英语词汇学教程参考答案杨信彰
- 格式:docx
- 大小:252.58 KB
- 文档页数:19

试题一第一部分选择题I. Each of the statements below is followed by four alternative answers. Choose the one that would best complete the statement and put the letter in the bracket.(30%)1.In Old English there was _______ agreement between sound form.A. moreB. littleC. lessD. gradual2.Both LDCE and CCELD are _______.A. general dictionariesB. monolingual dictionariesC. both A and BD. neither A and B3.The word "MINISKIRT" is _______.A. morphologically motivatedB. etymologically motivatedC. semantically motivatedD. none of the above4.The most important way of vocabulary development in present-day English is _______.A. borrowingB. semantic changeC. creation of new wordsD. all the above5.Generalization is a process by which a word that originally had a specialized meaning has now become ________.A. generalizedB. expandedC. elevatedD. degraded6.Some morphemes have _______ as they are realized by more than one morph according to their position in word.A. alternative morphsB. single morphsC. abstract unitsD. discrete units7.Old English vocabulary was essentially _______ with a number of borrowings from Latin and Scandinavian.A. ItalicB. GermanicC. CelticD. Hellenicpounds are different from free phrases in all the following ways EXCEPT _______.A. semanticsB. grammarC. phoneticsD. lexicology9.If two main constituents of an idiom share the same initial sound, it is called _______.A. repetitionB. alliterationC. rhymeD. none of the above10.Which of the following words is a functional word?A. OftenB. NeverC. AlthoughD. Desk11.Rhetorical features are shown in such respects of phonetic and lexical manipulation as well as _______.A. semantic unityB. structural stabilityC. idiomatic variationD. figure of speech12.The advantage of classifying idioms according to grammatical functions is to _______.A. use idioms correctly and appropriatelyB. understand idioms correctlyC. remember idioms quicklyD. try a new method of classification13.Borrowing as a source of homonymy in English can be illustrated by _______.A. long(not short)B. ball(a dancing party)C. rock(rock'n'roll)D. ad(advertisement)14.The change of word meaning is brought about by the following internal factors EXCEPT _______.A. the influx of borrowingB. repetitionC. analogyD. shortening15.Which of the following is NOT a component of linguistic context?A. Words and phrases.B. SentencesC. Text or passageD. Time and place第二部分非选择题II. Complete the following statements with proper words or expressions according to thecourse book.(10%)16.Word-meaning changes by modes of extension, narrowing, degradation, elevation and ___________________.17.The language used in England between 450 and 1150is called _________________.ELD is a ________________ dictionary.19.In the phrase "the mouth of the river",the word "mouth" is _________________ motivated.20.Physical situation or environment relating to the use of words is ________________ context.Ⅲ. Match the words or expressions in Column A with those in Column B according to1)types of meaning changes;2)types of meaning;3)language branches and 4)meaning and context.(10%)A B21.Scandinavian() l(place where things are made)22.Germanic() B.grammatical23.extension() C.double meaning24.narrowing() D.Swedish25.linguistic() prehend/understand26.ambiguity() F.Dutch27.participants()G.degermined28.difference in denotation()H.pigheaded29.appreciative()I.non-linguistic30.pejorative()J.iron(a device for smoothing clothes)Ⅳ. Study the following words or expressions and identify 1)types of bound morphemes underlined, and 2)types of word formation or prefixes.(10%)31.predict()32.motel()33.potatoes()34.blueprint()35.preliminaries()36.Southward()37.demilitarize()38.hypersensityve()39.retell()40.multi-purposes()Ⅴ.Define the following terms.(10%)41.acronymy42.native words43.elevation44.stylistic meaning45.monolingral dictionaryⅥ.Answer the following questions. Y our answers should the clear and short. Write your answers in the space given below.(12%)46.How many types of motivation are there in English? Give ONE example for each type.47.What are the major sources of English synonyms? Illustrate your points.48.What are the clues generally provided in verbal context?Ⅶ.Analyze and comment on the following. Write your answers in the space given below.(18%)49.analyze the morphological structures of following words and point out the types of the morphemes.Recollection, nationalist, unearthly50.Pick out the idioms in the following extract and explain its origin and the effect of using this form."Well, it's the old story of the stitch in time," he said.参考答案Ⅰ.(3%)1.A2.C3.A4.C5.A6.A7.B8.D9.B10.C11.D12.A13.B14.B15.DⅡ.(10%)16.transfer17.OLD English18.monolingual19.semantically20.extralinguistic/non-linguisticⅢ.(10%)21.D22.F23.A24.J25.B26.C27.I28.E29.G30.HⅣ.(10%)31.bound root32.(head+tail)blinding33.inflectional affix/morpheme34.a+n35.full conversion36.suffix37.reversative prefix38.prefix of degree39.prefix40.number prefixⅤ.(10%)41.The process of forming new words by joining the initial letters of names of organizations or special noun phrases and technical terms.42.Native words, also known as Anglo-Saxon words, are words brought to Britian in the 5th century by the Germanic tribes.43.The process by which words rise from humble beginnings to positions of importance.44.The distinctive stylistic features of words which make them appropriate for different context.45.A dictionary written in one language, or a dictionary in which entries are defined in the same language.Ⅵ.(12%)46.There are four types of motivation:1)Onomatopoeic motivation, e.g. cuckoo, squeak, quack, etc.2)Morphological motivation, e.g. airmail, reading-lamp, etc.3)Semantic motivation, e.g. the mouth of the river, the foot of the mountain, etc.4)Etymological motivation, e.g. pen, laconic, etc.47.Key points:borrowing; dialects and regional English; figurative and euphemistic use of words; coincidence withidiomatic expressions.48.Key points:definition; explanation; example; synonymy; antonymy; hyponymy; relevant details and word structure.Ⅶ.(18)49.1)Each of the three words consists of three morphemes, recollection(re+collect+ion),nationalist(nation+al+ist),unearthly(un+earth+ly).2)Of the nine morphemes, only "collect","nation" and "earth" are free morphemes as they can exist by themselves.3)All the rest re-,-ion,-al,-ist,un- and -ly are bound as none of them can stand alone as words. 50.1)the stitch in time ----- a stitch in time saves nine(3分)2)proverbs are concise, forcible and thought-provoking(1分)3)using an old saying is more persuasive(2分)4)the short form saves time, more colloquial(2分)5)indicates intimacy or close relationship(1分)。

《英语词汇学》课程教学大纲课程编码:30615008 学分: 2 总学时:36说明【课程性质】《英语词汇学》为英语专业的专业任意选修课程。
【教学目的】本课程是英语专业高年级阶段的一门专业任意选修课。
本课程的教学目的在于要求学生掌握英语词汇学的基本知识和基本理论,从而更科学地学习英语词汇,运用词汇学中所学到的基本知识和理论来分析和理解英语词汇,正确地使用英语词汇。
【教学任务】《英语词汇学》以帮助学生扩大词汇量,有效运用英语词汇;更深入的理解词义,更有效的组织划分和贮存词汇;增强学生对词义和用法的了解,使学生准确使用词汇;使学生掌握使用参考书的技能,增加解决问题的能力和学习英语的有效性;提高学生的语言接受能力和语言使用能力为教学任务。
【教学内容】词的基本知识、英语的亲属关系与英语词汇的形成和发展、词的形态结构和构成方法、词的意义、语义关系、词义的演变、英语习语、英语词典【教学原则和方法】教学原则:本课程采用张维友编写的《英语词汇学教程》(华中师范大学出版社)为主要教材,在教学过程中坚持以学生为主体,教师为指导的原则,以教材为中心,并适时地向学生介绍英语词汇学的研究动态和最新方向,让学生对词汇学有一个全面系统的了解。
教学方法:在教学过程中,采用论述式、概述式和指引式讲解相结合对教学内容的新信息点、重点、难点进行论述式讲解,深入浅出地详述理论原理,用恰当的例证加以说明,以此帮助学生充分理解理论知识。
对容易懂的内容则进行简明扼要地讲解。
教学中以学习指定的教材为主,适当穿插一些相关的信息材料。
通过对英语词汇学中相关的概念即理论知识的学习和理解,要求学生尽量独立完成教材各部分后面所附的练习,必要时教师可给予适当的指导。
教学手段主要是抽取各部分中的精华部分进行讲解,并适时地采用专题讨论的方式进行学习。
【先修课程要求】要求学生具备英语语音、英语语法、基础英语、英语阅读、英语写作以及翻译等课程知识。
教材:张维友《英语词汇学教程》华中师范大学出版社,2004年。
![18秋西南大学[0057]《英语词汇学》作业答案](https://uimg.taocdn.com/b27c090f6c175f0e7dd1370a.webp)
1、This story is a _________ to divert the public attention away from the issue.1. blue moon2. black horse3. red herring4. green hand2、Come on! Cheer up! Don’t just sit here as stiff as a ________.1. poker2. patient3. queen4. king3、Overjoyed to see his long-lost friend, Jimmy ________ a toast to the health of them all.1. suggested2. spoke3. proposed4. raised4、You were not seriously injured. Don’t make a _________ out of a _________.1. mountain, molehill2. mount, molehill3. hill, molehill4. molehill, mountain5、The figure of speech employed in “The past is a bucket of ashes” is _________.1. euphemism2. litotes3. irony4. metaphor6、Our work calls for mutual support. We shouldn’t _________ each other's efforts.1. active2. interact3. counteract4. activate7、They all thought that she and her boyfriend were ________.1. birds of a kind2. birds of a type3. birds of a breed4. birds of a feather8、After a meal in a restaurant, you ask the waiter for the _________.1. note2. receipt3. bill4. menu9、Exercise seems to benefit the brain power of the healthy and the sick, the young and the old ________.1. alike2. included3. alive4. through10、Words with such clusters as “ch”, “ph”, “pn”, “rh” as in chasm, phone, pneumatic and rhetoric are most prob1. German2. Chinese3. Greek4. Latin11、I waited for Tom for ages, but he didn’t _________.1. turn in2. turn up3. turn on4. turn out12、He was ________ of having asked such a silly question.1. miserable2. guilty3. sorry4. ashamed13、I took only a _________ of beans with me and left.1. hand2. handful3. handy4. handed14、1. According to the divine-source theory, language ________.1. the result of our ancestors imitating natural sounds around them2. originated from human physiological adaptation3. originated from the link between physical gestures and orally produced sounds4. is given by God15、Choked traffic has been a(n) ________ to urban transportation system.1. archenemy2. main enemy3. major enemy4. primary enemy16、Flying in an airplane was once thought to be an impossible ________.1. task2. problem3. promise4. profession17、No new ideas _______ from the meeting.1. merged2. submerged3. emerged4. immerged18、The scientists realized it would be too ________ to ship all people in one boat because it was fragile.1. dangerous2. risky3. daring4. bold19、I took the children to the zoo to ________ for the party they missed yesterday.1. make away2. make up3. make it4. make of20、The Old English word stān means ________ in modern English.1. stalig2. stole3. stain4. stone21、In “Elizabeth could hear voices through the open door”, the word door means ________.1. the moveable barrier in the entrance to a building, room, cupboard, car, etc.2. the channel to a certain place3. None of the above4. the panel board22、Communication is the process of ________ a message from a source to an audience via a channel.1. transforming2. transmitting3. switching4. submitting23、Which of the following usually appears in poems?_________1. nag2. steed3. horse4. gee-gee24、According to ________, human language is the result of evolution.1. the divine-source theory2. the oral-gestural theory3. the glossogenetic theory4. the natural-sound theory25、Among the four prefixes in the following, ________ is NOT a quantity prefix.1. an-2. di-3. multi-4. mono-判断题26、In the Middle English period, English lost most of its inflections.1. A.√2. B.×27、Human languages are derived from the natural sounds around and are thus onomatopoeic in nature.1. A.√2. B.×28、There exists a natural relation between the sound and meaning of a word.1. A.√2. B.×29、Words can be moved around without destroying the grammaticality of the sentence.1. A.√2. B.×30、Farewell is shortened from Fare thee well.1. A.√2. B.×31、With the aid of jargons, people of certain field can communicate effectively and economically.1. A.√2. B.×32、There is no principled clear-cut between the lexicon of a language and its grammar.1. A.√2. B.×33、The synchronic approach to word meaning focuses on the semantic changes over time.1. A.√2. B.×34、In the sentence, “I presume that you are Dr. Livingstone”,presume can be replaced by “suppose”.1. A.√2. B.×35、The meaning of words can be equated with what they refer to in the real world.1. A.√2. B.×36、Words loved, cherished, fainted and swirled all share the same grammatical meaning, i.e., “past tense”.1. A.√2. B.×37、“sense”, as a term in semantics, denotes the relationship between words within language.1. A.√2. B.×38、Absolute synonyms are not easy to found in any language.1. A.√2. B.×39、In standard AmE, the letter r is pronounced wherever it appears as in bar, board, park, etc.1. A.√2. B.×40、Lexicology is focused exclusively on lexical words or contents words.1. A.√2. B.×41、Man is a word, a root, a stem and a free morpheme as well.1. A.√2. B.×42、There is no direct link between a linguistic form and what it refers to.1. A.√2. B.×43、webinar is formed by blending web and seminar, meaning “an online seminar or conference”.1. A.√2. B.×44、Compared with horse, gee-gee is stylistically more formal.1. A.√2. B.×45、The prototype of a category is independent from context.1. A.√2. B.