FRM一级练习题(3)答案
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:198.02 KB
- 文档页数:4
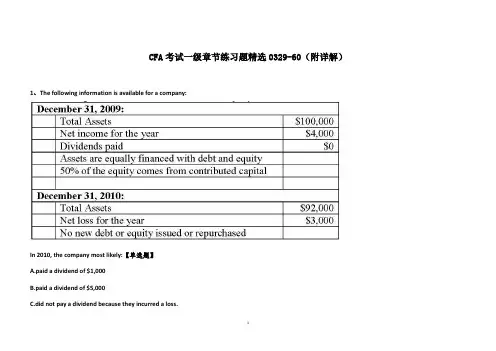
CFA考试一级章节练习题精选0329-60(附详解)1、The following information is available for a company:In 2010, the company most likely:【单选题】A.paid a dividend of $1,000B.paid a dividend of $5,000C.did not pay a dividend because they incurred a loss.正确答案:B答案解析:“Financial Reporting Mechanics,” Thomas R. Robinson, CFA, Jan Hendrik van Greuning, CFA, Karen O’Connor Rubsam, CFA, R. Elai ne Henry, CFA, and Michael A. Broihahn, CFA2010 Modular Level 1, Vol.3, pp. 43Study Session: 7-30-b, cExplain the accounting equation in its basic and expanded forms.Explain the process of recording business transactions using an accounting system based on the accounting equations.2、An analyst does research about gross profit margin and gathers the following informationabout a company in 2012 :● Average inventory is $2 000● Ending inventory of the year is $2 500● Total revenue is $20 000● Inventory turnover ratio is 5.5● Ta x rate is 40%The gross profit margin for the company is closest to:【单选题】A.27%B.31%C.45%正确答案:C答案解析:inventory turnover ratio = cost of goods sold/ average inventorygross profit = revenue - cost of goods soldgross profit margin = gross profit/ revenue所以,边际毛利率的计算如下:($20 000 - 5.5 × $2 000)/$20 000 = 45%。

FRM一级模拟题1 .If the daily returns of two assets are positively correlated, then:A. the covariance of their daily returns must be positiveB. the covariance of their daily returns must be zeroC. the covariance of their daily returns must be negativeD. nothing can be said about the covariance of their daily returnsAnswer: AIf variables are positively correlated, the covariance between the Variables will also be positive.2 .You are given that X and Y are random variables, and each of which follows a standard normal distribution with Covariance (X, Y) = 0.4. What is the variance of (5X+2Y)?A. 11.0B. 29.0C. 29.4D. 37.0Answer: DSince each variable is standardized, its variance is one. Therefore, Var(5X+2Y) = 25 x Var(X)+4xVar(Y)+2 x 5x2x Cov(X,Y) =25+4+8 = 373 . What is the covariance between populations A and B?If the variance ofA is 12, what is the variance of B?A. 10.00B. 2.89C. 8.33D. 14.40Answer:C5 . Which one of the following statements about the correlation coefficient is FALSE?A. It always ranges from -1 to +1B. A correlation coefficient of zero means that two random variables are independentC. It is a measure of linear relationship between two random variablesD. It can be calculated by scaling the covariance between two random variables Answer:BCorrelation describes the linear relationship between two variables. While we would expect to find a correlation of zero for independent .variables, finding a correlation of zero does not mean that two variables are independent.。

FRM一级模拟题1 . Assuming other things constant, bonds of equal maturity will still have different DV01 per USD 100 face value. Their DV01 per USD 100 face value will be in the following sequence of highest value to lowest value:A. Premium bonds, par bonds, zero coupon bondsB. Zero coupon bonds, Premium bonds, par bonds .C. Premium bonds, zero coupon bonds, par bondsD. Zero coupon bonds, par bonds, Premium bondsAnswer: ADVOI=PxMD/10000, price influences DVOI is larger than MD influence DVOI, zero-coupon bond have largest modified duration,premium bond smallest, But premium bond price is largest.So A is right not answer D.Duration2 .3 . What is the best estimate of the market value of a portfolio of USD 100 million invested in recently issued 6% 10-year bonds (its duration 7.802) and USD 100 million of long l0-year zero coupon bond if interest rates decline by 0.50%.A. USD 219 millionB. USD 195 millionC. USD 209 millionD. USD 206 m川ionAnswer: CStep I Total market initial value of the ponfolio =l00m+l00m=200mStep 2 WA=WB=l00m/200m=0.5Step 3 modified duration of the ponfolio = WA DA + WBDB =0.5x7.802+0.5x 10=8.901 Step4 AP = -MD x Po x Ay = -8.90lx200Mx(-50BP)/10000=8.901 MStep5 Total best estimate total market value =200 M+8.901 M=208.901 M209 M is close t0 208.901 M, so choice C4 . Which of the following is not a property of bond duration?A. For zero-coupon bonds, Macaulay duration of the bond equals its years to maturity.B. Duration is usually inversely related to the coupon of a bond.C. Duration is usually higher for higher yields to maturity.D. Duration is higher as the number of years to maturity for a bond selling at par or above increases.Answer: CIn general, the longer the term to maturity, all else equal, the greatei- the bond's duration. The greater the yield to maturity, all else equal, the lower the bond's duration. As yield decrease, theduration of bond increase at an increasing rate. So the convexity increases as the yieldsHolding yield constant, the lower the coupon, the higher the duration and the groater the convexity.So A, B and D are all right, we choice C.5 . A money markets desk holds a floating-rate note with an eight-year maturity. The interest rate is floating at three-month LIBOR rate, reset quarterly. The next reset is in one week. What is the approximate duration of the floating-rate note?A. 8 years .B. 4 yearsC. 3 months 'D. 1 weekAnswer: DDuration is not related to maturity when coupons are not fixed over the life of the investment. We know that at the next reset, the coupon on the FRN will be set at the prevailing rate. Hence, the market value of the note will be equal to par at that time. The duration or price risk is only related to the time to the next reset, which is I week here.。

FRM一级模拟题1 . Which one of the following long positions is more exposed to an increase in interest rates?A. A treasury billB. 10-year fixed coupon bondC. 10-yearfloaterD. 1 0-year reverse floaterAnswer: D ,The l0-year reverse floater has the highest effective duration and hence the most exposure to an increase in interest rates. Both the l0-year floater and the T-bill have short durations (bills have maturities of 52-weeks or less, while floaters, and have average durations equal to the time to reset). The l0-year fixed coupon bond falls in between the bill and the reverse floater2 . What can cause the total duration of a bond index to decrease even as the durations of each subsector (short, mid, and long) increase?A. There is a coupon payment on the largest bond in the indexB. Some bonds in the index rollover from long to mid, and some from mid to shortC. The whole yield curve shifts down by a substantial amountD. This cannot happenAnswer: BAs a bond rolls from one sub-sector to. another, it can increase the duration of each subsector, while lowering the duration for the portfolio as a whole. For example, if the portfolio has asub-sector of bonds with maturities of 2-10 years, and a bond rolls from die longer maturitysub-sector to the mid-maturity one, it is removing a bond from the longer maturity sub-sector that has z lower duration as compared to others in that sub-sector, and adding it to the mid-maturity sub-sector with a duration value that is greater than the other bonds in the mid-maturity sub-sector. The aging of the bond lowers the duration for the portfolio as a whole.3 . Which of the following fixed-income securities most likely has negative effective duration?A. A range accrual noteB. A floating rate noteC. An interest-only tranche of a CMOD. A principal-only tranche of a CMOAnswer: CAn I-O tranche has negative duration because a decline in interest rates causes the I-O price to fall. As rates fall and mortgages begin to prepay, the flows of an I-O tranche vanish. (Whenever some of the principal is paid-off there is less available from which to collect interest.) When rates are very high and prepayments are low, the I-O is like a security with a fixed set of cash flows. Jt has greater notional amount based on which interest will be calculated. The price of an interest-only tranche wⅢmost likely increase as interest rate increases, leading to a negative effective duration.to maturity of 8%. Assume par value of the bond to be $1,000:A. 2.00 yearsB. 1.94 yearsC. 1.87 yearsD. 1.76 years5 . The option-adjusted duration of a callable bond will be close to the duration of a similar non-callable bond when the:A. Bond trades above the call priceB. Bond has a high volatilityC. Bond trades much lower than the call priceD. ' Bond trades above parity。

FRM一级模考FRM一级模拟题1 .Which concept gives a measure of historical value added per unit of risk taken and can be useful, among other tools, to risk managers?A. Trackingerror' B. Model alphaC. Information ratioD. HeteroskedasticityAnswer: CWilliam Sharpe developed the concept of information ratio to describe the value added per unit of risk by a manager or activity. It is usually developed by analyzing at least 36 months of returns. Tracking error is an estimate ofhow much risk a manager takes as a measure ofthe deviation from a benchmark.2.A stack-and-roti hedge as described in the Metallgesellschaft case is best described as:A. Buying futures contracts of different expirations and allowing them to expire in sequence.B. Buying futures contracts of different expirations and closing out the position shortly before expiration.C. Using short-term futures to hedge a long-term risk exposure by replacing them with longer-term contracts shortly before they expire.D. Using short-term futures contracts with a larger notional value than the long-term risk they are meant to hedge.Answer: CA stack is a bundle of futures contracts with the same expiration. Over time, a firm may acquire stacks with variousexpiry dates. To hedge a long-term risk exposure, a firm would close out each stack as it approaches expiry and enter into a contract with a more distant delivery, known as a roll.This strategy is called a stack-and-roll hedge and is designed to hedge long-term risk exposures with short-term contracts. Using short-term futures contracts with a larger notional value than the. long-term risk they are meant to hedge could result in over hedging" depending on.the hedge ratio.3 . Past financial disasters have resulted when a firm allows a trader to have dual roles as both the head of trading and the head of the back-office support function. Which of the following case studies did not involve this particular operational risk oversight?IDrysdale SecuritiesII DaiwaIII AlliedIrish BankIV BaringsA. IonlyB. II and IVC. I and IIIAnswer: CThe rogue traders for both Daiwa and Barings had dual rojes as both the head of trading and the head of the back-office support function. This operational risk oversight allowed them to hide millions in losses from senior management. In the Allied Irish Bank case, John Rusnak did not run the back-office operations. The Drysdale Securities case did not deal with a rogue trader.4 .Which of the following reasons does not help explain the problems -of LTCM inAugust and September 1998:A. A spike in correlationsB. An increase in stock index volatilitiesC. A drop in liquidity ' 'D. An increase in interest rates on on-the-run TreasuriesAnswer: DIncreased volatility and higher correlations led to substantial losses in LTCM's highly-leveraged portfolio. A significant drop in market liquidity forced LTCM to liquidate these highly-leveraged positions at substantial discounts. An increase in the spread between U.S. treasury rates and Russian government rates resulted in significant losses.5 .The following is not a problem of having one employee perform trading functionsand back office function s:A. The employee gets paid more because he performs two functions.B. The employee can hide trading mistakes when processing the trades.C. The employee can hide the size of his book.D. The employee firm may not know its true exposure.Answer: ATo minimize operational risk, trading and back office functions should not be performed by the same employee. The risks of doing so include hiding trading mistakes and hiding the size of exposures in the trading book. The extra direct compensation cost of paying the same employee to perform both functions is minimal compared to the potential operational risk costs.。

