中科院博士入学英语试卷 2002年3月
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:9.08 MB
- 文档页数:16


2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C OR D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 1 . As was discussed before, it was not 2 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic_ 3 _ ,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 4 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 5 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 6 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 7 the 20th century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that Process in 8 . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, 9 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not immediately 12 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became “personal” too, as well as 13 , with display becoming sharper and storage 14 increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance between generations much 16 .It was within the computer age that the term “information society” began to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 view about its economic, political, social and cultural implication s. “Benefits” have been weighed 20 “harmful” outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.1. [A]between [B]before [C]since [D]later2. [A]after [B]by [C]during [D]until3. [A]means [B]method [C]medium [D]measure4. [A]process [B]company [C]light [D]form5. [A]gathered [B]speeded [C]worked [D]picked6. [A]on [B]out [C]over [D]off7. [A]of [B]for [C]beyond [D]into8. [A]concept [B]dimension [C]effect [D]perspective9. [A]indeed [B]hence [C]however [D]therefore10. [A]brought [B]followed [C]stimulated [D]characterized11. [A]unless [B]since [C]lest [D]although12. [A]apparent [B]desirable [C]negative [D]plausible13. [A]institutional [B]universal [C]fundamental [D]instrumental14. [A]ability [B]capability [C]capacity [D]faculty15. [A]by means of [B]in terms of [C]with regard to[D]in line with16. [A]deeper [B]fewer [C]nearer [D]smaller17. [A]context [B]range [C]scope [D]territory18. [A]regarded [B]impressed [C]influenced [D]effected19. [A]competitive [B]controversial [C]distracting [D]irrational20. [A]above [B]upon [C]against [D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing [A], [B], [C] or [D]. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different. If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses’ convention, of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. “Who is that?”the new arrival asked St. Peter. “Oh, that’s God,” came the reply, “but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties. With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman. You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that it becomes more natural. Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner. Often it’s the delivery which causes theaudience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor. It often comes from the unexpected. A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don’t succeed, give up”or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatement. Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.21. To make your humor work, you should .[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience[B] make fun of the disorganized people[C] address different problems to different people[D] show sympathy for your listeners22. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are .[A] impolite to new arrivals[B] very conscious of their godlike role[C] entitled to some privileges[D] very busy even during lunch hours23. It can be inferred from the text that public services .[A] have benefited many people[B] are the focus of public attention[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor[D] have often been the laughing stock24. To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered .[A] in well-worded language[B] as awkwardly as possible[C] in exaggerated statements[D] as casually as possible25. The best title for the text may be .[A] Use Humor Effectively[B] Various Kinds of Humor[C] Add Humor to Speech[D] Different Humor StrategiesText 2Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor. Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for thetransaction. Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers. And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge. “While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error," says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program at NASA, “we can't yet give a robot enough ‘common sense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. Despite a spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated—than previously imagined. They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.26. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in .[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.[C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D] the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.27. The word “gizmos” (line 1, paragraph 2) most probably means .[A] programs[B] experts[C] devices [D] creatures28. According to the text, what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robotthat can .[A] fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B] interact with human beings verbally.[C] have a little common sense.[D] respond independently to a changing world.29. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also .[A] make a few decisions for themselves.[B] deal with some errors with human intervention.[C] improve factory environments.[D] cultivate human creativity.30. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are .[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D] best used in a controlled environment.Text 3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return? Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March, the price of crude oil has jumped to almost $26 a barrel, up from less than $10 last December. This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the 1973 oil shock, when prices quadrupled, and 1979-1980, when they also almost tripled. Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline. So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth, at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere, could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the 1970s. In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the 1970s. In Europe, taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price, so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were, and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price. Energy conservation, a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy, energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption. Software, consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production. For each dollar of GDP (in constant prices) rich economies now use nearly 50% less oil than in 1973. The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that, if oil prices averaged $22 a barrel for a full year, compared with $13 in 1998, this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5% of GDP. That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in 1974 or 1980. On the other hand, oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive, and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that, unlike the rises in the 1970s, it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand. A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline. The Economist’s commodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago. In 1973 commodity prices jumped by 70%, and in 1979 by almost 30%.31. The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[A] global inflation. [B] reduction in supply.[C]fast growth in economy. [D] Iraq’s suspension of exports.32. It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go updramatically if______.[A] price of crude rises. [B] commodity prices rise.[C] consumption rises. [D] oil taxes rise.33. The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.[B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.[C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.[D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.34. We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.[B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.[C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.[D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.35. From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.[A]optimistic. [B]sensitive. [C]gloomy. [D]scared.Text 4The Supreme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide, the Court in effect supported the medical principle of “double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain, even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.Nancy Dubler, director of Montefiore Medical Center, contends that the principle will shield doctors who “until now have very, very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten death”.George Annas, chair of the health law department at Boston University, maintains that, as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose, the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death. “It’s like surgery,” he says. “We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients, although they risked their death. If you’re a physician, you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”On another level, many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’s ruling on physician-assisted suicide, theNational Academy of Science (NAS) released a two-volume report, Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life. It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of “ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong and even dishonor the period of dying” as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies, to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care, and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care. “Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”, to the extent that it constitutes “systematic patient abuse”. He says medical licensing boards “must make it clear...that painful deaths are presumptiv ely ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension”.36. From the first three paragraphs, we learn that .[A] doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’pain[B] it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C] the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D] patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37. Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[A] Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’death.[B] Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C] The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can beprescribed.[D] A doctor’s medication is no longer justified by his intentions.38. According to the NAS’s report, one of the problems in end-of-life care is .[A] prolonged medical procedures [B] inadequate treatment of pain[C] systematic drug abuse [D] insufficient hospital care39. Which of the following best defines the word “aggressive”(line 4, paragraph7)?[A] Bold. [B] Harmful. [C] Careless. [D] Desperate40. George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they .[A] manage their patients incompetently[B] give patients more medicine than needed[C] reduce drug dosages for their patients[D] prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese. Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior, and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone. What is needed is a technology of behavior, but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technology might be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind, feelings, traits of character, human nature, and so on. Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them. (42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find. The environment is obviously important, but its role has remained obscure. It does not push or pull, it selects, and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago, and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied. As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood, however, effects once assigned to states of mind, feelings, and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions, and a technology of behavior may therefore become available. It will not solve our problems, however, until it replaces traditional prescientific views, and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty. (44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory, and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements. A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment. It also raises questions concerning “values”. Who will use a technology and to what ends? (45)Until these issues are resolved, a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected, and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46. Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an es say entitled “Cultures National and International”.In the essay you should1. describe the picture and interpret its meaning, and2. give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about 200 words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
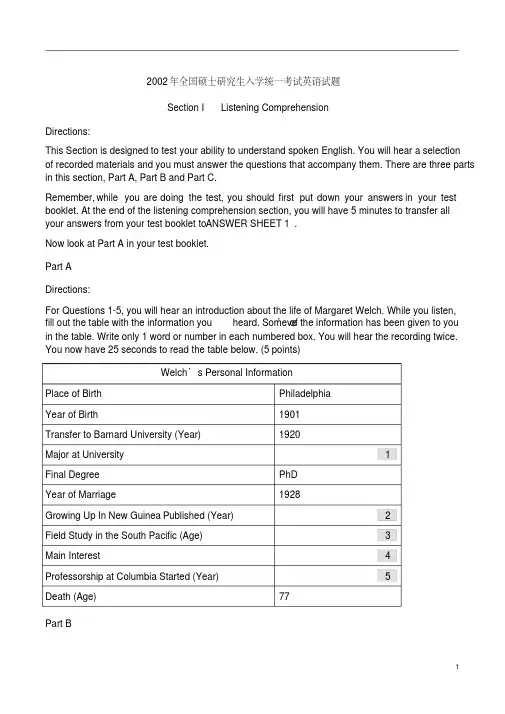
2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题Section I Listening ComprehensionDirections:This Section is designed to test your ability to understand spoken English. You will hear a selectionof recorded materials and you must answer the questions that accompany them. There are three parts in this section, Part A, Part B and Part C.Remember, while you are doing the test, you should first put down your answers in your test booklet. At the end of the listening comprehension section, you will have 5 minutes to transfer allyour answers from your test booklet to A NSWER SHEET 1.Now look at Part A in your test booklet.Part ADirections:For Questions 1-5, you will hear an introduction about the life of Margaret Welch. While you listen,heard. Some of the information has been given to youfill out the table with the information you’vein the table. Write only 1 word or number in each numbered box. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the table below. (5 points)Welch’s Personal InformationPlace of Birth PhiladelphiaYear of Birth 1901Transfer to Barnard University (Year) 1920Major at University 1Final Degree PhDYear of Marriage 1928Growing Up In New Guinea Published (Year) 2Field Study in the South Pacific (Age) 3Main Interest 4Professorship at Columbia Started (Year) 5Death (Age) 77Part BDirections:For questions 6-10, you will hear a talk by a well-known U.S. journalist. While you listen, completethe sentences or answer the questions. Use not more than 3 words for each answer. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the sentences and questions below. (5 points)Besides reporters, who else were camped out 6for days outside the speaker’s home?apartmentOne reporter got to the speaker’s 7pretending to pay.The speaker believed the reporter wanted a 8picture of her lookingWhere is a correction to a false story usually 9placed?According to the speaker, the press will lose10readers unless the editors and the newsdirectorsPart CDirections:You will hear three pieces of recorded material. Before listening to each one, you will have time to read the questions related to it. While listening, answer each question by choosing [A], [B], [C] or[D]. After listening, you will have time to check your answers. You will hear each piece once only.(10 points)Questions 11-13 are based on a report about children’s healthy development. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 11-13.11. What unusual question may doctors ask when giving kids a checkup next time? [A] How muchexercise they get every day.[B] What they are most worried about.[C] How long their parents accompany them daily.[D] What entertainment they are interested in.12. The academy suggests that children under age two ________.[A] get enough entertainment[B] have more activities[C] receive early education[D] have regular checkups13. According to the report, children’s bedrooms should ________.[A] be no place for play[B] be near a common area[C] have no TV sets[D] have a computer for studyQuestions 14-16 are based on the following talk about how to save money. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 14-16.14. According to the speaker, what should one pay special attention to if he wants to save up?[A] Family debts.[B] Bank savings.[C] Monthly bills.[D] Spending habits.15. How much can a person save by retirement if he gives up his pack-a-day habit?[A] $190,000.[B] $330,000.[C] $500,000.[D] $1,000,000.16. What should one do before paying monthly bills, if he wants to accumulate wealth?[A] Invest into a mutual fund.[B] Use the discount tickets.[C] Quit his eating-out habit.[D] Use only paper bills and save coins.Questions 17-20 are based on an interview with Herbert A. Glieberman, a domestic-relations lawyer. You now have 20 seconds to read Questions 17-20.17. Which word best describes the lawyer’s prediction of the change in divorce rate?[A] Fall[B] Rise[C] V-shape[D] Zigzag18. What do people nowadays desire to do concerning their marriage?[A] To embrace changes of thought.[B] To adapt to the disintegrated family life.[C] To return to the practice in the ‘60s and ‘70s.[D] To create stability in their lives.19. Why did some people choose not to divorce 20 years ago?[A] They feared the complicated procedures.[B] They wanted to go against the trend.[C] They were afraid of losing face.[D] they were willing to stay together.20. Years ago a divorced man in a company would have ________.[A] been shifted around the country.[B] had difficulty being promoted.[C] enjoyed a happier life.[D] tasted little bitterness of disgrace.You now have 5 minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET 1.THIS IS THE END OF SECTION IDO NOT READ OR WORK ON THE NEXT SECTIONUNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO CONTINUE全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(二)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。

2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or Don ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points).Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 1 . As was discussed before, it was not 2 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic 3 , following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 4 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 5 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 6 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 7 the 20th-century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that process in 8 . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, 9 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not immediately 12 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became "personal" too, as well as 13 , with display becoming sharper and storage 14 increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance b e tween generat10ns much 16It was within the computer age that the term "information society" began to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 views about its economic, political, social and cultural implications. "Benefits" have been weighed 20 "harmful" outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.。

THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES ENGLISH ENTRANCE EXA MINATIONFORDOCTORAL CANDIDATES PAPER ONEPART I LISTENING COMPREHENSION (20 minutes, 20 points) Section A (10 points, 1 point each)Directions: In this section, you will hear ten short conversations betwee n two speakers. At the end of each conversation, a question will be as feed about what was said. The question will be spoken only once. Ch oose the best answer from the four choices given by marking the corre sponding letter with a single bar across the square brackets on your M achine-scoring Answer Sheet.1. A, She is sick.B. She is hungry.C. She was bitten by an ant.D. She had a long bicycle ride.2. A. He's outgoing.B. He's considerate.C- He's successful.D. He's nice to all,3. A. 30 minutesB. 25 minutesC. 20 minutesD. 15 minutes4. A. take the airB. park the carC. fill in the formD. work on a text5. A. apply for a credit cardB. get a driver's licenseC. buy an insuranceD. rent a vehicle6. A, Crime needs to be treated as a disease.B. Primitive punishment will do no good.C. Severe punishment is necessary to stop crime.D. Primitive people had trouble with crime treatment.7. A, the sale of the old housesB. the pulling down of the gas companyC. the proposal of the councilD. the building of the office blocks8. A. He will not be able to many Cindy.B. He has financial problems.C. He has yet to buy furniture.D. He may not be recovered until the wedding.9. A. Both are having a cold.B. Both are on holidays.C. The woman feels sorry for the man.D. The woman hopes to see the man in the school.10. A. He felt sympathy for the Vietnamese.B. He used to come to the U.S. unlawfully.C. He aided illegal immigration to the U.S.D. He dealt with 7,000 immigration cases.Section B (10 points, 1 point each)Directions: In ihis section, you will hear three short passages. At the e nd of each passage, there will be a few questions. Both the passage and the questions will be read to you only once. After each question, t here will be a pause. During the pause, you must choose the best ans wer from the four choices given by marking the corresponding letter wit h a single bar across thesquare brackets on your Machine-scoring Answer Sheet.11. A. to make children grow tall and strongB. to keep the soul in the bodyC. to prevent someone from saying evil thingsD. to protect someone against catching a cold12. A. They think a good spirit may help the child grow,B. They want to drive away the devil "sneeze."C. They say it as a curse for the child to stop sneezing.D. They consider a sneeze an obstacle to the child's growth.13. A. the GermanB. the ItalianC. the JapaneseD. the Hindus14. A. All peoples are afraid of sneezing.B. Some people never sneeze in their lives.C. The moment of sneezing is very dangerous.D. Many people say prayers when they sneeze.15. A. a lack of available flightsB. long delays at the airportC. boredom on long flightsD. long trips to and from the airport16. A. on short tripsB. on long tripsC. when flying over citiesD. when flying at high altitudes17. A. It fuels with nuclear energy.B. It rests on a cushion of pressurized air.C. It flies above magnetically activated tracks.D. It uses a device similar to a jet engine-18. A. She is poor in school grade.B, Her major is thought to be useless.C, Her job expectation is too high.D, There is now an economic recession.19. A, undergraduatesB. experienced M.B.A.sC. laid-off workersD. liberal-arts majors20. A. Unemployment rate will get still higher.B. There will be no multiple job offers.C. 2 million job seekers will compete for jobs.D. First-time job requirements will be lowered.