MTI英汉对照_各种主义的翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:27.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

哲学术语英汉对照-CAL-FENGHAI.-(YICAI)-Company One1a prioria posteriori distinction 先验-后验的区分 abstract ideas 抽象理念abstract objects 抽象客体ad hominem argument 谬误论证 alienation/estrangement 异化,疏离altruism 利他主义analysis 分析analyticsynthetic distinction 分析-综合的区分aporia 困惑argument from design 来自设计的论证artificial intelligence (AI) 人工智能association of ideas 理念的联想autonomy 自律axioms 公理Categorical Imperative 绝对命令categories 范畴Category mistake 范畴错误causal theory of reference 指称的因果论causation 因果关系certainty 确定性chaos theory 混沌理论class 总纲、类clearness and distinctness 清楚与明晰cogito ergo sum 我思故我在concept 概念consciousness 意识consent 同意consequentialism 效果论conservative 保守的consistency 一致性,相容性constructivism 建构主义contents of consciousness 意识的内容 contingentnecessary distinction 偶然-必然的区分 continuum 连续体continuum hypothesis 连续性假说contradiction 矛盾(律)conventionalism 约定论counterfactual conditional 反事实的条件句criterion 准则,标准critique 批判,批评Dasein 此在,定在deconstruction 解构主义defeasible 可以废除的definite description 限定摹状词deontology 义务论dialectic 辩证法didactic 说教的dualism 二元论egoism 自我主义、利己主义eliminative materialism 消除性的唯物主义empiricism 经验主义Enlightenment 启蒙运动(思想)entailment 蕴含essence 本质ethical intuition 伦理直观ethical naturalism 伦理的自然主义eudaimonia 幸福主义event 事件、事变evolutionary epistemology 进化认识论expert system 专门体系explanation 解释fallibilism 谬误论family resemblance 家族相似fictional entities 虚构的实体first philosophy 第一哲学form of life 生活形式formal 形式的foundationalism 基础主义free will and determinism 自由意志和决定论function 函项(功能)function explanation 功能解释good 善happiness 幸福hedonism 享乐主义hermeneutics 解释学(诠释学,释义学)historicism 历史论(历史主义)holism 整体论iconographic 绘画idealism 理念论ideas 理念identity 同一性illocutionary act 以言行事的行为imagination 想象力immaterical substance 非物质实体immutable 不变的、永恒的individualism 个人主义(个体主义)induction 归纳inference 推断infinite regress 无限回归intensionality 内涵性intentionality 意向性irreducible 不可还原的Leibnizs Law 莱布尼茨法则logical atomism 逻辑原子主义logical positivism 逻辑实证主义logomachy 玩弄词藻的争论material biconditional 物质的双向制约materialism 唯物论(唯物主义)maxim 箴言,格言method 方法methodologica 方法论的model 样式modern 现代的modus ponens and modus tollens 肯定前件和否定后件 natural selection 自然选择necessary 必然的neutral monism 中立一无论nominalism 唯名论nonEuclidean geometry 非欧几里德几何nonmonotonic logics 非单一逻辑OckhamRazor 奥卡姆剃刀omnipotence and omniscience 全能和全知ontology 本体论(存有学)operator 算符(或算子)paradox 悖论perception 知觉phenomenology 现象学picture theory of meaning 意义的图像说pluralism 多元论polis 城邦possible world 可能世界postmodernism 后现代主义prescriptive statement 规定性陈述presupposition 预设primary and secondary qualities 第一性的质和第二性质 principle of noncontradiction 不矛盾律proposition 命题quantifier 量词quantum mechanics 量子力学rational numbers 有理数real number 实数realism 实在论reason 理性,理智recursive function 循环函数reflective equilibrium 反思的均衡relativity (theory of) 相对(论)rights 权利rigid designator 严格的指称词Rorschach test 相对性(相对论)rule 规则rule utilitarianism 功利主义规则Russells paradox 罗素悖论sanctions 制发scope 范围,限界semantics 语义学sense data 感觉材料,感觉资料set 集solipsism 唯我论social contract 社会契约subjectiveobjective distinction 主客区分sublation 扬弃substance 实体,本体sui generis 特殊的,独特性supervenience 偶然性syllogism 三段论thingsinthemselves 物自体thought 思想thought experiment 思想实验threevalued logic 三值逻辑transcendental 先验的truth 真理truth function 真值函项understanding 理解universals 共相,一般,普遍verfication principle 证实原则versimilitude 逼真性vicious regress 恶性回归Vienna Circle 维也纳学派virtue 美德。

翻译分类词汇A.经济类economist 经济学家socialist economy 社会主义经济capitalist economy 资本主义经济collective economy 集体经济planned economy 计划经济controlled economy 管制经济rural economics 农村经济liberal economy 自由经济mixed economy 混合经济political economy 政治经济学protectionism 保护主义autarchy 闭关自守primary sector 初级成分private sector 私营成分,私营部门public sector 公共部门,公共成分economic channels 经济渠道economic balance 经济平衡economic fluctuation 经济波动economic depression 经济衰退economic stability 经济稳定economic policy 经济政策economic recovery 经济复原understanding 约定concentration 集中holding company 控股公司trust 托拉斯cartel 卡特尔rate of growth 增长economic trend 经济趋势economic situation 经济形势infrastructure 基本建设standard of living 生活标准,生活水平purchasing power, buyingpower购买力scarcity 短缺stagnation 停滞,萧条,不景气underdevelopment 不发达underdeveloped 不发达的developing 发展中的B. 农业land, soil 土壤arable land, tilled land 耕地dry soil 旱田fertile soil 沃土,肥沃的土壤humus 腐殖质irrigable land 水浇地lean soil, poor soil 贫瘠土壤wasteland, barren land 荒地grass 草grassland 草地meadow 草甸prairie 大草原pasture land 牧场to lie fallow 休闲fallow 休闲地stubble, stubble field 亩茬地straw, hay 稿杆rural population 农村人口rural exodus 农村迁徙land reform, agrarian reform 土地改革mechanization of farming 农业机械化mechanized farming 机械化耕作farm 农场cattle farm 奶牛场ranch 大农场,牧场hacienda 庄园holding 田产plot, parcel, lot 地块cooperative farm 合作农场collective farm 集体农场country, countryside 农村countryman 农民,农民countrywoman 农民,农妇agronomist 农学家latifundium, large landed大农场主estatefarmer 农户producer 农业工人settle 佃户landowner 地主,土地拥有者absentee landlord 外居地主smallholder, small farmer 小农rancher 牧场主tenant farmer, leaseholder 土地租用人sharecropper 佃农ploughman 农民,犁田者farm labourers 农场工人,农业工人(美作:farm laborers)farm hand 农场短工cattle farmer 牧场工人cowherd, cowboy 牛仔shepherd 牧人fruit grower 果农vinegrower 葡萄栽植者vintager 采葡萄者farming, husbandry 农业animal husbandry, animalbreeding畜牧业dairy farming 乳品业,乳牛业horticulture 园艺market gardening 商品蔬菜种植业fruit growing 果树栽培vinegrowing, viticulture 葡萄栽培olive growing 油橄榄栽培arboriculture 树艺学silviculture 造林学agricultural products, farmproducts农产品foodstuffs 食品dairy produce, dairy products 乳制品dairy industry 乳品加工业crop year, farming year 农事年season 季节agricultural, commoditiesmarket农业市场livestock 牲畜C. 文学classical literature 古典文学contemporary literature 现代文学popular literature 大众文学light literature 通俗文学folklore 民间文学saga (river) novel 长篇小说short novel, long short 中篇小说叮叮小文库storyshort story 短篇小说love story 爱情小说deterctive story 侦破小说mystery story 怪诞小说whodunit 推理小说humorous story 幽默小说historical novel 历史小说essay 随笔book of travels 游记reportage 报告文学criticism 评论best seller 畅销书anthology 选集the complete works(of) 全集edition, printing 版masterpiece 杰作copyright 版权, 著作权deluxe binding 精装flat stitching 平装smyth sewed 线装humanities 人文学科writer 作家book 书volume 卷theatre 戏剧(美作:theater)drama 话剧comedy 喜剧tragedy 悲剧farce 滑稽剧play 剧本the three unities 三一律(一个情节,一个地点,一个时间)playwright 编剧act 幕scene 场plot 情节intrigue 错综复杂的剧情story 故事episode 逸事ending, denouement 结局poetry 诗歌poet 诗人poem 诗叮叮小文库epic poetry 史诗epopee 叙事诗ode 颂歌sonnet 十四行诗verse, stanza (诗)节line (诗)行rhyme 韵脚,押韵metrics 韵律学,格律学prose 散文novel 小说biography 自传allegory 寓言science fiction 科幻,科学幻想小说satire 讽刺诗essay 杂文composition 学术著作rhetoric 修辞学oratory 讲演术declamation 朗诵技巧improvisation 即席讲演criticism 批判主义critic 批评家wit 才智,创作才能eloquence 文才lyricism 抒情性D. 法律crime 犯法offence 违法(美作:offense)attempt 未遂罪unfulfilment 未实现nonobservance 未遵守injustice 不法行为threat, menace 恐吓high treason 叛国罪adultery 通奸forgery, forging, counterfeiting 伪造perjury 伪证to bear false witness, to commitperjury犯伪证罪attempted murder 谋杀未遂assassination, murder 暗杀,行刺homicide 杀人罪叮叮小文库infanticide, child murder 杀婴罪assault and battery 殴打,侵犯人身罪kidnapping, abduction 诱拐,拐骗highjacking 劫持(飞机)piracy 海盗罪rape, violation 强奸conspiracy, plot 结伙阴谋,共谋theft, larceny 盗窃armed robbery 持械抢劫housebreaking, burglary 入室行窃contraband, smuggling 走私swindle 诈骗embezzlement 贪污公款prevarication 推诿bribery, suborning 行贿,受贿,贿赂breach of contract 违约,违反合同fraud 欺诈tax evasion 偷税misuse of authority 滥用职权corruption 贪污腐化usurpation 强夺blackmail 敲诈,勒索calumny, slander 诽谤intoxication 酗酒disturbance of the peace 扰乱治安E. 外交Ministry of Foreign Affairs 外交部Protocol Department 礼宾司Information Department 新闻司diplomatic mission 外交代表机构embassy 大使馆legation 公使馆consulate-general 总领事馆consulate 领事馆office of the chargé d'affaires 代办处military attaché's office 武官处commercial counsellor's office 商务处press section, in formationservice新闻处liaison office 联络处F. 联合国叮叮小文库International Court of Justice 国际法院Security Council 安全理事会General Assembly 联合国大会Secretariat 秘书处Office of the Secretary General 秘书长办公室Office of Legal Affairs 法务局Department of Political and Security CouncilAffairs证治安全局Department of Economic and Social Affairs 经济社会局Office of Public Information 公共资料处Department of Conference Services 会议局Office of General Services 总务处United Nation Conference on Trade andDevelopment Secretariat联合国贸易开发事物局Unite Nation Industrial DevelopmentOrganization联合国工业开发机构United Nations Administrative Tribunal 联合国行政裁判所International Law Commission 国际法委员会United Nation s Commission on InternationalTrade Law国际贸易法委员会Committee on the peaceful Uses of the Seabed and the Ocean Floor beyond the Limits of National Jurisdiction 公海海底海床和平利用非凡委员会Enlarged Committee for Program andCoordination, ECPC扩大计划调整委员会Economic and Social Council 经济社会理事会Statistical Commission 统计委员会Population Commission 人口委员会Commission for Social Development 社会开发委员会Commission on Human Rights 人权委员会Commission on the Status of Women 妇女地位委员会Commission on Narcotic Drugs 麻醉药委员会Council Committee on Non-GovernmentalOrganizations民间机构委员会Committee on Housing, Building and Planning 住宅建筑企划委员会Committee for Development Planning 开发计划委员会Special Committee on Peace-Keeping Operations 维护和平活动非凡委员会United Nations Conference on Trade andDevelopment联合国贸易开发会议Trade and Development Board, TDB 联合国开发委员会United Nations Development Program, UNDP 联合国开发计划处United Nation Children's Fund, UNICEF 联合国儿童基金会United Nations Industrial Development 联合国工业开发组织Organization, UNIDOUnited Nations Capital Development Fund,UNCDF联合国资本开发基金会United Nations Institute for Training andResearch, UNITR联合国调查练习研究所United Nations FAO Intergovernmental Committee of the World Food Program 联合国FAO世界粮食计划国际委员会International Narcotics Control Board, INCB 国际麻醉药管制委员会Trusteeship Council 信托投资理事会International Labor Organization, ILO 国际劳工组织Food and Agriculture Organization, FAO 联合国粮食农业组织United Nation Educational Scientific and Culture Organization, UNESCO 联合国教育科学文化组织International Civil Aviation Organization, ICAO 国际民间航空组织World Health Organization, WHO 世界卫生组织International Telecommunications Union, ITU 国际电信同盟World Meteorological Organization, WMO 世界气象组织Universal Postal Union, UPU 万国邮政联盟International Maritime ConsultativeOrganzation, IMCO国际海事协议组织International Finance Corporation, IFC 国际金融组织International Monetary Fund, IMF 国际货币基金会International Bank for Reconstruction andDevelopment, IBRD世界银行International Development Association, IDA 国际开发协会General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, GATT 有关关税贸易一般规定International Atomic Energy Agency, IAEA 国际原子能组织World Federation of Trade Unions, WFTU 世界劳工组织International Confederation of Free TradeUnions, ICFTU国际自由劳工联盟International Chamber of Commerce, ICC 国际工农商会International Federation of AgriculturalProducers, IFAC国际农业生产联盟Inter-Parliamentary Union, IPU 诸国会议同盟International Organization of Employers, IOE 国际雇佣者组织World Veterans Federation, WVF 世界退伍军人联盟International Union of Local Authorities, IULA 世界地方自治联盟United Towns Organization, UTO 姊妹市团体联盟G. 地震词汇地震相关英语词汇:地震-earthquake,temblor(美语),seism['saiz?m];余震-aftershock;海啸-tsunami;打击、袭击-hit,strike;破坏-destroy,devastate;粉碎、摧毁-shatter;灾难性的-devastating;颠簸、摇晃-jolt;death toll 死亡人数;survivors 幸存者;victims 受灾者英语中表示地震的名词有:earthquake、quake、shake、shock、tremor和temblor (此词为美语)的动词)有:英语中表示地震的动词(即意为“地震发生于...”hit 袭击,打击,使遭受strike 突然发生shake 摇;摇动;摇撼jolt 使颠簸,摇晃rock 摇,摇动,使振动roll across 波动,起伏,横摇rip through 裂开,破开;突进,横撞直闯形容地震的破坏程度的动词有(按破换程度从小到大排序):damage 损害,损伤;〔口语〕伤害,毁坏destroy 毁坏,破坏;摧残shatter 破坏;捣毁;破灭devastate 蹂躏,破坏;使荒废;毁灭level 推倒,夷平flatten 夷为平地national day of mourning 全国哀悼日mourning ceremony 哀悼仪式national flags fly at half-mast 降半旗致哀silent tribute 默哀online tribute 网上悼念赈灾earthquake relief 赈灾post-disaster reconstruction 灾后重建altitude sickness 高原反应quake victims 遇难者relief work 救援工作叮叮小文库Tibetan treatment 藏医疗法medical team 医疗队relief goods 救援物资slide-proof rug 防滑垫cold-proof coat 防寒大衣heat sensor 生命探测仪signs of life 生命迹象plague prevention 防疫plague prevention 鼠疫防疫oxygen deprivation 缺氧oxygen supply 氧源,供氧oxygen mask 氧气罩募捐gala devoted to quake relief 赈灾晚会telethon 为募捐播放的长时间的电视节目campaign-style donation activity 大型募捐活动charity donor 慈善捐赠者donation agreement 捐赠协议charity sale 义卖giveaway buffet 慈善餐会地震aftershock 余震epicenter 震中magnitude 震级earthquake monitoring 地震监控earthquake wave / seismic wave 地震波earth tremor 轻微地震Richter Scale(1-10) 里氏震级at a scale of 7 on the Richter calculations 里氏7级地震叮叮小文库seismology 地震学11。

