名词单复数,数词,量词,some_any
- 格式:doc
- 大小:61.00 KB
- 文档页数:5

初中英语语法知识之数量词1. 数量词的定义:表示数量多少的词语,如one, two, three等。
2. 基数词和序数词:- 基数词表示数量的大小,如one, two, three等。
- 序数词表示顺序的大小,如first, second, third等。
基数词(Cardinal Numbers)是表示数量的词,如1、2、3、4、5等。
序数词(Ordinal Numbers)则是表示顺序的词,如第一、第二、第三、第四、第五等。
3. 数量词的用法:- 用于表示具体的数量,如two books, three apples等。
- 用于表示抽象的数量,如a lot of, many, few等。
- 用于表示时间、日期、年龄等,如two o'clock, the second of May, a three-year-old child等。
4. 数量词的变化:- 在表示单数时,一般不加-s,如one book, two books。
- 在表示复数时,一般加-s,如two books, three apples。
- 在表示序数时,一般加-th,如fourth, fifth。
- 在表示百分数时,一般加-percent,如50%。
5. 特殊的数量词:- a/an:表示“一个”,但只用于单数可数名词前。
- some:表示“一些”,用于肯定句中。
- any:表示“任何”,用于否定句和疑问句中。
- much:表示“许多”,用于不可数名词前。
- many:表示“许多”,用于可数名词前。
- several:表示“几个”,用于可数名词前。

some和any的用法区别一、什么是some和any?二、用法区别1. 意义不同2. 肯定和否定用法3. 疑问句用法三、具体应用场景举例1. 肯定陈述句2. 否定陈述句3. 疑问句四、总结一、什么是some和any?在英语中,some和any都属于数量词(quantifiers),用于描述或指示数量。
它们既可以修饰可数名词,也可以修饰不可数名词。
二、用法区别:1. 意义不同:- some通常表示“一些”、“几个”或“某些”,强调存在,并且常带有肯定的意味;- any则表示“任何”、“无论哪个”、“无论哪些”,强调对选择的不限制,并且通常带有否定或疑问的意味。
2. 肯定和否定用法:- some多用于肯定句和表示请求、建议、邀请等语境中,如“I have some books to read.”(我有一些书要读。
);- any则多用于否定句和疑问句中,如“I don't have any money.”(我没有钱。
)、“Do you have any questions?”(你有任何问题吗?)3. 疑问句用法:- some的疑问句常用于征求意见、询问期望等语境下,如“Would you like some tea?”(你想要一些茶吗?);- any的疑问句则常用于询问是否有任何可能性或可行性,如“Is there any way I can help you?”(我可以帮你做些什么吗?)三、具体应用场景举例:1. 肯定陈述句:- There are some bananas in the fridge. (冰箱里有些香蕉。
)- She bought some flowers for her mother's birthday. (她为母亲的生日买了一些花。
)2. 否定陈述句:- I don't have any money with me. (我身上没有钱。
)- There aren't any apples left in the basket. (篮子里没有苹果了。

一、some 和 any 的基本用法1. "Some" 和 "any" 都是英语中的量词,用于表示数量或程度。
2. "Some" 通常用于肯定句和疑问句中,表示肯定的数量或程度。
3. "Any" 通常用于否定句和疑问句中,表示任何数量或程度。
二、"Some" 和 "Any" 的具体用法4. "Some" 的具体用法:a. 用于肯定句中表示肯定的数量或程度,例如:“She has some books to read.”(她有一些书要读)b. 用于疑问句中请求肯定的答复,例如:“Would you like some tea?”(你想喝一些茶吗)c. 用于提议或请求时,例如:“Could I have some water, please?”(我可以喝点水吗)5. "Any" 的具体用法:a. 用于否定句中表示任何数量或程度,例如:“I don't have any money.”(我没有任何钱)b. 用于疑问句中请求否定的答复,例如:“Is there any food left?”(还有剩下的食物吗)c. 用于条件句或假设句中表示任何可能的情况,例如:“You can take any seat you like.”(你可以选择任何一个座位)三、"Some" 与 "Any" 的区别6. "Some" 用于肯定句和疑问句中,表示肯定的情况或提议请求;"Any" 用于否定句和疑问句中,表示否定的情况或假设情况。
7. "Some" 常用于可数名词和不可数名词;"Any" 一般用于可数名词的复数和不可数名词。
8. "Some" 带有一种积极的、自信的语气;"Any" 带有一种消极的、条件性的语气。

小学生的英语知识小学生必备的英语知识集锦小学生开始学习英语的时间越来越早,很多家长都知道小学是孩子打好英语基础的黄金阶段,所以特别重视小学英语的学习。
下面是店铺为大家整理的小学生必备的英语知识集锦,希望对大家有用!小学生的英语知识篇1名词:名词单复数,名词的格(一)名词单复数1.一般情况,直接加-s,如:book-books,bag-bags,cat-cats,bed-beds2.以s.x.sh.ch结尾,加-es,如:bus-buses,box-boxes,brush-brushes,watch-watches3.以“辅音字母+y”结尾,变y为i,再加-es,如:family-families,strawberry-strawberries4.以“f或fe”结尾,变f或fe为v,再加-es,如:knife-knives5.不规则名词复数:man-men,woman-women,policeman-policemen,policewoman-policewomen,mouse-micechild-children,foot-feet,tooth-teeth,fish-fish,people-people,Chinese-Chinese,Japanese-Japanese不可数名词的复数就是原型: paper,juice,water,milk,rice,tea(二)名词的格(1)有生命的东西的名词所有格:a)单数后加’s 如: Lucy’s ruler my father’s shirtb)以s 结尾的复数名词后加’如: his friends’ bagsc)不以s 结尾的复数后加’s children’s shoes并列名词中,如果把’s加在最后一个名词后,表示共有,如:Tom and Mike’s car 汤姆和迈克共有的小汽车要表示所有物不是共有的,应分别在并列名词后加’sTom’s and Mike’s cars 汤姆和麦克各自的小汽车(2)表示无生命东西的名词通常用“ of +名词”来表示所有关系:如:a picture of the classroom a map of China小学生的英语知识篇2.