
英语语法
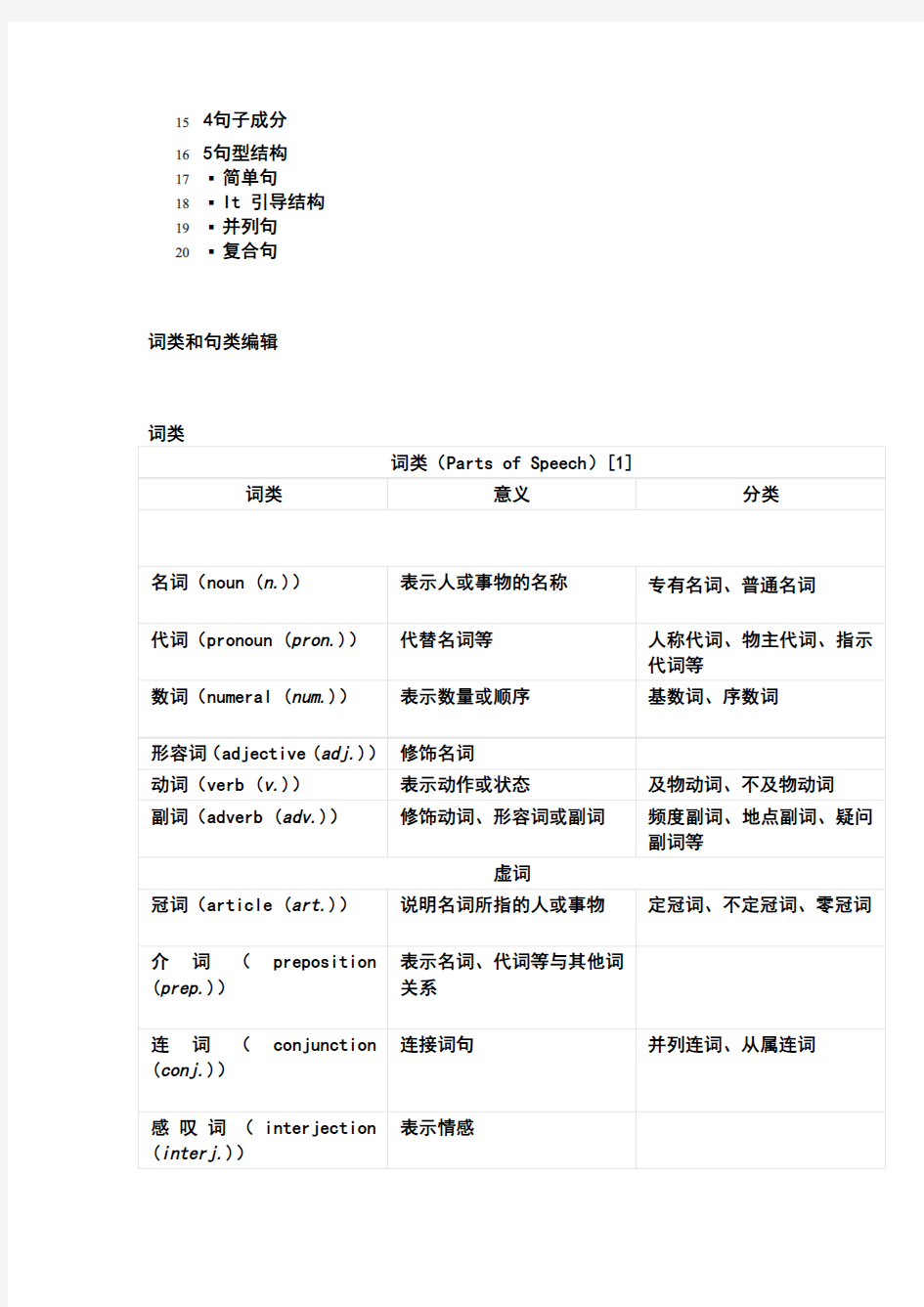
英语语法是针对英语语言的语法进行的研究。语法是组词造句的规则,是把合适的词放进合适位置的艺术文化底蕴,语法可以分成为两大部分:分别为词法和句法。词法包括各类词的形态及其变化,句法主要讲句子的种类和类型,句子成分以及遣词造句的规律。
中文名
英语语法
外文名
English grammar
类型
语法[1]
语言
英语
分类
词法、句法
词语
句子
目录
11词类和句类
2?词类
3?句类
42词语
5?名词
6?代词
7?数词
8?动词
9?感叹词
10?其他
113时态、语态和语气
12?时态
13?语态
14?语气
154句子成分165句型结构
17?简单句
18?It 引导结构19?并列句
20?复合句
词语编辑
名词
名词(noun)是指人或事物的名称。名词一般分为专有名词(proper noun)和普通名词(common noun)。专有名词是个别的人、事物、地点、团体、机构等专有的名称,首字母通常大写。名词按其所表示的事物的性质也可以分为可数名词(countable noun)和不可数名词(uncountable noun),可数名词有单数和复数形式。[1]
1.名词的数
2.名词所有格(possessive case of nouns)
名词所有格表示所属关系。
代词
代词(pronoun)用于代替名词等。代词分为人称代词(personal pronoun)、物主代词(possessive pronoun)、指示代词(demonstrative pronoun)、反身代词(reflexive pronoun)、相互代词(reciprocal pronoun)、疑问代词(interrogative pronoun)、关系代词(relative pronoun)、连接代词(conjunctive pronoun)和不定代词(indefinite pronoun)。
3.反身代词
数词
数词表示数量或顺序等。分为基数词(cardinal number)和序数词(ordinal number)。[1]
1.基数词表示数目的多少。[1]
2.序数词表示事物的先后顺序,常与定冠词the连用。[1]
动词
动词的第三人称单数形式[1]
动词-ing形式[2]
/s/,/z/,/?/,/t?/,/d?/等后读/iz/
情态动词本身就具有一定的词义,但要与动词原形以及其被动语态一起使用,给谓语动词增添情态色彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能、应该或必要等。情态动词后面加动词原形。
1)情态动词不能表示正在发生或已经发生的事情,只表示期待或估计某事的发生。
2)情态动词除ought 和have外,后面只能接不带to的不定式。
3)情态动词不随人称的变化而变化,即情态动词的第三人称单数不加-s。
4)情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式、分词等形式。
感叹词
感叹词是用来表示说话时表达的喜、怒、哀、乐等情感的词。它不构成后面句子的一个语法成分,却在意义上与它有关联,后面的句子一般说明这种情绪的性质、原因。感叹词是英语口语中最富有表现力的词语之一,用途甚广。下面是感叹词的用法:
Oh 表示惊讶、指责、痛苦、称赞、懊恼等,可译为“哦”、“哎呀”、“噢”“啊”、“呀”等。例如:
(1). "Oh, who was that?" Mr. Black asked. “哦,是谁?”布莱克先生问。
(2). "Oh, how blind you are!" he cried. “哎呀,你难道瞎了吗!”他大声道。
(3)."Oh,what that?!!!" I asked。“噢,那是什么?”我问道。
其他
1、动名词V-ing:动名词是一种兼有动词和名词特征的非限定动词。它可以支配宾语,也能被副词修饰。动名词有时态和语态的变化。
2、动词不定式:由to+动词原形构成。不定式是一种非限定性动词。而非限定动词是指那些在句中不能单独充当谓语的动词,可分为不定式、动名词、
现在分词和过去分词。
3、分词[participle]:具有动词及形容词二者特征的词;尤指以ing、ed、
d、t、en或n结尾的英语动词性形容词,具有形容词功能,同时又表现各种动词性特点,如时态,语态、带状语性修饰语的性能及带宾词的性能。
时态、语态和语气编辑
时态
时态(tense)是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同的时间与方式。
动词时态是表示行为、动作和状态在各种时间条件下的动词形式。因此,当我们说时态结构的时候,指的是相应时态下的动词形式。
