《法律专业外语》课程教学大纲
一、《法律专业外语》课程说明
(一)课程代码:02130016
(二)课程英文名称:Legal English
(三)开课对象:法学专业
(四)课程性质:
本课程是法学专业必选学科选修课程之一,一般在大学三年级开设。法学专业本科学生通过两年的大学英语的学习,已掌握了普通英语的基本语汇、语汇和句型,为法律专业英语的学习打下了良好的基础。法律专业英语课程的开设一方面为学生继续学习英语提供了良好的机会,另一方面也能使学生运用英语来表达自己所学的法律专业知识,从而为他们将来直接运用英语获得本专业的最新信息奠定基础。其前导课程有综合英语、基本法律课程等。
在课程类别中属于专业教育课程、专业必修课。
(五)教学目的:
通过这门课的教学与学习,将使学生了解和掌握法律英语的阅读与写作方法,并从众多节选于国外名著名篇中的课文里,了解国外尤其是英美法系国家里的法律制度,并培养学生运用已学的英语知识和相关法律原理来分析、处理和解决实际案例的能力。
(六)教学内容:
本课程要求学生,首先必须熟知相关的法律知识,即英美法律制度,然后通过教师对某些课文的讲解和学生自身根据教师提问对某些课文的阅读,掌握相关法律词汇,包括法律英语中基本词汇,以及学生已熟悉,但在法律语境下,与日常用义大相径庭的词汇;掌握法律英语中长句的理解和翻译,从而熟悉和掌握法律英语的特点。
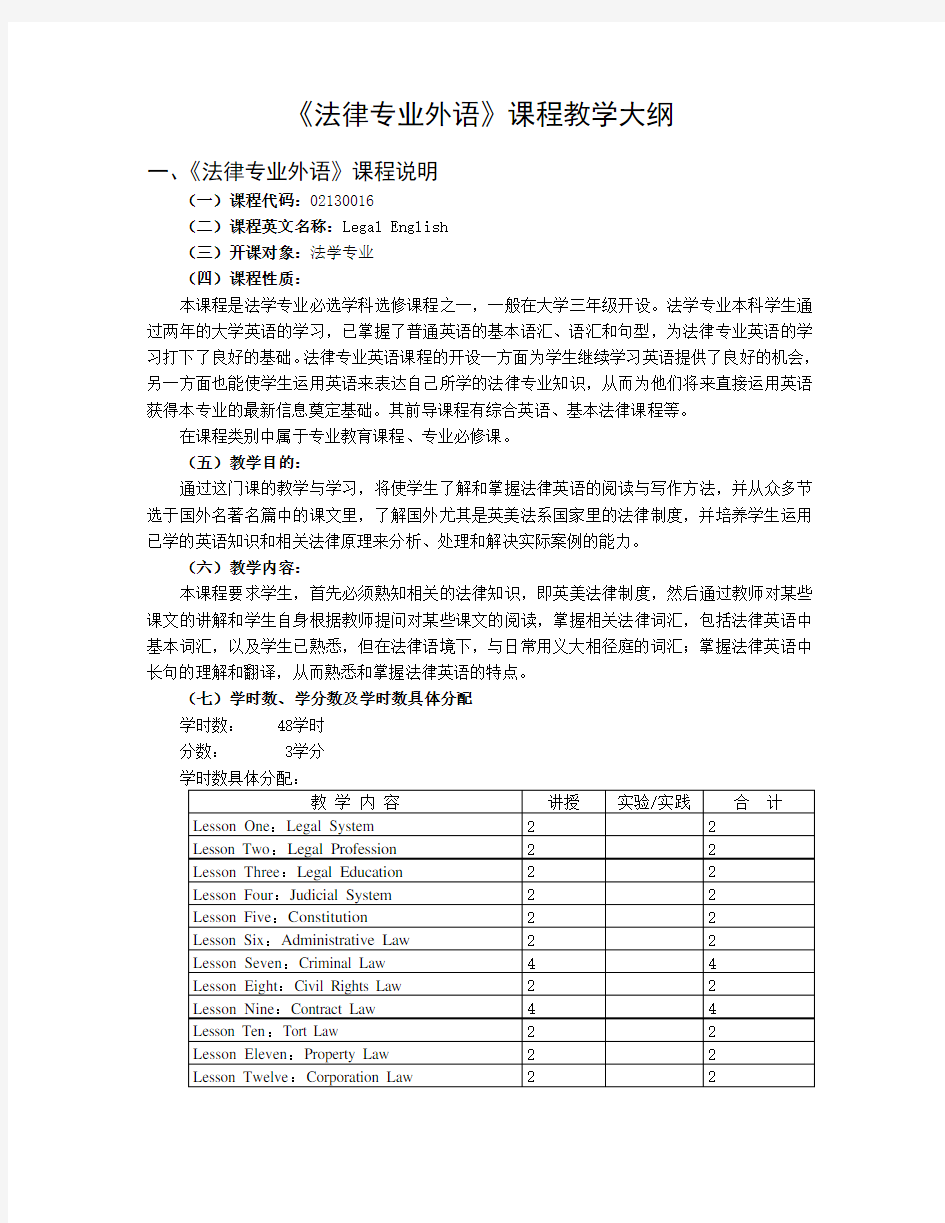
(七)学时数、学分数及学时数具体分配
学时数: 48学时
分数: 3学分
(八)教学方式
教学方式以课堂教学为主。
(九)考核方式和成绩记载说明
考核方式为考查。严格考核学生出勤情况,达到学籍管理规定的旷课量取消考试资格。综合成绩根据平时成绩和期末成绩评定,平时成绩占40% ,期末成绩占60% 。
二、讲授大纲与各章的基本要求
Lesson One:Legal System法律制度
教学要点:
Pre-reading tasks
1.What legal systems do you know about? Can you say something about them?
2.What is Russia’s legal system? And The Scandinavian countries’?
Comprehension of the text: Answer the following questions
1.How did civil-law system come into being?
2.What countries does the civil-law family have influence on?
3.What counties does the common law system have influence on?
4.What is the characteristic of the civil-law family?
5.What is the doctrine of common law?
6.Does the development of a country have a close relationship with the country’s law?
What is the difference between the civil-law family and the common law system?
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Legal systems
Clusters/families/groups of legal systems
Civil-law family
Common law system
Common law differs from civil law
考核要求:
Students will be able to:
1. know something about the two big legal systems, their differences and also will know that
every society has a legal system ;
2. master some related legal terms;
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities related to the theme of the
unit.
Lesson Two:Legal Profession法律职业
教学要点:
The personnel of the prosecutorial system in the US include both federal prosecutors and local prosecutors. In addition, assistant prosecutors at both the federal level and the local level are the most important part of the prosecutorial profession.
The basic qualification for a prosecutor in the United States is that he or she must be a member of the bar in that jurisdiction. In other words,all the prosecuting attorneys,including federal attorneys and local attorneys,the chief of a prosecutor’s office and the assistants,should have had a law degree and passed the Bar Examination in the jurisdiction.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
The training of attorneys and the practice of law have evolved over time in the United States. Today American lawyers practice in a variety of settings and circumstances.
Government Attorneys in the Judicial Process:1.Federal Prosecutors. 2.Prosecutors at the State Level. 3.Public Defenders.4.Other Government Lawyers. 5.The U.S. Department of Justice.6.U.S. Solicitor General. 7.State Attorneys General.
Private Lawyers in the Judicial Process Assigned Defense Counsel. Private Defense Counsel.
The Courtroom Workgroup
Legal Services for the Poor
考核要求:
1. How many types of lawyers are there in America? What are they?
2. What kind of lawyer do you want to be?(If you are a lawyer)What kind of work do you do ?
3.What roles do lawyers play in society? Which of them is the most important in your view?
4. If a lawyer knows much about law but very little about anything else,will he be a good
lawyer.
Lesson Three:Legal Education法律教育
教学要点:
legal education: an overview
Today, in nearly all states, completion of a degree program at an accredited law school is required for admission to practice as a lawyer. It normally takes three years of full time work to receive a law degree. Unlike the case in nearly all other countries of the world this required degree program must follow a basic four year college or university degree. In the United States there are 175
law schools accredited by the . Most states do not accept bar applications from graduates of law schools not on that list.
In the first year of law school students generally are required to take broad introductory topics. These may include , , , , property, and constitutional law. Many schools also require courses in and .
The second and third years of law school allow a student to concentrate on particular areas of the law such as business, litigation, , or family law. A number of courses may still be recommend or required such as , , , and . In addition, the second and third years often provide the student with the chance to get some legal experience through legal aid clinics and internships.
Law students usually participate in extra-curricular activities that provide them with further useful experience. Law reviews are legal academic journals edited and in part written by students. Membership in law review is usually granted on the basis of first year grades or a writing competition. Moot Court provides students with the opportunity to compete with one another by giving mock oral arguments before a panel of judges.
