LabWindowsCVI教程(1)PPT课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:364.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

l a b w i n d o w s-C V I-教程本页仅作为文档封面,使用时可以删除This document is for reference only-rar21year.MarchLabWindows/CVI基础教程序言LabWindows/CVI是National Instruments公司推出的一套面向测控领域的软件开发平台。
它以ANSI C为核心,将功能强大,使用灵活的C语言平台与数据采集,分析和表达的测控专业工具有机地接和起来。
它的集成化开发平台,交互式编程方法,丰富的控件和库函数大大增强了C语言的功能,为熟悉C语言的开发人员建立检测系统,自动测量环境,数据采集系统,过程监控系统等提供了一个理想的软件开发环境。
本教程面向的是那些从未使用过LabWindows/CVI的读者,但是假设读者以有了C语言的基础并且熟悉Windows 2000/9x/NT操作系统。
在每一章节的学习中,作者都是通过一个具体的实例让读者迅速的掌握本章的知识点;而不是长篇大论,述及边枝细叶,反而使读者望而却步,只见树木,不见森林。
想信通过对本教程的学习,读者可迅速掌握LabWindows/CVI编程思想及步骤,为读者日后进一步学习打下基础。
本书约定:“File>>Page Setup>>Options”File 这一种黑色斜体字是指多级菜单名,按扭名,窗口名或者是关键性词汇。
“>>”是指打开一个多级菜单或对话框。
如:File>>Page Setup>>Options是指你首先打开File 菜单,然后选择Page Setup项,最后从弹出的对话框中选择Options 项。
“说明:通过这种方式你可以修改Panel顶端所显示的名字。
”该种字体所写的文字是值得读者注意并记忆的内容。
“该椭圆形框所框住的内容是读者需修改的地方。
第一部分 CVI快速入门本部分通过编制一个简单的LabWindows/CVI程序,使读者对CVI编程环境,思想及步骤有一初步的认识。
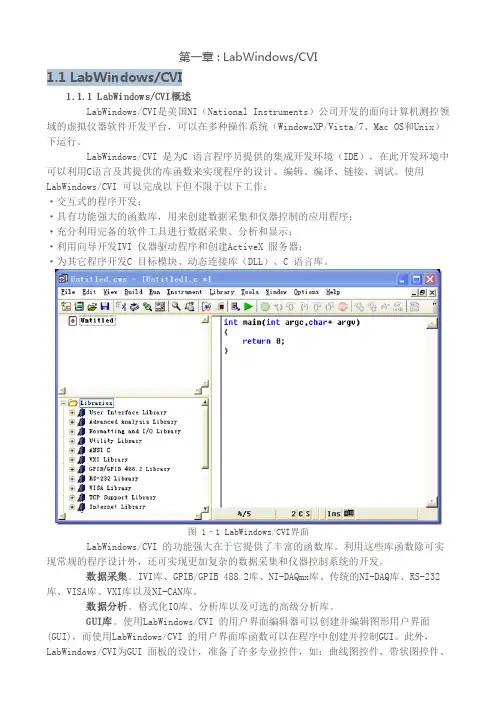
第一章 : LabWindows/CVI1.1 LabWindows/CVI1.1.1 LabWindows/CVI概述LabWindows/CVI是美国NI(National Instruments)公司开发的面向计算机测控领域的虚拟仪器软件开发平台,可以在多种操作系统(WindowsXP/Vista/7、Mac OS和Unix)下运行。
LabWindows/CVI 是为C 语言程序员提供的集成开发环境(IDE),在此开发环境中可以利用C语言及其提供的库函数来实现程序的设计、编辑、编译、链接、调试。
使用LabWindows/CVI 可以完成以下但不限于以下工作:·交互式的程序开发;·具有功能强大的函数库,用来创建数据采集和仪器控制的应用程序;·充分利用完备的软件工具进行数据采集、分析和显示;·利用向导开发IVI 仪器驱动程序和创建ActiveX 服务器;·为其它程序开发C 目标模块、动态连接库(DLL)、C 语言库。
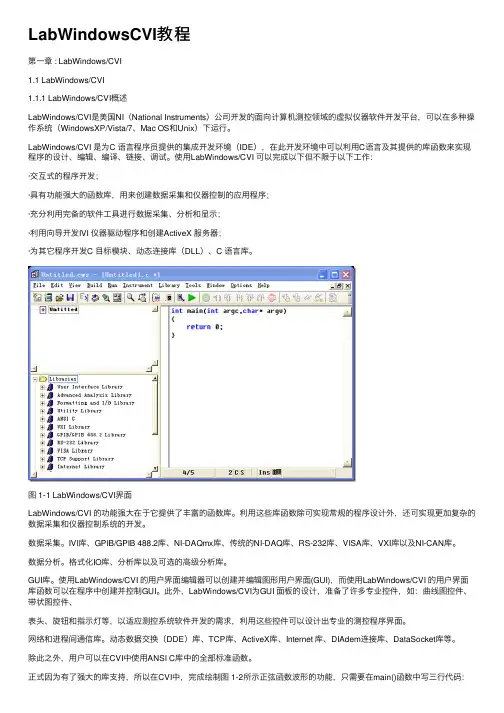
图 1‐1 LabWindows/CVI界面LabWindows/CVI 的功能强大在于它提供了丰富的函数库。
利用这些库函数除可实现常规的程序设计外,还可实现更加复杂的数据采集和仪器控制系统的开发。
数据采集。
IVI库、GPIB/GPIB 488.2库、NI-DAQmx库、传统的NI-DAQ库、RS-232库、VISA库、VXI库以及NI-CAN库。
数据分析。
格式化IO库、分析库以及可选的高级分析库。
GUI库。
使用LabWindows/CVI 的用户界面编辑器可以创建并编辑图形用户界面(GUI),而使用LabWindows/CVI 的用户界面库函数可以在程序中创建并控制GUI。
此外,LabWindows/CVI为GUI 面板的设计,准备了许多专业控件,如:曲线图控件、带状图控件、表头、旋钮和指示灯等,以适应测控系统软件开发的需求,利用这些控件可以设计出专业的测控程序界面。


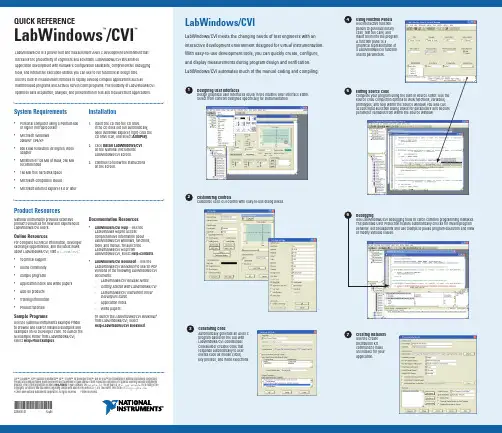
QUICK REFERENCELabWindows/CVI™™System Requirements•Personal computer using a Pentium 600or higher microprocessor• Microsoft Windows2000/NT SP6/XP• 800 x 600 resolution (or higher) videoadapter• Minimum of 128 MB of RAM, 256 MBrecommended•150 MB free hard disk space•Microsoft-compatible mouse•Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or laterInstallation1.Insert the CD into the CD drive.If the CD does not run automatically,open Windows Explorer, right-click theCD drive icon, and select AutoPlay.2. Click Install LabWindows/CVIon the National