电子工程专业外语考试题
- 格式:doc
- 大小:57.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

《电子技术专业英语》课程期末考试考试时间:100分钟,考核方式:笔试Part ІVocabulary and GrammarDirections:There are 20 incomplete sentences in this part.For each sentence there are four choices marked A,B,C and D.Choose the ONE answer that best completes the sentence.(20 points)( )1. -Where is Frank now?- He _______his bike in the yard.A.fixes upB. fixing upC. is fixing upD. fixed( )2. -You’ve left the light on, Tracy.-Oh, yes. _________ to turn it off right now.A. I’d goB. I’ve goneC. I’ll goD. I go( )3.“The World Without Thieves” is a very moving film. I ____ it twice already.A. will seeB. seeC. sawD. have seen( )4. The Oriental Pearl TV Tower ________ tens of thousands of visitors since l995.A. attractedB.attractsC. has attractedD.will attract( )5. -Did you see the traffic accident yesterday?-Yes. It happened when I past the museum.A. walkB. am walkingC. will walkD. was walking( )6. -Have you read this book?-Yes.I____ it two weeks ago.A.is reading B.have read C.will read D.read( )7.- What are you doing ,Jim?-I _________a beautiful horse.A. drawB. drewC. am drawingD. was drawing( )8. They______ all their money, so they have to walk home now.A. have spentB. spendC. spentD. are spending( )9. Jim is a student and ________in Town High School.A. studiesB. studiedC. had studiedD.study( )10.Sandy ________his old friend Tom when he was crossing the street.A. had metB. has metC. metD.meet( )11.A FET has three terminals: a souce,a drain and a ________.A.gateB.substractC.baseD.collector( )12.Transistor may be roughly grouped into two major divisions: ________ and field-effect. A.single B.polar C.bipolar D.collector( )13.In general,all material may be classified in three major catagories:conductors, ________and insulators.A.conductivityB.carbonC.diamondD.semiconductors( )14.A diode is an electrical device allowing current to move through it in ________ direction(s) with far greater ease than in the other.A one. B.two C.three D.four( )15.A diode may be thought of as a kind of switch:” ________” when forward-biased. Aopen. B. on C.closed D. off( )16.The BJT consists of ________region(s) of semiconductor material.A one. B.two C.three D.four( )17.VLSI is short form of “very large-scale________”.A.integratingB.integrationC.integrateD.integrator( )18.Bipolar transistors work as ________-controlled current regulators.A. currentB.voltageC.potentialD.drop( )19.Tomorrow we________ go for an outing unless it rains.A.willB.shallC.shouldD.would( )20.I ________ eighteen years old next year.A.am going toB.shall beC.should beD.would bePart ІІClozeDirections: Read the following text. Choose the best word or phrase for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C, or D.(10 points)The United States is a confederation(联邦)of states. Each state has the (26) to make laws with regard to the state. (27) , based on public opinion, states can (28) policies regarding education, and they may (29) a state income tax; they also determine the speed (30) , housing codes, and the drinking age.In most parts of the United States, you (31) be 21 years old to buy alcohol in a liquor (液体,溶液)store, bar, (32) restaurant. In some states you may buy beer in a grocery (杂货,食品)store. If a store sells alcohol to a minor, the (33) of the store is usually (34) a large sum of money. (35) , many areas have an open-container law, (36) means that people may not drink alcohol on the street or in a car. Anyone (37) with an open container of alcohol may be arrested.(38) , with all of these laws, the (39) of alcohol is a serious (40) in the United States and Canada. Drinking on college campuses, (41) there are many underage drinkers has (42) greatly. In fact, alcohol sales have gone up (43) the legal drinking age was (44) from 18 to 21. Some people believe that if there were no legal drinking age, (45) in some other countries, North American youth would drink less.( )21.A privilege B advantage C right D tradition( )22.A As a result B For example C In other words D In this case( )23.A demand B disagree C discuss D determine( )24.A collect B issue C demand D implement( )25.A limit B control C stop D regulation( )26.A can B shall C will D must( )27.A and B or C also D not( )28.A clerk B salesperson C owner D host( )29.A fined B charged C punished D suffered( )30.A In addition B In fact C In reality D In general( )31.A that B this C it D which( )32.A exposed B suspected C caught D detected( )33. A nevertheless B Anyway C Moreover D Therefore( )34.A application B consumption C expenditure D usage( )35.A condition B crisis C question D problem( )36.A though B as C where D which( )37.A raised B increased C peaked D climaxed( )38.D climaxed B since C before D after( )39.A shifted B upgraded C uplifted D changed( )40.A same B for C as D likePart ШReading ComprehensionDirections: Read the following text. Answer the questions on each text by choosing A,B,C or D. (10 points)The ostrich(鸵鸟), the largest bird in the world at present, lives in the drier regions of Africa outside the actual deserts. Because of its very long, powerful legs and the floating effect of its extended wings, it is able to run at great speed over considerable distances.The female(雌性的)ostrich normally produces about twenty eggs every rainy season. When the female ostrich begins to lay her eggs, however, she does not begin in her own nest(巢、窝).Instead she goes off in search of the nests of neighboring females and lays two or three eggs in each of them. By the time she has laid eight or nine eggs, she returns and lays the rest in her own nest.Because of the size of the eggs, the female ostrich cannot lay more than one every two days, so it takes her three weeks to finish laying in her own nest. During that period, she spends a lot of time away from her nest looking for food. And while she is off her nest, other females visit it tolay their eggs amongst hers. By the time she is ready to sit on the eggs to hatch(孵化)them, there could be up to thirty eggs in her nest, over half of which are not her own.The female ostrich can comfortably cover only about twenty eggs when she is sitting on the nest so before settling down she pushes the surplus(剩余,过剩的)ten or so eggs out of the nest. The rejected eggs, however, never include any of her own. Each female is remarkably consistent in the size and shape of the eggs she produces, so