冠词:不定冠词,定冠词种类:(1)不定冠词:a / an元音开头的可数名词前用an :an egg / an apple / an orange / an eraser / an answer / an ID card / an alarm clock / an actor / an actress / an e-mail / an address / an event / an example / an opera / an houran old man / an interesting book / an exciting sport / an action movie / an art lesson /(2)定冠词:the定冠词的用法:(1)特指某(些)人或某(些)物: The ruler is on the desk.(2)复述上文提到的人或物:He has a sweater.The sweater is new.(3)谈话双方都知道的人或物:The boys aren’t at school.(4)在序数词前:John’s b irthday is February the second.(5)用于固定词组中: in the morning / afternoon / evening不用冠词的情况:(1)专有名词前:China is a big country.(2)名词前有定语:this ,that ,my ,your ,some,any ,no 等:This is my baseball.(3)复数名词表示一类人和事:Monkeys can’t swim.They are teachers.(4)在节日,日期,月份,季节前:T oday is Christmas Day.It’s Sunday.(5)一日三餐前:We have breakfast at 6:30.(6)球类棋类运动前:They often play football after class.He plays chess at home.但乐器前要用定冠词:I play the guitar very well.(7)学科名称前:My favorite subject is music.(8)在称呼或头衔的名词前:This is Mr Li.(9)固定词组中:at noon at night by bus小学生的'英语知识篇3一、定义名词是表示人或事物名称的词。


英语词法全解英语中的词可以根据词义、语法功能和形式特征分为十大类,即名词(noun)、代词(pronoun)、形容词(adjective)、副词(adverb)、动词(verb)、数词(numeral)、冠词(article)、介词(preposition)、连词(conjunctions)和感叹词(interjection)。
一、名词(n.) 表示人、事物或抽象概念的名称的词(一)名词的分类名词分为普通名词和专有名词,其中普通名词包括可数名词和不可数名词,可数名词可用作单数,也可用作复数。
可数名词包括个体名词(表示一类人或物的个体。
如:boy,desk,cat,window)和集体名词(由若干个体组成的集合体。
如:family,class,police)。
不可数名词包括物质名词(表示无法分为个体的实物。
如:water,paper,silk,money)和抽象名词(表示性质、行为、状态、感情或其它抽象概念。
如:work,happiness,music,difficulty,housework)专有名词表示个人、地方、机构、组织等。
如:Tom,the Great Wall,the Spring Festival,France,the United States)(二)名词的数1.可数名词有单数和复数两种形式,其复数形式的构成主要有以下几种:(1)一般情况下,在词尾加s。
E.g.:book——books,dog——dogs,pen——pens,boy——boys以清辅音结尾的名词后的s的读音为[s),以浊辅音和元音结尾名词后的s读音为〔z〕。
(2)以s,x,ch,sh结尾的词名词变复数时,要在词尾加es。
e.g. beach——beaches,brush——brushes,bus——buses,box—boxes(es读音为〔iz〕(3)以“辅音字母+y”结尾的名词,先变y为i,再加es。
e.g. city——cities,family——families,documentary——documentaries,country——countries,strawberry——strawberries(ies读音为[iz]) (注:以“元音字母+y”结尾的词,直接在词尾加-s。

英语名词的数:定义、分类、用法和特点摘要英语名词的数是指名词表示一个或多个人或事物的形式。
英语名词分为可数名词和不可数名词两大类。
可数名词有单数和复数两种形式,不可数名词只有单数形式。
本文介绍了可数名词和不可数名词的定义、分类、用法和特点,并举例说明了可数名词的单数变复数的规则和不规则变化,以及不可数名词的量化表示方法。
本文还介绍了名词所有格的形式和用法,以及一些特殊情况下的注意事项。
一、可数名词和不可数名词1.1 可数名词可数名词是指可以用数目计算的名词,表示一个或多个人或事物。
可数名词有单数和复数两种形式,单数形式表示一个,复数形式表示多个。
例如:a book 一本书two books 两本书a dog 一只狗three dogs 三只狗可数名词的单数形式可以和不定冠词a/an连用,也可以和one, two, three等基数词连用。
例如:a pen 一支笔an apple 一个苹果one car 一辆车two cats 两只猫1.2 不可数名词不可数名词是指不能用数目计算的名词,表示一种物质、品质、状态或抽象概念。
不可数名词只有单数形式,没有复数形式。
例如:water 水milk 牛奶air 空气beauty 美丽love 爱health 健康music 音乐不可数名词不能和不定冠词a/an连用,也不能和one, two, three等基数词连用。
例如:a water 错误an air 错误one love 错误two musics 错误二、可数名词的单复数变化2.1 规则变化大多数可数名词的复数形式是在其单数形式后面加-s或-es构成。
具体规则如下:2.1.1 在词尾直接加-s一般情况下,在可数名词的单数形式后面直接加-s就可以构成复数形式。
