能源与动力工程专业英语
- 格式:doc
- 大小:20.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

专业英语四级(听写听力)模拟试卷124(题后含答案及解析)题型有:1. DICTATIONPART I DICTATIONDirections: Listen to the following passage. Altogether the passage will be read to you four times. During the first reading, which will be done at normal speed, listen and try to understand the meaning. For the second and third readings, the passage will be read sentence by sentence, or phrase by phrase, with intervals of 15 seconds. The last reading will be done at normal speed again and during this time you should check your work.1.正确答案:New Renewable Energy Sources Scientists and engineers are constantly working / to make new renewable energy sources. / Three of the most promising are as follows. / The first one is tidal energy, / which exploits the power of tides to produce electricity. / Some tidal energy projects use the moving tides / to turn the blades of an engine. / Other projects use small dams to control the flow of water. / The next is wave energy, which uses waves from the ocean, lakes, or rivers. / Some wave energy projects use the same equipment that tidal energy projects do. / Other wave energy projects float directly on waves. / The water’s constant movement over and through the floating pieces of equipment can create electricity. / The last one is algae fuel, a type of energy / that uses the unique chemicals in seaweed to create a clean and renewable fuel. / And it does not require acres of crop land to get this kind of fuel. /解析:新的可再生能源科学家和工程师不断致力于开发出新的可再生能源。

化学工程专业英语词汇(整理版)
1. 介绍
本文档整理了一些化学工程专业常用的英语词汇,旨在帮助学生更好地理解和应用相关词汇。
2. 词汇列表
- Chemical Engineering: 化学工程
- Reactor: 反应器
- Heat Exchanger: 热交换器
- Distillation: 蒸馏
- Extraction: 提取
- Polymerization: 聚合
- Crystallization: 结晶
- Filtration: 过滤
- Evaporation: 蒸发
- Drying: 干燥
- Mass Transfer: 质量传递
- Fluid Mechanics: 流体力学
- Thermodynamics: 热力学
- Reaction Kinetics: 反应动力学
- Process Control: 过程控制
- Chemical Plant: 化工厂
- Safety Regulations: 安全法规
- Waste Management: 废物管理
- Environmental Impact: 环境影响
- Sustainable Development: 可持续发展
- Renewable Energy: 可再生能源
以上是一些化学工程专业常用的英语词汇,希望对学生们的研究和研究有所帮助。
3. 结束语
本文档提供了一个简单的化学工程专业英语词汇列表,供学生们参考和学习使用。
通过掌握这些词汇,学生们将能够更好地理解和应用化学工程相关的知识。
希望本文档对学生们有所帮助,祝大家学业进步!。

大连海洋大学能源与动力工程专业培养方案能源与动力工程专业培养方案一、培养目标本专业以热工、力学和机械科学理论为基础,以计算机和控制技术为工具,培养德、智、体全面发展,具备能源生产、转化、利用与动力系统研发基本理论和应用技术,以及具备节能减排理念,适应国家能源与动力工程行业的人才需求和社会发展需要,并具有较强的能源与动力工程实践能力和一定创新精神,能在工业、国防、民用等领域从事能源动力、人工环境、新能源研究开发、优化设计、先进制造、智能控制、应用管理等工作的高级应用型人才。
二、基本培养规格1. 综合素质基本要求(1)热爱祖国,有为国家富强、民族昌盛而奋斗的理想,有事业心和责任感;努力学习,初步树立科学的世界观和为人民服务、为社会服务的人生观。
(2)崇尚科学,崇尚实践;具有一定的创新意识、求真务实精神和相应能力;确立终身学习观念,具有一定的知识更新能力;具有较宽广的基础知识面,较强的进取潜力和发展后劲。
(3)养成良好的生活和锻炼习惯,具有健康的体魄和良好的心理素质,受到必要的军事训练。
(4)具有一定的人文、艺术和社会科学基础,具备良好的口头和文字表达能力。
2. 专业基本要求(1)掌握本专业所必需的数学、物理、力学、材料、机械、热工、电工电子以及自动控制等工程科学基础知识,掌握计算机及控制技术等现代工具。
(2)具有本专业必需的绘图、计算、实验、测试、文献检索和基本工艺操作等基本技能。
(3)掌握一门外国语,能顺利阅读本专业书刊,有初步的听、说、写能力。
(4)了解能源生产、转化和利用的行业需求动态,熟悉能源高效转化和利用技术的理论前沿和应用背景,贯彻执行节能减排的方针政策和技术路线。
(5)了解能源与动力工程技术的发展趋势,及时掌握并应用相关新技术为社会服务,成为具备创新精神和创新能力,善于解决实际问题的工程技术人才。
(6)具有专门针对能源动力系统提出、分析及解决问题的能力,能进行能源新产品和新系统的设计与开发、运行维护以及相关制造,具有集成创新能力。

机电工程专业英语答案【篇一:机电工程专业英语】r (rotating member) in an electric motor has rotational inertia,and a torque is required to bring it up to speed when the motoris started. if the motor shaft is rigidly connected to a load witha large rotational inertia, and the motor is started suddenly by closing a switch, the motor may not have sufficient torquecapacity to bring the motor shaft up to speed before thewindings in the motor are burned out by the excessive current demands . a clutch between the motor and the load shafts will restrict the starting torque on the motor to that required to accelerate the rotor and parts of the clutch only.电机的转子(转动元件之一)是有惯性的。
当电机启动时,需要一个力矩使转子提升速度。
如果电机轴与负荷是刚性连接,就会有更大的惯性。
这样启动,电机在还没有足够的力矩使转子提升到一定速度,可能就被过电流烧毁了线圈。
在电机和负荷之间的离合器,会限制启动转矩来保证有足够的力矩只加速转子和离合器。
有些机床,可以非常方便的在电机连续运转时,通过操作离合器来启动或停止机器的。

能源动力硕士专业学位一、专业介绍能源动力硕士专业学位是一种面向能源与动力领域的高级学位,旨在培养具备较高的理论水平和实践能力,能够在能源与动力领域开展研究、管理和应用工作的高层次人才。
该专业涵盖了能源与环境、新能源技术、节能减排、燃气轮机等多个方向。
