翻译-金属基复合材料注射成型工艺总结
- 格式:docx
- 大小:1.19 MB
- 文档页数:10

材料成型工艺基础部分(中英文词汇对照)材料成型工艺基础部分0 绪论金属材料:metal material (MR)高分子材料:high-molecular material陶瓷材料:ceramic material复合材料:composition material成形工艺:formation technology1 铸造铸造工艺:casting technique铸件:foundry goods (casting)机器零件:machine part毛坯:blank力学性能:mechanical property砂型铸造:sand casting process型砂:foundry sand1.1 铸件成形理论基础合金:alloy铸造性能:casting property工艺性能:processing property收缩性:constringency偏析性:aliquation氧化性:oxidizability吸气性:inspiratory铸件结构:casting structure使用性能:service performance浇不足:misrun冷隔:cold shut夹渣:cinder inclusion粘砂:sand fusion缺陷:flaw, defect, falling流动性:flowing power铸型:cast (foundry mold)蓄热系数:thermal storage capacity 浇注:pouring凝固:freezing收缩性:constringency逐层凝固:layer-by-layer freezing 糊状凝固:mushy freezing结晶:crystal缩孔:shrinkage void缩松:shrinkage porosity顺序凝固:progressive solidification 冷铁:iron chill补缩:feeding等温线法:constant temperature line method 内接圆法:inscribed circle method铸造应力:casting stress变形:deforming裂纹:crack机械应力:mechanical stress热应力:heat stress相变应力:transformation stress气孔:blow hole铸铁:ingot铸钢:cast steel非铁合金:nonferrous alloy灰铸铁:gray cast-iorn孕育处理:inoculation球墨铸铁:spheroidal球化处理:sheroidisation可锻铸铁:ductile cast iron石墨:graphite蠕墨铸铁:vermicular cast iron热处理:heat processing铝合金:Al-alloy熔炼:fusion metallurgy铜合金:copper alloy氢脆:hydrogen brittleness1.2 铸造方法(casting method)手工造型:hand moulding机器造型:machine moulding金属型:metal mold casting金属模:permanent mould压力铸造:press casting熔模铸造:investment moulding蜡膜:cere离心铸造:centrifugal casting低压铸造:casting under low pressure 差压铸造:counter-pressure casting 陶瓷型铸造:shaw process1.3 铸造工艺设计浇注位置:pouring position分型面:mould joint活块:loose piece起模:patter drawing型芯:core型芯撑:chaplet工艺参数:processing parameter下芯:core setting合型:mould assembly冒口:casting head尺寸公差:dimensional tolerance尺寸公差带:tolerance zone机械加工余量:machining allowance 铸孔:core hole非标准:nonstandard label收缩率:rate of contraction线收缩:linear contraction体收缩:volume contraction起模斜度:pattern draft铸造圆角:curving of castings芯头:core register芯头间隙:clearance芯座:core print seat分型线:joint line分模线:die parting line1.4 铸造结构工艺性加强筋:rib reinforcement撒砂:stuccoing内腔:entocoele2 金属塑性加工塑性加工:plastic working塑性:plastic property锻造:forge work冲压:punching轧制:rolling拉拔:drawing挤压:extruding细化晶粒:grain refinement热锻:hit-forging温锻:warm forging2.1 金属塑性加工理论基础塑性变形:plastic yield加工硬化:work-hardening韧性:ductility回复温度:return temperature 再结晶:recrystallize再结晶退火:full annealing冷变形:cold deformation热变性:heat denaturation锻造比:forging ratio镦粗:upset拔长:pull out纤维组织:fibrous tissue锻造性能:forging property可锻性:forgeability变形抗力:resistance of deformation化学成分:chemical constitution热脆性:hot brittleness冷脆性:cold-shortness变形速度:deformation velocity应力状态:stress condition变形温度:deformation temperature过热:overheating过烧:burning脱碳:carbon elimination始锻温度:initiation forging temperature 终锻温度:final forging temperature2.2 金属塑性加工方法自由锻:flat-die hammer冲孔:jetting弯曲:bend弯曲半径:bending radius切割:cut扭转:twist rotation错移:offsetting锻接:percussion基本工序:basic process辅助工序:auxiliary process精整工序:finishing process模锻:contour forging锻模:forging die胎膜锻:fetal membrane forging剪床:shearing machine冲床:backing-out punch冲裁:blanking弹性变形:elastic distortion塑性变形:plastic yield剪切变形:shearing deformation最小弯曲半径:minimum bending radius 曲率:angularity弯裂:rupture回弹:rebound辊轧:roll forming辊锻:roll forging斜轧:oblique rolling横轧:transverse rolling辗压:tamping drum挤压:extruding拉拔:draft2.3 塑性加工工艺设计工艺规程:process specification锻件图:forging drawing敷料:dressing锻件余量:forging allowance锻件公差:forging tolerance工夹具:clamping apparatus加热设备:firing equipment加热规范:heating schedule冷却规范:cooling schedule后续处理:after treatment分模面:die parting face冲孔连皮:punching the wad模锻斜度:draft angle圆角半径:radius of corner圆饼类锻件:circumcresent cake-like forging 长轴类锻件:long axis-like forging2.4 锻件结构工艺性锥体:cone斜面:cant空间曲线:curve in space粗糙度:degree of roughness2.5 冲压件结构工艺性3 焊接焊接:welding铆接:riverting熔焊:fusion welding压焊:press welding钎焊:braze welding3.1 焊接理论基础冶金:metallurgy电弧焊:arc welding气焊:acetylene welding电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能束焊:high energy welding 电子焊:electronic welding激光焊:laser welding等离子焊:plasma welding电弧:electric arc阳极区:anode region阴极区:negative polarity弧柱区:arc stream正接法:electrode negative method反接法:opposition method脱氧剂:deoxidizing agent焊缝:welded seam焊缝区:weld zone熔合区:fusion area热影响区:heat-affected zone脆性断裂:brittle fracture过热区:overheated zone正火区:normalized zone相变区:phase change zone焊接应力:welding stress收缩变形:contraction distortion角变形:angular deformation弯曲变形:bend deformation扭曲变形:warping deformation波浪变形:wave transformation反变形法:reversible deformation method 刚性固定法:rigid fixing method预热:warming-up缓冷:slow cool焊后热处理:postweld heat treatment矫形处理:shape-righting3.2 焊接方法埋弧焊:hidden arc welding气体保护焊:gas shielded arc welding氩弧焊:argon welding熔化极氩弧焊:consumable electrode argon welding 钨极氩弧焊:argon tungsten-arc welding二氧化碳气体保护焊:CO2 gas shielded arc welding 碳弧焊:carbon arc welding碳弧气刨:carbon arc air gouging电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能焊:high grade energy welding等离子弧切割:plasma arc cutting (PAC)堆焊:bead weld电阻焊:resistance welding电焊:electric welding缝焊:seam welding压焊:press welding多点凸焊:multiple projection welding对焊:welding neck摩擦焊:friction welding扩散焊:diffusion welding硬钎料:brazing alloy软钎料:soft solder3.3 常用金属材料的焊接焊接性:weldability焊接方法:welding method 焊接材料:welding material 焊条:electrode焊剂:flux material碳素钢:carbon steel低碳钢:low carbon steel中碳钢:medium carbon steel 高碳钢:high carbon steel低合金钢:lean alloy steel不锈钢:non-corrosive steel 有色金属:nonferrous metal 3.4 焊接工艺设计型材:sectional bar药皮:coating焊丝:soldering wire连续焊缝:continuous weld断续焊缝:intermittent weld应力集中:stress concentration焊接接头:soldered joint坡口:groove对接:abutting joint搭接:lap joint角接:corner joint4 粉末冶金(power metallurgy)粉末冶金成品:finished power metallurgical product 铁氧体:ferrite硬质合金:sintered-carbide高熔点金属:high-melting metal陶瓷:ceramic4.1 粉末冶金工艺理论基础压坯:pressed compact扩散:diffusion烧结:agglomeration固溶:solid solubility化合:combination4.2 粉末冶金的工艺流程制备:preparation预处理:anticipation还原法:reduction method电解法:electrolytic method雾化法:atomization粒度:grain size松装密度:loose density流动性:flowing power压缩性:compressibility筛分:screen separation混合:compounding制粒:pelletization过烧:superburning欠烧:underburnt5 金属复合成型技术自蔓延焊接:SHS welding热等静压:HIP准热等静压:PHIP5.1 液态成型技术与固态成型技术的复合高压铸造:high-pressure casting电磁泵:magnetic-pump压射成型:injection molding柱塞:plunger piston冲头:drift pin凝固法:freezing method挤压法:extrusion method转向节:knuckle pivot制动器:arresting gear5.2 金属半凝固、半熔融成型技术凝固:freezing半熔融:semi-vitreous触变铸造:thixotropy casting触变锻造:thixotropy forging注射成型:injection molding5.3 其他金属成型新技术快速凝固:flash set非晶态:amorphous溢流法:press over system喷射沉积:ejecting deposit爆炸复合法:explosion cladding method 扩散焊接:diffusion welding挤压:extruding轧制:roll down6 非金属材料成型技术6.1 高分子材料成型技术高分子材料:non-metal material耐腐蚀:resistant material绝缘:insulation老化:ageing耐热性:heat-durability粘弹性:viscoelasticity塑料:plastic material橡胶:rubber合成纤维:synthetic fibre涂料:covering material粘结剂:agglomerant粘度:viscosity热塑性塑料:thermoplastic plastics 热固性塑料:thermosetting plastic 通用塑料:general-purpose plastics 工程塑料:engineering plastic薄膜:thin film增强塑料:reinforced plastics浇注塑料:pouring plastics注射塑料:injiection plastics挤出塑料:extrusion plastics吹塑塑料:blowing plastics模压塑料:die pressing plastics聚合物:ploymer semiconductor吸湿性:hygroscopic cargo定向作用:directional action生胶:green glue stock填料:carrier丁苯橡胶:SBR顺丁橡胶:BR氯丁橡胶:CR丁腈橡胶:NBR硅橡胶:Q聚氨酯橡胶:U压延:calender硫化:sulfuration胶粘剂:adhesive胶接:glue joint刹车片:brake block零件修复:parts renewal蜂窝夹层:honeycomb core material 6.2 工业陶瓷制品的成型技术干燥:drying坯料:blank润滑剂:anti-friction结合剂:binder热压铸:hot injiection moulding 6.3 非金属材料成型技术的新进展热压烧结:hot pressed sintering7 复合材料的成型技术复合材料:composite material树脂:resin7.1 金属复合材料的成型技术硼纤维:boron fiber钛合金:titanium alloy碳纤维:carbon filter等离子喷涂:plasma spraying浸渍法:immersion method锭坯:ingot blank7.2 聚合物基复合材料的成型技术晶须:whisker缠绕成形:enwind forming湿法缠绕:wet method enwind 7.3 陶瓷复合材料成型技术料浆:slurry溶胶-凝胶法:sol-gel method化学气相沉积:chemical vapor deposition (CVD) 原位:in situ8 材料成型方法的选择粉末冶金:powder metallurgy工程塑料:engineering plastics工程陶瓷:engineering ceramics。

