货币银行学 (2)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:165.91 KB
- 文档页数:13

货币银行学练习题第一章判断题:1、与货币的起源密不可分的是贫富分化。
2、价格标准是各种商品在质上同一、在量上可以比较的共同基础。
3、用纸做的货币,比如银行券和国家发行的纸币,在性质上都是一致的。
4 、钱、货币、通货、现金都是一回事,银行卡也是货币。
5 、发挥支付手段职能的货币同发挥流通手段职能的货币一样,都是处于流通过程中的现实的货币。
所谓流通中的货币,指的就是这两者的总体。
流通中的任一货币,往往是交替地发挥这两种职能。
67造。
1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A12A13A14A 、银行吸收存款B 、汽车购买C 、工资支付D 、商品购买15 、经济对货币的需求包括对:A 、世界货币的需求B 、储藏手段的需求C 、流通手段的需求D 、支付手段的需求第二章三、判断1、信用的形式特征是以收回为条件的付出,或以归还为义务的取得;而且贷者之所以贷出,是因为有权取得利息(interest)。
借者之所以可能借入,是因为承担了支付利息的义务。
2、高利贷者除了货币需要者的负担能力和抵抗能力以外,再也不知道别的限制。
3、个人的货币收入总额,通常情况下就是个人可以支配的货币收入。
4、银行券无非是向银行家开出的、持票人随时可以兑现的、由银行家用来代替私人汇票的一种汇票。
四、不定项选择1、信用活动中的货币发挥的职能是:A、储藏手段B、支付手段C、流通手段D、价值尺度2、商业信用最典型的做法是:A、赊销B、有借有还C、票据化D、挂账3、由债权人开出承诺到期付款的有价证券是:A、商业票据B、支票C、商业汇票D、商业期票4、一直在我国占主导地位的信用形式是:A、银行信用B、国家信用C、消费信用D、民间信用5、信用的基本特征有:A、所有权转移B、偿还性C、使用权转移D、付息性6、在商业信用中采用的商业票据有:A、支票B、传票C、期票D、汇票7、消费信贷的基本类型有:A、银行信用B、合作信用C、商业信用D、国家信用8、在典型的商业信用中实际包括两个同时发生的经济行为,亦即A、买卖行为B、借贷行为C、分配行为D、生产行为91011A121314A15161。





ExamName___________________________________MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.1) Everything else held constant, when prices in the art market become more uncertain, 1) _______A) the demand curve for bonds shifts to the right and the interest rate falls.B) the supply curve for bonds shifts to the right and the interest rate falls.C) the demand curve for bonds shifts to the left and the interest rate rises.D) the demand curve for bonds shifts to the left and the interest rate falls.2) Which of the following $1,000 face-value securities has the highest yield to maturity? 2) _______A) A 5 percent coupon bond selling for $1,000B) A 10 percent coupon bond selling for $1,000C) A 12 percent coupon bond selling for $1,100D) A 12 percent coupon bond selling for $1,0003) The recent Enron and Tyco scandals are an example of 3) _______A) the principal-agent problem. B) the adverse selection problem.C) the "lemons problem." D) the free-rider problem.4) A change in perceived risk of a stock changes 4) _______A) the expected dividend growth rate. B) the expected sales price.C) the current dividend. D) the required rate of return.5) ________ policy involves decisions about government spending and taxation. 5) _______A) Systemic B) Financial C) Fiscal D) Monetary6) The ________ of the term structure of interest rates states that the interest rate on a long-term bond will equal the average of short-term interest rates that individuals expect to occur over the life of the long-term bond, and investors have no preference for short-term bonds relative to long-term bonds. 6) _______A) liquidity premium theory B) segmented markets theoryC) separable markets theory D) expectations theory7) The ________ problem helps to explain why the private production and sale of information cannot eliminate ________. 7) _______A) free-rider; moral hazard B) free-rider; adverse selectionC) principal-agent; adverse selection D) principal-agent; moral hazard8) If the interest rate on a bond is below the equilibrium interest rate, there is an excess ________ of bonds and the bond price will ________. 