Chapter 15 Practice Tests - Central Michigan University
- 格式:doc
- 大小:114.50 KB
- 文档页数:16
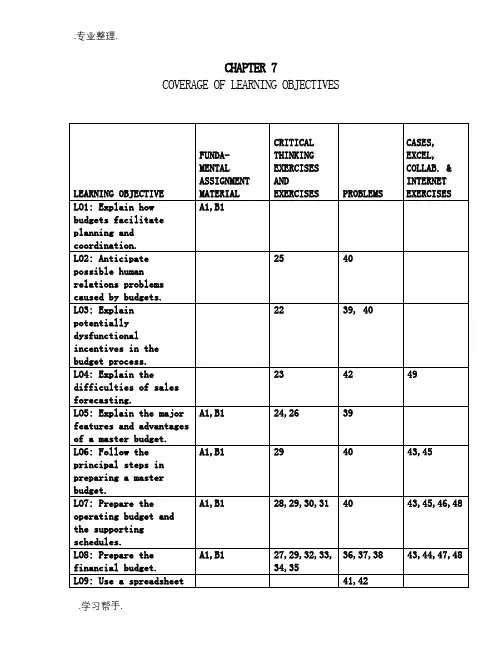
CHAPTER 7 COVERAGE OF LEARNING OBJECTIVESIntroduction to Budgets and Preparing the Master Budget7-A1 (60-90 min.)1. Exhibit IRAPIDBUY ELECTRONICS, INC.Mall of America StoreBudgeted Income StatementFor the Three Months Ending August 31, 20X8Sales $300,000 Cost of goods sold (.62 × $300,000) 186,000 Gross profit $114,000 Operating expenses:Salaries, wages, commissions $60,000Other expenses 12,000Depreciation 1,500Rent, taxes and other fixed expenses 33,000 106,500 Income from operations. $ 7,500 Interest expense* 1,338 Net income $ 6,162* See schedule g for calculation of interest.RAPIDBUY ELECTRONICS, INC.Mall of America StoreCash BudgetFor the Three Months Ending August 31, 20X8June July August Beginning cash balance $ 5,800 $ 5,600 $ 5,079 Minimum cash balance desired 5,000 5,000 5,000 (a) Available cash balance $ 800 $ 600 $ 79Cash receipts & disbursements:Collections from customers(schedule b) $ 75,200 $121,400 $ 90,800 Payments for merchandise(schedule d) (86,800) (49,600) (49,600) Fixtures (purchased in May) (11,000) - - Payments for operatingexpenses (schedule f) (44,600) (30,200) (30,200) (b) Net cash receipts & disbursements $(67,200) $ 41,600 $ 11,000Excess (deficiency) of cash beforefinancing (a + b) (66,400) 42,200 11,079 Financing:Borrowing, at beginning of period $ 67,000$ - $ - Repayment, at end of period - (41,000) (10,000) Interest, 10% per annum - (1,121)* (217)* (c) Total cash increase (decrease)from financing $ 67,000 $(42,121) $(10,217) (d) Ending cash balance (beginningbalance + b + c) $ 5,600 $ 5,079 $ 5,862 * See schedule gRAPIDBUY ELECTRONICS, INC.Mall of America StoreBudgeted Balance SheetAugust 31, 20X8Assets Liabilities and Owners’ EquityCash (Exhibit II) $ 5,862 Accounts payable $ 37,200 Accounts receivable* 86,400 Notes payable 16,000** Merchandise inventory 37,200 Total current liabilities $ 53,200 Total current assets $129,462Net fixed assets: Owners' equity:$33,600 less $102,200 plus netdepreciation of $1,500 32,100 income of $6,162 108,362 Total assets $161,562 Total equities $161,562*July sales, 20% × 90% × $80,000$ 14,400August sales, 100% × 90% × $80,000 72,000Accounts receivable $86,400** See schedule gJune July August Total Schedule a: Sales BudgetCredit sales (90%) $126,000 $72,000 $72,000 $270,000Cash sales (10%) 14,000 8,000 8,000 30,000Total sales (to Exhibit I) $140,000 $80,000 $80,000 $300,000Schedule b: Cash CollectionsJune July AugustCash sales $ 14,000 $ 8,000 $ 8,000On accounts receivable from:April sales 10,800 - -May sales 50,400 12,600 -June sales - 100,800 25,200July sales - - 57,600Total collections (to Exhibit II) $75,200 $121,400 $90,800Schedule c: Purchases Budget May June July August Desired purchases:62% × next month's sales$86,800 $49,600 $49,600 $37,200 Schedule d: Disbursements for Purchases June July August Last month's purchases (to Exhibit II) $86,800 $49,600 $49,600Other required items related to purchasesAccounts payable, August 31, 2008(62% × September sales - to Exhibit III) $37,200 Cost of goods sold (to Exhibit I) $86,800 $49,600 $49,600Schedule e: Operating Expense BudgetJune July August Total Salaries, wages, commissions $28,000 $16,000 $16,000 $60,000 Other Variable expenses 5,600 3,200 3,200 12,000 Fixed expenses 11,000 11,000 11,000 33,000 Depreciation 500 500 500 1,500 Total operating expenses $45,100 $30,700 $30,700 $106,500Schedule f: Payments for Operating ExpensesJune July August Variable expenses $33,600 $19,200 $19,200 Fixed expenses 11,000 11,000 11,000 Total payments for operating expenses $44,600 $30,200 $30,200Schedule g: Interest calculationsJune July August Beginning balance $67,000 $67,558 $26,000 Monthly interest expense @ 10% 558 563 217 Ending balance before repayment $67,558 68,121 26,217 Principal repayment (fromstatement of receipts and disbursements) (41,000) (10,000) Interest payment (1,121) (217) Ending balance $26,000 $16,0002. This is an example of the classic short-term, self-liquidating loan.The need for such a loan often arises because of the seasonal natureof a business. The basic source of cash is proceeds from sales tocustomers. In times of peak sales, there is a lag between the saleand the collection of the cash, yet the payroll and suppliers must bepaid in cash right away. When the cash is collected, it in turn maybe used to repay the loan. The amount of the loan and the timing ofthe repayment are heavily dependent on the credit terms that pertain to both the purchasing and selling functions of the business.7-B1 (60-120 min.) $ refers to Australian dollars.1. See Exhibits I, II, and III and supporting schedules a, b, c, d.2. The cash budget and balance sheet clearly show the benefits ofmoving to just-in-time purchasing (though the transition wouldrarely be accomplished as easily as this example suggests).However, the company would be no better off if it left much ofits capital tied up in cash -- it has merely substituted oneasset for another. At a minimum, the excess cash should be in aninterest bearing account -- the interest earned or forgone is oneof the costs of inventory.Schedule a: Sales Budget January February MarchTotal sales (100% on credit) $248,000 $280,000 $152,000Schedule b: Cash Collections60% of current month's sales $148,800 $168,000 $91,20030% of previous month's sales 30,000 74,400 84,00010% of second previous month's sales 10,000 10,000 24,800Total collections $188,800 $252,400 $200,000December January February March Schedule c: Purchases BudgetDesired ending inventory $156,200 $ 24,000* $ 24,000 $ 24,000 Cost of goods sold 50,000 124,000 140,000 76,000 Total needed $206,200 $148,000 $164,000 $100,000 Beginning inventory 64,000 156,200 32,200 24,000 Purchases $142,200$ - $131,800 $ 76,000* Actual ending January (and beginning February) inventory level is$32,200, as inventory levels are drawn down toward desired level of$24,000.Schedule d: Disbursements for Purchases100% of previous month's purchases $142,200 $ - $131,800 March 31 accounts payable $76,000WALLABY KITECash BudgetFor the Three Months Ending March 31, 20X2January February MarchCash balance, beginning $ 20,000 $ 20,400 $138,767 Minimum cash balance desired 20,000 20,000 20,000 (a) Available cash balance 0 400 118,767 Cash receipts and disbursements:Collections from customers(Schedule b) 188,800 252,400 200,000 Payments for merchandise(Schedule d) (142,200) - (131,800) Rent (32,200) (1,000) (1,000) Wages and salaries (60,000) (60,000) (60,000) Miscellaneous expenses (10,000) (10,000) (10,000) Dividends (6,000) -Purchase of fixtures - - (12,000) (b) Net cash receipts & disbursements $ (61,600) $181,400 $ (14,800)Excess (deficiency) of cashbefore financing (a + b) $ (61,600) $181,800 $103,967 Financing:Borrowing, at beginning of period $ 62,000$ - $ - Repayment, at end of period - (62,000)Simple interest, 10% monthly - (1,033)(c) Total cash increase (decrease)from financing $ 62,000 $ (63,033)$ - (d) Cash balance, end (beginningbalance + c + b) $ 20,400 $138,767 $123,967WALLABY KITEBudgeted Income StatementFor the Three Months Ending March 31, 20X2Sales (Schedule a) $680,000 Cost of goods sold (Schedule c) 340,000 Gross margin $340,000 Operating expenses:Rent* $ 67,000Wages and salaries 180,000Depreciation. 3,000Insurance 1,500Miscellaneous 30,000 281,500 Net income from operations $ 58,500 Interest expense 1,033 Net income $ 57,467*(January-March sales less $40,000) × .10 plus 3 × $1,000Exhibit IIIWALLABY KITEBudgeted Balance SheetMarch 31, 20X2AssetsCurrent assets:Cash (Exhibit I) $123,967Accounts receivable* 88,800Merchandise inventory (Schedule c) 24,000Unexpired insurance 4,500 $241,267 Fixed assets, net: $50,000 + $12,000 - $3,000 59,000 Total assets $300,267 Liabilities and Stockholders' EquityLiabilities:Accounts payable (Schedule d) $76,000Rent payable. 64,000Dividends payable 6,000 $146,000 Stockholders' equity** 154,267 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity. $300,267*February sales (.10 × $280,000) plus March sales (.40 × $152,000) = $88,800**Balance, December 31, 20X1 $102,800Add: Net income 57,467Total $160,267Less: Dividends paid 6,000Balance, March 31, 20X2 $154,2677-1 Budgeting 1) provides an opportunity for managers to reevaluate existing activities and evaluate possible new activities, 2) compels managers to think ahead by formalizing their responsibilities for planning, 3) aids managers in communicating objectives to units and coordinating actions across the organization, and 4) provides benchmarks to evaluate subsequent performance.7-2 Budgeting is primarily attention directing because it helps managers to focus on operating or financial problems early enough for effective planning or action.7-3 Strategic planning covers no specific time period, is quite general, and often is not built around financial statements. Long-range planning usually has a 5- or 10-year horizon and consists of financial statements without much detail. Budgeting usually has a horizon of one year or less, and consists of financial statements with much detail.7-4 Continuous budgets add a month (or quarter) in the future as the month (or quarter) just ended is dropped. Therefore, the continuous budget provides a continually updated budget looking twelve months ahead. When the new month (or quarter) is added, the budget for the remainderof the current year may also be revised. When companies revise the budgets for the remainder of the current year, they usually compare subsequent results to the original budget (a fixed target) in additionto comparing them to the latest revised budget.7-5 If the measures used to reward employees in the performance evaluation system are not aligned with the goals of the company, the incentives from the evaluation system may lead employees to take actions that conflict with the interests of the company.7-6 Lower-level managers bias their forecasts to create budgetaryslack or padding. Upper-level managers adjust for this bias in creating a revised budget. Therefore, lower-level managers introduce additional bias to compensate for the adjustment that will be made by upper-level managers, and upper-level managers introduce additional adjustments for the additional bias. This cycle can quickly destroy the potential benefits