QC080000新旧版本比对表中文版
- 格式:xls
- 大小:37.50 KB
- 文档页数:3

IECQ危害物质过程管理及QC080000标准介绍世界范围内许多现行或待决的法规中有许多要求消除所确定的一系列危害物质,包括电子电气产品中含有的铅、汞、镉、六价铬、多溴联苯、多溴联苯醚。
但是,各种法规对危害物质要求控制的法规多种多样,客户对危害物质的要求更是各有差异,要想以不变应万变地解决这个问题,必须有世界范围内权威的标准或规范出台,让所有相关各方有一个统一而明确的遵循准则,从而达到国际间产品贸易的技术壁垒最小化。
为解决上述的危害物质管理标准化的问题,IEC委托其下属的电子元器件质量评定委员会(IECQ)制订了专门的危害物质过程管理(HSPM)标准——“电子电器元件和产品危害物质减免标准和要求(EIA/ECCB-954)”,并为开展这一过程管理体系的认证制定了专门的程序规则——“危害物质过程管理要求(QC 001002-5)”,从而为危害物质管理和认证提供了权威性选择。
IEC及IECQ简介IEC是国际电工委员会的英文缩写,是非政府性国际组织,正式成立于1906年,是世界上成立最早的专业国际标准化机构,负责有关电工、电子领域的国际标准化工作,在标准的制订方面与国际标准化组织紧密合作。
IECQ即国际电工委员会电子元器件质量评定体系,隶属于国际电工委员会,是世界范围内唯一对电子元器件进行全面质量评估的批准和认证机构,负责对电工产品和材料以及生产过程进行质量评估,是在IEC、ISO内第一个实现具体产品质量认证国际化的国际性的认证组织。
IECQ的宗旨是:建立国际性的权威管理机构,制定统一的技术标准和实施质量评定的程序规则,以标准为依据,根据程序规则对生产厂的技术能力和管理水平进行全面的检查批准。
IECQ-HSPM体系IECQ-HSPM体系即IECQ危害物质过程管理体系,其依据的标准是EIA/ECCB-954,该标准在IECQ的标准编号为QC080000,即“电子电器元件和产品危害物质减免标准和要求”。
I ECQ-HSPM与QC080000标准之间的关系类似于ISO质量管理体系与ISO9001:2000之间的关系。

![[实用参考]QC080000-2017中文版](https://uimg.taocdn.com/dfa26a7d2b160b4e777fcf2b.webp)
前言 (7)1 范围 (8)1.1 总则 (8)1.2 应用 (8)2 规范性引用文件 (8)4 组织环境 (10)4.1 理解组织及其环境 (10)4.2 理解相关方的需求和期望 (11)4.3 确定HSPM体系的范围 (11)4.4 HSPM体系及其过程 (11)4.4.1 总则 (11)5 领导作用 (11)5.1 领导作用和承诺 (11)5.1.1总则 (11)5.1.2 以顾客为关注焦点 (11)5.2 HSF方针 (12)5.2.1 制定HSF方针 (12)5.2.2 沟通HSF方针 (12)5.3 组织的岗位、职责和权限 (12)6 策划 (12)6.1 应对风险和机遇的措施 (12)6.1.1 HSPM体系的策划 (12)6.1.2 组织 (12)6.2 HSF目标及其实现的策划 (12)6.2.1 HSF目标 (12)6.2.2 HSF目标的策划 (12)6.3 变更的策划 (13)7 支持 (13)7.1 资源 (13)7.1.1总则 (13)7.1.2人员 (13)7.1.3基础设施 (13)7.1.4 过程运行环境 (13)7.1.5监视和测量资源 (13)7.1.5.1总则 (13)7.1.5.2测量溯源 (13)7.1.6组织的知识 (13)7.2能力 (14)7.3意识 (14)7.5成文信息 (14)7.5.1 总则 (14)7.5.2创建和更新 (15)7.5.3成文信息的控制 (15)8 运行 (15)8.1 运行的策划和控制 (15)8.2产品和服务的HSF要求 (15)8.2.1顾客沟通 (15)8.2.2产品和服务HSF要求的确定 (16)8.2.3产品和服务要求的评审 (16)8.2.4产品和服务要求的更改 (16)8.3产品和服务的设计和开发 (16)8.3.1总则 (16)8.3.2设计和开发策划 (16)8.3.3设计和开发输入 (17)8.3.4设计和开发控制 (17)8.3.5设计和开发输出 (17)8.3.6设计和开发更改 (17)8.4外部提供的过程、产品和服务的控制 (18)8.4.1总则 (18)8.4.2控制类型和程度 (18)8.4.3提供给外部供方的信息 (18)8.5生产和服务提供 (19)8.5.1生产和服务提供的控制 (19)8.5.2标识和可追溯性 (19)8.5.3顾客或外部供方的财产 (19)8.5.4防护 (19)8.5.5交付后活动 (19)8.5.6更改控制 (20)8.6产品和服务的放行 (20)9 绩效评价 (20)9.1 监视、测量、分析和评价 (20)9.1.2顾客满意 (21)9.1.3 分析与评价 (21)9.2内部审核 (21)9.3管理评审 (21)9.3.1总则 (21)9.3.2管理评审输入 (21)9.3.3管理评审输出 (22)10 改进 (22)10.1总则 (22)10.2不合格和纠正措施 (22)10.3持续改进 (22)附录A(规范性附录)欧盟RoHS要求 (23)附录B(规范性附录)中国RoHS 2要求 (25)参考文献 (27)有害物质过程管理(HSPM)体系要求前言本出版物由IECQ管理委员会(MC)制订。

广东德豪润达电气股份有限公司珠海制造中心QC O80000标准部分内容略4 质量管理体系4.1 总要求在ISO9001的要求之外附加的要求如下:4.1.1 总则组织应包括ISO9001:2000要求的质量管理体系必要的程序、文件、实施过程管理来达到HSF产品和生产过程。
组织应:a) 对组织正在使用的有毒物质加以识别并形成文件;b) 识别与HSF目标有关的管理的特殊过程;c) 确定这些过程的相互依存和相互作用并制定一套合适的HSF过程管理计划;d) 建立客观确定组织HSF过程管理有效性的准则;e) 确保可以获得必要的资源和信息,以支持有效的HSF过程管理;f) 监视、测量和分析这些过程;g) 实施措施,以保证在达到HSF方面的过程持续改进。
h) 建立一个过程,以限制和/或消除产品和过程使用有毒物质。
4.1.2 与ISO9001的关系文件的目的是HSF过程管理与ISO9001:2000要素相适应。