InstrumentsLabWindows/CVI screen.3. Continue to follow the instructionson the screen.LabWindows/CVI is a proven test and measurement ANSI C development environment thatincreases the productivity of engineers and scientists. LabWindows/CVI streamlinesapplication development with hardware configuration assistants, comprehensive debuggingtools, and interactive execution utilities you can use to run functions at design time.Use the built-in measurement libraries to rapidly develop complex applications such asmultithreaded programs and ActiveX server/client programs. The flexibility of LabWindows/CVIoptimizes data acquisition, analysis, and presentation in test and measurement applications.LabWindows/CVILabWindows/CVI meets the changing needs of test engineers with aninteractive development environment designed for virtual instrumentation.With easy-to-use development tools, you can quickly create, configure,and display measurements during program design and verification.LabWindows/CVI automates much of the manual coding and compiling.CVI™, DIAdem™, IVI™, National Instruments™, NI™, ™, NI Developer Zone™, and NI-DAQ™ are trademarks of National Instruments Corporation.Product and company names mentioned herein are trademarks or trade names of their respective companies. For patents covering National Instrumentsproducts, refer to the appropriate location: Help»Patents in your software, the patents.txt file on your CD, or /patents. For a listing of thecopyrights, conditions, and disclaimers regarding components used in USI (Xerces C++, ICU, and HDF5), refer to the USICopyrights.chm.© 2003–2004 National Instruments Corporation. All rights reserved.Printed in Ireland.*323551B-01*323551B-01Sep04Product ResourcesNational Instruments provides extensiveproduct resources for new and experiencedLabWindows/CVI users.Online ResourcesFor complete technical information, developerexchange opportunities, and the latest newsabout LabWindows/CVI, visit /cvi:•Technical support•Online community•Sample programs•Application notes and white papers•Add-on products•Training information•Product tutorialsSample ProgramsUse the National Instruments Example Finderto browse and search installed examples andexamples on NI Developer Zone. To launch theNI Example Finder from LabWindows/CVI,select Help»Find Examples.Documentation Resources•LabWindows/CVI Help—Use theLabWindows Help to accesscomprehensive information aboutLabWindows/CVI windows, functions,tools, and menus. To launch theLabWindows/CVI Help fromLabWindows/CVI, select Help»Contents.