所谓“时”就是行为发生的时段或状态存在的时段,即:"现在、过去、将来、过去将来"四种;所谓“态”就是行为或状态发生时所呈现的状态,有一般状态、进行状态、完成状态和完成进行状态四种。由时态结合,便形成下列十六种时态:
一般时态
一般现在时(Simple Present Tense)表示现在的状态、经常的或习惯性的
动作、主语具备的性格和能力等。[1]
1.时间状语:Always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…),once a week(day, year, month…),on Sundays(on Mondays …).
2.基本结构:主语+be/do+其他;(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要改为第三人称单数形式)。
否定形式:主语 + am/is/are + not + 其他(此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词)。
一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
一般过去时(Simple Past Tense)表示过去某个时间内(或某一段时间内)发生的动作或存在的状态,过去经常或反复发生的动作。[2]
2.时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week, last(year, night, month…),in 1989,just now, at the age of 5,one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc.
3.基本结构:主语 + 动词的过去式或be的过去式+名词。
4.否定形式:主语 + was/were + not + 其他(在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词)。
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
6.例句:(1)She often came to help us in those days.那些天她经常来帮助我们。
(2) I didn't know you were so busy.我不知道你是这么忙。
一般将来时
1.概念:表示将要发生的动作、打算、计划或准备做某事。
2.标志:Tomorrow, soon, in a few minutes, ,the day after tomorrow, etc.
3.基本结构:(1)主语 + am/is/are + going to + do sth
(2)主语 + will/shall + do sth
4.否定句:在系动词is/am/are或情态动词will/shall后加not
5.一般疑问句:be放于句首;will/shall提到句首。{首字母大写}
6.例句:They are going to have a competition with us in studies.他们将有一场比赛和我们一起研究。
It is going to rain.天要下雨了。
一般过去将来时
1.概念:立足于过去某一时刻,从过去看将来,常用于宾语从句中。
2.时间状语:The next day (morning \, year…),the following month(week…),etc.
3.基本结构:主语 + was/were + going to + do + 其它;主语 + would/should + do +其它
4.否定形式:主语 + was/were + not + going to + do; 主语 + would/should + not + do.
5.一般疑问句:was或were放于句首;would/should 提到句首。
6.例句:(1)He said he would go to Beijing the next day.他说他第二天要去北京。
(2) I asked who was going there.我问,谁要去那里。
进行时态
现在进行时(Present Progressive Tense)表示现在(说话时)或当前阶段正在进行或发生的动作。[2]
2.时间状语:Now, at this time, days, etc. look, listen
3.基本结构:主语+ be + doing + 其它
4.否定形式:主语 + be + not +doing + 其它
5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
6.例句:How are you feeling today? 你今天感觉如何?
