胶体免维护蓄电池说明书0
- 格式:doc
- 大小:752.50 KB
- 文档页数:7


蓄电池使用手册
第一章:蓄电池简介
1.1 蓄电池的定义和作用
蓄电池,又称为蓄电池或电瓶,是一种能够储存电能的装置。
它通过将化学能转化为电能,稍后再将其放出,以满足电力设备供
电的需求。
蓄电池在众多领域中都有广泛的应用,包括汽车、太阳
能光伏系统、船只等。
1.2 蓄电池的分类
蓄电池可以根据其化学成分、外形结构和用途进行分类。
其中,最常见的蓄电池类型有铅酸蓄电池、锂离子电池和镍氢电池等。
第二章:蓄电池的使用与保养
2.1 蓄电池的储存和搬运
2.1.1 储存前的准备
在长时间不使用蓄电池之前,应该将其充满电,并存放在干燥、通风良好的环境中。
此外,还应定期检查蓄电池的接线,确保其正
常工作。
2.1.2 蓄电池的搬运
在搬运蓄电池时,应遵循以下注意事项:
- 使用合适的工具和装备,以确保安全搬运。
- 避免将蓄电池摔落或碰撞,以防损坏。
- 尽量避免磁性物品和金属物品接触蓄电池。
2.2 蓄电池的安装和连接
2.2.1 安装前的准备
在安装蓄电池之前,应确保以下几点:
- 确定蓄电池的安装位置和方向,以便于接线和维护。
- 清洁和检查安装位置,确保无积尘和腐蚀物。
2.2.2 连接蓄电池
在连接蓄电池时,应按照以下步骤进行操作:。

胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池结构好啦,今天咱们聊聊一个大家都听过但可能并不太了解的东西——胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池。
说到电池,很多人脑袋里第一个浮现的就是手机电池、汽车电池这种家喻户晓的玩意儿。
胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池也是电池家族中的一员,不过它有点“与众不同”,不像其他电池那样需要频繁保养,很多时候它能“自给自足”,不需要我们操太多心。
这么说吧,它就像一个勤劳的“小家伙”,不用天天给它喂水,也不用时刻担心它的健康状态。
这个胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池到底是什么呢?为什么它那么“懒”?我们一起来拆解一下它的秘密。
胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池,说白了就是一种在结构和设计上有了优化的铅酸蓄电池。
你可能会问,铅酸蓄电池不都是一样的吗?哪里有啥区别?嘿嘿,这就得说说它的内部结构了。
普通的铅酸电池里,电解液是液态的,看起来跟水差不多。
用起来虽然方便,但容易出现泄漏、腐蚀的问题。
而胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池呢,它的电解液是凝胶状的,这就像是把普通的液体变成了“果冻”,不仅更稳定,还不容易外泄。
你想想,液体泄漏了怎么办,可能车厢里一团糟,或者还可能损坏电池本身。
胶体版的就能避免这些麻烦,聪明得很。
再说到免维护。
哈哈,说到这个词儿,你肯定知道,很多传统铅酸电池的维护工作可不少。
电池使用一段时间后,电解液会自然蒸发,得定期检查水位,不然电池可能会干涸,直接“罢工”。
而胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池就没这么麻烦了。
因为电解液的状态是胶体的,蒸发的速度大大减缓,基本不用担心水位下降啥的。
听起来是不是特别省事儿?没错,就是省心又省力。
你要知道,很多车主和电池用户抱怨说,电池使用得差不多了,得去给它加水,做个小检查,这不光浪费时间,也挺麻烦的。
胶体免维护电池就避免了这些烦恼,打破了“每年一检查”的陈规,真的算是“懒人福音”。
胶体免维护铅酸蓄电池的使用寿命也比较长。
你想想,电池在长期使用中,液态电解液的酸性会对电池内部的铅板产生腐蚀,导致容量逐渐下降。
但胶体电解液的设计有效地减少了这种腐蚀,提升了电池的耐久性。

汽车免维护蓄电池MF一汽-大众汽车有限公司生产的宝来、高尔夫、捷达车均装有密封全免维护蓄电池。
免维护蓄电池又叫MF蓄电池,从20世纪70年代后期进入国际市场以来,已得到迅猛的发展。
免维护蓄电池由于自身结构上的优势,电解液的消耗量非常小,在使用寿命内基本不需要补充蒸馏水。
它还具有耐震、耐高温、体积小、自放电小的特点。
使用寿命一般为普通蓄电池的两倍。
免维护蓄电池与普通铅蓄电池的最大区别是极板材料不同,免维护蓄电池的栅架是用铅-钙-锡合金或铅-低锑合金﹙含锑2%-3%﹚制作的,后者的性能比前者的稍差,称为少维护蓄电池。
结构方面在孔盖内部设置了一个氧化铝过滤器,它既可以是氢气和氧气顺利溢出又可以阻止水蒸气和硫酸气体通过,股电解液中蒸馏水的消耗很少,在使用过程中,几乎不要加蒸馏水,这是无需维护蓄电池的最大特点。
正极板装在袋式微孔塑料隔板中,可以取消壳体的底部的凸筋部分,降低极板组的高度,是极板上部的容积增大33%,电解液的储存量相对增加。
由于正极板装在塑料袋中,活性物质脱落造成机板短路的现象大为减少,自放电的可能性大为减弱。
特点(1)免维护蓄电池失水量少,使用中一般不需添加蒸馏水。
(2)免维护蓄电池的栅架采用的是铅钙合金,特点是晶粒较细,耐腐蚀,不易形成微电池,自行放电量小。
(3)免维护蓄电池有集气室和新型的通气装置,可避免水分散失,有效的防止酸气外逸,从而很大程度的降低了硫酸气对极桩连接件的腐蚀。
(4)免维护蓄电池的起动电流比普通铅蓄电池大,起动性能好,一方面是由于铅钙合金的导电性能比铅锑合金好,蓄电池内阻小,输出电流大;另一方面是由于免维护蓄电池采用内连式连接,缩短了连线长度,功率损失小,放电电压高。
(5)免维护蓄电池采用铅钙合金制作栅架,增加了机械强度,提高了耐充性,还有效的防止活性物质脱落,提高了使用寿命。
一、保养要求1、检查蓄电池在车上是否固定好,外壳表面是否有磕碰伤;2、蓄电池电缆是否连接可靠,排气孔是否有灰尘;3、通过蓄电池上的电眼检查充电情况和质量状态,绿色表示合格,黑色表示亏电,白色表示电池损坏需要更换。

胶体免维护蓄电池说明书一、标准:胶体免维护蓄电池符合如下标准:1、JIS C 8707—1992 阴极吸收式密封固定型铅酸蓄电池标准2、JB/T 8451—96 中华人民共和国机械行业标准3、YD/T 799—2002 中华人民共和国通信行业标准4、DL/T 637—1997 中华人民共和国电力行业标准二、应用范围:⑴电话交换机⑼办公自动化系统⑵电器设备、医疗设备及仪器仪表⑽无线电通讯系统⑶计算机不间断电源⑾应急照明⑷输变电站、开关控制和事故照明⑿便携式电器及采矿系统⑸消防、安全及报警监测⒀交通及航标信号灯⑹通信用备用电源⒁发电厂、水电站直流电源⑺变电站开关控制⒂铁路用直流电源⑻胶体、风能系统⒃移动机站三、主要特点;⑴寿命长采用耐腐蚀性好的特殊铅钙合金制成的极板,可以具有较长的浮充寿命;采用特殊胶体电液,增加电池酸量,防止电液分层,阻止极板支晶短路,确保电池使用寿命长。
胶体电池是在阀控式密封铅酸蓄电池技术的基础上实现了长寿命化。
所以12V系列胶体电池设计寿命为6~8年(25℃);2V系列胶体电池设计寿命为10~15年(25℃)。
⑵自放电少使用特殊铅钙合金制成的板栅,将自放电量限制到最小,可长期保存。
⑶维护容易由于浮充电时,电池内部产生的氧气大部分被阴极板吸收还原成电解液,基本上没有电解液的减少,所以完全不必象一般蓄电池那样测量电解液的比重和补水。