专注国际财经教育FRM一级模拟题1 . When a bank decides to lend amount of money to borrowers, several considerations must be taken into account, based on the following statement which one is incorrect.A. Outstanding represent the total credit available to the borrower.B. Borrowers in distress often draw down on their unused commitment, so the adjusted exposure is outstanding plus usage given default times unused commitment.C. Credit optionality denotes the call option the borrower has purchased on the commitment for "a commitment fee".D. Collateral and seniority are the two most important factors in assessing recovery rates. Answer: ACommitment is the total credit available to the borrower.2 . Suppose ABC bank has booked a loan with following characteristics, it has total commitment of 3,000,000, 2,000,000 is outstanding. T he bank estiamate l% default probability (EDF) in one year, and draw down on default is 65%. The bank is currently experienced 60% of loss given default. The standard deviation of EDF and LGD is 5% and 30%, respectively. Please find the adjusted exposure.3 . The one-day Credit at Risk (CaR) of a portfolio is $1,000,000. What is the ten-day credit at risk?A. $10,000,000B. $3,162,278C. $5,136,498' .D. $1,923,657Answer: B。

FRM一级练习题(1)1、An investment manager is given the task of beating a benchmark. Hence the risk shoul d be measured in terms ofA. Loss relative to the initial investmentB. Loss relative to the expected portfolio valueC. Loss relative to the benchmarkD. Loss attributed to the benchmark2、Based on the risk assessment of the CRO, Bank United's CEO decid ed to make a large investment in a levered portfolio of CDOs. The CRO had estimated that the portfolio had a 1% chance of l osing $1 billion or more over one year, a loss that would make the bank insolvent. At the end of the first year the portfolio has lost $2 billion and the bank was cl osed by regulator. Which of the foll owing statement is correct?A. The outcome d emonstrates a risk management failure because the bank did not eliminate the possibility of financial distress.B. The outcome demonstrates a risk management failure because the fact that an extremely unlikely outcome occurred means that the probability of the outcome was poorly estimated.C. The outcome demonstrates a risk management failure because the CRO failed to go to regulators to stop the shutd own.D. Based on the information provid ed, one cannot determine whether it was a risk management failure.3、An analyst at CARM Research Inc. is projecting a return of 21% on Portfolio A. The market risk premium is 11%, the volatility of the market portfolio is 14%, and the risk-free rate is 4.5%. Portfolio A has a beta of 1.5. According to the capital asset pricing model which of the foll owing statements is true?A. The expected return of Portfolio A is greater than the expected return of the market portfolio.B. The expected return of Portfolio is less than the expected return of the market portfolio.C. The return of Portfolio A has l ower volatility than the mark t portfolio.D. The e peered return of Portfolio A is equal to the expected return of the market portfolio.4、Suppose Portfolio A has an expected return of 8%, volatility of 20%, and beta of 0.5. Suppose the market has an expected return of 10% and volatility of 25%. Finally suppose the risk-free rate is 5%. What is Jensen’s Alpha for Portfolio A?A. 10.0%B. 1.0%C. 0.5%D. 15%5、Which of the foll owing statement about the Sharpe ratio is false?A. The Sharpe ratio consid ers both the systematic and unsystematic risk of a portfolio.B. The Sharpe ratio is equal to the excess return of a portfolio over the risk-free rate divided by the total risk of the portfolio.C. The Sharpe ratio cannot be used to evaluate relative performance of undiversified portfolios.D. The Sharpe ratio is derived from the capital market line.6、A portfolio manager returns 10% with a volatility of 20%. The benchmark returns 8% with risk of 4%. The correlation between the two is 0.98. The risk-free rate is 3%. Which of the foll owing statement is correct?A. The portfolio has higher SR than the benchmark.B. The portfolio has negative IR.C. The IR is 0.35.D. The IR is 0.29.7、In perfect markets risk management expenditures aimed at reducing a firm' diversifiable risk serve toA. Make the firm more attractive to sharehol ders as long as costs of risk management are reasonable.B. Increase the firm's value by lowering its cost of equity.C. Decrease the firm's value whenever the costs o f such risk management are positive.D. Has no impact on firm value.8、By reducing the risk of financial distress and bankruptcy, a firm's use of d erivatives contracts to hedge it cash fl ow uncertainty willA. Lower its value due to the transaction costs of derivative trading.B. Enhance its value since investors cannot hedge such risks by themselves.C. Have no impact on its value as investor costless diversify this risk.D. Have no impact as only systematic risks can be hedged with derivatives.参与FRM的考生可按照复习计划有效进行,另外高顿网校官网考试辅导高清课程已经开通,还可索取FRM 考试通关宝典,针对性地讲解、训练、答疑、模考,对学习过程进行全程跟踪、分析、指导,可以帮助考生全面提升备考效果。

FRM一级模拟题1 . A covered call writing position is equivalent to:A a long position in the stock and a long position in the call optionB. a short put positionC. a short position in the stock and a long position in the call optionD. a short call positionAnswer: BA covered call position is a long position in the stock and a short position on the call option. The payoff to this position is equivalent to a short put position, in which both have eliminated the upside potential but still have the downside exposure.2 . A portfolio manager wants to hedge his bond portfolio against changes in interest rates. He intends to buy a put option with a strike price below the portfolio's current price in order to protect against rising interest rates. He also wants to sell a call option with a strike price above the portfolios current price in order to reduce the cost of buying the put option. What strategy is the manager using?A.Bear spreadB. StrangleC. CollarD. StraddleAnswer: CA. Incorrect. The description is not for bear spread. A bear spread is created by buying a nearby put and selling a more distant put. A bear spread can also be set up using calls.B. Incorrect. The description is not for box spread. If the options are correctly priced, then the risk free rate will be earned for a box spread.C. Correct. The description is for a collar strategy which limits changes in the portfolio value in either direction. In other words, a collar is defined around the current portfolio value.D. Incorrect. The description is not for straddle. A straddle is created by buying a put and a call atthe same strike price and expiration to take advantage of significant portfolio moves in either direction.3 . A butterfly spread involves positions in options with three difference strike prices. It can be created by buying a call option with a low strike of _Xi; buying a call option with a high strike X3; and selling two call options with a strike X2 halfway between X] and X3. What can be said about the upside and downside of the strategy?A. Both the upside and downside is unlimitedB. Both the upside and downside is limitedC. The upside is unlimited but the downside is limitedD. The upside is limited but the downside is unlimitedAnswer: BThe pay-off structure to this strategy leaves the upside and downside potential 'at the difference between the premium collected on the calls sold and the premium paid on the calls purchased4 . Which of the following will create a bull spread?A. Buy a put with a strike price of X = 50, and sell a put with a strike price of 55.B. Buy a put with a strike price of X= 55, and sell a put with a strike price of 50.C. Buy a call with a premium of 5, and sell a call with a premium of 7D. . Buy a call with a strike price of X = 50, and sell a put with a strike price of 55.Answer: AIf an investor buys a put with a mike _of 50 and sells a put with a strike of 55, he or she will gain the value of the premium on the put sold at 55 less the call of the premium purchased at 50j as long as the value of the stock is 55 0r more. If the value falls below 50, the most he or she will lose is $5.00.。

frm一级考试真题一级考试主要是看理解与掌握金融资产定价理论与方法,同时也是对金融资产定价相关知识的一个检验。
一级考试最大的特点是题目的难度较大;但相对来说难度也是中等的。
本次的试题以“新冠肺炎疫情”为主题,考察了金融资产定价理论与方法中涉及到的风险评估与风险管理。
本题共有11个问题:新冠肺炎疫情对金融资产估值影响的分析方法以及影响?新冠肺炎疫情对市场利率与金融资产定价体系会有什么影响?金融资产定价模型有哪些关键要素?1.对于新冠肺炎疫情的分析,以下哪个因素会影响新冠肺炎的估值?对于疫情的相关分析,需要考虑两个变量:政府对疫情的反应程度(paradox)和新冠肺炎对经济的影响(predictive)。
对于政府做出的反应程度,需要考虑两个因素:一是政府对疫情管控力度是否足够(rasmust);二是新冠肺炎对经济的影响(value)。
答案:政府对疫情反应程度对疫情结束后股市的估值产生巨大影响,进而影响到股市盈利水平。
此外,疫情在不同国家之间存在较大差异。
所以,应该考虑各国政府采取的不同应对措施对股市价值产生影响而决定股市估值水平。
2.对新冠肺炎疫情估值影响,下列哪种分析方法能充分说明?【答案】 C。
解析:对于新冠肺炎疫情,目前采用的技术并不能完全预测风险变化结果。
对于风险调整后的收益(长期),其影响主要体现在两个方面:对未来现金流折现)的影响;以及投资价值损失)。
但并不是所有的疫情冲击都会对收益产生影响(有正面影响的也有负面影响)。
对未来现金流(长期)影响最大的是疫情冲击导致的投资价值下降问题。
因此,虽然疫情冲击可以直接影响现金流(长期),但短期内还是会对投资价值产生一定影响。
对于投资价值损失)的影响,根据 FRM理论(最优经济参数)并考虑企业正常运营可能面临的不确定性和非线性风险后,最终确定长期投资价值影响系数并求得相应的参数范围。
因此本题可以说采用了最优经济参数作为判断标准进行相关分析。
3.从疫情爆发到疫苗研发成功,至少需要一个周期?答:如果想要研发出一种有效的疫苗,至少需要一个周期。

FRM一级模考试题(一)——答案1.Answer: CThe historical simulation method may not recognize changes in volatility and correlations from structural changes.2.Answer: CThe dirty price of the bond is calculated as N = 10; I/Y = 2.5; PMT = 30; FV = 1,000; CPT→PV = 1,043.76. Adjusting the PV for the fact that there are only 90 days until the receipt of the first coupon gives $1,043.76×(l.025)90/180 = $1,056.73. Clean price = dirty price - accrued interest = $1056.73 - $30(90/180) = $1,041.73.3.Answer: BGamma (not theta) represents the expected change in delta for a change in the value of the underlying. In-the-money options are more sensitive to changes in rates (rho is higher) than out-of-the-money options.4.Answer: AAssuming no default risk, the domestic return is 7.35%. The return on the UK investments, however, is equal to the amount invested today, (USD$2,000,000)/(USD1.62GBP)= GBP1,234,568, which turns into GBP1,234,568×1.08 = GBP1,333,333 one year from now. Since the forward contract guarantees the exchange rate in the future, this translates into GBP1,333,333 ×USD1.5200/GBP = USD2,026,666. This is a dollar return to the bank of USD2,026,666/ USD2,000,000-1 = 1.33%. Hence, the weighted average return to the bank’s investments is (0.5)×(7.35%) + (0.5)×(1.33%) = 4.34%. Since the cost of funds for the bank is 5.5%, the net interest margin for the bank is 4.34-5.50 = -1.16%.5.Answer: DAll of the statements are correct except choice d: the value of the firm’s equity should be the present value of its expected free cash flows (not net income).6.Answer: D± So youWith a known variance, the 95% confidence interval is constructed as Xknow that 33.23307.Answer: DA 6% rate compounded annually is approximately equivalent to a 5.8269% rate (rounded to four decimal places) compounded continuously. In (1 + 0.06) = 0.058268908 Using put-call parity:0.0582690 4.1027.5025$5.04rTp c XeS e −−=+−=+−=8.Answer: AV AR measures the expected amount of capital one can expect to lose within a given confidence level over a given period of time. One of the problems with V AR is that it does not provide information about the expected size of the loss beyond the V AR. V AR is often complemented by the expected shortfall, which measures the expected loss conditional on the loss exceeding the V AR. Note that since expected shortfall is based on V AR, changing the confidence level may change both measures. A key difference between the two measures is that V AR is not sub-additive, meaning that the risk of two funds separately may be lower than the risk of a portfolio where the two funds are combined. Violation of the sub-additive assumption is a problem with V AR that does not exist with expected shortfall. 