•LabWindows/CVI Bookshelf—Use theLabWindows/CVI Bookshelf to search PDFversions of the following LabWindows/CVIdocuments:–LabWindows/CVI Release Notes–Getting Started with LabWindows/CVI–LabWindows/CVI Instrument DriverDevelopers Guide–Application notes–White papersTo launch the LabWindows/CVI Bookshelffrom LabWindows/CVI, selectHelp»LabWindows/CVI Bookshelf.Designing User InterfacesDesign graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in the intuitive User Interface Editor.Select from controls designed specifically for instrumentation.1Customizing ControlsCustomize each GUI control with easy-to-use dialog boxes.2Generating CodeAutomatically generate an ANSI Cprogram based on the GUI withLabWindows/CVI CodeBuilder.CodeBuilder creates code thatresponds automatically to userevents such as mouse clicks,key presses, and menu selections.3Using Function PanelsUse interactive functionpanels to generate librarycalls, test the calls, andinsert them into the program.A function panel is agraphical representation ofa LabWindows/CVI functionand its parameters.4Editing Source CodeComplete your program using the built-in source editor. Use thesource code completion options to view functions, variables,prototypes, and help within the Source window. You also canaccess input selection dialog boxes for parameters and declareparameter variables from within the Source window.5Creating InstallersUse the CreateDistribution Kitcommand to makean installer for yourapplication.7DebuggingUse LabWindows/CVI debugging tools to catch common programming mistakes.The patented User Protection feature automatically checks for invalid programbehavior. Set breakpoints and use tooltips to pause program execution and viewor modify variable values.6Server Functions Client Functions Support FunctionsTCP Support LibraryThe TCP Support Library contains functions that provide support for a platform-independent interface to the reliable, byte-stream oriented, network connection capabilities of TCP/IP .ActiveX LibraryThe ActiveX Library contains functions that create and control ActiveX servers. Use these functions in conjunction with the ActiveX Controller Instrument Drivers, which you can generate using the Create ActiveX Controller Wizard. Also use theActiveX Library functions with ActiveX server code, which you can generate using the Create ActiveX Server Wizard.LabWindows/CVIUse built-in instrumentation libraries to