部分作业答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:116.50 KB
- 文档页数:3
1、某发电厂有3台300MW 发电机和三条500kV 出线,其中发电机和双绕组主变压器采用单元接线,变压器高压侧的一次接线拟采用一台半断路器接线。
试画出该发电厂的电气主接线图。
解:电气主接线图如下:2、画出两个电源,四条引出线的单母线分段带旁路接线的电气主接线图,并写出线路断路器QF3检修后,恢复线路WL1送电的基本操作步骤。
解:电气主接线图如下:基本操作步骤:(1)恢复WL1供电:合上31QS ,然后合上32QS ,再合上3QF (2)退出旁路母线WP :先断开1QSP ,然后断开QFP ,再断开1QSP 。
3、图示为什么形式的主接线?说明图中9QS 、10QS 的作用.解:图示为内桥接线9QS 、10QS 的作用:组成跨条,为了减少开环及满足一回进线或出线停运时桥断路器需退出运行。
4、某发电厂厂用电高、低压母线电压等级分别为6kV 和0.38kV 。
高压母线供电的负荷中含有高压电动机,在电动机自启动时,6kV 母线最低电压标幺值为0.83。
高压母线还通过一台额定容量N S 为1MVA ,短路电压%K U 为10的双绕组无激励变压器给低压母线供电。
低压母线上自启动电动机功率为500kW,电动机效率为0.9,功率因数8.0cos =ϕ,启动电流倍数为5,试问:厂用电低压母线和高压母线串接自启动时,低压电动机能否自启动?解:示意图:如图所示,变压器2T 的电抗标幺值为11.0100101.1100%1.1*=×=×=K t U X 低压母线上的合成负荷标幺值为288.09.08.0/500100051cos /11t av t *=××=⋅⋅=⋅=ΣΣϕηP S K S S K X av D 低压母线电压标幺值为:%55%06.60288.0288.011.083.0***1*2*>=×+=⋅+=D D t X X X U U 根据上式可知,低压电动机能自启动。

绪论部分一、填空1、通常认为说出来的话是口语,用笔写下来的是书面语,而从语言学的角度看口语和书面语的差别主要在_________________________方面。
风格2、周秦时代的书面语就是一般所说的文言文,汉魏以后出现了一种跟口语比较接近的书面语,如唐宋时代的语录、宋代的平话、元明清的戏曲和__________________等。
小说3、现代汉语有两种含义,其一是指以北京语音为标准音、以北京话为基础方言、以____________________________________________________为语法规范的普通话。
典范的现代白话文著作4、现代汉语的存在方式包括_______________、_________________、___________________。
口语、书面语、文学语言5、汉语是联合国规定的六种工作语言之一,这六种工作语言分别是__________________、______________、______________、______________、______________、_____________。
汉语、英语、法语、俄语、西班牙语、阿拉伯语6、英语和汉语的句子中都可以有修饰语,但两种语言的修饰语的位置不同,汉语的修饰语包括定语和状语一般在中心语__________________。
前面7、语言的规范化要解决两个问题:一个是__________________;一个是_________________。
规范不明确、规范不普及8、从方言区划分上,上海话属于_____________,南京话属于_____________,广州话属于_____________,南昌话属于________________。
吴方言、北方方言、粤方言、赣方言9、春秋时代,汉民族共同语被称作___________,汉代起被称作___________,明代改称___________,辛亥革命后称为___________,新中国成立后被称作___________。

作业一 一、名词解释 样品 买方样 卖方样 复样 对等样 参考样品 定牌中性 无牌中性 商品品质 商品数量 商品包装 中性包装 指示性标志 警告性标志、选择题1. 在国际贸易中,对于某些品质变化较大而难以规定统一标准的农副产品,其表示品质的方法常用。
( A )A. 良好平均品质B. 看货买卖C. 上好可销品质D. 凭说明书买卖2. 在国际上,对冷冻鱼或冻虾等没有公认规格和等级的商品,其交货时规定品质的方法常用。
( B )良好平均品质 B. 上好可销品质 C. 看货买卖 D. 凭样品买卖 对工业制成品交易,一般在品质条款中灵活制定品质指标,通常使用。
品质公差 B. 品质机动幅度 C. 交货品质与样品大体相等 D. 规定一个约量 买卖6. 对等样品也称之为 ( BC )7. 在国际贸易中最常见的计量办法。
(度不超过。
( C )A. 3%B. 5%C. 10%D. 15% 500 号出版物之规定, 在以信用证支付方式进行散装货物的买卖,若合同中未明确规定机动幅度,其交货数量可有的增减幅度为。
10. 目前,国际贸易中通常使用的度量衡制度有。
( ABCD ) A. 公制 B. 英制 C. 美制 D. 国际单位制 E. 法制11. 在货物买卖合同中,数量机动幅度的选择权可由 ( ABC )A. 船方行使B. 卖方行使C. 买方行使D. 保险公司行使E. 开证银选择12. 数量条款主要涉及 ( ABCD )A. 成交数量确定B. 计量单位确定C. 计量方法确定D. 数量机动幅度的掌握E. 品质公差确定A. 3. A.4. 以实物表示商品品质的方法有 ( AB )A. 看货买卖B. 凭样品买卖C. 凭规格买卖D. 凭等级买卖E. 凭标准买卖5. 在国际贸易中,按样品提供者的不同凭样品成交可分为。
( ABC )A. 凭买方样品买卖B. 凭卖方样品买卖C. 凭对等样品买卖D. 凭图样买卖E. 凭参考样品A. 复样B. 回样C. 确认样D. 卖方样品E. 买方样品A. 毛重B. 净重C. 理论重理D. 法定重量8. 根据国际商会《跟单信用证统一惯例》 500 号出版物之规定,对于“约量”允许其增减幅9. 根据国际商会 《跟单信用证统一惯例》 A. 3% B. 5% C. 10% D. 15%13. 根据包装程度的不同,目前绝大多数商品采用( A )A. 全部包装B. 局部包装C. 软性包装D. 硬性包装14. 直接接触商品并随商品进入零售网点与消费者见面的包装叫( B )A. 运输包装B. 销售包装C. 中性包装D. 定牌15. “唛头”是运输标志中的( A )A. 主要标志B. 目的地标志C. 原产地标志D. 件号标志16. 按照国际贸易惯例,在合同中不作规定时运输标志的提供方一般是( B )A. 开证行B. 卖方C. 买方D. 船方17. 运输包装的主要作用在于( AB )A. 保护商品B. 防止货损货差C. 促进销售D. 宣传商品E. 吸引客户18. 销售包装的标志和说明主要有( ABCD )A. 包装的装潢画面B. 包装上的文字说明C. 包装上的标签D. 条形码E. 唛头19. 按国际标准化组织的建议和推荐,标准运输标志的内容包括( ABCD )A. 收货人的英文缩写字母或简称B. 参考号C. 目的地D. 件数号码E. 条形码20. 包装条款的内容主要包括( ABCDE )A. 包装材料B. 包装方式C. 包装规格D. 包装标志E. 包装费用21. 在卖方同意接受买方提供包装时,合同中包括条款除一般内容外还要订明( ABCD )A. 寄送包装的方法B. 包装送达的日期C. 送交包装迟延的责任D. 运费包括费用的负担E. 包装的技术性能三、判断题1. 国际贷物买卖合同中,品名条款是合同中的次要条款。

过滤作业(书本P357~359)1、为什么粒径小于滤层孔隙尺寸的颗粒会被滤层拦截下来?答:粒径小于滤层孔隙尺寸的颗粒会被滤层拦截下来,不是滤层的机械筛滤作用,而是水中颗粒的迁移作用和颗粒粘附作用。
在过滤时,小颗粒会因重力作用、惯性作用,布朗运动的扩散作用和颗粒表面的水动力作用而使颗粒与滤料层接触,此即为迁移作用;当颗粒与滤料层接触后,则在范德华引力和静电斥力的相互作用下,以及某些化学键和化学吸附力下,被粘附于滤料表面或滤料表面上原先粘附的颗粒上。
2、从滤层中杂质分布规律,分析改善快滤池的几种途径和发展趋势。
答:滤层杂质分布规律:过滤初期,滤料较干净,孔隙率大,空隙流速较小,水流剪力较小,因而粘附作用占优势。
随着时间的延长,滤层中杂质逐渐增多,孔隙率逐渐减小,水流剪力逐渐增大,以至最后粘附颗粒先脱落下来,或则不再有粘附现象,于是,悬浮颗粒便向下层推移,下层滤料截留作用渐次得到发挥。
然而,滤料经过反冲洗后,滤层因膨胀而分层,表面滤料粒径最小,粘附比表面积大,截留悬浮颗粒量最多,而孔隙尺寸又小,因而,过滤一段时间后,表面滤料间孔隙将逐渐被堵塞,使过滤阻力剧增,造成下层滤料截留悬浮颗粒作用远未得到充分发挥时,过滤就停止。
为了改善滤料层中杂质分布状况,提高滤层含污能力,而采取双层、三层或均质滤料。
5、什么叫等速过滤和变速过滤?两者分别在什么情况下形成?分析两种过滤方式的优缺点。
答:等速过滤:当滤池过滤速度保持恒定不变的过滤方式;变速过滤:滤速随过滤时间而逐渐减少的过滤方式。
当滤料粒径,形状滤层级配和厚度以及水温已定时,随着过滤时间的延长,滤层中截留的悬浮物量逐渐增多,滤层孔隙率逐渐减少,在水头损失保持不变的条件下,将引起滤速减少;反之,滤速保持不变时,将引起水头损失的增加,这样就产生了等速过滤和变速过滤。
优缺点:等速过滤各层滤料水头损失的不均匀可能会导致某一深度出现负水头而影响过滤,采用虹吸滤池和无阀滤池的出水口高于滤层的方式可以解决负水头的问题;变速过滤滤后水质较好,过滤初期,滤速较大可使悬浮杂质深入下层滤料,过滤后期滤速减少,可防止悬浮颗粒穿透滤层,普通快滤池和V形滤池即是。

高电压工程第八周作业答案
张灵2012-04-18
4-15绝缘在冲击电压作用下常常是电击穿而不是热击穿,在高频电压下常常是热击穿而不是电击穿,为什么?
