英语语法大攻克--直接引语改为间接引语
- 格式:doc
- 大小:44.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

练习I. 将下面的直接引语变成间接引语。
1. She said, “I am tired.”2. They said, “We are in Grade 4.”3. My mother said, “I have washed the clothes for you.”4. The girl said, “My favorite star is Feixiang.”5. Our teacher said to us, “The moon moves round the earth.”6. The boy said, “I like football very much.”7. The student said, “He is feeling a little under the weather.”8. The doctor said, “The patient needs an X-ray.”9. Mr. Smith said, “I caught the bus.”10. The w oman said, “I have finished the work.”11. The little boy said, “I can skate now.”12. Anna said, “I will be watching TV at seven o’clock tonight.”13. The teacher said, “The classroom must be cleaned.”14. She said, “The film had started when I got to the cinema.”15. He asked me, “Have you seen him before?”16. They asked us, “What have you told him?17. The girl asked us, “What do you usually do in the evening?”18. The man said to me, “Cook dinner for me.”19. The teacher said to the s tudent, “Don’t be late for school next time.”20. The commander ordered, “Stand up!”II. Fill in the blanks with the best answer.1. He said that he______ English for four years.A. has learnedB. had learnedC. is learningD. was learning2. Mr. Smith said he ______ very grateful to us for our kindness.A. wereB. wasC. isD. am3. John said that ______ wife always ______ coffee for breakfast.A. him…drankB. her…drankC. his…drinkD. his…drank4. The teacher told Tom to finish_____ homework on time.A. his…B. himC. herD. hers5. The teacher said that he must bring _____ book to the classroom.A. heB. himC. hisD. she6. He said he ______ this book.A. likeB. likesC. likedD. liking7. He said that he ______ her the day before.A. sawB. seenC. seesD. had seen8. He said to me he ______tired.A. isB. wasC. wereD. be9. She said that he _______ waiting for an hour.A. has beenB. have beenC. had beenD. have been10. He said the I _____ changed much.A. haven’tB. hasn’tC. hadn’tD. to be haven’t11. The teacher told us that the sun ______ in the east.A. riseB. risesC. roseD. rising12. He said that he _____ at six.A. was comingB. cameC. has comeD. comes13. He said that the rain ______ the day before.A. is fallingB. were fallingC. had been fallingD. has been falling14. She said that she ______ reading the book by the end of that week.A. would have finishedB. will have finishedC. would have finishD. will have finish15. He said that he would come and_______ me sometime the next year.A. will be seeingB. will seeC. would seeD. see16. She said that she _____ dance very well.A. canB. couldC. willD. is17. He asked me ______ I _____ going away that day.A. what…wasB. what…amC. if…amD. if…was18. She asked me_____ he was ______ brother.A. if…myB. if…herC. that …myD. that …her19. She asked me who would help____ finish the job.A. myB. sheC. ID. me20. The foreigner asked me _____ the nearest hospital_____.A. how…wasB. how…isC. where…isD. where…was21. The boss ordered me _____ for the work.A. not…beB. beC. notD. not…to be22. My mother always tells me _____ for the job.A. be on timeB. in on timeC. be to on