
四级语法讲义
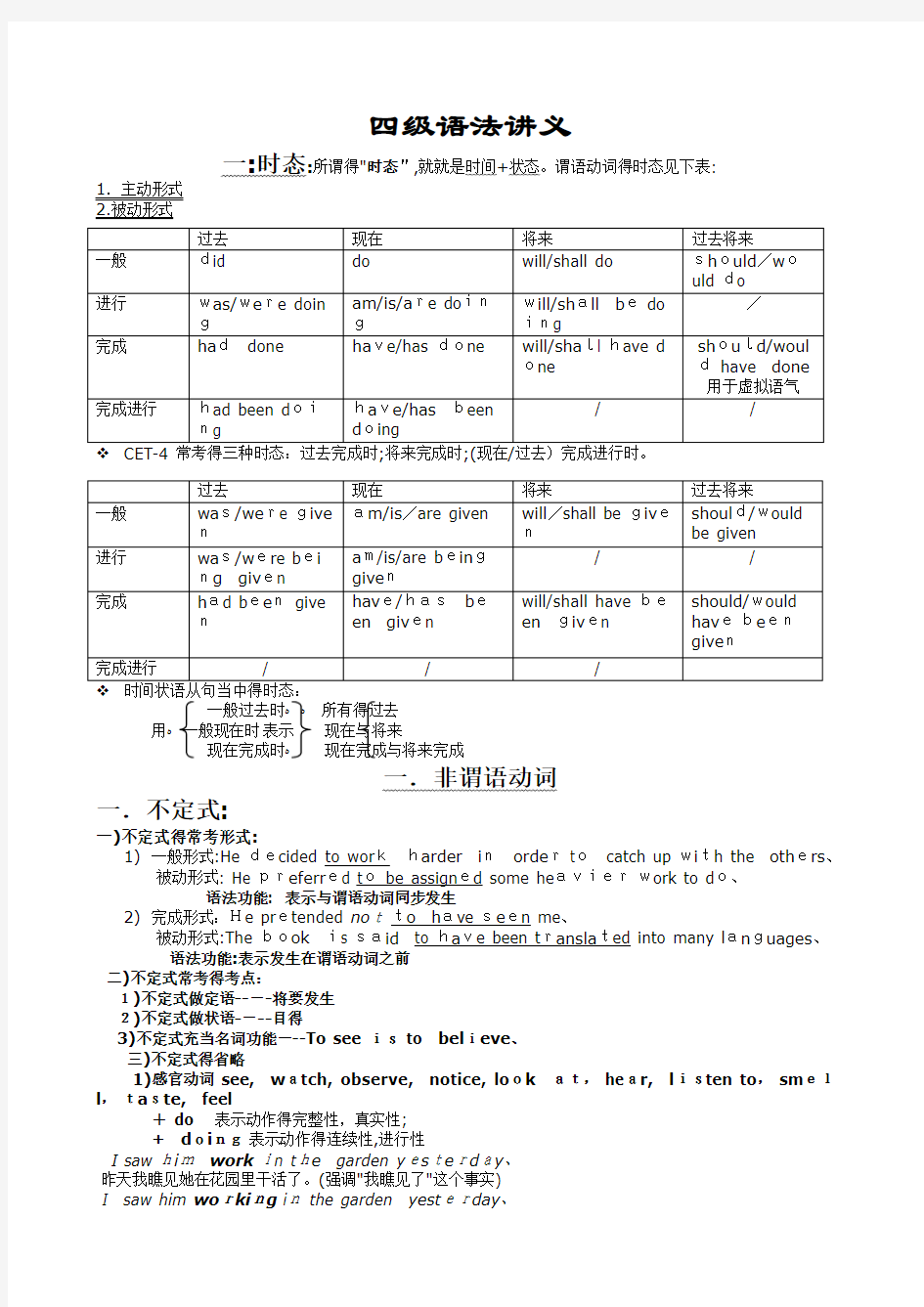
一:时态:所谓得"时态",就就是时间+状态。谓语动词得时态见下表:
1.主动形式
2.被动形式
一般过去时??所有得过去
用?一般现在时表示现在与将来
现在完成时?现在完成与将来完成
一.非谓语动词
一.不定式:
一)不定式得常考形式:
1)一般形式:He decided to workharder inorder tocatch up with the others、
被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavierwork to do、
语法功能: 表示与谓语动词同步发生
2)完成形式:He pretended notto have seen me、
被动形式:The bookis said to have been translated into many languages、
语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前
二)不定式常考得考点:
1)不定式做定语----将要发生
2)不定式做状语----目得
3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe、
三)不定式得省略
1)感官动词 see,watch, observe,notice, lookat, hear,listen to, smell,taste,feel
+ do表示动作得完整性,真实性;
+doing表示动作得连续性,进行性
I saw himworkin the garden yesterday、
昨天我瞧见她在花园里干活了。(强调"我瞧见了"这个事实)
I saw him working in the garden yesterday、
昨天我见她正在花园里干活。(强调"我见她正干活"这个动作)
?感官动词后面接形容词而不就是副词:The cake tastesgood;It feelsfortable、
2)使役动词 have bidmake let等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原to
I‘d like to have John do it、
I havemy package weighed、
Paul doesn’t have to bemade to learn、
3)help help sbdo help sb to do help do help todo
四)有些动词后只跟不定式如:
want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan, offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do ,permit sb to do,enablesbto do
force sb to do、 be more likely to do love to dowarn sb to do be able to dobe ambitious to do、begin to do 、start to do
五) 有得时候to后面要接-ing形式
accustom(oneself) to; be accustomed to; face up to; in addition to; look forward to; object to;be reduced to; resign oneself to; be resigned to; resort
to; sink to; be usedto;bealternative to;be close/closeness to; be dedication/dedicated to; be opposition/opposedto;besimilarity/similarto、
三、need/want 后得-ing形式具有被动得意思。其中,want不太常用。
He needs(a lot of) encouraging、
二、动名词: 具有动作性特征得名词
1)
2)具有动词性特征可以带宾语starvingtroops is necessary、
一)动名词得形式:
一般形式:I don't like yousmoking、
完成形式:Iregret not having taken your advice、
被动形式:This question is far from being settled、
二) 动名词常考得点
1)动名词做主语谓语动词为单数
2)在动名词与不定式中,做为介词得宾语就是动名词
3)动名词得否定直接在其前加否定词,通过代词得宾格或所有格形式给出逻辑主语、
Iwould appreciate_______ back this afternoon.
