振动与波(Oscillation and Wave)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.66 MB
- 文档页数:57
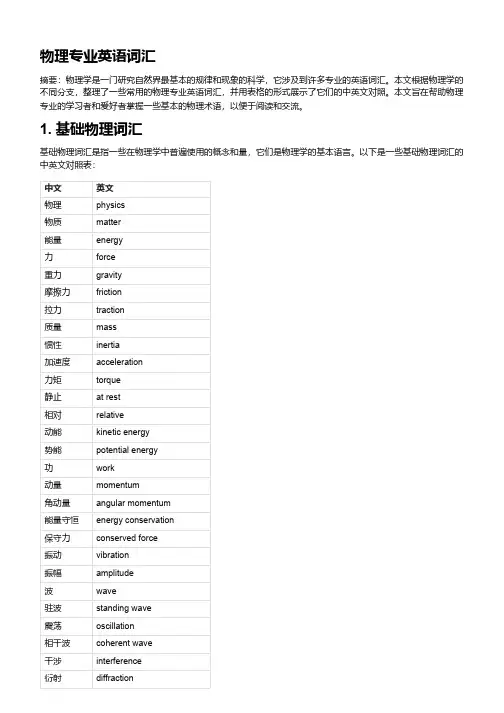
物理专业英语词汇摘要:物理学是一门研究自然界最基本的规律和现象的科学,它涉及到许多专业的英语词汇。
本文根据物理学的不同分支,整理了一些常用的物理专业英语词汇,并用表格的形式展示了它们的中英文对照。
本文旨在帮助物理专业的学习者和爱好者掌握一些基本的物理术语,以便于阅读和交流。
1. 基础物理词汇基础物理词汇是指一些在物理学中普遍使用的概念和量,它们是物理学的基本语言。
以下是一些基础物理词汇的中英文对照表:中文英文物理physics物质matter能量energy力force重力gravity摩擦力friction拉力traction质量mass惯性inertia加速度acceleration力矩torque静止at rest相对relative动能kinetic energy势能potential energy功work动量momentum角动量angular momentum能量守恒energy conservation保守力conserved force振动vibration振幅amplitude波wave驻波standing wave震荡oscillation相干波coherent wave干涉interference衍射diffraction轨道orbit速度velocity速率speed大小magnitude方向direction水平horizontal竖直vertical相互垂直perpendicular坐标coordinate直角坐标系Cartesian coordinate system极坐标系polar coordinate system2. 电学和磁学词汇电学和磁学是研究电荷、电流、电场、磁场等现象和规律的物理学分支,它们与光学、热学、原子物理等有着密切的联系。
以下是一些电学和磁学词汇的中英文对照表:中文英文电子electron电荷charge电流current电场electric field电通量electric flux电势electric potential导体conductor电介质dielectric绝缘体insulator电阻resistor电阻率resistivity电容capacitor3. 物理专业英语词汇物理专业英语词汇是指在物理学的学习和研究中经常使用的一些专业术语,它们涵盖了物理学的各个分支和领域,如力学、电磁学、光学、热学、量子力学等。

§5惠更斯原理波的衍射波的反射与折射一、惠更斯原理OS 1S 2u ∆tu ∆tS 1S 2在均匀的自由空间波传播时,任一波面上的每一点都可以看作发射子波的点波源,以后任意时刻,这些子波的包迹就是该时刻的波面。
——波沿直线传播t+∆t 时波面t 时波面t+∆t 时波面S1i 2三、波的反射与折射介质1MN反射波与入射波在同一介质中传播tu MD AN ∆==i容易算出i i '=(n 1)(n 2)A B C DMNi 1i1tu MD ∆1=tu AN ∆2=21u u AN MD =2sin i AD AN =1sin i AD MD =11u c n =22u c n =2211sin sin i n i n =介质2A B C D1122sin sin i u i u =21n =介质2相对于介质1的折射率折射波与入射波在不同介质中传播介质相对于空气的折射率声波—机械纵波一、声压媒质中有声波传播时的压力与无声波传播时的静压力之差纵波—疏密波稀疏区域:实际压力小于静压力,声压为负值稠密区域:实际压力大于静压力,声压为正值§7声波与声强级次声波可闻声超声波声压是仪器所测得的物理量定义声压:p = p -p 0对某声波媒质无声波——静压力p 0 、密度ρ0有声波——压力p 、密度ρ)(Hz ν2020000p+pV+∆V ∆V。



瞬时速度instantaneous velocity[,nstn'teinjs]圆柱形cylinder['silind]械振动mechanical vibration [va'bren]简谐振动simple harmonic oscillation [hɑ:'mnik]振幅amplitude ['mpl,tu:d, -,tju:d]频率frequency ['fri:kwnsi]xxhertz [h:ts]单摆simple pendulum ['pendjulm]受迫振动forced vibration共振resonance ['reznns]机械波mechanical wave介质medium ['mi:djm]横波transverse wave [trns'v:s]纵波longitudinal wave [lndi'tju:dinl]波长wavelength ['wev,lekθ]超声波supersonic wave [,sju:p'snik]速率speed[spi:d]v-t图象v-t graph[ɡrɑ:f]加速度acceleration [k,sel'ren]xxPlanck匀变速直线运动uniform variable rectilinear motion['ju:nif:m] ['vribl] [,rekti'lini]初速度initial velocity[i'nil] [vi'lsiti]自由落体运动free-fall motion自由落体加速free-fall acceleration[k,sel'ren]重力加速度gravitational acceleration [,ɡrvi'teinl] xxGalileo Galilei力force[f:s]xxNewton['nju:tn]重力gravity['ɡrviti]重心center of gravity['sent]万有引力gravitation[,grv'ten]电磁相互electromagnetic interaction[,lektrmg'netk] 强相互作用strong interaction[,ntr'kn]弱相互作用weak interaction形变deformation[,di:f:'men,]弹性形变elastic deformation[i'lstik] [,di:f:'men,]弹性限度elastic limit[i'lstik] ['limit]弹力elastic force[i'lstik] [f:s]劲度系数coefficient of stiffness[,k'fnt] ['stfns] xxHooke law[l:]摩擦力friction force['frikn]静摩擦力static frictional force['sttik] ['frikn]滑动摩擦力sliding frictional force['slaidi]动摩擦因数dynamic friction factor[dai'nmik]合力resultant force[ri'zltnt]分力component force[km'punnt]力的合成composition of forces[,kmp'zin]力的分解resolution of force[,rez'lu:n] 三角形定则triangular