8) _______A) supply; rise B) demand; rise C) demand; fall D) supply; fall9) Government regulations require publicly traded firms to provide information, reducing 9) _______A) transactions costs. B) the need for diversification.C) the adverse selection problem. D) economies of scale.10) Because of their ________ liquidity, ________ U.S. government securities are called secondary reserves.10) ______A) low; short-term B) low; long-termC) high; short-term D) high; long-term11) A discount bond 11) ______A) pays the bondholder the face value at maturity.B) pays the face value at maturity plus any capital gain.C) pays all interest and the face value at maturity.D) pays the bondholder a fixed amount every period and the face value at maturity.12) As a source of funds for nonfinancial businesses, stocks are relatively more important in 12) ______A) Japan. B) the United States.C) Canada. D) Germany.13) Although the dominance of ________ over ________ is clear in all countries, the relative importance of bond versus stock markets differs widely. 13) ______A) financial intermediaries; securities marketsB) government agencies; securities marketsC) financial intermediaries; government agenciesD) government agencies; financial intermediaries14) When short-term interest rates are expected to fall sharply in the future, the yield curve will 14) ______A) be an inverted U shape. B) be inverted.C) slope up. D) be flat.15) The higher a security's price in the secondary market the ________ funds a firm can raise by selling securities in the ________ market. 15) ______A) more; secondary B) more; primaryC) less; secondary D) less; primary16) Banks earn profits by selling ________ with attractive combinations of liquidity, risk, and return, and using the proceeds to buy ________ with a different set of characteristics. 16) ______A) securities; deposits B) assets; liabilitiesC) liabilities; assets D) loans; deposits17) Net profit after taxes per dollar of assets is a basic measure of bank profitability called 17) ______A) return on equity. B) return on assets.C) return on capital. D) return on investment.18) The largest percentage of banks' holdings of securities consist of 18) ______A) state and local government securities.B) Treasury and government agency securities.C) corporate securities.D) tax-exempt municipal securities.19) The global financial crisis lead to a decline in stock prices because 19) ______A) of a lowered expected dividend growth rate.B) higher expected future stock prices.C) of a lowered required return on investment in equity.D) higher current dividends.20) If an individual moves money from a savings deposit account to a money market deposit account, 20) ______A) M1 decreases and M2 stays the same.B) M1 stays the same and M2 increases.C) M1 stays the same and M2 stays the same.D) M1 increases and M2 decreases.21) During the Great Depression years 1930-1933 there was a very high rate of business failures and defaults, we would expect the risk premium for ________ bonds to be very high. 21) ______A) municipal B) U.S. Treasury C) corporate Aaa D) corporate Baa22) When tax revenues are greater than government expenditures, the government has a budget. 