He is doing well in his lessons.在课上他表现得很好。
过去进行时
1.概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
2.时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
3.基本结构主语+was/were +doing +其它
4.否定形式:主语+was/were + not +doing+其它
5.一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。(第一个字母大写)
6.例句:At that time she was working in a PLA unit.那段时间她在人民解放军部队工作。
When he came in, I was reading a newspaper.他进来时,我正在读报纸。
将来进行时
1.概念:表示将来某一时间正在进行的动作,或表示要在将来某一时间开始,并继续下去的动作。常用来表示询问、请求等。
2.时间状语:Soon, tomorrow, this evening,on Sunday, by this time,in two days, tomorrow evening
3.基本结构:主语 + shall/will + be + 现在分词 + 其它
4.否定形式:主语 + shall/will + not + be + 现在分词 + 其它
5.例句:This time next day they will be sitting in the cinema.下一天的这个时间,他们正坐在电影院。
He won’t be coming to the party.他不去参加聚会了。
过去将来进行时
1.概念:表示就过去某一时间而言,将来某一时刻或某一段时间正在进行的动作,主要用于宾语从句中,尤其多用于间接引语中。
2.基本结构:should/would + be + 现在分词
3.例句:He said he could not come because he would be having a meeting.他说他不能来因为要开会。 They said they would be coming.他们说了他们将要来。
完成时态
现在完成时
1.概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:yet, already ,just, never, ever, so far, by now, since + 时间点,for + 时间段,recently, lately, in the past few years, etc.
3.基本结构:主语 + have/has + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
4.否定形式:主语 + have/has + not + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
5.一般疑问句:have或has放句首。
6.例句:The countryside has changed a lot in the past few years.
在过去的几年,农村发生了巨大的变化。
I've written an essay.我已经写了一篇论文。
过去完成时
1.概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
2.时间状语:Before, by the end of last year (term, month…),etc.
3.基本结构:主语 + had + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
4.否定形式:主语 + had + not +p.p(过去分词) + 其它
5.一般疑问句:had放于句首。
6.例句:As soon as we got to the station, the train had left.当我们到车站的时候,火车已经开走了。
By the end of last month, we had reviewed four books.到上个月底,我们已经复习了四本书。
基本结构:主语 + had + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
①肯定句:主语 + had + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
②否定句:主语 + had + not + p.p(过去分词) + 其它
③一般疑问句:Had +主语 + p.p(过去分词)+其它
④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词 + 一般疑问句
将来完成时
1.概念:在将来某一时刻之前开始的动作或状态。
2.时间状语:by the time of; by the end of + 时间短语(将来);by the time + 从句(将来)
3.基本结构:主语 + be going to/will/shall + have + p.p(过去分词)+ 其它
4例句:By the time you get back, great changes will have taken place in this area
.到你回来的时候,就将发生巨大的变化。
过去将来完成时
1.概念:表示在过去某一时间对将来某一时刻以前所会发生的动作,常用在虚拟语气中,表示与过去的事实相反。
2.基本结构:should/would have done sth.
3.例句:I thought you'd have left by this time.我想这会儿你已经走了。
He told them he would have finished it by 8 o'clock.他告诉他们他会在8点以前干完。
完成进行时态
现在完成进行时
1.概念:表示从过去某一时间开始一直延续到现在的动作。这一动作可能刚刚开始,也可能仍在继续,并可能延续到将来。
2.基本结构:主语 + have/has + been + doing + 其它
3.时间状语:since + 时间点,for + 时间段等。
4.例子:I have been sitting here for an hour.我已经在这里坐了一个小时。
The children have been watching TV since six o'clock.从6点起,孩子们一直看电视。
过去完成进行时
1.概念:表示某个正在进行的动作或状态,持续到过去某个时刻,还未完成,一直持续到之后的当前才结束。
2.基本结构:主语 + had + been + doing + 其它
3.例子:She had been suffering from a bad cold when she took the exam.她在考试之前一直患重感冒。
Had they been expecting the news for some time? 他们期待这个消息有一段时间了吧?
4.特殊含义:①尚未完成:He had been writing the novel.他已经在写小说了。(他没写完)
②企图:He had been studying the meaning of this proverb.他曾经学习过这个谚语。(他曾努力学习过它)
③未得结果:We had been studying what our enemy had said.我们一直致力于敌人所说的。(但是我们没有理解)
④最近情况:He had been quarrelling with his wife.他和他的妻子吵了一场架。(最近)
⑤反复动作:He had been asking me the same question.他一直问我相同的问题。(屡次)
⑥情绪:What had he been doing?他做了什么
将来完成进行时
1.概念:表示动作从某一时间开始一直延续到将来某一时间。是否继续下去,要视上下文而定。
2.基本结构:shall/will have been doing
3.例子:I shall have been working here in this factory for twenty years by the end of the year.到今年年底,我将在这个工厂工作20年了。
If we don't hurry up the store will have been closing before we get there. 咱们如不快一点儿,等我们到了那儿,店门就会关了。
过去将来完成进行时
1.概念:表示从过去某时看至未来某时以前会一直在进行的动作。
2.基本结构:should/would + have + been +现在分词
3.例子:He told me that by the end of the year he would have been living there for thirty years.他告诉我,到年底时,他就在那住了30年了。