二、课程设置1.必修课程(1)工程热力学基础(2)传热学基础(3)流体力学基础(4)燃烧理论与技术(5)内燃机原理与技术(6)发电厂系统分析与设计2.选修课程(1)新型储能技术及应用(2)清洁化石能源利用技术及应用(3)核电站系统设计及安全分析三、就业前景1.行业前景广阔:随着国家对清洁能源的重视和环保政策的不断加强,能源动力行业将迎来更加广阔的发展前景。
2.职业选择多样:毕业生可在各大企事业单位从事能源与动力领域的研究、开发、设计、管理等工作,也可在政府、科研院所、高校等单位从事相关领域的教学和研究工作。
3.薪资待遇优厚:能源动力行业属于高新技术领域,毕业生的薪资待遇相对较高。
四、就业单位1.国家电网公司2.中石化集团3.中海油集团4.华电集团5.华能集团五、就业岗位1.能源与环境工程师2.新能源技术研究员3.节能减排技术专家4.燃气轮机设计师六、就业要求1.具备扎实的理论基础和实践经验;2.掌握相关领域的前沿知识和技术;3.具备较强的分析和解决问题的能力;4.具备良好的沟通和协调能力;5.具备一定的英语水平。
七、学习建议1.注重理论学习:掌握扎实的理论基础是成为一名优秀专业人才的必要条件。
2.注重实践能力:能源动力行业需要的不仅是理论水平,还需要具备一定的实践经验和动手能力。
3.注重团队合作:在专业学习过程中,要多参加团队合作的项目,培养良好的沟通和协调能力。
4.注重英语学习:英语是国际通用语言,在专业学习和职业发展中都有着重要的作用。

太原理工大学各学院及专业(方向)中英文对照表【机械工程学院】College of Mechanical Engineering机械设计制造及其自动化Mechanical Design & Manufacturing and Automation1.机械制造及其自动化Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation2.机械设计及理论Mechanical Design and Theory3.机械电子工程Mechatronics Electronics Engineering4.车辆工程Vehicle Engineering工业设计Industrial Design机械系Department of Mechanical Engineering机械制造工艺及设备Machinery Manufacturing Process and Equipment【材料科学与工程学院】College of Materials Science and Engineering材料成型及控制工程Materials Processing and Controlling Engineering金属材料工程Metallic Materials Engineering无机非金属材料工程Inorganic Non-metallic Materials Engineering冶金工程Metallurgical Engineering高分子材料与工程Macromolecular Materials and Engineering材料物理Materials Physics材料化学Materials Chemistry1.材料物理与化学Materials Physics and Chemistry2.材料科学与工程Materials Science and Engineering3.材料加工工程Materials Processing Engineering4.钢铁冶金Iron and Steel Metallurgy5.有色金属冶金Nonferrous Metallurgy【电气与动力工程学院】College of Electrical and Power Engineering电气工程及其自动化Electrical Engineering and Automation热能与动力工程Thermal Energy and Power Engineering培养方向:1.热动力工程Thermo Power Engineering2.动力机械及工程Power Machinery and Engineering3.电机与电器Electrical Machinery and Appliances4.电力系统及其自动化Electrical System and its Automation5.高压电绝缘技术High-V oltage Electricity an Insulation Technology6.电气,电子和传动装置Electrical, Electronics and Transmission7.电工理论与新技术Theory and New Technology of Electrical Engineering 【信息工程学院】College of Information Engineering自动化Automation培养方向:电路系统Electric Circuit and System电子信息工程Electronic Information Engineering测控技术与仪器Measurement Control Technology and Instruments培养方向:1.检测技术与自动化设备Detecting Technology and Automatic Equipment2.系统工程Systems Engineering3.模式识别与智能系统Pattern Recognition and Intellectual System通讯工程Telecommunication Engineering培养方向:1.通信与信息系统Communication and Information System2.信号与信息处理Signal and Information Processing电子科学与技术Electronic Science and Technology培养方向:控制理论与控制工程Control Theory and Control Engineering 【计算机科学与技术学院】College of Computer Engineering and Software 计算机科学与技术Computer Science and Technology物联网工程Internet of Things Engineering【软件学院】College of Software软件工程Software Engineering【建筑与土木工程学院】College of Architecture and Civil Engineering建筑学Architecture城市规划Urban Planning土木工程Civil Engineering【水利科学与工程学院】College of Water Conservancy Science and Engineering水利水电工程Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Engineering农业水利工程(含水利信息化方向)Agricultural Water Conservancy Engineering水文与水资源工程Hydrology and Water Resources EngineeringAgricultural Soil and Water EngineeringHydrology and Water ResourcesHydraulics and River DynamicsWater Engineering and Structural EngineeringWater Conservancy and Hydroelectric EngineeringHarbor Beach and Inshore Engineering【化学化工学院】College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering化学工程与工艺Chemical Engineering and Technology(化学工艺、能源化工、精细化工、高分子化工方向)Chemical Engineering and Technology (Chemical Process、Chemical Energy、Fine Chemical、Polymer Chemistry)应用化学Applied Chemistry生物工程Bioengineering制药工程(化学与生物制药工程方向)Pharmaceutical Engineering过程装备与控制工程Process Equipment and Control Engineering化学和生物制药工程方向Chemical and Biological Pharmaceutical Engineering Direction【矿业工程学院】College of Mining Engineering采矿工程Mining Engineering安全工程Safety Engineering资源勘查工程Resource Prospecting Engineering测绘工程Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering地理信息系统工程Geographical Information System Engineering矿物加工工程Mineral Processing