0 绪论金属材料:metal material (MR)高分子材料:high-molecular material 陶瓷材料:ceramic material复合材料:composition material成形工艺:formation technology1 铸造铸造工艺:casting technique铸件:foundry goods (casting)机器零件:machine part毛坯:blank力学性能:mechanical property砂型铸造:sand casting process型砂:foundry sand铸件成形理论基础合金:alloy铸造性能:casting property工艺性能:processing property收缩性:constringency偏析性:aliquation氧化性:oxidizability吸气性:inspiratory铸件结构:casting structure使用性能:service performance浇不足:misrun冷隔:cold shut夹渣:cinder inclusion粘砂:sand fusion缺陷:flaw, defect, falling流动性:flowing power铸型:cast (foundry mold)蓄热系数:thermal storage capacity浇注:pouring凝固:freezing收缩性:constringency逐层凝固:layer-by-layer freezing糊状凝固:mushy freezing结晶:crystal缩孔:shrinkage void缩松:shrinkage porosity顺序凝固:progressive solidification冷铁:iron chill补缩:feeding等温线法:constant temperature line method内接圆法:inscribed circle method 铸造应力:casting stress变形:deforming裂纹:crack机械应力:mechanical stress热应力:heat stress相变应力:transformation stress 气孔:blow hole铸铁:ingot铸钢:cast steel非铁合金:nonferrous alloy灰铸铁:gray cast-iorn孕育处理:inoculation球墨铸铁:spheroidal球化处理:sheroidisation可锻铸铁:ductile cast iron石墨:graphite蠕墨铸铁:vermicular cast iron热处理:heat processing铝合金:Al-alloy熔炼:fusion metallurgy铜合金:copper alloy氢脆:hydrogen brittleness铸造方法(casting method)手工造型:hand moulding机器造型:machine moulding金属型:metal mold casting金属模:permanent mould压力铸造:press casting熔模铸造:investment moulding蜡膜:cere离心铸造:centrifugal casting低压铸造:casting under low pressure 差压铸造:counter-pressure casting 陶瓷型铸造:shaw process铸造工艺设计浇注位置:pouring position分型面:mould joint活块:loose piece起模:patter drawing型芯:core型芯撑:chaplet工艺参数:processing parameter下芯:core setting合型:mould assembly冒口:casting head尺寸公差:dimensional tolerance 尺寸公差带:tolerance zone机械加工余量:machining allowance 铸孔:core hole非标准:nonstandard label收缩率:rate of contraction线收缩:linear contraction体收缩:volume contraction起模斜度:pattern draft铸造圆角:curving of castings芯头:core register芯头间隙:clearance芯座:core print seat分型线:joint line分模线:die parting line铸造结构工艺性加强筋:rib reinforcement撒砂:stuccoing内腔:entocoele2 金属塑性加工塑性加工:plastic working塑性:plastic property锻造:forge work冲压:punching轧制:rolling拉拔:drawing挤压:extruding细化晶粒:grain refinement 热锻:hit-forging温锻:warm forging金属塑性加工理论基础塑性变形:plastic yield加工硬化:work-hardening韧性:ductility回复温度:return temperature 再结晶:recrystallize再结晶退火:full annealing 冷变形:cold deformation热变性:heat denaturation锻造比:forging ratio镦粗:upset拔长:pull out纤维组织:fibrous tissue锻造性能:forging property可锻性:forgeability变形抗力:resistance of deformation化学成分:chemical constitution热脆性:hot brittleness冷脆性:cold-shortness变形速度:deformation velocity应力状态:stress condition变形温度:deformation temperature过热:overheating过烧:burning脱碳:carbon elimination始锻温度:initiation forging temperature 终锻温度:final forging temperature金属塑性加工方法自由锻:flat-die hammer冲孔:jetting弯曲:bend弯曲半径:bending radius切割:cut扭转:twist rotation错移:offsetting锻接:percussion基本工序:basic process辅助工序:auxiliary process精整工序:finishing process模锻:contour forging锻模:forging die胎膜锻:fetal membrane forging剪床:shearing machine冲床:backing-out punch冲裁:blanking弹性变形:elastic distortion塑性变形:plastic yield剪切变形:shearing deformation最小弯曲半径:minimum bending radius 曲率:angularity弯裂:rupture回弹:rebound辊轧:roll forming辊锻:roll forging斜轧:oblique rolling横轧:transverse rolling辗压:tamping drum挤压:extruding拉拔:draft塑性加工工艺设计工艺规程:process specification锻件图:forging drawing敷料:dressing锻件余量:forging allowance锻件公差:forging tolerance工夹具:clamping apparatus加热设备:firing equipment加热规范:heating schedule冷却规范:cooling schedule后续处理:after treatment分模面:die parting face冲孔连皮:punching the wad模锻斜度:draft angle圆角半径:radius of corner圆饼类锻件:circumcresent cake-like forging 长轴类锻件:long axis-like forging锻件结构工艺性锥体:cone斜面:cant空间曲线:curve in space粗糙度:degree of roughness 冲压件结构工艺性3 焊接焊接:welding铆接:riverting熔焊:fusion welding压焊:press welding钎焊:braze welding焊接理论基础冶金:metallurgy电弧焊:arc welding气焊:acetylene welding电渣焊:electro-slag welding 高能束焊:high energy welding 电子焊:electronic welding激光焊:laser welding等离子焊:plasma welding电弧:electric arc阳极区:anode region阴极区:negative polarity弧柱区:arc stream正接法:electrode negative method反接法:opposition method脱氧剂:deoxidizing agent焊缝:welded seam焊缝区:weld zone熔合区:fusion area热影响区:heat-affected zone脆性断裂:brittle fracture过热区:overheated zone正火区:normalized zone相变区:phase change zone焊接应力:welding stress收缩变形:contraction distortion角变形:angular deformation弯曲变形:bend deformation扭曲变形:warping deformation波浪变形:wave transformation反变形法:reversible deformation method 刚性固定法:rigid fixing method预热:warming-up缓冷:slow cool焊后热处理:postweld heat treatment矫形处理:shape-righting焊接方法埋弧焊:hidden arc welding气体保护焊:gas shielded arc welding氩弧焊:argon welding熔化极氩弧焊:consumable electrode argon welding 钨极氩弧焊:argon tungsten-arc welding二氧化碳气体保护焊:CO2 gas shielded arc welding 碳弧焊:carbon arc welding碳弧气刨:carbon arc air gouging电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能焊:high grade energy welding等离子弧切割:plasma arc cutting (PAC)堆焊:bead weld电阻焊:resistance welding电焊:electric welding缝焊:seam welding压焊:press welding多点凸焊:multiple projection welding对焊:welding neck摩擦焊:friction welding扩散焊:diffusion welding 硬钎料:brazing alloy软钎料:soft solder常用金属材料的焊接焊接性:weldability焊接方法:welding method焊接材料:welding material 焊条:electrode焊剂:flux material碳素钢:carbon steel低碳钢:low carbon steel中碳钢:medium carbon steel 高碳钢:high carbon steel 低合金钢:lean alloy steel 不锈钢:non-corrosive steel 有色金属:nonferrous metal 焊接工艺设计型材:sectional bar药皮:coating焊丝:soldering wire连续焊缝:continuous weld 断续焊缝:intermittent weld应力集中:stress concentration焊接接头:soldered joint坡口:groove对接:abutting joint搭接:lap joint角接:corner joint4 粉末冶金(power metallurgy)粉末冶金成品:finished power metallurgical product 铁氧体:ferrite硬质合金:sintered-carbide高熔点金属:high-melting metal陶瓷:ceramic粉末冶金工艺理论基础压坯:pressed compact扩散:diffusion烧结:agglomeration固溶: solid solubility化合:combination粉末冶金的工艺流程制备:preparation预处理:anticipation还原法:reduction method电解法:electrolytic method雾化法:atomization粒度:grain size松装密度:loose density流动性:flowing power压缩性:compressibility筛分:screen separation混合:compounding制粒:pelletization过烧:superburning欠烧:underburnt5 金属复合成型技术自蔓延焊接:SHS welding热等静压:HIP准热等静压:PHIP液态成型技术与固态成型技术的复合高压铸造:high-pressure casting 电磁泵:magnetic-pump压射成型:injection molding柱塞:plunger piston冲头:drift pin凝固法:freezing method挤压法:extrusion method转向节:knuckle pivot制动器:arresting gear金属半凝固、半熔融成型技术凝固:freezing半熔融:semi-vitreous触变铸造:thixotropy casting触变锻造:thixotropy forging注射成型:injection molding其他金属成型新技术快速凝固:flash set非晶态:amorphous溢流法:press over system喷射沉积:ejecting deposit爆炸复合法:explosion cladding method 扩散焊接:diffusion welding挤压:extruding轧制:roll down6 非金属材料成型技术高分子材料成型技术高分子材料:non-metal material耐腐蚀:resistant material绝缘:insulation老化:ageing耐热性:heat-durability粘弹性:viscoelasticity塑料:plastic material橡胶:rubber合成纤维:synthetic fibre涂料:covering material粘结剂:agglomerant粘度:viscosity热塑性塑料:thermoplastic plastics 热固性塑料:thermosetting plastic 通用塑料:general-purpose plastics 工程塑料:engineering plastic薄膜:thin film增强塑料:reinforced plastics浇注塑料:pouring plastics注射塑料:injiection plastics挤出塑料:extrusion plastics吹塑塑料:blowing plastics模压塑料:die pressing plastics 聚合物:ploymer semiconductor吸湿性:hygroscopic cargo定向作用:directional action生胶:green glue stock填料:carrier丁苯橡胶:SBR顺丁橡胶:BR氯丁橡胶:CR丁腈橡胶:NBR硅橡胶:Q聚氨酯橡胶:U压延:calender硫化:sulfuration胶粘剂:adhesive胶接:glue joint刹车片:brake block零件修复:parts renewal蜂窝夹层:honeycomb core material 工业陶瓷制品的成型技术干燥:drying坯料:blank润滑剂:anti-friction结合剂:binder热压铸:hot injiection moulding 非金属材料成型技术的新进展热压烧结:hot pressed sintering7 复合材料的成型技术复合材料:composite material树脂:resin金属复合材料的成型技术硼纤维:boron fiber钛合金:titanium alloy碳纤维:carbon filter等离子喷涂:plasma spraying浸渍法:immersion method锭坯:ingot blank聚合物基复合材料的成型技术晶须:whisker缠绕成形:enwind forming湿法缠绕:wet method enwind陶瓷复合材料成型技术料浆:slurry溶胶-凝胶法:sol-gel method化学气相沉积: chemical vapor deposition (CVD)原位:in situ8 材料成型方法的选择粉末冶金:powder metallurgy工程塑料:engineering plastics工程陶瓷:engineering ceramics。