语态
主动语态
主语是谓语动作的使动方。也就是说谓语的动作源自主语,而施加于宾语。相反,被动语态中,主语是谓语动作的受动方,如果有宾语的,宾语往往是谓语动作的使动方。
在语法机构上,主动语态和被动语态的区别主要在于,主动语态直接使用动词原形作为谓语,然后再在该动词原形的基础上施加时态和其他语法;而被动语态则使用系词+动词的过去分词作为谓语,各种时态和其他语法也施加在系词上。
被动语态
英语中的被动语态使用得比汉语要多,要普遍,许多课本及考试乃至实际应用中都常常涉及到这个问题。一般说来,当强调动作承受者,不必说出执行者或含糊不清的执行者时,多用被动式。须注意的是,许多地方与汉语不同。注意那些汉语中没有"被……"的意思,英语却应该用被动态。还要注意,英语的被动态往往由"by"引出,而有用介词"by"的短语往往又不是被动态,而是系表结构。还有些特殊现象,如:known to man(人类......所知),on foot步行(美国人有时用by foot),in carriage (乘四轮马车)等等。还有假主动,真被动的十几个常用词的用法,以及so heavy to carry而不用so heavy to be carried 等习惯用法。有关这类情况,做到心中有数对全面掌握被动态,准确无误地解答习题非常关键,被动态必须涉及的是动词的各种时态变化的问题。英语的时态本来很复杂,怎样记住各自的被动形式呢? 首先要明确"将来进行无被动,现在完成进行同"。这两种时态无被动形式。
另外,不及物动词带有同源宾语的动词,反身代词的动词和系动词都无被动形式。即便如此,还有不定式,动名词,分词,以及它们的复合结构)的被动态,再加上情态动词,助动词以及它们的疑问式和否定式从中掺杂,真是令人头痛,眼花缭乱。下面口诀就以动词do为例,即do did过去式done过去分词,以口诀形式总结各种时态的被动态,一定对你有所启示。
一、被动语态的用法
1.一般现在时的被动语态构成:is / am / are +及物动词的过去分词
Our classroom is cleaned every day. 我们教室每天都被打扫。
2.一般过去时的被动语态构成:was / were +及物动词的过去分词
A new shop was built last year. 去年修了一座新商店。
3.一般将来时的被动语态构成:will+ be + 及物动词的过去分词
A new hospital will be built in our city. 我们城市将要修建一家新医院。
4.现在进行时的被动语态构成:am / is / are + being +及物动词的过去分词
Uncle Wang is mending my bike now.→
My bike is being repaired by Tom now. 王叔叔正在修理我的自行车。
5.现在完成时的被动语态构成:has / have + been +及物动词的过去分词
This book has been translated into many languages. 这本书被翻译成多种文字。
Many man-made satellites have been sent up into space by many countries. 在许多国家有许多人造卫星被送上了太空。
6.过去进行时的被动语态构成:was/were + being +及物动词的过去分词
The new road was being made.这条新路正在修筑。
7.过去完成时的被动语态构成:had + been +及物动词的过去分词
The classroom hadn’t been cleaned before the teacher came. 在老师来之前,教室尚未打扫。
8.将来完成时的被动语态构成:shall/will + have been done
They will have been married for 20 years by then. 届时,他们结婚将满20周年。
9.含有情态动词的被动语态构成:情态动词 + be +及物动词的过去分词
Young trees must be watered often. 小树需要经常浇水。
二、主动语态改成被动语态
1. 先找出谓语动词;
2. 再找出谓语动词后的宾语;
3. 把宾语用作被动语态中的主语;
4. 注意人称、时态和数的变化。
例:1. Bruce writes a letter every week. →A letter is written by Bruce every week. 布鲁斯每星期写一封信。
2. Li Lei mended the broken bike this morning. →The broken bike was mended by Li Lei this morning. 李雷今天上午在修理坏的自行车。
3. He has written two novels so far. →Two novels have been written by him so far. 至今他已写了两部小说。
4. They will plant ten trees tomorrow. →Ten trees will be planted by them tomorrow. 他们明天将要种植十棵树。
5. Lucy is writing a letter now. →A letter is being written by Lucy now. 露西正在写信。
6. You must lock the door when you leave. →the door must be locked when you leave. 当你离开的时候你必须把门锁上。
三、使用被动语态应注意的几个问题:
1.不及物动词无被动语态。
What will happen in 100 years?一百年里会发生什么事?
2. 有些动词用主动形式表示被动意义。
This pen writes well. 这支钢笔很好写。
3.感官动词或使役动词使用省略to的动词不定式,主动语态中不带to ,但变为被动语态时,须加上to。
(1)Make somebody do something →somebody+ be +made to do something
(2)See somebody do something →somebody +be +seen to do something
例句:(1) A girl saw my wallet drop when she passed by. →My wallet was seen to drop by a girl when she passed by. 当一个女孩经过的时候,看到我的钱夹掉了。
(2)The boss made the little boy do heavy work. →The little boy was made to do heavy work by the boss. 这个老板让这小男孩干重活。
4. 如果是接双宾语的动词改为被动语态时,直接宾语(物)做主语,那么动词后要用介词,这个介词是由与其搭配的动词决定。
He gave me a book. →A book was given to me by him. 他给了我一本书。
He showed me a ticket. →A ticket was shown to me by him. 他给我展示了一张票。
My father bought me a new bike. →A new bike was bought for me by my father. 我父亲给我买了一辆新自行车。
5. 一些动词短语用于被动语态时,动词短语应当看作一个整体,而不能丢掉其中的介词或副词。
We can’t laugh at him. →He can’t be laughed at by us. 我们不能嘲笑他。
四、新兴形式的被动语态
Get+过去分词也可以构成被动语态,用这种结构的句子侧重于动作的结果而不是动作本身。如:The man got hurt on his way home. 那个男人在回家的路上受伤了。How did the glass get broken? 杯子怎么破了?著名学者周海中教授在论文《Get-Passive研究》中指出:Get+过去分词的被动语态是一种新兴的被动语态形式;相对来说它的使用还没有Be+过去分词构成的被动语态那么广泛,一般限于口语和非正式书面语;但它却有着用得愈来愈多的趋势,是一种生气蓬勃的语言现象。
语气
在英语中,语气是动词的一种形式,它表示说话人对某一行为或事情的看法和态度。
陈述语气
陈述语气表示动作或状态是现实的、确定的和符合事实的,用于陈述句、疑问句和某些感叹句。
如:(1)We are not ready. 我们没准备好。(陈述句)
(2)What a fine day it is! 多好的天气啊!(感叹句)
祈使语气
祈使语气表示说话人的建议、请求、邀请、命令等。
如:(1)Open the door,please.请打开门。(请求)
(2)Turn down the TV.关掉电视机。(命令)
虚拟语气
