表面活性剂的结构与性能
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.55 MB
- 文档页数:48










表面活性剂基础知识详解1、表面张力分子在液体表面相对高速运动,分子之间存在内聚力,表面分子向本体进行收缩,我们把液体表面任意单位长度的收缩力称为表面张力,单位为N•m-1。
2、表面活性和表面活性剂将能降低溶剂表面张力的性质称为表面活性,而具有表面活性的物质称为表面活性物质。
把能在水溶液中分子发生缔合且形成胶束等缔合体,并具有较高的表面活性,同时还具有润湿﹑乳化﹑起泡﹑洗涤等作用的表面活性物质称为表面活性剂。
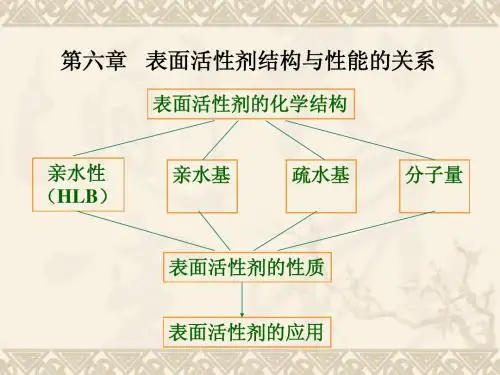
3、表面活性剂的分子结构特点表面活性剂是一种具有特殊结构和性质的有机化合物,它们能明显地改变两相间的界面张力或液体(一般为水)的表面张力,具有润湿﹑起泡﹑乳化﹑洗涤等性能。
就结构而言,表面活性剂都有一个共同的特点,即其分子中含有两种不同性质的基团,一端是长链非极性基团,能溶于油而不溶于水,亦即所谓的疏水基团或憎水基,这种憎水基一般都是长链的碳氢化合物,有时也为有机氟﹑有机硅﹑有机磷﹑有机锡链等。
另一端则是水溶性的基团,即亲水基团或亲水基。
亲水基团必须有足够的亲水性,以保证整个表面活性剂能溶于水,并有必要的溶解度。
由于表面活性剂含有亲水基和疏水基,因而它们至少能溶于液相中的某一相。
表面活性剂的这种既亲水又亲油的性质称为两亲性。
4、表面活性剂的类型表面活性剂是一种既有疏水基团又有亲水基团的两亲性分子。
表面活性剂的疏水基团一般是由长链的碳氢构成,如直链烷基C8~C20,支链烷基C8~C20,烷基苯基(烷基碳原子数为8~16)等。
疏水基团的差别主要是在碳氢链的结构变化上,差别较小,而亲水基团的种类则较多,所以表面活性剂的性质除与疏水基团的大小﹑形状有关外,主要还与亲水基团有关。
亲水基团的结构变化较疏水基团大,因而表面活性剂的分类一般以亲水基团的结构为依据。
这种分类是以亲水基团是否是离子型为主,将其分为阴离子型﹑阳离子型﹑非离子型﹑两性离子型和其他特殊类型的表面活性剂。
5、表面活性剂水溶液的特性①表面活性剂在界面上的吸附表面活性剂分子中具有亲油基和亲水基,为两亲分子。
表面活性剂的结构对去污性能的影响在去污机理中已经谈到,表面活性剂的去污作用是通过其在非极性表面上的吸附、使被清洗表面成为亲水性表面后实现的。
因此从原则上可以认为,吸附量越大去污能力会越好。
然而由于洗涤温度、水硬度、基质和污垢的种类及性质对表面活性的作用都有相当大的影响,同时吸附也不是决定表面活性剂去污作用的惟一因素。
所以不能仅从表面活性剂的表面活性(即吸附能力)来考虑,而应综合各方面的影响因素。
一、表面活性剂疏水基(也称亲油基)结构的影响(1)链长的影响表面活性剂在基质和污垢上吸附的量及其吸附方式对污垢的去除和防止再沉积均有重要作用。
在给定浓度下,亲水基相同的表面活性剂,其疏水基越长,吸附量大。
对于阴离子表面活性剂而言,疏水链长者去污性能较好,但也不是越长越好,而是有一个最佳链长范围。
此范围的确定与洗涤温度和水硬度有密切关系。
