
动词的时和体(Tense and Aspect)
1.1 时,体概说
1)时(Tense):
时(Tense)是一个语法范畴,它是表示时间区别的动词形式。英语动词只有“现在时”和“过去时”,而没有“将来时”。在现代英语中,能用以表示“将来”的语法手段是多种多样的。2)体(Aspect):
体(Aspect)也是一个语法范畴,它表示动作或过程在一定时间内处于何种状态的动词形式。英语动词有两个体:进行体(Progressive Aspect)和完成体(Perfective Aspect)。进行体是由助动词be的一定形式加主动词的- ing分词构成。完成体是由助动词have的一定形式加主动词的-ed分词构成
3)时和体:
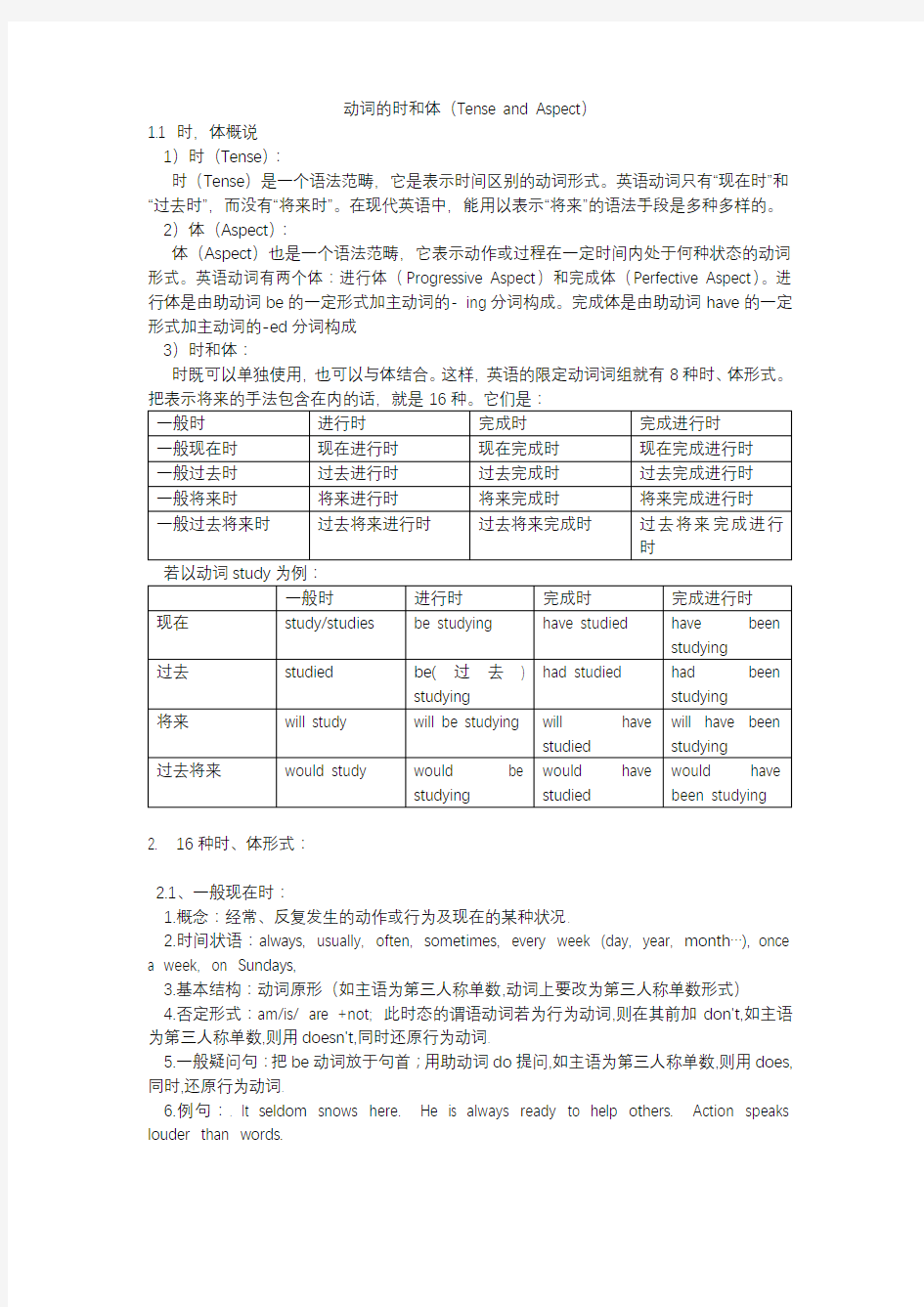
时既可以单独使用,也可以与体结合。这样,英语的限定动词词组就有8种时、体形式。
2. 16种时、体形式:
2.1、一般现在时:
1.概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况.
