
宾语补足语讲解
Document number:NOCG-YUNOO-BUYTT-UU986-1986UT
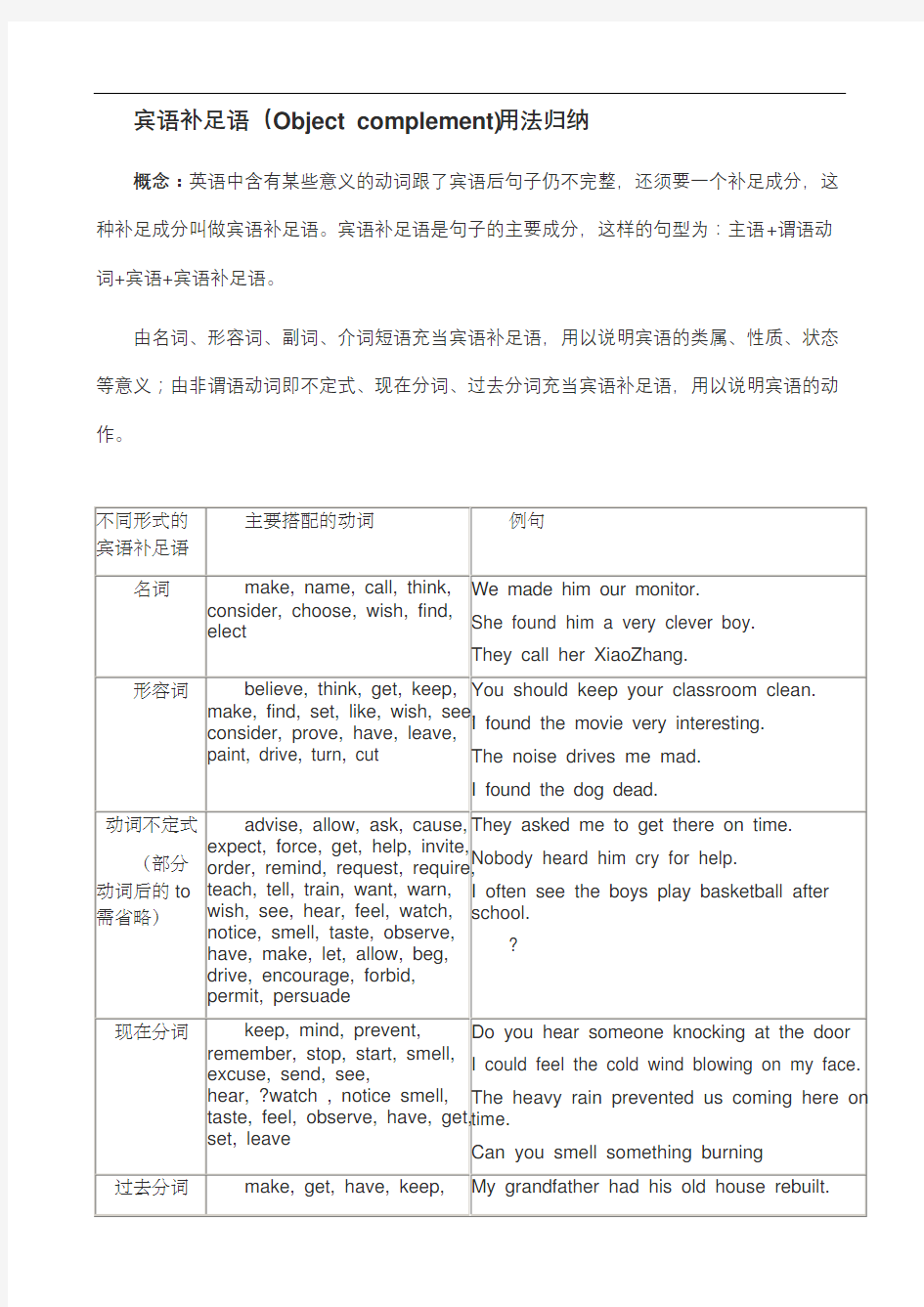
宾语补足语(Object complement)用法归纳
概念:英语中含有某些意义的动词跟了宾语后句子仍不完整,还须要一个补足成分,这种补足成分叫做宾语补足语。宾语补足语是句子的主要成分,这样的句型为:主语+谓语动词+宾语+宾语补足语。
由名词、形容词、副词、介词短语充当宾语补足语,用以说明宾语的类属、性质、状态等意义;由非谓语动词即不定式、现在分词、过去分词充当宾语补足语,用以说明宾语的动作。
宾语补足语使用注意事项:
①当感官动词和使役动词,如:see hear notice watch hear observe, listen to, feel(感官动词)make have let get(使役动词)接宾补时,不定式的符号to必须省略。但在被动语态中,动词后要加to。
主动语态:The policeman made him tell everything.
