形容词的比较级和一般过去时语法专项
- 格式:doc
- 大小:58.00 KB
- 文档页数:4


形容词比较级、-ing形式(现在进行时)、-ed形式(一般过去时)规则与用法不规则形容词比较等级的形式变化good-----better------best 好的well------better------best 身体好的bad------worse------worst 坏的ill--------worse-------worst 病的many--------more------most 许多much------more--------most 许多few------less-------least 少数几个little-------less------least 少数一点儿far------further------furthest 更进一步,程度far------farther------farthest 更远,路程old-------older------oldest 年老的(指年纪)old------elder-------eldest 年老的(指兄弟姐妹的排行)规则变化单音节词(只读一个元音,两个辅音间有多个元音也读成一个元音)和少数双音节词,加词尾-er,-est来构成比较级和最高级。
1.一般单音节词未尾加-er,-est。
great(巨大的) greater greatest tall(高的) taller tallest2.以不发音的e结尾的单音词和少数以- le结尾的双音节词只加-r,-st。
nice(好的) nicer nicest large(大的) larger largest able(有能力的) abler ablest3.以一个辅音字母结尾的闭音节单音节词,双写结尾的辅音字母,再加-er,-est。
big(大的) bigger biggest hot热的) hotter hottest4."以辅音字母+y"结尾的双音节词,改y为i,再加-er,-est。

形容词、副词的比较级和最高级比较级一、在英语中,对两者进行比较时,形容词或副词要用比较形式。
二、常用比较级的句型有:1.“than”,译为“......比......更......”2.“比较级and 比较级”,译为“越来越......”3.“the +比较级,the +比较级”,译为“越......越......”4.“as +原级+as”,译为“和......一样”5.“much+比较级”。
译为“......得多”三、单音节和少数双音节词的比较级的变化规则:1.一般直接在词尾加er。
如:tall--taller2.以字母e结尾的形容词加r。
如:nice--nicer3.以重读闭音节结尾的形容词如末尾只有一个辅音字母即辅音+元音+辅音,应先双写该末尾字母,再加er。
如:big--bigger4.以“辅音字母+y”结尾的形容词,先把y变成i,再加er。
如:busy--busier四、熟记不规则的比较级形式good/well ---better bad/ill,badly--worse many/much--morelittle--less far--farther/further五、部分双音节和多音节词,在词前加more构成比较级。
如:beautiful--more beautiful最高级一、当句子需要三者或三者以上进行比较时,要用最高级。
(注意:最高级前一般加the)二、最高级的规则变化:1.一般直接在词尾加est。
如:long --longest2.以“e”结尾的,直接加st。
如:nice--nicest3.以重读闭音节结尾的,先双写末尾字母,再加est。
如:big--biggest4.以辅音字母+y结尾的,先把y改为i,再加est。
如:busy--busiest5.多音节和部分双音节词,在词前加most构成最高级。
如:interesting--most interesting6.不规则的变化:good/well--best ill/bad/badly--worst many/much--mostlittle--least far--farthest/furthest练习一、写出下列词的比较级形式。

形容词的比较级和最高级专项讲解Ⅰ.常见的形容词及比较级和最高级的构成(1)规则变化:①单音节和部分双音节的形容词一般在词尾加-ercalm---calmer---calmesttall---taller---tallestsmart---smarter---tallest②以字母e结尾的直接在词尾加-rnice---nicer---nicestfine---finer---finestlarge---larger---largest③以“辅音+y结尾的词,变y为i,再加-er”early---earlier---earliesthappy---happier---happiestbusy---busier---busiest④以重读闭音节的单个辅音字母结尾的词,双写辅音字母,再加-erbig---bigger---biggestthin---thinner---thinnesthot---hotter---hottestfat ---fatter---fattestwet---wetter---wettestred---redder---reddestsad---sadder---saddestslim---slimmer---slimmest⑤多音节或部分双音节的形容词在原级前面加morepopular---more popular---most popularimportant---more important---mostimportant(2)非凡变革:原级good / wellmany/ muchbad / badly/ill(坏地)littleoldfar比较级bettermoreworselessolder(年岁)elder(辈份)最高级bestmostworstleastoldest/ eldestFarther(间隔)/ further(水平)farthest/ furthestⅡ.描述词比力级的用法:透露表现二者(人或物)的比力。