4.1.3 外包过程在组织选择任何影响其产品HSF特性的外包过程,将来自自己运作之外的过程产品纳入到自己的运作中的情况下,组织应确保对其过程进行管理和控制。
4.2 文件要求在ISO9001的要求之外附加的要求如下:4.2.1 总则质量管理体系文件应包括:a) HSF要求应为组织的质量管理体系的一部分,应包括b) 一份组织内使用的所有有毒物质清单;c) 形成文件的HSF方针和目标,适宜时包括消除使用所有有毒物质的期限;d) 组织的质量手册中包括HSF过程管理计划、目标和HSF形成文件的程序的引用。
e) 组织的HSF过程管理计划要求的形成文件的程序,包括执行ISO9001:2000中4.2.4条款要求的文件;f) 组织HSF过程管理执行的记录。
注1:与ISO9001保持一致性,本标准出现“形成文件的程序”之处,即要求建立该程序,形成文件,并加以实施和保持。
注2:不同组织的质量管理体系文件的多少与详略程度取决于:a) 组织的规模和活动的类型;b) 过程及其相互作用的复杂程度;c) 人员的能力。

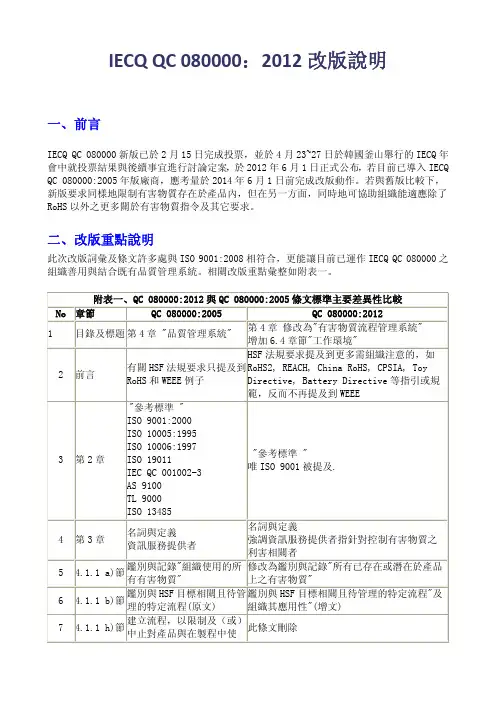
IECQ QC 080000:2012改版說明一、前言IECQ QC 080000新版已於2月15日完成投票,並於4月23~27日於韓國釜山舉行的IECQ 年會中就投票結果與後續事宜進行討論定案,於2012年6月1日正式公布,若目前已導入IECQ QC 080000:2005年版廠商,應考量於2014年6月1日前完成改版動作。
若與舊版比較下,新版要求同樣地限制有害物質存在於產品內,但在另一方面,同時地可協助組織能適應除了RoHS 以外之更多關於有害物質指令及其它要求。
二、改版重點說明此次改版詞彙及條文許多處與ISO 9001:2008相符合,更能讓目前已運作IECQ QC 080000之組織善用與結合既有品質管理系統。
相關改版重點彙整如附表一。
附表一、QC 080000:2012與QC 080000:2005條文標準主要差異性比較 No章節 QC 080000:2005 QC 080000:2012 1目錄及標題 第4章 "品質管理系統" 第4章 修改為"有害物質流程管理系統" 增加6.4章節"工作環境" 2前言 有關HSF 法規要求只提及到RoHS 和WEEE 例子 HSF 法規要求提及到更多需組織注意的,如RoHS2, REACH, China RoHS, CPSIA, Toy Directive, Battery Directive 等指引或規範,反而不再提及到WEEE 3第2章 "參考標準 " ISO 9001:2000 ISO 10005:1995 ISO 10006:1997 ISO 19011 IEC QC 001002-3 AS 9100 TL 9000 ISO 13485 "參考標準 " 唯ISO 9001被提及. 4第3章 名詞與定義 資訊服務提供者 名詞與定義 強調資訊服務提供者指針對控制有害物質之利害相關者 54.1.1 a)節 鑑別與記錄"組織使用的所有有害物質" 修改為鑑別與記錄"所有已存在或潛在於產品上之有害物質" 64.1.1 b)節 鑑別與HSF 目標相關且待管理的特定流程(原文) 鑑別與HSF 目標相關且待管理的特定流程"及組織其應用性"(增文) 7 4.1.1 h)節 建立流程,以限制及(或)中止對產品與在製程中使此條文刪除用的有害物質8 4.2節 a)HSF要求必須列入組織ISO 9001:2000中e)組織HSF流程管理計劃要求所需文件化之程序a) 此條文刪除e)修改"為組織HSF流程管理計劃要求、法規及顧客要求等所需相關文件或紀錄"9 5.6.1節 管理階層審查 增加"管理階層審查輸入":a) HSF政策及目標之適用性及落實,b)可能影響HS管理改變之法規及顧客要求 d) 稽核結果,包含其HSF不符合事項及矯正措施e) 組織HS管理績效評估及顧客回饋f) 實現HSF產品與過程所需資源g) 改善計畫10 6.3節 基礎設施 增加說明a) 建築物、工作空間及相關的公共設施;b) 過程設備(硬體與軟體兩者)c) 支援服務(諸如運輸、溝通或資訊系統)11 6.4節 2005年版無此條文 增加"6.4工作環境"組織應決定、提供與維持為達成符合HSF產品要求所需之工作環境12 7.1節 HSF流程與產品實現的規劃增加"組織對於可能造成HSF產品屬性改變之變更,應建立及維持相關程序。


国际电工委员会IECQ QC080000 ( IECQ )国际电工委员会电子元器件质量评定体系(IECQ )电子电器元件和产品有害物质过程管理体系要求(HSPM )目录前言0 、引言1 、范围2 、规范性引用文件3 、术语和定义4 、质量管理体系4.1 总要求4.2 文件要求5 、管理职责5.1 管理承诺5.2 以顾客为关注焦点5.3 HSF方针5.4 策划5.5 职责、权限和沟通5.6 管理评审6 、资源管理6.1 资源提供6.2 人力资源6.3 基础设施7 、产品实现7.1 HSF过程和产品实现的策划7.2 与顾客有关的过程7.3 设计和开发7.4 HSF产品的采购7.5 生产和服务提供7.6 HSF过程中使用的监视和测量设备的控制8 、测量、分析和改进8.1 总则8.2 HSF程的监视和测量8.3 不符合的HSF产品的控制8.4 HSF数据分析8.5 HSF程管理体系的改进国际电工委员会电子电器元件和产品有害物质过程管理体系要求(HSPM )前言本IECQ规范及其要求基于以下理念:不有效地综合应用管理科学,将无法实现有害物质减免(HSF)产品和生产过程。
本标准是ISO9001-2000质量管理体系框架的补充,与其协调一致,为的是对过程全面、系统、透明的管理和控制。
本规范以EIA/ECCB-954 “电器电子元件和产品HSF 标准和要求”为基础,为制造商满足HSF 要求和顾客要求提供指导。
这些要求包括法规要求如欧洲议会和欧盟理事会2003 年1 月27 日的2002 /95/EC 关于在电气电子设备中限制使用某些有害物质指令及2002 / 96 /EC 关于报废电子电气设备指令。
注:全世界许多现行或待决的法规中有许多要求消除所确定的一系列有害物质,包括许多产品中含有的铅、汞、锅、六价铬、多溴联苯、多溴联苯醚。
这就要求电子电器元件的制造商和使用商必须能够知道他们的产品是否是HSF产品;如果不是时,必须清楚地知道有害物质含量是多少。

![[最新]qc080000 标准中文版本](https://uimg.taocdn.com/1d4ed88a964bcf84b9d57b90.webp)