Law school teaching tends to be far more interactive than is common in undergraduate education, despite large classes. In the classic "Socratic Method" the law professor asks a student a series of questions about assigned cases.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Part one: Curriculum and the case method
Part two: Law school hierarchy
考核要求:
Which teaching method is better forlaw study:case method or lecture method?
Lesson Four:Judicial System司法系统
教学要点:
1st period pre-reading activities (familiar with new words, terms, and background information)
2nd period while reading (highlights of the text)
3th period after-reading activities
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Part one:Courts
--the Supreme Court
--Court of Appeals
--District Court
Part two:Judges
--Justice
--Judge
--Justice of Peace/Magistrate
考核要求:
1.How many court systems are there in the United States? And what are they?
2.How many judges generally are there in a federal district court?
3.How are state court judges usually selected?
Lesson Five:Constitution宪法
教学要点:
Warming-up questions
1. How much do you know about English constitution?
2. Can you guess what the theme of this unit refers to?
3. Can you say something about the organ of the English government?
Comprehension of the text.
1. What is the form of government based on in Britain?
2. According to the text, which of the following does not hold power?
3. Which of the following causes a new election of the Cabinet?
4. Where are the policies of the government warmly discussed and closely watched?
5. How often is the election for seats in Commons held?
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Constitution
Unwritten constitution
Sovereign
Monarch
Executive branch
Cabinet
House of Commons
House of Lords
考核要求:
Students will be able to:
1.understand the main idea (the function of each organ of the government and their relationship in England)of the text;
2. master some related legal terms; understand how the government work
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities related to the theme of the unit.
Lesson Six:Administrative Law行政法
教学要点:
Administrative law encompasses laws and legal principles governing the administration and regulation of government agencies (both Federal and state).Generally, administrative agencies are created to protect a public interest rather than to vindicate private rights.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Administrative law
Agency action
Administrative unit
Adjudication
Rulemaking
discretionary
考核要求:
1.What is the scope of administrative law?
2.What is agency action?
3.What is interpretation in administrative law?
4.What are the central tasks of administrative law?
Lesson Seven:Criminal Law刑法
教学要点:
Students will be able to:
1. understand the main idea (the general knowledge of crimes and punishment) of the
text;
2. master some related legal terms;
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities
related to the theme of the unit.
4. try to understand the criminal procedure
教学时数:4 学时
教学内容:
Justice
1. the ideal of fair and beneficent treatment of all people by each other and by their governments, which law in a democratic society attempts to serve
2. the system of law and administration of law
Criminal justice
Justice of the peace
Fraud
Statute
Code
Self-defense
Misdemeanor
--a crime less serious than a felony, usually one punishable by incarceration for up to one year, in some states misdemeanors include some offenses punishable only by a fine
考核要求:
1. Comprehension of the text.
1) Which aspect of law are ordinary people most familiar with?
2) What kind of criminal conduct can be found in a federal government code?
3) In which country was it illegal to own gold in the past?
2. Vocabulary
Compare and contrast the following pair of words
crime/criminal vary/variable threat/threaten violate/violation
burglar/burglary
3. Grammar
Lesson Eight:Civil Rights Law民权法
教学要点:
A civil right is an enforceable right or privilege, which if interfered with by another gives rise to an action for injury. Examples of civil rights are freedom of speech, press, assembly, the right to vote, freedom from involuntary servitude, and the right to equality in public places. Discrimination occurs when the civil rights of an individual are denied or interfered with because of their membership in a particular group or class. Statutes have been enacted to prevent discrimination based on a persons race, sex, religion, age, previous condition of servitude, physical limitation, national origin and in some instances sexual preference.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
The most important expansion of civil rights in the United States was the enactment of the Thirteenth and Fourteenth Amendments.
The most prominent civil rights legislation since reconstruction is the Civil Rights Act of 1964.
The judiciary, most notably the Supreme Court, plays a crucial role in interpreting the extent of the civil rights.
The existence of civil rights and liberties are recognized internationally by numerous agreements and declarations.
International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights.
考核要求:
1.What is the common form of racial discrimination in the workplace?
2.What is the Walker v. IRS about?
Lesson Nine:Contract Law合同法
教学要点:
Students will be able to:
1. understand what makes a valid contract;
2. master some related legal terms;
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities related to the theme
of the unit.
教学时数:4 学时
教学内容:
In legal terms, a contract is:
1.A promise (or set of promises) that the law protects and enforces. e.g.
2.seller: promise to deliver a carload of lumber
3.buyer: promises to pay the seller a certain price
4.If one party breached the contract, the other party can choose to sue.
A valid contract
“offer” and “acceptance” are promises and must be supported by “consideration”,which is: --a mysterious substance,
--an intricate legal concept
--underlying idea: each pa rty makes his promise “in consideration” of something the other party promises.
--e.g. I offer to sell my old car for $2,000, the buyer accepts (promising to pay $2,000) --- consideration on each side is clear.
--e.g. I promise to give my daughter a handful of diamonds --- there is no “consideration” for my promise.
考核要求:
Pre-reading tasks
1.What is a contract?
2.What can people do with contracts?
After-reading activities
Comprehension of the text: Answer the following questions
1.How to understand “from status to contract”?
2.What is a contract in legal terms?
3.What are the factors in a valid contract?
4.What is consideration?
5.Why do businessmen tend to sidestep contract law in the world of affairs?
6.What is the relationship between contract law and commercial law?
Lesson Ten:Tort Law侵权法
教学要点:
Students will be able to:
1.understand the main idea (the knowledge of tort law)of the text;
2.master some related legal terms;
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities
related to the theme of the unit.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Tort
Tortfeasor
Wrong
Fellow servant rule/doctrine
Negligence
Recover
Reasonable man/person
Strict liability
考核要求:
Pre-reading tasks
1. How much do you know about Torts law?
2. What can be covered in torts law?
After-reading activities
Comprehension of the text.
1.What is the common characteristic of the behaviors defined as civil wrongs?
2. Which category of civil wrongs has not grown rapidly in the 20th century?
3. As for the product liability, to whom the court judgments are favorable in the 20th century?
4. According to the text, what is the fundamental concept of tort law?
Lesson Eleven:Property Law财产法
教学要点:
Property signifies dominion or right of use, control, and disposition which one may lawfully exercise over things, objects, or land. One of the basic dividing lines between property is that between real property and personal property. Generally, the term real property refers to land. Land, in its general usage, includes not only the face of the earth but everything of a permanent nature over or under it. This includes structures and minerals.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
There are further divisions within the real property classification. The most important are freehold estates, nonfreehold estates, and concurrent estates. (Others are future interests, specialty estates, and incorporeal interests).
---Freehold estates are those in which an individual has ownership for an indefinite period of time. An example of a freehold estate is the "fee simple absolute", which is inheritable and lasts as long as the individual and his heirs wants to keep it. Another example is the "life estate", in which the individual retains possession of the land for the duration of his or her life.
---Nonfreehold estates are property interests of limited duration. They include tenancy for years, tenancy at will, and tenancy at sufferance.
---Concurrent estates exist when property is owned or possessed by two or more individuals simultaneously
考核要求:
1.What are the roles of government in the field of property law?
2.What are the lawyers in the field of property law?
3.What are the major areas in real property law?
Lesson Twelve:Corporation Law公司法
教学要点:
A corporation is a legal entity created through the laws of its state of incorporation. Individual states have the power to promulgate laws relating to the creation, organization and dissolution of corporations. The law treats a corporation as a legal "person" that has standing to sue and be sued, distinct from its stockholders. The legal independence of a corporation prevents shareholders from being personally liable for corporate debts. It also allows stockholders to sue the corporation through a derivative suit and makes ownership in the company (shares) easily transferable. The legal "person" status of corporations gives the business perpetual life; deaths of officials or stockholders do not alter the corporation's structure.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Corporation Law
Part one: Introduction
Part two: Forms of business
A.Proprietorships
B.Partnerships
C.Corporations
考核要求:
1.What are the main classes of business enterprises in the United States?
2.What are the main categories of laws applicable to business enterprises in the United States?
3.What are Blue Sky Laws?