⑷安装简单电池立式、侧卧安装使用均可,无电液渗漏之患,而且在正常充电过程中电池不会产生酸雾。
因此可将电池安装在办公室或配套设备房内,而无需另建专用电池房,降低工程造价.⑸安全性高为预防产生过多的气体,电池装有安全阀。
另外,还装有防爆过滤器,在构造上即使有火花接近,亦能防止引火至电池内部。
⑹使用方便电池出厂时已经完全充电,用户拿到电池后即可安装投入使用.四、胶体电池外形尺寸及其重量参数五、胶体蓄电池特性曲线1、放电曲线10小时率(0.1CA)、5小时率(0.17CA)、3小时率(0.25CA)放电终止电压为:1。

德国Sonnenschein(阳光)胶体阀控式铅酸蓄电池Dryfit A400系列使用维护手册目录第一节前言---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2 第二节安全守则---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------2 第三节产品验货---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 第四节蓄电池的储存---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------3 第五节蓄电池额定数据------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4 第六节蓄电池安装------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------4 第七节蓄电池充电方式------------------------------------------------------------------------------------5 第八节蓄电池初始充放电---------------------------------------------------------------------------------6 第九节蓄电池使用后的充电方式------------------------------------------------------------------------6 第十节蓄电池使用后的容量测试------------------------------------------------------------------------7 第十一节蓄电池的维护与检查---------------------------------------------------------------------------7 第十二节数据记录------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------7 第十三节技术数据------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------8 第十四节蓄电池极柱漏液确认方法---------------------------------------------------------------------9 第十五节关于电池塑性形变的说明---------------------------------------------------------------------9一前言在正常使用时,Sonnenschein(阳光)Dryfit A400系列胶体阀控式固定型铅酸免维护蓄电池(为方便起见,在以下叙述中,若无特殊说明均简称“蓄电池”)不会释放酸雾或泄漏电解液。

免维护蓄电池的产品性能参数免维护蓄电池是一种常见的电池类型,被广泛应用于各种领域,如UPS系统、太阳能发电系统、电动工具等等。
相对于传统的蓄电池,免维护蓄电池具有更高的性能和更长的使用寿命。
下面是关于免维护蓄电池的一些产品性能参数的详细介绍。
1.容量:容量是指蓄电池能够存储的能量的大小,通常以安时(Ah)为单位。
免维护蓄电池的容量通常在12V到200V之间,不同的应用需求可以选择不同容量的蓄电池。
2.额定电压:额定电压是指蓄电池正常工作时的电压。
免维护蓄电池的额定电压通常为12V,但也有其他额定电压的免维护蓄电池可供选择。
3.循环寿命:循环寿命是指蓄电池能够进行充放电循环的次数,在循环寿命内,蓄电池仍然能够保持一定的容量。
免维护蓄电池通常具有较长的循环寿命,可以达到数千次甚至上万次。
4.自放电率:自放电率是指蓄电池在不进行充放电时自然放电的速率。
免维护蓄电池通常具有较低的自放电率,能够在长时间不使用时保持较高的容量。
5.快速充电性能:快速充电性能是指蓄电池在充电状态下能够快速充电的能力。
免维护蓄电池通常具有良好的快速充电性能,能够在短时间内迅速充满电。
6.温度适应性:温度适应性是指蓄电池能够在不同温度下正常工作的能力。
免维护蓄电池通常具有较好的温度适应性,可以在较低或较高的温度条件下正常工作。
7.安全性能:安全性能是指蓄电池在正常使用或意外情况下能够确保安全的能力。
免维护蓄电池通常具有较高的安全性能,采用了多种安全措施来预防过充、过放、短路等问题。
综上所述,免维护蓄电池具有较高的性能参数,包括容量、额定电压、循环寿命、自放电率、快速充电性能、温度适应性和安全性能等。
这些性能参数决定了免维护蓄电池在各种应用中的可靠性和持久性。
用户在选择免维护蓄电池时,应根据具体的需求和应用场景来考虑这些性能参数,以确保选择适合的产品。

免维护蓄电池使用说明书使用方法:全密封免维护:1、将电池置于电池架上固定牢靠,正确连接正负极端子,应先将蓄电池正极和汽车发动机正极连接,再将蓄电池负极与发动机负极相连,防止松动和短路,保持电池、端子及接线清洁,在正负极端子上涂上凡士林以免腐蚀。
2、电池的充电电压应严格限定在13.8V—14.2V范围内。
超过此范围,可能引起不良后果。
充电电压过高会导致电解液损耗,长期过充电会导致电解液干枯和电池温度升高并可能发生爆炸,充电电压过低会导致充电不足。
干荷免维护:1、撕去电池排气孔的胶带,注入电池标准液(20℃时比重为1.28硫酸)至高水位线(max)、旋紧排气孔,用电压表检查电池正负极电压是否正确,静止20分钟即可使用(如气温低于15℃,则应适当延长)。
2、保持电池表面清洁和干净,防止电池短路,排气孔应畅通。
3、单个电池用于汽车时,汽车充电电机输出电压因为13.8V—14.4V,低于13.8V时电池会亏电,高于14.4V时,电池水分急剧分解,可能导致爆裂电池,用于应急电源,单个电池浮充电压为13.8V。
注意事项:1、电池应放在5—25℃干燥、清洁和通风良好的环境中,无阳光直射,离热源至少2m以上。
2、每个6个月应检查显示器,如电量不足,应补充电。
3、电池安装和库存保管时,倾斜度不得超出45度,以免侧面排气孔漏出液体,不得受任何机械冲击和重压。
4、安装电池时,请不要用锤子等敲打端子。
附录:1、充电存储器:干荷电池储存期为一年,带液电池储存期三个月,超过期限使用时应补充电。
充电方法如下:恒流充电:充电电流为0.1C20(C20:20小时率容端),端电压达到14.4V后,在充电5小时左右。
恒压充电:充电电压14.4±0.1V,允许最大电流0.5C20,充电16小时。
2、电解液的配置方法①电解液应由符合GB/T625-2007标准的蓄电池硫酸与蒸馏水(纯水)配置而成。