it is not difficult for her to distinguish her own from those of strangers.Of all the eggs laid by a colony of (群体)ostriches, only a very small number hatch into young birds. There are times when nests are left unprotected, for there are too few males to sit on all the nests at night. Thus there are ample(充足的)opportunities for their natural enemies to raid (袭击)the nests and eat the eggs. In fact, nearly 80% of the nests are destroyed. But even if a particular female’s nest suffers this fa te, there is a good chance that one or two of her eggs will be hatched in the nest of one of her neighbors.56.We learn from the text that an ostrich can go a long distance at high speed as ______.A.it is a special kind of birdB.it lives in large desert areasC.it has special wings and legsD.it is the largest bird in the world57.Normally, in every rainy season, the female ostrich produces about ______.A.12 eggs in her nestB.18 eggs in her nestC.20 eggs in her nestD.30 eggs in her nest58.The female ostrich would push some of the eggs out of her nest because ______.A.she can only hatch her own eggsB.those eggs are unlikely to be hatchedC.those eggs are to be hatched by othersD.she can only hatch a limited number of eggs59.The female ostrich identifies her own eggs by their size and ______.A.colorB.numberC.shapeD.weight60.The female ostrich lays her eggs in her neighbors' nests most probably because ______.A.her nest is not big enoughB.she cannot protect all her eggsC.she cannot tolerate all her eggsD.her nest is not comfortable enoughPart IV TranslationSection ADirections:There are 10 phases in this part.You are to translate the phases into Chinese or vice verse,and write them down in the blank.(20 points)1.threshold voltage( ) 6.运算放大器( )2.Schottky diode( ) 7.正向偏置( )3.differential amplifier( ) 8.电阻系数( )4.unity-gain buffer( ) 9.电容( )5.negative feedback( ) 10.电感( )Section BDirections:There are 2 passages in this part.You are to translate the passages into Chinese or vice verse,and write them down in the blank.(20 points)Passage 1The resistance of an electrical conductor depends on 4 factors, these being:(a) The length of the conductor. Resistance, R, is directly proportional to length, l, of a conductor, i.e. R∝l.(b) The cross-sectional area of the conductor. Resistance, R, is inversely proportional to cross-sectional area, a, of a conductor, i.e. R∝1/a.(c) The type of material.(d) The temperature of the material.Passage 2The only functional difference between a p-n-p transistor and an n-p-n transistor is the proper biasing (polarity) of the junctions when operating. For any given state of operation, the current directions and voltage polarities for each type of transistor are exactly opposite each other.Part V WritingDirections:For this part,you should write a short essay entitled How to Learn Electronic ESP Well.You should write at least 100 words following the outline given below.(20 points)1.电子专业英语学习的重要性2.电子专业英语学习的内容3.如何学好专业英语How to Learn Electronic ESP Well。
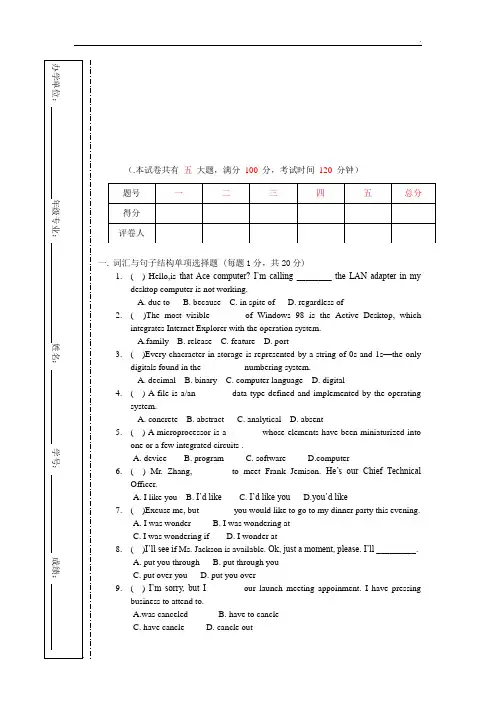
(.本试卷共有 五 大题,满分 100 分,考试时间 120 分钟)一. 词汇与句子结构单项选择题 (每题1分,共20分)1. ( ) Hello,is that Ace computer? I’m calling ________ the LAN adapter in mydesktop computer is not working.A. due toB. becauseC. in spite ofD. regardless of2. ( )The most visible_______ of Windows 98 is the Active Desktop, whichintegrates Internet Explorer with the operation system.A.familyB. releaseC. featureD. port3. ( )Every chacracter in storage is represented by a string of 0s and 1s —the onlydigitals found in the _________ numbering system.A. decimalB. binaryC. computer languageD. digital4. ( ) A file is a/an _______ data type defined and implemented by the operatingsystem.A. concreteB. abstractC. analyticalD. absent5. ( ) A microprocessor is a _______ whose elements have been miniaturized intoone or a few integrated circuits .A. deviceB. programC. softwareputer6. ( ) Mr. Zhang, _______ to meet Frank Jemison. He’s our Chief TechnicalOfficer.A. I like youB. I’d likeC. I’d like youD.you’d like7. ( )Excuse me, but _______ you would like to go to my dinner party this evening. A. I was wonder B. I was wondering atC. I was wondering ifD. I wonder at8. ( )I’ll see i f Ms. Jackson is available. Ok, just a moment, please. I’ll _________. A. put you through B. put through youC. put over youD. put you over9. ( ) I’m sorry, but I _______ our launch meeting appoinment. I have pressingbusiness to attend to.A.was canceledB. have to cancleC. have cancleD. cancle out10.( ) Well, I suggest all our employees_________ uniforms during business hours.A. puts onB. put offC. shall put onD. should put on11. ( )A FET has three terminals: a souce,a drain and a ________.A.gateB.substractC.baseD.collector12. ( )Transistor may be roughly grouped into two major divisions: ________ andfield-effect.A.singleB.polarC.bipolarD.collector13. ( )In general,all material may be classified into three major catagories:conductors,________and insulators.A.conductivityB.carbonC.diamondD.semiconductors14. ( )A diode is an electrical device allowing current to move through it in ________direction(s) with far greater ease than in the other.A one. B.two C.three D.four15. ( )A diode may be thought of as a kind of switch:” ________” when forward-biased.A. open.B. onC.closedD. off16. ( )The BJT consists of ________region(s) of semiconductor material.A one. B.two C.three D.four17. ( )VLSI is short form of “very large-scale________”.A.integratingB.integrationC.integrateD.integrator18. ( )Bipolar transistors work as ________-controlled current regulators.A. currentB.voltageC.potentialD.drop19. ( )Tomorrow we________ go for an outing unless it rains.A.willB.shallC.shouldD.would20. ( )I ________ eighteen years old next year.A.am going toB.shall beC.should beD.would be二.完型填空 (每题1分,共10分)One year Miss Wyatt decided to have a holiday in Italy. She did not speak 1 Italian, but wherever she went, she was fortunate enough to find people who knew 2 English to be able to 3 what she wanted, until one day she decided to have lunch in a charming little restaurant in a village 4 the south of Italy.She had seen some nice mushrooms in the market of another village near there and thought they would taste very 5 , so when the waiter came to take her 6 for lunch, she inquired whether she could have some 7 for her meal, but she had great 8 in explaining to him, because 9 did not know the Italian word for mushrooms.At last she took out a pencil and drew a picture of a mushroom. The waiter’s face 10 at once, and hastened out to the kitchen. A minute later he returned, carrying an umbrella.