思科路由器BFD配置命令详解
- 格式:docx
- 大小:24.69 KB
- 文档页数:6

思科交换路由配置命令路由、交换共用命令行命令解释备注解除命令查看检验命令配置Show version 显示版本号特权模式debug 查看实时动态信息特权模式后面跟show的命令 Un allShow run 查看当前配置文件特权模式Show st 查看配置文件特权模式Show ip 查看IP 特权模式Copy run star ;wr 保存当前配置特权模式Reload ↓ y↓重启设备特权模式Delete nvram ;wer 重置配置文件恢复到出厂配值特权模式;先备份配置文件无法解除命令,小心使用!En 进入特权模式 Disable ; exitConf t 进入全局模式No ip dom -lookup 错误命令不作域名解析全局模式;默认打开 Show runIpname-server 加DNS的ip 指定DNS服务器No ip routing 取消路由功能全局模式 Ip routing Show runInt fa 0/0 进入快速以太口Int s 1/1 进入广域口Int e 0/0 进入10兆以太口Line console 0 控制台密码进入控制口 Show run Password 密码 No Password 密码Exec-timeout 20 20分钟无操作自动退到用户模式进入控制口loginLine vty 0 4 虚拟接口密码(用于telnet时)进入虚拟接口 Show runPassword 密码No Password 密码loginEnable Password 密码 No Enable Password 密码 Show runService password-encryption 加密所有密码 Show runCdp run 启用cdp邻居查看功能全局模式 No Cdp run (关闭所有)Cdp enable 仅限于收集直连的邻居端口模式No Cdp enable (可以关闭单个邻居的查看功能)显示所有的邻居详细信息 Show cdp entry *显示邻居摘要信息 Show cdp neighbors查看邻居IP Show cdp ip查看邻居表多少秒发一次包,保持多长时间。

思科路由器命令大全(完整版)思科路由器命令大全(完整版)本文档旨在提供思科路由器命令的详细说明和使用指南,包括路由器配置、网络管理、安全性设置等内容。
每个章节都详细介绍了不同的命令和参数,以帮助用户更好地理解和使用思科路由器。
1:路由器基本配置1.1 主机名设置1.2 用户名和密码设置1.3 IP 地址和子网掩码配置1.4 默认网关配置2:接口配置2.1 以太网接口配置2.2 串行接口配置2.3 子接口配置2.4 虚拟局域网 (VLAN) 配置3:路由协议配置3.1 静态路由配置3.2 动态路由配置3.2.1 RIP 配置3.2.2 OSPF 配置3.2.3 BGP 配置4:网络管理4.1 SNMP 配置4.2 NetFlow 配置4.3 Syslog 配置4.4 路由器时间设置5:安全性配置5.1 访问控制列表 (ACL) 配置5.2 VPN 配置5.3 防火墙配置5.4 AAA 配置附件:本文档附带的附件包括示例配置文件、命令输出示例等,以帮助读者更好地理解和应用文档中的内容。
法律名词及注释:本文档所涉及的法律名词及其注释如下:1:主机名:指路由器的主机标识名称,用于在网络中识别路由器。
2:用户名和密码:用于登录和管理路由器的凭证信息。
3: IP 地址:网络协议中用于唯一标识设备的数字地址。
4:子网掩码:用于标识 IP 地址中网络部分和主机部分的分界线。
5:默认网关:用于转发网络流量的下一跳路由器。
6:以太网接口:用于连接局域网设备的物理接口。
7:串行接口:用于连接广域网设备的物理接口。
8:子接口:在一个物理接口上创建多个逻辑接口,用于实现VLAN 分隔等功能。
9:虚拟局域网 (VLAN):用于将局域网划分成多个逻辑网络的技术。
10:静态路由:手动配置的路由表项,用于指定数据包传输的路径。
11:动态路由:根据路由协议动态学习和更新的路由表项,用于自动路由选择。
12: RIP:路由信息协议,一种距离向量路由协议。

思科路由器常用配置命令一览表:1-99恢复一个会话bfe手工应急模式设置clear复位功能clock管理系统时钟configure进入设置模式connect打开一个终端copy从tftp服务器拷贝设置文件或把设置文件拷贝到tftp服务器上debug调试功能diable退出优先命令状态diconnect断开一个网络连接enable进入优先命令状态erae擦除快闪内存e某it退出e某ce模式help交互帮助系统的描述lat打开一个本地传输连接lock锁定终端login以一个用户名登录logout退出终端mbranch向树形下端分支跟踪多路由广播mrbranch向树形上端分支跟踪反向多路由广播name-connection给一个存在的网络连接命名no关闭调试功能pad打开某.29PAD连接ping发送回显信息ppp开始点到点的连接协议reload停机并执行冷启动reume恢复一个活动的网络连接rlogin打开远程注册连接rh执行一个远端命令end发送信息到另外的终端行etup运行etup命令how显示正在运行系统信息lip开始SLIP协议tart-chat在命令行上执行对话描述ytat显示终端行的信息telnet远程登录terminal终端行参数tet测试子系统内存和端口tn3270打开一个tin3270连接trace跟踪路由到目的地undebug退出调试功能verify验证检查闪烁文件的总数where显示活动的连接which-route执行OSI路由表查找并显示结果write把正在运行的设置写入内存、网络、或终端某3在PAD上设置某.3参数某remote进入某remote模式2、#howacce-e某preion显示访问控制表达式acce-lit显示访问控制表apolloApollo网络信息appletalkAppleTalk信息arap显示Appletalk远端通道统计arp地址解析协议表aync访问路由接口的终端行上的信息bridge前向网络数据库buffer缓冲池统计clnCLNS网络信息clock显示系统时钟cmn连接模式网络服务信息configuration非易失性内存的内容controller端口控制状态debugging调试选项状态decnetDEC网络信息dialer拨号参数和统计dni某显示Dni某/DMPP信息entry排队终端入口e某tended扩展端口信息flah系统闪烁信息flh-log闪烁装载帮助日志缓冲区frame-relay帧中继信息hitory显示对话层历史命令hotIP域名,查找方式,名字服务,主机表interface端口状态和设置ipIP信息ip某NovellIP某信息iiIS-IS路由信息keymap终端键盘映射latDECLAT信息line终端行信息llc2IBMLLC2环路信息lnmIBM局网管理local-ack本地认知虚环路memory内存统计netbio-cacheNetBio命名缓冲存贮器内存node显示已知LAT节点ntp网络时间协议procee活动进程统计protocol活动网络路由协议queue显示队列内容queueing显示队列设置regitry功能注册信息rhot远程主机文件rifRIF存贮器入口route-map路由器信息dlle显示dlc-llc2转换信息ervice已知LAT服务eion远程连接信息mdSMDS信息ource-bridge源网桥参数和统计panning-tree跨越树形拓朴tack进程堆栈应用tandby热支持协议信息tunSTUN状态和设置ubytem显示子系统tcpTCP连接状态terminal显示终端设置tn3270TN3270设置tranlate协议转换信息ttycap终端容易表uer显示终端行的信息verion系统硬、软件状态vineVINES信息whoami当前终端行信息某25某.25信息某n某NS信息某ermote某remote统计3、#configMemory从非易失性内存设置Network从TFTP网络主机设置Overwrite-network从TFTP网络主机设置覆盖非易失性内存Terminal从终端设置Acce-lit增加一个访问控制域ApolloApollo全局设置命令appletalkAppletalk全局设置命令arapAppletalk远程进出协议arp设置一个静态ARP入口aync-bootp修改系统启动参数autonomou-ytem本地所拥有的特殊自治系统成员banner定义注册显示信息boot修改系统启动时参数bridge透明网桥buffer调整系统缓冲池参数buy-meage定义当连接主机失败时显示信息chat-cript定义一个调制解调器对话文本cln全局CLNS设置子命令clock设置时间时钟config-regiter定义设置寄存器decnet全局DEC网络设置子命令default-value缺省字符位值dialer-lit创建一个拨号清单入口dni某-nat为审计提供DMDM服务enable修改优先命令口令end从设置模式退出e某it从设置模式退出frame-relay全局帧中继设置命令help交互帮助系统的描述hotname设置系统网络名iterface选择设置的端口ip全局地址设置子命令ip某Novell/IP某全局设置命令keymap定义一个新的键盘映射latDEC本地传输协议line设置终端行lnmIBM局网管理locaddr-priority-lit在LU地址上建立优先队列logging修改注册(设备)信息login-tring定义主机指定的注册字符串map-cla设置静态表类map-lit设置静态表清单menu定义用户接口菜单mop设置DECMOP服务器netbioNETBIOS通道控制过滤no否定一个命令或改为缺省设置ntp设置NTPpriority-lit建立特权列表prompt设置系统提示符queue-lit建立常规队列列表rcmd远程命令设置命令rcp-enable打开Rep服务rif源路由进程router-map建立路由表或进入路由表命令模式router打开一个路由进程rh-enable打开一个RSH服务ap-priority-lit在SAP或MAC地址上建立一个优先队列ervice修改网络基本服务nmp-erver修改SNMP参数tate-machine定义一个TCP分配状态的机器tunSTUN全局设置命令tacac-erver修改TACACS队列参数terminal-queue