(THIS IS THE END OF LISTENING COMPREHENSION.)PART II VOCABULARY (15 minutes, 10 points)Section A (0.5 point each)Directions: Choose the word or expression below each sentence shot b est completes the statement, and mark the corresponding letter of your choice with a single bar across the square brackets on your Machine-scaring Answer Sheet,21. His trick convinced none but the mostA. credulousB. plausibleC. trustworthyD. feasible22. Many people proposed that a national committee be formed to disc uss toexisting mass transit systems.A. substitutesB. measuresC, duplicates D. alternatives23. He is a hypocrite, a liar, a thief—, he is the greatest devil I ever know.A. as a consequenceB. as a ruleC, as a matter of fact D. as a matter of routine24. Since she was alone, she opened the door . leaving the chain lock fastened.A. warilyB. consciouslyC. audaciouslyD. recklessly25. In the last few minutes the conversation has become seemingly as ifthe discussion were of some minor domestic matter and not survival its elf,A. crucialB. centralC. casualD. causal26. I didn't listen to Mom and 1 was not surprised at the look of on her face.A. indifferenceB. complimentC, negligence D. reproach27. The victims of drunken driving in America over the past decade___ __ anincredible 250,000, with three killed every hour of every day on averag e.A. Sake upB. add up toC, count for D. turn out to28. He is believed to have been shot by a rival gang in for the shooti ngslast week.A. revenge B, reserveC. reverseD. remedial29. These pollutants can be hundreds and even thousands of kilometer s bylarge air masses.A. containedB. conveyedC. contaminatedD. conserved30. There are a few small things that I don't like about my job, but _ i t'svery enjoyable.A. all at onceB. once and for allC. so much asD. by and large31. In a divorce, the mother usually is granted___________ of her chil dren.A. supportB. retentionC. perseveranceD. custody32. What he had in mind to nothing less than a total reversal of the tr aditional role of the executive.A. contributedB. dedicatedC. amountedD. added33. Some Heads of Government now fear that negotiations will beforea settlement is reached.A. wear outB. come alongC. break offD. end up34. A of soap and two brightly colored towels were left beside the bat h, then the women smiled politely at Nicole and withdrew carefully from the room.A. loaf B, barC. stick D, block35. Of the 1200 million people who call themselves Chinese, a very s mallnumber speak what is referred to as standard Chinese.A. none butB. but forC. all butD. but then36.___________ recent brain and behavioral research. Dr. Goleman wr ote a fascinating book entitled "Emotional Intelligence."A. Drawing upB. Drawing onC. Putting upD. Putting on37. Many people think of deserts as regions, but numerous species of plants and animals have adapted to life there,A. remoteB. irginC. alienD. barren38. Attempts to persuade her stay after she felt insulted were __,A, of no avail B. out of focusC. at a loss D, in no way39. Scientists are certain that there is a cancer-inhibiting agent in the blood of the shark.A. dubiouslyB. virtuallyC. queerlyD. randomly40. The integration of staff for training has led to a good exchange of i deas, greater enthusiasm, and higher staff .________ ,A. moral B, mortalC. moraleD. moresPART III CLOZE TEST (IS minutes, 15 points)Directions: There are 15 questions in this part of the test. Read the pa ssage through-Then, go back and choose one suitable word or phrase marked A, B, C, or D for each blank in the passage. Mark the corresp onding tetter of the word or phrase you have chosen with a single bar across she square brackets on your Machine-scoring Answer Sheet.It is appropriate on an anniversary of the founding of a university to re mind ourselves of its purposes. It is equally appropriate at such time fo r students to 4j why they have been chosen to attend and to consider how they can best 42.__ the privilege of attending.At the least you 95 students can hope to become 43 in subject matter which may be useful to you in later life. There is, 44 , much more to be gained. It is now that you must learn to exercise your mind suffici ently __45_ learning becomes a joy and you thereby become a student for life. 46 this may require an effort of will and a period of self-discip line. Certainly it is not 47 without hard work. Teachers can guide and encourage you, but learning is not done passively. To learn is your48. There is 49 the trained mind satisfaction to be derived from exploring the ideas of others, mastering them and evaluating them. But there is 5 0 level of inquiry which I hope that some of you will choose. If your st udy takes you to the 51 of understanding of a subject and, you have r eached so far, you find that you can penetrate to 52 no one has been before, you experience an exhilaration which can't be denied and whic h commits you to a life of research.Commit mem to a life of scholarship or research is 53 many other lau dable goals. It is edifying, and it is a source of inner satisfaction even 54 other facets of life prove disappointing. I strongly 55 it,41.A. count42. A, benefit from43. A. efficient44. A. however45. A. if46. A. Of late47. A. acquired48. A. ambition49. A. to50.A. any51.A. ends52. A. elsewhere53. A. compatible with54. A. shall55. A. declareB. reflect t B.ake over B.excellent t B.herefore B.because B.Consequently B.accomplished B.conscience B.onB. oneB.limitsB.whatB. responsible forB. willB. recommendC. depend C.apply for C.professional C.indeedC. so that C.Afterwards C.approached C.responsibility C. in C. another C, bordersC. whicheverC. followed byC. wouldC, adviseD. comment D. go hrough D. proficient D. after all D.before D. At first D.assuredD.challenge D. byD. noD. edgesD. relevant toD.whereD. shouldD. contendPART IV READING COMPREHENSION (60 minutes, 30 points) Directio ns: Be low each of the following passages you will find some question s or incomplete statements. Each question or statement is followed by four choices market! A, B, C. end D. Read each passage carefully, an d then select (he choice that bear answers the question or completes (he statement Mark (fie teller of your choice with a single bar across (he square brackets on your Machine-scoring Answer Sheet.Passage ISmall, pink and very ugly. Hardly the qualities of a star, but they descr ibe the deformed mouse that was the media darling at a recent scienc e exhibition in Beijing. With a complex tissue structure in the shape of a human ear grafted on to its back, the rosy rodent was a stunning sy mbol of the serious strides China is making in the field of biotechnology.China is fast applying the latest life-science techniques learned from th e West to aggressively pursue genome research. It's establishing its ow n centers of technical excellence to build a scientific base to compete directly with the United States and Europe. With a plentiful supply of s mart young scientists at home and lots of interest abroad biotechnology is on the brick of a boom in China. And in the view of foreign scienti sts, Beijing is playing a clever hand, maximizing the opportunities open to them.For the moment, the cooperation exists mostly with Europe and the U. S. But Asia's other biotech leaders, Japan, Singapore and Korea, also are recognizing China's potential as an attractive low-cost base to cond uct research. These partnerships—and China's advancement in the field of biotechnology—could help benefit the rest of Asia: China's rapid pro gress in improving crop yields will address food-security concerns in the region, In addition, China is more likely to focus on developing chea p technology that its predominantly poor population—and those of other Asian countries—-can afford.There remain, however, serious barriers to the development qf a strong biotech industry. Among them are a poor domestic legal framework, w eak enforcement of intellectual-property rights and loose adherence to i nternational standards, China is a signatory of the International Bio Saf ety Protocol, which should mean adherence to global standards governi ng the conduct of field trials. But some observers are skeptical. 'The re gulations look good, but I haven't met one scientist who believes they are being fully adhered to," says a European science analyst.If shortcuts are taken, then some of the recent scientific achievements trumpeted in the official press may never make it to market. But no m atter how strict lab tests are. other problems lie in waii. For example, t here is a number of tasks it would take years :o fulfill in the patents of fice, says one lawyer, leaving innovators with little protection if they tak e a product to market in China.56, The mouse on display is most significant in that _ _.A. it has an ear in the shape of a human earB. it is unusually small and ugly as a starC. it is the focus of the media at the exhibitionD. it indicates China's progress in biotechnology57. The phrase "on the brink of a boom" (in boldface in Paragraph 2) i n the contextmeans .A. having an edge in competitionB. in great demandC. on the way to successD. preparing for challenge58. In the field of biotechnology China is thought to .A. have been making an utmost effort learning from the WestB. have become a country among the advancedC. have been able to rival the United Sates and EuropeD. have launched a biotechnological revolution59. Japan, Singapore, and Korea will also be interested in cooperating with China in biotechnology because________ .A. it has made extraordinary contributions to the worldB. it has large supplies of talents and advanced research centersC. its research focuses on the benefits of all Asian countriesD. its cooperation with the US and Europe proves profitable60. Science analysts are worried that China, in the course of biotech d evelopment,A. might refuse to join efforts to adhere to global standardsB. may put too much emphasis on developing cheap technologyC. cannot afford to fulfill years of tasks in assessing patentsD. may not seriously follow the International Bio Safety Protocol61. As implied in the context, the shortcuts that might be taken include ___________ .A. publicizing recent achievements in the official pressB. the protection of innovators with their productsC. the violation of intellectual-property rightsD. making lab tests as strict as possiblePassage 2The sizzling streams of sunlight were just beautifully glimmering down o n the crisp green schoolyard. Such a wonderful day that was. Nothing could have ruined it.Little Jimmy, since it was such a wonderful day, decided to go to the corner store and buy himself a little treat. As Jimmy started walking ov er to the store, Clouds flocked over the dazzling sun and the sudden p itch dark meant no trouble, On the other side of the road were three white boys from Jimmy's same school. Upon recognizing Jimmy, the bo ys ran over the street to where he was."Hey Negro, what's up?" one of the white boys said,"Did your mamma pack you enough to eat today? "another hooted. "Ju st leave me alone," Little Jimmy said." Oh no, Jimmy's really getting pist off!?" the first boy retaliated. "Just shove off and let me be," Jimmy answered.It is like this everyday, everywhere, and every time, people suffer discri mination. All because they have differences amongst each other. Differe nt beliefs, different cultures, different skin colors, all of these act like b uilding blocks to help construct what we know as Racism.Racism has become one of the many burdens amongst multi-cultural w orlds like Canada and the States. Racism is a part of each and every one of us. No doubt, we are all racist, but the term racism has been u sed too loosely. Racism has been mutated to such an extent that ii co uld be a reason for war, a symbol of terrorism, and even an excuse fo r neglecting.Is that all there is to it? No, actually it is just the beginning. Racism is just like warfare in which there is no shelter and nobody is neutral. Nobody is exempt from this demon. He has haunted us with a bitter c urse. On one occasion I remember, nobody would play with me at sch ool. 1 would walk around by myself and ask people if we could play to gether. Everywhere that 1 went, like the process of induction, everyone would avoid me. Like two inducted poles with the some polarity, they would just shimmer off into the distance and continue to do whatever t hey're doing. Because of racial differences, they neglect me.People are afraid of the unknown, and it is this difference amongst peo ple that spread rumors and distrust amongst people. Corrupting our tho ughts and reasons, we get accustomed to thinking differences are ome ns. Amongst smaller kids, there is no difficulty in getting them to all pl ay together, Their thoughts are not totally corrupted as others. Probably the demon has no time to bother with smaller children.62. With the description of the weather and Jimmy's teeling about it the author intends to show that_________ .A. what a happy world it is for humansB. what an innocent boy Jimmy wasC. what an unusual thing that was to happen to JimmyD. what a wonderful world that people have ignored63. From the conversation with the three white boys, we learn that Jim myA. must have offended them beforeB. was a pleasant boy to be talked toC. was being humiliated for being blackD. must have got used to their behaviors64, According to the author, RacismA. leads to a world with no varietyB. does not see the differences between culturesC. hinders rhe world's economic developmentD. does not tolerate coexistence of different cultures65. By saying ''No doubt, we are alt racist" (in boldface in Paragraph3) the author admits that .A. we are all warlike by natureB. we all discriminate against other peoplesC. we are all proud of our own race and nationD. we all focus on the difference between races66, To be continued, the passage would probably be followed by a par agraph that deals withA. how children's thoughts are corrupted by racism as they growB. the author's far more miserable experience of being neglectedC. how the black people should unite to fight against the WhitesD. the education of smaller children to behave pleasantly to each other67. Which of the following can best describe the tone of the passage?A. provocativeB. indignantC. sentimentalD. sarcasticPassage 3This week marks the 10th anniversary of the Alar apple scare, in whic h many American consumers were driven into a panic following the rel ease of a report by an environmental organization claiming that apples containing the chemical Alar posed a serious health threat to preschoolers. The report was disseminated through a PR (Problem Report) camp aign and bypassed any legitimate form of scientific peer review. Introdu ced to the American public by CBS' "60 Minutes," the unsubstantiated claims in the report led some school districts to remove apples from th eir school lunch programs and unduly frightened conscientious parents t rying to develop good eating habits for their children.Last month, Consumers Union released a report warning consumers of the perils of consuming many fruits and vegetables that frequently cont ained '"unsafe" levels of pesticide residues. This was especially true for children, they claimed. Like its predecessor 10 years earlier, the Cons umers Union report received no legitimate scientific peer review and th e public's first exposure to it was through news coverage.Not only does such reporting potentially drive children from consuming healthful fruits and vegetables, the conclusions were based on a mislea ding interpretation of what constitutes a "safe" level of exposure. Briefl y, the authors used values known as the "chronic reference doses," set by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, as their barometers of s afety. Used appropriately, these levels represent the maximum amount of pesticide that could be consumed daily for life without concern. For a 70-year lifetime, for example, consumers would have to ingest this av erage amount of pesticide every day for more than 25,000 days. It is c lear, as the report points out. that there are days on which kids may b e exposed to more; it is also clear that there are many more days wh en exposure is zero. Had the authors more appropriately calculated the cumulative exposures for which the safety standards are meant to app ly, there would have been no risks and no warnings.Parents should feel proud, rather than guilty, of providing fruits and veg etables for their children. It is well established that a diet rich in such f oods decreases the risk of heart disease and cancer. Such benefits dr amatically overwhelm the theoretical risks oftiny amounts of pesticides in food. So keep serving up the peaches, a pples, spinach, squash, grapes and pears.68. In the Alar apple scare, many Americans were frightened because ,A. scientists warned that apples were dangerousB. many school children became ill after eating applesC. it was reported that apples were harmful to healthD. apples were discovered to have too much pesticide69. The warning message about the Alar apple was given .A. by Consumers UnionB. by a health centerC. through an news agencyD. through the government70. The last month report parallels that on the Alar apple scare in that .A. neither really caused worry among the publicB. neither underwent a scientific peer reviewC. neither provided statistical supportsD. neither aimed for the public good71. The ''chronic reference doses" (in boldface in Paragraph 3) refer to .A, the safe levels of pesticide exposureB. the amount of fruits one can safely eatC, one's digestive capacity for fruitsD. health values of fruits and vegetables72. With regard to the pesticides in food, this passage seems to argue thatA. parents should keep their children from the food with pesticidesB. they should be applied to fruits and vegetables with cautionC. more research needs to be done on their harmfulness to healthD. they are not as threatening as said to children most of the time73, The primary purpose of this passage is to explain that___A. not all reports on food are scientifically soundB. it is important for the public to know the risks of pesticidesC. vegetables and fruits can be harmful to children's healthD. there should be no public concern over pesticidesPassage 4Abortion. The word alone causes civil conversation to flee the room. Th is is largely because the pro-choice and pro-life positions are being defi ned by their extremes, by those who scream accusations instead of ar guments.More reasonable voices and concerns, on both sides of the fence, are given little attention.For example, prolife extremists seem unwilling to draw distinctions betw een some abortions and others, such as those resulting from rape with an underage child. They would make no exception in the recent real-li fe case of a woman who discovered in her fifth month that her baby w ould be bom dead due to severe disabilities.On the other hand, pro-choice extremists within feminism insist on holdi ng inconsistent positions. The pregnant woman has an unquestionable r ight to abort, they claim. Yet if the biological father has no say whatso ever over the woman's choice, is it reasonable to impose legal obligati ons upon him for child support? Can absolute legal obligation adhere without some son of corresponding legal rights?The only hope for progress in the abortion dialogue lies in the great ex cluded middle, in the voices of average people who see something wro ng with a young girl forced to bear the baby of a rapist.Any commentary on abortion should include a statement of the writer'sposition, I represent what seems to be a growing "middle ground" in pr o-choice opinion. Legally, 1 believe in the right of every human being t o medically control everything under his or her own skin. Many things people have a legal right to do, however, seem clearly wrong to me: a dultery, lying to friends, walking past someone who is bleeding on the street. Some forms of abortion fall into that category. Morally speaking, my doubts have become so extreme that I could not undergo the pro cedure past the first three months and 1 would attempt to dissuade frie nds from doing so.Partial-birth abortion has thrown many pro-choice advocates into moral chaos. I find it impossible to view photos of late-term abortion—the fetu s's contorted features, the tiny fully formed hands, the limbs ripped apa rt—without experiencing nausea. This reaction makes me ineffectual in advocating the absolute right to abortion. 1 stand bytlie principle, "a woman's body, a woman's right" but I don't always like myself for do ing so.Fanatics on both sides are using reprehensible and deceitful tactics. An honest dialogue on abortion must start by re-setting the stage, by den ouncing the approaches that block communication.74. According to the passage, the pro-life and pro-choice positions on abortion areA. complementary to each otherB. opposed to each otherC. similar in natureD. reconcilable in a way75. To a pro-life extremist, .A. all babies should be carried to termB. babies resulting from rape should not be bomC. deformed babies can be aborted when detectedD. an underage girl has no right to give birth76. According to the pro-choice position,_____A. a pregnant woman cannot abort her baby if its father agrees to kee p itB. a pregnant woman has an absolute right of choice over an abortionC. the baby's father also has a say over its mother's choice of abortio nD. the baby's father has an unalienable obligation to support the baby 77, Who would insist that the baby be born whether or not it is the chi ld of a rapist?A. the authorB. average peopleC. a pro-choice advocateD. a pro-life extremist78. The author doubts the legal right to lie to friends as well as the one toA. abort a fetus in its fifth monthB. view the photos of late-term abortionC. give birth to a baby in one's teenageD. dispose of whatever under one's skin79. The author, as a "middle ground" person,___________ .A. actually holds a mild pro-life opinionB. proposes that a rapist's baby never be bornC. advocates a serious dialogue on abortionD. denies the principle "a woman's body, a woman's right"Passage 5In the absence of optimism, we are left with nothing but critics, naysay ers, and prophets of doom. When a nation expects the worst from its people and institutions, and its experts focus exclusively on faults, hope dies. Too many people spend too much time looting down rather than up, Finding fault with their country's political institutions, economic syst em, educational establishment, religious organizations, and—worst of all —with each other.Faultfinding expends so much negative energy that nothing is left over for positive action. It takes courage and strength to solve the genuine problems that afflict every society. Sure, there will always be things tha t need fixing. But the question is, Do you want to spend your time and energy tearing things down or building them up?The staging of a Broadway show could illustrate my point. Let's say a new production is about to open, A playwright has polished the script, i nvestors have put up the money, and the theater has been rented, A director has been chosen, actors have been auditioned and selected, a nd the cast has been rehearsing for weeks. Set, lighting, and sound e ngineers have been hard at work. By the time opening night arrives, n early a hundred people have labored tirelessly—all working long hours t o make magic for iheir audience.On opening night, four or five critics sit in the audience, [f they pan it, the play will probably close in a matter of days or weeks. If they prai se it, the production could go on for a long and successful run. In the end, success or failure might hinge on the opinion of a single person—someone who might be in a bad mood on opening night! What's wrong with this scene? In one sense, nothing. Critics have a legitimate role. The problem arises when we make critics our heroes or put them in c ontrol of our fate. When we empower the critic more than the playwrig ht, something is wrong. It is much easier to criticize than to create. Wh en we revere the critics of society, we eventually become a society of critics, and when that happens, there is no room left for constructive o ptimism.。