例如:单数复数book bookstree treescap capsdesk desksworker workers2.1.2 在词尾加-es以下几种情况下,在可数名词的单数形式后面加-es来构成复数形式:(1) 名词以s, x, ch, sh或z结尾的,在其后加-es例如:单数复数glass glassesbox boxeswatch watchesbrush brushestopaz topazes(2) 名词以辅音字母加o结尾的,在其后加-es例如:单数复数hero heroespotato potatoestomato tomatoesecho echoesvolcano volcanoes(3) 名词以辅音字母加y结尾的,把y改为i,再加-es例如:单数复数story storiesbaby babiescity citiesfactory factorieslady ladies2.1.3 在词尾加-ves以下几种情况下,在可数名词的单数形式后面加-ves来构成复数形式:(1) 名词以f或fe结尾的,把f或fe变为v,再加-es例如:单数复数self selveswife wivesknife kniveslife liveswolf wolves(2) 名词以o结尾的,如果是表示动物的名词,一般在其后加-ves例如:单数复数buffalo buffaloescalf calveself elveshalf halvesloaf loaves2.2 不规则变化有些可数名词的复数形式是不规则的,需要单独记忆。

there be句型some和any用法
“There be”句型是英语中常用的一种句型,表示存在关系,其中“some”和“any”是常用的量词短语,用于表示数量。
“Some”通常用于肯定句中,表示“一些”,可以用于可数名词或不可数名词之前。
例如,“There are some apples on the table.”(桌子上有一些苹果。
)“There is some water in the bottle.”(瓶子里有一些水。
)
“Any”通常用于否定句或疑问句中,表示“一些”,也可以用于可数名词或不可数名词之前。
例如,“There aren’t any books on the shelf.”(书架上没有书。
)“Are there any apples on the table?”(桌子上还有苹果吗?)“Is there any water in the bottle?”(瓶子里还有水吗?)
需要注意的是,“some”也可以用于表示请求、建议或请求的疑问句中,表示希望得到肯定回答。
例如,“Can you lend me some money?”(你能借给我一些钱吗?)“Could you give me some advice?”(你能给我一些建议吗?)“Will you share some ideas with me?”(你能和我分享一些想法吗?)
综上所述,“some”通常用于肯定句,“any”通常用于否定句、疑问句,但在表示请求、建议或请求的疑问句中,“some”也可以使用。
在选择使用“some”或“any”时,应该根据句子的时态、主语的人称和数进行判断。

名词的复数及some/any的用法语法点拨1. 名词的复数名词分可数名词和不可数名词,不可数名词没有复数形式,通常表示量的多少,可以用much,a little,some,any及a lot of修饰。
许多物质名词属于不可数名词,如milk,water,bread,meat,rice等。
可数名词有复数形式,具体变化规则如下:1) 一般情况在词尾加–s例如:map-mapsboy-boys girl-girls pen-pens bag-bagscar-cars2) 以s, sh, ch, x等结尾的词加–es例如:bus-buses watch-watches box-boxes brush-brushes3) 以辅音字母+y结尾的词,变y 为i再加-es例如:baby-babies city-cities country-countries但以元音字母加-y 结尾的名词变复数时,直接加-s。
如:monkey-monkeys holiday-holidays以o结尾的部分名词,变复数时加-es例如:photo-photos tomato—tomatoes hero- heroes Negro-Negroes 可以总结为“黑人英雄吃西红柿马铃薯”其余的一般直接加“s”,例如:piano-pianos radio-radioszoo-zoos;potato- potatoes4)以f或fe 结尾的名词变复数时:改f, fe 为ves,例如:half—halves knife—knives leaf—leaves wolf—wolves wife—wives life—lives thief—thieves;2.名词变复数的不规则变化1) child—children , foot—feet, tooth—teeth mouse—mice, man—-men ,woman—women注意:由一个词加man 或woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men 和-women,如an Englishman,two Englishmen。

小学英语知识点汇总—名词(通用版)1. 单数变复数1.1 规则变化1.1 单数变复数规则变化在英语中,将名词从单数形式变为复数形式是一项基本的语法规则。
下面是一些常见的规则变化:1.名词以辅音字母+y结尾,将y变为i,再加es。
–例如:baby -> babies, city -> cities2.名词以“o”结尾,通常加es,但也有例外。
–例如:potato -> potatoes, tomato -> tomatoes3.名词以“f”或“fe”结尾,通常将f或fe变为ves。
–例如:leaf -> leaves, knife -> knives4.名词以“s”,“sh”,“ch”,“x”或“z”结尾,加es。
–例如:bus -> buses, brush -> brushes, watch -> watches5.名词以“man”或“woman”结尾,将man变为men,woman变为women。
–例如:man -> men, woman -> women6.有些名词没有规则变化,直接加s。
–例如:book -> books, dog -> dogs下表是一些常见名词的单数变复数规则变化示例:单数形式复数形式baby babiescity citiespotato potatoestomato tomatoesleaf leavesknife knivesbus busesbrush brusheswatch watchesman men单数形式复数形式woman womenbook booksdog dogs通过了解这些规则,学生们可以更好地掌握将名词从单数形式变为复数形式的技巧。
1.2 不规则变化1.2 不规则变化不规则名词的复数形式不遵循一般的规则,需要记忆和熟练掌握。
以下是一些常见的不规则名词复数形式的示例:1.man(男人):men(男人们)2.woman(女人):women(女人们)3.child(孩子):children(孩子们)4.tooth(牙齿):teeth(牙齿们)5.foot(脚):feet(脚们)6.mouse(老鼠):mice(老鼠们)7.goose(鹅):geese(鹅们)8.sheep(羊):sheep(羊们)需要注意的是,有些不规则名词的复数形式与其单数形式相同,例如sheep。
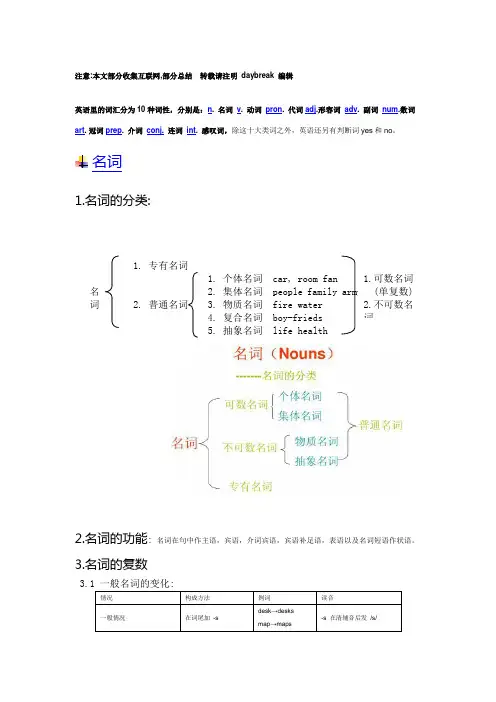
注意:本文部分收集互联网,部分总结转载请注明daybreak 编辑英语里的词汇分为10种词性,分别是:n. 名词v. 动词pron. 代词adj.形容词adv. 副词num.数词art. 冠词prep. 介词conj.连词int. 感叹词,除这十大类词之外,英语还另有判断词yes和no。
