药学英语名词解释
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:248.73 KB
- 文档页数:4

药学英语名词解释整理(3)药学英语名词解释整理18. 最小有效量/最小有效浓度(minimal effective dose/concentration):引起效应的最小药量或最小药物浓度,即阈剂量或阈浓度。
19. 治疗量(常用量,therapeutic dose)比最小有效量大比最小中毒量小得多的量20. 极量(最大治疗量 maximal dose)疗效最大的剂量21. 最小中毒量:出现中毒症状的最小剂量。
22. 量反应:效应强弱随剂量增减呈连续性量的变化;形成足直型曲线。
23. 质反应:药理效应随剂量表现为反应性质变。
用阳性率或阴性率表示效应。
形成S型曲线。
24. 半数有效量(ED50):量反应中能引起50%最大效应强度的药量;质反应中引起50%实验对象出现阳性反应的药量。
(尽可能小则好)25. 半数致死量(LD50):引起50%实验对象死亡的药量。
(尽可能大则好)26. 治疗指数(therapeutic index/TI):以药物LD50与ED50的比值来表示药物的安全性。
一般TI值大于3称药物安全。
27. 最大效应(Emax)/效能(efficacy):药理效应达到的不再随剂量或浓度的增加而增强的极限效应。
28. 效价强度(potency):引起等效应的相对浓度或剂量。
剂量越小,效价强度越大。
(亲和力:药物与受体结合的能力。
内在活性:药物与受体结合时发生效应的能力。
)29. 激动药(agonist):既有亲和力又有内在活性的药物,能与受体结合并激动受体产生效应。
30. 部分激动药:较强的亲和力但内在活性不强(α<1)。
特点:只引起较弱的激动效应,增加浓度也达不到Emax;31. 拮抗药(antagonist):有较强的亲和力而无内在活性(α=0)的药物,与受体结合不激动受体,反因占据受体而拮抗激动药效应。
32. 竞争性拮抗药:可逆性地与激动药竞争相同的受体;增加激动药的浓度可与拮抗药竞争结合部位,可使激动药量效曲线平行右移,但斜率和最大效应不变。

药学常见的英文名词解释导语:药学是研究药物的性质、制备、性能评价、临床应用以及药物的副作用等方面的学科。
在药学领域中,有许多常见的英文名词需要解释。
本文将对其中一些常见的名词进行解释,以帮助读者更好地理解药学知识。
一、Active ingredient(活性成分)活性成分是指药物中能够对人体产生治疗作用的化学物质。
药物的活性成分通常是通过药物的提取、合成或者其他方法制备而成。
例如,阿司匹林的活性成分是乙酰水杨酸。
二、Drug delivery system(药物给药系统)药物给药系统是指药物在进入人体后发挥作用的方式和途径。
药物可以通过口服、注射、贴剂等多种途径给予患者。
药物给药系统的选择与药物的性质、患者的病情以及治疗需求等因素有关。
三、Pharmacokinetics(药物动力学)药物动力学是研究药物在人体内的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄过程的科学。
了解药物动力学可以帮助我们更好地理解药物在体内的作用和影响。
药物动力学涉及到吸收速度、生物利用度、药物的分布范围以及半衰期等参数。
四、Pharmacodynamics(药物动力学)药物动力学是研究药物在体内的生理和生化作用的科学。
药物动力学研究药物与生物体的相互作用以及药物在分子水平上的作用机制。
通过研究药物的动力学原理,可以预测药物在人体内的药效和副作用。
五、Adverse drug reaction(药物不良反应)药物不良反应是指在正常使用或治疗范围内,药物对人体产生的有害的、非预期的反应。
药物不良反应可以包括过敏反应、中毒反应、药物相互作用等。
了解药物不良反应对于合理用药和提高药物安全性至关重要。
六、Pharmaceutical formulation(药物制剂)药物制剂是指将活性成分与辅料以一定比例混合,经过制备工艺制成的制剂形式,便于患者使用的药物形式。
药物制剂包括片剂、注射剂、栓剂、乳剂等。
药物制剂的选择将根据药物的性质和治疗的需要来确定。

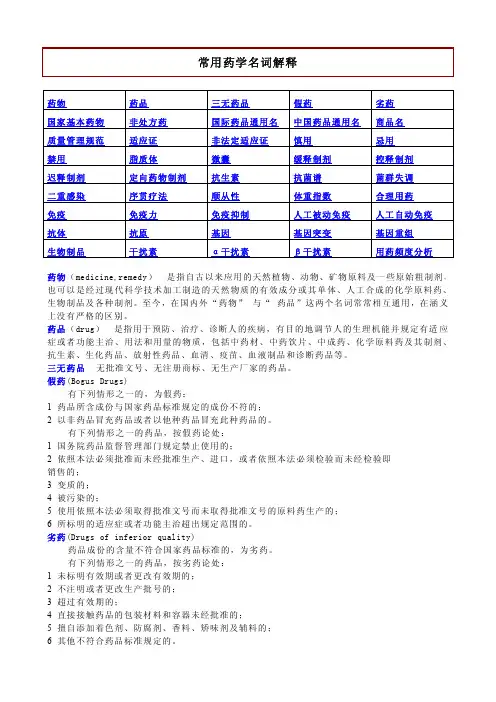
药剂学名词解释第一篇:药剂学名词解释绪论1.Pharmaceutics(Pharmacy)药剂学: 是研究药物制剂的基本理论,处方设计,制备工艺,质量控制,合理使用等内容的综合性应用技术科学.2.Dosage forms 剂型: 适合于疾病的诊断、治疗或预防的需要而制备的与一定给药途径相适应的给药形式,就叫做药物剂型,简称剂型.3.Pharmaceutical preparations 药物制剂:各种剂型中的具体药物或者为适应治疗或预防的需要而制备的不同给药形式的并规定有适应症、用法和用量的具体品种,简称制剂.4.DDS 指在防治疾病的过程中所采用的不同于普通剂型的各种新型的给药形式和方法5.Pharmacopoeia 药典:是一个国家记载药品标准,规格的法典,一般由国家药典委员会组织编著,出版,并由政府颁布,执行,具有法律约束力.6.Formulation 生产处方:是制剂生产或者调配的重要书面文件,是配料和成本核算的依据,包括药物,用量,配制方法以及工艺等内容。
7.Prescription 医师处方: 医生对病人用药的重要书面文件,包括药品的种类,数量和用法。
8.Prescritption(Ethical)drug 处方药: 必须凭执业医师或执业助理医师的处方才可调配,购买并在医生指导下使用的药品.9.OTC 非处方药: 不需凭执业医师或执业助理医师的处方,消费者可以自行判断,购买和使用的药品.液体制剂10.Liquid preparations 液体制剂: 指药物分散在适宜的分散介质中形成的供内服或外用的液体形态的制剂。
11.Solubilizer 增溶剂: 指具有增溶能力的表面活性剂.Solubilization增溶: 指某些难溶性药物在表面活性剂作用下,在溶剂中溶解度增大并形成澄清溶液的过程12.Hydrotropy agents 助溶剂: 指难溶性药物与加入的第三种物质在溶剂中形成可溶性分子间的络合物,复盐或缔合物等,以增加药物在溶剂中的溶解度,这第三种物质称为助溶剂。

药学英语词汇药学英语词汇是药学领域中不可或缺的一部分。
它涵盖了许多不同的概念和术语,涉及药物的研发、生产、管理和使用等方面。
下面将介绍一些常用的药学英语词汇,并对其进行拓展说明。