interface test applications to the outside bWindows/CVI includes a large set of run-time libraries for instrument control, data acquisition, analysis, and user interface creation. This chart illustrates classes in each library. To find specific functions, use <Ctrl-Shift-P> in the Source window. You also can use the Library Tree to browse to and search for functions.NI-DAQmx LibraryThe NI-DAQmx Library contains functions that communicate with and control data acquisition devices.PanelsMenu StructuresMenus and Submenus User Interface LibraryThe User Interface Library contains functions that programmatically control the user interface.Pop-up PanelsKeyPress Event Functions Callback FunctionsUser Interface Management PrintingMouse and Cursor Rectangles and PointsBitmaps Clipboard MiscellaneousLW DOS Compatibility Functions MonitorsUtility LibraryThe Utility Library contains functions that perform various operations, including using the system timer, managing disk files, launching another executable, and using multiple threads.VISA LibraryThe VISA Library provides a single interface library for controlling VXI, GPIB, USB, and serial instruments.VXI LibraryThe VXI Library contains functions that communicate with and control VXI devices.GPIB/GPIB 488.2 LibraryThe GPIB/GPIB 488.2 Library contains functions thatcommunicate with GPIB instruments, control GPIB boards, and acquire GPIB status information.IVI LibraryThe IVI Library contains functions that program and control IVI drivers. IVI-compliant drivers have a standard interface, so you can interchange similar instruments without changing your code.Formatting and I/O LibraryThe Formatting and I/O Library contains functions that read from and write to disk files and manipulate the format of data in a program.Open/Close Input/Output XModem Control Status Callbacks ExtensionRS-232 LibraryThe RS-232 Library contains functions that control multiple RS-232 ports using interrupt-driven I/O.Note Refer to the Library Tree for a list of the Traditional NI-DAQ Library classes.Character Handling Date and Time Localization Mathematics Nonlocal Jumping Signal Handling Input/Output General Utilities String HandlingLow-Level IO Multibyte CharactersANSI C LibraryThe ANSI C Library contains standard ANSI C functions,which you can use in LabWindows/CVI.Advanced Analysis LibraryThe Advanced Analysis Library contains functions that simulate and analyze large sets of numerical data quickly and efficiently.Controls/Graphs/Strip