化学专业英语学习Word版
- 格式:doc
- 大小:249.50 KB
- 文档页数:20

第一章单词表E u b a c t e r i a真细菌Prokaryote 原核生物A r c h a e b a c t e r i a原细菌Eukaryote 真核生物G r a m-po s i t i v e革兰氏阳性菌f r a c t i o n a t i o n分级、分馏G r a m n e g a t i v e b a c t e r i a革兰氏阴性菌b i o m o l e c u l e生物分子C y a n ob a c t e r i a蓝细菌o r g a n i s m生物体、有机体P l a s m a细胞浆m e m b r a n e膜M e s o s o m e间体nu c l e u s细胞核N u l e o i d拟核c o cc i球菌S y t o s o l细胞质、原生质b a c illi杆菌B il a y e r双分子层(膜)s p i r ill a螺旋菌P r o t e i n蛋白质L i p i d脂类Refresh 更新Carbohydrate 糖类、碳水化合物M i t o c h o n d r i a线粒体o s m o t i c p r e ss u r e渗透压o x i d a t i v e p h o s p h o r y l a t i o n氧化磷酸化P e p t i dog l y c a n肽聚糖f a tt y a c i d脂肪酸S u b c e ll u l a r亚细胞的d e g r a d a t i o n降解G a n e ll e细胞器C h l o r op l a s t s叶绿体G e n e t i c遗传的t h y l ak o i d v e s i c l e s类囊体C h r o m o s o m e染色体p h o t o s y n t h e s i s光合作用r i bo s o m a l r i bo nu c l e i c a c i d r R N A L y s o s o m e s溶酶体E n dop l a s m i c r e t i c u l u m内质网M a c r o m o l e c u l e大分子P h o s p h o li p i d磷脂Enzyme 酶D e t o x i f i c a t i o n解毒C y t o s k e l e t o n细胞支架G o l g i a pp a r a t u s高尔基体M e t a bo li c新陈代谢的C e n t r i f u g a t i o n离心A li p h a t i c脂肪族的I s o l a t e分离A r o m a t i c芳香族的E q u ili b r i u m平衡P o l a r极性的D e n s i t y密度Charged 带电荷的F r i c t i o n摩擦力G l y c i n e G l y,甘氨酸V e l o c i t y速率a l a n i n e A l a,丙氨酸Supernatant 上清夜v a li n e V a l,缬氨酸P e ll e t沉淀l e u c i n e L e u,亮氨酸第二章A m i n o a c i d氨基酸E n a n t i o m e r s对映体T e t r a h e d r a l正四面体的H y d r op h ob i c疏水的、憎水的i s o l e u c i n e I l e,异亮氨酸m e t h i o n i n e M e t,甲硫氨酸p r o li n e P r o,脯氨酸c y s t i n e C y s,半胱氨酸P h e n y l a l a n i n e P h e,苯丙氨酸T y r o s i n e T y r,酪氨酸T r y p t op h a n T r p,色氨酸A s p a r a g i n e s A s n,天冬酰胺G l u t a m i n e G l n,谷氨酰胺S e r i n e S e r,丝氨酸T h r e o n i n e T h r,苏氨酸V a r g i n i n e A r g,精氨酸L y s i n e L y s,赖氨酸H i s t i d i n e H i s,组氨酸a s p a r t i c a c i d A s p,天冬氨酸g l u t a m i c a c i d G l u,谷氨酸base 碱c a r bo x y l羧基i s o e l e c t r i c po i n t等电点po s i t i v e正的、阳性的n e g a t i v e负的、阴性的b u ff e r i n g缓冲p h y s i o l og i c a l生理的P r i m a r y s t r u c t u r e一级结构Secondary structure 二级结构T e r t i a r y s t r u c t u r e三级结构Q u a t e r n a r y s t r u c t u r e四级结构p e p t i d e bo n d肽键sequence 顺序、序列c o v a l e n t Bo n d共价键po l y p e p t i d e多肽t e r m i n a l末端c a r bo n y l羰基resonance structures 共振结构r i g i d刚性的rotate 旋转t r a n s c o n f i g u r a t i o n顺式构象d i s u l f i d e bo n d s二硫键α-h e li xα-落选hydrogen bond 氢键β-p l e a t e d s h ee tβ-折叠片p a r a ll e l平行的a n t i p a r a ll e l反平行的r a n do m c o il无规卷曲un i q u e唯一的s p a t i a l空间的a rr a n g e m e n t排列、安排li n e a r s e q u e n c e线性序列r e s i d u e残基H y d r op h ob i c i n t e r a c t i o n疏水相互作用I n t e r i o r内部的E l e c t r o s t a t i c f o r c e静电力s a l t b r i dg e盐桥、盐键v a n d e r W aa l s f o r c e范德华力s u b un i t亚基a ll o s t e r i c e ff e c t变构效应N o n c o v a l e n t i n t e r a c t i o n s非共价相互作用p r o t e i n s t a b ili t y蛋白质的稳定d i m e n s i o n a l空间的、维的proton 质子donor 供体、赠与者l o n e p a i r o f e l e c t r o n s孤对电子c o lli n e a r在同一直线上H yd r op h ob i c f o r c e疏水力N o n po l a r非极性M i n i m i z e最小化p r o t e i n f o l d i n g蛋白质折叠A cc e ss o r y p r o t e i n辅助蛋白质m o l e c u l a r c h a p e r o n e s分子伴侣M y og l ob i n肌红蛋白H e m og l ob i n血红蛋白p r o s t h e t i c g r o u p辅基e ss e n t i a l必需的heme 血红素c r e v i c e缝隙p r o t opo r p h y r i n原卟啉po r p h y r i n卟啉ferrous 含铁的p r o x i m a l最接近的c oop e r a t i v e协同的n o n c oop e r a t i v e非协同的d i ss o c i a t i o n c u r v e解离曲线s i g m o i d a l S形曲线h y p e r bo li c双曲线C o ll a g e n胶原蛋白a ff i n i t y亲和性S k i n皮肤b l oodc a p ill a r i e s血管Bone骨骼Bohr effect波尔效应Tendon腱2,3-b i p h o s p h og l y c e r a t e2,3-二磷酸甘油酸C a r t il a g e软骨M e c h a n i s m机制b l ood v e ss e l血管R e l a x e d s t a t e松弛状态m a mm a l哺乳动物tense state紧张状态f i b r o u s纤维状的h e m og l ob i n op a t h i e s血红蛋白分子病t r i p e p t i d e三肽的S i c k l e-c e ll a n e m i a镰刀形细胞贫血症t r i p l e-h e li c a l三股螺旋的Erythrocyte红血球c r o ss-li n k e交联s t i c k y p a t c h粘性小区A ll y s i n e醛基赖氨酸t h e r a p e u t i c治疗的A n t i bod i e抗体i mm un e s y s t e m免疫系统pathogen 病原体t r i gg e r引发、触发response 响应、应答a n t i g e n抗原a n t i g e n i c d e t e r m i n e抗原决定簇e p i t op e抗原决定簇I mm un o l o c a li z a t i o n免疫定位A n t i bod y抗体E n z y m e-li n k e d i mm un o s o r b e n t a ss a yE L I S A酶联免疫吸附测定p u r i f i c a t i o n提纯、纯化H o m og e n i z a t i o n匀浆s o l u b ili z a t i o n溶解A mm o n i u m s u l f a t e硫酸铵P r e c i p i t a t i o n沉淀D i a l y s i s透析C h r o m a t og r a p h i c t e c h n i q u e s层析技术g e l f il t r a t i o n凝胶过滤a ff i n i t y c h r o m a t og r a p h y亲和层析E l e c t r op h o r e t i c t e c h n i q u e s电泳技术i s o e l e c t r i c f o c u s i n g等电聚焦S D S po l y a c r y l a m i d e g e l e l e t r op h o r e s i sSDS 聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳s e m i-p e r m e a b l e半透性2-m e r c a p t o e t h a n o l2-巯基乙醇li g a n d配基n i n h y d r i n茚三酮i n e r t惰性的f l u o r e s c a m i n e荧光胺m a t r i x基质f l u o r od i n i t r ob e n z e n e二硝基氟苯e l u t e洗出、流出d a n s y l c h l o r i d e丹磺酰氯l e c t i n外源凝集素p h e n y l i s o t h i o c y a n a t e P I T C苯异硫氰酸g l y c op r o t e i n糖蛋白酯m o l e c u l a r s i e v e分子筛f r a g m e n t片断、碎片po l y a m p h o l y t e s聚两性电解质e n c od i n g编码g r a d i e n t梯度d e c i p h e r解读、破译m i g r a t e迁移、移动anchor 锚定c h y m o t r y p s i n胰凝乳蛋白酶s e q u e n c i n g测序第三章b i oc a t a l y s t生物催化剂a c t i v e s i t e活性中心R i bo z y m e核酶substrate底物Abzyme抗体酶T h e i n d u c e d–fit m od e l诱导契合学说c a t a l y t i c a n t i bod y抗体酶S t e r e o s p e c i f i c i t y立体异构专一性a n a l og类似物S p e c i f i c i t y专一性assay 化验、测定T r y p s i n胰蛋白酶op t i m a l最佳的E l a s t a s e弹性蛋白酶Coenzyme辅酶O x i do r e d u c t a s e氧化还原酶Cofactor 辅因子Transferase 转移酶apoenzyme脱辅酶H y d r o l a s e水解酶h o l o e n z y m e全酶Lyase 裂合酶a c e t y l c h o li n e s t e r a s e乙酰胆碱酯酶I s o m e r a s e异构酶N i c o t i n a m i d e烟酰胺L i g a s e连接酶A d e n i n e腺嘌呤D i nu c l e o t i d e二核苷酸I s o e n z y m e s同功酶Phosphate 磷酸K i n e t i c动力学O x i d a t i o n氧化l a c t a t e d e h y d r og e n a s e乳酸脱氢酶r e d u c t i o n还原p r opo r t i o n a l成比例的F l a v i n黄素saturate使饱和M o n o nu c l e o t i d e单核苷酸t h e r m a l热的A c y l酰基d e n a t u r a t i o n变性t h i a m i n e p y r op h o s p h a t e焦磷酸硫胺素op t i m u m最适宜的d e c a r bo x y l a s e脱羧酶d i v e r s i t y多样性P y r i do x a l吡哆醛M i c h a e li s-M e n t e n e q u a t i o n米氏方程P y r i do x a m i n e吡哆胺do u b l e-r e c i p r o c a l p l o t双倒数作图法P y r i do x i n e吡哆醇i n h i b i t i o n抑制U b i q u i n o n e泛醌I n h i b i t o r抑制剂M e t a bo li t e代谢物Branched 分支的I rr e v e r s i b l e不可逆的C o n f o r m a t i o n a l构象的R e v e r s i b l e可逆的h o m o t r op i c e ff e c t同促效应C o m p e t i t i v e竞争性的h e t e r o t r op i c e ff e c t异促效应N o n c o m p e t i t i v e非竞争性的P h o s p h o f r u c t o k i n a s e磷酸果糖激酶Probe 探测C i t r a t e柠檬酸盐C li n i c a ll y临床上F r u c t o s e2,6b i s p h o s p h a t e2,6-二磷酸果糖R e g u l a t i o n调节p h o s p h o r y l a t i o n磷酸化c o mm i tt ed s te p关键步骤d e p h o s p h o r y l a t i o n去磷酸化a c t i v a t o r激活剂h y d r o x y l羟基A d j u s t调节h o r m o n e激素Feedback反馈G l y c og e n p h o s p h o r y l a s e糖原磷酸化酶S e q u e n t i a l连续的P h o s p h o r y l a t e使磷酸化g l y c og e n s y n t h a s e糖原合酶boundary 边界un p h o s p h o r y l a t e使去磷酸化c o m p a r t m e n t s小室p r o t e o l y t i c蛋白质水解的M e c h a n i c a l机械的p r o e n z y m e s酶原s i g n a li n g发信号zymogen酶原i n s o l u b l e不可溶的h y d r o l y s i s水解g l y c e r op h o s p h o li p i d s甘油磷脂类p a n c r e a t i c胰腺的s p h i n go li p i d s鞘脂类pancreas 胰腺s t e r o l s固醇类s m a ll i n t e s t i n e小肠g l y c e r o l甘油b l oodc l o tt i n g血液凝固s p h i n go s i n e鞘氨醇a m p li f i c a t i o n扩大s p h i n go m y e li n s鞘磷脂cascade 级联c h o l e s t e r o l胆固醇第四章s t e r o i d类固醇A m p h i p a t h i c两性的H y d r op h ili c亲水的B u l k y体积大的s e l f-a ss e m b l e自组装的f l u i d i t y流动性r o t a t i o n a l转动的l a t e r a l侧向的F l u i d m o s a i c m od e l流体镶嵌模型I n t e g r a l整体的、内在的F li p翻跟头i n t e g r a l m e m b r a n e p r o t e i n s内在膜蛋白p e r i p h e r a l m e m b r a n e p r o t e i n s外周膜蛋白a s y mm e t r y不对称a s y mm e t r i c a ll y不对称地m e mb r a n e-s p a n i n g p r o t e i n跨膜蛋白M u l t i p l e多重的L i p i d-a n c h o r e d p r o t e i n s脂锚定蛋白H e t e r o ka r y o n异核体F u s i o n融合R e c o n s t i t u t i o n重建R e i n c o r po r a t e d重新合并E x t r a c e ll u l a r细胞外的I n t e r c e ll u l a r细胞内的P a ss i v e t r a n s po r t被动运输a c t i v e t r a n s po r t主动运输c o n c e n t r a t i o n浓度受体介导的内吞作d i ff u s i o n扩散用s a t u r a b l e可饱和的d e b r i s碎片f a c ili t a t e d协助的、推动的t r a n s d u c t i o n转导s y m po r t同向运送L i pop h ili c亲脂性的a n t i po r t逆向运送Receptors 受体e p i t h e li a l c e ll s上皮细胞s e c o n d m e ss e n g e r s第二信使e x o c y t o s i s分泌作用e n do c y t o s i s内吞作用p h a go c y t o s i s吞噬作用p i n o c y t o s i s胞饮作用R e c e p t o r m e d i a t e d e n do c y t o s i sf u s i o n 第五章N u c l e i c a c i d核酸R e p li c a t i o n复制N u c l e o t i d e核苷酸P y r i m i d i n e嘧啶G u a n i n e鸟嘌呤T h y m i n e胸腺嘧啶t e m p l a t e模板C y t o s i n e胞嘧啶p r i m e r引物N u c l e o s i d e核苷fork叉D e o x y r i bo nu c l e o s i d e脱氧核糖核苷B i d i r e c t i o n a l双向的r i bo nu c l e o s i d e核糖核苷O ka z ak i f r a g m e n t s冈崎片段d e o x y r i bo nu c l e o t i d e脱氧核糖核苷酸s e m i-d i s c o n t i nu o u s半不连续的genes 基因strand 链、一股c o m p l e m e n t a r il y互补地h y b r i d i z a t i o n杂交nu c l e o s o m e核小体m e l t i n g t e m p e r a t u r e熔融温度l oop突环r e n a t u r a t i o n复性rosette玫瑰花结l a b e l e d标记的s e m i-c o n s e r v a t i v e半保留的f l u o r e s c e n t荧光的po l y m e r a s e聚合酶tag 标记、标签a nn e a li n g退火a m p li f y增强、扩大T h e c e n t r a l dog m a中心法则g e n e t i c c od e遗传密码i n t e r m e d i a t e中间的、媒介codons 密码子T r a n s c r i p t i o n转录un a m b i g u o u s明确的i n i t i a t i o n起始correspond 相应、符合E l o n g a t i o n延伸degenerate 简并的t e r m i n a t i o n终止m u t a t i o n变异p r o m o t e r s启动子i n c o r po r a t i o n合并p a li n d r o m e回文结构n o n o v e r l a pp i n g不相重叠的p r o c e ss i n g加工r e a d i n g f r a m e s阅读框s p li c i n g拼接a m i n o a c y l-t R N A氨酰-t R N A r e v e r s e t r a n s c r i p t i o n逆转录p e p t i d y l-t R N A肽酰-t R N A 第六章s t e m茎、干、臂a n t i c odo n反密码子C e ll u l o s e纤维素t r a n s l o c a t i o n移位D e x t r a n葡聚糖第七章A m y l o s e直链淀粉m e t a bo li s m代谢a m y l op e c t i n支链淀粉S a cc h a r i d e s糖类G l y c o l y s i s糖酵解m o n o s a cc h a r i d e s单糖C y t op l a s m细胞质a l d e h y d e g r o u p醛基G l u c o s e葡萄糖ketone group 酮基G a l a c t o s e半乳糖S t e r e o i s o m e r s立体异构体M a nn o s e甘露糖O li go s a cc h a r i d e s寡糖Sucrose 蔗糖G l y c o s i d i c bo n d糖苷键T r e h a l o s e海藻糖P o l y s a cc h a r i d e s多糖Lactose 乳糖Starch 淀粉H e x o k i n a s e己糖激酶Fructose 果糖e n o l a s e烯醇化酶P h o s p h og l u c o i s o m e r a s e磷酸葡萄糖变位酶pyruvate 丙酮酸B i s p h o s p h a t e二磷酸G l u c o n e og e n e s i s糖异生g l y c e r a l d e h y d e s甘油醛N o n c a r b h y d r a t e非糖的d i h y d r o x y a ce t o n e二羟丙酮L i v e r肝脏a l do l a s e醛缩酶s k e l e t a l m u s c l e骨骼肌t r i o s e丙糖p h o s p h o r y l a s e磷酸化酶1,3-b i s p h o s p h og l y c e r a t e1,3二磷酸甘油酸P h o s p h o r o l y s i s磷酸化dehydrogenase 脱氢酶p y r op h o s p h o r y l a s e焦磷酸化酶3-p h o s p h og l y c e r a t e3-磷酸甘油酸g l u c o s y l葡萄糖基k i n a s e激酶n o n r e d u c i n g e n d非还原端m u t a s e变位酶E p i n e p h r i n e肾上腺素p h o s p h o e n o l p y r u v a t e磷酸烯醇式丙酮酸g l u c a go n胰高血糖素I n s u li n胰岛素k e t o n e bod i e s酮体第八章acetoacetate 乙酰乙酸f a tt y a c i d脂肪酸D-3-h y d r o x y b u t y r a t e D-3-羟基丁酸hydrocarbon 烃、碳氢化合物Acetone 丙酮c a r bo x y li c a c i d羧酸d i a be t e s糖尿病Unsaturated 不饱和的t o x i c有毒的T r i a c y l g l y c e r o l三酰甘油l e t h a l致命的A c e t y l乙酰基m u l t i f un c t i o n a l多功能的T h i o e s t e r硫酯m a l o n y l丙二酰基C a r n i t i n e肉(毒)碱c a r bo x y l a t i o n羧化H y d r a t i o n水合作用c o n d e n s a t i o n缩合T h i o l y s i s硫解a c e t o a c e t y l乙酰乙酰基C o n s u m e消耗h y d r o x y b u t y r y l羟丁酰基c r o t o n y l丁烯酰基i s o c i t r a t e异柠檬酸酸盐b u t y r y l丁酰基α-k e t og l u t a r a t eα-酮戊二酸h yd r o l y z a t i o n水解作用s u cc i n a t e琥珀酸盐p a l m i t o y l软脂酰基s u cc i n y l琥珀酰基p a l m i t a t e软脂酸f u m a r a t e延胡索酸盐li pop r o t e i n s脂蛋白m a l a t e苹果酸盐g l ob u l a r球状的o x a l o a c e t a t e草酰乙酸盐m i c e ll e胶束、微囊c y t o c h r o m e细胞色素第九章o x i d a s e氧化酶R e s p i r a t i o n呼吸作用reductase 还原酶c i t r i c a c id c y c l e柠檬酸循环、三羧酸Rotatory 旋转的循环e n g i n e发动机c o n c o m i t a n t伴随的第十章N i t r og e n氮urea 尿素D i e t常吃的食物vertebrates脊椎动物Erythrose 赤藓糖o r n i t h i n e鸟氨酸R i bo s e核糖a r g i n i n e精氨酸T r a n s a m i n a t i o n转氨基作用c i t r u lli n瓜氨酸D e a m i n a t i o n脱氨基作用p e r m a n e n t l y不变地T r a n s d e a m i n a t i o n联合脱氨基作用A mm o n i a氨Excrete 排泄A q u a t i c水生u r i c a c i d尿酸t e rr e s t r i a l陆生的r e p t il e爬行动物。