A.you to call B.you call C.youcalling D.you're calling(Key:C your calling 也对)I regret not having taken youradvice、
4)有些词后只能接动名词
admit; appreciate;avoid;celebrate;consider;contemplate; defer; delay; deny;detest; discontinue;dislike; dispute; enjoy;it entails; escape; excuse;explain; fancy; feel like; finish; forgive;can't help; hinder; imagine; it involves;keep; it means; mention; mind;miss;it necessitates; pardon; postpone;practice;prevent;recall; report; resent; resist;risk; su ggest; understand、、、
另外还有一些接-ing形式得常用说法:
it's no good;it's no/little/hardly any/ use;it's not/hardly/scarcely use; it'sworthwhile; spend money/time; there's no; there'sno point in;there's noth ing worse than; what'sthe use/point、、、
5有些词后加不定式与动名词均可
remember,forget, try,stop, go on,cease, mean后面用不定式与-ing形式,意义截然不容。
Iremembered to post the letters、(指未来/过去未来得动作)
I remembered posting/having postingthe letters(我记得这个动作)
forgot与remember得用法类似。
I regret toinformyou that…我很遗憾地通知您…
I regrettedhavingleft the firmafter twenty years、为了"二十年前得离
开"而遗憾。
try to努力You really must try to overe your shyness、
try–ing试验Try practicing five hoursaday、
I mean to go, but my fatherwould not allow me to、[打算、想]我想去,但我父
亲不让我去。
To raise wage means increasing purchasing power、[意味着]赠加工资意味
着增加购买力。
prefer得用法:
我宁愿在这里等。
I prefertowait here、(所以啊,您不介意得话,我就等下去。)
I preferwaiting here、(我正在这里等,我就喜欢这么做。)
I preferswimming to cycling、(这个句子里面就不能用不定式了。)
3 分词:
,过去分词被动状态
现在分词得形式:
1)一般式: Do you see the mantalking to the dean(主任)? (与谓语动词同步发生)
2)完成形式:Not having madeadequate preparations, they failed、 (发生谓语动词之前)
3)完成被动形式:Having been adapted, thescript seems perfect、(发生谓语动词之
前且表示被动)
过去分词
1)过去分词表示被动:Fight no battle unprepared、
2)过去分词得进行形式:You'll findthe topic being discussed everywhere、(强调正在被做)
这三种非谓语动词,都可以构成复合结构,非谓语动词所修饰得成分就是这些非谓语动词得逻辑主语。她们
之间得一致关系——主动还就是被动,往往就就是考点。独立主格结构中,要注意得就是分词与她前面得逻辑
主语之间得主动被动得关系。
二:虚拟三:虚拟语气
情态动词所表达得可能性程度:must/can't → should/shouldn't → might/may(not)
另外两个"类情态词得形式:"need/needn't; haveto/don't have to
?最自然得虚拟状态:由should/would+原型时态(不含时间只含状态)
本质上就是过去将来时:即,时间固定在过去将来,状态不同:一般、进行、完成、完成进行。
这时"虚拟语气"得产生往往就是因为我们要表达"本来应该……"(而现在却还没有……)
(本来可以……,本来能……)
I should go!(… but I'm still here!)?(一般)
I shouldbe working now!??(进行)
I should have practiced more (than I did)!???(完成)
我应该多多练习!(言下之意,现在我练习得不多。)
I shouldn't dream away my timetoo much! (完成得否定)
(actuallyIdid dream away my timetoo much!)
It shouldn't have been leaking for such a long time! (完成进行)
I may/might/could have finished!??(完成)
一些常见得句型中,就会出现这种虚拟语气,而处于从句之中,should 常常被省略掉
o suggest, advise,propose, remend, plan;
o demand, order, direct, arrange, mand, decide;
o require, request;
o think,expect, believe, insist, suspect、
由于她们得含义中包含"建议,假设,应该"这类得含义,所以,由她们引起得从句中,就会包含有should+原型时态构成得虚拟语气。
这些动词(以及她们得名次形式,分词形式)引起得从句还有其她得变形:
主语从句,表语从句,同位语从句
It's suggested that…
My suggestion isthat…
Theonly suggestion that、、、
The only suggestion I can give you now is that…
一些形容词引起得表语从句中,也会有同样得情况
?important; necessary; essential
It'snatural ; strange; incredible??that
apity; a shame; no wonder
?由lest, for fear that, incase引起得从句中多使用should
?表达与事实相反
1与现在相反:使用[过去时]:
I wish I werenot here!?(一般现在→一般过去)
Suppose we were not here、
He loved me as if I were his own son、?(一般现在→一般过去)
HopeI weren't always losingthings!?(现在进行→过去进行)
If only/IfIhadn't beenthere! (现在完成→过去完成)
What if I hadn't been waiting righthere! (现在完成进行→过去完成进行)
常考句型:It's (high) time(that)…;would rather (that)…
,只能表达对现在得瞧法,所以,从句中只有一般过去时。
2、与过去相反:过去完成时;
How niceit is if Ihad past the test!
How nice it is if I had slept a little more this morning!
3、与将来相反?将来得事情没有发生,所以只能推测。
If it rains tomorrow, we'll have to stayone day more、
不过,由于可以用be to表示将来;所以,虚拟语气中经常出现were to;也就是CET-4得常考语法点。
?虚拟条件句
o if 部分,做一个与事实相反得假设(所以只有一般过去与过去完成);
o主句部分,这就是表示基于这个假设得推测,,少数情况下使用could/might/may。
o注意:两个部分之间,就是有逻辑关系,而在两部分得谓语动词时态上,没有必然得联系。
?注意,虚拟条件句中得if可以省略,造成were/had提前,产生倒装。
?隐含得非真实条件
What would you do with 50 thousand dollar?
How could I be happy withoutyou?