名词1.名词的分类:2.名词的功能:名词在句中作主语,宾语,介词宾语,宾语补足语,表语以及名词短语作状语。
3.名词的复数3.1 一般名词的变化:情况构成方法例词读音一般情况在词尾加-sdesk→desksmap→maps -s 在清辅音后发/s/1.专有名词2.普通名词1.个体名词 car, room fan2.集体名词 people family army3.物质名词 fire water4.复合名词 boy-frieds5.抽象名词 life health名词1.可数名词 (单复数) 2.不可数名词ex: tooth→teeth(牙)mouse—mice 老鼠ox—oxen 公牛goose—geese 鹅单复数同形ex: deer sheep fish chinese japanese swiss means species3.3 集体名词以单数名词出现,实际为复数ex: cattle police people 不能用a+以上名词ok: a person a policeman ahead of cattle a english a chinese a french 3.4 ex: maths politics physics 都为单数名词(虽然以s结尾)ex: news 为不可数名词3.5 有两部分构成的东西ex: glasses clothes trousers裤子通常可以用数量词表示: a pair of glasses3.6 名词的复数形式另有引申意思ex: foods goods3.7 定语名词的复数: ex: sports meeting students reading-room talks table数词+名词一般名词要单数: two-dozen eggs a ten-mile walk two-hundred trees4.名词所有格1.一般的,所有格后面为’s 结尾为es 或s 的单词 直接加’2.名词的双重所有格公式: “a,an,this,that +名词+of +名词性物主代词”动词3.8不可数名词1.物质名词a 当物质名词转换成个体名词时为可数b 当物质名词表示该物质的种类 名词可数c 当物质名词表示份数 名词可数 2.抽象名词 有时候可数ex fourfreedoms a piece of advice代词分类:1.人称代词单数单数复数复数主格宾格主格宾格第一人称I me we us第二人称you you you you他he him they them她she her they them它it it they them不定one one ones ones物主代词我的你的他的她的它的我们的你们的他们的形容词性物主代词my your his her its our your their 名词性物主代词mine yours his hers its ours yours theirs 指示代词this这that那these这些those 那些it,such,some 可以做主语,宾语,表语,定语等反身代词第一人称第二人称第三人称第三人称第三人称单数myself yourself himself herself itself复数ourselves yourselvesthemselves themselvesthemselves疑问代词who谁what什么which哪个whose用法:疑问代词用于特殊疑问句中,疑问代词一般放在句子的最前面,在句中可用作主语,宾语,表语,定语不定代词all,any,another,both,each,every,either,every,few,little,many,much,no,none,neither,one,other,some以及由some,any,no,every 和body,one,thing 构成的复合词。
数量限定词一、英文中的数量词常用的有:1、只与可数名词连用、只接单数的:one each every one boy each boy every boy2、只接复数的:two,three,etc. both a couple of a pair of a few few several many a number of two boys both boys a couple of boys a pair of glasses a few boys few boys several boys many boys a number of boys3、只与不可数名词连用:a little little much a great deal ofa large amount of a little water little water much water a great deal of water a large amount of water4、与可数名词复数或不与可数名词连用均可:not any some a lot of lots of plenty of most all not any boys, not any water some boys, some water a lot of boys, a lot of water lots of boys, lots of water plenty of boys, plenty of water most boys, most water all boys, all water二、数量词 a few,few / a little,little1、与名词搭配:a few,few后面只能接可数名词复数;而a little,little后面只能接不可数名词。
例如:a few days,few boys a little water,little water 2、肯定/否定之别:a few,a little意思是肯定的,相当于some,表示“有一些”。
带有量词的英语单复数规则
在英语中,有许多带有量词的名词需要根据数量来决定其单复数形式。
以下是一些常见的带有量词的名词及其单复数规则:
1. 不可数名词(uncountable nouns)通常没有单复数形式,例如:water(水)、information(信息)等。
2. 可数名词的单复数形式通常是通过在名词后面加上不同的量词来表示的。
例如:
一些(some)、许多(many)、任何(any)等不定量词通常用于单数形式,例如:some books(一些书)、many students(许多学生)、any help(任何帮助)等。
一些(some)、许多(many)等不定量词通常用于复数形式,例如:some apples(一些苹果)、many cars(许多汽车)等。
具体的数量词(如one, two, three等)通常用于单数形式,例如:one book(一本书)、two apples(两个苹果)等。
一些特殊的量词(如all, both, each等)通常用于单数形式,例如:all students(所有学生)、both apples(两个苹果)、each student(每个学生)等。
需要注意的是,有些量词的单复数形式是相同的,例如:a lot of(许多)、lots of(许多)等,它们既可以用于单数形
式,也可以用于复数形式。