形容词比较级和最高级的用法及练习(一)一般句式的构成: A + is / are+ 形容词比较级+ than + BA 是主格B 是宾格如: She is taller than me.(二)英语形容词比较级的构成英语形容词比较等级有三个:原级,比较级和最高级。
形容词比较等级形式变化有规则的和不规则的两种。
规则变化1)单音节词末尾加-er(比较级),-est(最高级)2)单音节如以e结尾,只加-r(比较级),-st(最高级)3)闭音节单音节词如末尾只有一个辅音字母,须先双写这个辅音字母,再加-er(比较级),-est(最高级)4)少数以-y,-er,ow,-ble结尾的双音节词,末尾加-er(比较级),-es t(最高级)。
以-y结尾的词,如-y前是辅音字母,则变y为-i,再加-er和-est。
以-e结尾的词只加-r和-st。
5)其它双音节和多音节词皆在前面加单词more和most。
不规则变化常用的不规则变化的形容词的比较级和最高级:原级------比较级------最高级good------better------bestmany------more------mostmuch------more------mostbad------worse------worstfar------farther, further------farthest, furthest 形容词前如加 less 和 least 则表示"较不"和"最不"important 重要 less important 较不重要 least important 最不重要注:有些形容词一般没有比较等级。
如: right, wrong, woolen等。
形容词的比较等级的用法:比较级用于二者的比较。
There are more students in Class One than in Class Two.一班比二班学生多。
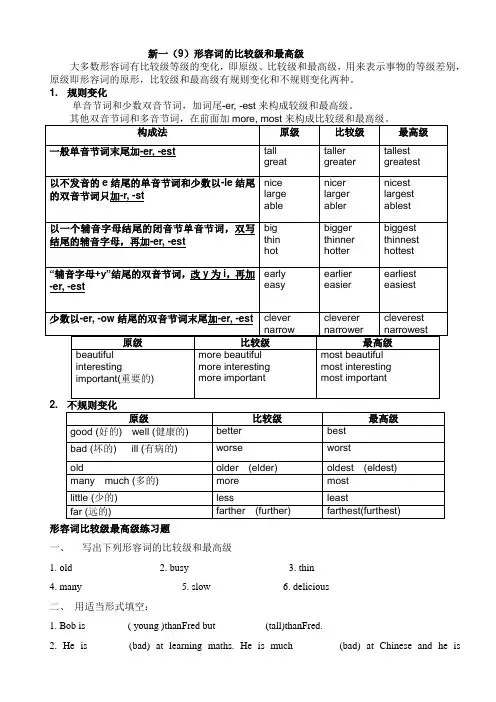
新一(9)形容词的比较级和最高级大多数形容词有比较级等级的变化,即原级、比较级和最高级,用来表示事物的等级差别,原级即形容词的原形,比较级和最高级有规则变化和不规则变化两种。
1. 规则变化单音节词和少数双音节词,加词尾-er, -est来构成较级和最高级。
形容词比较级最高级练习题一、写出下列形容词的比较级和最高级1. old ______ ________2. busy _________ _________3. thin ________ ________4. many _________ _________5. slow ________ _____6. delicious _________ ______二、用适当形式填空:1. Bob is ________( young )thanFred but__________(tall)thanFred.2. He is ______ (bad) at learning maths. He is much _______ (bad) at Chinese and he isthe _________ (bad) at English.3. Annie says Sally is the ________ (kind) person in the world.4 A dictionary is much _________ (expensive) than a story-book.5. An orange ia a little ______ (big) than an apple, but much ________ (small) than a watermelon.6. Playing computer games is______ _____ _____ of all the activities.(interesting).7. The Nile(尼羅河) is ______ ________river in the world. (long)8. Good health is _______ _______ ________thing life. (important)9. Taking a taxi is ______ _______ way to get to the airport. (easy)10. She is_______ than all the other students. (young)11. Where is the ________bus-stop? (near)12. Tom drives much ________ ________than John. (careful)13. The white flower is ________(beautiful). The yellow flower is ______ _______ (beautiful)than the white flower. The red flower is the _____ ______ of the three.三、选择题1. She is ________ than ________ .A. busier / usB. busier / weC. more busy / usD. more busy / we2. China is ________ country in the world.A. the third largestB. the largest thirdC. the third largeD. a third largest3. -Which is ____ season in Beijing?