2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text.Choose the best word(s)for each numbered blank and mark A,B,C ORD on ANSWER SHEET1.(10points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the20th century and the diffusion of printing in the15th and16th centuries.Yet much had happened 1.As was discussed before,it was not2the19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic_3_,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the4of the periodical.It was during the same time that the communications revolution5up,beginning with transport,the railway,and leading6through the telegraph,the telephone,radio,and motion pictures7 the20th century world of the motor car and the air plane.Not everyone sees that Process in8.It is important to do so.It is generally recognized,9,that the introduction of the computer in the early20th century,10by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s,radically changed the process,11its impact on the media was not immediately12.As time went by,computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became“personal”too,as well as13,with display becoming sharper and storage14increasing.They were thought of,like people,15 generations,with the distance between generations much16.It was within the computer age that the term“information society”began to be widely used to describe the17within which we now live.The communications revolution has18both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time,but there have been19view about its economic,political,social and cultural implications.“Benefits”have been weighed20“harmful”outcomes.And generalizations have proved difficult.1.[A]between[B]before[C]since[D]later2.[A]after[B]by[C]during[D]until3.[A]means[B]method[C]medium[D]measure4.[A]process[B]company[C]light[D]form5.[A]gathered[B]speeded[C]worked[D]picked6.[A]on[B]out[C]over[D]off7.[A]of[B]for[C]beyond[D]into8.[A]concept[B]dimension[C]effect[D]perspective9.[A]indeed[B]hence[C]however[D]therefore10.[A]brought[B]followed[C]stimulated[D]characterized11.[A]unless[B]since[C]lest[D]although12.[A]apparent[B]desirable[C]negative[D]plausible13.[A]institutional[B]universal[C]fundamental[D]instrumental14.[A]ability[B]capability[C]capacity[D]faculty15.[A]by means of[B]in terms of[C]with regard to[D]in line with16.[A]deeper[B]fewer[C]nearer[D]smaller17.[A]context[B]range[C]scope[D]territory18.[A]regarded[B]impressed[C]influenced[D]effected19.[A]competitive[B]controversial[C]distracting[D]irrational20.[A]above[B]upon[C]against[D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts.Answer the questions below each text by choosing[A], [B],[C]or[D].Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET1.(40points)Text1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile,you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems.Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view.Depending on whom you are addressing,the problems will be different.If you are talking to a group of managers,you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries,you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example,which I heard at a nurses’convention,of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors.A man arrivesin heaven and is being shown around by St.Peter.He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens,sunny weather,and so on.Everyone is very peaceful,polite and friendly until,waiting in a line for lunch,the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat,who rushes to the head of the line,grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself.“Whois that?”the new arrival asked St.Peter.“Oh,that’sGod,”came the reply,“but sometimes he thinks he’sa doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing,you will be in a positionto know the experiences and problems which are commonto all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’snotorious bad taste in ties.With other audiences you mustn’tattempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman.You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous,you must practice so that it becomes more natural.Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner.Often it’sthe delivery which causes theaudience to smile,so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor.It often comes from the unexpected.A twist on a familiar quote“If at first you don’tsucceed,give up”or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatement.Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.21.To make your humor work,you should.[A]take advantage of different kinds of audience[B]make fun of the disorganized people[C]address different problems to different people[D]show sympathy for your listeners22.The joke about doctors implies that,in the eyes of nurses,they are.[A]impolite to new arrivals[B]very conscious of their godlike role[C]entitled to some privileges[D]very busy even during lunch hours23.It can be inferred from the text that public services.[A]have benefited many people[B]are the focus of public attention[C]are an inappropriate subject for humor[D]have often been the laughing stock24.To achieve the desired result,humorous stories should be delivered.[A]in well-worded language[B]as awkwardly as possible[C]in exaggerated statements[D]as casually as possible25.The best title for the text may be.[A]Use Humor Effectively[B]Various Kinds of Humor[C]Add Humor to Speech[D]Different Humor StrategiesText2Since the dawn of human ingenuity,people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous,boring,burdensome,or just plain nasty.That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines.And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction,they have begun to come close.As a result,the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor.Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms.Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for thetransaction.Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers.And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics,there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility,they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge.“While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error,"says Dave Lavery,manager of a robotics program at NASA,“we can't yet give a robot enough‘common sense’to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results.Despite a spell of initial optimism in the1960s and1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year2010,researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found,in attempting to model thought,is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are muchmore talented—and humanperception far more complicated—than previously imagined.They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment.But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the98percent that is irrelevant,instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd.The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability,and neuroscientists still don’tknow quite how we do it.26.Humaningenuity was initially demonstrated in.[A]the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B]the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.[C]the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D]the elite’scunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.27.The word“gizmos”(line1,paragraph2)most probably means.[A]programs[B]experts[C]devices[D]creatures28.According to the text,what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robotthat can.[A]fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B]interact with human beings verbally.[C]have a little commonsense.[D]respond independently to a changing world.29.Besides reducing human labor,robots can also.[A]make a few decisions for themselves.[B]deal with some errors with human intervention.[C]improve factory environments.[D]cultivate human creativity.30.The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are.[A]expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B]able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C]far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D]best used in a controlled environment.Text3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return?Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March,the price of crude oil has jumped to almost$26a barrel, up from less than$10last December.This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the1973oil shock,when prices quadrupled,and1979-1980,when they also almost tripled.Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline.So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth,at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere,could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the1970s.In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the1970s.In Europe,taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price,so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were,and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price.Energy conservation,a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy,energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption.Software,consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production.For each dollar of GDP(in constant prices)rich economies now use nearly50%less oil than in1973.The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that,if oil prices averaged$22a barrel for a full year,compared with $13in1998,this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5%of GDP.That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in1974or1980. On the other hand,oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have becomemore energy-intensive,and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that,unlike the rises in the1970s,it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand.A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline.The Economist’scommodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago.In1973commodity prices jumped by70%,and in1979by almost30%.31.The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[A]global inflation.[B]reduction in supply.[C]fast growth in economy.[D]Iraq’ssuspension of exports.32.It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go updramatically if______.[A]price of crude rises.[B]commodity prices rise.[C]consumption rises.[D]oil taxes rise.33.The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.[B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.[C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.[D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.34.We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.[B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.[C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.[D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.35.From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.[A]optimistic.[B]sensitive.[C]gloomy.[D]scared.Text4The Supreme Court’sdecisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide,the Court in effect supported the medical principle of“double effect”,a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—agood one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain,even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.Nancy Dubler,director of Montefiore Medical Center,contends that the principle will shield doctors who“until now have very,very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten death”.George Annas,chair of the health law department at Boston University,maintains that,as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose,the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death.“It’slike surgery,”he says.“We don’tcall those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’tintend to kill their patients,although they risked their death.If you’re a physician,you can risk your patient’ssuicide as long as you don’tintend their suicide.”On another level,many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’sruling on physician-assisted suicide,the National Academy of Science(NAS)released a two-volume report,Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life.It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of“ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong andeven dishonor the period of dying”as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies,to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care,and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care.“Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”,to the extent that it constitutes“systematic patient abuse”.He says medical licensing boards“must make it clear...that painful deaths are presumptively ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension”.36.From the first three paragraphs,we learn that.[A]doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’pain[B]it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C]the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D]patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37.Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[A]Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’death.[B]Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C]The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can beprescribed.[D]A doctor’smedication is no longer justified by his intentions.38.According to the NAS’sreport,one of the problems in end-of-life care is.[A]prolonged medical procedures[B]inadequate treatment of pain[C]systematic drug abuse[D]insufficient hospital care39.Which of the following best defines the word“aggressive”(line4,paragraph7)?[A]Bold.[B]Harmful.[C]Careless.[D]Desperate40.George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they.[A]manage their patients incompetently[B]give patients more medicine than needed[C]reduce drug dosages for their patients[D]prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese.Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET2.(10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior,and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone.What is needed is a technology of behavior,but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technologymight be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind,feelings,traits of character, human nature,and so on.Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them.(42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find.The environment is obviously important,but its role has remained obscure.It does not push or pull,it selects,and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago,and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied.As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood,however,effects once assigned to states of mind,feelings,and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions,and a technology of behavior may therefore become available.It will not solve our problems,however,until it replaces traditional prescientific views,and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty.(44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory,and they are essentialto practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements.A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment.It also raises questions concerning“values”.Who will use a technology and to what ends?(45)Until these issues are resolved,a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected,and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46.Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an essay entitled“Cultures National and International”.In the essay you should1.describe the picture and interpret its meaning,and2.give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about200words neatly on ANSWER SHEET2.(20points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。

中国科学院博士研究生入学考试英语试卷构成试卷一:小计110分钟65分Ⅰ 词汇15分钟10分Ⅰ 完形填空15分钟15分Ⅰ 阅读80分钟40分试卷二:小计70分钟35分Ⅰ 英译汉30分钟15分Ⅰ 写作40分钟20分2006年3月PAPER ONEPART I VOCABULARY (15 minutes, 10 points, 0.5 point each)1. The problem is that most local authorities lack the to deal sensibly in this market.A. anticipationB. perceptionC. prospectD. expertise2. Awards provide a(n) for young people to improve their skills.A. incentiveB. initiativeC. fugitiveD. captive3. The profit motive is inherently with principles of fairness and equity.A. in lineB. in tradeC. at timesD. at odds4. Oil is derived from the of microscopic sea creatures, and is even older, according to most geologists.A. layoutsB. remindersC. remainsD. leftovers5. Successful students sometimes become so with grades that they never enjoy their school years.A. passionateB. involvedC. immersedD. obsessed6. Apparently there were between police reports taken from the same witnesses at different times.A. distortionsB. discrepanciesC. disordersD. distractions7. It had been a terrible afternoon for Jane, at about six o’clock in her father’s sudden col unconsciousness.A. convergingB. culminatingC. finalizingD. releasing8. The 12-year-old civil war had 1.5 million lives.A. declaredB. proclaimedC. claimedD. asserted9. The tribe has agreed to contribute 2 percent of net to charitable activities in the county.A. expensesB. revenuesC. budgetsD. payments10. This will make schools more directly and effectively to parents, and more responsive to their criticisms and wishes.A. accountableB. submittedC. subjectedD. available11. Make up your mind that whatever the short-term temptations may be, you will never from the highest standards of honor.A. deviateB. escapeC. deriveD. refrain12. They teach the vocabulary of the English used in computer science, which is also listed in the glossary.A. in sumB. in totalC. in generalD. in full13. This brings a feeling of emptiness that can never be filled and leaves us with a for more.A. scarcityB. commandC. hungerD. request14. Job fairs are usually very lively and informal, and you can roam , surveying what is on offer and gathering literature on jobs you might not have considered in the everyday run of things.A. at peaceB. at leisureC. at restD. at speed15. The closest to English and Welsh grammar schools are called grammar secondary schools; they can, however, accept some fee-paying pupils.A. equalityB. equationC. equivalentD. equity16. At first the university refused to purchase the telescope, but this decision was_____ revised.A. consecutivelyB. consequentlyC. successivelyD. subsequently17. He us as consistently fair and accurate about the issues we are concerned about.A. confusesB. regardsC. strikesD. knocks18. The water was so clear that it the trees on the river bank.A. shadowedB. shadedC. representedD. reflected19. Some 121 countries may be designated“developing”, and of this 121, seventeen countries___ than four-fifths of energy consumption.A. amount toB. account forC. add upD. take away20. The researchers found the age at which young people first fall to bullies seems to determine how much it affects them.A. sacrificeB. shortC. witnessD. victimPART Ⅰ CLOZE TEST (15 minutes, 15 points)Given the choice between spending an evening with friends and taking extra time for his schoolwork, Andy Klise admits he would probably 21 for the latter. It’s not that he doesn’t like to have fun; it desire to excel 22 drives his decision-making process.A 2001 graduate of Wooster High School and now a senior biology major at The College of Wooster, Klise acknowledges that he may someday have 23 thoughts about his decision to limit the time he has spent 24 ,25 out as well as they have, Ibut for now, he is comfortable with the choices he has made. “If things had notwould have had some regrets,” says Klise, who was a Phi Beta Kappa inductee as a junior.extra time studying has been well worth the 26 . I realized early on that to be successful, I had to make certain27 .”28 the origin of his intense motivation, Klise notes that it has been part of his makeup for as long as he3029 ,” he says. “This internal drive has caused me to give my all can remember. “I’ve always been goalpretty much everything I do.”Klise 31 Wooster’s nationally recognized Independent Study (I.S.) program with preparing him for hishoping that my I.S.next 32 in life: a research position with the National Institute of Health (NIH).“I amexperience will help me 33 a research position with NIH,” says Klise. “The yearlong program giv a chance to work with some of the nation’s 34 scientists while making the 35 from undergraduate t o graduate studies or a career in the medical field.”21. A. intend B. prefer C. opt D. search22.A. academically B. professionally C. socially D. technically23.A. different B. certain C. second D. other24.A. entertaining B. socializing C. enjoying D. sporting25.A. developed B. appeared C. occurred D. worked26.A. investment B. reward C. payment D. compensation27.A. devotions B. concessions C. sacrifices D. attempts28. A. Besides B. As for C. Out of D. Despite29.A. directed B. oriented C. conducted D. guided30.A. about B. with C. at D. in31.A. credits B. registers C. selects D. observes32. A. run B. step C. pace D. leap33.A. hold B. occupy C. anchor D. land34.A. leading B. advanced C. nominated D. marvelous35. A. achievement B. transition C. position D. vocationPART Ⅲ READING COMPREHENSIONSection A (60 minutes, 30 points)Passage OneShe’s cute, no question. Symmetrical features, flawless skin, looks to be 22 years oldmarket bar, a woman lucky enough to have this face would turn enough heads to stir a breeze. But when Victor Johnston points and clicks, the face on his computer screen changes into a state of superheated, crystallized beau “You can see it. It’s just so extraordinary,” says Johnston, a professor of biopsychology at New University who sounds a little in love with his creation.The transformation from pretty woman to knee-weakening babe is all the more amazing because the changeswrought by Johnston’s software are, objectively speaking, quite subtle. He created the original face by digitally averaging 16 randomly selected female Caucasian faces. The changing program then exaggerated the ways in which female faces differ from male faces, creating, in human-beauty-science field, a“hyp grew a bit larger, the nose narrowed slightly and the lips plumped. These are shifts of just a few millimeters, but experiments in this country and Scotland are suggesting that both males and females find“averaged faces more beautiful.Johnston hatched this little movie as part of his ongoing study into why human beings find some people attractive and others homely. He may not have any rock-solid answers yet, but he is far from alone in attemptingto apply scientific inquiry to so ambiguous a subject. Around the world, researchers are marching into territory formerly staked out by poets and painters to uncover the underpinnings of human attractiveness.The research results so far are surprising—and humbling. Numerous studies indicate that human not be simply in the eye of the beholder or an arbitrary cultural artifact. It may be ancient and universal, wrought through ages of evolution that rewarded reproductive winners and killed off losers. If beauty is not truth, it mayskin may fascinate moviegoers because, at s ome deep level, itbe health and fertility: Halle Berry’s flawlesspersuades us that she is parasite-free.Human attractiveness research is a relatively young and certainly contentious field—th females, for example, is still hotly debated—but those on its front lines agree on one point: We wonidea that beauty is until we understand its source. As psychologist Nancy Etcoff puts it:“The“looks-ism” unimportant or a cultural construct is the real beauty myth. We have to understand beauty, or we will always be enslaved by it.”36.The woman described in the very beginning of the text is .A. in fact in her late twentiesB. Johnston’s ideal girlfriendC. a stunning beautyD. is a professional prostitute37. Victor Johnston synthesized a new face by combining the features of 16 .A. beautiful European womenB. different women around the worldC. casually chosen white womenD. ordinary western women38. Through a few tiny changes made by Johnston, the synthesized face became even more .A. masculineB. averageC. feminineD. neutral39.Victor Johnston has produced such an attractive face in order to .A. give his computer a beautiful screenB. study the myth of human attractivenessC. prove the human capacity to create beautiesD. understand why Caucasian faces are special40. Paragraph 4 suggests that human beauty may be .A. culturally differentB. a disease-free idolC. individual-dependentD. a world agreed value41.It’s a consensus among the researchers that humans are still unconscious of .A. why they look attractiveB. when attractiveness is importantC. how powerful beauty isD. what constitutes beautyPassage TwoIt’s becoming something of a joke along the Maine-Canada border. So many busloads of retired people crisscross the line looking for affordable drugs that the roadside stands should advertise,Lipitor. Coumalin.” Except, of course, that such a market in prescription drugs would be illegal.These senior long-distance shopping sprees fall in a legal gray zone. But as long as people cross the border with prescriptions from a physician and have them filled for no more than a three-month supply for personal use, customs and other federal officials leave them alone. The trip might be tiring, but people can save an average of 60 percent on the cost of their prescription drugs. For some, that’s the difference between tak doing without. “The last bus trip I was on six months ago had 25 seniors,” says Chellie Ping state senator and now president of Common Cause.