×主观题46、grammatical meaning参考答案:Grammatical meaning refers to that part of meaning which indicates grammatical relationships of functions, such as tense mea plural meanings of words, etc.47、melioration参考答案:Melioration refers to the process whereby words with humble origins are gradually used in positive, or at least neutral conte xts woman”, but now it is used to refer to the female ruler of a state.48、semantic loan参考答案:A semantic loan is a word or expression that has developed a new meaning or new meanings due to the influence of a related w English word “dream”, for instance, which originally meant joy, music, has taken its moder n meaning from the Norse.49、jargon参考答案:Jargon are languages peculiar to a trade, profession, or other group. For example, RAM, ROM, Hard Disk, CPU, etc. are all ja50、free phrase参考答案:Free phrases refer to any group of words or expressions carrying meaning. For example, “three British experts” is a free phras needed, can be altered, such as “two Chinese students”, “100 African men”, “20 read apples”, etc., each of which carries a me51、morpheme参考答案:Morpheme is the minimal unit of meaning or grammatical function that cannot be further analyzed, e.g. -ly, dog, hand, etc.52、root参考答案:A root is the morpheme in a word functioning as the core of the meaning. For example, in “disliked”, “like” is the part left wi but “like”carries the meaning common to both “dislike”, and “liked”.53、subjectification参考答案:Subjectification refers to the process by which the meaning of a given word changes from relatively objective to increasingly s meant “true”or “real”, which are objective descriptive, such a s , very knight meant “true knight”. Presently, “very” is mainly a When I say “It is very hot”, the degree of “hotness” is out of my own personal evaluation.54、What is lexical meaning and what are its different types?参考答案:Lexical meaning is the meaning of an isolated word in a dictionary. This component of meaning is regarded as being identical can be divided into five different types, i.e. conceptual meaning, connotative meaning, social meaning, affective meaning and c illustrated in the following:1) Conceptual meaning, also known as denotative meaning or logical meaning, is assumed to be the most basic and central fac the core of semantic study. The conceptual meaning of a word indicates the concept, and is thus relatively stable. See the followbachelor: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, +MALE, –MARRIED]spinster: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, –MALE,–MARRIED]wife: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, –MALE, +MARRIED]2) Connotative meaning or connotation is the additional meaning that a word possesses beyond its central or conceptual meani associations suggested by the conceptual meaning of the word. See the following examples:boy conceptual meaning [+HUMAN, +MALE, –ADULT]connotative meaning lovable, naughty, noisy, irritating, etc.Connotative meanings or connotations often tend to be variable according to society, time, culture, and even the experience of e.g. “西风” vs. “west wind”: share the same denotation, the wind blowing from the west“西风”: sadness, bitterness, coldness, departure, etc.“west wind” in Britain: agreeable figure associated with spring and flowers3) Social meaning of words refers to the information about the potential social circumstances where the words are appropriate the following factors:DIALECT (e.g. the language of geographical region or of a social class)TIME (e.g. the language of the eighteenth century, etc.)PROVINCE (e.g. language of law, of science, of advertising, etc.)STATUS (e.g. polite, colloquial, slang, etc.)SINGULARITY (e.g. the style of Dickens, of Hemingway, etc.)4) Affective meaning conveys the personal emotions and attitudes of a language user, including his attitude to the listener, or h about. In the following, words in Column A are affective positive while those in Column B are negative in meaning.A Bslim skinnynew unproveninexpensive cheap5) Collocative meaning is part of the word meaning suggested by its relations with the words it can co-occur. It refers to the gr words can be used together.e.g. pretty vs. handsome.Although these two words share common ground in expressing the meaning of “good-looking”, they may be distinguished by t linguists’ term) collocate with.55、What is a compound and what is a free phrase? How can compound and free phrases be distinguished?参考答案:Compounds refer to words formed by compounding or combining two or more stems. Free phrase is similar to “expression”. It idiomatic meaning. Compounds are similar to free phrases in structure, but compounds and free phrases are essentially differen features, semantic features and grammatical features.1) Phonetic difference: Stress in compounds tends to fall on the initial element while that of free phrases is apt to fall on the fin Compounds Free phrases'green house green 'house'blackboard black 'board'White House white 'houseThis rule of distinction is not always reliable.e.g. scholar 'activist, Mansion 'Avenue, May 'Flowers, silk 'tie.2) Semantic differences: A compound is a semantic gestalt/gəˈʃtɑ:lt/ that expresses a single idea just like a word.e.g. green house : a building with glass walls and roof for the cultivation and exhibition of plants under controlled conditions o the free phrase green house means a house in green color.The meanings of the constituents in compounds form an inseparable semantic whole. The change of any element will result in considerable amount of compounds are transparent in meaning, that is, their meaning is the combination of the meanings of the scarlet fever, etc.3) Grammatical difference: A compound is supposed to perform a single grammatical role in a sentence like a noun, a verb or a compounds, blackboard and White House cannot be modified by the adverb very, but it is acceptable in phrases a very black b56、He was brainwashed into believing money made defines the means.参考答案:他被洗脑了,相信为了钱可以使用一切手段。

Chapter 3 Morphological Structure of English Words We have discussed the historical, cultural and social factors that facilitate (使……容易;推动)the development of the English vocabulary. Borrowing, as we see, has been playing an active role in the expansion of vocabulary。
In modern times,however, vocabulary is mainly enlarged on an internal basis. That is, we use word—building material available in English to create new words。
But before we discuss the actual ways and means to make new words, we need to have a clear picture of the structure of English words and their components (成分)—word-forming elements. This chapter will discuss morphemes(语素;词素), their classification(分类)and identification(辨别), the relationship between morphemes and word—formation(构词法)。
3。
1 MorphemesTraditionally,words are usually treated as the basic and minimal units of a language to make sentences,which are combinations of words according to syntactic rules(句法规则). Structurally,however, a word is not the smallest unit because many words can be separated into even smaller meaningful units. Take decontextualization for example。
![17秋西南大学[0057]《英语词汇学》作业答案](https://uimg.taocdn.com/867894c933d4b14e8424680e.webp)
1、“lose face” is a(n) _________.1. semantic loan2. denizen3. alien4. translation loan2、The United Nations has appealed for help from the ________ community.1. A. within-national2. intra-national3. international4. in-national3、Come on! Cheer up! Don’t just sit here as stiff as a ________.1. poker2. patient3. queen4. king4、You were not seriously injured. Don’t make a _________ out of a _________.1. mountain, molehill2. mount, molehill3. hill, molehill4. molehill, mountain5、After a meal in a restaurant, you ask the waiter for the _________.1. note2. receipt3. bill4. menu6、W ords with such clusters as “ch”, “ph”, “pn”, “rh” as in chasm, phone, pneumatic and rhetoric are most proba1. German2. Chinese3. Greek4. Latin7、In “Tom’s family keep a good table”, the word table means ________.1. food and drinks served at meals2. none of the above3. people assembled around a table, as at meals4. the piece of furniture with a flat horizontal surface supported by one or more vertical legs8、We eventually ran out of patience with his ________ behaviour.1. childish2. childlike3. child4. childy9、He was ________ of having asked such a silly question.1. miserable2. guilty3. sorry4. ashamed10、I took only a _________ of beans with me and left.1. hand2. handful3. handy4. handed11、The missiles missed their _________, so the research group did not reach its _________.1. target, target2. goal, goal3. goal, target4. target, goal12、No new ideas _______ from the meeting.1. merged2. submerged3. emerged4. immerged13、Which of the following words has gone through the semantic change of subjectification?1. corn2. gossip3. maid4. very14、Having lost the match, the team went home in ________ spirits.1. D. dark2. deep3. low4. empty15、The Old English word stān means ________ in modern English.1. stalig2. stole3. stain4. stone16、After his recovery from illness, he ________ his former position.1. C. presumed2. resumed3. assumed4. consumed17、In “Elizabeth could hear voices through the open door”, the word door means ________.1. the moveable barrier in the entrance to a building, room, cupboard, car, etc.2. the channel to a certain place3. None of the above4. the panel board18、Among the synonymous group, old man, daddy, dad, father and male parent, ________ would most probably u1. B. male parent2. father3. old man4. dad19、Which of the following usually appears in poems?1. nag2. steed3. horse4. gee-gee20、The main characters in the novel seem so true to life, but actually, they are entirely ________.1. imaginative2. imagined3. imaginable4. imaginary判断题21、Old English is a non-inflectional language.1. A.√2. B.×22、Many words in English vocabulary are compositional.1. A.√2. B.×23、In “I haven’t seen you for ages”, hyperbole is employed.1. A.√2. B.×24、The word nice has gone through a semantic change called “generalization”.1. A.√2. B.×25、In the Middle English period, English lost most of its inflections.1. A.√2. B.×26、Latin element was first brought into English by Germanic tribes.1. A.√2. B.×27、Connotative meaning of a word is relatively stable and insensitive to the change of context.1. A.√2. B.×28、London dialect began to spread as Standard English in the Middle English period.1. A.√2. B.×29、Farewell is shortened from Fare thee well.1. A.√2. B.×30、AmE and BrE shares all grammatical rules.1. A.√2. B.×31、Comparatively speaking, ask is more formal than interrogate.1. A.√2. B.×32、“Just a second!” is a case of litotes (understatement).1. A.√2. B.×33、Answering the question “Will you marry me?”with “Yes, I will”, the speaker is using su bstitution.1. A.√2. B.×34、The vocabulary of any language never remains stable; it is constantly changing.1. A.√2. B.×35、In the sentence, “I presume that you are Dr. Livingstone”,presume can be replaced by “suppose”.1. A.√2. B.×36、air-conditioner is a word derived from adding –er to air-condition.1. A.√2. B.×37、A word, car for example, may mean differently to different people.1. A.√2. B.×38、According to cognitive semantics, our mind can be explored via the study of linguistic meanings.1. A.√2. B.×39、Compared with horse, gee-gee is stylistically more formal.1. A.√2. B.×40、For an English word, the shift of stress may indicate a change of part of speech; export is a perfect example.1. A.√2. B.×主观题41、grammatical meaning参考答案:Grammatical meaning refers to that part of meaning which indicates grammatical relationships of functions, such as tense mea plural meanings of words, etc.42、translation loan参考答案:A translation loan is a word or an expression formed from the material already existing in the English language but according t way of literal word-for-word or root-for-root translation. Examples are “land-reform”, “mutual-aid” team, “national bourgeoisi43、blending参考答案:Blending refers to process of making a new word by combining parts of two or more words. For example, the word “brunch”“lunch”.44、jargon参考答案:Jargon are languages peculiar to a trade, profession, or other group. For example, RAM, ROM, Hard Disk, CPU, etc. are all ja45、free phrase参考答案:Free phra ses refer to any group of words or expressions carrying meaning. For example, “three British experts” is a free phras needed, can be altered, such as “two Chinese students”, “100 African men”, “20 read apples”, etc., each of which carries a me46、Stylistics参考答案:The systematic study of styles of words, expressions and text.47、meronymy参考答案:Meronymy refers to the part-whole sense relationship. For example, the word “body”and “head”, “arm”, “leg”, etc. have a pa relationship is called “meronymy”.48、affix参考答案:An affix is the morpheme added to a root and contributes to the meaning of a word as a whole. According to its position, an a word, or suffix, because it appears following the word. For example, in “enlarge”, the affix “en”is a prefix, because it is adde because of the ad dition of “en”that the new verb “enlarge” is made with causative meaning.49、What is lexical meaning and what are its different types?