rule[tra'gjl] [ru:l]运动学kinematics[kini'mtiks]动力学dynamics[dai'nmiks]牛顿第一定律Newton first law['nju:tn] [l:]惯性inertia [i'n:j]惯性定律law of inertia[i'n:j]质量mass[ms]惯性系inertial system['sistm]牛顿第二定律Newton second law单位制system of units国际单位制Le Systeme International Unites SI[,nt'nnl]作用力action['kn]反作用力reaction[ri'kn]牛顿第三定律Newton third law超重overweight[,v'wet]失重weightlessness['wetls]误差error['er]偶然误差accidental error[,ksi'dentl]系统误差systematic error [,sist'mtik]绝对误差absolute error['bslu:t]相对误差relative error['reltiv]亚里士多德Aristotle曲线运动curvilinear motion[k:vi'lini]基尔霍夫Kirchhoff切线tangent['tndnt]抛体运动projectile motion[pr'dektl,]抛物线parabola[p'rbl]线速度linear velocity['lini]匀速圆周运动uniform circular motion['ju:nif:m] ['s:kjul] 角速度angular velocity['gjl]弧度radian['reidjn]周期period['pirid]向心加速度centripetal acceleration[sen'trptl]向心力centripetal force[sen'trptl]开普勒Kepler引力常量gravitational constant [,ɡrvi'teinl] ['knstnt]万有引力定律law of universal gravitation[,ju:ni'v:sl]第一宇宙速度first cosmic velocity['kzmik]第二宇宙速度second cosmic velocity第三宇宙速度third cosmic velocityxxblack hole能力energy['endi]势能potential energy[p'tenl]动能kinetic energy[k'netk, ka-]功work[w:k]瓦特watt['pau]重力势能gravitational potential energy [,ɡrvi'teinl] [p'tenl]弹性势能elastic potential energy[i'lstik] [p'tenl]动能定理theorem of kinetic energy['θi:rm]机械能mechanical energy[mi'knikl] [k'netk]机械能守恒定律law of conservation of mechanical energy[,kns'vein] [mi'knikl]能量守恒定律law of energy conservation[,kns'vein]亥姆霍兹Helmholtz['helmhults]力force拉力traction['trkn]力矩torque[t:k]动量momentum[mu'mentm]角动量angular momentum ['gjl]振动vibration[va'bren]振幅amplitude['mpl,tu:d, -,tju:d] xxwave[weiv]驻波standing wave['stnd]震荡oscillation[,s'len]相干波coherent wave[ku'hirnt]干涉interference[,nt'firns]衍射diffraction[di'frkn]轨道obital大小magnatitude方向direction[di'rekn]水平horizental竖直vertical['v:tikl]相互垂直perpendicular[,p:pn'dkjl]坐标coordinate[ku':dineit]直角坐标系cersian coordinate system 极坐标系polar coordinate system['pul] 弹簧spring[spri]球体sphere[sfi]环loop[lu:p]盘型disc。

2011年技术物理学院08级(激光方向)专业英语翻译重点!!!作者:邵晨宇Electromagnetic电磁的principle原则principal主要的macroscopic宏观的microscopic微观的differential微分vector矢量scalar标量permittivity介电常数photons光子oscillation振动density of states态密度dimensionality维数transverse wave横波dipole moment偶极矩diode 二极管mono-chromatic单色temporal时间的spatial空间的velocity速度wave packet波包be perpendicular to线垂直be nomal to线面垂直isotropic各向同性的anistropic各向异性的vacuum真空assumption假设semiconductor半导体nonmagnetic非磁性的considerable大量的ultraviolet紫外的diamagnetic抗磁的paramagnetic顺磁的antiparamagnetic反铁磁的ferro-magnetic铁磁的negligible可忽略的conductivity电导率intrinsic本征的inequality不等式infrared红外的weakly doped弱掺杂heavily doped重掺杂a second derivative in time对时间二阶导数vanish消失tensor张量refractive index折射率crucial主要的quantum mechanics 量子力学transition probability跃迁几率delve研究infinite无限的relevant相关的thermodynamic equilibrium热力学平衡(动态热平衡)fermions费米子bosons波色子potential barrier势垒standing wave驻波travelling wave行波degeneracy简并converge收敛diverge发散phonons声子singularity奇点(奇异值)vector potential向量式partical-wave dualism波粒二象性homogeneous均匀的elliptic椭圆的reasonable公平的合理的reflector反射器characteristic特性prerequisite必要条件quadratic二次的predominantly最重要的gaussian beams高斯光束azimuth方位角evolve推到spot size光斑尺寸radius of curvature曲率半径convention管理hyperbole双曲线hyperboloid双曲面radii半径asymptote渐近线apex顶点rigorous精确地manifestation体现表明wave