ASRs软件架构需求模板
- 格式:doc
- 大小:1.12 MB
- 文档页数:16

![[实用参考]SAAS平台需求规格说明书.doc](https://uimg.taocdn.com/081f5f6fad02de80d4d84091.webp)
SAAS平台项目需求规格说明书版本历史目录第一章、概述 (1)1.1 总体要求 (1)1.2 文档编写约定 (1)1.3 系统介绍 (2)1.4 系统用户 (2)1.5 任务描述 (3)1.6 系统运行环境 (3)1.6.1系统拓扑结构图 (3)1.6.2硬件环境要求 (3)1.6.3软件环境要求 (3)1.7 系统总体设计要求 (4)1.7.1结构设计要求 (4)1.7.1.1 相关要求和标准 (4)1.7.1.2 外观、组装及包装设计要求 (4)1.7.2硬件设计要求 (4)1.7.2.2 硬件设计总体要求 (4)1.7.3软件设计要求 (4)1.7.3.1 相关要求和标准 (4)1.7.3.2 软件总体设计要求 (5)1.7.4其他设计要求 (5)1.8 词汇表 (5)1.9 参考资料 (5)第二章、功能性需求 (6)2.1 需求一览表 (6)2.1.1系统管理 (6)2.1.1.1 系统管理需求一览表 (6)2.1.2应用管理 (7)2.1.2.1 系统管理需求一览表 (7)2.1.3客服社区 (8)2.1.3.1 系统管理需求一览表 (8)2.1.4用户管理 (10)2.1.4.1 系统管理需求一览表 (10)2.1.5信息发布 (11)2.1.5.1 系统管理需求一览表 (11)2.1.6运维管理 (12)2.1.6.1 系统管理需求一览表 (12)2.1.7在线调查 (13)2.1.7.1 在线调查需求一览表 (13)2.1.8.1 系统管理需求一览表 (14)2.2 系统管理 (14)2.2.1系统管理 (14)2.2.1.1 数据源配置 (14)2.2.1.2 帐套建立 (16)2.2.2应用注册 (18)2.2.2.1 应用注册 (18)2.2.2.2 功能注册 (20)2.2.2.3 应用与帐套关联 (22)2.2.3权限管理 (24)2.2.3.1 操作员管理 (24)2.2.3.2 修改密码 (26)2.2.3.3 用户登录 (28)2.2.3.4 用户组管理 (29)2.2.3.5 操作员与用户组关联 (31)2.2.3.6 权限分配 (33)2.3 应用管理 (36)2.3.1应用管理 (36)2.3.1.1 应用类型定义 (36)2.3.1.2 应用类型和应用关联 (38)2.3.2计费管理 (40)2.3.2.1 服务项目 (40)2.3.2.2 计费类型定义 (42)2.3.2.3 应用标准计价表 (44)2.3.3.1 积分规则 (47)2.3.4应用组合 (50)2.3.4.1 应用组合定义 (50)2.3.4.2 组合应用 (52)2.3.4.3 分配应用功能 (55)2.3.4.4 应用组合定价 (57)2.4 用户管理 (60)2.4.1用户注册 (60)2.4.1.1 用户注册 (60)2.4.1.2 操作员注册 (63)2.4.1.3 修改密码 (65)2.4.1.4 用户登录 (67)2.4.1.5 用户组管理 (69)2.4.1.6 操作员与用户组关联 (70)2.4.1.7 权限分配 (73)2.4.2用户服务 (75)2.4.2.1 积分查询 (75)2.4.2.2 应用申请 (76)2.4.2.3 服务申请 (80)2.4.2.4 试用延期申请 (82)2.5 在线调查 (85)2.5.1创建问卷 (85)2.5.1.1 创建问卷 (85)2.5.1.2 添加题目 (88)2.5.2发布问卷 (92)2.5.2.1 发布问卷 (92)2.5.2.2 发布问卷回收 (94)2.5.3问卷分析 (95)2.5.3.1 问卷分析 (95)2.5.3.2 问卷明细查看 (97)2.6 运维管理 (98)2.6.1运维管理 (98)2.6.1.1 收款管理 (98)2.6.1.2 积分兑换管理 (103)2.6.1.3 服务申请审批 (106)2.6.1.4 应用申请审批 (109)2.6.1.5 试用延期申请审批 (111)2.6.2开通管理 (114)2.6.2.1 应用试用期限定义 (114)2.6.2.2 试用延期开通 (116)2.6.2.3 应用开通 (118)2.6.3运维服务 (120)2.6.3.1 操作日志 (120)2.6.3.2 系统日志 (123)2.6.3.3 数据导出 (125)2.6.3.4 数据导入 (127)2.6.3.5 数据备份 (128)2.6.3.6 数据恢复 (130)2.7.1库表管理 (132)2.7.2栏目管理 (133)2.7.2.1 栏目新建 (134)2.7.2.2 栏目管理 (136)2.7.3模板管理 (137)2.7.3.1 模板类别新建 (138)2.7.3.2 模板新建 (138)2.7.3.3 模板管理 (141)2.7.4附件管理 (142)2.7.4.1 附件上传 (142)2.7.4.2 附件管理 (143)2.7.5内容管理 (144)2.7.5.1 内容发布 (144)2.7.5.2 内容审核 (146)2.8 客服系统 (148)2.8.1客服系统 (148)2.8.1.1 创建问题 (148)2.8.1.2 问题回复 (151)2.8.1.3 问题查询 (153)2.9 客服社区 (155)2.9.1帖子管理 (155)2.9.2帖子批量管理 (155)2.9.3论坛设置 (156)2.9.4替换/限制设置 (156)2.9.6发布帖子 (157)2.9.7回复帖子 (158)2.9.8论坛内部邮箱和短信 (158)第三章、性能需求 (159)3.1 系统容量要求 (159)3.2 系统响应时间要求 (159)3.3 系统健壮性要求 (159)第四章、用户界面需求及界面原型 (160)4.1 用户界面设计原则要求 (160)4.2 易用性、易操作性要求 (160)4.3 界面原型 (160)4.3.1车辆新增 (160)4.3.1.1 界面描述 (160)4.3.1.2 界面元素说明 (161)第五章、安全性需求 (163)5.1 系统安全性需求 (163)5.2 数据安全性需求 (163)5.3 权限需求 (163)第六章、需进一步落实的问题(TBD) (164)第一章、概述1.1总体要求(1)需求规格说明书必须完整、准确描述业务需求及其环境要求(2)需求规格说明书作为一种契约,界定了系统的范围及内容;(3)通过该说明书,即使没有软件系统,按其内容而不需其它材料的情况下,手工处理也可实现;(4)通过培训讲解,软件开发人员、系统测试人员可以依此设计或测试系统,而不需要再去了解业务(5)子系统、功能模块和功能项的划分(即2.1部分)及其相互关系(即2.2部分)必须清晰、合理(6)对于功能项,特别是关键业务功能项(即2.G)的流程、输入输出必须清楚、完备;(7)对于关键数据元素的描述(即2.3部分)必须完备、准确。

软件需求规格说明书模板软件需求规格说明书模板1. 产品的目标1.1 该项目工作的用户问题或背景[对引发开发任务的工作和情况的描述。
同时也应描述用户希望用将要交付的软件来完成的工作。
][该节内容为该项目提供了合法的理由,你应该考虑用户的问题是否严重,是否应该解决和为什么应该解决。
]1.2 产品的目标[用一句话或很少的几句话来说明“我们希望该产品做什么?”换言之,即开发该产品的真正原因。
[项目如果没有一个表述清晰、易于理解的目标,就会迷失在产品开发的沙漠中。
产品必须带来某种优势。
典型的优势是产品会增加组织在市场上的价值,减少运作成本,或提供更好的客户服务。
这个优势应该是可度量的,这样才能够让您确定交付的产品是否达到目标。
]2. 客户、顾客和其它风险承担者2.1 客户是为开发付费的人,并将成为所交付产品的拥有者[ 这一项必须给出客户的姓名,三个以内是合理的。
][客户最终将接受该产品,因此必须对交付的产品满意。
如果你无法找到一个客户的姓名,那么也许你就不应该构建该产品。
]2.2 顾客是将花钱购买该产品的人[ 也给出姓名和相关的信息]2.3 其它风险承担者[其他的一些人或组织的名称,他们或者受到产品的影响,或影响产品。
]1) 经理或项目负责人;2) 业务领域专家;3) 技术人员;4) 系统开发者;5) 市场人员;6) 产品经理;7) 测试和质量保证人员;8) 审查员,诸如安全审查员或审计人员;9) 律师;10) 易用性专家;11) 你所处行业的专业人员。
3. 产品的用户3.1 产品的用户[产品的潜在用户或操作员的列表。
针对每种类型的用户,提供以下信息:]1) 用户分类2) 用户工作的任务;3) 主要相关的经验;4) 技术经验;5) 其他用户特征:包括身体、智力、工作态度、对技术的态度、教育程度、语言技能、年龄、性别等。
[用户是为了完成工作而与产品交互的人,你了解用户,就越可能提交适合用户工作方式的产品。
]3.2 对用户设的优先级[ 在每类用户后面附上一个优先级,这区别了用户的重要性和优先地位:]1) 关键用户:对产品的后续成功至关重要;2) 次要用户:他们使用产品,但对产品的长期成功并无影响;3) 不重要的用户:不常用、未授权和没有技能的用户。

1引言 (2)1.1编写目的 (2)1.2背景 (2)1.3定义 (2)1.4参考资料 (2)2任务概述 (3)2.1目标 (3)2.2用户的特点 (3)2.3假定和约束 (3)3需求规定 (3)3.1对功能的规定 (3)3.2对性能的规定 (5)3.2.1精度 (5)3.2.2时间特性要求 (5)3.2.3灵活性 (5)3.3输人输出要求 (5)3.4数据管理能力要求 (6)3.5故障处理要求 (6)3.6其他专门要求 (6)4运行环境规定 (6)4.1设备 (6)4.2支持软件 (6)4.3接口 (7)4.4控制 (7)5 其他需求 (7)XXXX软件需求说明书1引言1.1编写目的说明编写这份软件需求说明书的目的,指出预期的读者。
1.2背景说明:a.待开发的软件系统的名称;b.本项目的任务提出者、开发者、用户及实现该软件的计算中心或计算机网络;c.该软件系统同其他系统或其他机构的基本的相互来往关系。
1.3定义列出本文件中用到的专门术语的定义和外文首字母组词的原词组。
1.4参考资料列出用得着的参考资料,如:a.本项目的经核准的计划任务书或合同、上级机关的批文;b.属于本项目的其他已发表的文件;c.本文件中各处引用的文件、资料、包括所要用到的软件开发标准。
列出这些文件资料的标题、文件编号、发表日期和出版单位,说明能够得到这些文件资料的来源。
2任务概述2.1目标叙述该项软件开发的意图、应用目标、作用范围以及其他应向读者说明的有关该软件开发的背景材料。
解释被开发软件与其他有关软件之间的关系。
如果本软件产品是一项独立的软件,而且全部内容自含,则说明这一点。
如果所定义的产品是一个更大的系统的一个组成部分,则应说明本产品与该系统中其他各组成部分之间的关系,为此可使用一张方框图来说明该系统的组成和本产品同其他各部分的联系和接口。
|2.2用户的特点列出本软件的最终用户的特点,充分说明操作人员、维护人员的教育水平和技术专长,以及本软件的预期使甩频度。
软件系统系统需求规格说明书模板附件三系统需求规格说明书版本历史1.引⾔1.1.⽬的例如:规定系统的边界和⽬标,描述系统的功能性需求和⾮功能性需求。
1.2.读者对象及阅读建议说明:指明本⽂档⾯向的读者群,及相应的阅读意见。
1.3.⽂档范围【可选】说明:对本⽂的范围做阐述,本⽂档改动时,受到影响的范围,例如,本⽂引⽤到的⽤例模型,系统原型,系统测试⽤例等⽂档。
1.4.参考⽂档说明:列出本⽂档的所有参考⽂献(可以是⾮正式出版物),包括计划任务书、合同、批⽂、引⽤到的⽂件、资料及软件开发标准等。
1.5.术语与缩写解释说明:列出本⽂件中⽤到的专门术语的定义和缩写词的原词组,并给予解释,以便于所有读者达成共识。
2.综合描述2.1.系统背景【可选】说明:介绍系统的预期效果、历史原因。
2.2.问题说明【可选】提供⼀段说明,总结此项⽬需要解决的问题。
可以采⽤以下格式:2.3.系统范围说明:阐述本项⽬“适⽤的业务领域”和“不适⽤的业务领域”,本产品“应当包含的内容”和“不包含的内容”。
说清楚系统范围的好处是:(1)有助于判断什么是需求,什么不是需求;(2)可以将开发精⼒集中在产品范围之内;(3)有助于控制需求的变更。
●完整⽽准确的定义本产品的⼲系⼈;●明确本产品所影响到的部门和业务;⽤图表或者⽂字描述产品的范围,概要的定义产品的功能。
2.4.⼲系⼈与⽤户说明【可选】2.4.1.⽤户环境【可选】详细说明⽬标⽤户的⼯作环境。
以下是⼏项建议:该任务由多少⼈来完成?是否总在变化?⼀个任务周期需要多长时间?执⾏每项活动要⽤多长时间?是否总在变化?是否有特殊的环境约束:移动、户外、乘机旅⾏等?⽬前使⽤的是哪些系统平台?以后会使⽤哪些平台?还在使⽤哪些应⽤程序?您的应⽤程序是否需要和这些应⽤程序集成?在此处可以从业务模型中摘录⼀些内容来概述所涉及的任务和⾓⾊等等。
2.4.2.⼲系⼈简档【可选】通过在下表中填写各⼲系⼈的相关信息来说明系统中的各个⼲系⼈,详尽的简档应包括各种⼲系⼈在以下⽅⾯的信息:2.4.3.关键的⼲系⼈/⽤户需要列出⼲系⼈认为现有解决⽅案存在的关键问题。
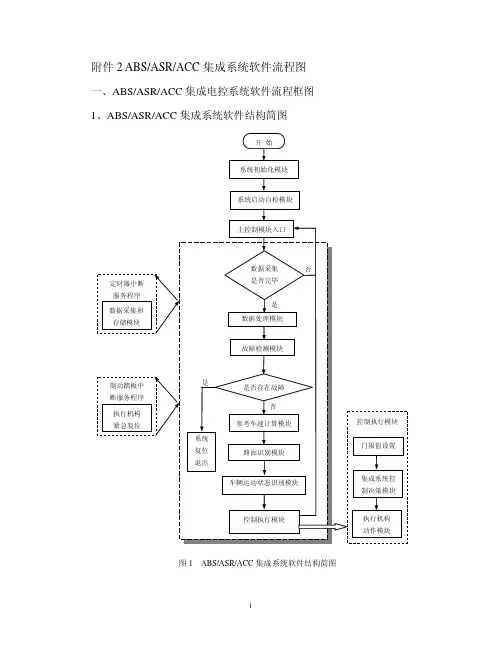
附件2 ABS/ASR/ACC集成系统软件流程图一、ABS/ASR/ACC集成电控系统软件流程框图1、ABS/ASR/ACC集成系统软件结构简图图1 ABS/ASR/ACC集成系统软件结构简图2、集成系统初始化Init.h图2 集成系统初始化程序框图3、系统启动自检模块图3 系统自检和故障诊断程序框图4、轮速数据处理模块框图图4 轮速数据处理程序流程图5、故障诊断模块框图图5 故障诊断程序框图6、参考车速确定模块框图图6 参考车速确定框图图7 工作模式识别程序框图集成系统按照左前、右前、左后、右后车轮的顺序调用ABS单轮独立控制模块。
图8 单轮独立ABS控制模块程序流程图s1为滑移率下门限值;s2为滑移率上门限值;a1为减速度下门限值;a2为减速度上门限值;慢减压指令指减压与保压指令以短暂周期交替四次,慢增压指令指增压与保压指令以短暂周期交替四次。
由于车辆的实际行驶工况复杂、多变,为了提高控制效果,结合ASR控制系统的特点,将ASR分为若干控制模式,在不同的模式下采用不同的控制方法,表9-1为ASR控制模式划分,其中参考车速15km/h为第一门限值,参考车速45km/h为第一门限值。
9.1 ASR模式选择程序图9-1 ASR模式选择程序框图设置了dkg1两侧车轮都滑转计数器,dkg2只有右侧车轮滑转计数器,dkg3为只有左侧车轮滑转计数器,dkg4为两侧车轮都不滑转计数器。
dkgt1_1、dkgt2_1、dkg3_1和dkg4_1为各自的门限值。
利用各门限值,可进行ASR控制过程中的路面识别。
9.2 ASR工作模式81控制逻辑框图以工作模式81为例说明ASR控制过程。
