外文翻译--人工智能
- 格式:doc
- 大小:48.00 KB
- 文档页数:11

人工智能与智能翻译智能化的语言翻译随着科技的发展,人工智能(Artificial Intelligence,AI)的应用范围越来越广泛。
其中,智能翻译(Machine Translation,MT)作为人工智能领域的一项重要应用,正逐渐引起人们的关注。
智能翻译利用计算机技术实现不同语言之间的翻译,减轻了人工翻译的工作负担,提高了翻译效率。
本文将探讨人工智能与智能翻译的关系,并对智能化的语言翻译进行分析和讨论。
一、人工智能与智能翻译的关系人工智能是一门研究如何使计算机能够像人类一样思考、理解、学习和决策的科学。
而智能翻译作为人工智能的应用之一,旨在通过计算机自动化地实现不同语言之间的翻译。
人工智能和智能翻译的关系可以用以下几个方面来描述:1. 自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing,NLP):智能翻译依赖于自然语言处理技术,通过识别和理解源语言的语义和语法结构,将其转化为目标语言。
人工智能在NLP方面的发展,为智能翻译提供了更加精确和高效的语言处理能力。
2. 机器学习(Machine Learning):智能翻译的一个重要组成部分是机器学习算法。
机器学习是人工智能的核心技术之一,在智能翻译中可以通过训练模型,使计算机根据大量的翻译样本自动学习翻译规则和模式,提高翻译准确性和效率。
3. 深度学习(Deep Learning):深度学习是机器学习的一个分支,通过模拟人类神经网络的方式,实现对复杂任务的学习和处理。
在智能翻译领域,深度学习可以应用于机器翻译模型中,提升翻译质量和流畅性。
二、智能化的语言翻译分析与讨论智能化的语言翻译是指基于人工智能的技术手段,实现对不同语言之间的翻译,以达到高效、准确、流畅的翻译效果。
智能化的语言翻译在以下几个方面展现了其独特的优势和挑战:1. 翻译效率的提高:相比传统的人工翻译方式,智能化的语言翻译利用计算机和人工智能的技术手段,可以实现快速、自动化的翻译过程。

人工智能英语领域研究论文人工智能(Artificial Intelligence, AI)作为当今科技领域的热点之一,其在英语领域的应用和研究也日益受到重视。
本文将探讨人工智能在英语领域的研究进展,包括自然语言处理(Natural Language Processing, NLP)、机器翻译、语音识别、情感分析等方面,并展望这一领域的未来发展趋势。
引言随着人工智能技术的快速发展,其在语言处理领域的应用越来越广泛。
英语作为世界上使用最广泛的语言之一,其研究和应用尤为关键。
人工智能在英语领域的研究不仅能够提高语言处理的效率和准确性,还能够为语言教学、跨文化交流等提供新的工具和方法。
自然语言处理自然语言处理是人工智能领域的一个重要分支,它致力于使计算机能够理解、解释和生成人类语言。
在英语领域,NLP技术的应用包括但不限于文本分析、信息抽取、问答系统等。
例如,通过使用深度学习技术,计算机可以更好地理解英语文本的语义和上下文,从而提高信息检索和文本分类的准确性。
机器翻译机器翻译是利用计算机技术将一种语言的文本自动翻译成另一种语言。
随着神经网络和机器学习技术的发展,机器翻译的质量得到了显著提升。
在英语领域,机器翻译系统能够处理大量的双语文本数据,通过学习语言之间的对应关系,实现高质量的翻译输出。
然而,机器翻译仍面临诸如处理复杂语言结构、保持原文风格等挑战。
语音识别语音识别技术使得计算机能够将人类的语音转化为文本。
在英语领域,语音识别技术的应用场景广泛,包括语音助手、自动字幕生成等。
随着深度学习技术的发展,语音识别的准确率得到了显著提升。
然而,对于带有口音、语速快或背景噪音的语音,语音识别系统仍需进一步优化。
情感分析情感分析是分析文本或语音中的情感倾向,如正面、负面或中性。
在英语领域,情感分析技术可以应用于社交媒体监控、客户反馈分析等场景。
通过分析用户在社交媒体上的发言,企业可以更好地了解消费者的情感倾向,从而优化产品和服务。

人工智能技术在翻译服务领域的应用案例一、引言随着全球化进程的加快和跨国交流的增加,翻译服务成为促进跨文化沟通的重要环节。
而随着人工智能技术的快速发展,其在翻译服务领域的应用也越来越成熟。
本文将介绍几个人工智能技术在翻译服务领域的应用案例,展示其在提高翻译效率、准确性和便利性方面的巨大潜力。
二、机器翻译1. 案例一:谷歌翻译谷歌翻译是目前最著名的机器翻译工具之一。
它基于神经网络技术,通过对大量的双语文本进行学习和训练,实现自动翻译。
谷歌翻译的优点是可以实现多语种的翻译,并能根据上下文进行准确的翻译。
例如,当输入一句中文“我爱你”的时候,谷歌翻译可以根据上下文自动识别并进行正确的翻译,如“我 love 你”(中文拼音)或“我愛你”(中文繁体)。
2. 案例二:DeepL翻译DeepL翻译是一款基于深度学习技术的机器翻译工具。
相对于传统的基于规则的机器翻译系统,DeepL翻译能更好地理解上下文和语义,并生成更准确的翻译结果。
它通过大量的已翻译文本进行训练,不断优化自身的翻译能力。
不仅如此,DeepL还提供了多种语言之间的翻译服务,覆盖了全球多个主要语种。
三、语音翻译1. 案例一:微软翻译微软翻译是一款结合了语音识别和机器翻译的语音翻译工具。
用户可以通过输入语音、拍摄翻译文本或手写输入等方式进行翻译。
该工具通过语音识别技术将语音内容转化为文字,然后再进行翻译。
微软翻译支持多种语言之间的翻译,让跨语言交流更加方便快捷。
2. 案例二:百度识图翻译百度识图翻译是一款结合了图像识别和机器翻译的翻译工具。
用户可以通过拍摄外文文本图片,然后将图片上传至该应用中,系统将自动识别图片中的文字并进行翻译。
这在旅行或者学习外语时非常有用,能够帮助用户快速获取外文资讯,并理解其含义。
四、智能辅助翻译工具1. 案例一:SDL Trados StudioSDL Trados Studio是一款专业的翻译记忆工具,它结合了人工智能技术,帮助译员更高效地进行翻译工作。

人工智能(AI)革命外文翻译中英文英文The forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolution:Its impact on society and firmsSpyros MakridakisAbstractThe impact of the industrial and digital (information) revolutions has, undoubtedly, been substantial on practically all aspects of our society, life, firms and employment. Will the forthcoming AI revolution produce similar, far-reaching effects? By examining analogous inventions of the industrial, digital and AI revolutions, this article claims that the latter is on target and that it would bring extensive changes that will also affect all aspects of our society and life. In addition, its impact on firms and employment will be considerable, resulting in richly interconnected organizations with decision making based on th e analysis and exploitation of “big” data and intensified, global competition among firms. People will be capable of buying goods and obtaining services from anywhere in the world using the Internet, and exploiting the unlimited, additional benefits that will open through the widespread usage of AI inventions. The paper concludes that significant competitive advantages will continue to accrue to those utilizing the Internet widely and willing to take entrepreneurial risks in order to turn innovative products/services into worldwide commercial success stories. The greatest challenge facing societies and firms would be utilizing the benefits of availing AI technologies, providing vast opportunities for both new products/services and immense productivity improvements while avoiding the dangers and disadvantages in terms of increased unemployment and greater wealth inequalities.Keywords:Artificial Intelligence (AI),Industrial revolution,Digital revolution,AI revolution,Impact of AI revolution,Benefits and dangers of AI technologies The rise of powerful AI will be either the best or the worst thing ever to happento humanity. We do not yet know which.Stephen HawkingOver the past decade, numerous predictions have been made about the forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) Revolution and its impact on all aspects of our society, firms and life in general. This paper considers such predictions and compares them to those of the industrial and digital ones. A similar paper was written by this author and published in this journal in 1995, envisioning the forthcoming changes being brought by the digital (information) revolution, developing steadily at that time, and predicting its impact for the year 2015 (Makridakis, 1995). The current paper evaluates these 1995 predictions and their impact identifying hits and misses with the purpose of focusing on the new ones being brought by the AI revolution. It must be emphasized that the stakes of correctly predicting the impact of the AI revolution arefar reaching as intelligent machines may become our “final invention” that may end human supremacy (Barrat, 2013). There is little doubt that AI holds enormous potential as computers and robots will probably achieve, or come close to, human intelligence over the next twenty years becoming a serious competitor to all the jobs currently performed by humans and for the first time raising doubt over the end of human supremacy.This paper is organized into four parts. It first overviews the predictions made in the 1995 paper for the year 2015, identifying successes and failures and concluding that major technological developments (notably the Internet and smartphones) were undervalued while the general trend leading up to them was predicted correctly. Second, it investigates existing and forthcoming technological advances in the field of AI and the ability of computers/machines to acquire real intelligence. Moreover, it summarizes prevailing, major views of how AI may revolutionize practically everything and its impact on the future of humanity. The third section sums up the impact of the AI revolution and describes the four major scenarios being advocated, as well as what could be done to avoid the possible negative consequences of AI technologies. The fourth section discusses how firms will be affected by these technologies that will transform the competitive landscape, how start-up firms are founded and the way success can be achieved. Finally, there is a brief concluding section speculating about the future of AI and its impact on our society, life, firms and employment.1. The 1995 paper: hits and missesThe 1995 paper (Makridakis, 1995) was written at a time when the digital (at that time it was called information) revolution was progressing at a steady rate. The paper predicted that by 2015 “the information revolution should be in full swing” and that “computers/communications” would be in widespread use, whi ch has actually happened, although its two most important inventions (the Internet and smartphones) and their significant influence were not foreseen as such. Moreover, the paper predicted that “a single computer (but not a smartphone) can, in addition to its traditional tasks, also become a terminal capable of being used interactively for the following:” (p. 804–805)• Picture phone and teleconference• Television and videos• Music• Shopping• On line banking and financial services• Reservations• Medic al advice• Access to all types of services• Video games• Other games (e.g., gambling, chess etc.)• News, sports and weather reports• Access to data banksThe above have all materialized and can indeed be accessed by computer,although the extent of their utilization was underestimated as smartphones are now being used widely. For instance, the ease of accessing and downloading scientific articles on one's computer in his/her office or home would have seemed like science fiction back in 1995, when finding such articles required spending many hours in the library (often in its basement for older publications) and making photocopies to keep them for later use. Moreover, having access, from one's smartphone or tablet, to news from anywhere in the world, being able to subscribe to digital services, obtain weather forecasts, purchase games, watch movies, make payments using smartphones and a plethora of other, useful applications was greatly underestimated, while the extensive use of the cloud for storing large amounts of data for free was not predicted at all at that time. Even in 1995 when the implications of Moore's law leading to increasing computer speed and storage while reducing costs were well known, nevertheless, it was hard to imagine that in 2016 there would be 60 trillion web pages, 2.5 billion smartphones, more than 2 billion personal computers and 3.5 billion Google searches a day.The paper correctly predicted “as wireless telecommunications will be possible the above list of capabilities can be accessed from anywhere in the world without the need for regular telephone lines”. What the 1995 paper missed, however, was that in 2015 top smartphones, costing less than €500, would be as powerful as the 1995 supercomputer, allowing access to the Internet and all tasks that were only performed by expensive computers at that time, including an almost unlimited availability of new, powerful apps providing a large array of innovative services that were not imagined twenty years ago. Furthermore, the paper correctly predicted super automation leading to unattended factories stating that “by 2015 there will be little need for people to do repetitive manual or mental tasks”. It also foresaw the decline of large industrial firms, increased global competition and the drop in the percentage of labour force employed in agriculture and manufacturing (more on these predictions in the section The Impact of the AI Revolution on Firms). It missed however the widespread utilization of the Internet (at that time it was a text only service), as well as search engines (notably Google), social networking sites(notably Facebook) and the fundamental changes being brought by the widespread use of Apple's iPhone, Samsung's Galaxy and Google's Android smartphones. It is indeed surprising today to see groups of people in a coffee shop or restaurant using their smartphones instead of speaking to each other and young children as little as three or four years of age playing with phones and tablets. Smartphones and tablets connected to the Internet through Wi-Fi have influenced social interactions to a significant extent, as well as the way we search for information, use maps and GPS for finding locations, and make payments. These technologies were not predicted in the 1995 paper.2. Towards the AI revolutionThe 1995 paper referred to Say, the famous French economist, who wrote in 1828 about the possibility of cars as substitutes for horses:“Nevertheless no machine will ever be able to perform what even the worst horses can - the service of carrying people and goods through the bustle and throng of a great city.” (p. 800)Say could never have dreamed of, in his wildest imagination, self-driving cars, pilotless airplanes, Skype calls, super computers, smartphones or intelligent robots. Technologies that seemed like pure science fiction less than 190 years ago are available today and some like self-driving vehicles will in all likelihood be in widespread use within the next twenty years. The challenge is to realistically predict forthcoming AI technologies without falling into the same short-sighted trap of Say and others, including my 1995 paper, unable to realize the momentous, non-linear advancements of new technologies. There are two observations to be made.First, 190 years is a brief period by historical standards and during this period we went from horses being the major source of transportation to self-driving cars and from the abacus and slide rules to powerful computers in our pockets. Secondly, the length of time between technological inventions and their practical, widespread use is constantly being reduced. For instance, it took more than 200 years from the time Newcomen developed the first workable steam engine in 1707 to when Henry Ford built a reliable and affordable car in 1908. It took more than 90 years between the time electricity was introduced and its extensive use by firms to substantially improve factory productivity. It took twenty years, however, between ENIAC, the first computer, and IBM's 360 system that was mass produced and was affordable by smaller business firms while it took only ten years between 1973 when Dr Martin Cooper made the first mobile call from a handheld device and its public launch by Motorola. The biggest and most rapid progress, however, took place with smartphones which first appeared in 2002 and saw a stellar growth with the release of new versions possessing substantial improvements every one or two years by the likes of Apple, Samsung and several Chinese firms. Smartphones, in addition to their technical features, now incorporate artificial intelligence characteristics that include understanding speech, providing customized advice in spoken language, completing words when writing a text and several other functions requiring embedded AI, provided by a pocket computer smaller in size than a pack of cigarettes.From smart machines to clever computers and to Artificial Intelligence (AI) programs: A thermostat is a simple mechanical device exhibiting some primitive but extremely valuable type of intelligence by keeping temperatures constant at some desired, pre-set level. Computers are also clever as they can be instructed to make extremely complicated decisions taking into account a large number of factors and selection criteria, but like thermostats such decisions are pre-programmed and based on logic, if-then rules and decision trees that produce the exact same results, as long as the input instructions are alike. The major advantage of computers is their lightning speed that allows them to perform billions of instructions per second. AI, on the other hand, goes a step further by not simply applying pre-programmed decisions, but instead exhibiting some learning capabilities.The story of the Watson computer beating Jeopardy's two most successful contestants is more complicated, since retrieving the most appropriate answer out of the 200 million pages of information stored in its memory is not a sign of real intelligence as it relied on its lightning speed to retrieve information in seconds. What is more challenging according to Jennings, one of Jeopardy's previous champions, is“to read clues in a natural language, understand puns and the red herrings, to unpack just the meaning of the clue” (May, 2013). Similarly, it is a sign of intelligence to improve it s performance by “playing 100 games against past winners”. (Best, 2016). Watson went several steps beyond Deep Blue towards AI by being able to understand spoken English and learn from his mistakes (New Yorker, 2016). However, he was still short of AlphaGo that defeated Go Champions in a game that cannot be won simply by using “brute force” as the number of moves in this game is infinite, requiring the program to use learning algorithms that can improve its performance as it plays more and more gamesComputers and real learning: According to its proponents, “the main focus of AI research is in teaching computers to think for themselves and improvise solutions to common problems” (Clark, 2015). But many doubt that computers can learn to think for themselves even though they can display signs of intelligence. David Silver, an AI scientist working at DeepMind, explained that “even though AlphaGo has affectively rediscovered the most subtle concepts of Go, its knowledge is implicit. The computer parse out these concepts –they simply emerge from its statistical comparisons of types of winning board positions at GO” (Chouard, 2016). At the same time Cho Hyeyeon, one of the strongest Go players in Korea commented that “AlphaGo seems like it knows everything!” while others believe that “AlphaGo is likely to start a ‘new revolution’ in the way we play Go”as “it is seeking simply to maximize its probability of reaching winning positions, rather than as human players tend to do –maximize territorial gains” (Chouard, 2016). Does it matter, as Silver said, that AlphaGo's knowledge of the game is implicit as long as it can beat the best players? A more serious issue is whether or not AlphaGo's ability to win games with fixed rules can extend to real life settings where not only the rules are not fixed, but they can change with time, or from one situation to another.From digital computers to AI tools: The Intel Pentium microprocessor, introduced in 1993, incorporated graphics and music capabilities and opened computers up to a large number of affordable applications extending beyond just data processing. Such technologies signalled the beginning of a new era that now includes intelligent personal assistants understanding and answering natural languages, robots able to see and perform an array of intelligent functions, self-driving vehicles and a host of other capabilities which were until then an exclusive human ability. The tech optimists ascertain that in less than 25 years computers went from just manipulating 0 and 1 digits, to utilizing sophisticated neural networkalgorithms that enable vision and the understanding and speaking of natural languages among others. Technology optimists therefore maintain there is little doubt that in the next twenty years, accelerated AI technological progress will lead to a breakthrough, based on deep learning that imitates the way young children learn, rather than the laborious instructions by tailor-made programs aimed for specific applications and based on logic, if-then rules and decision trees (Parloff, 2016).For instance, DeepMind is based on a neural program utilizing deep learning that teaches itself how to play dozens of Atari games, such as Breakout, as well or better than humans, without specific instructions for doing so, but by playing thousands ofgames and improving itself each time. This program, trained in a different way, became the AlphaGo that defeated GO champion Lee Sodol in 2016. Moreover, it will form the core of a new project to learn to play Starcraft, a complicated game based on both long term strategy as well as