参考答案:Lexical meaning is the meaning of an isolated word in a dictionary. This component of meaning is regarded as being identical can be divided into five different types, i.e. conceptual meaning, connotative meaning, social meaning, affective meaning and c illustrated in the following:1) Conceptual meaning, also known as denotative meaning or logical meaning, is assumed to be the most basic and central fact the core of semantic study. The conceptual meaning of a word indicates the concept, and is thus relatively stable. See the followbachelor: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, +MALE, –MARRIED]spinster: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, –MALE,–MARRIED]wife: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, –MALE, +MARRIED]2) Connotative meaning or connotation is the additional meaning that a word possesses beyond its central or conceptual meani associations suggested by the conceptual meaning of the word. See the following examples:boy conceptual meaning [+HUMAN, +MALE, –ADULT]connotative meaning lovable, naughty, noisy, irritating, etc.Connotative meanings or connotations often tend to be variable according to society, time, culture, and even the experience of e.g. “西风” vs. “west wind”: share the same denotation, the win d blowing from the west“西风”: sadness, bitterness, coldness, departure, etc.“west wind” in Britain: agreeable figure associated with spring and flowers3) Social meaning of words refers to the information about the potential social circumstances where the words are appropriate the following factors:DIALECT (e.g. the language of geographical region or of a social class)TIME (e.g. the language of the eighteenth century, etc.)PROVINCE (e.g. language of law, of science, of advertising, etc.)STATUS (e.g. polite, colloquial, slang, etc.)SINGULARITY (e.g. the style of Dickens, of Hemingway, etc.)4) Affective meaning conveys the personal emotions and attitudes of a language user, including his attitude to the listener, or h about. In the following, words in Column A are affective positive while those in Column B are negative in meaning.A Bslim skinnynew unproveninexpensive cheap5) Collocative meaning is part of the word meaning suggested by its relations with the words it can co-occur. It refers to the gr words can be used together.e.g. pretty vs. handsome.Although these two words s hare common ground in expressing the meaning of “good-looking”, they may be distinguished by t linguists’ term) collocate with.50、What is a word?参考答案:A word can be simple defined as the minimal meaningful free unit of language. This definition is to be understood in the from1) A word is the sound unit of language.(1) A word is a sound unit (or unit of speech) for the purpose of communication. In this sense, a word sound in nature and eac purpose(s). Even the first word uttered by a baby is for communication.(2) A word is a sound cluster conventionally sequenced. In this sense, the order of sound elements in a word is fixed and abid example, for the word /ɡəu/, the sequence /ɡ/must precede /əu /, otherwise, it is not the word “go” at all.(3) A word is a combination of sound and meaning according to the conventions of specific languages. For example, the soun “enough (够)” in Chinese.2) A word is the smallest free form of language.(1) Words are free forms of a language, i.e., forms that can be moved without destroying the grammaticality of the sentence. I “saw”and “Bill” can all move freely and each sentence is grammatically correct.(2) In contrast, the letters that form a word are fixed with rigid sequential order. A word is the smallest free form of language its meaning or even its status as a word. For example, only “John”is a boy’s name, but not “Jonh”, “Jhon”, “Jhno”or “Joan”.3) A word is the building block for phrase and sentence.When separate d from the phrase, sentence or passage, a word will be difficult to understand since it is no more than a “dead” d sentences and passages are contexts for the interpretation of words. In sum, words are the building blocks out of which phrases51、Once in the office, President Obama embarked right away on de-Clintonization.参考答案:就职以后,奥巴马总统立即着手去克林顿化。

英语词汇学夏洋版课后答案1、--What are you going to be in the future?--I want to be _______ actor. [单选题] *A. aB. an(正确答案)C. theD. /2、--What would you like to say to your _______ before leaving school?--I’d like to say"Thank you very much!" [单选题] *A. workersB. nursesC. waitersD. teachers(正确答案)3、More than one student_____absent from the class yesterday due to the flu. [单选题] *A.areB.hasC.isD.was(正确答案)4、( ) What _____ fine weather we have these days! [单选题] *A. aB. theC. /(正确答案)D. an5、Alice is a ______ girl. She always smiles and says hello to others.()[单选题] *A. shyB. strictC. healthyD. friendly(正确答案)6、—Why is Mary asking Bob about the school trip? —Because she wants to know ______.()[单选题] *A. how does he think of the tripB. what does he think of the tripC. what he likes the tripD. how he likes the trip(正确答案)7、I’m so tired after _______ walk. [单选题] *A. three hour’sB. three hours’(正确答案)C. three hoursD. three hour8、—Could you take out the rubbish, Jim?—______. I have too much homework to do. You can ask Sally to do it. ()[单选题] *A. Sorry, I can’t(正确答案)B. No problemC. I disagreeD. No, thanks9、We are very hungry now. Can you _______ us something to eat? [单选题] *A. carryB. takeC. borrowD. bring(正确答案)10、The manager gave one of the salesgirls an accusing look for her()attitude towards customers. [单选题] *A. impartialB. mildC. hostile(正确答案)D. opposing11、I walked too much yesterday and ()are still aching now. [单选题] *A. my leg's musclesB. my leg muscles(正确答案)C. my muscles' of legD. my legs' muscles12、A small village cuts across the river. [单选题] *A. 切B. 穿过(正确答案)C. 划船D. 踢13、Is there going to ______ a football match in the stadium next month?()[单选题] *A. beingB. haveC. be(正确答案)D. having14、John suggest _____ anything about it until they found out more facts. [单选题] *A not to sayB. not sayC to say notD not saying(正确答案)15、—Where ______ you ______ for your last winter holiday?—Paris. We had a great time. ()[单选题] *A. did; go(正确答案)B. do; goC. are; goingD. can; go16、Every means _____ but it's not so effective. [单选题] *A. have been triedB. has been tried(正确答案)C. have triedD. has tried17、If by any chance someone comes to see me, ask him to leave a _____. [单选题] *A. message(正确答案)B. letterC. sentenceD. notice18、My sister gave me a _______ at my birthday party. [单选题] *A. parentB. peaceC. patientD. present(正确答案)19、Let us put the matter to the vote,()? [单选题] *A. will youB. can weC. may ID. shall we(正确答案)20、I should like to rent a house which is modern, comfortable and _____, in a quiet neighborhood. [单选题] *A.in allB. after allC. above all(正确答案)D. over all21、______ my great joy, I met an old friend I haven' t seen for years ______ my way ______ town. [单选题] *A. To, in, forB. To, on, to(正确答案)C. With, in, toD. For, in, for22、( ) They have_____ useful dictionary. They want to lend it___ us. [单选题] *A. an; forB. a; fromC. an; toD. a; to(正确答案)23、Was()that I saw last night at the concert? [单选题] *A. it you(正确答案)B. not youC. youD. that yourself24、58.—How much is Lucy's skirt?—She________320 yuan for it. I think it's a little dear. [单选题] *A.tookB.paid(正确答案)C.spentD.bought25、?I am good at schoolwork. I often help my classmates _______ English. [单选题] *A. atB. toC. inD. with(正确答案)26、My watch usually _______ good time, but today it is five minutes fast. [单选题] *A. goesB. makesC. keeps(正确答案)D. gains27、______ visitors came to take photos of Hongyandong during the holiday. [单选题] *A. ThousandB. Thousand ofC. ThousandsD. Thousands of(正确答案)28、John and Jack had looked for the key, but _____ of them found it. [单选题] *A. noneB. neither(正确答案)C. bothD. either29、Don’t _______ to close the door when you leave the classroom. [单选题] *A. missB. loseC. forget(正确答案)D. remember30、I used to take ____ long way to take the bus that went by ____ tunnel under the water. [单选题] *A. a, aB. a. theC. a, /(正确答案)D. the, a。

词汇学练习参考答案I. Some of the following statements are true, and others are false. Mark your answer by writing T or F in the bracket at the end of each sentences.1. T2. F3. F4. T5. F6. F7. T8. T9. F 10. F 11. T 12. F 13. T 14. F15. T 16. T 17. T 18. T 19. F 20. F 21. F 22. F 23. T 24. F 25. F 26. T27. T 28. F 29. F 30. F 31. T 32. F 33. F 34. T 35.T 36. F 37. F 38. F 39. F40. T 41. F 42. T 43. F 44. T 45. F 46. F 47. T 48. T 49. F 50. T 51. T 52. F53. F 54. T 55. F 56. T 57. T 58. F 59. F 60. T 61. T 62. T 63. F 64. T 65. T66. F 67. T 68. F 69. T 70. T 71. F 72. F 73. T 74. T 75. F 76. T 77. T 78. F79. T 80. F 81. T 82. T 83. T 84. F 85. T 86. T 87. T 88. F 89. T 90. F 91. T92. F 93. F 94. T 95. F 96. T 97. T 98. T 99. F 100. F 101. T 102. T 103. T104. T 105. F 106. T 107. T 108. T 109. F 110. F 111. F 112. T 113. T 114. T115. F 116. F 117. T 118. T 119. F 120. F 121. T 122. F 123. F 124. F 125. T126. F 127. FII. The following are multiple-choice questions. Mark your answer by circling A, B, C, or D which best completes the sentence.1. C2. B3. A4. B5. D6. B7. D8. B9. B 10. D 11. A 12. D 13. A 14. A15. B 16. C 17. C 18. B 19. D 20. D 21. A 22. D 23. B 24. C 25. B 26. A27. A 28. B 29. C 30. B 31. B 32. D 33. C 34. D 35. C 36. B 37. A 38. B39. B 40. B 41. B 42. C 43. B 44. C 45. C 46. B 47. C 48. C 49. B 50. D51. D 52. B 53. C 54. A 55. A 56. B 57. B 58. C 59. A 60. D 61. D 62. A63. D 64. C 65. B 66. A 67. A 68. D 69. C 70. D 71. D 72. D 73. A 74. D75. D 76. A 77. C 78. A 79. D 80. D 81. B 82. D 83. D 84. D 85. B 86. A87. B 88. C 89. C 90. A 91. B 92. C 93. B 94. A 95. C 96. D 97. D 98. B199. B 110. C 101. A 102. A 103. B 104. B 105. C 106. C 107. DIII. 连线题Section A1. J2. A3. B4. H5. E6. D7. F8. I9. G 10. CSection B1. G2. E3. H4. F5. I6. C7. B8. J9. A 10. DSection C1. D2. B3. E4. G5. A6. C7. F8. I9. J 10. HIV. 填空题Section A1. aliens2. intrinsic3. Denizens4. common5. stable6. Conversion7. polysemy8. compounding9. pejorative 10. Reference 11. arbitrary12. imperfect 13. reversative 14. French 15. lexical 16. extension/generalization 17. 1500Section B18. mositure 19. rigid 20. deserted 21. innocent 22. old-fshioned 23. loosen 24. completely 25. similarity 26. indifferent 27. fruitful 28. special 29. essential 30. depressed/sadV. Complete the following sentences by choosing phrases from the list and using them intheir proper forms.Section A31. stood out against 32. approve of 33. get over with 34. looking into35. come up with 36. comply with 37. cashed in on 38. go without39. will profit by/from 40. put down toSection B41. close 42. cold 43. narrow 44. cardinal 45. burning 46. capital47. circumstantial 48. cool 49. double-minded 50. fair 51. green-eyed52. happy 53. hollow 54. open-ended 55. random 56. roundVI.1. b2. i3. c4. f5. a6. h7. e8. d9. g 10. j 11. r 12. p 13.s 14. k 15. o 16. m 17. l 18. n 19. qIX分析题(问题)1. As homonyms are identical in sound or spelling, particularly homophones, they are often employed to create puns for desired effect of, say, humor, sarcasm or ridicule. Consider the following conversation that takes place between a waitress and a customer in a restaurant: “You are not eating the fish,”the waitress said to him, “Anything wrong with it?”“Long time no sea,”the man replied.:Long time no see is usually said as a form of greeting between two friends when they meet 答案after a long time of separation. Here the customer cleverly employed the structure of the idiom to2his advantage to criticize in a humorous way the bad quality of the food served at the restaurant.Long time no sea implies that the “sea food kept for a long time is not fit for eating.”(问题)2. Collocation can affect the meaning of words答案:Collocation refers to the words before or after the word in discussion, and collocative meaning consists of the associations the word acquires in its collocation. Words with the same conceptual meaning may have different meanings due to the range of words they may collocate with. In other words, collocation can affect the meanings of words. For example, “pretty”and “handsome”share the conceptual meaning of “good looking”, but are distinguished by the range of nouns they collocate with: pretty girl (boy/woman/flower) and handsome man (car/airline, etc.).(问题)3. The “pen”is mightier than the “sword”.Explain what “pen”and “sword”mean respectively using the theory of motivation.答案:(1). Motivation accounts for the connection between the linguistic symbol and its meaning. (2). Semantic motivation, one of the four major types of motivation, explains the connection between the literal sense and figurative sense of the word. (3). In this sentence, “pen”reminds one of the tool to write with, thus suggesting writing; “sword”reminds one of the weapon to fight with, thus suggesting war.