
常见溶剂的化学位移
常见溶剂的1H在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值
常见溶剂的化学位移
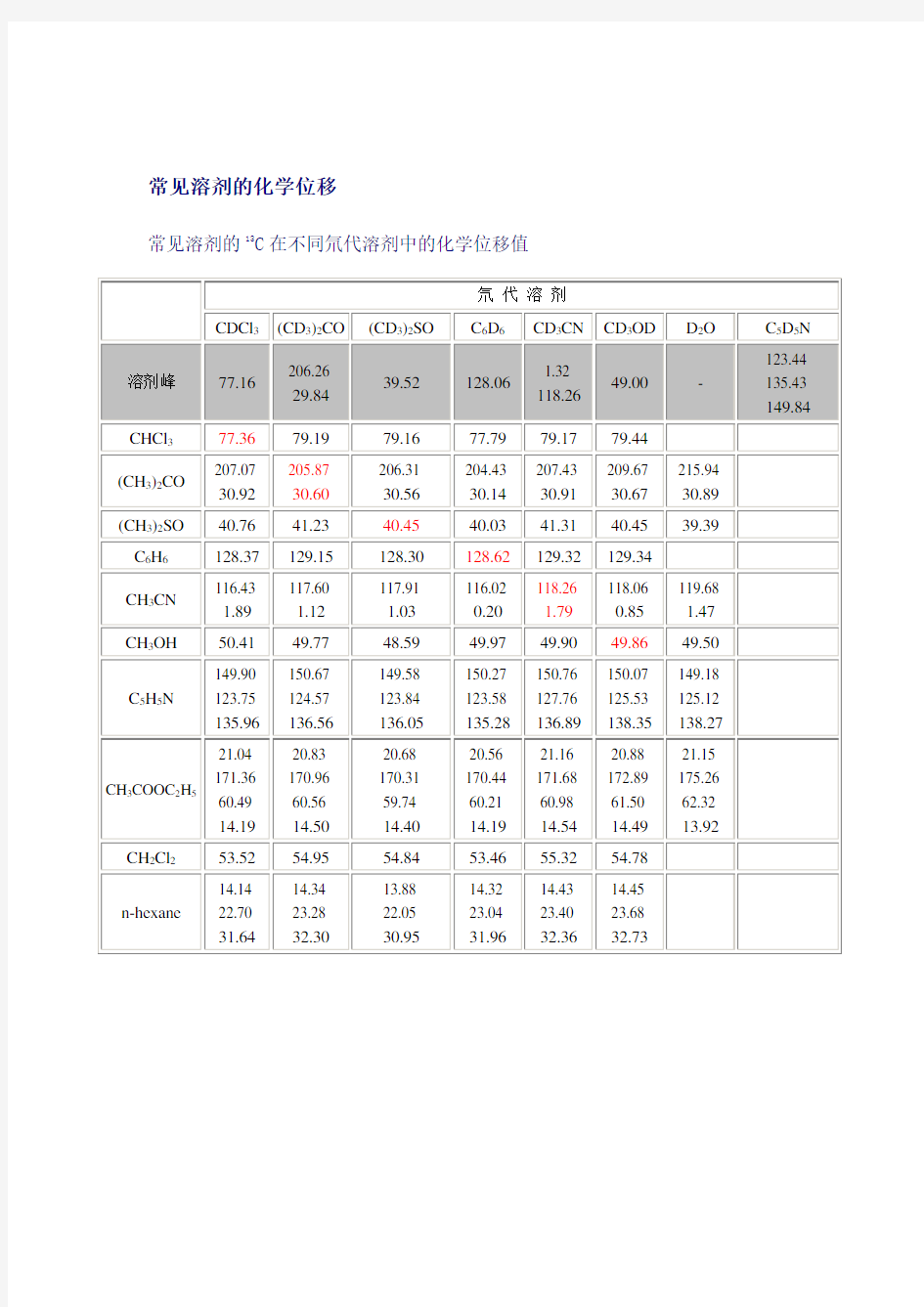
常见溶剂的13C在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值
注:JHD为溶剂本身的其他1H对与之相对应的1H之间的耦合常数,JCD为溶剂本身1H对13C的耦合常数,H2O和交换了D的HOD上的1H产生的即水峰的化学位移 氯仿:小、中小、中等极性 DMSO:芳香系统(日光下自然显色、紫外荧光)。对于酚羟基能够出峰。芳香化合物还是芳香甙,都为首选。 吡啶:极性大的,特别是皂甙 对低、中极性的样品,最常采用氘代氯仿作溶剂,因其价格远低于其它氘代试剂。极性大的化合物可采用氘代丙酮、重水等。 ??? 针对一些特殊的样品,可采用相应的氘代试剂:如氘代苯(用于芳香化合物、芳香高聚物)、氘代二甲基亚砜(用于某些在一般溶剂中难溶的物质)、氘代吡啶(用于难溶的酸性或芳香化合物)等。 丙酮:中等极性 甲醇:极性大 氯仿—甲醇: 石:乙 5;1小极性 石:丙 2:1——1:1中等极性 氯仿:甲醇6:1极性以上含有一个糖 2:1 含有两个糖 含有糖的三萜皂甙:一般用吡啶
常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的1H在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值 常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的13C在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值
核磁知识(NMR) 一:样品量的选择 氢谱,氟谱,碳谱至少需要5mg. 1H-1H COSY, 1H-1H NOESY, 1H-13C HMBC, 1H-13C HSQC需要10-15mg. 碳谱需要30mg. 二:如何选择氘代溶剂 常用氘代溶剂: CDCl3, DMSO, D2O, CD3OD.特殊氘代溶剂: CD3COCD3, C6D6, CD3CN。 极性较大的化合物可以选择用D2O或CD3OD,如果想要观察活泼氢切记不能选择D2O和CD3OD。CDCl3为人民币2-3元,D2O为人民币6元,DMSO为人民币10元,CD3OD为人民币30元。Solvent 化学位移(ppm) 水峰位移(ppm) CDCl3 7.26 1.56 DMSO 2.50 3.33 CD3OD 3.31 4.87 D2O 4.79 CD3COCD3 2.05 2.84
API 5CT石油套管 化学成分: 外径、薄厚、重量偏差
长度范围 描述:油管 标准:API SPEC 5CT、API SPEC 5B、ISO 11960 用途:油管用于油井中抽取石油或天然气。 油管规格:
注:P--平头;N--不加厚;U--外加厚;T&C--车螺纹带接箍;I--整体接头。描述:石油套管 标准:API SPEC 5CT、API SPEC 5B、ISO 11960 套管规格:
注:P--平端;S--短圆螺纹;L--长圆螺纹;B--偏梯形螺纹 接箍 Coupling: 1、标准接箍 Stabdard Coupling 2、特殊间歇接箍 Special Space Coupling 3、特殊倒角接箍 Special Bevellde Coupling 4、改进型带密封环接箍 API Improved Seal-Ring Coupling(SR13) 5、组合接箍或异径接箍 Combination Coupling or Special Diameter Coupling 短节或连接管 Pup Joint or Connector: 包括所有油套管规格、螺纹或其他组合 All Size,thread or their combination of tubing and casing are supplied.
尺寸偏差 Dimensions and Tolerances: 外径、壁厚、重量允许偏差 Outside Diameter,Wall Thickness and Weight Tolerances: 螺纹参数允许偏差 Thread Parameter Tolerances: 注a:p---螺距 Note 啊:p---Pitch.
API 5CT石油套管 Home--Parameter 化学成分: 外径、薄厚、重量偏差
长度范围 描述:油管 标准:API SPEC 5CT、API SPEC 5B、ISO 11960 用途:油管用于油井中抽取石油或天然气。 油管规格:
注:P--平头;N--不加厚;U--外加厚;T&C--车螺纹带接箍;I--整体接头。 描述:石油套管 标准:API SPEC 5CT、API SPEC 5B、ISO 11960 套管规格:
注:P--平端;S--短圆螺纹;L--长圆螺纹;B--偏梯形螺纹 接箍 Coupling: 1、标准接箍 Stabdard Coupling
2、特殊间歇接箍 Special Space Coupling 3、特殊倒角接箍 Special Bevellde Coupling 4、改进型带密封环接箍 API Improved Seal-Ring Coupling(SR13) 5、组合接箍或异径接箍 Combination Coupling or Special Diameter Coupling 短节或连接管 Pup Joint or Connector: 包括所有油套管规格、螺纹或其他组合 All Size,thread or their combination of tubing and casing are supplied. 尺寸偏差 Dimensions and Tolerances: 外径、壁厚、重量允许偏差 Outside Diameter,Wall Thickness and Weight Tolerances: 螺纹参数允许偏差 Thread Parameter Tolerances:
L80(13Cr)资料整理手册(根据API Spec 5CT标准)一.化学成分 二.物理性能 2.1 拉伸性能,屈服强度,伸长率, 硬度要求 表2—油管(L80)拉伸性能,屈服强度,硬度要求表 伸长率: 最小伸长率由下式确定:e=k(A0.2/U0.9) 式中:e——标距为50.8mm时的最小伸长率; K——常数:1944; A——拉伸式样的横截面积; U——规定的最小抗拉强度。 L80(13Cr)拉伸试样的最小伸长率见API Spec 5CT附表C7,E7。 最大硬度: 对于要求的每个拉伸试样,硬度试样(环或块)应如图1所指明的产品部位。所获得的硬度值应满足表2。 2 管子CVN吸收能要求 表3-L80管子横向夏比V 型吸收能要求
表4-L80管子纵向夏比V 型吸收能要求 a)横向:Cv(J)=YSmin(0.00118t+0.01259), 或14(J),取较大者。 b)纵向:Cv(J)=YSmin(0.00236t+0.02518), 或27(J),取较大者。 三.热处理要求 工艺:Q&T e(淬火+回火),可采用空气淬火,最低回火温度为593℃。 当回火温度低于620℃时,可能会脆化。当产品同时满足夏比V型缺口(CVN)冲击试验性能(见1材料要求),具有ISO/API螺纹的接箍毛坯、接箍半成品和接箍的CVN吸收性能要求、冲击实验和全尺寸试样最低吸收能要求时,无需采取进一步预防措施。 对于加厚管子,应在加厚以后再进行全长热处理。要求热处理的管子应进行全长热处理。接箍半成品可单个进行热处理。若终扎温度高于上临界(Ar3),且管子是经过空冷时,则应认为所有经热张力扎制过的管子均为正火过的。 四.尺寸和公差 ①管子的规格,壁厚和重量:按表C.24-C.29或表E.24-E.29(API-5CT)。 ②管子外径的测量及公差:对于代号大于6-5/8时,API-5C采用一位小数的精 度;采用美国惯用单位制单位时,直径应被圆整至三位小数。
NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities Hugo E.Gottlieb,*Vadim Kotlyar,and Abraham Nudelman* Department of Chemistry,Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan52900,Israel Received June27,1997 In the course of the routine use of NMR as an aid for organic chemistry,a day-to-day problem is the identifica-tion of signals deriving from common contaminants (water,solvents,stabilizers,oils)in less-than-analyti-cally-pure samples.This data may be available in the literature,but the time involved in searching for it may be considerable.Another issue is the concentration dependence of chemical shifts(especially1H);results obtained two or three decades ago usually refer to much more concentrated samples,and run at lower magnetic fields,than today’s practice. We therefore decided to collect1H and13C chemical shifts of what are,in our experience,the most popular “extra peaks”in a variety of commonly used NMR solvents,in the hope that this will be of assistance to the practicing chemist. Experimental Section NMR spectra were taken in a Bruker DPX-300instrument (300.1and75.5MHz for1H and13C,respectively).Unless otherwise indicated,all were run at room temperature(24(1°C).For the experiments in the last section of this paper,probe temperatures were measured with a calibrated Eurotherm840/T digital thermometer,connected to a thermocouple which was introduced into an NMR tube filled with mineral oil to ap-proximately the same level as a typical sample.At each temperature,the