timeD. to be on time23. I asked her ____ give_____ a glass of water.A. be…myB. to…meC. be…meD. to…my24. She told him _____ a brave boy _____ was.A. how…heB. what…heC. how…sheD. what…she25. The man told _____ that he ______me very much.A. I…missB. me…missedC. I…missingD. me…miss26. They told us they ______ the price ____ the meter.A. pay…forB. pay…onC. paid…onD. paid…for27. She asked us _______A. what she doing at eight last night.B. what was he doing at eight last night.C. what we were doing at eight last night.D. what were we doing at eight last night.28. Mother told us _______ with fire.A. don’t playB. not playC. to not playD. not to play29. The girl said that she __________ in 1989.A. is bornB. was bornC. has been bornD. had been born30. The old man told us that he ________.A. has never been aboard beforeB. had never been aboard beforeC. was never aboard beforeD. is never aboard before。

英语语法:直接引语变间接引语英语语法:直接引语变间接引语英语语法是针对英语语言进行研究后,系统地总结归纳出来的一系列语言规则。
英语语法的精髓在于掌握语言的使用。
在英语六级的学习过程中有哪些直接引语变间接引语的方法呢?下面就让店铺为大家整理的英语语法:直接引语变间接引语,一起来看看吧。
一、概述引用或转述别人说的话时有两种方法:直接引述别人的原话,这叫做直接引语(direct speech)。
用自己的话转述别人的话,叫间接引语(indirect speech)。
一般地讲,直接引语前后要加引号,间接引语不用引号,而用宾语从句来表达。
Mr. Black said, “I'm busy.”布菜克先生说:“我很忙”。
(直接引语)Mr. Black said that he was busy.布菜克先生说他很忙。
(宾语从句是间接引语)从上例看来,直接引语改为间接引语时,除将直接引语改为宾语从句之外,还须对直接引语中的人称和时态进行相应的变化,如上例直接引语中的I改成了he, am则改成了was。
现将由直接引语改为间接引语时应注意的问题,分述如下:二、直接引语是陈述句时直接引语如果是陈述句,变为间接引语时,用连词that引导(that 在口语中常省去),that从句之前用say、tell等动词,从句中的人称、时态、指示代词、时间状语、地点状语等要作相应的变化。
1、人称的变化直接引语改为间接引语人称要相应的变化,把直接引语中的第一人称(如:I,me,my,mine,we,us,our,ours)变为与主句的主语相一致的人称。
把直接引语中的第二人称(you,your,yours)变为和主句的间接宾语(即听话人,如无听话人,可根据上下文的体会人为确定一个人称)相一致的人称。
直接引语中的第三人称(he,him,his,she,her,hers,it,its,they,their,theirs,them)变为间接引语时,人称不变。

直接引语变间接引语的方法技巧时间:2010-02-22 作者:佚名来源:网络资源一祈使句方法是:使用ask [tell, order] sb to do sth这一结构进行转换,若祈使句为否定式,则用ask [tell, order] sb not to do sth,其中ask, tell, order的选择视句子的语气而定。
如:“Come early tomorrow, Jim.” he said. 他说。
如:“吉姆,明天早点来。
”→He told Jim to come early the next day. 他叫吉姆第二天早点来。
“Don’t be late again, Mary.” he said. 他说。
如:“玛丽,不要再迟到了。
”→He told Mary not to be late again. 他叫玛丽不要再迟到了。
注意:(1)除动词ask, tell, order外,有时也可能用其他动词。
如:“Don’t go out at night, Jim.” he said. 他说。
如:“吉姆,晚上别出去。
”→He warned Jim not to go out at night. 他警告吉姆晚上不要出去。
(2)若祈使句中没有呼语,应根据句意给动词ask, tell, order等补上适当的宾语。
如:“Watch carefully.” he said. 他说。
如:“仔细看着。
”→He tol d us to watch carefully. 他叫我们仔细看着。
二陈述句将直接引语变为由that引导的宾语从句跟在引述动词之后(that也可省略)。
如:“I don’t love her.” he says. 他说。
如:“我不爱她。
”→He says that he doesn’t love her. 他说他不爱她。
注意:(1)若引述动词用的是say to sb,则通常改为tell sb。

英语直接引语变间接引语的讲解
将英语直接引语转换为间接引语需要进行几个关键步骤,主要包括缩进、时态和人称的转换。
以下是详细的讲解:
1. 缩进:在直接引语转变为间接引语时,通常需要从第二行开始缩进。
通常使用两个或更多的空格或制表符来实现这一目的。
2. 时态:通常来说,间接引语中的时态应与主要句子的时态一致。
例如,如果主句使用一般现在时,间接引语也应当使用一般现在时。
然而,如果直接引语中的动作发生在过去,并且与主句的动作发生在同一时间,间接引语可以使用过去进行时来代替过去时态。
3. 人称:在直接引语转变为间接引语时,人称需要进行相应的转换。
例如,直接引语中的“I”在间接引语中应变为“he”或“she”。
4. 指示词和动词:指示词如“this”和“that”在直接引语转变为间接引语时通常需要省略。
此外,动词如“say”和“tell”在间接引语中通常可以省略,除非它们在句子中起到其他作用。
5. 标点符号:在直接引语转变为间接引语时,标点符号也需要进行相应的转换。
例如,直接引语的句号在间接引语中应变为逗号,而直接引语的感叹号在间接引语中应变为句号。
以下是一个示例:
直接引语:“I love you!”he said.
间接引语:“He said that he loved me.”