[最新]qc080000 标准中文版本IECQ危害物质过程管理及QC080000标准介绍世界范围内许多现行或待决的法规中有许多要求消除所确定的一系列危害物质,包括电子电气产品中含有的铅、汞、镉、六价铬、多溴联苯、多溴联苯醚。
但是,各种法规对危害物质要求控制的法规多种多样,客户对危害物质的要求更是各有差异,要想以不变应万变地解决这个问题,必须有世界范围内权威的标准或规范出台,让所有相关各方有一个统一而明确的遵循准则,从而达到国际间产品贸易的技术壁垒最小化。
为解决上述的危害物质管理标准化的问题,IEC委托其下属的电子元器件质量评定委员会(IECQ)制订了专门的危害物质过程管理(HSPM)标准——“电子电器元件和产品危害物质减免标准和要求(EIA/ECCB-954)”,并为开展这一过程管理体系的认证制定了专门的程序规则——“危害物质过程管理要求(QC001002-5)”,从而为危害物质管理和认证提供了权威性选择。
IEC及IECQ简介IEC是国际电工委员会的英文缩写,是非政府性国际组织,正式成立于1906年,是世界上成立最早的专业国际标准化机构,负责有关电工、电子领域的国际标准化工作,在标准的制订方面与国际标准化组织紧密合作。
IECQ即国际电工委员会电子元器件质量评定体系,隶属于国际电工委员会,是世界范围内唯一对电子元器件进行全面质量评估的批准和认证机构,负责对电工产品和材料以及生产过程进行质量评估,是在IEC、ISO内第一个实现具体产品质量认证国际化的国际性的认证组织。
IECQ的宗旨是:建立国际性的权威管理机构,制定统一的技术标准和实施质量评定的程序规则,以标准为依据,根据程序规则对生产厂的技术能力和管理水平进行全面的检查批准。
IECQ-HSPM体系IECQ-HSPM体系即IECQ危害物质过程管理体系,其依据的标准是EIA/ECCB-954,该标准在IECQ的标准编号为QC080000,即“电子电器元件和产品危害物质减免标准和要求”。
Changes of QC080000:2012 against QC080000:2005Moro Chen 陈庆今2Background for the updating of QC080000:2005Legal requirements are upgraded tremendously •EU REACH•EU recasted RoHS•……Strong industry appeal to upgrading•To improve it for better HS management ,such as 7.1,7.3, etc;•To revise some minor defects for better recognition by industry;•……ISO9001 upgraded from version2000 to version2008•ISO9001 is framework for QC080000;•To align the clauses with those of ISO9001,such as 6.4,7.2,7.4,7.5.4, 7.5.5, etc3Summary of the Main differences between version 2005 and 2012---1 version 2012 is applicable to much more legal requirements•in version 2005, only EU RoHS and WEEE mentioned;•IECQ-HSPM certificate can show compliance with only limited HS-relevant regulations, while version 2012 covers all HS-relevant legal requirements;•Version 2005 concerns mainly limitation requirements on HS within products; HS management requirements provided in some new regulations are not embodied very well, such as–SVHC notification and information communication in EU REACH;–Technical file, compliance assessment, compliancedeclaration, CE marking, internal production control, change management, marking and recall, non-conforming product, corrective measures of RoHS2,–China RoHS marking, voluntary certification, information declaration, etc 4Summary of the Main differences between version 2005 and 2012 ---2Intention of some definitions or clauses clarified , such as:•“restricted substance” deleted; “hazardous substance” used in all clauses under a new definition;•HSs to be identified are those with potential to entering into products rather than all HSs used by the organization;•staff to be competent are those who will have impact on the HSF characteristic of product rather than the product itself;•while planning the product realization, organization need to determine the HSF objective and requirements rather than other quality requirements;•no mandatory requirement on