
新概念第一册 知识点总结(全)
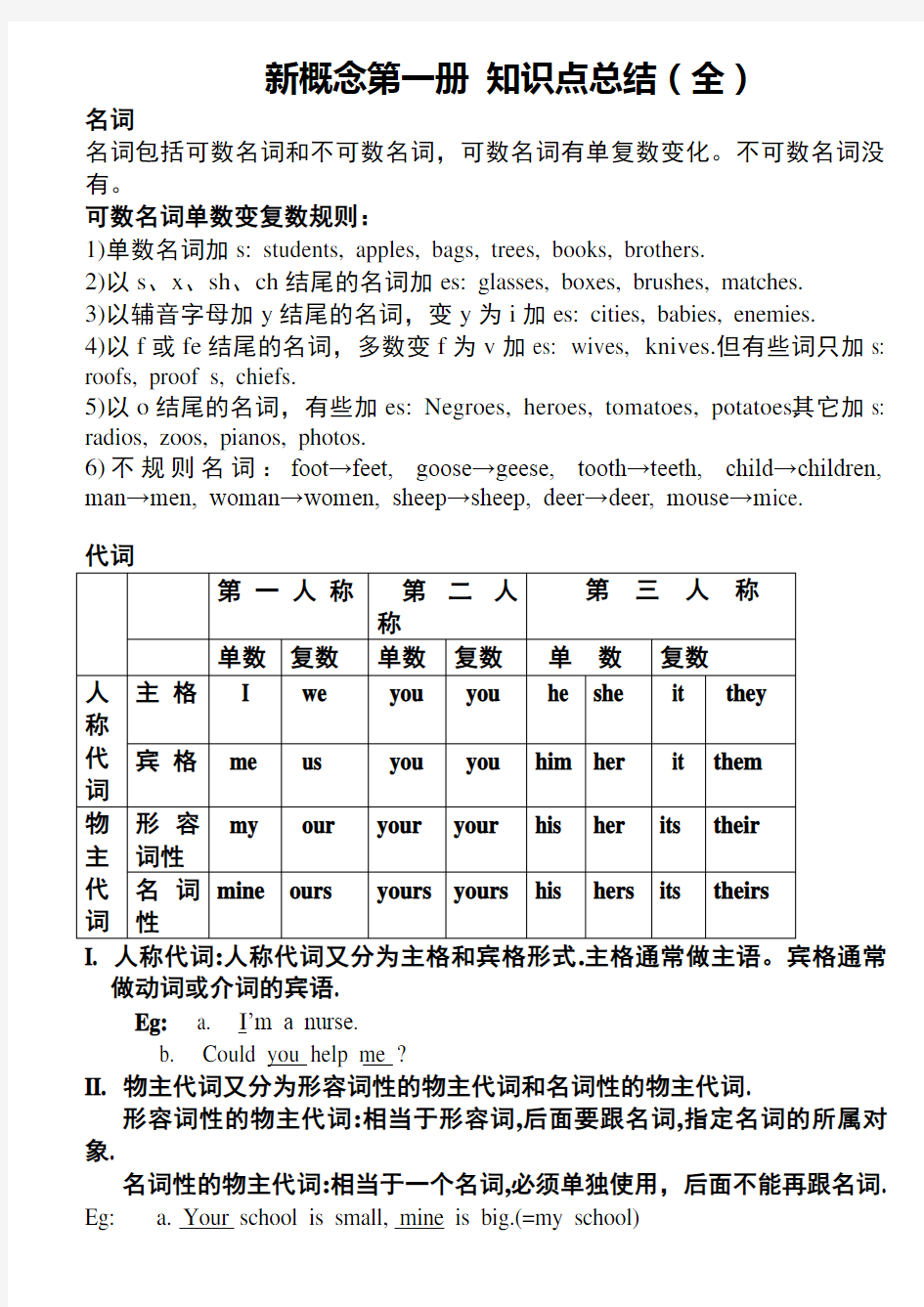
名词
名词包括可数名词和不可数名词,可数名词有单复数变化。不可数名词没有。
可数名词单数变复数规则: 1)
单数名词加 2)以s 、x 、sh 、ch
结尾的名词加 3)以辅音字母加y 结尾的名词,变y 为i
加 4)以f 或fe 结尾的名词,多数变f 为v 加es: wives, knives.但有些词只加
s:
5)以o 结尾的名词,有些加es: Negroes, heroes, tomatoes, potatoes.其它加
s:
6)不规则名词:foot→feet, goose→geese, tooth→teeth, child→children, man→men, woman→women, sheep→sheep, deer→deer, mouse→m ice.