(问题)4. Connotative meaning is not stable. Comment on this statement with one example.答案:(1).Connotative meaning, known as connotation, refers to the overtones or associations suggested by the conceptual meaning. (2). Connotative meanings are not given in the dictionary,but associated with the word in actual context to particular readers or speakers. Thus they are unstable, varying considerably according to culture, historical period and the experience of the individual. (3). For example, the word “home”may remind one child of warmth, safety or love, while to another child who is often scolded or beaten at home, it may mean indifference, hatred, or even hell.(问题)5. Grammatical meaning, lexical meaning, stylistic meaning, affective meaning, connotative meaning, collocative meaning, conceptual meaning, associative meaning, denotative meaning, formal, neutral, informal, appreciative, pejorative答案:Meaning—grammatical meaning—lexical meaning—conceptual meaning(denotative meaning)—associative meaning—connotative meaning—collocative meaning—stylistic meaning(formal, neutral, informal)—affective meaning(appreciative, pejorative)(问题)6. Analyze the morphological structures of the following words and point out the types of the morphemes.recollection, nationalist, unearthly3答案:(1). Each of the three words consists of three morphemes, recollection (re+collection), nationalist (nation+al+ist), unearthly (un+earth+ly).(2). Of the nine morphemes, only “collect”, “nation”and “earth”are free morphemes as they can exist by themselves.(3) All the rest re-, -ion, -al, -ist, un- and-ly are bound as none of them can stand alone aswords.(问题)7. Analyze and comment on the following.He has been sick since this fall.Tell what “sick”and “fall”mean respectively and explain why they take on those meanings in modern American English.答案:(1). ”sick”means “ill”and “fall”means “autumn”in present American English;(2). These words no longer have such meanings in presnet British English;(3). American English has revived the old meaning of “sick”and that of “fall”. This is the revival of archaic or obsolete words.(问题)8. Find blends from the following sentence and give the explanation of which types of blendings they belong to respectively.“There is a set of hi-fi in the motel. ”答案:(1). Blends: hi+fi=high+fidelity, motel=motor+hotel;(2). hi+fi: head+head, motel: head+tail.(问题)9. Explain the rhetoric use of homonyms in B's speech. Give the two possible Chinese translations.A. “What color would you paint the sun and the wind?”B. “The sun rose and the wind blue.”答案:(1). Rose can be defined in two ways: color of rose and the past form of the verb rise.(2). Blue in two ways too: the color blue and the past form of the verb blow (in pronunciation).a). 粉红的太阳,蓝色的风。

Unit 11. The Labor Party’s electoral strategy, which was based on a tactical alliance with other minor parties, has proved successful.劳动党的选择策略已经证明是成功地,这个策略主张和其他的小党派组成一个策略联盟。
2. The government troops recaptured the city from the rebels at the cost of two thousand casualties政府部队以二万人的伤亡为代价,从版乱者手中重新占领了这所城市。
3. By a stroke of good luck, Genelle, who had been buried in the rubble for more than 26 hours, came our alive. 。
非常侥幸地是,Genelle在瓦砾里埋了26个小时,竟然活着。
4. My brother wasn’t badly hurt, but he injured his leg and had to limp around for a few weeks.我的兄弟伤得不重,但他伤了腿,不得不跛行好几周。
5. The aircraft was subjected to a test of temperatures of minus65 degrees and plus 120 degrees.飞行物要能承受零下65度和120多度温度的考验。
6. Tax incentives combined with cheap labor will attract companies to the western regions of our country away from the east coast.有廉价劳动力的税收刺激将吸引更多的公司到我国远离东海岸的西部地区。

英语词汇学教程课后练习题含答案1. 填空题单选题1.My sister is flirting with a man _______ her father.–☐ like–☐ resembling–☒ unlike–☐ beyond2.She always tells me that she is proud of her _______ family.–☐ physical–☐ biological–☐ imaginary–☒ adopted3.The actor’s performance in the movie is _______ incredible.–☒ absolutely–☐ barely–☐ partly–☐ relatively多选题1.The following words can all mean ‘people’, which one(s)is/are the most formal?–☐ folks–☒ populace–☐ crowd–☒ citizens2.Which of the following words can mean both ‘friendly’ and‘creepy’ depending on the context?–☒ charming–☐ mundane–☐ thrifty–☐ clueless3.Which word shows ‘seclusion’, ‘retreat’, ‘privacy’,and ‘withdrawal’ at the same time?–☐ sacrifice–☐ obedience–☒ seclusion–☒ retreat2. 辨析题选择合适的单词或者词组填写下列空格1.He couldn’t _______ the time he had wasted in his youth. Hetried to make it up by working harder.2.The candidate promised to _______ healthcare, education, andsecurity for the citizens if he were elected.3.Don’t _______ the importance of speaking a foreign languagefluently, it can bring you many benefits.答案1.retrieve2.provide3.underestimate3. 翻译题将下列句子翻译成英语 1. 那个女士是一位伟大的母亲,她时刻为孩子们着想。

新编英语词汇学教程课后答案蔡增亮1、John is fond of playing _____ basketball and Jack is keen on playing _____ piano. [单选题] *A./…the(正确答案)B.the…/C./…/D.the…the2、7.—________ is the Shanghai Wild Animal Park?—It’s 15km east of the Bund. [单选题] *A.WhoB.WhatC.WhenD.Where (正确答案)3、During the Spring Festival, people in Northern China usually eat _______ as a traditional Chinese food. [单选题] *A. pizzaB. dumplings(正确答案)C. hamburgersD. noodles4、64.Would you like to drink ________?[单选题] *A.something else(正确答案)B.anything elseC.else somethingD.else anything5、The yellow bag _______ me. [单选题] *A. belong toB. belongs to(正确答案)C. belongD. belongs6、—How do you find()birthday party of the Blairs? —I should say it was __________ complete failure.[单选题] *A.a; aB. the ; a(正确答案)C.a; /D.the; /7、80.Thousands of ________ from other countries visit the village every year. [单选题] *A.robotsB.postcardsC.tourists(正确答案)D.bridges8、My friends will _______ me at the airport when I arrive in London. [单选题] *A. takeB. meet(正确答案)C. receiveD. have9、—Can you play tennis? —______, but I’m good at football.()[单选题] *A. Yes, I can(正确答案)B. Yes, I doC. No, I can’tD. No, I don’t10、38.These workers ___________ this bridge since one year ago. [单选题] * A.buildB.are buildingC.have built (正确答案)D.built11、48.—________ is your new skirt, Lingling?—Black. [单选题] * A.HowB.What colour(正确答案)C.WhichD.Why12、_______ your help, I can’t finish my job. [单选题] *A. withB. without(正确答案)C. inD. into13、_____ the plan carefully,he rejected it. [单选题] *A. To have consideredB.To considerC. Having considered(正确答案)D. Considering14、25.—I ______ Beijing for a holiday.—________. [单选题] * A.will go;GoodbyeB.will go;Have a good time(正确答案)C.will go to;Have a good timeD.am going to;Have a fun15、Ships can carry more goods than _____ means of transport. [单选题] *A. the otherB. anotherC. any other(正确答案)D. any16、It’s one of _______ means of transportation. [单选题] *A. cheapB. convenientC. second-handD. the most convenient(正确答案)17、_______ a busy afternoon! [单选题] *A. HowB. What(正确答案)C. WhichD. Wish18、I do not have my own room,_____. [单选题] *A. neither does Tom(正确答案)B. neither has TomC. so does TomD. so has Tom19、I could ______ control my feelings and cried loudly when I heard the bad news. [单选题] *A. hardly(正确答案)B. ?reallyC. clearlyD. nearly20、There ______ a football match and a concert this weekend.()[单选题] *A. isB. haveC. will be(正确答案)D. will have21、—Look at those purple gloves! Are they ______, Mary?—No, they aren’t. ______ are pink. ()[单选题] *A. you; IB. your; MyC. yours; Mine(正确答案)D. you; Me22、When you have trouble, you can _______ the police. They will help you. [单选题] *A. turn offB. turn to(正确答案)C. turn onD. turn over23、The more he tried to please her, _____she seemed to appreciate it. [单选题] *A.lessB.lesserC.the less(正确答案)D.the lesser24、--What’s the _______ like today?--Cloudy. [单选题] *A. skyB. airC. landD. weather(正确答案)25、( ) No matter _____ hard it may be, I will carry it out. [单选题] *A whatB whateverC how(正确答案)D however26、4.—Let's fly a kite when you are ________ at the weekend.—Good idea. [单选题] * A.warmB.kindC.smallD.free(正确答案)27、_____ of the teachers in this district are women teachers. [单选题] *A. Four fifthB. Four fifths(正确答案)C. Fourth fifthsD. Four five28、—It’s too noisy outside. I can’t fall asleep.—I can’t, either. We have to ______ new ways to solve the problem.()[单选题] *A. come up with(正确答案)B. get on withC. make up withD. catch up with29、_______ hard, _______ you’ll fail in the exam. [单选题] *A. Studying; forB. Study; or(正确答案)C. To study; andD. Study; and30、He has two sisters but I have not _____. [单选题] *A. noneB. someC. onesD. any(正确答案)。
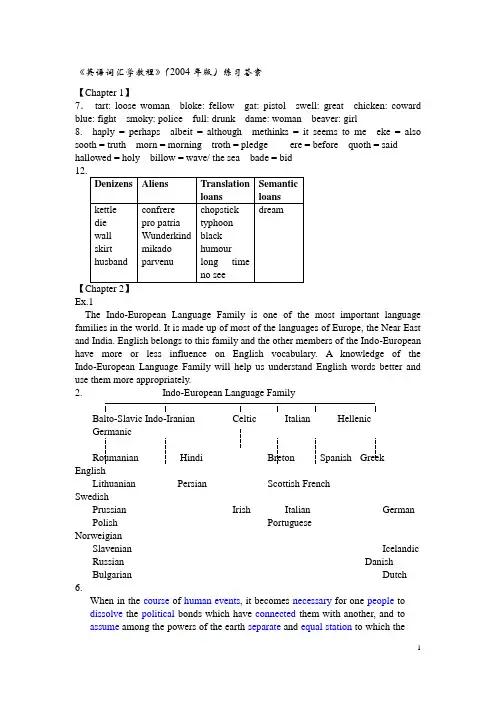
《英语词汇学教程》(2004年版)练习答案【Chapter 1】7.tart: loose woman bloke: fellow gat: pistol swell: great chicken: coward blue: fight smoky: police full: drunk dame: woman beaver: girl8. haply = perhaps albeit = although methinks = it seems to me eke = also sooth = truth morn = morning troth = pledge ere = before quoth = said hallowed = holy billow = wave/ the sea bade = bid【Ex.1The Indo-European Language Family is one of the most important language families in the world. It is made up of most of the languages of Europe, the Near East and India. English belongs to this family and the other members of the Indo-European have more or less influence on English vocabulary. A knowledge of the Indo-European Language Family will help us understand English words better and use them more appropriately.2. Indo-European Language FamilyBalto-Slavic Indo-Iranian Celtic Italian HellenicGermanicRoumanian Hindi Breton Spanish Greek EnglishLithuanian Persian Scottish FrenchSwedishPrussian Irish Italian German Polish PortugueseNorweigianSlavenian Icelandic Russian DanishBulgarian Dutch 6.When in the course of human events, it becomes necessary for one people to dissolve the political bonds which have connected them with another, and to assume among the powers of the earth separate and equal station to which thelaws of nature and of nature's God entitle them, a decent respect to the opinions of mankind requires that they should declare the causes which impel them to the separation.Most of the content words are either of Greek or Latin origin. What are left are mostly functional words. This shows that Greek and Latin play a very important part in the English vocabulary.8. eventful [Latin + English] hydroplane [Greek + Latin]falsehood [ Latin + English] pacifist [Latin + Greek]saxophone [German + Greek]heirloom [ French + English]joss house [ Portuguese + English] television[Greek + Latin]9.amateur (late) finacé (late) empire (early)peace (E) courage (E) garage (L)judgement (E) chair (E) chaise (L)grace (E) servant (E) routine (L)jealous (E) savaté (L) genre (L)gender (E) début (L) morale (L)state (E) chez (L) ballet (L)11.allegro, f轻快andante, j 行板diminuendo, g 渐弱largo, d 缓慢pianoforte, a轻转慢alto, i女低音crescendo, b渐强forte, e 强piano, h轻soprano, c女高音12.cherub (Hebrew) snorkel (G)coolie (Hindi) tulip (Turk)lasso (Sp) wok (Ch)shampoo (Indian) chocolate (Mex)tepee (Am Ind) jubilee (Gr)kibitz (G) Sabbath (Heb)chipmunk (Am Ind) tamale (Mex)cotton (Arab) voodoo (Afr)loot (Hindi) sauerbraten (G)13.a. alligatorb. lococ. rodeod. bonanzae. igloof. blitzkriegg. wigwam h. canoei. hurricane j. boomerangk. panchos【Chapter 3】1. a. morpheme b. allomorphc. bound morphemed. free morphemee. affixf. informational affixg. derivational affix h. rooti. stem j. base3. individualisticindividualist + ic [stem, base]individual + ist [stem, base]individu + al [stem, base]in + dividu [root, stem, base]undesirablesun + desirable [stem, base]desir + able [root, stem, base]free morpheme = free rootmorpheme bound rootbound morpheme inflectional affixaffix prefixderivational affixsuffix 【Chapter 4】Affixation5. non-smoker incapable impracticaldisobey insecurity irrelevantimmature inability/disability unofficiallyunwillingness illegal disagreement illogical disloyal inconvenientnon-athletic6. harden horrify modernizememorize falsify apologizedeepen glorify sterilizelengthen intensify beautifyfatten sympathizea. apologizedb. beautifyc. lengtheningd. sympathizede. fattenf. falsifyg. memorizing h. Sterilize7. a. employee b. politician c. participantd. waitresse. conductorf. teacherg. pianist h. examinee/examiner8.trans- = across: transcontinental, trans-worldmono- = one: monorail, monoculturesuper- = over, above: superstructure, supernaturalauto- = self: autobiography, automobilesub- = bad, badly: malpractice, malnutritionmini- = little, small: minicrisis, miniwarpre- = before: prehistorical, preelectionex- = former: ex-teacher, ex-filmerCompoundingheartbeat [S + V] brainwashing [V + O]movie-goer [place + V] baking powder [ V +adv]far- reaching [V + Adv] dog-tired [adv + a]lion-hearted [adv + a] love-sick [adv + a]boyfriend [S + complement] peace-loving [V +O]snap decision [V + O] easy chair [ a + n]on-coming [V +adv] tax-free [adv +a]light-blue [a + a] goings-on [V +adv]4. well-bred/well-behaved culture-bound/homeboundneedle work/homework praiseworthy/respectworthybar-woman/sportswoman nation-wide/college-wideclear-minded/strong-minded military-style/newstyleself-control/self-respect budget-related/politics-related water-proof/fire-proof once-fashionable/once-powerful news-film/news-letter mock-attack/mock-sadnesssister-in-law/father-in-law home-baked/home-producedhalf-way/half-done ever-lasting/ever-greenage-conscious/status-conscious campus-based/market-based Conversion7. a. stomach [n → v]b. room [n → v]c. wolf [n → v]d. come/go [v → n]e. familiar [a → n]f. innocent [a → n]g. flat [a → n]h. ah/ ouch [int → v]i. warm [a → n]j. has-been/might-have-been [finite v → n]k. Hamlet [proper n → v]l. buy [v → n]m. smooth [a → v]Blendingmotel (mo tor + ho tel)humint (hum an + int elligence)advertisetics (advertise ment + statis tics)psywarrior (psy chological warrior)hoverport (hover craft + port)chunnel (ch annel + t unnel)hi-fi (hi gh + fi delity)cinemactress (cinem a + actress)Clippingcopter (heli copter) dorm (dorm itory)lab (lab oratory) prefab (pref abricated house)活动板房gas (gas oline) prof (prof essor)scope (tele scope) champ (champ ion)sarge (serge ant) mike (mic rophone)ad (ad vertisement) tec (de tec tive)Acronymy2. kg = k ilo g ram ft = f oo t cf = c on f er授予cm = c enti m eter $ = dollaribid = ibid em etc. = et c eteraVIP = v ery i mportant p ersonOPEC = O rganization of P etroleum E xporting C ountriesTOEFL = t eaching o f E nglish as a f oreign l anguage3. a. SALTb. radarc. AIDSd. BASICe. Laserf. WHOg. sonarh. G-manBackformation2. lase (laser)escalate (escalator)babysit (babysitter)peeve (peevish易怒的)orate (orator)commute (commuter)Commonization of Proper Namesa. tantalize使干着急—Tantalus A king who for his crimes was condemned inHades to stand in water that receded when he tried to drink, and with fruit hanging above him that receded when he reached for it.