ChartsPictures Axis Label Strings CanvasGeneral FunctionsList/Tree (Label/Value) ControlsText BoxesGraphs and Strip ChartsMenu BarsMessage/Prompt Popups File/Directory Popups Graph Popups Windows Interrupt Support Creating and ModifyingRetrieving and Comparing Values Timers Tables SplittersActiveX Controls Data Binding Functions Drawing Batch Drawing Pens ClippingAccessing Pixel Values MiscellaneousMenu Items Control MenusTrees Graph Plotting and Deleting Graph Cursors Graph Legend Strip Chart TracesDigital Waveform Graph Plotting Axis Scaling Font Popups Signal Generation1D Operations 2D Operations Complex Numbers1D Complex Operations Frequency Domain Time Domain One-Step Filter Functions Old-Style Filter Functions FIR Digital Filters Windows Filter Information Utilities Measurement BasicsProbability DistributionsAnalysis of Variance Nonparametric Statistics Old-Style Functions InterpolationVector & Matrix AlgebraReal Matrices Complex Matrices Additional Numerical MethodsStatisticsCurve FittingCascade Filter FunctionsIIR Digital FiltersSignal ProcessingComplex OperationsArray OperationsTimer/WaitDate/Time Keyboard File Utilities Directory Utilities MultithreadingThread PoolExternal Modules Port IOStandard Input/Output Window Runtime Error ReportingOld-Style FunctionsInterruptsPhysical Memory Access Task Switching Extended Functions MiscellaneousGeneral Functions Reading/Writing Callbacks Thread Safe Variable Thread LockThread Local Variable Advanced FunctionsThread Safe QueueLaunching ExecutablesCall Scheduling Functions CallbacksVariant Related FunctionsPassing Values as Variants Assigning Values to Variants Querying the Type of a Variant Retrieving Values from Variants Array FunctionsC Array to SafeArray Conversion SafeArray to C Array Conversion Querying SafeArrays BSTR Functions Resource Management Error Processing ConfigurationLocales Multithreading Low-level FunctionsCreating ActiveX Objects Calling Methods and Properties EventsServer Creation FunctionsObject Functions Advanced FunctionsObject Helper Functions IUnknown Functions IDispatch Functions DLL Server Entry PointsTask Configuration/ControlAdvancedChannel Creation/ConfigurationCreate Analog Input ChannelsPositionCreate T EDS Analog Input ChannelsPositionPositionWatchdog Timer External Calibration DSA Calibration Create Analog Output Channels Create Digital Input Channels Create Digital Output Channels Create Counter Input ChannelsCreate Counter Output Channels Advanced S