I. 人称代词:人称代词又分为主格和宾格形式.主格通常做主语。宾格通常做动词或介词的宾语. Eg: a. I ’m a nurse.
b. Could you help me ?
II. 物主代词又分为形容词性的物主代词和名词性的物主代词.
形容词性的物主代词:相当于形容词,后面要跟名词,指定名词的所属对象.
名词性的物主代词:相当于一个名词,必须单独使用,后面不能再跟名词. Eg: a. Your school is small, mine is big.(=my school)
b. This is not your pen. Yours is on the desk.(=your pen)
时态
一、一般现在时:
概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。
时间状语:
always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays…
基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词
否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。
一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。
My father is a doctor.
Tom isn’t at home.
Are they policemen?
I often get up at 7 o’clock every morning.
He doesn’t like apples.
Do you always read before going to bed?
What do you usually do on Sundays?
一般现在时句中,如果主语是第三人称时,动词要变第三人称单数,变化规则如下:
1) 一般情况下,动词后面直接加 -s. 例如:
works gets says reads
2) 以s,x ,ch,sh或 o 结尾的动词,在后面加 -es。例如:
goes teaches washes
3) 以辅音字母 + y结尾的动词,把 y变为 i 再加 -es. 例如:
studies tries carries
特殊情况:动词 have 的第三人称单数是 has。
例如:He has an interesting book.
二、一般过去时:
概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。
时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, the other day, long long ago, once upon a time, ….
基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词
否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。
I was at my mother’s last week.
Once upon a time, there was a beautiful girl whose name was Snow White. Lucy went to America five months ago.
I didn’t go to the cinema last night.
Did Lily dance at the party?
What did you do yesterday?
动词的过去式变化:
be动词:am/is-----was are---were
规则动词:
1. 直接在词尾加-ed。如: want—wanted, work—worked, need—needed, clean—cleaned
2. 以不发音的e结尾的在词尾加-d。如:like—liked, live—lived, use—used, move—moved
3. 以一个元音字母加一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,先双写结尾的辅音字母,再加-ed。如:stop—stopped, trip—tripped
4. 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先把y变成i,再加-ed。如:study—studied, carry—carried, hurry—hurried, marry—married
不规则动词:
Have-had eat-ate drink-drank go-went come-came see-saw hear-heard put-put cut-cut 等等
三、现在进行时:
概念:表示此时此刻或现阶段正在进行的动作及行为。
时间状语:now, at this time, these days, …
基本结构:am/is/are+doing
否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing.
一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。
They are playing basketball on the playground.
I am not reading anything.
Is he waiting for the bus?
What are you doing now?
动词ing形式的变化规则:
1 一般情况下,直接在动词后加-ing
work ---- working sleep ----- sleeping study ----- studying
2 动词以不发音的-e结尾,要去-e加-ing
take ----- taking make ----- making dance ----- dancing
3 重读闭音节的动词,要双写词尾字母,再加-ing
cut ----- cutting put ----- putting begin ------ beginning
4 以-ie结尾的动词,把变成y再加-ing
lie ----- lying tie ----- tying die ----- dying
四、过去进行时:
概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。
时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状语等。
基本结构:was/were+doing
否定形式:was/were + not + doing.
一般疑问句:把was或were放于句首。
I was listening to the radio at 7 this morning.
He was cleaning the car when I arrived.
What was he doing at this time yesterday?
五、现在完成时:
概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。
时间状语:already, just,yet, since…, for…,….
基本结构:have/has + done
否定形式:have/has + not +done.
一般疑问句:have或has。
He has lost his wallet.
I have already had my lunch.
David hasn’t finished his homework yet.
Have you seen this film?
Mary has been a translator for 20 years.
They have lived here since 1987.
How long have you lived here?