-I think it's autumn.A.goodB.betterC.bestD.the best4.- Which is__________ , the sun, the moon or the earth?-- Of course, the moon is.A.smallB.smallerC.smallestD.the smallest5.The air in Beijing is getting much _____ now than a few years ago.A. cleanB. cleanerC. cleanestD. the cleanest6. Mobile phones are very popular now and they are _____ than before.A. cheapB. cheaperC. cheapestD. the cheapest7 Which is _____ , a bicycle or a computer?A. expensiveB.more expensiveC.the most expensive8. The Yellow River is one of ______rivers in China A long B longer C the longest9.She is the second _______student in our class. A. tall B. taller C. tallest。

译林版6B语法知识归类在译林版6B 的英语学习中,语法知识是构建语言能力的重要基石。
掌握好这些语法,能够帮助我们更准确、更流畅地表达自己的想法。
下面,让我们一起来对译林版 6B 的语法知识进行归类梳理。
一、一般过去时一般过去时是表示过去发生的动作或存在的状态。
其标志性的时间状语有:yesterday(昨天),last week(上周),last month(上个月),last year(去年),ago(以前)等。
动词在一般过去时中的变化规则是需要重点掌握的。
规则动词一般在词尾加 ed,例如:work worked,play played。
但也有一些不规则动词,如:go went,come came,do did,have had 等,需要特别记忆。
在句子构成上,一般过去时的肯定句结构是“主语+动词过去式+其他”,例如:I played football yesterday 否定句结构是“主语+ didn't +动词原形+其他”,例如:He didn't go to school last Monday 疑问句结构是“Did +主语+动词原形+其他?”,例如:Did you watch TVlast night?二、一般将来时一般将来时用于表示将来要发生的动作或存在的状态。
常与tomorrow(明天),next week(下周),next month(下个月),next year(明年),soon(不久)等时间状语连用。
一般将来时有两种常见的表达形式:“be going to +动词原形”和“will +动词原形”。
“be going to”表示计划、打算做某事,例如:I'm going to visit my grandparen ts this weekend “will”则更侧重于表示意愿或对未来的预测,例如:It will be sunny tomorrow三、现在进行时现在进行时表示正在进行的动作。

新概念英语第一册语法点归纳新概念一共144课,其中单课为课文,双课为语法和练习。
整本书是以单数课为正课,并附带有插图而双数课则是针对单数课所讲的内容有针对性地进行练习,从此出展现出整个新概念一教材区别于其他教材的独特之处。
以下是对新概念一整本教材的理解和剖析,以供各位对整个课本的理解和把握上参考和借鉴。
首先根据课本中出现的时态来分析:本册书的语法出现层次性和规律性是很强的,首先我们先来整本书中都出了哪些时态,这些时态的具体分布和讲解时我们大家需要注意的递进性。
Lesson 31—34 现在进行时Lesson 37—40 第一次出现be going to 的将来时Lesson 51—56 一般现在时Lesson 67—76 为一般过去式Lesson 83—90 为现在完成时Lesson 91—96 为一般将来时 (will)Lesson 117—118 过去进行时Lesson 119—120 过去完成时除去前面所有时态和句型所占据的76课我们一起来看一下以下的68课,每一课小的语言点,语法点都是在什么地方,应该用什么样的方式来讲解。
在这里告诉学员新概念一的每一个单课的重点都是出现双课的标题和课后的练习题里面。
Lesson1—2语言点:与陌生人说话或引起别人的注意。
Excuse me. Yes? Pardon? Thank you very much.语法点:主系表结构this为主语,名词做表语1的一般疑问句以及它的肯定回答。
Is this your handbag? Yes, it is.Lesson 5—6语言点:如何介绍别人。
This is Miss Sophie Dupont. Nice to meet you.语法点:主语为第三人称单数的主系表结构。
She is French. He is German. It’s a Volvo.(L6)a/an 的使用。
Lesson 7—8语言点:如何自我介绍和相互认识。

形容词的比较级:
1、两个事物或人的比较用比较级,比较级后面一般带有单词than。
than后的人称代词用宾格。
结构:形容词+er than...