“Those 25 people saved $19,000 on their supplies o Pingree sponsored Maine RX, which authorizes a discounted price on drugs for Maine residents who lackinsurance coverage. The law was challenged by drug companies but recently upheld by the U.S.Supreme Court.It hasn’t yet taken effect.Figuring out ways to spend less on prescription drugs has become a multifaceted national movement of consumers, largely senior citizens. The prescription drug bill in America is $160 billion annually, and people over 65 fill five times as many prescriptions as working Americans on average.“But they do it on he are half as good and on incomes that are half as large,” says Richard Evans, senior analyst at Sa an investment research firm. What’s more, seniors account for 20 percent of the voting public.little wonder that the May 19 Supreme Court ruling got the attention of drug manufacturers and It’spoliticians across the country. The often-over-looked state of 1.3 million tucked in the northeast comer of the country became David to the phar-maceutical industry’s Goliath. The face-off began three years ago legislators like Pingree began questioning why Maine’s elderly population had to take all those bus t42.The elderly Americans cross the Maine-Canada border in order to get drugs that are .A. sold wholesaleB. over the counterC. less expensiveD. tax-free43.We can learn from the second paragraph that .A. people can buy as many drugs for personal useB. the cross-border drug shopping has been out of the federal controlC. Chellie Pingree used to be one of the cross-border shoppers for drugsD. the cross-border shopping is the only way for some Americans to get drugs44. Maine Rx mentioned in Paragraph Two is a .A. billB. drug companyC. customs officeD. seniors society45. Most cross-border shoppers are retired people, rather than working Americans, because the former .A.have more leisure timeB.fill more prescriptionsC.mostly enjoy long tripsD.are fond of street shopping46. Politicians were interested in the May 19 Supreme Court ruling because .A. they couldn’t improve the well-being of the elderlyB. they couldn’t afford to ignore the elderly’s votesC. they saw the elderly as the greatest contributorsD. they saw the elderly as deserving a special care47. David and Goliath are names used to describe a situation in which_____.A. the two groups are evenly matched in strengthB. a more powerful group is fighting a less powerful groupC. a less powerful group is fighting a more powerful groupD. both of the two groups are losersPassage ThreeIt’s navel gazing time again, that stretch of the year when many of us turn our attention inward and think about how we can improve the way we live our lives. But as we embark on this annual ritual of introspection, we would do well to ask ourselves a simple question: Does it really do any good?The poet Theodore Roethke had some insight into the matter:“Self-contemplation is a curse tha old confusion worse.” As a psychologist, I think Roethke had a point, one that’s supported controlled psychological studies.In a study I conducted with Dolores Kraft, a clinical psychologist, and Dana Dunn, a social psychologist, people in one group were asked to list the reasons their relationship with a romantic partner was going the way it was, and then rate how satisfied they were with the relationship. People in another group were asked to rate their satisfaction without any analysis; they just gave their gut reactions.It might seem that the people who thought about the specifics would be best at figuring out how they really felt, and that their satisfaction ratings would thus do the best job of predicting the outcome of their relationships.In fact, we found the reverse. It was the people in the“gut feeling”group whose ratings they were still dating their partner several months later. As for the navel gazers, their satisfaction ratings did not predict the outcome of their relationships at all. Rather, too much analysis can confuse people about how they really feel.Self-reflection is especially problematic when we are feeling down. Research by Susan Nolen Hoeksema, a clinical psychologist at Yale University, shows that when people are depressed, ruminating on their problems makes things worse.For years it was believed that emergency workers like police officers and firefighters should undergo a debriefing process to focus on and relive their experiences; the idea was that this would make them feel better and prevent mental health problems down the road. But did it do any good? In an extensive review of the research, a team led by Richard McNally, a clinical psychologist at Harvard, concluded that debriefing procedures havelittle benefit and might even hurt by interrupting the normal healing process. People often distract themselvesfrom thinking about painful events right after they occur, and this may be better than mentally reliving the events.48.According to the author, why do people tend to look inward at the end of a year?A. They want to know if they get prepared for the future.B. They consider it beneficial to their future lives.C. They pay too much attention to their self-improvement.D. They overemphasize their progress in the past year.49.The author agrees with Theodore Roethke on that_____.A. people need self-reflection when they feel blueB. people are reluctant to confide in romantic partnersC. people may be more depressed by recalling the painful pastD. people would become sober when clearing up the confusions50.The findings of the study on the satisfaction ratings in romantic relationship reveal that_____.A. meditation can keep the relationship at its peakB. retrospection helps people feel satisfied with the partnerC. specific analysis can foretell the future of the relationshipD. thinking about details makes one uncertain about the relationship51.The phrase“the navel gazers”in Paragraph 5 refers to people who_____.A. boast of their own successB. hesitate in romantic relationshipsC. worry about their futureD. focus on their past52. Which of the following is the best way to help firefighters relieve their trauma?A. Leave them alone to adjust their emotions.B. Provide them with consultation about their jobs.C. Help them figure out what has happened.D. Discuss with them how to do it better next time.53.According to the passage, _____can help people get over a painful experience.A. pouring out their feelings about itB. distracting their attention from itC. discussing it with specialistsD. recalling the specificsPassage FourPublic speaking fills most people with dread. Humiliation is the greatest fear; self-exposure and failing to appeal to the audience come a close second. Women hate it most, since girls are pressurized from an early age to be concerned with appearances of all kinds.Most people have plenty of insecurities, and this seems like a situation that will bring them out. If parents, teachers or peers mocked your foibles as a child, you fear a repeat. If you were under pressure to be perfect, you are terrified of failing in the most public of ways.While extroverts will feel less fear before the ordeal, it does not mean they will necessarily do it better. Some very shy people manage to shine. In fact, personality is not the best predictor of who does it well. Regardless of what you are like in real life, the key seems to be to act yourself.Actual acting, as in performing the scripted lines of a character other than yourself, does not do the job. While politicians may limit damage by having carefully rehearsed, written screeds to speak from, there is alwaysa hidden awareness among the audience that the words might not be true.Although, as Earl Spencer proved at his sister Princess Diana’s funeral, it is possible both to word and to act naturally, a script rarely works and it is used as a crutch by most people. But, being yourself doesn’t work either. If you spoke as if you were in your own kitchen, it would be too authentic, too unaware of the need to communicate with an audience.I remember going to see British psychiatrist RD Laing speak in public. He behaved like a seriously odd person, talking off the top of his head. Although he was talking about madness and he wrote on mental illness, he seemed to be exhibiting rather than explaining it.The best psychological place from which to speak is an unselfconscious self-consciousness, providing theas psychologists call it, is very satisfying. illusion of being natural. Studies suggest that this state of“flow”,Whether in normal life or making speeches, the key is to remind yourself that, contrary to what your teachers or parents may have implied, your best is good enough. In the zone, a strange place of authentic falsehood and shallow depth, play is possible.54.For most people the biggest fear for public speaking is_____.A. looking foolishB. failing in wordsC. not attracting attentionD. appearing pressurized55.According to the passage shy people_____A. have greater difficulty than extrovert onesB. are not good at actingC. may well do a good job in a speechD. are better speakers in the public eye56.A successful speech maker is usually one who_____.A. can act naturallyB. makes careful preparationsC. rehearses adequatelyD. can get across easily57.The example of the British psychiatrist in Paragraph 6 shows a failure in_____.A. showing modesty in publicB. talking about one’s own tradeC. presenting the topic logicallyD. communicating with the audience58.“Shallow depth” in the last paragraph implies_____.A. being yourself in the performanceB. trying to look seriousC. pretending to be well-preparedD. being seemingly knowledgeable59.From the passage, we get the impression that public speaking is something_____.A. hard to do wellB. scary but manageableC. tough but rewardingD. worthwhile to challengePassage FiveAfrican American women’s search for societal acceptance often encompasses struggle between natural a socially constructed ideas of beauty. As an essential component in traditional African societies, cosmetic modification is ritualized to emphasize natural features of blackness. Defined by social occasion such as childhood development to maturity, indicators of marital status or the group to which you belong, beautificationof the hair and body play an essential role. In our racially conscious society, presenting a physical image and being accepted is a complex negotiation between two different worlds.Hair is an outward expression of culture and heritage. It also represents a sense of personal style. In the search for the African American identity, blacks have undergone many different changes in hairstyle. Hairstyles are cultural classifiers of what African Americans consider beautiful. Hairstyles are a representation of the African American soul, all of their confidence and dignity show in how they present themselves on Sundays and on adaily basis.“Duringthe sixties, white American youth used their hair to make a variety of political and philosophical statements,”young blacks joined thereafter.“The natural hairstyle not only was eas but also gave African Americans a closer tie to their heritage. Natural style serves as a visible imprimatur of blackness; a tribute to group unity; a statement of self-love and personal significance.”standards of beauty, black Americans halted the processes of using chemical straighteners or hot irons.A woman talks about her struggle.“I remember battling with the idea of going natural for several year never had the courage because every time I pictured myself with my natural hair, I never saw beauty. Now myhair is natural, thick and healthy.”African American women are finding confidence within themselves t their hair naturally and feel beautiful about it. Many contemporary African Americans are avoiding high maintenance and feeling confident in their natural beauty.It was a different story in the past. African Americans were pressed. Shame was the motivation behind blacks losing their roots and ethnic identity. By being brainwashed into believing black people arepeople are“superior”African Americans have mutilated and adjusted their bodies to try to lookstandards.Hair is as different as the people it belongs to. People are finally recognizing that beauty is what helps to create our individual identities. Ultimately, individual confidence shapes and strengthens the culture of theAfrican American community.60.The first paragraph tells us that African Americans_____.A. have been trying hard to be socially acceptedB. have been changing their value about beautyC. have maintained their identity of traditional AfricansD. have modified their hairstyles to fit into the society61. What kind of problem do African Americans face in society?A. They would look ugly if they don’t change their hairstyles.B. Their natural image may not be accepted by white Americans.C. They would never find a suitable hairstyle in the hair salons.D. Their cultural heritage may risk being abandoned by themselves.62.The word“imprimatur”in Paragraph 2 most probably means_____.A. dislikeB. betrayalC. approvalD. suspicion63. African Americans stopped using chemical straighteners or hot irons because_____.A. they reversed the attitude the white people had towards themB. they started to see beauty in their thick curly hairC. they feel good and comfortable in being differentD. they accepted the white standards of beauty64.Why did some African Americans accept the white standards of beauty?A. Because they tried to keep socially fashionable.B. Because they did not have their own standards of beauty.C. Because they were not well educated as white Americans.D. Because they wanted to become part of the mainstream.65.To African Americans, hair is a significant indicator of_____.A. their cultural identityB. their aesthetic tasteC. their social recognitionD. their challenge against the societySection B (20 minutes, 10 points)Passage OneFrancois Jacob wrote that“an age or culture is characterized less by the extent of its knowledge than b66 .nature of the questions it puts forward.” Admittedly, the most brilliant cultures are developed during the days of knowledge acquirement. 67 . Many convincing examples can be given when looking back to the cultural development of these countries. The most influential Chinese culture flourished during Tang Dynasty, which was established a thousand years ago. This influence can be traced by the word“Tang Street”, another name for Chinatown. And it was du time that the Chinese acquired more knowledge than they had before.68 However, when compared with the knowledge people have acquired and are acquiring today, the knowledge of the ancient Tangs and Arabs is unquestionably limited. But in all history books, the cultures of the Tang Dynasty and the ancient Arab are introduced in detail, while the cultures of the Peopleand the Arab League are seldom mentioned.69 . For instance, the ancient Greeks and Romans’knowledge about nature was definitely insu but they are still recognized as the founders of the most magnificent ages and cultures in human history because the questions put forward and thought about by them were profound and meaningful. In the works of the Greeks and Romans represented by The Iliad, The Odyssey and The Aeneid, the questions concerning life and death, love and hatred, benevolence and malevolence and individual and society are raised. People can always draw inspirations from Achilles’s different attitudes towards death in the Iliad and the Odyssey and Aeneas from love and glory. 70 .The importance of an era or civilization can never be diminished because of its lack of knowledge. The essence of an age or culture should be the exploration in the spiritual world and the thoughtful questions posed.A. The Arabian culture thrived when the Arabians learnt the application of arithmetic and created Arabic numbers.B. These remain the questions people face, contemplate and discuss till today.C. In general, cultures are developed during the time of knowledge acquirement.D. This statement reveals that the nature of an epoch or civilization is decided by the things that are thought about, rather than the things that are already known.E. This is probably a universal truth for all countries and nations that boast impressive histories.F. Compared with knowledge, the questions put forward are more significant in an age or culture.Passage TwoOver the past two decades, the lives of American women have undergone unparalleled change. The VirginiaSlims Opinion Poll has chronicled that change in national surveys conducted six times since 1970. 71 .One of the most striking findings of the 1990 Virginia Slims Opinion Poll is the degree of consensusthan conflict—in women’s and men’s attitudes about the changing roles of women. In many respects, thesexes agree. Men express strong and consistent support for women’s improved status in society.72 And they agree that the most tangible way in which they could help women balance jobs and family is to take on more household work.But men are also a major cause of resentment and stress for American women. 73 Now, a generation of sweeping change later, women’s expectations have outpaced the change in men’s behavior. Tok74 .dishes or the children no longer inspires women’s gratitude.Increasingly, the kitchen table has become that bargaining table. 75 Next to money, “how much mymate helps around the house”is the single biggest cause of resentment among women who are married or li as if married, with 52 percent citing this as a problem. Improvement in this area is one of the top things womencite when they consider what would make their lives better.A. There is evidence in the poll that waiting for men to live up to the ideal of equal responsibility is a major irritant for most women today.B. Together, these surveys provide a comprehensive picture of women’s changing status, and of the future.C. In 1970, most women were concerned about getting men to share household chores.D. They, like women, believe that sex discrimination remains an important problem in the workplace.E. Over the past three generations, expectationns of men as rulers and protectors of the household havechanged.F. Instead, as women contribute more to the family income, they expect in return a more equal division ofthe household responsibilities.PAPER TWOPART IV TRANSLATION(30 minutes, 15 points)As we enter the 21st century, the gap between the world’s rich and poor is widening, both with countries. 1)The vast majority of the world’s population is receiving an ever-decreasing share of its c wealth, while the share claimed by a few rich nations and individuals is steadily growing. In 2001 Forbesmagazine counted 538 billionaires with a total net worth of 1.7 trillion dollars, while the United Nations identified2.8 billion people surviving on less than two dollars a day. Overall, the richest 20 percent of the worldcontrol 86 percent of global income, while the poorest 20 percent control barely one percent.The impacts of this widening rich-poor gap are varied and worrisome. 2) They include environmental nations and individuals can afford to over-consume resources, while poorer nations and destruction—richerindividuals are forced to over-exploit the environment just to survive. They include migrationto move in search of adequate resources. And they include conflict—wealthier nations and individkeep what they have, while those suffering a lack of resources fight to obtain them. 3) Because poorer groups typically lack the assets and technology to conduct large-scale conventional war to obtain their goals, they often resort to low-intensity conflict and terrorism. The causes of this global disparity are diverse and complex, but include colonial era trading patterns that favor industrialized nations; the globalization of economies and economic structures, in which poor nations struggle to compete; a growing“digital divide”of access to information technology; inadequate governance and protection of law; and lack of access to education healthcare, and social safety nets, especially for women and girls.4) Individuals and nations need not remain in poverty indefinitely, however. With an awareness o f theinterdependence o f our modern world and a concerted political will, it is possible to reverse this trend that。

2002年考研英语作文真题English:In 2002, the Postgraduate Entrance Examination for English majors required candidates to write an essay on the topic of "Learning is a Change". This topic encouraged candidates to reflect on the transformative power of learning in one's personal growth and development. Learning is not merely acquiring knowledge or skills, but it is a journey of continuous self-improvement and evolution. Through learning, individuals can expand their horizons, challenge their beliefs, and cultivate critical thinking skills. It is through the process of learning that individuals can adapt to changing circumstances, overcome challenges, and ultimately thrive in an ever-evolving world. In essence, learning is a catalyst for change, enabling individuals to reach their full potential and make a positive impact on society.中文翻译:2002年,英语专业研究生入学考试要求考生写一篇关于“学习是一种变化”的文章。