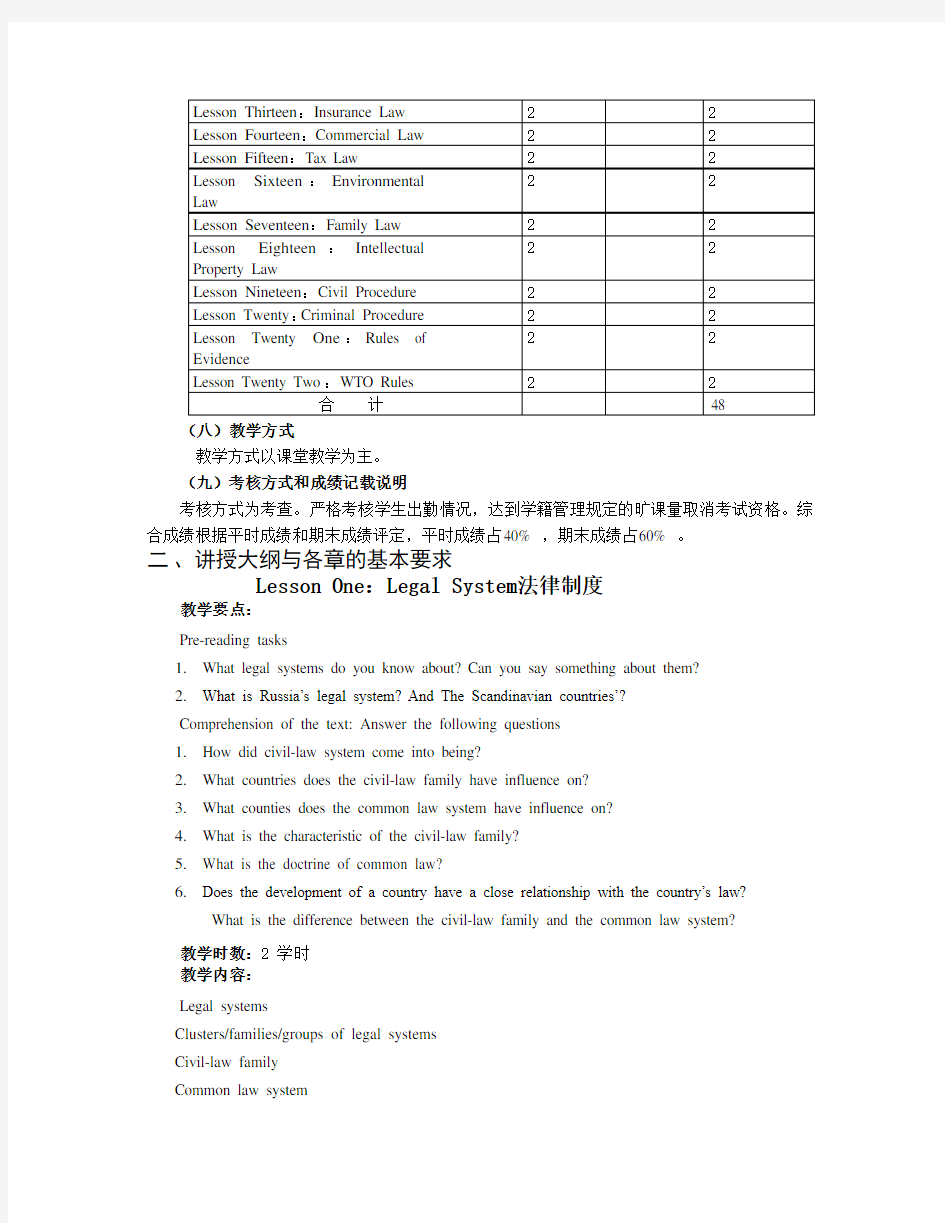
Lesson Thirteen:Insurance Law保险法
教学要点:
In the absence of insurance, three possible individuals bear the burden of an economic loss; the individual suffering the loss; the individual causing the loss via negligence or unlawful conduct; or lastly, a particular party who has been allocated the burden by the legislature, such as employers under Workmen's Compensation statutes. While types of insurance vary widely, their primary goal is to allocate the risks of a loss from the individual to a great number of people.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
In general, insurance companies are the safekeepers of the premiums. Because of its importance in maintaining economic stability, the government and the courts use a heavy hand in ensuring these companies are regulated and fair to the consumer.
Each individual pays a "premium" into a pool, from which losses are paid out. Regardless of whether the particular individual suffers the loss or not the premium is not returnable.
Up until 1944, insurance was not considered "commerce" and not subject to federal regulation. But in United States v. South-Eastern Underwriters Association, the Supreme Court held that Congress could regulate insurance transactions that were truly interstate.
考核要求:
1.Why do people purchase group insurance for personal needs?
2.What are the important of insurance for business?
3.What is “key man ” insurance?
Lesson Fourteen:Commercial Law商法
教学要点:
Commercial law governs the broad areas of business, commerce, and consumer transactions. Specific law has developed in a number of commercial fields. The Uniform Commercial Code, which has been substantially adopted as statutory law in nearly every state, governs numerous areas of commercial law.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Banks and bank accounts are regulated by both state and federal statutory law. Bank accounts may be established by national and state chartered banks and savings associations. All are regulated by the law under which they were established.
Bankruptcy law provides for the development of a plan that allows a debtor, who is unable to pay his creditors, to resolve his debts through the division of his assets among his creditors.
Credit allows consumers to finance transactions without having to pay the full cost of the merchandise at the time of the transaction.
Negotiable instruments are mainly governed by state statutory law.
Real estate transactions are governed by a wide body of federal statutes and state statutory and common law.
考核要求:
1.What is the history of the commerce clause adjudication?
2.What does the Supreme Court interpret the commerce clause?
Lesson Fifteen:Tax Law税法
教学要点:
The focus of this lesson is on tax and related issues. Tax includes income
(corporate and personal), excise and other taxation devices. Commercial law, trade,
intellectual property, etc. deal with the transactions giving rise to tax. Business
organizations focuses upon the entities themselves.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Part one:Federal taxation
1.Introduction
2.Generalscope of the taxing power
3.Direct v. indirect taxes
4.Federal taxing and due process
5.Federal taxes as regulatory measures
Part two:State taxation
1.Death taxes
2.Income taxes
考核要求:
1.What are the two limitations upon the exercise of Congress’ taxation power?
2.What are the principles of due process with respect to jurisdiction to impose income taxes
upon individuals and corporations in the United States?
Lesson Sixteen:Environmental Law环境保护法教学要点:
The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) was passed in 1970 along with the Environmental Quality Improvement Act, the Environmental Education Act, and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The main objective of these federal enactments was to assure that the environment be protected against both public and private actions that failed to take account of costs or harms inflicted on the eco-system.
The EPA was supposed to monitor and analyze the environment, conduct research, and work closely with state and local governments to devise pollution control policies. NEPA (really enacted in 1969) has been described as one of Congress's most far reaching environmental legislation ever passed. The basic purpose of NEPA is to force governmental agencies to consider the effects on the environment of their decisions.
State laws also reflect the same concerns and common law actions in nuisance allow adversely affected property owners to seek a judicial remedy for environtal harms harms.
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Part one: National environmental policy act
(Enacted in 1970;Amended in 1975)
Title one DECLARATION OF NATIONAL ENVIRONMENTAL POLICY Part two :Federal actions to address environmental justice in minority populations and low-income populations
(Executive order 12898,1994)
考核要求:
1.Why did the Congress make the Declaration of National Environmental Policy?
2.What is the continuing policy of the Federal Government?
3.What are main contents of an environmental impact statement?
Lesson Seventeen:Family Law家庭法
教学要点:
The right to freedom of choice in marriage and family relationships lies at the heart of the right to privacy. Family relationships, by their nature involve deep attachments and commitments to the necessarily few other individuals with whom one shares not only a special community of thoughts, experiences, and beliefs but also distinctly personal aspects of one’s life.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Domestic relations law
--Marriage
-husband-wife relation
--divorce
--separation
--parent-child relation
--adoption
--custody
--support
考核要求:
1.Should Abortion Be Legal?
2.What is the relationship between the right to privacy and the right to freedom of
choice in marriage and family relationships?
Lesson Eighteen:Intellectual Property Law知识产权法
教学要点:
Pre-reading tasks
1.What is copyright?
2.What rights does Copyright Law protect?
3.How can an owner get protected by Copyright Law?
Comprehension of the text: Answer the following questions
1.What rights does Copyright Law protect?
2.What is a prescribed copyright notice made up of?
3.How can an owner get protected by Copyright Law?
4.What remedies may a copyright owner have if infringement is proved?
5.As to the exception to the copyright infringement, what activities are in the realm of fair
use?
6.What has been done to protect the copyright owners in the world?
教学时数:2 学时
教学内容:
Copyright
Copyright can be sold or licensed to others
Formalities requirement under U.S. law
UCC (the Universal Copyright Convention)
To secure copyright protection in the USA and UCC member nations
Other international conventions
考核要求:
Students will be able to:
1. understand what makes a valid contract;
2. master some related legal terms;
3. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activities related to the theme
of the unit.
Lesson Nineteen:Civil Procedure民事诉讼程序教学要点:
Broadly speaking, civil procedure consists of the rules by which courts conduct civil trials. "Civil trials" concern the judicial resolution of claims by one individual or group against another and is to be distinguished from "criminal trials", in which the state prosecutes an individual for violation of criminal law.
"Procedure" is to be distinguished from "substantive law" in that substantive law defines the rights and duties of everyday conduct. Substantive law includes , tort law, and so on.
In America, civil procedure usually takes the form of a series of rules and judicial practices. The federal courts follow the Federal Rules of Civil Procedure; the state courts follow their own state rules of civil procedure.