2.形容词加er的规则:
⑴直接在词尾加er ;如:tall --- taller
⑵以字母e 结尾,加r ;如:nice---nicer
⑶以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y变i,再加er 。
如:heavy----heavier
⑷重读,辅元辅,双写末尾的辅音字母,再加er ;如:big--- bigger thin---- thinner 3.不规则形容词比较级:good/well-----better
例句:(1).It's taller than both of us together.它比我俩加起来还高。
(2).Your feet are bigger than mine.你的脚比我的大。
(3). I’m heavier than you.我比你重。
过去式规则变化
(1)直接+“ed ”。
如:walk →walked(走)
(2)以字母e 结尾,加“-d”。
如:live →lived (住)like →liked (喜欢)
(3)以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y变i,再加ed ;
若是词尾为“元音字母+y”,只加“ed ”。
如:study →studied (学习)play→played (游戏)
(4)原形动词词尾为重读闭音节时,先双写该辅音字母再+ “ed”
如:stop →stopped(停止)。

形容词比较级的变化规则及例题形容词比较级用于比较两个事物的特征或属性。
它们可以帮助我们描述事物之间的差异。
以下是形容词比较级的变化规则及例题。
规则一:单音节形容词对于单音节形容词,我们通常在形容词后面加上-er来表示比较级。
例如:- Tall(高)— Taller(更高)- Fast(快)— Faster(更快)- Big(大)— Bigger(更大)规则二:部分双音节形容词和少数单音节形容词对于部分双音节形容词以及少数单音节形容词,我们需要在形容词前面加上more来表示比较级。
例如:- Beautiful(美丽)— More beautiful(更美丽)- Modern(现代的)— More modern(更现代的)- Important(重要的)— More important(更重要的)规则三:多音节形容词和不规则形容词对于多音节形容词以及一些不规则形容词,他们的比较级形式与原形形式不同。
例如:- Expensive(昂贵的)— More expensive(更昂贵的)- Good(好的)— Better(更好的)- Bad(坏的)— Worse(更坏的)例题:1. The blue car is (big) than the red car.(big) than the red car.2. She is much (tall) than her brother.(tall) than her brother.3. The book is (interesting) than the movie.(interesting) than the movie.参考答案:1. bigger2. taller3. more interesting希望本文档能够帮助您理解形容词比较级的变化规则,并能够熟练运用于实际写作中。
如果您还有其他疑问,请随时提问。

形容词比较级,一般过去时语法记忆口诀(一)形容词比较级
形容词比较级,记住口诀就简单。
一般情况加er,末尾e只加r。
遇到重读闭音节,末尾双写加er。
辅音加Y来结尾,变y为i加er。
(二)一般过去时
一般过去时并不难,表示过去动作,状态记心间。
动词要用过去式,时间状语句末站。
否定句很简单,didn’t 站在动词原形前,其它部分不要变。
一般疑问句也好变,did放在句子前,
主语,动词原形,其它部分依次站。
特殊疑问句也简单,疑问词加一般疑问句记心间。
最后一条请注意,动词过去式要牢记。
形容词的比较级和最高级一、含义绝大多数形容词有三种形式,原级,比较级和最高级,以表示形容词说明的性质在程度上的不同。
(1)形容词的原级:形容词的原级形式就是词典中出现的形容词的原形。
例如: poor,tall,great,bad。
(2)形容词的比较级:形容词的比较级表示“更……”,用于两者之间的比较,用来说明“前者比后者更……”,其句式为:“比较级+than”,即:物体A + be动词+ 形比+ than + 物体B。
She is more beautiful than my sister. 她比我的姐姐漂亮。
This bottle is bigger than that one. 这瓶子比那瓶子大。
(3)形容词的最高级:形容词的最高级表示“最......”,表示在三者或三者以上中程度最高,其句式为:the+形容词最高级+(名词)+表示范围的短语或从句,即:物体A + be动词+ the + 形最高级+(名词)+比较范围(of + 人/物,in +地方)Lucy is the most beautiful girl in her school. 露西是她学校最漂亮的女孩。
Jim is the thinnest of the three boys. 吉姆是这三个男孩中最瘦的。
二、比较级和最高级的规则变化(1)单音节和少数双音节形容词变化规则如下:(2)多音节词和部分双音节词变化规则如下:(3)少数不规则变化如下:二、形容词的比较形式1. 比较级:(1) be动词+比较级+than 用于表达“...比...更如何”I am taller than you. 我比你高。
(2) the + 比较级+ of the two表示“两个中比较……的He is the better of the two . 他是这两个人中比较好的。
2. 最高级:be动词+ the + 最高级+ (名词) +比较范围(of + 人/物,in +地方) 用于表达“在...中最......”I am the tallest in our class. 我是我们班里个子最高的。
可编辑修改精选全文完整版形容词、副词的比较级与最高级用法详解一、形容词、副词比较级、最高级构成大多数的形容词、副词都具有原级、比较级和最高级三种形式。
而形容词、副词的比较级、最高级构成方式分规则变化和不规则变化。
其规则变化的方式详见下面个表:(一)规则变化:(1) 直接在词尾加-er, -est(2) 以不发音字母e 结尾的,在词尾加-r , -st(3)以“辅音字母+y“结尾的,把y 变i,再加-er , -est(4) 以辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词汇,双写最后一个辅音字母,再加-er , -est(5) 部分双音节和多音节词,在其前加more, most(二)、不规则变化:比较级、最高级具有不规则变化形式的形容词和副词比较少,因此,需要大家逐一认真记忆。