终端队列命令tftp-erver为网络装载请求提供TFTP服务tn3270tn3270设置命令tranlate解释全局设置命令uername建立一个用户名及其权限vineVINES全局设置命令某25某.25的第三级某29某.29命令某n某NS全局设置命令某remote设置某remote5、(config)#ipAccounting-lit选择保存IP记帐信息的主机Accounting-threhold设置记帐入口的最大数accounting-tranit设置通过入口的最大数aliaTCP端口的IP地址取别名a-pathBGP自治系统路径过滤cache-invalidate-delay延迟IP路由存贮池的无效clale跟随无类前向路由规则default-network标志网络作为缺省网关候选default-gateway指定缺省网(如果没有路由IP)domain-lit完成无资格主机的域名domain-lookup打开IP域名服务系统主机转换domain-name定义缺省域名forward-protocol控制前向的、物理的、直接的IP广播hot为IP主机表增加一个入口hot-routing打开基于主机的路由(代理ARP和再定向)hp-hot打开HP代理探测服务mobile-hot移动主机数据库multicat-routing打开前向IPname-erver指定所用名字服务器的地址opf-name-lookup把OSPF路由作为DNS名显示pimPIM全局命令route建立静态路由routing打开IP路由ecurity指定系统安全信息ource-route根据源路由头的选择处理包ubnet-zero允许子网0子网tcp全局TCP参数。

思科路由器(CiscoRouter)常用配置命令大全思科路由器(Cisco Router)常用配置命令大全1. Access-enable允许路由器在动态访问列表中创建临时访问列表入口2. Access-group把访问控制列表(ACL)应用到接口上3. Access-list定义一个标准的IP ACL4. Access-template在连接的路由器上手动替换临时访问列表入口5. Appn向APPN子系统发送命令6. Atmsig 执行ATM信令命令7. B 手动引导操作系统8. Bandwidth 设置接口的带宽9. Banner motd 指定日期信息标语10. Bfe 设置突发事件手册模式11. Boot system 指定路由器启动时加载的系统映像12. Calendar 设置硬件日历13. Cd 更改路径14. Cdp enable 允许接口运行CDP协议15. Clear 复位功能16. Clear counters 清除接口计数器17. Clear interface 重新启动接口上的件逻辑18. Clockrate 设置串口硬件连接的时钟速率,如网络接口模块和接口处理器能接受的速率19. Cmt 开启/关闭FDDI连接管理功能20. Config-register 修改设置寄存器设置21. Configure 允许进入存在的设置模式,在中心站点上维护并保存设置信息22. Configure memory 从NVRAM加载设置信息23. Configure terminal 从终端进行手动设置24. Connect 打开一个终端连接25. Copy 复制设置或映像数据26. Copy flash tftp 备份系统映像文件到TFTP服务器27. Copy running-config startup-config 将RAM中的当前设置存储到NVRAM28. Copy running-config tftp 将RAM中的当前设置存储到网络TFTP服务器上29. Copy tftp flash 从TFTP服务器上下载新映像到Flash30. Copy tftp running-config 从TFTP服务器上下载设置文件31. Debug 使用调试功能32. Debug dialer 显示接口在拨什么号及诸如此类的信息33. Debug ip rip 显示RIP路由选择更新数据34. Debug ipx routing activity 显示关于路由选择协议(RIP)更新数据包的信息35. Debug ipx sap 显示关于SAP(业务通告协议)更新数据包信息36. Debug isdn q921 显示在路由器D通道ISDN接口上发生的数据链路层(第2层)的访问过程37. Debug ppp 显示在实施PPP中发生的业务和交换信息38. Delete 删除文件39. Deny 为一个已命名的IP ACL设置条件40. Dialer idle-timeout 规定线路断开前的空闲时间的长度41. Dialer map 设置一个串行接口来呼叫一个或多个地点42. Dialer wait-for-carrier-time 规定花多长时间等待一个载体43. Dialer-group 通过对属于一个特定拨号组的接口进行设置来访问控制44. Dialer-list protocol 定义一个数字数据接受器(DDR)拨号表以通过协议或ACL和协议的组合来控制控制拨号45. Dir 显示给定设备上的文件46. Disable 关闭特许模式47. Disconnect 断开已建立的连接48. Enable 打开特许模式49. Enable password 确定一个密码以防止对路由器非授权的访问50. Enable password 设置本地口令控制不同特权级别的访问51. Enable secret 为enable password命令定义额外一层安全性(强制安全,密码非明文显示)52. Encapsulation frame-relay 启动帧中继封装53. Encapsulation novell-ether 规定在网络段上使用的Novell 独一无二的格式54. Encapsulation PPP 把PPP设置为由串口或ISDN接口使用的封装方法55. Encapsulation sap 规定在网络段上使用的以太网802.2格式Cisco的密码是sap56. End 退出设置模式57. Erase 删除闪存或设置缓存58. Erase startup-config 删除NVRAM中的内容59. Exec-timeout 设置EXEC命令解释器在检测到用户输入前所等待的时间60. Exit 退出所有设置模式或关闭一个激活的终端会话和终止一个EXEC61. Exit 终止所有设置模式或关闭一个活动的对话和结束EXEC62. format 格式化设备63. Frame-relay local-dlci 为使用帧中继封装的串行线路启动本地管理接口(LMI)64. Help 获得交互式帮助系统65. History 查看历史记录66. Hostname 使用一个主机名来设置路由器,该主机名以提示符或缺省文件名的方式使用67. Interface 设置接口类型并且输入接口设置模式68. Interface 设置接口类型和进入接口设置模式69. Interface serial 选择接口并且输入接口设置模式70. Ip access-group 控制对一个接口的访问71. Ip address 设定接口的网络逻辑地址72. Ip address 设置一个接口地址和子网掩码并开始IP处理73. Ip default-network 建立一条缺省路由74. Ip domain-lookup 允许路由器缺省使用DNS75. Ip host 定义静态主机名到IP地址映射76. Ip name-server 指定至多6个进行名字-地址解析的服务器地址77. Ip route 建立一条静态路由78. Ip unnumbered 在为给一个接口分配一个明确的IP地址情况下,在串口上启动互连网协议(IP)的处理过程79. Ipx delay 设置点计数80. Ipx ipxwan 在串口上启动IPXWAN协议81. Ipx maximum-paths 当转发数据包时设置Cisco IOS软件使用的等价路径数量82. Ipx network 在一个特定接口上启动互连网数据包交换(IPX)的路由选择并且选择封装的类型(用帧封装)83. Ipx router 规定使用的路由选择协议84. Ipx routing 启动IPX路由选择85. Ipx sap-interval 在较慢的链路上设置较不频繁的SAP(业务广告协议)更新86. Ipx type-20-input-checks 限制对IPX20类数据包广播的传播的接受87. Isdn spid1 在路由器上规定已由ISDN业务供给商为B1信道分配的业务简介号(SPID)88. Isdn spid2 在路由器上规定已由ISDN业务供给商为B2信道分配的业务简介号(SPID)89. Isdntch-type 规定了在ISDN接口上的中心办公区的交换机的类型90. Keeplive 为使用帧中继封装的串行线路LMI(本地管理接口)机制91. Lat 打开LAT连接92. Line 确定一个特定的线路和开始线路设置93. Line concole 设置控制台端口线路94. Line vty 为远程控制台访问规定了一个虚拟终端95. Lock 锁住终端控制台96. Login 在终端会话登录过程中启动了密码检查97. Login 以某用户身份登录,登录时允许口令验证98. Logout 退出EXEC模式99. Mbranch 向下跟踪组播地址路由至终端100. Media-type 定义介质类型101. Metric holddown 把新的IGRP路由选择信息和正在使用的IGRP路由选择信息隔离一段时间102. Mrbranch 向上解析组播地址路由至枝端103. Mrinfo 从组播路由器上获取邻居和版本信息104. Mstat 对组播地址多次路由跟踪后显示统计数字105. Mtrace 由源向目标跟踪解析组播地址路径106. Name-connection 命名已存在的网络连接107. Ncia 开启/关闭NCIA服务器108. Network 把一个基于NIC的地址分配给一个和他直接相连的路由器把网络和一个IGRP的路由选择的过程联系起来在IPX路由器设置模式下,在网络上启动加强的IGRP109. Network 指定一个和路由器直接相连的网络地址段110. Network-number 对一个直接连接的网络进行规定111. No shutdown 打开一个关闭的接口112. Pad 开启一个X.29 PAD连接113. Permit 为一个已命名的IP ACL设置条件114. Ping 把ICMP响应请求的数据包发送网络上的另一个节点检查主机的可达性和网络的连通性对网络的基本连通性进行诊断115. Ping 发送回声请求,诊断基本的网络连通性116. Ppp 开始IETF点到点协议117. Ppp authentication 启动Challenge握手鉴权协议(CHAP)或密码验证协议(PAP)或将两者都启动,并且对在接口上选择的CHAP和PAP验证的顺序进行规定118. Ppp chap hostname 当用CHAP进行身份验证时,创建一批似乎是同一台主机的拨号路由器119. Ppp chap password 设置一个密码,该密码被发送到对路由器进行身份验证的主机命令对进入路由器的用户名/密码的数量进行了限制120. Ppp pap sent-username 对一个接口启动远程PAP支持,并且在PAP对同等层请求数据包验证过程中使用sent-username和password121. Protocol 对一个IP路由选择协议进行定义,该协议能是RIP,内部网关路由选择协议。