动词过去分词变化规则:
规则动词:规则动词的过去分词变化规则与过去式变化规则相同,包括4条。
1. 直接在词尾加-ed。如: want—wanted, work—worked, need—needed, clean—cleaned
2. 以不发音的e结尾的在词尾加-d。如:like—liked, live—lived, use—used, move—moved
3. 以一个元音字母加一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节动词,先双写结尾的
辅音字母,再加-ed。如:stop—stopped, trip—tripped
4. 以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,先把y变成i,再加-ed。如:study—studied,
carry—carried, hurry—hurried, marry—married
不规则动词:需要特殊记忆。
Be动词-been have-had go-gone come-come eat-eaten drink-drunk 等等
六、过去完成时:
概念:以过去某个时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。
时间状语:before, after….
基本结构:had + done.
否定形式:had + not + done.
一般疑问句:had放于句首。
The bus had already left before I arrived at the station.
He went to the park after he had finished his work.
七、一般将来时:
概念:表示将要发生的动作或存在的状态及打算、计划或准备做某事。
时间状语:tomorrow, next day(week, month, year…),soon, in a few minutes, the day after tomorrow, …
基本结构:①am/is/are going to + do;②will + do.
否定形式:①am/is/are not going to + do;②will not + do
一般疑问句:①be放于句首;②will提到句首。
My family are going to Beijing next week.
It is going to rain.
He will be 11 years old next year.
We will leave in two hours.
情态动词
我们学过的情态动词有can, could, may, must, had better, have to
情态动词没有人称和数的变化,后面跟动词原形。
Can
1, 表示能力,“能够…”
I can swim very well.
He can’t sing or dance.
2, 表示请求,“可以…吗?”
Can I help you?
Can you give the glass to me, please?
Could
1, can的过去式,表示过去的能力,“能够…”
He could climb the mountain 30 years ago, but now he can’t.
2, 表示请求,比can 更加委婉客气,此时could非can的过去式。Could you help me, please?
Could you bring the book to me?
Could I borrow your bike?
May
表示请求,比can稍加委婉客气。“可以…吗?”
May I come in?
May I use your pen?
Must
1, 表示“必须…”
I must go now.
You must finish your work before you leave the company.
2, mustn’t表示“禁止…”
Kate,you mustn’t play with the knife, because it is too dangerous.
You mustn’t smoke in the classroom.
Had better “最好…”
否定形式:had better not
You had better put on more clothes. It is cold outside.
We’d better leave at once.
You had better not eat eggs.
You’d better not go out at this time.
Have to “不得不…”
David has to take care of his litter sister because his parents are not at home.
They have to stay at home because it is raining heavily outside.
形容词的原级,比较级和最高级
(一)规则变化:
1.绝大多数的单音节,词尾加-er ,-est
tall—taller—tallest
2.以不发音的e结尾的单音节词只加-r,-st
nice—nicer—nicest , able—abler—ablest
3.以辅音字母加y结尾的双音节词,改y为i再加-er,-est
easy—easier—easiest
4.只包含一个元音,并且以一个辅音字母结尾的重读闭音节词,双写结尾的辅音字母,再加-er,-est
big—bigger—biggest hot-hotter-hottest
5.少数以-er,-ow结尾的双音节词末尾加-er,-est
clever—cleverer—cleverest, narrow—narrower—narrowest
6.其他双音节词和多音节词,在前面加more,most来构成比较级和最高级
Beautiful---more beautiful---most beautiful
Expensive---more expensive---most expensive
(二)不规则变化
常见的有:
good / well—better—best ; bad /badly/ ill—worse—worst ;
many / much—more—most ; little—less—least ;
用法:
1.原级:as + 形容词原级+as(否定为not so/as + 形容词原级+as)
“…和…一样…”
This room is as big as that one.
I have as many books as you have.
You are not as tall as I.
2.比较级+ than 用于两者之间的比较
“…比…更…”
This shirt is cheaper.
He is older than I.
Lucy is more beautiful than her sister.
7.the + 最高级+ 比较范围
He is the tallest of the boys.
He is the tallest in his class.
This is the largest dress in the shop.
I want the most expensive shoes.
Have用作实义动词时的用法。
1.Have 作为“有”的意思,表示某人“拥有”某物。例如:
Do you have a soccer ball? 你有一个足球吗!
Does he have a ping-pong ball? 他有一个乒乓球吗!
I have a new alarm clock. 我有一个新的闹钟。
Mary has two pen pals in Canada. 玛丽在加拿大有两个笔友。2.Have 有“吃、喝”的意思,有时相当于动词“eat”或者“drink”。例如:I often have milk and eggs for breakfast.我早饭经常喝牛奶吃鸡蛋。
Do you usually have tea in the afternoon?你通常下午喝茶吗?