2.时间状语:always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…),once
a week, on Sundays,
3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)
4.否定形式:am/is/ are +not; 此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词.
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词.
6.例句:. It seldom snows here. He is always ready to help others. Action speaks louder than words.
2.2、一般过去时:
1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为.
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week,last(year, night, month…),in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
3.基本结构:be动词;行为动词的过去式
4.否定形式:was/were +not; 在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词.
6.例句:She often came to help us in those days. I didn't know you were so busy.
2.3、现在进行时:
1.概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为.
2.时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc.
3.基本结构:am/is/are +doing
4.否定形式:am/is/are +not +doing.
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首.
6.例句:How are you feeling today? He is doing well in his lessons.
2.4、过去进行时:
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作.
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等.
3.基本结构:was/were +doing
4.否定形式:was/were + not + doing.
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首.
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit. When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.
2.5、现在完成时:
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态.
2.时间状语:recently, lately, since…for…,in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:have/has + done
4.否定形式:have/has + not +done.
5.一般疑问句:have或has.
6.例句:I've written an article.
The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years.
2.6、过去完成时:
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”.
2.时间状语:before, by the end of last year(term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:had + done.
4.否定形式:had + not + done.
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首.
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left. By the end of last month. We had reviewed four books
2.7、一般将来时:
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事.
2.时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon,in a few minutes, by…,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:am/is/are/going to + do;will/shall + do.
4.否定形式:was/were + not; 在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词.
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首.
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies. It is going to rain.
2.8、过去将来时:
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中.
2.时间状语:the next day(morning, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:was/were/going to + do;would/should + do.
4.否定形式:was/were/not + going to + do; would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首.
6.例句:He said he would go to Beijing the next day. I asked who was going there .
2.9.将来完成时:
1.概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态
2.时间状语:by the time of; by the end of+时间短语(将来);by the time+从句(将来)
3.基本结构:be going to/will/shall + have done
2.10. 现在完成进行时:
1.概念:在过去某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态一直持续到说话为止
2.基本结构:have/has +been+ doing
3. 几种常见时态的相互转换
英语中的几种时态在一定情况下可以互相转换,以下是几种常见的转换形式:
3.1 一般过去时与现在完成时的转换:
在现在完成时中,延续性动词能与表示一段时间的状语连用,瞬间动词却不能.但是,可用别的表达方式:
①瞬间动词用于“一段时间+ ago”的一般过去时的句型中;
②瞬间动词可改成与之相对应的延续性动词及短语,与一段时间连用;
③瞬间动词用于“It is + 一段时间+ since + 一般过去时”的句型中,表示“自从……以来有……时间”的意思,主句一般用it is来代替It has been;
④瞬间动词用于“Some time has passed since + 一般过去时”的句型中.
请看:
A. He joined the League two years ago.
B. He has been in the League for two years.
C. It is two years since he joined the League.
D. Two years has passed since he joined the League.
3.2 一般现在时与现在进行时的转换:
在一般现在时中,at加上名词表示“处于某种状态”,如at work(在工作), at school(上学、上课)等.此短语可与进行时态转换.请看:Peter is at work, but Mike is at play. Peter is working, but Mike is playing.
3.3 现在进行时与一般将来时的转换:
在现在进行时态中go, come, leave, start, arrive等动词常与表示将来的时间状语连用表示将要发生的动作.如:I am coming, Mum! 意为“我就来,妈妈!”
请看:The train is leaving soon.
The train will leave soon.