被动语态:He was made to tell everything by the policeman.
②感官动词see, hear, watch, notice, observe后面的宾语补足语既可跟不带to的动词不定式,也可跟现在分词,其区别在于前者表示“经常性的,习惯性的动作”,后者表示“正在发生的瞬间动作”。
I often hear her sing English songs in the room.
Suddenly, Zhang Hua heard someone shouting “Fire! Fire!”
③在help后,不定式可以带to,也可不带。
Lucy often helps her brother (to) learn English.
④有些动词只能用现在分词作宾语补足语,如:keep, mind, prevent, stop。动词find, catch等的宾语可由现在分词作宾语补足语。
She caught her son smoking a cigarette.
We’d better keep the fire burning.
I don’t mind you joking. I like it.
The heavy rain prevented us coming here on time.
I found him drinking my whisky.
⑤hope, demand, suggest等动词后面不能接不定式作宾语补足语。
错误:I hope you to come here tomorrow.
正确:I hope you can come here tomorrow.
⑥表示心理状态的动词consider, think, believe, discover, find, imagine, judge, suppose, prove等动词后的不定式通常是“to be+形容词或名词”结构,to be常可省略。
We consider him (to be) a good teacher.
He proved that theory (to be) very important.
I thought her (to be) nice and honest the first time I met her.
⑦当宾语是不定式、动名词或宾语从句时,往往把宾语放在它的补足语后,而用it作句子的形式宾语,放在宾语补足语之前,将真正的宾语置于补足语之后。如:
I think it wrong to smoke in public.
I find it hard to learn English well.
She kept it secret that she hadn’t passed the exam.
I think it important that we should keep calm.
宾语补足语10 年高考真题汇总 1.(2015·浙江卷·18)Listening to music at home is one thing, going to hear it live is quite another. A. perform B. performing C. to perform D. being performed 2.(2015·陕西卷·18)Back from his two-year medical service in Africa, Dr. Lee was very happy to see his mother good care of at home. A. taking B. taken C. take D. be taken 3.(2014·江西卷·34).He is thought foolishly. Now he has no one but himself to blame for losing the job. A. to act B. to have acted C. acting D. having acted 4.(2013·北京卷·T29)When we saw the road with snow, we decided to spend the holiday at home. A. block B. to block C. blocking D. blocked 5.(2013·陕西卷·T13)Let those in need that we will go all out to help them. A.to understand B. understand C. understanding D. understood 6.H e is very popular among his students as he always tries to make them in his lectures.江苏A.interested B.interesting C.interest D.to interest 7.My parents have always made me about myself, even when I was twelve. A.feeling well B.feeling good C.feel well D.feel good 8.—Come on, please give me some ideas about the project. —Sorry. With so much work my mind, I almost break down.(07 福建卷) A.filled B.filling C.to fill D.being filled 9.John received an invitation to dinner, and with his work he gladly accepted it.(07 安徽A.finished B.finishing C.having finished D.was finished 10.I couldn’t to my homework with all the noise .(05 北京) A.going on B.goes on C.went on D.to go on 11.Jenny hopes that Mr. Smith will suggest a good way to have her written English in a short period. A.improved B.improving C.to improve D.improve 12.—Did Peter fix the computer himself? —He , because he doesn’t know much about computers.