22) ______A) crisis. B) revision. C) surplus. D) deficit.23) In Japan in 1998 and in the U.S. in 2008, interest rates were negative for a short period of time because investors found it convenient to hold six-month bills as a store of value because 23) ______A) of the high inflation rate.B) these bills sold at a discount from face value.C) the bills were denominated in small amounts and could be stored electronically.D) the bills were denominated in large amounts and could be stored electronically.24) A person's house is part of her 24) ______A) income. B) liabilities. C) money. D) wealth.25) In the generalized dividend model, a future sales price far in the future does not affect the current stock price because 25) ______A) the present value cannot be computed.B) the stock may never be sold.C) the sales price does not affect the current price.D) the present value is almost zero.26) If there are five goods in a barter economy, one needs to know ten prices in order to exchange one good for another. If, however, there are ten goods in a barter economy, then one needs to know ________ prices in order to exchange one good for another. 26) ______A) 20 B) 25 C) 30 D) 4527) Financial institutions search for ________ has resulted in many financial innovations. 27) ______A) higher profits B) respect C) higher risk D) regulations28) If the liquidity effect is smaller than the other effects, and the adjustment to expected inflation is immediate, then the 28) ______A) interest rate will rise immediately above the initial level when the money supply grows.B) interest rate will rise.C) interest rate will fall immediately below the initial level when the money supply grows.D) interest rate will fall.29) In actual practice, short-term interest rates and long-term interest rates usually move together; this is the major shortcoming of the 29) ______A) segmented markets theory. B) expectations theory.C) liquidity premium theory. D) separable markets theory.30) What is the return on a 5 percent coupon bond that initially sells for $1,000 and sells for $1,200 next year?30) ______A) -5 percent B) 5 percent C) 25 percent D) 10 percent31) According to the liquidity premium theory of the term structure, a flat yield curve indicates that short-term interest rates are expected to 31) ______A) rise in the future. B) remain unchanged in the future.C) decline moderately in the future. D) decline sharply in the future.32) People hold money even during inflationary episodes when other assets prove to be better stores of value. This can be explained by the fact that money is 32) ______A) a unique good for which there are no