diffraction波衍射aperture孔径complex beam radius复光束半径lenslike medium类透镜介质be adjacent to与之相邻confocal beam共焦光束a unity determinant单位行列式waveguide波导illustration说明induction归纳symmetric 对称的steady-state稳态be consistent with与之一致solid curves实线dashed curves虚线be identical to相同eigenvalue本征值noteworthy关注的counteract抵消reinforce加强the modal dispersion模式色散the group velocity dispersion群速度色散channel波段repetition rate重复率overlap重叠intuition直觉material dispersion材料色散information capacity信息量feed into 注入derive from由之产生semi-intuitive半直觉intermode mixing模式混合pulse duration脉宽mechanism原理dissipate损耗designate by命名为to a large extent在很大程度上etalon 标准具archetype圆形interferometer干涉计be attributed to归因于roundtrip一个往返infinite geometric progression无穷几何级数conservation of energy能量守恒free spectral range自由光谱区reflection coefficient(fraction of the intensity reflected)反射系数transmission coefficient(fraction of the intensity transmitted)透射系数optical resonator光学谐振腔unity 归一optical spectrum analyzer光谱分析grequency separations频率间隔scanning interferometer扫描干涉仪sweep移动replica复制品ambiguity不确定simultaneous同步的longitudinal laser mode纵模denominator分母finesse精细度the limiting resolution极限分辨率the width of a transmission bandpass透射带宽collimated beam线性光束noncollimated beam非线性光束transient condition瞬态情况spherical mirror 球面镜locus(loci)轨迹exponential factor指数因子radian弧度configuration不举intercept截断back and forth反复spatical mode空间模式algebra代数in practice在实际中symmetrical对称的a symmetrical conforal resonator对称共焦谐振腔criteria准则concentric同心的biperiodic lens sequence双周期透镜组序列stable solution稳态解equivalent lens等效透镜verge 边缘self-consistent自洽reference plane参考平面off-axis离轴shaded area阴影区clear area空白区perturbation扰动evolution渐变decay减弱unimodual matrix单位矩阵discrepancy相位差longitudinal mode index纵模指数resonance共振quantum electronics量子电子学phenomenon现象exploit利用spontaneous emission自发辐射initial初始的thermodynamic热力学inphase同相位的population inversion粒子数反转transparent透明的threshold阈值predominate over占主导地位的monochromaticity单色性spatical and temporal coherence时空相干性by virtue of利用directionality方向性superposition叠加pump rate泵浦速率shunt分流corona breakdown电晕击穿audacity畅通无阻versatile用途广泛的photoelectric effect光电效应quantum detector 量子探测器quantum efficiency量子效率vacuum photodiode真空光电二极管photoelectric work function光电功函数cathode阴极anode阳极formidable苛刻的恶光的irrespective无关的impinge撞击in turn依次capacitance电容photomultiplier光电信增管photoconductor光敏电阻junction photodiode结型光电二极管avalanche photodiode雪崩二极管shot noise 散粒噪声thermal noise热噪声1.In this chapter we consider Maxwell’s equations and what they reveal about the propagation of light in vacuum and in matter. We introduce the concept of photons and present their density of states.Since the density of states is a rather important property,not only for photons,we approach this quantity in a rather general way. We will use the density of states later also for other(quasi-) particles including systems of reduced dimensionality.In addition,we introduce the occupation probability of these states for various groups of particles.在本章中,我们讨论麦克斯韦方程和他们显示的有关光在真空中传播的问题。


