专四语法词汇总结
- 格式:doc
- 大小:186.50 KB
- 文档页数:32

专四必备语法一、时态、语态时态、语态需要掌握的要点:1.表达将来时的形式:(1)在时间、条件、让步从句中,一般现在时代替将来时,但要注意区别从句的类型,如:I'll tell him when you will ring again。
我告诉他你什么时候再来电话。
(宾语从句)比较:I’ll tell him when you ring again。
你再打电话时我告诉他。
(状语从句)(2)在make sure,make certain, see (to it) 后的that从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时代替将来时,如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn't know the answer to last time。
(include 不能用will include或其他形式)2.完成时是时态测试的重点,注意与完成时连用的句型和时间状语:(1)by/between/up to/till +过去时间、since、by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,主句用过去完成时。
如:We had just had our breakfast when an old man came to the door。
Between 1897 and 1919 at least 29 motion pictures in which artificial beings were portrayed had been produced.(表示1919年时已发生的情况)(2)by +将来时间、by the time/ when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,主句用将来完成时.如:By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed in Europe for two weeks.I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back next year.(3)by now、since +过去时间、in/during/for/over/the past/last few(或具体数字)years/days/months,主句用现在完成时, 但在it is +具体时间since/before这一句型中,主句更多的时候不用完成时。

英语专业四级语法、词汇知识1.语法考题的涉及面宽,近年考题曾经考到:几乎所有词类;三种动词的非谓语形式;各种从句及关系词的用法;动词时态、虚拟语气、情态动词的用法;独立主格,主谓一致,倒装,强调、并列结构等基本语法知识。
2.语法考试的重点突出,语法考试的重点为内容庞杂较难掌握的项目,这些项目还反复出现,如:虚拟语气,状语从句,定语从句,独立主格,情态动词。
3.具体考查重点为以上项目中的特殊用法,不常用的情况1)虚拟语气的考点为: would rather+that从句+一般过去时:It is vital/necessary/important / urgent / imperative/desirable/advisable/natural/essential+that+动词原形; It is time/about time/high time+that+一般过去时:proposal/suggestion+that +动词原形; lest + that +should +动词原形; if only+that+would+动词原形。
2)状语从句的考点为:非if引导的条件状语从句,此类句子多用at times ,provided ,so long as, in case , once 等来替代 if ;由 even if/so,now that,for all等引导的让步状语从句;just /hardly...when引导的时间状语从句;more than,as...as,not so muchas,the same as,as much as 等引导的比较状语从句。
3)独立主格结构多以逻辑主语+分词的形式出现。
4)情态动词多与完成时形式连用。
5)定语从句重点考查介词+关系代词(which )和 as 作为关系代词。
专业四级考试的词汇部分要求考生能灵活正确运用教学大纲语法结构表一至四级的全部内容,熟练掌握教学大纲词汇表中一至四级规定的 5000— 6000 个认知词汇及其最基本的搭配。