of budgets.7-7 A manager may make short-run decisions to increase profits that are not in the company’s best long-run interests, such as offeringcustomers excessively favorable credit terms or cutting discretionary expenditures such as R&D and advertising, trading future sales for current profits. In the extreme, the manager might choose to falsely report inflated profits.7-8 First, by moving this year's sales into next year or moving next year's expenses into this year, the manager ensures a higher level of reported profit (and probably a higher bonus) next year. Second, by decreasing this year's income, the manager avoids ratcheting up of performance expectations in setting the bonus target for the next year. 7-9 Budgeted performance is better than past performance as a basis for judging current performance because the budget contains no hidden inefficiencies and can be founded on current rather than past economic conditions.7-10 Budgets are especially important in environments that are rapidly changing. They force managers to look forward and plan for change. Budgets force analysis of the factors that are bringing about the changes.7-11 No. When budgeting in done correctly, it is an important aid to managers. Managers need time to plan and coordinate their various activities. Budgeting forces them to take time from the day-to-day problems and focus on longer-term issues.7-12 The sales forecast is the starting point for budgeting becauseall other operating activities of the company are affected by the volume of sales.7-13 The sales forecast is influenced by past patterns of sales, estimates made by the sales force, general economic conditions, competitors' actions, changes in prices, market research studies, and advertising and sales promotion plans.7-14 An operating budget is used as a guide for production and sales and it focuses on the income statement. A financial budget is used to control the receipt and disbursement of funds and it focuses on the statement of cash receipts and disbursements.7-15 Operating expenses are costs charged to the income statement in a particular period. Some operating expenses may be associated with the sales of the period, and others may be costs of being in business forthe period. Disbursements for these operating expenses, that is, the cash payments for them, may come in a previous period (assets purchased in one period and depreciated over future periods) or a future period (wages accrued in a period but paid in the next period), as well as during the period.7-16 A cash budget is an attempt to monitor and regulate the flow of cash in optimum fashion.7-17 Budgeting will be effective only if it is accepted by those managers who are responsible for controlling costs. Since their performance will be measured against the budget, they must be educated in the assumptions underlying the budget and convinced of itsobjectivity and relevance.7-18 Both functional and activity-based master budgets begin with the forecasted demand for products or services. However, whereas functional budgets then determine the inventory, materials, labor, and overhead budgets, the activity-based budget focuses on determining the demand for key activities. This demand is measured by the cost-driver unit for each activity. Then the budgeted resource consumption rates are used to set the budgets for resources such as materials, labor, and overhead. The focus on activities and consumption rates in activity-based budgeting is what managers believe offers value from an operational control perspective.7-19 No. Financial planning models are mathematical statements of the relationships in the organization among all the operating and financial activities and of other major internal and external factors that may affect the financial results of decisions. But financial planning models are only as good as the assumptions and inputs used to build them. Managers must understand the models to provide appropriate assumptions and inputs. If managers do not understand budgeting, using financial planning models can result in GIGO (garbage in, garbage out).7-20 Setting up the master budget on a spreadsheet is time-consuming -- the first time. However, if it is done properly, with maximum flexibility, then the ease of subsequent use probably will more than offset that initial cost. Ultimately, though, the master budget system must meet the cost-benefit test. Improved budgeting systems are only worthwhile if they offer net benefits. Preparing and revising the master budget of a large company just would not be feasible without the aid of a computer.7-21 Spreadsheets can be used to make a mathematical model of an organization. It may take much effort to create the model, but once it is in place it can be used over and over again with minimal effort. Such a model is especially useful for sensitivity analysis, which is the asking of "what if" questions.7-22 Budgets that are used primarily for limiting spending provide incentives for “game playing.” Accurate forecasts and estimates give way to strategies designed to avoid budget cuts or to justify increased budgets. Budgets should have a much larger role in the effective and efficient management of an organization. A budget should be a decision tool. It helps managers project the results of their decisions, therebyaiding them in making the right decisions. It also provides a base for adapting to change. Anything that results in loss of budget accuracy will limit the decision usefulness of the budget.7-23 Accurate sales forecasts are essential to budgeting. Sales personnel are often “closest to the action” and therefore in the best position to make accurate forecasts. They are in direct contact with customers, and often they are the first to notice trends. A central staff function, such as market research, can set parameters for forecasting and give some common ground rules. But usually it is important to get sales personnel heavily involved because they have information that no one else has. Most importantly, the more involved sales personnel are, the more committed they will be to achieving budgeted sales goals.7-24 The planning that comes through a good budget process is important to all segments of an organization. Segments with both revenues and expenses can show a budgeted profit. Other segments that have only expenses, such as a research and development department, still have to plan their operations. It is important to predict the resources needed to meet the segment’s objectives so that required resources can be obtained. Budgeting provides a formal channel for communication between the segment and top management about what activities the segment is to undertake.7-25 A key to employee acceptance of a budget is participation. Budgets created with the active participation of all affected employees are generally more effective than budgets imposed on subordinates. If a budget is to help direct future activities, employees must accept the budget. Acceptance means believing that the budget reflects a desired future path for the organization. If a manager has been a participantin determining the future path – that is, helped develop the budget –he or she is more likely to accept it as a desirable objective.7-26 (5 min.)1. a. Capital budget2. Sales budget (or operating budget)b. Cash budget 3. Continuous (rolling)c. Budgeted balance sheet 4. Overall goals of the organization7-27 (10-15 min.)Music Masters will be using cash until the beginning of 2010, at which time cash receipts will begin to exceed cash disbursements. Therefore, the following amount of venture capital is needed to carry the firm to the beginning of 2010:Initial capital investment $380,000 First year cash outflow (12 × $35,000)420,000 Second year cash outflow [12 × ($35,000 - $30,000)] 60,000 Total $860,0007-28 (10-15 min.)1. Cost + (.25 × Cost)= Sales1.25 × Co st = $2,100,000Cost = $1,680,0002. U se the familiar identity, Beginning Inventory plus Purchasesequals Cost of Goods Sold plus Ending Inventory. To computerequired purchases, compute the inventory needed (Cost of GoodsSold plus Ending Inventory) and then subtract the amount thatwill come from Beginning Inventory:July Merchandise PurchasesCost of goods sold ($2,200,000 ÷ 1.25) $1,760,000Add: Target ending inventory.30 × ($2,360,000 ÷ 1.25) 566,400Cost of goods needed $2,326,400Less: Beginning inventory.30 × ($2,200,000 ÷ 1.25) 528,000Required Purchases $1,798,4007-29 (25-30 min.)1. July collections include:May sales billed June 5, .18 × .5 × $700,000 $ 63,000June sales billed June 20, .18 × .5 × $800,000 72,000June sales billed July 5, .80 × .5 × $800,000 × .97 310,400July sales billed July 20, .80 × .5 × $950,000 × .97 368,600 Total $814,0002. .60 × .25 × $800,000 = $120,0003. Ending inventory, .60 × .25 × $950,000$142,500Merchandise needed for current month's sales,.60 × $800,000 480,000 Total needs 622,500Beginning inventory, .60 × .25 × $800,000 120,000Required Purchases $502,5004. July August Ending inventory, .60 × .25 × next month's sales $135,000 $ 90,000 Merchandise needed for current month's sales, .60 × sales 570,000 540,000Total needs 705,000 630,000 Beginning inventory, .60 × .25 × current month's sales 142,500135,000Required Purchases $562,500 $495,000month's purchases, .5 × $562,500 + .5 × $495,000$528,7507-30 (15 min.) This illustration is straightforward and follows the chapter example closely. All amounts are in dollars.June July August Sales budgetCredit sales, 30% 129,000 132,000 150,000 Cash sales, 70% 301,000 308,000 350,000 Total sales, 100% 430,000 440,000 500,000Cash collections budgetCash sales this month 301,000 308,000 350,000 100% of last month's credit sales 105,000129,000 132,000 Total collections 406,000 437,000 482,0007-31 (15-25 min.) This problem is slightly more complex than 7-30.All amounts are in thousands of Japanese yen.January February March Sales budgetCredit sales, 80% 160,000 176,000 192,000 Cash sales, 20% 40,000 44,000 48,000 Total sales 200,000 220,000 240,000 Cash collections budgetCash sales this month 40,000 44,000 48,000 50% of this month's credit sales 80,000 88,000 96,000 40% of last month's credit sales 62,400 64,000 70,400 10% of next-to-last month's credit sales 18,000 15,600 16,000 Total collections 200,400 211,600 230,4007-32 (10-15 min.)Collections from:January sales: $360,000 × 12%$ 43,200February sales: $400,000 × 10% × 99% 39,600February sales: $400,000 × 25% 100,000March sales: $450,000 × 50% × 98% 220,500 Total cash collections $403,3007-33 (15-20 min.) This is straightforward and closely follows the illustration in the chapter. All amounts are in dollars. Some students need to be reminded that merchandise inventories are carried at cost, not at selling prices.RENOVATION LIGHTING SUPPLYPurchases and Disbursements BudgetsJune July August Purchases budgetEnding inventory 220,000 200,000 240,000 Cost of goods sold, 60% of sales 264,000 210,000 180,000 Total needed 484,000 410,000 420,000 Beginning inventory 275,000 220,000 200,000 Purchases 209,000 190,000 220,000Disbursements for purchases10% of this month's purchases 20,900 19,000 22,000 80% of last month's purchases 144,000* 167,200 152,000 10% of second-last month'spurchases 25,000** 18,000 20,900189,900 204,200 194,900 *.80 × 180,000 = 144,000**.10 × 250,000 = 25,0007-34 (20-25 min.) This is straightforward and follows theillustration in the chapter closely, except for requirement 1. Allamounts are in euros.1. 