substitutes.B) extremely liquid.C) the only thing accepted in economic exchange.D) backed by gold.33) One way of describing the solution that high net worth provides to the moral hazard problem is to say that it 33) ______A) collateralizes the debt contract.B) removes all of the risk in the debt contract.C) state verifies the debt contract.D) makes the debt contract incentive compatible.34) If additional information is not used when forming an optimal forecast because it is not available at that time, then expectations are 34) ______A) formed equivalently. B) obviously formed irrationally.C) still considered to be formed rationally. D) formed adaptively.35) Assuming the same coupon rate and maturity length, when the interest rate on a Treasury Inflation Protected Security is 3 percent, and the yield on a nonindexed Treasury bond is 8 percent, the expected rate of inflation is 35) ______A) 3 percent. B) 5 percent. C) 8 percent. D) 11 percent.36) Banks can lower the cost of information production by applying one information resource to many different services. This process is called 36) ______A) asymmetric information. B) economies of scope.C) economies of scale. D) asset transformation.37) If prices in the bond market become more volatile, everything else held constant, the demand curve for bonds shifts ________ and interest rates ________. 37) ______A) left; fall B) right; rise C) left; rise D) right; fall38) Savings and loan associations are regulated by the 38) ______A) Office of Thrift Supervision.B) Federal Reserve System.C) Office of the Comptroller of the Currency.D) Securities and Exchange Commission.39) If in an efficient market all prices are correct and reflect market fundamentals, which of the following is a false statement? 39) ______A) A stock that has done poorly in the past is more likely to do well in the future.B) One investment is as good as any other because the securities' prices are correct.C) A security's price reflects all available information about the intrinsic value of the security.D) Security prices can be used by managers to assess their cost of capital accurately.40) A lower level of income causes the demand for money to ________ and the interest rate to ________, everything else held constant. 40) ______A) decrease; increase B) decrease; decreaseC) increase; decrease D) increase; increase41) Which of the following $1,000 face-value securities has the lowest yield to maturity? 41) ______A) A 15 percent coupon bond selling for $900B) A 5 percent coupon bond selling for $1,000C) A 10 percent coupon bond selling for $1,000D) A 15 percent coupon bond selling for $1,00042) According to the liquidity premium theory of the term structure 42) ______A) bonds of different maturities are not substitutes.B) if yield curves are downward sloping, then short-term interest rates are expected to fall by so much that, even when the positive term premium is added, long-term rates fall below short-term rates.C) yield curves should never slope downward.D) interest rates on bonds of different maturities do not move together over time.43) Everything else held constant, if the expected return on RST stock declines from 12 to 9 percent and the expected return on XYZ stock declines from 8 to 7 percent, then the expected return of holding RST stock________ relative to XYZ stock and demand for XYZ stock ________. 