英语专四语法术语(中英对照)英语专四语法术语名词:noun个体名词:individual noun 集体名词: collective noun物质名词:material noun抽象名词: abstract noun可数名词:countable noun 不可数名词:uncountable noun动词:verb动态动词:dynamic verb静态动词:stative verb情态动词:modal verb助动词:auxiliary非谓语动词:non-finite verbs(分词,participle; 不定式, infinitive; 动名词,gerund) 数词:numeral代词:pronoun人称代词:personal pronoun 物主代词:possessive pronoun 反身代词:reflexive pronoun 指示代词:demonstrative pronoun 关系代词:relative pronoun不定代词:indefinitepronoun形容词:adjective副词:adverb冠词:article连词:conjunction介词:preposition感叹词:interjection限定词:determiner短语:phrase不定式短语:infinitive phrase动名词短语:gerundial phrase分词短语:participial phrase 主语:subject谓语:predicate主谓一致:subject-verb agreement宾语:object补语:complement定语:attribute状语:adverbial同位语:appositive主语从句:subject clause表语从句:predicative clause 宾语从句:object clause定语从句:attributive clause 先行词:antecedent限制性定语从句:restrictive attributive clause非限制性定语从句:non-restrictive attributive clause状语从句:adverbial clause 陈述句:Declarative sentence 疑问句:interrogative sentence祈使句:imperative sentence 感叹句:exclamatorysentence时态(各种时态) tense语态:voice主动语态:active voice被动语态:passive voice虚拟语气:subjunctive mood 反义疑问句:tag question倒装:inversion部分倒装:partial inversion 省略:ellipsis。

专四常考语法点
英语专业四级考试常考的语法点包括:
1.虚拟语气:虚拟语气是英语语法中的一个重要部分,包括条件句、
虚拟语气的使用等。
2.时态和语态:英语中的时态和语态是非常重要的,包括现在时态、
过去时态、将来时态等。
3.非谓语动词:非谓语动词包括不定式、动名词和分词,是英语语
法中的一个难点。
4.从句:从句包括定语从句、状语从句和名词性从句等,是英语语
法中的一个重要部分。
5.倒装句:倒装句是英语语法中的一种特殊句型,包括完全倒装和
部分倒装等。
6.主谓一致:主谓一致是指句子中的谓语动词和主语在人称和数上
保持一致。
7.比较级和最高级:比较级和最高级是英语语法中的一个重要部分,
包括形容词和副词的比较级和最高级等。
这些语法点是英语专业四级考试中经常出现的,考生需要熟练掌握这些语法知识,才能在考试中取得好成绩。

英语专业四级语法、词汇知识1.语法考题的涉及面宽,近年考题曾经考到:几乎所有词类;三种动词的非谓语形式;各种从句及关系词的用法;动词时态、虚拟语气、情态动词的用法;独立主格,主谓一致,倒装,强调、并列结构等基本语法知识。
2.语法考试的重点突出,语法考试的重点为内容庞杂较难掌握的项目,这些项目还反复出现,如:虚拟语气,状语从句,定语从句,独立主格,情态动词。
3.具体考查重点为以上项目中的特殊用法,不常用的情况1)虚拟语气的考点为:would rather+that从句+一般过去时:It is vital/necessary/important /urgent/imperative/desirable/advisable/natural/essential+that+动词原形;It is time/about time/high time+that+一般过去时:proposal/suggestion+that+动词原形;lest+that+should+动词原形;if only+that+would+动词原形。
2)状语从句的考点为:非if引导的条件状语从句,此类句子多用at times,provided,so long as,in case,once等来替代if;由even if/so,now that,for all等引导的让步状语从句;just/hardly...when引导的时间状语从句;more than,as...as,not so much as,the same as,as muchas等引导的比较状语从句。
3)独立主格结构多以逻辑主语+分词的形式出现。
4)情态动词多与完成时形式连用。
5)定语从句重点考查介词+关系代词(which)和as作为关系代词。
专业四级考试的词汇部分要求考生能灵活正确运用教学大纲语法结构表一至四级的全部内容,熟练掌握教学大纲词汇表中一至四级规定的5000—6000个认知词汇及其最基本的搭配。