tart Trigger Reference Trigger Advance Trigger AdvancedSwitch Functions Signal Routing Device ControlCalibrationSystem Configuration TEDSError HandlingExport HW Signals Scale ConfigurationInternal Buffer Configuration AdvancedWrite FunctionsTiming TriggeringRead FunctionsInstrument Driver SessionLocking ChannelsRepeated Capabilities Attribute CreationAdd AttributeAdd Repeated Attribute Invalidation Lists Comparison Precision CallbacksSet Read Callback Set Write Callback Set Check Callback Set Coerce Callback Set Compare Callback Set/Get/Check AttributeSet Attribute Get Attribute Check AttributeCaching/Status-Checking ControlRange TablesRange Table EntriesGet ViInt32 Entry Get Range Table Num Entries Get ViReal64 Entry Range Table Ptr Dynamic Range Tables Error InformationInstrument Specific Error Queue Memory Allocation Helper FunctionsString Callbacks Direct Instrument I/O S tring/Value Tables Value Manipulation Default Callbacks Attribute Information Interchangeability Warnings Logical Names ConfigurationInherent Attribute Accessors Resource TemplateResource ManagementResource-Specific OperationsBasic Message-Based I/OFormatted I/OMemory-Based I/O (High Level)Memory-Based I/O (Low Level)Shared MemoryInterface-Specific OperationsOpen/Close Configuration I/ODevice Control Bus ControlBoard Control Callbacks LockingThread-Specific StatusGPIB 488.2 FunctionsDevice I/OTrigger and ClearSRQ and Serial PollsParallel PollsRemote/LocalSystem ControlLow-level I/OFile I/OString Manipulation Data FormattingFormatting Functions Scanning Functions Status FunctionsSystem Configuration Commander Word Serial Servant Word Serial Low-Level VXIbus Access High-Level VXIbus Access Local Resource Access VXI Signals VXI InterruptsVXI Triggers System Interrupts VXIbus Extenders Backward CompatibilityCommander Word Serial Servant Word SerialNote The Advanced Analysis Library is part of the LabWindows/CVI Full Development System. The LabWindows/CVI Base Package includes the standard LabWindows/CVI Analysis Library. If you have the BasePackage installed, refer to the Library Tree for a list of the standard Analysis Library classes.DIAdem Connectivity LibraryThe DIAdem Connectivity Library contains functions thatdirectly transfer data between LabWindows/CVI and DIAdem.Object ManagementAdvanced Data Storage Data RetrievalEnumeration FTP (Client)Low Level FTP Telnet (Client)POP3 (Client)Internet LibraryThe Internet Library contains functions that communicate with and