D2O samples were left to equilibrate for at least 10min before the data were collected. In order to avoid having to obtain hundreds of spectra,we prepared seven stock solutions containing approximately equal amounts of several of our entries,chosen in such a way as to prevent intermolecular interactions and possible ambiguities in assignment.Solution1:acetone,tert-butyl methyl ether,di-methylformamide,ethanol,toluene.Solution2:benzene,di-methyl sulfoxide,ethyl acetate,methanol.Solution3:acetic acid,chloroform,diethyl ether,2-propanol,tetrahydrofuran. Solution4:acetonitrile,dichloromethane,dioxane,n-hexane, HMPA.Solution5:1,2-dichloroethane,ethyl methyl ketone, n-pentane,pyridine.Solution6:tert-butyl alcohol,BHT,cyclo-hexane,1,2-dimethoxyethane,nitromethane,silicone grease, triethylamine.Solution7:diglyme,dimethylacetamide,ethyl-ene glycol,“grease”(engine oil).For D2O.Solution1:acetone, tert-butyl methyl ether,dimethylformamide,ethanol,2-propanol. Solution2:dimethyl sulfoxide,ethyl acetate,ethylene glycol, methanol.Solution3:acetonitrile,diglyme,dioxane,HMPA, pyridine.Solution4:1,2-dimethoxyethane,dimethylacetamide, ethyl methyl ketone,triethylamine.Solution5:acetic acid,tert-butyl alcohol,diethyl ether,tetrahydrofuran.In D2O and CD3OD nitromethane was run separately,as the protons exchanged with deuterium in presence of triethylamine. Results Proton Spectra(Table1).A sample of0.6mL of the solvent,containing1μL of TMS,1was first run on its own.From this spectrum we determined the chemical shifts of the solvent residual peak2and the water peak. It should be noted that the latter is quite temperature-dependent(vide infra).Also,any potential hydrogen-bond acceptor will tend to shift the water signal down-field;this is particularly true for nonpolar solvents.In contrast,in e.g.DMSO the water is already strongly hydrogen-bonded to the solvent,and solutes have only a negligible effect on its chemical shift.This is also true for D2O;the chemical shift of the residual HDO is very temperature-dependent(vide infra)but,maybe counter-intuitively,remarkably solute(and pH)independent. We then added3μL of one of our stock solutions to the NMR tube.The chemical shifts were read and are presented in Table 1.Except where indicated,the coupling constants,and therefore the peak shapes,are essentially solvent-independent and are presented only once. For D2O as a solvent,the accepted reference peak(δ)0)is the methyl signal of the sodium salt of3-(trimeth-ylsilyl)propanesulfonic