除了条件状语从句之外,原因状语从句也会出现虚拟语气。
o由in order that,so that引起得从句,肯定得时候可以使用may/might; can/could;
否定得时候,多用shouldn't;
owhoever, whatever,no matter what引起得从句中,多用may+
情态动词得基本用法及其区别
最近几年高考试题中常常借助语境来考查情态动词得基本用法及其区别,因此在平时学习时准确
理解与掌握情态动词得基本用法十分重要。情态动词得用法复杂多变,在高考试题中,命题者常常利用语境与
句子之间意义上得细微差别来考查学生对情态动词得理解与掌握。对于情态动词,除了要求考生能够准确掌握
它们得基本用法外,还要充分利用高考试题所设置得语境来分析句子之间所体现得特殊关系。下面就近几年来
高考试题中出现得情态动词得考点进行归纳分析,以便同学们复习掌握。
一、用“情态动词+have+done”结构表示对过去动作得推测,高考试题中常用过去时态或过去得时间状
语给以暗示。情态动词得这一用法可以用“对立统一”来概括。
1.当试题得前句与后句在动作与意义上相互补充说明,且整个句意在动作与时间上就是一个整体时,我们可用“统一”关系来解决这样得试题。常见得结构有:
musthave done:
表示对过去动作得肯定推测,常译作“一定做了……”,只能用于肯定句中。其否定形式为can’
t/couldn’t have done
疑问式为Can/Could、、、have done﹖。
could /might havedone:表示对过去发生得动作得可能性推测,常译作“可能做了……”。如:
1)My sister met him at theGrand Theater yesterday afternoon, so he
_____ your lecture.
A.couldn’t have attended
B.needn’t have attended
C.mustn’t have attended
D. shouldn’t have attended
本题选A。
2) Jack ____yet,otherwise hewould have telephoned me.
A. mustn’thave arrived
B. shouldn’t have arrived
C.can’t have arrived
D. need not have arrived (C)
2.当试题得前后句在动作与意义上构成转折关系时,常借助“but,however,
instead”等词来表示过去得动作与客观事实不符,这时我们就可以用“对立”关系来解决这样得试题。这种结构常见得有:
should have done /oughtto have done:表示过去本应该做某事而实际上没有做。
should nothavedone / ought notto havedone:表示过去本不应该做某事但事实上却做了。
need have done:表示过去本来有必要去做某事,但事实上没有做。
need not have done:表示过去本来没有必要做某事,但事实上却做了。如:
3) I was really anxious about you. You _____homewithout a word.
(NMET2001)
A. mustn’t leave
B. shouldn’t have left
C. couldn’t have left
D.needn’t leave
“本不应该离家出走却走了”,故本题选B。
4)I told Sally how to get here, but perhaps I _____ for her.(NMET’94)
A. had to write it out
B. must have writtenitout
C.shouldhave written it out
D.ought to write it out
由句中得连词but可知前后句之间就是对立关系,分析题意可知本题应选C。
二、考查情态动词基本用法之间得比较与辨析。最近几年高考试题中常借助具体得语境来考查考生对那些最常见得情态动词得基本用法得理解与掌握,因此在做这样得试题时应认真分析语境中所含得实际意义,并结合情态动词得基本含义与用法做出正确得选择。
5) —Is John ing by train﹖
—He should, but he ______ not. He likes driving his car.
A. must
B. can
C. needD.may
mustn’t 表示“禁止、不准”;cannot 表示“不可能”;need not 表示“不必要”;may not表示“可能不”。分析语境可知本题应选D。
6) —I hearyou’ve got a set ofvaluableAustralian coins.______I
have a look﹖
—Yes, certainly.
A. Do
B. May C. Shall D. Should
分析语境可知这就是在征求对方得许可,may表示“允许、可以”,语气比较委婉shall常用于第一、三人称作主语得疑问句中,表示征求对方意见与指示,如果此空用shall,则意为“要(我)瞧一下吗?”,不符合上下文意思。故本题选B。
7)Mr Bush is on timefor everything.How ____ itbethat he was late for the opening ceremony﹖
A. canB.should C. may D.must
must be表示肯定得猜测,只能用于肯定句中,由题意可知本题应选A。
8)—Areyou ing to Jeff’s party﹖
—I’mnot sure. I ____ go tothe concert instead.
A. must B. would C. should D. might
由题意与下句中得“I’m not sure”
可知这段对话中存在一种可能性推测,might可以用来表示一种比较委婉得可能性判断,故本题选D。又如: I should have been there, but I _____ not find the time.
A. would B. could C. might D.should
分析题意可知第二个分句表示过去得某种能力;C 项只表示语气上得可能性,与题意不符。故本题选B。9)Johnny, you____ play with the knife,you ____ hurtyourself.
A.won’t; can’t
B. mustn’t; may
C.shouldn’t;must D. can’t; shouldn’t
mustn’t 表示“不可以;禁止”,分析题意可知第二个空表示某种可能性,故本题选B。
10) —Will you stay for lunch﹖
—Sorry,______.My brother is ing tosee me.
A. I mustn’t
B. I can’t
C. I needn’t
D. I won’t
分析题意可知因为“我弟弟要来瞧我”,所以“不能留下”,因此对别人得邀请或要求应给予礼貌得拒绝。A 项表示“禁止”;C项表示“不必要”;而D项表示“不会”,均不符合题意。故本题选B。又如: —Could Iborrow your dictionary﹖
—Yes,of course you _____.
A. might B. will C.can D. should(C)
11)—When can I eforthe photos﹖I needthem tomorrow afternoon.
—They _____be readyby 1200.
A. can B. should C. might D. need
该题考查情态动词should得基本含义,分析句意可知本题应选B。又如:
12) The fire spread through the hotel very quickly but everyone____ get out.( A. had toB. would C.couldD. was able to
该题考查了could与be able to得区别,二者都可表示过去时间得能力,但如果表示过去成功地做了某事只能使用was / were able to do,故本题选D。
13) —Shall I tell John about it﹖
—No,you _____. I’vetold himalready.
A.needn’t B.wouldn’t C. mustn’t D.shouldn’t
情态动词shall在试题中表示征询对方意见或请求指示。答句暗示“没有必要了”,故本题选A
三、一致关系
一)主谓一致
1. 主谓一致(与插入语无关) ?1主谓得分隔原则:主谓之间可以用定语从句或者省略得定语从句分隔。2定语从句中得主谓一致:?3随前一致:
n、 + together withn2
aswell as ?including ?alongwith
with / of ?acpanied with / by
4就近原则:n1 or n2 +v(就近原则)
either n1 or n2 ?5可数n1 and可数n2+v(pl)
不可数n1 and 不可数n2+v(pl)
例外:war and peace is…war and peace就是一个整体
但就是如果主语表示得就是同一个概念,同一人,同一事得时候,谓语动词用单数,这种结构得特征就是and连接得两个词只有一个冠词。
The ironand steel industryis very important to our country、
The head master and mathematical teacheris ing、
The head master and themathematical teacherare ing、
类似得还有:law and order bread and
butter black and white
To love and to be loved is …
A lawyer and a teacher are…?A lawyer and teacher is …
6随后原则:not A but B / not only A but also B+v、(与B一致)
7百分比结构:most , half , rest , some , majority , one+persent ?of+n1+v、(由n1决定)
8倒装结构得主谓一致:
a)There be +n 由名词决定动词
b)Among , between等介词位于句首引起倒装结构:
Among / Between…+系动词+n、(由名词决定动词)
9The+adj得主谓一致:
a)当表示“一类人”,
b)当表示某一抽象概念时
The good isalways attractive、
10 Todo/doing/主从+vs
*More than one+n
many a +n、? a day or two
二)、倒装
1 全部倒装
就是只将句子中得谓语动词全部置于主语之前。此结构通常只用与一般现在时与一般过去时。常见得结构
有:Up went the plane=the plane went up、
1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, e, go, lie,run。
2)表示运动方向得副词(back, down,off, up)或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动得动词。
注意:1)上述全部倒装得句型结构得主语必须就是名词,如果主语就是人称代词则不能倒装。Herehe es、Away they went、2) 谓语动词就是be得时候,不能倒装。Here it is、Here y
ou are、
3)形容词短语/分词短语位于句首,引起倒装
*typical of characteristic of ? *coincidingwith + n
4) 表示地点范围得介词短语位于句首,谓语动词为系动词,一定引起倒装?In…(表语)+系动词+主,主同。*在倒装句型答案中不能出现there?*常考介词要倒装:among between in at beneath ?