在这个例子中,我们可以看到“I”被转换为“he”,“said”被省略了,同时指示词“that”被添加到了句子中。
此外,“!”也被省略了,取而代之的是句号。
希望这个讲解能帮助你更好地理解如何将英语直接引语转换为间接引语。

直接引语变间接引语英语直接引语是指按照原文原话进行引述的句子,而间接引语则是将原文的意思转述为自己的话语,并用相应的语法变化。
在英语中,直接引语和间接引语的使用具有一定的规则和注意事项。
本文将对直接引语变为间接引语的相关内容进行介绍和说明。
首先,直接引语变为间接引语时,需要注意动词的变化。
根据引言动词的不同,需要根据时态和人称进行相应的变化。
例如,如果引言动词是现在时态,需要将直接引语中的动词改为相应的过去时态;如果引言动词是过去时态,需要将直接引语中的动词改为相应的过去完成时态等。
同时,人称也需要进行相应的变化,例如将第一人称变为第三人称等。
其次,间接引语中的句子结构也需要进行调整。
在直接引语中,常常会使用到引号和冒号等标点符号,而在间接引语中则不需要使用这些标点符号。
同时,如果直接引语中存在疑问句或感叹句,则在间接引语中需要将其变为陈述句。
另外,还需要注意引言介词的使用。
根据引言动词的不同,需要使用相应的引言介词来引导间接引语。
例如,常用的引言介词有"that"、"if"等。
最后,要特别注意句子之间的逻辑关系和语气。
在直接引语变为间接引语时,要保持原文中的逻辑关系和语气一致。
例如,如果直接引语中是陈述句,则在间接引语中也应保持陈述句的形式;如果直接引语中是疑问句,则在间接引语中也应保持疑问句的形式。
总的来说,直接引语变为间接引语是英语中常见的语法转换,需要注意动词、句子结构、引言介词和语气等方面的变化。
通过准确使用这些规则,可以使文本表达更加精确和生动,从而提高文章的质量和可读性。
以上就是关于直接引语变间接引语的介绍,希望能对您有所帮助。

直接引语改为间接引语(直接引语为一般疑问句)注意:1、用连词if/whether引导2、语序要改成陈述句语序3、人称的改变(一随主二随宾三不变)4、时态的变化 (主句用现在时或将来时,从句可用任何时态。
主句用过去时,从句用与过去相关的时态。
)例如:‘Do you like English?’ Jim asked Tom.→Jim asked Tom if/whether he liked English.→Jim asked Tom whether he liked English or not.(注意:当句中用了whether --- or not时,不能用if来替换whether。
)一、把直接引语改为间接引语1.‘Is your mother a doctor?’ Lucy asked me.Lucy asked me .2. The principal wants to know. ‘Do the students study hard?’The principal wants to know .3. I really don’t know. ‘Did they go to the park yesterday?’I really don’t know .4. They wondered. ‘Shall we buy some food before we go for a picnic?’They wondered .5.‘Does the little girl like to swim in the swimming pool?’ I wanted to know.I wanted to know .二、单项选择1. I wondered a famous singer.A. whether Lily would becomeB. if Lily will becomeC. weather Lily would becomeD. if would Lily become2. Cathy really doesn’t know or not.A. if they will come hereB. whether they will come hereC. if will they come hereD. weather they will come here3. Can you guess ?A. if the man in white is a footballerB. that is the man in white a footballerC. whether the man in white is a footballerD. if the man in white is a footballer or not4. Mother didn’t tell me .A. if you will go shopping with meB. whether you will go shopping with meC. that you will go shopping with meD. if you would go shopping with me。
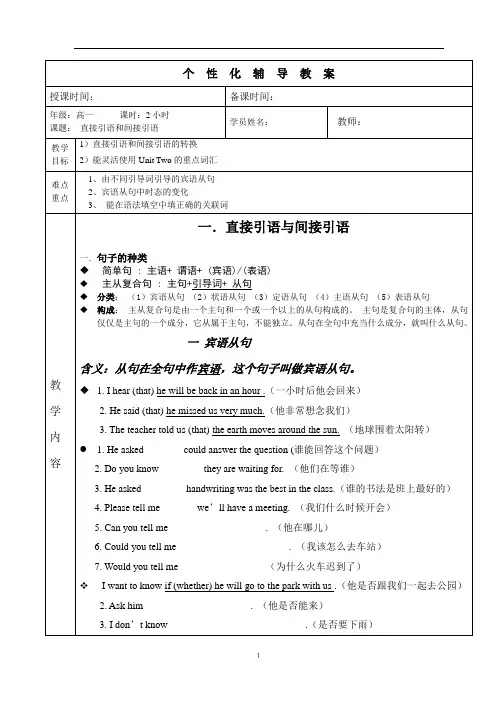
个性化辅导教案授课时间:备课时间:年级:高一课时:2小时课题:直接引语和间接引语学员姓名:教师:教学目标1)直接引语和间接引语的转换2)能灵活使用Unit Two的重点词汇难点重点1、由不同引导词引导的宾语从句2、宾语从句中时态的变化3、能在语法填空中填正确的关联词教学内容一.直接引语与间接引语一.句子的种类◆简单句 : 主语+ 谓语+ (宾语)/(表语)◆主从复合句 : 主句+引导词+ 从句◆分类:(1)宾语从句(2)状语从句(3)定语从句(4)主语从句(5)表语从句◆构成:主从复合句是由一个主句和一个或一个以上的从句构成的。
主句是复合句的主体,从句仅仅是主句的一个成分,它从属于主句,不能独立。
从句在全句中充当什么成分,就叫什么从句。
一宾语从句含义:从句在全句中作宾语,这个句子叫做宾语从句。
◆ 1. I hear (that) he will be back in an hour .(一小时后他会回来)2. He said (that) he missed us very much.(他非常想念我们)3. The teacher told us (that) the earth moves around the sun. (地球围着太阳转)● 1. He asked _______ could answer the question (谁能回答这个问题)2. Do you know_________they are waiting for. (他们在等谁)3. He asked ________ handwriting was the best in the class.(谁的书法是班上最好的)4. Please tell me _______we’ll have a meeting. (我们什么时候开会)5. Can you tell me ___________________. (他在哪儿)6. Could you tell me ______________________. (我该怎么去车站)7. Would you tell me _________________(为什么火车迟到了)I want to know if (whether) he will go to the park with us .(他是否跟我们一起去公园)2. Ask him _____________________. (他是否能来)3. I don’t know ___________________________.(是否要下雨)whether it is going to rain or not 总结: 根据什么来选择关联词?宾语从句用陈述语序连接词时态语序陈述句that,可省略,无意义如果主句是现在时态(一般现在时,一般将来时,现在进行时,现在完成时),从句时态不变。