中国科学院研究生院博士研究生学位英语考试样题Sample TestNON-ENGLISH MAJOR DOCTORATEENGLISH QUALIFYING EXAMINATION (DET)PAPER ONEPart I Listening Comprehension (35 minutes, 30 points)Section ADirections: In this part, you will hear 10 short conversations. At the end of each conversation, a question will be asked about what is said. Eachconversation and the question will be spoken only once. When you hearthe question, read the four choices of the answer given and choose thebest one by marking the corresponding letter A, B, C, or D on yourAnswer Sheet I.1. A. Go back home.B. Mail a letter.C. Do the shopping.D. Ask the way.2. A. Dennis always alters his idea about an outing.B. Dennis has no choice but to come with them.C. It’s surprising that Dennis would come with them.D. Dennis at last accepted the idea about going out.3. A. Go out for fun with the girl.B. Travel with the girl to Holland.C. Try not to spend so much money.D. Let the girl pay her own bill.4. A. The man should reschedule the trip.B. She has no idea when the semester ends.C. She’ll call the travel agency to confirm the date.D. The man should spend his holidays somewhere else.5. A. He forgot to mail the letter.B. He left the letter in his office.C. The letter slipped off his desk.D. He should have put the letter in his bag.6. A. He was exhausted.B. He was drunk.C. He was worried.D. He was late for work.17. A. In a mall.B. In a pharmacy.C. In the cleaner’s.D. In a department store.8. A. The woman argued for her innocence at court.B. The woman complained that she was forced to pay the fine.C. The woman has got away with many violations of traffic law.D. The woman pleaded ignorance this time of her violation of the traffic law.9. A. Jack has to meet a tight deadline.B. Jack has completed his assignmentC. Jack got himself burnt last night.D. Professor David is a pleasant figure.10 A. He does not like Beth.B. He thinks the world is too crowded.C. He is too excited to do anything about the party.D. He will not help arrange for the party.Section BDirections: In this part, you will hear two mini-talks. While you listen, complete the sentences in your Answer Sheet II for Questions 11 to 20 by writing NOMORE THAN THREE WORDS in each sentence. You will hear each talkor conversation TWICE.Questions 11 to 15 are based on a talk about the concept of community.You now have 30 seconds to read Questions 11 to 15.11.A village, or town, or ____________ can be called an area of social life.12.The speaker states that it is ____________ that people in a community shouldhave the sense of belonging together.13.In some countries ____________ form islands of their own peculiar life.14.The speaker holds that community means any circle of _______.15.When we use the term “____________” rather than “society”, we should think ofsomething greater than organization.You now have 30 seconds to check your answers to Questions 11 to 15.Questions 16 to 20 are based on an interview about “global warming.”You now have 30 seconds to read Questions 16 to 20.16.Scientists want to know whether global warming is caused by __________.17.Insulation may cause the Earth to ___________.218.There are many _________on the global climate.19.The _________does not remain static.20.We can not understand the global climate well without understanding _____.You now have 30 seconds to check your answers to Questions 16 to 20.Section CDirections: In this part, you will hear three mini-talks and each of them will be spoken only once. While listening to them, read the questions that follow eachtalk. At the end of each mini-talk you will hear the questions read to you.There will be a 40-second-pause after each question. During the pause,you will be asked to write down your answer on your Answer Sheet II,using one sentence only, either complete or incomplete. Your answershould be concise and to the point.Questions 21 to 23 are based on Mini-talk One:Mini-talk OneQuestion 21: How much grain do rats destroy each year in India?Question 22: Where do rats live?Question 23: How do rats spread diseases indirectly?Questions 24 to 26 are based on Mini-talk Two:Mini-talk TwoQuestion 24: What education does the vast majority of US Postal Service jobs require? Question 25: Where can one find the special requirements for some postal jobs? Question 26: In addition to the variety of paid leave, what other benefits are provided fora postal employee? (List at least two.)Questions 27 to 30 are based on Mini-talk Three:Mini-talk ThreeQuestion 27: Why is popular art said to be primarily entertainment?Question 28: What is the distinction in art between a professional and an amateur? Question 29: How does high art differ from popular art financially?Question 30: What are people interested in high art often required to do?Part II Use of English and Reading Comprehension (55 minutes, 40 points) Section ADirections: There are 15 blanks in the following passage. Read the passage carefully and fill in each of the blanks by choosing the right word or phrase fromthe list given below. Write your answer on the Answer Sheet II. Capitalizethe word when it is necessary. The words and phrases listed are twice as3many as the blanks. Once a word or phrase is chosen, it must be used onlyonce.Many of the most damaging and life-threatening types of weather—torrential rains, severe thunderstorm, and tornadoes—began quickly, strike suddenly, and dissipate rapidly, devastating small regions 31 leaving neighboring areas untouched. One such event, a tornado, struck the northeastern section of Edmonton, Alberta, in July 1987. Total damages from the tornado 32 $ 250 million, the highest 33 for any Canadian storm. Conventional computer models of the atmosphere have limited value in predicting short-lived local storms 34 the Edmonton tornado, because the available weather data are generally not detailed enough to allow computers to discern the subtle atmospheric changes that 35 these storms. In most nations, for example, weather-balloon observations are taken just 36 every twelve hours at locations typically 37 by hundreds of miles. With such limited data, conventional forecasting models do a much better job predicting general weather conditions over large regions 38 they do forecasting specific local events. Until recently, the observation—intensive approach needed for accurate, very short-range forecasts, or “Nowcast”, was not39 . The cost of equipping and operating many thousands of conventional weather stations was prohibitively high, and the difficulties involved in rapidly collecting and processing the raw weather data from such a network were insurmountable. 40 , scientific and technological advances have 41 most of these problems. Radar systems, automated weather instruments, and satellites are all capable of making detailed, nearly 42 observations over large regions at a relatively low cost. Communications satellites can transmit data around the world cheaply and 43 , and modern computers can quickly compile and analyze this large volume of weather information. Meteorologists and computer scientists now work together to design computer programs and video equipment capable of 44 raw weather data into words, symbols, and vivid graphic displays that forecasters can interpret easily and quickly. 45 meteorologists have begun using these new technologies in weather forecasting offices, nowcasting is becoming a reality.Section B (30minutes, 15 points)Directions: Read the following passages carefully and then select the best answer from among the four choices given to answer each of the questions or completeeach of the statements that follow each passage. Mark the letter of yourchoice on your Answer Sheet I.Passage 1For centuries, the gravel and sand of Georges Bank and the great canyons, muddy basins, and shallow ledges of the Gulf of Maine have supported one of the world’s most productive fishing regions. But big boulders have historically protected a41050-square-kilometer region at the bank’s northeastern tip from dredging boats in search of scallops and trawlers hunting down groundfish. However, those boulders are becoming less of a deterrent against improved and sturdier gear. So when geologist Page Valentine of the U.S. Geological Survey in Woods Hole, Massachusetts, stood before his colleagues last month and defended his proposal to safeguard this rare, undisturbed gravel bed, he knew that he was also standing at the crossroads of science and politics.Va lentine’s presentation was part of a 2-day workshop held at the New England Aquarium here to build support for Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), a controversial concept aimed at preserving biodiversity in coastal waters. The meeting, organized by Elliott Norse, founder of the Marine Conservation Biology Institute in Redmond, Washington, featured talks by 21 experts across a range of marine habitats and species and represented the marine community’s biggest push for MPAs.The discussion generated a map that nominated 29% of the ocean floor off the coast of New England and Canada’s Maritime Province for protection, as well as 25% of pelagic (open-ocean) waters. The next step will come in the fall, when the scientists discuss the plan with government officials, commercial stakeholders, and environmental activists—meetings that are likely to be contentious. “The conservation groups will want to see if various species are covered. And various fishermen will be convinced that their livelihood is threatened,” says Mik e Pentony, an analyst for the New England Fishery Management Council, who was an observer at last month’s workshop. The areas could be established by the National Marine Fisheries Service or under existing U.S. and Canadian laws to protect endangered species and habitats.46. Which of the following can be the best title of the passage?A.Fishery Industry in New England.B.Plan to Protect Coastal waters of New England.C.Restoration of Marine Life in the Gulf of Maine.D.Problems Critical to Ecological Balance in Georges Bank.47. The abundance of fish in the area has been a result of ________.A.the perpetual fishery closureB.the stringent ban on overfishingC.the effective fishery managementD.its unique geographic features48. Boulders used to be a deterrent to ________.A.scallopB.groundfishC.fishing boatsD.improved gear49. At the two-day workshop, the scientists reached an agreement on ______.A.the marine areas to be preservedB.how to rescue the endangered speciesC.the guarantee of the fishermen’s livelihoodD.what to discuss with the government officials550. Which of the following CANNOT be concluded from the last paragraph?A.The fishermen will be worried about their livelihood.B.A decision is soon to be made on the protected areas.mercial stakeholders may be at odds with scientists.D.Conflicting interests will arise between fishermen and scientists.Passage 2Some people are accustomed to thinking that facts must either be believed or they must be disbelieved—as if beliefs were like a light switch with only two positions, on or off. My use of the bathtub hoax is intended to illustrate that belief does not have to operate as a simple yes or no choice, all or nothing. Belief can be more conditional; it can be something that we decide to have “up to a point.” And so, the question we might ask ourselves while reading does not have to be “Should I believe it or not?”but instead can be “How much should I believe it?”This later question implies that the belief we have in any given fact, or in any given idea, is not determined by whether it sounds right or whether the source is an authority. It means that our beliefs are determined by the reasons that justify them. Belief is not a mechanical action, brought about by invariable rules of nature. It is a human activity, the exercise of judgment. With this in mind, we might say that we perform this action better when we know what the reasons are that have led to our belief, and why they are good reasons.These observations do not deprive us of our ability to believe in what we read. They are not intended to transform you from credulous believers into stubborn doubters. The process of weighing beliefs against the quality of reasons is one that you already go through all the time, whether you are aware of it or not. We all do. The practice of critical reading is the exercise of this kind of judgment on purpose. By doing it, we protect ourselves from being led into belief for inadequate reasons, but at the same time we open up our minds to the possibility of arriving at belief for adequate ones. If we decide to grant or withhold consent based on the quality of the reasons that we are given we admit at the same time that two things are possible: We admit that we might consent less in the future if we discover that the reasons are not so good after all; and we admit that we might consent more if we are ever presented with better reasons than we had formerly known. This attitude is not pure skepticism any more than it is pure credulity. It is somewhere in between. It is the attitude of an open-minded thinker, of someone who wishes to be responsible for deciding for herself or himself what to believe.51. The author’s use of the bathtub hoax is meant to suggest that __________.A.facts must be believed unconditionallyB.belief is more than a simple yes or no choiceC.nothing should be believed or disbelievedD.belief is nothing but a light switch52. To believe or disbelieve what you read should be based on ________.A.the facts that you are givenB.whether the author is an open-minded authorityC.the quality of reasons provided by the materialD.the assumption that you know everything about it653. As a human activity, weighing the facts about something is actually _______.A.determined by the rules of natureB. a performanceC.brought about even at birthD.experienced by everyone54. According to the author, which of the following is true?A.Our attitude toward what we read may change if we are given more reasons.B.An open-minded thinker is responsible for what he or she says.C.Critical reading can make us believe more in what we read.D.We ought to question the value of what we read if its source is notauthoritative.55. What is the topic of this passage?A.Judgment and Responsibility.B.Reading and Belief.C.Trust and Faith.D.Reading and Human Activity.Passage 3Things don’t come easily to Matteo, a 4-year-old New Yorker with brown bangs and cowboy bandanna. Afflicted by cerebral palsy, he moves awkwardly. He thinks slowly and doesn’t talk much. Small frustrations upset him terribly. But when Matteo visits Clive Robbins, his music therapist, he bangs gleefully on a snare drum, placing one hand on the rim to steady himself, he uses the other to rap in tempo to Robbins’s improvised song. As the tune progresses, Matteo moves his act to the piano, banging along with one or two fingers and laughing excitedly. By following the rhythm, he is learning to balance his body and coordinate the movement of his limbs. He’s also learning to communicate. “He is grown much more motivated and intent,” says Robbins, the co-founder of New York Univ ersity’s Nordoff-Robbins Center for Music Therapy.Disabled children aren’t the only ones feeling the therapeutic power of music. A 79-year-old stroke survivor listens to Viennese waltzes on his headphones to help him to relearn to walk. A woman in labor h ad LeAnn Rimes’ country tunes blaring from a stereo to help her keep in step with her contraction. And, yes, ostensibly healthy people are listening to airy New Age discs, and maybe lighting a candle or two, to lessen stress and promote well-being. They may all be on to something. Mounting evidence suggests that almost any musical stimulus, from Shostakovich to the Spice Girls can have therapeutic effects.Music therapy isn’t mainstream health care, but recent studies suggest it can have a wide range of benefits. In 1996, researchers at Colorado State University tried giving 10 stroke victims 30 minutes of rhythmic stimulation each day for three weeks. Compared with untreated patients, they shared significant improvements in their ability to walk steadily. P eople with Parkinson’s disease enjoyed similar benefits. A musical beat from any genre seemed to provide a rhythmic cue, stimulating the brain’s motor systems.7Other body systems seem equally responsive. Scottish researchers have found, for example, that a daily dose of Mozart or Mendelssohn significantly brightens the moods of institutionalized stroke victims. Using psychological tests, the Scottish team showed that patients receiving 12 weeks of daily music therapy were less depressed and anxious, and more stable and sociable, than other patients in the same facility. Music therapy has also proved useful in the management of Alzheimer’s and other neurological diseases. And Deforia Lane, a music therapist at University Hospitals in Cleveland, has shown that music can boost immune function in children. That’s consistent with a 1995 finding by Louisiana researchers that preemies exposed to lullabies in the hospital went home earlier.56.Which of the following would be the best title for this passage?A.Why Music is PowerfulB.Music and Pain MedicationC.Music and Disabled ChildrenD.The Medical Power of Music57.Which of the following statements is right about Matteo?A. He is suffering a paralysis of the brain.B. He is late in his ability to walk and talk.C. He plays music better by taking the advice.D. He’s ambitious to become a professional drummer.58.Paragraph 2 mainly tells that ________________.A.music helps pregnant women undergo contractionsB.music stimulates promotion of people’s well-beingC.music seems to have therapeutic effects on all peopleD.sick people benefit a lot from listening to music59.Based on the author’s description, the Spice Girls is taken asA.a classic example of music.B.a typical extreme of music.C.the most popular musical category.D.disgusting but having some medical effect.60.According to the context, the word “preemies” probably means________.A.sick children coming to see a doctorB.children with infectious diseasesC.newly recovered young patientsD.premature babiesSection C (10minutes, 10 points)Direction: In the following passage, five sentences have been removed from the original text. They are listed from A to F and put below the passage. Choosethe most suitable sentence fro the list to fill in each of the blanks numbered61 to 65. There is one sentence that does not fit in any of the blanks. Markyour answers on your Answer Sheet I.8Virtual reality engineers are space makers, to a certain degree they create space for people to play around in. A space maker sets up a world for an audience to act directly within, and not just so the audience can imagine they are experiencing a reality, but so they can experience it directly. “The film maker says, ‘Look, I’ll show you.’” The space maker says, “Here, I’ll help you discover.”61 Are virtual reality systems going to serve as supplements to our lives, or will individuals so miserable in their daily existence find an obsessive refuge in a preferred cyberspace? What is going to be included, deleted, reformed, and revised? Will virtual reality systems be used as a means of breaking down cultural, racial, and gender barriers between individuals and thus nurture human values? During this century, responsive technologies are moving even closer to us, becoming the standard interface through which we gain much of our experience. 62 Instead of a global village, virtual reality may create a global city, the distinction being that the city contains enough people for groups to form affiliations, in which individuals from different cultures meet together in the same space of virtual reality. 63 A special camera, possibly consisting of many video cameras, would capture and transmit every view of the remote locations. Viewers would receive instant feedback as they turn their heads. Any number of people could be looking through the same camera system. Although the example described here will probably take many years to develop, its early evolution has been under way for some time, with the steady march of technology moving from accessing information toward providing experience.64 Virtual Reality is now available in games and movies. An example of a virtual reality game is Escape From Castle Wolfenstein. In it, you are looking through the eyes of an escaped POW from a Nazi death camp. You must walk around in a maze of dungeons where you will eventually fight Hitler. One example of a virtual reality movie is Stephen King’s The Lawnmower Man. It is about a mentally retarded man that uses virtual reality as a means of overcoming his handicap and becoming smarter. He eventually becomes crazy from his quest for power and goes into a computer. From there he is able to control most of the world’s computers. This movie ends with us wondering if he will succeed in world domination. From all of this we have learned that virtual reality is already playing an important part in our world. 65A.Reality is to trick the human senses, to help people believe and uphold an illusion.B.The ultimate result of living in a cybernetic world may create an artificial globalcity.C.As well, it is probably still childish to imagine the adoption of virtual realitysystems on a massive scale because the starting price to own one costs about $300,000.D.The city might be laid out according to a three dimensional environment thatdictates the way people living in different countries may come to communicate and understand other cultures.E.Even though we are quickly becoming a product of the world of virtual reality, wemust not lose touch with the world of reality. For reality is the most important part of our lives.F.However, what will the space maker help us discover?9PAPER TWOWriting (60 minutes, 30 points)Section A (20 minutes, 10 points)Directions:Read the following article and write a summary of no more than 150 words on your Answer Sheet II.The label of world’s oldest spaceman sat uncomfortably with John Glenn. He insisted that he was simply another astronaut in the service of science, conducting experiments aboard the shuttle Discovery. But last week, before returning to Earth, a relaxed Glenn began to embrace what is likely to be his mission’s most lasting legacy: a redefinition of our image of aging. The nation’s No. 1 role model for seniority made jokes and even dispensed a bit of advice about not accepting a dull life (don’t “live by the calendar”) in old age.In a rapidly graying society, Americans are quick to celebrate heroes who defy stereotypes about aging: Glenn going up in space at 77, George Bush parachuting from an airplane at 72. We even made best-selling authors out of the Beardstown Ladies (average age: 70), until it was revealed that their investment returns were only mediocre. Why were we so eager to assume a bunch of novices could pick stocks better than a Wall Street pro? Because we want to believe that growing old is not as bad as we fear.Many who work with the elderly are reconsidering this adulation of senior overachievers. “John Glenn has taken us from our fear of aging to a fear of not being John Glenn in old age,” says Martha Holstein of Chicago’s Park Ridge Cente r for the Study of Health, Faith and Ethics. It’s one thing, she says, to knock down stereotypes that mark the elderly as enfeebled or befuddled. But raising unrealistic standards of vigor isn’t any better. Historian Theodore Roszak note s that along with the celebration of Glenn have come paroxysms of press about 90-year-old marathon runners and other aged mega-athletes. These “supermen images,” says Roszak, author of America the Wise, a new book about how the swelling ranks of the elderly will benefit America, give rise to the dangerous notion that “seniors need to achieve at the level of 30- or 40-year-olds” to win respect.Gerontologists talk about “productive aging,” the notion that one’s 60s and 70s constitute a new middle age as people live longer and healthier lives. Productive aging, with its roots in the social movements of the 1960s, began as a counter to prejudice against the elderly. But such well-intentioned efforts to bring new value to old age sometimes gloss over the fact that older hearts, lungs, ears, and eyes do start to wear out. Forty percent of Americans over age 65 have some chronic condition that limits such simple everyday activities as walking around the block or lifting a bag of groceries.One leading proponent of productive aging wants to use what we know about how proper exercise and diet can forestall illness and physical decline to encourage Americans to maintain healthier lifestyles. John Rowe of Mount Sinai-New York University Medical Center, coauthor of the new book Successful Aging, advocates an incentive program in which Medicare would pay a larger share of medical costs for individuals who quit smoking, drink moderately, or lose weight. That, he says, would10“enhance the well-being of older people” an d also cut the bill for Medicare.Others worry about creating ideals that the white, wealthy, and educated are most likely to live up to. The poor, minorities, and often women have the worst health in late life. A recent study reported in the Journal of the American Medical Association showed that the death rate among the poorest Americans is three times that of others of the same age—but not because they lead significantly less healthy lives. Rather, says Meredith Minkler of the University of California-Berkeley, poverty has “weathering” or cumulative effects. A woman who spends her life on her feet as a waitress or in some other physically demanding job—and then maybe also cares for her grandchildren—winds up in worse health than someone whose white-collar job lets her pay for membership in a health club.In reality, old age means to live with both vigor and limits. Barbara Toomer made that clear last week as she joined protesters in Washington who handcuffed their wheelchairs together at the doors of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to demand funding to live in their own homes. “We hear how marvelous it is for John Glenn to be in such great shape” says the 69-year-old Utah activist with American Disabled for Attendant Programs Today, “but we’re down here fighting to get everybody out of nursing homes, which is where you’re likely to get placed when you get old.”Section B (40 minutes, 20 points)Direction:Write an essay of no less than 250 words on the topic given below. Use the proper space on your Answer Sheet II.Topic: List three important problems facing the world today. Discuss these problems and offer your suggestions as to how to solve them.11Reference key to Sample TestNON-ENGLISH MAJOR DOCTORATE ENGLISH QUALIFYINGEXAMINATION (DET)PAPER ONEPart I Listening ComprehensionSection A1-10 C D A DA B C C B DSection B11.country12.inevitable13.immigrantsmon life.munity16.human activity /humans.17.get warmer.18.influences19.earth’s temperature20.(the) oceans.Section CMini-talk One21: Ten million tons of grain each year.22: Any place they can get into—homes, shops, farm buildings and farm and home storage areas.23: By carrying fleas, mites and other organisms that cause sickness.Mini-talk Two24: Four years of high school or less.25: Any special requirements will be stated on the announcement of examination.26: Retirement support, life insurance and health insurance.Mini-talk Three27: Many of them are hits for a few weeks then they disappear.28: A professional tries to make a living by working in art, while an amateur does all the artistic work just for pleasure.29: Popular art usually makes a lot of money, while high art often lacks funds.30: To give money to make future performances possible.12。