(07 安徽卷) A.has it fixed B.had fixed it C.had it fixed D.fixed it 13.You should understand the traffic rule by now. You’ve had it often enough.(05 天津) A.explaining B.to explain C.explain D.explained 14.A cook will be immediately fired if he is found in the kitchen.(03 全国卷) A.smoke B.smoking C.to smoke D.smoked 15.A good story does not necessarily have to have a happy ending, but the reader must not be left .(06 天津卷) A.unsatisfied B.unsatisfying C.to be unsatisfying D.being unsatisfied 16.After a knock at the door, the child heard his m other’s voice him.(07 上海卷) A.calling B.called C.being called D.to call 17.Even the best writers sometimes find themselves for words.(11 浙江) A. lose B. lost C. to lose D. having lost 18.Claire had luggage an hour before her plane left. A. check B. checking C. to check D. checked 19.Michael put up a picture of Yao Ming beside the bed to keep himself of his own dreams. A. reminding B. to remind C. reminded D. remind
“感使动词+宾语+宾语补足语”结构中宾语补足语的用法定义 1.所谓感官动词,是指表示人的大脑感觉器官所发出的动作的动词。如:notice / observe / see / look at / watch / hear / listen to / feel(常见的共8词). 2.使役动词是指具有使、让意义的动词。如:have/ let / make(常见的共3词)。 记忆与使用 难点一:如何系统、准确地熟记常见的感官、使役动词 口诀:“注意、观察、三看、二听、一感觉;三个使役半帮助。”注意:“半帮助”是为了易记加上去的(因help后接的to可省可不省,故叫“半帮助”)。 难点二:对感官、使役动词的主动结构后接非谓语动词作宾补的区别 先看感官动词主动结构的用法(以hear为例):hear sb. do/ doing/ done ' 即其后可接do(省to)/ doing/ done作宾补。区别是:1)do/ doing均表主动关系,done表被动关系。 2)do/ doing都可表主动,但do指整个动作,经常性动作或强调动作完成了。doing指动作正在进行或动作的某个片断。
3)done指某事由别人做(被做),也作“遭受”解。 试比较:A)I heared him sing a song. 我听他唱了一首歌(指自始至终整个过程)。 B)I heared him singing a song. 我听见他正在唱歌唱(指当时动作的某个片断)。 C)I heared a song sung.我听见(有人)唱歌(逻辑主语“歌”与“唱”是被动关系。) 再看使役动词主动结构的用法:have sb. do/ doing/ done, make/let sb. do/ done have后也接do(省to)/ doing/ done作宾补,区别是:1)do/ doing 均表主动关系,done表被动关系。 2)do/ doing虽然都表主动,但do指目前和将来或经常性、反复性的动作。Doidoing指目前正在进行的动作。 试比较:A)I won’t have you saying such things about my sister.(指目前正确进行的动作) B)I won’t have you saying such things about my sister.(指目前和将来的动作) C)I shouldn’t have him do that again.(指将来的动作,此处不用doing因do that again暗示将来) D)I am sorry to have had you waiting so long.(指目前正在进行的动作) E)I have had many friends visit me from time to time.
定语从句: 定义:在复合句中修饰名词或代词的从句。 先行词:被修饰的名词或代词。 引导定语从句的关系词: 关系代词:who, whom, whose, which, that, as 关系副词:when, where, why 定语从句关系词的选用 1.只能用that 不用which 作关系代词的情况
(1)当先行词是all, everything, anything, nothing, much, little, none, one 等不定代词时(something 除外)。 (2) 当先行词被all, every, no, some, any, little, much 等修饰 (3)当先行词被序数词或形容词最高级修饰时。 (4)如果出现两个或两个以上的先行词,并同时兼指人和物 (5) 当先行词被the only, the last, the very, the same 等修饰 6)在以疑问词who, which, what 开头的特殊疑问句中,为 了避免重复只用that。 7)当定语从句为there be 句型时,关系代词只能用that,也 可以省略。 (8)当指人或物的关系代词在定语从句中作表语时,关系代 词只能用that,也可以省略。 2.指物只能用which 不用that 的情况 (1)在非限制性定语从句中。如: St.Petersburg, which was once called Leningrad, is a very beautiful city. 圣彼得堡是一座非常美丽的城市,它曾被称作“列宁格勒”。 (2)在介词后面。如: This is the room in which we lived last year. 