虚拟语气表示动作或状态不是客观存在的事实,而是说话人的主观愿望、假设或推测等,它是专门表达"假设意义”(hypothetical meaning)及其他“非事实意义”(non-factual meaning)的动词形式。
虚拟词有wish(希望)、if(如果)、hope(希望)、want(想)、think(想、认为)等。
如:(1)I wish I was a bird.我希望我是一只鸟。(我不是一只鸟)
(2)If there were no gravity, we should not be able to walk.如果没有重力(我们有重力),我们就无法行走。
(3)If I were you,I would accept it.如果我是你(我永远不可能是你,表虚拟),我将接受它。
(4)If you had been here yesterday, you would have seen him.昨天你如果在这儿,就能见到他了。(事实是“昨天你没在这儿,未见到他”)
句子成分编辑
一个句子一般皆由两部分组成,即主语部分(subject group)和谓语部分
【英语语法分类汇总】存在句 存在句:又叫做“There be句型”,是一种表示“存在”的句式。 常见结构:“There + be + 主语+ 地点状语(或时间状语)”。存在句的“there”要弱读。 存在句的句型转换: 一. 肯定陈述句 例如:There is a dictionary on the desk.(桌子上有一本字典。)二. 否定陈述句 例如:There isn’t a dictionary on the desk.(桌子上没有字典。)三. 一般疑问句 例如:Is there a dictionary on the desk?(桌子上有一本字典吗?)四. 特殊疑问句 例如:How many dictionaries are there on the desk?(桌子上有几本字典?) What’s there on the desk?(桌子上有什么?) 五. 反意疑问句 例如:There is a dictionary on the desk, isn't there?(桌子上有一本字典,是吗?)
存在句的谓语动词和助动词连用: 例如:There have been many accidents in the past few weeks.(过去几个星期里发生了几个事故。) 存在句的数:在存在句中,只要紧靠“There be”的第一项不是复数,其谓语动词便可用单数形式。 一. 单数 例如:There was a dictionary, some pictures books and some magazines on the desk.(桌子上有一本字典,几本图画书,还有一本杂志。) 二. 复数 例如:There are two books on the desk.(桌子上有两本书。)
一、选择题 1.I share my room ______ a friend of _________. A.to, me B.with, mine C.with, me D.from, mine 2.I’m hungry. I want some _________. A.water B.bread C.toys D.homework 3.—Do _________ like going to ___________? —I don’t know. A.woman teachers, clothes shops B.women teachers, clothes shops C.woman teachers, sport shops D.women teachers, vegetables shops 4.---- _________ is it from Nanjing to Beijing? --- It’s less than three ___________ flight. A.How long, hour’s B.How far, hour’s C.How long, hours’D.How far, hours’ 5.People in western countries will get together to eat turkeys and celebrate harvest(丰收)on ________, just like our Mid-Autumn Day. A.Thanksgiving Day B.Christmas Day C.National Day 6.—Do you know Shanghai is one of _______ in the world? —Y es, it’s bigger than _______ city in China. A.the biggest city; any B.the biggest cities; any C.the biggest cities; any other D.the biggest cities; the other 7.—Why do you get up so early? —Because my home is far from the science museum. It’s ________bus r ide. A.fifty-minutes B.fifty minute’s C.fifty-minute’s D.fifty minutes’8.Some ________went to Japan to help when they knew that many ________ lost their homes in the earthquake. A.Germen; Japanese B.Frenchmen; Japaneses C.Germans; Japanese 9.Those _________ plans for the holiday sound great. How about ________? A.girl’s ; yours B.girls’; you C.girls ; your D.girls’; yours 10.There________some water in the bottle. A.is B.am C.are D.be 11.Peter would like a bowl of ________noodles. A.tomato and egg B.tomato and eggs C.tomatoes and eggs D.tomatoes and egg 12.________wild animals are disappearing because of the ________of their living areas. A.The number of; lost B.The number of; losing C.A number of; lose D.A number of; loss 13.—Let's ____________ some salad.
七年级外研版英语语法易错知识点归类 英语有很多很细小的知识点,而这些细小的知识点往往就是考点。同学们很容易由于注意不到而犯错误,下面就初一年级同学们比较容易犯错误的知识点做一个汇总。 [第一类] 名词类 1. 这些女老师们在干什么? [误] What are the woman teachers doing? [正] What are the women teachers doing? [析] 在英语中,当一名词作定语修饰另一名词(单或复数形式)时,作定语的名词一般要用其单数形式;但当man, woman作定语修饰可数名词复数形式时,要用其复数形式men, women. 2. 房间里有多少人? [误] How many peoples are there in the room? [正] How many people are there in the room? [析] people作“人、人们”解时,是个集合名词,其单复数同形。 3. 我想为我儿子买两瓶牛奶。
[误] I want to buy two bottle of milk for my son. [正] I want to buy two bottles of milk for my son. [析] 表示不可数名词的数量时,常用“a / an或数词+表量的可数名词+ of + 不可数名词”这一结构,其中当数词大于1时,表量的可数名词要用其复数形式。 [第二类] 动词类 4. 你妹妹通常什么时候去上学? [误] What time does your sister usually goes to school? [正] What time does your sister usually go to school? [析] 借助助动词do(或does)构成疑问句或否定句时,句中的谓语动词用其原形。 5. 琳达晚上经常做作业,但今晚她在看电视。 [误] Linda often do her homework in the evening, but this evening she watching TV. [正] Linda often does her homework in the evening, but this evening she is watching TV.