( ) 1. A. much B. a great deal C. a lot D. a little( ) 2. A. certain B. full C. enough D. special( ) 3. A. give B. get C. show D. understand ( ) 4. A. in B. to C. on D. outside( ) 5. A. well B. nicely C. soon D. good( ) 6. A. bill B. order C. dish D. check( ) 7. A. meat B. dishes C. mushrooms D. apples( ) 8. A. difficulty B. interest C. pleasure D. patience ( ) 9. A. she B. he C. they D. everybody ( ) 10. A. brightened B. astonished C. burned D. worried三、阅读理解(每题2分,共10分)Not very long ago, a special family system existed in certain parts of South India. In this system, th e actual head of a family unit was the mother’s eldest brother, though the mother also had an important position in the family. In families of this kind, a husband was actually no more than a visitor. He did not live with his wife , but with his own mother, brothers and sisters in another house. He saw his sons and daughters sometimes, but the man who actually fed and cared for them and acted as their father was their uncle—their mother’s brother.But this system, in which brothers and sisters take the place of the father, no longer exists in South India except in a few villages. Economic changes have had far-reaching effect on family life, so family life began to change when men sent out to work in factories and offices instead of working with their mothers, brothers, and sisters on the land. When a man went out to work he had money of his own and could buy his own land and build his own family, instead of depending on his mother and his brothers. He wanted to be independent. This is an example of the way in which economic relations can have an effect on family relationships.()1. The best title of this passage is .A.Husband Actually Visitor in FamilyB.Family System in South IndiaC.Wife Has Important Position in FamilyD.Economic Relations Affects Family Relationships()2. Who had the actual control of a family in South India not long ago?A.Mother.B.The mother’s eldest brother.C.The father.D.The father’s mother.()3. In this system, the husband lived together with his .A. wifeB. sons and daughtersC. mother, brothers and sistersD. wife’s brother()4. Now in South India there are of this system in which a husband has no control of his family.A. no familiesB. many more familiesC. very few familiesD. not any families()5. What has caused such a strange family system to die away?A.The fact that the mother has not got any brother.B.The fact that the father has got his own house and land.C.The changes in economic relations.D.The changes in family relationships.四、翻译(共40分)A.常用词组翻译(每题2分,共20分)1. 自由电子()2. nucleu of the atom ( )3. 集成电路()4. oprational amplifier ( )5. 反向输入端()6. digital electronics ( )7. 触发器()8. troubleshooting manuals ( )9. 中央处理器() 10. local area network ( )B.篇章翻译(每题10分,共20分)1. Starting the PC for the firsr timeYour PC has preinstalled software. This software is installed the first time you start the PC. The software initialization takes approximately three minutes, and:●sets up the software in your language.●Sets up the software to use the hardware installed in your computer—notethat you can change the settings after the sofeware has been initialized.2. Multimedia is not a new word. In fact, the concept of multimedia has been around for years. However, it appears that multimedia has finally started to play an increasingly important role in today’s computer world. Because of ever more powerful computer systems and the experience of creative programmers, multimedia is truly changing the way people are using computers.五、按照所给话题,写一篇不少于100字的小短文。

电子科技英语试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. Which of the following is not a feature of electronic components?A. High precisionB. High reliabilityC. Low power consumptionD. Large size答案:D2. What is the basic unit of digital information?A. BitB. ByteC. KilobitD. Megabyte答案:A3. In electronics, what does the term "analog" refer to?A. Continuous signalsB. Discrete signalsC. Digital signalsD. Binary signals答案:A4. Which of the following is not a type of semiconductormaterial?A. SiliconB. GermaniumC. PlasticD. Gallium arsenide答案:C5. What is the function of a transistor in an electronic circuit?A. To amplify signalsB. To store dataC. To convert light into electricityD. To filter signals答案:A6. What is the primary function of a capacitor in an electronic circuit?A. To block DC and allow ACB. To block AC and allow DCC. To store electrical energyD. To convert voltage into current答案:C7. What does the abbreviation "LED" stand for in electronics?A. Light Emitting DiodeB. Large Emitting DiodeC. Limited Emitting DiodeD. Low Emitting Diode答案:A8. What is the purpose of a resistor in an electronic circuit?A. To control voltageB. To control currentC. To store energyD. To amplify signals答案:B9. Which of the following is a type of passive component in electronics?A. TransistorB. DiodeC. RelayD. All of the above答案:D10. What is the term used to describe the flow of electric charge?A. VoltageB. CurrentC. ResistanceD. Capacitance答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. The smallest unit of electric charge is called an ________.答案:electron2. A ________ is a type of electronic component that can store energy in an electric field.答案:capacitor3. The process of converting sound into electrical signals is known as ________.答案:modulation4. In digital electronics, a ________ is a single digit number, either 0 or 1.答案:bit5. A ________ is a semiconductor device that can amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power.答案:transistor6. The unit of electrical resistance is the ________.答案:ohm7. An ________ is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow primarily in one direction.答案:diode8. The ________ is a passive component that opposes the flow of alternating current.答案:inductor9. A ________ is a type of display device that uses liquid crystals to produce images.答案:LCD10. The ________ is a type of electronic component that can store data.答案:memory三、简答题(每题10分,共20分)1. Explain the difference between an analog and a digital signal.答案:Analog signals are continuous and can represent a wide range of values, while digital signals are discrete and can only represent specific values, typically as a series of ones and zeros.2. Describe the role of a microprocessor in a computer system. 答案:A microprocessor is the central processing unit of a computer system, responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and controlling other system components to perform various tasks.四、翻译题(每题15分,共30分)1. Translate the following sentence into English: “在电子设备中,晶体管通常用作放大器或开关。