9.Answer: CThe fixed payments made by Cooper are (0.07/2)×$2,000,000 = $70,000. The present value of the fixed payments =0.0650.50.0681.0(0.0751.5)($70,000)($70,000)($70,000$2,000,000)$67,762$65,398$1,849,747$1,982,907e e e −×−×−×+++×=++=The value of the floating rate payments received by Cooper at the payment date is the value of the notional principal, or $2,000,000.The value of the swap to Cooper is ($2,000,000-$1,982,907) = $17,093. 10.Answer: CA stack is a bundle of futures contracts with the same expiration. Over time, a firm may acquire stacks with various expiry dates. To hedge a long-term risk exposure, a firm would close out each stack as it approaches expiry and enter into a contract with a more distant delivery, known as a roll. This strategy is called a stack-and-roll hedge and is designed to hedge long-term risk exposures with short-term contracts. Using short-term futures contracts with a larger notional value than the long-term risk they are meant to hedge could result in over hedging” depending on the hedge ratio. 11.Answer: BThe duration of a portfolio of bonds is the weighted average (using market value weights) of thedurations of the bonds in the portfolio. First let’s find the weights.Bond Price as Percentage of Par Face Value $ Market Value $1 95.5000 2,000,000 1,910,0002 88.6275 3,000,000 2,658,8253 114.8750 5,000,000 5,743,750 Total 10,312,575The weights based on market values are:Weight of bond 1 = 1,910,000 / 10,312,575 = 0.1852Weight of bond 2 = 2,658,825 / 10,312,575 = 0.2578Weight of bond 3 = 5,743,750 / 10,312,575 = 0.5570Bond Weights Duration WeightedDuration1 0.1852 6.95 1.28712 0.2578 9.77 2.51873 0.5570 14.81 8.2492Total 12.055012.Answer: CTo increase the beta of the portfolio from the market beta (1.0) to 1.5, the portfolio manager should take a long position:# of contracts =$250,000,000(1.5 1.0)4171,200250−×=×contracts13.Answer: BThe concessionality of a MYRA is defined as the difference between the present value of the loans before and after the restructuring.14.Answer: BThe formula is JB =2222(3)180(43)1[][0]30[]7.5 64644n KS−−+=+==Note that excess kurtosis is equal to K-3 so excess kurtosis of 1 means that kurtosis is 4.15.Answer: CThe rogue traders for both Daiwa and Barings had dual roles as both the head of trading and the head of the back-office support function. This operational risk oversight allowed them to hide millions in losses from senior management. In the Allied Irish Bank case, John Rusnak did not run the back-office operations. The Drysdale Securities case did not deal with a rogue trader.16.Answer: AThe fact that mean> median> mode is consistent with a distribution that is positively skewed. For all normal distributions, kurtosis = 3. Excess kurtosis = kurtosis-3, which is 0 for a normal distribution. In this case, excess kurtosis = 2, which means kurtosis = 5. This means that the distribution being examined is more peaked than the normal distribution and is said to be leptokurtic. 17.Answer: CA change from a Ba to Baa rating is an example of a credit upgrade. A credit upgrade will decrease the likelihood of default (EDF) reducing expected loss. Note that expected loss is an estimate of average future loss. Actual loss is by definition equal to zero until a credit event occurs. 18.Answer: BThe CAPM assumes that the market portfolio should be the portfolio with the highest Sharpe ratio of all possible portfolios and should include all investable assets. It also assumes that the expected excess returns for the market are assumed to be known in that investors have access to the same information. As well, it assumes that returns are normally distributed and investors’ expectations for risk and return ate identical. 19.Answer: CThe 3-month forward rate is calculated as follows:1()(0.0650.05)0.250,()$19$19.07r T T T F S e e δ−−==×=20.Answer: CThe farmer needs to be short the futures contracts. The two sources of basis risk confronting the farmer will result from the fact that he is using a cattle contract to offset the price movement of his buffalo herd, Cattle prices and buffalo prices may not be perfectly positively correlated. As a result, the correlation between buffalo and cattle prices will have an impact on the basis of the cattle futures contract and spot buffalo meat. The delivery date is a problem in this situation, because the farmer’s hedge horizon is winter, which probably will not commence until December or January. In order to maintain a hedge during this period, the farmer will have to enter into another futures contract, which will introduce an additional source of basis risk. 21.Answer: BA scattergram can help determine whether a relationship is positive or negative. Since the population and sample coefficients are almost always different, the residual will very rarely equal the corresponding population error term.Answer: C0.02(0.25)0.04(0.25)01,1001,08025.26qT rT S e Ke e e −−−−−=−=23.Answer: DPractitioners primarily use structural models, while academics are the primary users of statistical models. There are three types of structural models and one of them includes the need to forecast both factor returns and exposures. Factors in structural models are intuitive and well-known, while factors in statistical models are implied factors derived through a statistical operation. Structural models assume an underlying economic relationship between factors and stock returns. 24Answer: ABecause catastrophe bonds are riskier than straight bonds issued by the same firm, they usually have maturities less than three years and are usually non-investment-grade bonds. They also have potentially useful diversification qualities as their returns, being linked to operational losses, are not highly correlated with market returns. 25.Answer: AFor a risk management activity to have value, the firm must be able to do something for shareholders that they cannot do themselves. The risk of bankruptcy cannot be hedged by shareholders (as beta risk and output-price risk can), thus, it may be value increasing for the firm to hedge this risk. Note that it is not a question that bankruptcy costs are too expensive to hedge; they are impossible to hedge. Although Choices b and c may be correct, they are less relevant to the situation and are, therefore, not the best answers. 26.Answer: BIn this case, U = 1.1, D = 0.9, r = 0.035, and the value of the option is $1 if the stock increases and $0 if the stock decreases. The probability of an up movement, ∏U, can be calculated as0.0353/12(0.9)/(1.10.9)0.5439e ×−−=The value of the call option is therefore (0.0353/12)(0.5439$1)/$0.54e××=27.Answer: CStandards 2.1 and 2.2—Conflicts of Interest. Members and candidates must act fairly in all situations and must fully disclose any actual or potential conflict to all affected parties. Sell-side members and candidates should disclose to their clients any ownership in a security that they are recommending.28.Answer: BThe Treynor measure is most appropriate for comparing well-diversified portfolios. That is the Treynor measure is the best to compare the excess returns per unit of systematic risk earned by portfolio managers, provided all portfolios are well-diversified.All three portfolios managed by Donaldson Capital Management are clearly less diversified than the market portfolio. Standard deviation of returns for each of the three portfolios is higher than the standard deviation of the market portfolio, reflecting a low level of diversification.Jensen’s alpha is the most appropriate measure for comparing portfolios that have the same beta. The Sharpe measure can be applied to all portfolios because it uses total risk and it is more widely used than the other two measures. Also, the Sharpe ratio evaluates the portfolio performance based on realized returns and diversification. A less-diversified portfolio will have higher total risk and vice versa.29.Answer: DThe central limit theorem holds for any distribution (skewed or not) as long as the sample size is large (i.e., n >30). The mean of the population and the mean of the distribution of all sample means are equal. The standard deviation of the mean many observations is less than the standard deviation of a single observation.30.Answer: CUnexpected loss is a measure of the variation in expected loss. As a precaution, the bank needs to set aside sufficient capital in the event that actual losses exceed expected losses with a reasonable likelihood. For example, smaller recovery rates would be indicative of larger actual losses.31.Answer: CGiven that the economy is good, the probability of a poor economy and a bull market is zero. The other statements are true. The P(normal market) = (0.60×0.30) + (0.40×0.30) = 0.30. P(good economy and bear market)= 0.60×0.20 = 0.12. Given that the economy is poor, the probability of a normal or bull market = 0.30 + 0.20 = 0.50.32.Answer: DNone of the statements are correct. The historical approach uses historic data from past crisis events, the prospective scenario conditional approach includes correlations between risk factors, and the factor push method is a prospective approach not a historical approach.33.Answer: BRisk management activities can increase firm value when the firm’s claimholders cannot takeactions to replicate the results of hedging activity. Claimholders are willing to pay for the firm to do something they cannot do on their own accounts.34.Answer: CTop-down models rely primarily on aggregate historical data. Therefore, they are relatively simple and do not differentiate between high-frequency low-severity events and low-severity, high-frequency events because both are pooled together in the data. The aggregated nature of the data also limits the amount of data used in these models. A limitation of aggregated data, however, is that top-down models do not have diagnostic capabilities like bottom-up models that dissect processes into individual components.35.Answer: CBuying a call (put) option with a low strike price, buying another call (put) option with a higher strike price, and selling two call (put) options with a strike price halfway between the low and high strike options will generate the butterfly payment pattern. Two other wrong answer choices deal with bull and bear spreads, which can also be replicated with either calls or puts. A bull spread involves purchasing a call (put) option with a low strike price and selling a call (put) option with a higher exercise price. A bear spread is the exact opposite of the bull spread.36.Answer: DCaptive insurers are off-shore, wholly owned subsidiaries that may deduct for tax purposes the discounted value of all future expected losses stemming front a claim spanning several years. Essential this allows self-insurers to deduct losses before they have even occurred. Incurring costs to manage and control operational risk achieves the same result in principle as self-insurance. A contingent line of credit is a form of self-insurance that provides liquidity in the event of a loss rather than building up cash reserves in anticipation of a loss.37.Answer: DThe futures contract ended at 985 on the first day. This represents a decrease in value in the position of (1,000-985)×$250×20 = $75,000. The initial margin placed by the manager was $12,500×20 = $250,000. The maintenance margin for this position requires $10,000×20 = $200,000. Since the value of the position declined $75,000 on the first day, the margin account is now worth $175,000 (below the $200,000 maintenance margin) and will require a variation margin of $75,000 to bring the position back to the initial margin. It is not sufficient just to bring the position back to the maintenance margin.38.Answer: CWe are given that the forward exchange rate in one year is 1.200 and are asked to find the exchange rate in three years. This means we need to apply the 2-year forward rate one year fromtoday.The 2-year forward rate in the United States is:1.04811 4.81%==−=The 2-year forward rite in Europe is:1.022512.25%==−=Finally, we can apply interest rate parity:221.04811.200 1.2611.0225t F =×= 39.Answer: AStandards 3.1 and 3.2 relate to the preservation of confidentiality. The simplest, most conservative, and most effective way to comply with these Standards is to avoid disclosing any information received from a client, except to authorized fellow employees who are also working for the client. If the information concerns illegal activities by MTEX, Black may be obligated to report activities to authorities. 