一、选择题 1.My sister and I like eating two _______ and some _______ for dinner. They are really delicious. A.salad; eggs B.salads; eggs C.salad; eggs D.salads; egg 2.________the________Mike’ s and Jack’s? A.Is, rooms B.Are, room C.Are, rooms D.Is, room 3.Is it a picture_________ your school? A.of B.to C.and D.with 4.There are two________ near our school. A.shoe shops B.shoes shops C.shoe's shops D.shoes' shops 5.—What does your mother have for dinner? — A.Chickens and tomato B.Chicken and tomatoes.C.Chicken and tomato.6.There________some water in the bottle. A.is B.am C.are D.be 7.—Kate, I will go to the Guangzhou Zoo next week, because I will have a ________ holiday —You mean you can have ________ off? Oh, that’s great! A.three-day; three days B.three- day; three days’ C.three days’; three-day D.three days; three days 8.—Tom likes soccer.What club can he join? —He can join the ______ club. A.sport B.music C.sports D.swimming 9.—What is your _______, Lingling? —I really enjoy reading _______ stories at night. A.interests; interesting B.interests; interest C.interest; interesting D.interesting; interest 10.—What can I do for you? —Err, I want a glass of milk, some bread and . A.some chickens B.any chicken C.some chicken 11._______mother usually cooks for_______ at the weekend. A.Lily and Nick; their B.Lily's and Nick's; them C.Lily and Nick's; their D.Lily and Nick's; them 12.—Do you think it is _______good advice? —Yes, it’s really _______useful suggestion. A.a; an B./; a C.a; a D./; an 13.—Could you please give me ____? —Certainly. A.some advices B.any advices
一、选择题 1.It's about ten __________ walk from here. A.minutes' B.minute's C.minutes D.minute of 2.________wild animals are disappearing because of the ________of their living areas. A.The number of; lost B.The number of; losing C.A number of; lose D.A number of; loss 3.— Do you know all the names in your class, Mr King? —No, only part of them. A.student B.students C.student’s D.students’ 4.Alan usually goes to Harbin in .He likes playing with snow. A.May B.July C.September D.November 5.---- _________ is it from Nanjing to Beijing? --- It’s less than three ___________ flight. A.How long, hour’s B.How far, hour’s C.How long, hours’D.How far, hours’ 6.—I hear your family have made up their ________ to India next month. Have a pleasant journey. —Thank you. A.mind travelling B.minds travelling C.mind to travel D.minds to travel 7.—There are beautiful flowers everywhere to celebrate the National Day, and we have —________ holiday. That means we have seven days ________ for this public holiday. A.a seven-day; off B.a seven-days; away C.seven-day; over D.a seven-days’; off 8.Look! The Chinese national basketball team ________ a face-to-face interview with their fans in the hall. How excited the fans are! A.is having B.are having C.have D.has 9.—It’s convenient(方便的) to travel from Suzhou to Shanghai by car? —Yes. It’s said that_________is enough. A.two hours drive B.two-hours drive C.two hour’s drive D.two hours’ drive 10.Thanks for the two _______________you gave(给)to me. A.tape player B.tapes players C.tape players D.taper players 11._____________ mother usually cooks for ___________ at the weekend. A.Lily’s and Nick’s; them B.Lily and Nick’s; them C.Lily and Nick’s; their D.Lily and Nick; their 12.________the________Mike’ s and Jack’s? A.Is, rooms B.Are, room C.Are, rooms D.Is, room
专题一名词 考点一名词的固定搭配 ①[2016·天津]The dictionary is out of date:many words have been added to the language since it was published. 这本词典过时了:自从它出版以来,这种语言已经增加了许多单词。 ②[2015·江苏]Some schools will have to make adjustments in agreement with the national soccer reform. 这些学校将不得不作出一些调整来和国家足球改革保持一致。 1.动词have,keep,take,make,get,pay,play,give,put等加名词构成的短语 have a good reputation有个好的名声 have an idea of了解 have a sense of有……意识 have a feeling of有……感觉 have access to可以获得 have an advantage over胜过,优于 keep a balance保持平衡 take...into account考虑…… take advantage of利用;趁……之机 make fun of取笑,嘲弄 make the best of充分利用;妥善处理 get/lose contact with与……取得/失去联系 get relief得到缓解 give a solution给出解决方案 put...into practice将……付诸行动 2.介词后加名词构成的短语 in great demand需求量很大 in quantity大量,大批 in progress在进行中
一、选择题 1.Boys and girls, don′t lose in watching TV too much because it is bad for your eyes. A.himself B.yourself C.themselves D.yourselves 2.一I like the story of The Maze Runner better than of Tire Hunger Came. 一I agree. The fights are more exciting than in The Hunger Game. A.that; those B.those; those C.that; that D.those; that 3.—Did you buy a large house? —No, not really, at least not as large as ______. A.yours B.your C.you 4.—Hi, Anna. Are these your sister’s pencils? —Oh, no. The y’re not ______. A.her B.him C.hers D.his 5.The government is making an effort to improve the life of elderly people, many of whom are suffering(遭受) from either loneiness or poor health, or even___________. A.neither B.none C.all D.both 6.— Is there anything to drink in the fridge? — No, there is _____ left. A.all B.both C.neither D.none 7.—When is your father’s birthday? —________ birthday is on April 2nd. A.He B.She C.His D.Him 8.----Where would you like to go tomorrow, Beijing or Xi'an? ---- is OK. It’s up to you. A.Either B.Neither C.Both D.All 9.—Shall we sit in the corner or by the window? —. I don’t mind. A.Both B.Neither C.No D.Either 10.Not ______that is faced can be changed, but nothing can be changed until it is faced. A.everything B.anything C.something D.nothing 11.My parents showed some old pictures that brought back sweet memories. A.I B.me C.my D.mine 12.—How many friends of ________ can come to celebrate your birthday? —________, I think. They’re all preparing for the new term. A.you, No one B.yours, None C.you, None 13.Winning or losing is only half the game, __________half is learning how to communicate with your teammates and learning from your mistakes. A.another B.other C.the other 14.Life is full of ups and downs, and without the downs, the ups will mean A.something B.everything C.anything D.nothing