【答】冲击电压下,电压作用时间短,热量来不及积聚;高频下由于介损增大,介质发热严重,容易形成热击穿。
4-20为什么油纸组合绝缘的耐电强度比纸和油单一介质时都高?
【答】油纸绝缘的优点主要是优良的电气性能,干纸的耐电强度仅10kV/mm ~ 13kV/mm,纯油的耐电强度也仅是10kV/mm ~ 20kV/mm,二者组合以后,由于油填充了纸中薄弱点的空气隙,纸在油中又起了屏障作用,从而使总体耐电强度提高很多,油纸绝缘工频短时耐电强度可达50kV/mm ~ 120kV/mm。
4-21固体绝缘材料的耐热等级用什么表示,其含义是什么?
【答】国家标准GB 11021-1989“电气绝缘的耐热性评定和分级”将各种电工绝缘材料按其耐热程度划分等级,以确定各级绝缘材料的最高持续工作温度如表4-3 所示。
补充题:
〖批改情况〗本题同学们对于第(1)问都没有问题。
给大家留一个小思考问题:工程上一般采用哪些方法尽可能避免在法兰处的滑闪放电?
第(2)问错了一些同学,原因是对于题意没有正确理解。
原题中是在套管绝缘层中添加5层同心筒形极板,极板并不是绝缘层,不能混淆概念。
所以5层极板将绝缘层分成6层。

HTML4-7章作业1、CSS样式表不可能实现( )功能。
A将格式和结构分离B.一个CSS文件控制多个网页C.控制图片的精确位置D.兼容所有的浏览器2、可用来在一个网页中嵌入显示另一个网页内容的标记符是()A.<Marquee>B. <Iframe>C.<embed>D.<object>3.我们想要在框架中加入一个叫做list.htm的文件,应该在HTML中如何描述它?A、frame page="list.htm"B、frame target="list.htm"C、frame src="list.htm"D、frame framepage="list.htm"4.我们想要在页面中加入一个层,可以使用哪些HTML标记来描述它?(选择2项)A、<floor>B、<div>C、<span>D、<level>5 .下列哪种CSS样式定义的方式拥有最高的优先级?A、嵌入B、行内C、链接D、导入6 .以下的HTML中,哪个是正确引用外部样式表的方法?A、<style src="mystyle.css">B、<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">C、<stylesheet>mystyle.css</stylesheet>7.在HTML文档中,引用外部样式表的正确位置是?A)文档的末尾B)<head>部分C)文档的顶部D)<body>部分8.哪个HTML标签可用来定义内部样式表?A)<style>B)<script>C)<css>9.哪个HTML属性可用来定义内联样式?A)fontB)classC)stylesD)style10.下列哪个选项的CSS语法是正确的?A)body:color=blackB){body:color=black(body}C)body {color: black}D){body;color:black}11.如何在CSS文件中插入注释?A)// this is a commentB)// this is a comment //C)/* this is a comment */D)' this is a comment12 . CSS哪个属性可用来改变背景颜色?A)bgcolor:B)color:C)background-color:13.如何为所有的<h1>元素添加背景颜色?A)h1.all {background-color:#FFFFFF}B)h1 {background-color:#FFFFFF}C)all.h1 {background-color:#FFFFFF}14 . CSS如何改变某个元素的文本颜色?A)text-color:B)color:C)fgcolor:D)text-color=15 .哪个CSS属性可控制文本的尺寸?A)font-sizeB)text-styleC)font-styleD)text-size16 .以下的CSS中,可使所有<p>元素变为粗体的正确语法是?A)<p style="font-size:bold">B)<p style="text-size:bold">C)p {font-weight:bold}D)p {text-size:bold}17 .如何显示没有下划线的超链接?A)a {text-decoration:none}B)a {text-decoration:no underline}C)a {underline:none}D)a {decoration:no underline}18 .如何使文本以大写字母开头?A)text-transform:capitalizeB)无法通过CSS来完成C)text-transform:uppercase19 . css如何改变元素的字体?A)font=B)f:C)font-family:20 .如何改变元素的左边距?A)text-indent:B)margin-left:C)margin:D)indent:21.如何产生带有正方形的项目的列表?A)list-type: squareB)list-style-type: squareC)type: squareD)type: 222 .我们可以在下列哪个HTML元素中放置javascript代码?A)<script>B)<javascript>C)<js>D)<scripting>23.某一站点主页面index.html的代码如下所示,则选项中关于这段代码的说法正确的是()。
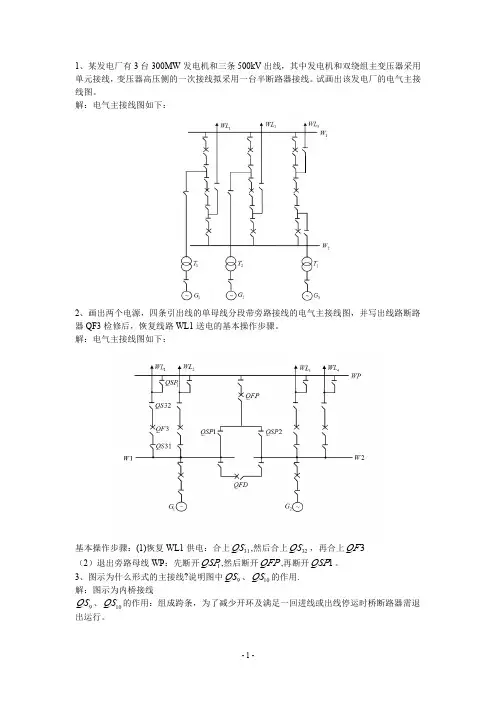
一、在图题1.3所示电路中,已知回路谐振频率0465kHz f =,0100Q =,160N =匝,140N =匝,210N =匝,200pF C =,16k Ωs R =,1k ΩL R =。
试求回路电感L 、有载Q 值和通频带B。
图题1.3i L答案1:002260000000322362223610115864 5.8410(171.2)11010()103.9110160401()10 3.9110(255.7)160161.361e e e L LLL ss s sL e f L uHf CCCQ g sR k g Q g sR g n g sg n g sR k g g g g πωω------∑=⇒===⇒==⨯=Ω=='==⋅=⨯'==⋅⨯=⨯=Ω''∴=++=⨯由并联谐振:折合到线圈两端:5000.70(73.2)4310.8e esR k CQ g f BW kH zQ ω-∑∑=Ω==答案2:答案3:二、在图题1.4所示电路中,0.8μH L =,1220pF C C ==,5pF S C =,10k ΩS R =,20pF L C =,5k ΩL R =,0100Q =。
试求回路在有载情况下的谐振频率0f 、谐振电阻p R (不计S R 和L R )、LQ 值和通频带B 。
图题1.4C L答案:三、设有一级单调谐回路中频放大器,其通频带4M Hz B =,10uo A =,如果再用一级完全相同的放大器与之级联,这时两级中放总增益和通频带各为多少?若要求级联后的总频带宽度为4M H z ,问每级放大器应如何改变?改变后的总增益是多少?四、 对于图题3.10所示各振荡电路:(1)画出高频交流等效电路,说明振荡器类型;(2)计算振荡频率。
图题3.10E 57ou (a)(b)E 68~125pF五、 试画出图题3.14所示各振荡器的交流等效电路,说明晶体在电路中的作用,并计算反馈系数F 。
液压传动的部分题目及答案 希望对大家有用!! 第1次部分作业答案1、用恩氏粘度计测得某液压油(ρ=850kg/m 3)200mL 在40℃时流过的时间为t 1=153s ;20℃时200mL 的蒸馏水流过的时间为t 2=51s ,求该液压油在40℃时的恩氏粘度°E,运动粘度v ,和动力粘度u 各为多少?351153210===sst t E sm s m EE v /1083.19/10)31.631.7(262600--⨯=⨯-= sPa sm •⨯=⨯⨯==-22-631069.1/1019.83 850kg/m ρνμ第二次 2:如图1-25所示,一具有一定真空度的容器用一根管子倒置于一液面与大气相通的水槽中,液体在管中上升的高度h=1m ,设液体的密度ρ=103kg/ m 3,试求容器内真空度。
解:由静力学基本方程得gh p p a ρ+=真空度gh p p a ρ=-=m s m m kg 1/8.9/10233⨯⨯ =9800a p3:如图1-25所示,有一直径为d ,质量为m 的活塞浸在液体中,并在力F 的作用下处于静止状态,若液体的密度为ρ,活塞浸入深度为h ,试确定液体在测压管内的上升高度x 。
解:取活塞底面得水平面为等压面(用相对压力)24)(d mgF h x g πρ+=+h gd mg F x -+=ρπ2)(4第3次作业 6、如图1-27所示,一抽吸设备水平放置,其出口与大气相通,细管处截面积A 2=4 A 1,h=1m 。
求开始抽吸时,A 1=24102.3m -⨯,水平管中必须通过的流量q (取a=1,不记损失)。
解:取截面1-1(与细管相交处),2-2(出口处),应用伯努利方程ghw u gh p u gh p +++=++22222211112/2/αραρ (1)121=αα、 0=ghw刚开始抽吸时,根据静力学基本方程有gh p p a ρ+=1 gh p p a ρ-=1=m s m m kg 1/8.9/1010233⨯⨯⨯- =a p 9800-1121222112410u u A A u A u A u p ====21h h =将以上条件代入式(1)得s m s mgh u /57.4/18.9153153221=⨯⨯==min)187(/1046.1102.3/57.4332411<⨯=⨯⨯==--s m m s m A u q7、如图1-28所示,液压泵的流量q=32L/min ,液压泵吸油口距离液面高度h=500mm ,吸油管直径d=20mm ,过滤器的压力降为0.01Mp a ,油液的密度ρ=900kg/m 3,油液的运动粘度v=20×10-6m 2/s 。

《微型计算机原理与接口技术》部分作业及补充题参考答案第7章存储器系统P2176.某SRAM存储芯片,其字位结构为512K×8bit,试问其地址、数据引脚各是多少个?答:∵219=512K,所以地址引脚需19根;数据引脚需8根(8bit)。
8.现有1024×1bit的存储芯片,若用它组成容量为16K×8bit的存储器。
试求:(1)实现该存储器所需的芯片数量答:(16K×8bit)/(1K×1bit)=128片(2)该存储器所需地址的地址码总位数是多少?其中几位选片?几位用作片内地址?答:∵214 =16K,所以地址码总位数为14位。
而1024×1bit存储芯片需要地址10位,因此选片地址为4位,片内地址为10位。
第8章输入/输出系统P2442.接口电路的作用是什么?I/O接口应具备哪些功能?参见教材P2193.什么是端口?端口有几类?参见教材P220 8.1.2 输入输出端口4.I/O端口有哪两种编址方式?PC系列机采用哪种编址方式?答:I/O端口和存储单元统一编址及I/O端口独立编址两种。
PC机采用I/O端口独立编址。
7. 定时/计数器的3个通道在PC系列机中是如何应用的?答:0#计数器用于系统时钟中断;1#计数器用于动态存储器刷新定时;2#计数器用于发声系统音调控制。
10.系统机定时/计数器的通道0定时周期最长是多少?要实现长时间定时,应采取什么措施?如果采用外扩8254定时/计数器实现长时间定时,应采取哪些措施?答:系统机定时/计数器通道0定时周期最长是55ms。
要实现长时间定时,只能使用 INT 1CH 中断的方法,通过对预先设定的中断次数进行计数,达到n倍55ms的定时目的。
采用外扩8254,可以使用三个通道硬件级联的方法实现长时间定时。
补充题:设PC 系统机外扩了一片8254 及相应的实验电路。
(1) 根据由门电路构成的译码电路,分析出该片8254 的四个端口地址。

CHAPTER 9 Virtual Memory Practice Exercises9.1 Under what circumstances do page faults occur? Describe the actions taken by the operating system when a page fault occurs.Answer:A page fault occurs when an access to a page that has not beenbrought into main memory takes place. The operating system verifiesthe memory access, aborting the program if it is invalid. If it is valid, a free frame is located and I/O is requested to read the needed page into the free frame. Upon completion of I/O, the process table and page table are updated and the instruction is restarted.9.2 Assume that you have a page-reference string for a process with m frames (initially all empty). The page-reference string has length p;n distinct page numbers occur in it. Answer these questions for any page-replacement algorithms:a. What is a lower bound on the number of page faults?b. What is an upper bound on the number of page faults?Answer:a. nb. p9.3 Consider the page table shown in Figure 9.30 for a system with 12-bit virtual and physical addresses and with 256-byte pages. The list of freepage frames is D, E, F (that is, D is at the head of the list, E is second, and F is last).Convert the following virtual addresses to their equivalent physical addresses in hexadecimal. All numbers are given in hexadecimal. (A dash for a page frame indicates that the page is not in memory.)