初中英语语法知识梳理-动词 动词是表示动作(study, find, swim 等)或状态(be, like, feel 等)的词。动词具有人称、数量、时态、语态和语态变化。 知识梳理:提纲挈领,抓住重点和难点! 动词分类:动词有助动词、情态动词、联系动词和行为动词四类。 一)助动词 助动词没有任何含义,不能单独做谓语,只能和行为动词一起构成谓语,帮助行为动词组成各种时态、语态、语气以及疑问或否定形式。常见的助动词有be, do, does, did, have, will, shall 等。具体用法如下: 1、助动词be的用法如下: 1)构成各种进行时态。如: It was raining all day yesterday. 昨天整天下雨。 2)构成被动语态。如: The meeting was held yesterday afternoon. 会议是昨天下午举行的。 3)与不定式连用表示按照计划、预先安排或规定要发生的动作。如: They are to see an English film this evening. 他们今天晚上看英语电影。 2、助动词do的用法如下: 1)构成疑问式或否定式。如: Does he think so? I didn’t say anything about the result. 2)在动词前加上do, does, did表示强调,意为“的确,确实”。如: They do study hard. She does love him. He did want to help the old man. 3、have: 助动词have 的过去式是had。have和had均可与动词过去分词一起构成完成时态。如: He has lived here for three years. As soon as the sun had set they returned. 4、shall, should: 助动词shall只用于第一人称的将来时态;助动词should 是shall的过去式,构成过去将来时。如:I shall send ten letters to my good friend. She wanted to know if I should go to the palace. 二)情态动词 情态动词本身有一定含义,但不能单独作谓语,要和行为动词一起构成谓语。它们也能表明句子的否定、疑问或时态上的区别。常见的情态动词有:can, may, must, need, should等。 表示能力 表示能力一般用can, could。如:Rose can speak now, but she couldn’t a week ago. be able to 也表示能力,它和can 的区别如下:
一、选择题 1.When did your father your mother? A.marry B.marry to C.marry with D.get married 2.—________ Mary________ fruit? —Of course. A.Is; like B.Does; likes C.Does; like D.Do; likes 3.Coffee is ready. How nice it ______! Would you like some? A.looks B.smells C.sounds D.feels 4.A group of little ducks __________ their mother into the river and swim away. A.follow B.miss C.help D.cross 5.Our school basketball team ________ in the final of the basketball competition. Another team from No.5 Middle School ________ doing very well too. A.is; isn’t B.are; aren’t C.is; are D.are; is 6.—What will the weather _______tomorrow? — It is going to_______ . A.be like; rainy B.be like; rain C.like; rain D.like; rainy 7.—How much ________ this pair of shoes? —Five dollars. A.am B.is C.are D.be 8.—William, your hat _______ nice. —Thanks. A.buys B.looks C.finds 9.—I am feeling ill. What should I do? — eating junk food and breakfast every day. A.Stop; having B.Stop; have C.To stop; have. D.To stop; to have 10.—Do you know whom they will have ________the parts of car together?—Sorry,I have no idea. A.fix B.fixed C.to fix D.fixing 11.Karen and Helen _______ my brother's friends. I know _______. A.is; her B.are; them C.are; her D.is; them 12.Many students are so crazy about mobile games that they lose interest in their schoolwork, which _________ their parents and teachers a lot. A.worries about B.is worried about C.worries D.is worried 13.Their eyes __________blue, but ours_________black. A.are; are B.is; are C.are; is . D.are; is 14.— Tom in the library? —Yes,and his friends Eric and Dale in the library,too. A.Is;are B.Is;is C.Are;is 15.—Who are you _______? — My mother.