quick tactical decisions to stay ahead of an opponent, which DeepMind plans to be its next target for advancing deep learning (Kahn, 2016). Deep learning is an area that seems to be at the forefront of research and funding efforts to improve AI, as its successes have sparked a burst of activity in equity funding that reached an all-time high of more than $1 billion with 121 projects for start-ups in the second quarter of 2016, compared to 21 in the equivalent quarter of 2011 (Parloff, 2016).Google had two deep learning projects underway in 2012. Today it is pursuing more than 1000, according to their spokesperson, in all its major product sectors, including search, Android, Gmail, translation, maps, YouTube, and self-driving cars (The Week, 2016). IBM's Watson system used AI, but not deep learning, when it beat the two Jeopardy champions in 2011. Now though, almost all of Watson's 30 component services have been augmented by deep learning. Venture capitalists, who did not even know what deep learning was five years ago, today are wary of start-ups that do not incorporate it into their programs. We are now living in an age when it has become mandatory for people building sophisticated software applications to avoid click through menus by incorporating natural-language processing tapping deep learning (Parloff, 2016).How far can deep learning go? There are no limits according to technology optimists for three reasons. First as progress is available to practically everyone to utilize through Open Source software, researchers will concentrate their efforts on new, more powerful algorithms leading to cumulative learning. Secondly, deep learning algorithms will be capable of remembering what they have learned and apply it in similar, but different situations (Kirkpatrick et al., 2017). Lastly and equally important, in the future intelligent computer programs will be capable of writing new programs themselves, initially perhaps not so sophisticated ones, but improving with time as learning will be incorporated to be part of their abilities. Kurzweil (2005) sees nonbiological intelligence to match the range and subtlety of human intelligence within a quarter of a century and what he calls “Singularity” to occur by 2045, b ringing “the dawning of a new civilization that will enable us to transcend our biological limitations and amplify our creativity. In this new world, there will be no clear distinction between human and machine, real reality and virtual reality”.For some people these predictions are startling, with far-reaching implications should they come true. In the next section, four scenarios associated with the AI revolution are presented and their impact on our societies, life work and firms is discussed.3. The four AI scenariosUntil rather recently, famines, wars and pandemics were common, affecting sizable segments of the population, causing misery and devastation as well as a large number of deaths. The industrial revolution considerably increased the standards of living while the digital one maintained such rise and also shifted employment patterns,resulting in more interesting and comfortable office jobs. The AI revolution is promising even greater improvements in productivity and further expansion in wealth. Today more and more people, at least in developed countries, die from overeating rather than famine, commit suicide instead of being killed by soldiers, terrorists and criminals combined and die from old age rather than infectious disease (Harari, 2016). Table 1 shows the power of each revolution with the industrial one aiming at routine manual tasks, the digital doing so to routine mental ones and AI aiming at substituting, supplementing and/or amplifying practically all tasks performed by humans. The cri tical question is: “what will the role of humans be at a time when computers and robots could perform as well or better andmuch cheaper, practically all tasks that humans do at present?” There are four scenarios attempting to answer this question.The Optimists: Kurzweil and other optimists predict a “science fiction”, utopian future with Genetics, Nanotechnology and Robotics (GNR) revolutionizing everything, allowing humans to harness the speed, memory capacities and knowledge sharing ability of computers and our brain being directly connected to the cloud. Genetics would enable changing our genes to avoid disease and slow down, or even reverse ageing, thus extending our life span considerably and perhaps eventually achieving immortality. Nanotechnology, using 3D printers, would enable us to create virtually any physical product from information and inexpensive materials bringing an unlimited creation of wealth. Finally, robots would be doing all the actual work, leaving humans with the choice of spending their time performing activities of their choice and working, when they want, at jobs that interest them.The Pessimists: In a much quoted article from Wired magazine in 2000, Bill Joy (Joy, 2000) wrote “Our most powerful 21st-century technologies –robotics, genetic engineering, and nanotech –are threatening to make humans an endangered species”. Joy pointed out that as machines become more and more intelligent and as societal problems become more and more complex, people will let machines make all the important decisions for them as these decisions will bring better results than those made by humans. This situation will, eventually, result in machines being in effective control of all important decisions with people dependent on them and afraid to make their own choices. Joy and many other scientists (Cellan-Jones, 2014) and philosophers (Bostrom, 2014) believe that Kurzweil and his supporters vastly underestimate the magnitude of the challenge and the potential dangers which can arise from thinking machines and intelligent robots. They point out that in the utopian world of abundance, where all work will be done by machines and robots, humans may be reduced to second rate status (some saying the equivalent of computer pets) as smarter than them computers and robots will be available in large numbers and people will not be motivated to work, leaving computers/robots to be in charge of making all important decisions. It may not be a bad world, but it will definitely be a different one with people delegated to second rate status.Harari is the newest arrival to the ranks of pessimists. His recent book (Harari, 2016, p. 397) concludes with the following three statements:• “Science is converging to an all-encompassing dogma, which says thatorganisms are algorithm s, and life is data processing”• “Intelligence is decoupling from consciousness”• “Non-conscious but highly intelligent algorithms may soon know us better than we know ourselves”Consequently, he asks three key questions (which are actually answered by the above three statements) with terrifying implications for the future of humanity: • “Are organisms really just algorithms, and is life just data processing?”• “What is more valuable –intelligence or consciousness?”• “What will happen to society, polit ics and daily life when non-conscious but highly intelligent algorithms know us better than we know ourselves?”Harari admits that nobody really knows how technology will evolve or what its impact will be. Instead he discusses the implications of each of his three questions: • If indeed organisms are algorithms then thinking machines utilizing more efficient ones than those by humans will have an advantage. Moreover, if life is just data processing then there is no way to compete with computers that can consult/exploit practically all available information to base their decisions.• The non-conscious algorithms Google search is based on the consultation of millions of possible entries and often surprise us by their correct recommendations. The implications that similar, more advanced algorithms than those utilized by Google search will be developed (bearing in mind Google search is less than twenty years old) in the future and be able to access all available information from complete data bases are far reachi ng and will “provide us with better information than we could expect to find ourselves”.• Humans are proud of their consciousness, but does it matter that self-driving vehicles do not have one, but still make better decisions than human drivers, as can be confirmed by their significantly lower number of traffic accidents?When AI technologies are further advanced and self-driving vehicles are in widespread use, there may come a time that legislation may be passed forbidding or restricting human driving, even though that may still be some time away according to some scientists (Gomes, 2014). Clearly, self-driving vehicles do not exceed speed limits, do not drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs, do not get tired, do not get distracted by talking on the phone or sending SMS or emails and in general make fewer mistakes than human drivers, causing fewer accidents. There are two implications if humans are not allowed to drive. First, there will be a huge labour displacement for the 3.5 million unionized truck drivers in the USA and the 600 thousand ones in the UK (plus the additional number of non-unionized ones) as well as the more than one million taxi and Uber drivers in these two countries. Second, and more importantly, it will take away our freedom of driving, admitting that computers are superior to us. Once such an admission is accepted there will be no limits to letting computers also make a great number of other decisions, like being in charge of nuclear plants, setting public policies or deciding on optimal economic strategies as their biggest advantage is their objectivity and their ability to make fewer mistakes than humans.One can go as far as suggesting letting computers choose Presidents/PrimeMinisters and elected officials using objective criteria rather than having people voting emotionally and believing the unrealistic promises that candidates make. Although such a suggestion will never be accepted, at least not in the near future, it has its merits since people often choose the wrong candidate and later regret their choice after finding out that pre-election promises were not only broken, but they were even reversed. Critics say if computers do eventually become in charge of making all important decisions there will be little left for people to do as they will be demoted to simply observing the decisions made by computers, the same way as being a passenger in a car driven by a computer, not allowed to take control out of the fear of causing an accident. As mentioned before, this could lead to humans eventually becoming computers’ pets.The pragmatists: At present the vast majority of views about the future implications of AI are negative, concerned with its potential dystopian consequences (Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla, says it is like “summoning the demon” and calls the consequences worse than what nuclear weapons can do). There are fewer optimists and only a couple of pragmatists like Sam Altman and Michio Kaku (Peckham, 2016) who believe that AI technologies can be controlled through “OpenAI” and effective regulation. The ranks of pragmatists also includes John Markoff (Markoff, 2016) who pointed out that the AI field can be distinguished by two categories: The first trying to duplicate human intelligence and the second to augment it by expanding human abilities exploiting the power of computers in order to augment human decision making. Pragmatists mention chess playing where the present world champion is neither a human nor a computer but rather humans using laptop computers (Baraniuk, 2015). Their view is that we could learn to exploit the power of computers to augment our own skills and always stay a step ahead of AI, or at least not be at a disadvantage. The pragmatists also believe that in the worst of cases a chip can be placed in all thinking machines/robots to render them inoperative in case of any danger. By concentrating research efforts on intelligence augmentation, they claim we can avoid or minimize the possible danger of AI while providing the means to stay ahead in the race against thinking machines and smart robots.The doubters: The doubters do not believe that AI is possible and that it will ever become a threat to humanity. Dreyfus (1972), its major proponent, argues that human intelligence and expertise cannot be replicated and captured in formal rules. He believes that AI is a fad promoted by the computer industry. He points out to the many predictions that did not materialize such as those made by Herbert A. Simon in 1958 that “a computer would be the world's chess champion within ten years” and those made in 1965 that “machines will be capable within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do” (Crevier, 1993). Dreyfus claims that Simon's optimism was totally unwarranted as they were based on false assumptions that human intelligence is based on an information processing viewpoint as our mind is nothing like a computer. Although, the doubters’ criticisms may have been valid in the last century, they cannot stand for the new developments in AI. Deep Blue became the world's chess champion in 1997 (missing Simon's forecast by twenty one years) while we are not far today from machines being capable of doing all the work that humans can do (missing。

外文翻译器外文翻译器外文翻译器(Machine Translation)是指使用计算机等技术对外文进行自动翻译的工具。
它利用计算机语言处理、人工智能和语言学等多个领域的知识和技术,将源语言(外文)自动转化为目标语言(母语)的过程。
外文翻译器可以帮助人们快速准确地将外文内容转化为自己熟悉的语言,提高工作效率和信息获取能力。
外文翻译器的研究和发展始于上世纪40年代,最早采用的是基于规则的翻译方法,即根据语法规则和词汇库对源语言进行分析和转换。
然而,这种方法存在很多限制,因为语法和词汇库可能无法覆盖所有的语言特点和用法,导致翻译结果不准确和不流畅。
随着计算机技术和人工智能的发展,神经网络机器翻译(Neural Network Translation)成为外文翻译器的主流方法。
这种方法利用大规模平行语料库训练神经网络模型,通过模仿人类学习语言的方式自动学习源语言和目标语言之间的映射关系。
神经网络机器翻译能够更好地处理语法结构和上下文信息,翻译结果更加准确和自然。
除了神经网络机器翻译,外文翻译器还可以采用统计机器翻译(Statistical Machine Translation)等其他方法。
统计机器翻译利用大量的双语语料进行统计分析,找到最佳的翻译候选,然后根据概率模型对其进行排序和选择。
虽然统计机器翻译在一定程度上改善了翻译质量,但由于依赖于大量的语料库,对于某些语言和领域的翻译效果仍然不理想。
当前外文翻译器的发展已经进入了深度学习时代,融合了自然语言处理、深度学习和人工智能的多种技术手段。
深度学习通过建立多层神经网络模型,能够从大规模语料中自动学习和提取特征,进一步提升了翻译质量和效率。
此外,人工智能的发展还带来了一系列辅助工具,如术语提取、句子结构分析和语音识别等,能够进一步提高翻译的准确性和流畅度。
虽然外文翻译器在很大程度上改善了翻译效率和准确性,但由于语言本身的复杂性和多义性,完全依靠机器翻译仍然存在一些局限性。
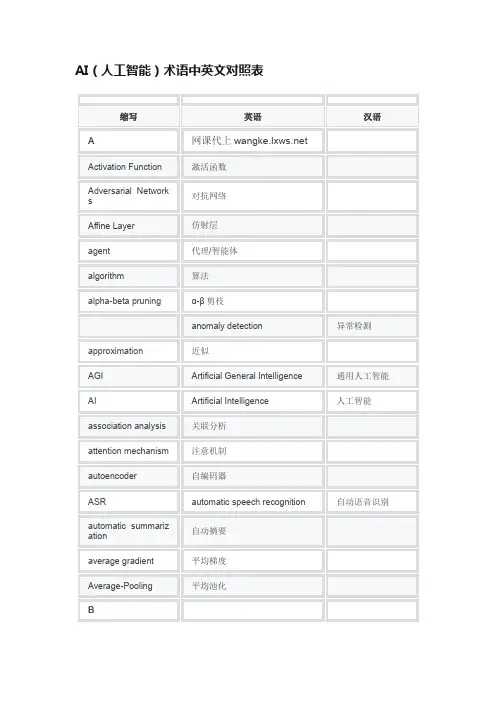
AI(人工智能)术语中英文对照表缩写英语汉语A网课代上Activation Function激活函数Adversarial Networks对抗网络Affine Layer仿射层agent代理/智能体algorithm算法alpha-beta pruningα-β剪枝anomaly detection异常检测approximation近似AGI Artificial General Intelligence通用人工智能AI Artificial Intelligence人工智能association analysis关联分析attention mechanism注意机制autoencoder自编码器ASR automatic speech recognition自动语音识别automatic summarization自动摘要average gradient平均梯度Average-Pooling平均池化BBP backpropagation反向传播BPTT Backpropagation Through Time 通过时间的反向传播BN Batch Normalization分批标准化Bayesian network贝叶斯网络Bias-Variance Dilemma偏差/方差困境Bi-LSTM Bi-directional Long-Short TermMemory双向长短期记忆bias偏置/偏差big data大数据Boltzmann machine玻尔兹曼机CCPU Central Processing Unit中央处理器chunk词块clustering聚类cluster analysis聚类分析co-adapting共适应co-occurrence共现Computation Cost计算成本Computational Linguistics计算语言学computer vision计算机视觉concept drift概念漂移CRF conditional random field条件随机域/场convergence收敛CA conversational agent会话代理convexity凸性CNN convolutional neural network卷积神经网络Cost Function成本函数cross entropy交叉熵DDecision Boundary决策边界Decision Trees决策树DBN Deep Belief Network深度信念网络DCGAN Deep Convolutional GenerativeAdversarial Network深度卷积生成对抗网络DL deep learning深度学习DNN deep neural network深度神经网络Deep Q-Learning深度Q学习DQN Deep Q-Network深度Q网络DNC differentiable neural computer可微分神经计算机dimensionality reduction algorithm降维算法discriminative model判别模型discriminator判别器divergence散度domain adaption领域自适应DropoutDynamic Fusion动态融合EEmbedding嵌入emotional analysis情绪分析End-to-End端到端EM Expectation-Maximization期望最大化Exploding GradientProblem梯度爆炸问题ELM Extreme Learning Machine超限学习机FFAIR Facebook Artificial IntelligenceResearchFacebook人工智能研究所factorization因子分解feature engineering特征工程Featured Learning特征学习Feedforward Neural Networks前馈神经网络Ggame theory博弈论GMM Gaussian Mixture Model高斯混合模型GA Genetic Algorithm遗传算法Generalization泛化GAN Generative Adversarial Networks生成对抗网络Generative Model生成模型Generator生成器Global Optimization全局优化GNMT Google Neural Machine Translation谷歌神经机器翻译Gradient Descent梯度下降graph theory图论GPU graphics processing unit 图形处理单元/图形处理器HHDM hidden dynamic model隐动态模型hidden layer隐藏层HMM Hidden Markov Model隐马尔可夫模型hybrid computing混合计算hyperparameter超参数IICA Independent Component Analysis独立成分分析input输入ICML International Conference for Machine Learning国际机器学习大会language phenomena语言现象latent dirichlet allocation隐含狄利克雷分布JJSD Jensen-Shannon Divergence JS距离KK-Means Clustering K-均值聚类K-NN K-Nearest Neighbours AlgorithmK-最近邻算法Knowledge Representation知识表征KB knowledge base知识库LLatent Dirichlet Allocation隐狄利克雷分布LSA latent semantic analysis潜在语义分析learner学习器Linear Regression线性回归log likelihood对数似然Logistic Regression Logistic回归LSTM Long-Short Term Memory长短期记忆loss损失MMT machine translation机器翻译Max-Pooling最大池化Maximum Likelihood最大似然minimax game最小最大博弈Momentum动量MLP Multilayer Perceptron多层感知器multi-document summarization多文档摘要MLP multi layered perceptron多层感知器multimodal learning多模态学习multiple linear regression多元线性回归NNaive Bayes Classifier朴素贝叶斯分类器named entity recognition命名实体识别Nash equilibrium纳什均衡NLG natural language generation自然语言生成NLP natural language processing自然语言处理NLL Negative Log Likelihood负对数似然NMT Neural Machine Translation神经机器翻译NTM Neural Turing Machine神经图灵机NCE noise-contrastive estimation噪音对比估计non-convex optimization非凸优化non-negative matrix factorization非负矩阵分解Non-Saturating Game非饱和博弈Oobjective function目标函数Off-Policy离策略On-Policy在策略one shot learning一次性学习output输出PParameter参数parse tree解析树part-of-speech tagging词性标注PSO Particle Swarm Optimization粒子群优化算法perceptron感知器polarity detection极性检测pooling池化PPGN Plug and Play Generative Network即插即用生成网络PCA principal component analysis主成分分析Probability Graphical Model概率图模型QQNN Quantized Neural Network量子化神经网络quantum computer量子计算机Quantum Computing量子计算RRBF Radial Basis Function径向基函数Random Forest Algorithm随机森林算法ReLU Rectified Linear Unit 线性修正单元/线性修正函数RNN Recurrent Neural Network循环神经网络recursive neural network递归神经网络RL reinforcement learning强化学习representation表征representation learning表征学习Residual Mapping残差映射Residual Network残差网络RBM Restricted Boltzmann Machine受限玻尔兹曼机Robot机器人Robustness稳健性RE Rule Engine规则引擎Ssaddle point鞍点Self-Driving自动驾驶SOM self organised map自组织映射Semi-Supervised Learning半监督学习sentiment analysis情感分析SLAM simultaneous localization and mapping同步定位与地图构建SVD Singular Value Decomposition奇异值分解Spectral Clustering谱聚类Speech Recognition语音识别SGD stochastic gradient descent随机梯度下降supervised learning监督学习SVM Support Vector Machine支持向量机synset同义词集Tt-SNE T-Distribution Stochastic Neighbour EmbeddingT-分布随机近邻嵌入tensor张量TPU Tensor Processing Units张量处理单元the least square method最小二乘法Threshold阙值Time Step时间步骤tokenization标记化treebank树库transfer learning迁移学习Turing Machine图灵机Uunsupervised learning无监督学习VVanishing Gradient Problem梯度消失问题VC Theory Vapnik–Chervonenkis theory 万普尼克-泽范兰杰斯理论von Neumann architecture 冯·诺伊曼架构/结构WWGAN Wasserstein GANW weight权重word embedding词嵌入WSD word sense disambiguation词义消歧XYZZSL zero-shot learning零次学习zero-data learning零数据学习。