oscillation/vibration振动spring弹簧oscillator振子pendulum单摆compound pendulum复合摆damp阻尼resonance共振friction摩擦力equilibrium position平衡位置restoring force回复力driving force驱动力amplitude振幅period周期frequency频率angular frequency角频率instric properties固有属性simple harmonic motion(SHM)简谐振动be proportional(directly)to与…成正比interference干涉diffraction衍射reflection反射refraction折射wavelength波长wedge劈尖intensity强度coherent wave相干波transmission透过boundary边界mechanical waves机械波phase difference相位差standing waves驻波traveling waves行波crest(peak)波峰trough(valley)波谷transverse wave横波longitudinal wave纵波identical frequency相同的频率interference of waves波的干涉destructive interference相消干涉constructive interference相涨干涉wavepath difference波程差opticalpath difference光程差half—wavelength loss半波损失Huygen’s Principle惠更斯原理Double-slit Interference杨氏双缝干涉optics光学geometric optics几何光学physical optics物理光学wave optics波动光学quantum optics粒子光学polarization偏振wave surface波面wave line波线wave front波前spherical wave球面波plane wave平面波wavelet子波isotropic各项同性instant时刻incident入射的normal line法线double slit双缝bright fringe明纹dark fringe暗纹Newton’s ring牛顿环adjacent相邻的equal inclination interference等倾干涉equal thickness interference等厚干涉high-resolution高精度resolution分辨率overlap重叠grating光栅fixed固定的(确定的)secondary maxima次极大diffraction angle衍射角grating constant光栅常数grating function光栅方程diffraction grating衍射光栅transmission grating透射光栅reflection grating反射光栅missing order of diffraction grating光栅的缺级TEM透射电子显微镜SEM隧道扫瞄电子显微镜unpolarized light非偏振光polarized light偏振光natural light自然光crystal晶体Polaroid sheet/ polarizer起偏片analyzer检偏器vertical垂直的polarization偏振completely polarized light完全偏振光partly polarized light部分偏振光ellipse/circle polarized light椭圆/圆偏振光polarization of light光的偏振a stack of glass plates玻璃片堆quantum量子blackbody黑体anode阳极cathode阴极photon光子atom原子exert施加linear线性的eject激发illuminate使照亮radiation辐射electric field电场ammeter电流表photoelectron光电子circuit电路hypothesis假设/假说instantaneity瞬时性undulatory property波动性corpuscular property粒子性atomatic spectra原子光谱absorption spectra吸收光谱emission spectra发射光谱photoelectric effect光电效应thermal radiation热辐射electromagnetic wave电磁波photoelectric current光电流absolute temperature绝对温度cut-off voltage截止电压work function逸出功/功函数cut-off frequency截止频率conservation of energy能量守恒angular momentum角动量conservation of momentum动量守恒main quantum number主量子数ionization energy电离能excited state激发态high energy state/higher state高能态Thermal radiation in equilibrium平衡热辐射The supposition of stationary state定态假设The Uncertainty Principle不确定关系/测不准原理The condition of orbital quantization轨道量子化条件。

wave物理定义-概述说明以及解释1.引言1.1 概述引言是一篇文章中非常重要的部分,它能够为读者提供一个关于文章主题的整体概念。
在这篇长文中,我们将讨论有关波的物理定义。
波是物理学中一个核心概念,广泛应用于各个领域。
我们将探讨波的定义、波的特征、波的传播以及波的应用。
通过对这些方面的研究,我们可以更好地理解波在自然界中的运作方式,从而开拓出更广阔的应用领域。
在本文的正文部分,我们将首先对波进行详细的定义。
波是一种能量在空间中传播的物理现象。
它可以是机械波,如声波和水波,也可以是电磁波,如光波和无线电波。
波具有特定的振幅、频率和波长等特征,这些特征决定了波的形态和性质。
接下来,我们将介绍波的一些特征。
波可以表现出传播、干涉、衍射和折射等特性。
通过对这些特征的理解,我们可以更好地解释波的行为和现象,如声音的传播和光的折射。
同时,我们还将研究波的传播方式。
波可以通过介质传播,如空气中的声波和水中的水波,也可以通过真空传播,如电磁波。
了解波的传播方式对我们理解波的行为和应用非常重要。
最后,我们将探讨波的应用。
波在各个领域都有着广泛的应用,如声波在通信和医学领域的应用,光波在光学和信息技术方面的应用等。
通过研究这些应用,我们可以深入了解波的价值和潜力。
通过对波的定义、特征、传播和应用的探讨,我们可以更好地理解波在物理学中的重要性和作用。
这篇长文旨在为读者提供关于波的全面而深入的理解。
通过对波的研究,我们将能够更好地把握自然界的规律,为未来的科学研究和技术发展做出更多贡献。
文章结构部分的内容可以是以下内容:1.2 文章结构本文共分为引言、正文和结论三个部分,具体结构如下:引言部分包括概述、文章结构和目的三个小节。
在概述中介绍了本文要探讨的主题“wave物理定义”,并简要说明了波的重要性。
接着,在文章结构一节中,详细介绍了本文的组织结构,包括引言、正文和结论部分的内容及其相互关系。
最后,在目的一节中,明确了本文的目的,即对wave物理定义进行全面的分析和论述。