常考得系动词:be lieexist remain rest
部分倒装
1. 否定 adv位于句首,引起倒装:not only, not until, hardly, scarcely, ?seldom, rar
ely, no sooner…than?1) not until + 时间 + 主谓倒装,not until + 句子+主谓倒装
2) only+状语位于句首
only +ad、 eg: recently ?prep、短短语eg: in recently years
3) 在比较级结构中,than后面可以倒装,也
从句 eg: when clause ?only一个词本身不倒装?
可以不倒装。
部分倒装就是指将谓语得一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。如果句中得谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则
需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
?1)Neither, nor,so 表示前面句子得共同否定或者肯定,产生倒装,一般主动词提前,谓语动词得其她部分就
4)as /though引导得让步从句必须将表语或状语提前 (形容词, 副词, 分词,实义动词提前)。
as〔让步〕虽然,尽管〔词序倒装。语气比 though强〕。
Successful ashe is,heis not proud、她虽成功,却不骄傲。
Women as she is, she'severy brave、
Tryhard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily、
注意:A) 句首名词不能带任何冠词。B)句首就是实义动词,其她助动词放在主语后。如果实义动词有宾语
与状语,随实义动词一起放在主语之前。
5)其她部分倒装
a)so…that 句型中得so; such… that句型中得such位于句首时,需倒装。
So frightened was hethat he did not dare to move an inch、
b)在某些表示祝愿得句型中:May you all be happy、
c)在虚拟语气条件句中从句谓语动词有were, had,should等词,可将if 省略,把were, had,
should移到主语之前,采取部分倒装。WereI you,I wouldtry it again、
四、复合句
从句可分为:
?名词性从句→主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句
?形容词性从句→定语从句
?副词性从句→状语从句
?常考得关系代词:that;which; who/whom/whose; where;when;what; as。
?常见得同位语从句现行词(that之前得抽象名词):fact, idea, news, hope, conclusion, evidence, opinion, problem, thought, understanding…
?常用得引导词
o时间状语从句:while; when;before; whenever; as;after;till; until; since;
once; ever since;as/solong as;as soon as; no sooner…than; hardl
y… when; scarcely/barely… when; the moment/minute/instant;on (the point of) doing…
o地点状语从句:where; wherever
o原因状语从句:because;since;as; seeing that;considering that; now that;
in that; for fear that;lest;owing to the fact that; because ofthe f
act that; due to the fact that…
o方式状语从句:as; as if;as though; how; save that…
o比较状语从句:as; than; as… as;not so…as; hardly… than;
o结果状语从句:so that; so… that;such…that;so asto…
o条件状语从句:if;unless; incase; so long as; so far as; provided/providing/that; supposing; granted/granting that…; giving that…、o让步状语从句:though; although; even if;even though; whether; as; however;no matter(what, how, when); for all that; in spite of the fact that; grante
d that;regardless of the factthat…
o目得状语从句:that; so that;in order that; lest; for the fear that; in case…
定语从句:
which 引导得定语从句结构
1)which就是关系代词,which后面应该加缺主语或者宾语得句子,
在这个句子中,which要作成分,作主语或者宾语
2)in which+完整得句子
which在定语从句中作in得宾语,所以不能作后面句子得主语
3)名词+of which+谓语动词
of which来修饰名词,名词在定语从句中作主语,所以后面直接跟谓语动词
I have fivebooks three of which are borrowed from Mary、
4)介词+which +to do其功能相当于定语从句。
The key with which to openthe door is lost、
5)定语从句得省略结构:
1. 如果that/which在定从中作宾语,可以省略、
sub+vt+n+(which / that)+sub+vt ?→s+vt+n+s+v ? s+vt+n1+n2+vt ?*当做题
6)时,若发现两个名词在一起,但就是似乎连不上,则一定省略that / ?which,则动词为vt,做谓语。?
定从得特殊省略
the way (in which) +句子?the reason (why that)+句子均为完整句
the time (that / when)+句子?Ido remember the first time (that
省) I ever heard the sweetest voice inthe world、
7)定从得主系省略(主+系可同时省)
By the time省that+句子,句子。?
