状语从句(表格)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:268.90 KB
- 文档页数:5
状语从句状语从句是副词性从句,它在句子中担任状语,修饰主句的动词、形容词、副词或句子。
根据修饰的方面,状语从句可以分为以下九种。
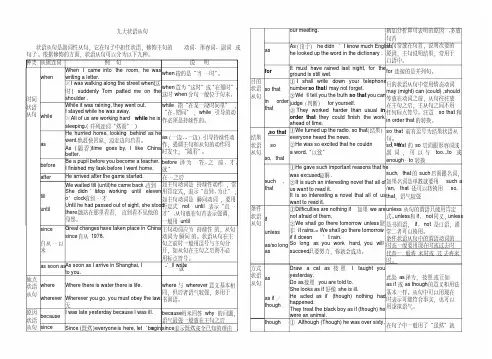
种类从属连词例句要点归纳时间状语从句whenWhen I came into the room, he was writing a letter. when指的是“当…时”。
从句中的动词可表延续性动作,也可表瞬间性动作※I was walking along the street when(这时) suddenly Tom patted meon the shoulder .when意为“这时”或“在那时”,这时when分句一般位于句末。
whileWhile it was raining, they went out.※All of us are working hard while he is sleeping.( 并列连词“然而”)while指“在某一段时间里”,“在…期间”,while引导的动作必须是持续性的。
asHe hurried home, looking behind as he went.他赶快回家,边走边向后看。
As (随着)time goes by, I like China better.as(一边...一边)引导持续性动作,强调主句和从句的动作同时发生;“随着”。
beforeBe a pupil before you become a teacher.I finished my task before I went home.before译为“在…之前, 才, 就”after He arrived after the game started. 在…之后tilluntilWe waited till (until)he came back .直到She didn’t stop working until eleven o’clock .直到…才主句谓语动词为延续性,常用肯定式;主句谓语动词为瞬间性,常用否定式,可用before替换since, Great changes have taken place in China since 1978.It’s 8 years since I taught here.其从句通常用一般过去时,主句谓语动词通常用完成时常用于It is /was …since句型as soon as As soon as I arrive in Shanghai, I’ll write to you.No sooner had he reached home than it began to rain“一…就”同:i mmediately, directly, instantly, the minute / moment , nosooner…than, hardly (scarcely)…whenthe first time The first time I saw him, he was a school teacher同理:every time, each time, any time ,the last time, by the time可引导时间状语从句地点状语从句wherewhereverWhere there is water there is life.Wherever you go, you must obey the law.where与wherever意义基本相同,但后者语气较强。




虚拟语气(一)状语从句中的虚拟语气虚拟语气在 if 引导的从句(条件)主句(目的)条件句中的用法三点:If+主语 +动词的过去式(be 用 were )主语 +would(should could might)+ 动词表示于现在事实相If I had time, I would attend the原型反的虚拟条件句meeting.If+主语 +had+ 动词的过去分词主语 +would ( should could might )表示与过去事实相If he had hurried, he could have+have+ 动词的过去分词反的拟条件句caught the train.1、 If+主语 +动词过去式主语 +would (could should might )+表示与将来事实相2、 If+主语 +were to+ 动词原形动词原型反的虚拟条件句3、 If+主语 +should + 动词原形If I were to go abroad, I would goto America.错综时间条件句—有时条件从句中的动作与主句中的动作,发生的时间不一致,这是动作的形—主从句时间不一式应根据它所表示的时间加以调整。
致的情况下的虚拟If you had followed my advice, you would be better now.语气If you had studied hard before, you would be a college student now.有时虚拟条件句并没用 if 从句表示出来,而是用介词短语(otherwise , or,without ,but for )上下文或其他方式来表示。
含蓄条件句She would have died without my help.。
在 if 引导的表示虚拟的条件状语从句中,有时可以把虚拟条件中的连词if 省去,而将 had ,should ,were 等助动词提到主语之前。
![[八年级英语]初中状语从句表格整理--原创](https://uimg.taocdn.com/557663d802d276a200292e9b.webp)
状语从句是副词性从句,它在句子中担任状语,修饰主句的动词、形容词、副词或状语从句although ②We were not tired though (although)we had worked all day.以与yet或still连用。
though /although意义相同,用法基本一样,前者通俗、口语化,后者正式多放主句的前面。
even i f/thoughI’ll go even if (though) it rains tomorrow.even if 和even though的意思为“即使”多用于书面语中。
asChild as he is , he knows a lot .Cold as it is, (= Though it is cold,)thechildren play outdoors.as引出的状语从句多用于书面语,它比用though或although引导的从句,语气强,更有表现力,从句常放在句首,语序部分倒装。