第一章化学专业英语词汇化学化工词汇有专业词汇量大和合成词汇多的特点。
由科学出版社1984年出版的“英汉化学化工词汇”就收集了相关词汇12万余条。
掌握一定的化学化工专业词汇和构词方法是学好化学专业英语的基础。
1 无机化合物1.1tetra-, mono- 后缀中的a, o在后一o之前省去,在不会引起歧义时,这些前缀都尽可能被省去。
如:1.2 后缀1.2.1 二元化合物(含有两种元素)(1)阳离子部分是固定价态的金属元素,阴离子部分为非金属元素阳离子用元素名表示,阴离子需加后缀-ide。
如:fluoride,chloride,bromide,iodide,oxide ,sulfide ,(2)阳离子部分是可变价态的金属元素,阴离子部分为非金属元素在Stock/IUPAC 命名法中阳离子用元素名表示,并在元素名后的括号中用罗马数字注明价态数,阴离子需加后缀-ide。
-ic,阴离子加后缀-ide。
(3)由两种非金属组成的化合物除了水和氨气使用俗称water,ammonia以外,其它的非金属化合物阳离子用元素名表示,阴离子需加后缀-ide。
对于卤族和氧族氢化物,H在对于其它族的非金属氢化物,H在化学式中写在后面,可加后缀-ane,氮族还可加-ine。
(4)以-ide结尾的特殊情况OH,CN,NH的化合物阴离子部分也以-ide为后缀。
(5) 23),表示酸时,H原子用前缀-hydro表示,阴离子以后缀-ic结尾,并加上词acid表示酸。
命名规则:hydro-词根-ic acid。
如HCl: hydrochloric acid.在无机酸(盐)中的偏、焦、连等有相应的词缀偏meta- 如meta-arsenic acid 偏砷酸HAsO3原(正)ortho- 如ortho-tungstic acid 原钨酸焦pyro- 如pyro-phosphorate 焦磷酸盐连、次hypo 如hypoboric acid 连二硼酸;hypohloric acid 次氯酸过(高)per 如perchloric acid 高氯酸重di 如dichromate 重铬酸盐1.2.2 三元化合物(含有三种元素)三元化合物阳离子部分是金属元素或氢,阴离子部分是一个多原子离子。

化学专业英语培训资料unite 1. Inorganic chemistry1.1 what is chemistry(1). 重点专业词汇讲解:Chemical: adj . 化学的、化学药品Transformation: 变化,化学转变,转化Dye: n. 染料染色,或者vt. 染Charcoal: ['t?ɑk??l] 木炭Cellulose :纤维素细胞的['selj?l??z; ]Fat:n. 脂肪肥肉adj . 肥大的alkalis:碱adj . 碱性的glycerin: 甘油丙三醇alkalis: n. 碱金属alloy: 合金使成合金bronze:青铜色的n. 青铜(铜和锡的合金)brass:[brɑs] n. 黄铜(铜和锌)要求学生会区别黄铜及青铜的不同翻译Poison:毒物毒药t. 毒害放毒下毒Proton:n. 质子Nulei: n. 核(nucleus的复数形式)['njukl??s]Identical : adj . 同一的Chirality n. 手性手征和Handeness的区别Amino acid :n. 氨基酸Alanine: n.丙氨酸2. 课文中重点词组(phrase)Chemical change: 化学变化physical change:物理变化Explore: 探险研究research investigate studyIsolate: 分离chemical bonds 化学键chemical reaction:化学反应Natural substance 天然物质Coke :焦炭carbon monoxide 一氧化碳Carbon Dioxide 二氧化碳Chemical bond 化学键fundamental principle 基本原理The periodic table of elements :元素周期表numbers of protons 质子数atomic number 原子序数covalent bonds 共价键positive 正阳性negative 负阴性3. 课文中重点句子The first and most important principle is that chemical substances are made up of molecules in which atoms of various elements are linked in well-defined ways. 需要着重给学生讲解第一条也是最重要的原理是化学物质是有分子组成的,分子中的不同元素的原子是以一定的方式连接在一起的。

(完整word版)有机化学专业英语烷基Alkyl [ˈælkil ]芳基aryl [ˈæril ]甲基methyl [ˈmeθil]亚甲基methylene [ˈmeθili:n ]乙基ethyl [ˈeθil,ˈeθəl]丙基propyl [ˈprəupil]异丙基isopropyl [ˌaisəuˈprəupil]丁基butyl [ˈbju:til]戊基pentyl [ˈpentil]己基hexyl [ˈheksil]庚基heptyl [ˈheptil]辛基octyl [ˈɔktəl]壬基nonyl [ˈnɔnil]奎基decyl [’desəl][di:’s i l]叔丁基tert-butyl异丁基iso-butyl环戊基cyclopentyl []环己基cyclohexyl []甲氧基methoxyl [’metɒksɪl]乙氧基ethoxyl [eˈθɔksil]丁氧基butoxyl酰基 acyl [ˈæsil]甲酰基formyl [ˈfɔ:mil]乙酰基acetyl [ˈæsitil]乙烯基vinyl [ˈvaɪnəl]或ethenyl丁烯基butenyl [ˈbjutənil]己烯基hexenyl庚烯基heptenyl [ˈheptəˌnil]烯丙基allyl [ˈælil]乙炔基ethinyl [eˈθainil]或alkynyl硝基nitro [ˈnaitrəu]亚硝基nitroso [naiˈtrəusəu]氨基amino [əˈmi:nəʊ,ˈæməˌnəʊ] 二氨基diamino亚氨基imino [ˈiminəu,iˈmi:nəu]重氮基diazo [daiˈæzəu]苯基phenyl [ˈfenəl,ˈfi:nəl,ˈfi:nil] 苄基benzyl [ˈbenzil]或phenmethyl [ˌfinˈmeθil]苯乙基phenethyl [fenˈeθəl]乙氧苯基ethoxyphenyl 苯胺基anilino [ˈænili:n]羰基carbonyl [ˈkɑ:bənil]羧基carboxyl [kɑ:ˈbɔksil]联苯基biphenyl [baiˈfenl]甲酰基formyl [ˈfɔ:mil]苯酰,苯甲酰benzoyl [’benzəʊɪl]脒基guanyl [il]羟基hydroxyl [haiˈdrɔksil]烷氧基alkoxy [ælˈkɔksi]或alkoxyl group芳基 aryl group二芳基diaryl group [daiˈæril]吡啶基pyridyl [ˈpiridil]三苯甲基trityl[’traɪtl]二苯甲基benzhydryl [benaɪd’raɪl]氨基甲酰基carbamoyl[kɑ:'bæməɪl]三甲基硅基trimethylsilyl炔丙基propargyl [prəʊ’pɑ:dʒɪl]丙酮基(乙酰甲基)acetonyl ['æsɪtənɪl]正n,normal异iso邻位ortho—[ˈɔ:θəu]间位meta- ['mɛtə]对位para—[ˈpɑ:rə]伯Primary [’praimәri]仲Secondary [’sekәndәri]叔Tertiary ['tә:ʃәri] tert-季碳quaternary [kwəˈtə:nəri] carbon一,单mono-二di-,双bis ,bi(化学中只有碳酸氢根才用bi,如bicarbonate [baiˈkɑ:bənit])三tri-,tris四tetra- 四quadric-五penta—五quinque—六hexa—七hepta—七septi八octa-九nona—十deca- [’dɛkə]十一undeca ,hendeca-十二dodeca-十三trideca-十四tetradeca(完整word版)有机化学专业英语十五pentadeca-十六hexadeca—十七heptadeca-顺式,cis—同,共syn反式trans有机化合物类名Aliphatic compound 脂肪族化合物[]Hydrocarbon 碳氢化合物[ˌhaɪdr əˈkɑ:b ən ]Alkane 烷[]Wax 蜡[]Paraffin wax 石蜡arene 芳烃[]Alkene 烯[]Alkyne 炔[ˈælkain]Acetylide 炔化物[]Active hydrogen compounds 活泼氢化合物acid [ˈæsid]Carbon acid 碳氢酸Super acid 超酸Diene 双烯[ˈdaii:n]Triene 三烯[ˈtraii:n ]Allene 丙二烯[ˈæli:n]Propylene丙烯[]cumulene 累积多烯[]Enyne 烯炔[eˈni:n]Diyne 二炔Alkyl halide 卤代烷[ˈælkil ˈhælaid]Alcohol 醇[]Homoallylic alcohol 高烯丙醇Ether 醚[ˈi:θə]Ester 酯[ˈestə]Ketone 酮Aldehyde 醛[ˈældihaid]Epoxide 环氧化物[eˈpɔksaid]Sulfone 砜[ˈs ʌlf əun]Sulfoxide 亚砜Sulfonic acid 磺酸Carboxylic acid 羧酸Cellosolve 溶纤剂Crown ether 冠醚Nitro compound 硝基化合物Amine 胺[]Quaternaryammonium compound 季铵化合物[][]Amine oxide 氧化胺Diazoalkane 重氮烷[daɪ,æzəʊ’ælkeɪn]Mercaptan 硫醇[]Aldehyde hydrate 醛水合物Ketone hydrate 酮水合物Hemiacetal 半缩醛[ˌhemiˈæsitæl]Acetal 缩醛acetal [化]乙缩醛, 乙缩醛二乙醇[ˈæsitæl] Ketal 缩酮[ˈki :tæl]thiazole 噻唑[ˈθai əˌzəul]Dithiane 二噻烷[daiˈθai ən]Aminal 缩醛胺;动物imine 亚胺[]Aldimine 醛亚胺Oxime 肟[]nitroso compound 亚硝基化合物aldoxime 醛肟,乙醛肟[ælˈdɔksi:m]Hydrazone 腙[ˈhaidrəˌzəun]Azine 嗪[ˈæzi:n]Semicarbazone 缩氯基脲Cyanohydrin 羟腈, 氰醇[ˌsaiənəuˈhaidrin] Pinacol 频哪醇Enol 烯醇[ˈi:nɔl]Enol ether 烯醇醚Enol ester 烯醇酯[ˈi:nɔl][ˈest ə] Enamine 烯胺[i ˈn æmin]Ynamine 炔胺Mannich base 曼尼希碱orthoester 原酸酯Acyl halide 酰卤[ˈæsil]Acyl fluoride 酰氟[] Acyl chloride 酰氯Acyl bromide 酰溴Acyl iodide 酰碘[ˈaiədaid]Carbobenzoxy chloride 苄氧甲酰氯Acyl tosylate 酰基对甲苯磺酸酐Ketene 乙烯酮[ˈki:ti:n]Peracid 过酸Perester 过酸酯Acyl peroxide 酰基过氧化物Nitrile 腈[ˈnaitrail](完整word版)有机化学专业英语acetonitrile 乙腈[ˌæsitəuˈnaitril]或met hyl cyanide [ˈsaɪəˌnaɪd]Nitrile oxide 氧化腈Isonitrile 异腈,异氰化物Amide 酰胺[ˈæmaid]Imide 二酰亚胺[ˈimaid]N—bromo compound N—溴化物Hydrazide 酰肼[]Azide 叠氮化物[ˈæzaid,ˈeizid]Acyl azide 酰基叠氮[ˈæsil][ˈæzaid,ˈe izid]Amidine 脒[ˈæmiˌdi:n]Keto ester 酮酸酯Acyl cyanide 酰腈[ˈæsil][ˈsaɪəˌnaɪd]Carbon suboxide 二氧化三碳Glycidic acid 环氧丙酸Carbammic acid 氨基甲酸Carbamate 氨基甲酸酯[ˈkɑ:bəmeit]Urea 脲,尿素[]Cyanamide 氨腈[saiˈænəmaid]Carbodiimide 碳二亚胺[,kɑ:bədai'imaid] Allophanate 脲基甲酸酯Thioester 硫代酸酯[ˌθaiəuˈestə]Thiol acid 硫羰酸[ˈθaiəu]Lactone 内酯[ˈlæktəun]Lactol 内半缩醛[ˈlæktəl]Macrolide 大环内酯[ˈmækrəlaid]Amino acid 氨基酸Zwitterion两性离子[ˈtsvitəraiən]Inner salt 内盐Betaine 甜菜碱[ˈbi:təi:n]Lactam 内酰胺[ˈlæktæm]Hydantoin 或glycolylurea 乙内酰脲[haiˈdæntəwin]Hydration水合,水合作用[haɪ'dreʃən] Peptide 肽[ˈpepˌtaɪd]Glycol 乙二醇[]Aldol 羟醛[ˈældəul]Acyloin 偶姻,酮醇[əˈsiləuin]acyloin condensation 酮醇缩合Carbohydrate 碳水化合物Aldose 醛糖[ˈældəus]Ketose 酮糖[ˈki:təus]Furanose 呋喃糖[ˈfjuərəˌnəus]Pyranose 吡喃糖[ˈpaiərənəus]Glycoside 糖苷[ˈɡlaikəˌsaid]Glucoside 葡[萄]糖苷Aglycon 苷元[əˈɡlaikɔn]Saccharide 糖类[ˈsækəraid]Oligosaccharide 寡糖[ˌɔliɡəuˈsækəraid] Polysaccharide 多糖[pɔliˈsækəraid]Alditol 糖醇[ˈælditɔl]Osazone 脎[ˈəusəˌzəun]Alicyclic compound 脂环化合物[æliˈsiklik]Cycloalkane 环烷Cycloalkene 环烯Spirane 螺烷[ˈspaiərein]Cage compound 笼型化合物Propellane 螺桨烷Rotazane 轮烷Catenane 索烃[ˈkætnein ]Fused ring 稠环[fju:zd riŋ]化学专业英语词汇常用前后缀—acetal 醛缩醇acetal—乙酰acid 酸-al 醛alcohol 醇-aldehyde 醛alkali- 碱allyl 丙烯基'alkoxy- 烷氧基Methoxy甲氧基的-amide 酰胺[]amino- 氨基的[əˈmi:nəʊ,ˈæməˌnəʊ]-amidine 脒[ˈæmiˌdi:n]—amine 胺—ane 烷anhydride 酐[ænˈhaidraid]anilino- 苯胺基[ˈænili:n]aquo—含水aqueous水的,水成的[ˈeikwiəs]-ase 酶—ate 含氧酸的盐、酯-atriyne 三炔azo- 偶氮[ˈæzəu]azoxy—氧化偶氮—N=N(O)—(完整word版)有机化学专业英语hydrazo—氢化偶氮 -NH-NH—benzene 苯[ˈbenˌzi:n, benˈzi:n] bi —在盐类前表示酸式盐bis- 双-borane 硼烷[ˈbəurein]bromo—溴butyl 丁基.—carbinol 甲醇carbonyl 羰基-caboxylic acid 羧酸centi- 10-2chloro—氯代cis—顺式condensed 缩合的、冷凝的cyclo- 环deca—十deci 10—1di二-dine 啶dodeca- 十二—ene 烯epi—表epoxy- 环氧[]-ester 酯—ether 醚ethoxy- 乙氧基[]ethyl 乙基fluoro—或fluor—氟代—form 仿—glycol 二醇hemi- 半hendeca—十一hepta- 七heptadeca- 十七hexa—六hexadeca—十六-hydrin 醇hydro—氢或水hydroxyl 羟基hypo—低级的,次-ic 酸的,高价金属-ide 无氧酸的盐,酰替胺,酐-il 偶酰—imine 亚胺/iodine 碘[] iodo—碘代iso—异,等,同-ite 亚酸盐keto—酮ketone 酮—lactone 内酯mega —106meta- 间,偏methoxy—甲氧基methyl 甲基micro—10-6milli- 10-3mono—( mon—) 一,单nano- 10-9nitro- 硝基nitroso—亚硝基nona- 九nonadeca—十九octa- 八octadeca —十八-oic 酸的-ol 醇9 a $f! Q, H: [5 n& G—one 酮ortho—邻,正,原—ous 亚酸的,低价金属oxa- 氧杂—oxide 氧化合物-oxime 肟[]oxo- 酮[]oxy- 氧化[]-oyl 酰para—对位,仲penta- 五pentadeca- 十五per- 高,过petro- 石油phenol 苯酚[ˈfi:nəl]phenyl 苯基[]pico—10—12poly—聚,多(完整word版)有机化学专业英语quadri- 四quinque- 五semi- 半septi- 七sesqui 一个半sulfa—磺胺[]sym- 对称syn —顺式,同,共ter—三—tetra- 四tetradeca—十四tetrakis—四个thio- 硫代[]trans- 反式,超,跨tri- 三trans- 反式,超,跨tri- 三trideca- 十三tris- 三个undeca- 十一。

专业英语词汇Unit 1TEXT A : Chemical Reactions and Group Reactionscustomary a. 通常的,惯例的handle n.柄vt.触摸handling n.处理,管理derive vt.取得,得到,衍生oxidate vt.使氧化oxidation n.satisfactory a.令人满意的,符合要求的rapid a.快的,迅速的,动作快的combustion n.燃烧somewhat pron. ad. 一点点,几分,有点effort n.努力commercial a.商业的,商务的undesirable a不.合需要的,不受欢迎的,讨厌的retard vt.延迟,放慢,使停滞transformer n.变压器transform vt.改变,转变automotive a.自动的,机动的,汽车的cracked裂化的sluge n.软泥,淤泥stiff a.硬的,强烈的extent 广度,程度distillation n.蒸馏distill vt.vi.unrefined a.未精致,未提炼的acidity n.酸味,酸性acidify vt. Vi.Involve vt. 包缠,卷缠Fell=followingIndividual a.个人的,个体的Presumable a可.假定的,可推测的Destruction n.破坏,毁灭Overall n。
a.全面的,综合的Exceed 超过,胜过Isolate vt.隔离,孤立,使离析iso—构词成分“均匀”“异构”“苯”Analyse vt. 分析,分解Carbonyl 羰基Carboxyl羧基Hydroxyl羟基Decomposition分解Alkyl烷基,烃基Ketone 酮Aldehyde n.醛Yield vt. 出产,产出Explosive a. 爆炸Vapor n.蒸汽, vi.蒸发Propagation 繁殖,增殖;传播Dehydrate vt.使脱水Acet 构词成分Acetaldehyde乙醛Resin n.树脂Resinous a.树脂的Carboxylic a.羟基的Substantial a.物质的,实质的Susceptible a易.受感动的,敏感的Analogous a.类似的,相似的( to)Response n.作答,回答,响应,反应Readily ad.乐意地,很快地Readiness n准.备就绪,愿意Extent n.广度长度Steric 空间的,位的Likewise ad.同样的,照样地;也,又Suffer vt.遭受,经历Progressive a进.步的,长进的,渐次的Adjacent a.邻近的,紧挨着的Terminal a.末端的,终点的MethyleneBromide n.溴化物Substitute n.代替物(人),代用品substitution n.代替,替换Remote a相.隔较远的Acetone n.丙酮Ether n.醚,乙醚Correspond vi.符合,一致;相当,相应Reservation n保.留,预定Tend vi.走向,趋向。

01 THE ELEMENTS AND THE PERIODIC TABLE01 元素和元素周期表The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is referred to as the atomic number, or proton number, Z. The number of electrons in an electrically neutral atom is also equal to the atomic number, Z. The total mass of an atom is determined very nearly by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. This total is called the mass number, A. The number of neutrons in an atom, the neutron number, is given by the quantity A-Z.在一个原子核中的质子数量被称为原子序数,或质子数,Z。
在一个电中性原子中的电子数量也等于原子序数,Z。
一个原子的总质量被测定是非常接近于原子核中质子和中子的总数。
这个总数被称为质量数,A。
在一个原子中的中子数量等于A – Z的数量。