表9-1 ASR系统控制模式变量数值说明模式名称10 车速高于第一门限小于第二门限,车辆在单一附着系数路面上加速。
MODE1021 车速高于第一门限小于第二门限,车辆在对开路面上加速,左侧车轮处于低附着系数路面MODE2122 车速高于第一门限小于第二门限,车辆在对开路面上加速,右侧车轮处于低附着系数路面MODE2270 车速低于第一门限,车辆在单一附着系数路面上加速MODE7081 车速低于第一门限,车辆在对开路面上加速,左侧车轮处于低附着系数路面MODE81ConMode82 车速低于第一门限,车辆在对开路面上加速,右侧车轮处于低附着系数路面MODE82图9-2 ASR模式81程序框图10、压力执行机构动作模块流程图集成系统液压系统原理图见论文正文图2,集成系统按照左前、右前、左后、右后的顺序调用压力执行机构动作。

软件需求规格说明(SRS) ................................................................................ 错误!未定义书签。
1范围 .. (3)1.1标识 (3)1.2系统概述 (3)1.3文档概述 (3)1.4基线 (3)2引用文件 (3)3需求 (3)3.1所需的状态和方式 (4)3.2需求概述 (4)3.2.1目标 (4)3.2.2运行环境 (4)3.2.3用户的特点 (4)3.2.4关键点 (4)3.2.5约束条件 (4)3.3需求规格 (5)3.3.1软件系统总体功能/对象结构 (5)3.3.2软件子系统功能/对象结构 (5)3.3.3描述约定 (5)3.4CSCI能力需求 (5)3.5CSCI外部接口需求 (6)3.5.1接口标识和接口图 (6)3.6CSCI内部接口需求 (7)3.7CSCI内部数据需求 (8)3.8适应性需求 (8)3.9保密性需求 (8)3.10保密性和私密性需求 (8)3.11CSCI环境需求 (8)3.12计算机资源需求 (8)3.12.1计算机硬件需求 (8)3.12.2计算机硬件资源利用需求 (9)3.12.3计算机软件需求 (9)3.12.4计算机通信需求 (9)3.13软件质量因素 (9)3.14设计和实现的约束 (9)3.15数据 (9)3.16操作 (10)3.17故障处理 (10)3.18算法说明 (10)3.19有关人员需求 (10)3.20有关培训需求 (10)3.21有关后勤需求 (10)3.22其他需求 (10)3.23包装需求 (11)3.24需求的优先次序和关键程度 (11)4合格性规定 (11)5需求可追踪性 (11)6尚未解决的问题 (12)7注解 (12)附录 (12)1范围1.1标识本条应包含本文档适用的系统和软件的完整标识,(若适用)包括标识号、标题、缩略词语、版本号和发行号。

软件架构需求文档AASRs产品/系统名称修改历史记录目录1.引言 (1)1.1目的 (1)1.2围 (2)1.3定义、缩写和缩略语 (2)1.4引用文件 (3)1.5概述 (3)2.商业目标 (3)3.功能需求 (4)3.1用例一名称 (4)3.2例子:查询 (5)3.3例子:客户身份验证 (5)3.4例子:提款 (6)3.5例子:转账 (7)4.质量需求 (8)4.1可用性(A VAILABILITY) (8)4.2可靠性(R ELIABILITY) (8)4.3性能(P ERFORMANCE) (10)4.4安全性(S ECURITY) (11)4.5可修改性(M ODIFIABILITY) (11)4.6可移植性(P ORTABILITY) (11)4.7可测试性(T ESTABILITY) (11)4.8可维护性(M AINTAINABILITY) (12)4.9互操作性(I NTEROPERABILITY) (12)4.10可复用性(R EUSABILITY) (12)4.11可伸缩性(S CALABILITY) (12)4.12可变化性(V ARIABILITY) (12)4.13可分解性(S UBSETABILITY) (12)4.14概念完整性(C ONCEPTUAL INTEGRITY) (12)4.15可集成性(I NTEGRATION) (12)4.16可管理性(M ANAGEABILITY) (13)4.17可支持性(S UPPORTABILITY) (13)4.18用户体验/易用性(U SER E XPERIENCE) (13)5.其他需求 (13)5.1技术环境需求 (13)5.2系统集成需求 (13)5.3文化与政治需求 (13)6.设计约束 (14)7.附录 (14)1.引言1.1目的Architecturally significant requirements(ASRs) are those requirements that play an important role in determining the architecture of the system. Such requirements require special attention. Not all requirements have equal significance with regards to the architecture.Architecturally significant requirements are a subset of the requirements that need to be satisfied before the architecture can be considered "stable". Typically, these are requirements that are technically challenging, technically constraining, or central to the system's purpose. Furthermore, the system will generally be more sensitive to changes against architecturally significant requirements, so identifying and communicating this subset will help others understand the potential implications of change.Requirements can be explicitly or implicitly architecturally significant. Explicitly significant requirements are often overtly technical in nature, such as performance targets; the need to interface to other systems; the number of users that must be supported; or security requirements. Implicitly significant requirements may define the essence of the functional behaviour of the system (for example, making a purchase from an on-line store).Deciding whether a specific requirement is architecturally significant is often a matter of judgment. The selection of requirements that are considered "architecturally significant" is driven by several key driving factors:The benefit of the requirement to stakeholders: critical, important, or useful.The architectural impact of the requirement: none, extends, or modifies. There may be critical requirements that have little or no impact on the architecture and low-benefit requirements that have a big impact. Low-benefit requirements with big architectural impacts should be reviewed by the project manager for possible removal from the scope of the project.The risks to be mitigated: performance, availability of a product, and suitability of a component.The completion of the coverage of the architecture.Other tactical objectives or constraints, such as demonstration to the user, and so on.There may be two requirements that hit the same components and address similar risks. If you implement A first, then B is not architecturally significant. If you implement B first, then A is not architecturally significant. Thus these attributes can depend on the order the requirements are realized, and should be re-evaluated when the order changes, as well as when the requirements themselves change.The following are good examples of Architecturally Significant Requirements:The system must record every modification to customer records for audit purposes.The system must respond within 5 seconds.The system must deploy on Microsoft Windows XP and Linux.The system must encrypt all network traffic.The ATM system must dispense cash on demand to validated account holders with sufficient cleared funds.Architecturally significant requirements also describe key behaviors that the system needs to perform. Such scenarios represent the important interactions between key abstractions.and should be identified as architecturally significant requirements. For example, for an on-line book store describing the way the software handles the scenarios for ordering a book and checking out the shopping cart are often enough to communicate the essence of the architecture.[描述ASRs的目的;说明ASRs的预期读者。

X X X X项目软件需求规格说明书XXXXXXX科技有限公司20XX年XX月目录第一章引言 (5)1编写目的 (5)2软件需求分析理论 (5)3软件需求分析目标 (5)4参考文献 (6)第二章需求概述 (6)1.项目背景 (6)2.需求概述 (7)3.条件与限制(可选) (7)4.移动办公系统结构 (8)5.移动办公网络拓扑图 (9)第三章系统功能需求 (9)1.移动办公系统升级改造需求 (9)✓界面显示要求 (11)✓待办公文列表 (11)✓待办公文列表排序 (11)✓公文详细信息界面元素 (11)✓网站信息审批 (11)✓会议申请 (11)✓意见录入 (12)✓移动邮件 (12)✓会议管理 (12)✓通知通告 (13)✓通讯录管理 (13)2.车辆管理模块升级改造需求 (13)✓系统功能架构 (14)✓网络拓扑结构 (15)3.电子公文预览需求 (15)✓电子公文交换网络 (16)✓电子公文交换流程 (17)4.政务信息管理系统平台功能需求 (18)第四章软硬件或其他外部系统接口需求 (20)1.用户界面 (20)2.硬件需求 (21)3.网络需求 (21)4.接口需求 (22)5.通信需求 (22)6.运行环境 (23)第五章其他非功能需求 (23)1.性能需求 (23)2.安全设施需求 (24)3.安全性需求 (24)4.扩展性需求 (25)5.可移植性需求 (25)第一章引言1编写目的为明确软件需求、安排项目规划与进度、组织软件开发与测试,撰写本文档。
2软件需求分析理论软件需求分析(Software Reguirement Analysis)是研究用户需求得到的东西,完全理解用户对软件需求的完整功能,确认用户软件功能需求,建立可确认的、可验证的一个基本依据。
软件需求分析是一个项目的开端,也是项目实施最重要的关键点。
据有关的机构分析结果表明,设计的软件产品存在不完整性、不正确性等问题80%以上是需求分析错误所导致的,而且由于需求分析错误造成根本性的功能问题尤为突出。