考验翻译学习资料:学科、专业名称中英文互译及相关词汇哲学Philosophy逻辑学Logic伦理学Ethics美学Aesthetics宗教学Science of Religion科学技术哲学Philosophy of Science and Technology经济学Economics 理论经济学Theoretical Economics 政治经济学Political Economy经济思想史History of Economic Thought经济史History of Economic西方经济学Western Economics世界经济World Economicss国民经济学National Economics 区域经济学Regional Economics计量经济学Quantitative Economics应用经济学Applied Economic财政学(含税收学)Public Finance (including Taxation)金融学(含保险学)Finance (including Insurance)统计学Statistics (注意也可能为“统计数据”)法学Law / Science of Law/ Legal Science法律史Legal History宪法学与行政法学Constitutional Law and Administrative Law刑法学Criminal Jurisprudence民商法学(含劳动法学、社会保障法学)Civil Law and Commercial Law (including Science of Labour Law and Science of Social Security Law )诉讼法学Science of Procedure Laws经济法学Science of Economic Law国际法学(含国际公法学、国际私法学、国际经济法学、) International law (including International Public law, International Private Law and International Economic Law)军事法学Science of Military Law政治学Political Science国际政治学International Politics政治制度Political Institution外交学Diplomacy (注意diplomatism 外交手段,外交手腕)国际关系学International Relations社会学Sociology人口学Demography人类学Anthropology教育学Education/ Education Science 教育学原理Educational Principle心理学Psychology 应用心理学Applied Psychology行为学behaviorism文学Literature 语言学Linguistics应用语言学Applied Linguistics新闻传播学Journalism and Communication电影学Film历史学History专门史History of Particular Subjects近现代史Modern and Contemporary History世界史World History考古学Archaeology博物馆学Museology数学Mathematics应用数学Applied Mathematics概率论与数理统计Probability and Mathematical Statistics运筹学与控制论Operational Research and Cybernetics物理学Physics 理论物理Theoretical Physics粒子物理与原子核物理Particle Physics and Nuclear Physics原子与分子物理Atomic and Molecular Physics 等离子体物理学Plasma Physics 凝聚态物理学Condensed Matter Physics声学Acoustics光学Optics化学Chemistry 无机化学Inorganic Chemistry有机化学Organic Chemistry天文学Astronomy 天体物理学Astrophysics 天体测量学Astrometry地球物理学Geophysics大气科学Atmospheric Sciences气象学Meteorology大气物理学与大气环境Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment海洋科学Marine Sciences (另:oceanology 海洋资源开发研究,海洋地理研究) 地质学Geology构造地质学Structural Geology生物学Biology微生物学Microbiology植物学Botany 动物学Zoology生理学Physiology 遗传学Genetics生物化学与分子生物学Biochemistry and Molecular Biology生物物理学Biophysics生态学Ecology系统科学Systems Science力学Mechanics固体力学Solid Mechanics 流体力学Fluid Mechanics理学Natural Science 工学Engineering机械工程Mechanical Engineering机械制造及其自动化Mechanical Manufacture and Automation测试计量技术及仪器Measuring and Testing Technologies and Instruments材料学Materialogy材料加工工程Materials Processing Engineering电气工程Electrical Engineering信息与通信工程Information and Communication Engineering计算机科学与技术Computer Science and Technology计算机应用技术Computer Applied Technology建筑学Architecture城市规划与设计Urban Planning and Design水利工程Hydraulic Engineering矿业工程Mineral Engineering采矿工程Mining Engineering石油与天然气工程Oil and Natural Gas Engineering油气井工程Oil-Gas Well Engineering油气田开发工程Oil-Gas Field Development Engineering交通运输工程Communication and Transportation Engineering航空宇航科学与技术Aeronautical and Astronautical Science and Technology核科学与技术Nuclear Science and Technology核技术及应用Nuclear Technology and Applications农业工程Agricultural Engineering农业机械化工程Agricultural Mechanization Engineering 兽医学Veterinary Medicine 临床兽医学Clinical Veterinary Medicine林学Forestry水土保持Soil and Water Conservation荒漠化防治Desertification Combating医学Medicine 基础医学Basic Medicine临床医学Clinical Medicine免疫学Immunology内科学Internal medicine外科学Surgery老年医学Geriatrics神经病学Neurology精神病学Psychiatry护理学Nursing康复医学与理疗学Rehabilitation Medicine & Physical Therapy运动医学Sports Medicine 急诊医学Emergency Medicine公共卫生Public Health营养与食品卫生学Nutrition and Food Hygiene中医学Chinese Medicine 方剂学Formulas of Chinese Medicine药学Pharmaceutical Science管理学Management Science 工商管理学Science of Business Administration会计学Accounting情报学Information Science通用前缀:比较-comparative应用-applied临床-clinic后-post相关:广义general 狭义restricted/ special辩证法/辩证法的,辩证的dialectic悖论paradox 谬论fallacy边缘学科/交叉学科interdisciplinary 跨学科cross-disciplinary实地研究/现场研究field study 理论研究theoretical study文献研究literary study/research评论criticism方法论methodology女权主义feminism现代主义modernism 后现代主义post-modernism现实主义realism 唯物主义materialism 唯心主义idealism (有时为理想主义)内涵connotation(文化内蕴)/ intension 外延denotation(字面意义)/extension归纳induction 演绎deductionhumanism 人本主义,人文主义humanitarianism 人道主义,博爱主义relativism 相对主义(注意不等于物理学中的“相对论”!) 这学名词A theory that conceptions of truth and moral values are not absolute but are relative to the persons or groups holding them.相对主义:认为真理的概念及道德价值不是绝对的而是相对于持有它们的人或集团的理论relativity 相对论(物理学名词)Encyclopedia 百科全书Renaissance 文艺复兴(时期的)各种学位名称B.A. or BA 文学士(Bachelor of Arts)B.S. or BS 理学士(Bachelor of Science)M.A. or MA 文科硕士(Master of Arts)M.S. or MS 理科硕士(Master of Science)M.B.A. 工商管理硕士(Master of Business Administration)Ph.D 哲学博士(Doctor of Philosophy)(注意并非所有的博士都是Ph. D)D.S. 理学博士(Doctor of Science)M. D. 医学博士(Doctor of Medicine)Eng.D 工学博士(Doctor of Engineering)。

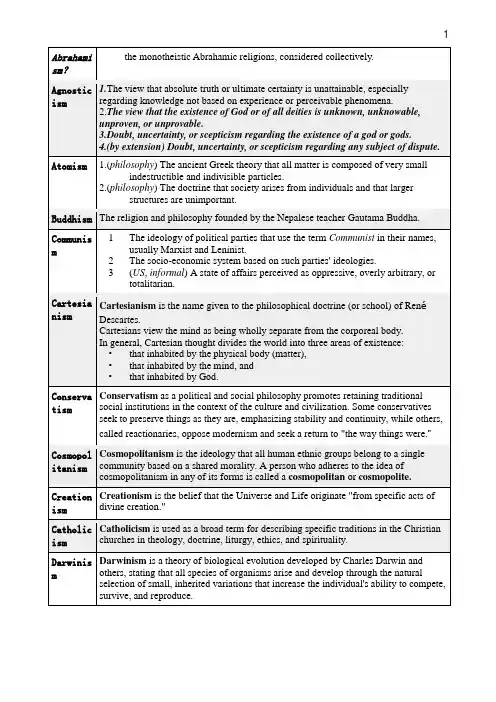
各种主义的名词中英文翻译封建主义 feudalism专制主义 absolutism社会主义 socialism资本主义 capitalism奴隶主义 slaverism集体主义 collectivism个人主义 individualism享乐主义 gastronomy共产主义 communism党派主义 factionalism国家主义 nationalism自由主义 liberalism宗派主义 sectarianism理性主义 rationalism理想主义 idealism科学社会主义 scientific socialism民主主义 democratism投机主义 opportunism公理主义 congregationalism地方自治主义 communalism工会主义 unionism反种族主义 antiracism反社会主义 antisocialism社会民主主义 social democracy种族主义 racialism工团主义 syndicalism商业主义 commercialism教条主义 doctrinairism黑权主义 black power军国主义 militarism公式主义 formulism法西斯主义 fascism平均主义 levellism专业主义 professionalism新艺术主义 ant nouveau消极主义 passivism新殖民地主义 neocolonialism新重商主义 neomercantilism实利主义 utilitariantilism实用主义 pragmatism实证主义 positivism怀疑主义 scepticism神秘主义 occultism无政府主义 anarchism地方主义 localism人文主义 humanism人道主义 humanitarianism抽象主义 abstractionism国家资本主义 state capitalism国际主义 internationalism形式主义 formalism产业主义 industrialism排他主义 exclusionism大男子主义 male chauvinism未来主义 futurism权力主义 authoritarianism联邦主义 unionism独身主义 bachelorism世界主义 cosmopolitanism金钱主义 venality自然主义 naturalism自我中心主义 autism独裁主义 tarianism黑人人权主义 negroism折中主义 eclecticism废除主义 abolitionism废奴主义 abolitionism霸权主义 hegemonism内省主义 introspections修正主义 revisionist印象主义 impressionism虚无主义 nihilism三民主义 the Three Principles of the People put forward by Dr. Sun Yat-sen 地方保护主义 regional protectionism男权主义 male chauvinism女权主义feminism权贵资本主义 crony capitalism工具主义 instrumentalism表现主义expressionism 本本主义bookishness 结构主义constructivism 浪漫主义romanticism 认知主义cognitivism唯美主义aestheticism 存在主义existentialism 无为主义quietism世俗主义secularism恐怖主义terrorism道德主义moralism立体主义cubism沙文主义chauvinism现代主义modernism。

封建主义feudalism 专制主义absolutism社会主义socialism 资本主义capitalism奴隶主义slaverism 集体主义collectivism 个人主义individualism 享乐主义gastronomy共产主义communism党派主义factionalism国家主义nationalism 自由主义liberalism宗派主义sectarianism理性主义rationalism理想主义idealism科学社会主义scientific socialism民主主义democratism投机主义opportunism公理主义congregationalism地方自治主义communalism工会主义unionism 反种族主义antiracism反社会主义antisocialism社会民主主义social democracy种族主义racialism工团主义syndicalism商业主义commercialism教条主义doctrinairism黑权主义black power军国主义militarism公式主义formulism法西斯主义fascism 平均主义levellism专业主义professionalism新艺术主义ant nouveau消极主义passivism新殖民地主义neocolonialism 新重商主义neomercantilism实利主义utilitariantilism实用主义pragmatism实证主义positivism怀疑主义scepticism神秘主义occultism无政府主义anarchism地方主义localism人文主义humanism人道主义humanitarianism抽象主义abstractionism国家资本主义state capitalism国际主义internationalism形式主义formalism产业主义industrialism排他主义exclusionism大男子主义male chauvinism未来主义futurism权力主义authoritarianism联邦主义unionism独身主义bachelorism世界主义cosmopolitanism金钱主义venality自然主义naturalism自我中心主义autism独裁主义tarianism黑人人权主义negroism折中主义eclecticism废除主义abolitionism废奴主义abolitionism霸权主义hegemonism内省主义introspections修正主义revisionist印象主义impressionism虚无主义nihilism三民主义the Three Principles of the People put forward by Dr. Sun Yat-sen 地方保护主义regional protectionism男权主义male chauvinism女权主义feminism权贵资本主义crony capitalism工具主义instrumentalism表现主义expressionism本本主义bookishness结构主义constructivism浪漫主义romanticism认知主义cognitivism唯美主义aestheticism存在主义existentialism 无为主义quietism世俗主义secularism恐怖主义terrorism道德主义moralism立体主义cubism沙文主义chauvinism 现代主义modernism。

翻译硕士(MTI)考研英语口译符号:字母、图像二、字母、图像Z 表示"人"people/person,因为"Z"看上去像个人头,它通常被写在一个词或符号的右上角。
例如:日本人:JZ。
C 表示政府,统治:governm ent,govern希腊字母C读/ga:ma/,近似government, 所以就用C来表示govern, governm ent。
governm ental officia l可以表示为CZP 表示政治:politic s, political希腊字母P读/pai/,近似politi cs, politic al。
那么politi cian就可以表示为 P ZE 表示总数:total, totally, entire, entirel y, on the whole, all in all, to sum up, ect. E 数学符号表示总值。
G 表示效率:efficie nt, effecti ve。
G为效率符号。
Q 表示"通货膨胀":inflati on因为这个符号酷似一个上升的气球。
A表示农业: agricul ture. agricul ture经常用到,所以用首字母代替。
B 表示商业:business。
C×表示冲突,矛盾:conflic t,confron tation "C×"中的"×"表示反对,字母"C"将反对的概念缩小为conflict 和confron tation。
W 表示工作,职业: work, employ等。
它是work的第一个字母。
所以WZ就可以用来表示wo rker, 而W(Z在字母上方表示emplo yer, 在字母下方表示e mployee)。

2. Alliteration:The repetition of the initial consonant sounds in poetry..10. Anapest抑抑扬: It’s made up of two unstressed and one stressed syllables, with the two unstressed ones in front.12 Antithesis:(a figure of speech) The balancing of two contrasting ideas, words phrases, or sentences. An antithesis is often expressed in a balanced sentence, that is, a sentence in which identical or similar grammatical structure is used to express contrasting ideas.17.Assonance(半韵, 半谐音元音相同而辅音不同的韵, 如late与make): The repetition of similar vowel sounds, especially in poetry. Assonance is often employed to please the ear or emphasize certain sounds.19. Autobiography(自传;自传文学): A person’s account of his or her own life. An autobiography is generally written in narrative form and includes some introspection.21.Ballad stanza (民谣体诗节): A type of four-line stanza. The first and third lines have four stressed words or syllables; the second and fourth lines have three stresses. Ballad meter is usually iambic. The number of unstressed syllables in each line may vary. The second and fourth lines rhyme.29.Classicism(古典主义): A movement or tendency in art, literature, or music that reflects the principles manifested in the art of ancient Greece and Rome. Classicism emphasizes the traditional and the universal, and places value on reason, clarity, balance, and order. Classicism, with its concern for reason and universal themes, is traditionallyopposed to Romanticism, whichis concerned with emotions andpersonal themes.32. Conceit(奇喻,妙喻): A kind of metaphorthat makes a comparison betweentwo startlingly different things. Aconceit may be a brief metaphor,but it usually provides theframework for an entire poem. Anespecially unusual and intellectualkind of conceit is themetaphysical conceit.35.Consonance: The repetition ofsimilar consonant sounds in themiddle or at the end of words.36.Couplet(双行体、双偶体): Twoconsecutive([kən'sekjutiv] 连续不断的;连贯的)lines of poetrythat rhyme. A heroic couplet is aniambic pentameter couplet.37Critical Realism:The criticalrealism of the 19th centuryflourished in the fouties and in thebeginning of fifties. The realistsfirst and foremost set themselvesthe task of criticizing capitalistsociety from a democraticviewpoint and delineated thecrying contradictions of bourgeoisreality. But they did not find away to eradicate(根除,根绝;消灭)social evils.42. Diction(措词): A writer’s choice of words,particularly for clarity,effectiveness, and precision.47.Enlightenment(启蒙主义):With the advent of the 