一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时
- 格式:docx
- 大小:32.41 KB
- 文档页数:17
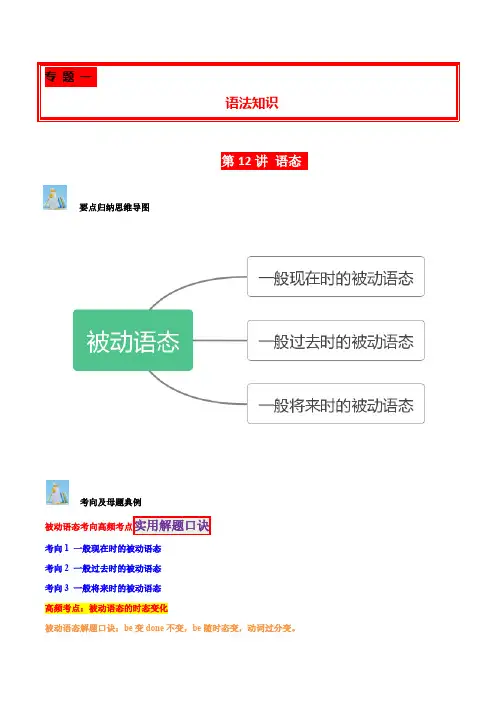
专题一语法知识语法知语法知识识第12讲语态要点归纳思维导图考向及母题典例被动语态考向高频考点实用解题口诀考向1 一般现在时的被动语态考向2 一般过去时的被动语态考向3 一般将来时的被动语态高频考点:被动语态的时态变化被动语态解题口诀:be变done不变,be随时态变,动词过分变。
被动语态各时态构成:结论:be变done不变,be随时态变,动词过分变。
(一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时三种时态的被动语态为中考考核内容)口诀解题典例::Many trees and flowers______in our school last year and they made our school a beautiful garden.A. have plantedB.are plantedC. were plantedD.will be planted口诀识别题目中需要对被动语态的不同时态进行区分时,用此口诀解题。
口诀解题答案解析根据题干中的last year并结合大招“be随时态变”可知,此处用一般过去时的被动语态,故选C。
解题坑点学生判断时态时容易失误,需要注意be要根据时态和主语的单复数而发生变化。
时态变化有时不一定有明显的标志词,需要根据具体语境判断。
(2023·江苏徐州·中考真题)The Monkey King is a traditional Chinese character. It ________ by people of all ages.A.is loved B.was loved C.will love D.is loving【答案】A【详解】句意:孙悟空是中国的一个传统人物。
它受到所有年龄段的人的喜爱。
考查被动语态及动词时态。
根据“by”可知,此处是被动语态,指孙悟空被人们喜爱。
本句陈述事实,故为一般现在时。
故选A。
母题2(2023·四川乐山·统考中考真题)—Who’s the little girl in the photo?—It’s me. The photo ________ when I was five years old.A.took B.was taken C.is taken【答案】B【详解】句意:——照片里的小女孩是谁?——是我。


一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、一般将来时专题训练复习七年级已经学过的时态(一)一般现在时、现在进行时、一般将来时、一般过去时重难点讲解:1. 一般现在时:用法:表示经常发生的事情或经常存在的状态。
常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
It often rains in summer.表示预定的行为/事情;The class begins at 9 a.m..描述客观真理/存在;The sun is bigger than the moon.表内心活动、感情等;I think that’s a good idea.用于表将来的从句。
If it is fine tomorrow, we will go.注意:(1)第三人称单数。
(2)频度副词的位置及使用。
alwa ys, usually, often, sometimes, seldom, never I’ll never forget the day when I met him.2. 现在进行时:表达现在正在发生的事情或正在进行的行为They are having a meeting now.表示现阶段正在进行的事情。
He is writing a book these months.注意:(1)表示来或去的动词:如go, come, leave, arrive等的现在进行时表示将要发生的动作。
Tomorrow I’m leaving for Shanghai.(2)时间状语:now, 具体某一时间点3. 一般过去时:表达过去发生的事情、行为或存在状态It was 11 o’ clock when I went to bed last night.表达过去经常发生的事情。
He got up very early when he was in middle school.注意:动词的过去式时间状语:yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982,just now等。
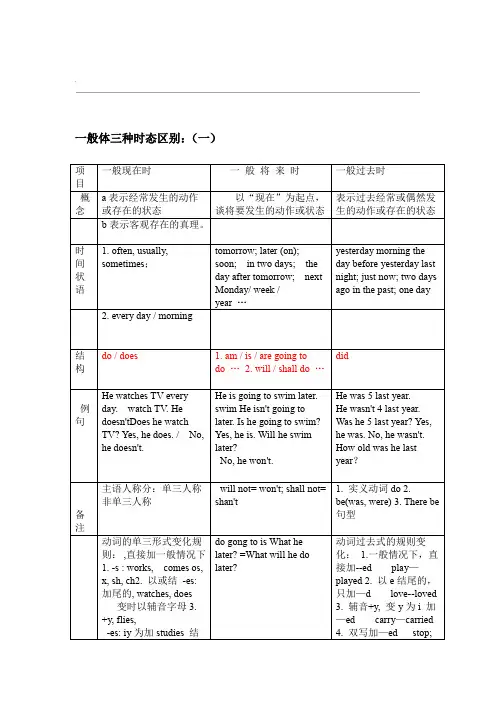
.一般体三种时态区别:(一);...一般体三种时态综合练习:(一)1. _____ he _____ to the park at 6:30 in the morning? No,he _____ .A. Does; goes; doesB. Does; go; doesn'tC. Does; go; does2. What colour _____ you _____ this bookcase? I _____ it pink.A. are; going to paint; am going to paintB. do; paint; paintC. did; paint; painted3. Tim always _____ a picture at home. He _____ a car now.A. draws; is drawingB. draw; drawC. draws; draw4. She usually _____ her friends. They often _____ tea.A. see; drinkB. sees; drinksC. sees; drink5. He usually _____ the dishes at night, but tonight he _____ clothes.A. wash; washB.washes; is going to washC. is washing; washes6. Mr. Green usually _____ his newspaper in the evening, but he and his wife _____ television yesterday evening.A.reads; watchesB.reads; is going to watchC.reads; watched7. Where are the man and the woman? They _____ near the tree.A. sitB. satC. are sitting8. _____ your pen pal _____ diving? No, he _____ .He ______ writing stories.A. Does; like; doesn't; likesB. Does; likes; doesn't; likeC. Do; like; don't; likes9. _____ you _____ fishing yesterday? No, we _____ .A. Does; go; doesn'tB. Did; go; didn'tC. Do; go; don't10. Open the window, Please. Look! He _____ it.A. opensB. is openningC. is opening11. I usually _____ some milk every day. But I _____ coffee yesterday.A. drink; drankB. is drinking; drinkC. drank; am drinking12. Mr. Green often __ his newspapers at night. But he ___ an interesting book tonight.A. reads; readsB. reads; readC. reads; is going to read13. The old man _____ playing sports in the park. He _____ morning exercise now.A. likes; is doingB. likes; doesC. like; doing14. What _____ you usually _____ in the evening? I ______ computer games. What _____ you _____ last