专四词汇全面总结大全对于英语专业的学生来说,通过专业四级考试(TEM4)是一项重要的任务。
而词汇量的积累在备考过程中起着至关重要的作用。
下面为大家带来一份专四词汇的全面总结。
首先,我们来谈谈名词。
名词是英语词汇中最基本的一类。
像“abundance”(丰富;充裕)、“access”(通道;机会)、“accommodation”(住处;膳宿)等,都是常见且重要的名词。
在记忆名词时,不仅要记住其词义,还要注意其单复数形式以及与其他词的搭配。
动词也是不可忽视的一部分。
“acquire”(获得;取得)、“adapt”(适应;改编)、“adjust”(调整;校准)等动词在句子中往往起着关键的作用。
对于动词,需要了解其不同的时态、语态以及固定搭配。
形容词能够使描述更加生动和准确。
“adequate”(足够的;适当的)、“admirable”(令人钦佩的;值得赞扬的)、“advantageous”(有利的;有益的)等形容词在写作和翻译中经常用到。
副词可以修饰动词、形容词和其他副词,增强语言的表达效果。
例如“abruptly”(突然地;意外地)、“absolutely”(绝对地;完全地)、“accurately”(准确地;精确地)。
接下来是一些容易混淆的词汇。
比如“adapt”和“adopt”,“adapt”是“适应;改编”的意思,而“adopt”则是“采用;收养”。
“affect”和“effect”,“affect”是动词,意为“影响”;“effect”是名词,意为“效果;影响”。
再说说一些高频词汇。
“accompany”(陪伴;伴随)、“accumulate”(积累;积聚)、“accurate”(精确的;准确的)等,在阅读理解、听力和写作中出现的频率都很高。
记忆词汇的方法也有很多种。
可以通过制作单词卡片,将单词、词义和例句写在上面,随时拿出来复习。
也可以通过阅读英语文章,在语境中理解和记忆单词。
还可以利用一些记忆软件,根据遗忘曲线来安排复习。

专业四级语法重点有哪些对于英语专业的学生来说,专业四级考试是一个重要的关卡。
而语法作为英语学习的基础和关键,在考试中占据着相当重要的地位。
那么,专业四级语法的重点究竟有哪些呢?首先,时态和语态是必不可少的重点。
时态包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、将来进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、将来完成时以及过去将来时等。
每一种时态都有其特定的用法和时间标志词。
比如,现在完成时常常与“since”、“for”等词连用,表示从过去某一时间点开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
而过去完成时则强调“过去的过去”,在使用时需要有一个明确的过去时间作为参照。
语态方面,主要有主动语态和被动语态。
被动语态的构成是“be +过去分词”,在理解和运用时需要注意不同时态下被动语态的形式变化。
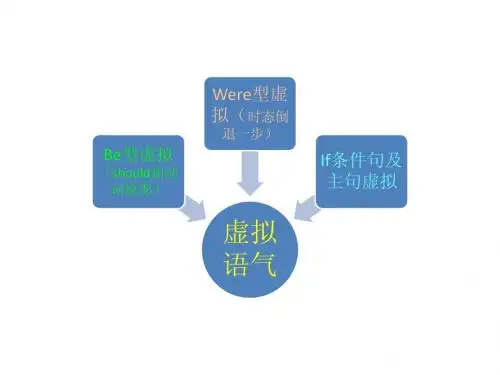
其次,虚拟语气也是一个重要的语法点。
虚拟语气用于表示假设、愿望、建议等与事实不符或不太可能发生的情况。
它分为三种情况:与现在事实相反、与过去事实相反以及与将来事实相反。
每种情况的虚拟语气形式都有所不同。
例如,与现在事实相反的虚拟语气,主句用“would / could / should / might +动词原形”,从句用“一般过去时(be 动词用 were)”。
再者,非谓语动词也是经常考查的内容。
非谓语动词包括动词不定式、动名词和分词(现在分词和过去分词)。
动词不定式可以作主语、宾语、定语、状语等;动名词具有名词的性质,可以作主语、宾语等;分词可以作定语、状语、补语等。
在使用非谓语动词时,需要根据句子的结构和语境来判断其具体的用法。
从句也是专业四级语法的重点之一。
定语从句用于修饰名词或代词,关系代词和关系副词的选择是关键;状语从句包括时间状语从句、条件状语从句、原因状语从句、结果状语从句等,需要掌握不同状语从句的引导词及其用法;名词性从句包括主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句,要清楚其在句子中的作用和构成方式。

专四必备语法一、时态、语态时态、语态需要掌握的要点:1.表达将来时的形式:(1)在时间、条件、让步从句中,一般现在时代替将来时,但要注意区别从句的类型,如:I ll tell him whe n you will ring aga in.我告诉他你什么时候再来电话。
(宾语从句)比较:I 'll tell him whe n you ring agai你再打电话时我告诉他。