In federal courts, evidentiary rules are governed by the The state courts follow their own state rules of evidence.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
adersary system
jury system
Federal Rule of Civil Procedure
Jury Trial
1.In general
2.Scope of jury rights
3.Means of controlling the jury
考核要求:
1.What were the there types of courts in the English legal history?
2.What are the distinctive characteristics of the adversary trial system?
3.Writing a legal memorandum
Lesson Twenty:Criminal Procedure刑事诉讼程序教学要点:
The rules of criminal procedure are different from those of civil procedure, because the two areas (criminal and civil) have different objectives and results. In criminal cases, the state brings the suit and must show guilt beyond a reasonable doubt, while in civil cases the plaintiff brings the suit and must only show the defendant is liable by a preponderance of the evidence.
The American criminal system is an adversarial and accusatorial model. Criminal procedure must balance the defendant's rights and the state's interests in a speedy and efficient trial with the desire for justice. Therefore, the rules of criminal procedure are designed to ensure that a defendant's rights are protected.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Part one : the adversary system
Part two: the accusatorial system
The burden of proof
The burden of going forward with the evidence
Presumption of innocence
Part three: standards of proof
考核要求:
1.How does an adversary system arrive at a decision?
2.What is an inquisitorial system?
3.How many standards of proof are critical legal standards and what are they?
4.What is the key to an accusatorial process of proof?
Lesson Twenty One:Rules of Evidence证据规则教学要点:
There are two principal questions about evidence that have to be answered.First, what matters and what materials should be admitted into evidence for the jury to consider?Secondly, what use can properly be made by the jurors of those matters and materials that are ruled admissible?
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
Rules of evidence: Admissibility; Relevancy;Weight;Sufficiency;Burden of proof
Types of evidence : direct evidence; indirect evidence
Forms of evidence
--Testimonial evidence
--Tangible evidence
--Judicial notice
考核要求:
1.What do the rules of evidence apply to?
2.What is ‘RELEV ANT EVIDENCE”?
3.What evidence is not admissible?
4.What are the court direct a party to predicate error upon a ruling?
Lesson Twenty Two:WTO Rules世贸组织规则
教学要点:
The WTO’s procedure for resolving trade quarrels under the Dispute Settlement Understanding is vital for enforcing the rules and therefore for ensuring that trade flows smoothly.
A dispute arises when a member government believes another member government is violating an agreement or a commitment that it has made in the WTO. The authors of these agreements are the member governments themselves —the agreements are the outcome of negotiations among members. Ultimate responsibility for settling disputes also lies with member governments, through the Dispute Settlement Body.
教学时数: 2 学时
教学内容:
A unique contribution
Dispute settlement is the central pillar of the multilateral trading syste m, and the WTO’s unique contribution to the stability of the global economy. Without a means of settling disputes, the rules-based system would be less effective because the rules could not be enforced. The WTO’s procedure underscores the rule of law, and it makes the trading system more secure and predictable. The system is based on clearly-defined rules, with timetables for completing a case. First rulings are made by a panel and endorsed (or rejected) by the WTO’s full membership. Appeals based on points of law are possible.
---Principles: equitable, fast, effective, mutually acceptable
---First stage: consultation (up to 60 days).
--- Second stage: the panel (up to 45 days for a panel to be appointed, plus 6 months for the panel to conclude).
---Appeals
考核要求:
1.How are disputes settled?
2.What is DSU?
3.What is DSB?
三、推荐教材和参考书目
1.《法律英语》,何家弘,第二版,法律出版社,2004
2.《法律英语教程》,沙丽金、林萍,中国政法大学出版社,2000
3.《法律英语》,董世忠、赵建,复旦大学出版社,1997
4.《法律英语核心教程》,杜金榜、张新红,对外经济贸易大学出版社,2002
执笔人:申静审核人:张道功审定:法学院
《英语教学法》课程教学大纲 英文名称:English Teaching Methodology 课程代码:0452117 学时数:32学时学分:2 课程类别: 课程性质:必修 适用专业:英语(教育方向) 先修课程:教育学、心理学、综合英语、英语听力、英语口语、 考核方式:闭卷笔试 一、课程的性质、地位和作用 《英语教学法》是英语(教育方向)专业必修课程,也是专业核心课程,在本专业的课程体系中具有举足轻重的作用。它在学生掌握一定的英语语言基本知识与基本技能以及教育学心理学基本理论的基础上,帮助学生形成英语教与学的理论素养与实践技能,直接为学生的顺利就业打下基础。本课程立足于培养优秀的中小学英语教学应用型人才,除了让学生掌握扎实学习教学理论知识之外,还让其具备较强的实际教学能力,较强的分析能力、合作能力和创新创业能力。本课程的作用是使学生系统地掌握英语教学的基本理论以及各教学层面的基本路子和方法,形成科学的教学观、语言观、学习观和方法观等,并具备一定的基本操作能力,旨在引导学生以本书阐述的理论为线索,了解英语教学的基本方法,初步掌握英语教学的理论知识,为将来从事英语教育打下坚实的基础。 二、教学内容及要求 第1章导论 【教学要求】 了解教学法的研究对象和意义以及英语教师的专业发展过程 重点和难点:教学法的内涵和教师专业发展 【教学内容】