no matter(who,whatwhen,how…)Do it no matter what不管什么otherssay.No matter how无论多么busy he was,he studied English every day.no matter……与who-ever引导的让步状语从句意义基本一样,no matter……引导的从句可是以位于主句前或主句后。
wh-ever(whateverwhoever…)Whatever happens / may happen , weshall not lose heart.Whoever comes, he will be welcome.比较状语从句as…asnotso/as…asMary is as old as my sister.He doesn’t run so (as) fast as Jack (does).连词表示同程度级的比较,肯定句用as…as否定句可用notas (so)…asthanHe bought fewer books than I (did).He runs less fast than me.表示不同程度之比较,主句中用比较级的形容词或副词。

初中状语从句表格整理状语从句是一种副词性从句,用于修饰主句的动词、形容词或副词。
根据修饰的方面,状语从句可以分为九种不同类型。
当表示“当。
时”的状况时,我们可以使用when引导的从句。
例如:“当我进入房间时,他正在写信。
”XXX引导的从句表示“在某一段时间里”或“在。
期间”。
例如:“他们在下雨的时候出去了,而我则一直待在家里。
”使用as引导的从句表示随着时间的推移,某种情况逐渐发生或变化。
例如:“随着时间的推移,我越来越喜欢中国。
”XXX表示“在。
之前”或“才。
”。
例如:“成为一名老师之前,你需要成为一名学生。
”使用after表示“在。
之后”。
例如:“他比赛开始后才到达。
”till或until表示“直到。
为止”,但是要注意主句的动词类型。
如果是持续性动作,我们需要使用肯定式;如果是瞬间动作,我们需要使用否定式。
例如:“我等到他回来才停止工作。
”或者“直到十一点钟,她都没有停止工作。
”状语从句可以帮助我们更加准确地表达自己的意思,使语言更加流畅自然。
因此,在写作或口语中,我们应该尽可能地熟练掌握各种类型的状语从句。
Since 1978.China has XXX。
The verb in the main clause should be continuous。
while the XXX by "since" should have an instantaneous verb。
A comma should be used to separate the subordinate clause from the main clause when the subordinate clause comes before the main clause。
If the subordinate clause comes after the main clause。
XXX needed.As soon as I arrive in Shanghai。
表格“话”状语从句状语从句是在复合句中充当状语,用来修饰谓语动词、形容词和副词的句子。
状语从句按其意义和作用可以分为时间、地点、原因、条件、结果、方式、让步状语从句等。
在高考中主要考查一下几个方面:①引导状语从句的从属连词;②主从句的时态、语态;③与其他从句和句型的区别;④从句中的省略。
考点例析1.___________ the Internet is bridging the distance between people, it may also be breaking some homes or will cause other family problems.2. The cost of living in Glasgow is among the lowest in Britain, _________ the quality of life is probably one of the highest.3. It was not until near the end of the letter ________ she mentioned her own plan.4. One Friday, we were packing to leave for a weekend away ________ my daughter heard cries for help.5. I have heard a lot of good things about you _________ I came back from abroad.6. ________ I really don‟t like art, I find his work impressive.7. You must learn to consult your feelings and your reasons _________ you reach any decision.表二地点状语从句考点例析1. A number of high buildings have arisen ________ there was nothing a year ago but ruins.2.In peace too, the Red Cross is expected to send help ___________ there is human suffering.3.Everything was placed exactly___________ he wanted it for the graduation ceremony.1.Mark needs to learn Chinese ____________ his company is opening a branch in Beijing.2.He found it increasingly difficult to read, _________ his eyesight was beginning to fail.句型转换He is so young that he can‟t join the army.= He is ________ ___________ __________ join the army.= He is ________ ___________ __________ to join the army.= He is so young __________ ___________ ___________ join the army.表五方式状语从句考点例析考点例析1.I don ‟t believe we ‟ve met before, __________ I must say you do look familiar.2. _____________ I have to give a speech, I get extremely nervous before I start.3. One can always manage to do more things, no matter _____________ full one ‟s schedule is in life.4. —— Look at those clouds!—— Don ‟t worry. __________ it rains, we …ll still have a great time.表八 比较状语从句动词。