②配置电解液时应将浓硫酸缓缓倒入蒸馏水中,严禁将蒸馏水倒入浓硫酸中,以免飞溅烫伤。

阀控式全密闭免维护胶体铅酸蓄电池技术规格书1 总则1.1 本技术规格书适用于阀控式全密封免维护胶体铅酸蓄电池物资招标,提出了该物资生产、检验、试验、验收、运输、试用和售后服务等方面的基本技术要求;1.2 本设备技术规格书提出的是最低限度的技术要求,并未对一切技术细节作出规定,也未充分引述有关标准和规范的条文,投标人应提供符合本规范书和工业标准的优质产品。
1.3 如果供方没有以书面形式对本协议的条文提出异议,则意味着卖方提供的设备完全符合本协议的要求。
1.4 本电池技术协议所使用的标准如遇与供方所执行的标准不一致时,按较高标准执行。
1.5本技术规格书未尽事宜,由供、需双方协商确定。
2 执行标准:GB/T 19638.1-2014 固定型阀控式铅酸蓄电池DL/T 637-1997 阀控式密封铅酸蓄电池订货技术YD/T 1360-2005 通信用阀控式密封胶体蓄电池GB/T 2900.41-2008 电工术语原电池和蓄电池JB/T 2599-2012 铅酸蓄电池名称、型号编制与命名办法以上标准均执行最新版本。
这些法则和标准提出了最基本要求,如果根据需方的意见并经用户接受,使用优于或更为经济的设计或材料,并能使卖方设备良好地、连续地在本规范所规定的条件下运行时,则这些标准也可以由供方超越。
当标准、规范之间出现矛盾时,需方应将矛盾情况提交用户,以便在开始生产前制定解决方案。
3 供货范围4 技术规格4.1设备名称:阀控式全密封免维护胶体铅酸蓄电池4.2 基本参数4.2.1 设备型号:见供货范围4.2.2 单体电池额定电压: 12V4.2.3 单体电池浮充电电压:13.38~13.62V(12V)4.2.4 单体电池均衡充电电压: 14.1~14.4V(12V)4.2.5 25℃蓄电池浮充设计寿命:≥15年(12V)4.2.6 80%放电深度的循环寿命:≥500次4.2.7 放电终止电压:10.5V(12V)4.2.8 外壳材料:ABS或PP 外壳阻燃4.2.9 每月自放电率:< 3%4.2.10 密封反应效率:≥99.5%4.2.11 电池开路压差:≤0.1V(12V)4.2.12 蓄电池开阀压力:10kPa~30kPa闭阀压力在1~10kPa5 主要技术要求5.1蓄电池要求为原装进口胶体蓄电池,需提供原厂项目授权以及报关单、原产地证明。
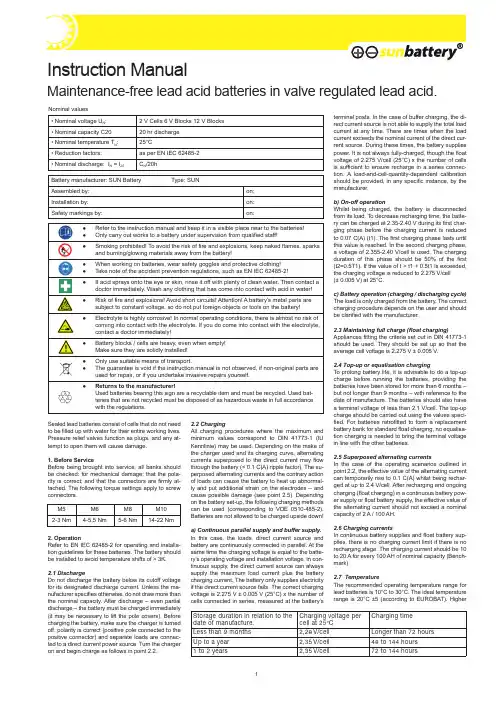
Sealed lead batteries consist of cells that do not need to be filled up with water for their entire working lives. Pressure relief valves function as plugs, and any at -tempt to open them will cause damage.1. Before ServiceBefore being brought into service, all banks should be checked: for mechanical damage; that the pola -rity is correct; and that the connectors are firmly at -tached. The following torque settings apply to screw connectors.2. OperationRefer to EN IEC 62485-2 for operating and installa -tion guidelines for these batteries. The battery should be installed to avoid temperature shifts of > 3K.2.1 DischargeDo not discharge the battery below its cutoff voltage for its designated discharge current. Unless the ma -nufacturer specifies otherwise, do not draw more than the nominal capacity. After discharge – even partial discharge – the battery must be charged immediately (it may be necessary to lift the pole covers). Before charging the battery, make sure the charger is turned off, polarity is correct (positive pole connected to the positive connector) and separate loads are connec -ted to a direct current power source. Turn the charger on and begin charge as follows in point 2.2.2.2 ChargingAll charging procedures where the maximum and minimum values correspond to DIN 41773-1 (IU Kennlinie) may be used. Depending on the make of the charger used and its charging curve, alternating currents superposed to the direct current may flow through the battery (< 0.1 C(A) ripple factor). The su -perposed alternating currents and the contrary action of loads can cause the battery to heat up abnormal -ly and put additional strain on the electrodes – and cause possible damage (see point 2.5). Depending on the battery set-up, the following charging methods can be used (corresponding to VDE 0510-485-2). Batteries are not allowed to be charged upside down!a) Continuous parallel supply and buffer supply. In this case, the loads, direct current source and battery are continuously connected in parallel. At the same time the charging voltage is equal to the batte -ry’s operating voltage and installation voltage. In