金属粉末的注射成型金属粉末的注射成型,也被称为金属粉末注射成型(Metal Powder Injection Molding,简称MIM),是一种先进的制造技术,将金属粉末与有机物相结合,通过注射成型和烧结工艺,制造出高密度、精确尺寸、复杂形状的金属零件。
在金属粉末注射成型过程中,首先将金属粉末与有机粘结剂和其他添加剂混合均匀,形成金属粉末/有机物混合物。
其次,在高压下,将混合物通过注射机注射到具有细微孔隙和管道的模具中。
模具通常采用两片结构,上模和下模之间形成的形状即为所需制造的零件形状。
注射机将足够的压力用于将混合物推进模具的每一个细微空间,以确保零件形状准确,毛边小。
注射后,模具中的混合物开始固化,形成绿色零件。
最后,通过烧结处理,去除有机物并使金属颗粒结合成整体,形成具有理想密度和力学性能的金属粉末零件。
相对于传统的金属加工方法,金属粉末注射成型具有以下优势:首先,MIM可以制造复杂形状的金属零件,包括薄壁结构、内外复杂曲面和细小结构,满足了一些特殊零件的制造需求。
其次,MIM的材料利用率高,废料少,可以减少原材料和能源的浪费。
此外,零件的尺寸稳定性好,需要的加工工序少,可以降低生产成本。
最重要的是,对于一些其他制造工艺难以实现的金属材料,例如高强度不锈钢、钨合金和钛合金,MIM可以实现高质量的制造。
然而,金属粉末注射成型也存在应用范围的限制。
首先,相对较高的制造成本使得该技术在一些低成本产品上难以应用。
其次,较大的尺寸限制了MIM在制造大尺寸、高精度的零件上的应用。
此外,与其他成型方法相比,MIM的制造周期较长,对行业响应速度要求较高的场景不适用。
尽管如此,金属粉末注射成型技术已经在汽车、电子产品、医疗器械、工具和航空航天等领域得到了广泛的应用。
随着制造技术的进步和材料属性的改进,金属粉末注射成型有望在更多领域发挥其优势,并带来更多创新的解决方案。

材料成型工艺基础部分0 绪论金属材料:metal material (MR)高分子材料:high-molecular material陶瓷材料:ceramic material复合材料:composition material成形工艺:formation technology1 铸造铸造工艺:casting technique铸件:foundry goods (casting)机器零件:machine part毛坯:blank力学性能:mechanical property砂型铸造:sand casting process型砂:foundry sand1.1 铸件成形理论基础合金:alloy铸造性能:casting property工艺性能:processing property收缩性:constringency偏析性:aliquation氧化性:oxidizability吸气性:inspiratory铸件结构:casting structure使用性能:service performance浇不足:misrun冷隔:cold shut夹渣:cinder inclusion粘砂:sand fusion缺陷:flaw, defect, falling流动性:flowing power铸型:cast (foundry mold)蓄热系数:thermal storage capacity 浇注:pouring凝固:freezing收缩性:constringency逐层凝固:layer-by-layer freezing 糊状凝固:mushy freezing结晶:crystal缩孔:shrinkage void缩松:shrinkage porosity顺序凝固:progressive solidification 冷铁:iron chill补缩:feeding等温线法:constant temperature line method 内接圆法:inscribed circle method铸造应力:casting stress变形:deforming裂纹:crack机械应力:mechanical stress热应力:heat stress相变应力:transformation stress气孔:blow hole铸铁:ingot铸钢:cast steel非铁合金:nonferrous alloy灰铸铁:gray cast-iorn孕育处理:inoculation球墨铸铁:spheroidal球化处理:sheroidisation可锻铸铁:ductile cast iron石墨:graphite蠕墨铸铁:vermicular cast iron热处理:heat processing铝合金:Al-alloy熔炼:fusion metallurgy铜合金:copper alloy氢脆:hydrogen brittleness1.2 铸造方法(casting method)手工造型:hand moulding机器造型:machine moulding金属型:metal mold casting金属模:permanent mould压力铸造:press casting熔模铸造:investment moulding蜡膜:cere离心铸造:centrifugal casting低压铸造:casting under low pressure 差压铸造:counter-pressure casting 陶瓷型铸造:shaw process1.3 铸造工艺设计浇注位置:pouring position分型面:mould joint活块:loose piece起模:patter drawing型芯:core型芯撑:chaplet工艺参数:processing parameter下芯:core setting合型:mould assembly冒口:casting head尺寸公差:dimensional tolerance尺寸公差带:tolerance zone机械加工余量:machining allowance 铸孔:core hole非标准:nonstandard label收缩率:rate of contraction线收缩:linear contraction体收缩:volume contraction起模斜度:pattern draft铸造圆角:curving of castings芯头:core register芯头间隙:clearance芯座:core print seat分型线:joint line分模线:die parting line1.4 铸造结构工艺性加强筋:rib reinforcement撒砂:stuccoing内腔:entocoele2 金属塑性加工塑性加工:plastic working塑性:plastic property锻造:forge work冲压:punching轧制:rolling拉拔:drawing挤压:extruding细化晶粒:grain refinement 热锻:hit-forging温锻:warm forging2.1 金属塑性加工理论基础塑性变形:plastic yield加工硬化:work-hardening 韧性:ductility回复温度:return temperature 再结晶:recrystallize再结晶退火:full annealing 冷变形:cold deformation热变性:heat denaturation锻造比:forging ratio镦粗:upset拔长:pull out纤维组织:fibrous tissue锻造性能:forging property可锻性:forgeability变形抗力:resistance of deformation化学成分:chemical constitution热脆性:hot brittleness冷脆性:cold-shortness变形速度:deformation velocity应力状态:stress condition变形温度:deformation temperature过热:overheating过烧:burning脱碳:carbon elimination始锻温度:initiation forging temperature 终锻温度:final forging temperature 2.2 金属塑性加工方法自由锻:flat-die hammer冲孔:jetting弯曲:bend弯曲半径:bending radius切割:cut扭转:twist rotation错移:offsetting锻接:percussion基本工序:basic process辅助工序:auxiliary process精整工序:finishing process模锻:contour forging锻模:forging die胎膜锻:fetal membrane forging剪床:shearing machine冲床:backing-out punch冲裁:blanking弹性变形:elastic distortion塑性变形:plastic yield剪切变形:shearing deformation最小弯曲半径:minimum bending radius 曲率:angularity弯裂:rupture回弹:rebound辊轧:roll forming辊锻:roll forging斜轧:oblique rolling横轧:transverse rolling辗压:tamping drum挤压:extruding拉拔:draft2.3 塑性加工工艺设计工艺规程:process specification锻件图:forging drawing敷料:dressing锻件余量:forging allowance锻件公差:forging tolerance工夹具:clamping apparatus加热设备:firing equipment加热规范:heating schedule冷却规范:cooling schedule后续处理:after treatment分模面:die parting face冲孔连皮:punching the wad模锻斜度:draft angle圆角半径:radius of corner圆饼类锻件:circumcresent cake-like forging 长轴类锻件:long axis-like forging2.4 锻件结构工艺性锥体:cone斜面:cant空间曲线:curve in space粗糙度:degree of roughness2.5 冲压件结构工艺性3 焊接焊接:welding铆接:riverting熔焊:fusion welding压焊:press welding钎焊:braze welding3.1 焊接理论基础冶金:metallurgy电弧焊:arc welding气焊:acetylene welding电渣焊:electro-slag welding 高能束焊:high energy welding 电子焊:electronic welding激光焊:laser welding等离子焊:plasma welding电弧:electric arc阳极区:anode region阴极区:negative polarity弧柱区:arc stream正接法:electrode negative method反接法:opposition method脱氧剂:deoxidizing agent焊缝:welded seam焊缝区:weld zone熔合区:fusion area热影响区:heat-affected zone脆性断裂:brittle fracture过热区:overheated zone正火区:normalized zone相变区:phase change zone焊接应力:welding stress收缩变形:contraction distortion角变形:angular deformation弯曲变形:bend deformation扭曲变形:warping deformation波浪变形:wave transformation反变形法:reversible deformation method 刚性固定法:rigid fixing method预热:warming-up缓冷:slow cool焊后热处理:postweld heat treatment矫形处理:shape-righting3.2 焊接方法埋弧焊:hidden arc welding气体保护焊:gas shielded arc welding氩弧焊:argon welding熔化极氩弧焊:consumable electrode argon welding 钨极氩弧焊:argon tungsten-arc welding二氧化碳气体保护焊:CO2 gas shielded arc welding 碳弧焊:carbon arc welding碳弧气刨:carbon arc air gouging电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能焊:high grade energy welding等离子弧切割:plasma arc cutting (PAC)堆焊:bead weld电阻焊:resistance welding电焊:electric welding缝焊:seam welding压焊:press welding多点凸焊:multiple projection welding对焊:welding neck摩擦焊:friction welding扩散焊:diffusion welding硬钎料:brazing alloy软钎料:soft solder3.3 常用金属材料的焊接焊接性:weldability焊接方法:welding method 焊接材料:welding material 焊条:electrode焊剂:flux material碳素钢:carbon steel低碳钢:low carbon steel中碳钢:medium carbon steel 高碳钢:high carbon steel低合金钢:lean alloy steel不锈钢:non-corrosive steel 有色金属:nonferrous metal 3.4 焊接工艺设计型材:sectional bar药皮:coating焊丝:soldering wire连续焊缝:continuous weld断续焊缝:intermittent weld应力集中:stress concentration焊接接头:soldered joint坡口:groove对接:abutting joint搭接:lap joint角接:corner joint4 粉末冶金(power metallurgy)粉末冶金成品:finished power metallurgical product 铁氧体:ferrite硬质合金:sintered-carbide高熔点金属:high-melting metal陶瓷:ceramic4.1 粉末冶金工艺理论基础压坯:pressed compact扩散:diffusion烧结:agglomeration固溶:solid solubility化合:combination4.2 粉末冶金的工艺流程制备:preparation预处理:anticipation还原法:reduction method电解法:electrolytic method雾化法:atomization粒度:grain size松装密度:loose density流动性:flowing power压缩性:compressibility筛分:screen separation混合:compounding制粒:pelletization过烧:superburning欠烧:underburnt5 金属复合成型技术自蔓延焊接:SHS welding热等静压:HIP准热等静压:PHIP5.1 液态成型技术与固态成型技术的复合高压铸造:high-pressure casting电磁泵:magnetic-pump压射成型:injection molding柱塞:plunger piston冲头:drift pin凝固法:freezing method挤压法:extrusion method转向节:knuckle pivot制动器:arresting gear5.2 金属半凝固、半熔融成型技术凝固:freezing半熔融:semi-vitreous触变铸造:thixotropy casting触变锻造:thixotropy forging注射成型:injection molding5.3 其他金属成型新技术快速凝固:flash set非晶态:amorphous溢流法:press over system喷射沉积:ejecting deposit爆炸复合法:explosion cladding method 扩散焊接:diffusion welding挤压:extruding轧制:roll down6 非金属材料成型技术6.1 高分子材料成型技术高分子材料:non-metal material 耐腐蚀:resistant material绝缘:insulation老化:ageing耐热性:heat-durability粘弹性:viscoelasticity塑料:plastic material橡胶:rubber合成纤维:synthetic fibre涂料:covering material粘结剂:agglomerant粘度:viscosity热塑性塑料:thermoplastic plastics 热固性塑料:thermosetting plastic 通用塑料:general-purpose plastics 工程塑料:engineering plastic薄膜:thin film增强塑料:reinforced plastics浇注塑料:pouring plastics注射塑料:injiection plastics挤出塑料:extrusion plastics吹塑塑料:blowing plastics模压塑料:die pressing plastics聚合物:ploymer semiconductor吸湿性:hygroscopic cargo定向作用:directional action生胶:green glue stock填料:carrier丁苯橡胶:SBR顺丁橡胶:BR氯丁橡胶:CR丁腈橡胶:NBR硅橡胶:Q聚氨酯橡胶:U压延:calender硫化:sulfuration胶粘剂:adhesive胶接:glue joint刹车片:brake block零件修复:parts renewal蜂窝夹层:honeycomb core material 6.2 工业陶瓷制品的成型技术干燥:drying润滑剂:anti-friction结合剂:binder热压铸:hot injiection moulding 6.3 非金属材料成型技术的新进展热压烧结:hot pressed sintering7 复合材料的成型技术复合材料:composite material树脂:resin7.1 金属复合材料的成型技术硼纤维:boron fiber钛合金:titanium alloy碳纤维:carbon filter等离子喷涂:plasma spraying浸渍法:immersion method锭坯:ingot blank7.2 聚合物基复合材料的成型技术晶须:whisker缠绕成形:enwind forming湿法缠绕:wet method enwind 7.3 陶瓷复合材料成型技术溶胶-凝胶法:sol-gel method化学气相沉积:chemical vapor deposition (CVD) 原位:in situ8 材料成型方法的选择粉末冶金:powder metallurgy工程塑料:engineering plastics工程陶瓷:engineering ceramics。