1、教学法研究的对象、内容; 2、学习英语教学法的意义; 3、何为一名合格的英语教师 4、如何成长为一名合格的英语教师 【教学重点与难点】 教学法的内涵与本质;语言教师的专业发展过程 第2章、语言与语言教学 【教学要求】 了解语言的性质;了解语言学习的过程;了解语言教学的主要流派及其理论基础;了解语言教学的新趋势; 【教学内容】 1)语言、语言教学的性质; 2)英语教学的语言学基础 3)英语教学的心理学基础 4)语言教学的主要流派及其理论基础; 【教学重点与难点】 语言教学的主要流派及其理论基础;语言教学的新趋势; 第3章、英语教学方法 【教学要求】 理解交际能力的内涵;了解交际教学和任务性语言教学的发展历程和基本特征;基本掌握交际教学原则在教学实践中的运用;正确评价交际教学法和任务型语言教学; 【教学内容】 1、交际能力的内涵及对英语教学的启示; 2、交际能力的内涵 3、交际教学的基本特征; 4、交际教学活动的创设; 5、对交际教学法的评价;
《口译2》课程教学大纲 课程代码:070141032 课程英文名称:Interpretation 2 课程总学时:16 讲课:16 实验:0 上机:0 适用专业:英语 大纲编写(修订)时间:2017. 10 一、大纲使用说明 (一)课程的地位及教学目标 本课程为英语专业第六学期口译课,为英语专业三年级的主要课程,是一门综合性的英语知识与技能课,主要讲授口译基础知识,训练包括听、说、读、记、译在内的口译能力;帮助学生建立合理的知识结构和获得运用英语语言的基本能力;提高学生的听、说、译等综合能力;为高级英语和其他专业课的学习打下坚固的基础。 (二)知识、能力及技能方面的基本要求 本课程主要讲授口译基础知识,对学生进行全面、严格的听、说、读、记、译基本技能训练,培养学生实际运用语言的能力,即:正确、自然、流畅地运用本阶段所学的语言,恰当、灵活地予以使用。并通过基础训练与实例讲解分析,使学生逐步提高口译能力,了解英语各种问题的表达方式和特点,扩大词汇量和熟悉英语常用句型。同时,培养学生养成良好的学习作风和正确的学习方法,提高学生的逻辑思维能力和独立工作的能力,丰富学生社会文化知识,增强学生对文化差异的敏感性。 (三)实施说明 本课程为英语专业本科生第六学期课程,共计16学时。改变过去以教师为中心的课堂模式,展开形式多样的教学活动,鼓励学生成为课堂主体,培养学生的学习能力和研究能力。采用启发式、讨论式、发现式和研究式的教学方法,激发学生的学习动机。引导学生主动积极地利用现有图书资料和网上信息获得知识,掌握查阅文献、检索资料的基本方法。 (四)对先修课的要求 无 (五)对习题课、实验环节的要求 各类原版英文视听材料为基本,使学生达到在一般及个别专业翻译场合能胜任外事翻译。专业八级以上难度的段落及篇章。 (六)课程考核方式 1. 考核方式:考查 2. 考核目标:在考核学生对口译基础知识掌握的基础上,重点考核学生具体场合口译能力。 3. 成绩构成:本课程的总成绩由两部分构成:平时考核(包括出勤、课堂表现等)占30%;小测验、作业占70%。 (七)主要参考书目: 《高级口译教程》,梅德明、戴炜栋编,上海外语教育出版社,2010 《口译教程》,梅德明编,上海外语教育出版社,2008 《翻译精要》,陈定安编,中国青年出版社,2004 《翻译变体研究》,黄忠廉编,中国对外翻译出版公司,2000 《轻松掌握英语翻译》,马光编,中国书籍出版社,2002
《英语口语1》课程教学大纲 课程编号:072401 课程名称:英语口语1 总学时数:24 实训学时:12 学分:2 后续课: 《英语口语2》 一、说明部分 1、课程性质 《英语口语1》是英语专业的基础必修课,帮助学生打下良好的口语基础。 2、教学目标和意义 《现代大学英语口语1》的教学目的是通过大量的国际音标训练、初级口语练习和实践,逐步培养和提高学生用英语进行口头交际的能力,同时帮助学生了解主要英语国家的文化背景和生活习俗,为其英语初级水平打下牢固的基础。 3、教学内容和要求 (1)教学内容及学时分配 (2)教学要求 《英语口语1》首先要求学生能够掌握准确的语音语调。其次,要求学生能够表达较复杂的观点。最后,要求学生注重思辨能力的发展。 通过本课程的教学,要求学生能够听懂一定难度的英语对话和篇章,并能运用简单的日常英语进行对话,能就所听、读的材料回答问题和复述,做到语音、语调、语法基本正确,能就一般日常生活话题进行简单的交谈;能就熟悉的话题经一定准备后作2-3分钟连贯性发言,学生能在发言中表达比较复杂的观点。《口语1》旨在为学生提高英语口语水平打下扎实的语言基础。 4、教学重点、难点: 教学重点;首先训练语音语调以使学生一开始就能掌握准确的发音。要求学生能够表达有一定难度的观点。最后,要求学生注重思辨能力的发展。 教学难点;少部分学生发音不够准,语法基础差,口语表达能力不尽理想。
5、教学方法和手段:本课程主要采取英语交际法和情境教学法教学,体现以学生为主体、教师为主导的教学理念。每一堂课以PPT形式的主题讲座开始,其中包括热身问题的讨论、课文主题词汇的补充和丰富以及主题内容补充读物以扩展学生的主题知识面,尤其加深对内容的理解。课文的教授主要发展学生的英语口语能力,但是也始终着重训练和提高他们的听力技能。通过个人叙/陈述、双人对话、小组讨论、角色扮演等多种口语实践形式,让学生理解单元课文内容和巩固语言点和知识点。通过要求学生课后讨论难度更深一层、与主题相关的问题,发展学生对主题内容进行深层次讨论的英语口语能力、创新和思辨能力。 本课程以实践教学为主,通过就所教主题进行口语训练、多媒体音频和视频等教学方式和手段,提高教学效果。 6、教材及主要参考书: 使用教材:《现代大学英语口语1》总主编:杨立民外语教学与研究出版社 2012年4月第11次印刷 教学参考书目: 1)《新标准大学英语视听说教程1》总主编:Simon Greenall 文秋芳外语教学 出版社2013年7月第3次印刷 2)《英语口译技能教程——听辨》卢朝信北京语言大学出版社2012年 3)《英语口译笔记法实战指导》吴钟明主编武汉大学出版社2005年 4)《口译教程》林郁如编审雷天放陈菁主编上海外语教育出版社2006年 5)Supplementary materials downloaded from the Internet 二、正文部分 Unit 1 First Day in College 一、教学要求 通过本单元学习,要求学生能够用英语作自我介绍、打招呼并讨论中学、大学生活。 二、教学内容 1. 训练部分国际音标,以帮助学生打好语音语调基础。 2. 第一单元“First Day in College”,讲解如何介绍、打招呼,如何过好大学生活。学生 学习介绍大学生活、比较中学大学生活等。 三、本单元学时数 4学时。 Unit 2 Hometown 一、教学要求 通过本单元学习,要求学生能够用英语介绍自己家乡、介绍自己曾经参观游览过的名胜古迹。 二、教学内容 1. 训练部分国际音标,以帮助学生打好语音语调基础。 2. 第二单元“Hometown”, 讲解名胜古迹,传授如何描写某地方和讨论气候等。学生 学习介绍家乡、介绍自己旅游过的地方。 三、本单元学时数 4学时。 Unit 4 Let’s Go Shopping 一、教学要求
《高职高专英语》课程教学大纲 一、课程的基本信息 1、课程名称:高职高专英语 2、课程学时:240 (理论教学学时180+技能教学学时60) 3、适用专业:全校三年制高职非英语专业 二、课程的定位和教学目标 本大纲依据教育部制定的《高职高专教育英语课程教学基本要求》编写而成,以传授英语基础知识和培养应用能力为教育目标。在教学过程中,从高职高专教育的培养目标出发,遵循“以应用为目的”和“以必需、够用为度”的原则,使学生具备基本的听、说、读、写、译的能力。能在日常活动和业务活动中进行简单的口头和书面交流,并为今后进一步提高英语的交际能力打下基础。 鉴于目前高职高专学生入学时的水平差异较大,本课程的教学要求分为A、B两级。A级是标准要求,B级是过渡要求。入学水平较高的学生应达到A级要求,入学水平较低的学生应达到或接近B级要求。分级不分班进行教学。教学过程中教师应考虑不同层次学生的不同要求,加强分类指导。 本课程在加强英语语言基础知识和基本技能训练的同时,重视培养学生实际使用英语进行交际的能力。通过240课时的学习,学生应该达到下列要求: 1、词汇 A级:认知3400个英语单词(包括入学时要求掌握的1600个单词)以及由这些词构成的常用词组,并具有按照基本构词法识别生词的能力。对其中2000个左右的单词能正确拼写,英汉互译。学生还应结合专业英语学习,认知400个专业英语词汇。 B级:认知2500个英语单词(包括入学时要求掌握的1000个词)以及由这些词构成的常用词组,对其中1500个左右的单词能正确拼写、英汉互译。 2、语法
掌握基本的英语语法规则,在听、说、读、写、译中能正确运用所学语法知识。 3、听力 A级:能听懂日常和涉外业务活动中使用的结构简单、发音清楚、语速较慢(每分钟120词左右)的英语对话和不太复杂的陈述,理解基本正确。 B级:能听懂涉计日常交际的结构简单、发音清楚、语速较慢(每分钟90词左右)的英语简短对话和陈述,理解基本正确。 4、口语 A级:能用英语进行一般的课堂交际,并能在日常和涉外业务活动中进行简单的交流。 B级:掌握一般的课堂用语,并能在日常涉外活动中进行简单的交流。 5、阅读 A级:能阅读中等难度的一般题材的简短英文资料,理解正确。在阅读生词不超过总词数3%的英文资料时,阅读速度不低于每分钟70词。能读懂通用的简短实用文字材料,如信函、技术说明书、合同等,理解正确。 B级:能阅读难度较低的一般题材的简短英文资料,理解正确。在阅读生词不超过总词数3%的英文资料时,阅读速度不低于每分钟50词。基本能读懂通用的简短实用文字材料,如信函、产品说明等,理解基本正确。 6、写作 A级:能就一般性题材,在30分钟内写出80-100词的命题作文;能填写和模拟套写简短的英语应用文,如填写表格与单证、套写简历、通知、信函等,词句基本正确,无重大语法错误,格式恰当,表达清楚。 B级:能运用所学词汇和语法写出简单的短文;能用英语填写表格、套写便函、简历等,词句基本正确,无重大语法错误,格式基本恰当,表达比较清楚。 7、翻译(英译汉) A级:能借助词典将中等难度的一般题材的文字材料和对外交往中的一般业务文字材料译成汉语。理解正确,译文达意,格式恰当。在翻译生词不超过总词数5%的实用文字材料时,笔译速度每小时250个英语词。