Marvel Electronics and Home Entertainment实用文档E-Store ProjectSoftware Requirements SpecificationVersion <4.0>Table of Contents1.Introduction 51.1Purpose 51.2Scope 51.3Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations 61.4References 61.5Overview 62.Overall Description 63.Specific Requirements 63.1Functionality 73.1.1Sell Configured to Ordered Products. 73.1.2Provide comprehensive product details. 73.1.3Detailed product Categorizations 73.1.4Provide Search facility. 73.1.5Maintain customer profile. 83.1.6Provide personalized profile 83.1.7Provide Customer Support. 83.1.8Email confirmation. 93.1.9Detailed invoice for customer. 93.1.10Provide shopping cart facility. 93.1.11Provide multiple shipping methods. 93.1.12Online tracking of shipments 93.1.13Provide online Tax Calculations 103.1.14Allow multiple payment methods. 93.1.15Allow online change or cancellation of order. 103.1.16Allow Online Product reviews and ratings 103.1.17Offer financing options. 103.1.18Provide detailed sitemap. 103.1.19Offer online promotions and rewards. 113.1.20Online Purchase of products. 103.2Usability 113.2.1Graphical User Interface 113.2.2Accessibility 113.3Reliability & Availability 113.3.1Back-end Internal Computers 113.3.2Internet Service Provider 113.4Performance 123.5Security 123.5.1Data Transfer 123.5.2Data Storage 123.6Supportability 133.6.1Configuration Management Tool 133.7Design Constraints 133.7.1Standard Development Tools 133.7.2Web Based Product 133.8On-line User Documentation and Help System Requirements 133.9Purchased Components 133.10Interfaces 143.10.1User Interfaces 143.10.2Hardware Interfaces 143.10.3Software Interfaces 143.10.4Communications Interfaces 153.11Licensing Requirements 153.12Legal, Copyright, and Other Notices 153.13Applicable Standards 154.Supporting Information 15Software Requirements Specification1. IntroductionThe introduction of the Software Requirements Specification (SRS) provides an overview of the entire SRS with purpose, scope, definitions, acronyms, abbreviations, references and overview of the SRS. The aim of this document is to gather and analyze and give an in-depth insight of the complete Marvel Electronics and Home Entertainment software system by defining the problem statement in detail. Nevertheless, it also concentrates on the capabilities required by stakeholders and their needs while defining high-level product features. The detailed requirements of the Marvel Electronics and Home Entertainment are provided in this document.1.1 PurposeThe purpose of the document is to collect and analyze all assorted ideas that have come up to define the system, its requirements with respect to consumers. Also, we shall predict and sort out how we hope this product will be used in order to gain a better understanding of the project, outline concepts that may be developed later, and document ideas that are being considered, but may be discarded as the product develops.In short, the purpose of this SRS document is to provide a detailed overview of our software product, its parameters and goals. This document describes the project's target audience and its user interface, hardware and software requirements. It defines how our client, team and audience see the product and its functionality. Nonetheless, it helps any designer and developer to assist in software delivery lifecycle (SDLC) processes.1.2 ScopePrimarily, the scope pertains to the E-Store product features for making Marvel Electronics and Home Entertainment project live. It focuses on the company, the stakeholders and applications, which allow for online sales, distribution and marketing of electronics.This SRS is also aimed at specifying requirements of software to be developed but it can also be applied to assist in the selection of in-house and commercial software products. The standard can be used to create software requirements specifications directly or can be used as a model for defining a organization or project specific standard. It does not identify any specific method, nomenclature or tool for preparing an SRS.1.3 Definitions, Acronyms, and Abbreviations1.4 ReferencesThe references are:✓E-Store Structural Model✓E-Store Behavioral Model✓E-Store NFR Model✓Vision Draft 51.5 OverviewThe remaining sections of this document provide a general description, including characteristics of the users of this project, the product's hardware, and the functional and data requirements of the product. General description of the project is discussed in section 2 of thisdocument. Section 3 gives the functional requirements, data requirements and constraints and assumptions made while designing the E-Store. It also gives the user viewpoint ofproduct. Section 3 also gives the specific requirements of the product. Section 3 also discusses the external interface requirements and gives detailed description of functional requirements. Section 4 is for supporting information.2. Overall DescriptionThis document contains the problem statement that the current system is facing which is hampering the growth opportunities of the company. It further contains a list of the stakeholders and users of the proposed solution. It also illustrates the needs and wants of the stakeholders that were identified in the brainstorming exercise as part of the requirements workshop. It further lists and briefly describes the major features and a brief description of each of the proposed system. The following SRS contains the detail product perspective from different stakeholders. It provides the detail product functions of E-Store with user characteristics permitted constraints, assumptions and dependencies and requirements subsets.3. Specific RequirementsThe specific requirements are –3.1 FunctionalityIntroduction –This subsection contains the requirements for the e-store. These requirements are organized by the features discussed in the vision document. Features from vision documents are then refined into use case diagrams and to sequence diagram to best capture the functional requirements of the system. All these functional requirements can be traced using tractability matrix.3.1.1 Sell Configured to Ordered Products.3.1.1.1The system shall display all the products that can be configured.3.1.1.2The system shall allow user to select the product to configure.3.1.1.3The system shall display all the available components of the product to configure3.1.1.4The system shall enable user to add one or more component to the configuration.3.1.1.5The system shall notify the user about any conflict in the current configuration.3.1.1.6The system shall allow user to update the configuration to resolve conflict in the current