organization any longer to inform potential contamination or mixing to customers;•“traceability” is not only required in case that it is requested but also where appropriate;•In 7.6, to be controlled is not equipment used in HSF processes but for monitoring and measuring HSF characteristic;5Summary of the Main differences between version 2005 and 2012 ---3Some minor defects revised, such as•Definition for “Information service provider”;•“ISO14001, EPA” in the structure chart;• 4.2.1 e);•The incomplete expression in 8.2.1;•……some redundant expressions deleted, such as •definitions of common meaning in such as ISO9000;• 4.1 h);•“The requirements of ISO9001 shall apply along with the additional requirements below:”at the beginning of many clauses;•7.5.4:adapted into 7.5.5or 8.3.6Summary of the Main differences between version 2005 and 2012---4Consistency between the specification and ISO9001:2008 improved, such as• 6.4 recovered ;•Adapted 7.5.4into 7.5.4,7.5.5with the same theme as ISO9001;•follow the clause structure of ISO9001, such as –Re-structured 7.2 into 7.2.1,7.2.2,7.2.3;–Re-structured 7.4 into 7.4.1,7.4.2,7.4.3.7detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---1clause No.version 2005Version 2012contents list 4. QUALITYMANAGEMENT SYSTEM No 6.4 4. hazardous substance process management system"6.4 Work environment" added.forword only RoHS and WEEEmentioned much more legistration mentioned suchas RoHS2, REACH, China RoHS,CPSIA, toy directive, battery directive,etc, and WEEE is not mentioned anymore.00. introduction 1 scope1.1 General1 1. scope 1.1 General1.2 Application 82 2 Normative ReferencesISO 9001:2000ISO 10005:1995ISO 10006:1997ISO 19011IEC QC 001002-3AS 9100TL 9000ISO 13485are all referred.2 Normative References only ISO9001 referred.3 3 Terms and Definitionsgive definition forHSHSF Information services provider May Product customer Product manufacturer Product repairer Product supplier Product user Restricted SubstanceShouldShall3. Terms and Definitionsonly give definition forHS,HSF,Hazardous characteristic of product,Information services provider,which are specific for the control of hazardous substances.detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---294title "Quality Management System"title "Hazardous Substance ProcessManagement System"4.1.1 a)"all hazardous substances in use in the organization""all hazardous substances contained orwill potentially be introduced intoproducts"4.1.1 b)"and their application throughout theorganization" added at the end of thesentence.4.1.1 h)deleted4.1"The requirements of ISO9001 shall apply alongwith the additionalrequirements below:", thesame for clause 4.2, 5.1, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 6.1, 6.2, 6.3,7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6,8.1, 