人工智能翻译随着科技的飞速发展,人工智能(Artificial Intelligence,AI)在诸多领域中得到了广泛应用。
人工智能翻译作为其中一项重要应用之一,正在深刻地改变着我们的生活和交流方式。
本文将探讨人工智能翻译的原理、应用领域、优缺点以及未来发展前景。
一、人工智能翻译的原理人工智能翻译是指利用计算机技术和人工智能算法实现的语言翻译过程。
其基本原理是通过机器学习和深度学习技术,将源语言的句子转化为中间语言,再将中间语言翻译为目标语言,从而实现跨语言的翻译。
人工智能翻译的核心是训练和优化机器翻译模型,通过对大量的双语语料进行学习,使机器不断提高翻译准确度和效率。
二、人工智能翻译的应用领域人工智能翻译在许多领域中有着广泛的应用。
首先,人工智能翻译在跨国公司的业务交流中起到了重要的角色,可以帮助企业解决语言障碍问题,促进不同国家之间的合作和交流。
其次,人工智能翻译在旅游和跨文化交流中也发挥着重要作用,可以帮助游客和旅行者更好地理解和融入当地文化。
此外,人工智能翻译还应用于新闻报道、学术论文翻译、电子商务和在线内容翻译等领域,满足了人们对多语种信息获取的需求。
三、人工智能翻译的优缺点虽然人工智能翻译在很多方面有着显著的优势,但也存在一些限制和挑战。
首先,人工智能翻译的翻译准确度相对有待提高,尤其是对于复杂的句子结构和专业性较强的文本,机器往往无法达到与人类翻译相媲美的水平。
其次,人工智能翻译在处理上下文信息时还存在一定的困难,往往难以准确理解句子的背景和语境,导致翻译结果不够流畅和准确。
此外,人工智能翻译还面临着数据隐私和信息安全的问题,需要加强相应的技术和法律保护。
四、人工智能翻译的未来发展前景随着机器学习和自然语言处理技术的不断进步,人工智能翻译在未来将继续取得突破性的进展。
首先,随着语言模型的不断优化和增强,人工智能翻译的准确度和流畅度会逐渐提高,更好地满足多语种交流的需求。
其次,随着云计算和大数据技术的发展,人工智能翻译将越来越快速和高效,为用户提供更好的翻译体验。

人工智能英文文献译文在计算机科学里许多现代研究都致于两个方面:一是怎样制造智能计算机,二是怎样制造超高速计算机.硬件成本的降低,大规模集成电路技术(VLSI)不可思议的进步以及人工智能(AI)所取得的成绩使得设计面向AI应用的计算机结构极为可行,这使制造智能计算机成了近年来最”热门”的方向.AI 提供了一个崭新的方法,即用计算技术的概念和方法对智能进行研究,因此,它从根本上提供了一个全新的不同的理论基础.作为一门科学,特别是科学最重要的部分,AI的上的是了解使智能得以实现的原理.作为一种技术和科学的一部分,AI的最终目的是设计出能完全与人类智能相媲美的智能计算机系统.尽管科学家们目前尚未彀这个目的,但使计算机更加智能化已取得了很大的进展,计算机已可用来下出极高水平的象棋,用来诊断某种疾病,用来发现数学概念,实际上在许多领域已超出了高水平的人类技艺.许多AI计算机应用系统已成功地投入了实用领域.AI是一个正在发展的包括许多学科在内的领域,AI的分支领域包括:知识表达,学习,定理证明,搜索,问题的求解以及规划,专家系统,自然语言(文本或语音)理解,计算机视觉,机器人和一些其它方面/(例如自动编程,AI教育,游戏,等等).AI是使技术适应于人类的钥匙,将在下一代自动化系统中扮演极为关键的角色.据称AI应用已从实验室进入到实用领域,但是传统的冯·诺依曼计算机中,有更大的存储容量与处理能力之比,但最终效率也不是很高.无论使处理器的速度多快也无法解决这个问题,这是因为计算机所花费的时间主要取决于数据的处理器和存储器之间传送所需的时间,这被称之为冯·诺依曼瓶颈.制造的计算机越大,这个问题就越严重.解决的方法是为AI应用设计出不同于传统计算机的特殊结构.在未来AI结构的研究中,我们可以在计算机结构中许多已有的和刚刚出现的新要领的优势,比如数据流计算,栈式计算机,特征,流水线,收缩阵列,多处理器,分布式处理,数据库计算机和推理计算机.无需置疑,并行处理对于AI应用是至关重要的.根据AI中处理问题的特点,任何程序,哪怕只模拟智能的一小部分都将是非常复杂的.因此,AI仍然要面对科学技术的限制,并且继续需要更快更廉价的计算机.AI的发展能否成为主流在很大程度上取决于VLSI技术的发展.另一方面,并行提供了一个在更高性能的范围内使用廉价设备的方法.只要使简单的处理单元完全构成标准模式,构成一个大的并行处理系统就变得轻而易举,由此而产生的并行处理器应该是成本低廉的.在计算机领域和AI中,研究和设计人员已投入大量精力来考查和开发有效的并行AI结构,它也越来越成为吸引人的项目.目前,AI在表达和使用大量知识以及处理识别问题方面仍然没有取得大的进展,然而人脑在并行处理中用大量相对慢的(与目前的微电子器件比较)神经元却可十分出色地完成这些任务.这启发了人们或许需要某种并行结构来完成这些任务.将极大地影响我们进行编程的方法.也许,一旦有了正确的结构,用程序对感觉和知识表达进行处理将变得简单自然.研究人员因此投入大量努力来寻求并行结构.AI中的并行方法不仅在廉价和快速计算机方面,而且在新型计算方法方面充满希望.两种流行的AI语言是函数型编程语言,即基于λ算子的和逻辑编程语言,即基于逻辑的.此外,面向对象的编程正在引起人们的兴趣.新型计算机结构采用了这些语言并开始设计支持一种或多种编程形式的结构.一般认为结合了这三种编程方式可为AI应用提供更好的编程语言,在这方面人们已经作了大量的研究并取得了某些成就.人工智能的发展1 经典时期:游戏和定理证明人工智能比一般的计算机科学更年轻,二战后不久出现的游戏程序和解迷宫程序可以看作是人工智能的开始,游戏和解迷宫看起来距专家系统甚远,也不能为实际应用提供理论基础.但是,基于计算机的问题的最基本概念可以追溯到早期计算机完成这些任务的程序设计方法.(1)状态空间搜索早期研究提出的基本叫做状态空间搜索,实质非常简单.很多问题都可以用以下三个组成部分表述:1. 初始状态,如棋盘的初始态;2. 检查最终状态或问题解的终止测试;3. 可用于改变问题当前状态的一组操作,如象棋的合法下法.这种概念性状态空间的一种思路是图,图中节点表示状态, 弧表示操作.这种空间随着思路的发展而产生,例如,可以从棋盘的初始状态开始构成图的第一个节,白子每走一步都产生连向新状态的一条弧,黑子对白子每步棋的走法,可以认为是改变了棋盘状态的情况下连向这些新节点的操作,等等.(2)启发式搜索如果除小范围搜索空间以外,彻底的搜索不可能的话,就需要某些指导搜索的方法.用一个或多项域专门知识去遍历状态空间图的搜索叫做启发式搜索.启发是凭经验的想法,它不像算法或决策程序那样保证成功,它是一种算法或过程,但大多数情况下是有用的.2 现代时期:技术与应用所谓现代时期是从70年代半期延续到现在,其特征是日益发展的自意识和自批判能力以及对于技术和应用的更强的定位.与理解的心理学概念相联系似已不占据核心地位.人们也渐渐不再对一般问题方法(如启发式搜索)心存幻想,研究者们已经认识到,这种方法过高估计了”一般智能”的概念,这一概念一向为心理学家喜欢,其代价是未考虑人类专家所具有的某一领域内的能力.这种方法也过低地估计了人的简单常识,特别是人能够避免,认识和纠正错误的能力.解决问题的启发能力程序能够处理的相关知识的清晰表达,而非某些复杂的推理机制或某些复杂的求值函数,这一观点已被证实并接受.研究者已经研制出以模块形式对人的知识进行编码的技术,此种编码可用模式启动.这些模式可以代表原始的或处理过的数据,问题说明或问题的部分解.早期模拟人们解决问题的努力试图达到知识编码的一致性和推理机制的简单性.后来将该结果应用于万家系统的尝试主要是允许自身的多样性.INTRODCTION TO ARTIFICIALMuch modern research effort in computer science goes along two directions. One is how to make intelligent computers,the other how to make ultraly high-speed computers. The former has become the newest “hot ” direction in recent years because the decreasing hardware costs, the marvelous progress in VLSI technology,and the results achieved in Artificial Intelligence(AI) have made it feasible to design AI applications oriented computer architectures.AI,which offers a mew methodology, is the study of intelligence using the idead and methods of computation, thus offering a radically new and different basis for theory formation. As a science, essentially part of Cognitive Science, the goal of AI is to understand the principles thatmake intelligence possible. As a technology and as a part of computer science,the final goal of AI is to design intelligent computer systems that behave with the complete intelligence of human mind.although scientists are far from achieving this goal, great progress dose hae been made in making computers more intelligent . computers can be made to play excellint chess, to diagnose certain types of diseases, to discover mathematical comcepts, and if fact , to excel in many other areas requiring a high level of human expertise. Many Aiapplication computer systems have been successfully put into practical usages.AI is a growing field that covers many disciplines. Subareas of AI include knowledge representation ,learning, theorem proving,search,problem solving, and planning, expert systems, natural-language(text or speech)understanding,computer vision,robotics, and several others (such as automatic programming ,AI education,game playing, etc.) .AI is the key for making techmology adaptable to people. It will play a crucial role in the next generation of automated systems.It is a growing field that covers many disciplines.subbareas of AI include knowledge representation,learing,theorem proving,search,prroblem solving, and planning,expert systems,natural_language(text or speech ) understanding,computer vision,robotics , and severalothers (such as automatic programming, AI education, game playing,etc.).AI is the key for making technology adaptable to people. It will play a crucial role in the next generation of automated systems.It is claimed that AI applications have moved from laboratories to the real wortld. However ,conventional von Neumann computers are unsuitable for AI applications,because they are designed mainly for numerical processing. In a larger von Neumann computer, there is a larger tatio of memory to processing power and consequently it is even less efficient. This inefficiency remains no matter how fast we make the processor because the length of the computation becomes dominated by the time required to move data between processor and memory. This is called the von Neumann bottleneck. The bigger we build machines, the worse it gets. The way to solve the problem is to diverse from the traditional architectures and to design special ones for AI applications. In the research of future AI architectures, we can take advantages of many existing or currentlyemerging concepts in computer architecture, such as dataflow computation, stack machines, tagging,pipelining, systolic array,multiprocessing,distrbuted processing,database machines ,and inference machines.No doubt, parallel processing is of crucial importance for AI applications.due to the nature of problems dealt with in AI, any program that will successfully simulate even a small part of intelligence will be very complicated. Therefor,AI continuously confronts the limits of computer science technology,and there id an instatiable demand for fastert and cheaper computers.the movement of AI into mainstream is largely owned to the addevent of VLSI technology.parallel architectures,on the other han,provide a way of using the inexpensive device technology at much higher performance ranges.it ix becoming easier and cheaper to construc large parallel processing systems as long as they are made of fairly regular patterns of simpl processwing elements,and thus parallel processors should become cost effective.a great amount of effort has been devoted to inverstigating and developing effictive parallel AI architectures,ans this topic id becoming more and more attractive for reaseachers and designersin the areas of computers and AI.Currently, very little success has been achieved in AI in representing and using large bodies of knowledge and in dealing with recognition problems. Whereas human brain can perform these tasks temarkably well using a large number of relatively slow (in comparison with todays microelectronic devices) neurons in parallel. This suggests that for these tasks some kind of parllel architecture may be needed. Architectures can significantly influence the way we programming it for perception and knowledge representation would be easy and natural. This has led researchers to look into massively parallel architectures. Parallelism holds great promise for AI not only in terms of cheaper and faster computers. But also as a novel way of viewingcomputation.Two kinds of popular AI languages are functoional programming languages, which are lambda-based ,and logic programming is attracting a growing interest. Novel computer architects have considered these languages seriously and begun to design architectures supporting one or more of the programming styles. It has been recognized that a combination of the three programming styles mingt provide a better language for AI applications. There have already been a lot of research effort and achievements on this topic.Development of AI1 the classical period: game playing and theorem provingartificial inteligence is scarcely younger than conventional computer science;the bebinnings of AI can be seen in the first game-playing and puzzle-solving programs written shortly after World War Ⅱ. Gameplaying and puzzle-solving may seem somewhat remote from espert systems, and insufficiently serious to provide a theoretical basis for real applications. However, a rather basic notion about computer-based problem solving can be traced back to early attempts to program computers to perform shuch tasks.(1)state space searchThe fundamental idea that came out of early research is called state space search,and it is essentially very simple. Many kinds of problem can be formulated in terms of three important ingredients:(1)a starting state,such as the initial state of the chess board;(2)a termination test for detecing final states or sulutions to the problem,such as the simple rule for detecting checkmate in chess;(3)a set of operations that can be applied to change the current state of theproblem,such as the legal moves of chess.One way of thinking of this conceptual space of states is as a graph in which the states are nodes and the operations are arcs. Such spaces can be generated as you go . gor exampe, you coule gegin with the starting state of the chess board and make it the first node in the graph. Each of White’s possilbe first moves would then be an arc connecting this node to a new state of the board. Each of Black’s legal replies to each of these f irst moves could then be considered as operations which connect each of these new nodes to a changed statd of the board , and so on .(2)Heuristic searchHiven that exhaustive search is mot feasible for anything other than small search spaces, some means of guiding the search is required. A search that uses one or more items of domain-specific knowledge to traverse a state space graphy is called a heuristic search. Aheuristic is best thought of as a rule of thumb;it is not guaranteed to succeed,in the way that an algorithm or decision procedure is ,but it is useful in the majority of cases .2 the romantic period: computer understandingthe mid-1960s to the mid-1970s represents what I call the romantic period in artificial intelligence reserch. Atthis time, people were very concerned with making machines “understand”, by which they usually meant the understanding of natural language, especially stories and dialogue. Winograd’s (1972)SHRDLU system was arguably the climax of this epoch : a program which was capable of understanding a quite substantial subset of english by representing and reasoning about a very restricted domain ( a world consisting of children’s toy blocks).The program exhibited understanding by modifying its “blocksworld” represent ation in respinse to commands , and by responding to questions about both the configuration of blocks and its “actions” upon them. Thus is could answer questions like:What is the colour of the block supporting the red pyramid?And derive plans for obeying commands such as :Place the blue pyramid on the green block.Other researchers attempted to model human problem-solving behaviour on simple tasks ,such as puzzles, word games and memory tests. The aim war to make the knowledge and strategy used by the program resemble the knowledge and strategy of the human subject as closely as possible. Empirical studies compared the performance of progran and subject in an attempt to see how successful the simulation had been.。

文献信息:文献标题:Research Priorities for Robust and Beneficial Artificial Intelligence(稳健和有益的人工智能的研究重点)国外作者:Stuart Russell, Daniel Dewey, Max Tegmark文献出处:《Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence》,2015,36(4):105-114字数统计:英文2887单词,16400字符;中文5430汉字外文文献:Research Priorities for Robust and Beneficial Artificial Intelligence Abstract Success in the quest for artificial intelligence has the potential to bring unprecedented benefits to humanity, and it is therefore worthwhile to investigate how to maximize these benefits while avoiding potential pitfalls. This article gives numerous examples (which should by no means be construed as an exhaustive list) of such worthwhile research aimed at ensuring that AI remains robust and beneficial.Keywords:artificial intelligence, superintelligence, robust, beneficial, safety, societyArtificial intelligence (AI) research has explored a variety of problems and approaches since its inception, but for the last 20 years or so has been focused on the problems surrounding the construction of intelligent agents – systems that perceive and act in some environment. In this context, the criterion for intelligence is related to statistical and economic notions of rationality – colloquially, the ability to make good decisions, plans, or inferences. The adoption of probabilistic representations and statistical learning methods has led to a large degree of integration and cross-fertilization between AI, machine learning, statistics, control theory, neuroscience, and other fields. The establishment of shared theoretical frameworks, combined with the availability of data and processing power, has yielded remarkablesuccesses in various component tasks such as speech recognition, image classification, autonomous vehicles, machine translation, legged locomotion, and question-answering systems.As capabilities in these areas and others cross the threshold from laboratory research to economically valuable technologies, a virtuous cycle takes hold whereby even small improvements in performance are worth large sums of money, prompting greater investments in research. There is now a broad consensus that AI research is progressing steadily, and that its impact on society is likely to increase. The potential benefits are huge, since everything that civilization has to offer is a product of human intelligence; we cannot predict what we might achieve when this intelligence is magnified by the tools AI may provide, but the eradication of disease and poverty are not unfathomable. Because of the great potential of AI, it is valuable to investigate how to reap its benefits while avoiding potential pitfalls.Short-term Research PrioritiesOptimizing AI’s Economic ImpactThe successes of industrial applications of AI, from manufacturing to information services, demonstrate a growing impact on the economy, although there is disagreement about the exact nature of this impact and on how to distinguish between the effects of AI and those of other information technologies. Many economists and computer scientists agree that there is valuable research to be done on how to maximize the economic benefits of AI while mitigating adverse effects, which could include increased inequality and unemployment (Mokyr 2014; Brynjolfsson and McAfee 2014; Frey and Osborne 2013; Glaeser 2014; Shanahan 2015; Nilsson 1984; Manyika et al. 2013). Such considerations motivate a range of research directions, spanning areas from economics to psychology. Below are a few examples that should by no means be interpreted as an exhaustive list.Labor market forecasting:When and in what order should we expect various jobs to become automated (Frey and Osborne 2013)? How will this affect the wages of less skilled workers, the creative professions, and different kinds of informationworkers? Some have have argued that AI is likely to greatly increase the overall wealth of humanity as a whole (Brynjolfsson and McAfee 2014). However, increased automation may push income distribution further towards a power law (Brynjolfsson, McAfee, and Spence 2014), and the resulting disparity may fall disproportionately along lines of race, class, and gender; research anticipating the economic and societal impact of such disparity could be useful.Other market disruptions: Significant parts of the economy, including finance, insurance, actuarial, and many consumer markets, could be susceptible to disruption through the use of AI techniques to learn, model, and predict human and market behaviors. These markets might be identified by a combination of high complexity and high rewards for navigating that complexity (Manyika et al. 2013).Policy for managing adverse effects:What policies could help increasingly automated societies flourish? For example, Brynjolfsson and McAfee (Brynjolfsson and McAfee 2014) explore various policies for incentivizing development of labor-intensive sectors and for using AI-generated wealth to support underemployed populations. What are the pros and cons of interventions such as educational reform, apprenticeship programs, labor-demanding infrastructure projects, and changes to minimum wage law, tax structure, and the social safety net (Glaeser 2014)? History provides many examples of subpopulations not needing to work for economic security, ranging from aristocrats in antiquity to many present-day citizens of Qatar. What societal structures and other factors determine whether such populations flourish? Unemployment is not the same as leisure, and there are deep links between unemployment and unhappiness, self-doubt, and isolation (Hetschko, Knabe, and Scho¨ b 2014; Clark and Oswald 1994); understanding what policies and norms can break these links could significantly improve the median quality of life. Empirical and theoretical research on topics such as the basic income proposal could clarify our options (Van Parijs 1992; Widerquist et al. 2013).Economic measures: It is possible that economic measures such as real GDP per capita do not accurately capture the benefits and detriments of heavily AI-and-automation-based economies, making these metrics unsuitable