成都理工大学工程技术学院 《专业外语》课程教学大纲 核能系环境工程教研室编 2017年4月2日 一、课程简介 该课程主要讲授 二、Introduction This course mainly teaches 三、课程的目的和任务 1 目的和任务 本课程是对于水利水电工程专业学生专业英语能力训练和培养的一门重要课程,是对大学高年级学生继公共英语课程之后的一个重要补充和提高。 2 完成培养方案中哪项基本素质要求和业务培养要求 本课程着重从实用角度出发,使学生掌握水利类专业中大量的专业词汇、英语术语及用法,提高学生阅读和撰写英文科技文章的能力。通过教师讲解,结合学生课后查阅英文资料,培养学生听、说、写的综合能力,掌握本专业的当前动态和前沿发展。 四、课程学时分配表 总体安排:理论教学32学时,实验教学0学时。 课程主要教学内容及学时分配分别见下表:
五、课程教学内容和教学基本要求 1.教学内容及要求 (1)Chapter 1 Effective head of water turbine 基本要求:掌握水轮机工作的有效水头以及各种工作参数的定义。 (2)Chapter 2 Basic principles of turbine operation the Euler equation 基本要求:掌握水轮机的工作原理,特别是反击式水轮机的工作原理以及水轮机进口和出口速度三角形的描述与绘制。 (3)Chapter 3 Specific speed and classification of turbines 基本要求:掌握水轮机的比转速与水轮机的分类,以及他们之间的相互关系。 (4)Chapter 4 Turbine efficiency and speed regulation turbine 基本要求:掌握水轮机的效率与水轮机的转速调节装置,并通过不同的工况特点,合理调节水轮机转速。 (5)Chapter 5 Operation of the turbine under varying head 基本要求:掌握不同工况下,也就是不同水头情况下,水轮机运行变化特点。 (6)Chapter 6 Purpose of draft tubes 基本要求:掌握设置尾水管的目的,与尾水管的基本工作原理。 2.教学内容的重点、难点 重点:Basic principles of turbine operation the Euler equation 难点:各种生僻的专业词汇的掌握
《口译》教学大纲 英文名称:Interpretation 一、课程目标 1. 课程性质:《口译》为英语专业学科基础课程的后续课程,为英语专业本科四年级必修课程。口译活动是集听、说、读、写、记为一体的复杂言语交际活动,因而必须以精读、泛读、听力、口语等课程为基础,在掌握这些课程所传授的技巧的基础上才能顺畅完成教学任务,是培养英语专业学生的综合语言能力的课程。此外,口译课涉及内容大多与现实生活的方方面面相关,因此除了注重词汇、句式积累,该课程注重学生的知识面拓展,努力提高学生的语言综合及运用能力,该课程将为社会培养基础实用人才。 2.教学方法:课堂教学为主,课后练习为辅 3.课程学习目标和基本要求 《口译》课旨在通过讲授口译基本及其和逻辑推理能力训练,并结合口译实践,拓宽学生知识面,培养学生跨文化交际能力、口译相关及其的这运用能力、认知、推理能力及相应的心理素质。 课堂教学应以学生为主体,教师为主导,改变以教师为中心的教学模式。注重培养学生的学习能力,学习兴趣和语言应用能力。在教学中开展以任务为中心,形式多样的教学活动。教师更多采用采用启发式,讨论式,发现式和研究式等教学方法,充分调动学生的学习积极性和主动性。在精心组织课堂教学的同时,结合口译技巧教学部分开展丰富多彩的课内外实践活动,如英语讲演,辩论,田野采集等方式,并积极探索利用现代化的语言教学手段丰富课堂教学内容。 4.课程学时:36学时 5.课程学分:3学分 6.课程类型:学科专业课 7.考核方式:考试 8.适用专业与年级:英语专业本科四年级 二、课程结构 Chapter One A brief introduction to Interpretation(学时数: 2) 知识点:1) the history of interpretation 2) the criteria of interpretation 3)the process of interpretation 4)the patterns of interpretation 重点:the history of interpretation; the criteria of interpretation; the process of interpretation; the patterns of interpretation, etc 难点:interpretation skills, the cultural elements in interpretation Chapter Two Ceremonial interpretation and public speeches skills(学时数: 4)
英语教学法与测试 课程编码: 209009 课程英文名称: English Teaching Methodology and Evaluation 课程类别:英语专业学科基础选修课开课对象:英语专业三年级学生 开课学期:第六学期学分:2 总学时:32 教材: 王蔷,2000.《英语教学法教程》北京:高等教育出版社 参考书: 1. Jeremy Harmer. 1983. The Practice of English Language Teaching. London: Longman. 2. Tang Lixing. 198 3. TEFL in China: Methods and Teaching. Shanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press. 3. Richards, J. C. & David Nuan. 2000. Second Language Teacher Education. Beijing: Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press. 4. Fang Yi & Rui Yuping. 1998. Way Out. Chongqing: Chongqing Publish House. 一、课程的性质、目的和任务 英语教学法与测试是英语专业语言学方向课程之一,主要内容为英语教学与测试理论、课堂教学设计的方法、课堂教学技巧等。本课程还介绍与英语教学法与测试相关的假设、热点论题和现有的教学模式。课程的主要目的在于引导学生了解英语教学与测试的主要理论,掌握课堂设计和课堂教学的设计和操作技巧,使学生能够针对特定的学生、根据特定的学生备课和教学。 二、课程的基本要求: 要求学生通过本课程的学习,基本了解英语教学和测试的基本方法,了解有关的重要理论和其主要内容,熟悉一些主要术语;了解英语教学和测试的主要研究方向和前沿动态。掌握英语教学的主要方法,应用到将来的教学实践中去。 三、课程基本内容和学时分配 1.The Development, system and present status of English teaching methodology and the relation between it and other disciplines (2h); 2.Foreign language learning theories (2h); 3.Contrast analysis and error analysis (2h); 4.Major schools of foreign language teaching in the world (2h); 5.Teachers and students in English language teaching (2h); 6.ELT and mental development (2h); 7.English teaching syllabus and textbook in middle schools (2h); 8.Principles of ELT in middle schools (2h); 9.Classroom teaching of English (2h); 10.Teaching of English knowledge (2h); 11.Practice methods of English linguistic competence (2h); 12.Electrical teaching of English (2h); 13.Second classroom activities of English (2h); 14.Artistic teaching of English (2h); 15.English test and evaluation (2h); 16. Research of ELT (2h).
《工业工程专业英语》课程教学大纲 课程编号:0803701057 课程名称:工业工程专业英语 英文名称:Professional English for Industrial Engineering 课程类型:专业任选课 总学时:32 讲课学时:32 实验学时:0 学分:2 适用对象:工业工程专业 先修课程:大学英语 一、课程性质、目的和任务 专业英语是工业工程专业的一门专业课,通过对本课程的学习,进一步巩固和提高英语水平,特别是提高阅读科技英语及本专业英语资料的能力。其任务是培养学生阅读、写作科技英语等方面的能力,使其能以英语为工具顺利获取有关本专业所需要的信息。 二、教学基本要求 了解专业英语的语法特点、专业英语的词汇特点及专业英语的各种文体中常用的符号、公式及其他。掌握工业工程专业的英语文献阅读和理解,能快速阅读科技文章,迅速获取信息和中心思想。理解专业英语翻译的基本方法。 三、教学内容及要求 1.Introduction to Industrial Engineering 了解工业工程的角色,工业工程毕业生的需求,学习本书的目的,掌握工业工程的定义。了解工业工程涉及的学科,工业工程的发展。了解美国工业工程专业在学科中的地位与中国的不同。 2.Work Study 工作研究和作业测量是工业工程领域最传统的研究内容。通过本章的学习,对工作研究和作业测量有一个全面的认识和了解。 3.Manufacturing Systems 了解制造系统的含义,制造系统的各个组成部分,掌握几种典型的制造系统及成组技术、柔性制造系统、敏捷制造等先进制造系统各自应用范围及特点。了解CAD,CAM,CAPP 等辅助制造系统在各种制造系统中的应用。 4.Production Planning and Control 掌握生产计划的主要内容,体会生产计划在生产系统中的重要性,掌握生产预测、生产计划的制定、生产计划控制的各种原理及方法。 5.Logistics Engineering 掌握物流工程中的基本术语。了解物流工程的内容和特点。了解EOQ的概念。掌握仓库运作的术语。 6.Ergonomics 对人因学发展的历史进行简要介绍的基础上对基本的人因系统模型进行阐述,并对未来