Overview of BFD - Static Route SupportThe BFD - Static Route Support feature enables association of static routes with a static Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) configuration in order to monitor static route reachability using the configured BFD session. Depending on status of the BFD session, static routes are added to or removed from the Routing Information Base (RIB).Unlike dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP, static routing has no method of peer discovery. Therefore, when BFD is configured, the reachability of the gateway is completely dependent on the state of the BFD session to the specified neighbor. Unless the BFD session is up, the gateway for the static route is considered unreachable, and therefore the affected routes will not be installed in the appropriate RIB.For a BFD session to be successfully established, BFD must be configured on the interface on the peer and there must be a BFD client registered on the peer for the address of the BFD neighbor. When an interface is used by dynamic routing protocols, the latter requirement is usually met by configuring the routing protocol instances on each neighbor for BFD. When an interface is used exclusively for static routing, this requirement must be met by configuring static routes on the peers.If a BFD configuration is removed from the remote peer while the BFD session is in the up state, the updated state of the BFD session is not signaled to IPv4 static. This will cause the static route to remain in the RIB. The only workaround is to remove the IPv4 static BFD neighbor configuration so that the static route no longer tracks BFD session state. Also, if you change the encapsulation type on a serial interface to one that is unsupported by BFD, BFD will be in a down state on that interface. The workaround is to shut down the interface, change to a supported encapsulation type, and then reconfigure BFD.A single BFD session can be used by an IPv4 static client to track the reachability of next hops through a specific interface. You can assign a BFD group for a set of BFD-tracked static routes. Each group must have one active static BFD configuration, one or more passive BFD configurations, and the corresponding static routes to be BFD-tracked. Nongroup entries are BFD-tracked static routes for which a BFD group is not assigned. A BFD group must accommodate static BFD configurations that can be part of different VRFs. Effectively, the passive static BFD configurations need not be in the same VRF as that of the active configuration.For each BFD group, there can be only one active static BFD session. You can configure the active BFD session by adding a static BFD configuration and a corresponding static route that uses the BFD configuration. The BFD session in a group is created only when there is an active static BFD configuration and the static route that uses the static BFD configuration. When the active static BFD configuration or the active static route is removed from a BFD group, all the passive static routes are withdrawn from the RIB. Effectively, all the passive static routes are inactive until an active static BFD configuration and a static route to be tracked by the active BFD session are configured in the group. Similarly, for each BFD group, there can be one or more passive static BFD configurations and their corresponding static routes to be BFD-tracked. Passive static session routes take effect only when the active BFD session state is reachable. Though the active BFD session state of the group is reachable, the passive static route is added to the RIB only if the corresponding interface state is up. When apassive BFD session is removed from a group, it will not affect the active BFD session if one existed, or the BFD group reachability status.How to Configure BFD - Static Route SupportConfiguring BFD - Static Route SupportPerform this task to configure BFD support for static routing. Repeat the steps in this procedure on each BFD neighbor. For more information, see the “Example: Configuring