for policypurposes (Mokyr 2014). Research on improved metrics could be useful for decision-making.Law and Ethics ResearchThe development of systems that embody significant amounts of intelligence and autonomy leads to important legal and ethical questions whose answers impact both producers and consumers of AI technology. These questions span law, public policy, professional ethics, and philosophical ethics, and will require expertise from computer scientists, legal experts, political scientists, and ethicists. For example: Liability and law for autonomous vehicles: If self-driving cars cut the roughly 40,000 annual US traffic fatalities in half, the car makers might get not 20,000 thank-you notes, but 20,000 lawsuits. In what legal framework can the safety benefits of autonomous vehicles such as drone aircraft and self-driving cars best be realized (Vladeck 2014)? Should legal questions about AI be handled by existing (software-and internet-focused) ‘‘cyberlaw’’, or should they be treated separately (Calo 2014b)? In both military and commercial applications, governments will need to decide how best to bring the relevant expertise to bear; for example, a panel or committee of professionals and academics could be created, and Calo has proposed the creation of a Federal Robotics Commission (Calo 2014a).Machine ethics: How should an autonomous vehicle trade off, say, a small probability of injury to a human against the near-certainty of a large material cost? How should lawyers, ethicists, and policymakers engage the public on these issues? Should such trade-offs be the subject of national standards?Autonomous weapons: Can lethal autonomous weapons be made to comply with humanitarian law (Churchill and Ulfstein 2000)? If, as some organizations have suggested, autonomous weapons should be banned (Docherty 2012), is it possible to develop a precise definition of autonomy for this purpose, and can such a ban practically be enforced? If it is permissible or legal to use lethal autonomous weapons, how should these weapons be integrated into the existing command-and-control structure so that responsibility and liability remain associated with specific human actors? What technical realities and forecasts should inform these questions, and howshould ‘‘meaningful human control’’ over weapons be defined (Roff 2013, 2014; Anderson, Reisner, and Waxman 2014)? Are autonomous weapons likely to reduce political aversion to conflict, or perhaps result in ‘‘accidental’’ battles or wars (Asaro 2008)? Would such weapons become the tool of choice for oppressors or terrorists? Finally, how can transparency and public discourse best be encouraged on these issues?Privacy: How should the ability of AI systems to interpret the data obtained from surveillance cameras, phone lines, emails, etc., interact with the right to privacy? How will privacy risks interact with cybersecurity and cyberwarfare (Singer and Friedman 2014)? Our ability to take full advantage of the synergy between AI and big data will depend in part on our ability to manage and preserve privacy (Manyika et al. 2011; Agrawal and Srikant 2000).Professional ethics:What role should computer scientists play in the law and ethics of AI development and use? Past and current projects to explore these questions include the AAAI 2008–09 Presidential Panel on Long-Term AI Futures (Horvitz and Selman 2009), the EPSRC Principles of Robotics (Boden et al. 2011), and recently announced programs such as Stanford’s One-Hundred Year Study of AI and the AAAI Committee on AI Impact and Ethical Issues.Long-term research prioritiesA frequently discussed long-term goal of some AI researchers is to develop systems that can learn from experience with human-like breadth and surpass human performance in most cognitive tasks, thereby having a major impact on society. If there is a non-negligible probability that these efforts will succeed in the foreseeable future, then additional current research beyond that mentioned in the previous sections will be motivated as exemplified below, to help ensure that the resulting AI will be robust and beneficial.VerificationReprising the themes of short-term research, research enabling verifiable low-level software and hardware can eliminate large classes of bugs and problems ingeneral AI systems; if such systems become increasingly powerful and safety-critical, verifiable safety properties will become increasingly valuable. If the theory of extending verifiable properties from components to entire systems is well understood, then even very large systems can enjoy certain kinds of safety guarantees, potentially aided by techniques designed explicitly to handle learning agents and high-level properties. Theoretical research, especially if it is done explicitly with very general and capable AI systems in mind, could be particularly useful.A related verification research topic that is distinctive to long-term concerns is the verifiability of systems that modify, extend, or improve themselves, possibly many times in succession (Good 1965; Vinge 1993). Attempting to straightforwardly apply formal verification tools to this more general setting presents new difficulties, including the challenge that a formal system that is sufficiently powerful cannot use formal methods in the obvious way to gain assurance about the accuracy of functionally similar formal systems, on pain of inconsistency via Go¨ del’s incompleteness (Fallenstein and Soares 2014; Weaver 2013). It is not yet clear whether or how this problem can be overcome, or whether similar problems will arise with other verification methods of similar strength.Finally, it is often difficult to actually apply formal verification techniques to physical systems, especially systems that have not been designed with verification in mind. This motivates research pursuing a general theory that links functional specification to physical states of affairs. This type of theory would allow use of formal tools to anticipate and control behaviors of systems that approximate rational agents, alternate designs such as satisficing agents, and systems that cannot be easily described in the standard agent formalism (powerful prediction systems, theorem-provers, limited-purpose science or engineering systems, etc.). It may also be that such a theory could allow rigorous demonstrations that systems are constrained from taking certain kinds of actions or performing certain kinds of reasoning.ValidityAs in the short-term research priorities, validity is concerned with undesirable behaviors that can arise despite a system’s formal correctness. In the long term, AIsystems might become more powerful and autonomous, in which case failures of validity could carry correspondingly higher costs.Strong guarantees for machine learning methods, an area we highlighted for short-term validity research, will also be important for long-term safety. To maximize the long-term value of this work, machine learning research might focus on the types of unexpected generalization that would be most problematic for very general and capable AI systems. In particular, it might aim to understand theoretically and practically how learned representations of high-level human concepts could be expected to generalize (or fail to) in radically new contexts (Tegmark 2015). Additionally, if some concepts could be learned reliably, it might be possible to use them to define tasks and constraints that minimize the chances of unintended consequences even when autonomous AI systems become very general and capable. Little work has been done on this topic, which suggests that both theoretical and experimental research may be useful.Mathematical tools such as formal logic, probability, and decision theory have yielded significant insight into the foundations of reasoning and decision-making. However, there are still many open problems in the foundations of reasoning and decision. Solutions to these problems may make the behavior of very capable systems much more reliable and predictable. Example research topics in this area include reasoning and decision under bounded computational resources as Horvitz and Russell (Horvitz 1987; Russell and Subramanian 1995), how to take into account correlations between AI systems’ behaviors and those of their environments or of other agents (Tennenholtz 2004; LaVictoire et al. 2014; Hintze 2014; Halpern and Pass 2013; Soares and Fallenstein 2014c), how agents that are embedded in their environments should reason (Soares 2014a; Orseau and Ring 2012), and how to reason about uncertainty over logical consequences of beliefs or other deterministic computations (Soares and Fallenstein 2014b). These topics may benefit from being considered together, since they appear deeply linked (Halpern and Pass 2011; Halpern, Pass, and Seeman 2014).In the long term, it is plausible that we will want to make agents that actautonomously and powerfully across many domains. Explicitly specifying our preferences in broad domains in the style of near-future machine ethics may not be practical, making ‘‘aligning’’ the values of powerful AI systems with our own values and preferences difficult (Soares 2014b; Soares and Fallenstein 2014a).SecurityIt is unclear whether long-term progress in AI will make the overall problem of security easier or harder; on one hand, systems will become increasingly complex in construction and behavior and AI-based cyberattacks may be extremely effective, while on the other hand, the use of AI and machine learning techniques along with significant progress in low-level system reliability may render hardened systems much less vulnerable than today’s. From a cryptographic perspective, it appears that this conflict favors defenders over attackers; this may be a reason to pursue effective defense research wholeheartedly.Although the topics described in the near-term security research section above may become increasingly important in the long term, very general and capable systems will pose distinctive security problems. In particular, if the problems of validity and control are not solved, it may be useful to create ‘‘containers” for AI systems that could have undesirable behaviors and consequences in less controlled environments (Yampolskiy 2012). Both theoretical and practical sides of this question warrant investigation. If the general case of AI containment turns out to be prohibitively difficult, then it may be that designing an AI system and a container in parallel is more successful, allowing the weaknesses and strengths of the design to inform the containment strategy (Bostrom 2014). The design of anomaly detection systems and automated exploit-checkers could be of significant help. Overall, it seems reasonable to expect this additional perspective – defending against attacks from ‘‘within” a system as well as from external actors – will raise interesting and profitable questions in the field of computer security.ControlIt has been argued that very general and capable AI systems operating autonomously to accomplish some task will often be subject to effects that increasethe difficulty of maintaining meaningful human control (Omohundro 2007; Bostrom 2012, 2014; Shanahan 2015). Research on systems that are not subject to these effects, minimize their impact, or allow for reliable human control could be valuable in preventing undesired consequences, as could work on reliable and secure test-beds for AI systems at a variety of capability levels.If an AI system is selecting the actions that best allow it to complete a given task, then avoiding conditions that prevent the system from continuing to pursue the task is a natural subgoal (Omohundro 2007; Bostrom 2012) (and conversely, seeking unconstrained situations is sometimes a useful heuristic (Wissner-Gross and Freer 2013)). This could become problematic, however, if we wish to repurpose the system, to deactivate it, or to significantly alter its decision-making process; such a system would rationally avoid these changes. Systems that do not exhibit these behaviors have been termed corrigible systems (Soares et al. 2015), and both theoretical and practical work in this area appears tractable and useful. For example, it may be possible to design utility functions or decision processes so that a system will not try to avoid being shut down or repurposed (Soares et al. 2015), and theoretical frameworks could be developed to better understand the space of potential systems that avoid undesirable behaviors (Hibbard 2012, 2014, 2015).ConclusionIn summary, success in the quest for artificial intelligence has the potential to bring unprecedented benefits to humanity, and it is therefore worthwhile to research how to maximize these benefits while avoiding potential pitfalls. The research agenda outlined in this paper, and the concerns that motivate it, have been called ‘‘anti-AI”, but we vigorously contest this characterization. It seems self-evident that the growing capabilities of AI are leading to an increased potential for impact on human society. It is the duty of AI researchers to ensure that the future impact is beneficial. We believe that this is possible, and hope that this research agenda provides a helpful step in the right direction.中文译文:稳健和有益的人工智能的研究重点摘要寻求人工智能的成功有可能为人类带来前所未有的好处,因此值得研究如何最大限度地利用这些好处,同时避免潜在危险。

人工智能英文文献原文及译文附件四英文文献原文Artificial Intelligence"Artificial intelligence" is a word was originally Dartmouth in 1956 to put forward. From then on, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence is also expands. Artificial intelligence is a challenging job of science, the person must know computer knowledge, psychology and philosophy. Artificial intelligence is included a wide range of science, it is composed of different fields, such as machine learning, computer vision, etc, on the whole, the research on artificial intelligence is one of the main goals of the machine can do some usually need to perform complex human intelligence. But in different times and different people in the "complex" understanding is different. Such as heavy science and engineering calculation was supposed to be the brain to undertake, now computer can not only complete this calculation, and faster than the human brain can more accurately, and thus the people no longer put this calculation is regarded as "the need to perform complex human intelligence, complex tasks" work is defined as the development of The Times and the progress of technology, artificial intelligence is the science of specific target and nature as The Times change and development. On the one hand it continues to gain new progress on the one hand, and turning to more meaningful, the more difficult the target. Current can be used to study the main material of artificial intelligence and artificial intelligence technology to realize the machine is a computer, the development history of artificial intelligence is computer science and technology and the development together. Besides the computer science and artificial intelligence also involves information, cybernetics, automation, bionics, biology, psychology, logic, linguistics, medicine and philosophy and multi-discipline. Artificial intelligence research include: knowledge representation, automatic reasoning and search method, machine learning and knowledge acquisition and processing of knowledge system, natural language processing, computer vision, intelligent robot, automatic program design, etc.Practical application of machine vision: fingerprint identification,face recognition, retina identification, iris identification, palm, expert system, intelligent identification, search, theorem proving game, automatic programming, and aerospace applications.Artificial intelligence is a subject categories, belong to the door edge discipline of natural science and social science.Involving scientific philosophy and cognitive science, mathematics, neurophysiological, psychology, computer science, information theory, cybernetics, not qualitative theory, bionics.The research category of natural language processing, knowledge representation, intelligent search, reasoning, planning, machine learning, knowledge acquisition, combined scheduling problem, perception, pattern recognition, logic design program, soft calculation, inaccurate and uncertainty, the management of artificial life, neural network, and complex system, human thinking mode of genetic algorithm.Applications of intelligent control, robotics, language and image understanding, genetic programming robot factory.Safety problemsArtificial intelligence is currently in the study, but some scholars think that letting computers have IQ is very dangerous, it may be against humanity. The hidden danger in many movie happened.The definition of artificial intelligenceDefinition of artificial intelligence can be divided into two parts, namely "artificial" or "intelligent". "Artificial" better understanding, also is controversial. Sometimes we will consider what people can make, or people have high degree of intelligence to create artificial intelligence, etc. But generally speaking, "artificial system" is usually significance of artificial system.What is the "smart", with many problems. This involves other such as consciousness, ego, thinking (including the unconscious thoughts etc. People only know of intelligence is one intelligent, this is the universal view of our own. But we are very limited understanding of the intelligence of the intelligent people constitute elements are necessary to find, so it is difficult to define what is "artificial" manufacturing "intelligent". So the artificial intelligence research often involved in the study of intelligent itself. Other about animal or other artificial intelligence system is widely considered to be related to the study of artificial intelligence.Artificial intelligence is currently in the computer field, the moreextensive attention. And in the robot, economic and political decisions, control system, simulation system application. In other areas, it also played an indispensable role.The famous American Stanford university professor nelson artificial intelligence research center of artificial intelligence under such a definition: "artificial intelligence about the knowledge of the subject is and how to represent knowledge -- how to gain knowledge and use of scientific knowledge. But another American MIT professor Winston thought: "artificial intelligence is how to make the computer to do what only can do intelligent work." These comments reflect the artificial intelligence discipline basic ideas and basic content. Namely artificial intelligence is the study of human intelligence activities, has certain law, research of artificial intelligence system, how to make the computer to complete before the intelligence needs to do work, also is to study how the application of computer hardware and software to simulate human some intelligent behavior of the basic theory, methods and techniques.Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science, since the 1970s, known as one of the three technologies (space technology, energy technology, artificial intelligence). Also considered the 21st century (genetic engineering, nano science, artificial intelligence) is one of the three technologies. It is nearly three years it has been developed rapidly, and in many fields are widely applied, and have made great achievements, artificial intelligence has gradually become an independent branch, both in theory and practice are already becomes a system. Its research results are gradually integrated into people's lives, and create more happiness for mankind.Artificial intelligence is that the computer simulation research of some thinking process and intelligent behavior (such as study, reasoning, thinking, planning, etc.), including computer to realize intelligent principle, make similar to that of human intelligence, computer can achieve higher level of computer application. Artificial intelligence will involve the computer science, philosophy and linguistics, psychology, etc. That was almost natural science and social science disciplines, the scope of all already far beyond the scope of computer science and artificial intelligence and thinking science is the relationship between theory and practice, artificial intelligence is in the mode of thinking science technology application level, is one of its application. From the view of thinking, artificial intelligence is notlimited to logical thinking, want to consider the thinking in image, the inspiration of thought of artificial intelligence can promote the development of the breakthrough, mathematics are often thought of as a variety of basic science, mathematics and language, thought into fields, artificial intelligence subject also must not use mathematical tool, mathematical logic, the fuzzy mathematics in standard etc, mathematics into the scope of artificial intelligence discipline, they will promote each other and develop faster.A brief history of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence can be traced back to ancient Egypt's legend, but with 1941, since the development of computer technology has finally can create machine intelligence, "artificial intelligence" is a word in 1956 was first proposed, Dartmouth learned since then, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence, it expands and not in the long history of the development of artificial intelligence, the slower than expected, but has been in advance, from 40 years ago, now appears to have many AI programs, and they also affected the development of other technologies. The emergence of AI programs, creating immeasurable wealth for the community, promoting the development of human civilization.The computer era1941 an invention that information storage and handling all aspects of the revolution happened. This also appeared in the U.S. and Germany's invention is the first electronic computer. Take a few big pack of air conditioning room, the programmer's nightmare: just run a program for thousands of lines to set the 1949. After improvement can be stored procedure computer programs that make it easier to input, and the development of the theory of computer science, and ultimately computer ai. This in electronic computer processing methods of data, for the invention of artificial intelligence could provide a kind of media.The beginning of AIAlthough the computer AI provides necessary for technical basis, but until the early 1950s, people noticed between machine and human intelligence. Norbert Wiener is the study of the theory of American feedback. Most familiar feedback control example is the thermostat. It will be collected room temperature and hope, and reaction temperature compared to open or close small heater, thus controlling environmental temperature. The importance of the study lies in the feedback loop Wiener:all theoretically the intelligence activities are a result of feedback mechanism and feedback mechanism is. Can use machine. The findings of the simulation of early development of AI.1955, Simon and end Newell called "a logical experts" program. This program is considered by many to be the first AI programs. It will each problem is expressed as a tree, then choose the model may be correct conclusion that a problem to solve. "logic" to the public and the AI expert research field effect makes it AI developing an important milestone in 1956, is considered to be the father of artificial intelligence of John McCarthy organized a society, will be a lot of interest machine intelligence experts and scholars together for a month. He asked them to Vermont Dartmouth in "artificial intelligence research in summer." since then, this area was named "artificial intelligence" although Dartmouth learn not very successful, but it was the founder of the centralized and AI AI research for later laid a foundation.After the meeting of Dartmouth, AI research started seven years. Although the rapid development of field haven't define some of the ideas, meeting has been reconsidered and Carnegie Mellon university. And MIT began to build AI research center is confronted with new challenges. Research needs to establish the: more effective to solve the problem of the system, such as "logic" in reducing search; expert There is the establishment of the system can be self learning.In 1957, "a new program general problem-solving machine" first version was tested. This program is by the same logic "experts" group development. The GPS expanded Wiener feedback principle, can solve many common problem. Two years later, IBM has established a grind investigate group Herbert AI. Gelerneter spent three years to make a geometric theorem of solutions of the program. This achievement was a sensation.When more and more programs, McCarthy busy emerge in the history of an AI. 1958 McCarthy announced his new fruit: LISP until today still LISP language. In. "" mean" LISP list processing ", it quickly adopted for most AI developers.In 1963 MIT from the United States government got a pen is 22millions dollars funding for research funding. The machine auxiliary recognition from the defense advanced research program, have guaranteed in the technological progress on this plan ahead of the Soviet union. Attracted worldwide computer scientists, accelerate the pace of development of AI research.Large programAfter years of program. It appeared a famous called "SHRDLU." SHRDLU "is" the tiny part of the world "project, including the world (for example, only limited quantity of geometrical form of research and programming). In the MIT leadership of Minsky Marvin by researchers found, facing the object, the small computer programs can solve the problem space and logic. Other as in the late 1960's STUDENT", "can solve algebraic problems," SIR "can understand the simple English sentence. These procedures for handling the language understanding and logic.In the 1970s another expert system. An expert system is a intelligent computer program system, and its internal contains a lot of certain areas of experience and knowledge with expert level, can use the human experts' knowledge and methods to solve the problems to deal with this problem domain. That is, the expert system is a specialized knowledge and experience of the program system. Progress is the expert system could predict under certain conditions, the probability of a solution for the computer already has. Great capacity, expert systems possible from the data of expert system. It is widely used in the market. Ten years, expert system used in stock, advance help doctors diagnose diseases, and determine the position of mineral instructions miners. All of this because of expert system of law and information storage capacity and become possible.In the 1970s, a new method was used for many developing, famous as AI Minsky tectonic theory put forward David Marr. Another new theory of machine vision square, for example, how a pair of image by shadow, shape, color, texture and basic information border. Through the analysis of these images distinguish letter, can infer what might be the image in the same period. PROLOGE result is another language, in 1972. In the 1980s, the more rapid progress during the AI, and more to go into business. 1986, the AI related software and hardware sales $4.25 billion dollars. Expert system for its utility, especially by demand. Like digital electric company with such company XCON expert system for the VAX mainframe programming. Dupont, general motors and Boeing has lots of dependence of expert system for computer expert. Some production expert system of manufacture software auxiliary, such as Teknowledge and Intellicorp established. In order to find and correct the mistakes, existing expert system and some other experts system was designed,such as teach users learn TVC expert system of the operating system.From the lab to daily lifePeople began to feel the computer technique and artificial intelligence. No influence of computer technology belong to a group of researchers in the lab. Personal computers and computer technology to numerous technical magazine now before a people. Like the United States artificial intelligence association foundation. Because of the need to develop, AI had a private company researchers into the boom. More than 150 a DEC (it employs more than 700 employees engaged in AI research) that have spent 10 billion dollars in internal AI team.Some other AI areas in the 1980s to enter the market. One is the machine vision Marr and achievements of Minsky. Now use the camera and production, quality control computer. Although still very humble, these systems have been able to distinguish the objects and through the different shape. Until 1985 America has more than 100 companies producing machine vision systems, sales were us $8 million.But the 1980s to AI and industrial all is not a good year for years. 1986-87 AI system requirements, the loss of industry nearly five hundred million dollars. Teknowledge like Intellicorp and two loss of more than $6 million, about one-third of the profits of the huge losses forced many research funding cuts the guide led. Another disappointing is the defense advanced research programme support of so-called "intelligent" this project truck purpose is to develop a can finish the task in many battlefield robot. Since the defects and successful hopeless, Pentagon stopped project funding.Despite these setbacks, AI is still in development of new technology slowly. In Japan were developed in the United States, such as the fuzzy logic, it can never determine the conditions of decision making, And neural network, regarded as the possible approaches to realizing artificial intelligence. Anyhow, the eighties was introduced into the market, the AI and shows the practical value. Sure, it will be the key to the 21st century. "artificial intelligence technology acceptance inspection in desert storm" action of military intelligence test equipment through war. Artificial intelligence technology is used to display the missile system and warning and other advanced weapons. AI technology has also entered family. Intelligent computer increase attracting public interest. The emergence of network game, enriching people's life.Some of the main Macintosh and IBM for application software such as voice and character recognition has can buy, Using fuzzy logic,AI technology to simplify the camera equipment. The artificial intelligence technology related to promote greater demand for new progress appear constantly. In a word ,Artificial intelligence has and will continue to inevitably changed our life.附件三英文文献译文人工智能“人工智能”一词最初是在1956 年Dartmouth在学会上提出来的。

AI智能翻译随着科技的发展和人们对国际交流的需求日益增长,人工智能(Artificial Intelligence,简称AI)智能翻译技术应运而生。
AI智能翻译以其高效、准确的特点,逐渐改变了人们的翻译方式,成为了全球各行业交流中的重要工具。
本文将就AI智能翻译的应用领域、技术原理以及它对语言学习和文化交流的影响进行探讨。
一、AI智能翻译的应用领域AI智能翻译技术广泛应用于多个领域,尤其是在商务交流、旅游服务、学术研究以及跨文化交流等领域中发挥了重要作用。
在商务交流方面,AI智能翻译帮助企业与海外客户或供应商进行顺畅的沟通,打破了语言壁垒,有效提高了商务合作的效率。
例如,AI智能翻译可辅助企业的多语种客服团队进行即时翻译,为客户提供全天候、高质量的服务。
在旅游服务中,AI智能翻译成为了游客在异国他乡的得力助手。
通过智能翻译设备或手机应用程序,游客可将外语标牌、菜单、对话等即时翻译为自己的母语,方便了他们的旅行体验,减少了交流障碍。
在学术研究方面,AI智能翻译为研究人员提供了一个便捷、准确的翻译工具。
研究人员可以快速获取其他语言的研究文献、论文等信息,推动学术交流和合作。
在跨文化交流中,AI智能翻译扮演着桥梁的角色。
它通过自动翻译和语音识别技术,实现了不同母语人士之间的实时对话和理解,有力地促进了跨文化的交流与融合。
二、AI智能翻译的技术原理AI智能翻译技术的核心是机器翻译(Machine Translation,简称MT)。
它利用自然语言处理技术和大数据分析方法,将源语言的句子转化为目标语言的句子。
机器翻译主要分为统计机器翻译(Statistical Machine Translation,简称SMT)和神经机器翻译(Neural Machine Translation,简称NMT)两个阶段。
统计机器翻译通过分析大量双语平行语料库,基于统计概率模型来进行翻译。
它将源语言的句子切分成词或短语,然后将其翻译为目标语言。
附件四英文文献原文Artificial Intelligence"Artificial intelligence" is a word was originally Dartmouth in 1956 to put forward. From then on, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence is also expands. Artificial intelligence is a challenging job of science, the person must know computer knowledge, psychology and philosophy. Artificial intelligence is included a wide range of science, it is composed of different fields, such as machine learning, computer vision, etc, on the whole, the research on artificial intelligence is one of the main goals of the machine can do some usually need to perform complex human intelligence. But in different times and different people in the "complex" understanding is different. Such as heavy science and engineering calculation was supposed to be the brain to undertake, now computer can not only complete this calculation, and faster than the human brain can more accurately, and thus the people no longer put this calculation is regarded as "the need to perform complex human intelligence, complex tasks" work is defined as the development of The Times and the progress of technology, artificial intelligence is the science of specific target and nature as The Times change and development. On the one hand it continues to gain new progress on the one hand, and turning to more meaningful, the more difficult the target. Current can be used to study the main material of artificial intelligence and artificial intelligence technology to realize the machine is a computer, the development history of artificial intelligence is computer science and technology and the development together. Besides the computer science and artificial intelligence also involves information, cybernetics, automation, bionics, biology, psychology, logic, linguistics, medicine and philosophy and multi-discipline. Artificial intelligence research include: knowledge representation, automatic reasoning and search method, machine learning and knowledge acquisition and processing of knowledge system, natural language processing, computer vision, intelligent robot, automatic program design, etc.Practical application of machine vision: fingerprint identification, face recognition, retina identification, iris identification, palm, expert system, intelligent identification, search, theorem proving game, automatic programming, and aerospace applications.Artificial intelligence is a subject categories, belong to the door edge discipline of natural science and social science.Involving scientific philosophy and cognitive science, mathematics, neurophysiological, psychology, computer science, information theory, cybernetics, not qualitative theory, bionics.The research category of natural language processing, knowledge representation, intelligent search, reasoning, planning, machine learning, knowledge acquisition, combined scheduling problem, perception, pattern recognition, logic design program, soft calculation, inaccurate and uncertainty, the management of artificial life, neural network, and complex system, human thinking mode of genetic algorithm.Applications of intelligent control, robotics, language and image understanding, genetic programming robot factory.Safety problemsArtificial intelligence is currently in the study, but some scholars think that letting computers have IQ is very dangerous, it may be against humanity. The hidden danger in many movie happened.The definition of artificial intelligenceDefinition of artificial intelligence can be divided into two parts, namely "artificial" or "intelligent". "Artificial" better understanding, also is controversial. Sometimes we will consider what people can make, or people have high degree of intelligence to create artificial intelligence, etc. But generally speaking, "artificial system" is usually significance of artificial system.What is the "smart", with many problems. This involves other such as consciousness, ego, thinking (including the unconscious thoughts etc. People only know of intelligence is one intelligent, this is the universal view of our own. But we are very limited understanding of the intelligence of the intelligent people constitute elements are necessary to find, so it is difficult to define what is "artificial" manufacturing "intelligent". So the artificial intelligence research often involved in the study of intelligent itself. Other about animal or other artificial intelligence system is widely considered to be related to the study of artificial intelligence.Artificial intelligence is currently in the computer field, the more extensive attention. And in the robot, economic and political decisions, control system, simulation system application. In other areas, it also played an indispensable role.The famous American Stanford university professor nelson artificial intelligence research center of artificial intelligence under such a definition: "artificial intelligence about the knowledge of the subject is and how to represent knowledge -- how to gain knowledge and use of scientific knowledge. But another American MIT professor Winston thought: "artificial intelligence is how to make the computer to do what only can do intelligent work." These comments reflect the artificial intelligence discipline basic ideas and basic content. Namely artificial intelligence is the study of human intelligence activities, has certain law, research of artificial intelligence system, how to make the computer to complete before the intelligence needs to do work, also is to study how the application of computer hardware and software to simulate human some intelligent behavior of the basic theory, methods and techniques.Artificial intelligence is a branch of computer science, since the 1970s, known as one of the three technologies (space technology, energy technology, artificial intelligence). Also considered the 21st century (genetic engineering, nano science, artificial intelligence) is one of the three technologies. It is nearly three years it has been developed rapidly, and in many fields are widely applied, and have made great achievements, artificial