1七上语法二 名词单复数单数名词前有a/an 、the 或物主代词,如:a book 、the book 、his book1、一般情况,加s ,例如:bags2、以s 、sh 、x 、ch 结尾,加es, 例如:boxes, classes, watches规则变化 3、以 f 、fe 、结尾,把f 、fe 改为v 加es, 例如:shelf →shelves, knife →knives 可数 4、以辅音+y 结尾,把y 改为i, 加es, 例如:baby →babies5、以o 结尾,一般加s, 例如:pianos 、photos特殊加es, 例如:tomatoes 、potatoes1、单复数词形:sheep 、Chinese 、Japanese复数 不规则变化 2、复数名词:clothes 、people 、police 、family3、特殊变化:man →men ,woman →women ,child →children ,foot →feet ,名词 tooth →teeth ,policeman →policemen前面可用many (许多)、a lot of/lots of (许多)、some (一些)、a few (一 点)1、 没有复数形式2、 前不加a/an 、数字、many 、a few ,后不加s不可数 3、前可以加some 、any 、a lot of/much 、a little4、表数量用量词加of 词组:a cup of ice cream ,two cups of ice cream5、常用不可数名词:food 、dessert 、orange 、ice cream 、salad 、chicken 、fruit 、soccer 、tennis 、 ping-pong 、breakfast 、lunch 、dinner 、help 、work 、homework 、time 、Chinese 、Japanese 、English 练习一、写出下列词的复数形式baby potatoknife photo Chinese hamburger case key watch name strawberry tomato dollar orange people family boy classchild man this thatIshe busmonth Japanese二、划出下面单词中的不可数名词star 、dessert 、sock 、dollar 、help 、month 、art 、meat 、ice-cream 、dictionary 、card 、club 、fruit 、food 、sister 、chicken 、CD 、homework 、English 、runner 、science 、people 、collection 、bread 、sport 、baseball 、vegetable 、soccer 三、根据所给词的适当形式填空 1.There are fifteen (sheep). 2.The baby has two (tooth) now. 3.These two (child) are Jane ’s brothers. 4.Those (leaf) on the tree are yellow.- 2 -5.Let ’s have some (strawberry).6.We have some (chicken) for lunch.7.Jim doesn ’t have any (food) for breakfast.8.These are two (man) and those are three (women). 9.These are some (zoo) and those are some (class). 10.That is some (salad) on the table. 四、将下列句子变成复数形式 1.This is a bus.2.She has a nice dress.3.A musician has a watch on her hand.4.You are a Chinese.5.The girl likes salad.6.The running star wants to eat healthy food.7.A photo is on the wall.8.That is a banana.9.It is an action movie. 10.I am a student.。
名词复数的规则一、名词的数1、名词分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词——可以数的名词不可数名词——数不清(没有复数以下为不可数名词:①流动的液体:drink milk tea water orange juice coke coffee porridge②一些食物:food rice bread fruit cake③肉类:meat fish pork mutton beef④其他:rice, hair, money, …(金、木、水、火、土;米、面、肉、食、布,都是不可数gold, wood, water, fire, earth; rice, flour, meat, food, cloth2、可数名词与不定冠词a(an连用有复数的形式,不可数名词不能与不定冠词a(an连用,没有复数形式many+可数名词复数much/a little+不可数名词some, any , a lot of (lots of 都可以修饰修饰不可数名词。
其中some 一般用于肯定句中,any用于否定句和疑问句中,但是在W ould you like…句型中要用some,不能用any.W ould you like some te a?Would you like some drink?3、可数名词可以直接用数词来修饰对可数名词的数量提问用How many:例如:How many _________(fish are there in the river?对不可数名词的数量提问用How much例如:How much mutton do you have?英语中名词可分为可数名词和不可数名词。
可数名词在应用时有单数和复数形式。
表示一个用单数,表示两个或两个以上用复数。
复数名词的构成分为规则变化和不规则变化。
情况构成方法读音例词①一般情况加-s 1.清辅音后读/s/; map-maps2.浊辅音和元音后读/z/; bag-bagscar-cars②以s, sh, ch, x等结尾的词加-es读/iz/bus-buseswatch-watches③以ce,se,ze, (dge等结尾加-s读/iz/license-licenses④以辅音字母+y结尾变y 为i 再加es读/z/baby---babies三.规则变化:1 一般在名词词尾加s,map—maps地图 bird—birds鸟orange—oranges 桔子bike—bikes自行车;2 以s, x, ch, sh结尾的名词加es,box—boxes盒子class—classes班级,watch—watches手表 dish-dishes 盘,碟子,餐具;3 以O结尾的名词后面加s(无生命或es (有生命无生命:photo—photos相片 radio—radios收音机zoo—zoos动物园有生命:tomato—tomatoes西红柿 potato—potatoes土豆hero-----heroes英雄Negro—Negroes 黑人4 以辅音字母加y结尾的名词,变y为i+esbaby—babies婴儿 family—families家庭;以元音字母加y结尾的名词直接加sboy—boys男孩toy—toys 玩具;day-----days 日子5 以fe或f结尾的名词,把fe或f变为vesknife—knives小刀wife—wives妻子thief----thieves 小偷leaf—leaves树叶life—lives 生命shelf----shelves 书架四、名词复数的不规则变化1child---children foot---feet tooth---teeth goose----geesemouse---mice man---men woman---womenwoman teacher-----women teachers 女教师注意:与man 和woman构成的合成词,其复数形式也是-men 和-women。