18thcentury, in England, as in otherEuropean countries, there spranginto life a public movementknown as the Enlightenment. TheEnlightenment on the whole, wasan expression of struggle of thethen progressive class ofbourgeois against feudalism. Theinequality, stagnation, prejudicesand other survivals of feudalism.The attempt to place all branchesof science at the service ofmankind by connecting them withthe actual deeds and requirementsof the people.48Epic(史诗): Along narrative poem telling aboutthe deeds of a great hero andreflecting the values of the societyfrom which it originated. Manyepics were drawn from an oraltradition and were transmitted bysong and recitation before theywere written down.65.Foot(音步): It is a rhythmic unit, aspecific combination of stressedand unstressed syllables.67.FreeVerse(自由诗:不受格律约束的): V erse that has either nometrical pattern or an irregularpattern.69. Iamb(抑扬格): It isthe most commonly used foot inEnglish poetry, in which anunstressed syllable comes first,followed by a stressed syllable.70.Iambic pentameter(抑扬格五音步): A poetic line consisting offive verse feet, with each foot aniamb—that is, an unstressedsyllable followed by a stressedsyllable. Iambic pentameter is themost common verse line inEnglish poetry.71. Image(意象):We usually think with words,many of our thoughts come to usas pictures or imagined sensationsin our mind. Such imaginedpictures or sensations are calledimages.73.Imagism(意象派:1912年前后源于英美,主张主题和形式摆脱因袭之风): It’s apoetic movement of England andthe U.S. flourished from 1909 to1917.The movement insists on thecreation of images in poetry by“the direct treatment of the thing” and the economy of wording. The leaders of this movement were Ezra Pound and Amy Lowell. Lost Generation(迷惘的一代): This term has been used again and again to describe the people of the postwar years. It describes the Americans who remained in Paris as a colony of “expatriates” or exiles. It describes the writers like Hemingway who lived in semi poverty. It describes the Americans who returned to their native land with an intense awareness of living in an unfamiliar changing world. The young English and American expatriates, men and women, were caught in the war and cut off from the old values and yet unable to come to terms with the new era when civilization had gone mad. They wandered pointlessly and restlessly, enjoying things like fishing, swimming, bullfight and beauties of nature, but they were aware all the while that the world is crazy and meaningless and futile. Their whole life is undercut and defeated.Meter(韵律): A generally regular pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables in poetry.Metonymy: A figure of speech in which something very closely associated with a thing is used to stand for or suggest the thing itself.Myth:A story, often about immortals and sometimes connected with religious rituals, that is intended to give meaning to the mysteries of the world. Myths make it possible for people to understand and deal with things that they cannot control and often cannot see. A body of relatedmyths that is accepted by a peopleis known as its mythology. Amythology tells a people what itis most concerned about.Narrative poem(叙事诗):Apoem that tells a story. One kindof narrative poem is the epic, along poem that sets forth theheroic ideals of a particularsociety.Onomatopoeia:The useof a word whose sound in somedegree imitates or suggests itsmeaning.Oxymoron:a figure ofspeech that combines opposite orcontradictory ideas or terms. Anoxymoron suggests a paradox, butit does so very briefly, usually intwo or three words.Paradox: Astatement that reveals a kind oftruth, although it seems at first tobe self-contradictory anduntrue.Parallelism:(a figure ofspeech) The use of phrases,clauses, or sentences that aresimilar or complementary instructure or in meaning.Parallelism is a form ofrepetition.Poetry: The mostdistinctive characteristic of poetryis form and music. Poetry isconcerned with not only what issaid but how it is said. Poetryevokes emotions rather thanexpress facts. Poetry meanshaving a poetic experience.Imagination is also an essentialquality of poetry. Poetry oftenleads us to new perceptions, newfeelings and experiences of whichwe have not previously beenaware.Psychological Realism(心理现实主义): It is the realisticwriting that probes deeply into thecomplexities of characters’thoughts and motivations. HenryJames is considered the founderof psychological realism. Hisnovel The Ambassadors isconsidered to be a masterpiece ofpsychological realism.Realism(现实主义): The attempt inliterature and art to represent lifeas it really is, withoutsentimentalizing or idealizing it.Realistic writing often depicts theeveryday life and speech ofordinary people. This has led,sometimes, to an emphasis onsordid details.Rhythm(节奏;韵律): It is one of the three basicelements of traditional poetry. It isthe arrangement of stressed andunstressed syllables into a pattern.Rhythm often gives a poem adistinct musical quality. Poetsalso use rhythm to echomeaning.Sonnet(十四行诗;商籁体): A fourteen-line lyric poem,usually written in rhymed iambicpentameter. A sonnet generallyexpresses a single theme oridea.Stanza(诗节): It’s astructural division of a poem,consisting of a series of verselines which usually comprise arecurring pattern of meter andthyme.2. Alliteration:The repetition of the initial consonant sounds in poetry..10. Anapest抑抑扬: It’s made up of two unstressed and one stressed syllables, with the two unstressed ones in front.12 Antithesis:(a figure of speech) The balancing of two contrasting ideas, words phrases, or sentences. An antithesis is often expressed in a balanced sentence, that is, a sentence in which identical or similar grammatical structure is used to express contrasting ideas.17.Assonance(半韵, 半谐音元音相同而辅音不同的韵, 如late与make): The repetition of similar vowel sounds, especially in poetry. Assonance is often employed to please the ear or emphasize certain sounds.19. Autobiography(自传;自传文学): A person’s account of his or her own life. An autobiography is generally written in narrative form and includes some introspection.21.Ballad stanza (民谣体诗节): A type of four-line stanza. The first and third lines have four stressed words or syllables; the second and fourth lines have three stresses. Ballad meter is usually iambic. The number of unstressed syllables in each line may vary. The second and fourth lines rhyme.29.Classicism(古典主义): A movement or tendency in art, literature, or music that reflects the principles manifested in the art of ancient Greece and Rome. Classicism emphasizes the traditional and the universal, and places value on reason, clarity, balance, and order. Classicism, with its concern for reason and universal themes, is traditionally opposed to Romanticism, which is concerned with emotions and personal themes.32. Conceit(奇喻,妙喻): A kind of metaphor that makes a comparison between two startlingly different things. A conceit may be a brief metaphor, but it usually provides the framework for an entire poem. An especially unusual and intellectual kind of conceit is the metaphysical conceit.35. Consonance: The repetition of similar consonant sounds in the middle or at the end of words.36. Couplet(双行体、双偶体): Two consecutive([kən'sekjutiv] 连续不断的;连贯的)lines of poetry that rhyme. A heroic couplet is an iambic pentameter couplet.37 Critical Realism:The critical realism of the 19th century flourished in the fouties and in the beginning of fifties. The realists first and foremost set themselves the task of criticizing capitalist society from a democratic viewpoint and delineated the crying contradictions of bourgeois reality. But they did not find a way to eradicate(根除,根绝;消灭)social evils.42. Diction(措词): A writer’s choice of words, particularly for clarity, effectiveness, and precision.47. Enlightenment(启蒙主义): With the advent of the 18th century, in England, as in other European countries, there sprang into life a public movement known as the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment on the whole, was an expression of struggle of the then progressive class ofbourgeois against feudalism. The inequality, stagnation, prejudices and other survivals of feudalism. The attempt to place all branches of science at the service of mankind by connecting them with the actual deeds and requirements of the people.48Epic(史诗): A long narrative poem telling about the deeds of a great hero and reflecting the values of the society from which it originated. Many epics were drawn from an oral tradition and were transmitted by song and recitation before they were written down.65.Foot(音步): It is a rhythmic unit, a specific combination of stressed and unstressed syllables.67.Free Verse(自由诗:不受格律约束的): V erse that has either no metrical pattern or an irregular pattern.69. Iamb(抑扬格): It is the most commonly used foot in English poetry, in which an unstressed syllable comes first, followed by a stressed syllable.70. Iambic pentameter(抑扬格五音步): A poetic line consisting of five verse feet, with each foot an iamb—that is, an unstressed syllable followed by a stressed syllable. Iambic pentameter is the most common verse line in English poetry.71. Image(意象): We usually think with words, many of our thoughts come to us as pictures or imagined sensations in our mind. Such imagined pictures or sensations are called images.73.Imagism(意象派:1912年前后源于英美,主张主题和形式摆脱因袭之风): It’s a poetic movement of England and the U.S. flourished from 1909 to 1917.The movement insists on the creation of images in poetry by“the direct treatment of the thing”and the economy of wording. Theleaders of this movement wereEzra Pound and Amy Lowell.Lost Generation(迷惘的一代):This term has been used againand again to describe the peopleof the postwar years. It describesthe Americans who remained inParis as a colony of “expatriates”or exiles. It describes the writerslike Hemingway who lived insemi poverty. It describes theAmericans who returned to theirnative land with an intenseawareness of living in anunfamiliar changing world. Theyoung English and Americanexpatriates, men and women,were caught in the war and cut offfrom the old values and yetunable to come to terms with thenew era when civilization hadgone mad. They wanderedpointlessly and restlessly,enjoying things like fishing,swimming, bullfight and beautiesof nature, but they were aware allthe while that the world is crazyand meaningless and futile. Theirwhole life is undercut anddefeated.Meter(韵律): Agenerally regular pattern ofstressed and unstressed syllablesin poetry.Metonymy: A figure ofspeech in which something veryclosely associated with a thing isused to stand for or suggest thething itself.Myth:A story, oftenabout immortals and sometimesconnected with religious rituals,that is intended to give meaningto the mysteries of the world.Myths make it possible for peopleto understand and deal with thingsthat they cannot control and oftencannot see. A body of relatedmyths that is accepted by a peopleis known as its mythology. Amythology tells a people what itis most concerned about.Narrative poem(叙事诗):Apoem that tells a story. One kindof narrative poem is the epic, along poem that sets forth theheroic ideals of a particularsociety.Onomatopoeia:The useof a word whose sound in somedegree imitates or suggests itsmeaning.Oxymoron:a figure ofspeech that combines opposite orcontradictory ideas or terms. Anoxymoron suggests a paradox, butit does so very briefly, usually intwo or three words.Paradox: Astatement that reveals a kind oftruth, although it seems at first tobe self-contradictory anduntrue.Parallelism:(a figure