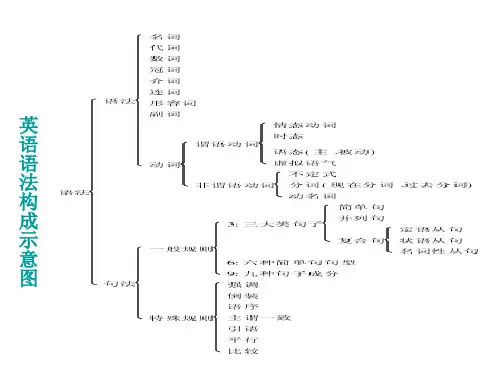
第9讲 虚拟语气
- 格式:doc
- 大小:434.00 KB
- 文档页数:30







一、虚拟语气(9).1、 It is high/about time that...+过去式 .2、 I would rather you 过去me now. .3、 I would rather I 过去的过去yesterday. .4、 I would rather you 过去tomorrow. .5、主语+propose/urge/suggest/require/demand/insist /that...+(should)+动词原形 .6、 The suggestion is that...(should)+动词原形 .7、 It is necessary/important/essential that+ (should) + 动词原 .8、 I wish I 过去ten years younger now. 9、 I wish I 过去的过去him yesterday. 虚拟语气在条件状语从句中的用法(必背)注意下延伸考点:1.as if /as though的相关考点现在用过去,过去用过去的过去 were,had,should 放到从句主语前面去,形成倒装,但是否定词not 不前移。
多见于书面语.二、时态(4)1.You’d better + do sth... / You’d better not do sth...2,by the time / end of主句+将来完成时by the end of next year 主句+过去将来完成时by the end of 1999 (关键句:By the middle of the 21st century, the vast majority of the world’s people 将来完成时in cities rather than in rural areas..3、 It is/has been +一段时间+since 自从......已有...... .4、 for, since, so far, till, until一般与完成时连用(完成时提示词) 三、固定句式(12) 1、 I have no doubt + that2、 I have trouble/difficulty + (in) doing sth3、 It is/was.... + that (强调句)4、 The more..., the more The more..., the less 5. make it( clear, one’s duty, possible),it不可以省略。


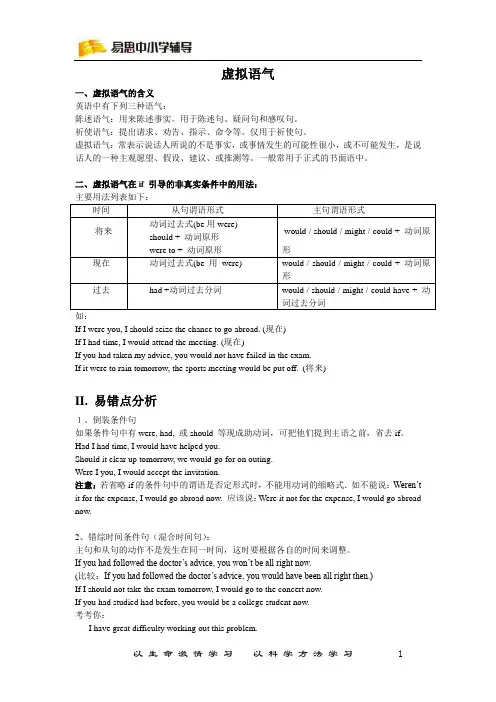
虚拟语气一、虚拟语气的含义英语中有下列三种语气:陈述语气:用来陈述事实。
用于陈述句、疑问句和感叹句。
祈使语气:提出请求、劝告、指示、命令等。
仅用于祈使句。
虚拟语气:常表示说话人所说的不是事实,或事情发生的可能性很小,或不可能发生,是说话人的一种主观愿望、假设、建议、或推测等。
一般常用于正式的书面语中。
二、虚拟语气在if 引导的非真实条件中的用法:主要用法列表如下:如:If I were you, I should seize the chance to go abroad. (现在)If I had time, I would attend the meeting. (现在)If you had taken my advice, you would not have failed in the exam.If it were to rain tomorrow, the sports meeting would be put off. (将来)II. 易错点分析1、倒装条件句如果条件句中有were, had, 或should 等现成助动词,可把他们提到主语之前,省去if。
Had I had time, I would have helped you.Should it clear up tomorrow, we would go for on outing.Were I you, I would accept the invitation.注意:若省略if的条件句中的谓语是否定形式时,不能用动词的缩略式.如不能说:Weren’t it for the expense, I would go abroad now. 应该说:Were it not for the expense, I would go abroad now.2、错综时间条件句(混合时间句):主句和从句的动作不是发生在同一时间,这时要根据各自的时间来调整。
第九节情态动词和虚拟语气〔真题演练〕1. (经典高考)I can’t find my purse. I could (leave)it in the supermarket yesterday, but I’m not sure.2. (经典高考)Truly elegant chopsticks might (make)of gold and silver with Chinese characters.3. (经典高考)What a pity! You missed the sightseeing, or we(have) a good time together.4. (经典高考)If we (catch)the flight yesterday, we would be enjoying our holiday on the beach now.〔必备知识〕考点一情态动词1.情态动词的基本用法情态动词用法例句can/could表示“能力”,意为“能,会”Samuel, the tallest boy in our class,can easily reach the books on the top shelf. Samuel是我们班最高的男孩,他能轻易地拿到书架顶层的书。
表示推测,意为“可能”,往往用于否定句或疑问句中。
can比could语气强That can’t be Mary—she is in London now.那不可能是玛丽——她现在在伦敦。
表示客观可能性,意为“有时候会”,多用于肯定句Credit cards provide us with lots of convenience, but sometimes they can lead to problems.信用卡给我们提供了许多方便,但有时候会带来一些问题。
表示礼貌地请求,意为“能,可以”。
在疑问句中could可代替can, 语气更委婉Can you tell us your recipe for happiness and a long life?你能告诉我们你幸福和长寿的秘诀吗?固定句式:can’t...too/enough“无论多么……也不过分”“越……越好”I can’t thank you too much for all your help to my son while we were away from home.我非常感谢你在我们不在家时对我儿子的帮助。
高中英语真题:第九讲情态动词和虚拟语气一、情态动词考点透析1.can (could),be able to。
can只有现在式can和过去式could两种形式, be able to可用于现在式、过去式、将来时、完成时。