这是我们去年住的那个屋子。 3.指人时只能用who 不用that 的情况 先行词为one, ones, those, anyone, he 时。如: Those who break the law must be punished. 那些违反法律的人必须受到惩罚。 4.“介词+关系代词”引导的定语从句 Is this the house in which Shakespeare was born? He paid the boy $10 for washing ten windows, most of which hadn't been cleaned for at least a year. In the dark street, there wasn't a single person to whom she could turn for help. 5.关系代词as 和which 的区别 (1)which 引导的定语从句只能位于主句后,但as 引导的 从句可位于主句前、中、后。如: David, as you know, is a photographer. 戴维是个摄影师, 你是知道的。(不可用which) Li Ming is late, as is often the case. 李明迟到了,这事是经常发生的。(不可用which) (2)as 在定语从句中作主语时,从句谓语通常要有be 或别 的系动词,但which 不受此限制。如: Li Ming was late, which ( =and this) made Mr. Zhang very angry. 李明迟到了,这件事使张先生非常生气。(不可用as) (3)as 引导的定语从句只表示一个众所周知或意料之中的 事,但which 不受此限制。如: He married her, which was unexpected. 他和她结婚了,这 是出乎意料的。(不可用as) (4)as 有“正如”之意,而which 则意为“这( 件事,一点)”,可用and this/that/it 来代替 (5)as 多用于固定搭配中:as is often the case(这是常有的 事),as was expected (不出所料),as often happens (正如经常发 生的那样),as is known to all (众所周知),as has been said before (如上所述),as is mentioned above (正如上面所提到的)等。 三、特殊句式 1.as 引导限制性定语从句常用句式 (1)such+名词+as... 像?-?-一样的,像?-?-之类的 We have found such materials as are used in their factory. (2)the same+名词+as... 和?-?-同样的 He is not the same man as he was. 2.当先行词是way,意为“方式、方法”,在定语从句中作状语时,引导词可以用that/in which/不填。如: The way that/in which/不填he explained the sentence to us was not difficult to understand. 定语从句的习题: 1. I?d skipped nearby Guilin,a dream place for tourists seeking the limestone mountain tops and dark waters of the Li River are pictured by artists in so many Chinese paintings.(2015全国Ⅰ) 2.When harvest came around, he was already selling herbs, vegetables and cotton in the market people from the towns met regularly.(2015广东). 3.Maybe you have a habit is driving your family crazy. (2014全国Ⅰ). 4.The next day, my brother and I went to the beach we watched some people play volleyball.(2014广东). 5.People should not do things will disturb their neighbors unnecessarily.(2014湖南). 6.In the following years ,there were fewer drop-outs and more college graduates in my village, I am proud of even today. 7. Is that the newspaper for you often write articles? 8.Can you explain to me how to use these idioms about I am not sure? 9.1949 was the year in our country was founded. 10. Do you know the man to I spoke just now? https://www.doczj.com/doc/8c2413215.html,st month, part of Southeast Asia was struck by floods from effects the people are still suffering. 12.The man pulled out a gold watch, the hands of were made of small diamonds. 13.The journey around the world took the old sailor nine months, of the sailing time was 226 days. 宾语补足语 有些动词如allow, advise, ask, beg, believe, call, cause, enable, encourage, get, invite, order, teach, tell 等后边常跟动词不定式作宾语补足语。 I invited him to come (come)here. He was invited (come) here. The teacher allowed me (finish) my homework on Friday.