intelligence has gradually become an independent branch, both in theory and practice are already becomes a system. Its research results are gradually integrated into people's lives, and create more happiness for mankind.Artificial intelligence is that the computer simulation research of some thinking process and intelligent behavior (such as study, reasoning, thinking, planning, etc.), including computer to realize intelligent principle, make similar to that of human intelligence, computer can achieve higher level of computer application. Artificial intelligence will involve the computer science, philosophy and linguistics, psychology, etc. That was almost natural science and social science disciplines, the scope of all already far beyond the scope of computer science and artificial intelligence and thinking science is the relationship between theory and practice, artificial intelligence is in the mode of thinking science technology application level, is one of its application. From theview of thinking, artificial intelligence is not limited to logical thinking, want to consider the thinking in image, the inspiration of thought of artificial intelligence can promote the development of the breakthrough, mathematics are often thought of as a variety of basic science, mathematics and language, thought into fields, artificial intelligence subject also must not use mathematical tool, mathematical logic, the fuzzy mathematics in standard etc, mathematics into the scope of artificial intelligence discipline, they will promote each other and develop faster.A brief history of artificial intelligenceArtificial intelligence can be traced back to ancient Egypt's legend, but with 1941, since the development of computer technology has finally can create machine intelligence, "artificial intelligence" is a word in 1956 was first proposed, Dartmouth learned since then, researchers have developed many theories and principles, the concept of artificial intelligence, it expands and not in the long history of the development of artificial intelligence, the slower than expected, but has been in advance, from 40 years ago, now appears to have many AI programs, and they also affected the development of other technologies. The emergence of AI programs, creating immeasurable wealth for the community, promoting the development of human civilization.The computer era1941 an invention that information storage and handling all aspects of the revolution happened. This also appeared in the U.S. and Germany's invention is the first electronic computer. Take a few big pack of air conditioning room, the programmer's nightmare: just run a program for thousands of lines to set the 1949. After improvement can be stored procedure computer programs that make it easier to input, and the development of the theory of computer science, and ultimately computer ai. This in electronic computer processing methods of data, for the invention of artificial intelligence could provide a kind of media.The beginning of AIAlthough the computer AI provides necessary for technical basis, but until the early 1950s, people noticed between machine and human intelligence. Norbert Wiener is the study of the theory of American feedback. Most familiar feedback control example is the thermostat. It will be collected room temperature and hope, and reaction temperature compared to open or close small heater, thus controlling environmentaltemperature. The importance of the study lies in the feedback loop Wiener: all theoretically the intelligence activities are a result of feedback mechanism and feedback mechanism is. Can use machine. The findings of the simulation of early development of AI.1955, Simon and end Newell called "a logical experts" program. This program is considered by many to be the first AI programs. It will each problem is expressed as a tree, then choose the model may be correct conclusion that a problem to solve. "logic" to the public and the AI expert research field effect makes it AI developing an important milestone in 1956, is considered to be the father of artificial intelligence of John McCarthy organized a society, will be a lot of interest machine intelligence experts and scholars together for a month. He asked them to Vermont Dartmouth in "artificial intelligence research in summer." since then, this area was named "artificial intelligence" although Dartmouth learn not very successful, but it was the founder of the centralized and AI AI research for later laid a foundation.After the meeting of Dartmouth, AI research started seven years. Although the rapid development of field haven't define some of the ideas, meeting has been reconsidered and Carnegie Mellon university. And MIT began to build AI research center is confronted with new challenges. Research needs to establish the: more effective to solve the problem of the system, such as "logic" in reducing search; expert There is the establishment of the system can be self learning.In 1957, "a new program general problem-solving machine" first version was tested. This program is by the same logic "experts" group development. The GPS expanded Wiener feedback principle, can solve many common problem. Two years later, IBM has established a grind investigate group Herbert AI. Gelerneter spent three years to make a geometric theorem of solutions of the program. This achievement was a sensation.When more and more programs, McCarthy busy emerge in the history of an AI. 1958 McCarthy announced his new fruit: LISP until today still LISP language. In. "" mean" LISP list processing ", it quickly adopted for most AI developers.In 1963 MIT from the United States government got a pen is 22millions dollars funding for research funding. The machine auxiliary recognition from the defense advanced research program, have guaranteed in the technological progress on this plan ahead of the Soviet union. Attracted worldwide computer scientists, accelerate the pace of development of AIresearch.Large programAfter years of program. It appeared a famous called "SHRDLU." SHRDLU "is" the tiny part of the world "project, including the world (for example, only limited quantity of geometrical form of research and programming). In the MIT leadership of Minsky Marvin by researchers found, facing the object, the small computer programs can solve the problem space and logic. Other as in the late 1960's STUDENT", "can solve algebraic problems," SIR "can understand the simple English sentence. These procedures for handling the language understanding and logic.In the 1970s another expert system. An expert system is a intelligent computer program system, and its internal contains a lot of certain areas of experience and knowledge with expert level, can use the human experts' knowledge and methods to solve the problems to deal with this problem domain. That is, the expert system is a specialized knowledge and experience of the program system. Progress is the expert system could predict under certain conditions, the probability of a solution for the computer already has. Great capacity, expert systems possible from the data of expert system. It is widely used in the market. Ten years, expert system used in stock, advance help doctors diagnose diseases, and determine the position of mineral instructions miners. All of this because of expert system of law and information storage capacity and become possible.In the 1970s, a new method was used for many developing, famous as AI Minsky tectonic theory put forward David Marr. Another new theory of machine vision square, for example, how a pair of image by shadow, shape, color, texture and basic information border. Through the analysis of these images distinguish letter, can infer what might be the image in the same period. PROLOGE result is another language, in 1972. In the 1980s, the more rapid progress during the AI, and more to go into business. 1986, the AI related software and hardware sales $4.25 billion dollars. Expert system for its utility, especially by demand. Like digital electric company with such company XCON expert system for the VAX mainframe programming. Dupont, general motors and Boeing has lots of dependence of expert system for computer expert. Some production expert system of manufacture software auxiliary, such as Teknowledge and Intellicorp established. In order to find and correct the mistakes, existing expert system and some other experts system was designed,such as teach userslearn TVC expert system of the operating system.From the lab to daily lifePeople began to feel the computer technique and artificial intelligence. No influence of computer technology belong to a group of researchers in the lab. Personal computers and computer technology to numerous technical magazine now before a people. Like the United States artificial intelligence association foundation. Because of the need to develop, AI had a private company researchers into the boom. More than 150 a DEC (it employs more than 700 employees engaged in AI research) that have spent 10 billion dollars in internal AI team.Some other AI areas in the 1980s to enter the market. One is the machine vision Marr and achievements of Minsky. Now use the camera and production, quality control computer. Although still very humble, these systems have been able to distinguish the objects and through the different shape. Until 1985 America has more than 100 companies producing machine vision systems, sales were us $8 million.But the 1980s to AI and industrial all is not a good year for years. 1986-87 AI system requirements, the loss of industry nearly five hundred million dollars. Teknowledge like Intellicorp and two loss of more than $6 million, about one-third of the profits of the huge losses forced many research funding cuts the guide led. Another disappointing is the defense advanced research programme support of so-called "intelligent" this project truck purpose is to develop a can finish the task in many battlefield robot. Since the defects and successful hopeless, Pentagon stopped project funding.Despite these setbacks, AI is still in development of new technology slowly. In Japan were developed in the United States, such as the fuzzy logic, it can never determine the conditions of decision making, And neural network, regarded as the possible approaches to realizing artificial intelligence. Anyhow, the eighties was introduced into the market, the AI and shows the practical value. Sure, it will be the key to the 21st century. "artificial intelligence technology acceptance inspection in desert storm" action of military intelligence test equipment through war. Artificial intelligence technology is used to display the missile system and warning and other advanced weapons. AI technology has also entered family. Intelligent computer increase attracting public interest. The emergence of network game, enriching people's life.Some of the main Macintosh and IBM for application softwaresuch as voice and character recognition has can buy, Using fuzzy logic, AI technology to simplify the camera equipment. The artificial intelligence technology related to promote greater demand for new progress appear constantly. In a word ,Artificial intelligence has and will continue to inevitably changed our life.附件三英文文献译文人工智能“人工智能”一词最初是在1956 年Dartmouth在学会上提出来的。
关于人工智能的外文文献
人工智能(Artificial Intelligence,简称 AI)是计算机科学和数学等相关学科的交叉学科领域,旨在研究、开发和应用智能计算机系统,使计算机具备模仿、实现和智能控制人类智能的能力。
AI 研究的历史可以追溯到上世纪 50 年代,但真正意义上的 AI 技术直至近年来才得到了飞跃式的发展。
AI 技术主要包括机器学习、自然语言处理、机器人技术等。
其中,机器学习是 AI 领域发展最快,应用最广泛的一个技术分支。
机器学习是一种能够让计算机自动学习和改进的算法,通过大量的数据训练模型、发现规律、优化算法,来实现某项特定任务的智能技术。
自然语言处理也是 AI 中一个极为重要的分支,旨在实现计算机对人类语言的自然理解和处理。
该技术被广泛应用于机器翻译、语音识别、智能客服等领域。
机器人技术则将 AI 技术应用于实际机器人的制造和智能控制,实现了人机交互、自主感知、自主导航等功能。
AI 技术的广泛应用,不仅能够提高生产效率,实现科学管理,还可以在医疗、教育、金融、民生等领域中解决眼下一系列难题,改善人类生活。
然而,AI 技术的应用同时也引发了一些问题和挑战。
例如,AI 技术的误判问题,即计算机因处理数据的不足而做出错误决策;AI 技术的隐私问题,即人们的信息可能被 AI 系统收集和利用;AI 技术的失业问题,即一些传统行业可能被 AI 技术替代。
因此,我们需要在推进 AI 技术发展的同时,加强监管和管理。
仅仅依靠技术本身解决问题是不够的,还需要法律法规的支持,严格控制 AI 技术的使用范围和标准,确保人类社会长远的发展。
基于人工智能的外文信息翻译技术研究随着全球化的推进和信息技术的快速发展,英语已成为全球最主要的商务和科技交流语言。
然而,不是所有人都能熟练掌握英语,这就导致了翻译这一行业的兴起。
然而,传统翻译方式需要大量人力物力支持,效率低下,成本高昂,而且还存在误译和遗漏等问题。
为此,基于人工智能的外文信息翻译技术应运而生,成为外语翻译领域的新一代技术。
人工智能即是让机器学习、自动化,以实现人类某些智能工作的技术。
在外文翻译方面,人工智能技术的应用可以分为两类:一是人机交互式翻译,另一种则是完全自动化的机器翻译。
在人机交互式翻译中,人工智能技术主要通过智能搜索、自然语言处理及机器学习等技术来辅助用户更快速、更准确地获得需要的翻译信息。
比如,用户可以通过输入关键词或者用英文描述相应信息的需求,SMARTCAT等软件就可以迅速地将相关的文章或者翻译资源检索出来。
这种翻译方式,可以大幅度提高人译速度,同时缩短了查找翻译资源的时间。
另一种机器翻译方式,则是完全由机器自动完成的翻译过程。
在机器翻译方面,人工智能技术主要应用于海量翻译语料库的构建、自然语言处理技术的优化及深度神经网络的训练,以从而实现机器翻译质量的提升。
虽然机器翻译目前还无法像人工翻译一样,精准而自然地翻译所有内容,但不可否认的是,基于人工智能的机器翻译技术已经在翻译行业中扮演着越来越重要的角色。
那么机器翻译技术的发展是如何实现的呢?我们可以从以下的三个方面来探讨:一、语料库的建立:语料库是机器翻译的核心资源。
获取数据、清洗数据及对数据进行标注,是语料库建立的最关键的前期工作。
同时随着数据的增多,我们可以获得更多的语言材料来作为机器翻译的参考资料,进而提高翻译的准确度。
二、自然语言处理技术的优化:自然语言处理技术主要涉及到对于文本的词性分析、命名实体识别、句法分析等。
所以,自然语言处理技术的优化,从而更好地把握语言文本的细节,是提升机器翻译水平的重要途径。
人工智能(AI)革命外文翻译中英文英文The forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) revolution:Its impact on society and firmsSpyros MakridakisAbstractThe impact of the industrial and digital (information) revolutions has, undoubtedly, been substantial on practically all aspects of our society, life, firms and employment. Will the forthcoming AI revolution produce similar, far-reaching effects? By examining analogous inventions of the industrial, digital and AI revolutions, this article claims that the latter is on target and that it would bring extensive changes that will also affect all aspects of our society and life. In addition, its impact on firms and employment will be considerable, resulting in richly interconnected organizations with decision making based on th e analysis and exploitation of “big” data and intensified, global competition among firms. People will be capable of buying goods and obtaining services from anywhere in the world using the Internet, and exploiting the unlimited, additional benefits that will open through the widespread usage of AI inventions. The paper concludes that significant competitive advantages will continue to accrue to those utilizing the Internet widely and willing to take entrepreneurial risks in order to turn innovative products/services into worldwide commercial success stories. The greatest challenge facing societies and firms would be utilizing the benefits of availing AI technologies, providing vast opportunities for both new products/services and immense productivity improvements while avoiding the dangers and disadvantages in terms of increased unemployment and greater wealth inequalities.Keywords:Artificial Intelligence (AI),Industrial revolution,Digital revolution,AI revolution,Impact of AI revolution,Benefits and dangers of AI technologies The rise of powerful AI will be either the best or the worst thing ever to happento humanity. We do not yet know which.Stephen HawkingOver the past decade, numerous predictions have been made about the forthcoming Artificial Intelligence (AI) Revolution and its impact on all aspects of our society, firms and life in general. This paper considers such predictions and compares them to those of the industrial and digital ones. A similar paper was written by this author and published in this journal in 1995, envisioning the forthcoming changes being brought by the digital (information) revolution, developing steadily at that time, and predicting its impact for the year 2015 (Makridakis, 1995). The current paper evaluates these 1995 predictions and their impact identifying hits and misses with the purpose of focusing on the new ones being brought by the AI revolution. It must be emphasized that the stakes of correctly predicting the impact of the AI revolution arefar reaching as intelligent machines may become our “final invention” that may end human supremacy (Barrat, 2013). There is little doubt that AI holds enormous potential as computers and robots will probably achieve, or come close to, human intelligence over the next twenty years becoming a serious competitor to all the jobs currently performed by humans and for the first time raising doubt over the end of human supremacy.This paper is organized into four parts. It first overviews the predictions made in the 1995 paper for the year 2015, identifying successes and failures and concluding that major technological developments (notably the Internet and smartphones) were undervalued while the general trend leading up to them was predicted correctly. Second, it investigates existing and forthcoming technological advances in the field of AI and the ability of computers/machines to acquire real intelligence. Moreover, it summarizes prevailing, major views of how AI may revolutionize practically everything and its impact on the future of humanity. The third section sums up the impact of the AI revolution and describes the four major scenarios being advocated, as well as what could be done to avoid the possible negative consequences of AI technologies. The fourth section discusses how firms will be affected by these technologies that will transform the competitive landscape, how start-up firms are founded and the way success can be achieved. Finally, there is a brief concluding section speculating about the future of AI and its impact on our society, life, firms and employment.1. The 1995 paper: hits and missesThe 1995 paper (Makridakis, 1995) was written at a time when the digital (at that time it was called information) revolution was progressing at a steady rate. The paper predicted that by 2015 “the information revolution should be in full swing” and that “computers/communications” would be in widespread use, whi ch has actually happened, although its two most important inventions (the Internet and smartphones) and their significant influence were not foreseen as such. Moreover, the paper predicted that “a single computer (but not a smartphone) can, in addition to its traditional tasks, also become a terminal capable of being used interactively for the following:” (p. 804–805)• Picture phone and teleconference• Television and videos• Music• Shopping• On line banking and financial services• Reservations• Medic al advice• Access to all types of services• Video games• Other games (e.g., gambling, chess etc.)