The term element refers to, a pure substance with atoms all of a single kind. To the chemist the "kind" of atom is specified by its atomic number, since this is the property that determines its chemical behavior. At present all the atoms from Z = 1 to Z = 107 are known; there are 107 chemical elements. Each chemical element has been given a name and a distinctive symbol. For most elements the symbol is simply the abbreviated form of the English name consisting of one or two letters, for example:这个术语(指chemical element)也可以指由相同质子数的原子组成的纯化学物质。

化学及化工专业词汇英语翻译(D-I)daguerreotype 达盖尔银版daily output 日产量dalton's law 道尔顿定律daltonide 道尔顿式化合物dammar 达玛尸dammar varnish 达玛胶漆damper 减震器daniell cell 丹聂耳电池dark color 深色dark line 暗线dark plaster 黑石膏dark reaction 暗反应database 资料库dative bond 配价键daturine 天仙子胺dawsom gas 半水煤气deacetylation 脱乙酰基deacidification 脱酸化deacon process 迪肯制氯法deactivation 去活dead burning 烧结dead burnt gypsum 烧石膏dead gold 消光金dead roasting 完全焙烧dead space 死空间dead time 无感时间deaeration 除汽deaerator 除汽器脱泡器dealkylation 脱烃酌deamidase 脱酰氨基酶deaminase 脱氨酶deamination 脱氨基酌deasphalting 脱沥青debenzolized oil 脱苯油deblooming 脱荧光debris 碎屑debromination 脱溴debye photograph 德拜摄影debye scherrer's method 德拜谢乐法debye's characteristic temperature 德拜特性温度decaborane 癸硼烷decahydronaphthalene 十氢化萘decalcification 脱钙decalin 十氢化萘decane 正十烷decanoic acid 癸酸decantation 倾析decanter 倾析器decarbonization 脱碳decarboxylation 脱羧酌decarburation 脱碳decatizing 蒸呢decay 衰变decay constant 衰变常数decay curve 衰变曲线dechlorinating agent 脱氯剂dechlorination 脱氯decinormal 十分之当量的decoction 煎decolorimeter 去色力计decoloring 脱色decolorization 脱色decolorizer 脱色剂decolorizing agent 脱色剂decolorizing carbon 脱色炭decomposition 分解;腐败decomposition heat 分解热decomposition point 分解点decomposition pressure 分解压力decomposition product 分解产物decomposition reaction 分解反应decomposition voltage 分解电压decontaminate 净化decontamination 消除污染decontamination agent 去污剂decortication 剥外皮decyl alcohol 癸醇decyl mercaptan 癸硫醇decylamine 癸胺decylene 癸烯decylic acid 癸酸decyltrichlorosilane 癸基三氯硅烷deep freeze refrigeration plant 深冷设备deep freezer 深冷器deep refrigeration 深度冷冻defecation 澄清defensive protein 防御蛋白质deferrization 除缺definite composition 一定组成deflagration 暴燃deflocculant 反絮凝剂deflocculating agent 反絮凝剂deflocculation 反絮凝defoamer 去沫剂defoaming agent 去沫剂deformation 变形deformation vibration 形变振动degasification 除气degasifier 除气器degassing 除气degeneracy temperature 简并温度degenerate rearrangement 退化重排degeneration 退化degradation 递降degras 油余物degreaser 脱脂器degreasing 脱脂degreasing agent 脱脂剂degreasing equipment 脱脂器degree of association 连带度degree of branching 支化度degree of crosslinking 交联度degree of dissociation 离解度degree of electrolytic dissociation 电离度degree of fineness 细度degree of freedom 自由度degree of hydrolysis 水解度degree of ionization 电离度degree of orientation 取向度degree of polycondensation 缩聚度degree of polymerization 聚合度degree of saturation 饱和度degree of superheat 过热度degree of swelling 溶胀度degree of tannage 度degree of vacuum 真空度degree of vulcanization 硫化度degumming 脱胶dehalogenation 脱卤酌dehumidifier 减湿器dehydrase 脱水酶dehydrated alcohol 无水酒精dehydrated castor oil 脱水蓖麻油dehydrating agent 脱水剂dehydrating gasoline 脱水汽油dehydrating tower 脱水塔dehydration 脱水dehydrator 脱水器dehydrochlorination 脱氯化氢dehydrocyclization 脱氢环化dehydrogenase 脱氢酶dehydrogenation 脱氢deicer 除冰剂deicing agent 除冰剂deionization 消电离deionized water 脱离子水delayed action 延迟酌delayed coagulation 缓凝delayed coking 延迟焦化delayed elasticity 延迟弹性delayed ignition 延迟点火delayed reaction 迟缓反应delignification 去木质素deliming 脱灰deliquescence 潮解delivery volume 排出容积delocalization energy 非定域能delphinidin 花翠素delphinine 翠雀宁苷delta metal 合金delustering 消光delustering agent 消光剂delustrant 消光剂demasking 解蔽demethylation 脱甲基demijohn 酸瓶demineralization 脱盐demineralizer 脱盐器demulsification 反乳化demulsification number 反乳化值demulsifier 反乳化剂denaturant 变性剂denaturation 变性denatured alcohol 变性酒精denatured protein 变性蛋白质denatured state 变性状态dendritic crystal 枝状晶体denier 旦尼尔denitration 脱硝denitrification 脱氮densimeter 密度计densimetric titration 密度滴定densitometer 密度计density 密度density bottle 比重瓶density gradient centrifugation 密度梯度离心法dental alloy 补齿合金dental cement 补齿水泥dental plaster 牙科石膏deobstruent 泻剂deodorant 脱嗅剂deodorization 脱嗅deodorizer 除嗅器deodorizing 脱嗅deoiling 脱油deoxidant 脱氧剂deoxidation 脱氧deoxidizer 脱氧剂deoxidizing agent 脱氧剂deoxy sugar 脱氧糖deoxyalizarin 去氧茜素deoxycorticosterone 去氧皮质甾酮deoxymannose 脱氧甘露糖deoxyribonuclease 脱氧核糖核酸酶deoxyribonucleic acid 脱氧核糖核酸deoxyribose 脱氧核糖dephlegmation 部分冷凝dephlegmator 分馏柱depilating agent 脱毛剂depilation 脱毛depilatory 脱毛剂depolarization 消偏振酌depolarization degree 去偏光度depolarizer 去极化剂depolymerization 解聚depolymerized rubber 解聚橡胶depolymerizing agent 解聚剂deposit 矿床;沉淀物deposition potential 沉积电位depot 贮藏物质depressimeter 冰点降低计depression of vapor pressure 蒸汽压下降depressor 抑制剂depropanizer 脱丙烷塔depropanizing column 脱丙烷塔deproteinization 脱蛋白质depside 缩酚酸depsidone 缩酚酸环醚depth type filtration 深度过滤derby red 铬红derivative 衍生物derivative polarography 微分极谱法derivative thermometric titration 微分温度滴定derived protein 衍生蛋白质derived unit 导出单位derris 鱼藤酮desalted water 脱盐水desalting 脱盐descending method 下行法desensitization 减敏现象desensitizer 减感剂desensitizing dye 减感染料desiccant 干燥剂desiccating agent 干燥剂desiccation 干燥desiccator 干燥器design of experiments 实验设计desilication 硅氧淋失酌desilverization 脱银desilylation 脱甲硅基desired value 预定值desizing agent 退浆剂desmine 束沸石desmo enzyme 不溶酶desmolase 碳链分解酶desmotrope 稳变异构物desmotropism 稳变异构性desolvation 去溶剂化desorption 解吸附destruction 破坏destructive distillation 分解蒸馏destructive distillation of wood 木材干馏desulfurating agent 脱硫剂desulfuration 脱硫desulfurizer 脱硫器deswelling 消溶胀detection 检验detection coefficient 检波系数detection limit 探测极限detector 检验器detergent 清洁剂deterioration 降解determinant 行列式determination 测定determination of molecular weight 分子量测定detonating cord 引爆线detonating fuse 引爆线detonating gas 爆鸣气detonating primer 雷管detonation 爆震detonation velocity 爆震速度detonator 雷管deuteration 氘化deuterium 氘deuterium oxide 氧化氘deuteron 氘核deuton 氘核devarda's alloy 迪氏铝铜锌合金developed dye 显色染料developer 显影剂developing agent 显影剂developing bath 显色浴developing out paper 显相纸developing solution 显影液development 显影development center 显影中心development factor 显影因素deviation 偏差deville furnace 德威尔炉devitrification 失透devulcanization 脱硫devulcanizer 脱硫器devulcanizing agent 脱硫剂dew point 露点dew point boundary 露点边界dew point depression 露点降低dew point pressure 露点压力dewar flask 杜瓦瓶dewar vessel 杜瓦瓶dewaxing 脱蜡dextran 葡萄聚糖dextrin 糊精dextrorotatory 右旋性dextrorotatory compound 右旋化合物dextrose 右旋糖diabase 辉绿岩diacetate 二醋酸盐diacetin 二醋精diacetone 双丙酮diacetone alcohol 双丙酮醇diacetyl 双乙酰diacetylene 丁二炔diacetylmorphine 二乙酰吗啡diacid base 二元碱diad 二价元素diagometer 电导计diagram 图表dialdehyde 二醛dialkyl sulfate 二烷基硫酸盐dialkylarsine 二烃基胂dialkylate 二烃化合物diallyl 联丙烯diallyl phthalate 己二烯酞酸酯diallyl sulfide 烯丙基硫醚dialuric acid 径尿酸dialysate 透析液dialysis 透析dialytic coefficient 可透系数dialyzator 渗析器dialyzer 渗析器diamagnetic substance 反磁物质diamagnetism 反磁性diamide 二酰胺diamine 二元胺diamine oxidase 二胺氧化酶diaminobenzene 二氨基苯diaminodiphenyl 联苯胺diaminophenol 二氨基苯酚diaminophenol hydrochloride 盐酸二氨基苯酚diamond 金刚石diamyl ether 二戊醚diamyl phenol 二戊基酚diamylamine 二戊胺dianisidine 邻联茴香胺diaphanometer 透闷diaphorase 心肌黄酶diaphragm 隔膜diaphragm cell 隔膜电解槽diaphragm manometer 膜片压力计diaphragm process 隔膜法diaphragm pump 隔膜泵diaphragm type pressure gauge 膜片压力计diapositive film 反底片diarsine 联胂diarylamine 二芳基胺diasolysis 溶胶渗析diaspore 水铝石diastase 淀粉糖化酶diastatic enzyme 糖化酶diastatic power 糖化力diastereoisomer 非对映异构体diastereoisomerism 非对映异构性diastereomer 非对映异构体diastimeter 距离测定计diathermancy 透热性diatom 硅藻diatom earth 硅藻土diatomaceous earth carrier 硅藻土载体diatomaceous earth support 硅藻土载体diatomic molecule 二原子分子diatomite 硅藻土diazinon 地亚农diazo reaction 重氮反应diazoamino compound 重氮氨基化合物diazoaminobenzene 重氮胺基苯diazobenzeneanilide 重氮胺基苯diazocompound 重氮化合物diazole 二唑diazomethane 重氮甲烷diazonium 重氮diazonium salt 重氮盐diazotate 重氮酸盐diazotation 重氮化diazotization 重氮化diazotization titration 重氮化滴定diazotype 重氮印相法dibasic 二元的dibasic acid 二元酸dibazol 地巴唑dibenzyl 二苄基diborane 乙硼烷dication 双阳离子dichlone 二氯萘醌dichloramine 二氮胺dichloride 二氯化物dichloroacetic acid 二氯醋酸dichlorobenzene 二氯苯dichloroethane 二氯乙烷dichloroethyl ether 二氯乙醚dichlorofluoromethane 二氯氟甲烷dichloromethane 二氯甲烷dichloropentane 二氯戊烷dichroism 二向色性dichromate 重铬酸盐dichromatic dye 双色染料dicyan 氰dicyandiamide 氰基胍dicyclohexyl adipate 己二酸二环己酯dicyclohexyl phthalate 酞酸二环己酯dicyclohexylamine 二环己基胺didecyl adipate 己二酸二癸基酯didecyl ether 二癸基醚didecyl phthalate 邻苯二甲酸二癸酯didymium 钕镨混合物die casting 压模铸造dieldrin 狄氏剂dielectric 电介质dielectric breakdown 介质哗dielectric constant 介电常数dielectric drying 高频烘烤dielectric loss 介电损耗dielectric polarization 电介质极化dielectrometer 介质测试仪dielectrometry 介电滴定diels alder reaction 二烯合成diene 二烯diene polymerization 二烯聚合diene synthesis 二烯合成diene value 二烯值dienestrol 双烯雌酚diesel engine 柴油机diesel fuel 柴油机燃料diesel oil 柴油diesterase 二酯酶diethanolamine 二乙醇胺diethyl ether 乙醚diethyl ketone 二乙酮diethyl maleate 马来酸二乙酯diethyl malonate 丙二酸二乙酯diethyl phenyl urea 二乙基苯基脲diethyl phthalate 酞酸二乙酯diethyl succinate 丁二酸二乙酯diethyl sulfate 硫酸二乙酯diethyl tartrate 酒石酸二乙酯diethyl thiourea 二乙硫脲diethylamine 二乙胺diethylbenzene 二乙苯diethylene glycol 二甘醇diethylurea 二乙脲differential chemical reactor 微分化学反应器differential equation 微分方程式differential extraction 微分萃取differential flotation 优先浮选differential flowmeter 差动量计differential manometer 差示压力计differential method 差动法differential polarography 差示极谱法differential refractometer 差示折光计differential solvent 差示溶剂differential staining 鉴别染色differential thermal analysis 示差热分析differential thermal analyzer 差热分析仪differential titration 差示滴定diffraction 衍射diffraction grating 衍射栅diffraction spectrum 衍射光谱diffusate 渗出物diffuse scattering 漫散射diffuser 扩散器diffusing glass 扩散玻璃diffusion 扩散diffusion analysis 扩散系数分析diffusion coefficient 扩散系数diffusion current 扩散电流diffusion heat 扩散热diffusion ion 扩散离子diffusion layer 扩散层diffusion potential 扩散电势diffusion process 扩散过程diffusion pump 扩散泵diffusion reaction 扩散反应diffusion transfer process 扩散转印法diffusion velocity 扩散速度diffusiophoresis 扩散电泳diffusivity 扩散率diffusivity analysis 扩散系数分析diformyl 乙二醛digallic acid 双没食子酸digester 蒸煮器digestibility 消化率digestion 消化;煮解digestive enzyme 消化酶digitalin 狄吉他林digitalis 毛地黄digitonin 毛地黄皂苷digitoxigenin 洋地黄毒苷元digitoxin 狄吉妥辛diglycolic acid 二甘醇酸digoxin 地谷新dihexyl 十二烷dihydrate 二水合物dihydric alcohol 二羟醇dihydrostreptomycin 二氢链霉素dihydroxyacetone 二羟基丙酮dihydroxyacetophenone 二羟基苯乙酮diiodomethane 二碘甲烷diiodothyrosine 二碘酪氨酸diisoamyl phthalate 邻苯二酸二异戊酯diisobutyl adipate 己二酸二异丁酯diisobutyl ketone 二异丁基甲酮diisobutylamine 二异丁胺diisobutylene 二异丁烯diisocyanate 二异氰酸盐diisodecyl adipate 己二酸二异癸酯diisodecyl phthalate 酞酸二异癸酯diisooctyl adipate 己酸二异辛酯diisooctyl azelate 壬二酸二异辛酯diisooctyl phthalate 邻苯二酸二异辛酯diisooctyl sebacate 癸二酸二异辛酯diisopropanolamine 二异丙醇胺diisopropylamine 二异丙基胺diketene 双烯酮diketone 二酮dilactone 双内酯dilatancy 膨胀性dilatation 膨胀dilatometer 膨胀计dilatometric curve 膨胀曲线dilatometry 膨胀测定法dilaurin 二月桂精diluent 稀释剂dilute acid 稀酸dilute solution 稀溶液dilute sulphuric acid 稀硫酸dilution 稀释dilution law 稀释律dilution refrigeration 稀释冷冻dimedrole 地麦德洛尔dimension 量纲dimensional analysis 量纲分析dimensional stability 尺寸恒定性dimensionless number 无因次数dimer 二聚物dimerization 二聚酌dimethyl ether 二甲醚dimethyl phthalate 酞酸二甲酯dimethyl sebacate 癸二酸二甲酯dimethyl sulfate 硫酸二甲酯dimethyl sulfoxide 二甲亚砜dimethyl terephthalate 对酞酸二甲酯dimethylacetal 二甲基缩醛dimethylacetamide 二甲基乙酰胺dimethylamine 二甲胺dimethylaniline 二甲基苯胺dimethylarsine 二甲胂dimethylbenzene 二甲苯dimethylbutadiene rubber 二甲基丁二烯橡胶dimethylether 二甲基乙醚dimethylformamide 二甲基甲酰胺dimethylhydrazine 二甲基肼dimethylolurea 二羟甲基脲dimethylpentane 二甲基成烷dimethylpyridine 卢剔啶dimethylsulphoxide 二甲亚砜dimethylterephthalate 二甲基对酞酸盐dimethylthiophene 二甲基噻吩dimorphism 二形dinas brick 硅酸盐砖dinitrite 双亚硝酸盐dinitrobenzene 二硝基苯dinitroglycerine 二硝基甘油dinitronaphthalene 