40.Answer: AThe liquidity preference theory suggests that the shape of the term structure is determined by the fact that most investors prefer short-term liquid assets, holding return constant. 41.Answer: AIn general, bond prices will tend to increase with maturity when coupon rates are above relevant forward rates. When short-term rates are below the forward rates utilized by bond prices, the investors who invest in longer-term investments will tend to outperform investors who roll over shorter-term investments. 42.Answer: CThe forward rate can be calculated as [(98.2240/96.7713)-1]×2 = 3%. 43.Answer: BThe price is calculated as $15 (0.992556) + $15 (0.982240) + $1,015 (0.967713) = $1,011.85. 44.Answer: AUnique among swaps, equity swap payments may be floating on both sides (and the payments not known until the end of the settlement period). Similar to options, premiums for swaptions are dependent on the strike rate specified in the swaption. The most common reason for entering into commodity swap agreements is to control the costs of purchasing resources, such as oil and electricity. A negative index return requires the fixed-rate payer to pay the percentage decline in the index. 45.Answer: BThe GARCH (1,1) estimate of volatility will be:220.000005(0.13)(0.03)(0.85)(0.022)0.0005330.0231 2.31%volatility ++====46.Answer: B0.04250.5($200.0349)($250.0263)$0.02582$0.03P e −×=××−×=≈47Answer: DThe minimum value for a European-style call option, c T is given by3/12max[0,/(1)]max[0,8680/(1.03)]$6.59T T F S X R −+=−=An American style call option must be worth at least as much as an otherwise identical European-style call option and has the same minimum value Note that this fact alone limits the possible correct responses to Choices a and d. Since the American style call is in the money and therefore must be worth more than the $6 difference between the strike price and the exercise price, you can eliminate Choice a and select Choice d without calculating the exact minimum value. 48.Answer: AThe appropriate test is an F-test, where the larger sample variance (Index A) is placed in the numerator. 49.Answer: DThe formula for the Treynor measure is ()[p FPE R R β−. Thus, the value for the Treynor measurein this case is (0.10 - 0.04)/0.75 = 0.08 50.Answer: DThe coefficient of variation, CV = standard deviation/arithmetic mean, is a common measure of relative dispersion (risk) CV W = 0.4/0.5 = 0.80, CV X = 0.7/0.9 = 0.78; CV Y = 4.7/l.2 = 3.92 and CV Z = 5.2/1.5=3.47 Because a lower relative risk, Security X has the lowest relative risk and Security Y has the highest relative risk.51.Answer: AThe probability of rescheduling sovereign debt is positively related to the debt-service ratio, the import ratio, the variance of export revenue, and the domestic money supply growth.52.Answer: BAccording to the cash-and-carry Formula, the futures price should be:(0.02750.01)0.25e−=1,010$1,014.43Hence, the futures is overvalued, indicating it should he sold and the index be purchased for a risk-free profit of $1,020 —$1,014.43 = $5.57.53.Answer: DHoffman has violated both Standard 1.2-independence and objectivity, which specially mentions that CARP Members must not offer, solicit, or accept any gift, benefit, compensation, or consideration that could be reasonably expected to compromise their own or another’s independence and objectivity, and Standard 2.2-Conflicts of Interest, which states the Members should make full and fair disclosure of all matters that could reasonably be expected to impair independence and objectivity or interfere with respective duties to their employer, clients, and prospective clients.54.Answer: DThe variability in the receipt of payments from the floating-rate asset is eliminated, as the floating payment of the floating rate leg of the swap offsets the receipt of the floating rate on the asset. The floating-rate payer is effectively left with a fixed-rate asset.55.Answer: DExpected value = (0.4)(10%) + (0.4)(12.5%) + (0.2)(30%) = 15%Variance = (0.4)(10-15)2 + (0.4)(12.5 -15)2 + (0.2)(30 - 15)2 = 57.5Standard deviation =56.Answer: D,,220.05 1.250.2S FS F F Cov HR Beta σ====57.Answer: AOption-free bonds have positive convexity and the effect of (positive) convexity is to increase the magnitude of the price increase when yields fall and to decrease the magnitude of the price decrease when yields rise. 358.Answer: CThe standard normal random variable, denoted Z, has mean equal to 0 and standard variation (and variance) equal to 1. Also, a multivariate distribution is meaningful only when the behavior of each random variable in the group is in some way dependent upon the behavior of others.59.Answer: DThe critical z-value for a one-tailed test of significance at the 0.01 level will be either +2.33 or -2.33. The test statistic for hypotheses concerning equality of variances is 2122S F S = The statement regarding p-value is true. A Type II error is failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false.60.Answer: BThe Taylor Series does not provide good approximations of price changes when the underlying asset is a callable bond or mortgage-backed security. The Taylor Series approximation only works well for “well-behaved” quadratic functions that can be approximated by a polynomial of order two.61.Answer: DLTCM believed that, although yield differences between risky and riskless fixed-income instruments varied over time, the risk premium (or credit spread) tended to revert (decrease) to average historical levels. This was similar to their equity volatility strategy. Also, their balance sheet leverage was actually in line with other large investments banks (but their true leverage, economic leverage, was not considered).62.Answer: BThe benchmark returns are not important here. The average of the portfolio returns is(6+9+4+12)14=31/4=7.75.0.4743==63.Answer: D Neither statement is correct. The appropriate number of contracts for the hedge is:$10,000,000() 1.0()36 1,100250portfolio portfolio value contracts futures price multiplierβ×=×≈×× However, since the manager is long the portfolio, he will want to take a short position in the 36 contracts.Change in value of portfolio = -0.01($10,000,000) = -$100,000.Change in value of futures position = 36(1,100 — 1,090)(250) = $90,000.Net payoff= -$100,000 + $90,000 = -$10,000 The net impact is a loss of $10,00064.Answer: CAt the end of year 1 there is a 0% chance of default and a 90% chance that the firm will maintain an Aaa rating. In year 2, there is a 0% chance of default if the firm was rated Aaa after 1 year (90%×0% = 0%), There is a 5% chance of default if the firm was rated Baa after 1 year (10%×5% = 0.5%). Also, there is a 15% chance of default if the firm was rated Caa after 1 year (0%× 15% = 0%) The probability of default is 0% from year 1 plus 0.5% chance of default from year 2 for a total probability of default over a 2-year period of 0.5%.65.Answer: AThe beta factors used in the standardized approach for operationa1 risk are as follows: trading and sales 18%, retail banking 12% agency and custody services 15%, asset management: 12%.66.Answer: AAccording to put-call parity:000rT c Xe p S −+=+The left-hand side=$4+$45e -0.06×0.5 = $47.67The right-hand side = $4 + $43 = $47Since the value of the fiduciary call is not equal to the value of the protective put, put-call parity is violated and there is an arbitrage opportunity.Sell overpriced and buy underpriced. That is, sell the fiduciary call and buy the protective put. Therefore, sell the call for $4, sell the Treasury bill for $43.67 (i.e., borrow at therisk-free rate), buy the put for $4 and buy the underlying asset for $43. The arbitrageprofit is $0.67.67.Answer: BThe 5-3-2 spread tells us the amount of profit that can be locked in by buying five barrels of oil and producing three barrels of gasoline and two barrels of heating oil.(61.5×3) + (58.5×2) - (55×5) = $26.50 for 5 barrels; $5.30/barrel68.Answer: CUse interest-rate parity to solve this problem. 1.1565 = Se (0.02-0.04)0.25, so S = 1.1623.69.Answer: AUnsystematic risk is asset-specific and, therefore, a diversifiable risk. The market risk premium is also known as the price of risk and is calculated as the excess of the expected return on the market over the risk-free rate of return. The risk premium of an asset is calculated as beta times the excess of the expected return on the market over the risk-free rate of return.70.Answer: C12[()][()] 6.523.56.520.325.88 3.5i i j j i j ij i j i j R E R R E R Cov Cov r σσσσ−×−========××Σ71.Answer: DMoral hazard refers to the fact that an insured party may engage in risky behavior (or at least behave in a less risk-averse manner) knowing that an insurance policy will insulate the party against the consequences of such behavior. The way that Eggenton can mitigate the moral hazard problem is to include a deductible or co-insurance feature that would force JT Cola to pay a portion of the cost should a claim be made against the policy. If a deductible feature were not included in the policy, JT Cola management would have been free to act in any manner they would choose, including manipulating the global cola market, and Federal Insurance Group would have assumed all of the risk.72.Answer: BWe can calculate the expected loss as follows.EL = AE×EDF×LGDMaximum lossAdjusted exposure = OS + (COM U - OS)×UGD= $8,000,000 + ($12,000,000)×(0.75)= 17,000,000EL = ($17,000,000)×(0.02)×(0.80) = $272,000Minimum lossAdjusted exposure = OS + (COM U - OS)×UGD= $8,000,000 + ($12,000,000)×(0.5)= $14,000,000EL = ($14,000,000)×(0.01)×(0.80) = $112,000Therefore, the difference between maximum and minimum loss is:$272,000 - $112,000 = $160,000.73.Answer: ASince the current position is short gamma, the action that must be taken is to go long the option in the ratio of the current gamma exposure to the gamma of the instrument to be used to create the gamma-neutral position (5,000/2 = 2,500). However, this will change the delta of