acid;one crystal of this was added to each NMR tube.This material has several disadvan-tages,however:it is not volatile,so it cannot be readily eliminated if the sample has to be recovered.In addition, unless one purchases it in the relatively expensive deuterated form,it adds three more signals to the spectrum(methylenes1,2,and3appear at2.91,1.76, and0.63ppm,respectively).We suggest that the re-sidual HDO peak be used as a secondary reference;we find that if the effects of temperature are taken into account(vide infra),this is very reproducible.For D2O, we used a different set of stock solutions,since many of the less polar substrates are not significantly water-soluble(see Table1).We also ran sodium acetate and sodium formate(chemical shifts: 1.90and8.44ppm, respectively). Carbon Spectra(Table2).To each tube,50μL of the stock solution and3μL of TMS1were added.The solvent chemical shifts3were obtained from the spectra containing the solutes,and the ranges of chemical shifts (1)For recommendations on the publication of NMR data,see: IUPAC Commission on Molecular Structure and Spectroscopy.Pure Appl.Chem.1972,29,627;1976,45,217. (2)I.e.,the signal of the proton for the isotopomer with one less deuterium than the perdeuterated material,e.g.,C H Cl3in CDCl3or C6D5H in C6D6.Except for CHCl3,the splitting due to J HD is typically observed(to a good approximation,it is1/6.5of the value of the corresponding J HH).For CHD2groups(deuterated acetone,DMSO, acetonitrile),this signal is a1:2:3:2:1quintet with a splitting of ca.2 Hz. (3)In contrast to what was said in note2,in the13C spectra the solvent signal is due to the perdeuterated isotopomer,and the one-bond couplings to deuterium are always observable(ca.20-30Hz). Figure1.Chemical shift of H DO as a function of tempera-ture. https://www.doczj.com/doc/4a5504740.html,.Chem.1997,62,7512-7515 S0022-3263(97)01176-6CCC:$14.00?1997American Chemical Society
油管标准: (1)API SPEC5CT (2)SY/T6194-1996 油管用途: ①、抽取油汽:油气井打完并固井之后,在油层套管中放置油管,以抽取油气至地面。 ②、注水:当井下压力不够,通过油管往井里注水。 ③、注蒸汽:在稠油热采过程中,要用隔热油管向井下输入蒸汽。 ④、酸化和压裂:在打井后期或为了提高油气井的产量,需要对油气层输入酸化和压裂的介质或固化物,介质和固化物都是通过油管输送的。 油管分类: 油管分为平式油管(NU)、加厚油管(EU)和整体接头油管。平式油管是指管端不经过加厚而直接车螺纹并带上接箍。加厚油管是指两管端经过外加厚以后,再车螺纹并带上接箍。整体接头油管是指一端经过内加厚车外螺纹,另一端经过外加厚车内螺纹,直接连接不带接箍。 油套管管柱结构 油套管管柱典型结构示意见图1。