二硝基萘dinitrophenol 二硝基苯酚dinitrotoluene 二硝基甲苯dinonyl phenol 二壬基苯酚dinonyl phthalate 酞酸二壬酯dioctyl ether 二辛醚dioctyl fumarate 反式丁烯二酸二辛酯dioctyl phthalate 酞酸二辛酯dioctyl sebacate 癸二酸二辛酯diol 二醇diolefin 二烯diolein 二油精diorite 闪绿岩diose 双糖diosgenine 地奥甙元dioxane 二氧六环dioxide 二氧化物dioxide peroxide 二氧化氯dioxindole 二氧吲哚dioxolane 二氧戊环dip dyeing 提浸染色dip oil 浸洗油dipentene 二戊烯dipeptidase 二肽酶dipeptide 二肽diphenic acid 联苯甲酸diphenol 联苯酚diphenyl 联二苯diphenyl carbonate 碳酸二苯酯diphenyl ether 二苯醚diphenyl oxide 二苯基氧diphenyl phthalate 酞酸二苯酯diphenyl urea 碳酰替diphenylacetonitrile 二苯基乙腈diphenylamine 二苯胺diphenylbenzidine 二苯联苯胺diphenylcarbinol 二苯基甲醇diphenylene oxide 联苯抱氧diphenylenemethane 芴diphenylguanidine 二苯胍diphenylhydrazine 二苯肼diphenylketone 二苯甲酮diphenylmethane 二苯甲烷diphenylurea 二苯脲diphosgene 双光气dipolar ion 偶极离子dipole 偶极子dipole molecule 偶极分子dipole moment 偶极矩dipping 浸渍dipping process 浸渍过程dipping refractometer 浸液折射计dipping varnish 浸渍清漆dipropyl ketone 二丙基甲酮dipropyl phthalate 酞酸二丙酯dipropyl sulfide 二丙硫dipropylene glycol 二丙二醇dipyridyl 联吡啶direct color 直接染料direct cotton dye 直接染棉染料direct current 直流direct dye 直接染料direct effect 直接效应direct fertilizer 直接肥料direct fired evaporator 直烧蒸发器direct pressure 定向压力direct reduction 直接还原direct steam 直接蒸汽direct titration 直接滴定direct writing oscillograph 直接记录式示波器direction coefficient 方向系数disaccharide 二糖disaggregation 解聚disazo dye 双偶氮染料disc crusher 盘式破碎机disc electrophoresis 圆盘电泳discharge 放电discharge hopper 卸料斗discharge liquor 排出液discharge rate 放电率discharge test 拔染试验discharge tube 放电管discharging agent 拔染剂discharging hopper 卸料斗discoloration 变色discontinuous operation 周期性操作discriminant analysis 判别分析disilane 乙硅烷disilicate 二硅酸盐disinfectant 消毒剂disinfection 消毒disinfector 消毒器disintegration 衰变disintegration constant 衰变常数disintegrator 粉碎机disk crusher 盘式破碎机disk electrophoresis 圆盘电泳disk type rotary vacuum filter 圆盘式旋转真空过滤器disk valve 圆板阀dislocation 错位dismutation 歧化过程disodium hydrogen arsenate 砷酸氢二钠disodium hydrogen phosphate 磷酸氢二钠dispensation 配方dispersant 分散剂disperse dye 分散染料dispersed material 分散质dispersed phase 分散相dispersed system 分散系dispersing agent 分散剂dispersion 分散dispersion force 分散力dispersion medium 分散介质dispersive power 分散本领dispersoid 分散胶体displacement 变位displacement chromatography 置换色谱法displacement law 位移定律displacement reaction 取代反应disproportion 不均衡disproportionation 歧化dissimilation 异化酌dissipation of energy 能量耗散dissipative structure 耗散结构dissociation 解离dissociation constant 离解常数dissociation energy 离解能dissociation pressure 离解压dissolution 溶解dissolved oxygen 溶解氧dissolving power 溶解力dissymmetry 非对称distance control 遥控distearin 二硬脂精distemper 水浆涂料distillate 馏出物distillation 蒸馏distillation apparatus 蒸馏装置distillation column 蒸馏塔distillation curve 蒸馏曲线distillation flask 蒸馏瓶distillation loss 蒸馏损失distillation still 蒸馏釜distillation tower 蒸馏塔distilled water 蒸馏水distributed load 分布负载distribution 分配distribution coefficient 配分系数distribution function 配分函数distribution law 分配律distribution of molecular weight 分子量分布distribution of polymerization degree 聚合度分布disulfide 二硫化物disulfonic acid 二磺酸diterpene 双萜dithiocarbamic acid 氨荒酸dithione 二硫酮dithionic acid 连二硫酸dithiooxamide 红氨酸dithizone 双硫腙diuretic 利尿剂diuretic hormone 利尿激素diuretin 利尿素divalent metal 二价金属divalent system 二变系divinyl 二乙烯divinyl sulfone 二乙烯砜divinylbenzene 二乙烯基苯djave butter 毒雾冰草油dna polymerase dna 聚合酶dnase 脱氧核糖核酸酶docosanoic acid 廿二烷酸doctor process 铅酸钠净化处理doctor solution 博士溶液doctor treatment 铅酸钠净化处理dodecane 十二烷dodecanoic acid 正十二烷酸dodecene 十二烯dodecyl acetate 醋酸十二酯dodecyl chloride 十二基氯dodecylbenzene 十二烷苯dodecylic acid 月桂酸dodecylphenol 十二烷苯酚dolomite 白云石dolomite clinker 白云石熔结dolomite plaster 白云石灰浆domain 晶畴domestic fuel 家用燃料dominant wave length 吱长donator 供体donnan's equilibrium 道南平衡donor 供体dopamine 多巴胺dopaoxidase 多巴氧化酶dope dyeing spun dyeing 原液染色doppler effect 多普勒效应dosage 剂量dose 剂量dose equivalent 剂量当量dose rate 放射量率dosimeter 剂量计dosimetry 剂量测定double arm kneader 双叶片捏和机double bond 双键double bond isomerism 双键异构性double cone mixer 双圆锥式混合机double decomposition 复分解double decomposition reaction 复分解反应double effect evaporator 双效蒸发器double exchange interaction 双重交换相互酌double exposure 双重曝光double fluid cell 双液电池double layer 双层double melting point 双重熔点double refraction 双折射double resonance 双共振double salt 复盐double solvent refining 双溶剂精炼double weighing method 双重秤量法doublet 双重线downdraft 向下通风downspout 下导管draft 通风draft chamber 通风室drain valve 排污阀draught 通风drawing of fiber 拉伸纤维drier 干燥机drinking water 饮水drop culture 点滴培养drop reaction 点滴反应drop sulfur 粒状硫droplet formation 点滴形成dropping bottle 滴瓶dropping electrode 滴液电极dropping funnel 滴液漏斗dropping mercury electrode 滴汞电极dropping point 滴点dropwise condensation 滴状凝结drug metabolism 药物代谢酌drug resistance 药物抗性drum 辊筒drum dryer 鼓式干燥器druse 晶簇dry air cure 干热硫化dry analysis 干法分析dry area 干摩擦点dry area spot 干摩擦点dry assay 干法试金dry blending 干搀和dry box 干箱dry cell 干电池dry cleaning 干洗dry cleaning fluid 干洗铃dry coloring 干颜料dry desiccant dehydration 干态干燥剂脱水酌dry distillation 干馏dry distillation of wood 木材干馏dry dyeing 干法染色dry friction 干摩擦dry gas 干气dry gas holder 干式气柜dry heat vulcanization 干热硫化dry hole 干钻孔dry ice 固体二氧化碳dry plate 干板dry point 干点dry process 干法dry reaction 干反应dry spinning 干纺dry steam 干燥蒸气dry sterilization 干热灭菌dry tack 干粘着性dry weight 干重dry yeast 干酵母dryer 干燥机drying 干燥drying agent 干燥剂drying apparatus 干燥装置drying chamber 干燥室drying efficiency 干燥效率drying oil 干性油drying oven 干燥炉drying plant 干燥设备drying temperature 干燥温度drying time 干燥时间dual gravity valve 双比重阀duboisine 天仙子胺ductility 延性ductilometer 拉伸度仪dulcin 对乙氧基苯脲dulcitol 卫矛醇dull finish 消光dull surface 无光面dulong petit's law 杜珀二氏定律duma's method 杜马斯法duplet 电子偶duplex printing 双面复合印花durability 耐久性duralumin 硬铝durene 杜烯duriron 杜里龙高硅钢durometer 硬度计durometer hardness 硬度计硬度dust chamber 除尘器dust coal 粉煤dust collector 除尘器dust powder 木炭粉dust sampler 粉尘采样器dust separator 除尘分离器dye 染料dye laser 染料激光器dyeing 染色dyeing assistant 染色辅助剂dyeing equilibrium 染色平衡dyeing power 染色力dyeing speed 上染速度dyestuff 染料dyestuff chemistry 染料化学dynameter 倍率计dynamic equilibrium 动态平衡dynamic isomerism 动态异构性dynamic modulus 动态模量dynamic pressure 动压dynamic viscosity 动态粘度dynamics 动力学dynamite 达纳炸药dypnone 缩二苯乙酮dysprosium 镝dysprosium bromide 溴化镝dysprosium carbonate 碳酸镝dysprosium chloride 氯化镝dysprosium hydroxide 氢氧化镝dysprosium nitrate 硝酸镝dysprosium oxide 氧化镝dysprosium oxychloride 氯氧化镝dysprosium phosphate 磷酸镝dysprosium sulfate 硫酸镝dystectic mixture 高熔混合物dystectic point 高熔点e bond e 键early strength cement 早强水泥earth acids 土酸类earth color 矿物颜料earth metals 土金属earth wax 木炭earthenware 陶器earthy humus 土状腐殖质ebonite 硬橡胶ebulliometer 酒精沸点计;沸点测定器ebullioscopic constant 沸点升高常数ebullioscopic method 沸点升高法ebullition 沸腾ecdysone 蜕化素ecgonine 芽子碱echelon grating 梯式格子eclipsing effect 重叠效应economizer 省煤器eddy 涡流eddy conductivity 涡寥导性eddy current 涡电流eddy viscosity 涡脸度edeleanu process 爱德林精炼法edestin 麻仁球蛋白edge runner 轮碾机edible fat 食用脂edible oil 食用油edison storage battery 爱迪生蓄电池editcoal gas 煤气editcyclotron 回旋加速器editmetallized carbon filament 金属化碳丝editmethacrylate resin 甲基丙烯酸尸editnitroglycerin 硝化甘油editpaint film 漆膜editpotassium cyanide 氰化钾editpour point 晶出点editsteric hindrance 立体阻碍editthixotropic gel 触变胶体edittrialkyl chlorosilane 三烷基氯硅烷editwater purification unit 净水设备edman degradation technique 埃德曼降解技术effect of extension 延伸效应effective angle 有效角effective area 有效面积effective collision number 有效碰撞数effective half life 有效半衰期effective head 有效扬程effective permeability 有效渗透率effective power 有效功率effective quantum number 有效量子数effective resistance 有效抵抗effective thermal conductivity 有效热传导率effective value 有效值effervescence 发泡efficiency 效率efficiency of dust collection 除尘效率efficiency of rectification tower 精馏塔效率efflorescence 风化effluent 瘤物efflux velocity 瘤速度efflux viscometer 瘤式粘度计effusiometer 打散计effusion 喷出effusive rock 喷出岩egg albumin 卵清蛋白egg white 蛋白egg yolk 蛋黄ehrlich's reagent 欧利布试剂eicosane 廿烷eicosanoic acid 花生酸eigen energy 本哲eigenfunction 本寨数eigenvalue 本盏eikonogen 显影剂einstein bohr equation 爱因斯坦玻尔方程einstein condensation 爱因斯坦凝聚einstein diffusion equation 爱因斯坦扩散方程einstein photochemical equivalenct law 爱因斯坦光化当量定律einstein photoelectric law 爱因斯坦光电定律einstein planck law 爱因斯坦普朗克定律einstein's equation for specific heat 爱因斯坦比热方程einstein's viscosity equation 爱因斯坦粘度方程式einsteinium 锿ejector 喷射器ejector condenser 喷射式冷凝器eka cesium 类铯eka element 待寻元素eka iodine 类碘eka tantalum 类钽elaeolite 脂光石elaeometer 油脂比重计elaeosacchara 油糖剂elaidic acid 反油酸elaidin 反油酸精elaidin test 反油酸检验elaidinization 反油酸转位elastase 弹性蛋白酶elastic aftereffect 弹性后效elastic body 弹性体elastic collision 弹性碰撞elastic constant 弹性常数elastic deformation 弹性变形elastic force 弹性力elastic gum 弹性胶elastic hysteresis 弹性滞后elastic limit 弹性极限elastic medium 弹性介质elastic modulus 弹性系数elastic recovery 弹性复原elastic rubber 弹性胶elasticity 弹性elastin 弹性硬朊elastomer 弹性体elastometer 弹性计elastoviscometer 弹性粘度计elastoviscometry 弹性粘度测量法elaterometer 气体密度计elatrometry 气体密度测量法elbs reaction 埃尔布斯反应electret 驻极体electric analysis 电分析法electric arc furnace 电弧炉electric calorimeter 电热量计electric charge 电荷electric conductivity 导电率electric conductor 导体electric current 电流electric desalting 电脱盐electric detonator 电爆管electric discharge 放电electric double layer 双电层electric drying apparatus 电干燥机electric dust precipitator 电集尘器electric energy 电能electric field 电场electric furnace 电炉electric heater 电热器electric heating 电热electric insulation 电绝缘electric potential 电位electric power 电力electric precipitation 电力沉淀electric resistance 电阻electric resistance furnace 电阻炉electric resistance manometer 电阻压力计electric resistance thermometer 电阻温度计electric susceptibility 电极化率electric thermostat 电热恒温器electric welding 电焊electrical carbonization 电法炼焦electrical dispersion 电分散法electrical property 电性质electroactive substance 电活性物质electroanalysis 电分析electrocapillarity 电毛细现象electrocapillary curve 电毛细管曲线electrocast brick 电熔耐火砖electrocasted refractories 电炉熔铸耐火物electrocasting 电铸electrocatalysis 电催化酌electroceramics 电陶瓷electrochemical cell 蓄电池electrochemical corrosion 电化学腐蚀electrochemical equivalent 电化当量electrochemical industry 电化工业electrochemical passivation 电化钝化electrochemical polarization 电化极化electrochemical process 电化法electrochemical protection 电化学防腐法electrochemical reaction 电化学反应electrochemical series 电化序electrochemistry 电化学electrochromatography 电气色层法electrocoagulation 电凝聚electroconductive glass 电导玻璃electrocyclic reaction 电环化反应electrode 电极electrode potential 电极势electrode process 电极过程electrode reaction 电极反应electrodecantation 电倾析electrodeposition 电极沉积electrodeposition analysis 电沉积分析electrodialysis 电渗析electroexplosive 电起爆炸药electrofocusing 等电点聚焦electroforming 电铸electrogeochemistry 电地球化学electrogravimetric analysis 电重量分析electrohydrometry 电液体比重测量法electrokinetic phenomena 界面电动学现象electrokinetic potential 界面动电势electroluminescence 电致发光electrolysis 电解electrolyte 电解质electrolytic aluminium 电解铝electrolytic analysis 电解分析electrolytic analysis apparatus 电解分析装置electrolytic bath 电解槽electrolytic bleaching 电解漂白electrolytic cell 电解槽electrolytic cleaning 电解清洗electrolytic condenser 电解质电容器electrolytic copper 电解铜electrolytic degreasing 电解去油electrolytic dissociation 电离electrolytic dissociation constant 电离常数electrolytic extraction 电解萃取electrolytic hardening 电解硬化electrolytic oxidation 电解氧化electrolytic polarization 电解极化electrolytic polishing 电解研磨electrolytic rectifier 电解整流electrolytic reduction 电解还原electrolytic refining 电解精炼electrolytic solution 电解溶液electrolytical surface treatment 电表面处理electrolytics 电解学electromagnet 电磁铁electromagnetic field 电磁场electromagnetic flowmeter 电磁量计electromagnetic gas analyzer 电磁气分析计electromagnetic induction 电磁感应electromagnetic oscillograph 电磁式示波器electromagnetic separation 电磁分离electromagnetic separator 电磁分离器electromagnetic