高考英语常用语法图解一、名词I. 名词的种类:II. 名词的数:1. 规则名词的复数形式:名词的复数形式,一般在单数形式后面加-s或-es。
现将构成方法与读音规则列表如下:2. 不规则名词复数:英语里有些名词的复数形式是不规则的,现归纳如下:III. 名词的所有格:名词在句中表示所有关系的语法形式叫做名词所有格。
所有格分两种:一是名词词尾加’s构成,二是由介词of加名词构成。
前者多表示有生命的东西,后者多表示无生命的东西。
1. ’s所有格的构成:2. ’s所有格的用法:3. of所有格的用法:用于无生命的东西:the legs of the chair, the cover of the book用于有生命的东西,尤其是有较长定语时:the classrooms of the first-year students用于名词化的词:the struggle of the oppressed二、冠词:冠词分为不定冠词(a, an),定冠词(the),和零冠词。
I. 不定冠词的用法:II. 定冠词的用法:III. 零冠词的用法:三、代词:1. one, some与any:1) one可以泛指任何人,也可特指,复数为ones。
some多用于肯定句,any多用于疑问句和否定句。
One should learn to think of others. / Have you any bookmarks? N o, I don’t have any bookmarks.I have some questions to ask.2) some可用于疑问句中,表示盼望得到肯定的答复,或者表示建议,请求等。
W ould you like some bananas? Could you give me some money?3) some 和any修饰可数名词单数时,some表示某个,any表示任何一个。
I have read this article in some magazine. Please correct the mistakes, if any.4) some和数词连用表示“大约”,any可与比较级连用表示程度。
在英语中,我们使用一些特定的短语来表示数量。
以下是一些常见的数量词短语:1."a" 用于单数可数名词前面,例如"a book"(一本书)。
2."an" 用于以元音音素开头的单词前面,例如"an hour"(一个小时)。
3."some" 用于肯定句中,表示“一些”,例如"I have some books"(我有一些书)。
4."any" 用于否定句或疑问句中,表示“一些”,例如"Do you haveany books?"(你有书吗?)。
5."no" 用于表示“没有”,例如"I have no books"(我没有书)。
6."many" 用于肯定句中,表示“许多”,例如"I have manybooks"(我有很多书)。
7."most" 用于肯定句中,表示“大部分”,例如"Most people liketo read books"(大部分人喜欢读书)。
8."few" 用于否定句中,表示“很少”,例如"Few people like toread books"(很少有人喜欢读书)。
9."little" 用于否定句中,表示“几乎没有”,例如"Little water isleft in the bottle"(瓶子里几乎没有水了)。
10."all" 用于肯定句中,表示“全部”,例如"All the books are here"(所有的书都在这里)。
名词的单数和复数单数复数变化规律(a) one pen two pensone apple three applesone cup four cupsone elephant five elephantsone American two Americans大部分名词的复数形式是在词尾加s.(b) baby babiescity citiesstory stories 以“辅音+-y”结尾的名词,变复数时要变y为i,再加-es.(c) boy boyskey keys 以“元音+-y”结尾的名词,变复数时直接在词尾加-s.(d) wife wivesthief thievesleaf leaves 以-fe或-f结尾的名词,变复数时要变fe 或f为v,再加-es.(e) dish dishesmatch matches watch watches class classes 以-sh, -ch, -ss, -x 结尾的名词,变复数时在词尾加-es,读作/ iz /.(f) tomato tomatoespotato potatoeszoo zoosradio radios 以“辅音+-o”结尾的名词,变复数时在词尾加-es.以“元音+-0”结尾的名词,变复数时在词尾加-s.(g) deer deersheep sheep单数与复数形式一样(h) man men child childrenfoot feet tooth teethgoose geese mouse miceox oxen不规则名词单数变复数A. Write out the plural forms.写出下列名词的复数形式。
1) box boxes 2) tomato3) zoo 4) pen ______5) baby 6) key7) city ______ 8) wife ______9) dish _______ 10) thief _______B. Choose the correct nouns and fill in the blanks with their plurals.从列表中选择恰当的名词,然后用其正确的复数形式完成下列句子。
child foot mouse tooth fish man sheep woman1) A dentist fixes teeth2) Cats like to catch3) Baby lambs become4) There are many different kinds of in the sea.5) We put shoes on our6) In your culture, do and women have the same freedoms?7) Some movies are very violent. They are not good for 8) Are men and very different?C. Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the nouns. Use “… of…”when necessary.用所给名词的正确形式填空,必要的时候用“…of…”结构。