详见下表:【妙记顺口溜】“坏”“病”两“多”和两“好”,一是“远”来,二是“老”,little 是“少”不是“小”。
二、形容词、副词比较级和最高级用法(一)形容词、副词比较级用法形容词、副词的比较级主要对两个的人或物在某种程度、性质上进行比较。
常见的形容词副词比较级用法如下:1.同级比较① A+be/v+as+原级+as+B A和B一样This room is as large as that one .这间房子和那间一样大(形容词)Tom writes as carefully as Kate.汤姆写字跟凯特一样认真。
(副词)②A+be/V+not+as(so)+级+as +B A 不如BTigers aren't as(so) dangerous as lions.老虎不如狮子危险。
(形容词)Mary didn't finish the work as(so) well as Lucy.玛丽完成这项工作不如露西好。
(副词)2.差极比较①A+be/v+比较级+B A比B更......This pen is newer than that one.这支钢笔比那支新。
中考语法专题篇之形容词(副词)的比较级与最高级形容词比较级和最高级一定义两者之间进行比较的时候,要用到形容词的比较级,通常than后接比较的对象。
三者及三者以上进行比较要用到形容词的最高级,形容词最高级前通常接要有定冠词the(副词最高级前the通常省略)He is taller than me.他比我高。
Tom is the tallest in his family.汤姆是他家里最高的。
[注意] 在英语中一些副词也是有比较级和最高级的,其构成与形容词的比较级和最高级一样,用法类似。
二构成1.[规则变化]2.[不规则变化]三比较级用法说明1.比较级(......)+than 的句型I have more money than you.2.原级比较as+adj/adv(原级)+as[在否定句第一个as可以换成so]My schoolbag is as big as yours.3.倍数的表达法[一倍是once,两倍是twice,三倍及以上是数词+times]①倍数+as +原级 +asMy school is three times as large as yours.②倍数+比较级+thanMy scores of this English exam is twice higher than those of Jack.③倍数+what 从句My homework is three times heavier what I used to have.④倍数+the seize/area/width/length/height/weight等+ofThis door is three times the width of that door.⑤倍数+that/those of +对象The length of this ruler is nearly three times that of that ruler.4.比较级表达最高级含义①Tom is the tallest in his class.=Tom is taller than any other student in his class.=Tom is taller than the other students in his class.=Tom is taller than the rest of the students in his class.[区分]any other+名词/any+名词any other 指比较的两个对象在同一个范围。
1.形容词比絞级的构成:(1)通常是在形容词后面加上弋讥形成比较级。
原级比较级原级比较级clean cleaner(比较干净的;更干净的)tall taller(比较高的;更高的)(2)原级, 比较级原级比较级nice nicer(比较好的;更好的)brave braver(比较勇敢的;更勇敢的)(3)原级比较级原级比较级happy■happierC比校快乐的;更快乐的)friendlyfriendlier(比较友善的;更友善的)(4)原形容词词尾有握辅元辅”现象(即后三个字母的排列是“辅音字母+元音字母+辅音字母”)时,则要双写词末的辅音字母,再加・e r.原级比较级原级比较级big bigger(比较大的;更大的)sad sadder(比较悲伤的;更悲伤的)(5)部分双音节形容词及三音节以上的形容词,只需在其前加more便构成比较级。
(注意:more后的形容词须用原级。
)原级比较级原级比较级beautifulmore beautiful(tt较美丽的;更美丽的)comfortablemore comfortable (比较舒适的;更舒适的〉(6)不规则变化形式,须一一记忆.原级比较级原级比较级many/much morc(比较多的;更多的)good/ well better(比较好的;更好的)bad worse (比较坏的;更坏的)little less(比校少的;更少的)比较级句型John is taller than Mary.约翰比玛丽高。
We are happier than they a re/them.我们比他们快乐.He is shorter than I am/me.他比我矮.Mary is more beautiful than Ann.玛丽比安漂亮.【注1)(1)这种句型中的动词不一定是be,也可以是一般动词;(2)比较级之后可视需要加名词.John has more books than Mary.约翰拥有的书比吗丽多.2.形容词最高级的构成:(1)通常只在形容词的原级后加上・esl即可.原级比较级最高级cold colder coldest(最冷的)young younger youngest(最年轻的)fast •faster fastest(最快的;最快地)cheap cheaper cheapestC最便宜的)(2)e•原级比较级最高级large larger largest (最大的)nice nicer nicestC最好的)(3)原级比较级最高级dry drier driest (最干的)easy easier easiest (最容易的)pretty prettier prettiestC最美丽的)(4)原级比较级最高级big bigger biggest (最大的)hot,>.hotter hottest (最热的)thin thinner thinnest(最瘦的)wet wetter wettest(最潮湿的)(5)原级比较级最高级beautiful more beautiful most beautiful(最漂亮的)comfortable more comfortable most comfortable(最舒适的)difficult more difficult most difficult(最困难的)expensive more expensive most expensiveC 最昂贵的)(6)原级比较级最高级bad worse worst (最差的)good/wellt better best(最佳的)many/much more most(最多的)【注竄】形容词最高级前须加the.形容词最离级的常见句型是,主语+动词贡秒形容词最高级( + in/on/at ・・・+群体)。