要表示“能够做某事”,可用can或be able to,但若要说过去的确运用了某种能力做成了某件事情,就只能用was/were able to,表将来具备的能力只能用will/shall be able to。
(1)If you study hard,you will be able to express freely in English in three months. (2)The fire spread through the hotel very quickly but everyone was able to get out.2.could是can的过去式,但是在很多情况下,特别是在口语中,它表示语气的委婉。
因此,用could提问时,不能用could 回答,而要用can或may。
would,might用于疑问句时也表委婉语气,回答时应该用will,may。
(1)-Could I borrow your dictionary?-Yes,of course you can.(2)-Could I call you by the first name?-Yes,you may.(3)-Would you be so kind as to explain the word?-Yes,I will.What is it?3.may/might,can/could都可表示可能,但may/might 不能用于问句,can/could用于否定句、疑问句、感叹句,表示惊异、怀疑,一般不用于肯定句。
如果用于肯定句,则表示偶尔发生某事的可能,或某人某物一时的特点。
(1)-Are you coming to Jeff's party?-I'm not sure.I might go to the concert instead.(2)-Where can Mr.Li be?-Sorry,I don't know.You can go to ask Mr.Zhang.He may help you.(3)Mr.Bush is on time for everything.How can it be that he was l ate for the opening ceremony?(4)We enjoy good weather in January,but sometimes it can be terribly cold.4.must表推测用于肯定句,其否定式要用can't。
高中英语语法学习/复习讲义虚拟语气语法知识点讲义09【精讲版·全国通用】英语的语气与虚拟语气知识点总结英语的语气与虚拟语气■关于动词的语气动词的语气与我们日常生活中说的“语气”有所不同,比如我们平常说的“委婉语气”“怀疑的语气”“生硬的语气”“害怕的语气”等等,这与“动词的语气”均没有关系。
动词的语气是动词的一种形式。
根据说话意图的不同,动词需要不同的形式,这就是所谓的语气(mood)。
关于语气的分类,不同的语法学有不同的看法,有的语法学家将语气分为陈述语气、疑问语气、祈使语气和虚拟语气四种,有的语法学家将语气分为陈述语气、祈使语气和虚拟语气三种(即将“疑问语气”并在“陈述语气”之中)。
■关于陈述语气陈述语气(indicative mood)用于陈述事实或提出看法。
英语中的句子绝大部分都是陈述语气。
我们在谈论时态和语态时,都主要是指陈述语气的动词变化。
如:He did very well in the examination. 他考得很好。
She heard the front door shut. 她听见大门给关上了。
I wonder if I might use your phone. 不知可否用一下你的电话。
He lived there happily for a year. 他在那儿愉快地居住了一年。
■关于疑问语气疑问语气(interrogative mood)用于提出问题。
英语中的疑问句均属于疑问语气。
如:Where do you come from? 你是哪里人?Why are you so nervous? 你为什么这样紧张?What did you do that for? 你做这个干什么?How many windows are broken? 打破了多少扇窗户?Why don’t you think more about other people?你怎么就不多为别人着想呢?■关于祈使语气祈使语气(imperative mood)用于提出命令、要求、请求、邀请、劝告或建议等。
奥风初中语法一:名词与数词I. 名词的种类:II. 名词的数:2. 不规则名词复数:英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,现归纳如下:III. 名词的所有格:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
3. of所有格的用法:用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed例题解析:1. ( ) His grandfather is _____.A) Robert Bob B) Tom Black C) Kate White D) Black Green2. ( ) _____ are playing tennis in the playground.A) The Browns B) The Brown's C) Browns D) Brown's3. ( ) Be careful. There is a _____ hole in the ground.A) two-foot-deep B) two-feet-deep C) two-foot deep D) two-feet deep4. ( ) He’s got bad toothache. He’d better go to _____.A) dentist B) the dentist C) the dentist’s D) see the dentists5. ( ) The _____ teachers wondered if the _____ students were in trouble.A) woman, boy B) woman, boys C) women, boy D) women, boys6. ( ) _____ came that Houston Rocket won again and Yao Ming got the most scores.A) A news B) Message C) Word D) Words7. ( ) All of a sudden, something on the ground caught _____.A) his eye B) his eyes C) his own eyes D) eyes of his own8. ( ) The lady with long _____ found her husband had already got three gray _____.A) hair, hair B) hair, hairs C) hairs, hair D) hairs, hair名词练习:习题训练:Choose the best answer (选择最恰当的答案,用A、B、C或D表示,填入空格内): ( ) 1. The police ______ running after the thief when I passed the street.A. areB. isC. wereD. was( ) 2. It’s seven o’clock. _____ are sitting at ta ble.A) Mr. Greens B) The Green's C) The Greens D) Greens( ) 3. Your brother is the same ______ me.A) old as B) age as C) old like D) age like( ) 4. ________ trees are cut down in the forests every year.A. ThousandB. ThousandsC. Thousand ofD. Thousands of( ) 5. ——What can I do for you?