2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C OR D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 1 . As was discussed before, it was not 2 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic_ 3 _ ,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 4 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 5 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 6 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 7 the 20th century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that Process in 8 . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, 9 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not immediately 12 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became “personal” too, as well as 13 , with display becoming sharper and storage 14 increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance between generations much 16 .It was within the computer age that the term “information society” began to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 view about its economic, political, social and cultural implications. “Benefits” have been weighed 20 “harmful” outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.1. [A]between [B]before [C]since [D]later2. [A]after [B]by [C]during [D]until3. [A]means [B]method [C]medium [D]measure4. [A]process [B]company [C]light [D]form5. [A]gathered [B]speeded [C]worked [D]picked6. [A]on [B]out [C]over [D]off7. [A]of [B]for [C]beyond [D]into8. [A]concept [B]dimension [C]effect [D]perspective9. [A]indeed [B]hence [C]however [D]therefore10. [A]brought [B]followed [C]stimulated [D]characterized11. [A]unless [B]since [C]lest [D]although12. [A]apparent [B]desirable [C]negative [D]plausible13. [A]institutional [B]universal [C]fundamental [D]instrumental14. [A]ability [B]capability [C]capacity [D]faculty15. [A]by means of [B]in terms of [C]with regard to [D]in line with16. [A]deeper [B]fewer [C]nearer [D]smaller17. [A]context [B]range [C]scope [D]territory18. [A]regarded [B]impressed [C]influenced [D]effected19. [A]competitive [B]controversial [C]distracting [D]irrational20. [A]above [B]upon [C]against [D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing [A], [B], [C] or [D]. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different. If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses’ convention, of a story which works we ll because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. “Who is that?” the new arrival asked St. Peter. “Oh, that’s God,” c ame the re ply, “but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and prob lems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties. With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman. You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that it becomes more natural. Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a r elaxed and unforced manner. Often it’s the delivery which causes the audience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor. It often com es from the unexpected. A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don’t succeed, give up” or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeratio n and understatement. Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.21. To make your humor work, you should .[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience [B] make fun of the disorganized people[C] address different problems to different people [D] show sympathy for your listeners22. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are .[A] impolite to new arrivals [B] very conscious of their godlike role[C] entitled to some privileges [D] very busy even during lunch hours23. It can be inferred from the text that public services .[A] have benefited many people [B] are the focus of public attention[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor [D] have often been the laughing stock24. To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered .[A] in well-worded language [B] as awkwardly as possible[C] in exaggerated statements [D] as casually as possible25. The best title for the text may be .[A] Use Humor Effectively [B] Various Kinds of Humor[C] Add Humor to Speech [D] Different Humor StrategiesText 2Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor. Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for the transaction. Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers. And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challeng e. “While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error," says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program at NASA, “we can't yet give a robot enough ‘common sense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. Despite a spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated—than previously imagined. They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.26. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in.[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.[C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D] the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.27. The word “gizmos” (line 1, paragraph 2) most probably means.[A] programs[B]experts[C]devices [D]creatures28. According to the text, what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robot that can.[A] fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B] interact with human beings verbally.[C] have a little common sense.[D] respond independently to a changing world.29. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also.[A] make a few decisions for themselves.[B] deal with some errors with human intervention.[C] improve factory environments.[D] cultivate human creativity.30. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are.[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D] best used in a controlled environment.Text 3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return? Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March, the price of crude oil has jumped to almost $26 a barrel, up from less than $10 last December. This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the 1973 oil shock, when prices quadrupled, and 1979-1980, when they also almost tripled. Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline. So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth, at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere, could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the 1970s. In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the 1970s. In Europe, taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price, so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were, and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price. Energy conservation, a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy, energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption. Software, consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production. For each dollar of GDP (in constant prices) rich economies now use nearly 50% less oil than in 1973. The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that, if oil prices averaged $22 a barrel for a full year, compared with $13 in 1998, this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5% of GDP. That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in 1974 or 1980. On the other hand, oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive, and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that, unlike the rises in the 1970s, it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand. A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline. The Economist’s co mmodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago. In 1973 commodity prices jumped by 70%, and in 1979 by almost 30%.31. The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[A] global inflation.[B] reduction in supply.[C]fast growth in economy.[D] Iraq’s suspension of exports.32. It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go up dramatically if______.[A] price of crude rises. [B] commodity prices rise.[C] consumption rises. [D] oil taxes rise.33. The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.[B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.[C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.[D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.34. We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.[B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.[C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.[D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.35. From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.[A]optimistic. [B]sensitive. [C]gloomy. [D]scared.Text 4The Su preme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide, the Court in effect supported the medical principle of “double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain, even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patien t.Nancy Dubler, director of Montefiore Medical Center, contends that the principle will shield doctors who “until now have very, very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten dea th”.George Annas, chair of the health law department at Boston University, maintains that, as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose, the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death. “It’s like surgery,” he says. “We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients, although they risked their death. If you’re a physician, you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”On another level, many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’s ruli ng on physician-assisted suicide, the National Academy of Science (NAS) released a two-volume report, Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life. It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of “ineffectual and forced medical p rocedures that may prolong and even dishonor the period of dying” as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies, to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care, and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care. “Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”, to the extent that it constitutes “systematic patient abuse”. He says medical licensing boards “must make it clear...that painful deaths ar e presumptively ones that are incompetently managed and should re sult in license suspension”.36. From the first three paragraphs, we learn that .[A] doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’pain[B] it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C] the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D] patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37. Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[A] Doctors will b e held guilty if they risk their patients’death.[B] Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C] The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can be prescribed.[D] A doctor’s medication is no longer justifi ed by his intentions.38. According to the NAS’s report, one of t he problems in end-of-life care is .[A] prolonged medical procedures [B] inadequate treatment of pain[C] systematic drug abuse [D] insufficient hospital care39. Which of the following best defines the word “aggressive” (lin e 4, paragraph 7)?[A] Bold. [B] Harmful. [C] Careless. [D] Desperate40. George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they .[A] manage their patients incompetently[B] give patients more medicine than needed[C] reduce drug dosages for their patients[D] prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese. Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior, and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone. What is needed is a technology of behavior, but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technology might be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind, feelings, traits of character, human nature, and so on. Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them. (42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find. The environment is obviously important, but its role has remained obscure. It does not push or pull, it selects, and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago, and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied. As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood, however, effects once assigned to states of mind, feelings, and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions, and a technology of behavior may therefore become available. It will not solve our problems, however, until it replaces traditional prescientific views, and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty. (44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory, and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements. A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment. It also raises questions concerning “values”. Who will use a technology and to what ends? (45)Until these issues are resolved, a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected, and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46. Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an essay entitled “Cultures National and International”.In the essay you should1. describe the picture and interpret its meaning, and2. give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about 200 words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)。

中国科学院2002-2005年研究生入学试题中国科学院2002年研究生入学试题《生物化学与分子生物学》一、是非题:15题,每题1分,共15分。
答"是"写"+",答"非"写"- ",写在题后的()中。
1.维生素对人体的生长和健康是必需的,但人体不能合成维生素。
()2.能被某种振奋分子识别,并与其特异和共价结合的原子,原子团和分子,称为配基。
()3.当不同分子大小的蛋白质混合物流经凝胶柱层析时,小分子物质因体积小最先被洗脱出来。
()4.酶的最适pH与酶的等电点是两个不同的概念,但两者之间有相关性,两个数值通常比较接近或相同。
()5.对于一个酶而言,其过渡态的底物类似物与底物的物相比较,是更有效的竞争性抑制剂。
()6.Km值是酶的牲常数之一,与酶浓度、pH值、离子强度等条件或因素无关。
()7.磷脂酶A水解脂生成磷脂酸。
()8.NAD 不能由细胞浆通过线粒体内膜进入线柆体内,而NADH能在通过线粒体内膜后被氧化。
()9.寡霉素是线粒体ATP合成酶的抑制剂。
()10.核苷磷酸化酶催化腺苷的磷酸化,生成腺嘌呤和核糖-5-磷酸。
()12.肿瘤RNA病毒的复制过程为RNA->DNA->RNA。
()13.肾上腺素能与细胞膜上专一受体结合,这种激素受体复合物能直接活化环化酶,使细胞cAMP浓度增加,引起级联反应。
()14.维生素E是一种抗氧化剂,对线体膜上的磷脂有抗自由的作用。
()15.吡哆醛、吡哆胺和吡哆醇的磷酸酯都可以作为转氨的辅酶。
()二、选择题:20题,每题1分,共20分。
请将选择答案的号码填入()中。
1.为稳定胶原三股螺旋结构,三联体的每三个氨基酸的位置必须是:()①丙氨酸;②谷氨酸;③甘氨酸2.分离含胡二硫键的肽段可以用()①SDS PAGE电泳;②对角线电泳;③琼脂糖电泳3.引起疯牛病(牛海绵脑病)的病原体是:()①一种DNA;②一种RNA;③一种蛋白质;④一种多糖4.胰岛素等激素的受体以及上成或表皮生长因子的受体都是一种:()①激酶;②脱氢酶;③转氨酶5.在酶的可逆抑制剂中,不影响酶的二级常数(Kcat/Km)的是:()①竞争性抑制剂;②非竞争性抑制剂;③反竞争性抑制剂;④都不是6.所谓"多酶体系"是指一个代谢过程中几个酶殗了一个反应链体系,多酶体系中的酶通常具有以下性质。
中国科学院博士学位研究生入学考试英语试题(2000年3月)THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCESENGLISH ENTRANCE EXAMINATION FORDOCTORAL CANDIDATESMarch 2000PAPER ONEPART ⅡSTRUCTURE & VOCABULARY (15 points, 25 minutes)Section A (0.5 point each)Directions: Choose the word or words below each sentence that best complete the statement, and mark the corresponding letter of your choice with a single bar across the square brackets on yourMachine-scoring Answer Sheet.16. Much I have traveled, I have never seen anyone to equal her for thoroughness, whatever the job.A. whenB. moreC. fartherD. as17. To support the general statement in the first sentence, each sentence in the paragraph provides adifferent example.A. relevantB. subsequentC. coherentD. antecedent18. A hefty 50% of those from ages 18 to 34 told the pollsters in the TIME/CNN survey that they“feminist” values.A. shareB. regardC. attachD. dominate19. I was not alone in my knowledge; the woman had also seen my father’s eyes gleaming withpride.A. contractedB. contestedC. contentedD. contrasted20. the writer’s craft through a consideration of rhetorical patterns is a useful way to study writing.A. ExploringB. ExploitingC. EmployingD. Embodying21. The first two assumptions made about the of TV were dead wrong: that it would bury radio and itwould be threat to movies.A. recessionB. adventC. diversityD. bias22. An education should enable a student to get a better job than be would be able to find or fill.A. consequentlyB. neverthelessC. otherwiseD. anyhow23. In addition to being physically sick, may dad was in the midst of a nervous , through none of us knew tocall it that at the time.A. breakupB. breakdownC. breakthroughD. breakout24. Although they are very succinct-that is why they caught on-cliches are wasted words because they are expression rather than fresh ones.A. staleB. stainlessC. stableD. spotted25. Though Americans do not currently abortions directly, costs are carried by other Americans through higher insurance premiums.A. implementB. terminateC. prohibitD. subsidize26. There are probably very few cases in which different races have lived in completein a single country for long periods.A. successB. revengeC. harmonyD. conscience27. In the last century and a half, scientific development has been breathtaking, but the understanding of thisprogress has changed.A. incidentallyB. dramaticallyC. rigorouslyD. temporarily28. It is always useful to have savings to .A. come out inB. live up toC. make a fuss ofD. fall back on29. We seek a society that has a respect for the dignity and worth of the individual.A. at its endB. at its handC. at its coreD. at its best30. Modern man is careless when disposing his garbage.A. ofB. toC. atD. about31. Negro slavery, many claimed, was good for all .A. concernedB. is concernedC. to concernD. that concerns32. To cry over spilled milk is to cry .A. in a vainB. in the vainC. in vainD. in no vain33. “Do you want to see my driver’s license or my passport?”“Oh, ”.A. either does wellB. either one will doC. each one is goodD. each will be fine34. The novel, which is a work of art, exists not by its life, but by its immeasurable difference from life.A. significance inB. imagination atC. resemblance toD. predominance over35. A 50-ft, wave travels at speeds 20 m.p.h., and anyone who’s too slow at the approach risks beingsmashed.A. in excess ofB. in the reach ofC. in exchange forD. in relation toSection B (0.5 point each)Directions: In each of the following sentences there are four parts underlined and marked A, B, C, and D. Indicate which of the four parts is incorrectly used by drawing a single bar across the square brackets on yourMachine-scoring Answer Sheet.36. Applicants will be considered provided that their files are complete due to theA B C Ddeadline.37. Elizabeth B. Browning, who has remembered for her love poems, published herA B Cfirst work at the age of twelve.D38.O n l y i f t e n m o r e s t u d e n t s r e g i s t e r t h i s a f t e r n o o n w i l l a n o t h e r p r o n u n c i a t i o nA B Csection be opening.D39.T h a t i n t e l l i g e n c e t e s t s a c t u a l l y g i v e a m e a s u r e m e n t o f t h e i n t e l l i g e n c e o fA BA individuals are questioned by some eminent.C D40. Track lighting is one of the most popular types, if not the most popular type, ofA B Clighting on market todary.D41. In fact, there is perhaps only one human being in a thousand who are passionatelyA Binterested in his job for the job’s sake.C D42. Watching films of what hate turned those people into made me choose to reject it,A Bto deal with people individual and not to spot all whites with the same obscene images.C D43. After a grueling review session, some confusing students asked the teaching assistant forA B Cstill more help.D44. Flourish in the thirteenth century, traveling musicians, called minstrels, played anA B Cimportant part in the cultural life of the time.D45.T h e r e w a s h a r d l y s o me b o d y i n t h e r o o m w h o p a i d a n y a t t e n t i o n t o h i m e v e nA B Cthough everyone knew who he was.C DPART ⅢCLOSE TEST (15 points, 15 minutes)Directions: For each blank in the following passage, choose the best answer from the choices given in the opposite column. Mark the corresponding letter of your choice with a single bar across the square brackets onyour Machine-scoring Answer Sheet.Faster than ever before, the human world is becoming an urban world. By the millions they come, the ambitious and the down-trodden of the world drawn by the strange magnetism of urban 46 . For centuries the progress of civilization has been 47 by the rigid growth of cities. Now the world is 48 to pass a milestone: more people will live in urban areas than in the countryside.Explosive population growth 49 a torrent of migration from the countryside are creating cities that dwarf the great capitals of the past. By the 50 of the century, there will be fifty-one “megacities” with populations of ten million or more. Of these, eighteen will be in 51 countries, including some of the poorest nations in the world. Mexico City already 52 twenty million people and Calcutta twelve million. According to the World Bank, 53 of Africa’s cities are growing by 10% a year, the swiftest 54of urbanization ever recorded.Is the trend good or bad? Can the cities cope? No one know 55 . Without question, urbanization has produced 56 so ghastly that they are difficult to comprehend. In Cairo, children who 57 might be in kindergarten can be found digging through clots of ox waste, looking for 58 kernels of corn to eat. Young, homeless thieves in Papua New Moresby may not 59 their last names or the names of the villages where they were born. In the inner cities of America, newspapers regularly report on newborn babies 60 into garbage bins by drug-addicted mothers.46. A. way B. life C. area D. people47. A. defined B. estimated C. created D. expected48. A. about B. up C. like D. already49. A. of B. like C. and D. or50. A. change B. wake C. beginning D. turn51. A. developing B. developed C. develop D. development52. A. makes B. has C. comes D. lives53. A. none B. few C. any D. some54. A. event B. work C. level D. rate55. A for good B. with clarity C. for sure D. in doubt56. A. miracles B. miseries C. mysteries D. misunderstandings57. A. elsewhere B. anywhere C. somewhere D. nowhere58. A. unrefined B. undigested C. unpolished D. unspoiled59. A. ask B. find C. have D. know60. A. dropped B. to drop C. dropping D. dropsPART IV READING COMPREHENSION (30 points, 60 minutes)Directions: Below each of the following passages you will find some questions or incomplete statements. Each question or statement is followed by four choices marked A, B, C, and D. Read each passagecarefully, and then select the choice that best answers the question or completes the statement. Markthe letter of your choice with a single bar across the square brackets on your Machine-scoringAnswer Sheet.Passage OneG ordon Shaw the physicist, 66, and colleagues have discovered what’s known as the “Mozart effect”, the ability of a Mozart sonata, under the right circumstances, to improve the listener’s mathematical and reasoning abilities. But the findings are controversial and have launched all kinds of crank notions about using music to make kids smarter. The hype, he warns, has gotten out of hand.But first, the essence: Is there something about the brain cells work to explain the effect? In 1978 the neuroscientist Ver non Mountcastle devised a model of the neural structure of the brain’s gray matter. Looking like a thick band of colorful bead work, it represents the firing patterns of groups of neurons. Building on Mountcastle, Shaw and his team constructed a model of t heir own. On a lark, Xiaodan Leng, who was Shaw’s colleague at the time, used a synthesizer to translate these patterns into music. What came out of the speakers wasn’t exactly toe-tapping, but it was music. Shaw and Leng inferred that music and brain-wave activity are built on the same sort of patterns.