油管钢级: 油管钢级有:H40、J55、N80、L80、C90、T95、P110。 N80分为N80-1和N80Q,二者的相同点是拉伸性能一致,二者的不同点是交货状态和冲击性能区别,N80-1按正火状态交货或当终轧温度大于临界温度Ar3且张力减径后经过空冷时,又可用热轧代替正火,冲击功和无损检验均不作要求;N80Q必须经过调质(淬火加回火)热处理,冲击功应符合API5CT规定,且应进行无损检验。 L80分为L80-1、L80-9Cr和L80-13Cr。它们的力学性能和交货状态均相同。不同之处表现在用途、生产难度和价格上,L80-1为普通型,L80-9Cr和L80-13Cr均为高抗腐蚀性油管,生产难度大,价格昂贵,通常用于重腐蚀油井。 C90和T95均分为1型和2型,即C90-1、C90-2和T95-1、T95-2。 油管化学成分: API5CT标准对油管化学成分要求见下表,这是一个范围很宽的指导性要求,其中J55、N80、P110等钢级油管只规定了硫、磷含量要求,其它主要元素均由生产厂家根据性能和使
DIR-10标准与API 5CT标准差异 一、化学成分: 1.DIR-10化学成分:包含管体与接箍元素重量百分比不大于表列数值 二、热处理: 1. DIR-10标准 Tempering Temperature: (回火温度) L80 Type 1 materials must have a tempering temperature not less than (不低于)621o C. 2.API 5CT标准 电焊管焊成后的焊缝,应加热至540 o C以上进行热处理,或采用某种处理方法使焊缝中没有未回火的马氏体组织。 三、硬度: 1. DIR-10标准 Hardness Requirements: (硬度,不大于表列数值)
(1) As per frequencies outlined in API Specification 5CT/ISO 11960. (测试频率按API 5CT) 2.API 5CT标准 第1组产品无要求。 公司内控:焊缝,母材,HAZ硬度变化范围:各处硬度值之差不超过40%,目标值不超过20%。 四、冲击试验: 1. DIR-10标准 Toughness Requirement (Charpy V-Notch): (冲击值) Directive 010 compliant materials must meet or exceed the Charpy impact full sized equivalent toughness values outlined below. Charpy impact testing must be conducted in accordance with API 5CT/ISO 11960. (按API 5CT/ISO 11960 规范进行测试,试样的全尺寸等值冲击值数据不小于表列数值。纵向或横向取样皆可) Pipe Body (管体) Coupling Stock (接箍料) Note: H40 pipe is normally supplied with grade K55 or J55 couplings. (H40套管通常配K55或J55 接箍) 2.API 5CT标准 H40、J55、K55钢级和N80钢级1类,没有强制性的CVN吸收能要求。 可选择的CVN冲击吸收能要求见A.10 SR16. 仅对H40钢级: 对于所有壁厚,全尺寸横向最低CVN吸收能为16J. 对于所有壁厚,全尺寸纵向最低CVN吸收能为20J. 仅对J55和K55钢级: 对于所有壁厚,全尺寸横向最低CVN吸收能为20J. 对于所有壁厚,全尺寸纵向最低CVN吸收能为27J.
常数,H2O和交换了D的HOD上的1H产生的即水峰的化学位移 氯仿:小、中小、中等极性 DMSO:芳香系统(日光下自然显色、紫外荧光)。对于酚羟基能够出峰。芳香化合物还是芳香甙,都为首选。 吡啶:极性大的,特别是皂甙 对低、中极性的样品,最常采用氘代氯仿作溶剂,因其价格远低于其它氘代试剂。极性大的化合物可采用氘代丙酮、重水等。 针对一些特殊的样品,可采用相应的氘代试剂:如氘代苯(用于芳香化合物、芳香高聚物)、氘代二甲基亚砜(用于某些在一般溶剂中难溶的物质)、氘代吡啶(用于难溶的酸性或芳香化合物)等。丙酮:中等极性 甲醇:极性大 氯仿—甲醇: 石:乙 5;1小极性 石:丙 2:1——1:1中等极性 氯仿:甲醇6:1极性以上含有一个糖 2:1 含有两个糖 含有糖的三萜皂甙:一般用吡啶
常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的1H在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值 常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的13C在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值
核磁知识(NMR) 一:样品量的选择 氢谱,氟谱,碳谱至少需要5mg. 1H-1H COSY, 1H-1H NOESY, 1H-13C HMBC, 1H-13C HSQC需要10-15mg. 碳谱需要30mg. 二:如何选择氘代溶剂 常用氘代溶剂: CDCl3, DMSO, D2O, CD3OD.特殊氘代溶剂: CD3COCD3, C6D6, CD3CN。 极性较大的化合物可以选择用D2O或CD3OD,如果想要观察活泼氢切记不能选择D2O和CD3OD。CDCl3为人民币2-3元,D2O为人民币6元,DMSO为人民币10元,CD3OD为人民币30元。Solvent 化学位移(ppm) 水峰位移(ppm) CDCl3 ? ? ? ? DMSO? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? CD3OD? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? D2O? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? CD3COCD3? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?