直接引语直接引用别人的原话叫做直接引语,直接引语通常置于引号内(“引用原话”)。
—“What is it all about?”—“究竟是什么事呢?”—“Nothing serious, just a storm in a teacup.”—“没有什么,大惊小怪而已。
”间接引语用自己的话转述别人的意思,或引用自己说过的话,都叫做间接引语。
间接引语多数用宾语从句来表达。
Mary said that she received a sugar report this morning.玛莉说她今天早上收到了一封情书。
He said that his hands were quite full at that moment. 他说那时他忙得不可开交。
直接引语间接引语的区别直接引语:直接引述别人的话(句子中有“”)。
间接引语:用自己的话转述别人的话,叫“间接引语”(句子中一般无“”)二.直接引语变间接引语A.一般不表示请求或祈使的句子改为一个宾语从句1.连词若直接引语引号里的内容是陈述句,那么改为间接时,要用连词that (可以省略)……………….一般疑问句,…….,要用连词if/whether (不可以省略)……………….特殊疑问句,…….,要用连词wh- 即特殊疑问词本身(不可省)2.变化(1)主句动词的变化一般说来,主句谓语动词常为said或said to,变为间接引语时,当直接引语是陈述句时,said不变。
当直接引语是一般疑问句和特殊疑问句时,则要把said或said to变为asked / asked sb. (2)从句人称的变化由直接引语变间接引语时,从句的主语人称要遵循一主、二宾、三不变的原则。
①直接引语的主语是第一人称变为间接引语时要和主句的主语保持一致。
②如果直接引语的主语是第二人称变为间接引语时要与主句的宾语保持一致。
③如果直接引语的主语是第三人称变为间接引语时,人称不变。
例如:①They said, “We will go there by bus.” →They said they would go there by bus.②She said to me, “Are you interested in science?” →She asked me if I was interested in science.③His mother said to me, “He can't go to school.” →His mother told me that he couldn't go to school. (3)、从句动词时态的变化a. 如果主句的时态是一般过去时,从句的时态则应是与主句时态相应的过去时态。

高中英语语法现象一直接引语变间接引语口诀一、当直接引语为陈述句,变成间接引语的“顺口溜”是:去掉引号加that,人称变化要灵活,时态向后退一步,状语变化按规则。
She said,“My brother doesn't want to go there.”→She said that her brother didn't want to go there.二、当直接引语为一般疑问句,变成间接引语的“顺口溜”是:去掉引号加if,陈述语序要记住,时态人称和状语,小心变化别马虎。
I asked her,“Do you study English here?”→I asked her if she studied English there.三、当直接引语是特殊疑问句,变成间接引语的“顺口溜”是:直接去引号,陈述莫忘掉,小心助动词,丢它最重要。
“What do you want?”he asked me. →He asked me what I wanted.四、当直接引语是祈使句,变成间接引语的“顺口溜”是:去掉引号要加to, ask,tell须记住,直引若是否定式,not加在to前部。
The teacher said to her mother,“Please give me the book.” →The teacher told her mother to give her the book.五、对于人称变化,要求学生们记住的“顺口溜”是:第一人称看主语,第二人称看宾语,宾语若是不存在,活用代词I,my,me。
He said to her,“Are you interested in English?”→He asked her if she wa s interested in English.The teacher said,“Where have you been?”→The teacher asked me(us) where I(we) had been.六、时态对应表:直接引语时态间接引语时态一般现在时→ 一般过去时一般将来时→ 过去将来时现在进行时→ 过去进行时一般过去时→ 过去完成时现在完成时→ 过去完成时(过去完成时时态不变)情态动词也要变成相应的过去式:can could; may might; must must/had to。

注意:1、通常直接引语里含有please表示请求,ask sb (not) to do sth.例如:He said to me,‘Shut the window,please.’改为:He asked me to shut the window.2、直接引语里不含please表示命令:tell sb (not) to do sth.例如:The teacher said to the student,‘Stop talking!’改为:The teacher told the students to stop talking.练习:1、The doctor said to me,‘Don’t drink too much.’The doctor me too much.\2、Mother said to him,‘Don’t cry!’Mother3、The doctor said to me,‘Don’t smoke.’The doctor4、Jim said to him,‘Start at once.’Jim him at once.5、Mother said to me,‘Don’t tell a lie.’Mother a lie.6、I said to him yesterday,‘Please come early.’Yesterday I him to come early7、‘Could you open the window,please?’Deming said to Yongxian.Deming Yongxian the window.8、The teacher said to the boy,‘Call the police right now.’The teacher9、His father said to him,‘Don’t leave the cat alone at home.’His father10、John said to the others,‘Keep quiet.’John the others注意:1、连词that引导2、人称的改变(一随主二随宾三不变)3、时态的变化(主句用现在时或将来时,从句可用任何时态;主句用过去时,从句用与过去相关的时态。