材料成型工艺基础部分0 绪论金属材料:metal material (MR)高分子材料:high-molecular material陶瓷材料:ceramic material复合材料:composition material成形工艺:formation technology1 铸造铸造工艺:casting technique铸件:foundry goods (casting)机器零件:machine part毛坯:blank力学性能:mechanical property砂型铸造:sand casting process型砂:foundry sand1.1 铸件成形理论基础合金:alloy铸造性能:casting property工艺性能:processing property收缩性:constringency偏析性:aliquation氧化性:oxidizability吸气性:inspiratory铸件结构:casting structure使用性能:service performance浇不足:misrun冷隔:cold shut夹渣:cinder inclusion粘砂:sand fusion缺陷:flaw, defect, falling流动性:flowing power铸型:cast (foundry mold)蓄热系数:thermal storage capacity 浇注:pouring凝固:freezing收缩性:constringency逐层凝固:layer-by-layer freezing 糊状凝固:mushy freezing结晶:crystal缩孔:shrinkage void缩松:shrinkage porosity顺序凝固:progressive solidification 冷铁:iron chill补缩:feeding等温线法:constant temperature line method 内接圆法:inscribed circle method铸造应力:casting stress变形:deforming裂纹:crack机械应力:mechanical stress热应力:heat stress相变应力:transformation stress气孔:blow hole铸铁:ingot铸钢:cast steel非铁合金:nonferrous alloy灰铸铁:gray cast-iorn孕育处理:inoculation球墨铸铁:spheroidal球化处理:sheroidisation可锻铸铁:ductile cast iron石墨:graphite蠕墨铸铁:vermicular cast iron热处理:heat processing铝合金:Al-alloy熔炼:fusion metallurgy铜合金:copper alloy氢脆:hydrogen brittleness1.2 铸造方法(casting method)手工造型:hand moulding机器造型:machine moulding金属型:metal mold casting金属模:permanent mould压力铸造:press casting熔模铸造:investment moulding蜡膜:cere离心铸造:centrifugal casting低压铸造:casting under low pressure 差压铸造:counter-pressure casting 陶瓷型铸造:shaw process1.3 铸造工艺设计浇注位置:pouring position分型面:mould joint活块:loose piece起模:patter drawing型芯:core型芯撑:chaplet工艺参数:processing parameter下芯:core setting合型:mould assembly冒口:casting head尺寸公差:dimensional tolerance尺寸公差带:tolerance zone机械加工余量:machining allowance 铸孔:core hole非标准:nonstandard label收缩率:rate of contraction线收缩:linear contraction体收缩:volume contraction起模斜度:pattern draft铸造圆角:curving of castings芯头:core register芯头间隙:clearance芯座:core print seat分型线:joint line分模线:die parting line1.4 铸造结构工艺性加强筋:rib reinforcement撒砂:stuccoing内腔:entocoele2 金属塑性加工塑性加工:plastic working塑性:plastic property锻造:forge work冲压:punching轧制:rolling拉拔:drawing挤压:extruding细化晶粒:grain refinement 热锻:hit-forging温锻:warm forging2.1 金属塑性加工理论基础塑性变形:plastic yield加工硬化:work-hardening 韧性:ductility回复温度:return temperature 再结晶:recrystallize再结晶退火:full annealing 冷变形:cold deformation热变性:heat denaturation锻造比:forging ratio镦粗:upset拔长:pull out纤维组织:fibrous tissue锻造性能:forging property可锻性:forgeability变形抗力:resistance of deformation化学成分:chemical constitution热脆性:hot brittleness冷脆性:cold-shortness变形速度:deformation velocity应力状态:stress condition变形温度:deformation temperature过热:overheating过烧:burning脱碳:carbon elimination始锻温度:initiation forging temperature 终锻温度:final forging temperature 2.2 金属塑性加工方法自由锻:flat-die hammer冲孔:jetting弯曲:bend弯曲半径:bending radius切割:cut扭转:twist rotation错移:offsetting锻接:percussion基本工序:basic process辅助工序:auxiliary process精整工序:finishing process模锻:contour forging锻模:forging die胎膜锻:fetal membrane forging剪床:shearing machine冲床:backing-out punch冲裁:blanking弹性变形:elastic distortion塑性变形:plastic yield剪切变形:shearing deformation最小弯曲半径:minimum bending radius 曲率:angularity弯裂:rupture回弹:rebound辊轧:roll forming辊锻:roll forging斜轧:oblique rolling横轧:transverse rolling辗压:tamping drum挤压:extruding拉拔:draft2.3 塑性加工工艺设计工艺规程:process specification锻件图:forging drawing敷料:dressing锻件余量:forging allowance锻件公差:forging tolerance工夹具:clamping apparatus加热设备:firing equipment加热规范:heating schedule冷却规范:cooling schedule后续处理:after treatment分模面:die parting face冲孔连皮:punching the wad模锻斜度:draft angle圆角半径:radius of corner圆饼类锻件:circumcresent cake-like forging 长轴类锻件:long axis-like forging2.4 锻件结构工艺性锥体:cone斜面:cant空间曲线:curve in space粗糙度:degree of roughness2.5 冲压件结构工艺性3 焊接焊接:welding铆接:riverting熔焊:fusion welding压焊:press welding钎焊:braze welding3.1 焊接理论基础冶金:metallurgy电弧焊:arc welding气焊:acetylene welding电渣焊:electro-slag welding 高能束焊:high energy welding 电子焊:electronic welding激光焊:laser welding等离子焊:plasma welding电弧:electric arc阳极区:anode region阴极区:negative polarity弧柱区:arc stream正接法:electrode negative method反接法:opposition method脱氧剂:deoxidizing agent焊缝:welded seam焊缝区:weld zone熔合区:fusion area热影响区:heat-affected zone脆性断裂:brittle fracture过热区:overheated zone正火区:normalized zone相变区:phase change zone焊接应力:welding stress收缩变形:contraction distortion角变形:angular deformation弯曲变形:bend deformation扭曲变形:warping deformation波浪变形:wave transformation反变形法:reversible deformation method 刚性固定法:rigid fixing method预热:warming-up缓冷:slow cool焊后热处理:postweld heat treatment矫形处理:shape-righting3.2 焊接方法埋弧焊:hidden arc welding气体保护焊:gas shielded arc welding氩弧焊:argon welding熔化极氩弧焊:consumable electrode argon welding 钨极氩弧焊:argon tungsten-arc welding二氧化碳气体保护焊:CO2 gas shielded arc welding 碳弧焊:carbon arc welding碳弧气刨:carbon arc air gouging电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能焊:high grade energy welding等离子弧切割:plasma arc cutting (PAC)堆焊:bead weld电阻焊:resistance welding电焊:electric welding缝焊:seam welding压焊:press welding多点凸焊:multiple projection welding对焊:welding neck摩擦焊:friction welding扩散焊:diffusion welding硬钎料:brazing alloy软钎料:soft solder3.3 常用金属材料的焊接焊接性:weldability焊接方法:welding method 焊接材料:welding material 焊条:electrode焊剂:flux material碳素钢:carbon steel低碳钢:low carbon steel中碳钢:medium carbon steel 高碳钢:high carbon steel低合金钢:lean alloy steel不锈钢:non-corrosive steel 有色金属:nonferrous metal 3.4 焊接工艺设计型材:sectional bar药皮:coating焊丝:soldering wire连续焊缝:continuous weld断续焊缝:intermittent weld应力集中:stress concentration焊接接头:soldered joint坡口:groove对接:abutting joint搭接:lap joint角接:corner joint4 粉末冶金(power metallurgy)粉末冶金成品:finished power metallurgical product 铁氧体:ferrite硬质合金:sintered-carbide高熔点金属:high-melting metal陶瓷:ceramic4.1 粉末冶金工艺理论基础压坯:pressed compact扩散:diffusion烧结:agglomeration固溶:solid solubility化合:combination4.2 粉末冶金的工艺流程制备:preparation预处理:anticipation还原法:reduction method电解法:electrolytic method雾化法:atomization粒度:grain size松装密度:loose density流动性:flowing power压缩性:compressibility筛分:screen separation混合:compounding制粒:pelletization过烧:superburning欠烧:underburnt5 金属复合成型技术自蔓延焊接:SHS welding热等静压:HIP准热等静压:PHIP5.1 液态成型技术与固态成型技术的复合高压铸造:high-pressure casting电磁泵:magnetic-pump压射成型:injection molding柱塞:plunger piston冲头:drift pin凝固法:freezing method挤压法:extrusion method转向节:knuckle pivot制动器:arresting gear5.2 金属半凝固、半熔融成型技术凝固:freezing半熔融:semi-vitreous触变铸造:thixotropy casting触变锻造:thixotropy forging注射成型:injection molding5.3 其他金属成型新技术快速凝固:flash set非晶态:amorphous溢流法:press over system喷射沉积:ejecting deposit爆炸复合法:explosion cladding method 扩散焊接:diffusion welding挤压:extruding轧制:roll down6 非金属材料成型技术6.1 高分子材料成型技术高分子材料:non-metal material 耐腐蚀:resistant material绝缘:insulation老化:ageing耐热性:heat-durability粘弹性:viscoelasticity塑料:plastic material橡胶:rubber合成纤维:synthetic fibre涂料:covering material粘结剂:agglomerant粘度:viscosity热塑性塑料:thermoplastic plastics 热固性塑料:thermosetting plastic 通用塑料:general-purpose plastics 工程塑料:engineering plastic薄膜:thin film增强塑料:reinforced plastics浇注塑料:pouring plastics注射塑料:injiection plastics挤出塑料:extrusion plastics吹塑塑料:blowing plastics模压塑料:die pressing plastics聚合物:ploymer semiconductor吸湿性:hygroscopic cargo定向作用:directional action生胶:green glue stock填料:carrier丁苯橡胶:SBR顺丁橡胶:BR氯丁橡胶:CR丁腈橡胶:NBR硅橡胶:Q聚氨酯橡胶:U压延:calender硫化:sulfuration胶粘剂:adhesive胶接:glue joint刹车片:brake block零件修复:parts renewal蜂窝夹层:honeycomb core material 6.2 工业陶瓷制品的成型技术干燥:drying润滑剂:anti-friction结合剂:binder热压铸:hot injiection moulding 6.3 非金属材料成型技术的新进展热压烧结:hot pressed sintering7 复合材料的成型技术复合材料:composite material树脂:resin7.1 金属复合材料的成型技术硼纤维:boron fiber钛合金:titanium alloy碳纤维:carbon filter等离子喷涂:plasma spraying浸渍法:immersion method锭坯:ingot blank7.2 聚合物基复合材料的成型技术晶须:whisker缠绕成形:enwind forming湿法缠绕:wet method enwind 7.3 陶瓷复合材料成型技术溶胶-凝胶法:sol-gel method化学气相沉积:chemical vapor deposition (CVD) 原位:in situ8 材料成型方法的选择粉末冶金:powder metallurgy工程塑料:engineering plastics工程陶瓷:engineering ceramics。