8.2.1, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5.deleted4.2a) deleted;"e) HSF documents or records specified by legal requirements or customerrequirements," is added;numbering is re-ordered;detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---3105.5.3 a)"HSF management requirements and changes" is requiredto be informed to the organization's personnel too.5.6.1the following points added:a) the suitability and realization of HSF policy and targets,b) the changes of legal and customer’s requirements withrespect to HS management,d) audit results with respect to HSF non-conformity andcorresponding corrective action, including audit results.e) evaluation and feedback from customers on the HSmanagement performance of the organization,f) resources needed for realizing HSF products andprocesses, andg) improvement plan.detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---4116.3infrastructure related to HS control are listed out as:a) buildings, workspace and associated utilities;b) process equipment and testing equipments (bothhardware and software), andc) supporting services (such as testing, data computing,communication or information systems).6.4none added as follows:6.4 Work environmentThe organization shall determine, provide and maintain thework environment needed to achieve HSF products.detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---5127.1 a paragraph on change management added as follows:"The organization shall establish and maintain procedurefor changes that will potentially lead to the change of HSFcharacteristic of products. The organization shall plan andimplement verification, validation and approval for suchchanges, and evaluate the results of changes. Changesthat have potential impact on HSF characteristic ofproducts can not be implemented without approval ofcustomers where necessary. Records shall be maintainedfor changes implemented.Note: changes include those within the organization andthose within the supply chain that the organization caninfluence."detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---6137.2.1 a paragraph added as follows:"The organization shall determine the responsibility andchannel for the collection, delivery and summarization of these requirements, and determine how these requirements apply to its products."7.2.2divided into 7.2.2 and 7.2.3, 7.2.2 C) is moved to 7.2.3 a), and7.2.3 read as:"7.2.3 Customer communicationThe organization shall determine and implement effectivearrangements for communication with customers in format andchannel specified by legal or customer requirements inrelation toa) any use of, contamination by or mixing with product orprocesses that contain hazardous substances,b) any information, records, documents or evidencesrequested by