the portfolio from zero to (2,500×0.7) = 1,750. This means that 1,750 of the underlying stock position will need to be said to maintain both gamma and delta neutrality.74.Answer: BYou have purchased a bull spread. You will exercise the call chat you purchased for a net profit of (34 - 25) - 3 = $6 per share. The call that you sold will not be exercised, so your net profit is the cost of $1 per share. Your total net profit is 6 + 1 = $7 per share.75.Answer: AIf the investor has written 15,000 call options, he must go long delta times the short option position to create a delta-neutral position. or buy $15,000×0.50 = 7,500 shares. Note that the delta of a call option, which is exactly at-the-money, is 0.5.76.Answer: BThe historical simulation V AR for 5% is the fifth lowest return, which is -1.59%; therefore, the correct V AR is: -79,500 = (-0.0159)×(5,000,000).77.Because firms tend to release good news more readily than bad news, downgrades may be more of a surprise, so downgrades affect stock prices more than upgrades when the firm reveals the good news associated with the upgrade prior to its occurrence.The “underrating” and “overrating” is seen more with the use of the through-the-cycle approach. As well, the ratings delivered by more specialized and regional agencies tend to be less homogeneous than those delivered by major players like S&P and Moody’s.78.Answer: BOperational risk economic capital is the difference between the loss at a given confidence level and the expected loss. In this case, $500,000 - $50,000 = $450,000.79.Answer: AThe head of the government bond trading desk at Kidder Peabody, Joseph Jett, misreported trades, which allowed him to report substantial artificial profits. After these errors were detected, $350 million in falsely reported gains had to he reversed.80.Answer: BThe R2 of the regression is calculated as ESS/TSS = (92.648/117.160) = 0.79, which means that the variation in industry returns explains 79% of the variation in the stock return. By taking the square root of R2, we can calculate that the correlation coefficient (r) = 0.889. The t-statistic for the industry return coefficient is 1.91/0.31 = 6.13, which is sufficiently large enough for the coefficient to be significant at the 99% confidence interval. Since we have the regression coefficient and intercept, we know that the regression equation is R stock= l.9X + 2.1. Plugging in a value of 4% for the industry return, we get a stock return of 1.9 (4%) + 2.1 = 9.7%.81.Answer: BFixed-rate coupon = 150,000,000×0.055 = $8,250,000B fixed = 8.25e-0.0575+158.25e-0.0625×2 = $147,440,000B floating = $150,000,000V swap= $150,000,000 - $147,440,000 = $2,560,00082.Answer: BThe rate of sampling error has no relation to the sample size; all things being equal, the likelihood of sampling error will be the same regardless of sample size. According to the central limit theorem, the sample mean for large sample sizes will be distributed normally regardless of the distribution of the underlying population.83.。

CFA考试一级章节练习题精选0329-39(附详解)1、An analyst does research about the limitations of cash flow yield.Which of thefollowing statements is least accurate to be a shortcoming in application of thecash flow yield measure?【单选题】A.The projected cash flows are assumed to be reinvested at the cash flowyield.B.The mortgage-backed or asset-backed security is assumed to be held untilthe final payoff of all the loans, based on some prepayment assumption.C.Because of principle prepayments, in order to project cash flow it is necessaryto make an assumption about the rate at which principle prepaymentswill occur.正确答案:C答案解析:选项A和B都是现金流收益率的局限性。
其中一个缺陷是现金流收益率假设以该收益率获得再投资收入,而实际情况可能不同。
另外一个缺陷是假设根据提前偿付的假设持有到期,但有可能会提前偿还本金。
选项C则不是现金流收益率的局限性。
2、An analyst does research about exchange trade funds (ETFs).Which of thefollowing statements is least accurate to describe exchange trade funds' characteristics?【单选题】A.Portfolio holdings of ETFs are transparent.B.ETF's structure prevents a significant premium or discount to NAV.C.Dividends are reinvested annually for open-end ETFs.正确答案:C答案解析:ETF不收取申购和赎回费用,可以卖空或者融资交易,同时组合的持仓是透明的。
CFA考试一级章节练习题精选0330-54(附详解)1、An analyst compares different real estate valuation methods.A factor common tothe sales comparison approach and the income approach is that both approachesrequire :【单选题】A.identification of benchmark properties.B.knowledge of investor's marginal tax rate.C.calculation of the property's net operating income.正确答案:A答案解析:销售比较法(sales comparison approach)不需要计算房地产项目的经营性净收入(NOI),所以也不需要知道投资者的边际税率(marginal tax rate)。
但销售比较法和收入法都需要定义一个标的资产,销售比较法需要寻找基准的房地产用来得到其销售价格,并用以计算该房地产的价格;收入法需要寻找基准的房地产用来得到市场的资本化率(marketcapitalization rate),并用来折现该房地产的经营性净收入,得到房地产的价格。
2、The real estate valuation approach that uses a perpetuity discount type model is the:【单选题】A.cost approach.B.income approach.C.sales comparison approach.正确答案:B答案解析:“Alternative Investments”, Global Investments, Sixth Edition, by Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey, CFA2011 Modular Level I, Volume 6, p. 205Study Session 18-74-eDescribe the various approaches to the valuation of real estate.B is correct. The income approach to real estate valuation values a property using a perpetuity discount type of model.3、Which of the following is least likely an aggregation vehicle for real estate ownership?【单选题】A.Leveraged equity rightsB.Real estate investment trusts (REITs)C.Real estate limited partnerships (RELPs)正确答案:A答案解析:“Alternative Investments,” Bruno Solnik and Dennis McLeavey2012 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, pp. 201–202Study Session 18-66-eDescribe the forms of real estate investment, and explain their characteristics as an investable asset class.A is correct because leveraged equity rights is not an aggregation vehicle. Leveraged equity does not give investors collective access to real estate investments.4、Adding alternative investments to a portfolio of traditional investments will most likely result in a new combined portfolio with returns and standard deviation that are, respectively:【单选题】A.B.C.正确答案:B答案解析:“Introduction to Alternative Investments”, Terri Duhon, George Spentzos, CFA, and Scott D. Stewart, CFA 2013 Modular Level I, Vol. 6, Reading 66, Section 2.3Study Session 18-66-cDescribe potential benefits of alternative investments in the context of portfolio management.B is correct because the risk/return profile of the overall portfolio will potentially improve. The overall risk will most likely drop, and the overall return will most likely rise.5、An analyst does research about interest rate risk of fixed income securities andgathers the following information about three option-free bonds selling at par:The bond with the lowest interest rate risk is:【单选题】A.Bond 1.B.Bond 2.C.Bond 3.正确答案:B答案解析:息票率(Coupon Rate)越低,利率风险越大,因为大部分比例的现金流在未来造成价格变动的可能性增加。
FRM 一级模考试题(一)——答案1. Answer: CThe historical simulation method may not recognize changes in volatility and correlations from structural changes.2. Answer: CThe dirty price of the bond is calculated as N = 10; I/Y = 2.5; PMT = 30; FV = 1,000; CPT →PV = 1,043.76. Adjusting the PV for the fact that there are only 90 days until the receipt of the first coupon gives $1,043.76×(l.025)90/180 = $1,056.73. Clean price = dirty price - accrued interest = $1056.73 - $30(90/180) = $1,041.73.3. Answer: BGamma (not theta) represents the expected change in delta for a change in the value of the underlying. In-the-money options are more sensitive to changes in rates (rho is higher) than out-of-the-money options.4. Answer: AAssuming no default risk, the domestic return is 7.35%. The return on the UK investments, however, is equal to the amount invested today, (USD$2,000,000)/(USD1.62GBP)= GBP1,234,568, which turns into GBP1,234,568×1.08 = GBP1,333,333 one year from now. Since the forward contract guarantees the exchange rate in the future, this translates into GBP1,333,333 ×USD1.5200/GBP = USD2,026,666. This is a dollar return to the bank of USD2,026,666/ USD2,000,000-1 = 1.33%. Hence, the weighted average return to the bank’s investments is (0.5)×(7.35%) + (0.5)×(1.33%) = 4.34%. Since the cost of funds for the bank is 5.5%, the net interest margin for the bank is 4.34-5.50 = -1.16%.5. Answer: DAll of the statements are correct except choice d: the value of the firm’s equity should be the present value of its expected free cash flows (not net income).6. Answer: DWith a known variance, the 95% confidence interval is constructed as X± So youknow that 33.2330=+7. Answer: DA 6% rate compounded annually is approximately equivalent to a 5.8269% rate (rounded to four decimal places) compounded continuously. In (1 + 0.06) = 0.058268908 Using put-call parity:0.0582690 4.1027.5025$5.04rTp c XeS e −−=+−=+−=8. Answer: AV AR measures the expected amount of capital one can expect to lose within a given confidence level over a given period of time. One of the problems with V AR is that it does not provide information about the expected size of the loss beyond the V AR. V AR is often complemented by the expected shortfall, which measures the expected loss conditional on the loss exceeding the V AR. Note that since expected shortfall is based on V AR, changing the confidence level may change both measures. A key difference between the two measures is that V AR is not sub-additive, meaning that the risk of two funds separately may be lower than the risk of a portfolio where the two funds are combined. Violation of the sub-additive assumption is a problem with V AR that does not exist with expected shortfall.9. Answer: CThe fixed payments made by Cooper are (0.07/2)×$2,000,000 = $70,000. The present value of the fixed payments =0.0650.50.0681.0(0.0751.5)($70,000)($70,000)($70,000$2,000,000)$67,762$65,398$1,849,747$1,982,907e e e −×−×−×+++×=++=The value of the floating rate payments received by Cooper at the payment date is the value of the notional principal, or $2,000,000.The value of the swap to Cooper is ($2,000,000-$1,982,907) = $17,093.10. Answer: CA stack is a bundle of futures contracts with the same expiration. Over time, a firm may acquire stacks with various expiry dates. To hedge a long-term risk exposure, a firm would close out each stack as it approaches expiry and enter into a contract with a more distant delivery, known as a roll. This strategy is called a stack-and-roll hedge and is designed to hedge long-term risk exposures with short-term contracts. Using short-term futures contracts with a larger notional value than the long-term risk they are meant to hedge could result in over hedging” depending on the hedge ratio.11. Answer: BThe duration of a portfolio of bonds is the weighted average (using market value weights) of the durations of the bonds in the portfolio. First let’s find the weights. BondPrice as Percentage of ParFace Value $Market Value $1 95.5000 2,000,000 1,910,0002 88.6275 3,000,000 2,658,8253 114.8750 5,000,000 5,743,750 Total10,312,575The weights based on market values are:Weight of bond 1 = 1,910,000 / 10,312,575 = 0.1852 Weight of bond 2 = 2,658,825 / 10,312,575 = 0.2578 Weight of bond 3 = 5,743,750 / 10,312,575 = 0.5570 Bond Weights Duration Weighted Duration 1 0.18526.951.28712 0.2578 9.77 2.51873 0.5570 14.81 8.2492 Total 12.055012. Answer: CTo increase the beta of the portfolio from the market beta (1.0) to 1.5, the portfolio manager should take a long position:# of contracts =$250,000,000(1.5 1.0)4171,200250−×=×contracts13. Answer: BThe concessionality of a MYRA is defined as the difference between the present value of the loans before and after the restructuring.14. Answer: BThe formula