“Gordon is a contrarian in his thinking”, says his longtime friend, Nobel Prize-winning Stanford physicist Martin Perl. “That’s important. In new areas of science, such as brain research, nobody knows how to do it.”What do neuroscientists and psychologists think of Shaw’s findings? They haven’t condemned it, but neither have they confirmed it. Maybe you have to take them with a grain of salt, but the experiments by Shaw and his colleagues are intriguing. In March a team led by Shaw announced that young children who had listened to the Mozart sonata and studied the piano over a period of months improved their scores by 27% on a test of ratios and proportions. The control group against which they were measured received compatible enrichment courses-minus the music. The Mozart-trained kids are now doing math three grade levels ahead of their peers, Shaw claims.Proof of all this, of course, is necessarily elusive because it can be difficult to do a double-blind experiment of educational techniques. In a double-blind trial of an arthritis drug, neither the study subjects nor the experts evaluating them know which ones got the test treatment and which a dummy pill. How do you keep the participants from knowing it’s Mozart on the CD?61. In the first paragraph Gordon Shaw’s concern is shown overA.the open hostility by the media towards his findings.B.his strength to keep trying out the “Mozart effect”.C.a widespread misunderstanding of his findings.D.the sharp disagreement about his discovery.62. Shaw and Leng’s experiment on the model of their own seems to be based on the hypothesis thatA.listening to Mozart could change the brain’s hardware.B.brain-waves could be invariably translated into music.C.listening to music could stimulate brain development.D.Toe-tapping could be very close to something musical.63. The remarks made by Martin Perl in Paragraph 3 about Gordon Shaw could be taken asA.neuroscientists and psychologists.B. Shaw and his colleagues.C. Shaw and his colleagues.D. the experiments by Shaw and his teamE. Shaw’s findings.66. According to the author, proof of what Shaw claims is difficult becauseA.the control group will also enjoy the same kind of Mozart.B.some educational techniques need re-evaluation.C.the double-blind experiment is not reliable and thus rejected by Shaw.D.participants cannot be kept from knowing what is used in the test.Passage TwoSometimes opponents of capital punishment horrify with tales of lingering death on the gallows, of faulty electric chairs, or of agony in the gas chamber. Partly in response to such protests, several states such as North Carolina and Texas switched to execution by lethal injection. The condemned person is put to death painlessly, without ropes, voltage, bullets, or gas. Did this answer the objections of death penalty opponents? Of course not. On June 22, 1984, The New York Times published an editorial that sarcastically attacked the new “hygienic” method of death by injection, and stated that “execution can never be made humane through science”. So it's not the method that really troubles opponents. It’s the death itself they consider barbaric.Admittedly, capital punishment is not a pleasant topic. However, one does not have to like the death penalty in order to support it any more than one must like radical surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy in order to find necessary these attempts at curing cancer. Ultimately we may learn how to cure cancer with a simple pill. Unfortunately, that day has not yet arrived. Today we are faced with the choice of letting the cancer spread or trying to cure it with the methods available, method that one day will almost certainly and would certainly delay the discovery of an eventual cure. We may not like the death penalty, but it must be available to punish crimes of cold-blooded murder, cases in which any other form of punishment would be inadequate and, therefore, unjust. If we create a society in which injustice is not tolerated, incidents of murder-the most flagrant form of justice-will diminish.67. How did Texas respond to the protests mentiond in Paragraph 1?A.No one was ever executed there later on.B.The criminal there was put to death in the gas chamber instead.C.Life of the condemned person there was terminated with a shot of drug.D.The murderer there was punished with life imprisonment instead.68. What is the main idea of Paragraph?A.The objections of death penalty have become less severe.B.The death itself is considered inhumane and unacceptable.C.Death penalty opponents only care about how one is put to death.D.The “hygienic” was of execution is even more barbaric.69. It can be safely inferred that the authorA.supports capital punishment.B.Is trying to learn how to cure cancer.C.Fears that someone might be punished by mistake.D.Likes radical surgery, radiation and chemotherapy.70. The author’s analogy between cancer and murder is made in order to showA.the lack of perfect solution to the present problems.B.the new discovery of modern science.C.the necessity of doing nothing till an ultimate cure is available.D.the availability of adequate punishment.71. Which of the following stands for the author’s attitude?A.Letting the injustice spread if we don't want to be barbarous.B.Minimizing incidents of murder by means of death penalty.C.Being tolerant of people’s choice of not having any medical treatment.D.Looking for a better form of punishment than death penalty.72. What type of writing is mostly adopted in this passage?A.Narration.B.Classification.C.Exemplification.D.Persuasion.Passage ThreeShyness is a nearly universal human trait. Almost everyone has bouts of it, and half of those surveyed describe themselves as shy. Perhaps because it’s so widespread, and because it suggests vulnerability, shyness is often an endearing trait: Princess Dian a, for example, won millions of admirers with her “Shy Di” manner. The human species might not even exist if not for an instinctive wariness of other creatures. In fact, the ability to sense a threat and a desire to flee are lodged in the most primitive regions of the brain.But at some life juncture, roughly 1 out of every 8 people becomes so timid that encounters with others turn into a source of overwhelming dread. The heart races, palms sweat, mouth grows dry, words vanish, thoughts become cluttered, an d an urge to escape takes over. This is the face of social phobia (also known as “social anxiety disorder”), the third most common mental disorder in the United States, behind depression and alcoholism. Some social phobics can hardly utter a sentence without obsession over the impression they are making. Others refuse to use public restrooms or talk on the telephone. Sometimes they go mute in front of the boss or a member of the opposite sex. At the extreme, they built a hermitic life, avoiding contact with others.Though social anxiety’s symptoms have been noted since the time of Hippocrates, the disorder was a nameless affliction until the late 1960s and didn’t make it way into psychiatry manuals until 1980. As it became better known, patients previously thought to suffer panic disorder were recognized as being anxious only in social settings. A decade ago, 40 percent of people said they were shy, but in today’s “nation of strangers” – in which computers and ATMs make face-to-face relations less and less common – that often favored by those who fear human interaction, greases the slope from shyness to social anxiety. If people were slightly shy to begin with, they can now interact less and less, and that will make the shyness much worse.73. According to Paragraph One, shyness isA.against human nature.B. completely an endearing trait.C. so widespread that a problem may arise.D. essential to the survival of the human species.74. The author suggests that our ability to sense a threat and desire to fleeA.are connected with types of shyness.B.make us more timid and less successfulC.distinguish humans from other creatures.D.are the results of the influence of our environment.75. Which is NOT mentioned as a sign of social anxiety disorder?A.Speechl ess in front of one’s supervisor.B.Unwilling to go to the public toilets.C.Getting drunk in social settings.D.The heart pumping fast.76. The term “social anxiety disorder” was coinedA. at the time of ancient meditation.B. in the 1960s.C. in 1980.D. a decade ago.77. It is shown that the most common mental disorder in the U.S. isA. depression.B. alcoholism.C. social phobia.D. panic disorder.78. What is the cited attitude of some psychologists towards the Internet culture?A.It is the main cause of social phobia.B.It is destructive and thus should be kept away from the youth.C.It encourages peple who are rather inhibited to communicate more freely.D.It helps accelerate the degradation from shyness to social phobia.Passage FourBenjamin Day was only 22 years old when he developed the idea of a newspaper for the masses and launched his New York Sun in 1833, which would profoundly alter journalism by his new approach. Yet, several conditions had to exist before a mass press could come into existence. It was impossible to launch a mass-appeal newspaper without invention of a printing press able to produce extremely cheap newspaper affordable almost to everyone. The second element that led to the growth of the mass newspaper was the increased level of literacy in the population. The then increased emphasis on education led to a concurrent growth of literacy as many people in the middle and lower economic groups acquired reading skills. The trend toward “democratization” of business and politics fostered the creation of a mass audience responsive to a mass press.Having seen others fail in their attempts to market a mass-appeal newspaper, he forged ahead with his New York Sun, which would be a daily and sell for a penny, as compared to the other dailies that went for six cents a copy. Local happenings, sex, violence, features, and human-interest stories would constitute his content. Conspicuously absent were the dull political debates t hat still characterized many of the six-cent papers. Within six months the Sun achieved a circulation approximately 8,000 issues, far ahead of its nearest competitor. Day’s gamble had paid off, and the penny press was launched.James Gordon Bennett, perhaps the most significant and certainly the most colorful of the individuals imitating Day’s paper, launched his New York Herald in 1835, even more of a rapid success than the Sun. Part of Bennett’s success can be attributed to his skillful reporting of crime news, the institution of a financial page, sports reporting, and an aggressive editorial policy. He looked upon himself a reformer, and wrote in one of his editorials: “I go for a general reformation of morals. … I mean to begin a new movement in the progress of civilization.”Horace Greeley was another important pioneer of the era. He launched his New York Tribune in 1841 and would rank third behind the Sun and Herald in daily circulation, but his weekly edition was circulated nationally and proved to be a great success. Greeley’s Tribune was not as sensational as its competitors. He used his editorial page for crusades and causes. He opposed capital punishment, alcohol, gambling and tobacco. Greeley also favored women’s rights. Greeley never talked down to the mass audience and attracted his readers by appealing to their intellect more than to their emotions.The last of the major newspapers of the penny-press era began in 1851. The New York Times,edited by Henry Raymond, promised to be less sensational than the Sun or Herald and less impassioned than Greeley. The paper soon established a reputation for objective and reasoned journalism. Raymond stressed the gathering of foreign news and served as foreign correspondent himself in 1859. The Times circulation reached more than 40,000 before the Civil war.79. Which is NOT mentioned as the contributing element in the launch of the mass press?A.The upgraded educational level of the masses.B.The increased wealth of the population as a whole.C.The democratic background and drive of the general publicD.The lowered cost of newspaper production.80. The New York Sun rarely featuredA.business newsB.women’s pages.C.lengthy discussion about politics.D.local shipment information.81. Which of the following papers issued a nationally circulated edition?A. The New York Tribune.B.The New York Sun.C.The New York Herald.D.The New York Times.82. Which of the following papers is viewed as the most dispassionate one?A The New York Tribune.B. The New York Sun.C. The New York Herald.D. The New York Times.83. The penny-press approach was pioneered byA.Henry Raymond.B. James Gordon Bennett.C. Benjamin day.D. Joseph Pulitzer84. It can be inferred thatA.the New York Times had the largest daily circulation at that time.B.the papers before the penny-press era only appealed to a small circle of readers.C.the success of the four papers lies in their endeavor to improve peple’s literacy.D.the paper’s being sensational was not favored by a majority of American readers.85. The main purpose of the passage is toA.give a brief introduction to the growth of the mass newspaper.B.trace the cause of the failures of the six-cent papers.C.find out which was the most significant newspaper of that time.D.show how a mass-appeal newspaper made a great fortune.Passage FiveInstead of advancing the public discussion of biotechnology, David Shenk succeeds merely in displaying his general ignorance and unfounded fears in his recent article “Biocapitalism”. His claim that “no living creature has ever before been able to upgrade its own operating system” ignores transduction (the act or process of transferring genetic material or characteristics from one bacterial cell to another) and bacterial conjugation (the temporary union of two bacterial cells), which are ways organisms have “upgraded” their own genomes with novel DNA f or hundreds of millions of years. A first-year biology major could have told him that. For Shenk to suggest that his daughter may someday use a before-birth genetic test for “quick-wittedness” is extremely dull-witted, ignoring the complexity of polygenetic traits while embracing a shallow genetic determinism. Nurture-utterly absent from his discussion-really does matter.Finally, worrying about the effects on the gene pool of a “culture in which millions choose the same desirable genes” is worse than point less. The United Nations projects an approximate human population of eight billion by the year 2020. Even if Shenk’s worst fears are realized, and the wealthy parents of 100 million children can and do select for a polygenetic trait-say, blue eyes-this would represent only a modest shift in the gene pool of 1 in 80, or 1.25 percent, assuming that none of those children would otherwise have been born with blue eyes. But what truly matters for the gene pool in the 1,000-year-long run is the capacity of this trait to grant reproductive success in subsequent generations. Whatever advantage blue eyes currently grant in acquiring a mate presumably derives in part from the trait’s relative scarcity. Elementary economics shows that if you flood the market with an asset, you diminish the relative value of that asset: more blue eyes will make blue eyes less sexy. Is it really too much to expect familiarity with either biology or economics from an essay entitled “Biocapitalism”?86. The purpose of David Shenk’s writing is most probably toA.draw the public’s attention to “biocapitalism”.B.cover his general ignorance about “biocapitalism”.C.show his approval of the advancement in biotechnology.D.Report his success in biotechnological research.87. According to the author, Dav id Shenk’s claim about the upgrading of living creaturesA.is obviously a fault.B. is comprehensible to college students.C. is identical to his own argument.D. will be testified by his daughter.88. What does David Shenk worry about?A.The capacity of the gene pool.B.The nurture of subsequent generations.C.The dramatic increase of world population.D.The consequences of excessive genetic shifts.89. The author’s explanation of people’s preference to blue eyes is thatA.blue eyes are purely inherited.B.few people have blue eyes.C.blue eyes are less sexy.D.people with blue eyes are usually wealthy.90. The tone of this passage is mainlyA. humorous.B. matter-of-fact.C. bitter and ruthless.D. emotional.PAPER TWOPART V TRANSLATION (10 points, 25 minutes)Directions: Put the following passage into Chinese. Write your English version in the proper space on Answer Sheet II.世界先进水平的一流大学应该是培养和造就高素质创造性人才的摇篮,应该是认识世界、探求客观真理、为人类解决面临的重大课题提供科学依据的前沿,应该是知识创新、推动科学技术成果向现实生产力转化的重要力量,应该是民族优秀文化与世界先进文明成果交流借鉴的桥梁。
清华04北大02年考博英语试题清华大学2004年博士研究生英语考试试题2006年8月Part Ⅰ Listening Comprehension (20%)Part Ⅱ Vocabulary (10%)21. The_____of the spring water attracts a lot of visitors from other parts of the country A. clash B.clarify C. clarity D. clatter22. Business in this area has been__________because prices are too high.A. prosperousB. secretiveC. slackD. shrill23. He told a story about his sister who was in a sad_______when she was ill and had nomoney. A.plight B. polarization C. plague D. pigment24. He added a__________to his letter by saying that he would arrive before 8 pm.A. presidencyB. prestigeC. postscriptD. preliminary25. Some linguists believe that the___age for children learning a foreign language is 5 to 8. A.optimistic B. optional C. optimal D. oppressed26. It all started in 1950, when people began to build their houses on the___of their cities. A.paradises B. omissions C. orchards D. outsk27.The meeting was__________over by the mayor of the city.A. presumedB. proposedC. presentedD. presided28. The crowd__________into the hall and some had to stand outside.A. outgrewB. overthrewC. overpassedD. overflew29. It was clear that the storm__________his arrival by two hours.A. retardedB. retiredC. refrainedD. retreated30. This problem should be discussed first, for it takes__________over all the other issues. A. precedence B. prosperity C. presumption D. probabilityer sadness was obvious, but she believed that her feeling of depression was__________.A. torrentB. transientC. tensileD. textured32. Nobody knew how he came up with this__________idea about the trip.A. wearyB. twilightC. unanimousD. weird33. The flower under the sun would__________quickly without any protection.A. winkB. withholdC. witherD. widower34. The__________of gifted children into accelerated classes will start next week according to their academic performance.A. segregationB. specificationC. spectrumD. subscription35. He__________himself bitterly for his miserable behavior that evening.A. repealedB. resentedC. relayedD. reproached36. Any earthquake that takes place in any area is certainly regarded as a kind of a __event. A.cholesterol B. charcoal C. catastrophic D. chronic37. He cut the string and held up the two__________to tie the box.A. segmentsB. sedimentsC. seizuresD. secretes38. All the music instruments in the orchestra will be__________before it starts.A. civilizedB. chatteredC. chamberedD. chorded39. When the air in a certain space is squeezed to occupy a smaller space, the air is said to be__________.A. commencedB. compressedC. compromisedD. compensated40. She made two copies of this poem and posted them__________to different publishers.A. sensationallyB. simultaneouslyC. strenuouslyD. simplyPart ⅢReading Comprehension (40%)Questions 41 to 45 are based on the following passage:Each year, millions of people in Bangladesh drink ground water that has been polluted by naturally high levels of arsenic poison. Finding safe drinking water in that country can be a problem. However, International Development Enterprises has a low-cost answer. This non-governmental organization has developed technology to harvest rainwater.e around the world have been harvesting rainwater for centuries. It is a safe, dependable source of drinking water. Unlike ground water, rainwater contains no minerals or salts and is free of chemical treatments. Best of all, it is free. The rainwater harvesting system created by InternationalDevelopment Enterprises uses pipes to collect water from the tops of buildings. The pipes stretch from the tops of buildings to a two-meter tall storage tank made of metal. At the top of the tank is a so-called “fir st-flush”device made of wire screen. This barrier prevents dirt and leaves in the water from falling inside the tank. A fitted cover sits over the “first-flush” device. It protects the water inside the tank from evaporating. The cover also prevents mosquito insects from laying eggs in thewater. Inside the tank is a low coat plastic bag that collects the water. The bag sits inside another plastic bag similar to those used to hold grains. The two bags are supported inside the metal tank. All total, the water storage system can hold up to three-thousand-five-hundred liters of water. International Development Enterprises says the inner bags may need to be replaced every two to three years. However, if the bags are not damaged by sunlight, they could last even longer.International Development Enterprises says the water harvesting system should be built on a raised structure to prevent insects from eating into it at the bottom. The total cost to build this rainwater harvesting system is about forty dollars. However, International Development Enterprises expects the price to drop over time. The group says one tank can provide a family of five with enough rainwater to survive a five-month dry season.41. People in Bangladesh can use__________as a safe source of drinking water.A. ground waterB. rainwaterC. drinking waterD. fresh water42. Which of the following contributes to the low-cost of using rainwater?A. Rainwater is free of chemical treatments.B. People have been harvesting rainwater for centuries.C. The water harvesting system is built on a platform.D. Rainwater can be collected using pipes.43. Which of the following actually prevents dirt and leaves from falling inside the tank?A. a barrierB. a wire screenC. a first-flushD. a storage tank44. The bags used to hold water are likely to be damaged by__________.A. mosquito insectsB. a fitted coverC. a first-flush deviceD. sunlight45. What should be done to prevent insects from eating into the water harvesting system at the bottom?A. The two bags holding the water should be put inside the metal tank.B. The inner bags need to be replaced every two years.C. The water harvesting system should be built on a platform.D. A cover should be used to prevent insects from eating it.Questions 46 to 50 are based on the following passage:Where one stage of child development has been left out, or not sufficiently experienced, the child may have to go back and capture the experience of it. A good home makes this possible,for example by providing the opportunity for the child to play with a clockwork car or toy railway train up to any age if he still needs to do so. This