物理英语词汇力force重力gravity摩擦力friction拉力traction质量mass惯量Interia加速度acceleration力矩torque静止at rest相对relative能量energy动能kenetic energy势能potential energy功work动量momentum角动量angular momentum能量守恒energy conservation保守力conserved force振动vibration振幅amplitude波wave驻波standing wave震荡oscillation相干波coherent wave干涉interference衍射diffraction轨道obital速度velocity速率speed大小magnatitude方向direction水平horizental竖直vertical相互垂直perpendicular坐标coordinate直角坐标系cersian coordinate system 极坐标系polar coordinate system弹簧spring球体sphere环loop盘型disc圆柱形cylinder电子electron电荷charge电流current电场electric field电通量electric flux电势electirc potential导体conductor电介质dieletric绝缘体insultalor电阻resistor电阻率resistivity电容capacitor无穷infinite横截面cross ection匀强电场uniform electric field分布ditribution磁场magnetic field磁通量magnetic flux电感inductance变压器transformer频率frequency周期period电磁波electomagnetic wave平面plane热平衡thermal equilibrium理想气体ideal gas热能thermal energy热量heat热容heat capacity外界surrounding准静态过程quasi-static process等体过程isochoric process 等压过程isobaric process等温过程isothermal process 绝热过程adiabatic process循环cycle光light光程optical path光强度light intensity偏振polarization波长wave length传播propagation原子atomic光子photon光电效应photo-electric effect物质波matter wave光谱spectrum激光laser衰减decay辐射radiation机械振动mechanical vibration简谐振动simple harmonic oscillation 振幅amplitude周期period频率ferquency赫兹hertz单摆simple pendulum受迫振动forced vibration能量守恒定律law of conservation of energy热力学第二定律second law of thermodynamics各向同性isotropy各向异性anisotropy单晶体single crystal(monocrystal)多晶体ploycrystal表面张力surface tension毛细现象capillarity液晶liquid crystal电荷electric charge电荷量queantity df electricity正电荷positive charg负电荷negative charg库仑定律Coulomb law静电感应electrostatic induction感应电荷inducde charge元电荷elementary charge电荷守恒定律law of conservation of charge库仑(电荷单位)coulomb电场electric fileld电场强度electric field strength电场线electric potential电势electric potential电势差/电压electric potential difference伏特volt电容capacitance电容器capacitor法拉(电容单位)farad电流electric current安培(电流单位)ampere电阻resistance欧姆(电阻单位)ohm 电动势electormotive force(e.m.f.)半导体semiconductor超导体superconductor磁性magnetism磁场magnetic field磁感线magnetic induction line安培定则Ampere rule安培力Ampere force磁感应强度magnetic induction左手定则left-hand rule洛伦兹力Lorentz force磁通量magnetic flux电磁感应elctromagnetic induction感应电流induction current感应电动势induction electromotive force电磁感应定律law of electromagnetic induction右手定则right-hand rule自感self-induction交流alternating current瞬时值instantaneous value峰值peak value有效值effective value电感inductance变压器transformer电能electric energy电磁场electromagnetic field电磁波electromagnetic wave雷达radar光线light ray平行光parallel light实象real image虚象virtual image折射refaction入射角incident angle反射角reflection angle折射角diffraction angle折射率diffraction index全反射total reflection临界角critical angle光导纤维optical fiber棱镜prism色散dispersion光谱spectrum波的衍射diffraction of wave 波的干涉interference of waves红外线infrared ray紫外线ultraviolet ray X射线X-ray电磁波谱electromagnetic effect光电效应photoelectric effect 光子photon普朗克常数Planck constant 波粒二象性wave-particle duality概率波probability wave物质波matter wave激光laser电子electron质子proton中子neutron核子nucleon同位数isotope原子核nucleus能级energy level基态ground state激发态excited state跃迁transition放射性radioactivityα射线αrayβ射线βrayγ射线γray衰变decay核反应nuclear reaction核能nuclear energy质能方程mass-energy equation 裂变fission链式反应chain reaction聚变fusion热核反应thermonuclear reaction 介子meson轻子lepton强子hadron合肥工业大学肖杨杨xiaoyangyang@。