第三节.动词的体 一. 下面句子中底划线的部分是动词的什么体?请输入( )内。 1) 上の実験で分かるように、広い水面は、いつも 鉛なまり直線ちょくせんと直角ちょっかく になっています。( 存续体,表示结果状态 ) 表示举例。 2) 湾岸わんがん戦争せんそう で毎日人々が死んでいる。( 持续体,表示反复 ) 3) 佐佐木先生は中国に行っている。( 存续体,表示结果状态 ) 4) 自転車はもう買っておいた。( 准备体,事先做好 ) 5) この小説を今週中に読んでしまう。( 完成体, ) 6) やっと支度したく ができて、出かけるところだ。( 即将体 ) 動詞基本形 表示正要做… 動詞た形 +ところだ 表示刚刚做完… 動詞ている形 表示正在做……之中 7) 止まっていたバスが動うご き出した。( 开始体 ) 動詞ます形+出す,表示动作开始,具有不可预料、意外、突然开始的语感 8) 弟は夜間大学に行っている。( 持续体,表示反复进行 ) 9) 10) 台風はゆっくり北上ほくじょう しつつある。( 持续体 ) 動詞ます形+つつある,表示动作情况持续不断的向某个方向进展,发展,书面用语。 11) たけのこはもうこんなに伸びている。( 存续体,表示结果状态 ) たけのこ(竹の子、筍):竹笋 12) 自動車が橋を渡っている。( 持续体,表示正在进行 ) 13) たくさん服を着ているから、暑くてたまらない。( 存续体,表示结果状态 ) 動詞て形+てたまらない,表示……得不行,太……而受不了。 14) 新しい工場がどしどし建っている。( 持续体,表示反复进行 ) どしどし:副词,连续不断地 15) みんなで大木たいぼく を倒している。( 持续体,表示正在进行 ) 二从下面A ?B ?C ?D 中选出正确的答案填入( )内 1) 新鮮な空気が入るように窓が( ) A 開けてある B 開いている C 開けている D 開いてある 2)山下さんの部屋は壁一面に絵がかけて( ) A ある B いる C おく D おる 3)明日は朝起きなければならないから。時計を15分進めて( ) A いこう B こよう C みよう D おこう 動詞準備体:ておく,事先提前做……, 意志形:ておこう,相当于ておきましょう 表示建议 4)経済成長とともに、心が失うしな われて( )ようなきがする。 A くる B いる C いく D ある とともに,与……同时 心が失うしな われている:丢失了心灵,存续体,结果状态
语法填空之动词解题技巧 教学目标: 1.巩固谓语动词和非谓语动词的用法; 2.探究语法填空中动词的解题思路及解题技巧。 教学重难点: 1. 辨别谓语动词和非谓语动词 2. 谓语动词和非谓语动词的解题思路 教学教具:多媒体,黑板,粉笔教学过程: StepI. Warm-up: 听一听,填一填______(hide) from the rain and snow ______(try) to forget but I won't let go Looking at a _____(crowd) street Listening to my own heart ______(beat) So many people all around the world …… Show me that wonders can be true They say nothing______(last)forever We're only here today Love is now or never …… Standing on a mountain high _____(look) at the moon through a clear blue sky I should go and see some friends But they don't really comprehend Don't need too much______ (talk) without saying anything All I need is someone who makes me wanna sing ……
第11讲动词的时和体(一) 11.1一般现在时的用法 一般现在时指未与进行体相结合的现在时形式,通常表示 1.表示不受时限的客观存在 包括客观真理、格言、科学事实及其他不受时限的事实。 2.表示现在习惯动作 这种用法常与频度副词always, ever, frequently, hardly ever, never, occasionally, often, rarely, seldom, sometimes, usually连用,频度副词通常位于主动词之前,如果主动词是be则通常位于其后,也可为了强调而位于其前。 3.表示现时状态和现在瞬间动作 表示现时状态通常都带有一定的持续性,因此只适用于静态动词。 表示现在瞬间的动作通常只适用于表示短暂动作的动态动词,常用于体育运动的实况报导中,也常见于一些戏法表演、技术操作表演等的解说词中,以及一些专门用语或日常用语中。上述用法一般都用第一人称。 4.表示将来时间 这种用法分为三种句型,第一种是在I hope, I bet 等后面的that-分句中可用一般现在时表示将来时间,第二种句型是see(to it)/make sure/make certain+ that-分句,第三种句型是由if/when 引导的条件分句和时间分句。 5.表示过去时间 能用一般现在时表示过去时间的动词有tell, say, hear, learn, gather 等,作为一种修辞手法也可用在叙事文或新闻报导中追述往事以增进描述的生动性和真实感,这就是所谓的“历史性现在时” 11.2一般过去时的用法 一般过去时是未与进行体或完成体相结合的过去时形式,可用于: 1.表示过去时间 主要用来表示在特定过去时间中一次完成的动作或一度存在的状态,也可表示过去的习惯动作。一般过去时所表示的过去时间都与现在时间不发生关系,动作或状态都已成为过去,现已不复存在。 2.表示现在时间和将来时间 一般过去时可用在特定句型中表示现在时间和将来时间,表示婉转口气或作想象性用法。 第一种情况是表示婉转语气,只限于want, wonder, think, hope 等少数几个动词。 第二种情况是在It’s time …, I wish …, I’d rather …等结构后面的that-分句中,以及在某些条件句中,表示主观设想。既可表示于现在事实相反主观设想,也可表示与现在事实相反或者表示对将来事态的主观设想,这种情况都不能改用一般现在时。 11.3现在进行体的用法 现在进行体是由助动词be的现在时形式(am,is,are)加-ing分词构成。可用于: 1.表示说话时正在进行的动作 表示现在在做什么,能用于现在进行体的动词一般都是表示持续动作的动态动词,往往带有暂时的含义 2.表示现阶段一直在进行的动作 这种动作在说话时不一定正在进行,这种用法也表示一种暂时性,常与always,continually,constantly,for ever等频度状语连用,对现阶段经常发生的动作表示某种感情色彩 3.表示按计划安排近期内即将发生的动作 这是表示将来的用法,通常是按照现在的计划安排近期内即将发生,还常见于某些时间