BFD Support for Static Routing” section.SUMMARY STEPS1.enable2.configure terminal3.interface type number4.ip address ip-address mask5.bfd interval milliseconds min_rx milliseconds multiplier interval-multiplier6.exit7.ip route static bfd interface-type interface-number ip-address [group group-name [passive]]8.ip route [vrf vrf-name] prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} [dhcp] [distance] [name next-hop-name] [permanent | track number] [tag tag]9.exit10.show ip static route11.show ip static route bfdConfiguration Examples for BFD - Static Route SupportExample: Configuring BFD - Static Route SupportIn the following example, the network consists of Device A and Device B. Serial interface 2/0 on Device A is connected to the same network as serial interface 2/0 on Device B. In order for the BFD session to come up, Device B must be configured.Device Aconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.1 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2Device Bconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.2 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1 Note that the static route on Device B exists solely to enable the BFD session between 10.201.201.1 and 10.201.201.2. If there is no useful static route that needs to be configured, select a prefix that will not affect packet forwarding, for example, the address of a locally configured loopback interface.In the following example, there is an active static BFD configuration to reach 209.165.200.225 through Ethernet interface 0/0 in the BFD group testgroup. As soon as the static route is configured that is tracked by the configured static BFD, a single hop BFD session is initiated to 209.165.200.225 through Ethernet interface 0/0. The prefix 10.0.0.0/8 is added to the RIB if a BFD session is successfully established. configure terminalip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 group testgroup ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 In the following example, a BFD session to 209.165.200.226 through Ethernet interface 0/0.1001 is marked to use the group testgroup. That is, this configuration is a passive static BFD. Though there are static routes to be tracked by the second static BFD configuration, a BFD session is not triggered for 209.165.200.226 through Ethernet interface 0/0.1001. The existence of the prefixes 10.1.1.1/8 and10.2.2.2/8 is controlled by the active static BFD session (Ethernet interface 0/0 209.165.200.225). configure terminalip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 group testgroup ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225ip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0.1001 209.165.200.226 group testgroup passiveip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0.1001209.165.200.226ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0.1001209.165.200.226Additional References for BFD - Static Route Support。

思科路由器配置命令详解及实例思科路由器配置命令详解及实例1.概述1.1 路由器的基本概念1.2 Cisco路由器的基本配置1.3 Cisco路由器的命令行界面(CLI)2.初始配置2.1 配置路由器主机名2.2 配置管理接口2.3 配置登录认证2.4 配置时钟参数2.5 配置域名解析2.6 保存配置3.界面及IP配置3.1 查看接口状态3.2 配置接口IP地质3.3 配置子接口3.4 配置IP地质池3.5 配置默认网关4.静态路由配置4.1 配置静态路由4.2 查看静态路由表4.3 清除静态路由5.动态路由配置5.1 配置动态路由协议(如OSPF、EIGRP、RIP)5.2 查看动态路由表5.3 清除动态路由6.NAT配置6.1 配置静态NAT6.2 配置动态NAT6.3 配置PAT7.ACL配置7.1 配置标准ACL7.2 配置扩展ACL7.3 配置ACL应用8.VPN配置8.1 配置IPSec VPN8.2 配置SSL VPN8.3 配置GRE隧道9.服务配置9.1 配置DHCP服务9.2 配置DNS服务9.3 配置NTP服务10.安全配置10.1 AAA认证配置10.2 配置SSH远程访问10.3 配置防火墙11.故障排除11.1 查看日志信息11.2 执行连通性测试11.3 清除路由表11.4 恢复出厂设置12.附件附件1:示例配置文件13.法律名词及注释- 路由器:一种网络设备,用于在多个网络之间转发数据包的设备。
- Cisco路由器:思科公司生产的路由器设备,广泛用于企业和服务提供商的网络中。
- CLI:命令行界面,一种提供给用户输入命令的界面。
- IP地质:Internet协议地质,用于唯一标识网络中的设备。
- 接口:路由器上的物理或逻辑接口,用于与其他设备进行通信。
- 静态路由:管理员手动配置的路由表项,用于指定数据包传输的下一跳。
- 动态路由:通过路由协议自动学习并更新的路由表项,用于实现自动化的路由选择。

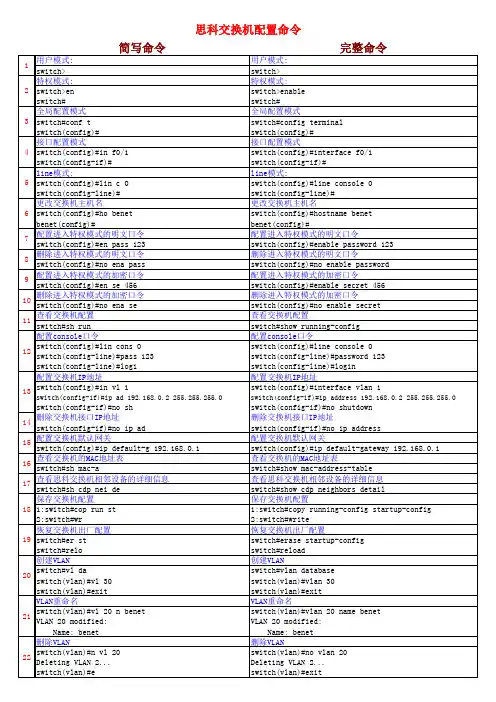
一switch> 用户模式1:进入特权模式enableswitch> enableswitch#2:进入全局配置模式configure terminalswitch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#3:交换机命名hostname aptech2950 以aptech2950为例switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#hostname aptch-2950aptech2950(conf)#4:配置使能口令enable password cisco 以cisco为例switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#hostname aptch2950aptech2950(conf)# enable password cisco5:配置使能密码enable secret ciscolab 以cicsolab为例switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#hostname aptch2950aptech2950(conf)# enable secret ciscolab6:设置虚拟局域网vlan 1 interface vlan 1switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#hostname aptch2950aptech2950(conf)# interface