形容词比较级和最高级1、形容词比较级的构成:(1)规则构成的变化变化规则例一般情况在词尾+ er; est great-greater-greatest以’e’结尾的单词直接在词尾+ r; st wide- wider-widest辅音加‘y’结尾的单词把y改为I + er; est happy- happier- happiest双写辅音字母+ er; est big- bigger- biggest 一个元音加辅音结尾的单词多音节的形容词在原词前+ more; most beautiful- more beautiful- mostbeautiful(2)不规则形容词副词比较级与最高级原级比较级最高级Bad/ badly/ill worse worstfar farther/further farthest/furthestGood/well better bestlate later latestlittle less leastOld elder/older eldest/oldestMuch more most2. 七种常用的比较级句型1)as + 原级+ as…和……一样English is as important as math.This coat is as cheap as that one.否定:not as (so) + 原级+ as…和……不一样;不如Kongfu Panda 2 is not as interesting as Kongfu Panda 1.2) 比较级+ and + 比较级, 表示“越来越……”When spring comes, days are getting longer and longer.My English is becoming better and better.3) the + 比较级,the + 比较级,表示“越……,就越……”The harder you work, the more successful you will be.4) less + 原级+ than, 表示“不如……”This book is less difficult than that one.5) least + 原级+ of (in),表示“最不……”This is the least useful of the four books.6) 比较级+ than any other + 单数名词,表示最高级的意义Mike is more hard-working than any other student in his class.7) one of + 比较级+ 复数名词,表示“最……之一”Transformer is one of the most popular films.3. 常用的修饰词1) 在very, quite, rather, too, so, pretty后用形容词原级:The story is quite interesting.You are quite right.This shirt is pretty good.2) 在much, a little, a bit, even, still, a great deal等词后用形容词比较级:He is much stronger than you.I feel even worse today.The shoes are a little bigger for me.3) 形容词最高级前一定要用定冠词the, 可以用形容词性物主代词、名词所有格、序数词以及by far, nearly, almost 等词修饰,前面有形容词性物主代词和名词所有格限定时,the 可以省略:This is my busiest day.Changjiang River is China’ s longest river.This hat is nearly the biggest.人称代词第一人称单数第二人称单数第三人称单数第一人称复数第二人称复数第三人称复数主格I you he/she/it we you they 宾格me you him/her/it us youthem形容词性物主代词my your his/her/its our yourtheir名词性物主代词mine yours his/hers/its ours yourstheirs汉语我的你的他的/她的/它的我们的你们的他(她、它)们的Exercise 1、不规则形容词的比较级和最高级good/ well- _________- _________ many/ much- __________ - __________ bad/ ill- __________ - __________ little –__________ - __________far-__________/_________-__________/________ old-__________/_________-__________/_________2、(1)This is my ________(old) sister.(2)The weather is ________(bad) than that of yesterday.(3)He goes to America for the _________(far) study(深造).(1)The summer is coming. The weather becomes _____ and ______(hot).(2)The ______ (many) books you read, the _______(much) knowledge you know.(3)The more you smile, the ______ (happy) you will feel.(4)Iphone is ______ ______ (expensive) than ______ ______ cellphone.Iphone比任何一部手机都昂贵。