principle, in fact, underlies all psychological treatment of children in difficulties with their development, and is the basis of work in child clinics.The beginnings of discipline are in the nursery. Even the youngest baby is taught by gradual stages to wait for food, to sleep and wake at regular intervals and so on. If the child feels the world around him is a warm and friendly one, he slowly accepts its rhythm and accustoms himself to conforming to its demands. Learning to wait for things, particularly for food, is a very importantelement in upbringing, and is achieved successfully only if too great demands are not made before the child can understand them.Every parent watches eagerly the child's acquisition of each new skill—the first spoken words, the first independent steps, or the beginning of reading and writing. It is often tempting to hurry the child beyond his natural learning rate, but this can set up dangerous feeling of failure and states of anxiety in the child. This might happen at any stage. A baby might be forced to use a toilet too early, a young child might be encouraged to learn to read before he knows the meaning o f the words he reads. On the other hand, though, if a child is left alone too much, or without any learning opportunities, he loses his natural zest for life and his desire to find out new things for himself.Learning together is a fruit source of relationship between children and parents. By playing together, parents learn more about their children and children learn more from their parents. Toys and games which both parents and children can share are an important means of achieving this co-operation. Building-block toys, jigsaw puzzles and crossword are good examples.Parents vary greatly in their degree of strictness or indulgence towards their children. Some may be especially strict in money matters, others are severe over times of coming home at night, punctuality for meals or personal cleanliness. In general, the controls imposed represent the needs of the parents and the values of the community as much as the child's own happiness and well-being.46. The principle underlying all treatment of developmental difficulties in children________A. is to send them to clinicsB. offers recapture of earlier experiencesC. is in the provision of clockwork toys and trainsD. is to capture them before they are sufficiently experienced47. The child in the nursery__________.A. quickly learns to wait for foodB. doesn't initially sleep and wake at regular intervalsC. always accepts the rhythm of the world around themD. always feels the world around him is warm and friendly48. The encouragement of children to achieve new skills__________.A. can never be taken too farB. should be left to school teachersC. will always assist their developmentD. should be balanced between two extremes49. Jigsaw puzzles are__________.A. too difficult for childrenB. a kind of building-block toyC. not very entertaining for adultsD. suitable exercises for parent-child cooperation50. Parental controls and discipline__________.A. serve a dual purposeB. should be avoided as much as possibleC. reflect the values of the communityD. are designed to promote the child's happinessQuestions 51 to 55 are based on the following passage:More than half of all Jews married in U. S. since 1990 have wed people who aren't Jewish. Nearly 480, 000 American children under the age of ten have one Jewish and one non-Jewish parent. And, if a survey compiled by researchers at the University of California at Los Angeles is any indication, it's almost certain that most of thesec hildren will not identify themselves as “Jewish” when they get older. That survey asked college freshmen, who are usually around age 18, about their own and their parents' religious identities. Ninety-three percent of those with two Jewish parents said they thought of themselves as Jewish. But when the father wasn't Jewish, the number dropped to 38 percent, and when the mother wasn't Jew, just 15 percent of the students said they were Jewish, too.“I think what was surprising was just how low the Jewish identification was in these mixed marriage families.” Linda Sax is a professor of education at UCLA. She directed the survey which was conducted over the course of more than a decade and wasn't actually about religious identity specifically. But Professor Sax says the answers to questions about religion were particularly striking, and deserve a more detailed study. She says it's obvious that interfaith marriage works against the development of Jewish identity among children, but says it's not clear at this point whythat's the case. “This new study is necessary to get more in-depth about their feelings about their religion. That's something that the study that I completed was not able to do. We didn't have information on how they feel about their religion, whether they have any concern about their issues of identification, how comfortable they feel about their lifelong goals. I think the new study's going to cover some of that,” she says.Jay Rubin is executive director of Hilel, a national organization that works with Jewish college students. Mr. Rubin says Judaism is more than a religion, it's an experience. And with that in mind, Hillel has commissioned a study of Jewish attitudes towards Judaism. Researchers will concentrate primarily on young adults, and those with two Jewish parents, and those with just one, those who see themselves as Jewish and those who do not. Jay Rubin says Hillel will then use this study to formulate a strategy for making Judaism more relevant to the next generation of American Jews.51. The best title of this passage is__________.A. Jewish and Non-Jewish in AmericanB. Jewish Identity in AmericaC. Judaism-a Religion?D. College Jewish Students52. Among the freshmen at UCLA__________thought themselves as Jewish.A. mostB. 93% of those whose parents were both JewishC. 62% of those only whose father were JewishD. 15% of those only whose mother were Jewish he phrase “interfaith marriage” in the Paragraph 3 refers tothe__________.A. marriage of people based on mutual beliefB. marriage of people for the common faithC. marriage of people of different religious faithsD. marriage of people who have faith in each other54. Which of the following statements is NOT true about professor Sax's research?A. The research indicates that most students with only one Jewish parent will not think themselves as Jewish.B. The survey was carried out among Jewish Freshmen.C. The research survey didn't find out what and how these Jewish students think about their religion.D. The research presents a new perspective for the future study.55. Which of the following is true according to the last paragraph?A. Mr. Rubin is the founder of Hillel.B. Mr. Rubin thinks that Judaism is not a religion and it's an experience.C. Hillel is an organization concerned with Jewish college students in the world.D. Hillel has asked certain people to carry out a study about Jewish attitudes towards Judaism.Questions 56 to 60 are based on the following passage:Governments that want their people to prosper in the burgeoning world economy should guarantee two basic rights: the right to private property and the right to enforceable contracts, says Mancur Olson in his book Power and Prosperity. Olson was an economics professor at the University of Maryland until his death in 1998.Some have argued that such rights are merely luxuries thatwealthy societies bestow, but Olson turns that argument around and asserts that such rights are essential to creating wealth. “In comes are low in most of the countries of the world, in short, be cause the people in those countries do not have secure in dividual rights,” he says.Certain simple economic activities, such as food gathering and making handicrafts, rely mostly on individual labor; property is not necessary. But more advanced activities, such as the mass production of goods, require machines and factories and offices. This production is often called capital-intensive, but it is really property-intensive, Olson observes.“No one would normally engage in capital-intensive production if he or she did not have rights that kept the valuable capital from being taken by bandits, whether roving or stationary,”he argues. “There is no private property without government—individuals may have possessions, the way a dog possesses a bone, but there is private property only if the society protects and defends a private right to that possession against other private parties and against the government as well.”Would-be entrepreneurs, no matter how small, also need a government and court system that will make sure people honor their contracts. In fact, the banking systems relied on by developed nations are based on just such an enforceable contract system. “We would not deposit our money in banks...if we could not rely on the bank having to honor its contract with us, and the bank would not be able to make the profits it needs to stay in business if it could not enforce its loan contracts with borrowers,” Olson writes.Other economists have argued that the poor economies of Third World and communist countries are the result ofgovernments setting both prices and the quantities of goods produced rather than letting a free market determine them. Olson agrees there is some merit to this point of view, but he argues that government intervention is not enough to explain the poverty of these countries. Rather, the real problem is lack of individual rights that give people incentive to generate wealth. “If a society has clear and secure individual rights, there are strong incentives (刺激,动力)to produce, invest, and engage in mutually advantageous trade, and therefore at least some economic advance,” Olson concludes.56. Which of the following is true about Olson?A. He was a fiction writer.B. He edited the book Power and Prosperity.C. He taught economics at the University of Maryland.D. He was against the ownership of private property.57. Which of the following represents Olson's point or view?A. Protecting individual property rights encourages wealth building.B. Only in wealthy societies do people have secure individual rights.C. Secure individual rights are brought about by the wealth of the society.D. In some countries, people don't have secure individual rights because they're poor.58. What does Olson think about mass production?A. It's capital intensive.B. It's property intensive.C. It relies on individual labor.D. It relies on individual skills.59. What is the basis for the banking system?A. Contract system that can be enforced.B. People's willingness to deposit money in banks.C. The possibility that the bank can make profits from its borrowers.D. The fact that some people have surplus money while some need loans.60. According to Olson, what is the reason for the poor economies of Third World countries?A. government interventionB. lack of secure individual rightsC. being short of capitalck of a free marketPart Ⅳ Cloze (10%)For the people who have never traveled across the Atlantic the voyage is a fantasy. But for the people who cross it frequently one crossing of the Atlantic is very much like another, and they do not make the voyage for the__61__of its interest. Most of us are quite happy when we feel__62__to go to bed and pleased when the journey__63__. On the first night this time I felt especially lazy and went to bed__64__earlier than usual. When I__65__my cabin, I was surprised__66__that I was to have a companion during my trip, which made me feel a little unhappy.I had expected__67__but there was a suitcase__68__mine in the opposite corner. I wondered who he could be and what he would be like. Soon afterwards he came in. He was the sort of man you might meet__69__, except that he was wearing__70__good clothes that I made up my mind that we would not__71__whoever he was and did notsay__72__. As I had expected, he did not talk to me either but went to bed immediately.I suppose I slept for several hours because when I woke up it was already the middle of the night. I felt cold but covered__73__as well as I could and tries to go back to sleep. Then I realized that a __74__was coming from the window opposite. I thought perhaps I had forgotten__75__the door, so I got up__76__the door but found it already locked from the inside. The cold air was coming from the window opposite. I crossed the room and__77__the moon shone through it on to the other bed.__78__there. It took me a minute or two to__79__the door myself. I realized that my companion__80__through the window into the sea.61. A. reason B. motive C. cause D. sake62. A. tired enough B. enough tired C. enough tiring D. enough tiring63. A. is achieved B. finish C. is over D. is in the end64. A. quite B. rather C. fairly D. somehow65. A. arrived in B. reached to C. arrived to D. reached at66. A. for seeing B. that I saw C. at seeing D. to see67. A. being lonely B. to be lonely C. being alone D. to be alone68. A. like B. as C. similar than D. the same that69. A. in each place B. for all parts C. somewhere D. anywhere70. A. a so B. so C. such a D. such71. A. treat together wel B. pass together well C. get on well together D. go by well together72. A. him a single word B. him not one word single word to hi m D. not one word to him73. A. up me B. up myself C. up to myself D. myself up74.A.draft B. voice C. air D. sound75. A. to close B. closing C. to have to close D. for closing76. A. to shut B. for shutting C. in shutting D. but shut77. A. while doing like that B. as I did like that C. as I did soD. at doing so78. A. It was no one B. There was no one C. It was anyone D. There was anyone79. A. remind to lock B. remember to lock C. remind lockingD. remember locking80. A. had to jump B. was to have jumped C. must have jumped D. could be jumpedPart Ⅴ Writing(20%) Directions: In this part, you are asked to write a composition on the title of “Effect of Research Event on My Later Life and Work” with no less than 200 English words. Your composition should be based on the following outline given in Chinese. Put your composition on the ANSWER SHEET.1. 在科研和学习中使我最难忘的一件事情是。
中科院博士学位英语考试Introduction:The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) is a renowned institution that plays a crucial role in scientific research and development in China. In order to obtain a doctoral degree, candidates who pursue academic excellence and wish to join the ranks of esteemed researchers are required to take the CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam. This exam is designed to assess the candidates' English language proficiency, which is essential for effective communication and collaboration in an increasingly globalized academic landscape. In this article, we will explore the importance of the CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam and provide insights into its format and preparation strategies.Overview of the CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam:The CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam consists of multiple sections that evaluate the candidates' reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills. Each section is carefully designed to assess specific language competencies that are crucial for academic research and professional communication. In order to pass the exam, candidates must demonstrate proficiency in all four areas.1. Reading Section:The reading section of the CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam assesses the candidates' ability to comprehend and analyze complex academic texts. Candidates are presented with a series of passages on various scientific and technological topics, ranging from physics and chemistry to biology andengineering. They must demonstrate their understanding of the key ideas, arguments, and evidence presented in these texts through answering questions and completing tasks that require critical thinking and inference skills.2. Writing Section:The writing section evaluates the candidates' ability to effectively convey their ideas and arguments in written English. Candidates are required to write an essay or a research paper on a given topic within a specified time limit. They must present a clear and logical argument, support it with evidence, and demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of the subject matter. Proper grammar usage, vocabulary selection, and organization of ideas are essential for success in this section.3. Listening Section:The listening section measures the candidates' ability to comprehend spoken English in an academic context. Candidates are played a series of recordings, such as lectures or presentations, and are required to answer questions based on the content. They must be able to understand the main points, details, and implications of the spoken information. Active listening skills, note-taking abilities, and the ability to follow complex academic discourse are critical for success in this section.4. Speaking Section:The speaking section assesses the candidates' ability to express their ideas and opinions in spoken English with clarity and coherence. Candidates are required to engage in a conversation or a presentation with the examiners,where they discuss a given topic, present arguments, and respond to questions. Fluency, pronunciation, and the ability to effectively communicate complex ideas are necessary for a high score in this section.Preparation Strategies:To excel in the CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam, candidates should adopt effective preparation strategies:1. Familiarize Yourself with the Format: Candidates should thoroughly understand the structure and requirements of each section of the exam. This will enable them to allocate their time and efforts accordingly during the actual test.2. Enhance Vocabulary and Grammar: Candidates should prioritize improving their vocabulary and grammar skills. Reading academic articles, scientific journals, and other relevant literature can help in expanding their knowledge base and enhancing their language proficiency.3. Practice Time Management: Time management is crucial during the exam. Candidates should practice completing tasks within the allocated time to ensure efficiency and accuracy. Regular mock exams can help identify areas of improvement and increase familiarity with the exam format.4. Develop Active Listening Skills: Engaging in listening activities, such as watching TED Talks or podcasts, can improve candidates' ability to understand and summarize complex information accurately. Taking notes while listening and practicing listening comprehension exercises are also beneficial.5. Engage in Oral Communication: Candidates should actively seek opportunities to practice speaking English in an academic or professional setting. Participating in discussions, debates, or joining language exchange programs can help develop fluency, coherence, and confidence.Conclusion:The CAS Doctoral Degree English Exam is a pivotal step for candidates aiming to obtain a Ph.D. degree from the esteemed Chinese Academy of Sciences. By demonstrating proficiency in reading, writing, listening, and speaking skills, candidates showcase their ability to effectively communicate in an international academic and research environment. Through proper preparation, continuous practice, and dedication, candidates can enhance their language skills and increase their chances of success in this important examination.。
中科院博士学位英语【1】博士学位英语的重要性在当今全球化时代,英语作为国际通用语言,在我国科研领域具有重要地位。
博士学位英语不仅是攻读博士学位的基本要求,也是提升个人综合素质、拓宽国际视野、促进学术交流的关键因素。
对于中科院博士生来说,掌握英语更是不可或缺的能力。
【2】中科院博士学位英语考试概述中科院博士学位英语考试主要测试考生在学术语境下的英语听、说、读、写能力。
考试内容包括听力、阅读、翻译、写作等部分。
为保证考试的公平性和专业性,中科院博士学位英语考试采用与国际接轨的题型和评分标准。
【3】备考中科院博士学位英语的建议1.制定合理的学习计划:根据自己的实际情况,合理安排学习时间,确保每天都有一定的学习时长。
2.夯实基础知识:加强词汇、语法、句型等英语基本功的训练,为学术英语打下坚实基础。
3.注重实践:通过参加英语角、与外国学者交流等方式,提高口语表达和听力理解能力。
4.扩大阅读面:阅读英文专业文献、学术论文,培养学术阅读和写作能力。
5.模拟测试:定期进行模拟考试,了解自己的薄弱环节,有针对性地进行改进。
【4】提高英语能力的实用技巧1.充分利用网络资源:搜索并订阅英语学习网站或APP,跟随课程学习,提高英语水平。
2.建立英语学习小组:与志同道合的朋友一起学习,相互督促、共同进步。
3.制定奖惩制度:为自己设定学习目标和奖励措施,提高学习积极性。
4.坚持每天学习:养成良好的学习习惯,持之以恒,必有收获。
【5】总结掌握英语对于中科院博士生至关重要。
通过制定合理的学习计划、夯实基础知识、注重实践、扩大阅读面和模拟测试等方法,有望提高英语水平。
全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(一)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则, 得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。
3. 全国硕士研究生入学考试英语分为试题(一) 、试题(二) 。
4. 本试题为试题(一), 共4页(1~4页) 。
考生必须在规定的时间内作答。
5. 试题(一) 为听力部分。
该部分共有A、B、C三节, 所有答案都应填写或填涂在答题卡1上。
A、B两节必须用蓝(黑) 圆珠笔答题, 注意字迹清楚。
C节必须用2B铅笔按照答题卡上的要求填涂, 如要改动, 必须用橡皮擦干净。
6. 听力考试进行时, 考生应先将答案写或标记在试题上, 然后在听力部分结束前专门留出的5分钟内, 将答案整洁地誊写或转涂到答题卡1上。
仅写或标记在试题上不给分。
Directions:Now look at Part A in your test booklet.Part ADirections:For Questions 1-5, you will hear an introduction about the life of Margaret Welch. While you listen, fill out the table with the information you’ve heard. Some of the information has been given to you in the table. Write only 1 word or number in each numbered box. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the table below. (5 points)Welch’s Personal InformationPlace of Birth PhiladelphiaYear of Birth 1901Transfer to Barnard University (Year) 1920Major at University1Final Degree PhDYear of Marriage 1928Growing Up In New Guinea Published (Year)2Field Study in the South Pacific (Age)3Main Interest4Professorship at Columbia Started (Year)Death (Age) 77Part BDirections:Besides reporters, who else were camped out for days outside the speaker’s home?6. ________One reporter got to the speaker’s apartment pretending to pay7. ________The speaker believed the reporter wanted a picture of her looking8. ________Where is a correction to a false story usually placed?9. ________According to the speaker, the press will lost readers unless the editors and the news directors10. ________Part CDirections:Questions 11-13 are based on a report about children’s healthy development. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 11-13.[B] What they are most worried about.[D] What entertainment they are interested in.12. The academy suggests that children under age two ________.[A] get enough entertainment[B] have more activities[C] receive early education[D] have regular checkups13. According to the report, children’s bedrooms should ________.[A] be no place for play[C] have no TV setsQuestions 14-16 are based on the following talk about how to save money. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 14-16.14. According to the speaker, what should one pay special attention to if he wants to save up?[A] Family debts.[B] Bank savings.[C] Monthly bills.[D] Spending habits.15. How much can a person save by retirement if he gives up his pack-a-day habit?[A] $190,000.[B] $330,000.[C] $500,000.[D] $1,000,000.16. What should one do before paying monthly bills, if he wants to accumulate wealth?[A] Invest into a mutual fund.[B] Use the discount tickets.[C] Quit his eating-out habit.[D] Use only paper bills and save coins.Questions 17-20 are based on an interview with Herbert A. Glieberman, a domestic-relations lawyer. You now have 20 seconds to read Questions 17-20.17. Which word best describes the lawyer’s prediction of the change in divorce rate?[A] Fall[B] Rise[C] V-shape[D] Zigzag18. What do people nowadays desire to do concerning their marriage?[A] To embrace changes of thought.[B] To adapt to the disintegrated family life.[C] To return to the practice in the ‘60s and ‘70s.[D] To create stability in their lives.19. Why did some people choose not to divorce 20 years ago?[B] They wanted to go against the trend.[C] They were afraid of losing face.[D] they were willing to stay together.[A] been shifted around the country.[B] had difficulty being promoted.[C] enjoyed a happier life.[D] tasted little bitterness of disgrace.You now have 5 minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET 1.THIS IS THE END OF SECTION IDO NOT READ OR WORK ON THE NEXT SECTIONUNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO CONTINUE全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(二)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。