con -tinuous supply, the direct current source can always supply the maximum load current plus the battery charging current. The battery only supplies electricity if the direct current source fails. The correct charging voltage is 2.275 V ± 0.005 V (25°C) x the number of cells connected in series, measured at the battery’sterminal posts. In the case of buffer charging, the di -rect current source is not able to supply the total load current at any time. There are times when the load current exceeds the nominal current of the direct cur -rent source. During these times, the battery supplies power. It is not always fully-charged, though the float voltage of 2.275 V/cell (25°C) x the number of cells is sufficient to ensure recharge in a series connec -tion. A load-and-cell-quantity-dependent calibration should be provided, in any specific instance, by the manufacturer.b) On-off operationWhilst being charged, the battery is disconnected from its load. T o decrease recharging time, the batte -ry can be charged at 2.35-2.40 V during its first char -ging phase before the charging current is reduced to 0.07 C(A) (t1). The first charging phase lasts until this value is reached. In the second charging phase, a voltage of 2.355-2.40 V/cell is used. The charging duration of this phase should be 50% of the first (t2=0.5T1). If the value of t > t1 + 0.5t1 is exceeded, the charging voltage is reduced to 2.275 V/cell (± 0.005 V) at 25°C.c) Battery operation (charging / discharging cycle) The load is only charged from the battery. The correct charging procedure depends on the user and should be clarified with the manufacturer.2.3 Maintaining full charge (float charging)Appliances fitting the criteria set out in DIN 41773-1 should be used. They should be set up so that the average cell voltage is 2.275 V ± 0.005 V.2.4 Top-up or equalisation chargingT o prolong battery life, it is advisable to do a top-up charge before running the batteries, providing the batteries have been stored for more than 6 months – but not longer than 9 months – with reference to the date of manufacture. The batteries should also have a terminal voltage of less than 2.1 V/cell. The top-up charge should be carried out using the values speci -fied. For batteries retrofitted to form a replacement battery bank for standard float charging, no equalisa -tion charging is needed to bring the terminal voltage in line with the other batteries.2.5 Superposed alternating currentsIn the case of the operating scenarios outlined in point 2.2, the effective value of the alternating current can temporarily rise to 0.1 C(A) whilst being rechar -ged at up to 2.4 V/cell. After recharging and ongoing charging (float charging) in a continuous battery pow -er supply or float battery supply, the effective value of the alternating current should not exceed a nominal capacity of 2 A / 100 AH.2.6 Charging currentsIn continuous battery supplies and float battery sup -plies, there is no charging current limit if there is no recharging stage. The charging current should be 10 to 20 A for every 100 AH of nominal capacity (Bench -mark).2.7 TemperatureThe recommended operating temperature range for lead batteries is 10°C to 