《英语口译》课程教学大纲 一、课程基本信息: 课程代码D0111007 D0111005 课程名称英语口译 课程性质英语专业选修课 适用专业英语专业(含各方向) 开课学期秋季学期 总学时34 先修课程:综合英语1-4 英语听力1-4 英语口语1-4 英语语法翻译理论与实践1-2 英语词汇学跨文化交际学英语语法英国文学美国文学英语语言学英文报刊阅读高级英语1-2 英语国家社会与 文化1-2 平行课程:英语测试英语论文写作教育科学研究方法基础教育英语新教材分析英语教师职业技能商务英语写作商务英语翻译导游业务模拟导游 后续课程:无 课程简介: 口译课是为高年级学生开设的英语基本技能课程。通过讲授口译基本理论、口译背景知识和口译基本技巧训练,使学生掌握口译的基本理论和专题连续传译的基本技能,初步学会口译记忆方法、口头概述、口译笔记及公众演讲等口译技巧,能够基本准确、流畅地进行汉英双语对译。 推荐教材:《口译教程》(雷天放,陈菁主编。新世纪高等院校英语专业本科生系列教材,上海外语教育出版社,2006。) 参考书目: 1、钟述孔,《实用口译手册》,中国对外翻译出版公司,1991. 2、吴冰,《汉译英口译教程》,外语与教学研究出版社,1995. 3. 冯建忠,《实用英语口译教程》,译林出版社2002.3 4、林超伦,《实战口译》,外语教学与研究出版社, 2004.9 5、仲伟合,《英语口译教程》,高等教育出版社,2006.1 6、 CHINA DAILY, CHINA TODAY, VOA,BBC,CRI,CCTV-9 等。 二、课程总目标 本课程旨在进一步加强英语专业高年级学生听、说、读、译等基本外语能力,并通过英语口译基本理论知识、基本技巧、口译背景知识的讲解和各种题材的口译练习,使学生初步了解口译的基本理论和基本方法,了解常用题材口译要运用到的词语、表达方式等,了解口译记忆方法、口头概述、口译笔记及公众演讲技巧,提高学生综合运用母语和外语的能力,使学生能够基本胜任一般性口头翻译工作;同时结合各项专题口译知识学习,扩大学生知识面,培养工作应变能力,开拓职业合作精神,为社会培养复合型外语人才。在课程结束时,学生对外事联络陪同口译工作有初步的了解,并能基本胜任这项工作。 三、理论教学内容与目标 课程主要以介绍基本口译技巧为主线,技巧主要包括:信息听辩、口译记忆、逻辑分析、口译笔记、公众演讲、数字口译、应对策略等。口译技巧训练不仅能培养从事口译工作所需要的技能,良好的逻辑思维能力、快速的语言组织和表达以及出色的公众演讲技巧,同时也是学生毕业后胜任实际工作的有利条件。
《经济学专业英语》教学大纲 大纲说明 课程代码: 3025050 总学时: 40 学时 总学分: 2.5 课程类别 : 必修 预修要求 : 西方经济学 一、课程性质、目的、任务: 本课程兼顾英语语言的学习应用和经济专业知识两个方面,学生在锻炼英语应用能力的 同时,又可学到经济学方面的知识。通过将英语与经济学方面的原理和基础知识相结合,培养学生具有较强的阅读能力、一定的会话及翻译能力,使他们能以英语为工具,顺利阅读本专业的英语材料、获取和交流本专业所需的信息、了解和熟悉经济学的最新发展与动态,并能在实践中加以运用。 二、课程教学的基本要求: 教学形式以课堂讲解为主,结合单元练习培养和提高学生应用英语的能力,能熟练掌握 经济学基本概念和基本理论以及专业术语。加强学生的口头交流能力和书面表达能力,个人发言和小组讨论相结合。除了完成课堂教学外,要求学生在课余进行广泛的相关内容的阅读。 三、大纲的使用说明: 1、推荐使用教材Pindyck和Rubinfeld合作编著的《Microeconomics》第6版,清华大学出版社 2、本课程建议学时为40 学时。根据计划课时的不同,授课内容可作适当调整。 大纲正文 Chapter 1 Preliminaries时间:4学时 Key points:limits;trade-offs;prices;markets; models; positive versus normative analysis Contents: ①The importance of limits for economic analysis ②Why people have to face trade-offs? ③Why economists think with models? ④What difference is positive economic analysis from normative economic analysis? Additional Text: Markets for prescription drugs
《计算机专业英语》 课程教学大纲 一、课程性质 《计算机专业英语》是学院物联网开发专业的公共必修课,也是物联网开发专业教学计划中的一门重要专业课。 二、课程目标 《计算机专业英语》教学目标在于扩大学生的专业词汇量,提高学生阅读国外计算机专业文章的能力,同时使学生获得更多的计算机信息方面的新知识和新的发展。 三、教学要求 根据中宣部和教育部的要求:本门课程要着重讲授计算机知识及英语运用能力,每篇文章之后都有与文章紧密联系的联系,具有一定的针对性,有利于检验学生掌握课文的程度,旨在达到即学、即练、即会的学习效果。精编介绍了计算机的最新技术及应用的自主阅读材料,在提高学生计算机专业英语阅读水平的同时,也扩展了学生的专业面知识。专业英语语言的结构特点、语法知识,科技英语文章的翻译方法,技巧等,能够帮助学生提高英语的读写能力。 大纲所列各部分的教学内容,提出三种不同要求: 第一种:要求学生“正确理解”并“牢固掌握”,或能“熟练运用”; 第二种:要求学生“理解”或“掌握”或“运用”; 第三种:只要求学生“有所了解” 四、教学方法和手段 1、文字教材 使用教材:书名《计算机专业英语》 作者:陈莉康丽军主编 宋学坤副主编 出版社:清华大学出版社 2013年版 2、上机实训 五、必要说明 1、本课程教学时间为一个学期 2、课程考核办法:教考分离,实行平时成绩和期末考查相结合的考核方式。 3、教材与主要参考书:《计算机专业英语》;21世纪高职高专规划教材《计算机专业英语》; 六、学时分配:理论学时72课时,实践学时: 授课学时分配表
七、章节内容 UNIT ONE INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS [教学目标] 本单元主要介绍计算机相关的基础知识,主要包括计算机的分类,计算机的发展过程,计算机的未来发展方向,计算机的正确使用及维护方法,使学生对计算机有一个全方位的了解和认知。 [教学重点和难点] 对计算机专业英语中的专业词汇重点考察,对计算机的专业知识有一个全方位的了解和认知。 [教学内容] PASSAGE ONE FOUR KINDS OF COMPUTERS PASSAGE TWO COMPUTER GENERATIONS PASSAGE THREE MAKE BETTER ULTRALIGHT COMPUTERS PASSAGE FOUR HOW TO KEEP YOUR PC STABLE
《计算机专业外语》课程教学大纲 课程名称:计算机专业英语 课程编码:0714232080 适用专业及层次:计算机应用技术专业(3G移动通信软件开发方向) 课程总学时:36学时 课程总学分: 一、课程的性质、目的与任务 1、本课程的性质 计算机专业外语是计算机科学与技术本科专业的必修课。通过本课程的学习,能够提高学生阅读和理解计算机英文资料的能力,增强学生科技英语的写作水平及对外交流能力,使学生能够加深相关计算机课程的理解,为学生以后进一步提高打下坚实的基础。 2、课程目的与任务: 通过本课程的教学,使学生掌握一定数量的常用现代计算机专业英语词汇,能够比较熟练地看懂计算机屏幕信息的英语提示、菜单、帮助文件及出错信息,并能够基本阅读和翻译计算机的软、硬件手册、资料和说明书;学习和巩固计算机专业的基本概念和知识,以提高学生的综合能力。 二、教学内容、教学要求及教学重难点 Chapter 1 Information Technology, the Internet, and You 【教学内容】:本章主要研究内容为 1.Five parts to an information system: 2.People 3. Software 4.Hardware 5.Data 6.Connectivity,The Wireless Revolution, and the Internet 【教学要求】:1.Explain the five parts of an information system: people, procedures, software, hardware, and data; 2.Distinguish between system software and application software; 3.Discuss the three kinds of system software programs; 4.Distinguish between basic and specialized application software 5.Identify the four types of computers and the six types of microcomputers. 6.Describe the different types of computer hardware including the system