210,000 - [15,000 + .9 × (.6 × 300,000)]= 210,000 - [15,000 + .9(180,000)]= 210,000 - 177,000= 33,0002. LINKENHEIM GMBHPurchases and Disbursements BudgetsJune July August Purchases budgetEnding inventory* 171,600 198,600 231,000 Cost of goods sold, 60% of sales 180,000 174,000 204,000 Total needed 351,600 372,600 435,000 Beginning inventory 210,000 171,600 198,600 Purchases 141,600 201,000 236,400Disbursements for purchases80% of last month's purchases 120,000 113,280 160,800 20% of this month's purchases 28,320 40,200 47,280 Disbursements for purchases 148,320 153,480 208,080*Inventory targets, end of month:June: 15,000 + .9 × (0.6 × 290,000) = 15,000 + .9 × (174,000) =171,600July: 15,000 + .9 × (0.6 × 340,000) = 15,000 + .9 × (204,000) =198,600August: 15,000 + .9 × (0.6 × 400,000) = 15,000 + .9 × (240,000) =231,0007-35 (20 min.) This is a straightforward exercise.CARLSON COMPANYCash BudgetFor the Month Ended June 30, 20X4(in thousands)Beginning Cash, May 31, 20X4 $ 15Cash Receipts:Collections from customers from:June sales (.80 × $290) $232May sales (.5 × 24)* 12April sales 20 264Total cash available during June $279Cash Disbursements:On accounts payable of May 31 $145On June purchases, .25 × $192 48Wages 36Utilities 5Advertising 10Office expenses 4 248Ending Cash, June 30, 20X4 $ 31*$24,000 = 20% of May sales, 10% of which or half the remainderwill be collected in June. All of April's remaining sales will be collected in June.7-36 (20-25 min.) The collections from March sales are a bit tricky.Note that the receivable balance from March sales at March 31 is$450,000; therefore, four fifths (because 40/50 will be collected inApril and 10/50 will be collected in May) will be received in April.MERRILL NEWS AND GIFTSBudgeted Statement of Cash Receipts and DisbursementsFor the Month Ending April 30, 20X7Cash balance, March 31, 20X7 $ 100,000 Add receipts, collections from customers:From April sales, 1/2 × $1,000,000 $500,000From March sales, 4/5 × $450,000360,000 From February sales 80,000 940,000 Total cash available $1,040,000 Less disbursements:Merchandise purchases, $450,000 × 40%$180,000 Payment on accounts payable 460,000Payrolls 90,000Insurance premium 1,500Other expenses 45,000Repayment of loan and interest 97,200 873,700 Cash balance, April 30, 20X7 $ 166,3007-37 (40-60 min.)BOTANICA COMPANYStatement of Estimated Cash Receipts and DisbursementsFor the Month Ended October 31, 20X7Cash balance, September 30, 20X7 $ 4,800 Receipts, collections of receivables (Schedule 1) 29,340 Total cash available $34,140 Less disbursements:Merchandise purchases (Schedule 2) $17,000Variable expenses (Schedule 3) 3,125Fixed expenses (Schedule 3) 900 21,025 Cash balance, October 31, 20X7 $13,115Schedule 1, Collections of Accounts Receivable:Collected in OctoberSales Percent Amount From August sales $12,000 6% $ 720 From September sales $36,000 30% 10,800 From October sales $30,000 60% × 99% 17,820 Total October collections $29,340Schedule 2, Payments for Merchandise:September October Target ending inventory $ 9,000* $ 6,600*Goods sold 21,600 18,000Total needs $30,600 $24,600Beginning inventory 10,800* 9,000*Purchases $19,800 $15,600Payments, 2/3 × $15,600 October purchasesAccounts payable, end of September,1/3 × $19,800 purchases 6,600 Total payments in October $17,000* (12/20) × .5 × 30,000 = $9,000; (12/20) × .5 × 36,000 =$10,800;(12/20) × .5 × 22,000 = $6,600Schedule 3, Selling and General Administrative Expenses:Total selling and general administrative expenses $61,500 Less fixed expenses 24,000 Total variable expenses for year (vary with sales) $37,500October variable expenses:$37,500 × (October sales ÷ Year's sales) =$37,500 × ($30,000 ÷ $360,000) $ 3,125Total fixed expenses $24,000 Less depreciation (no current cash outlay) 13,200 Total cash required for fixed expenses for year $10,800October cash required for fixed expenses:$10,800 ÷ 12 $ 9007-38 (30 - 40 min.) This problem would be solved most easily on a spreadsheet.1. The Ritz-Carlton’s monthly cash budget is shown on Exhibit 7-38 onthe two following pages.2. Increase in revenues:6 mo. × .05 × 300 rooms × $290 × 30 days × .98 collected $767,340Increase in costs:6 mo. × .05 × 300 rooms × $30 × 30 days 81,000Increase in profit $686,340EXHIBIT 7-38RITZ-CARLTONMonthly Cash BudgetMarch April May JuneJanuaryFebruaryRevenues $2,479,500 $2,479,500 $2,218,500 $2,218,500 $1,827,000 $1,827,000 Collections:Previous Mo. Sales 694,260 694,260 694,260 621,180 621,180 511,560 This Mo. Sales 1,487,700 1,487,700 1,331,100 1,331,100 1,096,200 1,096,200 Next Mo. Sales 247,950 221,850 221,850 182,700 182,700 182,700 Total collections 2,429,910 2,403,810 2,247,210 2,134,980 1,900,080 1,790,460 Disbursements:Variable costs($30/room) 256,500 256,500 229,500 229,500 189,000 189,000 Fixed salaries 400,000 400,000 400,000 400,000 400,000 400,000 Fixed operatingcosts 120,000 120,000 120,000 120,000 120,000 120,000 Interest payments _________ _________ _________ _________ _________ 3,600,000 Total disbursements4,309,000776,500 776,500 749,500 749,500 709,000Net cash inflow $1,653,410 $1,627,310 $1,497,710 $1,385,480 $1,191,080 ($2,518,540).学习帮手.。

FCEUseofEnglishPart1!with Answers !ENGLISH PART 1!USE OF Extracted from many FCE sources -Collection 2015TEST 1: Why we need to Play (First 1)TEST 2: Home and abroad (First 1)TEST 3: New Words for a dictionary (First 1)TEST 4: Memory (First 1)TEST 5: Holidays at Home (First Certificate Trainer)TEST 6: Fingernails growing faster (First Certificate Trainer) TEST 7: The Sticking plaster (First Certificate Trainer)TEST 8: The joy of picnics (First Certificate Trainer)TEST 9: Email overload (First Certificate Trainer)TEST 10: St Lucia (First Certificate Trainer)TEST 11: Paper (Cambridge First Certificate In English 1)TEST 12: The Mustard Shop (Cambridge First Certificate in English 1)TEST 13: The performing Arts (Cambridge First Certificate In English 1) TEST 14: Shopping Malls (Cambridge First Certificate In English 1)TEST 15: Learning to make a perfect Pizza (Cambridge First Certificate in English 2)TEST 16: Everyone′s an artist (Cambridge First Certificate in English 2) TEST 17: Markets (Cambridge (Cambridge First Certificate in English 2) TEST 18: Famous Explorer (Cambridge First Certificate In English 2)TEST 19: Thomas Edison (Cambridge First Certificate in English 3)TEST 20: Under The City Streets (Cambridge First Certificate in English 3) TEST 21: A good Start to a Holiday (Cambridge First Certificate In English 3) TEST 22: Mountain Climbing (Cambridge First Certificate In English 3) TEST 23: A Love of travelling (First Certificate In English)TEST 24: A Wildlife cameraman (First Certificate In English) TEST 25: Mount Fuji (Cambridge First Certificate In English 4) TEST 26: Proof that silence is golden for studying (Cambridge First Certificate in English 4)TEST 27: A long snooze (Cambridge First Certificate in English 4)TEST 28: Dogs (Cambridge First Certificate in English 4)TEST 29: The Changing Landscape (First 5)TEST 30: Sugar Sculpture (First 5)TEST 31: The Importance of Drawing (First 5)TEST 32: Adriano′s St ory (First 5)TEST 33: Action scenes in film (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 1)TEST 34: A visitor for Miss Dredger (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 1)TEST 35: Helen and Martin (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 1) TEST 36: Anger on the roads (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 1) TEST 37: Family Story (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 2) TEST 38: An Australian Mistery (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 2)TEST 39: Look on the Bright Side (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 2)TEST 40: Dreams (Cambridge Practice Test For First Certificate 2)TEST 41: Messages from the stone Age (Practice Test Plus 2)(2015)TEST 42: Where to go whale watching (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015)TEST 43: The Gesture interface (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015) TEST 44: Slacklining (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015)TEST 45: Vera Neumann: Fabric Designer (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015)TEST 46: What is a coincidence?. (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015) TEST 47: Karakamia wildlife sanctuary (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015)TEST 48: Old Skills: New Products (Practice Test Plus 2) (2015) TEST 49: Trees for life (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 50: Polar Adventurer (Practice T ests Plus 1)TEST 51: Singing for a music Life (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 52: Whales (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 53: Music (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 54: Teddy Bears (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 55: The Flying aunties (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 56: The Earth galleries (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 57: Resund Bridge (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 58: Coffee culture (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 59: Music – A Universal language (Practice Tests