configuration.3.1.1.7The system shall allow user to confirm the completion of current configuration3.1.2 Provide comprehensive product details.3.1.2.1The system shall display detailed information of the selected products.3.1.2.2The system shall provide browsing options to see product details.3.1.3 Detailed product CategorizationsThe system shall display detailed product categorization to the user.3.1.4 Provide Search facility.The system shall enable user to enter the search text on the screen.The system shall enable user to select multiple options on the screen to search.The system shall display all the matching products based on the searchThe system shall display only 10 matching result on the current screen.The system shall enable user to navigate between the search results.The system shall notify the user when no matching product is found on the search.3.1.5 Maintain customer profile.The system shall allow user to create profile and set his credential.The system shall authenticate user credentials to view the profile.The system shall allow user to update the profile information.3.1.6 Provide personalized profile.The system shall display both the active and completed order history in the customer profile. The system shall allow user to select the order from the order history.The system shall display the detailed information about the selected order.The system shall display the most frequently searched items by the user in the profile.The system shall allow user to register for newsletters and surveys in the profile.3.1.7 Provide Customer Support.The system shall provide online help, FAQ’s customer support, and sitemap options for customer support.The system shall allow user to select the support type he wants.The system shall allow user to enter the customer and product information for the support.The system shall display the customer support contact numbers on the screen.The system shall allow user to enter the contact number for support personnel to call.The system shall display the online help upon request.The system shall display the FAQ’s upon request.3.1.8 Email confirmation.The system shall maintain customer email information as a required part of customer profile. The system shall send an order confirmation to the user through email.3.1.9 Detailed invoice for customer.The system shall display detailed invoice for current order once it is confirmed.The system shall optionally allow user to print the invoice.3.1.10 Provide shopping cart facility.The system shall provide shopping cart during online purchase.The system shall allow user to add/remove products in the shopping cart.3.1.11 Provide multiple shipping methods.The system shall display different shipping options provided by shipping department.The system shall enable user to select the shipping method during payment process.The system shall display the shipping charges.The system shall display tentative duration for shipping.3.1.12 Online tracking of shipmentsThe system shall allow user to enter the order information for tracking.The system shall display the current tracking information about the order.3.1.13 Provide online Tax CalculationsThe system shall calculate tax for the order.The system shall display tax information for the order.3.1.14 Allow multiple payment methods..The system shall display available payment methods for payment.The system shall allow user to select the payment method for order.3.1.15 Allow online change or cancellation of order.The system shall display the orders that are eligible to change.The system shall allow user to select the order to be changed.The system shall allow user to cancel the orderThe system shall allow user to change shipping, payment method.The system shall notify the user about any changes made to the order.3.1.16 Allow Online Product reviews and ratingsThe system shall display the reviews and ratings of each product, when it is selected. The system shall enable the user to enter their reviews and ratings.3.1.17 Offer financing options.The system shall display all the available financing options.The system shall allow user to select the financing option.The system shall notify the use about the financing request.3.1.18 Provide detailed sitemap.The system shall allow user to view detailed sitemap.3.1.19 Offer online promotions and rewards.The system shall display all the available promotions to the user.The system shall allow user to select available promotion.3.1.20 Online Purchase of products.The system shall allow user to confirm the purchase.The system shall enable user to enter the payment information.3.2 Usability3.2.1 Graphical User InterfaceThe system shall provide a uniform look and feel between all the web pages.The system shall provide a digital image for each product in the product catalog.The system shall provide use of icons and toolbars.3.2.2 AccessibilityThe system shall provide handicap access.The system shall provide multi language support.3.3 Reliability & Availability3.3.1 Back-end Internal ComputersThe system shall provide storage of all databases on redundant computers with automatic switchover.The system shall provide for replication of databases to off-site storage locations.The system shall provide RAID V Disk Stripping on all database storage disks.3.3.2 Internet Service ProviderThe system shall provide a contractual agreement with an internet service provider for T3 access with 99.9999% availability.The system shall provide a contractual agreement with an internet service provider who can provide 99.999% availability through their network facilities onto the internet.3.4 PerformanceThe product shall be based on web and has to be run from a web server.The product shall take initial load time depending on internet connection strength which also depends on the media from which the product is run.The performance shall depend upon hardware components of the client/customer.3.5 Security3.5.1 Data TransferThe system shall use secure sockets in all transactions that include any confidential customer information.The system shall automatically log out all customers after a period of inactivity.The system shall confirm all transactions with the customer’s web browser.The system shall not leave any cookies on the customer’s computer containing the user’s password.The system shall not leave any cookies on the customer’s computer containing any of the user’s confidential information.3.5.2 Data StorageThe customer’s