1. Pharmacology (药理学): The study of how drugs interact with the body and how they produce therapeutic effects or side effects.2. Pharmaceutical (制药的): Relating to the production, development, and sale of drugs.3. Pharmacokinetics (药物动力学): The study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion in the body.4. Pharmacodynamics (药物动力学): The study of how drugs exert their effects on the body at the cellular and molecular level.5. Drug formulation (药物制剂): The process of developing the most suitable form of a drug for administration, such as tablets, capsules, or injections.6. Clinical trial (临床试验): A research study that tests the safety andeffectiveness of a new drug or treatment in humans.7. Drug interaction (药物相互作用): The effects that occur when two or more drugs are taken together, which can alter their individual therapeutic effects or cause adverse reactions.8. Adverse drug reaction (药物不良反应): Any harmful or unintended response to a drug, which may range from mild to severe.9. Pharmacist (药剂师): A healthcare professional who is knowledgeable about drugs, their uses, and their potential side effects, and who dispenses medications to patients.10. Prescription (处方): A written order from a healthcare provider fora specific medication, including dosage instructions and duration of treatment.11. Over-the-counter (OTC) (非处方药): Medications that can be purchased without a prescription, typically used to treat minor ailments and symptoms.12. Generic drug (仿制药): A medication that is equivalent to a brand-namedrug in terms of active ingredients, dosage form, strength, and route of administration, but is usually less expensive.13. Drug resistance (药物抗性): The ability of microorganisms or cancer cells to survive and multiply despite the presence of a drug, making the treatment less effective.14. Pharmacovigilance (药品监测): The science and activities related to the detection, assessment, understanding, and prevention of adverse effects or any other drug-related problems.15. Drug delivery system (药物输送系统): The technology or method by whicha drug is administered to the body, including oral, transdermal, inhalation, and intravenous routes.以上这些药学英语词汇不仅在医药领域中广泛使用,而且对于学习和理解药物的研发、使用和管理至关重要。

1. 药物(drug ):药物是人类用来预防、治疗、诊断疾病、或为了调节人体功能,提高生活质量,保持身体健康的特殊化学品。
2. 药物化学(medicinal chemistry ):药物化学是一门发现与发明新药、研究化学药物的合成、阐明药物的化学性质、研究药物分子与机体细胞(生物大分子)之间相互作用规律的综合性学科,是药学领域中重要的带头学科以及极具朝气的朝阳学科。
3. 国际非专有药名(international non-proprietary names for pharmaceutical substance ,INN ):是新药开发者在新药研究时向世界卫生组织(WHO )申请,由世界卫生组织批准的药物的正式名称并推荐使用。
该名称不能取得任何知识产权的保护,任何该产品的生产者都可使用,也是文献、教材及资料中以及在药品说明书中标明的有效成分的名称。
在复方制剂中只能用它作为复方组分的名称。
目前,INN 名称已被世界各国采用。
4. 中国药品通用名称(Chinese Approved Drug Names ,CADN ):依据INN 的原则,中华人民共和国的药政部门组织编写了《中国药品通用名称》(CADN ),制定了药品的通用名。
通用名是中国药品命名的依据,是中文的INN 。
CADN 主要有以下的一些规则:中文名使用的词干与英文INN 对应,音译为主,长音节可简缩,且顺口;简单有机化合物可用其化学名称。
5. 巴比妥类药物(barbiturates agents ):具有5,5二取代基的环丙酰脲结构的一类镇静催眠药。