丹达罗斯:一位国王,因其犯过罪而被打入阴间并被罚站立在水中,当他想去饮水时水即流走,其头上挂有水果,但当他想拿水果时却退开b. Argus-eyed—Argus Greek Mythology A giant with 100 eyes who was madeguardian of Io and was later slain by Hermes.【希腊神话】阿尔戈斯:守护艾奥的百眼巨人,后被赫耳墨斯所杀c. narcissism—Narcissusd. sabotage妨害, 破坏—sabots A wooden shoe worn in some Europeancountries.木履,木鞋:某些欧洲国家居民穿的一种木制鞋e. martinet—Martinet After Jean Martinet (died 1672), French army officer源自吉恩马提奈(卒于1672年),法国军官f. yahoo—Yahoo From Yahoo , member of a race of brutes having human formin Gulliver's Travels by Jonathan Swift 源自Yahoo ,格列弗游记中的一种人形兽,由乔纳森·斯威夫特著g. Shylock—Shylockh. hoovering—Hoover胡佛电动吸尘器i. utopia—Utopia New Latin Ua [imaginary island in ] Utopia by Sir ThomasMore 现代拉丁语Ua [在托马斯·莫尔所著的] 《乌托邦》中的想象出来的岛屿j. Uncle Tommism—Uncle Tom【Chapter 5】6. apes—b birds—acattle—m cricket—ndoves—c foxes—jgeese—k sheep—fwolves—g monkeys—epigs—l hyenas—hturkeys—d swans—i9. a. A scientist working in a project to develop industrial uses for nuclearpower might have all the positive associations with “atomic”, such as“benefit, energy”, etc.b. A Japanese resident of Hiroshima, victim of the atomic explosion at the endof World War II, might have all the negative associations with “atomic”, such as “suffering, killing, death, horror", etc.c. To a student of nuclear physics, “atomic” might be associated with “mystery,science, knowledge”, etc.10. talkative: implying a fondness for talking frequently and at length (neutral)articulate: expressing oneself easily and clearly (positive)gossip: indulging in idle talk or rumours about others (negative)rambling: talking aimlessly without connection of ideas (negative)fluent: speaking easily, smoothly, and expressively (positive)mouthy: overtly talkative, especially in a rude way (nagative)cow [-HUMAN -MALE +ADULT +BOVINE] calf [-HUMAN+MALE -ADULT +BOVINE] rooster [-HUMAN +MALE +ADULT +GALLINE] hen [-HUMAN -MALE +ADULT +GALLINE] chicken [-HUMAN +MALE +ADULT +GALLINE]【PolysemyHomonymy4. 1) Make both ends meat is a parody of make both ends meet which means “have enough money for one’s needs”. Here the butcher cleverly uses the pair of homonyms meat and meet to make a pun. It makes a proper answer to the lady’s question. (1) Butchers cannot make both ends meat (make whole sausages with all meat) because they cannot make both ends meet (If they made sausages with all meat, which is more costly, they would not earn enough money to survive.)( 2) Don’t complain. All the butchers do the same. I am not the only one who is making sausages with bread.2) Swallow is a bird which is seen in summer. But by one swallow we see, we cannot deduce that it is already summer time. Swallow can also mean a mouthful of wine. On a cold winter day, if one has a swallow of wine, one may feel warm.3) arms has two meanings: weapons; the human upper limbs. Since “a cannon ball took off his legs”, the soldier was not able to fight on, so he “laiddown his arms”, which means “surrender”. It can also mean he laid down his upper limbs.Synonymy3. avaricious: greedycourteously: politelyemancipate: set freecustomary: usualwidth: breadthadversary: opponentgullible: deceivedremainder: residueinnocent: sinlessobstacle: obstructionvexation: annoyance5. a. identifiable b. safetyc. motivatesd. delicatee. surroundingsf. artificialg. prestige h. perspirei. accomplishment j. silentk. impressive l. evaporate6. run move spinturn whirl roll7. a. stead b. gee-gee c. riped. maturee. effectivef. efficientg. fatigued, children h. tired, kidsi. declined j. refused k. rancidl. addled m. Penalties n. fineso. rebuked p. accusedAntonymy5. a. similar/same b. safec. sharp/ smartd. sende. stingy/ selfish h. simplef. significant/sensible i. sureg. skeptical/ suspicious l. smoothj. slipshod/ slovenly/ sloppyk. sleepiness/ sleep / slumberm. subjectiven. sob/ scowl6. a. old-fashioned b. completelyc. moistured. speciale. essentialf. similarityg. innocent h. rigidi. loosen j. clarityk. deserted l. fruitfulm. peremptory n. depressedo. indifferent7. a. feed—starve, cold-fever b. wisdom—folliesc. haste—leisured. penny—pound, wise—foolishe. speech—silencef. absence—presenceg. admonish—praise i. wise men—foolsh. young—old private—public saint—devilj. mind—body k. foul—fairl. danger—security m. deliberate--promptn. children—parents o. bully—cowardp. head—tail8. right—wrong single—returndry—sweet hard—easystrong—faint rough—calmlight—dark cold—warmhigh—low/deepHyponymy3. furniture: desk, chair, table, bedmatter: liquid, gas, solidmeat: pork, beef, muttongo: run, fly, walk4. profession workplacesurgeon: clinic, hospitalplumber: house, buildinglawyer: office, law courtsmechanic: garagephotographer: studioforeman: worksite, factory5.6. In Sentence 1, got, furniture, recently are superordinates because they are generaland convey a very vague idea whereas in Sentence 2, the three words are replaced respectively by bought, cupboard, three days ago, which are subordinates, conveying a definite and clear idea. So Sentence 2 is better than Sentence 1.In 3, it is said, magnificent building, destroyed, yesterday are superordinate terms, which are comparatively much more general than the news says, Royal Hotel, burnt down, last night respectively in 4, which can be described as subordinates.Since 4 is clearer than 3 in meaning, it is better.Semantic field3. Group 1 is synonymously semantic field and Group 2 is semantic filed. Thedifference lies: In 1 the words are synonyms, none of them covers the meaning of another, and they differ only in style and emotive values. In 2 the words are not synonyms, but each refers to a specific type of horse. Horse is a cover term or superordinate, and others are subordinates. These terms have no difference in style or affective meaning.【Chapter 7】4. 1) extension 2) extension3) narrowing 4) degradation5) elevation 6) narrowing7) extension 8) extension9) narrowing 10) elevation11) narrowing 12) degradation13) degradation 14) degradation5. a. associated transferb. abstract to concretec. abstract to concreted. abstract to concretee. abstract to concretef. abstract of concreteg. associated transferh. associated transferi. synesthesiaj. synesthesia6. a. objective b. subjective, objectivec. objectived. subjectivee. subjectivef. subjectiveg. subjective h. subjective, objective7. a. die b. graveyardc. bedlam疯人院d. old peoplee. strikef. Policemang. stupid pupil h. poor peoplei. toilet j. fat personk. unemployed mother【Chapter 8】2. a. to repairb. measurement and determination of one’s positionc. predicamentd. injectiona. a single complete dividing part (of a rocket)b. the theatre or acting as a professionc. a particular point or period in a process of developmentd. to plan, arrange and carry outa. interchange and discussion of ideas, esp. for mutual understanding orharmonyb. conversationc. a written conversation (of a play, etc.)3. a. synonymb. explanation/ definitionc. antonymd. examplee. relevant detailsf. relevant detailsg. relevant details4. a. stop people drinkingstop drinking by themselvesb. a stone house which is biga house built of big stonesc. a picture possessed by Bettya photograph of Bettyd. aunts who are visitingpaying a visit to auntse. take Jane as his wifepreside over Jane’s weddingf. a weapon that can fly over long distance and that it explodes when it h its thething it aims atan object that is thrown at somebody in order to hurt him【Chapter 9】6. a—2) b—9) c—3)d—6) e—1) f—8)g—5) h—4) i—7)j—10)7. a. stand out againstb. approve ofc. get … over withd. looking intoe. come up withf. comply withg. cashed in onh. go withouti. to profit by / fromj. dut do wn …to8. a cool cat = a really calm personblow one's stack = lose control over oneselffly off the handle = become excessively angrywhat's more = furthermoreget away with = commit an illegitimate act without penaltyof course = naturallyget on = get oldpepper and salt = grey (hair)make up for = compensate forlost time = time wastedtake it easy = relax, not worryget up = rise from bedturn in = go into bedtake care of = manage or look afterlike a breeze = without effort or easilytime off = time for restget it made = be successfulthis is it = be in a position or place, or have possession of an objectbeyond which more of the same is unnecessarySam is really a calm person. He never loses control of himself and hardly ever becomes too angry. Furthermore, he knows how to manage his business financially by using a few tricks… Needless to say, he, too, is getting older.His hair is beginning to turn grey, but he knows how to compensate for wasted time by relaxing. He rises early, exercises, and goes to bed early. He manages his frankfurter dispensary without visible effort, until it is someone else's turn to work there. Sam is successful, he has reached his life's goal.9. a. “Well, it's the old story of the stitch in t ime,” he said.A stitch in time saves nine.b. Fleur's head was lost in the tool-box, but her voice was heard saying: “Toomany cooks, better let me.”Too many cooks spoil the broth.c. But not many other people held that view discerning his finger still very largein every pie — so much so that there often seemed less pie than finger.have a finger in the pied. I’m thinking of putting up a “Silence is golden” placard in his office. Nobodycan hear themselves think.Speech is silver, silence is golden.e. They four had one likeness: their appearance and their work was as it were awheel in the middle of a wheel.wheel within wheelsf. He quotes them extensively nevertheless, together with other equally suspectevidence, because otherwise he would have no straw with which to make hisbricks.make bricks without straw10. wind and weather wheeling and dealingwaifs and strays town and gowntop and tail time after timerules and regulations rise and fallrags and tatters puff and blowpick and shovel peace and quietover and above one and onlyoff and on neck and neckshoulder to shoulder moan and groanmilk and water man and beast11. a. 好奇伤身。
第二单元基本构词方法一.派生法练习一例如:intervene,intervention,intervenor,intervenient练习二希腊语前缀拉丁语前缀half hemi- semi- demi- one mono- uni-two di- bi-three tri- tri-four tetra- quadri-five penta- quint-six hexa- sex- ,seven hepta- sept-eight oct- oct-nine ennea- nona-ten deca- deci-1. immature2. irregular3.inconsiderate4. ignoble5. noncontentious6. illegitimate7. nonmetal 8. impassive 9. nonferrous 10. inaccuracy 11. unendurable 12. invariance13. non-inductive 14. illegible 15. unreasonable16. irrational \ 17. unscrupulous 18. non-staple19. imbalance 20. illegalize练习四1. before2. near3. off4. in5. inside6. outside7. out 8. before 9. beneath 10. in 11. under 12. between 13. within 14. into 15. exceeding 16. beyond 17. after 18. before19. forward 20. back 21. below22. above 23. beyond 24. across 25. extreme练习五1. dispensable, convertible, tolerable, reversible2. assistant, resistant, consistent, persistent3. calculator, liar,subscriber, survivor4. confectionery, adversary, tributary, monastery5. capricious, presumptuous, momentous, spontaneous二.复合法A. 1. greenbelt 2. greengrocer3. greenhorn4. greenroomB. 1. handbag 2. handbook3. handbrake4. handrailC. 1. aftercare 2. aftereffect3. aftertaste4. afterthoughtD. 1. sleeping bag 2. sleeping car3. sleeping pill4. sleeping partnerE. 1. running mate 2. running hand3. running head4. running boardF. 1. washbasin 2. washboard3. washerwoman4. washclothG. 1. sunburn 2. sunburst3. sunset4. sunshineH. 1. breakdown 2. break-in3. breakthrough4. breakupI. 1. outbreak 2. outcry3. outlay4. outlet练习二A.1.火力2.火把3.燃烧弹4.消防队5.太平梯B.1.(空袭)紧急警报2.隆重的欢迎3.红色肉类4.官样文章5.鲑鱼C.1.流动资本2.工作负载3.工作状态4.计算5.工人D.1.(录音等的)播放2.花花公子3.(学校的)放假日4.操场5.剧作家练习三1. farfetched2. newborn3. heart-beat4. built-in5. clothes-washing6. dust-laden7. oncoming 8. fair-minded, good-hearted 9. self-evident 10. grown-up练习四1.修改,校订2.冷淡3,对……进行军法审判4.将……上手铐5. 骤然把……塞进6.用沙袋阻塞7.船只失事8’使短路9。