30°C. The ideal temperature range is 20°C ±5 (according to EUROBAT). Higher• Nominal voltage U N : 2 V Cells 6 V Blocks 12 V Blocks • Nominal capacity C2020 hr discharge • Nominal temperature T N :25°C• Reduction factors:as per EN IEC 62485-2• Nominal discharge: I N = I 20C N /20hBattery manufacturer: SUN Battery Type: SUNAssembled by:on:Installation by:on:Safety markings by:on:Nominal values M5M6M8M102-3 Nm4-5,5 Nm5-6 Nm14-22 Nm●●Refer to the instruction manual and keep it in a visible place near to the batteries!Only carry out works to a battery under supervision from qualified staff!●Smoking prohibited! To avoid the risk of fire and explosions, keep naked flames, sparks and burning/glowing materials away from the battery!●●When working on batteries, wear safety goggles and protective clothing!Take note of the accident prevention regulations, such as EN IEC 62485-2!●If acid sprays onto the eye or skin, rinse it off with plenty of clean water. Then contact a doctor immediately. Wash any clothing that has come into contact with acid in water!●Risk of fire and explosions! Avoid short circuits! Attention! A battery’s metal parts are subject to constant voltage, so do not put foreign objects or tools on the battery!●Electrolyte is highly corrosive! In normal operating conditions, there is almost no risk of coming into contact with the electrolyte. If you do come into contact with the electrolyte, contact a doctor immediately!●Battery blocks / cells are heavy, even when empty! Make sure they are solidly installed!●●Only use suitable means of transport.The guarantee is void if the instruction manual is not observed, if non-original parts are used for repair, or if you undertake invasive repairs yourself.●Returns to the manufacturer!Used batteries bearing this sign are a recyclable item and must be recycled. Used bat -teries that are not recycled must be disposed of as hazardous waste in full accordance with the regulations.Storage duration in relation to the date of manufacture.Charging voltage per cell at 25°C Charging time Less than 9 months 2,28 V/cell Longer than 72 hours Up to a year 2,35 V/cell 48 to 144 hours 1 to 2 years2,35 V/cell72 to 144 hoursMaintenance-free lead acid batteries in valve regulated lead acid.temperatures decrease battery life. The technical specifications apply to a nominal temperature of 25°C. Lower temperatures decrease available capa-city. Exceeding the maximum allowable temperature from 50°C is prohibited. Persistent operating tempe-ratures above 40°C should be avoided.2.8 Temperature-based float charging voltage and rapid dischargeThe float charging voltage of 2.275 V/cell ± 0.005 V/ cell applies to a temperature of 25°C. A temperatu-re-based recalibration of the float charging voltage is required to avoid over-charging at higher temperatu-res and under-charging at lower temperatures. The recommended recalibration factor is -3 mV/cell/V°C in a float charging situation. T o avoid a “thermal ru-naway”, for temperatures above 40°C the float char-ging voltage must be recalibrated to the temperature.A power-charging procedure can then be used if a rapid recharge is needed. In this case, the charging current should not exceed 0.01 