20世纪初问市的一类药物,主要由于5,5取代基的不同,有数十个各具药效学和药动学特色的药物供使用。
因毒副反应较大,其应用已逐渐减少。
6. 内酰胺-内酰亚胺醇互变异构(lactam- lactim tautomerism ):类似酮-烯醇式互变异构,酰胺存在酰胺-酰亚胺醇互变异构。
即酰胺羰基的双键转位,羰基成为醇羟基,酰胺的碳氮单键成为亚胺双键,两个异构体间互变共存。

药学综合名词解释药物分析1.药物(drug)是指用于预防、治疗、诊断人的疾病,有目的地调节人的生理功能并规定有适应症或者功能主治、用法用量的物质。
2.药品(medicinal products)由药物经一定的处方和工艺制备而成的制剂产品,是可供临床使用的商品。
3.药物分析(pharmaceutical analysis):利用分析测定手段,发展药物的分析方法,研究药物的质量规律,对药物进行全面检验与控制的科学。
4.中国药典(Chinese pharmacopoeia,ChP):由国家药典委员会组织编制、出版,政府颁布、执行,具有法律约束力的药品质量标准。
5.鉴别试验(Identification test):根据药物的某些物理、化学或生物学特性所进行的试验,以判定药物的真伪。
6.一般鉴别试验(General identification test):根据某一类药物的化学结构或理化性质,通过化学反应来鉴别药物的真伪。
7.专属鉴别试验(Specific identification test):根据药物分子中的特殊基团或官能团特殊反应或典型的有机官能团反应,在一般鉴别试验的基础上,区别同类药物或具有相同化学结构部分的各个药物单体。
8.杂质(Impurities):药物中存在的无治疗作用或影响药物稳定性和疗效,甚至对人体健康有害的物质。
9.杂质限量:药物中所含杂质的最大允许量。
10.特殊杂质(Related Substances):在特定药物的生产和贮藏过程中引入的杂质,这类杂质随药物的不同而不同。
11.有关物质:药物中可能存在的原料、中间体、降解物、异构体、聚合体、副反应产物和降解产物等。
12.干燥失重(loss on drying):药品在规定的条件下,经干燥后所减失的量,以百分率表示。
13.炽灼残渣(Residue on ignition):有机药物经炭化或挥发性无机药物加热分解后,高温炽灼所产生的非挥发性无机杂质的硫酸盐。

药物学名词解释药物学是研究药物的起源、性质、制备、使用、药理和毒理等方面的学科。
下面是一些药物学中常用的词汇的解释:1. 药物(drug):指能够治疗、预防或诊断疾病的物质。
药物主要有化学药物、天然药物和生物制品等类型。
2. 化学药物(chemical drug):由化学合成得到的药物。
化学药物通常具有明确的化学结构和药理活性。
3. 天然药物(natural drug):从植物、动物和微生物等自然界中提取得到的药物。
天然药物通常具有复杂的化学成分和药理活性。
4. 生物制品(biological product):由生物制备的药物,包括蛋白质药物、疫苗、基因治疗药物等。
生物制品通常具有与人体生物分子相似的结构和功能。
5. 药理学(pharmacology):研究药物在生物体内的作用机制、药效、药代动力学等方面的学科。
药理学研究的内容包括药物与受体相互作用、信号转导途径、药物代谢和排泄等。
6. 毒理学(toxicology):研究药物或其他化学物质对生物体的有害作用的学科。
毒理学研究的内容包括毒物的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄,以及毒物对器官和组织的损伤机制等。
7. 药代动力学(pharmacokinetics):研究药物在生物体内的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄过程的学科。
药代动力学可以帮助评估药物的药效持续时间、剂量调整和药物相互作用等。
8. 药物相互作用(drug-drug interaction):指多种药物同时使用时产生的一种影响药物代谢和药效的现象。
药物相互作用可能会导致药物的增效或减效,甚至出现不良反应。
9. 药效学(pharmacodynamics):研究药物在生物系统中产生的效应和药物与受体的关系的学科。
药效学可以帮助理解药物的作用机制和剂量-效应关系。
10. 药物剂型(pharmaceutical dosage form):指药物在制剂中的物理形态和制剂的剂型。
常见的药物剂型包括片剂、胶囊剂、注射剂、外用剂等。

药学英语名词解释整理文学1班庄亚勤1、HomeostasisThe progress of stabilization of the internal environment is called homeostasis and is essential if the cells of the body are to function normally.2、Super-infectionIt is an infection following a previous infection, especially when caused by microorganisms that are resistant or have become resistant to the antibiotics used earlier.3、Adverse reactionAdverse drug reactions are unwanted effects caused by normal therapeutic dose. There are 5 types of adverse drug reactions having been proposed.4、TITI refers to therapeutic index.It is a comparison of the amount of a therapeutic agent that causes the therapeutic effect to the amount that causes death (in animal studies) or toxicity (in human studies).The higher TI is, the safer the drug can be.5、Lead compoundIt is a chemical compound that has pharmacological or biological