日语动词“四大体” 一、持续体 形式:~ている 接续:动词连用形(て形)+~ 用法: ①表示动作的进行。 例:◇李さんはいま居間でテレビを見ています。 ◇待っていますから、早く来てください。 ②表示状态的持续(或结果的存留)。(多用于短暂性动词或状态性动词) 例:◇黄さんはもう教室に来ています。 ◇その金魚は死んでいる。 ◇たくさんの花が咲いている。 ◇花子さんは太っている。 ③表示经常反复的动作或状态。 例:◇毎朝ここで運動をしている人は王さんのおじいさんです。 ◇わたしは毎朝朗読をしているんです。 二、准备体 形式:~ておく 接续:动词连用形(て形)+~ 用法: ①表示“为……事先做好准备”。 例:◇人の家を訪ねる前に、電話を掛けておいた方がいいです。 ◇ともかく彼の意見を聞いておこう。 ◇この点は今皆さんにはっきりと言っておかなければならない。 ②表示“(使)某种状态保持下去”。 例:◇テレビはそのままにしておいてください。 ◇彼の才能を遊ばせておくのはもったいない。/不充分发挥他的才能是种浪费。 ◇記念に写真を撮っておきましょう。 注: 「~ておく」后项可以用命令,请求,意志等。 三、存续体 形式:~てある 接续:动词连用形(て形)+~ 用法:
①表示动作结果的存续,主语是动作涉及的对象,即他动词的宾语。 例:◇壁に地図が掛けてあります。 ◇庭には木が植えてある。 ◇窓が開けてあります。 注:A、表示现在的状态后项不用过去时。 B、动词前面的助词用「が」、不用「を」。 C、主语是物。 ②表示已做好了某事或做过了某事。 例:◇電話を掛けて、いくと言ってあるから、待っているだろう。 ◇すみません、李さんと約束をしてありますから。 ◇宿題はもうしてあります。 注:A、表示现在的状态后项不用过去时。 B、动词前面的助词可以用「を」。 C、主语是一般是人。 四、完成体 形式:~てしまう/~でしまう 接续:动词连用形(て形)+~ 用法: ①表示一种动作的完了。 例:◇その小説は一日で読んでしまった。 ◇両親からもらったお金はみな使ってしまった。 ◇三日で復習してしまうつもりで、今一所懸命勉強している。 ②表示一种不希望发生的事情,或发生了一种令人遗憾的事情。 例:◇うちのかわいい猫は死んでしまった。 ◇うっかりして指を切っちゃうよ。 ◇電車で財布を取られてしまったんです。 注:口语中「~てしまう」变成「~ちゃう」、「~でしまう」变成「~じゃう」。 一,什么是动词的体 动词所表现的动作,作用有的可以是一个过程,即存在着动作作用的开始, 进行和结束等阶段。动词的体就是记述动作,作用等处于何种进行情况的语法范畴。 体就其表现形式来讲非常丰富,这些表现形式有动词连用形+て+补助动词,
语法填空专项训练(动词) 一解法探究语法填空中,提示词为动词时,从几方面考虑? Group One 解题并思考,本组题的考点是什么? 1. After a four-day journey, the young man ______ (present) the water to the old man. His teacher took a deep drink, smiled warmly and thanked ...(2010广东) 2. Every few years, the coal workers _____(have) their lungs X-rayed to ensure their health. (2010 上海) 3. … people stepped on your feet or _____(push) you with their elbows, hurrying ahead to get to a bargain. (2009广东) 小结:本组题考查动词时态。如果一个句子没有谓语动词,或者虽然已有谓语动词,但所填的动词与之是并列关系,就确定填动词谓语,谓语动词首先要考虑时态。 Group Two:解题并思考,本组题的考点是什么? 3. Her mother was excited. “ Your father has at last decided to stop smoking,” Jane ____ (inform) (09 广东) 4. Linda, make sure the tables ______ (set) before the guests arrive. (2010全国II) 小结:本组题考被动语态。确定填谓语动词之后,不仅要考虑时态,也要考虑语态。 Group Th ree:解题并思考,本组题的考点是什么? 5. After the student left, the teacher let another student taste the water. He spit it out, ______ (say) it was awful. (2010广东) 6. With Father’s Day around the corner, I have taken some money out of the bank _______(buy ) presents for my dad. ((2010全国1) 7. Alexander tries to get his work _______ (recognize) in the medical circles. (2010 辽宁) 小结:本组题考查非谓语动词。如果一个句子已有谓语动词,且不是并列谓语, 就要考虑非谓语(-ing形式、过去分词或不定式), 然后分析该非谓语动词在句子中作什么成分,再根据非谓语动词各自的特点和用法,同时看谓语动词有没有特别的要求,再结合与逻辑主语是主动关系或被动关系,确定该填哪种形式。 Group Four:解题并思考,本组题的考点是什么? 8. John is very ______ (rely) --- if he promises to do something, he’ll do it. 9. The patient is seriously ill and is being kept under continuous _____ (observe). 小结:本组题考词语派生。分析句子结构,当所给动词不充当谓语或非谓语,必须弄清要填的词在句子中充当哪种句子成分,做该成分需要哪种词类的词,把括号中的词转换成相应的词类。 比较 (一) 1.The film which is popular among young people _____ (produce) last year. 2.The film ____ (produce) last year was popular. 3.We all like the film which ____ (produce) last year. (二) 1.I know Mr. Brown. We _____ (introduce) to each other at an international conference. 2.I know the man ______ (introduce) to me by my friend at an international conference.