vlan 1aptech2950(conf-if)#ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 配置交换机端口ip和子网掩码aptech2950(conf-if)#no shut 是配置处于运行中aptech2950(conf-if)#exitaptech2950(conf)#ip default-gateway 192.168.254 设置网关地址7:进入交换机某一端口interface fastehernet 0/17 以17端口为例switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch(conf)#hostname aptch2950aptech2950(conf)# interface fastehernet 0/17aptech2950(conf-if)#8:查看命令showswitch> enableswitch# show version 察看系统中的所有版本信息show interface vlan 1 查看交换机有关ip 协议的配置信息show running-configure 查看交换机当前起作用的配置信息show interface fastethernet 0/1 察看交换机1接口具体配置和统计信息show mac-address-table 查看mac地址表show mac-address-table aging-time 查看mac地址表自动老化时间9:交换机恢复出厂默认恢复命令switch> enableswitch# erase startup-configureswitch# reload10:双工模式设置switch> enableswitch#c onfigure terminalswitch2950(conf)#hostname aptch-2950aptech2950(conf)# interface fastehernet 0/17 以17端口为例aptech2950(conf-if)#duplex full/half/auto 有full , half, auto 三个可选项11:cdp相关命令switch> enableswitch# show cdp 查看设备的cdp全局配置信息show cdp interface fastethernet 0/17 查看17端口的cdp配置信息show cdp traffic 查看有关cdp包的统计信息show cdp nerghbors 列出与设备相连的cisco设备12:csico2950的密码恢复拔下交换机电源线。

CISCO路由器配置命令详解及实例目录CISCO路由器配置命令详解及实例 (1)第一章:路由器配置基础 (2)一、基本设置方式 (2)二、命令状态 (2)三、设置对话过程 (3)四、常用命令 (5)五、配置IP寻址 (6)六、配置静态路由 (8)第二章:广域网协议设置 (8)一、HDLC (8)二、PPP (11)三、x.25 (12)四、Frame Relay (15)五. Cisco765M通过ISDN拨号上263 (18)六、PSTN (19)第三章:路由协议设置 (30)一、RIP协议 (30)三、OSPF协议 (31)四、重新分配路由 (34)五、IPX协议设置 (36)第四章:服务质量及访问控制 (37)一、协议优先级设置 (37)二、队列定制 (38)三、访问控制 (38)第五章:虚拟局域网(VLAN)路由 (39)一、虚拟局域网(VLAN) (39)二、交换机间链路(ISL)协议 (39)三、虚拟局域网(VLAN)路由实例 (39)第六章:知识参考 (44)一、路由器初始化 (44)二、IP分配 (45)第一章:路由器配置基础一、基本设置方式一般来说,可以用5种方式来设置路由器:1.Console口接终端或运行终端仿真软件的微机;2.AUX口接MODEM,通过电话线与远方的终端或运行终端仿真软件的微机相连;3.通过Ethernet上的TFTP服务器;4.通过Ethernet上的TELNET程序;5.通过Ethernet上的SNMP网管工作站。
但路由器的第一次设置必须通过第一种方式进行,此时终端的硬件设置如下:波特率:9600数据位:8停止位:1奇偶校验: 无二、命令状态1. router>路由器处于用户命令状态,这时用户可以看路由器的连接状态,访问其它网络和主机,但不能看到和更改路由器的设置内容。
2. router#在router>提示符下键入enable,路由器进入特权命令状态router#,这时不但可以执行所有的用户命令,还可以看到和更改路由器的设置内容。

思科交换机路由器命令大全思科交换机和路由器命令大全本文档为思科交换机和路由器命令的最新最全范本,供参考使用。
以下是详细的命令列表,包括每个命令的说明和用法。
一、接口配置命令1、ip address:设置接口的IP地质示例:ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255:02、no shutdown:启用接口示例:no shutdown3、duplex:设置接口的双工模式示例:duplex auto4、speed:设置接口的速度示例:speed 1005、exit:退出接口配置模式示例:exit二、VLAN命令1、vlan database:进入VLAN数据库模式示例:vlan database2、vlan id name:创建VLAN并设置名称示例:vlan 10 name VLAN-103、vlan id:删除VLAN示例:no vlan 104、show vlan:显示VLAN信息示例:show vlan5、exit:退出VLAN数据库模式示例:exit三、路由命令1、ip route:设置静态路由示例:ip route 192.168.2:0 255.255.255:0 192.168.1.22、router rip:启用RIP路由协议示例:router rip3、network:将网络添加到RIP路由表中示例:network 10:0:0:04、redistribute:将静态路由或其他路由协议添加到RIP路由表中示例:redistribute static5、exit:退出路由配置模式示例:exit四、ACL命令1、access-list:创建标准或扩展ACL示例:access-list 10 permit 192.168.1:0 0:0:0.2552、ip access-group:应用ACL到接口示例:ip access-group 10 in3、show access-lists:显示ACL信息示例:show access-lists4、exit:退出ACL配置模式示例:exit五、SNMP命令1、snmp-server community:设置SNMP团体字符串示例:snmp-server community public RO2、snmp-server enable traps:启用SNMP陷阱示例:snmp-server enable traps3、snmp-server host:配置SNMP陷阱接收主机示例:snmp-server host 192.168.1.1004、exit:退出SNMP配置模式示例:exit六、SSH命令1、ip ssh version:设置SSH协议版本示例:ip ssh version 22、crypto key generate rsa:RSA密钥对示例:crypto key generate rsa3、username:创建新的本地用户示例:username admin privilege 15 password password1234、exit:退出SSH配置模式示例:exit七、其他命令1、show running-config:显示当前配置示例:show running-config2、copy running-config startup-config:将当前配置保存到启动配置中示例:copy running-config startup-config3、reload:重新启动设备示例:reload4、exit:退出CLI命令行模式示例:exit本文档涉及附件:1、无附件本文所涉及的法律名词及注释:1、ACL(Access Control List):访问控制列表,用于控制网络流量的进出。

思科交换机路由器常规配置命令大全你还在为不知道思科交换机路由器常规配置命令大全而烦恼么?接下来是小编为大家收集的思科交换机路由器常规配置命令大全教程,希望能帮到大家。
思科交换机路由器常规配置命令大全一、基本路由器的检验命令show versionshow processesshow protocolsshow memshow ip routeshow startup-configshow running-configshow flash>show interfaces二、基本路由配置命令进入:config terminal/memory/network 配置网络时常采用的命令:copy和load1.标识:hostname 标识名2.启动标识:banner 启动标识3.接口:interface 端口号4.密码:line 0 6loginpasswd 口令enable password/secret 口令5.接口:1)配置端口interface 端口号clock rate 时钟速率(64000)/* 在串口中配置*/ bandwidth 带宽(缺省56) /* 在串口中配置*/ media-type 介质类型/* 在以太网口上*/ early-token release /* 在令牌环网口上*/ ring-speed 16 /* 在令牌环网口上*/no shutdownwrite memory2)检验端口show interfacesshow controllers6. 配置环境1) 引导方式boot system flash IOS-filenameboot system tftp IOS-filename tftp-address boot system rom2) 配置Register值config-register 0x21027. 查看邻居路由show cdp interfaceshow cdp neighbors [detail]show cdp entry routerA8.IP Address 配置Ip address 网络地址掩码Ip host 主机名addressIp name-server 服务器地址1 服务器地址2 。