ofspeech) The use of phrases,clauses, or sentences that aresimilar or complementary instructure or in meaning.Parallelism is a form ofrepetition.Poetry: The mostdistinctive characteristic of poetryis form and music. Poetry isconcerned with not only what issaid but how it is said. Poetryevokes emotions rather thanexpress facts. Poetry meanshaving a poetic experience.Imagination is also an essentialquality of poetry. Poetry oftenleads us to new perceptions, newfeelings and experiences of whichwe have not previously beenaware.Psychological Realism(心理现实主义): It is the realisticwriting that probes deeply into thecomplexities of characters’thoughts and motivations. Henry James is considered the founderof psychological realism. His novel The Ambassadors is considered to be a masterpiece of psychological realism.Realism (现实主义): The attempt in literature and art to represent life as it really is, without sentimentalizing or idealizing it. Realistic writing often depicts the everyday life and speech of ordinary people. This has led, sometimes, to an emphasis on sordid details.Rhythm(节奏;韵律): It is one of the three basic elements of traditional poetry. It is the arrangement of stressed and unstressed syllables into a pattern. Rhythm often gives a poem a distinct musical quality. Poets also use rhythm to echo meaning.Sonnet(十四行诗;商籁体): A fourteen-line lyric poem, usually written in rhymed iambic pentameter. A sonnet generally expresses a single theme or idea.Stanza(诗节): It’s a structural division of a poem, consisting of a series of verse lines which usually comprise a recurring pattern of meter and thyme.2. Alliteration:The repetition of the initial consonant sounds in poetry..10. Anapest抑抑扬: It’s made up of two unstressed and one stressed syllables, with the two unstressed ones in front.12 Antithesis:(a figure of speech) The balancing of two contrasting ideas, words phrases, or sentences. An antithesis is often expressed in a balanced sentence, that is, a sentence in which identical or similar grammatical structure is used to express contrasting ideas.17.Assonance(半韵, 半谐音元音相同而辅音不同的韵, 如late与make): The repetition of similar vowel sounds, especially in poetry. Assonance is often employed to please the ear or emphasize certain sounds.19. Autobiography(自传;自传文学): A person’s account of his or her own life. An autobiography is generally written in narrative form and includes some introspection.21.Ballad stanza (民谣体诗节): A type of four-line stanza. The first and third lines have four stressed words or syllables; the second and fourth lines have three stresses. Ballad meter is usually iambic. The number of unstressed syllables in each line may vary. The second and fourth lines rhyme.29.Classicism(古典主义): A movement or tendency in art, literature, or music that reflects the principles manifested in the art of ancient Greece and Rome. Classicism emphasizes the traditional and the universal, and places value on reason, clarity,balance, and order. Classicism, with its concern for reason and universal themes, is traditionally opposed to Romanticism, which is concerned with emotions and personal themes.32. Conceit(奇喻,妙喻): A kind of metaphor that makes a comparison between two startlingly different things. A conceit may be a brief metaphor, but it usually provides the framework for an entire poem. An especially unusual and intellectual kind of conceit is the metaphysical conceit.35. Consonance: The repetition of similar consonant sounds in the middle or at the end of words.36. Couplet(双行体、双偶体): Two consecutive([kən'sekjutiv] 连续不断的;连贯的)lines of poetry that rhyme. A heroic couplet is an iambic pentameter couplet.37 Critical Realism:The critical realism of the 19th century flourished in the fouties and in the beginning of fifties. The realists first and foremost set themselves the task of criticizing capitalist society from a democratic viewpoint and delineated the crying contradictions of bourgeois reality. But they did not find a way to eradicate(根除,根绝;消灭)social evils.42. Diction(措词): A writer’s choice of words, particularly for clarity, effectiveness, and precision.47. Enlightenment(启蒙主义): With the advent of the 18th century, in England, as in other European countries, there sprang into life a public movement known as the Enlightenment. The Enlightenment on the whole, was an expression of struggle of the then progressive class ofbourgeois against feudalism. Theinequality, stagnation, prejudicesand other survivals of feudalism.The attempt to place all branchesof science at the service ofmankind by connecting them withthe actual deeds and requirementsof the people.48Epic(史诗): Along narrative poem telling aboutthe deeds of a great hero andreflecting the values of the societyfrom which it originated. Manyepics were drawn from an oraltradition and were transmitted bysong and recitation before theywere written down.65.Foot(音步): It is a rhythmic unit, aspecific combination of stressedand unstressed syllables.67.FreeVerse(自由诗:不受格律约束的): V erse that has either nometrical pattern or an irregularpattern.69. Iamb(抑扬格): It isthe most commonly used foot inEnglish poetry, in which anunstressed syllable comes first,followed by a stressed syllable.70.Iambic pentameter(抑扬格五音步): A poetic line consisting offive verse feet, with each foot aniamb—that is, an unstressedsyllable followed by a stressedsyllable. Iambic pentameter is themost common verse line inEnglish poetry.71. Image(意象):We usually think with words,many of our thoughts come to usas pictures or imagined sensationsin our mind. Such imaginedpictures or sensations are calledimages.73.Imagism(意象派:1912年前后源于英美,主张主题和形式摆脱因袭之风): It’s apoetic movement of England andthe U.S. flourished from 1909 to1917.The movement insists on thecreation of images in poetry by“the direct treatment of the thing”and the economy of wording. Theleaders of this movement wereEzra Pound and Amy Lowell.Lost Generation(迷惘的一代):This term has been used againand again to describe the peopleof the postwar years. It describesthe Americans who remained inParis as a colony of “expatriates”or exiles. It describes the writerslike Hemingway who lived insemi poverty. It describes theAmericans who returned to theirnative land with an intenseawareness of living in anunfamiliar changing world. Theyoung English and Americanexpatriates, men and women,were caught in the war and cut offfrom the old values and yetunable to come to terms with thenew era when civilization hadgone mad. They wanderedpointlessly and restlessly,enjoying things like fishing,swimming, bullfight and beautiesof nature, but they were aware allthe while that the world is crazyand meaningless and futile. Theirwhole life is undercut anddefeated.Meter(韵律): Agenerally regular pattern ofstressed and unstressed syllablesin poetry.Metonymy: A figure ofspeech in which something veryclosely associated with a thing isused to stand for or suggest thething itself.Myth:A story, oftenabout immortals and sometimesconnected with religious rituals,that is intended to give meaningto the mysteries of the world.Myths make it possible for peopleto understand and deal with things that they cannot control and often cannot see. A body of related myths that is accepted by a people is known as its mythology. A mythology tells a people what it is most concerned about. Narrative poem(叙事诗):A poem that tells a story. One kind of narrative poem is the epic, a long poem that sets forth the heroic ideals of a particular society.Onomatopoeia:The use of a word whose sound in some degree imitates or suggests its meaning.Oxymoron:a figure of speech that combines opposite or contradictory ideas or terms. An oxymoron suggests a paradox, but it does so very briefly, usually in two or three words.Paradox: A statement that reveals a kind of truth, although it seems at first to be self-contradictory and untrue.Parallelism:(a figure of speech) The use of phrases, clauses, or sentences that are similar or complementary in structure or in meaning. Parallelism is a form of repetition.Poetry: The most distinctive characteristic of poetry is form and music. Poetry is concerned with not only what is said but how it is said. Poetry evokes emotions rather than express facts. Poetry means having a poetic experience. Imagination is also an essential quality of poetry. Poetry often leads us to new perceptions, new feelings and experiences of which we have not previously been aware.Psychological Realism(心理现实主义): It is the realistic writing that probes deeply into the complexities of characters’ thoughts and motivations. Henry James is considered the founder of psychological realism. His novel The Ambassadors is considered to be a masterpiece of psychological realism.Realism (现实主义): The attempt in literature and art to represent life as it really is, without sentimentalizing or idealizing it. Realistic writing often depicts the everyday life and speech of ordinary people. This has led, sometimes, to an emphasis on sordid details.Rhythm(节奏;韵律): It is one of the three basic elements of traditional poetry. It is the arrangement of stressed and unstressed syllables into a pattern. Rhythm often gives a poem a distinct musical quality. Poets also use rhythm to echo meaning.Sonnet(十四行诗;商籁体): A fourteen-line lyric poem, usually written in rhymed iambic pentameter. A sonnet generally expresses a single theme or idea.Stanza(诗节): It’s a structural division of a poem, consisting of a series of verse lines which usually comprise a recurring pattern of meter and thyme.。

摘要:翻译硕士(MTI)经典素材-笔译常用词汇(文化)All Saint’s Day 万圣节American plan约能源 (旅馆的)美国式收费式a soft job 轻松的工作a widow’s mite 礼轻情义重beefcake 男性健美照be free to practice one’s religion 宗教信仰自由“bifocal” vision “双重”视野break with old customs 抛弃传统busboy (饭店的)洗碗擦桌子的杂工Catch-22 无法摆脱的困难;难以逾越的障碍civic values 大众价值观clash with civilizations 文明的碰撞consumerist creed 消费至上主义corporate culture 企业文化country fair 乡村博览会cross-cultural bridge 跨文化桥梁cross-cultural communication 跨文化交流cultural borrowing 文化借用cultural complex 文化情结cultural development 文化建设cultural devolution 文化退化cultural differences 文化差异cultural hegemony 文化霸权cultural heritage 文化遗产cultural identity 文化认同cultural impact 文化影响cultural insights 文化视角cultural lag 文化落后cultural life 文化生活cultural manifestation 文化诉求cultural misreading 文化误读cultural pluralism; multiculturalism 文化多元化cultural shock 文化冲击cultural traditions 文化传统culture area 文化区culture of tolerance 宽容的文化culture-oriented travel 文化旅游culture trait 文化特质dialogue among civilizations 文明间的对话dinner etiquette 餐桌礼仪dominant culture 主导文化ethnic origin 种族起源flower children 配花嬉皮士Flower Generation 花季的一代generation X (90年代的)未知的一代gold-collars 金领阶层hard drug 硬毒品;易成瘾的烈性毒品(如海洛因、可卡因、吗啡等)heterogenous culture 异质文化high culture 优等文化;高级文化human civilization 人类文明humane historical sites 人文历史遗址hyper-individualism 超级个人主义intercultural dialogue 跨文化对话isomorphic cultural community 同质文化群体King’s English 纯正英语language restriction 语言限制主义Lazy Susan (指一种盛食品的)自动转盘(方便顾客选用的食品)low culture 低等文化;低级文化low tea 晚餐前茶点mainstream culture 主流文化Mary Jane 大麻(烟叶)“me” generation (70年代的)“为我”的一代midriff 露脐装national identity and values 民族特性和价值观national sentiments 民族感情new-collars (指二战后的第一代婴儿潮中出生的人)Nobel laureate 诺贝尔获得者off license 售酒执照orphan book 孤本pot culture 大麻文化(指以吸用大麻为中心的生活方式)prejudice and misunderstanding 偏见和误解promote sociability 促进社会交往sample local culture 领略当地文化service station 加油站,服务站silent generation (指50年代成年的人)沉默的一代soft drug 软毒品;不宜成瘾的毒品spiritual enhancement 精神升华the beaten generation 垮掉的一代The Clash of Civilization 《文明冲突》the gilded age 镀金时代the lost generation 迷茫的一代the Millennials 千禧一代tolerance and mutual respect 互相宽容和尊重value of knowledge 知识的价值value proposition 价值主张Vietnam War generation 越战的一代(60年代成年的人)weekly-shoppers throwaways 每周购物一次的人看就随手扔掉的那种杂志Yaps (young aspiring professionals) 亚皮士/雅皮士/优皮士(少壮职业人士/年轻、不断得到升迁的专业人士)yellow boy 金币These two cultures, which were created in different areas, developed in parallel and without interference.这两种文化产生于不同的地区,他们的发展并行不悖,互不影响。