形容词和副词比较级形容词和副词有三个等级:原级,比较级,最高级(一)形容词、副词比较级的构成:1、单音节词和少数双音节词比较级规则变化:beautiful—more beautiful ;difficult—more difficult3、不规则变化:(二)使用原级一般有两种情况:1、当不进行比较时,在程度副词very, so, quite, too等后面的形容词或副词要用原级。
例如:This box is too heavy. 这个箱子太重了。
She speaks English very well. 她英语讲得很好。
2、在“as…as”或“not as/so…as”结构中,虽有比较的意思,但形容词或副词要用原形。
例如:This ruler is as long as that one. 这把尺子和那把尺子一样长。
Jim is not as/so tall as Tom. 吉姆不如汤姆高。
(三)比较级:表示两者(人或事物)之间的比较1、A+形容词比较级+than+ BSusan is happier than Jane.His brother is younger than me.Beijing is more beautiful than Osaka.(形容词或副词前有much, a lot, a little, far, still, even等词时,要用比较级)This story is much more interesting than that one. 这个故事比那个有趣的多。
2、在比较级的句子中有“of the two”之类意义的词组时,比较级前要用定冠词the。
Bill is the taller of the two boys. 比尔是两个男孩中个子较高的一个。
3、比较级+and+比较级,表示“越来越……”(多音节词要用“more+and+more+原级”)。
He is running faster and faster. 他跑得越来越快。
语法专项(预习篇)语法专项——☆形容词的比较级☆当我们需要对事物作出比较时,需要用到比较级。
英语中大多数形容词、副词是可以分等级的,一般有三个等级:原级,比较级和最高级。
形容词、副词的本来形式就是形容词的原级。
如:John is a tall boy.两者间进行比较用到形容词比较级。
如:Jim is taller than John.三者或者三者以上进行比较用形容词的最高级。
Mike is the tallest of the three boys.(形容词最高级前一定要加the)1. 形容词比较级:在英语中,两者进行比较,强调"一方比另一方……",可使用"形容词比较级+than" 结构比较级的句子结构通常是:什么+ 动词be (am ,is ,are )+ 形容词比较级+ than(比)+ 什么,如:I’m taller and heavier than you. (我比你更高和更重。
)An elephant is bigger than a tiger. (一只大象比一只老虎更大。
)形容词的比较级是在形容词的基础上变化而来的,它的变化规则是:①一般的直接在词尾加er ,如tall - taller ,strong - stronger ,②以e结尾的,直接加r ,如fine –finer ,③以辅音字母加y结尾的,先改y为i再加er,如funny - funnier④双写最后的字母再加er,如big –bigger,thin –thinner ,除此之外,还有几个特殊的单词,它的比较级和最高级都是不规则的,如:many / much(原形)–more(比较级)–most(最高级)good(原形)–better(比较级)–best(最高级)bad (原形)–worse(比较级)–worst(最高级)far(原形)–further–furthest附加:形容词的最高级变化类似于比较级,只是把词尾的er改成est,如:tall (原形)- taller (比较级)- tallest (最高级)long(原形)- longer(比较级)- longest(最高级)big (原形)- bigger(比较级)- biggest(最高级)2、需要掌握的形容词比较级的形式:tall-taller, short-shorter, old-older, young-younger, strong-stronger, heavy- heavier, long-longer, thin-thinner, big-bigger, small-smaller语法专项预习——一般过去时一、概念表示在的过去某个时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
通常在句子里找到表示过去时间的词或词组。
时间状语:yesterday,yesterday morning,yesterday afternoon,yesterday evening,the day before yesterday(前天),last night,last week,last month,last year,a moment ago(刚才),just now(刚才),two days ago,a week ago,in 1990等。
二、动词过去式的构成规律(一)规则动词的过去式1.一般情况下,在动词原形后面加-ed;look→looked play→played start→started visit→visited2.以不发音e结尾的动词,在词尾直接加-d;live→lived use→used3.以“辅音字母+ y”结尾的动词,先将y 改为i ,再加–ed;study→studied, tr y→tried fly→flied4.以重读闭音节(即辅音+元音+辅音)或r音节结尾,末尾只有一个辅音字母的动词,要先双写这个辅音字母后,再加–ed。
stop→stopped plan→planned, prefer→preferred(二)不规则动词的过去式1.改变动词中的元音;begin→began drink→drank come→came eat→ate grow→grew run→ran know→knew win→won speak→spoke take→took write→wrote get→got2.变词尾的–d 为–t ;build→built lend→lent send→sent spend→spent bend→bent3.与动词原形一样;cut→cut put→put cost→cost hurt→hurt shut→shut4.变-ay 为-aid (少数动词);say→said pay→paid lay→l aid5.采用不同词根;sell→sold teach→taught buy→bought6.其他。
am/is→was are→were have/has→had do→did三、加“-ed”后的读音方法1.ed加在清辅音后面读/t/。