API5CT标准J55和K55钢级油、套管的产品要求 1.热处理(PSL2和PSL1有区别) PSL1要求:J55和K55方式一样(可轧制态交货); PSL2要求:J55、K55产品应整体正火或正火加回火,若加厚,应在加厚之后正火或正火加回火。 2.矫直(无区别) 3.化学成分(控制无区别) 4.拉伸试验(最小抗拉强度有区别) J55:屈服强度379MPa~552MPa ;抗拉强度≥517MPa; K55: 屈服强度379MPa~552MPa ;抗拉强度≥655MPa; 由于抗拉强度不同,要求的最小伸长率J55是19%,K55是15%。 5.冲击试验(PSL2和PSL1有区别) 管体:PSL1 J55和K55无要求; PSL2 J55和K55要求全尺寸试样横向最小冲击功20J,全尺寸试样纵向最小冲击功27J。 接箍:J55和K55冲击试验必须做,尺寸试样横向最小冲击功20J,全尺寸试样纵向最小冲击功27J。 6.水压试验(无区别) 7.壁厚检测(PSL2和PSL1有区别) PSL1:对J55和K55壁厚无测量覆盖要求; PSL2:对J55和K55壁厚测量和记录应对全长进行,自动检测系统覆盖的表面积最好应达到25%。 8.无损检测(PSL2和PSL1有区别) PSL1:对J55和K55钢级管子没有做无损检测的强制要求; PSL2:对J55和K55钢级所有钢管应采用标准10.15.5所规定的一种或多种方法进行检验,以发现钢管外表面和内表面可以接收水平L4的纵向缺欠。 9.标识(色带有区别) J55钢级管体上喷一条明亮绿色带,接箍喷涂明亮绿色,上加一条白色带; K55钢级管体上喷两条明亮绿色带,接箍喷涂明亮绿色,无外加色带。
注:JHD为溶剂本身得其她1H对与之相对应得1H之间得耦合常数,JCD为溶剂本身1H对13C得耦合常数,H2O与交换了D得HOD上得1H产生得即水峰得化学位移 氯仿:小、中小、中等极性 DMSO:芳香系统(日光下自然显色、紫外荧光)。对于酚羟基能够出峰。芳香化合物还就是芳香甙,都为首选。 吡啶:极性大得,特别就是皂甙 对低、中极性得样品,最常采用氘代氯仿作溶剂,因其价格远低于其它氘代试剂。极性大得化合物可采用氘代丙酮、重水等。 针对一些特殊得样品,可采用相应得氘代试剂:如氘代苯(用于芳香化合物、芳香高聚物) 、氘代二甲基亚砜(用于某些在一般溶剂中难溶得物质) 、氘代吡啶(用于难溶得酸性或芳香化合物)等。 丙酮:中等极性 甲醇:极性大 氯仿—甲醇: 石:乙5;1小极性 石:丙2:1——1:1中等极性 氯仿:甲醇6:1极性以上含有一个糖 2:1 含有两个糖 含有糖得三萜皂甙:一般用吡啶 ?常见溶剂得化学位移 常见溶剂得1H在不同氘代溶剂中得化学位移值
常见溶剂得化学位移 常见溶剂得13C在不同氘代溶剂中得化学位移值
核磁知识(NMR)?一:样品量得选择??氢谱,氟谱,碳谱至少需要5mg、1H-1HCOSY,1H-1HN OESY, 1H-13C HMBC, 1H-13C HSQC需要10-15mg、碳谱需要30mg、 二:如何选择氘代溶剂? 常用氘代溶剂: CDCl3,DMSO,D2O,CD3OD、特殊氘代溶剂:CD3COCD3, C6D6, CD3C N。 极性较大得化合物可以选择用D2O或CD3OD,如果想要观察活泼氢切记不能选择D2O与CD3OD。 CDCl3为人民币2-3元,D2O为人民币6元,DMSO为人民币10元,CD3OD为人民币30元。 Solvent 化学位移(ppm) 水峰位移(ppm) CDCl3 7、26 1、56?DMSO 2、50 3、33?CD3OD 3、31 4、87?D2O4、79 CD3COCD3 2、052、84
N M R常见溶剂峰和水峰 Revised as of 23 November 2020
13C的耦合常数,H2O和交换了D的HOD上的1H产生的即水峰的化学位移 氯仿:小、中小、中等极性 DMSO:芳香系统(日光下自然显色、紫外荧光)。对于酚羟基能够出峰。芳香化合物还是芳香甙,都为首选。 吡啶:极性大的,特别是皂甙 对低、中极性的样品,最常采用氘代氯仿作溶剂,因其价格远低于其它氘代试剂。极性大的化合物可采用氘代丙酮、重水等。 针对一些特殊的样品,可采用相应的氘代试剂:如氘代苯(用于芳香化合物、芳香高聚物)、氘代二甲基亚砜(用于某些在一般溶剂中难溶的物质)、氘代吡啶(用于难溶的酸性或芳香化合物)等。 丙酮:中等极性 甲醇:极性大 氯仿—甲醇: 石:乙5;1小极性 石:丙2:1——1:1中等极性 氯仿:甲醇6:1极性以上含有一个糖 2:1含有两个糖 含有糖的三萜皂甙:一般用吡啶
常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的1H在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值 常见溶剂的化学位移 常见溶剂的13C在不同氘代溶剂中的化学位移值