政治学常见名词中英文对照政治学常见名词中英文对照一画一个数的绝对值 Absolute Value of a Number 一致C onsensus二画二元分类 Dichotomous Classification人格P ersonality三画个案研究 Case Study工程理论 Engineering Theory四画分析A nalysis分类C lassification分裂C leavage气质D ispositions方差分析 Analysis of Variance方法论 Methodology不对称 Asymmetry中心趋势测量 Central Tendency Measurement 中心极限理论 Central Limits Theorem内容分析 Content Analysis文化C ulture反馈F eedback场研究 Field Study历史研究方式 Historical Approach见解P erspective公共舆论 Public Opinion公共政策 Public Policy比率R atio比较研究 Comparative Study双尾检验 Two-Tailed Test五画生物政治学 Biopolitics代价-利益分析Cost-Benefit Analysis 目的-工具分析Ends-Means Analysis 平衡E quilibrium目标G oal归纳I nduction功能主义 Functionalism囚犯的困境 Prisoner's Dilemma主观互证 Intersubjectivity六画后行为主义 Postbehavioralism后验推理 A Posteriori先验推理 A Priori权威A uthority交易理论 Bargaining Theory交换E xchange行为模式 Behavior Pattern同型性 Isomorphism因果关系 Causality交互作用 Interaction行为主义 Behavioralism共同体 Community压制C oercion决策研究方式 Decision-making Approach 同期组 Cohort决定论 Determinism冲突C onflict自然实验 Natural Experiment自由度 Degrees of Freedom团体G roup团体理论 Group Theory机构I nstitution合法性 Legitimacy观察O bservation多元论 Pluralism权力P ower过程P rocess问卷Q uestionnaire地区研究 Regional Studies扩大S pillover传统研究方式 Traditional Approach价值V alue七画利益聚集 Aggregation of Interests连续统一体 Continuum利益表达 Articulation of Interests评价研究 Evaluation Research折衷研究方式 Eclectic Approach采访I nterview启发式设计 Heuristic Device纵向-横向研究方法投射法 Projective Methods 宏观-微观分析Macro-Micro AnalysisLongitudinal Versus Cross Section Methods投票行为 Voting Behavior还原论 Reductionism角色R ole社会自动平衡 Homeostasis社会控制 Social Control社会工程学 Social Engineering社会母体 Social Matrix社会科学 Social Science社会分层 Social Stratification社会系统 Social System社会S ociety社会计量学 Sociometry系统S ystem系统分析 System Analysis时间数列分析 Time Series Analysis八画态度A ttitude实力分析 Capability Analysis态度分级 Attitude Scaling实验E xperiment实验室研究方式 Laboratory Approach 经验主义 Empiricism环境E nvironment事实F act事件资料 Events Data规范N orm直觉I ntuition组织O rganization规范性 Normative和平研究 Peace Research组织理论 Organization Theory知觉P erception范例P aradigm命题P roposition知识社会学 Sociology of Knowledge 所属群体 Reference Group录用R ecruitment参与观察 Participant Observation参数P arameter抽样S ampling空间模型 Spatial Model刺激-反映Stimulus-Response刻板S tereotype非干扰性度量 Unobtrusive Measure 非参数统计 Nonparametric Statistics变量V ariable九画类比A nalogy相关C orrelation临界域 Critical Region指数I ndex Number重访法 Panel Study重言T autology点估计 Point Estimate政策科学 Policy Sciences政治行动 Political Action政治行动者 Political Actor政治人类学 Political Anthropology 政治行为 Political Behavior政治变化 Political Change政治通讯 Political Communication 政治共同体 Political Community 政治文化 Political Culture政治发展 Political Development政治生态学 Political Ecology政治一体化 Political Integration 政治哲学 Political Philosophy政治心理学 Political Psychology政治科学 Political Science政治社会化 Political Socialization政治社会学 Political Sociology政治系统 Political System政治理论 Political Theory政治P olitics政体P olity信度R eliability研究方式 Approach研究R esearch研究设计 Research Design科学S cience科学方法 Scientific Method科学哲学 Philosophy of Science语义差度 Semantic Differential战略S trategy统计学 Statistics结构-功能主义Structural-Functionalism 结构S tructure十画通讯理论 Communications Theory通则解释 Nomothetic Explanation 契约论 Contract Theory资料D ata差异检验 Deffierence Tests格特曼量表 Guttman Scale预测P rediction调查研究 Survey Research十一画假定A ssumption假设H ypothesis随大流效果 Bandwagon Effect偏性样本 Biased Sample偶然性 Chance控制组 Control Group控制变量 Control Variables控制论 Cybernetics描述D escription离散度量数 Dispersion Measures 推断I nference领导L eadership检验T esting检验的功效 Power of a Test随机R andom理想类型 Ideal Type理性选择范围 Rational Choice Paradigm 理性R ationality第一类错误 Type 1 Error十二画集体商品 Collective Goods集合S et量化Q uantification量表S cale量表转换 Scale Transformation趋势陈述 Tendency Statement散点图 Scatter Diagaram十三画概念C oncept概念组合 Conceptual Scheme概括G eneralization概率P robability解释E xplanation频数分布 Frequency Distrubution博弈论 Game Theory输入I nput。

汉语言文学专业词汇(英文版)FELIX2015-01-07 16:31:09文学思潮:Literature current of thought文学革命:Literature revolution古典文学:Classic literature维新运动:Reformist movement启蒙运动:Enlighten the sport价值领域:worth a realm外国文学:Foreign literature知识分子:Educated person浪漫主义:Romanticism唯美主义:Aestheticism百科全书:Cyclopeadia文艺复兴:Revival of learing发音器官:Speech organs功能名词:Function noun专有名词:Proper noun普通名词:Commen noun集合名词:Collective noun抽象名词:Abstract noun复合谓语:Compound predicate楔形文字:Arrowheaded character语法范畴:Grammatical category汉藏语系:Sino-Tibetan上层建筑:Superstructure意识形态:Ideology现代文学:Contemporary literature大众文学:Popular literature报告文学:Reportage批判主义:Criticism伊索寓言:Aesop`s Fables希腊文化:Hellenism形而上学:Metaphysis孔子学说:Confucian喜怒哀乐:Pleasure Anger Sorrow Joy发源地:Source爱美剧:Amateur修辞学:Rhetoric语音学:Phonetic助动词:Auxiliary verb感叹词:Interjection连接词:Link word-逻辑词:Logical word里程碑:Milestone拉丁语:Latin田园诗:Idyl无名氏:Annymous person真善美:Truth Goodness Beauty英语分类词汇:文学相关词汇classical literature 古典文学contemporary literature 现代文学popular literature 大众文学light literature 通俗文学folklore 民间文学saga (river) novel 长篇小说short novel, long short story 中篇小说short story 短篇小说love story 爱情小说deterctive story 侦破小说mystery story 怪诞小说whodunit 推理小说humorous story 幽默小说historical novel 历史小说essay 随笔book of travels 游记reportage 报告文学criticism 评论best seller 畅销书anthology 选集the complete works(of) 全集edition, printing 版masterpiece 杰作copyright 版权, 著作权deluxe binding 精装flat stitching 平装smyth sewed 线装humanities 人文学科writer 作家book 书volume 卷-theatre 戏剧(美作:theater)drama 话剧comedy 喜剧tragedy 悲剧farce 滑稽剧play 剧本the three unities 三一律(一个情节,一个地点,一个时间)playwright 编剧act 幕scene 场plot 情节Appendix 1 A Glossary of Linguistic TermsAabbreviation []n. 缩写.缩写词.略语ablative []n.夺格 a.夺格的absolute []a.独立的.独立成分absolute clause 独立从句abstract nouns 抽象名词accent []n.口音.重音.(诗歌中词或音节的)重读accidence []n.1.词形变化.字形变化 2. (学科的)初步.入门accommodation []n.调适.接纳accusative []a.直接宾格的n.直接宾格(受格)acoustic []a.听觉的.音响的.声学的(---feature/cue声学特征)acquisition []n.获得.习得acronym []n.首字母缩略字.缩略词active []n.主动语态actor []n.动作者.行动者(actor—action—goal)addition []n. 加.附加.添加address []n. 称呼(forms/terms of address 称呼语)addressee []n. 受话人,收信人,收件人addresser []n. 发话人,发言人,发信人.adjacency pair 相邻语对adjective []n.形容词 a.形容词的adjunct []n.附加语.修饰语.修饰成分adnominal []a.(定语)修饰名词的.形容词的.形容名词的adverb []n. 副词;状语adverbial []a. 副词的,作副词用的adversative []a.反意的.相反的n.反义字(转折语) affirmative []n.肯定词.肯定语affix []n1.附加物.添加物 2.字缀.词缀(affix hopping 词缀跳跃) affixation[]n. 附加.附加法.词缀附加法affricate []n.塞擦音agent (agentive) 施事agreement []n. (人称.性别.数.格的)一致airstream []n.气流alliteration []n.头韵(法)allomorph []n.同质异形体.词.语素变体allophone []n.同位音.音位变体allophonic variation 音位变体alveolar []n. 齿龈音,齿槽音.alveolar ridge 齿龈ambiguity []n.含混,歧义ambiguous歧义的anacoluthon []n.改变说法.错格.句法结构前后不一anadiplosis []n.反复法.顶真analogical []a.类似的.类推的analogical creation 类推造字anapaest []n.抑抑扬格.弱弱强格.短短长格anaphora []n. 复指.首语(句)重复法annotation []n. 注解.注释antecedent []n. (关系代词的)先行词antithesis []n. 1. 对立面;对立 2. (修辞学)对语,对偶,对句antonomasia []n. 代称,称呼替换antonym []n. 反义词,反义现象aphorism []n.格言.警句.箴言aposiopesis []n.话语中断,说话中断法apostrophe []n. 1.呼语 2.撇号 3.省略符号 4.所有格符号appellative []a.1.名称的 2.通称的n.通称名词.普通名词apposition []n. 1.同位语 2.并置appropriateness []n. 得体.适合.适当.相称arbitrariness []n. 任意性archaism []n.古体,拟古,古语argot []n.行语,暗语,黑话article []n.冠词articulation []n. (清楚的)发音.发出的(辅)音.发音动作articulator []n. 1.发音清楚的人或物 2.发音器官articulatory []a.发音清晰的.与发音有关的aside 旁白,私语,离题话aspect []n. (动词的) 体. 时态. 时间aspirated []a.伴有h音的.送气音的.吐气.送气assimilation []n.同化aureate []a.绚丽的(-- diction,绚丽辞令– style绚丽体)assonance []n. 1. 谐音 2. (诗的)准押韵.半谐音attributive []a. 1.归属的.属性的 2.定语的n.定语auxiliary []a. 辅助的.附属的.从属的n.助词auxiliary verb 助动词Bback-formation 逆构词法base form 基础形式base component 基础部分basic form 基本形式behaver 行为者behavioural process 行为过程behaviourism 行为主义bilabial []a.双唇音的n. 双唇音bilabial nasal 双唇鼻音bilateral []a.双边的.双边音bilateral opposition 双边对立bilingualism [] n.双语现象binary []a. 二元的.由二部分构成的(-- feature 二分特征) binomial []a. 二项式的n.二项式blade []n.舌叶.舌面前部blank verse 无韵诗bleaching []n.词义淡化blending []n.混合.混成法.裁切block language 块语、标题式语言(有限语境中使用缩略结构如No smoking) borrow(ing) 借用.借词bound clause粘附句bound morpheme 粘着语素bounding theory 界限理论bracketing 括号法broad transcription 宽式音标broadening 词义扩大Ccalque []n.语义转借.译借vt.转借(语义).仿造语cardinal[]n基数词cardinal vowel 基本元音category []n范畴(categorical component 范畴成分)causative []a.使役的n.使役动词cavity []n.腔clause 小句.从句click 吸气音.咂音clipping []n.缩略closure []n.关闭.闭塞cluster []辅音丛coarticulation 协同发音coda []n.节尾.韵尾code 语码.信码cognate []n.同源词.同根词.同系语言cognitive psycholinguistics 认知心理语言学cognitive psychology 认知心理学cognitive system 认知系统coherence 连贯.相关.关联cohension 衔接collapse [] 叠合collective []n.集合名词colligation []n. 概括.搭连collocation []n.组合.搭配command []命令(句)commissive 承诺语common普通的.共同的(--- core 共核)(--- noun 普通名词)comparative [] a比较的.比较级的-competence []n.语言能力complement(ation) 补语complementary互补.相反component 组成部分,成分componential 组成部分的composition 组构compound(ing) 复合;复合词(句)conative []a. 意动的concord []n. 协调.一致(关系)conditional []n.条件句.条件语congruence []n.重合conjugate []vt.列举(动词)的词形变化conjunct []a. 连接副词conjunction []n.连词.连接词connotation []n.含蓄.言外之意【逻】内涵consonant[]n.辅音.辅音字母 a.辅音的constative []a. 陈述的.表述的constituent []n.成分.结构成分construction (construct) 构建content (ive) 内容.实义(词)contrast(ive) 对立.对比convention(al) 常规;规约conversation 会话conversationalconversion 类转.变换coordinate /coordination/coordiative 并列copula []n.系词copulative []a.连系的.作系词的n.系词co-referential(ity) 同指coronal []n.舌冠(音).舌尖音corpus []n. 1.文集.全2..躯体(尤指尸体) 3.语料语料库.素材corpora[] (corpus的复数)correlative []a.相关的n.关联词count [] 可数的,countable/uncontable 可/不可数名词couplet []n. 对句.双韵covert []隐性的Ddactyl []n. (英诗的)扬抑抑格.长短短格dative []a.与格的n.与格.与格语dative movement 与格移动declarative []a. 1. 宣言的.布告的.申报的.陈述的 2.陈述的decode []vt. 译解(密码)deductive []a. 推论的.演绎的defeasibility 消除可行性definite []a.1. 明确的.确切的 2. 一定的.肯定的 3. 限定的deictic []a. 直证的.直指的(deixis)denotation []n. 1. 意义.本义2. 表示3. 名称.符号dental []a. 齿音的n.齿音dentalization 齿音化derivation []n.诱导.来历.起源调查.语言derivational []a.诱导的. 衍生的;引出的determiner []n.限定词deviant []a. 越轨的n.不正常者.变异物.变体deviation 偏离;变异devoice []vt.使(有声之音)变为无声之音devoicing 清音化diachronic []a.历时的diachronic linguistics 历时语言学diacritic []a.有区别的.能区分的.辨别的n.区别发音符号dialect []n. 方言.土话dialectology 方言学diphthong []n.双元音.复合元音direct object 直接宾语direct speech直接言语discourse []n.语段.语篇;话语discrete []a. 1. 分离的.不连接的 2.抽象的disjunction []n. 分离.分裂displacement []n.移位.置换.取代dissimilation []n. 1. 异化 2.异化作用 3.异化distinguish []vt.区别.识别把...区别分类distinguisher 辩义成分domain []n. 领域.范围dorsal []a.背部的.背侧的舌背音.舌中音dorsum []n.背.背状部分.舌面(舌尖以后之部分)dual []n. 1. 双数 2. 双数词dualistic []a. 二元的.二元论的duality 二重性Eejective []a. 喷出的.外射的n.外爆音ellipsis []n.省略.省略部分elliptic(al) []a. 1. 椭圆的 2.省略的encode []vt. 1. 把...译成电码(或密码)endocentric []a.向心的.内向的epenthesis []n.增音.插入字母epithet []n. 1. 表示特征的修饰词 2. (描述性的)称号equipollent []a.相等的n. 相等物equivalence 相等equivoque []n. 双关语.模棱两可的词句.语义双关euphemism []n.. 婉转说法.委婉(词)语euphony []n. 声音的和谐.谐音.悦耳语音exocentric []a. 外心的exocentric construction 外向结构extensive []引申的;扩展的Ffeasibility []n.可行性.可能性feature []n. 特征.特色felicity []n. 1. 幸福 2. (措辞等的)得体.巧妙.恰当的语句feminine []a.阴性的figurative []a. 1. 比喻的.象征的 2. (文章等)多比喻的figurative language 比喻性语言;象征性语言figures of speech 修辞手段;修辞格finite []a. 1. 有限的 2.有穷的 3.限定的n. 有限.有限之物flap [] 闪音flexibility []n. 易曲性.适应性.灵活性.弹性fricative []a. 摩擦的n. 摩擦音friction 摩擦function 功能fusion []n.溶合fuzzy []a. 1. 有绒毛的 2. 模糊不清的Ggender []n. 1.【语】性 2.性别gender difference 性别差异generalization []n. 普遍化.概括.综合.归纳generative []a.生殖的.有生产力的generative grammar 生成语法genitive []a.属格的n.属格global []a. 1. 球状的 2. 全世界的 3. 总体的global task 整体任务glottal []a. 1.声门的 2. 用声门发声的.喉音glottal stop 喉塞音gradable []a. (形容词)有比较级和最高级的grammar []n. 语法grammatical []a. 语法的group []n.群.组.类词组guttural []a.喉咙的.喉音的n. 喉音.喉音字腭音Hhead []n.中心词;中心成分headed construction 中心结构heptameter []n.七音步 a. 七音步的hierarchical []a.等级制度的.等级体系的hierarchical structure 等级结构hierarchical system 等级系统hierarchy []n.