wave 电磁波electromerism 电子异构electrometallurgy 电冶金学electrometer 电位计electrometer tube 电表管electrometric titration 电滴定electromigration 电迁移法electromotive force 电动势electron 电子electron affinity 电子亲合势electron beam 电子束electron capture 电子俘获electron cloud 电子云electron configuration 电子构型electron density 电子密度electron diffraction 电子衍射electron donor 电子供体electron emission 电子发射electron exchange 电子交换electron exchange resin 电子交换尸electron gas 电子气electron lattice interaction 电子点阵相互酌electron microscope 电子显微镜electron orbit 电子轨道electron oxidation reduction resin 电子交换尸electron pair 电子对electron pair bond 电子对键electron probe microanalysis 电子探针微量分析electron rays 电子束electron redox resin 电子交换尸electron shell 电子壳electron spectroscopy 电子能谱术electron transfer reaction 电子转移反应electron transport 电子转移electron transport system 电子传递体系electron tube 电子管electron volt 电子伏特electronegative element 阴电性元素electronegativity 电负度electronic charge 电子电荷electronic computer 电子计算机electronic conduction 电子传导electronic friction 电子摩擦electronic galvanometer 电子管检疗electronic oscillator 电子振荡器electronic polarization 电子极化electronic self balancing type recorder 电子自动平衡记录器electronic structure of molecule 分子的电子结构electronic tube glass 真空管玻璃electronic voltmeter 电子伏特计electronics 电子学electroosmosis 电渗透electrophilic agent 亲电子试剂electrophilic reaction 亲电子反应electrophilic rearrangement 亲电子换位electrophoresis 电泳electrophoresis apparatus 电泳器electrophoretic effect 电泳效应electrophotography 电照相术electroplating 电镀electropositive element 阳电性元素electropositive potential 阳电势electroscope 验电器electrosol 电溶胶electrostatic field 静电场electrostatic induction 静电感应electrostatic potential 静电势electrostatic separator 静电选矿机electrostatic valence rule 静电价规则electrostenolysis 细孔隔膜电解electrotechnical porcelain 电瓷electrothermic industry 电热工业electrothermics 电热学electrovalence 离子价electrowinning 电解沉积element 元素elementary analysis 元素分析elementary charge 电子电荷elementary particle 基本粒子elementary reaction 基本反应elemi 榄香脂eleolite 霞石eleolite syenite 霞石正长岩eleostearic acid 桐酸elevation of boiling point 沸点升高elgin extractor 埃尔金萃取器elimination reaction 消除反应ellagic acid 花烯ellipsometry 椭圆光度法elongation percentage 伸长率eluate 洗出液eluent 洗脱液elution 洗提elution analysis 淘析分析elution constant 淋洗常数elution curve 淘析曲线elutriation 淘析elutriator 淘析器emagram 埃玛图eman 埃曼emanation 射气emerald 纯绿宝石emerald green 巴黎绿emery 金刚砂emery cloth 研磨砂布。

Unit 1 Chemical Industry化学工业1。
Origins of the Chemical IndustryAlthough the use of chemicals dates back to the ancient civilizations, the evolution of what we know as the modern chemical industry started much more recently。
It may be considered to have begun during the Industrial Revolution, about 1800, and developed to provide chemicals roe use by other industries. Examples are alkali for soapmaking, bleaching powder for cotton, and silica and sodium carbonate for glassmaking。
It will be noted that these are all inorganic chemicals。
The organic chemicals industry started in the 1860s with the exploitation of William Henry Perkin’s discovery if the first synthetic dyestuff—mauve. At the start of the twentieth century the emphasis on research on the applied aspects of chemistry in Germany had paid off handsomely, and by 1914 had resulted in the German chemical industry having 75% of the world market in chemicals。

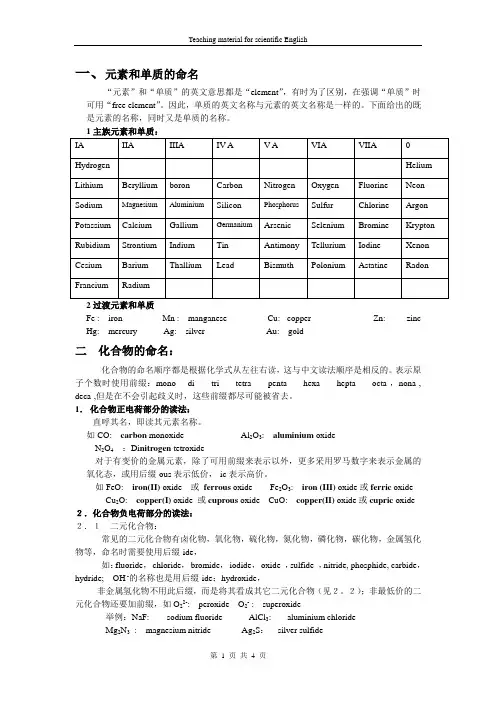
一、元素和单质的命名“元素”和“单质”的英文意思都是“element”,有时为了区别,在强调“单质”时可用“free element”。
因此,单质的英文名称与元素的英文名称是一样的。
下面给出的既是元素的名称,同时又是单质的名称。
2过渡元素和单质Fe : iron Mn : manganese Cu: copper Zn: zinc Hg: mercury Ag: silver Au: gold二化合物的命名:化合物的命名顺序都是根据化学式从左往右读,这与中文读法顺序是相反的。
表示原子个数时使用前缀:mono-di -tri- tetra -penta- hexa-hepta- octa-,nona-, deca-,但是在不会引起歧义时,这些前缀都尽可能被省去。
1.化合物正电荷部分的读法:直呼其名,即读其元素名称。
如CO: carbon monoxide Al2O3: aluminium oxideN2O4:Di nitrogen tetroxide对于有变价的金属元素,除了可用前缀来表示以外,更多采用罗马数字来表示金属的氧化态,或用后缀-ous表示低价,-ic表示高价。
如FeO: iron(II) oxide 或ferrous oxide Fe2O3: iron (III) oxide或ferric oxide Cu2O: copper(I) oxide 或cuprous oxide CuO: copper(II) oxide或cupric oxide 2.化合物负电荷部分的读法:2.1二元化合物:常见的二元化合物有卤化物,氧化物,硫化物,氮化物,磷化物,碳化物,金属氢化物等,命名时需要使用后缀-ide,如:fluoride,chloride,bromide,iodide,oxide ,sulfide ,nitride, phosphide, carbide,hydride; OH -的名称也是用后缀-ide:hydroxide,非金属氢化物不用此后缀,而是将其看成其它二元化合物(见2。

化学工程基础英文版Chemical Engineering Basics: Understanding Chemical FormulasI. Chemical BondsLet's start with chemical bonds. Think of atoms as little building blocks. Chemical bonds are like the "glue" or "hooks" that hold these building blocks together.1. Ionic Bond- Imagine ionic bonds as super - strong magnets. In an ionic bond, we have atoms that have an electric charge. Some atoms lose electrons and be positively charged (like cations), and some gain electrons and be negatively charged (like anions). For example, in sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium (Na) loses an electron and bes Na⁺, and chlorine (Cl) gains that electron and bes Cl⁻. These charged atoms, like a positive and negative end of a super - strong magnet, are attracted to each other very strongly. It's as if they have a really powerful force pulling them together.2. Covalent Bond- Covalent bonds are a bit different. Here, atoms share their "hooks." For instance, in a molecule of hydrogen gas (H₂), each hydrogen atom has one electron. They share these electrons with each other. It's like two people sharing a pair of tools. They both hold on to the same electrons to be stable. In a moreplex molecule like water (H₂O), the oxygen atom shares its "hooks" (electrons) with two hydrogen atoms.II. Chemical BalanceChemical balance is like a tug - of - war game.1. The Concept- In a chemical reaction, we have reactants (the starting materials) and products (the stuff that is made). Let's say the reactants are one team and the products are another team in the tug - of - war. At the beginning of the reaction, the "pull" (the rate of the reaction) is mostly in the direction of making products from reactants. But as the reaction goes on, the products start to "pull back" (react in the reverse direction).- Eventually, a point is reached where the "pull" in both directions is equal. The rate of the forward reaction (reactants turning into products) is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction (products turning back into reactants). At this point, the concentrations of the reactants and products don't change anymore. It's like in a tug - of - war when neither team can move the other because they are pulling with equal force.III. Molecular Polarity1. Polar Molecules- Think of a polar molecule like a little magnet or a smallpass needle. Take water (H₂O) for example. The oxygen atom in water is more "electron - greedy" than the hydrogen atoms. So, the electrons in the covalent bonds between oxygen and hydrogen are closer to the oxygen. This makes the oxygen end of the water molecule a bit more negative, like the south pole of apass needle. And the hydrogen ends are a bit more positive, like the north pole of apass needle.2. Non - Polar Molecules- Now, consider carbon dioxide (CO₂). It's a linear molecule, with the carbon atom in the middle and the two oxygen atoms on either side. The electrons are shared evenly between the carbon and oxygen atoms in a way that the molecule is symmetric. So, there is no "pole" or side that is more positive or negative. It's like a stick that is evenly balanced, not like a littlepass needle.IV. Coordination Compounds1. The Analogy- In a coordinationpound, we can think of the center ion as the main character at a party. For example, in aplex like [Cu(NH₃)₄]²⁺, the copper ion (Cu²⁺) is the "host" of the party. And the ligands, like ammonia (NH₃) in this case, are the "guests." The ligands have lone pairs of electrons that they can share with the center ion. It's like the guests bringing something special (their lone pairs of electrons) to share with the host at the party.V. Electron Transfer in Oxidation - Reduction Reactions1. The "Transaction" Analogy- Consider the reaction between zinc (Zn) and copper sulfate (CuSO₄). This is like a business transaction. Zinc atoms are like the "givers" and copper ions (Cu²⁺) are like the "receivers." The zinc atom gives away two electrons. By giving away these electrons, the zinc atom bes a zinc ion (Zn²⁺), and the copper ion (Cu²⁺) that receives these electrons bes a copper atom (Cu). It's like one person giving money (electrons) to another person.VI. Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction Rate1. Temperature- Temperature is like the weather. When it's warm (high temperature), people (atoms or molecules) are more active. In a chemical reaction, high temperature gives the atoms more energy.It's like in hot weather, people run around and move more. So, the atoms can collide with each other more often and with more energy, which makes the reaction happen faster.2. Concentration- Concentration is like the number of people on a running track. If there are more people (higher concentration of reactants) on the track, the chances of them bumping into each other (reacting) are higher. So, a higher concentration of reactants usually leads to a faster reaction because there are more opportunities for the reactant particles to collide.3. Catalyst- A catalyst is like a really smart coach. In a chemical reaction, the reactant molecules have to find a certain "path" to react. A catalyst shows the reactant molecules an easier or faster "path." It doesn't get used up in the reaction, just like a coach who doesn't actually run in the race but helps the runners (reactant molecules) perform better. So, with a catalyst, the reaction can happen more quickly.These are the basic concepts related to chemical formulas, and understanding them using these simple analogies can make the study of chemistry much more fun and accessible!。
(完整版)化学类专业英语词汇.doc专业英语词汇Unit 1TEXT A : Chemical Reactions and Group Reactions customary a. 通常的,惯例的handle n.柄vt.触摸handling n.处理,管理derive vt.取得,得到,衍生oxidate vt.使氧化oxidation n.satisfactory a.令人满意的,符合要求的rapid a.快的,迅速的,动作快的combustion n.燃烧somewhat pron. ad. 一点点,几分,有点effort n.努力commercial a.商业的,商务的undesirable a不.合需要的,不受欢迎的,讨厌的retard vt.延迟,放慢,使停滞transformer n.变压器transform vt.改变,转变automotive a.自动的,机动的,汽车的cracked裂化的sluge n.软泥,淤泥stiff a.硬的,强烈的extent 广度,程度distillation n.蒸馏distill vt.vi.unrefined a.未精致,未提炼的acidity n.酸味,酸性acidify vt. Vi.Involve vt. 包缠,卷缠Fell=followingIndividual a.个人的,个体的Presumable a可.假定的,可推测的Destruction n.破坏,毁灭Overall n。
a.全面的,综合的Exceed 超过,胜过Isolate vt.隔离,孤立,使离析iso—构词成分“均匀”“异构”“苯”Analyse vt. 分析,分解Carbonyl 羰基Carboxyl羧基Hydroxyl羟基Decomposition分解Alkyl烷基,烃基Ketone 酮Aldehyde n.醛Yield vt. 出产,产出Explosive a. 爆炸Vapor n.蒸汽, vi.蒸发Propagation 繁殖,增殖;传播Dehydrate vt.使脱水Acet 构词成分Acetaldehyde乙醛Resin n.树脂Resinous a.树脂的Carboxylic a.羟基的Substantial a.物质的,实质的Susceptible a易.受感动的,敏感的Analogous a.类似的,相似的( to)Response n.作答,回答,响应,反应Readily ad.乐意地,很快地Readiness n准.备就绪,愿意Extent n.广度长度Steric 空间的,位的Likewise ad.同样的,照样地;也,又Suffer vt.遭受,经历Progressive a进.步的,长进的,渐次的Adjacent a.邻近的,紧挨着的Terminal a.末端的,终点的MethyleneBromide n.溴化物Substitute n.代替物(人),代用品substitution n.代替,替换Remote a相.隔较远的Acetone n.丙酮Ether n.醚,乙醚Correspond vi.符合,一致;相当,相应Reservation n保.留,预定Tend vi.走向,趋向。