Engineering城市地下空间工程City Underground Space Engineering勘查技术与工程Exploration Technology and Engineering【轻纺工程学院】College of Textile Engineering with Academy of Fine Arts 纺织工程Textile Engineering服装设计与工程Apparel Design and Engineering艺术设计Artistic Design(2012级以前学生)服装与服饰设计Fashion Design【艺术学院】艺术设计Artistic Design(2012级以前学生)摄影Photography(2012级以前学生)绘画Painting动画Animation数字媒体艺术Digital Media Art文化产业管理Cultural Industry Management视觉传达设计Visual Communication Design环境设计Environment Design影视摄影与制作Photography and Video Production【环境科学与工程学院】College of Environmental Science and Engineering 给水排水工程Water Supply and Drainage Engineering环境工程Environmental Engineering建筑环境与设备工程Constructing Environment and Equipment Engineering 【数学学院】College of Mathematics数学与应用数学Mathematics and Applied Mathematics信息与计算科学Information and Computing Science统计学Statistics【物理与光电工程学院】College of Physics and Photo Electricity Engineering 光信息科学与技术Optical Information Science and Technology应用物理Applied Physics光源与照明Light Source and Lighting【力学学院】College of Mechanics工程力学Engineering Mechanics【外国语学院】College of Foreign Languages英语English【政法学院】College of Politics and Law法学Law行政管理Public Administration思想政治教育Ideological and Political Education【经济管理学院】College of Economics and Management 市场营销Marketing and Sales工程管理Construction Management会计学Accounting国际经济与贸易International Economics and Trade物流管理Logistics Management电子商务Electronic Business【体育学院】College of Physical Education体育教育Physical Education。

Be in versely (directly)proporti onal to 与. 合成反(正)比The computer system 计算机系统collect solar energy 搜集太阳能collect stamps 集邮Conventional sign 通用标志Conventional units of measurement 常用的计量单位Crank han dle(case )手摇曲柄(去冰箱)chemical power 化学能Diesel power plant 柴油发电厂Diesel engine generator 柴油发电机Direct(alternating) current (DC)直流电(交流电)a electrical power system 电力系统Electrical(mechanical)energy 电能(机械能)Electromagnetic principle 电磁原理a hydraulic turbine 水轮机Mechanical power 机械能A magnetic field 磁场a steam turbine 汽轮机synthetic gas (fiber)合成气体(纤维)petroleum products 石油产品petroleum equipment 石油设备pote ntial en ergy (resources)潜在的能量(资源)Prime mover(energy)原动机(原始能)light (heavy)nuclear particles 轻(重)荷粒子nu clear reaction s(weap ons)核反应(核武器)A thermal power station 火力发电站The thermal unit 热量单元Torque requirement 转矩要求The rotor shaft 转轴Rotor core 转子铁芯nuclear fission 核裂变nuclear safety 核安全chain letter 连锁反应chain reaction 连锁信号steam cycle 蒸汽循环steam power 蒸汽动力fluid medium 流质体fluid mechanics 流体力学nuclear fuel 核燃料solid fuel 固体燃料fissionable isotope 可裂变同位素fissionable materials 可裂变物质critical mass 临界质critical load 临界负载nu clear energy 核(原子)能thermal energy 热能commercial reactor 商用(核)反应堆atomic reactor 核反应堆heat source 热源redioactive source 放射源availability of machinery 机械的可用性availability of the equipment 设备的可用性high pressure zone 高压地带low pressure zone 低压地区commission of a nuclear power station 核电站的运行after commission 投产后precentage of outages 停机率percentage of maintenance 维修率instant loading 瞬间负载take full load 完全负载shutdowns for check 停机检查shutdowns for repairs and maintenance 停机保养13.self-replenishing energy 自行补充的能源self-replenishing water capacity 自行补充的水容量construction of a reservoir 修建水库construction of a dam 大坝的建筑a system of farm irrigation 农田灌溉系统a system of automatic drains 自动排水系统the multi-purpose harness of the Yellow Valley 黄河流域的综合治理the development of Yangtse Valley 长江流域的开发time invariant steady-state 时间恒定不变的稳定状态sinusoidal steady-state 正弦稳定状态conducting materials 导体原料conducting wires 导线maximum current density 最大电流密度weight density 重度a transmissionqd line 输电线路a transmission system 传输系统plane surface 平面quipotential surface 等势面额power system 电力系统power apparatus 电力仪表instantaneous value 瞬时值average value 平均值fluid insulation 液体绝缘solid insulation 固体绝缘resistance network 电阻网络network structure 网状组织allowable current 允许电流allowable load 许可负载the protective relay 继电保护器induction-type relays 感应型继电器voltage signal 电压信号current signal 电流信号measuring operation 测量动作instantaneous operation 瞬时动作alternating current circuits 交流电路direct-current circuits 直流电路static devices 静态设备rotating equipment 转动设备magnetic-induction typesv 磁感应型types of various