一、选择题 1.— How _______ is it from Xi'an to Dunhuang? — It's less than 3 _______ flight. A.long; hour's B.far; hour's C.long; hours' D.far, hours' 2.I’m hungry. I want some _________. A.water B.bread C.toys D.homework 3.—I hear your family have made up their ________ to India next month. Have a pleasant journey. —Thank you. A.mind travelling B.minds travelling C.mind to travel D.minds to travel 4.This is Mary and that is Kate.______ my______. A.She's; friend B.They're; friends C.They're; friend 5.Look, this is________ bedroom. A.my father and mother’s B.my father’s and mother’s C.my father’s and mother D.my father and mother 6.Those _________ plans for the holiday sound great. How about ________? A.girl’s ; yours B.girls’; you C.girls ; your D.girls’; you rs 7.My mother often________when she was a young girl. A.keep diaries B.keep diary C.kept diaries D.kept diary 8.Do you know the three ______ under the tree? Their mothers are all ______in our school. A.boy students; woman teachers B.boy students; women teachers C.boys students; women teachers D.boys students; woman teachers 9.—What can I do for you? —Err, I want a glass of milk, some bread and . A.some chickens B.any chicken C.some chicken 10.The computer is _______________. A.Amy's and Lily's B.Amy and Lily C.Amy's and Lily D.Amy and Lily's 11.—Could you please give me ____? —Certainly. A.some advices B.any advices C.some advice D.advices 12.Alan usually goes to Harbin in .He likes playing with snow. A.May B.July C.September D.November 13.—Let's ____________ some salad. —Sorry, I don't like ____________ . A.have; them B.to have; it C.have; it D.to have; them 14.—These days, more and more kids have problems with their sight. — They should do eye________and take________every day.
名词(一) 一、名词的概念:在我们身边存在着形形色色的人和事物,它们都有自己的称呼,我们用来称呼它们的词就是名词,概括来说表示人、事物、地方、现象等的名称的词都叫名词。 二、名词的分类: 1.专有名词:它的第一个字母通常大写。 a. 人名、地名、国名等例如:Lucy, Shanghai, China b.组织、团体、机构等例如: the United Nations c.语言、星期、月份等例如:English, Friday, March (注意介词in/on/at的用法) 注意:国家与人的对应 China----- Chinese America---- American(s) Australia---- Australian(s) Canada---- Canadian(s) Japan---- Japanese Germany---- German(s) France----Frenchman(Frenchmen) GB----Englishman(Englishmen) 2.普通名词: (1)不可数名词:不可以直接以数字计算的名词。例如:snow, air, water, rice, paper, work, news(新闻),food, rain, weather, juice, milk, meat, money ,English, fruit , information … 不可数名词要表示具体数量,必须借助of短语。如不能说one bread,但是可以说one piece of bread和two pieces of bread。 只能用来修饰不可数名词的表示数量的一些词或短语: little很少的(表示否定);a little一些(表示肯定),much(许多),how much (多少),a bit of(一些) 既能用来修饰可数名词又能用来修饰不可数名词的表示数量的一些词或短语:some(一些,用于肯定句), any(一些,用于否定和疑问句)a lot of (许多), lots of(许多) ★不可数名词量的表示方法:计量词+of 例如:a piece of news a cup of tea a piece of bread two pieces of news two cups of tea two pieces of bread 注意:a bag of apples
一、选择题 1.Karen and Helen _______ my brother's friends. I know _______. A.is; her B.are; them C.are; her D.is; them 2.Kay looked _________ at the guests who said that the food she cooked tasted _________. A.happily; wonderfully B.happily; wonderful C.happy; wonderful D.happy; wonderfully 3.I don’t have a baseball, but Alan A.do B.does C.have D.has 4.—Listen! I can hear someone __________ for help. —Is there __________? A.calling; anything wrong B.call; anything wrong C.calling; wrong anything D.call; wrong anything 5.Our school basketball team ________ in the final of the basketball competition. Another team from No.5 Middle School ________ doing very well too. A.is; isn’t B.are; aren’t C.is; are D.are; is 6.—Why ______ you so busy these days? —Because they arrived ______ London ______ the morning of July1. A.are; in , in B.are; in , on C.do; on , in D.do; at , on 7.A number of visitors ________visiting our school. The number of them________ about 180. A.is;are B.are; is C.is; is D.are; are 8.—William, your hat _______ nice. —Thanks. A.buys B.looks C.finds 9.This is a photo of my grandpa. He young A.looks B.feels C.sounds D.hears 10.Lily and Lucy _______ their mother. They have big eyes and yellow hair. A.like both B.both are like C.both like D.are both like 11.—He’s never been late for school. —________________. A.So have I B.So am I C.Neither have I D.Nor am I 12.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister. A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cry C.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry 13.This my sister and those my brothers. A.is, is B.are, are C.is, are 14.— Tom in the library? —Yes,and his friends Eric and Dale in the library,too. A.Is;are B.Is;is C.Are;is
一、选择题 1.— Is this room yours? —No, it's not__________.It's __________. A.mine; Lily's and Lucy's B.my; Lily and Lucy's C.my; theirs D.mine; Sally's 2.________wild animals are disappearing because of the ________of their living areas. A.The number of; lost B.The number of; losing C.A number of; lose D.A number of; loss 3.-Can I help you? -Yes. I'd like__________ rice. A.a small bar of B.a slice of C.a large bag of D.a piece of 4.With the ________ of society, our environment is becoming worse and worse. So we should do what we can ________ our environment. A.development; to protect B.developing; to protect C.development; protect D.develop; protect 5.People in western countries will get together to eat turkeys and celebrate harvest(丰收)on ________, just like our Mid-Autumn Day. A.Thanksgiving Day B.Christmas Day C.National Day 6.—There are beautiful flowers everywhere to celebrate the National Day, and we have —________ holiday. That means we have seven days ________ for this public holiday. A.a seven-day; off B.a seven-days; away C.seven-day; over D.a seven-days’; off 7.Look, this is________ bedroom. A.my father and mother’s B.my father’s and mother’s C.my father’s and mother D.my father and mother 8.Those _________ plans for the holiday sound great. How about ________? A.girl’s ; yours B.girls’; you C.girls ; your D.girls’; yours 9.My mother often________when she was a young girl. A.keep diaries B.keep diary C.kept diaries D.kept diary 10.—Kate, I will go to the Guangzhou Zoo next week, because I will have a ________ holiday —You mean you can have ________ off? Oh, that’s great! A.three-day; three days B.three- day; three days’ C.three days’; three-day D.three days; three days 11.—Look.There’re lots of______here. —Great.We can make______soup. A.egg;egg B.eggs;egg C.egg;eggs D.eggs;eggs 12.—Do you think it is _______good advice?