等级制度.统治集团.级系.阶系holophrastic []a.表句词的.单词句的holophrastic stage 单词句阶段homonym []n.同音异义字.同形同音异义字.同形异义字homophony []n. 同音异义hyperbole []n. 1.修辞的夸张法 2.夸张的语句hypercorrection []n.矫枉过正hyponym []n.下位的名称.下义词hypothesis []n.假说. 前提.假设Iiamb []n.抑扬格.短长格iambic pentameter 抑扬格五音步诗行idiom []n1. 惯用语.成语.习惯语 2. 方言.土话.(个人特有)用语ill-formed sentences 不合适的句子illocutionary []a.发语词内的.语内表现行为的illocutionary act 话中行为;施为性行为illocutionary force 言外作用;施为作用immediacy assumption 即时假定immediate constituent analysis 直接成分分析法imperative []a.祈使法的.祈使语气.命令的implicate []vt.意味着.暗指n. 包含的事物.暗含的论断implication 蕴涵;含义implosive []a.闭塞音的n.内爆发音inanimate []a.无生命的indefinite []a.不定的.未定的indicative []a.陈述的n.陈述语气.陈述语气的动词形式inference []n. 推论.推断[inferential []a. 推理的.推论的infinitive []n.不定式 a.不定式的infix []n. 插入词.中缀inflection []n. 1. 变音.转调 2. 弯曲.向内弯曲innateness []n. 天生.天赋intensifier []n. 1. 增强器.增强剂 2. 加强者 3.强调成分intensive []a. 加强的.密集的.加强语意的n.强调成分interdental []a. 在牙齿间的 2.齿间音的n.齿间音interface []n. 界面.分界面interjection []n. 感叹词.感叹语interlanguage []n. 国际语言Interlingua []n.人工国际语之一interlocutor []n. 对话者internal []a. 内的.内部的international phonetic alphabet. IPA 国际音标interpersonal []a. 人与人之间的interpersonal function 人际功能interrogative []a. 疑问的.质问的n.疑问词intonation []n. 语调.声调intransitive []a.不及物的n.不及物动词intrinsic []a.本身的.本质的.固有的.内在的invariable []a. 不变的.恒定的.一律的inversion []n.反向.倒置.倒转 2.倒装法IPA chart 国际音标图IPS symbol 国际音标符号J K Ljargon []n.黑话;行语kernel []n.核心.要点keyword关键词label []n. 标记.符号. 称号.绰号labial []a. 唇的.唇音的n. 唇音labiodental 唇齿音language []n.语言larynx []n.喉lateral []a.旁流音的.侧音的lateral sounds侧音lax []a. (元音)松弛的n.松弛的元音lax vowel 松元音letter []n字母level []n. 层,级,平面lexeme []n. 词汇.语汇单位.词位;词素lexical []a. 1. 词汇的.语词的 2. 词典的.词典编纂的lexicon []n. 1. 词典 2. 语汇 3. 词素lexis []n. (某一语言的)词语(层)liaison [] 连音linear []a. 线的.直线的linguistic []a.. 语言的.语言学的lip rounding 圆唇化literal []a. 照字面的.原义的loan translation 翻译借词loanblend 混合借词loanshift 转移借词loanword 借词Mmacro []a. 1. 巨大的.大量的 2. 宏观的.main clause 主句manner of articulation 发音方式marked 标记的masculine []a. 1. 男性的.男子的2阳性的maxim []n. 格言.箴言.座右铭manner maxim 方式准则meaning 意义meaning potential 意义潜势meaning shift 转移mental (processs) 思维过程;心理过程mentalism []n.心灵主义message 信息metafunction 元功能metalinguistic 元语言的metaphor 隐喻metathesis []n. 1.音位转换 2.交换反应.置换metonymy []n.转喻metre []n.格律.韵律.拍子metrical patterning 韵律格式9.3.3mind 思维minimal []a.最小的.极微的n.极简抽象派艺术(或其作品) mirror maxim 镜像准则mistake 错误modal []a. 1.形态上的.形式的 2.语气的.情态的 3.典型的modal subject 语气主语modal verb 情态动词modality []n. 1. 形式.情态程序 3.物理疗法 4. 主要的感觉modification []n.修饰.变异modifier []n.1. 修改者 2. 修饰词语 3.修饰基因 4.改性剂monomorphemic 单语素的monophonemic 单音位的monophthong 单元音monosyllabic 单音节的mood 语气morpheme []n.语素.词素(语言中最小的字义单位)morphemic []a.词素的.语素的morphological []a.形态学的.形态的morphology []n.形态学morphophonemics []n词素音位结构 2. 词素音位学mother tongue 母语;本族语motivation 动因;动机multilingualism 多语制;多语现象Nnasal []a.1. 鼻的2. 鼻音的n.. 鼻音.鼻音字母nasal cavity 鼻腔nasal sound 鼻音nasal stop 鼻塞音nasal tract 鼻道nasality 鼻音性nasalization 鼻音化negation []n. 1. 否定 2. 反对.反驳 3. 不存在 4. 对立面negative []a.否定的.否认的. 反面的.消极的n.否定语negative interference 负面干扰negative marker 否定标记negative transfer 负转移neutralize []vt. 1. 使无效.抵消2. 使中立化neutralizable opposition 可中立对立node []n. 1. 结.节2. 中心点.交叉点nominal []a.名词性的n. 名词性的词nominal group 名词词组nominalization 名词化nominative []a.主格的n.主格.主格词non-conventionality 非规约性non-detachability非可分离性non-linear phonology 非线性音系学non-linguistic entity 非语言实体non-pulmonic sound 非肺闭塞音non-reciprocal discourse 非交替性语篇non-reflexive pronoun 非反身代词nonsense word stage 无意义词语阶段nonverbal cues 非言语提示norm 规范notation system 标写系统notion 意念noun phrase 名词短语noun 名词Oobject 宾语object-deletion 宾语省略objective case 宾格objectivity 客观性obligatory 强制性observational adequacy 观察充分性abstruction 阻塞octametre 八音步诗行onomatopoeia []n. 1.拟声.象声词 2.拟声法onset 节首辅音open class 开放类open syllable 开音节operative 可操作性operator 操作词oppositeness relation 对立关系opposition 对立optimal relevance 最适宜关联option 选择optional 可选择的oral cavity 口腔oral stop 口阻塞音ordinal numeral 序数词origin of language 语言起源orthography []n.1. 正字法.拼字法 2. (几何)正射影(法) ostensive communication 直示交际overgeneralization 过分法则化Ppalate []n. 1.上颚 2. 味觉 3. 趣味.嗜好palatal []a.上颚(音)的.颚(音)的n. 上颚音.颚音palatal-alveolar 腭齿龈音palatalization []n.腭音化paradigm []n.1.范例 2. (名词或动词)词形变化(表) paradigmatic []a.1.范例的 2.词形变化(表)的paradigmatic relation 聚合关系paraphrase []n. 1. 释义.意译.改述vt. vi.. 释义.意译participant 参与者particle []n.虚词(包括某些副词.冠词.介词.连词等).字首.字尾partitive []a. 1. 区分的 2.表示部分的n.表示部分的词passive []n.被动语态被动态的动词pattern 模式patterning 制定模式pause 停顿peak (节)峰perceptual []a.感知的.知觉的perceptual span 感知时距perfectionism 完善主义perfective 完成体performative (verb) 行事性动词person 人称personal (function) 自指性功能pharyngeal []a.1.咽部的 2.喉音的n.喉音pharynx []n.咽头phatic []a. 交流感情的.应酬的phatic (communion) 寒暄交谈;phoneme []n.音素.音位phonetic []a. 1.语音的.语音学的 2. 语音差异的phonetic alphabet 音标phonetic form component 语音形式部分phonetic similarity 语音相似性phonetic symbol 语音符号phonetic transcription 标音(法)phonetics []n. (用作单)语音学phonologic []a.音位学的.语音体系的phonological process 音位过程phonology []n. 音位学.语音体系phrase []n. 短语.词组pidgin []n.1. (并用两种或多种语言的)混杂语.洋泾浜语 2.事儿plosion []n】爆破发音.爆破plosive []n.a.破裂音(的)plural []a.复数的pluralism []n.1.兼职.兼任 2.多重性.多元论plurality []n.1. 复数.多数.多重性 2.复数(形式) polysyllabic []a. 多音节的Portugese 葡萄牙语positive transfer 正移转possessive []a.1.拥有的.占有的 2.所属关系的.所有格的postdeterminer 后限定词pragmatic []a.1. 实际的.实干的 2. 实用主义的pragmatics 语用学Prague School 布拉格学派predeterminer 前限定词predicate []n..谓语.述部 a.谓语的.述部的prefix []n.字首.前缀(人名前的)称谓premodifier 前修饰语preposition []n.1.介词.前置词prepositional []a.. 介词的.前置词的prepositional phrase 介词短语prescriptive []a. 规定的.因时效而获得的presupposition []n.预想.假定.前提primary []a. 首要的.主要的priva principle []n. 原则.原理process 过程pro-form 代词形式;替代形式pronominal []a. 代词的pronoun 代词pronunciation 发音pronunciation dictionary 发音词典proposition 命题prosodic []a. 作诗法的.韵律学的psycholinguistics 心理语言学psycholinguistic-sociolinguistic approach 心理-社会语言学方法pulmonic []a. 肺病的pulmonic sound 肺闭塞音Putonghua 普通话Qquality 质量quality maxim 质量准则quantity 数量-quantity maxim 数量准则quantifier 数量词quantitative analysis 定量分析quantitative paradigm 数量变化表quatrain []n. 四行诗quirk []n.1. 突然的转变 2. 字的花体 3. 怪癖 4. 借口Rrange 范围rank 级rationalism 理性主义raw data 原始素材R-based implicature 基于关联的涵义realisation 体现received pronunciation. RP 标准发音receiver 受话者;信息接受者recency effectrecognition 识别recursion []n.【数】递回.递回式.循环.可溯recursive []a.】递归的.可溯的;还原的recursiveness 递归性reference 所指参照referential []a.1 指示的所指的reflexive []n..反身动词.反身代词 a.反身的regional dialect 地域方言register []n.语域regressive []a.1.后退的.逆行的.退化的 2. 回归的relative clause 关系分句.关系从句relative pronoun 关系代词relative uninterruptibility 相对的非间断性relevance theory 关联理论reliability 信度repetition 重复residue []n.残余.剩余.剩余成分restricted []a. 受限制的.被限定的restricted language 限制性语言retrieval []n.1. 取回.恢复 2. 纠正.补偿检索retroflex []a.1. 反折的.后翻的 2. 卷舌(音)的n. 卷舌音reverse rhyme 反陨rhyme 韵;韵角;压韵rhythm 韵律;节奏role 角色root 词根root morpheme 词根语素round vowel 圆元音rules of language 语言规则Ssameness relation 相同关系Sanskrit []n. 梵文.梵语 a. 梵文的.梵语的Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis 萨丕尔-沃夫假设Saussure 索绪尔scale of delicacy 精密阶schema []n.1. 轮廓.概要.略图2.先验图式 3.图式second language acquisition 第二语言习得secondary cardinal vowel 次要基本元音secondary stress 次重音segment []n.语流中的一个音素(或单个音)selection restriction 选择限制selectional rules 选择规则self-reflexive 自反身semantic []a.. 语义的.语义学的semantic triangle 语义三角semantics 语义学semi-consonant 半辅音semiotic []a.1.符号学的 2.症状的semiotics 符号学semi-vowel 半元音sense 意义sentence 句子sentence fragments 句子成分sentence meaning 句义sentence memory 句子记忆sentence stress 句重音sentence structure 句子结构sentential calculus 句子演算setting 场景sibilant []a.1.丝丝作响的 2.发丝音的n.1.丝丝音 2.发丝音辅音sign 符号signified 所指.受指signifier 能指.施指simile []n. (修辞)直喻.明喻simultaneity 同时性singular 单数slot 空缺soft palate 软腭sonnet 十四行诗sonorant []n..响音sonority []n.1. 响亮 2. (声音的)响亮程度sound 语音Spanish 西班牙语Speaker 说话者speech 言语spelling 拼写.拼法split infinitives 分裂的不定式spoken corpus 口语语料库spoken language 口语spondee []n.扬扬格spoonerism []n.斯本内现象(即字音的无意互换现象) Standard English 标准英语standardization 标准化statistical analysis 统计分析status 地位stem 词干stimulus 刺激stimulus-response 刺激反应stop 闭塞音stratification []n.成层.阶层的形成stress 重音structure 结构stylistics 文体学subcategorize 次范畴subject 主语subject-deletion 主语省略subjectivity 主观性subjunctive []a.虚拟的n.虚拟语气subordinate construction 从属结构subordination 从属substitutability 替代性substitution 替换suffix 后缀superlative degree 最高级superordinate 上坐标词suprasegmental feature超语段特征syllabic []a.1. 音节的.构成音节的n.音节主音syllabification []n.1. (语音)分音节 2. 分音节法syllable []n. 音节syllabus []n. 教学大纲.课程大纲 2.要目syllogism []n.1.三段论.演绎推理 2.推断 3.诡辩.狡辩symbol 符号synchronic []a. 同时的.共时的synonym []n. 同义字.类义字(分类学中的)同物异名synonymous []a. 同义的.同义词性质的synonymy []n. 同义.同义词研究syntax []n.语法.句法 2. (组成部分的)有条理(或系统)的排列syntactic []a. 按照句法的.句法的Ttacit []a1. 缄默的.不说话的 2. 不明言的.默示的tacit knowledge 默契的知识tagmeme []n.法位.序位tagmemics 法位学tautology []n. 同义反复.重复.赘述template []n. 模块tense vowel 紧元音tense 时态tetrameter []n. 四音步诗行text 语篇textual 语篇功能theme []n. 1.论题.话题.题目 2.主题.主题思想.题材 3.词干.主位tone 声调.音调tongue height 舌高tongue position 舌位tongue tip 舌尖topic 主题trace theory 轨迹论transcription []n. 1.抄写.誊写 2.副本音标.标音transfer 移转transformation 转换transitivity []n.动词的及物性trill []n.颤音trochee []n.扬抑格.长短格trope []n.转义.比喻truth condition 真值条件truth value 真值tu/vous distinction 你/您区别turn length 话语轮次长度turn quantity 话语轮次数量turn-taking 依次发言two-place predicate 二位谓语two-word utterance 二词话语typology 类型学UUnaspirated 不松气的underlying form 底层形式underlying representation 底层表达uninterruptibility 非中断性universal quantifier 普遍限量词universal 普遍现象universality 普遍性universals of language 语言的普遍现象unmarked 未标记的unrounded vowel 非圆元音urban dialectology 都市方言学utterance []n.1.发声.表达 2.说话方式.语调3言辞.言论.话语utterance meaning 语句意义uvula []n. 悬雍垂.小舌uvular []a.小舌的.小舌音的Vvalidity 效度variable 可变化的variable word 可变化词variation变异variety 变体;语体velar []a.1膜的 2.软颚音的n. 软颚音velarization 腭音化velum []n.1.软颚 2.菌膜.缘膜verb 动词verb phrase 动词短语verbal communication 言语交际verbal process 言语过程verbiage []n.1. 废话.冗词 2. 用语.措词vernacular []n.本国语.本地话.方言.行话.日常用语.白话vernacular language education 本地化教育vocabulary 词汇vocal []a.声的.声音的.元音的.浊音的n.元音.浊音vocal cord 声带vocal organ 发音器官vocal tract 声道vocative []a. 称呼的.呼格的n.呼格voice 语态voiced consonant 浊辅音voiced obstruent 浊塞音voiced (sound) 浊音voiceless consonant 清辅音voiceless obstruent 清塞音voiceless(sound) 清音voicing 浊音化,有声化vowel []n. 1.元音 2. 元音字母vowel glide 元音音渡WWh-interrogative 特殊疑问句women register 女性语域-word 词word class 词类word formation 词语形成word group 词组word meaning 词义word order 词序word recognition 词语识别word formation 词语形成word-for-word 逐词翻译wording []n. 措辞.用语written language 书面语written text 篇章XY ZYes--no interrogative 是非问句yes--no question 是非问句zero 零.零形式zeugma []n. 轭式搭配,轭式修饰法欢迎下载21。
翻译硕士(MTI)考研必备:常见词汇表-W小编网上查找中国日报常用词汇表A-Z,希望对大家词汇掌握有所帮助。
以下为汉语W开头的单词,希望大家认真记忆。