night? I _____ a book.A. do; do; play; did; do; readB. did; do; played; do; do; readC. does; do; plays; do; do; am reading15. Where ______ the boy _____ ? He _____ across the river now.A. does; swim; swimsB. is; swimming; is swimmingC. is; swimming; is swimming;...16. _____ you _____ to music now? Yes, we _____ .A. Do; listen; doB. Did; listen; didC. Are; listening; are17. Put on you coat, please. OK. I ___ it on.A. am puttingB. am going to putC. Put18. _____ you ______ coffee? Yes, I ______ .A. Do; like; doB. Did; like; didC. Are; like; am19. Look! Two cats ______ across the wall.A. runB. runsC. are running20. She ____ tea, but he ___ .A. likes; doesn't B; like; don't C. like; doesn't21. ---How many ________ in the tree? ---There are two.A. bird are therB. birds is therC. birds are thereD.birds are their22.. Mr Johnson usually goes to the hospital ________.A. by his carB. by the black carC. by carD. by the new car23. Does your brother play ping-pong __________?A. on every afternoonB. every afternoonC. in every afternoonD. at every afternoon24. ________ do you usually come to school?A. HowB. WhatC. WhichD. How much25. ---Don't you usually come to school by bike? ---_________. But I sometimes walk. A. Yes, I do B. No, I don't C. Yes, I do D. No, I don't26. What ____ Tom and his mother like ?A. doesB. doC. isD. are27. What's your hobby? My hobby is ______ model plane.A. makingB. makeC. makingD. made28. ---Did you go to the park on Sunday morning? ---___, I went there in the afternoon.A. YesB. NoC. SureD. Sorry29. I don't think he's so great, but my mom _________.A. doB. doesC. isD. are30. A kid ______ breakfast every morning, because it's good for his health.A. have toB. has toC. has to haveD. has to has;...一般体三种时态综合练习:(二)1.Listen ! Someone ______ in the room.A. criedB. cryingC. is crying2.Could you tell me where the bus station______?A. wasB. isC. be3.He often ______ his clothes on Sundays.A. washingB. washesC. wash4.I'm Chinese. Where ______ from?A. do you comeB. you are comingC. you comeD. are you coming5.Don't talk so loudly . Your father ______.A. sleepsB. is sleepingC. sleptst week John ______ his leg.A. brokenB. brokeC. breaks7.——Can I speak to Mr. Green?——I'm afraid not. He __________a meeting at the moment.A. havingB. is havingC. hasD. had8.——What are the old men under the tree doing?——They ______________ happily.A. is chatingB. is chattingC. are chatingD. are chatting9. My father _______ the Party twenty years ago.A. joinB. joinsC. joinedD. will join10. Gina often ________her homework in the evening. But at the moment this evening she________ TV.A. does; watchesB. is doing; is watchingC. does; is watchingD. is doing; watches11. He _________ to school on Sundays.A. don't goB. doesn't goC. isn't goD. not go12. He sometimes _________ some novels on Sunday.A. seeB. readsC. watchesD. look13. My father _______ to work at eight.A. usually goB. usually goesC. goes usuallyD. go usually14. Jenny ____ in an office. Her parents ____in a hospital.A. work works B works workC. work are workingD. is working work15. He said the sun ____in the east and ____in the west.A rose; setB rises; setsC rises; setD rise; sets16. Wang Mei ____ music and often ____ to music.A like; listenB likes; listensC like; are listeningD liking ; listen17. Jenny____ English every evening.A has studyB studiesC studyD studied18. Every year many foreigners _________to China to learn Chinese.A. have comeB. comesC. cameD. come;...19.——Where's Susan, Mike?——She _________ in the kitchen.A. cooksB. cookedC. is cooking20.——What's your brother doing in his room now?——He ____________ a kite.A. makesB. madeC. is makingD. will make21. Yesterday,Tony's family _________ a good time.A. hasB. haveC. hadD. haven't22.——Where's the cake I made this morning?