即:which be , who be , that be可同时省
状语从句省略结构
这种省略从句主语得方式理论上需要满足以下两个条件:
第一、特定得状语从句引导词:althoughthough even though when while if as 第二、从句主语与主句主语必须保持一致;
第三、从句得谓语必须就是be动词,主语与be动词同进同出,
声明:本资料由 STUGD、收集整理,转载请注明出自、stugd、
大学英语四级考试语法:—定语从句 很多同学在大学英语四级考试中会存在一些误区,认为语法不那么重要,其实英 语语法是学习英语的指南,对我们帮助很大。以下是小编给大家整理的大学英语四级 考试语法:—定语从句,希望可以帮到大家 1、mary is a beautiful girl. 名词的扩展靠限定,最基本的就是在名词的前面增加一个形容词这样的定语,上 面的句子就是表语girl的前面加了一个形容词。显然,如果只是mary is a girl这样的 句子会让人觉得非常枯燥,没有什么意义,所传递的信息量极其有限。所以,名词前 面加定语,可以使被限定的名词更加生动,更加形象而富有生命。如果要对名词给出 更多限定,挖掘更多内部信息,我们可以在名词前面加多个定语来限定,如mary is a beautiful chinese girl. 放在名词前面起到限定作用的定语有很多种形式,形容词,名词,动词现在分词,动词过去分词等。虽然形式多样,但是这类定语还是比较好理解,只要顺着句子的顺序,就基本可以明白是怎么回事。 2、the computer that i bought yesterday works well. 有时候,我们需要对名词给出很多的说明,用大量的信息来限定名词。这时,如 果还是把长长的限定成分放在名词前面,就会头重脚轻,所以英语中会用跟在名词后 面的定语从句来限定前面的名词。根据定语的功能还可以分为限制性定语从句和非限 制性定语从句。两者的区别在于前者与被限定名词之间没有逗号,而后者则有逗号隔开;前者起到限定作用,不可或缺,后者起到补充作用,舍去后对剩余部分影响不大。 本句子通过“that i bought yesterday”这个that引导的定语从句,使得主语the computer得到限定而明确,是我昨天买的计算机而不是别的。如果明白了这个名词可 以通过后面加定语从句来扩展,我们的句子马上可以变得复杂起来,请看下例:another popular spectator sport, which is known as the sport of kings, is horse-racing, which is controlled by the jockey club. 译文:另一种以特大型运动著称的流行观赏运动是赛马,这种比赛由赛马总会控制。
大学英语四级语法题大全 1、_____all our kindness to help her, Sara refused to listen. A.At B.In C.For D.On 2、____beforewe depart the day after tomorrow, we should have a wonderful dinner party. A.Had they arrived B.Would they arrive C.Were they arriving D.Were they to arrive 3、____ conflict among city-states caused the eventual decline of Greek civilization. A.Continuous B.Continual C.Constant D.Contrary 4、____ he's already heard the news. A.Chances are B.Chance is C.Opportunities are D.Opportunity is 5、____ his knowledge and academic background, he is basically stupid. A.But for B.According to C.For all D.Thanks to 6、____ man can now create radioactive elements, there is nothing he can do to reduce their radioactivity. A.As B.Whether C.While D.Now that
大学英语四级语法精要 一、动词(时态,语态,用法,省略,一致性等) (一)时态 1、主动形式 过去现在将来过去将来一般did do will/shall do should/would do 进行was/were doing am/is/are doing will/shall be doing / 完成had done have/has done will/shall have done should/would have done 用于虚拟语气完成进行had been doing have/has been doing / / 2、被动形式 过去现在将来过去将来 一般was/were given am/is/are given Will / shall be given should/would be given 进行was/were being given am/is/are being given / / 完成was/were being given am/is/are being given / / 完成进行/ / / / · CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。 ·时间状语从句当中的时态: 一般过去时所有的过去 用一般现在时表示现在和将来 现在完成时现在完成和将来完成 3、现在完成进行时态(have/has been + -ing 分词构成): 动作或状态从过去某时开始,继续到现在,可能继续下去,也可能刚刚结束. · I’ve been writing letters for an hour. I’ve bee n sitting in the garden. 4、过去完成进行时(由had been + ing分词构成): 过去某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作 · We had been waiting for her for two hours by the time she came. 5、将来完成进行时: 将来某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作. · By next summer, he will have been working here for twenty years. 6、将来完成时(由shall/will have + 过去分词构成): 将来某时会业已发生的事. · I shall have finished this one before lunch. They’ll have hit the year’s target by the end of October. (二)语态 1、可以有两种被动结构的类型,例如: · He was said to be jealous of her success. It was said that he was jealous of her success. ·能同时适用于上述两个句型的主动词通常都是表示“估计”,“相信”等意义的动词,常见的
大学英语四级写作资料 一、大学英语四级考试大纲(2006 修订版)对写作的要求 写作选用考生所熟悉的题材。考生根据规定的题目和所提供的提纲、情景、图片或图表等,写出一篇不少于120词的短文。写作要求是思想表达准确、意义连贯、无严重语法错误。考试时间30分钟。 写作部分要求考生用英语进行短文写作,思想表达准确、意义连贯、无重大语法错误。写作部分考核的技能是: A.思想表达 1.表达中心思想 2.表达重要或特定信息 3.表达观点、态度等 B.篇章组织 4.围绕所给的题目叙述、议论或描述,突出重点 5.连贯地组句成段,组段成篇 C.语言运用 6.运用恰当的词汇 7.运用正确的语法 8.运用合适的句子结构 9.使用正确的标点符号 10.运用衔接手段表达句间关系(如对比、原因、结果、程度、目的等) D.写作格式 11.运用正确的符合英语表达习惯的写作格式 大学英语四级考试写作部分要求考生达到《教学要求》中的一般要求,即“能完成一般性写作任务,能描述个人经历、观感、情感和发生的事件等,能写常见的应用文,能就一般性话题或提纲在半小时内写出至少120词的短文,内容基本完整,用词恰当,语意连贯。能掌握基本的写作技能。” 二、四级考试写作评分标准 (1)本题满分为15分。 (2)阅卷标准共分四等:2分、5分、8分、11分及14分。各有标准样卷1-2份。 (3)阅卷人根据阅卷标准,对照样卷评分,若认为与某一分数(如8分)相似,即定为该分数(即8分); 若认为稍优或稍劣于该分数,则可以加一分(即9分)或减一分(即7分)。但不得加或减半分。(4)评分标准 ?2分:条理不清,思路紊乱,语言支离破碎或绝大部分句子均有错误,且多数为严重错误。 ?5分:基本切题。思想表达不清楚,连贯性差。有较多的严重语法错误。 ?8分:基本切题。思想表达清楚,文章尚连贯,但语法错误较多,其中有一些是严重错误。 ?11分:切题。思想表达清楚,文字连贯,但有少量语法错误。 ?14分:切题。思想表达清楚,文字通顺,连贯性较好,基本上无语法错误。仅有个别小错误。 ?注:白卷、所写内容与题目毫不相关或只有几个孤立的词而无法表达思想,则给0分。 (5)字数不足应酌情扣分。 题目中给出主题句、起始句和结束句,均不得记入所写字数。 只写一段者:0-4分;只写两段者,0-9分(指规定三段的作文) (6)各档作文相当于百分制的得分,列表如下,称为得分率。其中9分的得分率为60分(相当于百分制的60分)。
英语专业四级语法词汇练习题(6) 所属:专四专八阅读:1021 次评论:7 条[我要评论] [+我要收藏] 有关否定 1)双重否定最常见的形式有: no(not)...but...没有……不…… no(not)...without...没有……不,除……不 no(not)...unless没有……就不…… not...until直到……才…… 例如:There is no one but knows it.没有一个人不知道此事。 2)can not与副词too,enough, sufficiently, over,too much等词连用时,意为“无论怎样也不过分”,“越…越”。例如: You cannot be too careful.你越仔细越好。 We cannot praise him too much.我们无论怎样赞扬他也不过分。 近义词辨析 break, crack, crush, shatter,break, smash 这组词均含有“打破”或“挤碎”的意思。 break 是这组词中最常用的,指使某件东西破碎。 If you break that vase, you’ll have to pay for it.如果打破了那只花瓶,你就得赔偿。crack 指打裂某物,但不一定打碎,因而通常不会成为碎片。 You may crack these nuts with a hammer.你可以用锤子把这些坚果敲开。 crush
强调挤压或踩的动作,毁坏程度取决于被压物的组织结构,或变形,或成小块,或可恢复原状。 To make wine, you first crush the grapes.若要造酒,需先将葡萄压碎。 shatter 打破某物,力大到使碎片飞出很远,常指整件东西完全被毁。 The explosion shattered most of the windows in the building.爆炸震碎了那座大楼 的大部分窗玻璃。smash 突出暴力,击打时动作较猛,被击打的东西往往完全报废。 He smashed the window with a brick.他用砖块击碎窗玻璃。 全真模拟试题 1. ____ native to North America, corn has now spread all over the world. A. In spite of B. That it is C. It was D. Although 2. Our civilization cannot be thought of as ____ in a short period of time. A. to have been created B. to becreated C. having been created D. beingcreated 3. We feel it is high time that the Government ____something to check the inflation. A. did B. do do D. would do 4. It has been proposed that we ____ our decision until the next meeting. C. can delay D. are to delay 5. Hurricanes are severe cyclones with winds over seventy-five miles an hour____ originate over tropical ocean waters. A. which B. who to 6. ____ is announced in the papers, our country has launched a large-scale movement against smuggling and fraudulent activities in foreign currency exchange deals.