语法----直接引语改为间接引语一、选择正确答案完成下列宾语从句。
( )1 .The children said they themselves very much .A .if ,enjoyB .why ,enjoyedC .what ,enjoyD .that ,enjoyed( )2 .I don’t think I out the problem .A .if , can workB .how , will workC .that , can workD .when , will work( )3 .She is afraid he cold at night .A .that , will catchB .that , catchesC .whether , will catchD .if , catches( )4 .We are sure he to speak French well .A .that , learnedB .that , has learnedC .if , learnedD .if ,has learned( )5 .The boy asked I any noise from outside .A .when , heardB .why , had heardC .whether , had heardD .what ,heard( )6 .Who can tell us about over there ?A .what they talkB .what do they talkC .what are they talkingD .what they are talking( )7 .We couldn’t find out ,so we asked a policeman .A .whose bike it wasB .whose bike was itC .whose it was bikeD .whose was it bike( )8 .Do you know take to get to the hospital ?A .which way must weB .which must we wayC .which way we mustD .which we must way( )9 .Tom asked to school late .A .who did often comeB .who often did comeC .who often comeD .who often came( )10 .I don’t remember the boy by himself .A .why did she leaveB .why she leftC .why had she leftD .why she had left( )11 .Have you forgotten when he died ?A .how old he wasB .how old was heC .what did he sayD .what he did say( )12 .Nobody knows to visit our school .A .when will he comeB .when does he comeC .when he will comeD .when he does come( )13 .Please tell us to the science museum .A .how can we reachB .how we can reachC .how can we getD .how we can get( )14 .Don’t you believe to the moon by spaceship ?A .that man did flyB .how did man flyC .if man flyD .whether man fly( )15 .I don’t know.A .what is the matter with himB .what the matter is with himC .what with him the matter isD .what the matter with him is( )16 .He doesn’t tell me if he .If he .I’ll telephone you .A .will come , comesB .will come , will comeC .comes , will comeD .comes , comesⅡ .选择括号内正确的关联词语填空。
如何把直接引语转换为间接引语引述别人的话时,一般采用两种方式:一是引用别人的原话,把它放在引号内,称为直接引语;二是用自己的话加以转述,被转述的话不放在引号内,称为间接引语。
间接引语在大多数情况下是一个宾语从句。
直接引语变成间接引语时,要注意以下几点:人称变化、时态变化、宾语从句要用陈述句语序。
1. 直接引语是陈述句,变成间接引语时,由连词that....引导,很多时候可省略that。
例如:She said, "I am very happy to help you."→She said she was very happy to help me.She said, “I will go to Guangzhou tomorrow.”→She said that she would go to Guangzhou the next day/the following day.She said, “I have lived in Foshan for several years.”→She said that she had lived in Foshan for several years.She said, “ I am reading a book now.”→She said that she was reading a book at that time/moment.John said, “I am leaving for Paris on Wednesday”→John said that he was leaving for Paris on Wednesday.2. 直接引语是一般疑问句,变成间接引语时,由连词whether.......或if..(是否)引导。
先把直接引语变为陈述句语序,再放在whether或if后面。