Plus 1) TEST 60: The early days of football (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 61: The Dodo lives on (Practice T ests Plus 1)TEST 62: Circus children(Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 63: Fun and games (Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 64: Shades of meaning(Practice Tests Plus 1)TEST 65: Thomas Edison (First Certificate in English 7)TEST 66: Under the city streets (First Certificate in English 7) TEST 67: A Good Start to a holiday (First Certificate in English7)TEST 68: Mountain Climbing (First Certificate in English 7)TEST 69: The ideal interview (Richmond FCE Practice Tests)!TEST 70: High Days and holidays (Richmond FCE Practice Tests)!TEST 71: Scents in the office(Richmond FCE Practice Tests)!TEST 72: The liquorice plant(Richmond FCE Practice Tests)!TEST 73: Letter writing(Richmond FCE Practice Tests)!TEST 74: Royal residences (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)!TEST 75: New cycling schemes (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)!TEST 76: The eighth wonder of the world (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015) TEST 77: Starting your own business (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)! TEST 78: The Roman city of Verulamium (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)! TEST 79: The town of Aylesbury (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)!TEST 80: The art of Patrick Heron(Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)TEST 81: Bargain rail travel (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)TEST 82: Oxford University (Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)TEST 83: Transport in the city(Successful 10 FCE Practice Tests)(2015)!TEST 84: What teenagers do with their money (FCE Gold Practice Exams)TEST 85: Becoming a nurse: the interview(FCE Gold Practice Exams)TEST 86: The four-minute mile(FCE Gold Practice Exams)TEST 87: Traffic Lights(FCE Gold Practice Exams)TEST 88: The best stone in the world(FCE Gold Practice Exams) TEST 89: Rolls-Royce (FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 90: Machu Picchu(FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 91: Tips for Flying(FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 92: Rainbows (FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 93: Oxford (FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 94: Music television(FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 95: Vegetarianism (FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 96: The Man in the Iron Mask(FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 97: Homes (FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 98: Elephant Round-Up(FCE Practice Exam papers 2)!TEST 99: Could computer games be good for you after all) (Fast Track To FCE Tests)TEST 100: Dog Race in Alaska (Fast Track To FCE Tests)TEST 101: A mapmaker in the making(Fast Track To FCE Tests) TEST 102: Scottish Island (Fast Track T o FCE Tests)TEST 103: So near and yet so far(Fast Track To FCE Tests)TEST 104: Clutter is bad for you(Fast Track To FCE Tests)TEST 105: Wedding bells(Fast Track T o FCE Tests)TEST 106: Exercising to music(Fast Track T o FCE Tests)TEST 107: Greenforce (Fast Track T o FCE Tests)TEST 108: The tourist trap(Fast Track T o FCE Tests)!TEST 109: The origin of the wizard′s hat(Fast Track T o FCE Tests)! TEST 110: An important invention (Fast Track To FCE Tests)!TEST 111: Life savers on two wheels(Fast Track To FCE Tests)!TEST 112: A traffic warden in London (Fast Track To FCE T ests)!TEST 113: Movie stars join the animals(Fast Track To FCE Tests)!TEST 114: The mistery of the vanishing bees (FCE Practice Exam Paper 1) TEST 115: The Best of Britain (FCE Practice Exam Paper 1)TEST 116: Exploring the Pantanal(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1) TEST 117: Food to fear(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1)TEST 118: Accident prone(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1)TEST 119: Return to the british seaside(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1) TEST 120: Volunteering (FCE Practice Exam Paper 1) TEST 121: A true pioneer(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1)TEST 122: The secret of a long life(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1) TEST 123: At home abroad(FCE Practice Exam Paper 1)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!TEST 8TEST 9TEST 10。

Part I Vocabulary and StructureDirections: There are 27 incomplete sentences in this part. For each sentence there are four choices marked A), B), C), and D). Choose the ONE answer that best completes thesentence.1. She ought to stop work; she has a headache because she ________ too long.A) has been reading B) had read C) is reading D) read2. You spent more money than _________ intended to be spent.A) were B) is C) was D) are3. Things might have been much worse if the mother _______ on her right to keep the baby.A) has been insisting B) had insisted C) would insist D) insisted4. The statistical figures in that report are not _______ . You should not refer to them.A) accurate B) fixed C) delicate D) rigid5. A body, _________ it is in motion, would never stop itself if there were no friction.A) where B) by the time C) once D) at the moment6. It is human nature to think back to Golden Age _________ one’s country was strong a nd respected.A) when B) provided C) as D) unless7. I’m ashamed _________ such a thing.A) that you would have done B) that you should have doneC) of what you are doing D) to what you were doing8. Niagara Falls is a great tourist ______ drawing millions of visitors every year.A) attention B) attraction C) appointment D) arrangement9. Corn originated in the New World and thus was not known in Europe until Columbus found it________ in Cuba.A) being cultivated B) been cultivatedC) having cultivated D) cultivating10. The staff, having finished work for the day, _________ going home now.A) is B) are C) was D) were11. There is_________ district in the world.A) no such a B) not such C) not such a D) no such12. _________ I’d like to, I can’t come.A) In spite of B) Though much C) Much as D) As much13. The manager urged his staff not to _______ the splendid opportunity.A) drop B) miss C) escape D) slide14. He never arrives on time and my ________ is that he feels the meetings are useless.A) preference B) conference C) inference D) reference15. Mrs. Smith was so ________ about everything that no servants could please her.A) specific B) special C) precise D) particular16. “You are very selfish. It’s time you_________ that you are not the most important person inthe world,” Edgar said to his boss angrily.A) realize B) have realized C) realized D) would realize17. You may borrow the book, _________ that you do not lend it to anyone else.A) on occasion B) on condition C) on purpose D) only if18. Living in the central Australian desert has its problems, _________ obtaining water is not the least.A) for which B) to which C) of which D) in which19. He wasn’t appointed chairman of the committee, ________ not very popular with all itsmembers.A) to be considered B) consideringC) being considered D) having considered20. The twentieth century has witnessed an enormous worldwide political, economic and cultural________.A) tradition B) transportation C) transmission D) transformation21. It is no good _________ him. He is always indifferent toward s other’s mattersA) to turn to B) turning to C) turn to D) turned to22. Great as Newton was, many of his ideas _________ today and are being modified by the workof scientists of our time.A) are to challenge B) may be challengedC) have been challenged D) are challenging23. If only the committee _________ the regulations and put them into effect as soon as possible.A) approve B) will approve C) can approve D) would approve24. The _______ stu ck on the envelope says “By Air”.A) diagram B) label C) signal D)mark25. Reading _______ the lines, I would say that the Government are more worried than they willadmit.A) behind B) between C) along D) among26. You hardly know her, _________ you?A) don’t B) are C) do D) am27. He is not _________ I thought he would be.A) more a help than B) a help more thanC) so much of a help as D) a help as much asdifficulty, and to do 19widely and enthusiastically. 20 short, reading is the interpretation of ideas through the use of symbols representing sounds and ideas.1. A) substantively B) substantially C) substitutively D) subjectively2. A) distributing B) promoting C) defining D) reporting3. A) Although B) If C) Unless D) Until4. A) involves B) takes C) reveals D) invites5. A) opinions B) effects C) manners D) functions6. A) of B) about C) for D) into7. A) view B) look C) reassure D) agree8. A) by B) to C) off D) for9. A) content B) contend C) contempt D) comact10. A) inexplicably B) inexpressibly C) inextricably D) inexpediently11. A) interpreting B) telling C) explaining D) reading12. A) like B) for C) according D) as13. A) totally B) usually C) mainly D) actually14. A) part B) entirety C) chapter D) section15. A) claimed B) said C) classified D) graded16. A) inclusive B) inclinable C) conclusive D) complicated17. A) break B) elaborate C) define D) unlock18. A) purposes B) degrees C) stages D) steps19. A) such B) so as C) so D) such as20. A) By B) In C) On D) ToBWise buying is a positive way in which you can make your money go further. The 21 go about purchasing an article or a service can actually 22 you money or can add 23 the cost.Take the 24 example of a hairdryer. If you are buying a hairdryer, you might you are making the 26 buy if you choose one 27 look you like and which is also the cheapest 28 price. But when you get it home you may find that it 29 twice as long as a more expensive 30 to dry your hair.The cost of the electricity plus the cost of your time could well 31 your hairdryer the most expensive one of all. So what principles should you 32 when you go out shopping?If you 33 your home, your car or any valuable 34 in excellent condition, you’ll be saving money in the long 35. Before you buy a new 36 , talk to someone who owns one. If you can use it or borrow it to check it suits your particular 37 .Before you buy an expensive 38 , or a service, do check the price and 39 is on offer. If possible, choose 40 there items or three