customer, andc) changes that may have impact on the HSF characteristic of product."detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---7147.3.1"The suitable stage and method shall be determined for thereview, verification and validation of the HSF characteristic ofproduct during design and development." added.7.3.2"Inputs shall include legal and customer requirements onhazardous substance control and be in line with the internalHSF acceptance criteria for HSF product (see 7.1)." added.7.3.3"Where appropriate, the HSF outputs shall provide appropriate information for customer communication, purchasing,production, product marking, information releasing, and service provision. The outputs shall contain or refer to productacceptance criteria.“"a restricted substance" is replaced by "a hazardous substance or processes of risk of contamination by or mixing withhazardous substance"detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---8157.3.5"Verification shall be performed in accordance with planned arrangements to ensure the HSF characteristicof product and process has met the design anddevelopment input requirements. Methods used forverification shall be determined and validated." added.7.3.6"Validation shall be performed in accordance with plannedarrangements to ensure the compliance of HSFcharacteristic, and the resulting product is capable ofmeeting the requirements for the specified application orintended use, where known.The result of design and development shall be approvedby customer where necessary." added.detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---9167.4re-phrased to make it more consistent with ISO9001, andthe following requirements are added:"The type and extent of control applied to the supplier andthe purchased product shall be dependent upon the HSFrisk of the purchased product and the ability of thesupplier in HSF management.""The organization shall establish a list of qualified HSFsuppliers and validated HSF purchased products.""The organization shall ensure effective control overchanges in supply chain.""The organization shall establish and communicate theHSF requirements to suppliers.""c) Without specific approval, the organization shall notpurchase products from outside of the list of qualifiedHSF suppliers and validated HSF purchased products forHSF production."detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---10177.5.1"in which processes that have the potential of contamination or mixture are identified and preventivemeasures documented," added in the end of b);"c) the validated HSF purchased products for HSFproduction," added.7.5.3b)...toprevent combinat ion with HSF product.b) …to prevent HSF product from contamination by ormixing with hazardous substances."e) The organization shall ensure