电子信息工程专业英语Part 1第一课关于电子技术一、课文习题参考答案Ⅰ. (1)alternating current circuits (2) semiconductor diodes(3) passive component(4) the combinatorylogic electric circuit(5) rectification(6) Laplace transform(7) inductor(8) Fourier series andFourier transformⅡ.(1)控制理论(2)场效应管三极管(3)布尔代数(4)稳压(5)相关性和功率谱密度(6)滤波器类型(7)模/数转换器(8)时序逻辑电路的分析与综合Ⅲ.(1)Electronics is a part of the largerfield of electricity. The basic principles of electricity are also common to electronics.Modern advances in the field of computer,control system, communications have a close relationship with electronics. The field of electronics includes the electron tube,transistor, integrated circuit and so on.(2) Direct current circuits & Alternating current circuits,Analog electronics,Digital electronics,signal and systems,Circuit theory and design, Control theory, Microcontroller systems,Computer programming for engineering applications.(3) This curriculum mainly introduces the characteristics of semiconductor devices in linear application scope.The content involved in semiconductor diodes (PN junction diodes, special purpose diodes), transistors (field effects and bipolar transistors), signal amplifiers, practical amplifiers, biasing circuits, operational amplifiers circuit and other circuits (rectification, regulation and DC power supplies).(4) This partial studies take the basic electric circuit theory and the operational amplifier knowledge as the foundation. The main study goal is to enhance understanding of the electric circuit theory. Its main contentincludes the elementary theory in circuit theory (network functions, characteristic frequencies), types of filter (lowpass,bandpass), review of operational amplifiers (design of first and second order using operational amplifiers, cascade design), filter characteristics(Butterworth, Chebyshev, frequency transformations in design, sensitivity design of passive LC ladder filters and a brief introduction to switched capacitor filters).(5) Perfect.二、参考译文电子学的发展电子学是电学的一部分。
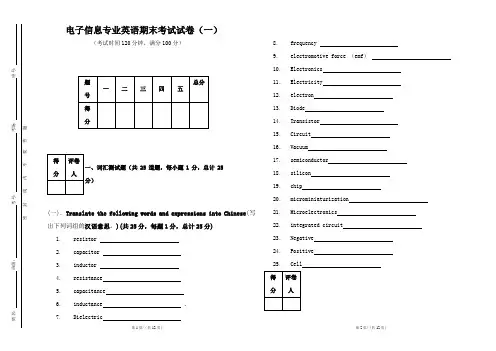
电子信息专业英语期末考试试卷(一)(考试时间120分钟,满分100分)一、词汇测试题(共25道题,每小题1分,总计25分)(一).Translate the following words and expressions into Chinese (写出下列词组的汉语意思。
)(共25分,每题1分,总计25分)1. resistor 2. capacitor 3. inductor 4. resistance 5. capacitance 6. inductance . 7.Dielectric8. frequency9.electromotive force (emf )10. Electronics 11. Electricity12. electron 13. Diode14. Transistor 15. Circuit 16. Vacuum 17. semiconductor 18. silicon 19. chip20. microminiaturization 21. Microelectronics 22. integrated circuit 23. Negative 24. Positive 25. Cell(共25题,每题1分,总计25分)1.黑白电视机2.基本原理3.硅晶体管4.电子元件5. 锗晶体管6. 真空二极管7. 信息时代 8. 单片 9.电源 10.负极 11.正极 12.干电池 13.串联 14.并联 15.电压降16.固定电阻 17.电阻值18.电场 19.容抗 20. 对电流的阻力21. 非线性电阻23.一个二端元件24.一个闭合回路 25. 事实上(三)填空题Choose one word from the word list below to fill in the blank in each of the following sentences. Change the form of the word where necessary: (共8道题,每题1分,总计8分)resistors capacitance nonlinear resistance electricity inductor electrical capacitor1. Capacitor’s basic function is to store _____ energy.2. A _____ is a device designed to have capacitance.3. The property of a capacitor to oppose any change in voltage across that capacitor is called ______.4. Resistors used for special applications are ______.5. Ohm is used as a unit of ______.6. Some _____ are made to have a variable resistance.7. The larger is the emf, the more ______ the capacitor stores. 8. Any _____ is made of wire having resistance.(四)单项选择题Choose the one that best completes each of the following statements according to the text: (共12题,每题1分,共12分)1. Electronics is a part of _______.A. electronsB. technologyC. electricityD. science2. The field of electronics includes _____.A. transistorB. electron tubeC. integrated circuitD. All above3. Thomas Edison invented ______ in 1883.A. vacuum tubeB. diodeC. triodeD. lamp4. The first transistors were made from ______.A. siliconB. germaniumC. copperD. gold5. ______ created a new future in electronics.A. Integrated circuitB. SemiconductorC. Electron tubeD. Computer6. Due to the invention of ______, microelectronics was created in 1950s.A. electron tubeB. transistor 7. Power supply, the conductor, the control device and ______ are fourbasic parts of an electric circuit.A. batteryB. wireC. switchD. load8. The energy conversion can take place _______.A. in the circuitB. in a cellC. within the loadD. along the wire9. Electric circuit is a combination of a conductor and of a source of e.m.f.which permits electrons to flow along a ______.A. streamB. wireC. terminalD. pathway10. The electrons move in a fixed way in a _____ direction.A. definiteB. differentC. variousD. appropriate11. The electric current flows from ______ to ______.A. negative , positiveB. positive, negativeC. minus, plusD. A and C12. When the current flows, it is a ______ circuit.A. closedB. openC. combinationD. electric(五)翻译题(共10题,每题2分,总计20分)1. Each lamp filament representing an independent path from the minus main wire to the plus wire.2. Silicon transistors began to replace germanium transistors in the late 1950s, which made possible the next revolutionary step in electronics.3. Electronics began in 1883, when Thomas Edison discovered the vacuum diode as part of his research on materials for a practical electric light. proportional to the current passing through it.5. Such circuits make it possible to combine the different voltage characteristic of a series circuit with the different current characteristic of a parallel circuit within a single network.6. Jack Kilby, an American scientist, made the first single IC in the late 1950s, which laid foundation of microminiaturization and integration.7. Digital computers are essentially machines for recording numbers, operating with numbers and giving the result in numerical forms.8. Integrated circuits are more of a science, than of a technology.9. Bandwidth of transistor amplifiers vary from about 250 MHz in the L band to 1000 MHz in the X band.10. The main device failure mode is secondary breakdown。