(1) I can see two __________ (bus) on the road.(2) How many __________ (mango) are there in the fridge?(3) Paul is drinking two ______________ (tin, cola).(4) Please give me three _________________ (slice, bread).(5) The police caught two ________ (thief) last night.(6) There are many __________ (country) in Asia.(7) My father told us some _______ (story) before we went to bed.(8) There are two _________________ (bowl, soup) on the table.(9) I want to have four ___________________ (plate, fried rice).A. Write out the plural forms.写出下列名词的复数形式。
1) photo photos 2) watch3) key 4) leaf ______5) story 6) mouse7) foot ______ 8) potato ______9) sheep _______ 10) brush _______B. Fill in the blanks with the correct forms of the nouns.用所给名词的正确形式填空。
(1) There are many __________ (packet) of chips.(2) How much __________ (peanut butter) is there in the fridge?(3) Paul is eating two ______________ (longan).(4) Please give me three _________________ (glass) of juice.(5) Two _______ (thief) were caught by two brave _______ (man).(6) There are many __________ (city) in China.(7) My father told us a story about three _________ (mouse).(8) She picked a few beautiful__________ (leaf) on the ground.(9) There are a lot of _________ (sheep) eating grass.量词(1)常见的表示数量的限定词有: some, any, enough, many, much, a few, a little, few, little等;(2)some 和any表示一些,位于复数名词或不可数名词之前。
some通常用于肯定句,any主要用于否定句或疑问句中。
e.g. There’s some milk in the fridge.We haven’t got any milk in the fridge.当表示主动帮忙和请求时,通常用some。
e.g. Would you like some coffee?Can you give me some tea?(3)a lot of/many/much/plenty of 表示大量的,多的;a few/a little表示少量;few/little表示否定概念,几乎没有;enough表示足够。
(4)many, too many(太多), a few(一些), few(几乎没有)用来修饰可数名词复数;much, too much(太多), a little(一些), little(几乎没有)用来修饰不可数名词;a lot of, plenty of, enough, some, any既可以修饰可数,也可以修饰不可数名词。
e.g. There are too many carrots but there are only a few peas.There is too much salt but there is only a little sugar.There are a lot of biscuits and plenty of milk.There is enough food but there are not enough drinks.(5)常常会用到many, much, few, little的比较级与最高级:much/many more mostlittle less leastfew fewer feweste.g. I have many clothes.Sam has more clothes than me.Ken has the most clothes of us allA. Circle the correct words.(1) I have a little (water/books).(2) Ryan’s cat has too much (hair/fleas).(3) There are many (people/orange juice) in the kitchen.(4) Angel has too many (milk/dresses) in the closet.(5) There are a few (children/paper) in the room.(6) We have little (dollars/money). It’s not enough for lunch.(7) There is not much (bread/apples) on the table.(8) They have too much (pets/heat) in their room.(9) There are (a little/plenty of) things to learn in the new school. Ineed (a little/a few) help.(10) There are quite (a little/a few) restaurants nearby. We have (llittle/enough) choices.(11) There is (a little/plenty of) rain this summer. Some places are flooded.(12) We have invited (plenty of/a little) guests for dinner. Please makesure we have prepared (a little/enough) food.(13) There is (a few/ plenty of) work to do this week. I will have a fewdays off next week.