C(A) and constantly decreases until it’s below 0.01 C(A). Once a level of ±0.1 V/cell has been reached, it should be switched to float voltage charging.2.9 ElectrolyteThe electrolyte is diluted sulphuric acid suspended in mats.3. Battery care and inspectionThe battery must always be kept in a clean and dry condition to avoid leakage currents.The battery should be cleaned according to the ZVEI information leaflet “Cleaning of Batteries”. The batte-ry’s plastic parts should only be cleaned using water without additives; using organic cleaning products is not recommended. The following should be checked and recorded at least every 6 months:- Battery voltage- Voltage of some individual cells/battery blocks- Surface temperature of some cells- Battery room temperatureIf the cell voltage differs from the average float char-ging voltage by ±0.1 V/cell, or if the surface tempe-rature of different cells/blocks differ from each other by more than 5 K, please contact customer services. The following must be measured and recorded yearly: - Voltage of all cells/battery blocks- Surface temperature of all cells- Battery room temperature- Leakage resistance according to EN 60896-21Annual visual inspection:- Screw connections. Unfixed screw connections should be checked that they are firmly attached.- The battery rack / storage area- Ventilation (both aeration and extraction) according to EN IEC 62485-24. InspectionsInspections should be carried out according to EN 60896-21. Please also refer to additional guidelines e.g. EN 50172 and VDE 0100-710. Refer to the afo-rementioned EN. In order to ensure a reliable power supply, the whole battery should be replaced once its expected service life – given its operating conditions and temperature – has expired.5. ProblemsIf you identify errors with the battery or the charging set-up, contact customer services without delay. The measurement specifications in point 3 enable easier fault-checking and troubleshooting. A maintenance contract helps with the timely identification of problems.6. Storage and decommissioningIf cells/batteries are put in storage or taken out ofservice for a significant amount of time, they shouldbe kept in a dry, frost-free room. T o avoid damage,maintenance charging should be carried out as spe-cified in point 2.4.7. TransportSun batteries are not hazardous materials as long asthey are secured against short circuits, slipping, fallingover and damage (Hazardous Material Act, GGVS, vo-lume No. 2801a). This applies to transport by road, rail,sea and air, and to IATA rules (Rule A67), ADR (Rule598), IMDG (Rule 238.2), and UN 2800 special provisi-ons. The transported goods should not carry any dan-gerous traces of acid. All sealed lead batteries and cellswhose containers are no longer leak-proof or damagedare subject to the corresponding special provisions.Temperature(°C)ChargingVoltage(V/Z)Float chargingvoltage(V/Z)- 102,532,36 02,482,33 102,452,30 202,402,28 302,372,24 402,342,218. Technical specificationsCapacities (Cn) at various discharge times (tn) until the relevant cutoff voltage (US) at a temperature of 25°C.Description20hr10hr5hr3hr1hrType SUN1,80 V/Z1,80 V/Z1,75 V/Z1,75 V/Z1,60 V/ZSB6-1,21,2 Ah 1,12 Ah 