宾语补足语总汇 六、具体说明: (一)副词作宾语补足语 I found him in yesterday. (二)常接形容词作宾语补足语的动词有:keep, make, find等。 如:We must keep our classroom clean. (三)常接名词作宾语补足语的动词有:call, name, make, think等。 如:We call them mooncakes. (四)常接动词-ing形式作宾语补足语的动词有:see, watch, hear, find, keep等。如:In the country, we can hear birds singing. (五)常接介词短语作宾语补足语的动词有:keep, find, leave等。如:I left my pen on my desk at home. (六)不定式作宾语补足语 1. 常接带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语的动词有:ask, tell, want, teach, wish等; 2. 接不带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语的动词有:see, watch, hear, make, let advise, allow, ask, beg, command, tell, invite, force, oblige, get, help, encourage, persuade, permit, remind, request, order, warn, cause等。如: I often see him play football. She often asks me to help her. We don't allow such things to happen again. Most of the parents agree to forbid their children to smoke. She asked me to answer the phone in her absence. Please remind me to leave her this note. She requested him to go with her. 3. 用不定式作宾语补足语的几种说明: ①help后面作宾语补足语的动词不定式可以带to也可以不带to。 如:I often help my mother(to) do some housework. ②在使役动词后作宾语补足语,不定式不带to。有些动词跟不定式作宾语补足语时省去了to,这些动词有:一感二听三让四观看。 一感:feel 二听:hear, listen to 三让:let, have, make 四观看:observe, see, watch, look at 这类动词有:make, let, have等。转为被动语态时,其后通常都用带to的不定式(have没有被动语态)。What would you have me do? 你要我做什么?She made him give up smoking. 她让他戒了烟。Let him do whatever he wishes to do. 他想干什么就让他干吧。 Though he had often made his little sister cry, today he was made to cry by his little sister.虽然经常是他弄哭小妹妹,但今天他却被小妹妹弄哭了 3. 掌握“使役动词have + 宾语+过去分词”的几种含义 在“ hav e +宾语+过去分词”结构中,过去分词作宾语补足语,have 也可用get 。这一结构具有以下几种含义:
【中考解读】 【考点分布】1.副词的语法作用及分类 2.副词的比较级 3.副词的词义辨析 【考点内容】掌握副词在句中充当的成分及副词比较级的变化规则,包括规则变化和不规则变化,掌握副词的词义辨析及具体用法 【命题趋势】1.副词的比较级和最高级运用 2.副词与动词的搭配使用 3.对具体副词及疑问副词的辨析 【副词定义】副词是用来说明事情发生的时间、地点、原因、方式等含义或说 明其他形容词或副词程度的词。 第一讲副词的语法作用及分类 一、副词的句法功能 1.作状语 副词作状语,修饰动词、形容词、副词、介词短语或句子。 ①修饰动词It’s raining heavily.天正下着大雨。 He speaks English well. 他英语说得非常好。 【德州1】I carried the bowl with both hands___, so that I wouldn’t break it. A. carefully B. happily C. quickly D. carelessly 【山西3】— Jack, I have to have a talk with your father today. —Sorry, Mrs King. He is going on business and won’t be ___ until next week. A. out B. away C. back 【盐城4】It was raining _______when my sister and I got to the museum. ②修饰形容词I am quite busy now. ③修饰其他副词Don’t drive too fast.别骑得太快。 ④修饰介词短语,—Where is the book?书在哪儿? —Just on the desk.. 就在桌子上。 ⑤修饰句子Luckily , I passed the final exam. 幸运的是,我通过了期末考试。【注】修饰句子的副词,一般放在句首。 【湖北咸宁4】—As we know it’s difficult to live in a foreign country. —_______if you can’t understand the language there. D. Especially 2.作表语 副词作表语主要指主语的方位、方向、动作或状态. 如:in. out. on. back. down. up. off. away. upstairs等 My father is out this morning, but he will be in this afternoon I'll be back in five minutes. 我五分钟后就回来。 3.作定语 有些地点副词和时间副词可以作定语,放在所修饰的名词或代词之后。 The people there were very friendly.那儿的人很友好。 4.作宾语补足语 副词可以作主语或宾语的补足语,说明主语或宾语的状态。
Contents 英语宾语补足语用法详解 (2) 一、概念 (2) 二、何时用现在分词、何时用过去分词作主语(宾语)补足语 (2) 三、可以用分词作主语或宾语补足语的动词 (3) 典例精析: (4)
英语宾语补足语用法详解 一、概念 分词作主语补足语和宾语补足语其实是同一成分用于两种不同的句式中。具体地说,主动态句子中的宾语补足语就是被动态句子中的主语补足语。先了解宾语补足语,则很容易了解主语补足语。 宾语补足语:在英语中,某些及物动词不仅需要宾语,而且还要求某个词或词组来补充说明宾语,即表示宾语代表的人或物所发出的动作或所处的状态,这个词或短语称为宾语补足语。有些语法书把宾语和补足语称为复合宾语。 句型:及物动词+宾语(n./pron.)+宾语补足语(n./adj./adv./to do/-ing/-ed/介词短语共7种表示法) 该句型若变成被动语态,即将宾语提到句首作主语,原主动语态中的宾语补足语此时在被动语态中起到补充说明主语的作用,所以改称主语补足语。例如: A cook will be immediately fired if he is found smoking in the kitchen. 此句中smoking是主语he的补足语,所以称为主语补足语。 二、何时用现在分词、何时用过去分词作主语(宾语)补足语 分词作主语(宾语)补足语时,若主语(宾语)与分词之间是主动关系,则用现在分词表示主动; 如果主语(宾语)与分词之间是被动关系,则用过去分词表示被动。例如: He was heard singing in the next room. He was singing.主语he与补足语“唱歌”之间是主动关系,故用现在分词singing。 One of the glasses was found broken. One of the glasses was broken.主语one of the glasses与补足语“打破”之间是被动关系,故用过去分词broken。 Don‘t leave the water running while you brush your teeth.