英语专业词汇学课本及标准答案Chapter 3 Morphological Structure of English Words We have discussed the historical, cultural and social factors that facilitate (使……容易;推动) the development of the English vocabulary. Borrowing, as we see, has been playing an active role in the expansion of vocabulary. In modern times, however, vocabulary is mainly enlarged on an internal basis. That is, we use word-building material available in English to create new words. But before we discuss the actual ways and means to make new words, we need to have a clear picture of the structure of English words and their components (成分) —word-forming elements. This chapter will discuss morphemes(语素;词素), their classification(分类) and identification(辨别), the relationship between morphemes and word-formation(构词法).3.1 MorphemesTraditionally, words are usually treated as the basic and minimal units of a language to make sentences, which are combinations of words according to syntactic rules(句法规则). Structurally, however, a word is not the smallest unit because many words can be separated into even smaller meaningful units. Take decontextualization for example. This is one word, but can be broken down into de-, con-, text, -a/ , -iz(e), -ation , each having meaning of its own. These segments (部分) cannot be furtherdivided; otherwise, none of them would make any sense. Though -ation has a number of variants (变体) such as -tion, -sion, -ion, they belong to the same suffix as they have the same meaning and grammatical function and occur owing to (因为;根据) different sound environment. These minimal meaningful units are known as morphemes (morphe is the Greek word for 'form'; -eme as in 'phoneme' (⾳素) means 'class of' ). In view of word-formation, the morpheme is seen as 'the smallest functioning unit in the composition of words' (Crystal 1985). Syntactically(从句法上看), however, a morpheme is the minimal form of grammatical analysis (语法分析). For instance, each of the word-forms studies, studying, studied, consists of the morpheme study + ; the forms -es in studies, -ing in studying, -ed in studied are morphemes, which express grammatical concepts (语法概念) instead of deriving new words (See Classifying Morphemes).3.2 Morphs and Allomorphs(词素变体)Morphemes are abstract units, which are realized in speech by discrete units (具体单位) known as morphs(形素). 'They are actual spoken, minimal carriers of meaning' (Bolinger and Sears 1981:43). In other words the phonetic or orthographic strings(语⾳串或拼写字串)or segments (切分成分;节) which realize morphemes are termed 'morphs' (Bauer 1983:15). The morpheme isto the morph what a phoneme (⾳位) is to a phone (⾳素). Most morphemes are realized by single morphs like bird, tree, green , sad, want, desire, etc. . These morphemes coincide (巧合) with words as they can stand by themselves and function freely in a sentence. Words of this kind are called mono-morphemic words. Some morphemes, however, are realized by more than one morph according to their position in a word. For instance, the morpheme of plurality {-s} has a set of morphs in different sound context, e. g. in cats /s/, in bags /z/, in matches /iz/. The alternates (作为替换的事物) /s/, /z/ and /iz/ are three different morphs. The same is true of the link verb morpheme {be}. Its past tense is realized by two distinct orthographic forms was , were, each of which happens to be a word-form, realizing {preterit} and {singular}, and {preterit} and {plural} respectively and each has its own phonetic form /woz/ or /w?:/. Therefore, both was, were and their phonetic forms /woz/ and /w?: / are morphs (See discussion i n Bauer, p15).An allomorph refers to a member of a set of morphs, which represent one morpheme. Just as we class phones(⾳素) together as allophones (⾳位变体) of a single phoneme(⾳位), so we class morphs together as allomorphs of a single morpheme. Take the plural morpheme {-s} again. Phonetically, it is realized by /s/, /z/, /iz/, all of which are allomorphs. In English, many morphemes canThen what is the difference between morphs and allomorphs? The relationship can be illustrated by the diagram below. Morpheme{would}morph morph morph morph →allomorph/wud/ /w?d/ /?d/ /d/3.3 Classifying MorphemesMorphemes vary in function. Accordingly, we can classify morphemes into several general categories: free versus bound,derivational versus inflectional, and lexical versus grammatical. However, their boundaries are not as clear-cut as they appear to be due to some overlapping(重叠). For the sake of discussion, we shall define each type in terms of its characteristics.1. Free versus Bound Morphemes(⾃由词素与粘着词素)This is the easiest and most preferred classification in morphological studies, discussed in Hatch and Brown (1995), Crystal (1985), Fromkin and Rodman (1983), Bauer (1983), Bolinger and Sears (1981) and Matthews (2000). Morphemes which are independent of other morphemes are free. These morphemes have complete meanings in themselves and can be used as free grammatical units in sentences. They are identical with(与……完全相同) words, for example, man, earth, wind, car and anger.Morphemes which cannot occur as separate words are bound. They are so named because they are bound to other morphemes to form words or to perform a particulargrammatical function.Bound morphemes are chiefly found in derived words (派⽣词). Let us take recollection, idealistic and ex-prisoner for example. Each of the three words comprises three morphemes: recollection (re- collect-ion) , idealistic (ideal-ist-ic) , ex-prisoner (ex- prison -er). Of the nine morphemes, collect, ideal and prison can stand by themselves and thus are free morphemes. All the rest re-, -ion , -ist, -ic, ex-and -er are bound as none of them are freestanding units.Free morphemes are all roots, which are capable of being used as words or as word-building elements to form new words like collect, ideal, prison , whereas bound morphemes consist of either roots or affixes, most of which can be used to create new words like -dict- , -ced- (接近;去), re-, -ion, -ist, -ic and ex-(前). But there are a few affixes which can only indicate such grammatical concepts as tense, aspect, number and case, for example, the -ing in watching, -er in easier, -s in books, and -ed in worked.The English language possesses a multitude of (⼤量的) words made up of merely bound morphemes, e. g. antecedent, which can be broken down into ante-, -ced- and -ent. Among them, -ced- is a root meaning 'approach, go to', ante-, a prefix meaning 'before' and -ent, a noun suffix meaning 'a person, a thing', thus the whole word antecedent meaning 'something that goes before'(前例;前事;先⾏词;祖先). These examples show clearly that bound morphemes include two types: bound root (See Root, Stem, Base) and affix.2. Derivational versus Inflectional MorphemesMorphemes which are used to derive new words are known as derivational morphemes (派⽣词素) because when these morphemes are conjoined, new words are derived.In English, derivatives and compounds are all formed by such morphemes. For example, a + mor + ai, clear + ance, Life + Like and homo + gen + eous are results of such morphological processes.Inflectional morphemes(屈折词素), in contrast, indicate the syntactic relationships between words and function as grammatical markers. Inflectional morphemes are confined to suffixes. There is the regular plural suffix -s (-es) which is added to nouns such as machines, fridges, desks, radios and potatoes; the same forms can be added to verbs to indicate the simple present for the third person singular such as likes, works and goes; the form -'s is used to denote the possessive case of nouns such as the children ' s library, the man ' s role and the mother-in-law' s complaints; the suffixes -er, -est are usually attached to simple adjectives or adverbs to show their comparative or superlative degrees like happier—happiest,。
A word of warning: Not all the keys provided here are correct. Use your brainsUnit 1 pp. 9-16P.9 Check Your Understanding: a-d: F e. TIn-Class Activities 1 … f. Word has it they’re divorcing.a. Something he would talk aboutb. things that are said, contrasted with things that are donec. the promise one has maded. spoken command or signale. informationf. piece of news; messageP10 2. (1) five criteria:Potential pause: The pause , which happens when you say a sentence, will tend to fall between words, and not within words.Indivisibility: The extra items will be added between the words and not within them.Minimal free forms: the smallest units of speech that can meaningfully stand on their own.Phonetic boundaries: It is sometimes possible to tell from the sound of a word where it begins or ends.Semantic units: each word in a sentence has a clear meaning.(2) Do you think these criteria are questionable in any way? Can they be applied to the identification of zi, the roughChinese equivalent of the English “word”?No, as the above analysis explained. No, they cannot. For example, 流连and 蹒跚are danchuci (单纯词) which cannot be analyzed independently.P11 3. (1)Suppose we want to know what are the ten most frequently used English words. What are they, as far as you can tell? How about Chinese?The, of, to, and, a, in, is, it, you, that的、一、是、在、了、不、和、有、大、着3. (2)They are basically functional words.possessive words (of, 的)number words (a,一)copula words (is, 是)conjunctions (and, 和) andlocalizers (in, 在);English has the definite article the and several pronouns, you, that and it which are absent in Chinese.4.words are arbitrary (i.e. not motivated)onomatopoeic words “sl-” is highly suggestive of the meaning of the words that contain it, such as “slide”, “slip”, and “slush”.(1) Babble, bang, grunt, splash; 噼啪、嗡嗡、滴滴哒、吱嘎吱No, these words are only a small part of English or Chinese vocabulary(2) Football and handball concern the body part which kick/pass the ball from one place to another, and basketball isnamed after a basket into which the ball is put.(3) People have bodily embedded knowledge to infer these motivations of such usage. The first example concerns themetaphor and second metonymy.(4) Some figurative usages are also highly motivated. For example: Necessity is the mother of invention.5.British English (BE for short) and American English (AE for short)P13(1) half, advance, advantage, after, answer, ask, glance, glass, grasp(2) grammatical differences: In American English we say “graduate from school”; while in British English, we say“leave school”. In American English, it has “put up price”, while in British English, it is “raise price”(3) distinctive spellings:For Chinese characters “博览会”, British English has “fair”while American English users trade show. “L ift and elevator” , and “autumn and fall” are more examples.(4) same words with different meanings:one billion/ first floor/ pantsone billion(Brit) the number 1000000000000 万亿之数(US) the number 1000000000十亿之数first floorIn British English the floor of a building at street level is the ground floor and the floor above that is the first floor.In US English the street-level floor is the first floor and the one above is the second floorpants(Brit) men's underpants; women's or children's knickers(US) trousers6. Barack Obama’s choice of words(1) Empathy means identification with and understanding of another's situation, feelings.The ability to stand in somebody else’s sho esSympathy is defined as feeling of pity and sorrow (for sb.)(2) Hope, according to Obama, is that something better is waiting for us if we’re willing to work for it and fight for it, if we are willing to believe. He differentiates hope from what is blind optimism or willful ignorance of the problems we face(3) “As fathers and parents”, why not as fathers and mothers: Open to discussionPost-Class Tasks” in the sentence “The word is that he's left the country. (据说他已经离开这个国家了).” But actually, we will not write the sentence, esp., say the sentence in daily conversations. By this example, we show that receptive lexical knowledge concerns what you learned and productive lexical knowledge concerns what you would put into practice. Reading vocabulary may be the largest type of vocabulary, because you may recognize the meaning of a word without using it in daily exchanges or in academic writing.3. No, lexical competence covers a larger scope that that of productive lexical knowledge.4. underline word equivalentsLanguage is composedof not just individualwords, but also wordequivalents, such asword groups (orcompound words),chunks such as idioms,formulaic sequences,and so. The latter isattracting more and more scholarly attention these days. Thus, lexicology is more precisely defined as the scientific study of the words and word equivalents in a language.Unit 2 pp. 24 -29Check Your Understanding: a-e. FIn-Class Activities 1.