——We _______ it, mum. Can you make another one for us?A. ateB. eatC. will itD. were eating23. Mary___________ the piano well.A. playB. playsC. playingD. played24. Don't turn off the radio. I _______ to the news.A. listenB. have listenedC. listenedD. am listening25. Don't turn on the TV. Grandma ____________ now.A. is sleepingB. will sleepC. sleptD. sleeps26.——What are you doing, Cathy?——I'm __________my cat. I can't find it.A. looking forB. looking atC. looking upD. looking after27.——What did you do after school yesterday?——I _________basketball with my friends.A. playB. playedC. will playD. am playing28. ---Hi, Kate. You look tired. What's the matter?---I ______well last night.A. didn't sleepB. don't sleepC. haven't sleptD. won't sleep29.Look!The twins_____their mother do the housework.(A)are wanting (B)help(C)are helping (D)are looking30._____are the birds doing? They are singing in a tree.(A)Who (B)What (C)How (D)Where31.Is she____something?(A)eat (B)eating (C)eatting (D)eats32.你在干什么?(A)What is you doing? (B)What are you do?(C)What are you doing? (D)What do you do?33.What are you listening_____?(A)/ (B)for (C)at (D)to34.我正在听他说话.(A)I listening to him. (B)I'm listening to him.C)I'm listen to him. (D)I'm listening him.35.They are_____their clothes.(A)makeing (B)putting (C)put away (D)putting on36.Listen! She____in the classroom.;...(A)is singing (B)sing (C)to sing (D)is sing37.The children_____football.(A)is playing (B)are playing (C)play the (D)play 38.They are flying kites.(A)他们喜欢放风筝. (B)他们在放风筝吗?(C)他们在放风筝. (D)他们常放风筝.39.Look,They are swimming in the river.I want_____you.(A)to go with (B)go with (C)helping (D)help40.Look.Lucy is_____a new bike today.(A)jumping (B)running (C)riding (D)takeing41. _____ you have a book?A. DoB. AreC. IsD. Have42. They _________ on a farm.A. workingB. is workC. workD. is worked43. Does Peter like to watch TV?__________.A. Yes, he likeB. No, he doesn'tC. Yes, he'd likeD. No, he likes44. She doesn't __________ her homework in the afternoon.A. doingB. to doC. doesD. do45. How ____________ Mr. Brown ___________ to America?A. do,goB. is,goC. does,goD. does,goes46. Where's my camera? I____________ it.A. am not findingB. am not seeingC. can't findD. can't look at47. How ___________ he go to work?He ___________ to work by bike.A. does ;goB. do;goesC. do ;goD. does;goes48. ______ you usually late for school?No, _____________.A. Do ; I amB. Does ;notC. Are ; I'm notD. Are ; I aren't49. _____ she _____ home at six every day?A. Is , leaveB. Does , leaveC. Is , leavesD. Does , left50. Mr. Yang ____________ English this term.A. teaches ourB. teaches usC. teachs usD. teach our51. _____Mike from Japan?A. AreB. DoC. DoesD.Is52. _____you come from Japan?A. AreB. DoC. DoesD.Is53. What language do you_______?A. sayB. talkC. tellD. speak54. They ________ an English evening next Sunday.A. are havingB. are going to haveC. will havingD. is going to have;...55. ________ your brother ________ a magazine from the library?A. Are; going to borrowB. Is; going to borrowC. Will; borrowsD. Are; going to borrows56. _____ he _____ to the park at 6:30 in the morning? No, he ____.A. Does; goes; doesB. Does; go; doesn'tC. Does; go; does57. What colour _____ you _____ this bookcase? I _____ it pink.A. are; going to paint; am going to paintB. do; paint; paintC. did;paint; painted58. Tim always _____ a picture at home. He _____ a car now.A. draws; is drawingB. draw; drawC. draws; draw59. She usually _____ her friends. They often _____ tea.A. see; drinkB. sees; drinksC. sees; drink60. He usually _____ the dishes at night, but tonight he _____ clothes.A. wash; washB. washes; is going to washC. is washing; washes61. Mr. Green usually _____ his newspaper in the evening, but he and his wife _____ television yesterday evening.A. reads; watchesB. reads; is going to watchC. reads; watched62. Where are the man and the woman? They _____ near the tree. A. sit