复合材料注射成型工艺
复合材料注射成型工艺是一种将纤维增强树脂复合材料注射到模具中,通过加热和压力使其固化形成所需的产品或零件的制造方法。
以下是复合材料注射成型工艺的一般步骤:
1. 材料准备:选择适当的纤维和树脂,并按照特定的配比进行混合和预处理。
2. 模具设计和制造:根据产品或零件的要求,设计和制造出适应的模具。
3. 模具准备:在开始注射成型之前,需要对模具进行准备,如涂抹模具表面的防粘剂,以确保成品的顺利脱模。
4. 注射成型:将预处理好的纤维增强树脂复合材料通过注射机注入到模具的空腔中。
注射时,可以施加一定的压力来促进树脂充填和纤维排列。
5. 固化:注射完成后,通过加热和固化剂等方式,使树脂快速固化。
固化过程中,可以控制温度、压力和时间等参数,以确保复合材料的质量。
6. 脱模和后处理:在树脂固化完全后,打开模具并取出成品。
根据需要进行修整、修边、打磨等后处理工序,以达到最终的产品要求。
复合材料注射成型工艺具有高效率、自动化程度高、产品质量稳定等优点,广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、电子、体育用品等领域的零部件制造中。
1。

金属粉末注射成型技术金属粉末注射成型(Metal Powder Injection Molding,简称MIM)是一种先进的金属加工技术,将金属粉末与有机粘结剂混合,经过注射成型、脱脂和烧结等多个工艺步骤,最终制造出高精度、复杂形状的金属零件。
MIM技术结合了传统的塑胶注射成型和粉末冶金工艺,可以在一次制造过程中实现高效的生产。
MIM技术的关键步骤是粉末的混合与注射成型。
首先,将金属粉末与有机粘结剂按一定比例混合,并进行干燥处理,确保粉末颗粒均匀分散。
然后,将混合物装入注射机中,通过高压将混合物注入到预先制作好的模具中。
注射成型后,零件进入下一步的脱脂处理。
脱脂是将注射成型后的零件中的有机粘结剂去除的过程。
通常使用热解脱脂方法,在高温下将有机粘结剂热解,通过挥发、分解等反应将其去除。
脱脂后的零件称为绿体,其具有一定的强度和形状稳定性。
接下来是烧结过程,即将脱脂后的绿体加热到金属粉末熔点以上,使粉末颗粒间相互结合,形成致密的金属零件。
烧结过程通过控制温度和时间,可以调节零件的致密度和性能。
烧结后的金属件通常还需要进行表面处理,如抛光、镀层等,以提高其表面质量和耐腐蚀性。
MIM技术具有以下几个优点:1.高精度:MIM技术可以制造出精度高、尺寸稳定的零件,其精度可以达到0.1%。
2.复杂形状:相比于传统的金属加工方法,MIM技术能够制造出更为复杂的形状,如螺纹、齿轮、细小结构等。
3.省材料:MIM技术可以最大限度地利用金属粉末,减少了废料产生,节约了原材料成本。
4.高效率:MIM技术能够一次成形多个零件,大大提高了生产效率。
而且由于是批量生产,可以降低单件成本。
MIM技术在很多领域都有广泛的应用,包括电子、汽车、医疗器械、航空航天等。
例如,在电子领域,MIM技术可以用于制造微型连接器、导电部件等;在汽车领域,可以制造发动机零件、传动系统零件等。
MIM技术还被广泛应用于医疗器械制造,如人工关节、牙科种植器械等。

金属注射成型综述要点金属注射成型(MIM)是一种通过将金属粉末与塑料注射成型技术相结合的新型金属加工方法。
它以其高效率、高精度和复杂形状制造能力而受到广泛关注。
本文将对金属注射成型技术的原理、工艺流程、优点和应用领域等进行综述。
1.技术原理金属注射成型是将金属粉末与有机聚合物混合后,在高温下进行塑性加工。
首先,将金属粉末与粘结剂混合,形成金属粉末/粘结剂浆料。
然后,通过注射成型机将该浆料注入金属注射模具中。
在注射模具中,通过压力和温度的作用,金属粉末与粘结剂烧结成型。
最后,通过去除粘结剂和烧结金属零件的后处理工艺,获得最终的金属注射成型零件。
2.工艺流程金属注射成型的工艺流程主要包括:原料准备、混合、注射成型、脱脂、烧结和后处理。
在原料准备阶段,需要准备金属粉末、粘结剂和其他辅助材料。
混合阶段是将金属粉末与粘结剂混合,并形成浆料。
注射成型阶段将浆料注入金属注射模具中,并在高温下进行塑性变形。
脱脂阶段是将注射成型的零件在高温下去除粘结剂。
烧结阶段是将零件在高温下烧结,以实现金属颗粒的结合和形状的固定。
最后,通过后处理工艺,如表面处理、加工和涂装等,得到最终的金属注射成型零件。
3.优点(1)高精度:金属注射成型可以制造出复杂形状的零件,并且具有高精度和低尺寸偏差。
(2)高效率:金属注射成型可以通过注射成型机实现大规模的连续生产,提高生产效率。
(3)材料利用率高:金属注射成型可以利用可回收的金属粉末制造零件,减少材料浪费。
(4)节省成本:金属注射成型可以减少后续加工工序,节省制造成本。
(5)材料性能优良:金属注射成型所制造的零件具有高密度、均匀组织和优良的机械性能。
4.应用领域金属注射成型技术已广泛应用于汽车、医疗器械、电子设备、航天航空等领域。
在汽车行业中,金属注射成型可以制造出发动机零件、变速器零件和车身零件等。
在医疗器械领域,金属注射成型可以制造出植入物、外科器械和牙科器械等。
在电子设备领域,金属注射成型可以制造出连接器、插头和传感器等。
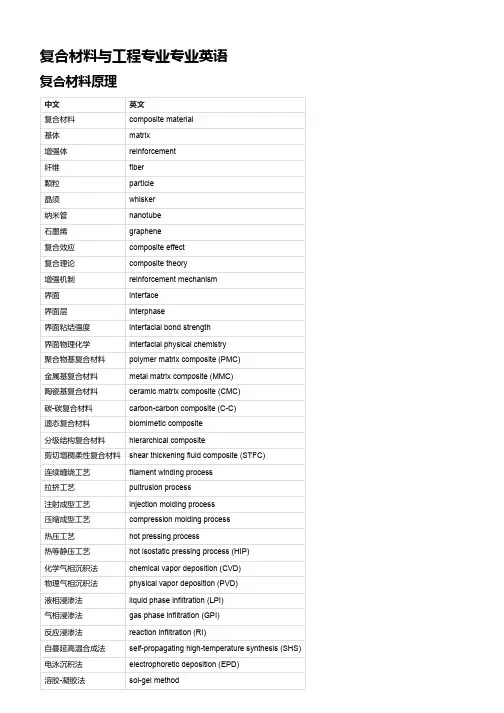
复合材料与工程专业专业英语复合材料原理中文英文复合材料composite material基体matrix增强体reinforcement纤维fiber颗粒particle晶须whisker纳米管nanotube石墨烯graphene复合效应composite effect复合理论composite theory增强机制reinforcement mechanism界面interface界面层interphase界面粘结强度interfacial bond strength界面物理化学interfacial physical chemistry聚合物基复合材料polymer matrix composite (PMC)金属基复合材料metal matrix composite (MMC)陶瓷基复合材料ceramic matrix composite (CMC)碳-碳复合材料carbon-carbon composite (C-C)遗态复合材料biomimetic composite分级结构复合材料hierarchical composite剪切增稠柔性复合材料shear thickening fluid composite (STFC)连续缠绕工艺filament winding process拉挤工艺pultrusion process注射成型工艺injection molding process压缩成型工艺compression molding process热压工艺hot pressing process热等静压工艺hot isostatic pressing process (HIP)化学气相沉积法chemical vapor deposition (CVD)物理气相沉积法physical vapor deposition (PVD)液相浸渗法liquid phase infiltration (LPI)气相浸渗法gas phase infiltration (GPI)反应浸渗法reaction infiltration (RI)自蔓延高温合成法self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS)电泳沉积法electrophoretic deposition (EPD)溶胶-凝胶法sol-gel method复合材料工艺中文英文复合材料工艺学composite material processing science复合材料加工技术composite material processing technology复合材料成型方法composite material forming method复合材料固化方法composite material curing method复合材料后处理方法composite material post-processing method复合材料接头技术composite material joint technology复合材料修复技术composite material repair technology复合材料表面处理技术composite material surface treatment technology复合材料工艺参数composite material process parameters复合材料工艺性能composite material process performance复合材料工艺缺陷composite material process defects复合材料工艺模拟composite material process simulation复合材料工艺优化composite material process optimization手糊法hand lay-up method喷射成型法spray-up method真空吸附法vacuum bagging method自动糊层机法automatic tape laying method (ATL)自动纤维放置法automated fiber placement method (AFP)树脂传输成型法resin transfer molding method (RTM)树脂膜层叠加成型法resin film infusion method (RFI)真空辅助树脂传输成型法vacuum assisted resin transfer molding method (VARTM)真空辅助树脂注射成型法vacuum assisted resin injection molding method (VARI)树脂浸渍拉挤成型法resin impregnation pultrusion method树脂浸渍缠绕成型法resin impregnation winding method树脂浸渍编织成型法resin impregnation weaving method预浸料成型法prepreg molding method预浸料自动糊层机法prepreg automatic tape laying method预浸料自动纤维放置法prepreg automated fiber placement method预浸料真空吸附法prepreg vacuum bagging method预浸料热压成型法prepreg hot pressing method预浸料热等静压成型法prepreg hot isostatic pressing method预浸料自动模具线成型法prepreg automatic mold line method (AML)模塑复合材料成型法molded compound molding method压缩模塑复合材料成型法compression molded compound molding method注射模塑复合材料成型法injection molded compound molding method转移模塑复合材料成型法transfer molded compound molding method挤出模塑复合材料成型法extrusion molded compound molding method热解复合材料制备方法pyrolysis composite preparation method复合材料结构设计中文英文复合材料结构设计composite material structural design复合材料结构分析composite material structural analysis复合材料结构优化composite material structural optimization复合材料结构可靠性composite material structural reliability复合材料结构失效模式composite material structural failure mode复合材料结构失效准则composite material structural failure criterion复合材料结构强度composite material structural strength复合材料结构刚度composite material structural stiffness复合材料结构稳定性composite material structural stability复合材料结构疲劳性能composite material structural fatigue performance 复合材料结构断裂韧性composite material structural fracture toughness 复合材料结构损伤容限composite material structural damage tolerance复合材料层合板composite material laminate复合材料夹层板composite material sandwich panel复合材料桁架composite material truss复合材料梁composite material beam复合材料板壳composite material plate-shell复合材料管壳composite material tube-shell复合材料网格壳composite material grid-shell复合材料蜂窝板composite material honeycomb panel纤维方向角fiber orientation angle层厚比thickness ratio层间剪切模量interlaminar shear modulus层间剪切强度interlaminar shear strength层间正应力强度因子interlaminar normal stress intensity factor层间剪应力强度因子interlaminar shear stress intensity factor层间断裂韧度interlaminar fracture toughness层间脱层interlaminar delamination层间裂纹扩展速率interlaminar crack propagation rate层间裂纹扩展阻力曲线interlaminar crack resistance curve (R-curve)层内应力分布intralaminar stress distribution层内应变分布intralaminar strain distribution层内失效模式intralaminar failure mode层内失效准则intralaminar failure criterion复合材料力学中文英文复合材料力学composite material mechanics复合材料弹性理论composite material elasticity theory复合材料弹塑性理论composite material elasto-plasticity theory复合材料粘弹性理论composite material viscoelasticity theory复合材料热弹性理论composite material thermoelasticity