43) ______A) falls; falls B) rises; rises C) falls; rises D) rises; falls44) Bank reserves include 44) ______A) vault cash and deposits at the Fed.B) deposits at other banks and deposits at the Fed.C) vault cash and short-term Treasury securities.D) deposits at the Fed and short-term treasury securities.45) Financial markets promote greater economic efficiency by channeling funds from ________ to ________.45) ______A) savers; borrowers B) borrowers; saversC) savers; lenders D) investors; savers46) When stock prices fall 46) ______A) an individual's wealth is not affected nor is their willingness to spend.B) an individual's wealth may decrease and their willingness to spend may decrease.C) a business firm will be more likely to sell stock to finance investment spending.D) an individual's wealth may decrease but their willingness to spend is not affected.47) The primary assets of credit unions are 47) ______A) municipal bonds. B) mortgages.C) business loans. D) consumer loans.48) The components of the U.S. M1 money supply are demand and checkable deposits plus 48) ______A) currency plus travelers checks plus money market deposits.B) currency plus savings deposits.C) currency plus travelers checks.D) currency.49) Property that is pledged to the lender in the event that a borrower cannot make his or her debt payment is called 49) ______A) points. B) good faith money.C) collateral. D) interest.50) ________ is the relative ease and speed with which an asset can be converted into a medium of exchange.50) ______A) Deflation B) Liquidity C) Efficiency D) Specialization1) A2) D3) A4) D5) C6) D7) B8) D9) C10) C11) A12) C13) A14) B15) B16) C17) B18) B19) A20) C21) D22) C23) D24) D25) D26) D27) A28) A29) A30) C31) C32) B33) D34) C35) B36) B37) C38) A39) A40) B41) B42) B43) C44) A45) A46) B47) D48) C49) C50) B。


第七章金融中介一、单项选择题1.金融机构适应经济发展需求最早产生的功能是()。
A.融通资金B.支付结算服务C.降低交易成本D.风险转移与管理2.在一个国家或地区的金融监管组织机构中居于核心位置的机构是()。
A.社会性公律组织B.行业协会C.中央银行或金融管理局D.分业设立的监管机构1999年4月20日,我国成立的首家经营商业银行不良资产的金融资产公司是()。
A.华融 B.长城 C.东方 D.信达3.我国的政策性金融机构主要有()。
A.国家开发银行B.中国建设银行C.中国农业银行D.农村信用合作社4.()是我国第一家全国性股份制商业银行。
A. 光大银行B. 招商银行C. 交通银行D. 华夏银行5.在我国,执行中央银行职能的是()。
A. 中国银行B. 中国人民银行C. 中国建设银行D. 中国工商银行6.中国人民银行专门行使中央银行职能是在()年。
A.1983B.1984C.1985D.19867.2003年,随着()的成立,银行、证券、保险——中国金融业“分业经营,分业监管”的框架最终完成,新中国成立50多年来中国人民银行集货币政策与银行监管于一身的“大一统”时代也宣告结束。
A. 中国人民银行B. 保监会C. 证监会D. 银监会8.国际货币基金组织的最高权力机构是()。
A.理事会B.董事会C.会员国协商D.监管机构二、简答题如何理解金融机构在各国社会经济中的主要功能?第八章商业银行一、名词解释1.巴塞尔协议2.中间业务3.存款派生倍数二、单项选择题1.在商业银行总分行制的外部组织形式中,()是指总部负责管理下属分支机构的业务活动,自身并不经营具体的银行对外业务。
A.总行制B. 单一制C.连锁制D. 管理处制2.根据我国《商业银行法》规定,在改革开放后逐步建立起来的我国现行的商业银行体系,目前采用的是()模式。