状语从句时状语从句连词引导从句的连词备注after, as, before, once, since, till, until, 1.hardly, no sooner 引导的从句要用过去完成时态,hardly 和 no sooner 在句首时,从句要部分倒装.Hardly had sb. done sth.+when/before... ;No sooner had sb. done sth. +than...间状语从句地点状语从句方式状语从句原因状语从句结果状语从句目的状语从句条件状语从句when,whenever,while,as soon as,hardly(scarcely)⋯ when,No sooner ⋯than, the time (moment, instant,minute, day ⋯ ),immediately,instantlywhere , whereveras, as if/thoughbecause, since, as, now (that)so ⋯ that,such (a)⋯that,so that,thatso that, in order thatif , unless, in case , as/as long as, only if,on (the)condition that,suppose/supposing(that),provided/providing (that)2.since 引导的从句注意看动词是瞬间动词还是延续性动词.Since句型 : It is /has been+time since sb+ 过去时态3.when 引导的从句注意其特殊用法.was about to do/was on the point of doing/was doing/had (not) done+when(就在那时)...4.before 的句型It will ( not ) be +time+before It was (not)+time before5.not ⋯ until 的在倒装句中和强调句中Not until+ 副词 / 介词短语 / 状语从句 +半倒装; It was not until+ 被强调部分 +that+句子其它部分后者表示强调 .as“按照”;“正如”语气一个比一个弱; for“因为”,引导的是并列句,表示非常明显的原因或者是作为推测的理由,但它只能位于句末. It must have rained last night, for the ground is wet. (推测的理由)The six blind men had never seen an elephant, for they were blind. (非常明显的原因)so ⋯ that和 such...that 中的 so 或 such 在句首,主句要部分倒装.So+形容词 / 副词 +半倒装 +that...so that 也可以引导结果状语从句“以至于...”注意分清 if 从句中是否该用虚拟语气.only if 位于句首 ,主句倒装比较状语从句让步状语从句as ⋯ as ;not so ⋯ as; the same as;such ⋯ as; thanthough, although, even though, as,while (“尽管”,只在句首) , nomatter how/wh-= -everHenry is not such a good worker as Peter .as 引导的让步状语从句要倒装; though 引导的让步状语从句可以倒装也可以不倒装名词 / 形容词 / 副词 / 动词原形 +as/though+ 主语 +谓语, +主句 .。
状语从句是副词性从句,它在句子中担任状语,修饰主句的动词、形容词、副词或句子。
根注意:时间状语从句(1)当主句是一般将来时、祈使句或主句中含有情态动词,这些词引导的从句要用一般现在时(主将从现)Don’t go to bed until you finish your homework.(2)When while as 的辨析A.相同点:都是“当。
时“不同点:when后用短暂性动词,指时间点,此时该从句的时态是一般现在时或一般过去时,后也可用延续性动词,指时间段,时态通常是进行时。
He was watching Tv when I came back.B.while引导的从句后必须是延续性动词,指时间段,常用进行时Someone knocked at the door while she was cooking.C.as着重指主从句同时发生“一边…一边“As we walked,we talked.(3)since 引导的从句一般用过去时,主句用现在完成时I have learnt English since I was 4 .目的状语和结果状语(1)目的状语从句引导词:so that. in order that从句中常用情态动词。
★so that既可引导目的状语从句,又可引导结果状语从句。
区别这两种从句的办法有两个:1)目的状语从句里往往带有情态动词can, could, may, mightwould等。
2)从意思上看,目的状语从句往往表示的目的很明确。
例如:Speak clearly so that they may understand you. (目的状语从句)Jack is badly ill so that he has to rest. (结果状语从句)(2)结果状语从句引导词:so...that,such...that.(3)so与such的区别①so+形+a/an+名单=such+a/an+形+名单②so+many/much/few/little+形+名(只能用so, 不用such)例如:Soon there were so many deer that they ate up all the wild roses.He has so little time that he can’t go to the cinema with you.③such+形+不可数名词/可数名词复数(4)so...that与too...to和...enough to间转换The apple is so dear that I can’t buy it.=The apple is too dear for me to buy.=The apple isn’t cheap enough for me to buy.。