• 9EF• 1112930 Chapter 9 Virtual Memory• 700• 0FFAnswer:• 9E F - 0E F• 111 - 211• 700 - D00• 0F F - EFF9.4 Consider the following page-replacement algorithms. Rank these algorithms on a five-point scale from “bad” to “perfect” according to their page-fault rate. Separate those algorithms that suffer from Belady’s anomaly from those that do not.a. LRU replacementb. FIFO replacementc. Optimal replacementd. Second-chance replacementAnswer:Rank Algorithm Suffer from Belady’s anomaly1 Optimal no2 LRU no3 Second-chance yes4 FIFO yes9.5 Discuss the hardware support required to support demand paging. Answer:For every memory-access operation, the page table needs to be consulted to check whether the corresponding page is resident or not and whether the program has read or write privileges for accessing the page. These checks have to be performed in hardware. A TLB could serve as a cache and improve the performance of the lookup operation.9.6 An operating system supports a paged virtual memory, using a central processor with a cycle time of 1 microsecond. It costs an additional 1 microsecond to access a page other than the current one. Pages have 1000 words, and the paging device is a drum that rotates at 3000 revolutions per minute and transfers 1 million words per second. The following statistical measurements were obtained from the system:• 1 percent of all instructions executed accessed a page other than the current page.•Of the instructions that accessed another page, 80 percent accesseda page already in memory.Practice Exercises 31•When a new page was required, the replaced page was modified 50 percent of the time.Calculate the effective instruction time on this system, assuming that the system is running one process only and that the processor is idle during drum transfers.Answer:effective access time = 0.99 × (1 sec + 0.008 × (2 sec)+ 0.002 × (10,000 sec + 1,000 sec)+ 0.001 × (10,000 sec + 1,000 sec)= (0.99 + 0.016 + 22.0 + 11.0) sec= 34.0 sec9.7 Consider the two-dimensional array A:int A[][] = new int[100][100];where A[0][0] is at location 200 in a paged memory system with pages of size 200. A small process that manipulates the matrix resides in page 0 (locations 0 to 199). Thus, every instruction fetch will be from page 0. For three page frames, how many page faults are generated bythe following array-initialization loops, using LRU replacement andassuming that page frame 1 contains the process and the other twoare initially empty?a. for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)A[i][j] = 0;b. for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)for (int j = 0; j < 100; j++)A[i][j] = 0;Answer:a. 5,000b. 509.8 Consider the following page reference string:1, 2, 3, 4, 2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 1, 2, 3, 7, 6, 3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 6.How many page faults would occur for the following replacement algorithms, assuming one, two, three, four, five, six, or seven frames? Remember all frames are initially empty, so your first unique pages will all cost one fault each.•LRU replacement• FIFO replacement•Optimal replacement32 Chapter 9 Virtual MemoryAnswer:Number of frames LRU FIFO Optimal1 20 20 202 18 18 153 15 16 114 10 14 85 8 10 76 7 10 77 77 79.9 Suppose that you want to use a paging algorithm that requires a referencebit (such as second-chance replacement or working-set model), butthe hardware does not provide one. Sketch how you could simulate a reference bit even if one were not provided by the hardware, or explain why it is not possible to do so. If it is possible, calculate what the cost would be.Answer:You can use the valid/invalid bit supported in hardware to simulate the reference bit. Initially set the bit to invalid. O n first reference a trap to the operating system is generated. The operating system will set a software bit to 1 and reset the valid/invalid bit to valid.9.10 You have devised a new page-replacement algorithm that you thinkmaybe optimal. In some contorte d test cases, Belady’s anomaly occurs. Is the new algorithm optimal? Explain your answer.Answer:No. An optimal algorithm will not suffer from Belady’s anomaly because —by definition—an optimal algorithm replaces the page that will notbe used for the long est time. Belady’s anomaly occurs when a pagereplacement algorithm evicts a page that will be needed in the immediatefuture. An optimal algorithm would not have selected such a page.9.11 Segmentation is similar to paging but uses variable-sized“pages.”Definetwo segment-replacement algorithms based on FIFO and LRU pagereplacement schemes. Remember that since segments are not the samesize, the segment that is chosen to be replaced may not be big enoughto leave enough consecutive locations for the needed segment. Consider strategies for systems where segments cannot be relocated, and thosefor systems where they can.Answer:a. FIFO. Find the first segment large enough to accommodate the incoming segment. If relocation is not possible and no one segmentis large enough, select a combination of segments whose memoriesare contiguous, which are “closest to the first of the list” andwhich can accommodate the new segment. If relocation is possible, rearrange the memory so that the firstNsegments large enough forthe incoming segment are contiguous in memory. Add any leftover space to the free-space list in both cases.Practice Exercises 33b. LRU. Select the segment that has not been used for the longestperiod of time and that is large enough, adding any leftover spaceto the free space list. If no one segment is large enough, selecta combination of the “oldest” segments that are contiguous inmemory (if relocation is not available) and that are large enough.If relocation is available, rearrange the oldest