With 结构(with+宾语+宾补)宾补可以是:过去分词,现在分词,不定式,副词,adj.,介词短语 可以做定语,伴随状语,原因状语,结果状语等等。 1. 1) With his key lost, he couldn’t get into his house.(钥匙丢了, 他进不了家门. ) 2) With his hair cut, Father looks much younger. (理了发,父亲看上去年轻多了.) 3) He sat there with his eyes closed. (他闭目坐在那儿。) 4) All the afternoon he worked with the door locked. (整个下午他都锁着门在房里工作。) 5) The meeting ended with all the problems settled. (问题解决了,会散了.) 2. 1) With the teacher standing beside, the girl felt a bit uneasy. (老师站在一旁,女孩子感到有点不自在.) 2) She was chatting with her friend, with her child playing beside her. (她在跟朋友闲聊,孩子在旁边玩。) 3) He felt uneasy with the whole class staring at him. (他感到很不安,因为所有的同学都盯着他。) 4) The boy lay on the grass, with his eyes looking into the sky. (小男孩躺在草地上,两眼望着天空。) 5) With night coming on, we started for home. 夜幕降临,我们动身回家。 6) I won’t be able to go on holiday with my mother being ill. (因为妈妈有病,我无法去度假。) 7) He fell asleep with the lamp burning. (他没熄灯就睡着了。) 3.1) I can’t go out with all these clothes to wash. (要洗这些衣服,我无法出去了。) 2) With so many people to help us, we are sure to finish the work in time.
语法汇总(基本句子成分) (本来想手写然后给你照照片的,不过写几个字之后发现自己的中文有点不会写了。个人觉得语法没什么用,可能是中国人比较喜欢系统的总结各种东西,初中高中也学了很多语法,不过等到学到稍高端之后就会发现,他们外国人写东西有语法不过更像是在跟感觉走。 I am never a big fun of grammar. Anyway, let’s get started.) 主语 主语表明这句话说的是谁和什么,主语主要由名词、代词或相当于名词的单词,短语或从句充当。 一、名词作主语 David arrived last night. 大卫昨晚到达。 Pride goes before a fall. 骄必败。 二、代词作主语 Who is speaking, please? (在电话中)请问您是谁? That's OK. 这没问题。 三、数词作主语 Two will be enough. 两个就够了。 Two-thirds of the workers are women. 三分之二的工人是女工。 四、ing形式作主语 Skating is good exercise. 溜冰是很好的运动。 Looking up all the new words in the dictionary took him a lot of time. 从字典里查所有的生词花费了他许多时间。 五、不定式作主语 To translate this ideal into reality needs hard work. 把理想转变成现实需要辛勤的劳动。 六、名词化的形容词作主语 The blind and the lame are well cared for in our country. 在我们国家,盲人和肢残人受到很好的照顾。 The unemployed usually lead a hard life. 失业的人生活一般很困难。 七、短语作主语 How to do well is an important question. 如何把这件事做好是一个重要问题。 Early to bed and early to rise makes a man healthy. 早睡早起身体好。 八、从句作主语 What has happened proves that our policy is right.
高考英语四种常考句型汇总总结动词不定式 ( 1)作主语 To learn a foreign language is not easy. It is not easy to learn a foreign language. ( 2)作宾语 They began to read. ( 3)作宾语补足语 Jim asked me to help him with his lessons. We often heard her sing. ( 4)作定语 I have an important meeting to attend. ( 5)作状语 She went to see her grandma yesterday. ( 6)用在how, when, where, what, which等之后 I don’t know how to use a computer.