第8单元动词(一) (一)动词的种类 动词是表示动作或状态的词,按其词义和在句子中的作用可分为行为动词,连系动词, 助动词和情态动词。 1.行为动词 行为动词可分为及物动词(vt)和不及物动词(vi),及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,后跟宾语;不及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作 谓语,但后面不能直接跟宾语,如要带宾语则与介词或副词构成短语。 『例』 Thestudentsarelisteningtotheteachercarefully.(vi) 2.连系动词 连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。常用的连 系动词有be,get,turn,become,look,feel,grow,seem,sound,taste,smell等。 『例』 3.助动词 助动词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能和主要动词一起构成谓语动词,表示否定, 疑问及动词的时态、语态、人称和数等语法特征,助动词有be,do,have,shall,will等。『例』 Thechildrenareplayingyo- 4.情态动词 情态动词本身有一定的意义,但不能独立作谓语,只能和主要动词原形一起构成谓语, 表示说话人的语气和情态。情态动词没有人称和数的变化。情态动词有can (could),may(might),must,need,oughtto,dare等。 『例』CanIhelpyou? -Mustwegonow? –No,youneedn’t. a.can与beableto的用法有所区别。can只用于一般现在时和过去时,指本身有能力的“能”;beableto用于各种时态均可,指须经过努力而“能”。 b.must与have/hasto的用法。must表示说话人主观认为“必须”,只用于一般现在时和一般将来时;have/hasto表示客观需要,意为“不得不”,它可用于各种时态。 c.need和dare既可作情态动词也可作行为动词。 (二)动词不定式 动词不定式todo没有人称和数的变化,在句中不能独立作谓语,但可以和助动词或情态动词构成谓语,又可以在句子中作宾语、宾语补足语、状语、定语、主语、表语等。但 它毕竟是动词,因此,具有动词的许多特点,如它可以有自己的宾语或状语构成不定式 短语。 1.作主语: 『例』 但实际上不定式作主语常用it来作形式主语,而将不定式移至谓语动词后作真正的主语。
一、选择题 1.—Would you like to try some pizza? —Yes, please. It lovely and nice. A.sounds, sees B.looks, smells C.hears, turns D.sounds, watches 2.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister. A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cry C.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry 3.These chicken wings taste ________. I want more. A.well B.wonderfully C.nice D.bad 4.Parents always hope their children a happy and healthy life. A.to live B.can live C.living D.should live 5.The teacher's smile made me ________ better. A.feel B.to feel C.feeling D.felt 6.—Listen! I can hear someone __________ for help. —Is there __________? A.calling; anything wrong B.call; anything wrong C.calling; wrong anything D.call; wrong anything 7.—_______everyone get tired today? —Yes, we_______very tired the whole afternoon. A.Does; are all B.Do; are all C.Does; all are D.Is; all are 8.The library ______ from 8 a.m. to 3 p.m. on weekdays. But it______ at 5 p.m. on Saturdays and Sundays. A.is open; closes B.opens; closed C.is opened; closes D.is opening; is closed 9.Which of the following sentences is right? A.My books on the desk B.Nice meet you, too C.These are my dictionaries D.Thanks you for your help. 10.—When you free last week? — Well, I have a free day because there was too much work. A.did; didn’t B.were; didn’t C.were; wasn’t D.did; wasn’t 11.The shopping mall near our school _________ for 12 hours a day. It _________ at 9:00 p.m.. A.opens; closes B.opens; is closed C.is open; is closed D.is open; closes 12.Hard work can bring you , but if you are lazy, you won’t become . A.success; success B.successful; success C.success; successful D.successful; succeed 13.—Where_______you come from? —I______from Japan A.are; am B.are; come C.do; come