N segments to be contiguous in memory and replace those with the new segment.9.12 Consider a demand-paged computer system where the degree of multiprogramming is currently fixed at four. The system was recently measured to determine utilization of CPU and the paging disk. The results are one of the following alternatives. For each case, what is happening? Can the degree of multiprogramming be increased to increase the CPU utilization? Is the paging helping?a. CPU utilization 13 percent; disk utilization 97 percentb. CPU utilization 87 percent; disk utilization 3 percentc. CPU utilization 13 percent; disk utilization 3 percentAnswer:a. Thrashing is occurring.b. CPU utilization is sufficiently high to leave things alone, and increase degree of multiprogramming.c. Increase the degree of multiprogramming.9.13 We have an operating system for a machine that uses base and limit registers, but we have modified the machine to provide a page table.Can the page tables be set up to simulate base and limit registers? How can they be, or why can they not be?Answer:The page table can be set up to simulate base and limit registers provided that the memory is allocated in fixed-size segments. In this way, the base of a segment can be entered into the page table and the valid/invalid bit used to indicate that portion of the segment as resident in the memory. There will be some problem with internal fragmentation.9.27.Consider a demand-paging system with the following time-measured utilizations:CPU utilization 20%Paging disk 97.7%Other I/O devices 5%Which (if any) of the following will (probably) improve CPU utilization? Explain your answer.a. Install a faster CPU.b. Install a bigger paging disk.c. Increase the degree of multiprogramming.d. Decrease the degree of multiprogramming.e. Install more main memory.f. Install a faster hard disk or multiple controllers with multiple hard disks.g. Add prepaging to the page fetch algorithms.h. Increase the page size.Answer: The system obviously is spending most of its time paging, indicating over-allocationof memory. If the level of multiprogramming is reduced resident processeswould page fault less frequently and the CPU utilization would improve. Another way toimprove performance would be to get more physical memory or a faster paging drum.a. Get a faster CPU—No.b. Get a bigger paging drum—No.c. Increase the degree of multiprogramming—No.d. Decrease the degree of multiprogramming—Yes.e. Install more main memory—Likely to improve CPU utilization as more pages canremain resident and not require paging to or from the disks.f. Install a faster hard disk, or multiple controllers with multiple hard disks—Also animprovement, for as the disk bottleneck is removed by faster response and morethroughput to the disks, the CPU will get more data more quickly.g. Add prepaging to the page fetch algorithms—Again, the CPU will get more datafaster, so it will be more in use. This is only the case if the paging action is amenableto prefetching (i.e., some of the access is sequential).h. Increase the page size—Increasing the page size will result in fewer page faults ifdata is being accessed sequentially. If data access is more or less random, morepaging action could ensue because fewer pages can be kept in memory and moredata is transferred per page fault. So this change is as likely to decrease utilizationas it is to increase it.10.1、Is disk scheduling, other than FCFS scheduling, useful in asingle-userenvironment? Explain your answer.Answer: In a single-user environment, the I/O queue usually is empty. Requests generally arrive from a single process for one block or for a sequence of consecutive blocks. In these cases, FCFS is an economical method of disk scheduling. But LOOK is nearly as easy to program and will give much better performance when multiple processes are performing concurrent I/O, such as when aWeb browser retrieves data in the background while the operating system is paging and another application is active in the foreground.10.2.Explain why SSTF scheduling tends to favor middle cylindersover theinnermost and outermost cylinders.The center of the disk is the location having the smallest average distance to all other tracks.Thus the disk head tends to move away from the edges of the disk.Here is another way to think of it.The current location of the head divides the cylinders into two groups.If the head is not in the center of the disk and a new request arrives,the new request is more likely to be in the group that includes the center of the disk;thus,the head is more likely to move in that direction.10.11、Suppose that a disk drive has 5000 cylinders, numbered 0 to 4999. The drive is currently serving a request at cylinder 143, and the previous request was at cylinder 125. The queue of pending requests, in FIFO order, is86, 1470, 913, 1774, 948, 1509, 1022, 1750, 130Starting from the current head position, what is the total distance (in cylinders) that the disk arm moves to satisfy all the pending requests, for each of the following disk-scheduling algorithms?a. FCFSb. SSTFc. SCANd. LOOKe. C-SCANAnswer:a. The FCFS schedule is 143, 86, 1470, 913, 1774, 948, 1509, 1022, 1750, 130. The total seek distance is 7081.b. The SSTF schedule is 143, 130, 86, 913, 948, 1022, 1470, 1509, 1750, 1774. The total seek distance is 1745.c. The SCAN schedule is 143, 913, 948, 1022, 1470, 1509, 1750, 1774, 4999, 130, 86. The total seek distance is 9769.d. The LOOK schedule is 143, 913, 948, 1022, 1470, 1509, 1750, 1774, 130, 86. The total seek distance is 3319.e. The C-SCAN schedule is 143, 913, 948, 1022, 1470, 1509, 1750, 1774, 4999, 86, 130. The total seek distance is 9813.f. (Bonus.) The C-LOOK schedule is 143, 913, 948, 1022, 1470, 1509, 1750, 1774, 86, 130. The total seek distance is 3363.12CHAPTERFile-SystemImplementationPractice Exercises12.1 Consider a file currently consisting of 100 blocks. Assume that the filecontrol block (and the index block, in the case of indexed allocation)is already in memory. Calculate how many disk I/O operations are required for contiguous, linked, and indexed (single-level) allocation strategies, if, for one block, the following conditions hold. In the contiguous-allocation case, assume that there is no room to grow atthe beginning but there is room to grow at the end. Also assume thatthe block information to be added is stored in memory.a. The block is added at the beginning.b. The block is added in the middle.c. The block is added at the end.d. The block is removed from the beginning.e. The block is removed from the middle.f. The block is removed from the end.Answer:The results are:Contiguous Linked Indexeda. 