blood 各种血型the pole face 极面the pole star 北极星a permanent magnet 永久磁铁a permanent committee 常设委员会a cooling system 冷却系统a railway system 铁路系统abnormal operation 非正常运行normal operation 正常运行Long-distance communication 远距离通信Long-distance transmission 远距离传递Voice band communications channel 音频通信信道Selecting the voice channel 选择信道Frequently modulation 频率调制Velocity modulation 速度调节Digital pulse 数字脉冲Error pulse 误差信号脉冲Give priority to the one computer 给一个计算机以优先权Give priority to women and children 给妇女儿童以优先权Have access to the central computer 有进入主计算机的通道Have access to the library 有权利使用图书馆Go out of commission 脱离了权限命令Go out of date 过时了Be identified as the primary 被标识为主机Be identified as transmission 被标识为信息传递Relay the information to its intended destination 将信息转发给预期的目的Relay TV programmes to foreign countries 将电视节目传播到国外Control system 控制系统eating system 加热系统H Physical quantity 物理量Known quantity 已知量Analog technique 模拟技术Digital technique 数字技术Data-handling capability 数据处理器能力Heat transfer capability 传热能力Desired value 理想值Given value 给定值Modify the system 调整系统Modify the design 修改设计Have no effect on 对。

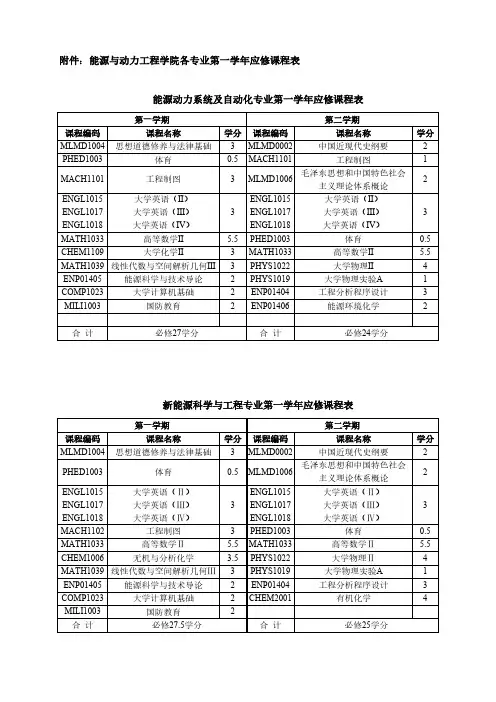
能源与动力工程专业课程设置
公共基础课:高等数学A1、高等数学A2、大学物理B、大学英语读写译1、大学英语读写译2、大学英语读写译3、大学英语读写译4、大学英语视听说(自主学习)1、大学英语视听说(自主学习)2、大学英语视听说(自主学习)3、大学英语视听说(自主学习)4、思想道德修养与法律基础、中国近现代史纲要、马克思主义基本原理概论、毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论、形势与政策、大学体育1、大学体育2、大学体育3、大学体育4
专业基础课:画法几何与机械制图B、工程化学基础、计算机程序设计基础—C 语言程序设计、工程力学B、线性代数A、机械设计基础A、概率论与数理统计A、工程热力学(能动)、流体力学B、传热学A
专业课:能源与动力工程专业导论、电工电子技术B、自动控制原理(能动)、燃料及燃烧学、制冷与低温原理、锅炉原理与设备、汽轮机原理、换热器原理与设计、热力发电厂、动力循环理论及技术
专业选修课:能源与环境工程、热工控制系统、热工测量及仪表、燃烧污染控制、供热工程B、燃气输配B、低温工艺与装置、空调工程B、热动专业仿真软件技术与应用、燃气轮机装置、专业英语(能动)、系统节能、能源与动力工程创新创业综合
专业实践课程:认识实习(能动)、金工实习B、生产实习(能动)、物理实验B、电子实习B、课程设计(锅炉原理与设备)、课程设计(制冷与低温原理)、课程设计(热力发电厂)、课程设计(小型冷库)、电厂运行、仿真训练、课程设计(换热器原理)、毕业设计(能动)
素质拓展与创新课程:大学生心理健康教育、创业基础、大学生就业创业指导、军事训练与国防教育、安全教育、军事理论。

能源与动力工程专业培养方案(工学,能源动力类,080501)一、培养目旳本专业以热工、力学和机械科学理论为基础,以计算机和控制技术为工具,以锅炉与热能供应、低温制冷、电厂为重要方向,培养具有能源生产、转化、运用与动力系统研发基本理论和应用技术,具有节能减排理念,能在工业、民用领域从事能源动力、人工环境、新能源研究开发、优化设计、先进制造、智能控制、应用管理等工作旳创新创业型高级工程技术人才。
二、培养规定1.知识规定(1)具有较扎实旳数学、物理等自然科学基础,纯熟掌握其基本原理与措施;(2)纯熟掌握一门外国语、计算机基础知识;(3)具有一定人文、社会科学基础,科学文献检索和文字表述能力;(4)比较系统、扎实地掌握本专业所必需旳自然科学基础和技术科学基础旳理论知识,具有一定旳专业知识,有关旳工程技术知识和技术经济、工业管理知识,对本专业范围旳科学技术新发展及其动向有一般旳理解;(5) 具有本专业所必需旳制图、运算、试验、测试、计算机应用等基本技能,以及一定旳基本工艺操作技能以及专业创新和创业能力。
2.能力规定(1)具有较强旳自学能力、具有综合应用多种手段(包括外语)查取资料、获取信息旳基本能力;具有应用语言、文字、图件进行工程体现和交流旳基本能力;至少掌握一门计算机高级语言,具有计算机应用、重要测试和试验仪器使用旳基本能力。
(2)本专业学生重要学习动力工程及工程热物理旳基础理论,学习多种能量转换及有效运用旳理论技术,得到现代动力工程师旳基本训练;具有进行动力机械与热工设备及系统旳设计、运行、试验研究旳基本能力。
(3)能比较纯熟地阅读本专业外文书刊,理解本学科国际前沿性旳科学技术最新发展动态,具有一定旳创新性思维和科学研究能力。
3.素质规定(1)热爱社会主义祖国,拥护中国共产党旳领导,掌握马列主义、毛泽东思想和邓小平理论旳基本原理;愿为社会主义现代化建设服务、为人民服务;有为国家富强、民族昌盛而奋斗旳志向和责任感;具有敬业爱岗、艰苦求实、热爱劳动、遵纪遵法、团结合作旳品质;具有良好旳思想品德、社会公德和职业道德。
风能与动力工程专业人才培养方案Undergraduate Program for Wind Energy & Power Engineering Major学科门类工学代码08Discipline Type: Engineering Code: 08类别能源动力类代码0805Type: Energy & Power Engineering Code: 0805专业名称风能与动力工程代码080507sTitle of the Major:Wind Energy & Power Engineering Code: 080507s一、学制与学位Length of Schooling and Degree学制:四年Duration:Four years学位:工学学士Degree:Bachelor of Engineering二、培养目标Educational Objectives本专业培养基础扎实,知识面宽,具有较强的实践能力和良好的发展潜力的高级专门人才。
学生毕业后能够从事风电场的规划、设计、施工、运行与维护,风力发电机组设计与制造,风能资源测量与评估,风力发电新技术开发等风能与动力工程专业的技术与管理工作,并能从事其它相关领域的专门技术工作。
The students of this major are educated into professionals with strong foundations, broad knowledge scopes, strong practical capabilities and great potentials. The graduates may find engineering or managerial positions in Wind Energy & Power Engineering (WEPE) for wind power plant planning, design, construction, operation and management, Wind Turbine Generator System design and manufacturing, wind resources measurement and assessment, wind power New technology design, etc. They can also undertake the professional posts in other fields.三、专业培养基本要求Skills Profile本专业主要学习流体、机械、电气等学科的基础理论,学习风资源测量与评估、空气动力学、机械设计与制造、自动控制的理论和技术,接受现代风力发电专业工程师的基本训练,使学生具有进行风电机组及风电场的设计、制造、运行、试验研究、项目投资与管理的基本能力,一定的创新能力,较强的实践能力和良好的发展潜力。