挖墙脚undermine the foundation of sth.; cut the ground from under sb's feet歪风邪气unhealthy practices and evil phenomena/外层空间outer space/外汇储备foreign exchange reserve (forex reserve)/外汇管理局Administration of Exchange Control外汇管制foreign exchange control外交庇护diplomatic asylum/外交斡旋diplomatic offices/外联网(计算机) extranet/外卖take-out外卖店take-out restaurant外贸单证员vouching clerk/外贸自营权power to engage in foreign trade/外企foreign company/外税局foreign-related tax bureau外滩(上海) The Bund外逃资本flight capital/外向型经济export-oriented economy外星人extraterrestrial being (ET)外需overseas market demand/外债foreign debt; external debt/顽固分子die-hard/万维网(计算机) World Wide Web(WWW)/汪辜会谈Wang Daohan-Koo Chen-fu Talks (Wang-Koo talks)王储,王太子Crown Prince王水aqua regia网吧Internet bar网虫netter; Internet geek网关gateway网恋online love affair网络出版online publishing网络管理员network administrator网络化networking网络经济cybereconomy网络恐怖主义cyberterrorism网络摄象机web cam网民netizen; net citizen; cyber citizen网上冲浪surf the Internet网上交易平台online trading platform网友net friend往返机票return ticket; round-trip ticket/往事如风The past has vanished (from memory) like wind.; What in past, is past.望子成龙hold high hopes for one's child/危房dilapidated building/威武之师,文明之师mighty force and civilized force/微软公司Micorsoft Corporation/微软移动构想Microsoft Vision for Mobility; Microsoft Mobility Initiatives违反合同breach of contract/围城》A Surrounded City围垦造田enclose tideland for cultivation; reclaim land from marshes唯利是图draw water to one's mill唯一致命的弱点Achilles' heel维护人权和不断改善人权状况safeguard human rights and steadily improve the human rights situation伪君子hypocrite; a wolf in sheep's clothing伪劣商品赔还法lemon law卫冕世界冠军reigning world champion卫星城satellite town/卫星导航satellilte navigation/慰安妇comfort woman/温饱工程Adequate Food and Clothing Program/温饱工程bring-warmth fill-bellies project温室气体greenhouse gases/文化产业culture industry/文化旅游culture-oriented travel/文科liberal arts文明街道model community文韬武略military expertise; military strategy纹身tattoo/稳定物价stabilize prices/稳定压倒一切Maintaining stability is of top priority问讯处information office; inquiry desk我们在国际上说话是算数的We always live up to our international commitments./乌拉圭回合Uruguay Round乌龙球own goal/污染指数pollution index/污水处理sewage treatment/ disposal/凯程2016年集训营考取北京地区翻译硕士学员30多人,成功率85%以上!屋顶花园broof garden屋漏又逢连阴雨Misfortunes never come singly. When it rains it pours./无风不起浪There are no waves without wind. There's no smoke without fire./无氟冰箱Freon-free refrigerator无公害蔬菜green vegetable/无力偿付的公司insolvent corporation/无人售票self-service ticketing无绳来电显示电话ordless telephone with caller ID无土栽培soil-less cultivation无为而治govern by doing nothing that is against nature; govern by non-interference无线应用协议W AP(wireless application protocol)无息贷款interest-free loan/无形资产intangible assets无形资产intangible assets; immaterial property/无源雷达passive radar/无源之水,无本之木water without a source, and a tree wiithout roots/无中生有make/create something out of nothing五保户household enjoying the five guarantees (childless and infirm old persons who are guarateed food, clothing, medical care, housing and burial expenses)/五讲四美三热爱the movement of five stresses, four points of beauty and three loves(The five stresses are: stress on decorum, manners, hygiene, discipline and morals. The four points of beauty are: beauty of the mind, language, behavior adn the enviornment. The three loves are: love of the motherland, socialism and the Communist Party.)/ 文联literary federation五金化工metals and chemicals武侠小说tales of roving knights; martial arts novel; kung fu novel物价局Price Bureau物流logistics; the interflow of goods and materials/物人human vegetable; vegetable物业管理estate management, property management物以类聚,人以群分Birds of a feather flock together./物质文明material progress/物质文明建设和精神文明建设一起抓pay attention to ethical as well as material progress/物种起源origin of species/凯程教育:凯程考研成立于2005年,国内首家全日制集训机构考研,一直从事高端全日制辅导,由李海洋教授、张鑫教授、卢营教授、王洋教授、杨武金教授、张释然教授、索玉柱教授、方浩教授等一批高级考研教研队伍组成,为学员全程高质量授课、答疑、测试、督导、报考指导、方法指导、联系导师、复试等全方位的考研服务。
All Saint’s Day 万圣节American plan约能源(旅馆的)美国式收费式a soft job 轻松的工作a widow’s mite 礼轻情义重beefcake 男性健美照be free to practice one’s religion 宗教信仰自由“bifocal” vision “双重”视野break with old customs 抛弃传统busboy (饭店的)洗碗擦桌子的杂工Catch-22 无法摆脱的困难;难以逾越的障碍civic values 大众价值观clash with civilizations 文明的碰撞consumerist creed 消费至上主义corporate culture 企业文化country fair 乡村博览会cross-cultural bridge 跨文化桥梁cross-cultural communication 跨文化交流cultural borrowing 文化借用cultural complex 文化情结cultural development 文化建设cultural devolution 文化退化cultural differences 文化差异cultural hegemony 文化霸权cultural heritage 文化遗产cultural identity 文化认同cultural impact 文化影响cultural insights 文化视角cultural lag 文化落后cultural life 文化生活cultural manifestation 文化诉求cultural misreading 文化误读cultural pluralism; multiculturalism 文化多元化cultural shock 文化冲击cultural traditions 文化传统culture area 文化区culture of tolerance 宽容的文化culture-oriented travel 文化旅游culture trait 文化特质dialogue among civilizations 文明间的对话dinner etiquette 餐桌礼仪dominant culture 主导文化ethnic origin 种族起源flower children 配花嬉皮士Flower Generation 花季的一代generation X (90年代的)未知的一代gold-collars 金领阶层hard drug 硬毒品;易成瘾的烈性毒品(如海洛因、可卡因、吗啡等)heterogenous culture 异质文化high culture 优等文化;高级文化human civilization 人类文明humane historical sites 人文历史遗址hyper-individualism 超级个人主义intercultural dialogue 跨文化对话isomorphic cultural community 同质文化群体King’s English 纯正英语language restriction 语言限制主义Lazy Susan (指一种盛食品的)自动转盘(方便顾客选用的食品)low culture 低等文化;低级文化low tea 晚餐前茶点mainstream culture 主流文化Mary Jane 大麻(烟叶)“me” generation (70年代的)“为我”的一代midriff 露脐装national identity and values 民族特性和价值观national sentiments 民族感情new-collars (指二战后的第一代婴儿潮中出生的人)Nobel laureate 诺贝尔获得者off license 售酒执照orphan book 孤本pot culture 大麻文化(指以吸用大麻为中心的生活方式)prejudice and misunderstanding 偏见和误解promote sociability 促进社会交往sample local culture 领略当地文化service station 加油站,服务站silent generation (指50年代成年的人)沉默的一代soft drug 软毒品;不宜成瘾的毒品spiritual enhancement 精神升华the beaten generation 垮掉的一代The Clash of Civilization 《文明冲突》the gilded age 镀金时代the lost generation 迷茫的一代the Millennials 千禧一代tolerance and mutual respect 互相宽容和尊重value of knowledge 知识的价值value proposition 价值主张Vietnam War generation 越战的一代(60年代成年的人)weekly-shoppers throwaways 每周购物一次的人看就随手扔掉的那种杂志Yaps (young aspiring professionals) 亚皮士/雅皮士/优皮士(少壮职业人士/年轻、不断得到升迁的专业人士)yellow boy 金币These two cultures, which were created in different areas, developed in parallel and without interference.这两种文化产生于不同的地区,他们的发展并行不悖,互不影响。
翻译必备词汇:艺术类相关词汇学习work 作品work of art 艺术作品masterpiece 杰作plastic arts 造型艺术graphic arts 形象艺术Fine Arts 美术art gallery 画廊,美术馆salon 沙龙exhibition 展览collection 收藏author 作者style 风格inspiration 灵感,启发muse 灵感purism 修辞癖conceptism 格言派,警名派Byzantine 拜占庭式Romanesaue 罗马式Gothic 哥特式expressionism 表现主义Fauvism 野兽派abstract art 抽象派,抽象主义Cubism 立体派,立体主义Dadaism 达达主义surrealism 超现实主义naturalism 自然主义existentialism 存在主义futurism 未来主义Baroque 巴洛克式Rococo 洛可可式classicism 古典主义,古典风格neoclassicism 新古典主义romanticism 浪漫主义realism 现实主义symbolism 象征主义impressionism 印象主义Art Nouveau 新艺术主义翻译必备词汇:地理常考词汇学习发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!earth'saxis 地轴latitude 纬度longitude 经度subtropical 亚热带的subfrigid 亚寒带的archipelago 群岛humidity 温度aircurrent 气流front 锋面earthquake 地震epicenter 震央erosion 侵蚀reef 矿脉glacier 冰河iceberg 冰山meander 曲折ributary 支流delta 三角洲heavenlybody 天体astronomy 天文学constellation 星座Galaxy 银河galacticnebula 银河星云satellite 卫星planet 行星asteroid 小行星meteor 流星meteorite 陨石翻译必备词汇:外贸相关词汇发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!债转股debt-to-equity swap通货紧缩deflation通货膨胀inflation非配额产品quota-free products风险基金venture capital国家补贴public subsidies季节性调价seasonal price adjustments千年问题millennium bug外援方式modality of foreign aid劳务合作labor service cooperation瓶颈制约bottleneck”restrictions放松银根ease monetary policy流动人口floating population贪图安逸crave comfort and pleasure消费膨胀inflated consumption信息化informationize无氟冰箱freon-free refrigerator无纸交易paperless transaction倒爷profiteer机构重叠organizational overlapping所有制形式forms of ownership经常性的财政收入regular revenues慢性萧条chronic depression就业前培训pre-job training岗位培训on-the-job training对外项目承包foreign project contracting部长级会议ministerial meeting公正合理equitable and rational减免债务reduce and cancel debts工程项目engineering project同步增长increase in the same pace隆重开会formal sitting全会plenary meeting来自 开会sitting, meeting(美作:session)会期session (美作:meeting)工作小组working party席位seat, headquarters主管团体governing body圆桌round table工业增加值industrial added value固定资产投资investment in the fixed assets建材building materials配件accessories备件spare parts进口环节税import linkage tax营业税turnover tax企业所得税corporate income tax抵免offset省会provincial capital超前消费deficit spending翻译必备词汇:海关类词汇发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!Customs Bond 海关担保Surety Company 担保公司Principle 本人Carrier 承运人Attorney 代理人/委托人Freight Forwarder 货运代理Liquidated Damages 违约赔偿金Solvency 偿付能力Security 抵押品/保证金Power of Attorney 委托书Make a Complete Entry 正式/完整申报Bill of Lading 提单Condemned Goods 有问题的货物Customs Liquidation 清关Customs Clearance 结关Court Costs 诉讼费用CFR(Code of Federal Regulations)美国联邦政府行政法规汇编Jointly and Severally Liable For负连带责任翻译必备词汇:河流相关词汇学习发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!source lake 河源湖rivulet 小溪creek, brook 小河canyon, gorge 峡谷waterfalls 瀑布tributaries, streams 支流rapids 急流valley 流域north fork 北叉branches 分支natural levee 天然堤岸river bed 河床valley 河谷gorge 峡谷V-shaped valley 幼年谷widened V-shaped valley 青年谷U-shaped valley 壮年谷synclinal valley 老年谷south fork 南叉point 汇合点alluvial fan 冲积扇right bank 右岸left bank 左岸oxbow lake 牛轭湖downstream 顺流而下upstream 逆流而上ait 江心岛swamp, marsh 沼泽flood land 河滩地main channel 主水道islands 岛distributaries 分流delta 三角洲sand bar 沙洲cross section of river 河流断面river channel 河道dike 堤翻译必备词汇:家庭有关英语词汇学习发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!my family 我家my people 我家人next of kin 近亲family life 家庭生活caste 社会地位generation 代branch 支,系tribe 部族,部落clan 氏族race, breed 种族lineage 宗族,世系stock 门第,血统of noble birth 贵族出身of humble birth 平民出身dynasty 朝代origin 出身ancestry 祖先,先辈extraction 家世descent, offspring 后代,后辈descendants 后代,晚辈progeny, issue 后裔succession 继承kinsmen by blood 血亲affinity 姻亲关系,嫡戚关系kinsmen by affinity 姻亲blood 血family tree 家谱consanguinity, blood relationship 血缘ancestors/forebears/forefathers 祖先relations/relatives/kinfolk/kin 亲属翻译必备词汇:酒店有关词汇学习发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!information desk 服务台hotel register book 旅客登记簿registration form 登记表newsstand 售报处postal service 邮局服务处shop 小卖部bar 酒吧间lounge 酒店大厅billiard-room 台球房dining-room, dining hall 餐厅men's room 男盥洗室ladies' room 女盥洗室cloak-room 寄存处basement 地下室cellar 地窖broom closet 杂物室room number 房间号码room key 房间钥匙suite 套房single room 单人房double room 双人房sofa, settee 长沙发easy chair 安乐椅armchair 扶手椅wicker chair 藤椅folding chair 叠椅swivel chair 转椅rocking chair 摇椅stool 凳子bench 板凳tea table 茶几wardrobe 衣柜built-in wardrobe, closet 壁橱screen 屏风hat rack 帽架rug 小地毯carpet 大地毯slipper 拖鞋single bed 单人床double bed 双人床mattress 褥子quilt 棉被blanket 毯子sheet 床单bedspread 床罩cotton terry blanket 毛巾被pillow 枕头pillowcase 枕套mat 席cushion 垫子翻译必备词汇:城市有关词汇学习发表日期:2011-4-1 来源:中大网校[在线考试]为了帮助广大考生系统的复习翻译资格考试,更好的掌握翻译资格考试的重点内容,小编特编辑汇总了2011年翻译资格考试的重点辅导资料,希望对您此次参加考试有所帮助!centre of population 城市city 城capital 首都metropolis 大都市centre 市中心(美作:center)shopping centre 商业区municipality 市政当局municipall 市的,市政的district 区residential area 居民区,住宅区urban 市区的suburb 近郊区outskirts 郊区slums 贫民窟,贫民区shantytown 贫民区village 村hamlet 小村hole, dump 狭小破旧的住房locality 所在地Chinese quarter 唐人街extension 范围,扩展house 房子building 楼房skyscraper 摩天楼flat 居住单元,套房shop, store 商店department stores 百货公司bazaar, bazaar 市场market 市场,集市junk shop 旧货店newsstand 报摊Commodity Exchange 商品交易所Stock Exchange 股票交易所town hall 市政厅Lawcourt 法院church 教堂cathedral 大教堂chapel 小礼拜堂cemetery 墓地,公墓grave, tomb 坟,墓school 学校university 大学library 图书馆theatre 剧院(美作:theater) museum 博物馆zoological garden 动物园fairground, fun fair 游乐园stadium 体育场general post office 邮局station 车站art museum 美术馆art gallery 画廊botanical garden 植物园monument 纪念碑public telephone 公共电话public lavatory 公共厕所national highway 国道traffic light 交通灯barracks 兵营。
1.Allegory (寓言)A tale in verse or prose in which characters, actions, or settings represent abstract ideas or moral qualities.寓言,讽喻:一种文学、戏剧或绘画的艺术手法,其中人物和事件代表抽象的观点、原则或支配力。
2.Alliteration (头韵)Alliteration is the repetition of the same initial consonant sound within a line or a group of words.头韵:在一组词的开头或重读音节中对相同辅音或不同元音的重复。
3.Allusion (典故)A reference to a person, a place, an event, or a literary work that a writer expects the reader to recognize and respond to.典故:作者对某些读者熟悉并能够作出反映的特定人物,地点,事件,文学作品的引用。
4.Analogy (类比)A comparison made between two things to show the similarities between them.类比:为了在两个事物之间找出差别而进行的比较。
5. Antagonist (反面主角)The principal character in opposition to the protagonist or hero or heroine of a narrative or drama.反面主角:叙事文学或戏剧中与男女主人公或英雄相对立的主要人物。
6. Antithesis (对仗)The balancing of two contrasting ideas, words, or sentences.对仗:两组相对的思想,言辞,词句的平衡。