activity. The lead compound is not intended to be used as a clinical agent.It is the starting point from which a clinically useful compound can be developed.6、IndicationsIndication is the disease that a certain drug can be used for.ContraindicationContraindication is the disease that a particular medicine or treatment should not ba used because it is or might be harmful.7、LD50The median lethal dose is the dose required to kill the half the members of a tested population after a specified test duration.LD50 figures are frequently used as general indicator of a substance’s acute toxicity.8、ED50ED50 refers to effective dose for 50% of people given it.It is commonly used as a measure of reasonable expectance of drug effect, but not necessarily the dose that a clinical might use.9、Dose- range studyIt is a clinical trial where different dose of an agent are tested against each other to establish whichdose works best or is the least harmful. Dose-range study is to estimate the response vs. dose given as to analyze the efficacy and safety of the drug.10、Controlled studyThere are many forms of controlled experiments. A relatively simple one separates research subjects or specimens into two groups: an experimental group and a control group. No treatment is given to the control group, while the experimental group is changed according to some key variable of interest and the two groups are otherwise kept under the same condition.11、INDA(investigational new drug application)INDA should be submitted to FDA before tests with people begin. It should include a report on toxicity and efficacy data gained from plant and animal test. In addition, a plan for clinical trial is also required. If FDA approves the INDA, the drug is allowed to test on people in clinical trials.12、ResistanceDrug resistance is the reduction in effectiveness of a drug in curing a disease or condition.。

1.药物(drug):是指可以改变或查明机体的生理功能及病理状态,可用以预防、诊断和治疗疾病的物质。
2.药理学(pharmacology):是研究药物与机体(含病原体)相互作用及作用规律的学科,包括药物代谢动力学和药物效应动力学两个方面。
3.药物代谢动力学(pharmacokinetics):研究药物在机体的影响下所发生的变化及其规律,又称药动学。
(研究药物在体内的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄过程,并运用数学原理和方法阐释药物在机体内的动态规律)4.药物效应动力学(pharmacodynamics):研究药物对机体的作用及作用机制,又称药效学。
5.首过消除(first pass elimination):有些药物在进入体循环之前在胃肠道或肝脏被代谢灭活,使进入全身血循环内的有效药物量明显减少,这种作用称为首过消除(首关消除)。
6.肝药酶诱导剂:苯巴比妥、苯妥英和保泰松等均属于肝药酶诱导剂,它们可使肝药酶的活性增强,从而加速自身或其他药物的代谢,最终使得药物的效应减弱。
7.肝药酶抑制剂:氯霉素、异烟肼和丙磺舒等均属于肝药酶抑制剂,它们可使肝药酶的活性减弱,从而降低自身或其他药物的代谢,最终使得药物的效应增强。
8.肝肠循环:经胆汁排入肠腔的药物部分可再经小肠上皮细胞吸收经肝脏进入血循环,这种肝脏、胆汁、小肠间的循环称为肝肠循环。
9.一级消除动力学:是体内药物在单位时间内消除的药物百分率不变,也就是单位时间内消除的药物量与血浆药物浓度成正比,是药物在体内消除的一种方式。
10.零级消除动力学:是药物在体内以恒定的速率消除,即不论血浆药物浓度高低,单位时间内消除的药物量不变,是药物在体内消除的一种方式。
11.清除半衰期(half life,t1/2):是血浆药物浓度下降一半时所需要的时间。
12.清除率(clearance,CL):是机体消除器官在单位时间内清除药物的血浆容积,即单位时间内有多少毫升血浆中所含药物被机体清除。

名词解释1、药剂学(Pharmaceuticals)药剂学是研究药物制剂的基本理论、处方设计、制备工艺和合理应用的综合性技术科学。