专业词汇整理一.Subject name: (学科名称)1. Calculus微积分(学) mathematics 数学2.physics物理(学):statistical physics统计物理(学) modern physics 近代物理(学)Classic physics 经典物理学 molecular physics 分子物理学3.electromagnetism 电磁学 acoustics声学 kinematics 运动学4.mechanics力学 quantum mechanics 量子力学5. dynamics 动力学 thermodynamics 热力学6.general theory of relativity 广义相对论Special theory of relativity 狭义相对论二.在数学中的术语1.基本词汇:Function 函数(linear function 线性函数)equation 方程(linear equations 线性方程组)(注解:linear 是“线性”之意)formula 公式 theorem 定理(Pythagorean theorem 勾股定理)define 定义Projection 投影 test 检验 Determinant 行列式 minimum 最小值maximum 最大值2.矢量代数中的术语Vector 矢量(向量)①向量的几个概念:magnitude of vector 矢量的大小 projectionof vector 矢量的投影②向量的运算:subtraction of vector 矢量的减法 addition of vector 矢量的加法Dot (inner, scalar) product 点积(内积,标量积)Cross (vector) product 叉积(向量积)Scalar triple product(mixed product) 三重内积(混合积)③向量的分类:in the plane vector 平面向量 in space vector 空间向量(unit) Tangent vector (单位)切向量 (unit) normal vector (单位)法向量(注解:unit 有单位之意,而且与中文中的单位一样都有双重含义)Unit vector单位向量zero vector 零向量component vector(component of a vector )分向量Orthogonal vector 正交向量 rotating vector 旋转向量④**向量 position vector 位置矢量velocity vector 速度矢量displacement vector位移矢量 acceleration vector 加速度矢量3.级数中的术语series 级数①基本概念:sequence 序列(Fibonacci sequence 斐波那契数列)convergence 收敛性Term (数列中的)项②较为常见的级数:p _ series P—级数 harmonic series 调和级数power series幂级数alternating series交错级数Taylor series泰勒级数 Geometric series几何级数 position term series正项级数③收敛性与发散性convergence of series 级数的收敛性 partial sum 部分和Divergence of series 级数的发散性Absolute convergence (theorem) 绝对收敛(定理)conditional convergence 条件收敛radius of convergence 收敛半径interval of convergence 收敛区间iterated integral 逐次积分④检验法(审收法)nth_term test 第N项检验法limit comparison test极限比较检验Ratio test 比值检验Root test根植检验 alternating series test 交错级数审敛法geometric series test 几何级数审敛法 integral test 积分检验Basic comparison test 基本比较审敛法Rorschach test 罗氏检验⑤逼近法 Taylor’s approximation 泰勒逼近Maclaurin’s approximation 麦克劳林逼近4 微积分中的术语①基本概念:Variable变量 invariable 不变量domain of definition 定义域composite function复合函数parametric equation 参数方程 extreme 极值addition 加法subtraction 减法communicative law 交换律associative law 结合律②微分概念:differentiation 微分 chain rule 链式法则Derivative 导数:Directional derivative (angle) 方向导数(方向角)Partial derivative 偏导数 mixed second partial二阶混合偏导数second partial二阶偏导数 Lagrange multiplier 拉格朗日乘数③积分概念:integration积分 definitive integral定积分Riemann sum黎曼和improper integral 反常积分 integral test 积分检验inner limits 积分内限outer limits积分外限integration integral积分区间Initial condition 初始条件integration constant 积分常数integral curve 积分曲线 source function 原函数Upper bound of integral积分上限lower bound of integral积分下限multiple integral多重积分 double integral 二重积分triple integral 三重积分④ Newton-Leibniz formula 牛顿—莱布尼兹公式Fundament theorem of calculus微积分基本定理5 场论中的术语Field 场①基本概念:scalar field 标量场 operator 算子vector field(vector-valued function )矢量场(矢量函数)curl旋度 divergence散度 gradient(del)梯度 flux通量②积分:line integral线积分 surface integral面积分Independent of path 与路径无关③定理:Green’s theorem 格林定理Gauss’s theorem 高斯定理Stoker’s theorem 斯托克斯定理6.