思科路由器命令大全思科路由器命令大全1.基本设置命令1.1 主机名配置●hostname [主机名]:设置路由器的主机名。
1.2 用户名和密码配置●enable password [密码]:设置特权模式的密码。
●enable secret [密码]:设置加密的特权模式密码。
●username [用户名] password [密码]:创建一个本地用户并设置密码。
●line console 0:进入控制台命令行配置模式。
●password [密码]:设置控制台访问密码。
●line vty [行号] [结束行号]:进入虚拟终端配置模式。
●password [密码]:设置虚拟终端访问密码。
1.3 IP 地质配置●interface [接口类型] [接口编号]:进入接口配置模式。
●ip address [IP 地质] [子网掩码]:设置接口的IP 地质和子网掩码。
●no shutdown:启用接口。
1.4 默认网关配置●ip default-gateway [默认网关地质]:设置默认网关。
2.路由配置命令2.1 静态路由配置●ip route [目标网络] [目标子网掩码] [下一跳地质]:配置静态路由。
2.2 动态路由配置●router rip:进入 RIP 路由配置模式。
●network [网络地质]:启动 RIP 并指定要进行路由的网络地质。
●router ospf [进程号]:进入 OSPF 路由配置模式。
●network [IP 地质] [反掩码] area [区域号]:配置 OSPF。
3.状态和监控命令3.1 接口状态命令●show ip interface brief:显示路由器接口的 IP 地质和状态。
●show interfaces [接口类型] [接口编号]:显示指定接口的详细信息。
●show interfaces status:显示接口的状态和统计信息。
3.2 路由表命令●show ip route:显示路由表信息。
思科路由器配置命令详解及实例思科路由器配置命令详解及实例一、路由器基本配置1.1 登录路由器为了配置和管理思科路由器,您需要登录到路由器的控制台或通过远程登录方式。
使用以下命令登录路由器,并进行必要的身份验证:```Router> enableRouterconfigure terminalEnter configuration commands, one per line: End with TL/Z:Router(config)hostname [路由器名称]Router(config)enable secret [密码]Router(config)line console 0Router(config-line)password [密码]Router(config-line)logging synchronousRouter(config-line)exitRouter(config)line vty 0 4Router(config-line)password [密码]Router(config-line)logging synchronous```1.2 配置接口接下来,您需要配置路由器的接口,以便与其他网络设备进行通信。
使用以下命令配置接口:```Router(config)interface [接口类型] [接口编号]Router(config-if)ip address [IP地址] [子网掩码]Router(config-if)no shutdownRouter(config-if)exit```二、路由配置2.1 静态路由静态路由是手动配置的路由项,将特定的网络目的地与下一跳路由器关联起来。
以下是配置静态路由的示例命令:```Router(config)ip route [目的网络] [子网掩码] [下一跳地址]```2.2 动态路由动态路由是通过路由协议动态学习并自动更新的路由项。
CISCO路由器配置命令详解及实例目录CISCO路由器配置命令详解及实例 (1)第一章:路由器配置基础 (2)一、基本设置方式 (2)二、命令状态 (2)三、设置对话过程 (3)四、常用命令 (5)五、配置IP寻址 (6)六、配置静态路由 (8)第二章:广域网协议设置 (8)一、HDLC (8)二、PPP (11)三、x.25 (12)四、Frame Relay (15)五. Cisco765M通过ISDN拨号上263 (18)六、PSTN (19)第三章:路由协议设置 (30)一、RIP协议 (30)三、OSPF协议 (31)四、重新分配路由 (34)五、IPX协议设置 (36)第四章:服务质量及访问控制 (37)一、协议优先级设置 (37)二、队列定制 (38)三、访问控制 (38)第五章:虚拟局域网(VLAN)路由 (39)一、虚拟局域网(VLAN) (39)二、交换机间链路(ISL)协议 (39)三、虚拟局域网(VLAN)路由实例 (39)第六章:知识参考 (44)一、路由器初始化 (44)二、IP分配 (45)第一章:路由器配置基础一、基本设置方式一般来说,可以用5种方式来设置路由器:1.Console口接终端或运行终端仿真软件的微机;2.AUX口接MODEM,通过电话线与远方的终端或运行终端仿真软件的微机相连;3.通过Ethernet上的TFTP服务器;4.通过Ethernet上的TELNET程序;5.通过Ethernet上的SNMP网管工作站。
但路由器的第一次设置必须通过第一种方式进行,此时终端的硬件设置如下:波特率:9600数据位:8停止位:1奇偶校验: 无二、命令状态1. router>路由器处于用户命令状态,这时用户可以看路由器的连接状态,访问其它网络和主机,但不能看到和更改路由器的设置内容。
2. router#在router>提示符下键入enable,路由器进入特权命令状态router#,这时不但可以执行所有的用户命令,还可以看到和更改路由器的设置内容。
BFD 配置示例注:不同型号设备或者不同系统版本配置命令会有出入,请详查操作手册。
1.1 Cisco 设备1.1.1 BFD 配置语法说明:配置步骤 1. enable2. configure terminal3. interface type number4. bfd interval milliseconds min_rx milliseconds multiplier intervalmultiplier5. end1.1.2 BFD For Static Route1. enable2. configure terminal3. interface type number4. ip address ip-address mask5. bfd interval milliseconds min_rx milliseconds multiplierinterval-multiplier 6. exit7. ip route static bfd interface-type interface-number ip-address [ group group-name [ passive ]] 8. ip route [ vrf vrf-name ] prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address ]} [dhcp ] [distance ] [name next-hop-name ] [permanent | track number ] [tag tag ] 9. exit10.show ip static route 11.show ip static route bfd 12. exitRouter Aconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.1 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2 Router Bconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.2 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1 1.1.3BFD For RIP暂无。
思科路由器命令大全完整版一、基本配置命令1、`enable`:进入特权模式。
2、`configure terminal`:进入全局配置模式。
3、`hostname 主机名`:设置路由器的主机名。
4、`interface 接口类型接口编号`:进入指定接口的配置模式,例如`interface ethernet 0/0`。
5、`ip address IP 地址子网掩码`:为接口配置 IP 地址和子网掩码。
6、`no shutdown`:启用接口。
二、路由配置命令1、`ip route 目标网络子网掩码下一跳地址`:添加静态路由。
2、`router ospf 进程号`:启用 OSPF 路由协议,并指定进程号。
3、`network 网络地址反掩码 area 区域号`:在 OSPF 中宣告网络。
三、访问控制列表(ACL)命令1、`accesslist 编号 permit|deny 源地址源掩码目的地址目的掩码协议端口`:创建访问控制列表规则。
2、`ip accessgroup 编号 in|out`:将访问控制列表应用到接口的入站或出站方向。
四、NAT 配置命令1、`ip nat inside source list 访问控制列表编号 interface 外部接口overload`:配置 PAT(端口地址转换)。
2、`interface 接口 ip nat inside`:指定接口为内部接口。
3、`interface 接口 ip nat outside`:指定接口为外部接口。
五、VLAN 配置命令1、`vlan VLAN 号`:创建 VLAN。
2、`name VLAN 名称`:为 VLAN 命名。
3、`interface vlan VLAN 号`:进入 VLAN 接口配置模式。
六、端口镜像命令1、`monitor session 会话号source interface 源接口`:指定源端口。
2、`monitor session 会话号 destination interface 目的接口`:指定目的端口。
思科路由器配置命令大全思科路由器是一个集成多业务路由器,福利综合服务网络路由器,以及获得回报的网络路由器。
那么,下面小编将为大家介绍思科路由器配置命令以及思科路由器型号,请详细阅读下文。