一、理论部分 四川大学志在培养“具有深厚的人文底蕴,扎实的专业知识,强烈的创新意识,宽广的国际视野”的国家栋梁和社会精英,本课程恰恰与学校的办学定位和人才培养目标相呼应,属专业基础课和核心课程,在进一步提高学生的双语听、说、译等实践技能和跨文化交流意识方面起着至关重要的作用,其最终目标是培养一专多能、文化素质好、专业水平高,双语实践能力强,信息技术运用能力强,具有国际视野、创新意识和跨文化交际意识,能直接参与国际竞争与合作的国际通用型、高效率人才。 本课程实践性很强,但也有由不同知识模块组成的理论部分的教学,包括对口译特点、口译分类、口译标准、口译的语言特点、合格译员的素质和各种口译技巧从理论角度进行的介绍。口译技巧涉及口译记忆、笔记、公共演讲、数字转换、综述、应急处理、习语成语和幽默笑话的译法、中外尊称和专有名称的译法、译前准备、跨文化交际技能等等,这些技巧对于培养学生的国际视野、创新意识、跨文化交际和人际交往意识,提高学生的整体素质有着十分重要的作用。 理论部分中知识模块的内容与后面实践课程的内容和学时对应 第6学期(周学时2) 第1-2周:知识模块—介绍口译课的教学安排、特点和目的;口译的定义、类型和标准;口译的语言特点;合格译员的素质; 第3-4周:知识模块—公共演讲技巧、外事礼仪、行为规范。 第5-6周:知识模块—意义听辨,译员的语言理解能力和分析能力。 第7-8周:知识模块—记忆技巧 第9周:实景模拟口译演练及点评。 第9-11周:知识模块—笔译技巧。 第12-13周:知识模块—跨文化交际技能。 第14-15周:知识模块—语言转换. 第16周: 自主口译演练和复习. 第 17 周: 期末考试 第7学期(周学时2) 第1-3周:知识模块—数字转换。 第 4周:知识模块—综述技巧。 第5周:知识模块—主旨口译。 第6周:知识模块—应急技巧。 第7-9周:话题练习及点评。 第10-11周:知识模块—译员角色。 第12周:知识模块—译前准备。 第13周:知识模块—口译教学法。 第14-15周:知识模块—口译研究 第16周:自主口译演练和复习。 第 17 周: 期末考试 二、实践部分
高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲 为了规范全国高等学校英语专业的英语教学,特制订本教学大纲。本大纲所作的各项规定,对全国各类高等学校的英语专业均有指导作用,也是组织教学、编写教材和检查与评估教学质量的依据。 一、培养目标 高等学校英语专业培养具有扎实的英语语言基础和广博的文化知识并能熟练地运用英语在外事、教育、经贸、文化、科技、军事等部门从事翻译、教学、管理、研究等工作的复合型英语人才。 21世纪是一个国际化的知识经济时代。我们所面临的挑战决定了21世纪我国高等学校英语专业人才的培养目标和规格:这些人才应具有扎实的基本功、宽广的知识面、一定的相关专业知识、较强的能力和较高的素质。也就是要在打好扎实的英语语言基本功和牢固掌握英语专业知识的前提下,拓宽人文学科知识和科技知识,掌握与毕业后所从事的工作有关的专业基础知识,注重培养获取知识的能力、独立思考的能力的创新的能力,提高思想道德素质、文化素质和心理素质。 二、课程设置 英语本科专业学制为4年。根据英语专业教学规律,一般将4年的教学过程分为两个阶段,即:基础阶段(一年级和二年级)和高年级阶段(三年级和四年级)。基础阶段的主要教学任务是传授英语基础知识,对学生进行全面的、严格的基本技能训练,培养学生实际运用语言的能力、良好的学风和正确的学习方法,为进入高年级打下扎实的专业基础。高年级阶段的主要教学任务是继续打好语言基本功,学习英语专业知识和相关心业知识,进一步扩大知识面,增强对文化差异的敏感性,提高综合运用英语进行交际的能力。在两个教学阶段中课程的安排可以有所侧重,但应将4年的教学过程视为一个整体,自始至终注意打好英语语言基本功。 英语专业课程分为英语专业技能、英语专业知识和相关专业知识三种类型,一般均应以英语为教学语言。三种类型的课程如下: (1)英语专业技能课程:指综合训练课程和各种英语技能的单项训练课程,如:基础英语、听力、口语、阅读、写作、口译、笔译等课程。 (2)英语专业知识课程:指英语语言、文学、文化方面的课程,如:英语语言学、英语词汇学、英语语法学、英语
---------------------------------------------------------------最新资料推荐------------------------------------------------------ 英语专业各课程教学大纲 英语教学法与测试课程编码: 209009 课程英文名称: English Teaching Methodology and Evaluation 课程类别:英语专业学科基础选修课开课对象:英语专业三年级学生开课学期:第六学期学分:2 总学时:32 教材: 王蔷,2000.《英语教学法教程》北京:高等教育出版社参考书: 1. Jeremy Harmer. 1983. The Practice of English Language Teaching. London: Longman. 2. Tang Lixing. 1983. TEFL in China: Methods and Teaching. Shanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press. 3. Richards, J. C. & David Nuan. 2000. Second Language Teacher Education. Beijing: Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press. 4. Fang Yi & Rui Yuping. 1998. Way Out. Chongqing: Chongqing Publish House. 一、课程的性质、目的和任务英语教学法与测试是英语专业语言学方向课程之一,主要内容为英语教学与测试理论、课堂教学设计的方法、课堂教学技巧等。 本课程还介绍与英语教学法与测试相关的假设、热点论题和现有的教学模式。 课程的主要目的在于引导学生了解英语教学与测试的主要理论,掌握课堂设计和课堂教学的设计和操作技巧,使学生能够针对特定的学生、根据特定的学生备课和教学。 二、课程的基本要求:要求学生通过本课程的学习,基本了解英 1/ 22
《地理信息系统专业英语》课程教学大纲 【课程代码】: 【英文译名】:Professional English for Geographic Information System 【适用专业】:地理信息系统 【学分数】:3 【总学时数】:48 一、本课程教学目的和课程性质 《专业英语》是地理信息系统专业的一门必修课。 本课程的目的是使学生在进行了两年的公共英语学习后,在巩固已有知识的基础上,掌握科技英语的特点,具备教好的英语资料查阅及专业英语交流的能力。也就是说,开设本课程,主要是让学生具备“以英语为工具通过阅读获取专业所需信息的能力”。 通过本课程的学习,学生应在科技词汇、专业英语文献阅读速度、准确理解和翻译专业文献、摘要写作上有较大的提高。 二、本课程的基本要求 要求学生在学习完本课程后,能熟悉常用专业词汇,较流利地阅读并准确理解一般难度的英语原文专业文献和参考资料,能正确地撰写论文的英语摘要。 具体而言,本课程结束时,学生应掌握常见的科技英语词缀,识记词汇表中常见的300个左右专业词汇;阅读速度70词/分钟、理解力正确率70%;翻译(笔译、英→汉)350词(英)/小时;毕业设计(论文)的英语摘要语法、句法、词汇准确率达70%。 三、本课程与其他课程的关系 先修《综合外语L》。 修完本课程并考试合格后,对后续专业课程的学习过程中查阅英文资料等很有帮助。四、课程内容 课程的学习以阅读为主,精读部分要求准确理解文章内容,理解文章细节文法结构,泛读部分则通过大量快速的阅读理解,形成较为强烈的语言环境氛围,用以强化专业英语意识。并在学习中以分类词汇学习和汉英,英汉翻译和摘要写作练习为辅。 重点:巩固和提高学生在基础英语阶段中获得的能力,扩大词汇量。提高阅读能力和理解能力。培养科技英语写作能力。本课程的内容安排如下所示:
《口译》课程教学大纲及教学计划 一.课程设置的目的与目标 2000年4月《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》经教育部高教司批准下发执行。新《大纲》规定高等院校英语专业的培养目标为:“具有扎实的英语语言基础和广博的文化知识并能熟练地运用英语在外事、教育、经贸、文化、科技、军事等部门从事翻译、教学、管理、研究等工作的复合型英语人才;其规格为:“扎实的基本功、宽广的知识面、一定的相关专业知识、较强的能力和较高的素质”。 口译是一门语言技能与专业知识相结合的课程。本课程以口、笔译理论和其他相关学科理论作指导,通过讲授口译基本技巧以及各种交际环境中语言的正确表达方式、全方位地对学生进行口译技巧和逻辑推理能力训练,并结合课外口译实践,拓宽学生知识面,培养学生跨文化交际能力、口译相关技巧的综合运用能力、认知、推理能力、独立工作能力、解决问题的能力以及相应的心理素质。 二.口译课开设年级及课时安排 第六、第七学期,周学时2。 三.课程教学对象 英语专业大三学生 四.口译课教学要求 为了更好地因材施教,根据我系生源、学生专业方向以及西部地区口译市场现状,我系口译教学大纲在教学要求上分为三个层次。 通过讲授口译基本理论、口译背景知识以及对学生进行口译基本技巧的训练,结合口译实践,使学生掌握口译的基本理论和专题连续传译的技能,初步学会口译记忆方法、口译笔记、口头概述、公众演讲等基本技巧和口译基本策略,培养学生的话语分析能力,提高学生的逻辑思维能力、语言组织
能力和双语表达能力,学生能担任一般外事活动的交替传译。注意培养学生 关心时事的信息意识,积累知识,掌握文献检索、资料查询的基本方法,具 有初步研究能力和实际工作能力,提高各项交际技能综合运用的能力,提高 学生的综合人文素质。 五.口译课教学原则 我系口译教学以国家教委颁布的《高等学校英语专业英语教学大纲》中 教学原则为指导原则,结合我系生源、学生专业方向以及西部地区翻译市场 现状,实行立体型、交叉式的口译教学模式。口译教学的重点放在培养学生 的跨文化交际能力、口译相关技巧的综合运用能力、认知、推理能力、独立 工作能力、解决问题的能力以及相应的心理素质。 六.口译课教学方法与教学手段 从“口译基本功”训练、“口译语言技能”训练、“口译对话翻译能力”训练、“口译实战”训练,一直到“口译专业技能训练”,“4+1”翻译班的“层次思维训练法”,以层次递进的方式,系统、有序和全方位地引导学员掌握口译的技能和能力;并通过交传和同传并重、普通班和翻班齐上的套餐形式,将学生从 听说的专业技能顺利地过渡到口译的专业技能的培训上,在一定程度上实现 相关专业与外语专业之间的复合、交融与渗透,使学生从语言的单一性向知 识的多元化、宽厚型方向转化。 七.口译教学参考文献 1、理论部分 1.《口译技巧—思维科学与口译推理教学法》,刘和平,北京:中国对外翻 译公司,2001年。 2.《口译理论与实践》,刘和平,中国对外翻译出版公司,2005年5月。 3.《口译理论概述》,鲍刚,北京:旅游教育出版社,1998。 4.《口译须知》<瑞士> 让·艾赫贝尔著,孙慧双译,北京:外语教学与研 究出版社1982年5月第一版。 5.《口译理论-实践与教学》<法> 达尼卡·塞莱斯科维奇、玛丽亚娜·勒代 雷著,汪家荣等译,北京:旅游教育出版社1990年。