is JB =2222(3)180(43)1[][0]30[]7.5 64644n KS−−+=+==Note that excess kurtosis is equal to K-3 so excess kurtosis of 1 means that kurtosis is 4.15. Answer: CThe rogue traders for both Daiwa and Barings had dual roles as both the head of trading and the head of the back-office support function. This operational risk oversight allowed them to hide millions in losses from senior management. In the Allied Irish Bank case, John Rusnak did not run the back-office operations. The Drysdale Securities case did not deal with a rogue trader.16. Answer: AThe fact that mean> median> mode is consistent with a distribution that is positively skewed. For all normal distributions, kurtosis = 3. Excess kurtosis = kurtosis-3, which is 0 for a normal distribution. In this case, excess kurtosis = 2, which means kurtosis = 5. This means that the distribution being examined is more peaked than the normal distribution and is said to be leptokurtic.17. Answer: CA change from a Ba to Baa rating is an example of a credit upgrade. A credit upgrade will decrease the likelihood of default (EDF) reducing expected loss. Note that expected loss is an estimate of average future loss. Actual loss is by definition equal to zero until a credit event occurs.18. Answer: BThe CAPM assumes that the market portfolio should be the portfolio with the highest Sharpe ratio of all possible portfolios and should include all investable assets. It also assumes that the expected excess returns for the market are assumed to be known in that investors have access to the same information. As well, it assumes that returns are normally distributed and investors’ expectationsfor risk and return ate identical.19. Answer: CThe 3-month forward rate is calculated as follows:1()(0.0650.05)0.250,()$19$19.07r T T T F S e e δ−−==×=20. Answer: CThe farmer needs to be short the futures contracts. The two sources of basis risk confronting the farmer will result from the fact that he is using a cattle contract to offset the price movement of his buffalo herd, Cattle prices and buffalo prices may not be perfectly positively correlated. As a result, the correlation between buffalo and cattle prices will have an impact on the basis of the cattle futures contract and spot buffalo meat. The delivery date is a problem in this situation, because the farmer’s hedge horizon is winter, which probably will not commence until December or January. In order to maintain a hedge during this period, the farmer will have to enter into another futures contract, which will introduce an additional source of basis risk.21. Answer: BA scattergram can help determine whether a relationship is positive or negative. Since the population and sample coefficients are almost always different, the residual will very rarely equal the corresponding population error term.22. Answer: C0.02(0.25)0.04(0.25)01,1001,08025.26qT rT S e Ke e e −−−−−=−=23. Answer: DPractitioners primarily use structural models, while academics are the primary users of statistical models. There are three types of structural models and one of them includes the need to forecast both factor returns and exposures. Factors in structural models are intuitive and well-known, while factors in statistical models are implied factors derived through a statistical operation. Structural models assume an underlying economic relationship between factors and stock returns.24. Answer: ABecause catastrophe bonds are riskier than straight bonds issued by the same firm, they usually have maturities less than three years and are usually non-investment-grade bonds. They also have potentially useful diversification qualities as their returns, being linked to operational losses, are not highly correlated with market returns.25. Answer: AFor a risk management activity to have value, the firm must be able to do something for shareholders that they cannot do themselves. The risk of bankruptcy cannot be hedged by shareholders (as beta risk and output-price risk can), thus, it may be value increasing for the firm to hedge this risk. Note that it is not a question that bankruptcy costs are too expensive to hedge;they are impossible to hedge. Although Choices b and c may be correct, they are less relevant to the situation and are, therefore, not the best answers.26. Answer: BIn this case, U = 1.1, D = 0.9, r = 0.035, and the value of the option is $1 if the stock increases and $0 if the stock decreases. The probability of an up movement, ∏U, can be calculated as0.0353/12(0.9)/(1.10.9)0.5439e ×−−=The value of the call option is therefore (0.0353/12)(0.5439$1)/$0.54e××=27. Answer: CStandards 2.1 and 2.2—Conflicts of Interest. Members and candidates must act fairly in all situations and must fully disclose any actual or potential conflict to all affected parties. Sell-side members and candidates should disclose to their clients any ownership in a security that they are recommending.28. Answer: BThe Treynor measure is most appropriate for comparing well-diversified portfolios. That is the Treynor measure is the best to compare the excess returns per unit of systematic risk earned by portfolio managers, provided all portfolios are well-diversified.All three portfolios managed by Donaldson Capital Management are clearly less diversified than the market portfolio. Standard deviation of returns for each of the three portfolios is higher than the standard deviation of the market portfolio, reflecting a low level of diversification.Jensen’s alpha is the most appropriate measure for comparing portfolios that have the same beta. The Sharpe measure can be applied to all portfolios because it uses total risk and it is more widely used than the other two measures. Also, the Sharpe ratio evaluates the portfolio performance based on realized returns and diversification. A less-diversified portfolio will have higher total risk and vice versa.29. Answer: DThe central limit theorem holds for any distribution (skewed or not) as long as the sample size is large (i.e., n >30). The mean of the population and the mean of the distribution of all sample means are equal. The standard deviation of the mean many observations is less than the standard deviation of a single observation.30. Answer: CUnexpected loss is a measure of the variation in expected loss. As a precaution, the bank needs to set aside sufficient capital in the event that actual losses exceed expected losses with a reasonable likelihood. For example, smaller recovery rates would be indicative of larger actual losses.31. Answer: CGiven that the economy is good, the probability of a poor economy and a bull market is zero. The other statements are true. The P(normal market) = (0.60×0.30) + (0.40×0.30) = 0.30. P(goodeconomy and bear market)= 0.60×0.20 = 0.12. Given that the economy is poor, the probability of a normal or bull market = 0.30 + 0.20 = 0.50.32. Answer: DNone of the statements are correct. The historical approach uses historic data from past crisis events, the prospective scenario conditional approach includes correlations between risk factors, and the factor push method is a prospective approach not a historical approach.33. Answer: BRisk management activities can increase firm value when the firm’s claimholders cannot take actions to replicate the results of hedging activity. Claimholders are willing to pay for the firm to do something they cannot do on their own accounts.34. Answer: CTop-down models rely primarily on aggregate historical data. Therefore, they are relatively simple and do not differentiate between high-frequency low-severity events and low-severity, high-frequency events because both are pooled together in the data. The aggregated nature of the data also limits the amount of data used in these models. A limitation of aggregated data, however, is that top-down models do not have diagnostic capabilities like bottom-up models that dissect processes into individual components.35. Answer: CBuying a call (put) option with a low strike price, buying another call (put) option with a higher strike price, and selling two call (put) options with a strike price halfway between the low and high strike options will generate the butterfly payment pattern. Two other wrong answer choices deal with bull and bear spreads, which can also be replicated with either calls or puts. A bull spread involves purchasing a call (put) option with a low strike price and selling a call (put) option with a higher exercise price. A bear spread is the exact opposite of the bull spread.36. Answer: DCaptive insurers are off-shore, wholly owned subsidiaries that may deduct for tax purposes the discounted value of all future expected losses stemming front a claim spanning several years. Essential this allows self-insurers to deduct losses before they have even occurred. Incurring costs to manage and control operational risk achieves the same result in principle as self-insurance. A contingent line of credit is a form of self-insurance that provides liquidity in the event of a loss rather than building up cash reserves in anticipation of a loss.37. Answer: DThe futures contract ended at 985 on the first day. This represents a decrease in value in the position of (1,000-985)×$250×20 = $75,000. The initial margin placed by the manager was $12,500×20 = $250,000. The maintenance margin for this position requires $10,000×20 = $200,000. Since the value of the position declined $75,000 on the first day, the margin account is now worth $175,000 (below the $200,000 maintenance margin) and will require a variation margin of $75,000 to bring the position back to the initial margin. It is not sufficient just to bringthe position back to the maintenance margin.38. Answer: CWe are given that the forward exchange rate in one year is 1.200 and are asked to find the exchange rate in three years. This means we need to apply the 2-year forward rate one year from today.The 2-year forward rate in the United States is:1.04811 4.81%==−=The 2-year forward rite in Europe is:1.022512.25%==−=Finally, we can apply interest rate parity:221.04811.200 1.2611.0225t F =×=39. Answer: AStandards 3.1 and 3.2 relate to the preservation of confidentiality. The simplest, most conservative, and most effective way to comply with these Standards is to avoid disclosing any information received from a client, except to authorized fellow employees who are also working for the client. If the information concerns illegal activities by MTEX, Black may be obligated to report activities to authorities.40. Answer: AThe liquidity preference theory suggests that the shape of the term structure is determined by the fact that most investors prefer short-term liquid assets, holding return constant.41. Answer: AIn general, bond prices will tend to increase with maturity when coupon rates are above relevant forward rates. When short-term rates are below the forward rates utilized by bond prices, the investors who invest in longer-term investments will tend to outperform investors who roll over shorter-term investments.42. Answer: CThe forward rate can be calculated as [(98.2240/96.7713)-1]×2 = 3%.43. Answer: BThe price is calculated as $15 (0.992556) + $15 (0.982240) + $1,015 (0.967713) = $1,011.85.44. Answer: AUnique among swaps, equity swap payments may be floating on both sides (and the payments notknown until the end of the settlement period). Similar to options, premiums for swaptions are dependent on the strike rate specified in the swaption. The most common reason for entering into commodity swap agreements is to control the costs of purchasing resources, such as oil and electricity. A