其原因在于,随链长的增加,表面活性剂在水中的溶解度迅速下降,同时其Krafft点上升明显,见表2-1.当洗涤温度低于Krafft点时,表面活性剂的溶解量很少,不能达到临界胶束浓度,得不到最好的去污效果。
因此欲配置在较低温度下使用的洗涤剂,就不能选择疏水基过长的表面活性剂。
表2-1 一些阴离子表面活性剂的Krafft点除洗涤温度外,水硬度对表面活性剂的溶解性能也有很大影响。
特别是阴离子表面活性剂,随水硬度增高,溶解中生成高Krafft点表面活性剂钙和镁盐的量也逐渐增多。
这些钙盐在水中的溶解度很低,见表2-2,从而大大影响了去污性能。
表2-2 烷基硫酸钙在水中的溶解度(25℃)10 250~300 14 0.03~0.04非离子表面活性剂的Krafft点一般都低于零度,对钙、镁离子的敏感性也较低。
但是尽管如此,非离子表面活性剂疏水基的链长也有一个最佳范围。
疏水基过长水溶性变差、浊点降低,去污性能也随之降低。
虽然增加长碳链非离子表面活性剂的乙氧基聚合度也可增加水溶性,但此时会大大影响表面活性剂吸附的扩散速度,以致在实际洗涤条件下达不到最大吸附量。
表面活性剂的基本理论知识1.表面张力把液体表面任意单位长度的收缩力称为表面张力,单位为N•m-1。
2.表面活性和表面活性剂将能降低溶剂表面张力的性质称为表面活性,而具有表面活性的物质称为表面活性物质。
把能在水溶液中分子发生缔合且形成胶束等缔合体,并具有较高的表面活性,同时还具有润湿﹑乳化﹑起泡﹑洗涤等作用的表面活性物质称为表面活性剂。
3.表面活性剂的分子结构特点表面活性剂是一种具有特殊结构和性质的有机化合物,它们能明显地改变两相间的界面张力或液体(一般为水)的表面张力,具有润湿﹑起泡﹑乳化﹑洗涤等性能。
就结构而言,表面活性剂都有一个共同的特点,即其分子中含有两种不同性质的基团,一端是长链非极性基团,能溶于油而不溶于水,亦即所谓的疏水基团或憎水基,这种憎水基一般都是长链的碳氢化合物,有时也为有机氟﹑有机硅﹑有机磷﹑有机锡链等。
另一端则是水溶性的基团,即亲水基团或亲水基。
亲水基团必须有足够的亲水性,以保证整个表面活性剂能溶于水,并有必要的溶解度。
由于表面活性剂含有亲水基和疏水基,因而它们至少能溶于液相中的某一相。
表面活性剂的这种既亲水又亲油的性质称为两亲性。
4.表面活性剂的类型表面活性剂是一种既有疏水基团又有亲水基团的两亲性分子。
表面活性剂的疏水基团一般是由长链的碳氢构成,如直链烷基C8~C20,支链烷基C8~C20,烷基苯基(烷基碳原子数为8~16)等。
疏水基团的差别主要是在碳氢链的结构变化上,差别较小,而亲水基团的种类则较多,所以表面活性剂的性质除与疏水基团的大小﹑形状有关外,主要还与亲水基团有关。
亲水基团的结构变化较疏水基团大,因而表面活性剂的分类一般以亲水基团的结构为依据。
这种分类是以亲水基团是否是离子型为主,将其分为阴离子型﹑阳离子型﹑非离子型﹑两性离子型和其他特殊类型的表面活性剂。
5.表面活性剂水溶液的特性①表面活性剂在界面上的吸附表面活性剂分子中具有亲油基和亲水基,为两亲分子。
水是强极性液体,当表面活性剂溶于水中时,根据极性相似相引﹑极性相异相斥原理,其亲水基与水相引而溶于水,其亲油基与水相斥而离开水,结果表面活性剂分子(或离子)吸附在两相界面上,使两相间的界面张力降低。