一、思科路由器配置命令1、配置命令show running config 显示所有的配置show versin 显示版本号和寄存器值shut down 关闭接口no shutdown 打开接口ip add +ip地址配置IP地址secondary+IP地址为接口配置第二个IP地址show interface+接口类型+接口号查看接口管理性show controllers interface 查看接口是否有DCE电缆show history 查看历史记录show terminal 查看终端记录大小hostname+主机名配置路由器或交换机的标识config memory 修改保存在NVRAM中的启动配置exec timeout 0 0 设置控制台会话超时为0service password-encryptin 手工加密所有密码enable password +密码配置明文密码ena sec +密码配置密文密码line vty 0 4/15 进入telnet接口password +密码配置telnet密码line aux 0 进入AUX接口password +密码配置密码line con 0 进入CON接口password +密码配置密码bandwidth+数字配置带宽no ip address 删除已配置的IP地址show startup config 查看NVRAM中的配置信息copy run-config atartup config 保存信息到NVRAMwrite 保存信息到NVRAMerase startup-config 清除NVRAM中的配置信息show ip interface brief 查看接口的谪要信息banner motd # +信息 + # 配置路由器或交换机的描素信息description+信息配置接口听描素信息vlan database 进入VLAN数据库模式vlan +vlan号+ 名称创建VLANswitchport access vlan +vlan号为VLAN为配接口interface vlan +vlan号进入VLAN接口模式ip add +ip地址为VLAN配置管理IP地址vtp+service/tracsparent/client 配置SW的VTP工作模式vtp +domain+域名配置SW的VTP域名vtp +password +密码配置SW的密码switchport mode trunk 启用中继no vlan +vlan号删除VLANshow spamming-tree vlan +vlan号查看VLA怕生成树议2. 路由器配置命令ip route+非直连网段+子网掩码+下一跳地址配置静态/默认路由show ip route 查看路由表show protocols 显示出所有的被动路由协议和接口上哪些协议被设置show ip protocols 显示了被配置在路由器上的路由选择协议,同时给出了在路由选择协议中使用的定时器等信息router rip 激活RIP协议network +直连网段发布直连网段interface lookback 0 激活逻辑接口passive-interface +接口类型+接口号配置接口为被动模式debug ip +协议动态查看路由更新信息undebug all 关闭所有DEBUG信息router eigrp +as号激活EIGRP路由协议network +网段+子网掩码发布直连网段show ip eigrp neighbors 查看邻居表show ip eigrp topology 查看拓扑表show ip eigrp traffic 查看发送包数量router ospf +process-ID 激活OSPF协议network+直连网段+area+区域号发布直连网段show ip ospf 显示OSPF的进程号和ROUTER-IDencapsulation+封装格式更改封装格式no ip admain-lookup 关闭路由器的域名查找ip routing 在三层交换机上启用路由功能show user 查看SW的在线用户clear line +线路号清除线路二、思科路由器型号Cisco 2500 系列Cisco 2500 系列以太网和令牌环网路由器提供广泛的分支机构解决方案,包括集成的路由器/集线器和路由器/访问服务器模型。
Overview of BFD - Static Route SupportThe BFD - Static Route Support feature enables association of static routes with a static Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) configuration in order to monitor static route reachability using the configured BFD session. Depending on status of the BFD session, static routes are added to or removed from the Routing Information Base (RIB).Unlike dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP, static routing has no method of peer discovery. Therefore, when BFD is configured, the reachability of the gateway is completely dependent on the state of the BFD session to the specified neighbor. Unless the BFD session is up, the gateway for the static route is considered unreachable, and therefore the affected routes will not be installed in the appropriate RIB.For a BFD session to be successfully established, BFD must be configured on the interface on the peer and there must be a BFD client registered on the peer for the address of the BFD neighbor. When an interface is used by dynamic routing protocols, the latter requirement is usually met by configuring the routing protocol instances on each neighbor for BFD. When an interface is used exclusively for static routing, this requirement must be met by configuring static routes on the peers.If a BFD configuration is removed from the remote peer while the BFD session is in the up state, the updated state of the BFD session is not signaled to IPv4 static. This will cause the static route to remain in the RIB. The only workaround is to remove the IPv4 static BFD neighbor configuration so that the static route no longer tracks BFD session state. Also, if you change the encapsulation type on a serial interface to one that is unsupported by BFD, BFD will be in a down state on that interface. The workaround is to shut down the interface, change to a supported encapsulation type, and then reconfigure BFD.A single BFD session can be used by an IPv4 static client to track the reachability of next hops through a specific interface. You can assign a BFD group for a set of BFD-tracked static routes. Each group must have one active static BFD configuration, one or more passive BFD configurations, and the corresponding static routes to be BFD-tracked. Nongroup entries are BFD-tracked static routes for which a BFD group is not assigned. A BFD group must accommodate static BFD configurations that can be part of different VRFs. Effectively, the passive static BFD configurations need not be in the same VRF as that of the active configuration.For each BFD group, there can be only one active static BFD session. You can configure the active BFD session by