B. satC. are sitting63. _____ your pen pal _____ diving? No, he _____ .He ______ writing stories.A. Does; like; doesn't; likes B. Does; likes; doesn't; like C. Do; like; don't; likes64. _____ you _____ fishing yesterday? No, we _____ .A. Does; go; doesn'tB. Did; go; didn'tC. Do; go; don't65. Open the window, please. Look! He _____ itA. opensB. is openningC. is opening66. I usually _____ some milk every day. But I _____ coffee yesterday.A. drink; drankB. is drinking; drinkC. drank; am drinking67. Mr. Green often _____ his newspapers at night. But he _____ an interesting book tonight.A. reads; readsB. reads; readC. reads; is going to read68. The old man _____ playing sports in the park. He _____ morning exercise now.A. likes; is doingB. likes; doesC. like; doing69. What _____ you usually _____ in the evening? I ______ computer games. What _____ you _____ last night? I _____ a book.A. do; do; playB. did; do; playedC. does; do; playsdid; do; read do; do; read do; do; am reading70. Where ______ the boy _____? He _____ across the river now.A. does; swim; swims B. is; swimming; is swimmingC. is; swimming; is swimming71. _____ you _____ to music now? Yes, we _____. A. Do; listen; do B. Did; listen; did C. Are; listening; are72. Put on you coat, please. OK. I ______ it on.A. am puttingB. am going to putC. put73. _____ you ______ coffee? Yes, I ______.;...A. Do; like; doB. Did; like; didC. Are; like; am74. Look! Two cats ______ across the wall.A. runB. runsC. are running75. She _____ tea, but he _____.A. likes; doesn't B; like; don't C. like; doesn't76. If it ________ tomorrow, we'll go roller-skating.A. isn't rainB. won't rainC. doesn't rainD. doesn't fine77. Jenny ____ in an office. Her parents ____in a hospitalA work; worksB works; workC work; are workingD is working; work78. ----I don't know if his uncle _____.---- I think he _____ if it doesn't rain.A will come; comesB will come; will comeC comes; comesD comes; will come80. There _____ a meeting tomorrow afternoon.A. will be going toB. will going to beC. is going to be三、按要求变换句型。
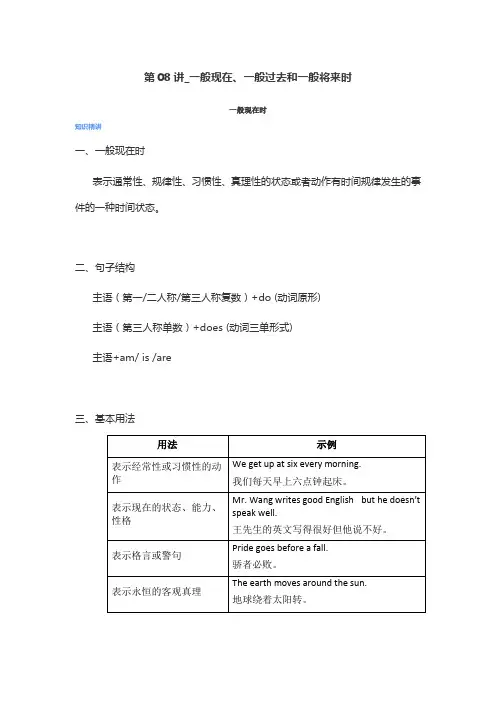
一般现在时知识精讲一、一般现在时表示通常性、规律性、习惯性、真理性的状态或者动作有时间规律发生的事件的一种时间状态。
二、句子结构主语(第一/二人称/第三人称复数)+do (动词原形)主语(第三人称单数)+does (动词三单形式)主语+am/ is /are三、基本用法四、时间状语1. 表示频率的副词: always, usually, often, sometimes, never, hardly, seldom…2. every/once+名词: every day/ week/ year, once a week/ month …3. 表示时间的短语: twice a day, on weekends, on Mondays…五、一般现在时动词三单的变化规律六、相关句式三点剖析一、考点:时态是英语学习中的核心内容之一,是英语学习的基础。
自然,时态考查是各种英语考试尤其是中考时的座上宾。
动作发生的时间决定时态,时态决定动词的形式,而考卷中的时态题通常没有给出明确的时间标志词,考试需领悟所提供的语境来做出判断。
只有推断出动作发出的正确时间,才可能正确答题,这就要求考生在熟练掌握时态结构、用法并牢记常用的时间状语的基础上,要充分利用上下文中隐含的信息来捕捉时间,找准答题的突破口。
二、重难点:一般现在时在考试中的重难点是:句子结构、基本用法、标志时间状语、动词三单的变化规则及相关句式的变化。
三、补充点:1. 表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。
但只限于start, begin, leave, go, come, arrive, return, take place等。
例:My train leaves at 7:00 this afternoon.我乘坐的火车将在今天下午7点离开。
2. 在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。

英语时态总共有16种,但是常见的9种,常用8种时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式.英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时,过去将来时,现在完成进行时。
常用的时态只有八种。
一:一般现在时的用法1..概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理.句中常用always, usually, often, sometimes, every we ek (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays等时间状语。
例如:He goes to school every day.(经常性动作)He is very happy.(现在的状态)The earth moves around the sun.(真理)2)在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来.例如:If you come this afternoon,we' ll have a meeting.When I graduate,I’ll go to the countryside.3)有时这个时态表示按计划、规定要发生的动作,(句中都带有时间状语)但限于少数动词如begin,come,leave,go,arrive,start,stop,return,open,close等.例如:The meeting begins at seven.The train starts at nine in the morning.4)表示状态和感觉的动词,如be,like,hate,think,remember,find,sound等常用一般现在时.例如:I like English very much.The story sounds very interesting.5)书报的标题,小说等情节介绍常用一般现在时.2.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加(e)S)。