A.从介词开始到其后跟的名词结束 B.从介词开始到动名词结束 C.从介词开始到动名词的宾语结束2018年12月大学英语四六级语法精讲课程讲义 一、识别句子成分必须记住的原理 1.衡量是否是一个句子的标准:是否有动词,有动词就是句子,反之不是句子。 2.英语构句原则规定:一个简单句中只能有一个谓语动词 3.长难句的构成:主句、从句、介词短语、非谓语动词 (1)主句的辨识:谓语动词 (2)从句的辨识:连词+与之匹配的谓语动词 (3)介词短语: (4)非谓语动词:4.衡量长难句划分是否正确的标准:整个句子中谓语动词的个数比连词多一个 5.长难句划分方法:连动切割法 ·连动切割法:将句子中的所有连词和动词(连词、动词的排列不分先后)作为切割长难句的基 础,断开主句和从句。 ·长难句划分的具体步骤: 【第一步】断开主句和从句 通读整个句子找出所有的连词或动词,并将连词和动词匹配起来(主要是针对从句而 言,主句不存在连词,从句连词和动词的匹配遵守就近原则),然后再给动词匹配主 语(主句的主语在谓语之前找;从句的主语在连词和与之匹配的谓语动词中间找,如 果它们中间没有任何词语,那么连词本身就是这个从句的主语。) 动名词(doing ) 动词不定式(to do ) 现在分词(doing ) 过去分词(done )
【第二步】断开介词短语和非谓语动词 二、总结复习句子的主要成分 1、主语 (1)定义:主语是动作的发出者。 (2)位置:在谓语动词之前。 (3)什么可以充当主语: 2、谓语 (1)定义:述说主语的动作或状态。 (2)位置:在主语之后。(3)什么可以充当谓语:实意动词。 3、宾语 (1)定义:(2)位置: (3)什么可以充当宾语:4、表语 (1)定义:表述主语的身份特征,性质状态的 (2)位置:在系动词之后 (3)什么可以充当表语: A.名词: B.代词: C.介词短语: D.非谓语动词: E.句子:A.动作的承受者B.介词所联系的对象,即介词宾语(简称介宾) A.名词: B.代词: C.介词短语: D.非谓语动词: E.句子: A.名词: B.代词: C.形容词 D.介词短语: E.非谓语动词: F.句子:A.在谓语动词之后B.在非谓语动词之后C.在介词之后
英语四级考试必备基础语法知识 动词时态 1)现在完成进行时态 (have/has been + -ing 分词构成): 动作或状态从过去某时开始,继续到现在,可能继续下去,也可能刚刚结束. I’ve been writing letters for an hour. I’ve been sitting in the garden. 2)过去完成进行时(由had been + ing分词构成): 过去某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作 I’d been working for some tim e when he called. We had been waiting for her for two hours by the time she came. 3)将来完成进行时: 将来某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作. By next summer, he will have been working here for twenty years. In another month’s time she’ll have been studying here for three years. 4)将来完成时(由shall/will have + 过去分词构成): 将来某时已发生的事. I shall have finished this one before lunch. They’ll have hit the year’s target by the end of October. 动词语态 可以有两种被动结构的类型,例如: He was said to be jealous of her success. It was said that he was jealous of her success. 能同时适用于上述两个句型的主动词通常都是表示“估计”,“相信”等意义的动词,常见的有assume,believe,expect,fear,feel,know,presume,report,say,suppose,understand等. It is supposed that the ship has been sunk. The ship is supposed to have been sunk. 担当be supposed to 与不定式的一般形式搭配时往往表示不同的意义.例如: Why are you driving so fast in this area? You are supposed to know the speed to know the speed limit. (你应该晓得速度限制) 双宾语及宾补结构的被动语态 双宾语结构的被动语态: 双宾语结构变为被动语态时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一个宾语仍然保留在谓语后面,但多数是把间接宾语变为主语. He was asked a number of questions at the press conference.
No matter what / who / which / how / when / where / whether引导的让步状语从句: No matter how much I tried to make things stay the same, even Jimmy grasped that the world he’d known was gone. (课文中) No matter what he is wearing, you must serve him. 这一结构大都可以由-ever 构成的合成词代替: Whatever(代词)he is wearing, you must serve him. 但no matter 结构只能引导让步状语从句,而-ever构成的合成词除了引导让步状语从句,还能引导主语从句、宾语从句。 Go to stamp sales and buy whatever you can afford.(引导宾语从句, 不能换成no matter what).