(1) S is pronounced as [s] [z and [iz]] when it is respectively attached to a voiceless consonant, a voiced consonant or avowel, and any words ending with s, z or pronouncing as [s] or [z].(2) Yes, for example,the plural form of sheep remains unchanged, and man has its plural form realized as “men”.(3) The usual allomorphs of the morpheme of the past tense may be realized as [t], [d] and [id]2. prefixes of negation: a-, un-, in- (ir-, il-), dis-, mis-, non-, de-symmetry→asymmetry typical→atypical forgettable →unforgettable tie→untiearticulate →inarticulate, discreet →indiscreet mature →immature, partial →impartiallegal →illegallegible →illegiblerelevant →irrelevantreverent →irreverentlike→dislikeable→disableuse →misuselead →misleadsense →nonsensecommercial→noncommercialform→deformconstruction→deconstruction(2) Un- is usually prefixed before transitive verbs, such as tie →untie, nouns, such as and adjectives, such asemployment→unemployment. Non- is often put before adjectives, such as essential→non-essential, and nouns, such as existence→non-existence. Both of the usage are possible because the word followed the above two prefixes has no ready-made acronyms in English lexical system.3.(1) No. unwoman is not a word in English. Un- is usually put before an abstract uncountable noun.(2) morphological structure:inaccessibilityinaccessible -ityin- accessibleaccess -ible(3) These words may connate sex inequality at first sight. But, In fact, we go too far if we hold this notion in mind.4. (1) Stop, bin, wear, suit(2) complete conversions5. (1) Tue →Tuesday, Sun →Sunday, PM →post meridiem(2) 1月January Jan 2月February Feb 3月March Mar. 4月April Apr. 5月May May 6月June Jun. 7月July Jul. 8月August Aug. 9月September Sept. 10月October Oct. 11月November Nov. 12月December Dec.6.(1) Marathon--telethon/ talkathon, hamburger--shrimpburger-(2) 无微不至-无胃不治;其乐无穷-棋乐无穷7. (1)a. flu virus: A caused Bb. safety line: B ensures Ac. night bird: A is the usual time when B is actived. spoon-feeding: A is one of the ways to realize B.e. potato pancake: A is the ingredient of Bf. man-made: B is realize by Ag toilet seat: B is part A.(2) “safety line” vs. “safe line”:NO, the former means that line can keep one safe, whereas the latter means the line is safe.(You can touch it)Security guard and secure guardPost-Class Tasks1. Supply the best answer from the four choices marked A, B, C, and D.a.D;b.B;c. A;d. C;e. A;f. D2. a. intangibility b. unevenlyin/tangible/ity un/even/lyc. friendlinessd. notwithstandingfriend/ly/ness not/with/stand/inge. overseasf. minimalistover/sea/s minim/al/istg. immigration h. Psychologistim/migrate/ion psych/ology/isti. occurrences j. assumptionoc/cur/rence as/sumpt/ion3. Safe: conversionCheck-out: CompositionDead: conversionValuable: conversion4. Adjectives like “poor”, “rich”, “fat”, “sick”, “wounded”, “deaf”, “mute”, “Chinese”, “Danish”, “best”, “most”, “least”, “latest”, “accused”, “condemned”, (for) “good”, “thick” (and) “thin”, etc. undergo partial conversion;stop, pause, halt, look, rest, check, try, taste, smell, etc, often undergo complete conversion.5. prince/princeling, under/underling, world/worlding, child/childish, self/selfish, fool/foolish6. Acronyms:NATO = North Atlantic Treaty OrganizationInitialisms:EU 欧盟= European Union;ABC = American Broadcasting Corporation 美国广播公司orAustralian Broadcasting Corporation 澳大利亚广播公司;U.S. =the United StatesKeys to Unit 3Check Your Understandinga. Fb. Fc. Td. Fe. FIn-class Activities1. (1) Yes. There is some difference between the words “clean” and “cleanly” in the sentences in Group A. In SentenceA-a, “clean” means “completely”, while in Sentence A-b, “cleanly” means “easily”.(2) Yes. There is some difference between the words “clean” and “cleanly” in the sentences in Group A. In Sentence A-a, “clean” means “completely”, while in Sentence A-b, “cleanly” means “easily”.(3) The words “high” and “highly” cannot be used interchangeably in the two sentences in Group C. In Sentence C-a,“high” is an adjective and functions as the complement, while in Sentence C-b, “highly” is an adverb and functions as the modifier.(4) a1. I felt pretty nervous going into the exam, but after I got started I loosened up some.a2. The woman chairing the meeting speaks prettily.b1. When he saw her, he stopped dead in his tracks.b2. I'm deadly serious. This isn't a game!c1. Someone left the back door wide open.c2. These laws were widely regarded as too strict.2. (1) a. The old man smiled his refusal to the young man request.b. He lived a long life and died a natural death.(2) a. 每听完一个笑话,那个老人都咯咯地笑出他的喜悦之情。
《英语词汇学》课程习题集一、单选题1. The word “humorousness” has _______ morphemes.A. oneB. twoC. threeD. four2. The word “nationalize” has _______ morphemes.A. oneB. twoC. threeD. four3. The word “decoding” has _______ morphemes.A. oneB. twoC. threeD. four4. Which of the following forms is not an allomorph of the morpheme “in-”?A. ig-B. ir-C. il-D. im-5. Which of the following forms does not contain an allomorph of the inflectional morpheme of plurality?A. booksB. pigsC. horsesD. expense6. According to ______, there is an intrinsic correspondence between sound and sense.A. naturalistsB. anthropologistsC. linguistsD. conventionalists7. According to ______ , there is not a logical connection between sound and sense.A. naturalistsB. anthropologistsC. linguistsD. conventionalists8. Most English words are _________ symbols.A. definiteB. arbitraryC. infiniteD. hereditary9. From the point of view of ________, a direct connection between the symbol and its sense can be readily observed in a small group of words.A. nationalismB. anthropologyC. linguisticsD. motivation10. Words motivated phonetically are called _________ words.A. onomatopoeicB. similarC. naturalD. symbolic11. In the sentence “John was asked to spy the enemy”, “spy” is considered an example of the word-formation process using _________.A. compoundingB. derivationC. conversionD. acronym12. In the sentence “John was doctored by Mr. Smith in the hospital”, “doctor” is considered an example of the word-formation process using _________.A. compoundingB. derivationC. conversionD. acronym13.In the sentence “John was asked to get into the office after a two-hour wait”, “wait”is considered an example of the word-formation process using _________.A. compoundingB. derivationC. conversionD. acronym14. In the sentence “John decided to nurse his sister himself”, “nurse” is considered an example of the word-formation process using _________.A. compoundingB. derivationC. conversionD. acronym15.In the sentence “John was asked to leave after his three-day stay in the town”, “stay”is considered an example of the word-formation process using _________.A. compoundingB. derivationC. conversionD. acronym16. Which of the following terms refers to the form which remains when all derivational and inflectional affixes have been removed?A. stemB. rootC. baseD. affix17. Which of the following terms refers to the form which remains when all derivational affixes have been removed?A. stemB. rootC. baseD. affix18. Which of the following terms refers to the form which remains when all inflectional affixes have been removed?A. stemB. rootC. baseD. affix19. Any root or stem can be termed as a _______.A. stemB. rootC. baseD. affix20.A _______ is a form which is not further analyzable, either in terms of derivational or inflectional morphology.A. stemB. rootC. baseD. affix21. The wo rd “wife” used to mean “woman”, now it means “married woman esp. in relation to her husband”. The word has undergone a sort of semantic change called _____.A. elevationB. degenerationC. extensionD. restriction22.The word “holiday” used to mean “holy day, a day of religious significance”, and now it refers to “day of recreation, when no work is done”. This is an example of _____ of meaning.A. extensionB. restrictionC. degenerationD. elevation23.The word “salary” used to mean “a sum of money given to Roman soldiers to enable them to buy salt”, and now it refers to “fixed payment made by employer at regular intervals to person doing other than manual work”. This is an example of _____ of meaning.A. extensionB. restrictionC. degenerationD. elevation24.The word “starve” used to mean “to die”, and now it refers to “to die of hunger”. This is an example of _____ of meaning.A. extensionB. restrictionC. degenerationD. elevation25.The word “shrewd” used to mean “evil, bad, wicked”, and now it refers to “clever or sharp in practical affairs”. This is an example of _____ of meaning.A. extensionB. restrictionC. degenerationD. elevation26. The Renaissance brought great changes to the English vocabulary _______.A. from 1100 to 1500 ADB. from 1500 to 1700 ADC. from 450 to 1100 ADD. from 1700 to 1900 AD27. French brought great changes to the English vocabulary _______.A. from 1100 to 1500 ADB. from 1500 to 1700 ADC. from 450 to 1100 ADD. from 1700 to 1900 AD28. The transitional period from Old English to Modern English is known as _________.A. Ancient EnglishB. Primordial EnglishC. Contemporary EnglishD. Middle English29. The English language from 1500 AD to the present is called ________ .A. Ancient EnglishB. Old EnglishC. Middle EnglishD. Modern English30. Which of the following is not a phase in the development of the English language?A. Old EnglishB. Middle EnglishC. Modern EnglishD. Contemporary English31.The word “tear”meaning “the drop of salty water from the eye”and the word “tear”meaning “to pull sharply apart” are called a pair of ________.A. homophonesB. perfect homonymsC. homographsD. polysemic words32. The word “lead” meaning “guide or take, esp. by going in front, etc.” and the word “lead”meaning “an easily melted metal of a dull bluish-grey color” are called a pair of ________.A. homophonesB. perfect homonymsC. homographsD. polysemic words33. The word “lie” meaning “make a statement that one knows to be untrue” and the word “lie”meaning “put oneself flat on a horizontal surface” are called a pair of ________.A. homophonesB. perfect homonymsC. homographsD. polysemic words34. The word “base” meaning “the thing or part on which something rests” and the word “base”meaning “having or showing little or no honour, courage or decency”are called a pair of ________.A. homophonesB. perfect homonymsC. homographsD. polysemic words35. The word “son” meaning “one’s male child” and the word “sun” meaning “a star that is the basis of the solar system and that sustains life on Earth, being the source of heat and light” are called a pair of ________.A. homophonesB. perfect homonymsC. homographsD. polysemic words36. When a word has a range of different meanings, it belongs to the words of ________.