Do you know when to start? He didn’t know what to do next. 句子种类 (1)陈述句 ( 肯定式和否定式) (2)疑问句 ( 一般疑问句、特殊疑问句、选择疑问句、反意疑问句) (3)祈使句 ( 肯定式和否定式) (4)感叹句 句子成份 1)主语 Betty likes her new bike. He gets up early every day. To learn a foreign language is not easy. 2)谓语 We work hard. The boy caught a bird.
He is my brother. They all look fine. 3)表语 Her sister is a nurse. It’s me. I’m ready. He got angry. We were at home last night. His cup is broken. 4)宾语 Tom bought a story-book. I saw him yesterday. He wanted to have a cup of tea. 5)直接宾语和间接宾语 He gave me some ink. Our teacher told us an interesting story. 6)宾语补足语
宾语补足语和主语补足 语 集团标准化小组:[VVOPPT-JOPP28-JPPTL98-LOPPNN]
宾语补足语:? 某些及物动词的宾语后面还需要有一个补足语,意思才完整,宾语和它的补足语构成复合宾语。而复合宾语的第一部分通常由名词或代词充当,第二部分表示第一部分的名词或代词发出的动作或身份、特征等,称为宾语补足语。? 宾语补足语有以下几类。? 1.由动词不定式充当。多数是带to的不定式,也有不带to 的不定式。1).要求带to的不定式作宾语补足语的动词有tell,ask,invite,force,get,beg,allow,wish,want,like,prefer,intend,expect,encourage,a d v i s e,p e r m i t,o r d e r,w a r n,c a u s e等。e g.? I would prefer you not to change your plan.? 我宁愿你不要改变计划。?
They encouraged me to try again.他们鼓励我再次尝试。? ? 2).某些动词如think,consider,believe,know,find 等后面作宾语补足语的不定式常用to be + adj.的结构。? e g.? We believed him to be stupid.我们认为他很笨。? He didn”t consider himsel f (to be) important.? 他并不认为自己重要。? ? 3).某些动词如make,have,let,see,hear,watch,notice,feel等后作宾语补足语的不定式不带to。? e g.? He made us stay for tea.他使我们留下来吃茶点。?
一. 形容词/副词的比较级和最高级 1. 形容词/副词的比较级和最高级的构成规则 (1)单音节词和少数以-er,-ow结尾的双音节单词,比较级在后面加-er,最高级在后面加-est。 ①单音节单词 small→smaller→smallest short→shorter→shortest tall→taller→tallest great→greater→greatest ②少数以-er,-ow结尾的双音节单词 clever→cleverer→cleverest narrow→narrower→narrowest (2)以不发音e结尾的单音节单词,比较级在原形后加-r,最高级在原级后加-st。
large→larger→largest nice→nicer→nicest able→abler→ablest (3)以一个辅音字母结尾的闭音节(即:辅音+元音+辅音)单词中,先双写末尾的辅音字母,比较级加-er,最高级加-est。 big→bigger→biggest hot→hotter→hottest fat→fatter→fattest (4)以“辅音字母+y”结尾的双音节词,把y改为i,比较级加-er,最高级加-est。 easy→easier→easiest heavy→heavier→heaviest busy→busier→busiest happy→happier→happiest (5)其他双音节词和多音节词,比较级在前面加more,最高级在前面加most。
beautiful→more beautiful→most beautiful different→more different→most different easily→more easily→most easily (6)有少数形容词、副词的比较级和最高级是不规则的,必须熟记。 good→better→best well→better→best bad→worse→worst ill→worse→worst old→older/elder→oldest/eldest many/much→more→most little→less→least far →further/farther→furthest/farthest 2. 形容词和副词比较级的用法 (1)“甲+be+(倍数)+形容词比较级+than+乙”表示“甲比乙…”或“甲比乙…几倍”。 Tom is taller than Kate. 汤姆比凯特高。