(课文中: Para6)He went wherever(副词)I went and seemed to adjust pretty well. (课文中:Para12)We were reminded that the constant love and support of our friends and family would get us through whatever life might present. However(程度副词,常与形容词和副词连用)rich people are, they always seem anxious to make more money. However carefully you drive, you will probably have an accident eventually. Whoever (代词)gains the most points wins the competition. Whichever(代词)of them gains the most points wins. Whichever (形容词) team gains…. 有时whatever, wherever可以表示说话人不知情或不关心 He lives in Wick, wherever that is.(…谁知道那地方在哪儿。)
四级语法知识点总结 一:时态:所谓的"时态",就是时间+状态。谓语动词的时态见下表: 1.主动形式 2.被动形式 CET-4 常考的三种时态:过去完成时;将来完成时;(现在/过去)完成进行时。 时间状语从句当中的时态: 一般过去时 所有的过去 用 一般现在时 表示 现在和将来 现在完成时 现在完成和将来完成 过去 现在 将来 过去将来 一般 did do will/shall do should/would do 进行 was/were doing am/is/are doing will/shall be doing / 完成 had done have/has done will/shall have done should/would have done 用于虚拟语气 完成进行 had been doing have/has been doing / / 过去 现在 将来 过去将来 一般 was/were given am/is/are given will/shall be given should/would be given 进行 was/were being given am/is/are being given / / 完成 had been given have/has been given will/shall have been given should/would have been given 完成进行 / / /
二:非谓语动词 1.不定式: 一)不定式的常考形式: 1)一般形式:He decided to work harder in order to catch up with the others. 被动形式: He preferred to be assigned some heavier work to do. 语法功能:表示与谓语动词同步发生 2)完成形式:He pretended not to have seen me. 被动形式:The book is said to have been translated into many languages. 语法功能:表示发生在谓语动词之前 二)不定式常考的考点: 1)不定式做定语----将要发生 2)不定式做状语----目的 3)不定式充当名词功能---To see is to believe. 三)不定式的省略 感官动词 see, watch, observe, notice, look at, hear, listen to, smell, taste, feel + do 表示动作的完整性,真实性; + doing表示动作的连续性,进行性 I saw him work in the garden yesterday. 昨天我看见他在花园里干活了。(强调"我看见了"这个事实) I saw him working in the garden yesterday. 昨天我见他正在花园里干活。(强调"我见他正干活"这个动作)感官动词后面接形容词而不是副词:The cake tastes good; It feels comfortable. 使役动词 have bid make let 等词后不定式要省略但同1)一样被动以后要还原to I ‘d like to have John do it. I have my package weighed. Paul doesn’t have to be made to learn. help help sb do help sb to do help do help to do 四)有些动词后只跟不定式如: want,wish,hope,manage,promise,refuse,pretend,plan,offer,decide,agree,expect allow sb to do, cause sb to do , permit sb to do, enable sb to do
第一章动词的时与体(Tense & Aspect) 时(tense)是个语法范畴,它是表示时间区别的动词形式。英语动词只有“现在时”和“过去时”,而没有“将来时”(在英语中,表示“将来”手段多种多样,但没有一种独特的、能与“现在时”和“过去时”平起平坐的专一表示“将来”的动词形式----“将来时”)。 体(aspect)也是一个语法范畴,它表示动作或过程在一定时间内处于何种状态的动词形式。英语有进行体(progressive aspect)和完成体(perfective aspect)。进行体是由助动词be的一定形式加主动词的-ing 分词构成;完成体由助动词have的一定形式加主动词的-ed分词构成。 现在时和过去时既可以单独使用,也可以和进行体或完成体结合使用,也可以同时与完成体和进行体结合使用。这样,英语的限定动词词组便有8种时、体形式。它们分别是:一般现在时(simple present)、一般过去时(simple past)、现在进行体(present progressive)、过去进行体(past progressive)、现在完成体(present perfective)、过去完成体(past perfective)、现在完成进行体(present perfective progressive)、过去完成进行体(past perfective progressive)。在这一章中,我们单独挑出完成体来加以详述。 1.1 必须使用完成体的结构 1)It (This, This evening, yesterday...) is (was, will be) first (second, third...) time (day, month…)…结构中的分句,要求用完成体。 Is this the first time you've been to Beijing? This was the first time he had been to Beijing. This is the eighth month that I have been out of work.. This was the eighth month that I had been out of work. This is the second time that the goods produced by our factory have been shown in the International Exhibition. This was the second time that the goods produced by our factory had been shown in the International Exhibition. 2)在no sooner…than, hardly/barely/scarcely…when,等的句型中,主句要用过去完成体。 He had no sooner seen me than he left the room. No sooner had he seen me than he left the room. The helicopter had hardly landed when the waiting crowd ran toward it. Scarcely had I seen the lightning when I heard a clap of thunder. 3)将来完成体用来表示在将来某一时间以前已经完成或一直持续的动作。经常与before+将来时间或by+将来时间连用,也可与before或by the time引导的现在时的分句连用。 I will have finished all the work by the time you are back this evening. I am sure he will have left Paris by this time tomorrow. I hope we will have got all the information before you come tomorrow. By the time you get to New York, I _______for London. (2002年1月) A) would be leaving B) am leaving C) have already left D) shall have left 本题时间状语为by+将来时间,考察将来完成体用法,应选择D)。 By the time he arrives in Beijing, we ________here for two days.(2001年6月) A) have been staying B) have stayed C) shall stay D) will have stayed 将来完成体用来可以表示在将来某一时间以前一直持续的动作,本句话的意思是:我们将在这里呆两天,因此谓语动词用将来完成体,答案为D)。 1.2 现在完成体与现在完成进行体 现在完成进行体兼有现在完成体和现在进行体二者基本特点。由于它有现在完成体的特点,所以它
大学英语四级考试语法指导 名词性从句中的虚拟语气 第一节:宾语从句(Subordinate Clasue)中的虚拟语气 一、在动词wish后的宾语从句中的虚拟语气 在动词wish后的宾语从句中的虚拟语气,常省去宾语从句的引导词that。 一)、对现在情况的虚拟(与现在的事实相反): 从句用过去式或过去进行式(时间上是同时的)。其句子结构为:宾语从句的谓语be和were(was),实义动词用过去式。例: 1. I wish (that可省略,下同)I knew the answer to the question.(wish, 动词过去式knew)我希望知道这个答案。(事实上是不知道) 2. I wish it were spring in my hometown all the year around.(wish, were)但愿我的家乡四季如春。(事实上不可能) 3. I wish I were a bird.(wish, were)但愿我是只小鸟。(事实上不可能) 4. When she was at the party,she wished she were at home.(wished,过去虚拟动词were)(事实上并不在家) 5. Now that he is in China, he wishes he understood Chinese.(wishes,过去虚拟动词understood)
现在他在中国,他希望能懂得中文。(事实上并不懂) 6. When we begin the trip, they will wish they were with us.(will wish,过去虚拟动词were)(事实上并不和我们在一起) 二)、对过去情况的虚拟(和过去的事实相反): 用wish表示对过去事情的遗憾。其句子结构为:宾语从句的谓语用过去完成时,或would, could, might+现在完成时。例: 1. I wish (that可省略,下同)I hadn't wasted so much time. 我后悔不该浪费这么多时间。(事实上已浪费了) 2. He wishes he hadn't lost the chance. 他真希望没有失去机会。(其实已失去) 3. We wished he had spoken to us. (wished,had + spoken)(事实上他并没同我们讲) 4. I wish you had called earlier. (wish, had + called)(事实上已迟了) 5. They will wish they had listened to us sooner. (will wish,had + listened)(事实上并不如此)
大学英语四级语法精要 Ⅰ动词(时态,语态,用法,省略,一致性等) 1. 时态 1)现在完成进行时态(have/has been + -ing 分词构成): 动作或状态从过去某时开始,继续到现在,可能继续下去,也可能刚刚结束. I’ve been writing letters for an hour. I’ve been sitting in the garden. 2)过去完成进行时(由had been + ing分词构成): 过去某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作 I’d been working f or some time when he called. We had been waiting for her for two hours by the time she came. 3)将来完成进行时: 将来某个时刻以前一直在进行的动作. By next summer, he will have been working here for twenty years. In another month’s time she’ll have been studying here for three yea rs. 4)将来完成时(由shall/will have + 过去分词构成): 将来某时会业已发生的事. I shall have finished this one before lunch.