补充Limit极限 limits 范围continuous连续的 continuous everywhere处处连续coordinate system (coordinates)坐标系 quadrant 象限rectangular coordinates 直角坐标系cylinder coordinates 柱面坐标系spherical coordinates 球面坐标系Cartesian coordinates 笛卡尔坐标系Polar coordinates 极坐标系三物理中的常见术语1.force (力)and interaction(相互作用)Weak interaction弱相互作用 strong interaction强相互作用electromagnetic interaction 电磁相互作用Normal force法向力 tangential force切向力 drag force 阻力coriolis force科里奥利力 Lorenz force洛伦兹力elastic force弹性力 internal force 内力impulsive force 冲力inertial force惯性力 centrifugal inertial force 离心惯性力centre of force力心 force of gravity 重力friction force 阻力 static friction 静摩擦sliding friction 动摩擦2.constant (常量,常数)gas constant 气体普适常数 absolute constant 绝对常数damping constant 阻力常数gravitation constant引力常数3.inertial (惯性) inertial force惯性力 inertial mass 惯性质量noninertial frame 非惯性系inertial reference frame 惯性参考系rotational inertia 转动惯量w(定律) , equation(方程) ,formula(公式) and theorem(定理)kinematical equation 运动学方程Bernoulli’s equation 伯努利方程 poiseuill’s formula 泊肃叶公式theorem of momentum 动量定理theorem of kinetic energy 动能定理Theorem of angular momentum 角动量定理Parallel axis theorem 平行轴定理Perpendicular axis theorem 垂直轴定理conservation law of momentum 动量守恒定律conservation law of energy 能量守恒定律conservation law of angular momentum 角动量守恒定律conservation law of mechanical energy 机械能守恒定律Newton’s first/second/third law 牛顿三定律Law of universal gravitational force 万有引力定律Principle of superposition 叠加原理principle of work and energy 功能原理principle of relativity 相对性原理Hubble’s law 哈勃定律Hooker’s law 胡克定律Kepler’s law 开普勒定律konig’s theorem 克尼希定理Newton-Leibniz formula 牛顿—莱布尼兹公式Mass-energy equation(relation) 质能方程(关系)Temporal behavior 暂态行为 chaotic behavior 混沌行为Doppler effect 多普勒效应 Compton effect 康普顿效应Two-body problem 两体问题statically indeterminate problem 超静定问题5.unit(单位) and dimension(量纲)system of units单位制fundamental unit 基本单位derived unit 导出单位6.oscillation(振动) and wave(波)①波中的概念; wave front 波前wave speed 波速wave equation 波方程wave length 波长Wave number 波数wave shape波形wave resistance 波阻node波节 antinode 波腹②波的类型Forced oscillation受迫振动parametric oscillation参数动 infrasonic wave次声波 supersonic wave超声波 sound wave 声波electromagnetic wave电磁波 surface wave表面波 plane wave平面波 elastic wave弹性波 inelastic wave 非弹性波transverse wave横波 longitudinal wave 纵波mechanical wave机械波 simple harmonic wave(motion) 简谐波(简谐振动)solitary wave(sol ton)孤立波(弧子)pressure wave压力波 gravitational wave 引力波shock wave击波 cosine wave余弦波 sinusoidal wave正弦波standing wave驻波七 reference frame(参考系)Inertial reference frame 惯性参考系ceter-of-mass frame of reference质心参考系Moving reference frame 运动参考系Laboratory reference frame 实验室参考系basic reference frame 基本参考系八.Work(功) ,power(功率) and energy(能量)Element work 元功principle of work and energy 功能原理 mechanical energy 机械能conservation law of mechanical energy 机械能守恒定律conservation law of energy 能量守恒定律Potential energy 势能(位能) gravitational potential energy 引力势能Kinetic energy 动能 theorem of kinetic energy 动能定理Mass-energy relation(equation) 质能关系(质能方程)Mass-energy equivalence 质能等价性九.Velocity (速度),acceleration(加速度), coordinate(坐标)and motion(运动)Absolute velocity 绝对速度 relative velocity相对速度terminal velocity 终极速度First/second/third cosmic velocity 第一/二/三宇宙速度Instantaneous velocity/acceleration 瞬时速度/加速度Angular velocity/acceleration/coordinate 