201 1 1b. 101 52 1c. 1 3 1d. 198 1 0e. 98 52 0f. 0 100 012.2 What problems could occur if a system allowed a file system to be mounted simultaneously at more than one location?Answer:4344 Chapter 12 File-System ImplementationThere would be multiple paths to the same file, which could confuse users or encourage mistakes (deleting a file with one path deletes thefile in all the other paths).12.3 Wh y must the bit map for file allocation be kept on mass storage, ratherthan in main memory?Answer:In case of system crash (memory failure) the free-space list would notbe lost as it would be if the bit map had been stored in main memory.12.4 Consider a system that supports the strategies of contiguous, linked, and indexed allocation. What criteria should be used in deciding which strategy is best utilized for a particular file?Answer:•Contiguous—if file is usually accessed sequentially, if file isrelatively small.•Linked—if file is large and usually accessed sequentially.• Indexed—if file is large and usually accessed randomly.12.5 One problem with contiguous allocation is that the user must preallocate enough space for each file. If the file grows to be larger than thespace allocated for it, special actions must be taken. One solution to this problem is to define a file structure consisting of an initial contiguous area (of a specified size). If this area is filled, the operating system automatically defines an overflow area that is linked to the initial contiguous area. If the overflow area is filled, another overflow areais allocated. Compare this implementation of a file with the standard contiguous and linked implementations.Answer:This method requires more overhead then the standard contiguousallocation. It requires less overheadthan the standard linked allocation. 12.6 How do caches help improve performance? Why do systems not use more or larger caches if they are so useful?Answer:Caches allow components of differing speeds to communicate moreefficiently by storing data from the slower device, temporarily, ina faster device (the cache). Caches are, almost by definition, more expensive than the device they are caching for, so increasing the numberor size of caches would increase system cost.12.7 Why is it advantageous for the user for an operating system todynamically allocate its internal tables? What are the penalties to the operating system for doing so?Answer:Dynamic tables allow more flexibility in system use growth — tablesare never exceeded, avoiding artificial use limits. Unfortunately, kernelstructures and code are more complicated, so there is more potentialfor bugs. The use of one resource can take away more system resources (by growing to accommodate the requests) than with static tables.Practice Exercises 4512.8 Explain how the VFS layer allows an operating system to support multiple types of file systems easily.Answer:VFS introduces a layer of indirection in the file system implementation.In many ways, it is similar to object-oriented programming techniques. System calls can be made generically (independent of file system type). Each file system type provides its function calls and data structuresto the VFS layer. A system call is translated into the proper specific functions for the target file system at the VFS layer. The calling program has no file-system-specific code, and the upper levels of the system callst ructures likewise are file system-independent. The translation at the VFS layer turns these generic calls into file-system-specific operations.。

第一部分作业题一、单项选择题(题中只有一个答案最符合题意)1、施工定额属于()性质。
A.计价性定额B. 生产性定额C. 通用性定额D. 计划性定额2、规费不包括()。
A. 工伤保险费B. 养老保险费 C .劳动保险费 D .住房公积金3、下列费用不属于措施费的有()A. 安全文明施工费B.医疗保险费 C. 临时保护设施费 D.垂直运输费4、下列不属于建筑安装施工机械使用费的是()A. 大型机械设备进出场及安拆费B.机上司机人工费C. 燃料动力费D. 大修理费5、下列不属于人工费的是()A. 管理人员工资B.生产工人高温津贴C. 生产工人产假工资D. 生产工人加班工资6、()是编制和确定项目建议书和可行性研究报告投资估算的基础和依据。
A、投资估算指标 B 、概算定额 C 、概算指标 D 、预算定额7、下列不属于企业管理费的是()A. 财产保险费B.职工教育经费 C. 失业保险费 D. 劳动保险费8、下列不属于材料费的是()A. 材料原价B.材料检验试验费 C. 材料采购保管费 D. 材料运杂费9、根据我国现行建筑安装工程费用项目组成的规定,下列人工费中不能构成分部分项工程费的有()。
A. 保管建筑材料人员的工资B.绑扎钢筋人员的工资C. 操作施工机械人员的工资D. 现场临时设施搭设人员的工资10、下列不属于措施项目费的是()A. 安全文明施工费B. 水泥材料费C. 脚手架工程费D. 二次搬运费11、下列不属于分部分项材料费的是()A. 水泥原价B. 粘土砖运杂费C. 模板费D. 钢筋采购保管费12、不应计入其他项目费的是()A. 总承包服务费B. 计日工C. 暂列金额D. 临时设施费13、下列不属于规费中的社会保险费的是()A. 劳动保险费B. 医疗保险费C. 生育保险费D. 养老保险费14、下列哪一项不是工程建设定额的特点()。
A、科学性 B 、先进性 C 、系统性 D 、统一性15、机械台班时间定额和产量定额之间的关系是()。
操作系统部分习题参考答案(孙钟秀版)操作系统部分习题参考答案第⼀章2. ⼀个计算机系统,有⼀台输⼊机和⼀台打印机,现有两道程序投⼊运⾏,且程序A先开始做,程序B后开始运⾏。
程序A的运⾏轨迹为:计算50ms、打印100ms、再计算50ms、打印100ms,结束。
程序B的运⾏轨迹为:计算50ms、输⼊80ms、再计算100ms,结束。
试说明(1)两道程序运⾏时,CPU有⽆空闲等待?若有,在哪段时间内等待?为什么会等待?(2)程序A、B有⽆等待CPU的情况?若有,指出发⽣等待的时刻。
答:画出两道程序并发执⾏图如下:(1) 两道程序运⾏期间,CPU存在空闲等待,时间为100⾄150ms之间(见图中有⾊部分)。
(2) 程序A⽆等待现象,但程序B有等待。
程序B有等待时间段为180ms⾄200ms间(见图中有⾊部分)。
5. 在单CPU和两台I/O(I1,I2)设备的多道程序设计环境下,同时投⼊三个作业运⾏。
它们的执⾏轨迹如下:Job1:I2(30ms)、CPU(10ms)、I1(30ms)、CPU(10ms)Job2:I1(20ms)、CPU(20ms)、I2(40ms)Job3:CPU(30ms)、I1(20ms)如果CPU、I1和I2都能并⾏⼯作,优先级从⾼到低为Job1、Job2和Job3,优先级⾼的作业可以抢占优先级低的作业的CPU。
试求:(1)每个作业从投⼊到完成分别所需的时间。
(2) 从作业的投⼊到完成CPU的利⽤率。
(3)I/O设备利⽤率。
答:画出三个作业并⾏⼯作图如下(图中着⾊部分为作业等待时间):(1) Job1从投⼊到运⾏完成需80ms,Job2从投⼊到运⾏完成需90ms,Job3从投⼊到运⾏完成需90ms。
(2) CPU空闲时间段为:60ms⾄70ms,80ms⾄90ms。
所以CPU利⽤率为(90-20)/80=77.78%。
(3) 设备I1空闲时间段为:20ms⾄40ms,故I1的利⽤率为(90-20)/90=77.78%。