电子信息工程专业英语教程任志刚课后习题答案1、—Is this ______ football, boy? —No, it is not ______.()[单选题] *A. yours; myB. your; mine(正确答案)C. your; meD. yours; mine2、Sometimes Americans are said to be _____. [单选题] *A superficially friendB superficial friendC. superficial friendlyD. superficially friendly(正确答案)3、What do you think of the idea that _____ honest man who married and brought up a large family did more service than he who continued single and only talked of _____ population. [单选题] *A. a, /B. an, /C. a, theD. an, the(正确答案)4、16.Lily is a lovely girl. We all want to ________ friends with her. [单选题] * A.haveB.make(正确答案)C.doD.take5、--Jenny, what’s your favorite _______?--I like potatoes best. [单选题] *A. fruitB. vegetable(正确答案)C. drinkD. meat6、( ) ____ eye exercises ___ good __ your eyes. [单选题] *A. Doing, is, for(正确答案)B. Doing, are, forC. Do, is, forD. Do, are, at7、He _______ walks to school, because he lives near school. [单选题] *A. sometimes(正确答案)B. neverC. doesn’tD. don’t8、40.Star wars is ______ adventure film and it is very interesting. [单选题] *A.aB.an (正确答案)C.theD./9、It took a long time to _______ Tom to go shopping with me. [单选题] *A. speakB. tellC. persuade(正确答案)D. talk10、Jack would rather spend time complaining than_____the problem by himself. [单选题] *A.solve(正确答案)B.solvedC.solvesD.to solve11、29.______ my free time, I like listening to music. [单选题] *A.AtB.OnC.In(正确答案)D.About12、They took _____ measures to prevent poisonous gases from escaping. [单选题] *A.efficientB.beneficialC.validD.effective(正确答案)13、My father?is _______ flowers. [单选题] *A. busy watering(正确答案)B. busy waterC. busy with wateringD. busy with water14、He was very excited to read the news _____ Mo Yan had won the Nobel Prize for literature [单选题] *A. whichB. whatC. howD. that(正确答案)15、This is not our house. lt belongs to _____. [单选题] *A. the Turners'B. the Turners(正确答案)C. Turner'sD. Turners16、—I can’t always get good grades. What should I do?—The more ______ you are under, the worse grades you may get. So take it easy!()[单选题] *A. wasteB. interestC. stress(正确答案)D. fairness17、The more he tried to please her, _____she seemed to appreciate it. [单选题] *B.lesserC.the less(正确答案)D.the lesser18、I don’t know how to improve my English. Can I ask you for some _______? [单选题] *A. answersB. advice(正确答案)C. questionsD. words19、--What are the young people doing there?--They are discussing how to _______?the pollution in the river. [单选题] *A. come up withB. talk withC. deal with(正确答案)D. get on with20、He asked for help from his friends who owned a computer company in New York. [单选题] *A. 拥有(正确答案)B. 经营D. 了解21、They all choose me ______ our class monitor.()[单选题] *A. as(正确答案)B. inC. withD. on22、78.—Welcome to China. I hope you'll enjoy the ________.—Thank you. [单选题] * A.tour(正确答案)B.sizeC.nameD.colour23、--What’s the _______ like today?--Cloudy. [单选题] *A. skyB. airC. landD. weather(正确答案)24、Every morning John takes a()to his office. [单选题] *A. 20-minutes' walkB. 20 minute ' walkC. 20-minutes walkD. 20-minute walk(正确答案)25、Having stayed in the United States for more than ten years, he got an American()[单选题] *A. speechB. accent(正确答案)C. voiceD. sound26、Neither she nor her friends ______ been to Haikou. [单选题] *A. have(正确答案)B. hasC. hadD. having27、I'm sorry I cannot see you immediately. But if you wait, I'll see you_____. [单选题] *A. for a momentB. in a moment(正确答案)C. for the momentD. at the moment28、My mother’s birthday is coming. I want to buy a new shirt ______ her.()[单选题] *A. atB. for(正确答案)C. toD. with29、You can't see many _____ in a hospital. [单选题] *A. man nurseB. men nurses(正确答案)C. men nurseD. man nurses30、_____you may do, you must do it well. [单选题] *A.WhichB.WheneverC.Whatever(正确答案)D.When。

电子科技英语试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. The term "semiconductor" refers to materials that have electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator.A) TrueB) False2. Which of the following is not a type of electronic component?A) ResistorB) CapacitorC) InductorD) Transistor3. The unit of electrical resistance is the ohm, symbolized by:A) ΩB) mAC) VD) A4. The process of converting analog signals to digital signals is known as:A) ModulationB) DemodulationC) Analog-to-Digital Conversion (ADC)D) Digital-to-Analog Conversion (DAC)5. In the context of electronic circuits, what is the purpose of a diode?A) To amplify signalsB) To block the flow of current in one directionC) To store energyD) To filter signals6. What does the acronym "CPU" stand for in computing?A) Central Processing UnitB) Central Power UnitC) Central Programming UnitD) Central Print Unit7. The term "bandwidth" in telecommunications refers to:A) The width of a transmission bandB) The speed of data transmissionC) The quality of a transmission lineD) The cost of a transmission service8. Which of the following is a type of programming language used in electronics?A) JavaB) C++C) Both A and BD) Neither A nor B9. The basic unit of information in digital systems is the:A) BitB) ByteC) KilobitD) Megabyte10. What does "RAM" stand for in computer memory?A) Random Access MemoryB) Rapid Access MemoryC) Read Access MemoryD) Recorded Access Memory二、填空题(每空1分,共10分)11. The ________ is the fundamental unit of electric charge.12. A ________ is a type of electronic device that can change resistance based on an input signal.13. The process of converting digital signals to analog signals is known as ________.14. In computer architecture, ________ refers to the internal communication pathways within a computer.15. The speed of a computer's processor is often measured in ________.三、简答题(每题5分,共20分)16. What are the three main components of a microprocessor?17. Explain the difference between a parallel and a serial communication system.18. What is the role of a filter in an electronic circuit?19. Describe the function of a transistor in an amplifier circuit.四、翻译题(每题5分,共10分)20. 将以下句子从英文翻译成中文:"The development of integrated circuits hasrevolutionized the electronics industry."21. 将以下句子从中文翻译成英文:“光纤通信具有传输速度快、抗干扰能力强等优点。