H海峡两岸交流基金会(海基会) Strait Exchange Foundation(基金会) of (Taiwan, China)(SEF)海峡两岸关系协会(海协会) the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS)行业信息发布制度 information release system for industries 行业准入制度 industry access system和平共处五项原则:互相尊重领土完整和主权、互不侵犯、互不干涉内政、平等互利、和平共处Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence: mutual respect for territorial integrity and sovereignty mutual non-aggression, non-interference in each other’s internal affairs, equality and mutual benefit, and peaceful coexistence和平解决台湾问题 peaceful settlement of the Taiwan question 和平大使 Messenger of Peace核心竞争力 core competitiveness鸿门宴 Hongmen banquet红楼梦户籍改革 household registry reform; residential system reform 户口簿 residence(合法居住资格,住处,居住,住宅) booklet ▲户口管理制度 "domicile(较正式,家,住所) system, residence registration(登记,挂号) system互联网服务提供商 Internet Service Provider (ISP)换届选举 election at expiration(期满,终止) of office terms 环太平洋地区 Pacific Rim环保专项治理 special projects to address(对付) serious environmental problems黄、赌、毒 pornography(黄), gambling and drug abuse and trafficking*(农产品国内支持)"黄箱"措施 Amber Box measures灰色收入 gray income汇率制度 currency regime(政治制度,政权)混合所有制 diversified ownership; mixed ownership婚前协议 premaritial agreement货币操纵国 currency manipulator(货币供应量 measure of money supply货币回笼 withdrawal of currency from circulation货币留成制度 currency retention scheme货到付款 cash on deliveryJ基本国策 basic state policy; basic national policy基本国情 fundamental realities of the country基本人权 fundamental human rights基本医疗保险制度 basic medical insurance system基层工作grass-roots work基层监督 grass-roots supervision基层民主 democracy at the grassroots level基层文化建设 primary-level cultural undertakings机场建设费 airport construction fee继承税 inheritance tax基础税率 base tariff level鸡蛋碰石头 like an egg striking a rock; attack… stronger than oneself基地组织 al-Qaeda group缉毒 investigate drug smuggling; capture drug smugglers缉毒 investigate drug smuggling; capture drug smugglers机构臃肿 overstaffing in organizations (government)计划单列市 city specifically designated in the state plan 计划生育责任制 responsibility system of family planning季节性调价 seasonal price adjustment吉尼斯世界记录 Guinness World Records即期消费 immediate consumption急人民所急,忧人民所忧 making the desires and worries of the people one's own吉日良辰 auspicious day纪实文学 documentary writing纪实小说 documentary fiction技术产权交易所 technology equity market; technology property right exchange技术成果商品化commercialization of technological achievements集资房 house built with fundscolected by the buyers技术密集产品 technology-intensive product缉私力量 the forces engaged in the fight against smuggling 纪委 discipline inspection commission绩优股 blue chip价格听证会 public price hearings甲骨文 oracle bone inscriptions(铭文,碑文,题字)假冒伪劣产品 counterfeit and shoddy products监管漏洞 supervision loopholes荐贤举能 recommend the virtuous and the able奖励工资制度 a bonus wages system; a system of higher pay for better performance江南水乡 the south of the lower reaches of the Yangze River 叫板 challenge; pick a quarrel脚踩两只船 sit on the fence矫情 use lame arguments教育部社政司 Social Science Research and Ideological Work Department of the Ministry of Education教育规划纲要 national education plan教育乱收费 unauthorized collection of fees by educational institutions教育体制 education bureaucracy加强水土保持 reinforce the conservation of water and soil 基层民主政治 democracy at the local level节能降耗减排 to save energy, lower energy consumption and reduce pollutants discharge金本位 gold standard金刚经 Vajracchedika-sutra进口差价税 import variable duties进口附加税 import surcharge进口环节税 import linkage tax金融寡头 financial oligarchy; financial magnate; financial tycoon金融货币危机 financial and monetary crisis金融衍生物financial derivative金融自由化financial liberalization禁渔期 closed fishing seasons; fishing moratorium; fishing ban靖国神社 Yasukuni Shrine经济刺激方案 economic stimulus bill*经济适用房 economically affordable housing经济一体化 economic integration京剧票友 Peking Opera fan京剧人物脸谱 types of facial make-up in Beijing opera金融监管责任制the responsibility system for financial supervision纠风办 State Council Office for Rectifying救灾物资 disaster relief materials居民委员会 residential committee; neighborhood committee; residents's committee局域网 local area network (LAN)军备竞赛 arms race军事对峙 military confrontation军事扩张 military expansion君子之交淡如水 the friendship between gentlemen is as pure as crystal; a hedge between keeps friendship greenK凯恩斯政策 Keynesian policy侃大山 shoot the breeze; chew the fat开放带动战略 strategy spearheaded by opening-up开后门under-the-counter deals; offer advantages to one's friends or relatives by underhand means开源节流 increase income and reduce expenditure抗日战争 War of Resistance Against Japan考勤 check on work attendance考勤制度 work attendance checking system可比价格 comparable prices可比经济指标 comparable economic targets可持续发展 sustainable development可持续发展战略 strategy of sustainable development科教兴国 rejuvenate our country through secience and education 客流量 volume of commuters; passenger volume科学发展观 Scientific Outlook on Development科教兴国战略 strategy of invigorating the country through science, technology and education可透支额度(信用卡) sky-high credit line科学发展观 Scientific Outlook on Development跨行转帐 inter-bank transfer service.快速消费品 fast-moving consumer goods宽带(ADSL技术即非对称数字用户环路技术) ADSL(Asymetric Digital Subscriber Line)跨越式发展 great-leap-forward development扩军备战 arms expansion and war preparation拉闸限电 power rationing垃圾分类收集 separate waste collection滥发纸币 excessive issue of bank notes; excessive note issue 劳保医疗制度 labor medicare system劳动合同制 labor contract system劳动力产权 labor property rights劳动力过剩 labor surplus;manpower surplus劳动力资源配置 allocation of labor resources劳动密集型产业 labor-intensive industry老年保险制度 endowment insurance劳务输出 export of labor services老油条 wily old bird; old slicker老字号 an old and famous shop or enterprise; time-honoured brand老龄化社会 aging society劳保 labor insurance累进税率 progressive tax rate冷战思维 Cold War mentality离岸价格 free on board(FOB)立法真空 legislation vacuum利改税 substitution of tax payment for profit delivery立国之本 the foundation underlying all efforts to build the country立体开放口岸 trading port open to sea, land and air离退办 office for the affairs of the retired workers离退休人员基本养老金 basic pensions for retirees恋父情结 Electra complex联产承包责任制 system of contracted responsibility linking remuneration to output; contract system with remuneration linked to output联合公报 joint communique联合国反腐败公约 UN Convention Against Corruption《联合国海洋法公约》 The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea联合国环境署 UNEP (United Nations Environment Program)联合国会费 the UN membership dues (fee)联合国开发计划署 UNDP (United Nations Development Program) 联合国粮农组织 FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation)联合国维持和平部队 United Nations Peace Keeping Forces联合国维和行动 UN peacekeeping operations恋母情结 Oedipus complex连锁反应 chain effect; domino effect练摊 to be a vendor廉政公署 Independent Commission Against Corruption (ICAC)廉租房 low-rent houses两岸民间行业组织 non-governmental trade organizations across the Straits两岸三地 the Mainland, Taiwan and Hong Kong两岸直航促进会 Association for Promotion of Cross-Straits Direct Transportation两岸直航 cross-Straits direct transportation link两岸直航包机 Direct Chartered Flight Across the Taiwan Straits 粮食风险基金 grain risk fund粮食流通体制 grain distribution system粮食收购部门 (government's) grain procurement (purchasing) agencies粮食主产区 major grain producing areas两伊战争 the Iran-Iraq War粮油关系 grain and oil rationing registration两院院士 academicians of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Academy of Engineering两岸关系 relations across the Taiwan Straits两岸周末包机直航 cross-Straits weekend charter flight《聊斋志异》 Strange Tales of a Lonely Studio临时政府 interim government零和博奕 zero-sum game; zero game临时价格干预措施 interim price control measure流动人口 transient population; floating population流动性负债 current liabilities流动性资产 current assets流动资产 current assets; liquid assets流动资金circulating fund; floating money; liquid fund; working fund六合彩 mark-six lottery六艺:礼、乐、射、御、书、数 "six classical arts: rites, music, archery, riding, writing, arithmetic"六方会谈 the Six-Party Talks《论语》 Analects of Confucius轮值主席 rotating chairman落地签证 visa upon arrival旅游黄金周 golden week for tourismM马尔萨斯人口论 Malthusian Theory of Population; Malthusianism 马太效应 the Matthew effect麦克马洪线 McMahon Line贸易和投资自由化和便利化TILF (Trade and Investment Liberalization and Facilitation)贸易纠纷 trade rows贸易逆差 adverse balance of trade; trade deficit; trade gap 贸易顺差 favorable balance; trade surplus贸易与发展委员会 Committee on Trade and Development贸易战 trade war贸易制裁 trade sanction贸易自由化 trade liberalization帽子戏法 hat trick煤矿爆炸 mine blast美食节 gourmet festival美元贬值 dollar depreciation门户开放政策 open-door policy门户网站 portal门罗主义 Monroe Doctrine免税商店 duty-free shop免税商品 tax-free commodities建设性伙伴关系 a constructive strategic partnership免验放行 pass without examination (P.W.E)民法通则 general provisions of the civil law民工潮 farmers' frenzied hunt for work in cities民间协商 consultation on a non-governmental basis民主集中制 democratic centralism民主监督 democratic supervision民主决策 make decisions through a democratic process民族国家 nation state民族凝聚力 national cohesion民族区域自治 regional autonomy of ethnic minorities民族事务委员会 Ethnic Affairs Commission民办高校 private higher learning institution名利双收 gain in both fame and wealth明码标价制度 system that commodity prices must be mar名人堂 walk of fame名人效应 celebrity charm明文 explicit terms明星代言 celebrity endorsement民间文化遗产 folk cultural heritage民意 will of the people民怨 social grievance模糊战略(美国在台湾问题上奉行的政策) indistinct strategy; ambiguous strategy默哀 silent tribute目标跟踪雷达 target-tracking radar(TTR)睦邻友好关系(合作) good-neighborly and friendly relations (cooperation)牧业税 livestock taxN纳税申报制度 tax declaration system纳斯达克 National Association of Securities Deal Automated Quotations (NASDAQ)耐用品 durable goods南北对话 North-South dialogue南南合作 South-South cooperation南水北调工程 South-to-North water diversion project南巡讲话 South Tour Speeches内阁成员 cabinet lineup内政部长 interior minister泥石流 mud-rock flow年度国家预算 annual State Budget年龄结构 age structure年夜饭 family reunion dinner年画 New Year painting农产品出口补贴 agricultural export subsidies农村剩余劳动力 surplus rural labour (labourers)农村信用社 rural credit cooperatives农工党 Chinese Peasants' and Workers' Democratic Party农药残留物 pesticide residue;agricultural chemicals residue 农业产业化经营the industrialization of agriculture; industrialized agricultural operation农业税费改革 reform of rural taxes and administrative charges 农业特产税 taxes on special agricultural products农业增加值 added value of agriculture农转非 rural residents become urban residents农村合作医疗 rural cooperative medical service农村养老金制度 rural pension system农村综合试点改革 trials of comprehensive rural reform女权运动 movement for women's rights。
封建主义feudalism
专制主义absolutism
社会主义socialism
资本主义capitalism
奴隶主义slaverism
集体主义collectivism
个人主义individualism
享乐主义gastronomy
共产主义communism
党派主义factionalism
国家主义nationalism
自由主义liberalism
宗派主义sectarianism
理性主义rationalism
理想主义idealism
科学社会主义scientific socialism
民主主义democratism
投机主义opportunism
公理主义congregationalism
地方自治主义communalism
工会主义unionism
反种族主义antiracism
反社会主义antisocialism
社会民主主义social democracy 种族主义racialism
工团主义syndicalism
商业主义commercialism
教条主义doctrinairism
黑权主义black power
军国主义militarism
公式主义formulism
法西斯主义fascism
平均主义levellism
专业主义professionalism
新艺术主义ant nouveau
消极主义passivism
新殖民地主义neocolonialism 新重商主义neomercantilism
实利主义utilitariantilism
实用主义pragmatism
实证主义positivism
怀疑主义scepticism
神秘主义occultism
无政府主义anarchism
地方主义localism
人文主义humanism
人道主义humanitarianism
抽象主义abstractionism
国家资本主义state capitalism 国际主义internationalism
形式主义formalism
产业主义industrialism
排他主义exclusionism
大男子主义male chauvinism 未来主义futurism
权力主义authoritarianism
联邦主义unionism
独身主义bachelorism
世界主义cosmopolitanism
金钱主义venality
自然主义naturalism
自我中心主义autism
独裁主义tarianism
黑人人权主义negroism
折中主义eclecticism
废除主义abolitionism
废奴主义abolitionism
霸权主义hegemonism
内省主义introspections
修正主义revisionist
印象主义impressionism
虚无主义nihilism
三民主义the Three Principles of the People put forward by Dr. Sun Yat-sen 地方保护主义regional protectionism
男权主义male chauvinism
女权主义feminism
权贵资本主义crony capitalism
工具主义instrumentalism
表现主义expressionism
本本主义bookishness
结构主义constructivism
浪漫主义romanticism
认知主义cognitivism
唯美主义aestheticism
存在主义existentialism
无为主义quietism
世俗主义secularism
恐怖主义terrorism
道德主义moralism
立体主义cubism
沙文主义chauvinism 现代主义modernism。