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. antonymyD. polysemy37. When many pairs or groups of words which are different in meaning are pronounced alike or spelled alike, or both, such words belong to the words of ________.A. antonymyB. synonymyC. homonymyD. polysemy38.When words are identical in sound but different in spelling and meaning are called ________ .A. homophonesB. homographsC.homoformsD. homogenes39. ________ is the most common cause of homophones.A. semantic divergenceB. phonetic convergenceC. shorteningD. foreign influence40. When words are involved in the relationship which obtains between specific and general lexical items, such that the former is included in the latter, the words belong to the words of ________.A. hyponymyB. synonymyC. polysemyD. antonymy41.We can use “a silver lining” for “every cloud has a silver lining”. The kind of usage of the idiom is known as _______.A. separationB. additionC. abbreviationD. extension42.We can use “pull an unhappy face” for “pull a long face”. The kind of usage of the idiom is known as _______.A. separationB. replacementC. abbreviationD. extension43.We can use “see too many trees, but not the forest” for “cannot see the wood for the trees”. The kind of usage of the idiom is known as _______.A. separationB. omissionC. abbreviationD. extension44.We can use “come of marriage age” for “come of age”. The kind of usage of the idiom is known as _______.A. separationB. replacementC. abbreviationD. extension45. What is the rhetoric style illustrated by the idiom “neck and neck”?A. comparisonB. rhymeC. alliterationD. repetition46. _______ is the central factor in a word describing what it is.A. Denotative meaningB. Connotative meaningC. Stylistic meaningD. Affective meaning47. _______ consists of word-class and inflectional paradigm.A. Denotative meaningB. Connotative meaningC. grammatical meaningD. lexical meaning48. _______ refers to the emotional association which a word suggests in one’s mind.A. Denotative meaningB. Connotative meaningC. Stylistic meaningD. Affective meaning49._______ is that which a piece of language conveys about the social circumstances of its use.A. Denotative meaningB. Connotative meaningC. Stylistic meaningD. Affective meaning50. _______ is concerned with the expression of feelings and attitudes of the speaker or writer.A. Denotative meaningB. Connotative meaningC. Stylistic meaningD. Affective meaning二、名词解释题51. proverbabsolute synonym52. function wordsonomatopoeic words53. homonymydegradation54. metaphorprefixation55. polysemyelevation of meaning三、Word-building processes56. IOC VIP fire-proof ad auto plane CIA BBC ID record-breaking raindrop newscast brunch botel motel beautility champ dorm steamboat honeybee57. sit-in TB phone shoulder-high bit somg stagflation comsat sitcom gym taxi memo vet TEFL SALT dropout setback UN OPEC crystal-clear58.round-the-clock NATO sci-fi telex proof-reader schoolboy chute bus copter PE ASEAN NASA TOEFL air-conditioning lion’s share dozer plane airtel faction lunarnaut59.sea-green flowerbed VOA bike fridge medicare Motown hi-fi tec scope quake NBC EPA UNESCO H-bomb air-tight silkworm peace-loving slimnastics docudrama60.morning person ROM CD flu brunch travelog workaholic motel telex nark pop biz math VCR sun-tanned arms race fire engine handwriting ABC RAM四、Rewriting the short paragraph61. First VersionEven since I was a CHILD, I have wanted to go on the stage and be an ACTRESS, like my elder sister. She is less PRETTY than I am and I hoped that if I was LUCKY, I, too, would have the chance to PERFORM three or four times a week at our little local theatre.Second VersionEver since my ____, I have wanted to go on the stage and ____, like my elder sister. I am ____ than she is, and I hoped that with ____, I, too, would have the chance to give ____ three or four times a week at our little local theatre.62. First Version“You should be CONFIDENT. You are ABLE to do it,” she told me, “but you may not have the PATIENCE. It takes a lot of hard work to be SUCCEESSFUL. You can ACHIEVE anything if you stick to it.”Second Version“You should have _____ in yourself. You’ve got the _____ to do it,” she told me, “but you may be too ____. It takes a lot of hard work to ____. You can make any ____ if you stick to it.”63. First VersionThen she would DESCRIBE in DETAIL of her CONFUSION and embarrassment when the man who was DIRECTING the play told her that she spoke and MOVE too slowly in one scene. Second VersionThen she would give me a ____ ____ of how _____ and embarrassed she’d been when the ____ of the play told her that her speech and ____ were too slow in one scene.64. First VersionShe was supposed to run across the stage and, after HESITATING for a moment, say “WELCOME!” to and old woman who was ENTERING from the other side. “But take CARE because the stage is SLIPPERY,” he said.Second VersionShe was supposed to run across the stage and, after a moment’s ____, to ____ an old woman who was making her ____ from the other side. “But be ____ not to ____,” he said.65. First VersionThere was no DOUBT that the stage was very slippery, but she would PROBABL Y have reached the other side SAFEL Y if she had not fallen over her long skirt, which was in FASHION that year, and tumbled right off the stage, to the ASTONISHMENT of the audience.Second VersionThe stage was ____ very slippery, but it’s ____ that she would have reached the other side in ____ if she had not fallen over her long skirt, which was ____ that year, and tumbled right off the stage. The audience was ____.五、简答题(略)……答案一、单选题1. C2. C3. C4. A5. D6. A7. D8. B9. D10. A11. C12. C13. C14. C15. C16. A17. C18. B19. C20. B21. D22. A23. A24. B25. D26. B27. A28. D29. D30. D31. C32. C33. B34. B35. A36. D37. C38. A39. B40. A41. C42. B43. A44. D45. D46. A47. C48. B49. C50. D二、名词解释题51. proverb: it is a well-known, supposedly wise saying usually in simple language expressinga fact or a truth which deals with everyday experience.e.g. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. / The early bird catches the worm.absolute synonyms: two words that are fully identical in meaning and interchangeable in any context without the slightest alteration in connotative, affective and stylistic meanings.e.g. word-formation and word-building or spirants and fricatives.52. function words: short words such as prepositions, conjunctions and so on. They don’t have much lexical meaning and serve grammatically more than anything else. They are in contrast to content words, which have independent lexical meaning and used to name objects, actions, states and so on. e.g. in, on and from.onomatopoeic words: They are the words imitating the sounds or sounding like natural sounds.e.g. cuckoo, tick, bang.53.homonymy: It is the relationship between words in the pairs which, though different in meaning, are pronounced alike, or spelled alike or both.e.g. lead (to guide) / lead (a gray metal), tear (drop of salty water coming from the eye) / tear (pull sharply to pieces), bear / baredegradation: It means that words once respectable or neutral shift to a less respectable even degraded meaning.e.g. genteel, terrific, accident54. metaphor: It is a figure of speech containing an implied comparison based on association of similarity.e.g. the teeth of a saw, a shower of stones, the tongue of a shoeprefixation: It is the word-formation process by the addition of a word element before an already existing word.e.g. multimedia, inconvenience, antiart55. polysemy: If a word has got more than two meanings, then it belongs to words of polysemy.e.g. rich, full, getelevation of meaning: Elevation is the process where words go uphill, shifting from words showing disrespectable meaning to better meaning. e.g. craftsman, shrewd三、Word-building processes56. compounding: fire-proof record-breaking raindrop steamboat honeybee acronymy: CIA IOC VIP BBC IDclipping: ad auto champ dorm planeblending: newscast brunch botel motel beautility57. compounding: sit-in dropout setback shoulder-high crystal-clearacronymy: TB UN OPEC TEFL SALTclipping: phone gym taxi memo vetblending: bit somg stagflation comsat sitcom58. compounding: round-the-clock air-conditioning proof-reader schoolboy lion’s share acronymy: NATO PE ASEAN NASA TOEFLclipping: chute bus copter dozer planeblending: sci-fi telex airtel faction lunarnaut59. compounding: sea-green flowerbed air-tight silkworm peace-lovingacronymy: VOA NBC EPA UNESCO H-bombclipping: bike fridge tec scope quakeblending: slimnastics docudrama medicare Motown hi-fi60. compounding: morning person sun-tanned arms race fire engine handwriting acronymy: ROM CD VCR ABC RAMclipping: flu nark pop biz mathblending: brunch travelog workaholic motel telex四、Rewriting the short paragraph61. 1. childhood 2. act 3. prettier 4. luck 5. performances62. 1. confidence 2. ability 3. impatient 4. succeed 5. achievement63. 1. detailed 2. description 3. confused 4. director 5. movement64. 1. hesitation 2. welcome 3. entrance 4. careful 5. slip65. 1. undoubtedly 2. probable 3. safety 4. fashionable 5. astonished五、简答题(略)……。
下列定义所表示的名称:1.a minimum unit of meaning :(morpheme)2。
a morpheme to which affixescan be added : (root)3。
a linguistic form that can occur as an independent word:(free form)4.a morpheme that must occur with at least one other morpheme:(bound form)5。
a bound morpheme attached to a base (root or stem):(affix)6。
an affix attached to the beginning of a base (root or stem ):(prefix)7.an affix attached to the end of a base (root or stem): (suffix)8。
an affix (in English,usually a suffix) that changes the form of a word without changing its part of speech or basic meaning:(inflectional affix)9.the process by which noninfectional affixes are added to roots to form words:(derivation)10。
the process of joining together two linguistic forms which can function independently :(compounding)各组单词中共同的粘着词根、其词源及语义:1。
acoustic,acoustical,acoumeter,acoustician,acoustics,acouphone:(acou—听,GK) 2aerodomestics,erodrome,erodynamic,aerofoil,aerogramme,aerolite,aerography,aeronautics,aerophysics,aeroplane,aerosphere: (aero—空气GK)3。
英语词汇学教程参考答案杨信彰
集团文件发布号:(9816-UATWW-MWUB-WUNN-INNUL-DQQTY-《英语词汇学教程》参考答案 Chapter 1
1. The three definitions agree that lexicology studies words. Yet, they have different focuses. Definition 1 focuses on the meaning and uses of words, while definition 2 on the overall structure and history. Definition 3 regards lexicology as a branch of linguistics and focuses on the semantic structure of the lexicon. It is interesting to note that the three definitions use different names for the object of study. For Definition 1, it is words, for Definition 2 the vocabulary of a language, and for Definition 3 the lexicon. 2. (1) They can go into the room, and if they like, shut the door.
(2) You boys are required to give in your homework before 10 o’clock. (3) I watch the football match happily and find it very interesting. 3. (1) When it follows ‘-t’ and ‘-d’, it is pronounced as [id]; (2) When it follows voiceless consonants, it is pronounced as [t]; (3) When it follows voiced consonants and vowels, it is pronounced as [d]. 4. (1) They are words that can be included in a semantic field of “tree”. (2) They represent the forms of the verb “fly” and have a common meaning. (3) They belong to a lexical field of “telephone communication”. (4) They are synonyms, related to human visual perception. Specifically, they denote various kinds of “looking”. 5. (a) 'blackboard: a board with a dark smooth surface, used in schools for writing with chalk (the primary stress in on black); 'blackbird: a particular kind of bird, which may not necessarily be black in color (the primary stress in on black); 'greyhound: a slender, swift dog with keen sight (the primary stress in on black); 'White House: the residence of the US President in Washington (the primary stress in on black). (b) 'black 'board: any board which is black in color (both words receive primary stress); 'black 'bird: any bird which is black in color (both words receive primary stress); 'grey 'hound: any hound that is grey in color (both words receive primary stress); 'white 'house: any house that is painted white (both words receive primary stress). 6. There are 44 orthographic words, i.e. sequences of letters bounded by space. There are 24 open class words and 20 closed class words. 7. (a) The ‘bull’ is literal, referring to a male bovine animal. (b) ‘Take the bull by the horn’ is an idiom, meaning (having the courage to) deal with someone or something directly. (c) ‘Like a bull in a china shop’ is an idiom, meaning doing something with too much enthusiasm or too quickly or carelessly in a way that may damage things or upset someone. (d) A ‘bull market’ is one where prices rise fast because there is a lot of buying of shares in anticipation of profits. 8. drinking vessels: cup, mug, glass, tumbler, tankard, goblet, bowl, beaker, wineglass, beer glass, sherry glass They can be organized in a number of ways, for example, by the drinks the vessel is used for. Non-alcoholic: glass, tumbler, cup, mug, beaker, bowl Beer: beer glass, tankard Wine: wineglass, goblet Spirits: sherry glass Chapter 2 1. Lexeme is an abstract linguistic unit with different variants, for example, sing as against sang, sung. Morpheme is the ultimate grammatical constituent, the smallest meaningful unit of language. For example, moralizers is an English word composed of four morphemes: moral+lize+er+s.
Any concrete realization of a morpheme in a given utterance is called a morph, such as cat, chair, -ing, -s, etc. Allomorphs are the alternate phonetic forms of the same morpheme, for example, [t], [d] and [id] are allomorphs of the past tense morpheme in English. 2. quick-ly, down-stair-s, four-th, poison-ous, weak-en, world-wide, inter-nation-al-ly, in-ject, pro-trude 3. island, surname, disclose, duckling, cranberry, reading, poets, flavourfulness, famous, subvert 4. (a) [?] (b) [-ai] 5. (1) -’s, -s (2) -est, -s (3) -ing (4) -ed 6. The connotations are as follows: (1) slang, carrying the connotation of reluctance, (2)informal, carrying the connotation that the speaker is speaking to a child, (3) beastie is used to a small animal in Scotland, carrying the connotation of disgust, (4) carrying the connotation of formalness, (5) carrying the connotation of light-heartedness. 7. { -?m; ~- n; ~- n; ~-i: ~-s; ~-z; ~-iz} 8. court: polysemy dart: polysemy fleet: homonymy jam: homonymy pad: homonymy steep: homonymy stem: homonymy stuff: polysemy watch: polysemy 9. (1)—(f), (2)—(g), (3)—(c), (4)—(e), (5)—(a), (6)—(d), (7)—(b)