Tom usually has lunch at school every day. 汤姆每天在学校吃午饭。
3.Have 还可以用来描述病情,构成诸如have a cold /have a toothache/ have a fever/have a sore back/have a pain in/on 等固定搭配,例如:
---“What’s the matter? ”你怎么了?
---“I have a toothache. ”我牙疼。
4.Have 与不定式符号“to”构成固定词组have to do something,用来表示义务必须做某事,其意思与must相当。例如:
---Jenny, can you come to my party on Sunday?
珍妮,星期天能来参加我的聚会吗?
---I’d love to. 我很乐意去。
---How about you? 你呢?
---I’m sorry, I have to help my parents.抱歉,我得照顾我的父母。
5.我们还常见到如下的固定搭配:have a walk /have a swim /have a rest /have a try/have a look at/ have a good time。比如:
Let’s lie down and have a rest. 让我们躺下休息一下吧
常见的介词的用法
On
1.在….上(有接触点)
There is a picture on the wall.
over, on表示“在……上”之间的区别
(1)over指“在……正上方”,表示垂直上方,其反义词为under。如:
The bridge is over the river.
(2)on表示“在……上面”,与物体表面接触,与beneath相对。如:
There is a map on the wall.
The earth felt soft beneath our feet.
2. 指时间
(1)在具体的某一天,如某日、某节日、星期几等。如:
On May 4th, there will be a celebration.
It will rain on Tuesday.
(2)在具体某一天的早晨、下午或晚上。如:
He arrived at 10 o’clock on the night of the 5th.
In
1.
2.在….里面
He is in the classroom.
2.
3.表示地点,在…。
My uncle lives in Shanghai.
Life is difficult in America.
3.表示时间。
(1)在某个较长的时间(如世纪、朝代、年、月、季节以及泛指的上午、下午或傍晚等)内。如:
in 2004, in March, in spring, in the morning, in the evening, 等等
(2)在一段时间之后。一般情况下,用于将来时,谓语动词为瞬间动词,意为“在……以后”。如:
He will arrive in two hours.
At
1. 指时间:时间的一点、时刻等。如:
They came home at ten o’clock .
另外注意一些固定搭配:at noon, at midnight, at night
4.指地点:在一些小地方。如:
At home at the butcher’s at the dentist’s at the hairdresser’s
in the front of是指某物(或某整体)内部的前部;
in front of指某物(或某整体)外部的前面.
例如:
The teacher is standing in the front of the classroom.
There is a tree in front of the house.
Behind 在…后面
The photo is behind the door.
Under 在….下面
Mary is sitting under the tree in the garden.
Across穿过…横渡…
Don’t walk across the road when the traffic lights are red.
Off 从…离开
Jump off the wall.
Take off your coat.
Into进
Many children are going into the school.
Out of出
He run out of the house.
英语中时间的表达方式
1. 表示整点:时间+o’clock
Seven o’clock
2、如果分钟在半小时以内(包括半小时),表示“几点过几分”,句式为“分
钟+past+小时”。如:
eleven past seven
3、如果分钟在半小时以上(不包括半小时),表示“几点差几分”,句式为
“(60—分钟)+to+(小时+1)”,如:
two to seven
a quarter to eight
4、quarter意思是“四分之一”,用在时间中表示“一刻钟, 15分钟”。three quarter表示“三刻钟”即“45分钟”。不过,半小时可不是two quarter!而是“half”
a quarter past eight 八点一刻
half past nine 九点半
5、日常生活中用口语表达时间时,可以直接照书面数字读。如:
7:15读作seven fifteen
11:30读作eleven thirty
3:53读作three fifty-three
6、时间后面的am指上午;pm则指下午。
9.p.m 下午9点
5.a.m 上午5点
7、表达“在几点几分”,用at+时间。如:
My father begins to work at eight. 我的爸爸八点开始工作。
英语中日期的表达方式
(一)书写方面
先看下面的两个例子:
1. 1986年10月23日→October 23rd, 1986
2. 2002年1月17日→Ja nuary 17th, 2002
从上面的例子可以看出,英语日期的表达与汉语不同。英语表达的顺序为\"月、日、年\"。
(二)朗读方面
在朗读时,"月份"一般直接用英语读出;"日"则要读成"the + 序数词";
读年份时,一般分为两个单位来读,前两个数为一个单位,后两个数为一个单位。如:1982年读作nineteen eighty-two, 1900年读作nineteen hundred。如果是三位数,先读第一位,再把后两个数合起来读。如:984年可读为nine eighty-four,757年读成seven fifty-seven。
另外,像2000年一般读成two thousand, 2001年则读成two thousand and one,以此类推,2004年应读成two thousand and four。