A.全能型B.混业经营C.单元型D.职能分工3.商业银行从事的不列入资产负债表内但能影响银行当期损益的经营活动,是商业银行的(),且其可以有狭义和广义之分。

2024年货币银行学学习心得货银作业学财经,学经济,总归是要从追根溯源的。
经济、贸易等早已渗透在人类生活的方方面面。
社会离不开金钱交易,而作为金钱交易的载体和媒介,货币这个复杂的东西更成为当今世界不可或缺的一项物品。
在高中政治书的经济生活部分,货币就出现在了那本书的开端。
作为了解经济生活的入门,货币的本质及基本职能等概念至今都能清晰地浮现。
而《货币》这部纪录片的第一集,展示的所有,说是《有价星球》,其实就是将货币对人类社会的渗透作用渲染得生动直观了些。
以我对货币现有的了解,也就像曾经书里给的概念一般,货币是人类社会发展过程中从商品中分离出来固定地充当一般等价物的商品,本质是一般等价物。
就如同纪录片里呈现出来的一般,货币也是促进文化交流沟通的一种工具,是可以推动社会发展的一种媒介。
而如果一定要给货币的职能赋予个说法,那么价值尺度和流通手段就是货币的基本职能。
纪录片里面一直在重复一个观点,“货币是一把尺子”,它能丈量社会生产的价值,往更小的方面看,就一个商品来说,该商品能直观地反映到人脑的价值也是通过商品的价格标签来达成的,即“观念上的货币”。
而当人们对这件商品感兴趣想去拥有它,人们就需要付出一定的货币去购买商品,往更大的方面看,社会不同领域的生产产物也需要通过货币来实现流通,即货币的“流通手段”职能。
除了最基本的这俩职能,货币还可以在赋税、地租、借贷以及工资和各种劳动报酬等支付中发挥“支付手段”职能;还能作为积累和保存价值的手段而存在,即发挥其“贮藏手段”职能;而随着经济全球化和贸易全球化的发展,国家经济不再是孤立的存在,货币服务于国际交往,即“世界货币”职能。
事物都有正反两面。
2024年货币银行学学习心得(2)学习货币银行学是我大学期间的一门重要课程,通过这门课程的学习,我深刻理解了货币和银行在现代经济中的重要性。
在____年的今天,我想分享我对货币银行学的学习心得。
货币在现代社会中扮演着非常重要的角色,它是人们进行经济交换的媒介和计量单位。

《货币银行学》试题及答案三、单项选择题(每小题1分,共10分):试卷A BBDAACDDAB1、下列最不可能作为货币的是()A、燕麦B、冰激凌C、香烟D、松香2、信用卡透支属于银行的何种业务?()A、贴现业务B、放款业务C、汇兑业务D、中间业务3、下列何者是货币市场上资金的供给者()A、商业银行B、工商企业C、个人D、以上都是4、下列属于长期信用工具的是()A、股票B、支票C、本票D、汇票5、对我国目前发行的1元硬币最准确的描述是:()A、本位币B、金属货币C、实物货币D、辅币6、商业银行与其他金融机构区别之一在于其能接受()。
A、派生存款B、定期存款C、活期存款D、储蓄存款7、LIBOR是指:()A、固定收益债券 B本币相对于其他国家货币的价值C、银行资产对利率的敏感性 D伦敦同业拆借利率8、下列不属于存款型金融机构的是()A .商业银行 B.储蓄银行 C.信用社 D.投资基金9、如果金银的法定比价为1:13,而市场比价为1:15,这是充斥市场的将是()A、银币B、金币C、金币和银币 D.都不是10、我国成立资产管理公司的目的是()A、管理国有资产B、管理和处置商业银行的不良资产C、受客户委托管理金融资产D、管理不动产补考试卷B 43442433121.单利是指()①按市场利率计算的利息②以年为期限单位计算的利息③银行对逾期贷款的加罚息④仅对本金计算利息,对本金所生利息不再计息2.利息率是指()①利息额与利润的比率②利息额与货币供应量的比率③一定时期内利息额与所贷金额的比率④利息额与金融资产的比率3.再贴现贷款是()①商业银行对企业的贷款②商业银行对其他非银行金融机构的贷款③商业银行对商业银行的贷款④中央银行对商业银行的贷款4.中国人民银行成立于()① 1949年10月1日② 1949年12月1日③ 1948年10月1日④ 1948年12月1日5.一定时期的商品可供量减少,则货币需要量()①增加②减少③不变④没有相关关系6.凯恩斯认为与利率变动存在着负相关关系的货币需求是()①交易性货币需求②预防性货币需求③营业性货币需求④投机性货币需求7.最早的标志着资本主义新式银行制度确立的银行是()①法兰西银行②德意志银行③英格兰银行④瑞士银行8.银行作为一种企业,与工商企业有共同点,表现为()①活动领域相同②经营的对象相同③经营活动的目的相同④资金来源相同9.政策性金融机构的经营目标是()①实现政府的政策目标②实现上级政策规定的利润目标③实现本机构的长远规划目标④实现本机构的利润最大化10.“劣币驱逐良币”这一规律出现的货币制度是()①平行本位制②双本位制③跛行本位制④银本位制试卷A卷ADBCBACADCBCACC1、我国的货币层次划分中一般将现金划入()层次:A、M0B、M1C、M2D、M32、名义利率、实际利率和通货膨胀率三者之间的关系可表述为()。
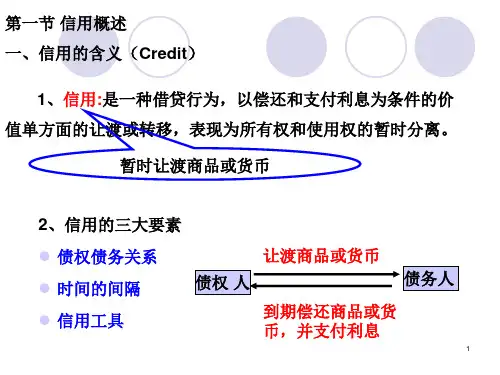
《货币银行学》试题及答案(一)1 信用是在私有制的基础上产生的。
√2 商业银行经营方针中安全性与盈利性是统一的。
×3 中国人民银行在1984年之后是复合式中央银行。
×4 国际收支是存量概念,货币供应量是流量概念。
×5 当法定存款准备金率降低时,存款货币的派生将扩张。
√6 自1984年至1995年《中华人民共和国中国人民银行法》颁布之前,我国事实上一直奉行双重货币政策目标,即(稳定物价,经济增长)。
7 决定债券收益率的因素主要有(期限、利率、购买价格)8 货币制度的基本类型有(复本位,银本位,不兑现的信用货币,金本位)。
9 《国务院关于金融体制改革的决定》明确指出,我国今后货币政策的中介指标有(信用总量、货币供应量,同业拆借利率,银行备付金率)10 国际货币基金组织会员国的国际储备,一般可分为(外汇、黄金、特别提款权,在IMF的储备头寸)。
11 关于会计主体和法律主体的区别,描述正确的是(只要是一个法律主体,无论其规模多大----------)。
12 业务收支以外币为主的企业,其记账本位币应为(两种方式均可)。
13 关于真实性原则的含义,下列不正确的是(在必要的情况下,真实性原则并非不可违背)。
14 会计核算所要反映和提供的会计信息必须有助于会计信息使用者正确地做出经济决策,即会计信息必须满足宏观经济管理的需要,满足各有关方面了解企业财务状况和经营成果的需要,满足加强内部经营管理的需要,这是(相关性原则)的要求。
15 在会计核算中,一个会计期间内的各项收入与其相关联的成本费用应当在同一会计期间内进行确认、计量,是(配比性原则)的要求。
16 按照历史成本原则,企业对资产、负债等项目的计量应当基于经济业务的(实行交易价格)。
17 谨慎性原则要求(意味着企业可以设置秘密准备)。
18 关于重要性原则,理解正确的是(可以不用全面反映,充分披露重要的事项即可)。
19 下列哪个不属于会计要素(成本)。