化学专业英语**Title: Introduction to Key Concepts in Chemistry**Chemistry, often referred to as the central science, is a multifaceted field that delves into the composition, structure, properties, and changes of matter. Understanding its key concepts is fundamental for students and professionals alike. This document aims to provide a comprehensive overview of essential terminology andprinciples in chemistry.**1. Matter and Its Properties**Matter, anything that occupies space and has mass, exists in various states—solid, liquid, gas, and plasma. Each state exhibits unique properties such as density, volume, and compressibility. Additionally, matter undergoes physical and chemical changes, altering its composition or structure.**2. Atoms and Elements**Atoms, the building blocks of matter, consist of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons. Elements, substances composed of a single type of atom, are organized in the periodic table based on atomic number and chemical properties. Understanding atomicstructure is crucial for comprehending chemical bonding and reactions.**3. Chemical Bonds and Molecular Structure**Chemical bonds, forces that hold atoms together in compounds, include covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons, while ionicbonds result from the transfer of electrons between atoms. Molecular structure refers to the arrangement of atoms in a molecule, influencing its properties and behavior.**4. Chemical Reactions and Stoichiometry**Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different properties. Reactants undergo transformation into products, following principles of conservation of mass and energy. Stoichiometry quantitatively describes the relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction, crucial for determining reaction yields and compositions.**5. Acids, Bases, and pH**Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) in aqueous solutions, while bases accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH⁻). The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14, with 7 considered neutral. Understanding acid-base properties is essential in various chemical processes, from industrial applications to biological systems.**6. Thermodynamics and Kinetics**Thermodynamics explores the energy changes accompanying chemical reactions and phase transitions. Concepts such as enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy govern reaction spontaneity and equilibrium. Kinetics, on the other hand, studies the rates of chemical reactions and factors influencing reaction rates, crucial for optimizing reaction conditions.**7. Organic Chemistry and Functional Groups**Organic chemistry focuses on the study of carbon-containing compounds, including hydrocarbons, alcohols, acids, and carbohydrates. Functional groups, specific arrangementsof atoms within molecules, impart characteristic properties and chemical reactivity to organic compounds. Understanding organic chemistry is vital for fields such as pharmaceuticals, materials science, and biochemistry.**8. Analytical Chemistry and Spectroscopy**Analytical chemistry involves the identification and quantification of chemical substances in various samples. Spectroscopic techniques, including UV-Vis, IR, NMR, and mass spectrometry, provide valuable information about molecular structures and compositions. Analytical methods play crucial roles in fields such as environmental monitoring, forensic analysis, and quality control.**Conclusion**Chemistry encompasses a vast array of concepts and principles essential for understanding the natural world and advancing technology. From the microscopic realm of atoms to the macroscopic world of materials and reactions, chemistry provides insights into the fundamental processes shaping our universe. By mastering its key concepts, individuals can unravel the mysteries of matter and contribute to scientific innovation and discovery.。
(完整版)化学专业英语一、基础词汇篇1. 原子与分子Atom(原子):物质的基本单位,由质子、中子和电子组成。
2. 化学反应Reactant(反应物):参与化学反应的物质。
Product(物):化学反应后的物质。
Catalyst(催化剂):能改变化学反应速率而本身不发生永久变化的物质。
3. 物质状态Solid(固体):具有一定形状和体积的物质。
Liquid(液体):具有一定体积,无固定形状的物质。
Gas(气体):无固定形状和体积的物质。
4. 酸碱盐Acid(酸):在水溶液中能电离出氢离子的物质。
Base(碱):在水溶液中能电离出氢氧根离子的物质。
Salt(盐):由酸的阴离子和碱的阳离子组成的化合物。
5. 溶液与浓度Solution(溶液):由溶剂和溶质组成的均匀混合物。
Solvent(溶剂):能溶解其他物质的物质。
Solute(溶质):被溶解的物质。
Concentration(浓度):溶液中溶质含量的度量。
二、专业术语篇1. 有机化学Organic Chemistry(有机化学):研究碳化合物及其衍生物的化学分支。
Functional Group(官能团):决定有机化合物化学性质的原子或原子团。
Polymer(聚合物):由许多重复单元组成的大分子化合物。
2. 无机化学Inorganic Chemistry(无机化学):研究不含碳的化合物及其性质的化学分支。
Crystal(晶体):具有规则排列的原子、离子或分子的固体。
OxidationReduction Reaction(氧化还原反应):涉及电子转移的化学反应。
3. 物理化学Physical Chemistry(物理化学):研究化学现象与物理现象之间关系的化学分支。
Chemical Bond(化学键):原子间相互作用力,使原子结合成分子。
Thermodynamics(热力学):研究能量转换和物质性质的科学。
4. 分析化学Analytical Chemistry(分析化学):研究物质的组成、结构和性质的科学。
完整版)化学专业英语Teaching Material for Scientific EnglishI。
Naming of XXX1.Naming of XXXThe English word for both "元素" and "单质" is "element"。
To distinguish een the two。
"free element" may be used when emphasizing "单质"。
Therefore。
the English names for XXX are the same。
The following are the names of elements that are also names of free elements:Group IA:XXXXXXSodiumGroup IIA:XXXMagnesiumGroup IIIA: Boron AluminumGroup IVA: Carbon Silicon GermaniumGroup VA: Nitrogen PhosphorusGroup VIA: Oxygen Sulfur XXXXXXPoloniumGroup VIIA: Fluorine Chlorine Bromine IodineXXXGroup 0: XXXNeon ArgonXXX Xenon RadonGroup IA: Potassium CalciumGroup IIA:RubidiumCesiumFranciumGroup IIIA:GalliumIndiumXXXGroup IVA:ArsenicXXXXXXXXXLead2.Naming of CompoundsCompounds are named from left to right according to their chemical formula。
1 CHEMISTRY AND CHEMISTWithout chemistry our lives would beunrecognisable, for chemistry is at work all aroundus. Think what life would be like without chemistry- there would be no plastics, no electricity and noprotective paints for our homes. There would be no synthetic fibres to clothe us and no fertilisers to help us produce enough food. We wouldn‟t be able to travel because there would be no metal, rubber or fuel for cars, ships and aeroplane. Our lives would be changed considerably without telephones, radio, television or computers, all of which depend on chemistry for the manufacture of their parts. Life expectancy would be much lower, too, as there would be no drugs to fight disease.Chemistry is at the forefront of scientific adventure, and you could make your own contribution to the rapidly expanding technology we are enjoying. Take some of the recent academic research: computer graphics allow us to predict whether small molecules will fit into or react with larger ones - this could lead to a whole new generation of drugs to control disease; chemists are also studying the use of chemicals to trap the sun‟s energy and to purify sea water; they are also investigating the possibility of using new ceramic materials to replace metals which can corrode.Biotechnology is helping us to develop new sources of food and new ways of producing fuel, as well as producing new remedies for the sick. As the computer helps us to predict and interpret results from the test tube, the speed, accuracy and quality of results is rapidly increasing - all to the benefit of product development.It is the job of chemists to provide us with new materials to take us into the next century, and by pursuing the subject, you could make your positive contribution to society.Here are some good reasons for choosing chemistry as a career.Firstly, if you have an interest in the chemical sciences, you can probably imagine taking some responsibility for the development of new technology. New ideas and materials are constantly being used in technology to improve the society in which we live. You could work in a field where research and innovation are of primary importance to standards of living, so you could see the practical results of your work in every day use.Secondly, chemistry offers many career opportunities, whether working in a public service such as a water treatment plant, or high level research and development in industry. Your chemistry-based skills and experience can be used, not only in many different areas within the chemical industry, but also as the basis for a more general career in business.1 As a qualification, chemistry is highly regarded as a sound basis for employment.You should remember that, as the society we live in becomes more technically advanced, the need for suitably qualified chemists will also increase. Although chemistry stands as a subject in its own right, it acts as the bond between physics and biology. Thus, by entering the world of chemistry you will be equipping yourself to play a leading role in the complex world of tomorrow.Chemistry gives you an excellent training for many jobs, both scientific and non-scientific. To be successful in the subject you need to be able to think logically, and be creative, numerate, and analytical. These skills are much sought after in many walks of life, and would enable you to pursue a career in, say, computing and finance, as well as careers which use your chemistry directly.Here is a brief outline of some of the fields chemists work in:Many are employed in the wealth-creating manufacturing industries - not just oil, chemical and mining companies, but also in ceramics, electronics and fibres. Many others are in consumer based industries such as food, paper and brewing; or in service industriessuch as transport, health and water treatment.In manufacturing and service industries, chemists work in Research and Development to improve and develop new products, or in Quality Control, where they make sure that the public receives products of a consistently high standard.Chemists in the public sector deal with matters of public concern such as food preservation, pollution control, defence, and nuclear energy. The National Health Service also needs chemists, as do the teaching profess ion and the Government‟s research and advisory establishments.Nowadays, chemists are also found in such diverse areas as finance, law and politics, retailing, computing and purchasing. Chemists make good managers, and they can put their specialist knowledge to work as consultants or technical authors. Agricultural scientist, conservationist, doctor, geologist, meteorologist, pharmacist, vet ... the list of jobs where a qualification in chemistry is considered essential is endless. So even if you are unsure about what career you want to follow eventually, you can still study chemistry and know that you‟re keeping your options open.What Do Chemistry Graduates Do?Demand for chemists is high, and over the last decade opportunities for chemistry graduates have been increasing. This is a trend that is likely to continue. Chemistry graduates are increasingly sought after to work in pharmaceutical, oil, chemical, engineering, textile and metal companies, but the range of opportunities also spans the food industry, nuclear fuels, glass and ceramics, optical and photographic industries, hospitals and the automotive industry. Many graduates begin in scientific research, development and design, but over the years, about half change, into fields such as sales, quality control, management, or consultancy. Within the commercial world it is recognised that, because of the general training implicit in a chemistry course, chemistry graduates are particularly adaptable and analytical - making them attractive to a very broad spectrum of employers. There has been a growth of opportunity for good chemistry graduates to move into the financial world, particularly in accountancy, retail stores, and computer software houses.