web browser shall never display a customer’s password. It shall always be echoed with special characters representing typed characters.The customer’s web browser shall never display a customer’s credit card number after retrieving from the database. It shall always be shown with just the last 4 digits of the credit card number.The system’s back-end servers shall never display a customer’s password. The customer’s password may be reset but never shown.The system’s back-end servers shall only be accessible to authenticated administrators.The system’s back-end databases shall be encrypted.3.6 Supportability3.6.1 Configuration Management ToolThe source code developed for this system shall be maintained in configuration management tool.3.7 Design Constraints3.7.1 Standard Development ToolsConfidential <Company Name>, 2023 Page 12The system shall be built using a standard web page development tool that conforms to either IBM’s CUA standards or Microsoft’s GUI standards.3.7.2 Web Based ProductThere are no memory requirementsThe computers must be equipped with web browsers such as Internet explorer.The product must be stored in such a way that allows the client easy access to it.Response time for loading the product should take no longer than five minutes.A general knowledge of basic computer skills is required to use the product3.8 On-line User Documentation and Help System RequirementsAs the product is E-store, On-line help system becomes a critical component of thesystem which shall provide –It shall provide specific guidelines to a user for using the E-Store system and within the system.To implement online user help, link and search fields shall be provided.3.9 Purchased ComponentsNot Applicable3.10 InterfacesThere are many types of interfaces as such supported by the E-Store software system namely; User Interface, Software Interface and Hardware Interface.The protocol used shall be HTTP.The Port number used will be 80.There shall be logical address of the system in IPv4 format.3.10.1 User InterfacesThe user interface for the software shall be compatible to any browser such as Internet Explorer, Mozilla or Netscape Navigator by which user can access to the system.The user interface shall be implemented using any tool or software package like JavaApplet, MS Front Page, EJB etc.3.10.2 Hardware InterfacesSince the application must run over the internet, all the hardware shall require to connect internet will be hardware interface for the system. As for e.g. Modem, WAN – LAN,Ethernet Cross-Cable.3.10.3 Software Interfaces1.The e-store system shall communicate with the Configurator to identify all theavailable components to configure the product.2.The e-store shall communicate with the content manager to get the productspecifications, offerings and promotions.3.The e-store system shall communicate with billPay system to identify availablepayment methods , validate the payments and process payment.4.The e-store system shall communicate to credit management system for handlingfinancing options.5.The e-store system shall communicate with CRM system to provide support.6.The e-store system shall communicate with Sales system for order management.7.The e-store system shall communicate with shipping system for tracking orders andupdating of shipping methods.8.The e-store system shall communicate with external Tax system to calculate tax.9.The e-store system shall communicate with export regulation system to validateexport regulations.10. The system shall be verisign like software which shall allow the users to completesecured transaction. This usually shall be the third party software system which is widely used for internet transaction.3.10.4 Communications InterfacesThe e-store system shall use the HTTP protocol for communication over the internet and for the intranet communication will be through TCP/IP protocol suite.3.11 Licensing RequirementsNot Applicable3.12 Legal, Copyright, and Other NoticesE-store should display the disclaimers, copyright, word mark, trademark and product Confidential <Company Name>, 2023 Page 14warranties of the Marvel electronics and home entertainment.3.13 Applicable StandardsIt shall be as per the industry standard.4. Supporting InformationPlease refer the following document:1.Vision document for E-store.e case analysis.3.Structural models.4.Behavioral models.5.Non functional requirements model.6.Traceability Matrix.7.Project Plan。

软件架构需求文档AASRs产品/系统名称修改历史记录目录1.引言 (1)1.1目的 (1)1.2范围 (2)1.3定义、缩写和缩略语 (2)1.4引用文件 (2)1.5概述 (3)2.商业目标 (3)3.功能需求 (4)3.1用例一名称 (4)3.2例子:查询 (4)3.3例子:客户身份验证 (5)3.4例子:提款 (6)3.5例子:转账 (7)4.质量需求 (8)4.1可用性(A VAILABILITY) (8)4.2可靠性(R ELIABILITY) (8)4.3性能(P ERFORMANCE) (9)4.4安全性(S ECURITY) (10)4.5可修改性(M ODIFIABILITY) (10)4.6可移植性(P ORTABILITY) (10)4.7可测试性(T ESTABILITY) (10)4.8可维护性(M AINTAINABILITY) (11)4.9互操作性(I NTEROPERABILITY) (11)4.10可复用性(R EUSABILITY) (11)4.11可伸缩性(S CALABILITY) (11)4.12可变化性(V ARIABILITY) (11)4.13可分解性(S UBSETABILITY) (11)4.14概念完整性(C ONCEPTUAL INTEGRITY) (11)4.15可集成性(I NTEGRATION) (11)4.16可管理性(M ANAGEABILITY) (12)4.17可支持性(S UPPORTABILITY) (12)4.18用户体验/易用性(U SER E XPERIENCE) (12)5.其他需求 (12)5.1技术环境需求 (12)5.2系统集成需求 (12)5.3文化与政治需求 (12)6.设计约束 (13)7.附录 (13)1.引言1.1目的Architecturally significant requirements(ASRs) are those requirements that play an important role in determining the architecture of the system. Such requirements require special attention. Not all requirements have equal significance with regards to the architecture.Architecturally significant requirements are a subset of the requirements that need to be satisfied before the architecture can be considered "stable". Typically, these are requirements that are technically challenging, technically constraining, or central to the system's purpose. Furthermore, the system will generally be more sensitive to changes against architecturally significant requirements, so identifying and communicating this subset will help others understand the potential implications of change.Requirements can be explicitly or implicitly architecturally significant. Explicitly significant requirements are often overtly technical in nature, such as performance targets; the need to interface to other systems; the number of users that must be supported; or security requirements. Implicitly significant requirements may define the essence of the functional behaviour of the system (for example, making a purchase from an on-line store).Deciding whether a