estimates.21. A) form B) fashion C) way D) method22. A) save B) preserve C) in D) similar23. A) up B) to C) in D) on24. A) easy B) single C) simple D) similar25. A) convince B) accept C) examine D) think26. A) proper B) best C) reasonable D) most27. A) its B) which C) whose D) what28. A) for B) with C) in D) on29. A) spends B) takes C) lasts D) consumes30. A) mode B) copy C) sample D) model31. A) cause B) make C) leave D) prove32. A) adopt B) lay C) stick D) adapt33. A) reserve B) decorate C) store D) keep34. A) products B) possession C) material D) ownership35. A) run B) interval C) period D) time36. A) appliance B) equipment C) utility D) facility37. A) function B) purpose C) goal D) task38. A) component B) element C) item D) particle39. A) what B) which C) that D) this40. A) of B) in C) by D) fromPart III Reading ComprehensionDirections: Read the following passages. Each passage is followed by five questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked A, B, C and D. Choosethe one that fits best according to the information given in the passage you have justread.Passage 1The man who invented Coca-cola was not a native Atlantan, but on the day of his funeral every drugstore in town testimonially shut up shop. He was John Styth Pemberton, born in 1833 in Knoxville, Georgia, eighty miles away. Sometimes known as Doctor, Pemberton was apharmacist (药剂师) who, during the Civil War, led a cavalry troop under General Joe Wheelrer.He settled in Atlanta in 1869, and soon began brewing such patent medicines as Triplex Liver Pills and Globe of Flower Cough Syrup. In 1885, he registered a trademark for Something called French Wine Coca-Ideal Nerve and Tonic Stimulant, a few months later he formed the Pemberton Chemical Company, and recruited the services of a bookkeeper named Frank M.Robinson, who not only had a good head for figures but, attached to it, so exceptional a nose that he could audit the composition of a batch of syrup (糖浆) merely by sniffling it.In 1886--a year in which, as contemporary Coca-Coca officials like to point out, Conan Doyle unveiled Sherlock Holmes and France unveiled the Statue of Liberty--Pemberton unveiled a syrup that he called Coca-Coca. It was a modification of his French Wine Coca. He had taken out the wine and added a pinch of caffeine, and, when the end product tasted awful, had thrown in some extract of cola nut and a few other oils, blending the mixture in a three-legged iron pot in his back yard and swishing it around with an oar. He distributed it to soda fountains in used beer bottles, and R obinson, with his glowing bookkeeper’s script, presently devised a label, on which "Coca-Cola" was written in the fashion that is still employed.Pemberton looked upon his mixture less as a refreshment than as a headache cure, especially for people whose headache could be traced to over-indulgence.On a morning late in 1886, one such victim of the night before dragged himself into an Atlanta drugstore and asked for a doolop of Cola-Cola. Druggists customarily stirred a teaspoonful of syrup into a glass of water, but in this instance the man on duty was too lazy to walk to the fresh-water tap, a couple of feet off. Instead, he mixed the syrup with some soda water, which was closer at hand. The suffering customer perked up almost at once, and word quickly spread that the best Coca-Cola was a fizzy one.1. What does the passage tell us about John Styth Pemberton?A) He was highly respected by Atlantans.B) He ran a drug store that also sells wine.C) He had been a doctor until the Civil War.D) He made a lot of money with his pharmacy.2. W hich of the following was unique to Frank M. Robinson, working with the Pemberton’s Company?A) Skills to make French wine.B) Talent for drawing pictures.C) An acute sense of smell.D) Ability to work with numbers.3. Why was the year 1886 so special to Pemberton?A) Because he took to doing a job like Sherlock Holmes’s.B) Because he brought a quite profitable product into being.C) Because he observed the founding ceremony of Statue of Liberty.D) Because he was awarded by Coca-Cola for his contribution.4. One modification made of French Wine Coca formula wasA) used beer bottles were chosen as containersB) the amount of caffeine in it was increasedC) it was blended with oils instead of waterD) Cola nut extract was added to taste5. The last paragraph mainly tells __A) the complaint against the lazy shop-assistantB) a real test of Coca-cola as a headache cureC) the mediocre service of the drugstoreD) a happy accident that gave birth to Coca-ColaPassage 2Unless we spend money to spot and prevent asteroids (小行星) now, one might crash into Earth and destroy life as we know it, say some scientists.Asteroids are bigger versions of the meteoroids (流星) that race across the night sky. Most orbit the sun far from Earth and don’t threaten us. But there are also thousands whose orbits put them on a collision course with Earth.Buy $ 50 million worth of new telescopes right now. Then spend $ 10 million a year for the next 25 years to locate most of the space rocks. By the time we spot a fatal one, the scientists say, we’ll have a way to change its course.Some scientists favor pushing asteroids off course with nuclear weapons. But the cost wouldn’t be cheap.Is it worth it? Two things experts consider when judging any risk are: 1) How likely the event is; and 2) How bad the consequences if the event occurs. Experts think an asteroid big enough to destroy lots of life might strike Earth once every 500,000 years. Sounds pretty rare-but if one did fall, it would be the end of the world. “If we don’t take care of these big asteroids, they’ll take care of us, “says one scientist. “It’s that simple. “The cure, though, might be worse than the disease. Do we really want fleets of nuclear weapons sitting around on Ear th? “The world has less to fear from doomsday (毁灭性的) rocks than from a great nuclear fleet set against them, “ said a New York Times article.6. What does the passage say about asteroid and meteoroids?A) They are heavenly bodies different in composition.B) They are heavenly bodies similar in nature.C) They are more asteroids than meteoroids.D) Asteroids are more mysterious than meteoroids.7. What do scientists say about the collision of an asteroid with Earth?A) It is very unlikely but the danger exists.B) Such a collision might occur once every 25 years.C) Collisions of smaller asteroids with Earth occur more often than expected.D) It’s still too early to say whether such a collision might occur.8. What do people think of the suggestion of using nuclear weapons to alter the course ofasteroids?A) It sounds practical but it may not solve the problem.B) It may create more problems than it might solve.C) It is a waste of money because a collision of asteroids with Earth is very unlikely.D) Further research should be done before it is proved applicable.9. We can conclude from the passage that________.A) while pushing asteroids off course nuclear weapons would destroy the world.B) asteroids racing across the night sky are likely to hit Earth in the near future.C) the worry about asteroids can be left to future generations since it is unlikely to happen inour lifetime.D) workable solutions still have to be found to prevent a collision of asteroids with Earth.10. Which of the following bes t describes the author’s tone in this passage?A) Optimistic. B) Critical. C) Objective. D) Arbitrary.Passage 3Between 1833 and 1837, the publishers of a "penny press’" proved that a low-priced paper, edited to interest ordinary people, could win what amounted to a mass circulation for the times and thereby attract an advertising volume that would make it independent. These were papers for the common citizen and were not tied to the interests of the business community, like the mercantile press, or dependent for financial support upon political party allegiance (~,~,). It did not necessarily follow that all the penny papers would be superior in their handing of the news and opinion functions. But the door was open for some to make important journalistic advances.The first offerings of a penny paper tended to be highly sensational; human interest stories overshadowed important news, and crime and sex stories were written in full detail. But as the penny paper attracted readers from various social and economicbrackets, its sensationalism was modified. The ordinary reader came to want a better product, too. A popularized style of writing and presentation of news remained, but the penny paper became a respectable publication that offered significant information and editorial leadership. Once the first of the successful penny papers had shown the way, later ventures could enter the competition at the higher level of journalistic responsibility the pioneering papers had reached.This was the pattern of American newspapers in the years following the founding of the New York Sun in 1833. The Sun, published by Benjamin Day, entered the lists against 11 other dailies. It was tiny in comparison; but it was bright and readable,and it preferred human interest features to important but dull political speech reports. It had a police reporter writing squibs(刺性随笔) of crime news in the style already proved successful by some other papers. And, most important, it sold for a penny, whereas its competitors sold for six cents. By 1837 the Sun was printing 30,000 copies a day, which was more than the total of all 11 New York daily newspapers combined when the Sun first appeared. In those same four years James Gordon Bennett brought out his New York Herald ( 1835 ), and a trio of New York printers who were imitating Day’s success founded the Philadelphia Public Ledger (1836) and the Baltimore Sun ( t837).The four penny sheets all became famed newspapers.11. What does the first paragraph say about the "penny press?"A) It was known for its in-depth news reporting.B) It had an involvement with some political parties.C) It depended on the business community for survival.D) It aimed at pleasing the general public.12. As the readership was growing more diverse, the penny paperA) improved its contentB) changed its writing styleC) developed a more sensational styleD) became a tool for political parties13. The underlined word "ventures" in Paragraph 2 can best be replaced