(14) Your diet is not balanced. You do not have (enough/a little)vegetables.(15) I am not ready yet. I still need (a few/a little) minutes to get dressed.(16) I want to play basket ball, but I have (a little/a few) homework todo.B. Fill in the blanks with the given words .many much a lot of too many too much enough(1) I don’t have money. Please buy me lunch.(2) Lucy does not have friends. She has spent time at work.(3) There is water in the bottle. You can have a drink.(4) There are people on the MTR. We are going to go there bytaxi instead.(5) You have sweets. Can I have one?(6) The bus was really slow. It stopped at stations.(7) There are shoes in your closet.(8) Harry has read books. Will she make progress in the coming test?(9) Ivy has bad teeth because she ate sugar.(10) We have flour to make cakes.(11) My father had toys when he was young.(12) She doesn’t need our help. She has food to eat now.(13) We don’t have stamps left. We have to buy some.C. Rearrange the words to form meaningful sentences. Add suitable punctuations.(1) a / for / vegetables / have / I / few / lunch(2) many / Kelvin / has / t-shirt / too(3) the / street / there / much / too / noise / in / is(4) meat / have / we / a little / only(5) this / are / many / wildlife park / animals / there / in(6) a / are / chairs / few / there // have / a / please / seat (two sentences)(7) few / I / to / have / shoes / wear(8) little / is / air / there // the / open/ please/ windowD. Read the passage and fill in the blanks with the correct forms of thegiven words.The weather is very nice today. The children go on a picnic in the countryside. They are enjoying their food and drinks now.Billy brings a big food basket. She has (1) (many/much) chicken wings and sandwiches than the other children. Brian likes soft drinks very much. He has (2) (many/much) Coke of all. But he has (3) (little/few) fresh fruit of all. He doesn’t like fruit. Adahas (4) (little/few) vegetables and (5) (little/few) soup than Cherry. But she has (6) (much/many) fried rice than her. They share their food together. Fred is the most unhealthy boy. Heeats (7) (much/many) meat and (8) (few/little) vegetables.A. Fill in the blanks with the given words.some too many too much a lot of a few a little(1)There is soft sand on the beach. I want to lie on it.(2)Paul has shoes. He can’t find a place to store them.(3)Mr Lee has money but he doesn’t spend it.(4)There are only pencils in the pencil holder.(5)I need salt so I am going to the grocery store.(6)If you drink coffee, you will feel unwell.B. Read the dialogue and finish the following dialogue with ‘a lot of’,‘not enough’, ‘some’, or ‘any’.Sam: Do you have (1) time, Polly?Polly: Oh, yes. I think you have (2) problems.Sam: Yes, I have (3) homework to do this week but I want to go hiking with my friends. So I am afraid I have (4) time to finishit.Polly: Then do you need (5) help?Sam: Yes, please. I have to find (6) pictures for my project butI only found (7) of them. That is (8) . Can youhelp me to find (9) more on the Internet?Polly: All right, but you have to help me back (10) other time. Sam: No problem。