角速度/角加速度/角坐标Rectilinear motion with constant velocity 匀速直线运动Rectilinear motion with constant acceleration 匀加速直线运动Circular motion圆周运动 plane motion (translation)平面运动(平动)Rolling motion 滚动Linear accelerator直线加速器 cyclotron回旋加速器十.Momentum(动量) and angular momentum (角动量)Orbital angular momentum 轨道角动量theorem of momentum 动量定理Theorem of angular momentum 角动量定理conservation law of momentum 动量守恒定律conservation law of angular momentum 角动量守恒定律十一,常见的小词Temperature温度 position位置 displacement位移mass质量weight 重量experiment 实验liquid液体Pressure 压力particle 质点 simple pendulum 单摆atom原子 echo 回声error误差satellite人造卫星。
oscillatory的工作原理Oscillatory的工作原理引言Oscillatory是一种常见的物理现象,广泛应用于各个领域,如电子学、光学、声学等。
本文将探讨oscillatory的工作原理,并对其应用进行简要介绍。
一、什么是oscillatory?Oscillatory(振荡)指的是物体或系统在一定的时间间隔内以往复的方式来回运动或变化的现象。
它可以是机械振动、电磁振荡、波动等。
振荡的基本特征是周期性的变化或周期性的交替。
二、机械振动的工作原理机械振动是最为常见的振荡形式之一,其工作原理可以用一个简单的弹簧振子来说明。
弹簧振子由一个质点和一个弹簧组成。
当质点受到外力作用时,会发生位移,弹簧产生回弹力,使质点向相反方向运动,形成振动。
三、电磁振荡的工作原理电磁振荡是指电场和磁场在空间中交替变化的现象。
典型的电磁振荡器是LC振荡电路,由电感和电容组成。
当电荷在电容器和电感之间来回流动时,电场和磁场相互作用,产生电磁振荡。
四、波动的工作原理波动是一种能量传播的方式,可以分为机械波和电磁波。
机械波是通过质点的振动来传播的,如水波、声波等;而电磁波是通过电场和磁场的振荡来传播的,如光波、无线电波等。
波动的工作原理是通过振动的物质粒子或电场磁场的相互作用来传递能量。
五、oscillatory的应用1. 电子学领域:振荡电路在电子设备中得到广泛应用,如时钟电路、无线电收发器等。
2. 光学领域:光的振荡性质是实现光学器件和光学通信的基础,如激光器、光纤通信等。
3. 声学领域:声波的振荡特性用于声学传感器、扬声器等。
4. 化学领域:化学振荡反应是某些化学反应中出现周期性变化的现象,如质子泵、质子传导等。
六、结论通过对oscillatory的工作原理的探讨,我们了解到它是物体或系统以周期性的方式来回运动或变化的现象。
机械振动、电磁振荡和波动都是oscillatory的具体表现形式。
在各个领域中,oscillatory都有着广泛的应用,为我们的生活和科学研究提供了重要的基础和工具。
oscillation 用法(一)Oscillation(振荡)的用法介绍什么是振荡?振荡(Oscillation)是指物体在固定时间内在两个或多个状态之间来回变化的过程。
在不同领域中,振荡都有不同的涵义和应用。
物理领域中的振荡1.机械振荡:机械振荡是指由于物体的弹性形变或势能的变化而产生的周期性运动。
例如,钟摆的摆动、弹簧的拉伸和压缩等都是机械振荡的例子。
2.电磁振荡:电磁振荡是指电荷或电磁场的能量在电路中周期性地来回转化的过程。
例如,交流电的频率就是电磁振荡的频率。
3.光学振荡:光学振荡是指光波在介质中传播时的周期性变化。
例如,激光器中的光波就是通过光学振荡来产生和放大的。
数学领域中的振荡1.正弦振荡:正弦振荡是指以正弦函数为基础的周期性变化。
在数学中,正弦函数是最基本的一类周期函数,描述了很多自然界中的变化规律。
2.傅里叶级数:傅里叶级数是把一个周期函数分解为多个正弦函数的和的方法。
利用傅里叶级数理论,我们可以分析和预测振荡的性质和特征。
3.振荡方程:振荡方程是描述振荡系统行为的方程。
例如,单摆的运动可以用简谐振动方程描述,而电路中的振荡行为可以用LCR电路的振荡方程表示。
其他领域中的振荡1.经济领域:在经济学中,振荡可以用于描述市场的周期性波动。
经济振荡往往与经济周期和商业周期有关,对于经济预测和政策制定有一定的指导意义。
2.生物领域:在生物学中,振荡现象广泛存在于生物体内。
例如,生物钟调控着生物体的昼夜节律,心脏的搏动也是一种生物振荡现象。
3.信息领域:在信息科学中,振荡可以用于描述信号的周期性变化。
例如,音频和视频信号中的波形振动就是一种经典的振荡现象。
以上只是振荡在不同领域中的一些常见应用和用法,振荡作为一个重要的概念和现象,还有许多其他领域中的应用和深入研究。
物理领域中的振荡的用法1. 机械振荡•弹簧振荡:当给弹簧施加力或变形后,会产生弹性形变,从而使弹簧发生周期性的振动。
•摆锤振荡:摆锤是一个具有一定质量的物体,在重力作用下能够以固定点为中心进行摆动。
ap物理1汇总物理1必考知识点梳理题型分布物理1&2考试的题型分为选择题和解答题,两门考试选择题的数目是一样的,都是50道题,其中包括45道单选题和5道双选题,要在90分钟内答完,占总分值的50%。
物理1的解答题共5道,明确将考察一道实验设计题,一道计算题,三道问答题,要求在90分钟内答完,占总分值的50%。
题型分配由此可见,解答题部分将不再局限于对学生计算能力的考察,而是更注重考察学生的理解能力,文字叙述和书面表达能力。
考点分析由于物理12是2015年刚刚改革的,所以参考资料比较少,很多同学这时候会比较纠结,不知道哪一部分是考试的重点,我这次主要是综合了一下CB官网给出的样题以及15、16这两年FR的真题,给出了一个考点分布,大家可以看出目前的考察重点,建议大家一定要重视这两年的真题和样题,虽然巴朗、普林斯顿等也是非常好的参考资料,但就出题的思路上毕竟跟官方有些差距,容易对学生造成一定的误导。
物理1考点AP物理1考试的覆盖范围可以大体上分为五大块1. 运动学&牛顿定律2. 功&能&动量3. 圆周运动&转动力学4. 振动&波5. 电场力&纯电阻电路物理1考点在简答题中的分布出题频率最高的分别是运动学&牛顿运动、功&能&动量、振动&波这三部分,这几乎可以说是必考的部分,需要引起大家的重视。
详细考点梳理:1. 运动学&牛顿定律(kinetics, dynamics)运动学和牛顿定律是力学的基础,往往跟力学的各个章节结合起来,也经常跟电磁学结合起来考查,是考试的重点。
这一部分的主要考点包括uniformly accelerated motion 匀加速运动velocity-time diagram 速度-时间图projectile motion 抛体运动Newton’s Law 牛顿定律Free-body diagram 受力分析图2. 功&能&动量(work,energy, impulse)功能这一部分是力学的核心,还特别容易和振动、摆部分综合出题。