specific requirement is architecturally significant is often a matter of judgment. The selection of requirements that are considered "architecturally significant" is driven by several key driving factors:The benefit of the requirement to stakeholders: critical, important, or useful.The architectural impact of the requirement: none, extends, or modifies. There may be critical requirements that have little or no impact on the architecture and low-benefit requirements that have a big impact. Low-benefit requirements with big architectural impacts should be reviewed by the project manager for possible removal from the scope of the project.The risks to be mitigated: performance, availability of a product, and suitability of a component.The completion of the coverage of the architecture.Other tactical objectives or constraints, such as demonstration to the user, and so on.There may be two requirements that hit the same components and address similar risks. If you implement A first, then B is not architecturally significant. If you implement B first, then A is not architecturally significant. Thus these attributes can depend on the order the requirements are realized, and should be re-evaluated when the order changes, as well as when the requirements themselves change.The following are good examples of Architecturally Significant Requirements:The system must record every modification to customer records for audit purposes.The system must respond within 5 seconds.The system must deploy on Microsoft Windows XP and Linux.The system must encrypt all network traffic.The ATM system must dispense cash on demand to validated account holders with sufficient cleared funds.Architecturally significant requirements also describe key behaviors that the system needs to perform. Such scenarios represent the important interactions between key abstractions.and should be identified as architecturally significant requirements. For example, for an on-line book store describing the way the software handles the scenarios for ordering a book and checking out the shopping cart are often enough to communicate the essence of the architecture.[描述ASRs的目的;说明ASRs的预期读者。
SAAS平台项目需求规格说明书版本历史目录第一章、概述 ................................................................ - 1 -1.1总体要求. (1)1.2文档编写约定 (1)1.3系统介绍 (2)1.4系统用户 (2)1.5任务描述 (3)1.6系统运行环境 (3)1.6.1系统拓扑结构图..................................................... - 3 -1.6.2硬件环境要求....................................................... - 3 -1.6.3软件环境要求....................................................... - 3 -1.7系统总体设计要求.. (4)1.7.1结构设计要求....................................................... - 4 -1.7.1.1相关要求和标准................................................... - 4 -1.7.1.2外观、组装及包装设计要求......................................... - 4 -1.7.2硬件设计要求....................................................... - 4 -1.7.2.1相关要求和标准................................................... - 4 -1.7.2.2硬件设计总体要求................................................. - 4 -1.7.3软件设计要求....................................................... - 4 -1.7.3.1相关要求和标准................................................... - 4 -1.7.3.2软件总体设计要求................................................. - 5 -1.7.4其他设计要求....................................................... - 5 -1.8词汇表 (5)1.9参考资料 (5)第二章、功能性需求........................................................... - 6 -2.1需求一览表.. (6)2.1.1系统管理........................................................... - 6 -2.1.1.1系统管理需求一览表............................................... - 6 -2.1.2应用管理........................................................... - 7 -2.1.2.1系统管理需求一览表............................................... - 7 -2.1.3客服社区........................................................... - 8 -2.1.3.1系统管理需求一览表............................................... - 8 -2.1.4用户管理.......................................................... - 10 -2.1.4.1系统管理需求一览表.............................................. - 10 -2.1.5信息发布.......................................................... - 11 -2.1.5.1系统管理需求一览表.............................................. - 11 -2.1.6运维管理.......................................................... - 12 -2.1.6.1系统管理需求一览表.............................................. - 12 -2.1.7在线调查.......................................................... - 13 -2.1.7.1在线调查需求一览表.............................................. - 13 -2.1.8客服系统.......................................................... - 14 -2.1.8.1系统管理需求一览表.............................................. - 14 -2.2系统管理 (14)2.2.1系统管理.......................................................... - 14 -2.2.1.1数据源配置...................................................... - 14 -2.2.1.2帐套建立........................................................ - 16 -2.2.2应用注册.......................................................... - 18 -2.2.2.1应用注册........................................................ - 18 -2.2.2.2功能注册........................................................ - 20 -2.2.2.3应用与帐套关联.................................................. - 22 -2.2.3权限管理.......................................................... - 24 -2.2.3.1操作员管理...................................................... - 24 -2.2.3.2修改密码........................................................ - 27 -2.2.3.3用户登录........................................................ - 28 -2.2.3.4用户组管理...................................................... - 30 -2.2.3.5操作员与用户组关联.............................................. - 32 -2.2.3.6权限分配........................................................ - 34 -2.3应用管理 (36)2.3.1应用管理.......................................................... - 36 -2.3.1.2应用类型和应用关联.............................................. - 38 -2.3.2计费管理.......................................................... - 41 -2.3.2.1服务项目........................................................ - 41 -2.3.2.2计费类型定义.................................................... - 42 -2.3.2.3应用标准计价表.................................................. - 44 -2.3.3积分规则.......................................................... - 47 -2.3.3.1积分规则........................................................ - 47 -2.3.4应用组合.......................................................... - 51 -2.3.4.1应用组合定义.................................................... - 51 -2.3.4.2组合应用........................................................ - 53 -2.3.4.3分配应用功能.................................................... - 56 -2.3.4.4应用组合定价.................................................... - 58 -2.4用户管理 (61)2.4.1用户注册.......................................................... - 61 -2.4.1.1用户注册........................................................ - 61 -2.4.1.2操作员注册...................................................... - 64 -2.4.1.3修改密码........................................................ - 66 -2.4.1.4用户登录........................................................ - 68 -2.4.1.5用户组管理...................................................... - 70 -2.4.1.6操作员与用户组关联.............................................. - 71 -2.4.1.7权限分配........................................................ - 74 -2.4.2用户服务.......................................................... - 76 -2.4.2.1积分查询........................................................ - 76 -2.4.2.2应用申请........................................................ - 77 -2.4.2.3服务申请........................................................ - 81 -2.4.2.4试用延期申请.................................................... - 83 -2.5在线调查 (86)2.5.1创建问卷.......................................................... - 86 -2.5.1.1创建问卷........................................................ - 86 -2.5.1.3添加题目选项.................................................... - 91 -2.5.2发布问卷.......................................................... - 93 -2.5.2.1发布问卷........................................................ - 93 -2.5.2.2发布问卷回收.................................................... - 95 -2.5.3问卷分析.......................................................... - 96 -2.5.3.1问卷分析........................................................ - 96 -2.5.3.2问卷明细查看.................................................... - 98 -2.6运维管理 (99)2.6.1运维管理.......................................................... - 99 -2.6.1.1收款管理........................................................ - 99 -2.6.1.2积分兑换管理................................................... - 104 -2.6.1.3服务申请审批................................................... - 107 -2.6.1.4应用申请审批................................................... - 110 -2.6.1.5试用延期申请审批............................................... - 112 -2.6.2开通管理......................................................... - 115 -2.6.2.1应用试用期限定义............................................... - 115 -2.6.2.2试用延期开通................................................... - 117 -2.6.2.3应用开通....................................................... - 119 -2.6.3运维服务......................................................... - 121 -2.6.3.1操作日志....................................................... - 121 -2.6.3.2系统日志....................................................... - 124 -2.6.3.3数据导出....................................................... - 126 -2.6.3.4数据导入....................................................... - 128 -2.6.3.5数据备份....................................................... - 129 -2.6.3.6数据恢复....................................................... - 131 -2.7信息发布.. (133)2.7.1库表管理......................................................... - 133 -2.7.2栏目管理......................................................... - 134 -2.7.2.1栏目新建....................................................... - 135 -2.7.3模板管理......................................................... - 138 -2.7.3.1模板类别新建................................................... - 139 -2.7.3.2模板新建....................................................... - 139 -2.7.3.3模板管理....................................................... - 142 -2.7.4附件管理......................................................... - 143 -2.7.4.1附件上传....................................................... - 143 -2.7.4.2附件管理....................................................... - 144 -2.7.5内容管理......................................................... - 145 -2.7.5.1内容发布....................................................... - 145 -2.7.5.2内容审核....................................................... - 147 -2.8客服系统.. (149)2.8.1客服系统......................................................... - 149 -2.8.1.1创建问题....................................................... - 149 -2.8.1.2问题回复....................................................... - 152 -2.8.1.3问题查询....................................................... - 154 -2.9客服社区.. (156)2.9.1帖子管理......................................................... - 156 -2.9.2帖子批量管理..................................................... - 156 -2.9.3论坛设置......................................................... - 157 -2.9.4替换/限制设置.................................................... - 157 -2.9.5查看帖子......................................................... - 158 -2.9.6发布帖子......................................................... - 158 -2.9.7回复帖子......................................................... - 159 -2.9.8论坛内部邮箱和短信............................................... - 159 -第三章、性能需求........................................................... - 161 -3.1系统容量要求. (161)3.2系统响应时间要求 (161)3.3系统健壮性要求 (161)第四章、用户界面需求及界面原型............................................. - 162 -4.1用户界面设计原则要求 (162)4.2易用性、易操作性要求 (162)4.3界面原型 (162)4.3.1车辆新增......................................................... - 162 -4.3.1.1界面描述....................................................... - 162 -4.3.1.2界面元素说明................................................... - 163 -第五章、安全性需求......................................................... - 165 -5.1系统安全性需求.. (165)5.2数据安全性需求 (165)5.3权限需求 (165)第六章、需进一步落实的问题(TBD).......................................... - 166 -第一章、概述1.1总体要求(1)需求规格说明书必须完整、准确描述业务需求及其环境要求(2)需求规格说明书作为一种契约,界定了系统的范围及内容;(3)通过该说明书,即使没有软件系统,按其内容而不需其它材料的情况下,手工处理也可实现;(4)通过培训讲解,软件开发人员、系统测试人员可以依此设计或测试系统,而不需要再去了解业务(5)子系统、功能模块和功能项的划分(即2.1部分)及其相互关系(即2.2部分)必须清晰、合理(6)对于功能项,特别是关键业务功能项(即2.X)的流程、输入输出必须清楚、完备;(7)对于关键数据元素的描述(即2.3部分)必须完备、准确。
ASRS介绍自动化仓储系统Automatic Storage and Retrieval System (AS/RS system)自动化立体仓库(Automatic Storage &Retrieval System)设计步骤,一般分为以下几步:一、收集、研究用户的原始资料,明确用户所要达到的目标,这些原始资料包括:1、明确自动化立体仓库与上游、下游衔接的工艺过程;2、物流要求:上游进入仓库的最大入库员、向下游转运的最大出库量以及所要求的库容量;3、物料的规格参数:物料的品种数、物料包装形式、外包装尺寸、重量、保存方式及其它物料的其它特性;4、立体仓库的现场条件及环境要求;5、用户对仓库管理系统的功能要求;6、其它相关的资料及特殊要求。
二、确定自动化立体仓库的主要形式及相关参数所有原始资料收集完毕后,可根据这些第一手资料计算出设计时所需的相关参数,包括:①对整个库区的出入库总量要求,亦即仓库的流量要求;②货物单元的外形尺寸及其重量;③仓库储存区(货架区)的仓位数量;④结合上述三点确定储存区(货架厂)货架的排数、列数及巷道数目其它相关技术参数。
三、合理布置自动化立休仓库的总体布局及物流图一般来说,自动化立体仓库包括:入库暂存区、检验区、码垛区、储存区、出库暂存区、托盘暂存区、不合格品暂存区及杂物区等。
规划时,立体仓库内不一定要把上述的每一个区都规划进去,可根据用户的工艺特点及要求来合理划分各区域和增减区域。
同时,还要合理考虑物料的流程,使物料的流动畅通无阻,这将直接影响到自动化立体仓库的能力和效率。