• News, sports and weather reports• Access to data banksThe above have all materialized and can indeed be accessed by computer,although the extent of their utilization was underestimated as smartphones are now being used widely. For instance, the ease of accessing and downloading scientific articles on one's computer in his/her office or home would have seemed like science fiction back in 1995, when finding such articles required spending many hours in the library (often in its basement for older publications) and making photocopies to keep them for later use. Moreover, having access, from one's smartphone or tablet, to news from anywhere in the world, being able to subscribe to digital services, obtain weather forecasts, purchase games, watch movies, make payments using smartphones and a plethora of other, useful applications was greatly underestimated, while the extensive use of the cloud for storing large amounts of data for free was not predicted at all at that time. Even in 1995 when the implications of Moore's law leading to increasing computer speed and storage while reducing costs were well known, nevertheless, it was hard to imagine that in 2016 there would be 60 trillion web pages, 2.5 billion smartphones, more than 2 billion personal computers and 3.5 billion Google searches a day.The paper correctly predicted “as wireless telecommunications will be possible the above list of capabilities can be accessed from anywhere in the world without the need for regular telephone lines”. What the 1995 paper missed, however, was that in 2015 top smartphones, costing less than €500, would be as powerful as the 1995 supercomputer, allowing access to the Internet and all tasks that were only performed by expensive computers at that time, including an almost unlimited availability of new, powerful apps providing a large array of innovative services that were not imagined twenty years ago. Furthermore, the paper correctly predicted super automation leading to unattended factories stating that “by 2015 there will be little need for people to do repetitive manual or mental tasks”. It also foresaw the decline of large industrial firms, increased global competition and the drop in the percentage of labour force employed in agriculture and manufacturing (more on these predictions in the section The Impact of the AI Revolution on Firms). It missed however the widespread utilization of the Internet (at that time it was a text only service), as well as search engines (notably Google), social networking sites(notably Facebook) and the fundamental changes being brought by the widespread use of Apple's iPhone, Samsung's Galaxy and Google's Android smartphones. It is indeed surprising today to see groups of people in a coffee shop or restaurant using their smartphones instead of speaking to each other and young children as little as three or four years of age playing with phones and tablets. Smartphones and tablets connected to the Internet through Wi-Fi have influenced social interactions to a significant extent, as well as the way we search for information, use maps and GPS for finding locations, and make payments. These technologies were not predicted in the 1995 paper.2. Towards the AI revolutionThe 1995 paper referred to Say, the famous French economist, who wrote in 1828 about the possibility of cars as substitutes for horses:“Nevertheless no machine will ever be able to perform what even the worst horses can - the service of carrying people and goods through the bustle and throng of a great city.” (p. 800)Say could never have dreamed of, in his wildest imagination, self-driving cars, pilotless airplanes, Skype calls, super computers, smartphones or intelligent robots. Technologies that seemed like pure science fiction less than 190 years ago are available today and some like self-driving vehicles will in all likelihood be in widespread use within the next twenty years. The challenge is to realistically predict forthcoming AI technologies without falling into the same short-sighted trap of Say and others, including my 1995 paper, unable to realize the momentous, non-linear advancements of new technologies. There are two observations to be made.First, 190 years is a brief period by historical standards and during this period we went from horses being the major source of transportation to self-driving cars and from the abacus and slide rules to powerful computers in our pockets. Secondly, the length of time between technological inventions and their practical, widespread use is constantly being reduced. For instance, it took more than 200 years from the time Newcomen developed the first workable steam engine in 1707 to when Henry Ford built a reliable and affordable car in 1908. It took more than 90 years between the time electricity was introduced and its extensive use by firms to substantially improve factory productivity. It took twenty years, however, between ENIAC, the first computer, and IBM's 360 system that was mass produced and was affordable by smaller business firms while it took only ten years between 1973 when Dr Martin Cooper made the first mobile call from a handheld device and its public launch by Motorola. The biggest and most rapid progress, however, took place with smartphones which first appeared in 2002 and saw a stellar growth with the release of new versions possessing substantial improvements every one or two years by the likes of Apple, Samsung and several Chinese firms. Smartphones, in addition to their technical features, now incorporate artificial intelligence characteristics that include understanding speech, providing customized advice in spoken language, completing words when writing a text and several other functions requiring embedded AI, provided by a pocket computer smaller in size than a pack of cigarettes.From smart machines to clever computers and to Artificial Intelligence (AI) programs: A thermostat is a simple mechanical device exhibiting some primitive but extremely valuable type of intelligence by keeping temperatures constant at some desired, pre-set level. Computers are also clever as they can be instructed to make extremely complicated decisions taking into account a large number of factors and selection criteria, but like thermostats such decisions are pre-programmed and based on logic, if-then rules and decision trees that produce the exact same results, as long as the input instructions are alike. The major advantage of computers is their lightning speed that allows them to perform billions of instructions per second. AI, on the other hand, goes a step further by not simply applying pre-programmed decisions, but instead exhibiting some learning capabilities.The story of the Watson computer beating Jeopardy's two most successful contestants is more complicated, since retrieving the most appropriate answer out of the 200 million pages of information stored in its memory is not a sign of real intelligence as it relied on its lightning speed to retrieve information in seconds. What is more challenging according to Jennings, one of Jeopardy's previous champions, is“to read clues in a natural language, understand puns and the red herrings, to unpack just the meaning of the clue” (May, 2013). Similarly, it is a sign of intelligence to improve it s performance by “playing 100 games against past winners”. (Best, 2016). Watson went several steps beyond Deep Blue towards AI by being able to understand spoken English and learn from his mistakes (New Yorker, 2016). However, he was still short of AlphaGo that defeated Go Champions in a game that cannot be won simply by using “brute force” as the number of moves in this game is infinite, requiring the program to use learning algorithms that can improve its performance as it plays more and more gamesComputers and real learning: According to its proponents, “the main focus of AI research is in teaching computers to think for themselves and improvise solutions to common problems” (Clark, 2015). But many doubt that computers can learn to think for themselves even though they can display signs of intelligence. David Silver, an AI scientist working at DeepMind, explained that “even though AlphaGo has affectively rediscovered the most subtle concepts of Go, its knowledge is implicit. The computer parse out these concepts –they simply emerge from its statistical comparisons of types of winning board positions at GO” (Chouard, 2016). At the same time Cho Hyeyeon, one of the strongest Go players in Korea commented that “AlphaGo seems like it knows everything!” while others believe that “AlphaGo is likely to start a ‘new revolution’ in the way we play Go”as “it is seeking simply to maximize its probability of reaching winning positions, rather than as human players tend to do –maximize territorial gains” (Chouard, 2016). Does it matter, as Silver said, that AlphaGo's knowledge of the game is implicit as long as it can beat the best players? A more serious issue is whether or not AlphaGo's ability to win games with fixed rules can extend to real life settings where not only the rules are not fixed, but they can change with time, or from one situation to another.From digital computers to AI tools: The Intel Pentium microprocessor, introduced in 1993, incorporated graphics and music capabilities and opened computers up to a large number of affordable applications extending beyond just data processing. Such technologies signalled the beginning of a new era that now includes intelligent personal assistants understanding and answering natural languages, robots able to see and perform an array of intelligent functions, self-driving vehicles and a host of other capabilities which were until then an exclusive human ability. The tech optimists ascertain that in less than 25 years computers went from just manipulating 0 and 1 digits, to utilizing sophisticated neural networkalgorithms that enable vision and the understanding and speaking of natural languages among others. Technology optimists therefore maintain there is little doubt that in the next twenty years, accelerated AI technological progress will lead to a breakthrough, based on deep learning that imitates the way young children learn, rather than the laborious instructions by tailor-made programs aimed for specific applications and based on logic, if-then rules and decision trees (Parloff, 2016).For instance, DeepMind is based on a neural program utilizing deep learning that teaches itself how to play dozens of Atari games, such as Breakout, as well or better than humans, without specific instructions for doing so, but by playing thousands ofgames and improving itself each time. This program, trained in a different way, became the AlphaGo that defeated GO champion Lee Sodol in 2016. Moreover, it will form the core of a new project to learn to play Starcraft, a complicated game based on both long term strategy as well as quick tactical decisions to stay ahead of an opponent, which DeepMind plans to be its next target for advancing deep learning (Kahn, 2016). Deep learning is an area that seems to be at the forefront of research and funding efforts to improve AI, as its successes have sparked a burst of activity in equity funding that reached an all-time high of more than $1 billion with 121 projects for start-ups in the second quarter of 2016, compared to 21 in the equivalent quarter of 2011 (Parloff, 2016).Google had two deep learning projects underway in 2012. Today it is pursuing more than 1000, according to their spokesperson, in all its major product sectors, including search, Android, Gmail, translation, maps, YouTube, and self-driving cars (The Week, 2016). IBM's Watson system used AI, but not deep learning, when it beat the two Jeopardy champions in 2011. Now though, almost all of Watson's 30 component services have been augmented by deep learning. Venture capitalists, who did not even know what deep learning was five years ago, today are wary of start-ups that do not incorporate it into their programs. We are now living in an age when it has become mandatory for people building sophisticated software applications to avoid click through menus by incorporating natural-language processing tapping deep learning (Parloff, 2016).How far can deep learning go? There are no limits according to technology optimists for three reasons. First as progress is available to practically everyone to utilize through Open Source software, researchers will concentrate their efforts on new, more powerful algorithms leading to cumulative learning. Secondly, deep learning algorithms will be capable of remembering what they have learned and apply it in similar, but different situations (Kirkpatrick et al., 2017). Lastly and equally important, in the future intelligent computer programs will be capable of writing new programs themselves, initially perhaps not so sophisticated ones, but improving with time as learning will be incorporated to be part of their abilities. Kurzweil (2005) sees nonbiological intelligence to match the range and subtlety of human intelligence within a quarter of a century and what he calls “Singularity” to occur by 2045, b ringing “the dawning of a new civilization that will enable us to transcend our biological limitations and amplify our creativity. In this new world, there will be no clear distinction between human and machine, real reality and virtual reality”.For some people these predictions are startling, with far-reaching implications should they come true. In the next section, four scenarios associated with the AI revolution are presented and their impact on our societies, life work and firms is discussed.3. The four AI scenariosUntil rather recently, famines, wars and pandemics were common, affecting sizable segments of the population, causing misery and devastation as well as a large number of deaths. The industrial revolution considerably increased the standards of living while the digital one maintained such rise and also shifted employment patterns,resulting in more interesting and comfortable office jobs. The AI revolution is promising even greater improvements in productivity and further expansion in wealth. Today more and more people, at least in developed countries, die from overeating rather than famine, commit suicide instead of being killed by soldiers, terrorists and criminals combined and die from old age rather than infectious disease (Harari, 2016). Table 1 shows the power of each revolution with the industrial one aiming at routine manual tasks, the digital doing so to routine mental ones and AI aiming at substituting, supplementing and/or amplifying practically all tasks performed by humans. The cri tical question is: “what will the role of humans be at a time when computers and robots could perform as well or better andmuch cheaper, practically all tasks that humans do at present?” There are four scenarios attempting to answer this question.The Optimists: Kurzweil and other optimists predict a “science fiction”, utopian future with Genetics, Nanotechnology and Robotics (GNR) revolutionizing everything, allowing humans to harness the speed, memory capacities and knowledge sharing ability of computers and our brain being directly connected to the cloud. Genetics would enable changing our genes to avoid disease and slow down, or even reverse ageing, thus extending our life span considerably and perhaps eventually achieving immortality. Nanotechnology, using 3D printers, would enable us to create virtually any physical product from information and inexpensive materials bringing an unlimited creation of wealth. Finally, robots would be doing all the actual work, leaving humans with the choice of spending their time performing activities of their choice and working, when they want, at jobs that interest them.The Pessimists: In a much quoted article from Wired magazine in 2000, Bill Joy (Joy, 2000) wrote “Our most powerful 21st-century technologies –robotics, genetic engineering, and nanotech –are threatening to make humans an endangered species”. Joy pointed out that as machines become more and more intelligent and as societal problems become more and more complex, people will let machines make all the important decisions for them as these decisions will bring better results than those made by humans. This situation will, eventually, result in machines being in effective control of all important decisions with people dependent on them and afraid to make their own choices. Joy and many other scientists (Cellan-Jones, 2014) and philosophers (Bostrom, 2014) believe that Kurzweil and his supporters vastly underestimate the magnitude of the challenge and the potential dangers which can arise from thinking machines and intelligent robots. They point out that in the utopian world of abundance, where all work will be done by machines and robots, humans may be reduced to second rate status (some saying the equivalent of computer pets) as smarter than them computers and robots will be available in large numbers and people will not be motivated to work, leaving computers/robots to be in charge of making all important decisions. It may not be a bad world, but it will definitely be a different one with people delegated to second rate status.Harari is the newest arrival to the ranks of pessimists. His recent book (Harari, 2016, p. 397) concludes with the following three statements:• “Science is converging to an all-encompassing dogma, which says thatorganisms are algorithm s, and life is data processing”• “Intelligence is decoupling from consciousness”• “Non-conscious but highly intelligent algorithms may soon know us better than we know ourselves”Consequently, he asks three key questions (which are actually answered by the above three statements) with terrifying implications for the future of humanity: • “Are organisms really just algorithms, and is life just data processing?”• “What is more valuable –intelligence or consciousness?”• “What will happen to society, polit ics and daily life when non-conscious but highly intelligent algorithms know us better than we know ourselves?”Harari admits that nobody really knows how technology will evolve or what its impact will be. Instead he discusses the implications of each of his three questions: • If indeed organisms are algorithms then thinking machines utilizing more efficient ones than those by humans will have an advantage. Moreover, if life is just data processing then there is no way to compete with computers that can consult/exploit practically all available information to base their decisions.• The non-conscious algorithms Google search is based on the consultation of millions of possible entries and often surprise us by their correct recommendations. The implications that similar, more advanced algorithms than those utilized by Google search will be developed (bearing in mind Google search is less than twenty years old) in the future and be able to access all available information from complete data bases are far reachi ng and will “provide us with better information than we could expect to find ourselves”.