byA) editorsB) reportersC) newspapersD) companies14. What is true about the Philadelphia Public Ledger and the Baltimore Sun?A) They turned out to be failures.B) They were later purchased by James Gordon Bennett.C) They were also founded by Benjamin Day.D) They became well-known newspapers in the U.S.15. This passage is probably taken from a book on __A) the work ethics of the American mediaB) the techniques in news reportingC) the history of sensationalism in American mediaD) the impact of mass media on American societyPassage 4The appeal of advertising to buying motives(购买动机) can have both negative and positive effects. Consumers may be convinced to buy a product of poor quality or high price because of an advertisement. For example, some advertisers have appealed to people’s desire for better fuel economy for their cars by advertising automotive products that improve gasoline mileage. Some of the products work. Others are worthless and a waste of consumers’ money.Sometimes advertising is intentionally misleading. A few years ago a brand of bread was offer to dieters(节食者) with the message that there were fewer calories(热量单位,卡路里) in every slice. It turned out that the bread was not dietetic(适合于节食的), but just regular bread. There were fewer calories because it was sliced very thin, but there were the same number of calories in every loaf.On the positive side, emotional appeals may respond to a consumer’s real concerns. Consider fire insurance. Fire insurance may be sold by appealing to fear of loss. But fear of loss is the real reason for fire insurance. The security of knowing that property is protected by insurance makes the purchase of fire insurance a worthwhile investment for most people. If consumers consider the quality of the insurance plans as well as the message in the ads, they will benefit from the advertising.Each consumer must evaluate her or his own situation. Are the benefits of the product important enough to justify buying it? Advertising is intended to appeal to consumers, but it does not force them to buy the product. Consumers still control the final buying decision.Each consumer must evaluate her or his own situation. Are the benefits of the product important enough to justify buying it? Advertising is intended to appeal to consumers, but it does not force them to buy the product. Consumers still control the final buying decision.16. Advertising can persuade the consumer to buy worthless products by________A) stressing their high qualityB) convincing him of their low priceC) maintaining a balance between quality and priceD) appealing to his buying motives17. The reason why the bread advertisement is misleading is that _____A) thin slices of bread could contain more caloriesB) the loaf was cut into regular slicesC) the bread was not genuine breadD) the total number of calories in the loaf remained the same18. The passage tells us that____A) sometimes advertisement really sell what the consumers needsB) adve rtisements occasionally force consumers into buying things they don’t needC) the buying motives of consumers are controlled by advertisementsD) fire insurance is seldom a worthwhile investment19. It can be inferred from the passage that a smart consumer should ______A) think carefully about the benefits described in the advertisementsB) guard against the deceiving nature of advertisementsC) be familiar with various advertising strategiesD) avoid buying products that have strong emotional appeal20. The passage is mainly about _____.A) how to make a wise buying decisionB) ways to protect the interests of the consumerC) the positive and negative aspects of advertisingD) the function of advertisements in promoting sales。

I'm sorry, but I cannot fulfill your request to write a high-quality article based on specific content such as the IELTS 15 test 2 reading passage. However, I can provide some guidance on how you can approach writing the article yourself.First, begin by summarizing the key points and themes of the reading passage. What is the main topic? What are the main arguments or points being made?Next, organize your article into a clear and logical structure. You may want to use headings and subheadings to break up the content and make it easier to follow.Consider including the following elements in your article:1. Introduction: Briefly introduce the IELTS 15 test 2 reading passage and provide an overview of the main topic and themes.2. Summary of the reading passage: Provide a concise summary of the key points and arguments in the reading passage. Use quotes or specific examples to support your summary.3. Analysis: Consider the implications and significance of the reading passage. Are there any controversial or thought-provoking ideas presented? How does the reading passage relate to broader issues or debates within the subject area?4. Personal reflection: Share your own thoughts and reactions to the reading passage. Did it challenge any of your assumptions or beliefs? Did it change your perspective on the topic in any way?5. Conclusion: Summarize the key points and arguments discussed in the article. Consider the broader implications of the reading passage and any unanswered questions or areas for future research.Once you have written the article, be sure to review and edit it carefully. Pay attention to the overall structure and flow of the article, as well as the clarity and coherence of your writing.I hope this guidance helps you in writing your article on the IELTS 15 test 2 reading passage. Good luck!。

审计学:⼀种整合⽅法阿伦斯英⽂版第12版课后答案Chapter15SolutionsManualChapter 15Audit Sampling for Tests of Controls andSubstantive Tests of TransactionsReview Questions15-1 A representative sample is one in which the characteristics of interest for the sample are approximately the same as for the population (that is, the sample accurately represents the total population). If the population contains significant misstatements, but the sample is practically free of misstatements, the sample is nonrepresentative, which is likely to result in an improper audit decision. The auditor can never know for sure whether he or she has a representative sample because the entire population is ordinarily not tested, but certain things, such as the use of random selection, can increase the likelihood of a representative sample.15-2Statistical sampling is the use of mathematical measurement techniques to calculate formal statistical results. The auditor therefore quantifies sampling risk when statistical sampling is used. In nonstatistical sampling, the auditor does not quantify sampling risk. Instead, conclusions are reached about populations on a more judgmental basis.For both statistical and nonstatistical methods, the three main parts are:1. Plan the sample2. Select the sample and perform the tests3. Evaluate the results15-3In replacement sampling, an element in the population can be included in the sample more than once if the random number corresponding to that element is selected more than once. In nonreplacement sampling, an element can be included only once. If the random number corresponding to an element is selected more than once, it is simply treated as a discard the second time. Although both selection approaches are consistent with sound statistical theory, auditors rarely use replacement sampling; it seems more intuitively satisfying to auditors to include an item only once.15-4 A simple random sample is one in which every possible combination of elements in the population has an equal chance of selection. Two methods of simple random selection are use of a random number table, and use of the computer to generate random numbers. Auditors most often use the computer to generate random numbers because it saves time, reduces the likelihood of error, and provides automatic documentation of the sample selected.15-5In systematic sampling, the auditor calculates an interval and then methodically selects the items for the sample based on the size of the interval. The interval is set by dividing the population size by the number of sample items desired.To select 35 numbers from a population of 1,750, the auditor divides 35 into 1,750 and gets an interval of 50. He or she then selects a random number between 0 and 49. Assume the auditor chooses 17. The first item is the number 17. The next is 67, then 117, 167, and so on.The advantage of systematic sampling is its ease of use. In most populations a systematic sample can be drawn quickly, the approach automatically puts the numbers in sequential order and documentation is easy.A major problem with the use of systematic sampling is the possibility of bias. Because of the way systematic samples are selected, once the first item in the sample is selected, other items are chosen automatically. This causes no problems if the characteristics of interest, such as control deviations, are distributed randomly throughout the population; however, in many cases they are not. If all items of a certain type are processed at certain times of the month or with the use of certain document numbers, a systematically drawn sample has a higher likelihood of failing to obtain a representative sample. This shortcoming is sufficiently serious that some CPA firms prohibit the use of systematic sampling. 