动词的时态动词的发生有一定的时间,这就是英语中动词的时态。
1、一般现在时的用法。
表示经常性或习惯性的动作或存在的状态。
常与often,usually,sometimes,once a week,every day等时间副词或时间状语连用。
例如:I often go to school by bike.表示客观事实或普遍真理。
例如:The earth goes around the sun.在条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表将来。
例如:If it rains, we won’t go to the park.实义动词的第三人称单数形式的变化:1. 在动词原形后面加s run s like s 2.以ch,sh,o,s,x结尾的动词,后面加es go es teach es3.以辅音字母加y结尾的,去y变i,加es stud ies tr ies4. 以元音字母加y结尾的,直接加s stay s play s5.不规则变化的动词have—has(一般来说,当主语是he,she,it,单个的人名或名词的单数时,统称为第三人称单数。
)一般现在时专项练习Ⅰ.用括号内动词的适当形式填空1. He often (have) dinner at home.2. Daniel and Tommy (be) members of the Reading Club.3. She and I (take)a walk together every evening.4. There (be) some water in the bottle.5. We (not watch) TV on weekdays.6. Nick (not do) his homework on Sundays.7. they (like) the World Cup?8. What they usually (do) on holidays?9. your parents (read) newspapers every day?10. The girl (teach) us English on Sundays.11. I don’t like ______________ (dance).Ⅱ.按照要求改写句子1. Daniel watches TV every evening. (改为否定句)Daniel TV every evening.2. I do my homework every day. (改为一般疑问句并作否定回答)——you homework every day?——No, I .3. She likes milk.(改为一般疑问句并作肯定回答)—— _______ she milk?—— Yes, she .4. Amy likes playing computer games. (改为一般疑问句并作否定回答)________ Amy ________ playing computer games? No, ________ ________.5. We go to school every morning . (改为否定句)We ________ ________ to school every morning.6. She is always ready to help others. (改为一般疑问句并作否定回答)________ she always ready to help others? No, ________ ________.Ⅲ.改错1. Is you brother speak English?2. Does he looks like his father?3. He likes play games after class.4. Mr. Wu teachs us English.5. She doesn’t her homework on Sundays.6. My mother often go to the shop on Sundays.7. She doesn’t likes bread or cakes.选择题:1.He is so careless that he always _______ his school things at home.A. forgetsB. forgotC. leavesD. left2. It ____usually ____at this time of year, but today it is raining heavily.A. is; rainingB. won’t; rainC. has; rainedD. doesn’t; rain3. When my dad comes back, he always_____ his shoes and leavesthem by the front door.A. tires onB. takes offC. takes swayD. puts on4. Light _____much faster than sound.A. travelB. travelsC. travelledD. travelling5. I will tell him the good news as soon as he ______ back.A. comesB. cameC. will comeD. is coming2、一般过去时。


教学内容知识点一:一般现在时【知识梳理】(1)一般现在时的基本结构和变化1.一般现在时的结构①be动词:主语+be(am, is, are)+其它。
e.g. I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
②行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
一般现在时主要用动词的原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数,则在动词原形后加"-s"或"-es"e.g. He gets up early in the morning.2.否定句和疑问句的变化①be动词的变化:A.否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。
He is not a worker.他不是工人。
B. 一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。
---Are you a student? ---Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.C. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
Where is my bike?②行为动词的变化:A.否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
I don't like bread. / He doesn't like bread.B. 一般疑问句:Do ( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
---Do you often play football? --- Yes, I do. / No, I don't.--- Does she go to work by bike? --- Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't.C. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
How does your father go to work?(注意回顾动词第三人称单数形式变化规则)一般情况下在词尾加s help→helps, clean→cleans, play→plays, wear→wears, give→gives; 以s, x, ch, sh结尾的动词在词尾加es dress→dresses, fix→fixes, watch→watches, finish→finishes;以“辅音字母加y”结尾的动词,把y变为i,再study→studies, carry→carries, fly→flies )(2)一般现在时的用法•1.表示经常性或习惯性的动作或行为。
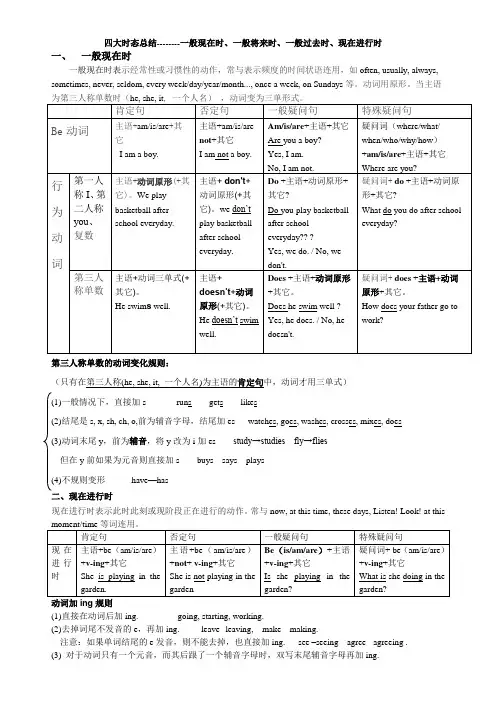