2、药典(Pharmacopoeia)药典是一个国家记载药品标准、规格的法典,一般由国家药典委员会组织编纂、出版,并由政府颁布、执行,具有法律约束力。
3、处方药(prescription drug)必须凭执业医师或执业助理医师的处方才能调配、购买,并在医生指导下使用的药品。
可以在国务院卫生行政部门和国务院药品监督管理部门共同指定的医学、药学专业刊物上介绍,但不得在大众传播媒介发布广告或者以其他方式进行以公众为对象的广告宣传。
4、非处方药(nonprescription drug)不需执业医师或执业助理医师处方,消费者可以自行判断、购买和使用的药品。
5、GMP(Good Manufacturing Practice)《药品生产质量管理规范》,是药品生产和质量管理的基本准则,适用于药品制剂生产的全过程和原料药生产中影响成品质量的关键工序。
6、助溶剂(hydrotropy agent)多为低分子化合物,与难溶性药物形成可溶性分子络合物、复盐或分子缔合物等,以增加药物在溶剂中溶解度。
7、潜溶剂(cosolvent)系指能形成氢键的混合溶剂。
(P23)在混合溶剂中各溶剂在某一比例时,药物的溶解度比在各单纯溶剂中的溶解度大,而且出现极大值,这种现象叫做潜溶(cosolvency),这种溶剂称为潜溶剂。
8、酊剂(tincture)指药物用规定浓度的乙醇浸出或溶解制成的澄清液体制剂,亦可用流浸膏或浸膏溶解稀释制成,可供内服或外用。
(P149)9、芳香水剂(aromatic waters)指芳香挥发性药物(多半为挥发油)的饱和或近饱和水溶液。
(P147)10、絮凝(flocculation)混悬微粒形成絮状聚集体的过程称为絮凝。
(P153)在一定条件下,微粒表面带有同种电荷时粒子间产生排斥力,而且双电层越厚,则排斥力越大,微粒越稳定。
药理学英文名词解释1.药物(drug):是指可以改变或查明机体的生理功能及病理状态,可用以预防、诊断和治疗疾病的物质。
2.药理学(pharmacology):是研究药物与机体(含病原体)相互作用及作用规律的学科,包括药物代谢动力学和药物效应动力学两个方面。
3.药物代谢动力学(pharmacokinetic):研究药物在机体的影响下所发生的变化及其规律,又称药动学。
(研究药物在体内的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄过程,并运用数学原理和方法阐释药物在机体内的动态规律)4.药物效应动力学(pharmacodynamic):研究药物对机体的作用及作用机制,又称药效学。
5.首过消除(firtpaelimination):有些药物在进入体循环之前在胃肠道或肝脏被代谢灭活,使进入全身血循环内的有效药物量明显减少,这种作用称为首过消除(首关消除)。
6.肝药酶诱导剂:苯巴比妥、苯妥英和保泰松等均属于肝药酶诱导剂,它们可使肝药酶的活性增强,从而加速自身或其他药物的代谢,最终使得药物的效应减弱。
7.肝药酶抑制剂:氯霉素、异烟肼和丙磺舒等均属于肝药酶抑制剂,它们可使肝药酶的活性减弱,从而降低自身或其他药物的代谢,最终使得药物的效应增强。
8.肝肠循环:经胆汁排入肠腔的药物部分可再经小肠上皮细胞吸收经肝脏进入血循环,这种肝脏、胆汁、小肠间的循环称为肝肠循环。
9.一级消除动力学:是体内药物在单位时间内消除的药物百分率不变,也就是单位时间内消除的药物量与血浆药物浓度成正比,是药物在体内消除的一种方式。
10.零级消除动力学:是药物在体内以恒定的速率消除,即不论血浆药物浓度高低,单位时间内消除的药物量不变,是药物在体内消除的一种方式。
11.清除半衰期(halflife,t1/2):是血浆药物浓度下降一半时所需要的时间。
12.清除率(clearance,CL):是机体消除器官在单位时间内清除药物的血浆容积,即单位时间内有多少毫升血浆中所含药物被机体清除。
1.What is pharmaceutics? How many branches of pharmaceutics ?2.What is a drug? Give some examplesA drug is defined as an agent intended for use in the diagnosis, mitigation, treatment, cure, or prevention of disease in humans or in other animals.药物是有目的地用于诊断、缓解、治疗、治愈或预防人类或动物疾病的物质。
●Emetic (induce vomiting催吐剂) and antiemetic (prevent vomiting止吐剂) drugs●Diuretic drugs (increase the flow of urine利尿剂)●Expectorant drugs (increase respiratory tract fluid除痰剂)●Cathartics or laxatives (evacuate the bowel泻药)●Other drugs decrease the flow of urine, diminish body secretions, or induce constipation (便秘)Drug standards●The united states pharmacopeia (药典) and the national formulary (国家药品标准)●Pharmakon, meaning “drug”; poiein, meaning “make”;●The combination indicates any recipe or formula or other standards required to make orprepare a drug.●Organized sets of monographs or books of these standards are called pharmacopeias orformularies.International Organization for standardization (ISO)is an international consortium of representative bodies constituted to develop and promote uniform or harmonized international standards.国际标准化组织是一个代表性的国际联合会,其设立是为了发展和增进国际标准的均一性和协调性。
药学名词解释整理版
1. 药学 (Pharmacy)