例如:He asked me, "Do you like playing football?"→→He asked me whether/if I liked playing football.He asked Mary, “Will you come to my birthday party?”→You will come to my birthday party.→He asked Mary whether/if she would come to his birthday party.注意:大多数情况下,if和whether 可以互换,但后有or not,或在动词不定式前,或放在介词后作连接词时,一般只用whether。
直接引语变间接引语(时间地点状语的转变)但要注意在以下几种情况下,在直接引语变为间接引语时,时态一般不变化。
①直接引语是客观真理或是谚语格言时,如:"The earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth, the teacher told me. → The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth。
He said,“Practice makes perfect.” ——>He said that practice makes perfect.②直接引语是过去进行时,时态不变。
如:Jack said, "John, where were you going when I met you in the street?" →Jack asked John where he was going when he met him in the street。
③直接引语中有具体的过去某年、某月、某日作状语,变为间接引语时,时态不变。
如:Xiao Wang said. "I was born on April 2l, 1980。
" →Xiao Wang said he was born on April 20, 1980。
④直接引语如果是一般现在时,表示一种反复出现或习惯性的动作,变间接引语,时态不变。
如:He said, "I get up at six every morning。
" →He said he gets up at six every morning。
⑤如果直接引语中的情态动词没有过去时的形式(例:ought to,had better, used to)和已经是过去时的形式时,(例:could, should, would, might)不再变。
直接引语变间接引语及其注意事项直接引语变间接引语(⼀)⼈称的转变1.直接引语中的第⼀⼈称,⼀般转换为第三⼈称,如:He said,“I am very sorry. ”He said that he was very sorry.2.直接引语中的第⼆⼈称,如果原话是针对转述⼈说的,转换为第⼀⼈称,如:“You should be more careful next time, ”my father told me.My father told me that I should be morecareful the next time.3.直接引语中的第⼆⼈称,如果原话是针对第三⼈称说的,转换成第三⼈称。
如:She said to her son, “I'll check your homework tonight. ”She said to her son that she would checkhis homework that night.4.⼈称的转换包括⼈称代词、物主代词和名词性物主代词等,如:He asked me, “Will you go to the station with me to meet a friend of mine this after noon?”He asked me whether I would go to the station with him to meet a friend of his that afternoon.总之,⼈称的转换不是固定的,具体情况,具体对待,要符合逻辑。
(⼆)时态的转换直接引语改为间接引语时,主句中的谓语动词如果是过去时,从句(即间接引语部分)的谓语动词在时态⽅⾯要作相应的变化,变成过去时范畴的各种时态(实际也是宾语从句的时态要求),变化如下:⼀般现在时⼀般过去时现在进⾏时过去进⾏时现在完成时过去完成时⼀般将来时过去将来时⼀般过去时过去完成时过去完成时不变过去进⾏时不变如:1.“I am very glad to visit your school”, shesaid.She said she was very glad to visit ourschool.2.Tom said, “We are listening to the pop music. ”Tom said that they were listening to the pop music.3.Mother asked, “Have you finished your homework before you watch TV?”Mother asked me whether I had finished my homework before I watched TV.4.He asked the conductor, “Where shall I get off to change to a No. 3 bus?”He asked the conductor where he would get off to change to a No. 3 bus.5.“Why did she refuse to go there?”the teacher asked.The teacher asked why she had refused to go there.6.Mother asked me, “Had you finished your homework before you watched TV?”Mother asked me whether I had finished my homework before I watched TV.7.Tom said, “We were having a football match this time yesterday. ”Tom said that they were having a football match that time the day before.8.He said,“I haven't heard from my parents these days. ” He said that he hadn't heard from his parents those days.(三)时间状语、地点状语的变化1.直接引语是客观事实、普遍真理等,主句尽管是过去时态,变成间接引语时,时态仍然⽤⼀般现在时态。