2010年中考英语汇总--动词的分类概念:表示动作中状态的词叫做动词。 动词的分类 1.按照在句子中的功能,动词可分为四类:实义动词、系动词、助动词、情态动词。 说明:某些情况下,有些动词既可做实义动词,又可做助动词,例如: We are having a meeting.我们正在开会。(having是实义动词。) He has gone to New York.他已去纽约。(has是助动词。) 2. 按照后面是否有宾语,分为两类:及物动词(vt)、不及物动词(vi)。 说明:同一动词有时可用作及物动词,有时可用作不及物动词。例如: She can dance and sing.她能唱歌又能跳舞。(sing在此用作不及物动词。) She can sing many English songs. 她能唱好多首英文歌曲。(sing用作及物动词。) 3. 根据是否受主语的限制,分两类:限定动词、非限定动词。例如: She sings very well. 她唱得很好。(sing受主语she的限制,故用第三人称单数形式sings.) She wants to learn English well. 她想学好英语。(to learn不受主语she的限制,没有词形变化,是非限定动词。) 说明:英语中共有三种非限定动词,分别是:动词不定式、动名词、分词。 在这里我们多说一下to+动词原型,和ing形式。英语不同于我们的汉语,不可以两个动词联用。如,我们汉语说,我喜欢吃苹果。其中“喜欢”和“吃”是两个动词,汉语这样说没有问题,如果翻译成英语,就变成了“I like eat apple.”这种说法按照英语的规定是不对的。那怎么办呢,于是就在两个动词之间多了一个“to”,或者把第二个词加上ing.于是就变成了“I like to eat apple.或者I like eatting apple”这样说来,动词是不是很简单啦! 4.根据动词的组成形式,可分为三类:单字词、短语动词、动词短语。例如: The English language contains many phrasal verbs and verbal phrases. 英语里有许多短语动词和动词短语。(contains是单字动词。) Students should learn to look up new words in dictionaries. 学生们学会查字典。(look up是短语动词。) The young ought to take care of the old. 年轻人应照料老人。(take care of是动词短语。) 5.动词有五种形态:原形、第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词、现在分词。
动词的时(tense)体(aspect)态(voice)式(mood)概说 1.动词的时、体形式 时是一个语法范畴,他是表示时间区别的动词形式。 体是一个语法范畴,他表示动作或过程在一定时间内处于何种状态的动词形式。英语动词有两个体,进行体和完成体。 由此可见,英语的限定动词词组有八种时、体形式。 一般现在时(simple present) She plays the piano very well. 一般过去时(simple past) She played the piano very well when she was young. 现在进行体(present progressive) She is playing the piano now. 过去进行体(past progressive) She was playing the piano this time yesterday. 现在完成体(present perfective) She has played the piano for half an hour. 过去完成体(past perfective) she had played the piano for an hour before went to lunch. 现在完成进行体(present perfective progressive) She has been playing the piano for a long time. 过去完成进行体(past perfective progressive)
By 10 o’clock she had been playing the piano for two hours. 2.主动态和被动态 语态是一个语法范畴,他表示主语和谓语动词之间的主动或被动关系的语法形式。英语动词有两种语态,主动态和被动态。 被动态可以由助动词be 的一定形式加及物动词的-ed分词构成. 被动语态也有不同的时体形式。 一般现在时 The boy is regarded as brilliant. 一般过去时 This book was published in 1998. 现在进行体 The visitors are being met at the airport. 过去进行体 He told me that the machine was being repaired. 现在完成体 The car has been repaired. 过去完成体 Last month, the new road had been opened to traffic. 被动态还可以由get+及物动词的-ed分词构成,在这里,get起助动词的作用。 The boy got hurt on his way home. get型被动态通常只适合动态动词,常用来表示某些未曾预料的突发事件,或者用于in the end,eventually,at last等连接性状语之后表示某种结局。 He got caught by the police driving at 60 km/s through Cambridge.