核磁知识(NMR) 一:样品量的选择 氢谱,氟谱,碳谱至少需要,1H-1HNOESY,1H-13CHMBC,1H-13CHSQC需要10-15mg.碳谱需要30mg. 二:如何选择氘代溶剂 常用氘代溶剂:CDCl3,DMSO,D2O,CD3OD.特殊氘代溶剂:CD3COCD3,C6D6,CD3CN。 极性较大的化合物可以选择用D2O或CD3OD,如果想要观察活泼氢切记不能选择D2O 和CD3OD。 CDCl3为人民币2-3元,D2O为人民币6元,DMSO为人民币10元,CD3OD为人民币30元。 Solvent化学位移(ppm)水峰位移(ppm) CDCl3 DMSO CD3OD D2O CD3COCD3
测试核磁的样品一般要求比较纯,并且能够溶解在氘代试剂中,这样才能测得高分辨率的图谱。 为不干扰谱图,所用溶剂分子中的氢都应被氘取代,但难免有氢的残余(1%左右),这样就会产生溶剂峰;除了残存的质子峰外,溶剂中有时会有微量的H2O而产生水峰,而且这个H2O峰的位置也会因溶剂的不同而不同;另外,在样品(或制备过程)中,也难免会残留一些杂质,在图谱上就会有杂质峰,应注意识别。 常用氘代溶剂和杂质峰在1H谱中的化学位移单位:ppm 溶剂—CDCl3 (CD3)2CO (CD3)2SO C6D6 CD3CN CD3OH D2O 溶剂峰—7.26 2.05 2.49 7.16 1.94 3.31 4.80 水峰— 1.56 2.84 3.33 0.40 2.13 4.87 — 乙酸— 2.10 1.96 1.91 1.55 1.96 1.99 2.08 丙酮— 2.17 2.09 2.09 1.55 2.08 2.15 2.22 乙腈— 2.10 2.05 2.07 1.55 1.96 2.03 2.06 苯—7.36 7.36 7.37 7.15 7.37 7.33 — 叔丁醇CH3 1.28 1.18 1.11 1.05 1.16 1.40 1.24 OH —— 4.19 1.55 2.18 —— 叔丁基甲醚 CCH3 1.19 1.13 1.11 1.07 1.14 1.15 1.21 OCH3 3.22 3.13 3.08 3.04 3.13 3.20 3.22 氯仿—7.26 8.02 8.32 6.15 7.58 7.90 — 环己烷— 1.43 1.43 1.40 1.40 1.44 1.45 — 1,2-二氯甲烷 3.73 3.87 3.90 2.90 3.81 3.78 — 二氯甲烷— 5.30 5.63 5.76 4.27 5.44 5.49 — 乙醚 CH3(t) 1.21 1.11 1.09 1.11 1.12 1.18 1.17 CH2(q) 3.48 3.41 3.38 3.26 3.42 3.49 3.56 二甲基甲酰胺 CH 8.02 7.96 7.95 7.63 7.92 7.79 7.92 CH3 2.96 2.94 2.89 2.36 2.89 2.99 3.01 CH3 2.88 2.78 2.73 1.86 2.77 2.86 2.85 二甲基亚砜— 2.62 2.52 2.54 1.68 2.50 2.65 2.71 二氧杂环— 3.71 3.59 3.57 3.35 3.60 3.66 3.75
1H NMR Data proton mult CDCl3(CD3)2CO (CD3)2SO C6D6 CD3CN CD3OD D2O solvent residual peak 7.26 2.05 2.50 7.16 1.94 3.31 4.79 H2O s 1.56 2.84a 3.33a 0.40 2.13 4.87 acetic acid CH3 s 2.10 1.96 1.91 1.55 1.96 1.99 2.08 acetone CH3 s 2.17 2.09 2.09 1.55 2.08 2.15 2.22 acetonitrile CH3 s 2.10 2.05 2.07 1.55 1.96 2.03 2.06 benzene CH s 7.36 7.36 7.37 7.15 7.37 7.33 tert-butyl alcohol CH3 s 1.28 1.18 1.11 1.05 1.16 1.40 1.24 OH c s 4.19 1.55 2.18 tert-butyl methyl ether CCH3 s 1.19 1.13 1.11 1.07 1.14 1.15 1.21 OCH3s 3.22 3.13 3.08 3.04 3.13 3.20 3.22 BHT b ArH s 6.98 6.96 6.87 7.05 6.97 6.92 OH c s 5.01 6.65 4.79 5.20 ArCH3 s 2.27 2.22 2.18 2.24 2.22 2.21 ArC(CH3)3 s 1.43 1.41 1.36 1.38 1.39 1.40 chloroform CH s 7.26 8.02 8.32 6.15 7.58 7.90 cyclohexane CH2 s 1.43 1.43 1.40 1.40 1.44 1.45 1,2-dichloroethane CH2 s 3.73 3.87 3.90 2.90 3.81 3.78 dichloromethane CH2 s 5.30 5.63 5.76 4.27 5.44 5.49 diethyl ether CH3 t, 7 1.21 1.11 1.09 1.11 1.12 