电子专业英语阶段测试试卷A.Words(35)1界面()2坐标()3十字准线()4指针()5撤销()6图层()7使自动化()8辅助()9实时的()10机器人技术()11自动控制()12完成()13普通地()14使成整体()15提示()16几何图形()17软件()18放大()19方位()20全体职员()21精炼()22仪器()23耗时的()24车间()25原始图()26设计图()27排除()28排除()29程序()30加工()31菜单()32草图()33图表()34标签()35重大的()B.Technical Terms.(30)1layout tab()2status bar()3computer aided manufacturing()4production process()5integrated CAD/CAM system()6computer aided design()7graphics editing command()8drawing instrument()9part drawing()10dialogue box()11default setting()12menu bar()13drawing area()14coordinate system()15model tab()C.Finish the dialogue.(15)John:Would you please tell me how to create a new drawing with AutoCAD? Mary:No().Open your AutoCAD window.John:()it open.Mary:(),choose New from the File menu.John:Yes,here comes the dialogue box.Mary:Secondly,choose Start from Scratch.John:How about the next step?Mary:Take it().Under Select Default Setting Select English and Metric, and then choose OK.John:The drawing opens()the default AutoCAD settings.Mary:You’re really a quick learner.Finally choose Save As from the File menu and enter a file name.Then you can save the drawing.D.Translation.(20)1.--Do you know who invented the CAD software?--Sorry,but I know this software is very helpful in drawing.2.--How often do you communicate with you parents in US?--We have a net chat each day through QQ.3.--Will you please tell me something about Computer-aided manufacturing?--Certainly.CAM is a system of using computer technology to assist the manufacturing process.4.–-Do you have any idea about CAD/CAM system?--The system takes the computer-generated design and feeds it directly into the manufacturing system..5.–Through the use of CAM,a factory can become highly automated. --Thanks for your clear explanation.。

2013~2014学年第一学期1106-1107班《电子信息技术专业英语》试卷(考试时间90分钟)一、单词翻译(20%)1. switch 11. component2. device 12. circuit3. instruction 13. resistor4. junction 14. capacitor5. combination 15. diode6. manufacture 16. transistor7. structure 17. current8. principle 18. voltage9. wafer 19. amplifier 10. analog20. insulator二、词组互译(20%) 1. 广泛应用于 11. electronic circuit 2. 把…. 分成…… 12. variable resistor 3. 打算…… 13. direct currents 4. 根据…… 14. integrated circuit 5. 将…..应用于 15. forward bias 6. 提到、指 16. N-type material 7.由……组成 17. electronic counter 8. 用做…… 18. frequency synthesizer 9. 被称做…… 19. digital instrument 10. 形成 20. operational amplifier三、判断正误,用“T ”或“F ” 表示(10%)1. The conductivity of semiconductors is higher than that of insulators But lower than that of conductors. ( )2. Silicon materials can conduct electricity when they are in purestate. ( )3. A semiconductor of n-type means that the pure material have been added impurities with three outer electrons. ( )班级 学号 姓名4. It is called forward bias if a diode is connected to an external voltage to make the p-type region positive and the n-type region negative. ( )5. An n-type and a p-type material created side by side can form a p-n junction. ( )四、回答问题(15%)1. What component can restrict the flow of electrons?2. What component can be used to change AC into DC?3. What component can amplify small signal?4. Material can be divided into three types, what are they?5. What function can integrated circuits perform?五、句子翻译(20%)1. The transistor acts as a switch.2. Diodes conduct electricity in only one direction.3. Digital ICs can be used in computers.4. ICs have a small size and low cost and therefore they are widely used in different fields.5. Substance can be divided into three types: conductors, semiconductors andinsulators.六、段落翻译(15%)An integrated circuit look like nothing more than a tiny chip of metal, perhaps one-half of a centimeter on a side, and not much thicker than a sheet of paper. It is so small that if it fell on the floor, it could be easily swept up with the dust. Although it is very small, it represents the most highly skilled technology at every step of its manufacture. At today’s level of development, it might comprise more than ten thousand separate electronic elements including elements of many different functions, such as diodes, transistors, capacitors and resistors.2013~2014学年第一学期1106-1107班《电子信息技术专业英语》补考答题卷(考试时间90分钟)一、单词翻译(20%)1.__________________________ 11. ________________________2.__________________________ 12._________________________3.__________________________ 13._________________________4. _________________________ 14. _________________________5.__________________________ 15.________________________ 6 ._________________________ 16.________________________ 7 ._________________________ 17.________________________8. _________________________ 18.________________________ 9 ._________________________ 19.________________________ 10._________________________ 20.________________________ 二、词组互译(20%)1.__________________________ 11. ________________________2.__________________________ 12._________________________3.__________________________ 13._________________________4. _________________________ 14. ________________________5.__________________________ 15.________________________ 6 ._________________________ 16.________________________ 7 ._________________________ 17.________________________8. _________________________ 18.________________________ 9 ._________________________ 19.________________________ 10._________________________ 20.________________________三、判断正误,用“T ”或“F ” 表示(10%)1._____2._____3.______4.______5.________(10%)。
郴州师范学校期末考试试卷 (2013学年第一学期) 课程名称 专业英语 适用班级 Z328—Z329 班 考试时量 60 分钟 满分 100 分
一、选择英语的汉语意思,并把序号填在题前的括号内。(1'×10) ( )1、battery A、电路 ( )2、resistor B、物理学家 ( )3、circuit C、电阻器 ( )4、voltage D、电压 ( )5、capacitance E、电池 ( )6、AC F、金属的 ( )7、metallic G、电容 ( ) 8、physicist H、法拉 ( )9、current I、交流电 ( )10、Farad J、电流
二、选择最佳答案的序号填在题前的括号内。(2'×15) ( )1、The most typical circuit are . A、series circuit B、parallel circuit C、series and parallel circuit ( )2、A current is the flow of . A、charges B、positive charges C、electrons ( )3、The value of can be altered to adjust the current in a circuit. A、thermistors B、variable resistors C、 LDR ( )4、The unit of the resistance is . A、volt B、ampere C、ohm ( )5、Ohm' Law expresses the relationship between resistance ,voltage and . A、charges B、current C、potential difference ( )6、A capacitor resists change in . A、current B、voltage C、 resistance ( )7、The inductor has properties of . A、inductance B、inductance and resistance C、resistance ( )8、Under opposite condition ,current will not abruptly decrease to . A、the highest B、the lowest C、zero ( )9、A semiconductor diode is a terminal device. A、one B、two C、three ( )10、A transistor can connected in to a in any one of the three ways. A、circuit B、line C、dot ( )11、Operating voltages range from 1.5 to volts DC for most applications. A、25 B、30 C、35 ( )12、A transformer cannot be called a machine ,for it has not .