业>>单选题1.to make2.be made3.making4.made1.unless2.if3.since4.as long as1.have I realized2.I have realized3.did I realize4.I realized1.relaxing2.relax3.relaxed4.to relax1.shall learn2.should learn3.learn4.learned1.look at2.look up3.look for4.look around1.leave2.left3.has left4.shall leave1.show2.showed3.shall show4.shown1.which2.what3.why4.that1.sequence2.time3.form4.shape1.seeing2.see3.be seeing4.have seen题1.which2.who3.that4.what1.led2.had3.got4.gave1.In many instances2.In much instance3.For many instances4.For much instance1.serious2.silent3.simple4.slight1.that2.which3.who4.what1.which chair should he take2.which chair he should take3.which chair he take4.which chair he took1.where2.when3.which4.that1.be obeyed2.is obeyed3.shall be obeyed4.obeyed1.extend2.explore3.express4.exercise1.would be injured2.will have been injured3.will be injured4.would have been injured1.could2.should3.would4.might1.surf2.to surf3.surfing4.surfed1.No sooner had I2.No sooner I had3.No sooner have I4.No sooner I have1.seeing2.see3.be seeing4.have seen1.write2.wrote3.writing4.written1.on which2.on that3.in which4.on whom1.unless2.as if3.when4.in order that1.look at2.look up3.look for4.look around1.where might be her son2.which might be her son3.where her son might be4.which her son might be1.where2.when3.which4.that1.warned2.warn3.warning4.having warned2:It is high time that you _____ English and computer well.1.shall learn2.should learn3.learn4.learned3:He asked me _______ after graduation?1.what did I intend to do2.what I intended to do3.what did I intend to4.what I intended to4:There have been complaints about the noise from the people ___ live in the flats.1.which2.whom3.whose4.who5:I used to ____ poems when I was his age.1.write2.wrote3.writing4.written6:They tried to think of a plan ____ they could fulfill their task ahead of time.1.by that2.by which3.in that4.in which7:He told me that I______be present at the ceremony.1.could2.should3.would4.might8:I spent all my spare time surfing the Internet. I am absolutely keen ___ it.1.on2.at3.in4.to9:Little______that they had made a great discovery in chemistry.1.they realized2.had they realized3.did they realize4.they had realized10:I can never forget the day ____ I got the first prize in the competition.1.that2.where3.which4.when11:If they were here tomorrow, the problem _____.1.would be solved2.would have been solved3.will be solved4.will have been solved12:If I were you, I ____ the job.1.accept2.accepted3.will accept4.would accept13:In Ireland, as in the rest of Europe, dates are usually written in the _____of day, month, and year.1.sequence2.time3.form4.shape14:The criminal didn’t realize the value of freedom______he had lost it.1.if2.as3.while4.until15:I spent all my spare time ___ the Internet.1.surf2.to surf3.surfing4.surfed16:There are two reasons ____ I do not want to go out tonight.1.why2.because3.so4.that17:The book was different______all the other books I’ve ever read.1.from2.to3.on4.among18:He is writing to______his appreciation of the hospitality you showed to him.1.extend2.explore3.express4.exercise19:______got home than it began to rain.1.No sooner had I2.No sooner I had3.No sooner have I4.No sooner I have20:The question______yesterday is of great importance.1.discussing2.discussed3.being discussed4.to be discussed1:Tell the taxi driver _______.1.where do you want to go2.where you want to go3.where do you want to4.you want to go2:Linda and Cheryle come from families which are______rich nor poor.1.both2.either3.neither4.as3:It seems ages since we ___ you.1.heard from2.heard about3.heard of4.heard4:I used to ____ poems when I was his age.1.write2.wrote3.writing4.written5:I spent all my spare time surfing the Internet. I am absolutely keen ___ it.1.on2.at3.in4.to6:Why does Tom want to leave the______job?1.present2.private3.public4.powerful7:The question______yesterday is of great importance.1.discussing2.discussed3.being discussed4.to be discussed8:Here is a notice______people not to litter the beach.1.warned2.warn3.warning4.having warned9:It is high time that you _____ English and computer well.1.shall learn2.should learn3.learn4.learned10:We wish that people everywhere ____ more concern for the environment around them.1.show2.showed3.shall show4.shown11:The children were______to see the performance.1.keen2.anxious3.eager4.sharp12:While_______in the factory, the students learnt a lot from theworkers.1.working2.worked3.is working4.having worked13:______, parents must set a good example for their children.1.Generally2.Obviously3.Fortunately4.Unnecessarily14:Let’s______ and see if we can find something particular.1.look at2.look up3.look for4.look around15:They were playing in the garden______they heard a scream.1.what2.when3.where4.so that16:Luckily I was wearing a seat belt. If I had n’t been wearing one, I ____ seriously.1.would be injured2.will have been injured3.will be injured4.would have been injured17:Things turned ____ to be exactly as the professor had foreseen1.up2.off3.down4.out18:Mr. Black is looking forward to______his Chinese partner soon.1.seeing2.see3.be seeing4.have seen19:He said ______.1.how the garden was beautiful2.how beautiful the garden was3.how beautiful was the garden4.the garden was how beautiful20:She wanted to know ___.1.what is his job2.what was his job3.what his job is4.what his job was1:He told me that I______be present at the ceremony.1.could2.should3.would4.might2:______you like to know something about Chinese acrobatics?1.Could2.Would3.Can4.Will3:The old couple ____ live next to us have four grandchildren.1.who2.which4.whose4:While_______in the factory, the students learnt a lot from the workers.1.working2.worked3.is working4.having worked5:The police do not allow him to go out of the city without ____.1.permit2.permission3.admit4.admission6:Her doctor insists that she ______ any longer.1.does not smoke2.will not smoke3.should not smoke4.has not smoked7:The book is______more difficult than the one I recommended to you.2.much3.very4.so8:The garden of his house has a lawn, ___ is very pleasant to sit on in summer.1.where2.when3.which4.that9:Modern business and industry demand that every manager ___ much about economic management.1.know2.knew3.shall know4.known10:This coat______ me one hundred and sixty yuan.1.spend2.cost3.take4.pay11:The audience, most of ____ were students, enjoyed the performance very much.1.whom2.who3.which4.that12:Luckily I was wearing a seat belt. If I hadn’t been wear ing one, I ____ seriously.1.would be injured2.will have been injured3.will be injured4.would have been injured13:The father was pleased to hear the child______that.1.to