1.18 1.17 CH2 q, 7 3.48 3.41 3.38 3.26 3.42 3.49 3.56 diglyme CH2 m 3.65 3.56 3.51 3.46 3.53 3.61 3.67 CH2 m 3.57 3.47 3.38 3.34 3.45 3.58 3.61 OCH3s 3.39 3.28 3.24 3.11 3.29 3.35 3.37 1,2-dimethoxyethane CH3 s 3.40 3.28 3.24 3.12 3.28 3.35 3.37 CH2 s 3.55 3.46 3.43 3.33 3.45 3.52 3.60 dimethylacetamide CH3CO s 2.09 1.97 1.96 1.60 1.97 2.07 2.08 NCH3 s 3.02 3.00 2.94 2.57 2.96 3.31 3.06 NCH3 s 2.94 2.83 2.78 2.05 2.83 2.92 2.90 dimethylformamide CH s 8.02 7.96 7.95 7.63 7.92 7.97 7.92 CH3 s 2.96 2.94 2.89 2.36 2.89 2.99 3.01 CH3 s 2.88 2.78 2.73 1.86 2.77 2.86 2.85 dimethyl sulfoxide CH3 s 2.62 2.52 2.54 1.68 2.50 2.65 2.71 dioxane CH2 s 3.71 3.59 3.57 3.35 3.60 3.66 3.75 ethanol CH3 t, 7 1.25 1.12 1.06 0.96 1.12 1.19 1.17 CH2 q, 7d 3.72 3.57 3.44 3.34 3.54 3.60 3.65 OH s c,d 1.32 3.39 4.63 2.47 ethyl acetate CH3CO s 2.05 1.97 1.99 1.65 1.97 2.01 2.07 C H2CH3 q, 7 4.12 4.05 4.03 3.89 4.06 4.09 4.14 CH2C H3t, 7 1.26 1.20 1.17 0.92 1.20 1.24 1.24 ethyl methyl ketone CH3CO s 2.14 2.07 2.07 1.58 2.06 2.12 2.19 C H2CH3 q, 7 2.46 2.45 2.43 1.81 2.43 2.50 3.18 CH2C H3t, 7 1.06 0.96 0.91 0.85 0.96 1.01 1.26 ethylene glycol CH s e 3.76 3.28 3.34 3.41 3.51 3.59 3.65“grease” f CH3 m 0.86 0.87 0.92 0.86 0.88 CH2 br s 1.26 1.29 1.36 1.27 1.29 n-hexane CH3 t 0.88 0.88 0.86 0.89 0.89 0.90 CH2 m 1.26 1.28 1.25 1.24 1.28 1.29 HMPA g CH3 d, 9.5 2.65 2.59 2.53 2.40 2.57 2.64 2.61 methanol CH3 s h 3.49 3.31 3.16 3.07 3.28 3.34 3.34 OH s c,h 1.09 3.12 4.01 2.16 nitromethane CH3 s 4.33 4.43 4.42 2.94 4.31 4.34 4.40 n-pentane CH3 t, 7 0.88 0.88 0.86 0.87 0.89 0.90 CH2 m 1.27 1.27 1.27 1.23 1.29 1.29 2-propanol CH3 d, 6 1.22 1.10 1.04 0.95 1.09 1.50 1.17 CH sep, 6 4.04 3.90 3.78 3.67 3.87 3.92 4.02 pyridine CH(2) m 8.62 8.58 8.58 8.53 8.57 8.53 8.52 CH(3) m 7.29 7.35 7.39 6.66 7.33 7.44 7.45 CH(4) m 7.68 7.76 7.79 6.98 7.73 7.85 7.87 silicone grease i CH3 s 0.07 0.13 0.29 0.08 0.10 tetrahydrofuran CH2 m 1.85 1.79 1.76 1.40 1.80 1.87 1.88 CH2O m 3.76 3.63 3.60 3.57 3.64 3.71 3.74 toluene CH3 s 2.36 2.32 2.30 2.11 2.33 2.32 CH(o/p) m 7.17 7.1-7.27.18 7.02 7.1-7.37.16 CH(m) m 7.25 7.1-7.27.25 7.13 7.1-7.37.16 triethylamine CH3 t,7 1.03 0.96 0.93 0.96 0.96 1.05 0.99 CH2 q, 7 2.53 2.45 2.43 2.40 2.45 2.58 2.57