能源与动力工程专业本科培养计划(卓越工程师教育培养计划实验班)Undergraduate Program for Specialty in Thermal and Power Engineering(Undergraduate Experimental Program for Exemplary Engineer Education)一、培养目标I . Educational Objectives培养具备能源与动力工程知识与现代信息技术及工程应用能力为一体的高级专门技术人才和管理人才。
能在电力、制冷低温、采暖空调、汽车、船舶、流体机械、电子信息、冶金、化工、铁路、医药等部门从事能源动力工程及自动化和相关方面的研究、设计、开发、教学、管理等工作。
This program is designed to prepare top-ranking technicians and managers of both energy and power engineeringknowledge and modern informationtechnique. Students can pursue a career in departments related to electricpower, cryogenic refrigenrationair conditioning,automotive ergineeringfluidmachinery, metallurgy,chemical industry,railways,medicine and other various sectors. Students are quealifiefor jobs concerning research, teaching, design, development, and management on energy and power engineering.二、基本规格要求II.Skills Profile1.具有数学、外语、自然科学和能源动力工程科学知识的应用能力;2.熟悉本专业领域内广2个专业方向或有关方面的专业知识,了解其学科前沿和发展趋势;3.具有本专业必需的制图、计算、测试、调研、查阅文献和基本工艺、操作、运行等基本技能;4.具有对于能源动力工程问题进行系统表达、建立模型、分析求解和论证的能力;5.具有制订实验方案、进行实验、分析和解释数据的能力6.具有较强的自学能力、分析能力和创新意识。
普通高等学校本科专业目录和专业介绍01 学科门类:哲学 Field of Study: Philosophical Sciences0101 哲学类 Philosophical Sciences010101 哲学 Philosophy010102* 逻辑学 Logic010103* 宗教学 Science of Religion02 学科门类:经济学 Field of Study: Economics Sciences0201 经济学类 Economics Sciences020101 经济学 Economics020102 国际经济与贸易 International Economics & Trade020103 财政学 Public Finance020104 金融学 Finance and Banking03 学科门类:法学 Field of Study: Law0301 法学类 Law030101 法学 Law0302 马克思主义理论类 Marxist Theoretical Studies030201* 科学社会主义与国际共产主义运动 Scientific Socialism & International Communist Movement030202* 中国革命史与中国共产党党史 History of the Chinese Revolution & History of the Communist Party of China0303 社会学类 Sociological Sciences030301* 社会学 Sociology030302 社会工作 Social Work0304 政治学类 Political Sciences030401 政治学与行政学 Political Science & Public Administration030402 国际政治 International Politics030403* 外交学 Science of Diplomacy030404 思想政治教育 Idea logical & Political Education0305 公安学类 Science of Public Security030501 治安学 Science of Public Order030502 侦察学 Science of Criminal Investigation030503 边防管理 Management of Frontier Order04 学科门类:教育学 Field of Study: Education0401 教育学类 Educational Studies040101 教育学 Pedagogy040102 学前教育 Preschool Education040103 特殊教育 Special Education040104 教育技术学 Educational Technology0402 体育学类 Physical Education And Sports Science040201 体育教育 Physical Education040202* 运动训练 Sports Training040203 社会体育 Social Sports040204* 运动人体科学 Human Kinesiology040205* 民族传统体育 Traditional and Ethnic Sport05 学科门类:文学 Field of Study: Literature0501 中国语言文学类 Chinese Language & Literature050101 汉语言文学 Chinese Language & Literature050102 汉语言 Chinese Language050103* 对外汉语 Chinese as a Second Language050104 中国少数民族语言文学 Chinese Minority Language & Literatures 050105* 古典文献 Chinese Classics And Classical Bibliography0502 外国语言文学类 Foreign Languages & Literature050201 英语 English050202 俄语 Russian050203* 德语 German050204* 法语 French050205* 西班牙语 Spanish050206* 阿拉伯语 Arabic050207 日语 Japanese050208△ 波斯语 Persian050209* 朝鲜语 Korean050210△ 菲律宾语 Tagalog050211△ 梵语巴利语 Sanskrit050212△ 印度尼西亚语 Indonesian050213△ 印地语 Hindi050214△ 柬埔寨语 Cambodian050215△ 老挝语 Laotian050216△ 缅甸语 Myanmese050217△ 马来语 Malay050218△ 蒙古语 Mongolian050219△ 僧加罗语 Singhalese050220* 泰语 Thai050221△ 乌尔都语 Urdu050222△ 希伯莱语 Hebrew050223* 越南语 Vietnamese050224△ 豪萨语 Hausa050225△ 斯瓦希里语 Swahili050226△ 阿尔巴尼亚语 Albanian050227△ 保加利亚语 Bulgarian050228△ 波兰语 Polish050229△ 捷克语 Czech050230△ 罗马尼亚语 Romanian050231* 葡萄牙语 Portuguese050232△ 瑞典语 Swedish050233△ 塞尔维亚—克罗地亚语 Serbo—Croatian050234△ 土耳其语 Turkish050235△ 希腊语 Greek050236△ 匈牙利语 Hungarian050237* 意大利语 Italian0503 新闻传播学类Journalism & Mass Medium050301* 新闻学 Journalism050302 广播电视新闻学 Radio & Television Science050303 广告学 Advertising050304 编辑出版学 Editing & Publishing Science0504 艺术类 A rts050401 音乐学 Musicology050402 作曲与作曲技术理论 Composition and Theories of Composition 050403 音乐表演 Music Performance050404 绘画 Painting050405 雕塑 Sculpture050406 美术学 Research of Fine Arts050407 艺术设计学 Artistic Design Theories050408 艺术设计 Artistic Designing050409 舞蹈学 Dancology050410 舞蹈编导 Choreography050411 戏剧学 Dramaturgy050412 表演 