四大时态总结--------一般现在时、一般将来时、一般过去时、现在进行时一、一般现在时一般现在时表示经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用,如often, usually, always, sometimes, never, seldom, every week/day/year/month..., once a week, on Sundays等。
动词用原形。
当主语第三人称单数的动词变化规则:(只有在第三人称(he, she, it, 一个人名)为主语的肯定句中,动词才用三单式)(1)一般情况下,直接加s runs gets likes(2)结尾是s, x, sh, ch, o,前为辅音字母,结尾加es watches, goes, washes, crosses, mixes, does(3)动词末尾y,前为辅音,将y改为i加es study→studies fly→flies但在y前如果为元音则直接加s buys says plays(4)不规则变形have—has二、现在进行时现在进行时表示此时此刻或现阶段正在进行的动作。
常与now, at this time, these days, Listen! Look! at this(1)直接在动词后加ing. going, starting, working.(2)去掉词尾不发音的e,再加ing. leave--leaving, make---making.注意:如果单词结尾的e发音,则不能去掉,也直接加ing. see –seeing agree - agreeing .(3) 对于动词只有一个元音,而其后跟了一个辅音字母时,双写末尾辅音字母再加ing.sitting, beginning run – running stop – stopping cut – cutting control – controlling(4)以ie结尾,把ie变y再加ing。

小学英语四大时态语法知识点小学英语主要是如下的四大时态:一般现在时、现在进行时、一般过去时、一般将来时。
01一般现在时一、标志词always(总是)usually(通常)often(经常)sometimes(有时)never(从不)every(每一)二、基本用法1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。
2.表示经常性、习惯性的动作。
3.表示客观现实。
三、构成1.be动词:主语+be动词(am isare)+其它.2.行为动词:主语+行为动词+其它。
四、句型肯定句:A. be 动词:be+主语+其它。
B. 行为动词:主语+动词(注意人称变化)+其它。
否定句:A.be动词:主语+be+not+其它。
B.行为动词:主语+助动词(do/does)+not+d动词原形+其它一般疑问句:A.be动词:be+主语+其它。
B.行为动词:助动词(Do/Does)+主语+动词原形+其他.特殊疑问词:疑问词+一般疑问句02现在进行时一、标志词now(现在), look(看),listen(听)二、基本用法表示现阶段正在进行的动作三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+be动词+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
2.否定句:主语+be动词+not+动词现在分词(ing)+其它。
3.一般疑问句:be动词+主语+现在分词(ing)+其它。
4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
03一般将来时一、标志词tomorrow(明天),soon(不久),will(将要=be going to)二、基本用法表示在在将来某个时间要发生的动作或存在的状态。
三、基本结构1.肯定句:主语+ be going to + 动词原形。
主语+will+动词原形。
2.否定句:主语+ be going to +动词原形。
主语+won’t + 动词原形3.一般疑问句:Be + 主语+ going to+动词原形Will + 主语+ 动词原形4.特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句04一般过去时一、标志词yesterday(昨天),ago(以前),before(在...之前)二、用法1.表示过去某个时间发生的动作或存在的状态,常和表示过去的时间状语连用。
初三英语时态汇总一般现在时【定义】一般现在时表示现在经常反复发生的动作、存在的状态或习惯性的动作。
即描述我们日常生活中的衣食住行等活动。
【用法】(1) 在实际应用中,一般现在时常与以下时间状语联用:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month, once a week, on Sundays ……例句:He usually plays football on Sundays.(2)没有时间状语,可以分以下四种类型:这一类型由be动词+名词、形容词、副词、代词、数词或介词短语等一起构成谓语,表示主语的个性、特征或状态。
如:①I am a student.(主语+be动词+名词)②They are hungry.(主语+be动词+形容词)③He is out.(主语+be动词+副词)④That pen is mine.(主语+be动词+代词)⑤I am fifteen.(主语+be动词+数词)⑥The bike is under the tree.(主语+be动词+介词短语)do型由行为动词充当谓语,表示经常性或习惯性的动作,其构成为。
如:①I know it. ②He believes me.there be型句子表示“某地存在…”,其构成为,表示客观事实。
用法遵循,即主语是单数或并列主语中的第一个主语是单数,则用there is;主语是复数或并列主语中的第一个主语是复数,则用there are。
如:(1)There is an eraser on the teacher's desk.(主语an eraser是单数)(2)There is an orange,five apples and eight bananas in the bag.(并列主语中的第一个主语an orange是单数)情态动词型句子的构成为,情态动词和动词原形一起构成谓语,表示说话人对所叙述的动作或状态的看法。
一般现在时、一般过去时、现在进行时、一般将来时专题训练一、单项选择()1. Look at these clouds, it _______________A. will be rainingB. is going to rainC. rainsD. is to rain()2. If you don’ t mind, I __________ off the TV set.A. will turnB. am turningC. would turnD. had turned()3. Shall I call a taxi for you?No, thanks. __________ one myselfA. I callB. I’ll callC. I ’d callD. I called() 4. She ________ him a lovely dog on his next birthday.A. givesB. gaveC. will givingD. is going to give() 5. He ________ in four days.A. coming backB. came backC. will come backD. is going to coming back() 6. We ________ the homework this way next time.A. doB. will doC. going to doD. will doing() 7. Tomorrow he ________ a kite, and then ________ boating.A. will fly; will goB. will fly; goesC. is going to fly; will goesD. flies; will go() 8. There __________ a meeting tomorrow afternoon.A. will be going toB. will going to beC. is going to beD. will go to be() 9. He ________ very busy this week, he ________ free next week.A. will be ; isB. is ; isC. will be ; will beD. is ; will be() 10. There ________ a dolphin show in the Dalian ’zoos tomorrow evening.A. wasB. is going to haveC. will haveD. is going to be() 11. The train ________ at six oc’ lock.A. going to arriveB. will be arriveC. is going toD. is arriving二、将括号里的词的相应形式进行填空1. We often___________(play) on the playgound.2.He _________(get) up at six o’ clock.3.