四、选择机械设备类型及相关参数1、货架货架的设计是立体仓库设计的一项重要内容,它直接影响到立体仓库面积和空间的利用率。
①货架形式:货架的形式有很多,而用在自动化立体仓库的货架一般有:横梁式货架、牛腿式货架、流动式货架等。
设计时,可根据货物单元的外形尺寸、重量及其它相关因素来合理选取。
②货格的尺寸:货格的尺寸取决于货物单元与货架立柱、横梁(牛腿)之间的间隙大小,同对,在一定程度上也受到货架结构型式及其它因素的影响。
XXXXXXXXXXXX设计 ——需求分析姓名:学号:邮箱:指导教师:2010年12月22日12:31:48目录1 文档概述1.1 编写目的1.2 背景1.3 定义1.4 参考资料2 任务概述2.1 目标2.2 用户特点分析2.3 相关事实与假定3 需求概述3.1 系统概述3.2 主题域13.2.1 概述3.2.2 业务事件3.2.3 报表4 具体需求4.1主题域14.1.1 用例模型4.1.2 领域模型5 总体设计5.1 项目规划5.2 系统功能结构图5.3 流程分析5.4 实体分析1 文档概述1.1 编写目的1.2 背景1.3 定义1.4 参考资料2 任务概述2.1 目标2.2 用户特点分析2.3 相关事实与假定3 需求概述3.1 系统概述3.2 主题域13.2.1 概述3.2.2 业务事件3.2.2.1业务事件1(1)业务流程分析(2)业务实体分析(3)用例分析3.2.2.2业务事件23.2.3 报表3.2.3.1报表1(1)概述部门/职位:目的:1.2.3.(2)数据内容(3)报表项3.2.3.2 报表24 具体需求4.1主题域14.1.1 用例模型4.1.1.1 UC_B_XX(用例)(1)概述【编号、名称、概述、相关Stakeholder】(2)事件流描述【前、后置条件,基本、扩展、子事件流】(3)相关需求与功能点(4)界面原型(5)规约与约束4.1.1.2 UC_R_xx(报表)(1)概述【名称、用户部门与职位、业务意图、相关场景】(2)报表内容【领域类图、数据项】(3)输入\输出格式(4)其他4.1.1.3 UC_I_xx(接口)(1)使用者【名称、业务目的、时机、频率】(2)内容与格式【交互过程、数据包说明】(3)设计与实现约束【性能要求、协议格式要求】4.1.2 领域模型4.1.2.1 XX领域类(1)概述【类名、别名】(2)数据窗口分析【涉及主题域、业务事件、各域数据】(3)数据组成与格式(4)其他5 总体设计5.1 项目规划5.2 系统功能结构图5.3 流程分析5.4 实体分析。
项目名称软件需求规格求说明书本说明书是系统客户和开发者对将要开发的软件系统的共同理解,是后续设计和实现工作的基础。
本说明书涉及的对《新生报到管理系统》的全部定义,经客户确认后,具有约束力,由系统设计人员贯彻。
客户(签名): 邓欢欢日期: 2010年10月24 日新生报到管理系统是经管院委托计算机系08网计开发的软件,集新生、材料录入、查询、统计分析,宿舍分配等功能于一体的应用软件。
根据合同规定,通过双方讨论协商,特编写本《新生报到管理系统需求规格说明书》。
1.编写目的本需求规格说明书主要目的是明确所要开发的软件应具有的功能、性能,使系统分析人员及软件开发人员能清楚地了解用户的需求,并在此基础上进一步提取概要设计说明书和完成后继续设计与开发工作,为软件开发范围、业务处理规范提供依据,也是应用软件进行合同终验的验收依据。
系统对新生各种材料进行录入(扫描、修改、查询、统计分析)同时系统根据宿舍基本情况给新生自动分配宿舍,由于在系统分析与分配宿舍等功能,所以要求系统有相应事物处理能力。
此外,系统还涉及系统安全和用户管理问题、各种代码使用和维护问题、数据安全和数据维护问题、统计报表生成和输出等问题,因此要求系统具有系统管理和维护事物处理功能。
总而言之,要求通过系统的开发,达到系统项输出总体目标是在校园网工程的构架下,结合学院管理的实际需要,实现对新生报到的全过程进行有效管理的信息系统,提供查询分析功能和管理、决策信息,用户界面友好,满足学院管理需要的软件,提高新生管理的效率。
2.项目背景开发软件名称:新生报到管理系统项目任务提出者:江西经管院项目开发者:08网计用户:江西经管院实现软件单位:08网计3.符号、缩略语和定义:NSMS:新生报到管理系统。
B/S(Browser):浏览器服务器。
4.参考资料《新生报到管理系统可行性研究报告》,08网计编。
《新生报到管理系统开发委托合同》,江西经管院。
1.待开发的系统的一般描述学院新生报到管理系统项目是校园网工程的构架下哦,结合学院新生报到管理的实际需要,对新生信息进行有效管理的信息系统,提供丰富的查询分析功能和管理、决策信息,用户界面友好,满足新生报到管理的软件,用以提高管理效率。
软件架构需求文档AASRs产品/系统名称修改历史记录目录1.引言 (1)1.1目的 (1)1.2范围 (2)1.3定义、缩写和缩略语 (2)1.4引用文件 (2)1.5概述 (2)2.商业目标 (2)3.功能需求 (3)3.1用例一名称 (3)3.2例子:查询 (4)3.3例子:客户身份验证 (4)3.4例子:提款 (5)3.5例子:转账 (6)4.质量需求 (7)4.1可用性(A VAILABILITY) (7)4.2可靠性(R ELIABILITY) (7)4.3性能(P ERFORMANCE) (9)4.4安全性(S ECURITY) (10)4.5可修改性(M ODIFIABILITY) (10)4.6可移植性(P ORTABILITY) (10)4.7可测试性(T ESTABILITY) (10)4.8可维护性(M AINTAINABILITY) (11)4.9互操作性(I NTEROPERABILITY) (11)4.10可复用性(R EUSABILITY) (11)4.11可伸缩性(S CALABILITY) (11)4.12可变化性(V ARIABILITY) (11)4.13可分解性(S UBSETABILITY) (11)4.14概念完整性(C ONCEPTUAL INTEGRITY) (11)4.15可集成性(I NTEGRATION) (11)4.16可管理性(M ANAGEABILITY) (11)4.17可支持性(S UPPORTABILITY) (12)4.18用户体验/易用性(U SER E XPERIENCE) (12)5.其他需求 (12)5.1技术环境需求 (12)5.2系统集成需求 (12)5.3文化与政治需求 (12)6.设计约束 (13)7.附录 (13)1.引言1.1目的Architecturally significant requirements(ASRs) are those requirements that play an important role in determining the architecture of the system. Such requirements require special attention. Not all requirements have equal significance with regards to the architecture.Architecturally significant requirements are a subset of the requirements that need to be satisfied before the architecture can be considered "stable". Typically, these are requirements that are technically challenging, technically constraining, or central to the system's purpose. Furthermore, the system will generally be more sensitive to changes against architecturally significant requirements, so identifying and communicating this subset will help others understand the potential implications of change.Requirements can be explicitly or implicitly architecturally significant. Explicitly significant requirements are often overtly technical in nature, such as performance targets; the need to interface to other systems; the number of users that must be supported; or security requirements. Implicitly significant requirements may define the essence of the functional behaviour of the system (for example, making a purchase from an on-line store).Deciding whether a specific requirement is architecturally significant is often a matter of judgment. The selection of requirements that are considered "architecturally significant" is driven by several key driving factors:The benefit of the requirement to stakeholders: critical, important, or useful.The architectural impact of the requirement: none, extends, or modifies. There may be critical requirements that have little or no impact on the architecture and low-benefit requirements that have a big impact. Low-benefit requirements with big architectural impacts should be reviewed by the project manager for possible removal from the scope of the project.The risks to be mitigated: performance, availability of a product, and suitability of a component.The completion of the coverage of the architecture.Other tactical objectives or constraints, such as demonstration to the user, and so on.There may be two requirements that hit the same components and address similar risks. If you implement A first, then B is not architecturally significant. If you implement B first, then A is not architecturally significant. Thus these attributes can depend on the order the requirements are realized, and should be re-evaluated when the order changes, as well as when the requirements themselves change.The following are good examples of Architecturally Significant Requirements:The system must record every modification to customer records for audit purposes.The system must respond within 5 seconds.The system must deploy on Microsoft Windows XP and Linux.The system must encrypt all network traffic.The ATM system must dispense cash on demand to validated account holders with sufficient cleared funds.Architecturally significant requirements also describe key behaviors that the system needs to perform. Such scenarios represent the important interactions between key abstractions.and should be identified as architecturally significant requirements. For example, for an on-line book store describing the way the software handles the scenarios for ordering a book and checking out the shopping cart are often enough to communicate the essence of the architecture.[描述ASRs的目的;说明ASRs的预期读者。
]1.2范围[通过名称识别要生产/开发的软件产品;说明软件产品将做或不做什么;描述规定的软件的应用,包括相关的收益、目标和目的;如下面例子:该文档是…,它主要描述了…,与之相关的文档有…。
部分内容的变更将会影响到相关两个文档更改。
]1.3定义、缩写和缩略语[提供对正确解释ASRs所要求的所有术语、简写和缩略语的定义,可以通过引用ASRs中一个或多个附录、或者引用其他文件的方式来提供]1.4引用文件[提供ASRs引用的所有文件的完整清单;标识出每个文件的名称、报告编号(适用时)、日期、出版组织;标明可以获得引用文件的来源。