第一单元元件与定律A.课文译文电阻器、电容器和电感器在电子电路中,电阻器、电容器和电感器是非常重要的元件。
电阻器和电阻电阻器是二端口元件。
电阻是阻止电流流动,更确切地说,是阻止电荷流动的能力。
在国际单位制中,电阻用欧姆来度量。
希腊字母Ω是欧姆的标准符号。
较大的电阻一般用千欧和兆欧来表示。
模拟这种特性常用的电路元件是电阻器。
图1.1表示电阻器的电路符号,R表示电阻器的电阻值。
图1.1 电阻器的电路符号为了进行电路分析,我们必须在电阻器中指明电流和电压的参考方向。
如果我们选择关联参考方向,那么电压和电流之间的关系是:v=iR(1.1) 这里v是电压,其单位是伏特,i是电流,其单位是安培,R是电阻,其单位是欧姆。
如果选择非关联参考方向,我们必须写成:v=-iR(1.2) 用在公式(1.1)和(1.2)中的代数式就是著名的欧姆定律。
欧姆定律表示了电压作为电流的函数。
然而,要表示电流是电压的函数也是非常方便的。
欧姆定律是电阻两端的电压和电流间的代数关系。
电容器和电容电能可以存储在电场中,存储电能的装置叫电容器。
电容器存储电能的能力叫做电容。
图1.2表示电容器的电路符号。
电容的电路参数用字母C表示,用法拉来度量。
因为法拉是相当大的电容量,实际上电容值通常位于皮法和微法之间。
图1.2 电容器的电路符号当电压随时间变化时,电荷的位移也随时间变化,引起了众所周知的位移电流。
在终端,位移电流和传导电流没有区别。
当电流参考方向和电压参考方向是关联参考方向时,电流正比于电容两端电压随时间的变化率的数学表达式为:dt dvC i = (1.3)这里 i 的单位是安培,C 的单位是法拉,v 的单位是伏特, t 的单位是秒。
电感器和电感众所周知,电感是电子电路中的模块之一。
所有的线圈都有电感。
电感是抵抗流过线圈电流的任何变化的性质。
电感用字母L 表示,其单位是亨利。
图1.3表示一个电感器。
图1.3 电感器的电路符号当电流和电压的参考方向关联时,有dt diL v = (1.4)这里v 的单位是伏特,L 的单位是亨利,i 的单位是安培,t 的单位是秒。
电子信息工程专业英语Part 1第一课关于电子技术一、课文习题参考答案Ⅰ. (1)alternating current circuits (2)semiconductor diodes(3)passive component(4)the combinatory logic electric circuit(5)rectification(6)Laplace transform(7)inductor(8)Fourier series and Fourier transformⅡ.(1)控制理论(2)场效应管三极管(3)布尔代数(4)稳压(5)相关性和功率谱密度(6)滤波器类型(7)模/数转换器(8)时序逻辑电路的分析与综合Ⅲ.(1)Electronics is a part of the larger field of electricity. The basic principles of electricity are also common to electronics. Modern advances in the field of computer, control system, communications have a close relationship with electronics. The field of electronics includes the electron tube, transistor, integrated circuit and so on.(2) Direct current circuits & Alternating current circuits,Analog electronics,Digital electronics,signal and systems,Circuit theory and design, Control theory, Microcontroller systems,Computer programming for engineering applications.(3) This curriculum mainly introduces the characteristics of semiconductor devices in linear application scope.The content involved in semiconductor diodes (PN junction diodes, special purpose diodes), transistors (field effects and bipolar transistors), signal amplifiers, practical amplifiers, biasing circuits, operational amplifiers circuit and other circuits (rectification, regulation and DC power supplies).(4) This partial studies take the basic electric circuit theory and the operational amplifier knowledge as the foundation. The main study goal is to enhance understanding of the electric circuit theory. Its main content includes the elementary theory in circuit theory (network functions, characteristic frequencies), types of filter (lowpass,bandpass), review of operational amplifiers (design of first and second order using operational amplifiers, cascade design), filter characteristics(Butterworth, Chebyshev, frequency transformations in design, sensitivity design of passive LC ladder filters and a brief introduction to switched capacitor filters).(5) Perfect.二、参考译文电子学的发展电子学是电学的一部分。
1. The advantages of the transistor over the vacuum tube wereenormous. Compared totheold technology ,transistors were much smaller ,faster ,and cheaper to manufacture . They were also far more reliable and used much less power . The transistor is what started the evolution of the modern computer industry in motion. 和真空管相比,晶体管存在着巨大优势:晶体管的尺寸小得多,切换速度快得多,生产成本低得多; 晶体管的性能更加可靠,耗能也更少。晶体管的发明带来了计算机工业的蓬勃发展。 2. A special material is used to make these integrated circuits. While most materials either insulate from electrical flow (air , glass ,wood )or conduct electricity readily (metals ,water ), there are some that only conduct electricity a small amount ,or only under certain conditions . These are called semiconductors . the most commonly used semiconductor is of course silicon . 制造集成电路需要使用一类特殊材料。多数材料要么对电流绝缘(如空气,玻璃,木头),要么很容易传导电流(如金属,水溶液), 但也有一些材料只能传到少量电流,或只在特定条件下传导电流 ------这种材料被称作“半导体”。 硅是最常用的半导体材料。 3. A flip-flop is basically a bi-state circuit in which either a 0 or 1 state can resides. beacause its simplicity ,the flip-flop is extremely fast . as a basic element , the flip-flop is used in digital circuits and Ics . A flip-flop will lose its state when the supply votage is removed.Therefore,itis volatile. 触发器是一种存储“0"或”1“ 的双态电路。由于结构简单, 所以触发器速度极快。触发器是数字电路和集成电路的基础构件。由于电源电压去掉后,触发器的原有状态就失去了,因此触发器是易失的. 4. RAMstandsforrandom-access memory . RAM contains bytes of information , and the microprocessor can read or write to those bytes depending on whether the RD or WR line is signaled . One problem with today’s RAM chips is that they forget everything once the power goer off . that is why the computer needs ROM . RAM 是随机存取存储器。RAM中包含着以字节为单位的信息,微处理器能够依据RD/WR 信号哪个有效来决定字节的读、写。