药学是研究药物的发现、制备、性质、使用和药物对生物体的作用与影响的科学领域。
2. 药物 (Medicine)
药物是指用来预防、诊断和治疗疾病的物质或产品。
药物可以是化学制剂、天然物质或生物制品。
3. 药理学 (Pharmacology)
药理学研究药物在生物体内的作用机制、药物与生物体之间的相互作用以及药物对生物体的影响。
4. 药代动力学 (ics)
药代动力学研究药物在生物体内的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄过程,以及这些过程对药物在生物体内的剂量与时间关系的影响。
5. 药剂学 (Pharmaceutics)
药剂学研究药物的制备、配方、稳定性和药物在给药系统中的释放。
6. 药效学 (Pharmacodynamics)
药效学研究药物如何影响生物体以及药物的作用机制。
7. 药用植物学 (___)
药用植物学研究天然植物的化学成分和药用价值,并将其应用于药物治疗中。
8. 药物相互作用 (Drug n)
药物相互作用指同时或连续使用两种或更多药物时,其中一种药物对另一种药物的药效或药代动力学产生影响。
9. 药品管理 (Pharmaceutical Management)
药品管理包括药品生产、流通、质量控制、合理使用和药物安全等方面的管理。
10. 药理毒理学 (Pharmacotoxicology)
药理毒理学研究药物对生物体产生的毒性效应以及药物引起的毒理学反应机制。
以上是一些常见的药学名词解释,希望对您有所帮助。
如有任何问题,请随时与我联系。
药学英语词汇汇总药学英语词汇是药学领域中使用最广泛的术语和词汇。
以下是一些常见的药学英语词汇及其含义:1、Pharmaceutical:药物的,药学的2、Drug:药物,药品3、Medicine:药物,医学4、Dosage:剂量,配药5、Dose:剂量,投药量6、Route:给药途径7、Administration:给药,投药8、Inhalation:吸入9、Oral:口服的10、Rectal:直肠的11、Topical:局部的,外用的12、Transdermal:透皮吸收的13、Intravenous:静脉注射的14、Intramuscular:肌肉注射的15、Subcutaneous:皮下注射的16、Administration:(给药的)方式,(药物的)投药途径17、Controlled-release dosage form:控释剂型18、Drug interaction:药物相互作用19、Drug resistance:药物耐受性,耐药性20、Toxicity:毒性21、Side effect:副作用22、Overdose:用药过量23、Drug tolerance:药物耐受性,耐药性24、Pharmacokinetics:药物代谢动力学25、Pharmacodynamics:药效学,药物作用动力学26、Pharmacologist:药理学家,药学家27、Pharmacy technician:药房技术员,药剂师助理28、Prescription:处方,药方29、Non-prescription drug:非处方药30、Generic drug:非专利药品,仿制药31、Brand-name drug:品牌药,专利药品32、Formulation:配方,制剂33、Dosage form:剂量形式,剂型在高中英语的学习过程中,词汇的学习是至关重要的环节。
拥有足够的词汇量不仅可以提高阅读理解能力,还能增强写作和口语的表达。
药学英语知识点归纳药学英语是指与药学相关的英语知识。
药学是研究药物的性质、合成、制备、分离、鉴定、药效、药代动力学以及其应用和临床评价的一门科学。
药学英语作为专业英语的一部分,主要包括药学常用词汇、句子结构、专业写作和专业交流等方面的内容。
1. 药学常用词汇在药学英语中,有许多常用的词汇需要掌握。
例如:- drug:药物- medicine:医学;药;医药- dosage:剂量- prescription:处方- pharmacy:药房- pharmaceutical:制药的- efficacy:药效- adverse effect:不良反应- overdose:过量服用- side effect:副作用- contraindication:禁忌症- drug interaction:药物相互作用2. 句子结构掌握药学英语的句子结构对于正确理解和表达药学领域的内容非常重要。
以下是一些常见的句子结构:- 简单句:包括主语、谓语和宾语,用来陈述一个简单的事实或观点。
例如:“The drug is effective for treating hypertension.”- 复合句:包括一个主句和一个或多个从句,用来表达复杂的观点、条件、原因等。
例如:“If the patient has a history of allergic reactions, the drug should be avoided.”- 并列连词:用于连接两个相对 ** 的句子或短语。
例如:“The drug is effective, but it may cause side effects.”- 介词短语:用于描述药物的用法、途径和目的等。
例如:“The medication sho uld be taken before meals.”- 被动语态:用于强调动作的承受者而不是执行者。
例如:“The drug is widely used in clinical practice.”3. 专业写作在药学领域,专业写作是一种常见的沟通方式。
1.药物(drug)是指能够影响机体(包括病原体)功能和(或)细胞代活动,用于疾病的治疗、预防和诊断,以及计划生育等方面的化学物质。
1.Drugs are chemicals that alter the function of living systems by interactionsat the molecular level and can be used to prevent, diagnose and treat disease.2.不良反应(adverse drug reaction ADR)是指上市的合格药品在常规用法、用量情况下出现的,与用药目的无关,并给患者带来痛苦或危害的反应。
3.副作用(side effect)是由于药物作用选择性低,作用围广,在治疗剂量引起的,与用药目的无关的作用。
4.毒性反应(toxic effect)是由于用量过大或用药时间过长引起的严重不良反应。