语法填空之动词 一、动词时态 1.一般现在时do,does 习惯性动作,客观事实,主语特征或状态,按时刻表发生的动作The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. 被动:am /is /are done She is loved by all her students.(强调动作被施加者) 2.一般过去时did 过去发生的动作,过去习惯性动作 When I was a child, I always went to that park and played there. 被动:was/ were done The book was published in 1932.(不知道动作施加者) 3.一般将来时will do, am/ is /are going to do 将要发生的动作或打算 Look at the dark clouds. It is going to rain. 被动:will be done When will the work be finished? 4.现在进行时am /is /are doing 说话时或现阶段正在进行的动作,强调赞叹厌恶等的情绪 Tom is always coming late for meetings.(总是迟到) Look, our friends are waiting for us outside. 被动:am /is /are being done Is the accident now being looked into? 5.现在完成时have/ has done 已完成的动作(对现在有影响),从过去开始持续到现在的动作He has made a lot of friends since he came to Beijing. 被动:have/ has been done The sports meeting has been put off until next Friday. 6.过去将来时would do,was/ were going to do 站在过去看将来 He said he would visit the Palace Museum the next week. 被动:would be done I was told that the press conference would be held the next day. 7.过去进行时was / were doing 过去某一时刻或阶段正进行的动作 They were watching TV when I came in. 被动:was/ were being done The car was being mended when you meant to drive it away. 8.过去完成时had done 过去的过去 They had learned Chinese for a year before they came to China. 被动:had been done The room had been broken before we came.
一、选择题 1.What a beautiful song! It ___________so sweet. A.feels B.sounds C.tastes D.smells 2.—Do you like watching cooking programs on TV? —No, I don’t , but my twin brother . He's very fond of cooking. A.does B.do C.is D.are 3.—________ Mary________ fruit? —Of course. A.Is; like B.Does; likes C.Does; like D.Do; likes 4.These chicken wings taste ________. I want more. A.well B.wonderfully C.nice D.bad 5.The strawberries delicious. You can have a try. A.eat B.drink C.taste D.sound 6.Parents always hope their children a happy and healthy life. A.to live B.can live C.living D.should live 7.The woman made her husband_______ outside the gate yesterday afternoon. A.wait B.waiting C.to wait D.waited 8.A group of little ducks __________ their mother into the river and swim away. A.follow B.miss C.help D.cross 9.I think the music is great , and it is worth________ A.to listen B.to listen to C.listening D.listening to 10.—William, your hat _______ nice. —Thanks. A.buys B.looks C.finds 11.Which of the following sentences is right? A.My books on the desk B.Nice meet you, too C.These are my dictionaries D.Thanks you for your help. 12.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister. A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cry C.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry 13.—The books on the table_________ Mike’s, right? —Yes, they are. A.am B.is C.are 14.— Tom in the library? —Yes,and his friends Eric and Dale in the library,too. A.Is;are B.Is;is C.Are;is 15.—Would you like to try some pizza? —Yes, please. It lovely and nice. A.sounds, sees B.looks, smells C.hears, turns D.sounds, watches
1)、15課ています动词的持续体 意义:一般在表示具体动作的动词后面时,动词持续体表示正在进行的动作或是经常、反复进行的动作。除此之外则表示动作结果的存续。 私は今お茶を飲んでいます。 私はセーターを着ています。 今日の新聞はまだ読んでいません。 その時、わたしは遊んでいませんでした。 田中さんはアパートに()でいます。―――――住む 2)、てあります(32課动词存续体108) 用他动词加“てあります”的形式,可以表示事物保持着某人动作的结果所造成的状态。事物用格助词が表示。 冷蔵庫に、肉やビールが入れてあります。(他動詞) 冷蔵庫に、肉やビールが入っています。(自動詞) テーブルの上に、食器が並べてあります。 日記には旅行について詳しく書いてあります。 3)、ておきます(33課122) 准备体 表示事先做好某种准备。 明日出発します。今日準備をしておきます。 友達が来るので、部屋を片付けておきましょう。 先に電話をかけておいて、友達を訪ねたほうがいいでしょう。
(给朋友先打个电话再去拜访比较好吧) 昼ご飯と晩ご飯を作っておいて、仕事に出掛けました。 (做午饭时把晚饭一起做了,然后才去上班) ふだんしっかり勉強しておけば、試験の前にそんなに遅くまで勉強しなくてもいいです。(如果平时好好学习的话,考试前就不用学到那么晚。) そのことはもう手紙で(頼んで)おきました。―――頼む 4)、てしまいます(33課122 ) 完成体 表示动作、作用全部结束。 この本はもう読んでしまいました。 有时表示无可挽回、遗憾的心情。 もう長い間使っていないから、使い方は忘れてしまうでしょう。 (已经好久没有用了,使用方法恐怕已经忘了吧。) 空港で両替するのを忘れてしまいました。 あの人は病気で三十五歳で死んでしまいました。 (那个人三十五岁就病逝了。)