• Humans are proud of their consciousness, but does it matter that self-driving vehicles do not have one, but still make better decisions than human drivers, as can be confirmed by their significantly lower number of traffic accidents?When AI technologies are further advanced and self-driving vehicles are in widespread use, there may come a time that legislation may be passed forbidding or restricting human driving, even though that may still be some time away according to some scientists (Gomes, 2014). Clearly, self-driving vehicles do not exceed speed limits, do not drive under the influence of alcohol or drugs, do not get tired, do not get distracted by talking on the phone or sending SMS or emails and in general make fewer mistakes than human drivers, causing fewer accidents. There are two implications if humans are not allowed to drive. First, there will be a huge labour displacement for the 3.5 million unionized truck drivers in the USA and the 600 thousand ones in the UK (plus the additional number of non-unionized ones) as well as the more than one million taxi and Uber drivers in these two countries. Second, and more importantly, it will take away our freedom of driving, admitting that computers are superior to us. Once such an admission is accepted there will be no limits to letting computers also make a great number of other decisions, like being in charge of nuclear plants, setting public policies or deciding on optimal economic strategies as their biggest advantage is their objectivity and their ability to make fewer mistakes than humans.One can go as far as suggesting letting computers choose Presidents/PrimeMinisters and elected officials using objective criteria rather than having people voting emotionally and believing the unrealistic promises that candidates make. Although such a suggestion will never be accepted, at least not in the near future, it has its merits since people often choose the wrong candidate and later regret their choice after finding out that pre-election promises were not only broken, but they were even reversed. Critics say if computers do eventually become in charge of making all important decisions there will be little left for people to do as they will be demoted to simply observing the decisions made by computers, the same way as being a passenger in a car driven by a computer, not allowed to take control out of the fear of causing an accident. As mentioned before, this could lead to humans eventually becoming computers’ pets.The pragmatists: At present the vast majority of views about the future implications of AI are negative, concerned with its potential dystopian consequences (Elon Musk, the CEO of Tesla, says it is like “summoning the demon” and calls the consequences worse than what nuclear weapons can do). There are fewer optimists and only a couple of pragmatists like Sam Altman and Michio Kaku (Peckham, 2016) who believe that AI technologies can be controlled through “OpenAI” and effective regulation. The ranks of pragmatists also includes John Markoff (Markoff, 2016) who pointed out that the AI field can be distinguished by two categories: The first trying to duplicate human intelligence and the second to augment it by expanding human abilities exploiting the power of computers in order to augment human decision making. Pragmatists mention chess playing where the present world champion is neither a human nor a computer but rather humans using laptop computers (Baraniuk, 2015). Their view is that we could learn to exploit the power of computers to augment our own skills and always stay a step ahead of AI, or at least not be at a disadvantage. The pragmatists also believe that in the worst of cases a chip can be placed in all thinking machines/robots to render them inoperative in case of any danger. By concentrating research efforts on intelligence augmentation, they claim we can avoid or minimize the possible danger of AI while providing the means to stay ahead in the race against thinking machines and smart robots.The doubters: The doubters do not believe that AI is possible and that it will ever become a threat to humanity. Dreyfus (1972), its major proponent, argues that human intelligence and expertise cannot be replicated and captured in formal rules. He believes that AI is a fad promoted by the computer industry. He points out to the many predictions that did not materialize such as those made by Herbert A. Simon in 1958 that “a computer would be the world's chess champion within ten years” and those made in 1965 that “machines will be capable within twenty years, of doing any work a man can do” (Crevier, 1993). Dreyfus claims that Simon's optimism was totally unwarranted as they were based on false assumptions that human intelligence is based on an information processing viewpoint as our mind is nothing like a computer. Although, the doubters’ criticisms may have been valid in the last century, they cannot stand for the new developments in AI. Deep Blue became the world's chess champion in 1997 (missing Simon's forecast by twenty one years) while we are not far today from machines being capable of doing all the work that humans can do (missing。
人工智能在外语翻译领域的应用前景如何在当今全球化的时代,语言交流的需求日益增长,外语翻译的重要性不言而喻。
而随着科技的迅猛发展,人工智能在这一领域的应用逐渐崭露头角,给传统的翻译方式带来了巨大的冲击和变革。
那么,人工智能在外语翻译领域的应用前景究竟如何呢?要探讨这个问题,我们首先得了解一下当前人工智能在外语翻译中的发展现状。
如今,各种翻译软件和在线翻译工具层出不穷,它们利用人工智能技术,能够在短时间内为用户提供翻译结果。
这些工具通常基于深度学习算法,通过对大量的双语语料进行学习和训练,从而掌握语言的规律和模式。
比如,谷歌翻译、百度翻译等知名的翻译工具,已经能够处理多种语言之间的翻译任务,并且在一些常见的领域,如旅游、商务等,能够提供较为准确和流畅的翻译服务。
然而,尽管人工智能在翻译方面取得了显著的进步,但它仍然存在一些局限性。
语言是极其复杂和灵活的,充满了文化内涵、隐喻、习语等难以捉摸的元素。
人工智能在处理这些具有文化和语境特定性的内容时,往往会出现偏差或不准确的情况。
例如,一些诗词、文学作品中的精妙表达,人工智能可能无法完全领悟其中的韵味和情感,从而导致翻译的生硬和缺乏美感。
另外,人工智能翻译在语法和语义的理解上也并非完美无缺。
有时候,它可能会因为对句子结构的误判或者对词汇多义性的理解不足,而给出错误的翻译结果。
而且,对于一些新出现的词汇和表达方式,由于没有在训练数据中出现过,人工智能可能无法及时做出准确的翻译。
尽管存在这些问题,但我们不能忽视人工智能在外语翻译领域所具有的巨大潜力和广阔的应用前景。
从效率方面来看,人工智能能够在极短的时间内处理大量的文本,这对于需要快速获取信息的场合,如新闻报道、商务文件的翻译等,具有无可比拟的优势。
相比之下,人工翻译需要耗费大量的时间和精力,难以满足这种对速度的要求。
在准确性方面,随着技术的不断进步和数据的不断丰富,人工智能翻译的质量也在逐步提高。
通过不断优化算法和增加训练数据的多样性,未来人工智能有望在更多领域提供更加准确和可靠的翻译服务。
is about, and this is presently possible only for very limited domains.Computer visionThe world is composed of three-dimensional objects, but the inputs to the human eye and computers' TV cameras are two dimensional. Some useful programs can work solely in two dimensions, but full computer vision requires partial three-dimensional information that is not just a set of two-dimensional views. At present there are only limited ways of representing three-dimensional information directly, and they are not as good as what humans evidently use.Expert systemsA “knowledge engineer” interviews experts in a certain domain and tries to embody their knowledge in a computer program for carrying out some task. How well this works depends on whether the intellectual mechanisms required for the task are within the present state of AI. When this turned out not to be so, there were many disappointing results. One of the first expert systems was MYCIN in 1974, which diagnosed bacterial infections of the blood and suggested treatments. It did better than medical students or practicing doctors, provided its limitations were observed. Namely, its ontology included bacteria, symptoms, and treatments and did not include patients, doctors, hospitals, death, recovery, and events occurring in time. Its interactions depended on a single patient being considered. Since the experts consulted by the knowledge engineers knew about patients, doctors, death, recovery, etc., it is clear that the knowledge engineers forced what the experts told them into a predetermined framework. In the present state of AI, this has to be true. The usefulness of current expert systems depends on their users having common sense.Heuristic classificationOne of the most feasible kinds of expert system given the present knowledge of AI is to put some information in one of a fixed set of categories using several sources of information. An example is advising whether to accept a proposed credit card purchase. Information is available about the owner of the credit card, his record of payment and also about the item he is buying and about the establishment from which he is buying it (e.g., about whether there have been previous credit card frauds at this establishment).Minimax Trees and Alpha-Beta PruningMoving on to another genre of games completely - board games. Board gaming AI has received a huge amount of publicity since the famous chess match between Deep Blue (IBM's master chess computer) and Kasparov - the first time a chess world champion has been beatenby a machine. Games like chess, checker, Pente, and Go require a great deal of thinking。
英文原文Artificial IntelligenceAdvanced Idea ,Anticipating Incomparability on Artificial Intelligence.Artificial intelligence(AI) is the field of engineering that builds systems ,primarily computer systems ,to perform tasks requiring intelligence .This field of research has often set itself ambitious goals, seeking to build machines that can outlook humans in particular domains of skill and knowledge ,and has achieved some success in this.The key aspects of intelligence around which AI research is usually focused include expert system ,industrial robotics,systems and languages language understanding ,learning ,and game playing,etc.Expert SystemAn expert system is a set of programs that manipulate encoded knowledge to solve problems in a specialized domain that normally requires human expertise . Typically,the user interacts with an expert system in a consultation dialogue,just as he would interact with a human who had some type of expertise,explaining his problem,performing suggested tests,and asking questions about proposed solutions. Current experimental systems have achieved high levels of performance in consultation tasks like chemical and geological data analysis,computer system configuration,structural engineering,and even medical diagnosis.Expert systems can be viewed as intermediaries between human experts,who interact with the systems in knowledge acquisition mode ,and human users who interact with the systems in consultation mode. Furthermore ,much research in this area of AI has focused on endowing these systems with the ability to explain their reasoning,both to make the consultation more acceptable to the user and to help the human expert find errors in the system´s reasoning when they occur.Here are the features of expert systems:①Expert systems use knowledge rather than data to control the solution process.②The know is encoded and maintained as an entity separated fromthe control program.Furthermore,it is possible in some cases to use differentknowledge bases with the same control programs to producedifferent types of expert system.Such system are known as expert systemshells.③Expert systems are capable of explaining how a particular concl-usion is reached,and why requested information is needed during a consultation.④Expert systems use symbolic representations for knowledge andperform their inference through symbolic computations.⑤Expert systems often reason with metaknowledge.Industrial RoboticsAn industrial robot is a general-purpose computer-controlled manipulator consisting of several rigid links connected in series by revolute or prismatic joints.Research in this field has looked at everything from the optimal movement of robot arms to methods of planning a sequence of actions to achieve a robot´s goals.Although more complex systems have been built,the thousands of robots that are being used today in industrial applications are simple devices that have been programmed to some repetitive task.Robots,when compared to humans,yield more consistent quality,more predictable output,and are more reliable.Robots has been used in industry since 1965.They are usually characterized by the design of the mechanical system.There are six recognizable robot configurations:①Cartesian Robots:A robot whose main frame consist of three Linear axes.②Gantry Robots:A Gantry robot is a type of artesian robot whose structure resembles a gantry.This structure is used to minimize deflection along each axis.③Cylindrical Robots:A cylindrical robot has two linear axes and one rotary axis.④Spherical Robots:A spherical robot has one linear axis and two rotary axes.Spherical Robots are used in a variety of industrial tasks such as welding and material handling.⑤Articulated Robots:An articulated robot has three rotational axes connecting three rigid links and a base.⑥Scara Robots:One style of robot that has recently become quite popular is a combination of the articulated arm and the cylindrical robot.The robot has more than three axes and is widely used in electronic assembly.Systems and LanguagesComputer-systems ideas like time-sharing,list processing,and interactive debugging were developed in the AI research environment.Specialized programming languages and systems,with features designed to facilitate deduction,robot manipulation,cognitive modeling,and so on, have often been rich sources of new ideas.Most recently,reveral knowledge-representation languages,computer languages for encoding knowledge and reasoning methods as data structure and procedures,which have been developed in the last few years to explore a variety of ideas about how to build reasoning programs.Problem SolvingThe first big success in AI was programs that could solve puzzles and play games like chess.Techniques like looking ahead several moves and dividing difficult problems into easier sub-problems evolved into the fundamental AI techniques of search and problem reduction.Today´s programs play championship-level checkers and backgammon,as well as verygood chess.Another problem-solving program that integrates mathematical formulates symbolically has attained very high levels of performance and is being used by scientists and engineers.Some programs can even improve their performance with experience.As discussed above,the open questions in this area involve capabilities that human players have but cannot articulate,like the chess master´s ability to see the board configuration in terms of meaningful patterns.Another basic open question involves the original conceptualization of a problem,called in AI the choice of problem representation.Humans often solve a problem by finding a way of thinking about it that makes the solution easy-AI problems,so far,must be told how to think about the problems they solve.Logical ReasoningClosely related to problem and puzzle solving was early work on logical deduction.Programs were developed that could prove assertions by manipulating a database of facts,each represented by discrete data structures just as they are represented by discrete formulas in mathematical logic.These methods,unlike many other AI techniques,could be shownto be complete and consistent.That is,so long as the original facts were correct,the programs could prove all theorems that followed from the facts,and only those theorems.Logical reasoning has been one of the most persistently investigated subareas of AI research.Of particular interest are the problems of finding ways of focusing on only the relevant facts of a large database and of keeping track of the justifications for beliefs and updating them when new information arrives.Language UnderstandingThe domain of language understanding was also investigated by early AI researchers and has consistently attracted interest.Programs have been written that answer questions posed in English from an internal database,that translate sentences from one language to another,that follow instruction given in English,and that acquire knowledge by reading textual material and building an internal database.Some programs have even achieved limited success in interpreting instructions spoken into a microphone instead of typed into the computer.Although these language systems are not nearly as good as people are at any of these tasks,they are adequate for some applications.Early successes with programs that answered simple queries and followed simple directions,and early failures at machine translation,have resulted in a sweeping change in the whole AI approach to language.The principal themes of current language-understanding research are the importance of vase amounts of general,commonsense world knowledge and the role of expectations,based on the subject matter and the conversational situation,in interpreting sentences.LearningLearning has remained a challenging area for AI.Certainly one of the most salient and significant aspects of human intelligence is the ability to learn.This is a good example of cognitive behavior that is so poorly understood that vary little progress has been made in achieving it in AI system.There have been several interesting attempts,including programs learn from examples,form their own performance,and from being told.An expert system may perform extensive and costly computations to solve a problem.Most expert systems are hindered by the inflexibility of their problem-solving strategies and the difficulty of modifying large amounts of code.The obvious solution to these problems is for programs to learn on their own,either from experience,analogy,and examples or by being told what to do.Game PlayingMuch of the early research in state space search was done using common board games such as checkers,chess,and the 15-puzzle.In addition to their inherent intellectual appeal,board games have certain properties that make them ideal subjects for this early work.Most games are played using a well-defined set of rules,this makes it easy to generate the search space and frees the researcher from many of the ambiguities and complexities inherent in less structured problems.The board configurations used in playing these games are easily represented on a computer,requiring none of the complex formalisms.ConclusionWe have attempted to define artificial intelligence through discussion of its major areas of research and application.In spite of the variety of problems addressed in artificial intelligence research,a number of important features emerge that seem common to all divisions of the field,these include:①The use of computers to do reasoning,learning,or some other form of intelligence.②A focus on problems that do not respond to algorithmic solutions.This underlies the reliance on heuristic search as an AI problem-solving technique.③Reasoning about the significant qualitative features of a situation.④An attempt to deal with issues of semantic meaning as well as syntactic form.⑤The use of large amounts of domain-specific knowledge in solving problems.This is the basis of expert systems.AbstractArtificial intelligence(AI) is the field of engineering that builds systems,primarily computer systems,to perform tasks requiring intelligence .This field of research has often set itself ambitious goals,seeking to build machines that can outlook humans in particular domains of skill and knowledge,and has achieved some success in this.The key aspects of intelligence around which AI research is usually focused include expert systems,industrial robotics,systems and languages,language understanding,learning,and game playing,machine translation,etc.中文译文人工智能先进的想法不断注入到人工智能的发展过程中,使其最新理念无与伦比。