5.后遗效应(residual effect)是指在停药后,血浆药物浓度下降至阈浓度以下时残存的药理效应。
6.变态反应(allergic reaction)是药物引起的免疫反应,反应性质与药物原有效应无关,其临床表现包括免疫反应的各种类型。
致敏原可以是药物本身或药物代产物,亦可能是制剂中的杂质或辅剂。
7.继发反应(secondary reaction)是继发于药物治疗作用之后的不良反应。
8.停药反应(withdrawal reaction)是指患者长期应用某种药物,突然停药后发生病情恶化的现象。
9.特异质反应(idiosyncrasy reaction)是指少数患者由于遗传因素对某些药物的反应性发生了变化。
特异质反应表现为对药物的反应特别敏感,或出现与在常人不同性质的反应。
10.依赖性(dependence)是药物与机体相互作用所造成的一种状态,表现出强迫要求连续或定期使用该药的行为或其他反应,其目的是感受药物的精神效应,或避免由于停药造成身体不适应。
Unit 2-A1.bacillus (复数:bacilli)杆菌,芽孢杆菌,细菌any rod(杆)-shaped or cylindrical (英[sɪ'lɪndrɪkəl] adj. 圆柱形的,圆筒状的)bacterium of the genus(英['dʒiːnəs] n. 类,种;[生物] 属)Bacillus, comprising spore-producing bacteria.芽孢杆菌属的任何杆状或圆柱形细菌,包括产孢子细菌。
2.clostridia (单数:clostridium)梭状芽孢杆菌any of several rod-shaped,spore-forming,anaerobic bacteria of the genus clostridium,found in soil and in the intestinal tract of humans and animals.梭菌属梭状芽孢杆菌中的任何一种杆状孢子形成的厌氧细菌,存在于土壤和人类和动物的肠道中。
ctobacillus 乳酸菌,乳杆菌属any long,slender,rod-shaped,anaerobic bacterium of the genus lactobacillus,that produces large amounts of lactic acid in the fermentation of carbohydrates,especially in milk.任何长的,细长的,杆状的乳酸杆菌属的厌氧细菌,在碳水化合物的发酵过程中产生大量的乳酸,特别是在牛奶中。
6.Prebiotics 益生元natural substances in some foods that encourage the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut.某些食物中的天然物质会促进肠道中健康细菌的生长Probiotics 益生菌A usually dairy food or a dietary supplement containing live bacteria that replace or add to the beneficial bacteria normally present in the gastrointestinal tract一种通常的乳制品或膳食补充剂,其中含有能替代或添加至胃肠道中, 通常存在于胃肠道Unit 3-A7.adenosine 腺苷,腺嘌呤核苷A nucleoside formed by the condensation of adenine and ribose. It is present in all living cells in a combined form,as in ribonucleic acid.腺嘌呤和核糖缩合形成的核苷。
它以组合形式存在于所有活细胞中,如在核糖核酸中。
8. anabolic adj.合成代谢的A metabolic process in which complex molecules are synthesized from simpler ones with the storages of energy; constructive metabolism.一种新陈代谢过程,其中复杂的分子由具有存储能量的简单分子合成;建设性的新陈代谢。
9.monomeric 单体的A compound whose can join together to form a polymer一种可以连接在一起形成聚合物的化合物monosaccharide 单糖simple sugar,such as glucose,that does not hydrolysis([haɪ'drɒlɪsɪs])to yield(生产)other sugar10.neurotransmitter 神经递质A chemical by which a nerve cell communicates with another nerve cell or with a muscle.神经细胞与另一个神经细胞或肌肉相通的化学物质。
nucleotidase n.核苷酸酶an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a nucleotide to a nucleoside and phosphoric acid一种催化核苷酸水解成核苷和磷酸的酶Unit 4-A14.biotransformation 生物转化The series of chemical changes occurring in a compound,especially a drug as a result of enzymatic or otheractivity by a living organism.化合物中发生的一系列化学变化,特别是由于生物体的酶活性或其他活性导致的药物。
15.pharmacognosy 生药学,药材学The branch of pharmacology concerned with crude drugs of plant and animals origin.药学的分支,涉及植物和动物的原料药。
16.pharmacokinetics 药代动力学The branch of pharmacology that studies the fate of pharmacological substances in the body,as their absorption,distribution,metabolism,and elimination.药学的一个分支,研究体内药理物质的命运,作为它们的吸收,分布,代谢和消除。