——I'd like two _______.A. box of appleB. boxes of applesC. box of applesD. boxes of apple( ) 6. What kind of ______ do you like best?A) watermelon B) the watermelon C) a watermelon D) watermelons( ) 7. Look at this magazine. Let’s do the ______ about eating habits.A) quiz B) list C) cooking D) dinner( ) 8.Help yourself to ______.A. some chickensB. a chickenC. some chickenD. any chicken( ) 9.________ it is today!A. What fine weatherB. What a fine weatherC. How a fine weatherD. How fine a weather( ) 10. Which is the way to the __________?A. shoe factoryB. shoes factoryC. shoe's factoryD. shoes' factory( ) 11.This class _______ now. Miss Gao teaches them.A. are studyingB. is studyingC. be studyingD. studying( ) 12. We will have a ______ holiday after the exam.A. two monthB. two-monthC. two month'sD. two-months( ) 13. Our bodies need food to give us ______.A) health B) strong C) energy D) taste( ) 14. Our sports meeting will be held ________.A. on 24, Tuesday, AprilB. in April 24, TuesdayC. on Tuesday, April 24D. in April Tuesday 24( ) 15._________ people here are very friendly to us.A. TheB. /C. AD. An( ) 16. .There is no enough ________ in the corner to put the table.A. placeB. roomC. floorD. ground( ) 17. He has got _____ to tell you.A) a good news B) some news C) a lot news D) many news( ) 18. Look! Those three _______ are talking with the three _______.A. Englishmen, GermenB. Englishmans, GermansC. Englishmen, GermansD. Englishmans, Germen数词数词分为两大类:基数词和序数词。
Ⅰ. 基数词基数词用来表示精确的数量,例如:one, two, three, twelve, eighteen, ninety, hundred, thousand, million, billion等。
基数词有两个后缀:-teen表示“+10”,例如:sixteen, thirteen等;-ty表示“×10”,例如:sixty, thirty等。
1.2. 100以上的大数词有:a hundred 一百(100)a thousand 一千(1,000)ten thousand 一万(10,000)a hundred thousand 十万(100,000)a million (= a thousand thousand) 一百万(1,000,000)ten million 一千万(10,000,000)a hundred million 一亿(100,000,000)a billion (= a thousand million) 十亿(1,000,000,000)在表示精确数量时不用复数形式,例如:two thousand people两千人,不能说two thousands people。
在表示含糊数量时要用复数形式,例如:thousands of people几千人,不能说thousand of people。
有时,可以在大数词(单数形式)前加上several, a few等词,表示含糊数量,例如:several hundred times好几百次,a few million years几百万年。
100以内的基数词有时也可用复数形式,表示一些特别的意义。
例如:They went to the theatre in twos and threes. 他们三三两两地来到了剧院。
The girl is in her teens. 这个女孩不到二十岁。
He became a professor in his thirties. 他三十多岁时成为了教授。
It was in the 1960s. 那是在二十世纪六十年代。
3. 混合数目的读法:百位以内的数目一般在个位和十位之间加一个and,例如:101 读作:a hundred and one320 读作:three hundred and twenty648 读作:six hundred and forty-eight千位以上的数目从右向左数起,每三位数加一个逗号。
从右开始,第一个逗号处读thousand,第二个逗号处读million,第三个逗号处读billion。
例如:2,648 读作:two thousand six hundred and forty-eight3,008 读作:three thousand and eight16,250,064 读作:sixteen million two hundred and fifty thousand sixty-four5,237,166,234 读作:five billion,two hundred and thirty-seven million,one hundred and sixty-six thousand,two hundred and thirty-four4. “名词+基数词”结构具有“序列”的意义,例如:Room Four四号房间,相当于the Fourth Room;Lesson Five = the Fifth Lesson第5课。