1,01 Ah 0,882 Ah0,728 AhSB6-1212 Ah11,2 Ah10,2 Ah9,2 Ah 7,54 AhMB12-0,80,8 Ah 0,74 Ah 0,67 Ah 0,588 Ah0,486 AhSB12-1,21,2 Ah 1,12 Ah 1,01 Ah 0,882 Ah0,728 AhSB12-2,12,3 Ah 2,14 Ah 1,93 Ah 1,69 Ah 1,40 AhSB12-3,43,4 Ah3,16 Ah 2,89 Ah2,60 Ah2,14 AhSB12-7,27,2 Ah 6,7 Ah 6,12 Ah 5,37 Ah 4,49 AhSB12-7,2L7,2 Ah 6,70 Ah 6,12 Ah 5,37 Ah 4,49 AhSB12-12L12,7 Ah12,0 Ah 10,4 Ah9,48 Ah7,38 AhSB12-1818 Ah16,7 Ah 15,3 Ah 13,4 Ah 11,2 AhSB12-2424 Ah 22,3 Ah 20,4 Ah 18,4 Ah 15,1 AhSB12-2626 Ah 24,2 Ah 22,1 Ah 19,9 Ah 16,3 AhSB12-3838 Ah 36,1 Ah 31,1 Ah 28,2 Ah 22 AhSB12-4545 Ah 42 Ah 36,6 Ah 32,7 Ah 26 AhSB12-6569,6 Ah 65 Ah 56,5 Ah 50,7 Ah 40,3 AhSB12-65S 65.0 Ah61.0 Ah51,5 Ah 46.8 Ah36.6 AhSB12-7578 Ah 75 Ah 64,5 Ah 58,5 Ah 45,8 AhSB12-100100 Ah 93,5 Ah 81,5 Ah 72,9 Ah 57,9 AhSB12-150160,5 Ah 150 Ah 130,5 Ah 117 Ah 93,0 AhSB12-200214 Ah 200 Ah 174,0 Ah156 Ah 124,0 AhHC12-9 T28,8 Ah8,2 Ah7,7 Ah6,6 Ah5,80 AhHC12-13 T212,56 Ah12,3 Ah10,65 Ah9,93 Ah9,17 AhHC12-22 M521,8 Ah21,8 Ah18,7 Ah16,47 Ah13,2 AhHC12-36 M635,0 Ah34,9 Ah31,55 Ah28,05 Ah24,2 AhHC12-50 M649,2 Ah46,7 Ah42,85 Ah36,9 Ah30,9 AhHC12-75 M675,0 Ah74,1 Ah67,0 Ah61,2 Ah49,5 AhHC12-80 M683,8 Ah80,0 Ah70,5 Ah63,0 Ah50,8 AhHC12-100 M8107,0 Ah106,0 Ah87,5 Ah75,0 Ah65,7 AhMB12-5HR6,1 Ah 5 Ah 4,47 Ah 4,05 Ah 3,74 AhMB12-7HR7,8 Ah 7,23 Ah 6,45 Ah 5,67 Ah 5,41 AhSB12-110A FT106 Ah 100 Ah 95,2 Ah 87 Ah 63,7 AhSB12-150A FT158,8 Ah 150 Ah 142,4 Ah 130,5 Ah 95,9 Ah Technical changes reserved.Updated 03/2021Battery-KutterBattery-Kutter GmbH & Co. KGRobert-Koch-Straße 19a · 22851 NorderstedtTelefon: +49 40 - 611 631 0 · Fax: +49 40 - 611 631 79E-Mail:**********************www.battery-kutter.de。

蓄电池使用说明书一、产品介绍蓄电池是一种能够存储电能并在需要时释放电能的装置。
它由一系列电化学反应组成,通过化学能转化为电能。
蓄电池常用于备用电源、储能系统、汽车和其他电动设备等领域。
二、安全注意事项1. 请勿将蓄电池直接暴露在高温环境下,以避免损坏电池性能。
2. 请勿将蓄电池投入水中或其他液体中,以免引起电池损坏或引发电击危险。
3. 当使用蓄电池时,请注意防止短路,避免金属物品接触电池两极。
4. 请勿将蓄电池与阳光直接接触,以免损坏电池外壳。
5. 如果电池出现损坏、漏液或发生异常情况,请立即停止使用并联系专业人员进行处理。
三、充电须知1. 在首次使用蓄电池之前,请先仔细阅读说明书,并确保了解正确的充电方式。
2. 使用正确的充电器进行充电,切勿使用不符合规定或低质量的充电器。
3. 在充电时,请确保充电器与电源的连接牢固,避免充电过程中出现意外情况。
4. 充电时请保持通风良好的环境,避免过热或过冷的环境。
5. 在充电过程中,如发现异常情况(如电池过热、充电时间过长等),请立即停止充电,并与厂家联系。
四、使用方法1. 在使用蓄电池之前,请先确保电池已充满电。
2. 将蓄电池正确安装在相应的设备或车辆中,确保极性正确连接。
3. 在正常使用过程中,如发现电池性能下降,电量不足等情况,请及时充电或更换电池。
4. 在存储蓄电池时,请避免长时间不使用导致电量耗尽,应定期检查电池的电量并充电。
5. 在长时间不使用蓄电池时,请将电池储存在干燥、通风的环境中,并定期充电以保持电池性能。
五、维护保养1. 定期清洁蓄电池的外壳,并确保其表面干燥。
2. 如果电池外壳有损坏,应及时更换,并避免继续使用,以免引发安全隐患。
3. 请勿拆卸或改装蓄电池,以免损坏电池性能或引发安全风险。
4. 当电池寿命结束时,请咨询专业人员进行处理,切勿随意丢弃。
六、故障排除1. 当蓄电池无法保持充电或电池寿命显著降低时,请联系专业人员进行检修或更换。
目录(一)使用须知及注意事项 (2)(二)使用前旳准备和检查事项 (2)(三)操作 (3)(四)维护和保养 (4)(五)储存 (5)(六)故障及排除 (5)附录一:充电操作规程 (6)附录2:车型、蓄电池、充电机适配表 (10)电动车蓄电池使用维护阐明(一)使用须知及注意事项1、请仔细阅读使用阐明。
2、只容许专业人员操作蓄电池。
3、在使用和充电过程中:禁烟、严禁明火、暗火或火花接近蓄电池,否则易发生爆炸和火灾危险。
4、操作人员应佩戴好防护眼镜,穿上防护服。
遵守操作规范。
5、在操作过程中,如有酸液溅入眼内或皮肤上,必须立即用冷水冲洗,并寻找医生进一步解决。
衣服上沾上酸液也请用水冲洗。
6、防爆、防火和防短路!电池旳金属件上始终带电!7、电解液具有强烈旳腐蚀性!8、请勿翻转蓄电池,使用准许旳吊装运送机械。
吊钩不得损坏电池或连接电缆。
(二)使用前旳准备和检查事项1、收货当货品送达时,收货人员必须及时验收、检查:A、有无任何漏电解液旳迹象,或电池有无遭受撞击旳变形及损毁。
B、电池壳面与否凹陷、破裂,连接线缆有否损毁。
C、电瓶塞、连接线缆及其他配件与否齐全。
D、对电池状况如有疑问,请做好记录并告知供应商。
2、初次使用——已灌注电解液及充电电池A、检查电解液液位与否在电池瓶塞盖可见液位。
对初次使用旳新蓄电池前十次旳充放电,毋须加补充水。
B、检查确认充电机与电池与否合适,如有需要与车辆制造商技术工程人员沟通确认。
C、按有关使用程序,连接电池与充电机。
注意:正负极位与否对旳!D、按有关使用守则对电池进行充电。
E、在初始有效期间,留意电池状况,避免深度放电(超过70%容量)。
车辆装有电量表,可清晰批示。