receive files and commands from remote servers.PropertiesFileChannel Group Channel MiscellaneousNote The LabWindows/CVI Base Package does not include the Internet Library.DDE Support LibraryThe DDE Support Library contains functions that create an interface between other Windows applications using the DDE standard.Server Functions Client FunctionsL a b W i n d o w s /C V I L i b r a r y R e f e r e n c e/cvi。
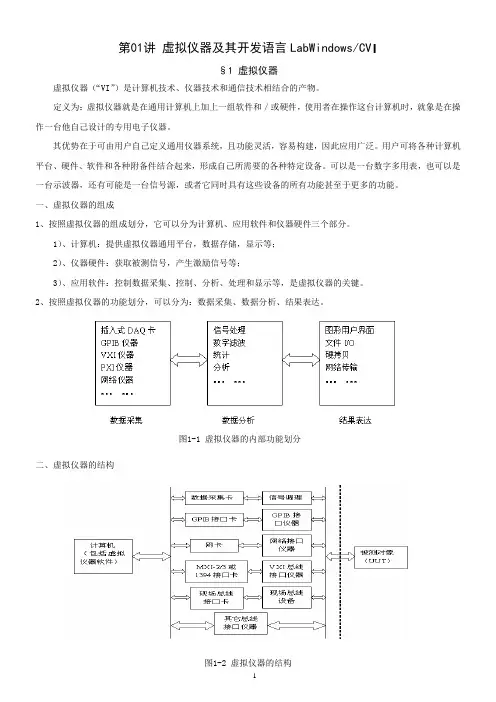
第01讲 虚拟仪器及其开发语言LabWindows/CV I§1 虚拟仪器虚拟仪器(“VI ”)是计算机技术、仪器技术和通信技术相结合的产物。
定义为:虚拟仪器就是在通用计算机上加上一组软件和/或硬件,使用者在操作这台计算机时,就象是在操作一台他自己设计的专用电子仪器。
其优势在于可由用户自己定义通用仪器系统,且功能灵活,容易构建,因此应用广泛。
用户可将各种计算机平台、硬件、软件和各种附备件结合起来,形成自己所需要的各种特定设备。
可以是一台数字多用表,也可以是一台示波器,还有可能是一台信号源,或者它同时具有这些设备的所有功能甚至于更多的功能。
一、虚拟仪器的组成1、按照虚拟仪器的组成划分,它可以分为计算机、应用软件和仪器硬件三个部分。
1)、计算机:提供虚拟仪器通用平台,数据存储,显示等; 2)、仪器硬件:获取被测信号,产生激励信号等;3)、应用软件:控制数据采集、控制、分析、处理和显示等,是虚拟仪器的关键。
2、按照虚拟仪器的功能划分,可以分为:数据采集、数据分析、结果表达。
二、虚拟仪器的结构图1-2 虚拟仪器的结构图1-1 虚拟仪器的内部功能划分虚拟仪器由仪器硬件平台和应用软件两大部分构成。
硬件平台包括:计算机、I/O接口设备(主要完成被测信号的采集、放大和模/数转换)。
见书上P5。
三、虚拟仪器的特点见书上P2。
四、常用术语VI: Virtual Instrument 虚拟仪器GPIB:General Purpose Interface Bus 通用接口总线VME:VersaModle Eurcaed Versa总线模块欧式卡(采用主控/目标结构,异步非复用传输模式)PCI:Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group ,PCISIG 简称PCI 外部设备互连VXI: VME Extensions for Instrumentation VME在仪器的扩展VPP: VXI Plug&Play VXI即插即用PXI: PCI Extensions for Instrumentation PCI在仪器的扩展DAQ: Data Acquire 数据采集GUI: Graphical User Interface 图形用户界面IDE: Integrated Development Environment 集成开发环境VISA:Virtual Instrument Software Architecture 虚拟仪器软件结构IVI: Interchangeable Virtual Instruments 可互换虚拟仪器SCPI:Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments 程控仪器标准命令LXI:LAN Extension for Instrumentation LXI在仪器的扩展§2 LabWindows/CVI的开发环境LabWindows/CVI是一个完全的ANSI C开发环境,用于仪器控制、自动检测、数据处理的应用软件。

LabwindowsCVI学习技巧与资料测控软件一般包括:用户界面、程序控制、数据采集和数据分析4部分。
CVI文件一般包括:工程文件(Pr)、源文件(.C)、头文件(h)和用户界面文件(.uir).Labwindows技巧学习必看(摘录)CVICVI是基于ANSI C的快速开发环境,适用于有C,C++基础。
使用VB,VC,BC运用控件式组织用户界面的工程师Build--Target Type--Dynamic Link LibraryCVI 是事件驱动式的运行方法,排除响应各个事件,造成显示滞后。
需要强制在函数中加入“Process system event()CVI对多线程的支持(1)概念篇每个进程至少有一人上基本线程(主线程)线程与数据一起隔离在某一物理区域,在进程中声明的数据可通过该线程进行访问。
如何实现CVI窗体的全屏?GetMonitorFromPanel(Main,&montior);//获得显示器IDGetMonitorAttribute(monitor,ATTR_HEIGHT,&height);//得到高度GetMonitorAttribute(monitor,ATTR)WIDTH,&width);//得到宽度SetPanelSize(Main,height-25,width);//设置窗口高宽度(高度需要去除任务栏的部分)SetPanelPos(Main,25,0);//设置窗口位置如何在LABWINDOWS中调用MATLAB程序?CVI和Matlab混合编程,必须要行安装Matlab在CVI中,建立ActiveX控制服务器,选择MatlabAutomatin Server type Library(Matlab必须在CVI之前安装才能看到这个选项),创建后将生成三个文件,XXX.FPxxx.C和XXX.h,将.C和.H文件包含在CVI工程中就可以了。