They’ll have hit the year’s target by the end of October. 2. 语态 1) 可以有两种被动结构的类型,例如: He was said to be jealous of her success. It was said that he was jealous of her success. 能同时适用于上述两个句型的主动词通常都是表示“估计”,“相信”等意义的动词,常见的有assume,believe,expect,fear,feel,know,presume,report,say,suppose,underst and等. It is supposed that the ship has been sunk. The ship is supposed to have been sunk. 担当be supposed to 与不定式的一般形式搭配时往往表示不同的意义.例如: Why are you driving so fast in this area? You are supposed to know the speed to know the speed limit. (你应该晓得速度限制) 2) 双宾语及宾补结构的被动语态 a) 双宾语结构的被动语态: 双宾语结构变为被动语态时,可以把主动结构中的一个宾语变为主语,另一个宾语仍然保留在谓语后面,但多数
大学英语四级常考语法总结 一、虚拟语气。应着重复习能引起虚拟语气的某些介词、介词短语和连词(如lest, in case, otherwise等);一部分表示建议、主张、命令等概念的词语,由于本身隐含说话人的主观愿望,其后的主语从句、宾语从句、同位语从句往往采用“should+动词原形”;虚拟倒装句;在would rather, wish, as if, it’s time that等句型中使用适当形式表达主观愿望;混合虚拟句。 二、独立主格题。一般说来,在句子中没有连接词的情况下,逗号是无力连接两个句子的,其中一个分句要么是非谓语形式,要么是独立主格结构。两种结构都做状语,不同的是独立主格结构有自己的逻辑主语。 三、时态。英语中共有16个时态。四级考试中出现最多的是将来完成时、现在完成时、过去完成时和完成进行时。 四、名词性从句。形容词性的定语从句是考核的重点,用什么引导词,引导词前面的介词形式,引导词在从句中做什么成分,从句的语序等均有可能成为考点。此外,主语从句、同位语从句、宾语从句也应适当复习。 五、主谓一致。这类考题灵活性大,需要根据实际情况判断谓语动词的单复数形式。一部分具有生命意义的集合名词做主语时谓语动词多采用复数形式,如people, poultry, militia等;用and连接的成分表单一概念时谓语动词用单数;就近原则:主语中含有某些连词(如as well as, besides, in addition to等)时,谓语动词的数同第一个主语保持一致。
六、倒装结构。分为全部倒装和部分倒装。那些否定词(组)、介词短语能引起倒装句,部分倒装和全部倒装有和区别,as在倒装结构中的用法及意义等等,都是考生应当重视的地方。 七、非谓语动词。①根据非谓语动词同其所修饰的名词或逻辑主语的一致关系,确定使用主动语态或被动语态,然后考虑采用现在分词、现在分词被动式或过去分词;②非谓语动词同主句谓语动词动作发生的先后关系。动作正在进行的用现在分词进行式,同时发生或不分先后发生的用现在现在分词一般式或过去分词;在主句谓语动词之前发生的用现在分词完成式、不定式完成式;发生在主句谓语动词之后的多用不定式一般式;③表状态多用分词,表目的多用不定式。
Exercise for Subject-verb Concord 1. Which of the following sentences is incorrect A. His sister rather than his parents is at home now. B. Every boy and every girl are excited to hear the news. C. His thanks were really sincere. D. Either Jack or John knows the truth. 2. Which of the following sentences is incorrect A. Poultry are very expensive in the city. B. New machinery were introduced in the factory. C. The police are investigating the murder case. D. The militia were called out to rescue flood victims. 3. Which of the following sentences is grammatically incorrect A. Politics are the art or science of government. B. Ten miles seems like a long walk to me. C. Mumps is a kind of infectious disease. D. All the furniture has arrived undamaged. 4. Which of the following sentences is grammatically incorrect A. Physics is an important school subject. B. The United States borders Canada. C. The Niagara Falls is in North America. D. Mumps is a kind of infectious disease. 5. Which of the following sentences is incorrect A. Only one out of six were present at the meeting. B. Ten dollars was stolen from the cash register. C. Either my sister or my brother is coming. D. Five miles seem like a long walk to me. 6. Which of the following sentences is grammatically incorrect A. John, rather than his roommates, is to blame. B. Either Tina or Carol are sure to know the answer. C. Three pints is not enough to get him drunk. D. Forty-five percent of the doctors were woman. 7. Which of the following sentences is grammatically incorrect A. This pair of trousers costs fifty dollars. B. Either my grandsons or their father is coming. C. The British police has only very limited powers. D. A committee of twelve men is to discuss the matter. 8. All President’s Men one of the important books for scholars who study the Watergate Scandal. A.remains B. remained C. remain D. remaining 9. Two years a long time for a patient who has to lie in bed, and do nothing. A. are B. is C. were D. was Answers: 1-5 b b a c d 6-9 b c a b