say2.to have said3.said4.say14:You will be full of confidence during the interview______you are well prepared.1.unless2.if3.since4.as long as15:The children were______to see the performance.1.keen2.anxious3.eager4.sharp16:_____ it is the inviter who pays the bill.1.In many instances2.In much instance3.For many instances4.For much instance17:He talked cheerfully about the film and the actress ___ interested him.1.who2.which3.that4.what18:He talked as if he______everything.1.knows2.knew3.have known4.had known19:______got home than it began to rain.1.No sooner had I2.No sooner I had3.No sooner have I4.No sooner I have20:She wanted to know ___.1.what is his job2.what was his job3.what his job is4.what his job was20:?Li Ming takes an active part in social work.1.So does each of us2.So each of us does3.So is each of us4.So has each of us窗体底端1:The old couple ____ live next to us have four grandchildren.1.who2.which3.whom4.whose2:The meeting must be important because the CEO says no one is allowed to be ______1.present2.appear3.absent4.attend3:Things turned ____ to be exactly as the professor had foreseen1.up2.off3.down4.out4:He is writing to______his appreciation of the hospitality you showed to him.1.extend2.explore3.express4.exercise5:I want to______the position advertised by ABC Company.1.apply in2.apply on3.apply4.apply for6:I would rather that Mr. Mike ____ the speech at the conference instead of the dean that day.1.make2.made3.has made4.had made7:______you like to know something about Chinese acrobatics?1.Could2.Would3.Can4.Will8:The father was pleased to hear the child______that.1.to say2.to have said3.said4.say9:When not on stage, he spends time______at home.1.relaxing2.relax3.relaxed4.to relax10:He asked ____.1.which chair should he take2.which chair he should take3.which chair he take4.which chair he took11:?Li Ming takes an active part in social work.1.So does each of us2.So each of us does3.So is each of us4.So has each of us12:This coat______ me one hundred and sixty yuan.1.spend2.cost3.take4.pay13:The criminal didn’t realize the value of freedom______he had lost it.1.if2.as3.while4.until14:It is advisable that she ____ for Madrid as soon as possible.1.leave2.left3.has left4.shall leave15:The child ____ parents died in the air crash is living with his aunt now.1.who2.whose3.whom4.which16:In the armchair______,reading a novel.1.his mother sat2.did his mother sit3.does his mother sit4.sat his mother17:Why does Tom want to leave the______job?1.present2.private3.public4.powerful18:He talked as if he______everything.1.knows2.knew3.have known4.had known19:They were playing in the garden______they heard a scream.1.what2.when3.where4.so that20:The invitation ___ to be something you’d hate to do.1.turns in2.turns on3.turns off4.turns out1.know2.knew3.shall know4.known1.serious2.silent3.simple4.slight1.turns in2.turns on3.turns off4.turns out1.rather2.much3.very4.so1.would be injured2.will have been injured3.will be injured4.would have been injured1.write2.wrote3.writing4.written1.even if2.so that3.in case4.as if1.on which2.on that3.in which4.on whom1.whom2.who3.which4.that1.which2.when3.that4.as1.how the garden was beautiful2.how beautiful the garden was3.how beautiful was the garden4.the garden was how beautiful1.why2.because3.so4.that1.make2.made3.has made4.had made1.apply in2.apply on3.apply4.apply for1.make2.to make3.making4.made1.present2.private3.public4.powerful1.both2.either3.neither4.as1.with2.of3.for4.to1.discussing2.discussed3.being discussed4.to be discussedmit2.conform3.admit4.adapt1.know2.knew3.shall know4.known2:The doctor came out of the patient’s room with a______look on his face.1.serious2.silent3.simple4.slight3:The invitation ___ to be something you’d hate to do.1.turns in2.turns on3.turns off4.turns out4:The book is______more difficult than the one I recommended to you.1.rather2.much3.very4.so5:Luckily I was wearing a seat belt. If I hadn’t been wearing one, I ____ seriously.1.would be injured2.will have been injured3.will be injured4.would have been injured6:I used to ____ poems when I was his age.1.write2.wrote3.writing4.written7:We moved to London______we could visit our friends more often.1.even if2.so that3.in case4.as if8:That is the player _____ we all rely.1.on which2.on that3.in which4.on whom9:The audience, most of ____ were students, enjoyed the performance very much.1.whom2.who3.which4.that10:It was in that small village______our president was born.1.which2.when3.that4.as11:He said ______.1.how the garden was beautiful2.how beautiful the garden was3.how beautiful was the garden4.the garden was how beautiful12:There are two reasons ____ I do not want to go out tonight.1.why2.because3.so4.that13:I would rather that Mr. Mike ____ the speech at the conference instead of the dean that day.1.make2.made3.has made4.had made15:You’d better______the buffet supper sumptuous.1.make2.to make3.making4.made16:Why does Tom want to leave the______job?1.present2.private3.public4.powerful17:Linda and Cheryle come from families which are______rich nor poor.1.both2.either3.neither4.as18:The Greeks believed that individuals must beresponsible______their own actions.1.with2.of3.for4.to19:The question______yesterday is of great importance.1.discussing2.discussed3.being discussed4.to be discussed20:If you want to be an actor you have to really _____ yourself to it.mit2.conform3.admit4.adapt11:ABC Company______a person for full-time sales in the clothing department.1.inquire2.require3.ask4.charge1:______by these success, they decided to expand the business.1.Encouraging2.Encouraged3.Having encouraged4.Being encouraging9:He asks ___3_ .1.when will they leave2.when they leave3.when they will leave4.they when will leave19:In the armchair______,reading a novel.1.his mother sat2.did his mother sit3.does his mother sit4.sat his mother。
作业习题答案《单片机应用技术》部分习题与参考答案第1章单片机概述1-1什么是嵌入式系统?嵌入式系统的硬件和软件各包括哪些内容?答: 以应用为中心,以计算机技术为基础,软/硬件可剪裁,针对具体应用系统,对功能、可靠性,成本、体积、功耗严格要求的专用计算机系统称为嵌入式计算机系统。
简称为嵌入式系统。
嵌入式系统的硬件包括:嵌入式处理器、存储器和外部设备器件、输入输出接口、图形控制器等。
软件包括操作系统和应用程序。
嵌入式系统是专用的计算机系统,嵌入式系统的核心是嵌入式处理器,单片机是嵌入式处理器的典型代表。
1-2 什么叫单片机?一个完整的单片机芯片至少有哪些部件?答:将微处理器(CPU)、存储器、定时/计数器及输入输出接口电路等部件集成在一块集成电路上,称为单片微型计算机,简称单片机。