3、初次使用——未灌注电解液旳未充电电池A、所有未灌注电解液没有启用旳新蓄电池必须寄存于干燥、通风、荫凉旳储存室。
B、未充电旳蓄电池投入使用,务必做好蓄电池旳初充电工作,初充电对蓄电池旳性能质量和寿命起着决定性旳作用!C、初充电操作环节(1)、灌液移除蓄电池注液孔塞,灌注电解液至液位盖覆电池极板15mm~20mm。
免维护蓄电池使用说明书使用方法:1、蓄电池使用前,请测量蓄电池端电压,电压在12.6V以上可直接使用;免维护蓄电池一般有荷电状态指示器(俗称电眼)。
蓄电池显示的荷电状态请参见以下指导或蓄电池上相关标记说明。
若电压较低或状态不足,请补充电后再使用。
2、蓄电池上标有“+”、“—”端,应分别于车辆的正负连接线连接,接线应牢固、可靠。
严禁反接,否则将会损坏车辆用电设备;接线不牢,会产生火花、引起爆炸或端柱烧毁。
另外,为避免损坏发动机,在没有接通蓄电池充电线路前,切勿运行发动机。
严禁敲击端柱,以免端柱松动造成电池渗酸。
3、蓄电池充电时,不许打开电池盖体,直接充电;蓄电池“+”、“—”端分别与充电机正负链接线链接。
具体充电方法按说明书中规定的“充电方法”充电。
4、蓄电池在使用或运输过程中不得倾斜或倒置。
维护和保养:1、蓄电池储存超过三个月需要进行一次补充电。
对于使用过程中因各种原因造成的亏电蓄电池,应及时进行充电,以防止蓄电池硫酸盐化造成的性能下降。
2、经常检查蓄电池上盖两侧的排气孔,切勿被灰尘、冰水等堵塞,以防壳体变形、炸裂。
3、蓄电池或车辆长时间不适用时,蓄电池应充足电再存放,否则会影响蓄电池使用寿命。
4、蓄电池充电结束时,请先关闭充电电源,再取掉充电机与蓄电池连接线,谨防炸裂伤人。
5、蓄电池端子烧损后不得再继续使用。
6、本系列产品在使用过程中无需加水,因此推荐恒压充电,尽量避免恒流充电法。
充电:优先采用恒压充电1、恒压充电:蓄电池采用充电电压16±0.10v,允许最大电流0.1C20A或0.1×(C5/0.8)(C20为电池20小时率容量,C5为电池5小时率容量,C5=0.8×C20)的恒压充电方法进行充电,充电电流接近零值,而且2-3小时不变为止。
2、恒流充电:蓄电池以0.1 C20A或0.1×(C5/0.8)的电流充电,在充电末期,当蓄电池电压变化≦0.05V/h,认为蓄电池已充足电。
“双登牌”胶体蓄电池说明书(2V 系列)一、品牌概念双登商标系目前业内唯一的“中国驰名商标”。
双登集团是国家级重点高新技术产业集团,国家AAA 级重合同守信用企业,中国化学与物理电源行业协会副理事长单位。
双登在同行业中首家通过ISO9001质量体系认证、ISO14001国际环保认证和国家一级计量体系认证。
生产许可证号QS :XK06-044-00398。
2005年在伦敦证交所挂牌上市,2006年获得了国家免检产品称号。
二、产品执行标准、型号编制方式及工作原理GFMJ 系列胶体蓄电池在充放电过程中产生如下反应:Pb ﹢PbO 2﹢2H 2SO 4 2Pb SO 4﹢2H 2O电池在充电后期或过充电情况下,正极析出氧气,负极析出氢气。
GFMJ 蓄电池负板栅采用了高纯度的铅钙合金板栅,提高了负极析氢过电位,从而抑制了氢气的析出。
GFMJ 系列电池采用了独特的胶体电解质技术,由于电池内的硅凝胶为三维多孔结构,并且存在许多细小裂缝(气体通道),在充电期间正极析出的氧气通过这些裂缝到达负极,与负极板上的海绵状铅发生反应复合成水又重新回到系统中,即电池内部实现了氧的循环复合,因此电池可以实现密封,电池内放电充电部几乎没有水的损失,无需补水维护。
产品工作步骤及化学反应方程式第一步:充电后期或过充电情况下,水在正极分解,并析出氧气:H2O→2H++1/2O2+2e-第二步:正极析出的氧气通过胶体的缝隙扩散到负极,并同负极的海绵状铅及硫酸发生反应,重新化和回到系统中:O2﹢2H2SO4﹢2Pb = 2Pb SO4﹢2H2O第三步:负极生成的硫酸铅在电池充电过程中生成铅和硫酸,参加充电反应: PbSO+2H++2e-→Pb﹢H2SO44三、产品用途●电信、移动、网络、铁道、机场等各种通信、信号系统备用电源。
●电力系统、核电站备用电源。
●太阳能、风能发电储能。
●UPS、医疗设备、应急照明等备用电源。
●舰船、海事等备用电源。
胶体免维护蓄电池说明书
一、标准:
胶体免维护蓄电池符合如下标准:
1、JIS C 8707-1992 阴极吸收式密封固定型铅酸蓄电池标准
2、JB/T 8451-96 中华人民共和国机械行业标准
3、YD/T 799-2002 中华人民共和国通信行业标准
4、DL/T 637-1997 中华人民共和国电力行业标准
二、应用范围:
⑴电话交换机⑼办公自动化系统
⑵电器设备、医疗设备及仪器仪表⑽无线电通讯系统
⑶计算机不间断电源⑾应急照明
⑷输变电站、开关控制和事故照明⑿便携式电器及采矿系统
⑸消防、安全及报警监测⒀交通及航标信号灯
⑹通信用备用电源⒁发电厂、水电站直流电源
⑺变电站开关控制⒂铁路用直流电源
⑻胶体、风能系统⒃移动机站
三、主要特点;
⑴寿命长
采用耐腐蚀性好的特殊铅钙合金制成的极板,可以具有较长的浮充寿命;
采用特殊胶体电液,增加电池酸量,防止电液分层,阻止极板支晶短路,确保电池使用寿命长。
胶体电池是在阀控式密封铅酸蓄电池技术的基础上实现了长寿命化。
所以12V系列胶体电池设计寿命为6~8年(25℃);2V系列胶体电池设计寿命为10~15年(25℃)。
⑵自放电少
使用特殊铅钙合金制成的板栅,将自放电量限制到最小,可长期保存。
⑶维护容易
由于浮充电时,电池内部产生的氧气大部分被阴极板吸收还原成电解液,基本上没有电解液的减少,所以完全不必象一般蓄电池那样测量电解液的比重和补水。
⑷安装简单
电池立式、侧卧安装使用均可,无电液渗漏之患,而且在正常充电过程中电池不会产生酸雾。
因此可将电池安装在办公室或配套设备房内,而无需另建专用电池房,降低工程造价。
⑸安全性高
为预防产生过多的气体,电池装有安全阀。
另外,还装有防爆过滤器,在构造上即使有火花接近,亦能防止引火至电池内部。
⑹使用方便
电池出厂时已经完全充电,用户拿到电池后即可安装投入使用。
四、胶体电池外形尺寸及其重量参数
五、胶体蓄电池特性曲线
1、放电曲线
10小时率(0.1CA)、5小时率(0.17CA)、3小时率(0.25CA)放电终止电压为:1.8V/单格;1小时率(0.55CA)放电终止电压为:1.75V/单格。
电池使用时放电终止电压最好不要低于1.0V/单格,以保证电池不会过放电。
12V系列胶体电池:
2V系列胶体电池:
2、充电曲线
蓄电池要求采用恒压限流的充电方式,充电电压在13.65±0.02V/台范围内,充电设备必须保持恒定功能且稳压精度小于1%,充电瞬间的最大电流不超过0.25C10A
2V系列胶体电池:
3、浮充电压与温度的关系曲线:
电池的浮充电压值应随着环境温度的降低而适量增加,随着环境温度的升高而适量减少,其关系曲线见下图:
(注明:不适宜在40℃以上的环境中长期使用)
12V系列胶体电池:(温度在25℃时,电池的浮充电压为:13.65±0.1V/台)
2V系列胶体电池:(温度在25℃时,电池的浮充电压为:2.23±0.1V/台)
4、容量与温度的关系曲线
蓄电池不同放电率的放电容量值都会随着环境温度的升高而缓慢增加,其关系曲线见下图:
5、蓄电池寿命与温度的关系曲线
环境温度对电池寿命有很大的影响,当环境温度每升高10℃,电池寿命约减少50%。
因此为了延长电池寿命,电池房应安装空调,使室温保持在15~25℃。
12V系列胶体电池:
2V系列胶体电池:。