theory复合材料非线性力学composite material nonlinear mechanics复合材料动力学composite material dynamics复合材料疲劳力学composite material fatigue mechanics复合材料断裂力学composite material fracture mechanics复合材料损伤力学composite material damage mechanics复合材料微观力学composite material micromechanics复合材料宏观力学composite material macromechanics复合材料多尺度力学composite material multiscale mechanics复合材料本构关系composite material constitutive relation复合材料本构方程composite material constitutive equation复合材料本构模型composite material constitutive model复合材料本构参数composite material constitutive parameter复合材料本构参数识别方法composite material constitutive parameter identification method纤维增强复合材料单元细胞模型fiber reinforced composite unit cell model纤维增强复合材料等效模量计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent modulus calculation method纤维增强复合材料等效泊松比计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent poisson ratio calculation method纤维增强复合材料等效热膨胀系数计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent thermal expansion coefficient calculation method纤维增强复合材料等效热导率计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent thermal conductivity calculation method 纤维增强复合材料等效电导率计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent electrical conductivity calculation method 纤维增强复合材料等效介电常数计算方法fiber reinforced composite equivalent dielectric constant calculation method 颗粒增强复合材料单元细胞模型particle reinforced composite unit cell model颗粒增强复合材料等效模量计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent modulus calculation method颗粒增强复合材料等效泊松比计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent poisson ratio calculation method颗粒增强复合材料等效热膨胀系数计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent thermal expansion coefficient calculation method颗粒增强复合材料等效热导率计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent thermal conductivity calculation method 颗粒增强复合材料等效电导率计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent electrical conductivity calculation method 颗粒增强复合材料等效介电常数计算方法particle reinforced composite equivalent dielectric constant calculation method 晶须增强复合材料单元细胞模型whisker reinforced composite unit cell model晶须增强复合材料等效模量计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent modulus calculation method晶须增强复合材料等效泊松比计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent poisson ratio calculation method晶须增强复合材料等效热膨胀系数计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent thermal expansion coefficient calculation method晶须增强复合材料等效热导率计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent thermal conductivity calculation method 晶须增强复合材料等效电导率计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent electrical conductivity calculation method晶须增强复合材料等效介电常数计算方法whisker reinforced composite equivalent dielectric constant calculation method 纳米复合材料中文英文纳米复合材料nanocomposite material纳米粒子nanoparticle纳米纤维nanofiber纳米管nanotube纳米线nanowire纳米带nanoribbon纳米棒nanorod纳米片nanosheet纳米球nanosphere纳米星nanostar纳米花nanoflower纳米棘轮nanoratchet纳米泡沫nanofoam纳米多孔材料nanoporous material纳米气凝胶nanoaerogel纳米海绵nanosponge纳米网格nanogrid纳米蜂窝结构nanohoneycomb structure纳米层状结构nanolayered structure纳米纤维素复合材料nanocellulose composite material石墨烯复合材料graphene composite material二维纳米材料复合材料two-dimensional nanomaterial composite material量子点复合材料quantum dot composite material全息纳米复合材料holographic nanocomposite material超分子纳米复合材料supramolecular nanocomposite material生物医用复合材料中文英文生物医用复合材料biomedical composite material生物相容性biocompatibility生物降解性biodegradability生物吸收性bioabsorbability生物活性bioactivity生物力学性能biomechanical performance生物功能化biofunctionalization药物缓释drug delivery组织工程tissue engineering骨组织工程bone tissue engineering软骨组织工程cartilage tissue engineering皮肤组织工程skin tissue engineering神经组织工程nerve tissue engineering血管组织工程vascular tissue engineering心脏组织工程cardiac tissue engineering肝脏组织工程liver tissue engineering肾脏组织工程kidney tissue engineering胰腺组织工程pancreas tissue engineering肺组织工程lung tissue engineering骨水泥复合材料bone cement composite material骨替代材料复合材料bone substitute material composite material 骨修复板复合材料bone fixation plate composite material骨钉复合材料bone screw composite material骨髓钉复合材料bone nail composite material骨髓钉复合材料bone nail composite material人工关节复合材料artificial joint composite material人工韧带复合材料artificial ligament composite material人工心脏瓣膜复合材料artificial heart valve composite material人工血管复合材料artificial blood vessel composite material 人工角膜复合材料artificial cornea composite material人工耳蜗复合材料artificial cochlea composite material人工牙齿复合材料artificial tooth composite material人工皮肤复合材料artificial skin composite material人工肝脏复合材料artificial liver composite material复合材料测试与评价中文英文复合材料测试与评价composite material testing and evaluation复合材料测试方法composite material testing method复合材料测试标准composite material testing standard复合材料测试仪器composite material testing instrument复合材料测试数据composite material testing data复合材料测试结果composite material testing result复合材料测试分析composite material testing analysis复合材料评价方法composite material evaluation method复合材料评价指标composite material evaluation index复合材料评价模型composite material evaluation model复合材料评价系统composite material evaluation system复合材料评价报告composite material evaluation report静态力学性能测试static mechanical performance test动态力学性能测试dynamic mechanical performance test疲劳性能测试fatigue performance test断裂性能测试fracture performance test热性能测试thermal performance test电性能测试electrical performance test光学性能测试optical performance test磁学性能测试magnetic performance test磁学性能测试magnetic performance test损伤性能测试damage performance test环境适应性能测试environmental adaptability performance test 耐腐蚀性能测试corrosion resistance performance test耐磨性能测试wear resistance performance test耐老化性能测试aging resistance performance test耐辐射性能测试radiation resistance performance test耐火性能测试fire resistance performance test耐水性能测试water resistance performance test耐化学品性能测试chemical resistance performance test。

一、实训背景随着我国经济和科技的快速发展,复合材料因其优异的性能和广泛的应用领域,逐渐成为我国新材料领域的研究热点。
为了提高我国复合材料成型技术水平和人才素质,培养具备实际操作能力的复合型技术人才,我校特开设了复合材料成型实训课程。
本实训课程旨在让学生了解复合材料的基本原理、成型工艺以及实际操作技能,提高学生的动手能力和综合素质。
二、实训目的1. 了解复合材料的基本原理、组成和性能;2. 掌握复合材料成型工艺的基本知识和操作技能;3. 培养学生的实际操作能力和团队协作精神;4. 提高学生的创新意识和综合素质。
三、实训内容1. 复合材料基础知识:讲解复合材料的基本原理、组成、性能、分类及应用领域等。
2. 复合材料成型工艺:介绍手糊成型、喷射成型、树脂传递模塑成型、袋压法、真空袋压成型、热压罐成型、液压釜法成型、热膨胀模塑法成型、夹层结构成型、模压料生产工艺、ZMC模压料注射技术、模压成型工艺、层合板生产技术、卷制管成型技术、纤维缠绕制品成型技术、连续制板生产工艺、浇铸成型技术、拉挤成型工艺、连续缠绕制管工艺、编织复合材料制造技术、热塑性片状模塑料制造技术及冷模冲压成型工艺、注射成型工艺、挤出成型工艺、离心浇铸制管成型工艺等。
3. 实际操作:学生在指导下进行复合材料成型操作,包括材料准备、模具设计、铺层、固化、脱模等环节。
4. 成型工艺优化:通过分析实验数据,优化成型工艺参数,提高复合材料制品的性能。
5. 成型设备操作:学习复合材料成型设备的使用方法和注意事项。
四、实训成果1. 学生对复合材料的基本原理、组成、性能和成型工艺有了深入的了解;2. 学生的实际操作能力得到提高,能够独立完成复合材料成型操作;3. 学生的团队协作精神得到锻炼,能够与他人共同完成实验任务;4. 学生的创新意识得到培养,能够提出优化成型工艺的建议。
五、实训体会1. 复合材料成型工艺是一门综合性很强的课程,涉及材料科学、力学、化学等多个学科;2. 实践是检验真理的唯一标准,通过实际操作,我们才能更好地掌握复合材料成型技术;3. 团队协作精神在实训过程中至关重要,只有大家共同努力,才能完成实验任务;4. 创新意识是提高复合材料成型技术的重要途径,我们要不断探索,寻求更好的成型工艺。

金属粉末注射成型金属粉末注射成型(Metal Powder Injection Molding,简称MIM)是一种高效、精确和经济的金属加工技术。
它结合了传统的塑料注射成型和金属粉末冶金工艺,可以生产出复杂形状的金属部件。
MIM技术在汽车、医疗、航空航天等行业中得到广泛应用,本文将介绍MIM的工艺原理、材料选择和应用领域。
MIM工艺原理可以分为四个步骤:混合、注射、脱模和烧结。
首先,将金属粉末与聚合物粉末、脱模剂等混合,并将其加热到高温使其熔化。
然后,将熔融的混合物喷射到模具中,形成所需的部件形状。
接下来,通过在高温和高压下使部件凝固,并将其从模具中取出。
最后,在高温下进行烧结,以消除聚合物,并在金属颗粒之间形成冶金结合。
在MIM中,材料选择是关键。
常用的金属材料包括不锈钢、工具钢、硬质合金、钻石等。
不锈钢具有良好的韧性和耐腐蚀性,常用于制造医疗器械、手表零件等高精度部件。
工具钢具有高强度和耐磨性,常用于制造汽车零部件、工具等。
硬质合金具有高硬度和耐磨性,常用于制造切削工具、注射模具等。
钻石是一种具有超硬性和导热性的材料,常用于制造高性能刀具。
MIM技术具有许多优点。
首先,MIM可以生产出复杂形状的部件,减少了后续加工的需要。
其次,MIM可以实现批量生产,提高了生产效率。
再次,MIM可以生产出高密度的部件,具有良好的力学性能和表面质量。
此外,MIM工艺还可以减少材料的浪费,提高了资源利用率。
MIM技术在许多领域中得到了广泛的应用。
在汽车行业中,MIM可以制造各种复杂形状的汽车零部件,如发动机零件、制动系统零件等。
在医疗行业中,MIM可以制造高精度医疗器械,如人工关节、牙科器械等。
在航空航天行业中,MIM可以制造轻量化部件,提高了飞机的燃油效率。
此外,MIM还可以应用于电子、军工等领域。
总之,金属粉末注射成型是一种高效、精确和经济的金属加工技术。
通过在MIM中选择合适的材料和工艺参数,可以生产出各种复杂形状的金属部件,并在汽车、医疗、航空航天等行业中得到广泛应用。
金属粉末冶金注射成型技术金属粉末冶金注射成型技术(Metal Powder Injection Molding,简称MIM)是近年来快速发展起来的一种先进的粉末冶金成形工艺。
它将金属粉末与有机蜡粉通过混合、热塑性制品注射成型、脱蜡、烧结等步骤制作成金属零件。