一个完整的单片机芯片至少有中央处理器(CPU)、随机存储器(RAM)、只读存储器(ROM)、定时/计数器及I/O接口等部件。
1-3嵌入式处理器有何特点?嵌入式处理器分为哪几类?答:嵌入式处理器对实时和多任务系统有和强的支持能力、对存储区保护功能强、具有可扩展的处理器结构及低功耗等特点。
嵌入式处理器分为:嵌入式微处理器、微控制器、嵌入式DSP处理器和片上系统等。
1-4 单片机系统的开发过程分为那几步进行?答:1.硬件的设计与调试。
2 应用程序的设计和调试。
3系统联调。
4程序的固化。
5.脱机运行。
1-5 Intel 公司的主要单片机产品分为哪几大系列?各系列的区别何在?答:Intel公司的MCS-48系列、MCS-51系列、MCS-96系列产品;48系列的单片机在片内集成4位CPU,片内含有多种I/O接口,有的根据不同用途还配有许多专用接口,价格便宜,控制功能强。
51系列的单片机在片内集成8位CPU、片内RAM为128字节,ROM为4K字节,4个并行I/O口、2个16位定时/计数器、串行接口、5个中断源。
96系列单片机CPU为16位,片内RAM为232字节,ROM为8K字节,片内带有高速输入输出部件,多通道10位A/D转换部件,中断处理为8级。
第一部分 绪论一、单选题1、 在ISO层次体系中,实现同步进程间对话的是( D )。
A、运输层B、应用层C、表示层D、会话层2、 TCP/IP代表传输控制协议/互联网协议,其实它代表一个标准协议组,下面不属于这个标准协议组的协议是( D )。
A、简单邮件传送协议SMTPB、文件传送协议FTPC、远程登录TelnetD、AppleTalk3、下面不属于网络拓扑结构的是:( D )。
A、环形结构B、总线结构C、网状结构D、层次结构4、实现通信协议的软件一般固化在 的ROM中( C )。
A、微机主板B、IDE卡C、网卡D、MODEM卡5、国际标准化组织制定了开放互连系统模型,其英文缩写为_______,它把通信服务分成________层( D )。
A、OSI/EM,4B、OSI/RM,5C、OSI/EM,6D、OSI/RM,76、Internet的前身是( A )。
A、ARPANETB、EthernetC、TelnetD、Intranet三、填空题1、同一计算机的相邻功能层(N/N+1)之间的通信规则称为( 接口)。
2、开放系统互连缩写为( OSI )。
3、服务质量缩写为( QoS )。
4、计算机网络一般分为(局域网(LAN) )、(城域网(MAN) )、( 广域网(WAN) )和(互联网(internet) )。
5、计算机网络的主要功能是(数据通信 )、(资源共享 )和提高系统可靠性。
第二部分 数据通信基础一、单向选择题1、对于带宽为3kHz的无噪声信道,假设信道中每个码元信号的可能状态数为16,则该信道所能支持的最大数据传输率可达( A)。
A、24KbpsB、48KbpsC、12KbpsD、72Kbps2、传输速率单位“bps”代表。
( B )A、BYTES PER SECONDB、BITS PER SECONDC、BAUD PER SECONDD、BILLION PER SECOND3、RS-232C的电气特性规定逻辑“0”的电平电压为。
第一部分绪论一、单选题1、在ISO层次体系中,实现同步进程间对话的是( D )。
A、运输层B、应用层C、表示层D、会话层2、 TCP/IP代表传输控制协议/互联网协议,其实它代表一个标准协议组,下面不属于这个标准协议组的协议是( D )。
A、简单邮件传送协议SMTPB、文件传送协议FTPC、远程登录TelnetD、AppleTalk3、下面不属于网络拓扑结构的是:( D )。
A、环形结构B、总线结构C、网状结构D、层次结构4、实现通信协议的软件一般固化在的ROM中( C )。
A、微机主板B、IDE卡C、网卡D、MODEM卡5、国际标准化组织制定了开放互连系统模型,其英文缩写为_______,它把通信服务分成________层( D )。
A、OSI/EM,4B、OSI/RM,5C、OSI/EM,6D、OSI/RM,76、Internet的前身是( A )。
A、ARPANETB、EthernetC、TelnetD、Intranet三、填空题1、同一计算机的相邻功能层(N/N+1)之间的通信规则称为( 接口 )。
2、开放系统互连缩写为( OSI )。
3、服务质量缩写为( QoS )。
4、计算机网络一般分为(局域网(LAN))、(城域网(MAN))、(广域网(WAN))和(互联网(internet))。
5、计算机网络的主要功能是(数据通信)、(资源共享)和提高系统可靠性。
第二部分数据通信基础一、单向选择题1、对于带宽为3kHz的无噪声信道,假设信道中每个码元信号的可能状态数为16,则该信道所能支持的最大数据传输率可达( A)。
A、24KbpsB、48KbpsC、12KbpsD、72Kbps2、传输速率单位“bps”代表。
( B )A、BYTES PER SECONDB、BITS PER SECONDC、BAUD PER SECONDD、BILLION PER SECOND3、RS-232C的电气特性规定逻辑“0”的电平电压为。
HTML4-7章作业1、CSS样式表不可能实现( )功能。
A将格式和结构分离 B.一个CSS文件控制多个网页C.控制图片的精确位置 D.兼容所有的浏览器2、可用来在一个网页中嵌入显示另一个网页内容的标记符是()A.<Marquee>B. <Iframe>C.<embed>D.<object>3.我们想要在框架中加入一个叫做list.htm的文件,应该在HTML中如何描述它?A、frame page="list.htm"B、frame target="list.htm"C、frame src="list.htm"D、frame framepage="list.htm"4.我们想要在页面中加入一个层,可以使用哪些HTML标记来描述它?(选择2项)A、<floor>B、<div>C、<span>D、<level>5 . 下列哪种CSS样式定义的方式拥有最高的优先级?A、嵌入B、行内C、链接D、导入6 . 以下的HTML中,哪个是正确引用外部样式表的方法?A、 <style src="mystyle.css">B、 <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="mystyle.css">C、 <stylesheet>mystyle.css</stylesheet>7. 在HTML文档中,引用外部样式表的正确位置是?A)文档的末尾B) <head>部分C)文档的顶部D) <body>部分8. 哪个HTML标签可用来定义内部样式表?A) <style>B) <script>C) <css>9. 哪个HTML属性可用来定义内联样式?A) fontB) classC) stylesD) style10. 下列哪个选项的CSS语法是正确的?A) body:color=blackB) {body:color=black(body}C) body {color: black}D) {body;color:black}11. 如何在CSS文件中插入注释?A) // this is a commentB) // this is a comment //C) /* this is a comment */D) ' this is a comment12 . CSS哪个属性可用来改变背景颜色?A) bgcolor:B) color:C) background-color:13. 如何为所有的<h1>元素添加背景颜色?A) h1.all {background-color:#FFFFFF}B) h1 {background-color:#FFFFFF}C) all.h1 {background-color:#FFFFFF}14 . CSS如何改变某个元素的文本颜色?A) text-color:B) color:C) fgcolor:D) text-color=15 . 哪个CSS属性可控制文本的尺寸?A) font-sizeB) text-styleC) font-styleD) text-size16 . 以下的CSS中,可使所有<p>元素变为粗体的正确语法是?A) <p style="font-size:bold">B) <p style="text-size:bold">C) p {font-weight:bold}D) p {text-size:bold}17 . 如何显示没有下划线的超链接?A) a {text-decoration:none}B) a {text-decoration:no underline}C) a {underline:none}D) a {decoration:no underline}18 . 如何使文本以大写字母开头?A) text-transform:capitalizeB)无法通过CSS来完成C) text-transform:uppercase19 . css如何改变元素的字体?A) font=B) f:C) font-family:20 . 如何改变元素的左边距?A) text-indent:B) margin-left:C) margin:D) indent:21. 如何产生带有正方形的项目的列表?A) list-type: squareB) list-style-type: squareC) type: squareD) type: 222 . 我们可以在下列哪个HTML元素中放置javascript代码?A) <script>B) <javascript>C) <js>D) <scripting>23.某一站点主页面index.html的代码如下所示,则选项中关于这段代码的说法正确的是()。
第七章 部分作业答案
7.4.8 已知Y100L1-4型异步电动机的某些额定技术数据如下:
kW 380V Y接法 1420r/min 82.0cos %81
试计算:
(1)相电流和线电流的额定值及额定负载时的转矩;
(2)额定转差率及额定负载时的转子电流频率。设电源频率为50Hz。
解:(1)AUPIIlNlP5%8182.038032200cos3
mNnPTNNN•8.1414202.295509550
(2)%33.5%100150014201500%100ONONnnnS
HzfSfN67.250%33.512
7.4.9 有台三相异步电动机,其额定转速为1470r/min,电源频率为50Hz。在(a)起动瞬间
(b)转子转速为同步转速32时(c)转差率为时三种情况下,试求:(1)定子旋转磁场对
定子的转速;(2)定子旋转磁场对转子的转速;(3)转子旋转磁场对转子的转速;(4)转子
旋转磁场对定子的转速;(5)转子旋转磁场对定子旋转磁场的转速。
解:(1)定子旋转磁场对定子的转速:在(a)(b)(c)三种情况下均为1500 r/min 。
(2)定子旋转磁场对转子的转速:
(a)起动瞬间:1500 r/min ;
(b)转子转速为同步转速32时:500 r/min;
(c)转差率为时:30 r/min。
(3)转子旋转磁场对转子的转速:
(a)起动瞬间:1500 r/min ;
(b)转子转速为同步转速32时:500 r/min;
(c)转差率为时:30 r/min。
(4)转子旋转磁场对定子的转速:在(a)(b)(c)三种情况下均为1500 r/min 。
(5)转子旋转磁场对定子旋转磁场的转速:在(a)(b)(c)三种情况下均为0。
说明:
定子旋转磁场和转子旋转磁场共同构成旋转磁场,转速均为同步转速。
7.4.11 已知Y132S-4型三相异步电动机的额定技术数据如下:
功率 转速 电压 效率 功率因数 NstII/ NstTT/ NTT/max
kW 1440r/min 380V %5.85 7 2
电源频率为50Hz。试求额定状态下的转差率NS、电流NI和转矩NT,以及起动电流stI、起
动转矩stT、最大转矩maxT。
解: %4%100150014401500%10000nnnSN
AUPIIlNlN6.11%5.8584.038035500cos3
mNnPTNNN•5.3614405.595509550
AIINst2.816.1177
mNTTNst•735.3622
mNTTN•3.805.362.22.2
max
7.4.13 某四极三相异步电动机的额定功率为30kW,额定电压为380V,三角形联接,频率为
50Hz。在额定负载下运行时,其转差率为,效率为90%,线电流为57.5A,试求:(1)转子
旋转磁场对转子的转速;(2)额定转矩;(3)电动机的功率因数。
解: (1) 由%10000nnnSN得:min/14701500)02.01()1(0rnsnNN
所以转子旋转磁场对转子的转速为:1500-1470=30 r/min
(2)mNnPTNNN•9.19414703095509550
(3)88.0%905.57380310303cos3llNIUP
7.5.4 在例中电动机的2.1/NstTT,7/NstII,试求:(1)用Y-Δ换接起动时的起动
电流和起动转矩;(2)当负载为额定转矩的60%和25%时,电动机能否起动
解:(1)直接起动时:
起动电流:AIINst5.4025.5777
起动转矩:mNTTNst•88.2339.1942.12.1
采用Y-Δ换接起动时:
起动电流:AIIstYst2.1345.4023131
起动转矩:mNTTstYst•96.7788.2333131
(2)当负载为额定转矩的60%时:
起动转矩:mNTYst•96.77;负载转矩:mNTTNL•94.116%60
起动转矩小于负载转矩,所以不能起动。
当负载为额定转矩的25%时:
起动转矩:mNTYst•96.77;负载转矩:mNTTNL•725.48%25
起动转矩大于负载转矩,所以能起动。
7.5.5 在例中,采用自耦变压器降压启动,而使电动机的起动转矩为额定转矩的85%,试求:
(1)自耦变压器的变比;(2)电动机的起动电流和线路上的起动电流各为多少
解: (1)设变压器的变比为K,由于电动机的起动转矩为额定转矩的85%,即:
%85)1(2
K
,则:085.1%851K
(2)电动机的起动电流AIkIstst3715.402085.111'2
线路上的起动电流AIkIstst3427.37208.111'2'