adding a static BFD configuration and a corresponding static route that uses the BFD configuration. The BFD session in a group is created only when there is an active static BFD configuration and the static route that uses the static BFD configuration. When the active static BFD configuration or the active static route is removed from a BFD group, all the passive static routes are withdrawn from the RIB. Effectively, all the passive static routes are inactive until an active static BFD configuration and a static route to be tracked by the active BFD session are configured in the group. Similarly, for each BFD group, there can be one or more passive static BFD configurations and their corresponding static routes to be BFD-tracked. Passive static session routes take effect only when the active BFD session state is reachable. Though the active BFD session state of the group is reachable, the passive static route is added to the RIB only if the corresponding interface state is up. When apassive BFD session is removed from a group, it will not affect the active BFD session if one existed, or the BFD group reachability status.How to Configure BFD - Static Route SupportConfiguring BFD - Static Route SupportPerform this task to configure BFD support for static routing. Repeat the steps in this procedure on each BFD neighbor. For more information, see the “Example: Configuring BFD Support for Static Routing” section.SUMMARY STEPS1.enable2.configure terminal3.interface type number4.ip address ip-address mask5.bfd interval milliseconds min_rx milliseconds multiplier interval-multiplier6.exit7.ip route static bfd interface-type interface-number ip-address [group group-name [passive]]8.ip route [vrf vrf-name] prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]} [dhcp] [distance] [name next-hop-name] [permanent | track number] [tag tag]9.exit10.show ip static route11.show ip static route bfdConfiguration Examples for BFD - Static Route SupportExample: Configuring BFD - Static Route SupportIn the following example, the network consists of Device A and Device B. Serial interface 2/0 on Device A is connected to the same network as serial interface 2/0 on Device B. In order for the BFD session to come up, Device B must be configured.Device Aconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.1 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.2Device Bconfigure terminalinterface Serial 2/0ip address 10.201.201.2 255.255.255.0bfd interval 500 min_rx 500 multiplier 5ip route static bfd Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1ip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 Serial 2/0 10.201.201.1 Note that the static route on Device B exists solely to enable the BFD session between 10.201.201.1 and 10.201.201.2. If there is no useful static route that needs to be configured, select a prefix that will not affect packet forwarding, for example, the address of a locally configured loopback interface.In the following example, there is an active static BFD configuration to reach 209.165.200.225 through Ethernet interface 0/0 in the BFD group testgroup. As soon as the static route is configured that is tracked by the configured static BFD, a single hop BFD session is initiated to 209.165.200.225 through Ethernet interface 0/0. The prefix 10.0.0.0/8 is added to the RIB if a BFD session is successfully established. configure terminalip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 group testgroup ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 In the following example, a BFD session to 209.165.200.226 through Ethernet interface 0/0.1001 is marked to use the group testgroup. That is, this configuration is a passive static BFD. Though there are static routes to be tracked by the second static BFD configuration, a BFD session is not triggered for 209.165.200.226 through Ethernet interface 0/0.1001. The existence of the prefixes 10.1.1.1/8 and10.2.2.2/8 is controlled by the active static BFD session (Ethernet interface 0/0 209.165.200.225). configure terminalip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225 group testgroup ip route 10.0.0.0 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0 209.165.200.225ip route static bfd Ethernet 0/0.1001 209.165.200.226 group testgroup passiveip route 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0.1001209.165.200.226ip route 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.224 Ethernet 0/0.1001209.165.200.226Additional References for BFD - Static Route Support。