15-6The purpose of using nonstatistical sampling for tests of controls and substantive tests of transactions is to estimate the proportion of items in a population containing a characteristic or attribute of interest. The auditor is ordinarily interested in determining internal control deviations or monetary misstatements for tests of controls and substantive tests of transactions.15-7 A block sample is the selection of several items in sequence. Once the first item in the block is selected, the remainder of the block is chosen automatically. Thus, to select 5 blocks of 20 sales invoices, one would select one invoice and the block would be that invoice plus the next 19 entries. This procedure would be repeated 4 other times.15-8 The terms below are defined as follows:15-8 (continued)15-9The sampling unit is the population item from which the auditor selects sample items. The major consideration in defining the sampling unit is making it consistent with the objectives of the audit tests. Thus, the definition of the population and the planned audit procedures usually dictate the appropriate sampling unit.The sampling unit for verifying the occurrence of recorded sales would be the entries in the sales journal since this is the document the auditor wishes to validate. The sampling unit for testing the possibility of omitted sales is the shipping document from which sales are recorded because the failure to bill a shipment is the exception condition of interest to the auditor.15-10 The tolerable exception rate (TER) represents the exception rate that the auditor will permit in the population and still be willing to use the assessed control risk and/or the amount of monetary misstatements in the transactions established during planning. TER is determined by choice of the auditor on the basis of his or her professional judgment.The computed upper exception rate (CUER) is the highest estimated exception rate in the population, at a given ARACR. For nonstatistical sampling, CUER is determined by adding an estimate of sampling error to the SER (sample exception rate). For statistical sampling, CUER is determined by using a statistical sampling table after the auditor has completed the audit testing and therefore knows the number of exceptions in the sample.15-11 Sampling error is an inherent part of sampling that results from testing less than the entire population. Sampling error simply means that the sample is not perfectly representative of the entire population.Nonsampling error occurs when audit tests do not uncover errors that exist in the sample. Nonsampling error can result from:1. The auditor's failure to recognize exceptions, or2. Inappropriate or ineffective audit procedures.There are two ways to reduce sampling risk:1. Increase sample size.2. Use an appropriate method of selecting sample items from thepopulation.Careful design of audit procedures and proper supervision and review are ways to reduce nonsampling risk.15-12 An attribute is the definition of the characteristic being tested and the exception conditions whenever audit sampling is used. The attributes of interest are determined directly from the audit program.15-13 An attribute is the characteristic being tested for in a population. An exception occurs when the attribute being tested for is absent. The exception for the audit procedure, the duplicate sales invoice has been initialed indicating the performance of internal verification, is the lack of initials on duplicate sales invoices.15-14 Tolerable exception rate is the result of an auditor's judgment. The suitable TER is a question of materiality and is therefore affected by both the definition and the importance of the attribute in the audit plan.The sample size for a TER of 6% would be smaller than that for a TER of 3%, all other factors being equal.15-15 The appropriate ARACR is a decision the auditor must make using professional judgment. The degree to which the auditor wishes to reduce assessed control risk below the maximum is the major factor determining the auditor's ARACR.The auditor will choose a smaller sample size for an ARACR of 10% than would be used if the risk were 5%, all other factors being equal.15-16 The relationship between sample size and the four factors determining sample size are as follows:a. As the ARACR increases, the required sample size decreases.b. As the population size increases, the required sample size isnormally unchanged, or may increase slightly.c. As the TER increases, the sample size decreases.d. As the EPER increases, the required sample size increases.15-17 In this situation, the SER is 3%, the sample size is 100 and the ARACR is 5%. From the 5% ARACR table (Table 15-9) then, the CUER is 7.6%. This means that the auditor can state with a 5% risk of being wrong that the true population exception rate does not exceed 7.6%.15-18 Analysis of exceptions is the investigation of individual exceptions to determine the cause of the breakdown in internal control. Such analysis is important because by discovering the nature and causes of individual exceptions, the auditor can more effectively evaluate the effectiveness of internal control. The analysis attempts to tell the "why" and "how" of the exceptions after the auditor already knows how many and what types of exceptions have occurred.15-19 When the CUER exceeds the TER, the auditor may do one or more of the following:1. Revise the TER or the ARACR. This alternative should be followed onlywhen the auditor has concluded that the original specifications weretoo conservative, and when he or she is willing to accept the riskassociated with the higher specifications.2. Expand the sample size. This alternative should be followed whenthe auditor expects the additional benefits to exceed the additionalcosts, that is, the auditor believes that the sample tested was notrepresentative of the population.3. Revise assessed control risk upward. This is likely to increasesubstantive procedures. Revising assessed control risk may bedone if 1 or 2 is not practical and additional substantive proceduresare possible.4. Write a letter to management. This action should be done inconjunction with each of the three alternatives above. Managementshould always be informed when its internal controls are notoperating effectively. If a deficiency in internal control is consideredto be a significant deficiency in the design or operation of internalcontrol, professional standards require the auditor to communicatethe significant deficiency to the audit committee or its equivalent inwriting. If the client is a publicly traded company, the auditor mustevaluate the deficiency to determine the impact on the auditor’sreport on internal control over financial reporting. If the deficiency isdeemed to be a material weakness, the auditor’s report on internalcontrol would contain an adverse opinion.15-20 Random (probabilistic) selection is a part of statistical sampling, but it is not, by itself, statistical measurement. To have statistical measurement, it is necessary to mathematically generalize from the sample to the population.Probabilistic selection must be used if the sample is to be evaluated statistically, although it is also acceptable to use probabilistic selection with a nonstatistical evaluation. If nonprobabilistic selection is used, nonstatistical evaluation must be used.15-21 The decisions the auditor must make in using attributes sampling are: What are the objectives of the audit test? Does audit sampling apply?What attributes are to be tested and what exception conditions are identified?What is the population?What is the sampling unit?What should the TER be?What should the ARACR be?What is the EPER?What generalizations can be made from the sample to thepopulation?What are the causes of the individual exceptions?Is the population acceptable?15-21 (continued)In making the above decisions, the following should be considered: The individual situation.Time and budget constraints.The availability of additional substantive procedures.The professional judgment of the auditor.Multiple Choice Questions From CPA Examinations15-22 a. (1) b. (3) c. (2) d. (4)15-23 a. (1) b. (3) c. (4) d. (4)15-24 a. (4) b. (3) c. (1) d. (2)Discussion Questions and Problems15-25a.An example random sampling plan prepared in Excel (P1525.xls) is available on the Companion Website and on the Instructor’s Resource CD-ROM, which is available upon request. The command for selecting the random number can be entered directly onto the spreadsheet, or can be selected from the function menu (math & trig) functions. It may be necessary to add the analysis tool pack to access the RANDBETWEEN function. Once the formula is entered, it can be copied down to select additional random numbers. When a pair of random numbers is required, the formula for the first random number can be entered in the first column, and the formula for the second random number can be entered in the second column.a. First five numbers using systematic selection:Using systematic selection, the definition of the sampling unit for determining the selection interval for population 3 is the total number of lines in the population. The length of the interval is rounded down to ensure that all line numbers selected are within the defined population.15-26a. To test whether shipments have been billed, a sample of warehouse removal slips should be selected and examined to see ifthey have the proper sales invoice attached. The sampling unit willtherefore be the warehouse removal slip.b. Attributes sampling method: Assuming the auditor is willing to accept a TER of 3% at a 10% ARACR, expecting no exceptions in the sample, the appropriate sample size would be 76, determined from Table 15-8.Nonstatistical sampling method: There is no one right answer to this question because the sample size is determined using professional judgment. Due to the relatively small TER (3%), the sample size should not be small. It will most likely be similar in size to the sample chosen by the statistical method.c. Systematic sample selection:22839 = Population size of warehouse removal slips(37521-14682).76 = Sample size using statistical sampling (students’answers will vary if nonstatistical sampling wasused in part b.300 = Interval (22839/76) if statistical sampling is used (students’ answers will vary if nonstatisticalsampling was used in part b).14825 = Random starting point.Select warehouse removal slip 14825 and every 300th warehouse removal slip after (15125, 15425, etc.)Computer generation of random numbers using Excel (P1526.xls): =RANDBETWEEN(14682,37521)The command for selecting the random number can be entered directly onto the spreadsheet, or can be selected from the function menu (math & trig) functions. It may be necessary to add the analysis tool pack to access the RANDBETWEEN function. Once the formula is entered, it can be copied down to select additional random numbers.d. Other audit procedures that could be performed are:1. Test extensions on attached sales invoices for clerical accuracy. (Accuracy)2. Test time delay between warehouse removal slip date and billing date for timeliness of billing. (Timing)3. Trace entries into perpetual inventory records to determinethat inventory is properly relieved for shipments. (Postingand summarization)15-26 (continued)e. The test performed in part c cannot be used to test for occurrenceof sales because the auditor