直接引语变间接引语的几点变化一、时态的变化直接引语变为间接引语时,若主句为过去时态,变为间接引语的宾语从句通常要将时态往后推一个,即一般现在时变为一般过去时,一般将来时变为过去将来时,现在进行时变为过去进行时,现在完成时变为过去完成时,一般过去时也变为过去完成时,等等(若直接引语为过去完成时,变为间接引语可以不变)。
另外,若直接引语中有情态动词can, may等,也应变成过去式could, might等(情态动词must可以变为had to,也可不变,should, ought to, had better 等可以不变)。
如:“I like to watch TV,” she said. 她说:“我喜欢看电视。
”→She said that she liked to watch TV. 她说她喜欢看电视。
He said, “I’m waiting for her.” 他说:“我在等她。
”→He said that he was waiting for her. 他说他在等她。
“It will rain soon,” he said. 他说:“很快就会下雨。
”→He said that it would rain soon. 他说很快就会下雨。
“She can swim,” he said. 他说:“她会游泳。
”→He said that she could swim. 他说她会游泳。
注意:(1)若直接引语为客观真理,则变为间接引语时时态不变:The teacher said, “The earth turns around the sun.” 老师说:“地球绕着太阳转。
”→The teacher said that the earth turns around the sun. 老师说地球绕着太阳转。
(2)有时由于直接引语有特定的过去时间状语,变为间接引语时时态也可不变:He said, “ was born in 1954.” 他说:“我是1954年生的。
直接引语和间接引语一、直接引语和间接引语:在陈述句中,直接引用说话人原来的语句,称为直接引语。
在书写时,直接引语用引号。
用自己的词语来转述表达原来说话人说的内容,称为间接引语。
二、直接引语改变为间接引语:1、直接引语如果是陈述句,变为间接引语时应注意以下各点:①不用引号,而用连接词that,但有时可省略(口语中)。
②人称作相应变化;③主句里的动词如果是过去时,间接引语中的时态一般应作相应改变:一般现在时变一般过去时;一般将来时变过去将来时;现在进行时变过去进行时;现在完成时变成过去完成时;一般过去时变成过去完成时;过去完成时不变;一般过去时如与一个具体的过去时间连用,则时态不变。
如:He says,"I am not from the USA.”→He says that he is not from the USA.Mr Smith said to his girl friend,“ I haven’ t seen you for a long time.”→Mr Smith said to his girl friend that he had not seen her for a long time.但要注意在以下几种情况下,在直接引语变为间接引语时,时态一般不变化。
(1)直接引语是客观真理。
“The earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth”, the teacher told me. → The teacher told me the earth moves around the sun and the moon moves around the earth .(2)直接引语中有具体的过去某年、某月、某日作状语,变为间接引语时, 时态不变。
Xiao Wang said. “I was born on April 2l, 1980.”→Xiao Wang said he was born on April 20, 1980.(3)直接引语中被引述的部分是反复出现的,习惯性的动作或说话时情况仍然存在的,变间接引语时, 时态保持不变。
“直接引语”如何变成间接引语?_现在进行时所谓直接引语,就是直接引述别人的话,不加任何改变,一般放在引号里。
如:He said, I willlearn English.所谓间接引语,就是转述别人的话,此时需要改变一些内容,比如主语、时态、地点等。
如:He said thathe wouldlearn English.一、直接引语变间接引语时,句式变化方法如下:1.陈述句直接引语:She said, I willstudy English.间接引语:She said thatshe wouldstudy English.既然转述别人的话,就不能再用人家的原话了,所以I就变成了she。
前面是said过去式,will也就变成过去时的would。
2.一般疑问句直接引语:She asked me, Can youspeak English?间接引语:She asked mewhether I couldspeak English.如果别人的原话是一般疑问句,变成间接引语时记得要加上whether,然后倒装变为陈述语序。
3.特殊疑问句直接引语:She asked me, Whencan youdo that?间接引语:She asked me whenI coulddo that.如果别人的原话是特殊疑问句,变成间接引语时不用加词,但要把倒装语序变成陈述语序。
4.祈使句直接引语:Shesaid tothe children, Dontplay outside.间接引语:Shetoldthe childrennot toplay outside.如果别人的原话是祈使句,don’t 要变成not to,后面正常。
二、其它变化1.指示代词直接引语间接引语指示代词this这that那指示代词these这些地点状语here这里there那里2.动词变化He said, I will go there.He said that he would come here.3.地点状语He said, I will go there.He said that he would come here.4.时间状语直接引语间接引语时间状语now现在then那时;当时时间状语that day那天时间状语tonight今晚that night那天晚上时间状语this week本周that week上周时间状语yesterday昨天the day before前一天时间状语the day before yesterday前天two days before前两天时间状语three days ago三天以前three days before前三天时间状语last week上周the l请看评论区eek前一周时间状语tomorrow明天the next day /the following day第二天时间状语next week下周the next week第二个星期时间状语next month下个月the following month第二个月时间状语this morning这个早晨that morning那个早晨时间状语ago/last以前/最后before之前。
注意:1、通常直接引语里含有please表示请求,ask sb (not) to do sth.