MIM技术具有成型精度高、加工复杂度高、生产效率高等优点,并且可以制造出形状复杂、尺寸精确的金属零部件,已经在汽车、电子、医疗器械等领域得到广泛应用。
金属粉末冶金注射成型技术的工艺流程主要包括:粉末配方、混合、成型、脱蜡、烧结和后处理。
首先,根据要生产的零件的要求选择合适的金属材料,对金属粉末进行配方,以获得所需的物理和化学性能。
然后,将金属粉末和有机蜡粉混合均匀,形成金属粉末和有机蜡的复合物料。
复合物料经过精密注射成型机注射到塑料型腔中,通过注射压力和模具温度的控制,使金属粉末和有机蜡混合物充分填充型腔,并形成零件的初始形状。
注射成型后,将模具中的零件放入脱蜡设备中进行脱蜡处理。
在脱蜡过程中,通过加热使有机蜡融化和蒸发,从而获得完全密实的金属粉末成型件。
然后,将脱蜡后的零件置入烧结炉中进行烧结处理。
在烧结过程中,通过控制炉内温度和气氛,使金属粉末颗粒相互结合,获得致密的金属零部件。
最后,对烧结后的零件进行后处理,如机械加工、热处理、表面处理等,以获得所需的工程性能和外观质量。
MIM技术的优势主要体现在以下几个方面:首先,MIM技术可以制造出形状复杂、尺寸精确的金属零部件,可以实现传统加工方法难以实现的形状和结构。
其次,MIM技术具有高度的自动化程度,生产效率高,能够大规模、高效率地生产金属零件。
再次,MIM的制造工艺具有较好的重复性和稳定性,能够确保产品的质量和性能的稳定性。
此外,MIM还可以利用强化纤维等增强材料提高零件的力学性能。
当前,MIM技术已经应用于广泛的领域。
在汽车行业,MIM技术可以用于制造汽车的发动机支架、齿轮、离合器等零部件;在电子行业,MIM技术可以用于制造手机、电视等电子产品的外壳、连接器等零部件;在医疗器械领域,MIM技术可以制造手术钳、植入物等高精度、高性能的医疗器械部件。
材料成型工艺基础部分0 绪论金属材料:metal material (MR)高分子材料:high-molecular material陶瓷材料:ceramic material复合材料:composition material成形工艺:formation technology1 铸造铸造工艺:casting technique铸件:foundry goods (casting)机器零件:machine part毛坯:blank力学性能:mechanical property砂型铸造:sand casting process型砂:foundry sand1.1 铸件成形理论基础合金:alloy铸造性能:casting property工艺性能:processing property收缩性:constringency偏析性:aliquation氧化性:oxidizability吸气性:inspiratory铸件结构:casting structure使用性能:service performance浇不足:misrun冷隔:cold shut夹渣:cinder inclusion粘砂:sand fusion缺陷:flaw, defect, falling流动性:flowing power铸型:cast (foundry mold)蓄热系数:thermal storage capacity 浇注:pouring凝固:freezing收缩性:constringency逐层凝固:layer-by-layer freezing糊状凝固:mushy freezing结晶:crystal缩孔:shrinkage void缩松:shrinkage porosity顺序凝固:progressive solidification 冷铁:iron chill补缩:feeding等温线法:constant temperature line method 内接圆法:inscribed circle method铸造应力:casting stress变形:deforming裂纹:crack机械应力:mechanical stress热应力:heat stress相变应力:transformation stress气孔:blow hole铸铁:ingot铸钢:cast steel非铁合金:nonferrous alloy灰铸铁:gray cast-iorn孕育处理:inoculation球墨铸铁:spheroidal球化处理:sheroidisation可锻铸铁:ductile cast iron石墨:graphite蠕墨铸铁:vermicular cast iron热处理:heat processing铝合金:Al-alloy熔炼:fusion metallurgy铜合金:copper alloy氢脆:hydrogen brittleness1.2 铸造方法(casting method)手工造型:hand moulding机器造型:machine moulding金属型:metal mold casting金属模:permanent mould压力铸造:press casting熔模铸造:investment moulding蜡膜:cere离心铸造:centrifugal casting低压铸造:casting under low pressure 差压铸造:counter-pressure casting 陶瓷型铸造:shaw process1.3 铸造工艺设计浇注位置:pouring position分型面:mould joint活块:loose piece起模:patter drawing型芯:core型芯撑:chaplet工艺参数:processing parameter下芯:core setting合型:mould assembly冒口:casting head尺寸公差:dimensional tolerance 尺寸公差带:tolerance zone机械加工余量:machining allowance 铸孔:core hole非标准:nonstandard label收缩率:rate of contraction线收缩:linear contraction体收缩:volume contraction起模斜度:pattern draft铸造圆角:curving of castings芯头:core register芯头间隙:clearance芯座:core print seat分型线:joint line分模线:die parting line1.4 铸造结构工艺性加强筋:rib reinforcement撒砂:stuccoing内腔:entocoele2 金属塑性加工塑性加工:plastic working塑性:plastic property锻造:forge work冲压:punching轧制:rolling拉拔:drawing挤压:extruding细化晶粒:grain refinement 热锻:hit-forging温锻:warm forging2.1 金属塑性加工理论基础塑性变形:plastic yield加工硬化:work-hardening韧性:ductility回复温度:return temperature 再结晶:recrystallize再结晶退火:full annealing 冷变形:cold deformation热变性:heat denaturation锻造比:forging ratio镦粗:upset拔长:pull out纤维组织:fibrous tissue锻造性能:forging property可锻性:forgeability变形抗力:resistance of deformation化学成分:chemical constitution热脆性:hot brittleness冷脆性:cold-shortness变形速度:deformation velocity应力状态:stress condition变形温度:deformation temperature过热:overheating过烧:burning脱碳:carbon elimination始锻温度:initiation forging temperature 终锻温度:final forging temperature2.2 金属塑性加工方法自由锻:flat-die hammer冲孔:jetting弯曲:bend弯曲半径:bending radius切割:cut扭转:twist rotation错移:offsetting锻接:percussion基本工序:basic process辅助工序:auxiliary process精整工序:finishing process模锻:contour forging锻模:forging die胎膜锻:fetal membrane forging剪床:shearing machine冲床:backing-out punch冲裁:blanking弹性变形:elastic distortion塑性变形:plastic yield剪切变形:shearing deformation最小弯曲半径:minimum bending radius 曲率:angularity弯裂:rupture回弹:rebound辊轧:roll forming辊锻:roll forging斜轧:oblique rolling横轧:transverse rolling辗压:tamping drum挤压:extruding拉拔:draft2.3 塑性加工工艺设计工艺规程:process specification锻件图:forging drawing敷料:dressing锻件余量:forging allowance锻件公差:forging tolerance工夹具:clamping apparatus加热设备:firing equipment加热规范:heating schedule冷却规范:cooling schedule后续处理:after treatment分模面:die parting face冲孔连皮:punching the wad模锻斜度:draft angle圆角半径:radius of corner圆饼类锻件:circumcresent cake-like forging 长轴类锻件:long axis-like forging2.4 锻件结构工艺性锥体:cone斜面:cant空间曲线:curve in space粗糙度:degree of roughness2.5 冲压件结构工艺性3 焊接焊接:welding铆接:riverting熔焊:fusion welding压焊:press welding钎焊:braze welding3.1 焊接理论基础冶金:metallurgy电弧焊:arc welding气焊:acetylene welding电渣焊:electro-slag welding 高能束焊:high energy welding 电子焊:electronic welding激光焊:laser welding等离子焊:plasma welding电弧:electric arc阳极区:anode region阴极区:negative polarity弧柱区:arc stream正接法:electrode negative method反接法:opposition method脱氧剂:deoxidizing agent焊缝:welded seam焊缝区:weld zone熔合区:fusion area热影响区:heat-affected zone脆性断裂:brittle fracture过热区:overheated zone正火区:normalized zone相变区:phase change zone焊接应力:welding stress收缩变形:contraction distortion角变形:angular deformation弯曲变形:bend deformation扭曲变形:warping deformation波浪变形:wave transformation反变形法:reversible deformation method 刚性固定法:rigid fixing method预热:warming-up缓冷:slow cool焊后热处理:postweld heat treatment矫形处理:shape-righting3.2 焊接方法埋弧焊:hidden arc welding气体保护焊:gas shielded arc welding氩弧焊:argon welding熔化极氩弧焊:consumable electrode argon welding 钨极氩弧焊:argon tungsten-arc welding二氧化碳气体保护焊:CO2 gas shielded arc welding 碳弧焊:carbon arc welding碳弧气刨:carbon arc air gouging电渣焊:electro-slag welding高能焊:high grade energy welding等离子弧切割:plasma arc cutting (PAC)堆焊:bead weld电阻焊:resistance welding电焊:electric welding缝焊:seam welding压焊:press welding多点凸焊:multiple projection welding对焊:welding neck摩擦焊:friction welding扩散焊:diffusion welding 硬钎料:brazing alloy软钎料:soft solder3.3 常用金属材料的焊接焊接性:weldability焊接方法:welding method焊接材料:welding material 焊条:electrode焊剂:flux material碳素钢:carbon steel低碳钢:low carbon steel中碳钢:medium carbon steel 高碳钢:high carbon steel 低合金钢:lean alloy steel 不锈钢:non-corrosive steel 有色金属:nonferrous metal 3.4 焊接工艺设计型材:sectional bar药皮:coating焊丝:soldering wire连续焊缝:continuous weld断续焊缝:intermittent weld应力集中:stress concentration焊接接头:soldered joint坡口:groove对接:abutting joint搭接:lap joint角接:corner joint4 粉末冶金(power metallurgy)粉末冶金成品:finished power metallurgical product 铁氧体:ferrite硬质合金:sintered-carbide高熔点金属:high-melting metal陶瓷:ceramic4.1 粉末冶金工艺理论基础压坯:pressed compact扩散:diffusion烧结:agglomeration固溶: solid solubility化合:combination4.2 粉末冶金的工艺流程制备:preparation预处理:anticipation还原法:reduction method电解法:electrolytic method雾化法:atomization粒度:grain size松装密度:loose density流动性:flowing power压缩性:compressibility筛分:screen separation混合:compounding制粒:pelletization过烧:superburning欠烧:underburnt5 金属复合成型技术自蔓延焊接:SHS welding热等静压:HIP准热等静压:PHIP5.1 液态成型技术与固态成型技术的复合高压铸造:high-pressure casting电磁泵:magnetic-pump压射成型:injection molding柱塞:plunger piston冲头:drift pin凝固法:freezing method挤压法:extrusion method转向节:knuckle pivot制动器:arresting gear5.2 金属半凝固、半熔融成型技术凝固:freezing半熔融:semi-vitreous触变铸造:thixotropy casting触变锻造:thixotropy forging注射成型:injection molding5.3 其他金属成型新技术快速凝固:flash set非晶态:amorphous溢流法:press over system喷射沉积:ejecting deposit爆炸复合法:explosion cladding method 扩散焊接:diffusion welding挤压:extruding轧制:roll down6 非金属材料成型技术6.1 高分子材料成型技术高分子材料:non-metal material耐腐蚀:resistant material绝缘:insulation老化:ageing耐热性:heat-durability粘弹性:viscoelasticity塑料:plastic material橡胶:rubber合成纤维:synthetic fibre涂料:covering material粘结剂:agglomerant粘度:viscosity热塑性塑料:thermoplastic plastics 热固性塑料:thermosetting plastic 通用塑料:general-purpose plastics 工程塑料:engineering plastic薄膜:thin film增强塑料:reinforced plastics浇注塑料:pouring plastics注射塑料:injiection plastics挤出塑料:extrusion plastics吹塑塑料:blowing plastics模压塑料:die pressing plastics 聚合物:ploymer semiconductor吸湿性:hygroscopic cargo定向作用:directional action生胶:green glue stock填料:carrier丁苯橡胶:SBR顺丁橡胶:BR氯丁橡胶:CR丁腈橡胶:NBR硅橡胶:Q聚氨酯橡胶:U压延:calender硫化:sulfuration胶粘剂:adhesive胶接:glue joint刹车片:brake block零件修复:parts renewal蜂窝夹层:honeycomb core material 6.2 工业陶瓷制品的成型技术干燥:drying润滑剂:anti-friction结合剂:binder热压铸:hot injiection moulding 6.3 非金属材料成型技术的新进展热压烧结:hot pressed sintering7 复合材料的成型技术复合材料:composite material树脂:resin7.1 金属复合材料的成型技术硼纤维:boron fiber钛合金:titanium alloy碳纤维:carbon filter等离子喷涂:plasma spraying浸渍法:immersion method锭坯:ingot blank7.2 聚合物基复合材料的成型技术晶须:whisker缠绕成形:enwind forming湿法缠绕:wet method enwind7.3 陶瓷复合材料成型技术溶胶-凝胶法:sol-gel method化学气相沉积: chemical vapor deposition (CVD) 原位:in situ8 材料成型方法的选择粉末冶金:powder metallurgy工程塑料:engineering plastics工程陶瓷:engineering ceramics。