__________you _________(brush) your teeth every morning.4.What(do) he usually (do) after school?5.Danny(study) English, Chinese, Maths, Science and Art at school.6.Mike sometimes __________(go) to the park with his sister.7.At eight at night, she ________(watch) TV with his parents.8.________ Mike________(read) English every day?9.How many lessons ______your classmate____(have) on Monday?10.What time ____his mother_________(do) the housework?11.Don ’ t make a noise. Grandpa __________(sleep).12.It ________(take) me two hours to finish my homework last night.13.-What ______ your mother _______(do) every evening?-She _______(wash) clothes.14._______ it ______ (rain)every day?15.There ________ (be) a football match on TV every morning.16. they often ________ (visit) the Great Wall.17. The earth __________ (move) round the sun.三、写出以下动词的第三人称单数形式:1.wash_________ match _______guess______ study______ finish_________ go________ snow______ carry_________2.stop______ see________ drive ________let_______ carry______ keep_____ join______ find_______ think________teach______ catch______3.stay_______ begin______ forget_______lie________die _______ run_______prefer______give________ring_______dance______ hope_______四、写出以下动词的过去式tell break build catch begin draweat come buy cut read putthink go get give keep know改句子1. Do you often play football after school? (必定答复 )2. I have many books. 〔改为否认句〕3.Gao Shan’ s sister likes playing table tennis〔改为否认句〕4.She lives in a small town near New York. 〔改为一般疑问句〕5.I watch TV every day. 〔改为一般疑问句〕6.David has a goal. 〔改为一般疑问句〕7.We have four lessons〔.否认句〕8.Nancy doesn ’ t run fast〔必定句〕9.My dog runs fast. (一般疑问句 )10.Su Yang usually washes some clothes on Saturday〔划.线提问〕11.Su Yang usually washes some clothes on Saturday〔.划线提问〕12.Mingming usually waters the flowers every day。
教学内容知识点一:一般现在时【知识梳理】(1)一般现在时的基本结构和变化1.一般现在时的结构①be动词:主语+be(am, is, are)+其它。
e.g. I am a boy.我是一个男孩。
②行为动词:主语+行为动词(+其它)。
一般现在时主要用动词的原形表示,如果主语是第三人称单数,则在动词原形后加"-s"或"-es"e.g. He gets up early in the morning.2.否定句和疑问句的变化①be动词的变化:A.否定句:主语+ be + not +其它。
He is not a worker.他不是工人。
B. 一般疑问句:Be +主语+其它。
---Are you a student? ---Yes. I am. / No, I'm not.C. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
Where is my bike?②行为动词的变化:A.否定句:主语+ don't( doesn't ) +动词原形(+其它)。
I don't like bread. / He doesn't like bread.B. 一般疑问句:Do ( Does ) +主语+动词原形+其它。
---Do you often play football? --- Yes, I do. / No, I don't.--- Does she go to work by bike? --- Yes, she does. / No, she doesn't.C. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句。
How does your father go to work?(注意回顾动词第三人称单数形式变化规则)一般情况下在词尾加s help→helps, clean→cleans, play→plays, wear→wears, give→gives; 以s, x, ch, sh结尾的动词在词尾加es dress→dresses, fix→fixes, watch→watches, finish→finishes;以“辅音字母加y”结尾的动词,把y变为i,再study→studies, carry→carries, fly→flies )(2)一般现在时的用法•1.表示经常性或习惯性的动作或行为。
常与always, sometimes, often, usually, never等副词连用。
e.g. I go to school every day except Saturdays and Sundays. My mother often gets up at 6 o’clock.2.表示现在的状态,能力,性格,个性。
e.g. My father teaches maths.Lin Yan dances well.3.表示普遍真理或客观事实。
e.g. The earth moves around the sun. The sun rises in the east.【注意】此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
如:Our physics teacher said that light travels much faster than sound. 我们的物理老师说光的传播速度比声音的传播速度快得多,在时间、条件、比较等状语从句中,用现在时表示将来的动作,从句的谓语动词用一般现在时。
如:I will e-mail you as soon as I get to Beijing. 我一到北京就给你发邮件。
If you come this afternoon, we will have a meeting. 如果你今天下午能来,我们就开会。