例如:He said to me,‘Shut the window,please.’
改为:He asked me to shut the window.
2、直接引语里不含please表示命令:tell sb (not) to do sth.
例如:The teacher said to the student,‘Stop talking!’
改为:The teacher told the students to stop talking.
练习:
1、The doctor said to me,‘Don’t drink too much.’
The doctor me too much.\
2、Mother said to him,‘Don’t cry!’
Mother
3、The doctor said to me,‘Don’t smoke.’
The doctor
4、Jim said to him,‘Start at once.’
Jim him at once.
5、Mother said to me,‘Don’t tell a lie.’
Mother a lie.
6、I said to him yesterday,‘Please come early.’
Yesterday I him to come early
7、‘Could you open the window,please?’Deming said to Yongxian.
Deming Yongxian the window.
8、The teacher said to the boy,‘Call the police right now.’
The teacher
9、His father said to him,‘Don’t leave the cat alone at home.’
His father
10、John said to the others,‘Keep quiet.’
John the others
注意:
1、连词that引导
2、人称的改变(一随主二随宾三不变)
3、时态的变化(主句用现在时或将来时,从句可用任何时态;主句用过去时,从句用与过去相关的时态。
)
4、如果直接引语是表示客观真理时,变为间接引语,一般现在时不改为一般过去时,如:The teacher said,‘The earth goes round the sun.’
改为:The teacher said that the earth goes round the sun.
一、把直接引语改为间接引语(主句为一般现在时)
1、‘We to to school on Saturday,too.’
They say to school on Saturday.
2、‘I want to give your sister a Christmas card.’
Kelly says to give sister a Christmas card.
3、‘I will visit my daughter in March.’
Professor Waths says visit daughter in March.
4、She says,‘I’m glad to meet you.’
She tells us glad to meet .
5、David says,‘I want to bear their songs.’
David says to bear
二、把直接引语改为间接引语(主句为一般过去时)
1、‘I am a soldier.’
He said a soldier.
2、‘We are at the race.’
They said at the race.
3、‘They don’t have any books about stamps.’
John told Annie have any books about stamps.
4、‘I need the cook’s telephone number.’
Zak said cook’s telephone number.
5、‘She is running along the street.’
She said along the street.
三、把直接引语改为间接引语(两种时态混用)。
6、Sally says,‘Our exam are starting this week.’
Sally says starting this week.
7、‘I am going to read these.’
My mother said .
8、‘I shall find an easier job.’
直接引语改为间接引语预习作业
请思考以下问题:
1、直接引语为祈使句时,直接引语怎样改为间接引语?
2、直接引语为陈述句时,直接引语改为间接引语要注意哪两个方面?
3、直接引语为陈述句时,直接引语改为间接引语,人称的变化有什么规律?
4、直接引语为陈述句时,直接引语改为间接引语,时态的变化有什么规律?
5、直接引语为特殊疑问句时,直接引语改为间接引语,要注意哪四个方面?
6、直接引语为一般疑问句时,直接引语改为间接引语,要注意哪四个方面?
预习作业一
完成下列练习,并简单归纳直接引语变为间接引语的类型。
1、T he doctor said to me,‘Don’t drink too much.’
The doctor me too much.
类别1:直接引语为
2、‘I want to give your sister a Christmas card.’
Kelly says to give sister a Christmas card.
类别2:直接引语为
3、‘How can I get to the park?’Can you tell me?
Can you tell me to the park?
类别3:直接引语为
4、‘Is your mother a doctor?’Lucy asked me.
Lucy asked me a doctor.
类别4:直接引语为
预习作业二
(Homework 1) 1、Mother said to him,‘Don’t cry!’
Mother him cry.
2、I said to him yesterday,‘please come early.’
Yesterday I him early.
(Homework 2) 1、‘We go to school on Saturday,too.’They say.
They say to school on Saturday,too.
2、M y teacher said,‘She is a good student.’
My teacher said was a good student.
3、‘You must be on time for your lessons.’He said to me.
He said to me on time for
lessons.
(Homework 3)1、Sally says,’Our exams are starting this week.’
Sally says exam starting this week.
2、‘She is running along the street.’
She said running along the street.
3、T he teacher said,‘the earth is round.’
The teacher said the earth round.
(Homework 4)1、‘When does the train arrive?’Please tell me.
Please tell me the train .
2、‘What time did he get up today?’I don’t know.
I don’t know what time up today.
(Homework 5) 1、‘Is your mother a doctor?’Lucy asked me.
Lucy asked me a doctor.
2、I really don’t know.‘Did they go to the park?’
I really don’t know to the park or not.。