金属注射成形技术:
金属注射成形 ( Metal injection Molding ,MIM ) 是一种将金属粉末与其粘结剂的增塑混合料注射于模型中的成形方法。
它是先将所选粉末与粘结剂进行混合,然后将混合料进行制粒再注射成形所需要的形状。
聚合物将其粘性流动的特征赋予混合料,而有助于成形、模腔填充和粉末装填的均匀性。
成形以后排除粘结剂,再对脱脂坯进行烧结。
有的烧结产品还可能要进行进一步致密化处理、热处理或机加工。
烧结产品不仅具有与塑料注射成形法所得制品一样的复杂形状和高精度,而且具有与锻件接近的物理、化学与机械性能。
该工艺技术适合大批量生产小型、精密、三维形状复杂以及具有特殊性能要求的金属零部件的制造。
由于粉末冶金技术的优点,它已成为解决新材料问题的钥匙,在新材料的发展中起着举足轻重的作用。
金属注射成形技术特点:
MIM技术作为一种制造高质量精密零件的近净成形技术,具有常规粉末冶金、机加工和精密铸造方法无法比拟的优势。
能象生产塑料制品一样生产形状复杂的小型金属零件(0.1-500g);制件各部分组织均匀、尺寸精度高、相对密度高;表面光洁度好;产品质量稳定,生产效率高,易于实现大批量、规模化生产。
生产流程
产品技术交流→产品设计→模具设计→模具制造
金属粉末、粘结剂→混炼→注射成形→分离粘结剂→烧结→深加工(根据强度需要)→检验→成品。
金属粉末注射成型技术(Metal Powder Injection Molding,简称MIM)是将现代塑料注射成形技术引入粉末冶金领域而形成的一门新型粉末冶金近净形成形技术。
其基本工艺过程是:首先将固体粉末与有机粘结剂均匀混练,经制粒后在加热塑化状态下(~150℃)用注射成形机注入模腔内固化成形,然后用化学或热分解的方法将成形坯中的粘结剂脱除,最后经烧结致密化得到最终产品。
与传统工艺相比,具有精度高、组织均匀、性能优异,生产成本低等特点,其产品广泛应用于电子信息工程、生物医疗器械、办公设备、汽车、机械、五金、体育器械、钟表业、兵器及航空航天等工业领域。
因此,国际上普遍认为该技术的发展将会导致零部件成形与加工技术的一场革命,被誉为“当今最热门的零部件成形技术”和“21世纪的成形技术”。
美国加州Parmatech公司于1973年发明,八十年代初欧洲许多国家以及日本也都投入极大精力开始研究该技术,并得到迅速推广。
特别是八十年代中期,这项技术实现产业化以来更获得突飞猛进的发展,每年都以惊人的速度递增。
到目前为止,美国、西欧、日本等十多个国家和地区有一百多家公司从事该工艺技术的产品开发、研制与销售工作。
日本在竞争上十分积极,并且表现突出,许多大型株式会社均参与MIM工业的推广,这些公司包括有太平洋金属、三菱制钢、川崎制铁、神户制钢、住友矿山、精工--爱普生、大同特殊钢等。
目前日本有四十多家专业从事MIM产业的公司,其MIM工业产品的销售总值早已超过欧洲并直追美国。
到目前为止,全球已有百余家公司从事该项技术的产品开发、研制与销售工作,MIM技术也因此成为新型制造业中最为活跃的前沿技术领域,被世界冶金行业的开拓性技术,代表着粉末冶金技术发展的主方向MIM技术金属粉末注射成型技术是集塑料成型工艺学、高分子化学、粉末冶金工艺学和金属材料学等多学科透与交叉的产物,利用模具可注射成型坯件并通过烧结快速制造高密度、高精度、三维复杂形状的结构零件,能够快速准确地将设计思想物化为具有一定结构、功能特性的制品,并可直接批量生产出零件,是制造技术行业一次新的变革。
金属粉末注塑成型技术金属粉末注射成型技术(Metal Powder ※※※※ction Molding,简称MIM)是将现代塑料注射成形技术引入粉末冶金领域而形成的一门新型粉末冶金近净形成形技术。
其基本工艺过程是:首先将固体粉末与有机粘结剂均匀混练,经制粒后在加热塑化状态下(~150℃)用注射成形机注入模腔内固化成形,然后用化学或热分解的方法将成形坯中的粘结剂脱除,最后经烧结致密化得到最终产品。
与传统工艺相比,具有精度高、组织均匀、性能优异,生产成本低等特点,其产品广泛应用于电子信息工程、生物医疗器械、办公设备、汽车、机械、五金、体育器械、钟表业、兵器及航空航天等工业领域。
因此,国际上普遍认为该技术的发展将会导致零部件成形与加工技术的一场革命,被誉为“当今最热门的零部件成形技术”和“21世纪的成形技术”。
美国加州Parmatech公司于1973年发明,八十年代初欧洲许多国家以及日本也都投入极大精力开始研究该技术,并得到迅速推广。
特别是八十年代中期,这项技术实现产业化以来更获得突飞猛进的发展,每年都以惊人的速度递增。
到目前为止,美国、西欧、日本等十多个国家和地区有一百多家公司从事该工艺技术的产品开发、研制与销售工作。
日本在竞争上十分积极,并且表现突出,许多大型株式会社均参与MIM工业的推广,这些公司包括有太平洋金属、三菱制钢、川崎制铁、神户制钢、住友矿山、精工--爱普生、大同特殊钢等。
目前日本有四十多家专业从事MIM产业的公司,其MIM工业产品的销售总值早已超过欧洲并直追美国。
到目前为止,全球已有百余家公司从事该项技术的产品开发、研制与销售工作,MIM技术也因此成为新型制造业中最为活跃的前沿技术领域,被世界冶金行业的开拓性技术,代表着粉末冶金技术发展的主方向MIM技术金属粉末注射成型技术是集塑料成型工艺学、高分子化学、粉末冶金工艺学和金属材料学等多学科透与交叉的产物,利用模具可注射成型坯件并通过烧结快速制造高密度、高精度、三维复杂形状的结构零件,能够快速准确地将设计思想物化为具有一定结构、功能特性的制品,并可直接批量生产出零件,是制造技术行业一次新的变革。
金属基复合材料注射成型工艺总结摘要金属注射成型(金属注射成型工艺)是一种成熟制造技术,是能够低成本高效益批量生产复杂零件的制造工艺。
这种独特处理方法能,使它对金属基复合材料的制造有吸引力。
在本文中,通过金属注射成型工艺制造金属基复合材料的研究和发展的状况进行总结,材料系统,制造方法,由此产生的材料特性和微观结构是主要的焦点。
此外,这种复合材料制造技术的不足在本文中也会介绍。
金属注射成型工艺工艺制备金属基复合材料的全部潜力有待探讨。
目录1. 介绍 (3)2. 金属基复合材料注射成型工艺 (4)2.1难熔金属基复合材料 (4)2.2 钛基复合材料 (6)2.3 金属化合物基复合材料 (6)2.4 钢基复合材料 (7)2.5双金属结构 (8)3.微注射成形 (9)4.总结 (10)1. 介绍粉末注射成型(PIM)是一种与塑料注塑成型相结合的成熟的制造技术。
粉末的能力冶金用于加工金属和陶瓷粉末(德国,1990年)。
PIM的过程通常包括四个步骤:混合,注塑成型,脱脂和烧结,如下图(图1)PIM技术的演变导致了许多变化,反映了不同的组合粉末,粘结剂,成型技术,脱脂路线,烧结做法。
金属注射成型,常用其简称金属注射成型工艺,是迄今为止使用最广泛的PIM的过程。
金属注射成型工艺吸引人的特点,非常有利于金属基复合材料的制造(MMC)或陶瓷基复合材料(CMC)。
虽然许多金属基复合材料具有独特的属性,但是无法正常实现制造工艺来实现材料,其商业用途往往受限于材料和制造成本。
通过采用金属注射成型工艺,使用复合材料的商业成本可显着降低。
在近年来,综合性的工作已进行到探索金属基复合材料的制造,并扩展到陶瓷基复合材料和部件。
金属注射成型工艺技术的复合材料制造公司甚至已建立并形成商业能力(德克尔,1989年,H. C. Starck的公司,2003年)。
最广泛的研究是PIM金属基复合材料,包括不锈钢钢,难熔金属,金属间化合物和钛合金。
虽然在理论上加强型复合材料可以采取或者连续(通常长纤维)或连续(颗粒和短纤维/晶须)的形式,流和充模的PIM程序的要求确定这是大多数应用性,为加工原料含有颗粒或短纤维。
因此,这并不奇怪迄今为止所有通过金属注射成型工艺制造的金属复合材料强度不断增加。
本文提供了一个通过金属注射成型工艺方式制造复合材料研究方法的总结。
为了保持完整性,双金属结构及表面工程金属注射成型工艺制造的组件中还包括金属基复合材料。
此外,由金属注射成型工艺制造的微结构将涵盖在本文中,即使它仍然是在实验室阶段。
2. 金属基复合材料注射成型工艺根据基体材料,复合材料的制备金属注射成型工艺可分为难溶金属基复合材料,钛基复合材料,金属间化合物基复合材料以及钢基复合材料。
双金属结构在本节也会讨论。
金属注射成型工艺的路线已启用含有成分的材料,难溶金属基复合材料的制备很难通过传统方法制造。
2.1难熔金属基复合材料钨钼是两个高熔融温度金属(3422◦C的钨和超过2623◦C的钼),在消费类电子产品,航空航天等行业得到应用,由于其优良耐热性引起电信,医疗和国防极大的兴趣。
然而,它是很难熔炼和铸造材料。
按照惯例,钨钼基合金复合材料制造方法为粉末冶金法,然后进行轻微的加工或研磨。
组件制造也是传统的粉末冶金工艺,通常仅限于简单的几何形状。
金属注射成型工艺的塑造优势使得它能够用于生产形状复杂的零件。
因此,金属注射成型工艺作为一种替代制造难熔金属材料的制造方式已被广泛探讨。
(Bruhn,Terselius ,1999年,王等,2001; Li等人,2003年;Tarata Ghita,2002年德国,1999年百色,2003年,杨等人,2000年宋等,1999年)一个重要的难熔金属基复合材料是钨铜系统,它具有优良的热管理属性和高微波的吸收能力。
它主要是用于重型电气接触和电弧耐电极。
钨铜的部分通常是编造由渗透铜成钨粉契约或液相烧结的铜粉末的混合物。
然而,传统的技术不适合小的复杂零件的批量生产。
金属注射成型工艺已实行批量生产小而精致的钨铜。
由金属注射成型工艺制备的钨镍铁复合材料已被广泛研究(Fan等,2001A,B,2002年,2004年,2005年,苏芮等等,2003;曲Huang等,2003; Li等,1998; Lee等人,2005年b;等人,2000年,2001年)钨镍铁复合材具有高密度,高强度,良好的延展性和耐腐蚀性等优点。
W - Ni- Fe体系的主要研究对象是金属注射成型工艺制造的90W -7Ni-3FE(风扇等,2001A,B,2002年,2005年;苏瑞等,2003; Huang等,2003; Lee等人,2005年;瞿等,2000,2001年)。
W-镍铁纳米复合粉体通常机械球磨制备多组分混合粘结剂,形成同质原料(苏里等。
2003年黄等,2003; Lee等人,2005年b; Fan等人,2001年,B)。
实验结果表明,铣床升级混合元素粉末,最大程度粉末装载量,同质化的原料,最终烧结。
在1350◦C至1450 ◦C的温度范围内,它具有高机械性能的完全致密的部分固态生产和极小的失真。
为了控制最终产品的尺寸偏差,范(Fan 等,2005)提出了一个考虑重量偏差的数学模型并通过实验调查核实。
此外,角色添加剂,如钼,钽和重新对组织和由金属注射成型工艺的W - Ni- Fe体系的力学性能审议通过了德国和百色(德国等,1989;百色等,1989年,1990年)。
他们的研究结果显示,即使是很小的重数量具有显着的固溶强化粮食炼油能力。
然而,转口成本高可能会限制只有特殊应用的添加剂除了。
类似的W - Cu复合,钼铜复合材料具有高导热和热膨胀密切配合,以及半导体材料的优越性。
吴铜钼铜的密度较低,在相同的重量体积较大。
在制造的复合材料过程中,烧结也是一个内在的问题。
虽然在烧结温度,基本上是没有的铜钼溶解度只有1-1.5%的Mo在熔融铜中的溶解度。
利用金属注射成型工艺工艺制备钼铜复合材料提高烧结由于在原料的超细颗粒使用。
此外,添加剂元素,具有较高的溶解度钼及与铜形成一个连续的固溶促进致密化。
柯克(柯克等人,1992年)发现,镍系统在烧结过程逐渐致密化。
然而,这是实现莫晶粒尺寸粗化的成本,并减弱热扩散。
使用超细粉末似乎更为有利因为它提出了复合材料的热扩散致密。
替代路线以改善复合材料的热扩散放大的高导电性的成分增加。
2.2 钛基复合材料钛的合金是最有前途的的金属生物材料由于其良好的医疗植入应用生物相容性,高化学稳定性,在生理环境,优良的机械性能。
他们是也因为广泛应用于航空航天应用特定的高强度和耐腐蚀性。
目前钛基复合材料的研究是通过金属注射成型工艺主要集中在生物医学领域的应用Thian和他的同事领导的研究人员在探索制造钛羟基磷灰石医疗植入应用的复合材料(Thian等,2001年)。
HA是一个磷酸钙复合[CA10(PO4)6(OH)]具有类似的组成自然骨矿物。
它是作为一种生物活性建立材料使用时。
然而,2HA本身很脆,并不能用于受载的地方。
发展钛合金复合材料的目的是结合HA 的生物活性和钛合金优良的机械性能,以避免HA的脆性和低韧性问题(Halouani 等,1994)。
要均匀的原料,Ti6Al4V的和HA粉末第一个混合浆的方法,使用聚乙烯醇(PVA)为载体(Thian等,2003)。
聚乙烯醇是通过加热删除及混合物粉末是粉碎成小颗粒,以获得Ti6Al4V/HA复合粉。
它是以Ti6Al4V为内在核心与外层包裹HA。
PAN- 250S,商业粘结剂系统还在实验阶段。
2.3 金属化合物基复合材料人们已经认识到,金属间化合物的基础上铝有吸引力的低密度的特点,高在高温下的强度,以及良好的耐腐蚀性和抗氧化能力,这是非常高的理想更换为高温合金的高温结构。
然而,它的脆性和较差的可加工性限制它们的应用范围。
不过复合强化可以提高机械性能。
PIM制造短纤维的一个独特的优势是的控制复合材料纤维的方向。
研究结果表明,扩张的流动趋向于使得纤维垂直流动方向,而压缩流趋向于使得纤维平行于流动方向,作为示意如图2(德国和Bose,1989年)。
通过适当控制注射过程中的原料流成型,沿着一定的方向的力学性能可以根据要求量身定做。
对齐成功的关键是起始粉末的大小和形态粉末对齐程度。
但是,这种方法有一些障碍,包括需要精细的球状粉末,加固和粘结剂的正确选择,并去除粘结剂。
然而,这个过程已经证明金属间化合物复合材料的潜力。
图2 注射过程中控制纤维的方向2.4 钢基复合材料相比在上一节所述的其他金属基复合材料的研究,钢基复合材料信息少的多。
这是因为钢可以相对容易地使用传统的制造加工流程,而且只需在广泛不同的合金成分,钢材属性可以控制。
因此,少数出版物上可以找到钢基复合材料的研究。
有色金属复合材料制造的主要目的金属注射成型工艺可以提高钢的耐磨性,再加塑造独特的金属注射成型工艺的优势。
TiN和TiC平均直径小于10维米可以作为增强相。
增加量控制在5%以下,以避免在注射过程中损害致密化和潜在损害。
钢粉和添加剂的粉末的起始原料混合在一起加入粘结剂。
蜡基粘结剂系统主要是在钢基体的制造以及使用。
表2表示在实验室成功地应用于一些粘合剂。
烧结通常是在还原气氛处理和温度是受到钢的基体,通常在1200°—1400°的范围内超过90%达到理论密度。
烧结钢基复合材料的一个主要挑战是在钢基体的碳含量的精确控制。
这可以通过选择粘结剂和控制部分脱脂和烧结气氛中CO气体的压力实现,但是这往往是一个试错的方法(三浦等人,1996年; Petzoldt等,1995)。
增加3-5%增加相得钢基复合材料可实现95-99%的相对密度。
(陆等人,2001年; Khakbiz等,2005年)这个密度范围内,钢材为主的金属基复合材料的耐磨性就可以大大提高。
例如,一个金属注射成型的复合材料与4140钢的基复合材料相比,磨损质量损失高10倍(三浦等,1996年)。
2.5双金属结构金属部件的使用环境一般都很恶劣。
双金属结构两种不同的材料层粘合在一起,对于这类应用有性能上的优势。
传统方式使双金属结构焊接或债券两个用料上在一起。
此外相关的高成本的二次操作,常规加入方法也有缺点。
加入的第三个材料(例如,焊接填料,粘合剂等)成为组件的危险点,从而损害了组件的性能。
压接或冷缩配合也可用于制造双金属结构,但这种方法只能适用于部分与某些特定形状(鲍姆加特纳和谭,2002年)。
金属注射成型提供另一种解决方案。
两个不同的化学性质和属性成型的金属材料可以克服这些问题。
金属注射成型生产的双金属结构在某个时候视为连续增强金属基复合材料(鲍姆加特纳谭谈,2001年,2002年等,2001; Pischang等,1994;阿尔科克等。