January 12th, 1993读成January the twelfth, nineteen ninety-three。
注意:
英语中月份和星期名称都是专有名词,它们的首字母必须大写,并且前面无需用冠词。
用英语表示日期,其顺序为“月+日+年”,日和年之间需用逗号隔开。
如:August 2nd,2003(2003年8月2日)。也可以用“日+月+年”来表示。如:10th May,2003(2003年5月10日)。
英语日期前介词的使用:若指在哪一年或哪一月,则用介词in,若具体到某一天,则需用介词on
不规则动词表
原形过去式过去分词意义
arise arose arisen 出现
be was, were been 是
beat beat beaten 击败
become became become 成为
begin began begun 开始
bend bent bent 弯曲
bet bet bet 打赌
bite bit bitten 咬
bleed bled bled 流血
blow blew blown 打击
break broke broken 打破
bring brought brought 带来
broadcast broadcast broadcast 广播
build built built 建设
burn burnt, burned burnt, burned 燃烧
burst burst burst 爆裂buy bought bought 购买can could - 可以catch caught caught 捕捉choose chose chosen 选择come came come 来cost cost cost 花费cut cut cut 切deal dealt dealt 处理dig dug dug 挖do did done 做draw drew drawn 画
dream dreamt,
dreamed
dreamt, dreamed 梦想
drink drank drunk 喝drive drove driven 开车eat ate eaten 吃fall fell fallen 下降feed fed fed 饲养feel felt felt 感觉fight fought fought 战斗find found found 发现fly flew flown 飞foresee foresaw foreseen 预见
forget forgot forgotten 忘记forgive forgave forgiven 原谅freeze froze frozen 冻结get got got 获得give gave given 给go went gone 去grow grew grown 增长hang hung ,hanged hung, hanged 挂have, has had had 有hear heard heard 听hide hid hidden 隐藏hit hit hit 击中hold held held 举行hurt hurt hurt 伤害keep kept kept 保持know knew known 知道lay laid laid 躺在lead led led 领导learn learnt, learned learnt, learned 学习leave left left 离开lend lent lent 借出let let let 让lie lay lain 撒谎light lit, lighted lit, lighted 照亮
lose lost lost 失去
make made made 使
may might - 可能
mean meant meant 意思
meet met met 见面
misread misread misread 误解
mistake mistook mistaken 错误
misundersta
misunderstood misunderstood 误会nd
must must - 必须
pay paid paid 付
put put put 放
read read read 读
rid rid, ridded rid, ridded 摆脱
ride rode ridden 骑
ring rang rung 响
rise rose risen 上升
run ran run 跑
say said said 说
see saw seen 看
seek sought sought 寻求
sell sold sold 出售
send sent sent 发送
set set set 放置
shake shook shaken 摇动shall should - 将shine shone, shined shone, shined 闪耀show showed showed, shown 显示shut shut shut 关闭sing sang sung 唱sink sank, sunk sunk, sunken 下沉sit sat sat 坐sleep slept slept 睡觉smell smelt, smelled smelt, smelled 闻sow sowed sown, sowed 播种speak spoke spoken 发言spell spelt, spelled spelt, spelled 拼写spellbind spellbound spellbound 迷惑spend spent spent 花spill spilt spilt 洒spin spun spun 旋转spit spat spat 吐spoil spoilt spoilt 溺爱spread spread spread 蔓延stand stood stood 站steal stole stolen 窃取stick stuck stuck 粘贴strike struck struck, stricken 打击
swell swelled swollen 膨胀sweep swept swept 扫swim swam swum 游泳swing swung swung 摆动take took taken 带走teach taught taught 教tell told told 告诉think thought thought 认为throw threw thrown 扔understand understood understood 明白upset upset upset 打乱
wake waked,woke waked,woken,woke
醒来
wear wore worn 穿weave wove woven 编织will would - 将win won won 赢write wrote written 写