Acting050413 导演 Directing050414 戏剧影视文学 Literature of Theatre Film & Television050415 戏剧影视美术设计 Artistic Design of Theatre Film & Television 050416 摄影 Photography050417 播音艺术 Recording Techniques050418 动画 Science of Animated Cartoon050419* 播音与主持艺术 Techniques of Broadcasting & Anchoring 050420 广播电视编导 Radio & Television Editing & Directing06 学科门类:历史学 Field of Study: History0601 历史学类 Historical Sciences060101 历史学 Historical060102* 世界历史 World History060103 考古学 Archaeology060104 博物馆学 Museology060105* 民族学07 学科门类:理学 Field of Study: Natural Sciences0701 数学类 Mathematical Sciences070101 数学与应用数学 Mathematics and Applied Mathematics070102 信息与计算科学 Information and Computing Science0702 物理学类 Physical Sciences070201 物理学 Physics070202 应用物理学Applied Physics0703 化学类 Chemical Sciences070301 化学 Chemistry070302 应用化学 Applied Chemistry0704 生物科学类Biological Sciences070401 生物科学 Biological Science070402 生物技术 Biotechnology0705 天文学类 Astronomical Sciences070501 天文学 Astronomy0706 地质学类 Geological Sciences070601 地质学 Geology070602 地球化学 Geochemistry0707 地理科学类 Geographical Sciences070701 地理科学 Geography070702 资源环境与城乡规划管理 Urban and Rural Planning & Resource management 070703 地理信息系统 Geographical Information System0708 地球物理学类 Geophysical Sciences070801 地球物理学 Geophysics0709 大气科学类 Atmospherical Sciences070901 大气科学 Atmospheric Science070902 应用气象学 Applied Meteorology0710 海洋科学类ceanographic Sciences071001 海洋科学 Marne Science071002 海洋技术 Marine Technology0711 力学类 Sciences of Mechenics071101 理论与应用力学 Theoretical and Applied Mechanics0712 电子信息科学类 Electronic and Information Science071201 电子信息科学与技术 Electronic and Information Science and Technology 071202 微电子学 Microelectronics071203* 光信息科学与技术 Optical Information Science and Technology0713 材料科学类 Material Science071301 材料物理 Material Physics071302 材料化学 Material Chemistry0714 环境科学类 Environmental Science071401 环境科学 Environmental Science071402 生态学 Ecology0715 心理学类 Psychological Sciences071501 心理学 Psychology071502 应用心理学 Applied Psychology0716 统计学类 Statistical Sciences071601 统计学 Statistics08 学科门类:工学 Field of Study: Engineering0801 地矿类 Geological Prospecting and Mining080101 采矿工程 Mining Engineering080102 石油工程 Petroleum Engineering080103 矿物加工工程 Mineral Processing Engineering080104 勘查技术与工程 Prospecting Techniques and Engineering080105 资源勘查工程 Natural Resources Prospecting Engineering0802 材料类 Materials080201 冶金工程 Metallurgical Engineering080202 金属材料工程 Metallic Materials Engineering080203 无机非金属材料工程 Inorganic Nonmetallic Materials Engineering 080204 高分子材料工程 Macromolecular Materials and Engineering0803 机械类 Machinery080301 机械设计制造及其自动化 Machine Design & Manufacturing and Their Automation080302 材料成型及控制工程 Material Processing and Control080303 工业设计 Industrial Design080304 过程装备与控制工程 Process Equipment and Control0804 仪器仪表类 Lnstrument and Apparatus080401 测控技术与仪器 Measuring & Control Technology and Instrumentations 0805 能源动力类 Energy and Power080501 热能与动力工程 Thermal Energy and Power Engineering080502 核工程与核技术 Nuclear Engineering and Technology0806 电气信息类Electrical and Information Science and Technology080601 电气工程及其自动化 Electrical Engineering and Automation080602 自动化 Automation080603 电子信息工程 Electronic and Information Engineering080604 通信工程 Telecommunications Engineering080605 计算机科学与技术 Computer Science and Technology080606 电子科学与技术 Electronic Science and Technology080607 生物医学工程 Biomedical Engineering0807 土建类 Civil Engineering and Architecture080701 建筑学 Architecture080702 城市规划 Urban Planning080703 土木工程 Civil Engineering080704 建筑环境与设备工程 Building Environment and Equipment Engineering 080705 给水排水工程 Water Supply and Sewerage Engineering0808 水利类Water Conservancy and Hydraulic Engineering080801 水利水电工程 Water Conservancy and Hydropower Engineering080802 水文与水资源工程 Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering080803 港口航道与海岸工程 Harbours, Water Channels and Coast Engineering0809 测绘类 Science of Surveying & Mapping080901 测绘工程 Surveying & Mapping Engineering0810 环境与安全类 Science of Environment & Safety Engineering081001 环境工程 Environmental Engineering081002 安全工程 Safety Engineering0811 化学与制药类 Science of Chemical & Pharmaceutical Engineering081101 化学工程与工艺 Chemical Engineering and Technology081102 制药工程 Pharmaceutical Engineering0812 交通运输类 Science of Traffic & Transportation081201 交通运输 Traffic and Transportation081202 交通工程 Traffic Engineering081203 油气储运工程 Petroleum and Gas Storage and Transportation Engineering 081204 飞行技术 Aviation Technology081205 航海技术 Navigation Technology081206 轮机工程 Marine Engineering0813 海洋工程类 Science of Ocean Engineering081301 船舶与海洋工程 Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering0814 轻工纺织食品类 Science of Textile & food Engineering081402 轻化工程 Light Chemical Engineering081403 包装工程 Packaging Engineering081405 纺织工程 Textile Engineering081406 服装设计与工程 Apparel Design and Engineering0815 航空航天类 Aeronautics081501 飞行器设计与工程 Flight Vehicle Design and Engineering081502 飞行器动力工程 Flight Vehicle Propulsion Engineering081503 飞行器制造工程 Flight Vehicle Manufacture Engineering081504 飞行器环境与生命保障工程 Flight Vehicle Environment and Life Support SystemEngineering0816 武器类 Weapons Systems081601 武器系统与发射工程 Weapon Systems and Launching Engineering081602 探测制导与控制技术 Detection, guidance and Control Technology 081603 弹药工程与爆炸技术 Ammunition Engineering and Explosion technology 081604 特种能源工程与烟火技术 Special energy and Pyrotechnics081605 地面武器机动工程 Ground Motor Weapon Engineering081606* 信息对抗技术 Information Countermeasure/Warfare Technology0817 工程力学类 Science of Engineering Mechanics081701 工程力学 Engineering Mechanics0818 生物工程类 Biotechnology081801 生物工程 Bioengineering/Biotechnology0819 农业工程类 Agricultural Engineering081901 农业机械化及其自动化 Agricultural mechanization and its automation 081903 农业建筑环境与能源工程 Agricultural structure, environment and energy engineering081904 农业水利工程 Agricultural water conservancy engineering0820 林业工程 Forestry Engineering082001 森林工程 Forest Logging Engineering082002 木材科学与工程 Wood Science and Engineering082003 林产化工 Chemical Processing of Forest Products0821 公安技术类 Public Security & Technology082101 刑事科学技术 Criminal Science and Technology082102 消防工程 Fire Prevention Engineering09 学科门类:农学Field of Study: Agricultural Sciences0901 植物生产类 Plant production sciences090101 农学 Agronomy090102 园艺 Horticulture090103 植物保护 Plant protection090104 茶学 Tea science0902 草业科学类 Pratacultural090201 草业科学 Prataculture science0903 森林资源类 Science of Forest resources090301 林学 Forestry090302 林资源保护与游憩 Forest Resources Conservation and Recreation 090303 野生动物与自然保护区管理 Wildlife and Natural Reserve Management0904 环境生态类 Environmental and Ecological Sciences090401 园林 Landscape gardening090402 水土保持与荒漠化防治 Soil and water conservation and combating desertification090403 农业资源与环境 Agricultural Resources and Environment0905 动物生产类 Animal production sciences090501 动物科学 Animal science090502 蚕学 Sericulture0906 动物医学类 Science of Veterinary Medicine090601 动物医学 Veterinary Medicine0907 水产类 Fishery Science090701 水产养殖学 Aquaculture090702 海洋渔业科学与技术 Marine fishery science and technology10 学科门类:医学 Field of Study: Medicine1001 基础医学类 Preclinical Medicine100101* 基础医学 Basic Medical Sciences1002 预防医学类 Preventive Medicine100201 预防医学 Public Health1003 临床医学与医学技术类 Clinical Medicine and Associated MedicalSciences100301 临床医学 Clinical Medicine100302* 麻醉学 Anaesthesiology100303* 医学影像学 Medical Imaging100304* 医学检验 Medical Laboratory Tests and Analyses1004 口腔医学类 Stomatology100401 口腔医学 Oral Medicine1005 中医学类 Traditional Chinese Medicine100501 中医学 Chinese Medicine100502 针灸推拿学 Acupuncture Moxibustion and Massage100503 蒙医学 Mongolian Medicine100504 藏医学 Tibetan Medicine1006 法医学类 Forensic Medicine100601* 法医学 Medical Jurisprudence1007 护理学类 Nursing Science100701 护理学 Nursing1008 药学类 Pharmacy100801 药学 Pharmacy100802 中药学 Traditional Chinese Pharmacy100803 药物制剂 Pharmaceutical Preparations11 学科门类:管理学 Field of Study: Management Sciences 1101 管理科学与工程类 Management Science and Engineering110101* 管理科学 Management Science110102 信息管理与信息系统 Information Management & Information System 110103 工业工程 Industrial Engineering110104 工程管理 Project Management1102 工商管理类 Business Administration110201 工商管理 Business Administration110202 市场营销 Marketing110203 会计学 Accounting110204 财务管理 Financial Management110205 人力资源管理 Human Resource Management110206 旅游管理 Tourism management1103 公共管理类 Public Administration110301 行政管理 General Administration110302 公共事业管理 Public Utilities Management110304* 土地资源管理 Land Resources Management1104 农业经济管理类Agricultural economy management110401 农林经济管理 Agricultural/forest economy management110402 农村区域发展 Rural regional development1105 图书档案学类 Library and Archive Science110501 图书馆学 Library Science110502 档案学 Archive Science。