一、 名词的分类 普通名词 可数名词 当不可数名词转化为可数名词时,词义常发生变化。 集体名词 专有名词 不可数名词 物质名词 抽象名词 二、 名词的性 1. 在英语中,大多数名词没有性的区别,只有一个共同的形式。部分名词具有性别差异,存在阴性和阳性两种不同的形式。 2. 在具有性别差异的名词中,有些名词在词尾直接加“-ess ”即可构成阴性名词(多数);有些名词在词尾直接加“-ette ”即可构成阴性名词(少数);有些名词以“-ter ”或“-tor ”结尾,须将结尾改为“-tress ”以构成阴性名词;有些名词以“-rer ”或“-ror ”结尾,须将结尾改为“-ress ”以构成阴性名词;有些名词以“-der ”结尾,须将结尾改为“-dress ”以构成阴性名词。(①“-ter ”/“-tor ”→“-tress ”;②“-rer ”/“-ror ”→“-ress ”;③“-der ”→“-dress ”。注:少数情况下存在例外) 3. 在现代英语中,对于无性别区分的名词,一般可通过在该词前加 he/she, male/female, man/woman, boy/girl, lord/lady, dog/bitch, bull/cow, jack/jenny, tom/tally, cock/hen, duck/doe, billy/nanny, father/mother, son/daughter 等词来区分性别。(强调尊敬时,可用 lady 表示女性,但只能用单数形式。) 4. 某些外来语中的名词在变为阴性名词时,须接固定的后缀。(Ref.P324<7>) 5. 惯用阳性的名词和惯用阴性的名词: 1) 阳性词:general, lawyer, fellow, lover, soldier, sailor 等 2) 阴性词:nurse, typist, dressmaker, housekeeper 等 3) 拟人化的阳性词:Time, Mountain, Wind, War, the Ocean, Storm, Thunder, Sleep, Winter, Summer, Autumn, Despair, Fear 等(代词用 he ) 4) 拟人化的阴性词:Moon, Spring, Night, Nature, Peace, Hope, Virtue, Truth, the Earth, Liberty, Justice, Fame, Victory, Faith, Humility, Pride, Mercy, Art, Science, Soul 等(代词用 she ) 5) 通常情况下,船、火车、国家、都市均视为阴性名词。 6. man 可以包括 woman ,统指一切人,代词用 he/his 。 三、 名词的数 1. 专有名词的复数形式 1) 有些专有名词变为复数时,仅在词尾加“-s ”即可。 Kansas City → Kansas Citys Mayor Brown → Mayor Browns the two Mr. Smiths, Lord Mayors, Queen Elizabeths (例外:Rockey → Rockies, Sicily → Sicilies )
七年级英语语法易错知识点分类例析 英语有很多很细小的知识点,而这些细小的知识点往往就是考点。同学们很容易由于注意不到而犯错误,下面就初一年级同学们比较容易犯错误的知识点做一个汇总。 [第一类] 名词类 1. 这些女老师们在干什么? [误] What are the woman teachers doing?[正] What are the women teachers doing? [析] 在英语中,当一名词作定语修饰另一名词(单或复数形式)时,作定语的名词一般要用其单数形式;但当man, woman作定语修饰可数名词复数形式时,要用其复数形式men, women. 2. 房间里有多少人? [误] How many peoples are there in the room? [正] How many people are there in the room? [析] people作“人、人们”解时,是个集合名词,其单复数同形。 3. 我想为我儿子买两瓶牛奶。 [误] I want to buy two bottle of milk for my son. [正] I want to buy two bottles of milk for my son. [析] 表示不可数名词的数量时,常用“a / an或数词+表量的可数名词+ of + 不可数名词”这一结构,其中当数词大于1时,表量的可数名词要用其复数形式 [第二类] 动词类 4. 你妹妹通常什么时候去上学? [误] What time does your sister usually goes to school? [正] What time does your sister usually go to school? [析] 借助助动词do(或does)构成疑问句或否定句时,句中的谓语动词用其原形。 5. 琳达晚上经常做作业,但今晚她在看电视。 [误] Linda often do her homework in the evening, but this evening she watching TV. [正] Linda often does her homework in the evening, but this evening she is watching TV.