(状语从句)(2)在make sure, make certain, see (to it)后的that 从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时代替将来时,如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn ' t know t answer to last time.(include 不能用will include 或其他形式)2.完成时是时态测试的重点,注意与完成时连用的句型和时间状语:(1)by/between/up to/till +过去时间、since、by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,主句用过去完成时。
女口:We had just had our breakfast when an old man came to the door.Between 1897 and 1919 at least 29 motion pictures in which artificial beings were portrayed had been produced.(表示1919年时已发生的情况)(2)by +将来时间、by the time/ when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,主句用将来完成时。
如:By the time you arrive in London, we will have stayed in Europe for two weeks.I hope her health will have improved greatly by the time we come back nextyear.(3)by now、since +过去时间、in/during/for/over/the past/last few(或具体数字)years/days/months主句用现在完成时,但在it is +具体时间since/before这一句型中,主句更多的时候不用完成时。

英语专四必考语法知识点总结如今,TEM4日益受到人们的关注与重视,其重要性不言而喻,本论文主要以近几年英语专业四级试题为例,针对词汇和语法两个方面,结合理论和实践对试卷命题进行分析,从而为教师教学及学生答题总结一些有效的方法。
英语专四必考知识点总结集体名词作主语主谓一致1)通常作复数的集体名词? 集体名词,如:police, people, cattle, militia, poultry等,通常作复数,用复数动词。
如:?Dome ...集体名词作主语主谓一致1)通常作复数的集体名词?集体名词,如:police, people, cattle, militia, poultry等,通常作复数,用复数动词。
如:?Domestic cattle provide us with milk, beef and hides.?2)通常作不可数名词的集体名词?有些集体名词,如foliage, machinery, equipment, furniture, merchandise,通常作不可数名词,随后的动词用单数。
例如:All the machinery in the factory is made in China.?3)既可作单数也可作复数的集体名词?集体名词,如audience, committee, class, crew, family, public, government等,既可作单数,也可作复数用。
?The city council is meeting to set its agenda.?4) a committee, etc. of +复数名词?如果主语是由a committee of /a panel of /a board of +复数名词构成,随后的动词通常用单数。
例如:?A committee of five men and three women is to consider the matter.?近义词辨析tired, exhausted, fatigued, weary, worn-out这组词均含有疲惫的的意思。
专四语法词汇总结 第 1 页 共 32 页 了解TEM4考试要求 专四作为全国各大专院校英语专业学生的水平测试,其测试要求与硕士研究生招生英语考试截然不同。前者属于水平性测试,意在考察考生是否达到高校英语专业教学大纲规定水平,这个水平包括听力理解、阅读理解、词汇语法、写作等等方面,在考纲和教学大纲中都有明确要求。而后者属于选拔性测试,意在为高校挑选一批具备一定研究能力和潜质的本科毕业生或相同学力人员。难怪在现实中经常出现这样一种“悖论”,专四优秀甚至是专八合格的英语专业学生并不一定能在考验公共英语测试轻而易举地拿到好成绩,更曾出现过不及格的情况。其实对此不必讶异,了解到考试的不同之处我们就能明白,专四需要的是考生夯实基本语言技能,在听、说、读、写、译等方面达到教学大纲要求,如此则能顺利通过水平性测试。因此对于通过考试,广大考生一定要充满信心。