17.pharmacodynamics 药效学The branch of pharmacology dealing with the course of action,effect and breakdown or drugs within the body.药学的分支,涉及体内的作用,作用和分解或药物的过程。
Unit 6-A21.bioavailability 生物利用度The extent to which a drug or other substances is taken up by a specific tissue or organ after administration.给药后特定组织或器官吸收药物或其他物质的程度。
22.biopharmaceutics 生物药剂学The study of the relationships between physical and chemical properties,dosage and administration of a drug and its activity in humans animals.研究药物的物理和化学性质,剂量和给药及其在人类动物中的活性之间的关系Unit 7-A23.elution 洗脱Elution to remove by dissolving,as absorbed material from an adsorbent.通过溶解从吸附剂中吸收的物质来洗脱24.hydrolysis 水解作用Chemical decomposition in which a compound is split into other compounds by reacting with water.化学分解,其中化合物通过与水反应分裂成其他化合物25.chromatgraphy 色谱法,层析A scientific method of finding what separate chemicals are in a substance by passing it through a material such as paper,which different substances will flow through at different speeds.一种科学的方法,通过使物质通过纸张等不同物质以不同速度流过的物质来查找物质中的单独化学物质。
immunoassay n.免疫测定identification of a substance (especially a protein) by its action as an antigen;通过物质(尤其是蛋白质)作为抗原的作用进行鉴定;Unit 7-Bplexometric 络合滴定的A chemical technique using the formation of a colored complex to indicate the end of a titration.一种化学技术,使用有色复合物的形成来指示滴定的结束。
27.reactant 反应物Any substance that undergoes a chemical change in a given reaction.在给定反应中经历化学变化的任何物质solubility n.溶解性the quality or property of being soluble; relative capability of being dissolved28.titration 滴定To ascertain the quantity of a given constituent of known strength and measuring the volume necessary to convert the constituent to another form.确定已知强度的给定成分的数量并测量将成分转换成另一种形式所需的体积Titrant滴定剂Standard concentration of reagent solution for titration, we judge the content of the sample to be tested by the amount of titrantSpectrometry光谱测定法,频谱测定法,能谱测定An optical device for measuring wavelengths, deviation of refracted rays, and angles between faces of a prism 用于测量波长,折射光线的偏差以及棱镜面之间的角度的光学装置Spectroscopy光谱法The science that deals with the use of the spectroscope ['spektrəskəʊp] and with spectrum analysis涉及光谱仪使用和光谱分析的科学standardize v.标定to bring to or make of an established standard size, weight, quality, strength, or the like使或达到既定的标准尺寸,重量,质量,强度等Unit 8-A29.pharmacophore 药效团,药效基团,药效结构The group of atoms in a drug molecule which is responsible for the biologic pharmacological interaction.药物分子中的原子团,负责生物学药理学相互作用Unit 8-B30.antifeedant 拒食素A chemical agent that causes a pest,as an insect,to stoping eating.一种化学试剂,可以使害虫作为昆虫停止进食31.broth 发酵液A liquid medium containing nutrients suitable for culturing microorganisms.含有适于培养微生物的营养素的液体培养基Unit 9-A34. antigen 抗原(删)Any substance that can stimulate the production of antibodies and combine specifically with them.任何可以刺激抗体产生并与之特异性结合的物质。