.C文件中包含着CVI和 Matlab的接口函数。

LabWindows/CVI实现
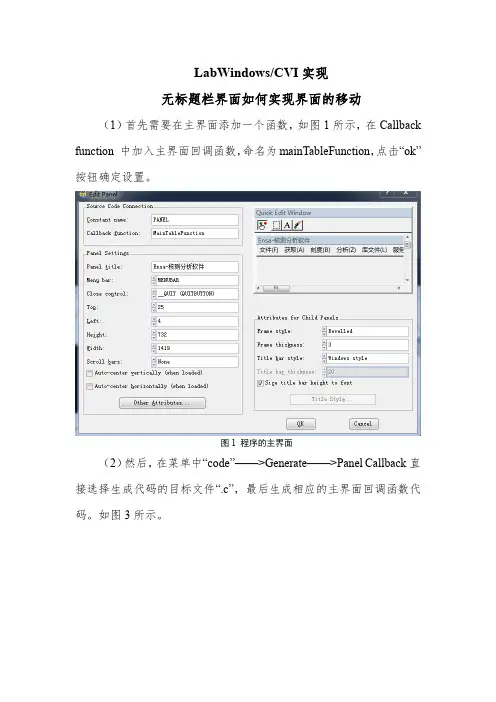
无标题栏界面如何实现界面的移动(1)首先需要在主界面添加一个函数,如图1所示,在Callback function 中加入主界面回调函数,命名为mainTableFunction,点击“ok”按钮确定设置。
图1 程序的主界面
(2)然后,在菜单中“code”——>Generate——>Panel Callback直接选择生成代码的目标文件“.c”,最后生成相应的主界面回调函数代码。
如图3所示。
图2 生成回调函数代码
图3 主界面回调函数代码
(3)第三步,在代码文件的开头,包含“windows.h”头文件,将需要的windows相关的函数引入,在引入的时候,需要注意将该头文件放在所有的头文件前面,否则会出现如图4所示错误信息。
图4 引用头文件不正确,导致错误
(4)补充关于鼠标左键移动界面的代码,在回调函数中加入以下代码,初始化变量:int hwnd;//窗口句柄
在switch中加入:
case EVENT_LEFT_CLICK: //长按鼠标左键,移动界面
GetPanelAttribute(panelHandle,ATTR_SYSTEM_WINDOW_HAN DLE,&hwnd); //获取窗口句柄
ReleaseCapture();//释放SendMessage(hwnd,WM_NCLBUTTONDOWN,HTCAPTION,0);
//发送系统消息
break;
(5)编译代码,最后可以实现鼠标左键移动界面的功能。

LabWindowsCVI教程第⼀章 : LabWindows/CVI1.1 LabWindows/CVI1.1.1 LabWindows/CVI概述LabWindows/CVI是美国NI(National Instruments)公司开发的⾯向计算机测控领域的虚拟仪器软件开发平台,可以在多种操作系统(WindowsXP/Vista/7、Mac OS和Unix)下运⾏。
LabWindows/CVI 是为C 语⾔程序员提供的集成开发环境(IDE),在此开发环境中可以利⽤C语⾔及其提供的库函数来实现程序的设计、编辑、编译、链接、调试。
使⽤LabWindows/CVI 可以完成以下但不限于以下⼯作:·交互式的程序开发;·具有功能强⼤的函数库,⽤来创建数据采集和仪器控制的应⽤程序;·充分利⽤完备的软件⼯具进⾏数据采集、分析和显⽰;·利⽤向导开发IVI 仪器驱动程序和创建ActiveX 服务器;·为其它程序开发C ⽬标模块、动态连接库(DLL)、C 语⾔库。
图 1‐1 LabWindows/CVI界⾯LabWindows/CVI 的功能强⼤在于它提供了丰富的函数库。
利⽤这些库函数除可实现常规的程序设计外,还可实现更加复杂的数据采集和仪器控制系统的开发。
数据采集。
IVI库、GPIB/GPIB 488.2库、NI-DAQmx库、传统的NI-DAQ库、RS-232库、VISA库、VXI库以及NI-CAN库。
数据分析。
格式化IO库、分析库以及可选的⾼级分析库。
GUI库。
使⽤LabWindows/CVI 的⽤户界⾯编辑器可以创建并编辑图形⽤户界⾯(GUI),⽽使⽤LabWindows/CVI 的⽤户界⾯库函数可以在程序中创建并控制GUI。
此外,LabWindows/CVI为GUI ⾯板的设计,准备了许多专业控件,如:曲线图控件、带状图控件、表头、旋钮和指⽰灯等,以适应测控系统软件开发的需求,利⽤这些控件可以设计出专业的测控程序界⾯。
@+labwindows+cvi测试技术及工程应用第一篇基础篇本篇主要介绍虚拟仪器的基本概念、虚拟仪器开发语言LabWindows/CVI的编程环境和程序结构以及基本控件的使用方法,并通过讲解简单实例,使初学者可以迅速掌握利用LabWindows/ CVI开发平台构建一般应用程序的基本思想、方法和步骤.本书使用的是LabWindows/CVI 8.0版本。
奢侈品保养虚拟仪器虚拟仪器(virtual instrument,简称“vi")是计算机技术、仪器技术和通信技术相结合的产物奢侈品维护.虚拟仪器的目的是利用计算机强大资源使硬件技术软件化,分立元件模块化,降低程序开发的复杂程度,增强系统的功能和灵活性。
奢侈品清洗1.1.1虚拟仪器的基本概念虚拟仪器基于计算机的软硬件测试平台,它可代替传统的测量仪器,如示波器、逻辑分析仪、信号发生器、频谱分析仪等:可集成自动控制、工业控制系统:可自由构建专有仪器系统。
它由计算机、奢侈品保养应用软件和仪器硬件组成。
虚拟仪器系统是将仪器硬件搭载到计算机平台,并辅以相应软件而构成的.奢侈品护理加盟虚拟仪器通过软件将计算机硬件资源与仪器硬件有机地融合为一体,从而把计算机强大的计算处理能力和仪器硬件的测量、控制能力结合在一起,大大降低了仪器硬件的成本,并通过软件实现对数据的显示、奢侈品维护存储以及分析处理功能。
从发展史看,电子测量仪器经历了由模拟仪器、智能仪器到虚拟仪器三个阶段。
奢侈品清洗如果在计算机中插入数据采集卡,利用计算机高速计算能力完成仪器信号的分析与处理、结果的输出,就可以把传统仪器的所有功能模块集成在一台计算机上,软件成为仪器系统的关键.在此基础上,美国国家仪器公司(National Instrument,简称“NI")提出了“软件就是仪器”的观点。
奢侈品保养奢侈品护理加盟虚拟仪器技术的优势在于可由用户自己定义通用仪器系统,且功能灵活,很容易构建,所以应用面极为广泛,尤其在科研、开发、.测量、检测、计量、控制等领域,更是不可多得的优秀开发工具。