finished /-t/ help /-t/ asked /-t/2.ed加在浊辅音或元音结尾的,读/d/。
played /-d/ lived /-d/ enjoyed /-d/3.ed加在/t/或/d/后面,读/id/。
wanted /-tid/ needed /-did/ visited /-tid/四、句型结构:1.在表示某个时间里存在的状态的句子,系动词用过式was,were构成。
如:(1)I was at home yesterday.昨天我在家。
(2)We were in the gym just now. 刚才我们在体育馆。
2.在表示过去某个时间里发生的动作,用动词的过去式构成。
如:I visited my uncle yesterday. 昨天我拜访了我的叔叔。
3.各种句式(1)一般过去时的肯定陈述句:主语+动词过去式+宾语或表语。
He worked in Shanghai ten years ago.(2)一般过去时的否定句:a.主语+didn’t +动词原形+宾语。
(did + not = didn't)He didn't do morning exercises yesterday.b.主语+wasn’t/weren’t +表语。
(was + not = wasn't were + not = weren't) He wasn't an English teacher ten years ago.(3)一般过去时的一般疑问句:a.Did +主语+动词原形+宾语?Did you study English in 1990 ?(肯定回答:Yes, I did. 否定回答:No,I didn’t.)b.Was/Were + 主语+表语?Was he a pupil five years ago ?(肯定回答:Yes, he was. 否定回答:No, he wasn’t.)(4)一般过去时的特殊疑问句:a.特殊疑问词+did + 主语+动词原形+宾语?Where did your parents live five years ago?What did you do last Sunday?b.特殊疑问词+were/was +表语?Who was at the zoo yesterday?五、句式变化(一)一般过去时的一般疑问句1.把was, were放在句首,其余位置不变。
由Was…?引导的一般疑问句,肯定答为:Yes,…was. 否定回答为:No,…. wasn’t. 由Were…?引导的一般疑问句,肯定回答为:Yes,… were. 否定回答为:No,… weren’t.如:(1)I was born in Shanghai. →Were you born in Shanghai?→Yes, I was. (肯定回答) →No, I wasn’t. (否定回答)(2)They were in Li Yan’s home last night. →Were they in Li Yan’s home last night?→Yes, they were. (肯定回答) →No, they weren’t. (否定回答)2.在行为动词的句子中,要用助动词词did来引导,其余的语序不变。
要注意的是,要把行为动词的过去式改为原形。
肯定回答为:Yes, …did. 否定回答:No, …didn’t.如:John played computer games last night.→Did John play computer games last night?→Yes, he did. (肯定回答) →No, he didn’t. (否定回答)(二)一般过去时的否定句1.在表示过去存在的状态的句子中,相接在was, were的后面加上not。
如:(1)He was in the park the day before yesterday.→He was not in the park the day before yesterday.(2)We were busy last week.→We were not busy last week.2.在表示过去的时间发生的动作的句子中,要在行为动词的前面加助动词didn’t.然后把过去式的行为动词改为动词原形。
即:didn’t + 动词原形。
如:(1)She played the violin last night.→She didn’t play the violin last night.(2)They swam in the lake yesterday.→They didn’t swim in the lake yesterday.(三)、一般过去式的特殊疑问句1.What did …?(主要是询问过去发生了什么事情,注意要把过去式改为动词原形。
)We ate Chinese food last night.→What did we eat last night?2.Where did ?( 主要是询问过去事情发生的地方。
)They sang and dance in the music room yesterday morning.→Where did they sing and dance yesterday morning?3.Who + 动词过去式…?( 主要是询问过去事情发生的人物。
)Mike and Tom climbed mountains last weekend.→Who climbed mountains last weekend?六.小结. 过去式的肯定、否定、疑问及简短回答1. 过去式的肯定、否定、疑问及简短回答的形式可表示如下:肯定句:I (He, She, We, You, They) went there by bus.否定句:I (He, She, We, You, They) didn't go there by bus.疑问句:Did I (he, she, we, you ,they) go the by bus?简短回答:Yes, I (He, She, We, You, They) did.No, I (He, She, We, You, They) didn't.2. 动词be的肯定、否定、疑问及简短回答形式如下:肯定句:I (He, She) was there.We (You, They) were there.否定句:I (He, She) wasn't there.We (You, They) weren't there疑问句:Was I (he, she) there?Were we (you, they) there?简短回答:No, I (he, she) wasn't.we (you, they) weren't.。