【例题精讲】例1.——Who is that lady?——She’s Miss Green. She ____ us music, and she is so good.A. taughtB. teachesC. will teachD. is teaching例2.——I think I’ll take a bus to the meeting.——The bus? If you ____, you will be late.A. doB. have doneC. will do例3. Unless the weather ____, we will have to cancel the picnic.A. improveB. improvesC. improvedD. will improve例4.We don’t know if our friend ____. If he ____, we’ll let you know.A. comes; comesB. comes; will comeC. will come; comes例5. Our geography teacher told us that the earth ____ the sun.A. went aroundB. goes aroundC. is going aroundD. was going around【课堂练习】1. Look! A dog ____ a blind man across the road.A. leadsB. leadC. is leadingD. led2. They usually ____ TV in the evening.A. watchB. will watchC. are watchingD. watches3. He hardly ____ up early.A. getsB. getC. doesn’t getD. don’t get4. John ____ football.A. likes playingB. likes playC. like play5. Frank usually ____ in touch with his primary school teachers by email.A. keepB. keepsC. keptD. will keep知识点二:一般过去时【知识梳理】(1)一般过去时的基本结构和变化1.定义:表示过去某时发生的动作或存在的状态。
2.结构:“主语 + 动词的过去式”3.句型转化:①be 动词的过去时的句型如下:A. 否定句:主语+ be动词的过去式(was, were)+ not…B. 疑问句:be动词的过去式(was, were)+ 主语…?a. He was busy yesterday. (肯定句) 他昨天很忙。
b. He was not busy yesterday. (否定句) 他昨天不忙。
c. Was he busy yesterday? (疑问句) 他昨天忙吗?d. There weren’t any boys in the room.房间里没有男孩儿。
e.g. There weren’t any boys in the room.房间里没有男孩儿。
Were there any boys in the room? 房间里有男孩儿吗?②行为动词的否定式和疑问式:A. 否定式:行为动词前加上did not或缩略式didn’t,并把这个行为动词改为动词原形。
a. I called Lin Tao yesterday afternoon.→I did not / didn’t call Lin Tao yesterday afternoon.b. I borrowed a book from Sun Yang last Sunday.B. 一般疑问式:若在陈述句中只有行为动词的过去式, 那就得在句首加上一个助动词did来帮助提问, 然后把句中的行为动词由过去式改为动词原形, 并在句末打上问号。
回答时别忘了还用did。
a. We stayed there for 10 days last month.→ Did you stay there for 10 days last month? Yes, we did. / No, we didn’t.b. Mary had a delicious dinner yesterday evening.→ Did Mary have a delicious dinner yesterday evening? Yes, she did. / No, we didn’t. •(2)规则动词的变化过去式(规则变化)一般情况下,直接在动词词尾加-ed。
watch →watchedplant →planted 以不发音字母e结尾的动词在词尾加-d。
like →likedmove →moved 以“辅音字母+ y”结尾的动词,先变y为i,再在词尾加-ed。
study →studiedcarry →carried重读闭音节动词且词尾只有一个辅音字母,先双写词尾的辅音字母,再在词尾加-ed。
stop →stoppedshop →shopped过去式(be动词) (不规则变化)am / is →was are →were do →did(3)不规则动词的过去式和过去分词第一组AAA1. cost—cost—cost2. cut—cut—cut3. hit—hit—hit4. let—let—let5. put—put—put6. set—set—set7. read—read—read第二组ABC1. break—broke—broken2. choose—chose—chosen3. speak—spoke—spoken4. steal—stole—stolen5. wake—woke—woken6. forget—forgot—forgotten7.take—took—taken 8.give—gave—given 9.hide—hid—hidden10. drive—drove—driven 11. write—wrote—written 12. rise—rose—risen13. ride—rode—ridden 14. eat—ate—eaten第三组ABC1. know—knew—known2. grow—grew—grown3. throw—threw—thrown4. fly—flew—flown5. show—showed—shown第四组ABB1. build—built—built2. burn—burnt—burnt3. mean—meant—meant4. lend—lent—lent5. send—sent—sent6. spend—spent—spent第五组ABB1. keep—kept—kept2. sweep—swept—swept3. sleep—slept—slept4. leave—left—left5. feel—felt—felt6. smell—smelt—smelt7. lose—lost—lost 8. learn—learnt—learnt (learned—learned)9. get—got—got 10. do—did—done 11. go—went—gone第六组ABB1. make—made—made2. hear—heard—heard3. have—had—had4. bring—brought—brought5. find—found—found6.buy—bought—bought7. think—thought—thought 8. teach—taught—taught第七组 ABB1. dig—dug—dug2. lead—led—led3. hold—held—held4. meet—met—met5. say—said—said6. pay—paid—paid7. win—won—won 8. sell—sold—sold 9. tell—told—told10. stand—stood—stood 11. understand—understood—understood12. sit—sat—sat 13. wear—wore—worn第八组ABC1. begin—began—begun2. swim—swam—swum3. sing—sang—sung4. ring—rang—rung5. drink—drank—drunk6. come—came—come7. become—became—become 8. see—saw—seen 9. run—ran—run11. lie—lay—lain—lying(躺)12. lie—lied—lied—lying(说慌)13. lay—laid—laid(放)(4)一般过去时的用法①表示过去某一时刻或某一段时间内所发生的动作或情况,常与明确的时间状语连用,如:yesterday, last week (month, year...), ago, just now, at the age of…, in 1980等连用。