强化词汇语法能力 高等学校英语专业教学大纲规定专四水平学生应认知词汇5,500-6,500个,正确而熟练地运用其中的3,000-4,000个及其最基本的搭配。词汇学习是英语学习的基石。对于英语专业学生而言这个要求自然会更高一些,故而在考试的词汇和语法部分出现超纲词汇也是理所应当。无论是单纯为了应付考试还是提高英语能力,我们的词汇学习都必须和语法联系在一起,达到通过词汇强化语法意识,通过语法熟练运用词汇的目的。我国著名英语教育专家张道真教授在其著作中也一再叮嘱英语学习者要把语法和词法结合在一起,其指导意义不言而喻。
日常词汇学习过程中首先要注意同义词的积累和辨析。同义词越多写作和翻译起来就会愈发得心应手,当然背得也更熟。举几个例子。“笑”一个词在英文中有laugh, smile, giggle, chuckle, chortle, guffaw等等,不一而足;“擦”这一个动词则有rub、 strike 、scratch、 wipe 、mop 、dry 、polish 、scrub、 oil 、clean等等一些。类似的情况当词汇量增长到6000左右时将会非常频繁。若一一背诵则不仅痛苦异常而且效率低下。若用中文含义接近这一点把它们串在一起构成词汇网络那么背词的效果将会显著提高。
在记住这些同义词之后就要通过查阅参考书或者日常阅读来辨明其区别,方便口头和笔头使用,使语言更加地道。比如“擦”这一组词,说擦地板常用mop the floor,擦火柴用strike a match, 擦眼泪是wipe one’s tears,等等。如果做了这样细致的比较工作,那么经过一段时间之后我们的语言运用将会更加纯熟,作对几道单选题就更不在话下了。 积累阅读量 要想在完形和阅读考试里面取得高分没有一定的阅读量积累是不可能完成的。专四的阅读考察重在阅读速度理解能力,要求考生在规定时间内读懂难度相当于Newsweek的新闻类或者Sons and Lovers的文学原著。不难理解平常如果只知死读精读课本,没有阅读大量鲜活的日常百科文章,或者没有养成定期阅读英文报刊文章(以及网络)的习惯训练良好的语感,那么在理解准确度和速度两个方面面对考试都会是望洋兴叹。 英语学习中的阅读应以精读和泛读相结合的方式进行。这也符合我们第二语言习得中所谓的输入—输出规律的要求。精读基本体现的是输入过程——大量密集语言养料的吸收、分析和记诵,还有语感的培养。在泛读中我们必须动用所有掌握的语法和词汇知识来迅速了解文章大意,知晓作者观点,或者根据要求有目的地提取出有用信息。这个输出过程在无形当中强化了语感意识提高了对各种篇章类型的熟悉程度,从而最终达到准确度和速度双丰收的目的。 如果在身边查阅英文报刊比较困难,大家可以上网浏览。英文各大门户网站都有新闻报导和深度报导。当然也可以通过Google in English直接查阅一天热点资讯,确实非常方便!和10年前比起来大家现在学习英语的渠道更多了,更丰富了,资料更新颖了,在全球化时代学习英语更是有得天独厚的优势。提醒大家注意的是,对国外网站的信息大家要学会批判性吸收,不可不假思索尽信无疑,对其中的失实报导要保持警惕。 专四语法词汇总结 第 2 页 共 32 页 问题一:请问专四考试要求的词汇量是多少?与大学英语六级相比,哪个考试词汇量要求更大? 高等学校英语专业教学大纲规定专四水平学生应认知词汇5,500~6,500个,正确而熟练地运用其中的3,000~4,000个及其最基本的搭配。而考生们比较熟悉的大学英语六级考试要求5,500个单词。从考纲规定来说,专四的词汇量比六级更大,而且专四对词汇搭配、词义辨析考查得更加细化和专业;由于新六级考试已经取消了词汇语法题,因此在词汇用法的掌握方面要求明显低于专四。 问题二:专四的词汇语法题和完形填空题包含哪些题型和考点?又该如何复习? 无论是词汇语法还是完形填空,主要包含以下六大题型,每一种题型的考点各具特色: 1.近义词辨析题 表示“真实的”的形容词可以有true, genuine, real等,不一而足,但含义上彼此有差异,用法也不尽相同,比如true强调“符合真理的,正确的”,genuine强调“非人造的,货真价实的”,real则强调“事件的真实性”,可理解为“显示的,并非虚假的”。此时就要注意结合考题的上下文,选择符合要求的词汇。 2.词根词缀辨析题 英语单词的构成可包含三个成分:前缀(prefix)+词根 (root)+后缀(suffix)。下面我们以respectable(体面的,高尚的,值得尊敬的)这个词为例:“re-”是前缀,表示“重复做某动作”;“spect”是词根,意思是一个动作——“看”;而“-able”是后缀,它首先揭示了该单词的词性是形容词,另外,这个形容词后缀的意思是“能够……的,值得……的”。而英语中,很多单词含有相同的词根,即含义上有一定的联系性,此时就比较难判断词义用法。如respectable的同根词有 respectful (态度恭敬的)和respective (各自的)。这三个单词的词根都是“spect”,拼写也有些相似,但词义相去甚远。平时复习时,考生应当重点积累这类含有相同词根的词汇,并且背单词时要学会掌握常见词根、前缀、后缀的含义,从而在解题时才可以运用构词法知识来判断词语含义。 3.