products are affixed with HSF marking and other elements according to legal or customer requirements applicable." added.7.5.4transferred into 7.5.5the whole 7.5.4 added and read as:"7.5.4 Customer propertyThe organization shall exercise care with customerproperty to protect the HSF characteristic while it is underthe organization’s control or being used by organization.The organization shall communicate to customer whereHSF nonconformity identified with customer property."detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---11187.5.5none the whole 7.5.5 re-wording as:"7.5.5 Preservation of producta) The organization shall protect the HSF characteristicand HSF identification status of product.b) HSF nonconforming materials and products shall besegregated and managed separately.c) The organization shall ensure purchased products arereleased correctly for HSF production.d) Records for storage and releasing of HSFnonconforming products shall be maintained."7.6"c) Measuring equipment for HSF characteristic shall bemanaged to ensure valid results." added.detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---12198.1adapted to the sub-clauses of 8.1, ISO9001.8.2.1deliberated as:"The organization shall monitor information relating tocustomer and interested party’s perception as to whetherthe organization has met their HSF requirements.Note: Interested Party may include competentauthorities, surveillance authorities, distributors,consumers, authorised representatives, etc., whereapplicable."8.2.2Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 90018.2.3Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 90018.2.4Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 90018.3Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 90018.4Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 90018.5Re-phrased to clarify the intention and align with 9001detailed differences between version 2005 and 2012---13。
iecq-qc-080000:-第四版标准(中文版)I E C Q-Q C-080000:2017-第四版标准(中文版)-CAL-FENGHAI-(2020YEAR-YICAI)_JINGBIAN有害物质过程管理(HSPM)体系要求前言本出版物由IECQ 管理委员会(MC)制订。
本出版物与包含 IECQ HSPM 方案程序规则的IECQ 03-5 直接相关。
本IECQ 国际规范(以下称为国际规范)及其要求源于以下理念:只有有效地融合管理规范,才能实现有害物质减免(HSF)产品和生产过程。
本国际规范是对ISO 9001 质量管理体系(QMS)框架的补充,与其协调一致,目的是对过程进行全面、系统、透明的管理和控制,以实现HSF 目标。
IECQ QC 080000 第四版针对第三版的使用反馈进行修订。
第四版中的变化包括:––与ISO 9001:2015 一致;––采用了ISO 附录SL 高层结构;––适应全球不断增加的有害物质法规。
如REACH1法规所规定的新增受控物质、变更控制、产品召回,供应链内的信息沟通,以及向ECHA2通报SVHC3;––响应适用的法律法规义务,强化了成文信息的要求。
如RoHS4指令改写后的要求(如符合性评定、技术文件的编写、自我声明的编制、标志的使用等)现在都可以通过IECQQC 080000 来管理。
IECQ QC 080000 规定了组织如何建立和实施关键过程来管理其有害物质,而不是强调如何去除和回避产品中的受限物质。
用于识别、控制、量化和报告电工产品或其部件中有害物质(HS)含量的各种过程,必须足够详尽地予以定义和理解,以便让所有相关方确信产品的HSF 状态。
这些过程必须适当成文,并以受控和一致的方式执行,从而:––有利于验证适用顾客要求和法规的符合性––可以进行高效且有效的符合性检查––有利于在组织及其供应链得到一致推广––使得符合性和执行方法能够相互协调这样,就能够在世界范围内最大限度地减少产品贸易的技术壁垒。