(Summarized from: A brief of the Royal Society of Chemistry,1992)2 NOMENCLATURE OF INORGANICCOMPOUNDSNaming elementsThe term element refers to a pure substance with atoms all of a single kind. At present 107 chemical elements are known. For most elements the symbol is simply the abbreviated form of the English name consisting of one or two letters, for example:oxygen = O nitrogen = N magnesium = MgSome elements, which have been known for a long time, have symbols based on their Latin names, for example:iron = Fe (ferrum) copper = Cu (cuprum) lead = Pb (Plumbum)A few elements have symbols based on the Latin name of one of their compounds, the elements themselves having been discovered only in relatively recent times1, for example: sodium = Na (natrium = sodium carbonate)potassium = K (kalium = potassium carbonate)A listing of some common elements may be found in Table 1.Naming Metal Oxides, Bases and SaltsA compound is a combination of positive and negative ions in the proper ratio to give a balanced charge and the name of the compound follows from names of the ions, for example, NaCl, is sodium chloride; Al(OH)3is aluminium hydroxide; FeBr2is iron (II) bromide or ferrous bromide; Ca(OAc)2is calcium acetate; Cr2(SO4)3is chromium (III) sulphate or chromic sulphate, and so on. Table 3 gives some examples of the naming of metal compounds. The name of the negative ion will need to be obtained from Table 2.Negative ions, anions, may be monatomic or polyatomic. All monatomic anions have names ending with -ide. Two polyatomic anions which also have names ending with -ide are the hydroxide ion, OH-, and the cyanide ion, CN-.Many polyatomic anions contain oxygen in addition to another element. The number of oxygen atoms in such oxyanions is denoted by the use of the suffixes -ite and -ate, meaning fewer and more oxygen atoms, respectively. In cases where it is necessary to denote more than two oxyanions of the same element, the prefixes hypo- and per-, meaning still fewer and still more oxygen atoms, respectively, may be used, for example,hypochlorite ClO-Chlorite ClO2-chlorate ClO3-perchlorate ClO4-Naming Nonmetal OxidesThe older system of naming and one still widely used employs Greek prefixes for both the number of oxygen atoms and that of the other element in the compound 2. The prefixes used are (1) mono-, sometimes reduced to mon-, (2) di-, (3) tri-, (4) tetra-, (5) penta-, (6) hexa-, (7) hepta-, (8) octa-, (9) nona- and (10) deca-. Generally the letter a is omitted from the prefix (from tetra on ) when naming a nonmetal oxide and often mono- is omitted from the name altogether.The Stock system is also used with nonmetal oxides. Here the Roman numeral refers to the oxidation state of the element other than oxygen.In either system, the element other than oxygen is named first, the full name being used, followed by oxide 3. Table 4 shows some examples.Naming AcidsAcid names may be obtained directly from a knowledge of Table 2 by changing the name of the acid ion (the negative ion ) in the Table 2 as follows:The Ion in Table 2Corresponding Acid-ate-ic-ite-ous-ide-icExamples are:Acid Ion Acidacetate acetic acidperchlorate perchloric acidbromide hydrobromic acidcyanide hydrocyanic acidThere are a few cases where the name of the acid is changed slightly from that of the acid radical; for example, H2SO4 is sulphuric acid rather than sulphic acid. Similarly, H3PO4 is phosphoric acid rather than phosphic acid.Naming Acid and Basic Salt and Mixed SaltsA salt containing acidic hydrogen is termed an acid salt.A way of naming these salts is to call Na 2HPO4disodiumhydrogen phosphate and NaH2PO4sodium dihydrogenphosphate. Historically, the prefix bi- has been used innaming some acid salts; in industry, for example, NaHCO3 iscalled sodium bicarbonate and Ca(HSO3)2 calcium bisulphite.Bi(OH)2NO3, a basic salt, would be called bismuthdihydroxynitrate. NaKSO4, a mixed salt, would be calledsodium potassium sulphate.3 NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDSA complete discussion of definitive rules of organic nomenclature would require more space than can be allotted in this text. We will survey some of the more common nomenclature rules, both IUPAC and trivial.AlkanesThe names for the first twenty continuous-chain alkanes are listed in Table 1.Alkenes and AlkynesUnbranched hydrocarbons having one double bond are named in the IUPAC system by replacing the ending -ane of the alkane name with -ene. If there are two or more double bonds, the ending is -adiene, -atriene, etc.Unbranched hydrocarbons having one triple bond are named by replacing the ending -ane of the alkane name with -yne. If there are two or more triple bonds, the ending is -adiyne, -atriyne etc. Table 2 shows names for some alkyl groups, alkanes, alkenes and alkynes.The PrefixesIn the IUPAC system, alkyl and aryl substituents and many functional groups are named as prefixes on the parent (for example, iodomethane). Some common functional groups named as prefixes are listed in Table 3.In simple compounds, the prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, etc. are used to indicate the number of times a substituent is found in the structure: e.g., dimethylamine for (CH3)2NH or dichloromethane for CH2Cl2.In complex structures, the prefixes bis-, tris-, and tetrakis- are used: bis- means two of a kind; tris-, three of a kind; and tetrakis-, four of a kind. [(CH3)2N]2is bis(dimethylamino) and not di(dimethylamino).Nomenclature Priority of Functional GroupsIn naming a compound, the longest chain containing principal functional group is considered the parent. The parent is numbered from the principal functional group to the other end, the direction being chosen to give the lowest numbers to the substituents. The entire name of the structure is then composed of (1) the numbers of the positions of the substituts (and of the principal functional group, if necessary); (2) the names of the substituts;(3) the name of the parent.The various functional groups are ranked in priority as to which receives the suffix name and the lowest position number1.A list of these priorities is given in Table 4.*-CKetonesIn the systematic names for ketones, the -e of the parent alkane name is dropped and -one is added. A prefix number is used if necessary.In a complex structure, a ketone group my be named in IUPAC system with the prefix oxo-. (The prefix keto- is also sometimes encountered.)AlcoholsThe names of alcohols may be: (1) IUPAC; (2) trivial; or, occasionally, (3) conjunctive. IUPAC names are taken from the name of the alkane with the final -e changed to -ol. In the case of polyols, the prefix di-, tri- etc. is placed just before -ol, with the position numbers placed at the start of the name, if possible, such as, 1,4-cyclohexandiol. Names for some alkyl halides, ketones and alcohols are listed in Table 5.EthersEthers are usually named by using the names of attached alkyl or aryl groups followed by the word ether. (These are trivial names.) For example, diethyl ether.In more complex ethers, an alkoxy- prefix may be used. This is the IUPAC preference, such as 3-methoxyhexane. Sometimes the prefix- oxa- is used.AminesAmines are named in two principal ways: with -amine as the ending and with amino- as a prefix. Names for some ethers and amines can be found in Table 6.Carboxylic AcidsThere are four principal types of names for carboxylic acids: (1) IUPAC; (2)trivial;(3)carboxylic acid; and (4)conjunctive. Trivial names are commonly used.AldehydesAldehydes may be named by the IUPAC system or by trivial aldehyde names. In the IUPAC system, the -oic acid ending of the corresponding carboxylic acid is changed to -al, such as hexanal. In trivial names, the -ic or -oic ending is changed to -aldehyde, such as benzaldehyde. Table 7 gives a list of commonly encountered names for carboxylic acids and aldehydes.Esters and Salts of Carboxylic AcidsEsters and salts of carboxylic acids are named as two words in both systematic and trivial names. The first word of the name is the name of the substituent on the oxygen. The second word of the name is derived from the name of the parent carboxylic acid with the ending changed from -ic acid to -ate.AmidesIn both the IUPAC and trivial systems, an amide is named by dropping the -ic or -oic ending of the corresponding acid name and adding -amide, such as hexanamide (IUPAC) and acetamide (trivial).Acid AnhydridesAcid anhydrides are named from the names of the component acid or acids with the word acid dropped and the word anhydride added, such as benzoic anhydride.The names for some esters, amides and anhydrides are shown in Table 8.Acid HalidesAcid halides are named by changing the ending of the carboxylic acid name from -ic acid to -yl plus the name of the halide, such as acetyl chloride.Some names of aryl compounds and aryls are as follows:benzenephenylbenzylarylbenzoic acid4. Introduction to Chemistry Department of FloridaUniversityProgram of StudyThe Department of Chemistry offers programs of study leading to the M.S. and Ph.D. degrees. Students may elect studies in analytical, inorganic, organic, and physical chemistry. Specialty disciplines, such as chemical physics and quantum, bioorganic, polymer, radiation, and nuclear chemistry, are available within the four major areas.The M.S. and Ph.D. degree requirements include a course of study, attendance at and presentation of a series of seminars, and completion and defense of a research topic worthy of publication1. Candidates for the Ph.D. degree must also demonstrate a reading ability of at least one foreign language and show satisfactory performance on a qualifying examination. The M.S. degree is not a prerequisite for the Ph.D. degree. A nonthesisdegree program leading to the M.S.T. degree is offered for teachers.Students are encouraged to begin their research shortly afterselecting a research director, who is the chairman of the supervisorycommittee that guides the student through a graduate career.Research FacilitiesThe chemistry department occupies 111,000 square feet of space in four buildings: Leigh Hall, the Chemical Research Building, Bryant Hall, and the Nuclear Science Building. Plans for a 65,000-square-foot addition to Leigh Hall are being prepared. A new central science library is located near the chemistry facilities. The University library system holds more than 2.2 million volumes.The major instrumentation includes ultraviolet-visible, infrared, fluorescence, Roman, nuclear magnetic resonance, electron spin resonance, X-ray, ESCA, and mass spectrometers. Many are equipped with temperature-control and Fourier-transform attachments, and some have laser sources. Data-storage and data-acquiring minicomputers are interfaced to some of the instruments, such as the recently constructed quadrupole resonance mass spectrometer. The chemistry department has V AX-11/780 and V AX-11/750 computers as well as multiple terminals connected to IBM machines in the main computer centre on campus.The departmental technical services include two well-equipped stockrooms and glassblowing, electronics, and machine shops to assist in equipment design, fabrication, and maintenance.Financial AidMost graduate students are given financial support in the form of teachingand research assistantships. Stipends range from $9400 - 11,000 for the1986-87 calendar year. State residents and assistantship holders pay