动词词组题 动词词组永远是考试的重点,尤其要注意同一个动词与不同介词组合,可结合成含义不同的词组,以动词give为例:“give out”表示“分发物品”;“give off”表示“散发出光芒或气味”;“give up”表示“放弃”;“give in”表示“屈服,投降,让步”。考题中常给出一个动词,而后面用什么介词与之搭配,则需要考生在选项中选词填空。因此,考生在背单词时,需要专门花时间积累“动词+介词”词组。 4.从句引导词题 英语的从句包括主语从句、表语从句、状语从句、定语从句、同位语从句、宾语从句等。根据从句部分在句子里不同的表情达意作用,又可细分为更多类型,如状语从句包含表示原因的原因状语从句、表示时间概念的时间状语从句、表示假设的条件状语从句;根据从句语义的重要性和语气的强弱又可进一步细分,比如定语从句可细分为限定性定语从句(此时从句含义与主句紧密相关)以及非限定性定语从句(此时从句含义与主句联系不紧密,仅起到补充说明作用)。综上所述,各种从句都有各自常用的引导词,如限定性定语从句常用that引导,非限定性定语从句常用which引导,条件状语从句常用if引导,主语从句常用what引导等。考生应该根据上述从句分类,搞清常用的引导词的用法。 5.逻辑连词题 这类题目通常在选项中出现表示不同逻辑关系的连词,如表示转折关系的but,表示递进关系的then,表示并列关系的and和or,表示因果关系的 because, since, therefore等。此类题目要求考生理解上下文的逻辑关系,再选择符合要求的连词。平时复习时考生要把上述常考的逻辑关系词反复熟悉并练习使用。 6.形近词辨析题 这类题目指在选项中故意安插拼写形式相近、具有混淆功能的单词,让考生辨别。如virtual专四语法词汇总结 第 3 页 共 32 页 与visual,前者表示“实质上的”,后者表示“视觉的”。对于这类题目考生只有具备扎实的词汇背记基本功,才能做到对单词的拼写形式有清晰的判断力。 问题三:能否推荐几种高效的背单词方法?每一种背单词方法适用于哪一种考试题型? 众所周知,捧着词汇手册死记硬背绝不是积累词汇的好方法。当然,也不能迷信所谓“一天背出500个词汇”的不切实际的方法。良好的词汇积累,应建立在英语构词法基础上,结合词组扩展、近义词对比及适当联想来强化记忆,从而编织出由点及面的知识网。现向各位专四考生推荐以下四大背单词方法。 1.词根词缀法 英语词根词缀的概念之前已经介绍过,这些构词成分往往都带有鲜明的含义特色,而很多英语单词就是各个词根词缀的排列组合。如果能够熟练了解词根词缀的含义,那么当考生看到时此类生词时就能马上推测出其含义了,比如respect这个词,“re-”前缀表示“重复做某事,再一次做某事”,“spect”则表示“看”,可由此想到:反复看某人或某事,表示心存尊敬,因此可轻松记住的单词含义。再比如前文所举例的 respectful和respectable这两个词,很多考生总记不清两者的含义区分,因为都是由同一个动词respect派生出来的形容词。此时,应抓住两者唯一的不同——后缀的区别来进行突破。“-able”后缀表示“值得……的”,所以respectable用以形容人或事物“值得尊敬的”;而 “-ful”后缀表示“充满……的”,因此respectful是形容一个人对待他人或事物的态度“充满尊敬的,恭敬的”。词根词缀法不仅是词汇记忆体系的基石,更能帮助考生有效应对词义辨析题目。 适用题型:词根词缀辨析题及其他所有词汇题 2.词组拓展法 此方法指背单词时,不能只背孤立的个别单词,而是要把与之相关联的搭配用法和词组一网打尽,从而使自己的词汇量在短期内成倍数增长。如 accordance (符合,依照),考生不应仅仅满足于把单词的拼写和中文意思记住,考试中真正常考的是词组 “in accordance with sth.”,只有记住了单词的用法,才能在考试中解答出题目。另外,也要特别关注一些看似简单的动词,如 give, take与不同介词搭配的词组。 适用题型:动词词组题 3.近义词串联法 每背一个单词或词组,就同时熟悉与之含义用法有类似的词汇,也是迅速而有效的背词法。如前面所提到的词组 “in accordance with sth.”, 与另一个词组“be in line with sth.”含义接近,都表示“符合,依照”,因此可把含义相似的词组串联在一起同时记。而如果同义词之间含义用法有细微差别,尤其要注意辨清。 适用题型:近义词辨析题 4.联想记忆法 此方法指结合单词拼写特征或者在发音上与汉语的谐音效果来辅助记忆,如strong这个单词,发音非常接近汉语“死壮”,且单词本身确实表示“强壮”之意,因此可巧妙地联想到中文来记忆。另外,对于一些拼写非常接近的词汇,尤其要利用联想来加以区分,比如:stationary是形容词,表示“静止不动的”;stationery是名词,表示“文具”。这两个单词发音完全相同,拼写仅在黑体字部分有一字母之差,确实很难记忆。此时可抓住唯一有区别的黑体字部分展开联想——由stationery中的字母e联想到时下文案工作最常用的email,因此可记住含有e的stationery是“文具”之意,而另一个同音词stationary就表示“静止不动的”。 适用题型:形近词辨析题