当前RAM芯片的一个问题是,掉电后,所有保存在RAM上的内容全部丢失。这就是计算机需要ROM 的原因。 5. The test register is a special latch that can hold values from comparisons performed in the ALU . An ALU can normally compare two numbers and determine if they are epual , if one is greater than the other , etc. The test register can also normally hold a carry bit from the last stage of the adder . It stores these values in flip-flops and then the instrucion decoder can use the values to make decisions. 测试寄存器; 一种保存ALU比较结果的专用锁存器。通常,ALU能够将两个数进行比较,并判断出二者是否相等或者哪个更大。测试寄存器也可以保存加法运算最后一步的进位位。这些数值保存在处罚期当中,指令译码器利用这些数值作出判决。 6. It is extremely hard to define dynamic range (DR) for an op amp, so let’s start with a digital-to-analog converter (DAC)where DR is defined as the ratio of the maximum output voltage to the smallest output voltage the DAC can produce . 由于很难定义运算放大器的”动态范围“,因此先给”数模转换器“的动态范围下定义。DAC的动态范围就是其最大输出电压和最小输出电压之比。 7. The switching regulator operates the power devices in the full-on and cutoff states. This then results in either large currents passed through the power devices with a low on voltage or no current flowing with high voltage across the devece . This results in a much lower power being dissipated within the supply. The average switching power supply exhibits efficiencies of between 70 to 90 percent,regardless of the input voltage . 开关电源中的功率器件工作在”全开“和”截断“状态。这样,要么在大电流流经功率器件时,导通电压很低;要么在大电压时,没有电流通过器件。因此,电源内部消耗的功率就很少。开关电源的平均效率为70%-90%,而且和输入电压无关。 8. Frequency synthesizers use one or more Phase-Locked Loops (PLL) to generate one to many different frequencies on their outputs, from one or more referencesources.The reference frequency is usually generated by a crystal attached to the synthesizer. The design goal of frequency synthesizers is to replace multiple oscillators in a system, and hence reduce board space and cost. 通过使用一个或多个”锁相环“,频率合成器从一个或多个参考时钟源产生一个或多个不同的输出频率。参考频率通常是由连接到合成器上的晶体产生的。设计频率合成器的目的是用以替代系统中的多个振荡器,从而减少了电路板空间,降低了系统成本。 9. A block buffer is a device in which th output waveform directly follows the input waveform. The input wavefom propagates through the device and is redriven by the output buffers. hence, such devices have a propagation delay associated with them .In addition ,due to the differences between the propagation delay through the device on each input-output path ,skew will exist on the outputs . 时钟缓冲器是一种输出波形直接跟随输入波形的器件。输入波形通过该器件并被输出缓冲器重新驱动。因此,该类器件存在传输延迟。此外,由于在每个输入,输出通道间存在传输延迟的差别,输出端将出现相位抖动 10. A resistor at high frequency acts like a series combination of inductance with the resistor in parallel with a capacitor. A capacitor at high frequency acts like an inductor and resistor in series combination with the capacitor plates . 工作在高频的电阻表现为电感和并联的电阻,电容之间的级联。工作在高频的电容表现为电感,电阻和电容的级联。 11. In an area where the number of users has grown to the point that the system is overloaded , the poer is reduced , and the overloaded cells are split int smller microcells to permit more frequency reuuse. Telephone companies sometimes create temporary microcells, using portable towers with satellite links at sporting events , rock concerts , and other places where large numbers of mobile users congregate for a few hours . 在用户数量达到导致系统过载程度的地区,为了实现更多的频率重用,需要降低功率并过载蜂窝小区分为更小的微蜂窝单元。在体育赛事,摇滚音乐会及其他在几个小时内有大量移动用户云集的场所,电话公司有时会使用卫星链接的便携发射塔创建临时'微蜂窝”。 12. CDMA is completely different from AMPS. D-AMPS, and GSM .instead of dividing the allowed frequency range into a few hundred narrow channels , CDMA allows each station to transmit over the entire frequency spectrum all the time .multiple simultaneous transmissions are separated using coding theory . CDMA also relaxes the assumption that colliding frames are totally garbled. instead, it assumes that multiple signals add linearly . CDMA和AMPS ,D-AMPS 及GSM完全不同。CDMA没有将可用频带分割为几百个窄带信道,而是允许信号在整个频谱范围内传送。利用编码原理,CDMA可以将多个同时传送的信号分离开来。在CDMA中,“相遇数据帧会造成数据混淆”的想法不存在了--CDMA认为多路信号之间是线性相加的。 13. A base station communicates with mobiles using two types of radio channels, control channels to carry control information and traffic channels to carry messages . 基站使用两类无线信道和移动用户进行通信:传送控制信息的“控制信道”和传送消息的”通信信道“ 14. In an FDMA scheme the available spectrum is divided into a number of frequency channels of certain bandwidth and individual calls use ifferent frequency channels. all first-generation cellular systems use this scheme . 在FDMA方式中,可用频谱划分为若干具有一定带宽的频道;每个呼叫都使用不同频道。第一代蜂窝系统采用的都是FDMA 方式。 15. Some digital logic Ics and their analog counterparts (analog/digital converters, for example ) are standard parts , or standard Ics . you can select standard Ics from catalogs and data books and buy them from distributors . systems manufacturers and designers can use the same