negative index return requires the fixed-rate payer to pay the percentage decline in the index.45. Answer: BThe GARCH (1,1) estimate of volatility will be:220.000005(0.13)(0.03)(0.85)(0.022)0.0005330.0231 2.31%volatility ++====46. Answer: B0.04250.5($200.0349)($250.0263)$0.02582$0.03P e −×=××−×=≈47. Answer: DThe minimum value for a European-style call option, c T is given by3/12max[0,/(1)]max[0,8680/(1.03)]$6.59T T F S X R −+=−=An American style call option must be worth at least as much as an otherwise identical European-style call option and has the same minimum value Note that this fact alone limits the possible correct responses to Choices a and d. Since the American style call is in the money and therefore must be worth more than the $6 difference between the strike price and the exercise price, you can eliminate Choice a and select Choice d without calculating the exact minimum value.48. Answer: AThe appropriate test is an F-test, where the larger sample variance (Index A) is placed in the numerator.49. Answer: D The formula for the Treynor measure is ()[p FPE R R β−. Thus, the value for the Treynor measurein this case is (0.10 - 0.04)/0.75 = 0.0850. Answer: DThe coefficient of variation, CV = standard deviation/arithmetic mean, is a common measure of relative dispersion (risk) CV W = 0.4/0.5 = 0.80, CV X = 0.7/0.9 = 0.78; CV Y = 4.7/l.2 = 3.92 and CV Z = 5.2/1.5=3.47 Because a lower relative risk, Security X has the lowest relative risk and Security Y has the highest relative risk.51. Answer: AThe probability of rescheduling sovereign debt is positively related to the debt-service ratio, the import ratio, the variance of export revenue, and the domestic money supply growth.52. Answer: BAccording to the cash-and-carry Formula, the futures price should be:(0.02750.01)0.251,010$1,014.43e −=Hence, the futures is overvalued, indicating it should he sold and the index be purchased for a risk-free profit of $1,020 —$1,014.43 = $5.57.53. Answer: DHoffman has violated both Standard 1.2-independence and objectivity, which specially mentions that CARP Members must not offer, solicit, or accept any gift, benefit, compensation, or consideration that could be reasonably expected to compromise their own or another’s independence and objectivity, and Standard 2.2-Conflicts of Interest, which states the Members should make full and fair disclosure of all matters that could reasonably be expected to impair independence and objectivity or interfere with respective duties to their employer, clients, and prospective clients.54. Answer: DThe variability in the receipt of payments from the floating-rate asset is eliminated, as the floating payment of the floating rate leg of the swap offsets the receipt of the floating rate on the asset. The floating-rate payer is effectively left with a fixed-rate asset.55. Answer: DExpected value = (0.4)(10%) + (0.4)(12.5%) + (0.2)(30%) = 15% Variance = (0.4)(10-15)2 + (0.4)(12.5 -15)2 + (0.2)(30 - 15)2 = 57.5Standard deviation =56. Answer: D,,220.051.250.2S FS F FCov HR Beta σ====57. Answer: AOption-free bonds have positive convexity and the effect of (positive) convexity is to increase the magnitude of the price increase when yields fall and to decrease the magnitude of the price decrease when yields rise. 358. Answer: CThe standard normal random variable, denoted Z, has mean equal to 0 and standard variation (and variance) equal to 1. Also, a multivariate distribution is meaningful only when the behavior ofeach random variable in the group is in some way dependent upon the behavior of others.59. Answer: DThe critical z-value for a one-tailed test of significance at the 0.01 level will be either +2.33 or-2.33. The test statistic for hypotheses concerning equality of variances is 2122S F S = Thestatement regarding p-value is true. A Type II error is failing to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false.60. Answer: BThe Taylor Series does not provide good approximations of price changes when the underlying asset is a callable bond or mortgage-backed security. The Taylor Series approximation only works well for “well-behaved” quadratic functions that can be approximated by a polynomial of order two.61. Answer: DLTCM believed that, although yield differences between risky and riskless fixed-income instruments varied over time, the risk premium (or credit spread) tended to revert (decrease) to average historical levels. This was similar to their equity volatility strategy. Also, their balance sheet leverage was actually in line with other large investments banks (but their true leverage, economic leverage, was not considered).62. Answer: BThe benchmark returns are not important here. The average of the portfolio returns is(6+9+4+12)14=31/4=7.75.0.4743==63. Answer: DNeither statement is correct. The appropriate number of contracts for the hedge is:$10,000,000() 1.0()36 1,100250portfolio portfolio valuecontracts futures price multiplierβ×=×≈××However, since the manager is long the portfolio, he will want to take a short position in the 36contracts.Change in value of portfolio = -0.01($10,000,000) = -$100,000.Change in value of futures position = 36(1,100 — 1,090)(250) = $90,000.Net payoff= -$100,000 + $90,000 = -$10,000 The net impact is a loss of $10,00064. Answer: CAt the end of year 1 there is a 0% chance of default and a 90% chance that the firm will maintain an Aaa rating. In year 2, there is a 0% chance of default if the firm was rated Aaa after 1 year(90%×0% = 0%), There is a 5% chance of default if the firm was rated Baa after 1 year (10%×5% = 0.5%). Also, there is a 15% chance of default if the firm was rated Caa after 1 year (0%× 15% = 0%) The probability of default is 0% from year 1 plus 0.5% chance of default from year 2 for a total probability of default over a 2-year period of 0.5%.65. Answer: AThe beta factors used in the standardized approach for operationa1 risk are as follows: trading and sales 18%, retail banking 12% agency and custody services 15%, asset management: 12%.66. Answer: AAccording to put-call parity:000rT c Xe p S −+=+The left-hand side=$4+$45e -0.06×0.5 = $47.67The right-hand side = $4 + $43 = $47Since the value of the fiduciary call is not equal to the value of the protective put, put-call parity is violated and there is an arbitrage opportunity.Sell overpriced and buy underpriced. That is, sell the fiduciary call and buy the protective put. Therefore, sell the call for $4, sell the Treasury bill for $43.67 (i.e., borrow at therisk-free rate), buy the put for $4 and buy the underlying asset for $43. The arbitrageprofit is $0.67.67. Answer: BThe 5-3-2 spread tells us the amount of profit that can be locked in by buying five barrels of oil and producing three barrels of gasoline and two barrels of heating oil.(61.5×3) + (58.5×2) - (55×5) = $26.50 for 5 barrels; $5.30/barrel68. Answer: CUse interest-rate parity to solve this problem. 1.1565 = Se (0.02-0.04)0.25, so S = 1.1623.69. Answer: AUnsystematic risk is asset-specific and, therefore, a diversifiable risk. The market risk premium is also known as the price of risk and is calculated as the excess of the expected return on the market over the risk-free rate of return. The risk premium of an asset is calculated as beta times the excess of the expected return on the market over the risk-free rate of return.70. Answer: C12[()][()] 6.523.56.520.325.88 3.5i i j j i j ij i j i j R E R R E R Cov Cov r σσσσ−×−========××Σ71. Answer: DMoral hazard refers to the fact that an insured party may engage in risky behavior (or at least behave in a less risk-averse manner) knowing that an insurance policy will insulate the party against the consequences of such behavior. The way that Eggenton can mitigate the moral hazard problem is to include a deductible or co-insurance feature that would force JT Cola to pay a portion of the cost should a claim be made against the policy. If a deductible feature were not included in the policy, JT Cola management would have been free to act in any manner they would choose, including manipulating the global cola market, and Federal Insurance Group would have assumed all of the risk.72. Answer: BWe can calculate the expected loss as follows.EL = AE ×EDF ×LGDMaximum lossAdjusted exposure = OS + (COM U - OS)×UGD= $8,000,000 + ($12,000,000)×(0.75)= 17,000,000EL = ($17,000,000)×(0.02)×(0.80) = $272,000Minimum lossAdjusted exposure = OS + (COM U - OS)×UGD= $8,000,000 + ($12,000,000)×(0.5)= $14,000,000EL = ($14,000,000)×(0.01)×(0.80) = $112,000Therefore, the difference between maximum and minimum loss is:$272,000 - $112,000 = $160,000.73. Answer: ASince the current position is short gamma, the action that must be taken is to go long the option in the ratio of the current gamma exposure to the gamma of the instrument to be used to create the gamma-neutral position (5,000/2 = 2,500). However, this will change the delta of the portfoliofrom zero to (2,500×0.7) = 1,750. This means that 1,750 of the underlying stock position will need to be said to maintain both gamma and delta neutrality.74. Answer: BYou have purchased a bull spread. You will exercise the call chat you purchased for a net profit of (34 - 25) - 3 = $6 per share. The call that you sold will not be exercised, so your net profit is the cost of $1 per share. Your total net profit is 6 + 1 = $7 per share.75. Answer: AIf the investor has written 15,000 call options, he must go long delta times the short option position to create a delta-neutral position. or buy $15,000×0.50 = 7,500 shares. Note that the delta of a call option, which is exactly at-the-money, is 0.5.76. Answer: BThe historical simulation V AR for 5% is the fifth lowest return, which is -1.59%; therefore, the correct V AR is: -79,500 = (-0.0159)×(5,000,000).77. Answer: BBecause firms tend to release good news more readily than bad news, downgrades may be more of a surprise, so downgrades affect stock prices more than upgrades when the firm reveals the good news associated with the upgrade prior to its occurrence.The “underrating” and “overrating” is seen more with the use of the through-the-cycle approach. As well, the ratings delivered by more specialized and regional agencies tend to be less homogeneous than those delivered by major players like S&P and Moody’s.78. Answer: BOperational risk economic capital is the difference between the loss at a given confidence level and the expected loss. In this case, $500,000 - $50,000 = $450,000.79. Answer: AThe head of the government bond trading desk at Kidder Peabody, Joseph Jett, misreported trades, which allowed him to report substantial artificial profits. After these errors were detected, $350 million in falsely reported gains had to he reversed.80. Answer: BThe R2 of the regression is calculated as ESS/TSS = (92.648/117.160) = 0.79, which means that the variation in industry returns explains 79% of the variation in the stock return. By taking the square root of R2, we can calculate that the correlation coefficient (r) = 0.889. The t-statistic for the industry return coefficient is 1.91/0.31 = 6.13, which is sufficiently large enough for the coefficient to be significant at the 99% confidence interval. Since we have the regression coefficient and intercept, we know that the regression equation is R stock= l.9X + 2.1. Plugging in a value of 4% for the industry return, we get a stock return of 1.9 (4%) + 2.1 = 9.7%.81. Answer: B。