第4章火力发电厂4.1 简介电站的生产过程利用的是一个封闭的蒸汽动力循环,在这个循环中伴随着水的各种热力过程。
有一半的循环包括锅炉(或热源)及其辅助设备;另一半的热力循环则包括汽轮机,发电机,凝汽器,给水泵及给水加热器。
在锅炉中给水被加热成干饱和蒸汽。
干蒸汽进一步过热并进入汽轮机的高压缸。
过热蒸汽在汽轮机中膨胀,很大比例的热能转化为带动汽轮机转子的动能。
汽轮机转子带动发电机产生电能。
做功后的蒸汽离开高压缸回到锅炉被再次加热。
再热蒸汽进一步在汽轮机中压缸和低压缸中膨胀做功,然后进入凝汽器。
蒸汽在凝汽器这个大型表面式换热器中,通过释放汽化潜热给冷却水(CW)从而被冷凝。
主蒸汽在凝汽器中被冷凝成很低压力下的接近饱和的水。
凝结成的水从凝汽器排入热井。
热井中的水被凝结水泵抽出,经过低压给水加热系统后进入锅炉给水泵。
在现代回热循环中,一部份蒸汽通过布置在汽轮机汽缸上的一系列位于选定的动叶级后的抽汽口进入到凝汽器和给水加热器中。
这些蒸汽被用来加热低压加热器中的凝结水及高压加热器中的给水,这些加热器都属于表面式换热器。
给水经锅炉给水泵增压到高于汽包的压力,以足够克服给水经过锅炉汽水系统和高压给水加热系统的压力损失。
至此整个循环就完成了。
4.1.1 应用过热的实际循环朗肯循环向一个更实际的蒸汽循环的首次改进包括提高进入汽轮机蒸汽的温度和压力。
在过热蒸汽循环中,干饱和蒸汽离开锅炉汽包并进一步过热后才能进入汽轮机。
由此,提高了循环的效率。
这种过热循环选择与先前的朗肯循环具有相同的汽轮机排汽条件。
然而,过热蒸汽的一个主要好处在于提高循环蒸汽的温度和压力,使得汽轮机的排汽湿度可以保持在所能承受的物理极限内。
4.1.2 再热循环由于希望进一步增加循环的条件并由此提高循环效率,于是在汽轮机内的膨胀过程中增加蒸汽的再热循环。
再热循环中,额定温度的蒸汽在汽轮机中部分地膨胀做功,然后回到锅炉,被再热到最初的额定温度左右。
再热蒸汽进入汽轮机其余部分继续做功,之后进入凝汽器冷凝。
For practical reasons,most impulse turbines mount their buckets on the rims of disks
(wheels),and nozzles feed steam from one side (Fig.6.9),Pressurized steam from the nozzle box
flows through parallel converging nozzles formed by vane or foils.Steam leaves as a broad
high-speed jet to flow through the slower moving-bucket passages,which turn the steam flow to
an axial direction as they absorb its kinetic energy.The steam leaves with lower internal energy
and speed.
由于实用性的原因,大部分冲击式汽轮机把他们的叶片安装在轮缘,并且喷嘴从一边提供蒸
汽。高压蒸汽从喷嘴室流过由叶片或翼形成的平行的渐缩喷嘴。蒸汽离开的时候是一个宽阔
的高速气流,它流过较慢的动叶片通道,把蒸汽换向流到一个轴线方向,在那里吸收他们的
动能。蒸汽带着较低的内能和速度离开。
Steam pressure and speed vary through the true impulse stage.When the impulse stage are
pressure-compouned,which are called Rateau stages,pressure drop occurs in steps and exhausted
steam from one-stage folws through following similar impulse stages,where it expands to a lower
pressure.If the impulse stages are velocity-compounded,which are called Curtiss stages,steam
velocity is absorbed in a series of constant-pressure steps.
流过一个完全的冲击级时,蒸汽压力和速度是不同的。当冲击级是压力复合的,这样的就被
称做压力级,在过程中发生压降,并且乏汽从一级流过相似的冲击级,在那里它膨胀成低压。
如果冲击级是复速的,那就被称作复速级,在一系列压力不变的过程中蒸汽速度被吸收。
In the reaction stage (Fig6.10),steam enters the fixed-blade passage;it leaves as a steam jet that
fills the entire rotor periphery.Steam flows between moving blades that form moving
nozzles.There it drops in pressure,and its speed rises relative to the blades,which creates the
reactive force that does work.Despite the rising relative speed,the overall effect reduces the
absolute steam speed through one stage.When the enthalpy drop is about equal in moving and
stationary blades,it is called a 50 percent reaction stage.
在反应级中,蒸汽进入静叶片通道,它作为一种蒸汽气流而离开,并且充满整个边缘。蒸汽
流经形成动的喷嘴的动叶片。在这里,压力下降,速度随着叶片而上升,这样就导致反冲击
力工作。尽管速度上升,通过一级的时候,
总的影响是减少绝对速度。在动叶片和静叶片
中焓降是相同的,那就被称作一个50%的反冲击级
Fig.6.11 shows a velocity-compounded control stage followed by two reaction stages.The high
speed steam jet gives up only part of its kinetic energy in the first row of moving buckets. The
come reversing blades that redirect the slowed-up steam into the second row of moving
buckets,where most of its remaining kinetic energy is absorbed.Steam then enters the series of
reaction stages.
图6.11展示了一个复速控制级随着反冲击级流动。在动叶片的第一行中,高速蒸汽气流仅
释放一部分动能。转向式叶片改变方向进入动叶片第二行,在那里他保留的动能被吸收。蒸
汽进入一系列反冲击级。
In practice,so-called impulse-stage turbine use about 5% to 10% reaction in their design.This
means there is a small steam pressure drop through the moving-blade passages.These
buckets,instead of taking the symmetrical shape, have a longer tail to form a slightly coverging
passage at the exit.
在实际中,这种被称作冲击级式的汽轮机在设计中有5%到10%的都使用反冲击式。这就是
说通过动叶片通道时会有一个小的蒸汽压降。这些叶片代替采用对称的形状,有一个较长的
尾巴为了在出口形成一个小的渐缩的通道。