一、定义:宾语补足语通常紧跟在宾语之后,对宾语进行补充说明。 二、句子结构是:主+谓+宾+宾补 三、两种结构: 1.主表型: 1) make our country beautiful (adjective) 2) call him Lao Li (noun) 3) find sb. out (adv.) 4) find sb. at home (Prep. phrase) 2. 主谓型: 1) ask sb. to do sth.(有to 不定式) 2) have sb. do sth. (无to 不定式) 3) see sb. doing sth. (现在分词) 4) have sth. done. (过去分词) 四、什么动词后可有宾语补足语: 1. 在表示心理状态的动词后作宾语补足语。这类动词有:consider, think, believe, discover, find, imagine, judge, suppose, prove等。这类动词后的不定式通常是"to be+形容词或名词"结构,think, consider, find后的to be常可省略。 We consider him (to be) a good teacher.我们认为他是一个好老师。 He proved that theory (to be) very important. 他证明那个理论是很重要的。 I thought her (to be) nice and honest the first time I met her. 我第一次见到她的时候就认为她人很好,很诚实。 2. 在表示情感状态的动词后作宾语补足语。这类动词有:love, like, prefer, hate, want, wish, expect等。 I'd prefer you to leave him alone. 我希望你不要打扰他。 I don't want there to be any trouble. 我不想有任何麻烦。 3. 注意:hope, demand, suggest等动词后面不能接不定式作宾语补足语。 I hope you can give me a hand. 我希望你能帮我一把。 I wish you to give me a hand. 我希望你能帮我一把。 He required us to be present at the meeting. 他要求我们出席会议。 Mr Li suggested that she should not go there alone.李先生建议她不要独自去那里。 五、可作宾语补足语的形式有: 不定式,现在分词,过去分词,名词,形容,副词,介词短语都能作补语。 六、具体说明: (一)副词作宾语补足语 I found him in yesterday. (二)常接形容词作宾语补足语的动词有:keep, make, find等。 如:We must keep our classroom clean. (三)常接名词作宾语补足语的动词有:call, name, make, think等。 如:We call them mooncakes. (四)常接动词-ing形式作宾语补足语的动词有:see, watch, hear, find, keep等。 如:In the country, we can hear birds singing. (五)常接介词短语作宾语补足语的动词有:keep, find, leave等。如:I left my pen on my desk at home. (六)不定式作宾语补足语 1. 常接带to的动词不定式作宾语补足语的动词有:ask, tell, want, teach, wish等;
英语五种基本句型小结 根据句子的基本结构,英语句子可简单的分为以下五种: 一、主语+谓语(S + V) “主语+不及物动词”构成句子的主体部分,后面不能跟宾语,但可以跟状语。 e.g. He cooks. 他烧饭。 They are drinking. 他们正在喝东西。 He runs in the park. 他在公园里跑步。 二、主语 + 谓语 + 宾语(S + V + O) 在这种句型中,谓语动词是及物动词。后面可以直接跟宾语。宾语一般是由名词、代词、动名词或动词不定式等来充当。 e.g. She made cakes. 她做了蛋糕。 They are eating meat. 他们正在吃肉。 She likes reading. 她喜欢读书。 I want to sleep. 我想睡觉。 三、主语 + 系动词 + 表语(S + V + P) 常见的系动词有以下几种: 1. be动词 (am / is / are / was / were / been) 2. 四变: get / become / turn / go 3. 感官动词: look / feel / taste / sound / smell 4. 另外还有keep, remain等都可以作为系动词。 表语一般由名词、形容词、介词短语、动词不定式等来承担。 e.g. We are students. 我们是学生。 The days get longer and longer.白天变得越来越长。 The food goes bad. 食物变质了。 He seems worried. 他似乎很着急。 You must keep healthy. 你必须保持健康。 Tom is in China now. 汤姆现在在中国。 四、主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语(S + V + IO+ DO) 这种结构就是我们所说的双宾语。其中前一个宾语指人,称为间接宾语,一般放在直接宾语的前面,也可以放在直接宾语后面,但要用介词to 或for 隔开。后一个是直接宾语,一般指物。 1. 与to连用的动词有give, pass, bring, send, tell, teach, take, show 等, to一般表示方向。 e.g. Please show me the photos.(=Please show the photos to me.)请让我看看那些照片。 I gave him a book. (=I gave a book to him.)我把书给了他。 2. 与for 连用的动词有buy, get, find, cook, make, grow, sing等,for一般表示对象。 e.g. My mother bought a birthday cake for me yesterday. (=My mother bought me a birthday cake yesterday.) 我妈妈昨天给我买了一个生日蛋糕。 The singer sang three songs for us just now.