in-statefees of about $1400 per calendar year. A limited number of full orsupplemental fellowships are available for superior candidates.Cost of StudyIn 1985-86, in-state students paid a registration fee of $48.62, per credit hour for each semester, out-of-state students paid an additional $ 94.50 ($ 143.12 per credit hour each semester). A small increase in fees is expected for 1986-87.5 ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTIONWith the coming of the Industrial Revolution the environmentalpollution increased alarmingly. Pollution can be defined as an undesirablechange in the physical, chemical, or biological characteristics of the air, water,or land that can harmfully affect health, survival, or activities of humans orother living organisms. There are four major forms of pollution - waste onland, water pollution (both the sea and inland waters), pollution of the atmosphere and pollution by noise.Land can be polluted by many materials. There are two major types of pollutants: degradable and nondegradable. Examples of degradable pollutantsare DDT and radioactive materials. DDT can decompose slowly buteventually are either broken down completely or reduced to harmless levels. For example, it typically takes about 4 years for DDT in soil to be decomposed to 25 percent of the original level applied. Some radioactive materials that give off harmful radiation, such as iodine-131, decay to harmless pollutants. Others, such as plutonium-239 produced by nuclear power plants, remains at harmful levels for thousands to hundreds of thousands of years.Nondegradable pollutants are not broken down by natural processes. Examples of nondegradable pollutants are mercury, lead and some of their compounds and some plastics. Nondegradable pollutants must be either prevented from entering the air, water, and soil or kept below harmful levels by removal from the environment.Water pollution is found in many forms. It is contamination of water with city sewage and factory wastes; the runoff of fertiliser and manure from farms and feed lots; sudsy streams; sediment washed from the land as a result of storms, farming, construction and mining; radioactive discharge from nuclear power plants; heated water from power and industrial plants; plastic globules floating in the world‟s oceans; and female sex hormones entering water supplies through the urine of women taking birth control pills.Even though scientists have developed highly sensitive measuringinstruments, determining water quality is very difficult. There are a largenumber of interacting chemicals in water, many of them only in trace amounts.About 30,000 chemicals are now in commercial production, and each yearabout 1,000 new chemicals are added. Sooner or later most chemicals end up in rivers, lakes, and oceans. In addition, different organisms have different ranges of tolerance and threshold levels for various pollutants. To complicate matters even further, while some pollutants are either diluted to harmless levels in water or broken down to harmless forms by decomposers and natural processes, others (such as DDT, some radioactive materials, and some mercury compounds) are biologically concentrated in various organisms1.Air pollution is normally defined as air that contains one or more chemicals in high enough concentrations to harm humans, other animals, vegetation, or materials. There are two major types of air pollutants. A primary air pollutant is a chemical added directly to the air that occurs in a harmful concentration. It can be a natural air component, such as carbon dioxide, that rises above its normal concentration, or something not usually found in the air,such as a lead compound. A secondary air pollutant is a harmful chemical formed in the atmosphere through a chemical reaction among air components.We normally associate air pollution with smokestacks and cars, but volcanoes, forest fires, dust storms, marshes, oceans, and plants also add to the air chemicals we consider pollutants. Since these natural inputs are usually widely dispersed throughout the world, they normally don‟t build up to harmful levels. And when they do, as in the case of volcanic eruptions, they are usually taken care of by natural weather and chemical cycles2.As more people live closer together, and as they use machines to produce leisure, they find that their leisure, and even their working hours, become spoilt by a byproduct of their machines – namely, noise,The technical difficulties to control noise often arise from the subjective-objective nature of the problem. You can define the excessive speed of a motor-car in terms of a pointer reading on a speedometer. But can you define excessive noise in the same way? You find that with any existing simple “noise-meter”, vehicles which are judged to be equally noisy may show considerable difference on the meter.Though the ideal cure for noise is to stop it at its source, thismay in many cases be impossible. The next remedy is to absorb iton its way to the ear. It is true that the overwhelming majority ofnoise problems are best resolved by effecting a reduction in thesound pressure level at the receiver. Soft taped music in restaurantstends to mask the clatter of crockery and the conversation at thenext table. Fan noise has been used in telephone booths to maskspeech interference from adjacent booths. Usually, the problem is how to reduce the sound pressure level, either at source or on the transmission path.6 ANALYTICAL INSTRUMENT MARKETThe market for analytical instruments is showing a strength only dreamed about as little as five years ago. Driven by the need for greater chemicalanalysis coming from quality control and government regulation, arobust export market, and new and increasingly sophisticatedtechniques, sales are increasing rapidly1.The analytical instrument business' worldwides sales arenearly double their value of five years ago, reaching $ 4.1 billion in1987. Such growth is in stark contrast to the doldrums of severalyears ago when economic recession held back sales growth to littleor nothing. In recent years, the instrumentation market hasrecovered, growing at nearly 9% per year, and it‟s expected t o continue at this rate at least until the 1990. With sales increases exceeding inflation, the industry has seen the real growth demonstrating the important role of chemical instrumentation in areas such as research and development, manufacturing, defense, and the environment in a technologically advancingworld2.Chromatography is the fastest-growing area, comprising 40%, or $ 1.5billion, in 1987 world sales. Chromatographic methods are used extensively inindustrial labs, which purchase about 70% of the devices made, for separation,purification, and analysis. One of the biggest words in all forms of chromatography is “biocompatibility.” Biocompatible instruments are designed to have chemically inert, corrosion-resistant surfaces in contact with the biological samples.Gas Chromatography sales are growing at about the same rate as the instrument market.Some of the newest innovations in GC technology are the production of more instruments with high-efficiency, high-resolution capillaries and supercritical fluid capability.Despite having only a 3% share of the GC market, supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC) has attracted a great deal of attention since its introduction around 1985 and production of the first commercial instrument around 1986. SFC, which operates using asupercritical fluid as the mobile phase, bridgesthe gap between GC and HPLC. The use ofthese mobile phases allows for higherdiffusion rates and lower viscosities thanliquids, and a greater solvating powerthan gases.Another area showing tremendous growth is ion chromatography (IC). From growth levels of 30% per year in the U.S. and similar levels worldwide, the rate is expected to drop slightly but remain high at 25%. The popularity of IC has been enhanced through extending its applicability from inorganic systems to amino acids and other biological systems by the introduction of biocompatible instruments.Mass spectrometry (MS) sales have been growing about 12% annually. Sales have always been high, especially since MS is the principal detector in a number of hyphenated techniques such as GC-MS, MS-MS, LC-MS, and GC-MS accounts for about 60% of MS sales since it is used widely in drug and environmental testing. Innovations in interface technology such as inductively coupled plasma/MS, SFC/MS, and thermospray or particle beam interfaces for LC-MS have both advanced the technology and expanded the interest in applications. Recent MS instruments with automated sampling and computerized data analysis have added to the attractiveness of the technique for first time users.Spectroscopy accounts for half of all instrument sales and is the largest overall category of instruments, as the Alpert & Suftcliffe study shows. It can be broken down evenly into optical methods and electromagnetic, or nonoptical, spectroscopies. These categories include many individual high-cost items such as MS, nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers, X-ray equipment, and electron microscopy and spectroscopy setups. Sales of spectroscopic instruments that are growing at or above the market rate include Fourier transform infrared (FTIR), Raman, plasma emission, and energy dispersive X-ray spectrometers. Others have matured and slowed down in growth, but may still hold a large share of the market.The future of analytical instrumentation does not appear to be without its new stars as there continue to be innovations and developments in existing technology. Among these are the introduction of FT Raman, IR dichroism, IR microscopy, and NMR imaging spectrometers. Hyphenated and automated apparatus are also appearing on the market more frequently. New analytical techniques like capillary electrophoresis, gel capillary electrophoresis, scanning tunneling microscopy for the imaging of conducting systems, atomic force microscopy for the imaging of biological systems, and other techniques for surface and materials analysis are already, or may soon be, appearing as commercialized instruments. And, if the chemical industry continues to do well in the next few years, so too will the sales of analytical instrumentation.The effect of alcohol have both medical and medicolegal implications. The estimationof alcohol in the blood or urine is relevant when the physician needs toknow whether it is responsible for the condition of the patient. From themedicolegal standpoint the alcohol level is relevant in cases of suddendeath, accidents while driving, and in cases when drunkenness is thedefense plea. The various factors in determining the time after ingestion showing maximum concentration and the quality of the alcohol are the weight of the subject,。
矿产资源开发利用方案编写内容要求及审查大纲
矿产资源开发利用方案编写内容要求及《矿产资源开发利用方案》审查大纲一、概述
㈠矿区位置、隶属关系和企业性质。
如为改扩建矿山, 应说明矿山现状、
特点及存在的主要问题。
㈡编制依据
(1简述项目前期工作进展情况及与有关方面对项目的意向性协议情况。
(2 列出开发利用方案编制所依据的主要基础性资料的名称。
如经储量管理部门认定的矿区地质勘探报告、选矿试验报告、加工利用试验报告、工程地质初评资料、矿区水文资料和供水资料等。
对改、扩建矿山应有生产实际资料, 如矿山总平面现状图、矿床开拓系统图、采场现状图和主要采选设备清单等。
二、矿产品需求现状和预测
㈠该矿产在国内需求情况和市场供应情况
1、矿产品现状及加工利用趋向。
2、国内近、远期的需求量及主要销向预测。
㈡产品价格分析
1、国内矿产品价格现状。
2、矿产品价格稳定性及变化趋势。
三、矿产资源概况
㈠矿区总体概况
1、矿区总体规划情况。
2、矿区矿产资源概况。
3、该设计与矿区总体开发的关系。
㈡该设计项目的资源概况
1、矿床地质及构造特征。
2、矿床开采技术条件及水文地质条件。