FRM一级模拟题1 . Consider the following 3-year currency swap, which involves exchanging annual interest of2.75% on 10 million US dollars for3.75% on 15 million Canadian dollars. The CAD/USD spot rate is l.52. The term structure is flat in both countries. Calculate the value of the swap in USD if interest rates in Canada are 5% and in the United States are 4%. Assume continuous compounding. Round to the nearest dollar.A. $152,000B. $145,693C. $131,967D. $127,8182 . Consider the following plain vanilla swap. Party A pays a fixed rate 8.2g% per annum on a semiannual basis (180/360), and receives from Party B LIBOR+30 basis point. The current six-month LIBOR rate is 7.35% per annum. T. he notional principal is $25M. What is the net swap payment of Party 'AA. $'20,000B. $40,000C. $80,000D. $110,0003 . What rate should be used to calculate the unwind value of a swap in which we are paying fixed?A. Bid swap rateB. Offer swap rateC. Mid swap rateD. Insufficient informationAnswer: ATo unwind this swap we will need to-receive fixed. So we should use the bid rate4 . Assume an investor has a position in a currency swap. He receives euro inexchange for paying yen. What are the conditions for the swap to bein-the-money?I The value of yen fallsII The value of yen risesIII The euro interest rate fallsIV The euro interest rate risesA. I and IIIB. I and IVC. II and IIID. II and IVAnswer: AThe swap is similar to a long position in euro denominated bond and a short position in Yen denominated bondThus, decrease in euro interest rate is beneficial to a holder of a long position. Likewise, the decrease in the value of yen makes the yen denominated bond less valuable (what is beneficial for a short position).5 . Which of the following constitutes an' advantage of swaps over physical capital markets transactions in hedging existing exposures?A. Low transaction costsB. Off-balance sheet natureC. Ease of transactionD. All of the aboveAnswer: DSwaps allow corporate hedgers to adjust their risk profiles far easier and at a lower cost than capital market transactions. Moreover, swaps being used for hedging' purposes can be held off balance sheet in most jurisdictions.。
FRM一级模拟题1 . Which of the following best describes the asset liability mix of a typical retail bank?A . Duration of assets is equal to duration of liabilities.B . Duration of assets is less than duration of liabilities.C . Asset and liability durations depend on interest rates.D . Duration of assets is more than duration of liabilities.Answer: DA large portion of the liabilities of a typical retail bank consist of demand deposits and other short term deposits. Whilst its assets consist of longer loans and bonds.2 . If interest rates rise which of the following statements is incorrect?A. A bank with a positive maturity gap will experience a gain in equiy capitalB. A bank with a positive maturity gap will experience a Joss in equiy capitalC. A bank with a negative maturity gap will experience a loss in equiy capitalD. A bank with a negative maturity gap will experience no change in equiyAnswer: BIf interest rates rise, a bank will experience a positive maturity gap .A. Incorrect. The Bank will experience a loss of equity capital. See .explanation in 'b' below.B. Correct. A loss of equity capital. lf the maturity gap is positive, the assets have a longerWeighted average maturity than the liabilities. If rates rise, the value of the liabilities will fall by less than the value of the assets, and equity capital wⅢdecrease.C. Incorrect. The Bank will experience a loss of equity capital. See explanation in 'b' above.D. Incorrect. The Bank will experience a loss of equity capital. See explanation in 'b' above. Modified Duration3.Calculate the Modified Duration of a bond with Macaulay duration of 13.083 years. Assume market interest rates are 11.5% and the coupon on the bond is paid semi-annually.A. 13.083B. 12.732C. 12.459 .D. 12.371Answer: DD Mod = D Mac/ (1 + y) =13.083/(1+11 .5%/2)=12.3714 . A 4.5-year 6% straight bond with annual coupon payments is traded at a clean price of 103.50. Calendar convention is 30E/360. The modified duration of the bond is 3.6. The PVBP (Price value of a Basis Point) is:A. 0.0383B. 0.0373C. 0.0414D. 0.03605 . Which attribute of a bond is not a reason for using effective duration instead of modified duration?A. Its life may be uncertain.B. Its cash flow may be uncertain.C. Its price volatility tends to decline as maturity approaches.D. It may include changes 'in adjustable rate coupons with caps or fl oors.Answer: CPrice volatility does not affect the calculation of duration of a bond, while each of the factors in A, B, and D will affect duration.。
FRM一级练习题(3)答案1. Here the t-reliability factor is used since the population variance is unknown. Since there are 30 observations, the degrees of freedom are 30 – 1 = 29. The t-test is a two-tailed test. So the correct critical t-value is2.045; thus the 95% confidence interval for the mean return is = [-3.464%, 11.464%].2. Assuming the l ong-run estimated variance remains unchanged, the reversion rate defined by the GARCH(1,1) model is (1- - ), which implies that the volatility term structure predicted by the GARCH(1,1) model reverts to the l ong-run estimated variance more sl owly.3. The cal culation is as foll ows:Two-thirds of the equity fund is worth USD 40 million. The optimal hedge ratio is given byh = 0.89 * 0.51 / 0.48 = 0.945The number of futures contracts is given byN = 0.945 * 40,000,000 / (910 * 250) = 166.26 c 167, rounded up to nearest integer.Incorrect:(A)—This is obtained if you hedge the full portfolio instead of two-thirds.Incorrect:(B)—This is obtained if you use the S&P 500 index l evel of 900 instead of the futures price of 910. Incorrect:(D)—This is obtained if the volatilities of the portfolio and the futures in the formula for the optimal hedge ratio are incorrectly invested.4. Due to the fact that the American option under consideration is on the stock, which does not pay dividends during the period, its value is equal to the European option with the same parameters. Thus, we can apply the put-call parity to determine the l evel of interest rates.C – P = S – K e – rT0.46 – 2.25 = 22 – 24 e – 0.25r–23.79 = –24e – 0.25rr = 3.52%(A) Incorrect answer.(B) Correct answer.(C) Incorrect answer: This is obtained if 0.5 year expiration is used instead of three months.(D) Incorrect answer: Because there are no dividends during the life of the option, put-call parity can be used and the interest rate can indeed be calculated.5. It is a butterfly spread strategy that can maximize the profit at the target level of USDJPY 97 while limiting the loss to the difference between the premiums of the two long and short calls. Incorrect:(A)—It is a strad dle strategy suitable for high expected volatility.Incorrect:(B)—It is a bull spread strategy suitable for bull expectation on USD.Incorrect:(C)—It is a bull spread strategy for USD.6. The key concept here is the box spread. A box spread with strikes at 120 and 150 gives you a payoff of 30 at expiration irrespective of the spot price. In a sense, it is like a zero coupon bond. Now recall the put-call parity relation:p + S = c + price of zero coupon bond with face value of strike red eeming at the maturity of the options.Since the strike is 120, the price of a zero coupon bond with face value of 120 can be expressed as four units of box spread.If there is any way you can sell any one side of the equation at a price higher than the other there is an arbitrage opportunity.(A) is correct.Short one put: +25Short one spot: +100Buy one call: –5Buy six box spreads: –120Net cash fl ow: 0At expiry, if spot is greater than 120, call is exercised, and if it is less than 120, put is exercised. In either case you end up buying one spot at 120. This can be used to cl ose the short position. The six spreads will provid e a cash fl ow of 6 * 30 = 180. The net profit is therefore = 180 – 120 = 60.(B) is incorrect.Buy one put: –25Short one spot: +100Short one call: +5Buy four box spreads: –80Net cash fl ow: 0At expiry, if spot is greater than 120, call is exercised, and if it is less than 120, put is exercised. In either case you end up selling one spot, at 120. However, you are already short one spot, which you have to cl ose. The four box-spreads provide a cash flow of 4 * 30 = 120. The net cash outfl ow = K – S – S – 120 = –2S. You have mad e a loss unless the spot price is zero.(C) is incorrect. This is exactly the reverse strategy of(A) And will give you a loss of 60.(D) is incorrect. You will choose this if you cannot figure out the similarity of the box-spread payoff to that of a zero coupon bond.7. The cheapest-to-deliver bond on maturity is defined as the one for which the adjusted spot price is the l owest. Adjusted spot price = Spot price/Conversion factor. Computation of adjusted price for each of the bonds is as foll ows:Bond A = (10214/32)/0.98 = 104.53%Bond B = (10619/32)/1.03 = 103.49%Bond C = (9812/32)/0.95 = 103.55%So, bond B is the cheapest-to-deliver bond, and option (B) is correct.8.(1) is false. Basis risk can also arise if the underlying asset and hedge asset are id entical. This can happen ifthe maturity of hedge contract and delivery date of asset does not match.(2) is true. Short hedge position or short forward contract benefits from unexpected decline in future prices and consequent strengthening of basis. The payoff to short hedge position is spot price at maturity (S2) and difference between futures price, i.e. (F1 – F2). Thus, payoff = S2 + F1 – F2 = F1 + b2, where b2 is the basis.(3) is false. Long hedge position benefits from weakening of basis.(A) is incorrect.(B) is incorrect.(C) is correct.(D) is incorrect.9.The value of the swap increases / decreases with an increase / decrease in the U.S. five-year fixed rate.The value of the swap increases / decreases with a d ecrease / increase in the USD-JPY rate.In(A), the value of the swap will increase.(A) is incorrect.In(B), the value of the swap will decrease.(B) is incorrect.In(C), the value of the swap will decrease.(C) is incorrect.In (D), both factors will cause a decrease in the value of the swap. Hence, (D) is correct.10. (A) is incorrect. The larger the debt repayments in hard currencies are in relation to export revenues, the greater the probability that the country will have to reschedul e its debt. (B) is incorrect. Since the first use of reserves is to buy vital imports, the greater the ratio of imports to foreign exchange reserves, the higher the probability that the country will have to reschedule its debt repayments. This is the case because the repayment of foreign debt hol ders is generally viewed by countries as being less important than supplying vital goods to the domestic population.(C) is correct. The investment ratio measures the d egree to which a country is all ocating resources to real investment in factories, machines, and so on, rather than to consumption. The higher this ratio is, the more productive the economy shoul d be in the future and the l ower the probability that the country will need to reschedul e its debt. An opposing view argues for a positive relationship, especially if the country invests heavily in import-competing industries. However, the relationship between the INVR and the probability of rescheduling is most likely to be negative among the four options given.(D) is incorrect. The more volatile a country's export earnings, the l ess certain creditors can be that at any time in the future it will be abl e to meet its repayment commitments. That is, there should be a positive relationship between VAREX and the probability of rescheduling.参与FRM的考生可按照复习计划有效进行,另外高顿网校官网考试辅导高清课程已经开通,还可索取FRM 考试通关宝典,针对性地讲解、训练、答疑、模考,对学习过程进行全程跟踪、分析、指导,可以帮助考生全面提升备考效果。