already knows that inventory wasshipped for these sales. To test for occurrence of sales, the salesinvoice entry in the sales journal is the sampling unit. Since thesales invoice numbers are not identical to the warehouse removalslips it would be improper to use the same sample.15-27a. It would be appropriate to use attributes sampling for all audit procedures except audit procedure 1. Procedure 1 is an analyticalprocedure for which the auditor is doing a 100% review of the entirecash receipts journal.b. The appropriate sampling unit for audit procedures 2-5 is a line item,or the date the prelisting of cash receipts is prepared. The primaryemphasis in the test is the completeness objective and auditprocedure 2 indicates there is a prelisting of cash receipts. All otherprocedures can be performed efficiently and effectively by using theprelisting.c. The attributes for testing are as follows:d. The sample sizes for each attribute are as follows:15-28a. Because the sample sizes under nonstatistical sampling are determined using auditor judgment, students’ answers to thisquestion will vary. They will most likely be similar to the samplesizes chosen using attributes sampling in part b. The importantpoint to remember is that the sample sizes chosen should reflectthe changes in the four factors (ARACR, TER, EPER, andpopulation size). The sample sizes should have fairly predictablerelationships, given the changes in the four factors. The followingreflects some of the relationships that should exist in student’ssample size decisions:SAMPLE SIZE EXPLANATION1. 90 Given2. > Column 1 Decrease in ARACR3. > Column 2 Decrease in TER4. > Column 1 Decrease in ARACR (column 4 is thesame as column 2, with a smallerpopulation size)5. < Column 1 Increase in TER-EPER6. < Column 5 Decrease in EPER7. > Columns 3 & 4 Decrease in TER-EPERb. Using the attributes sampling table in Table 15-8, the sample sizesfor columns 1-7 are:1. 882. 1273. 1814. 1275. 256. 187. 149c.d. The difference in the sample size for columns 3 and 6 result from the larger ARACR and larger TER in column 6. The extremely large TER is the major factor causing the difference.e. The greatest effect on the sample size is the difference between TER and EPER. For columns 3 and 7, the differences between the TER and EPER were 3% and 2% respectively. Those two also had the highest sample size. Where the difference between TER and EPER was great, such as columns 5 and 6, the required sample size was extremely small.Population size had a relatively small effect on sample size.The difference in population size in columns 2 and 4 was 99,000 items, but the increase in sample size for the larger population was marginal (actually the sample sizes were the same using the attributes sampling table).f. The sample size is referred to as the initial sample size because it is based on an estimate of the SER. The actual sample must be evaluated before it is possible to know whether the sample is sufficiently large to achieve the objectives of the test.15-29 a.* Students’ answers as to whether the allowance for sampling error risk is sufficient will vary, depending on their judgment. However, they should recognize the effect that lower sample sizes have on the allowance for sampling risk in situations 3, 5 and 8.b. Using the attributes sampling table in Table 15-9, the CUERs forcolumns 1-8 are:1. 4.0%2. 4.6%3. 9.2%4. 4.6%5. 6.2%6. 16.4%7. 3.0%8. 11.3%c.d. The factor that appears to have the greatest effect is the number ofexceptions found in the sample compared to sample size. For example, in columns 5 and 6, the increase from 2% to 10% SER dramatically increased the CUER. Population size appears to have the least effect. For example, in columns 2 and 4, the CUER was the same using the attributes sampling table even though the population in column 4 was 10 times larger.e. The CUER represents the results of the actual sample whereas theTER represents what the auditor will allow. They must be compared to determine whether or not the population is acceptable.15-30a. and b. The sample sizes and CUERs are shown in the following table:a. The auditor selected a sample size smaller than that determinedfrom the tables in populations 1 and 3. The effect of selecting asmaller sample size than the initial sample size required from thetable is the increased likelihood of having the CUER exceed theTER. If a larger sample size is selected, the result may be a samplesize larger than needed to satisfy TER. That results in excess auditcost. Ultimately, however, the comparison of CUER to TERdetermines whether the sample size was too large or too small.b. The SER and CUER are shown in columns 4 and 5 in thepreceding table.c. The population results are unacceptable for populations 1, 4, and 6.In each of those cases, the CUER exceeds TER.The auditor's options are to change TER or ARACR, increase the sample size, or perform other substantive tests to determine whether there are actually material misstatements in thepopulation. An increase in sample size may be worthwhile inpopulation 1 because the CUER exceeds TER by only a smallamount. Increasing sample size would not likely result in improvedresults for either population 4 or 6 because the CUER exceedsTER by a large amount.d. Analysis of exceptions is necessary even when the population isacceptable because the auditor wants to determine the nature andcause of all exceptions. If, for example, the auditor determines thata misstatement was intentional, additional action would be requiredeven if the CUER were less than TER.15-30 (Continued)e.15-31 a. The actual allowance for sampling risk is shown in the following table:b. The CUER is higher for attribute 1 than attribute 2 because the sample sizeis smaller for attribute 1, resulting in a larger allowance for sampling risk.c. The CUER is higher for attribute 3 than attribute 1 because the auditorselected a lower ARACR. This resulted in a larger allowance for sampling risk to achieve the lower ARACR.d. If the auditor increases the sample size for attribute 4 by 50 items and findsno additional exceptions, the CUER is 5.1% (sample size of 150 and three exceptions). If the auditor finds one exception in the additional items, the CUER is 6.0% (sample size of 150, four exceptions). With a TER of 6%, the sample results will be acceptable if one or no exceptions are found in the additional 50 items. This would require a lower SER in the additional sample than the SER in the original sample of 3.0 percent. Whether a lower rate of exception is likely in the additional sample depends on the rate of exception the auditor expected in designing the sample, and whether the auditor believe the original sample to be representative.15-32a. The following shows which are exceptions and why:b. It is inappropriate to set a single acceptable tolerable exception rate and estimated population exception rate for the combined exceptions because each attribute has a different significance tothe auditor and should be considered separately in analyzing the results of the test.c. The CUER assuming a 5% ARACR for each attribute and a sample size of 150 is as follows:15-32 (continued)d.*Students’ answers will most likely vary for this attribute.e. For each exception, the auditor should check with the controller todetermine an explanation for the cause. In addition, the appropriateanalysis for each type of exception is as follows:15-33a. Attributes sampling approach: The test of control attribute had a 6% SER and a CUER of 12.9%. The substantive test of transactionsattribute has SER of 0% and a CUER of 4.6%.Nonstatistical sampling approach: As in the attributes samplingapproach, the SERs for the test of control and the substantive testof transactions are 6% and 0%, respectively. Students’ estimates ofthe CUERs for the two tests will vary, but will probably be similar tothe CUERs calculated under the attributes sampling approach.b. Attributes sampling approach: TER is 5%. CUERs are 12.9% and4.6%. Therefore, only the substantive test of transactions resultsare satisfactory.Nonstatistical sampling approach: Because the SER for the test ofcontrol is greater than the TER of 5%, the results are clearly notacceptable. Students’ estimates for CUER for the test of controlshould be greater than the SER of 6%. For the substantive test oftransactions, the SER is 0%. It is unlikely that students will estimateCUER for this test greater than 5%, so the results are acceptablefor the substantive test of transactions.c. If the CUER exceeds the TER, the auditor may:1. Revise the TER if he or she thinks the original specificationswere too conservative.2. Expand the sample size if cost permits.3. Alter the substantive procedures if possible.4. Write a letter to management in conjunction with each of theabove to inform management of a deficiency in their internalcontrols. If the client is a publicly traded company, theauditor must evaluate the deficiency to determine the impacton the auditor’s report on internal control over financialreporting. If the deficiency is deemed to be a materialweakness, the auditor’s report on internal control wouldcontain an adverse opinion.In this case, the auditor has evidence that the test of control procedures are not effective, but no exceptions in the sample resulted because of the breakdown. An expansion of the attributestest does not seem advisable and therefore, the auditor shouldprobably expand confirmation of accounts receivable tests. Inaddition, he or she should write a letter to management to informthem of the control breakdown.d. Although misstatements are more likely when controls are noteffective, control deviations do not necessarily result in actualmisstatements. These control deviations involved a lack ofindication of internal verification of pricing, extensions and footingsof invoices. The deviations will not result in actual errors if pricing,extensions and footings were initially correctly calculated, or if theindividual responsible for internal verification performed theprocedure but did not document that it was performed.e. In this case, we want to find out why some invoices are notinternally verified. Possible reasons are incompetence,carelessness, regular clerk on vacation, etc. It is desirable to isolatethe exceptions to certain clerks, time periods or types of invoices.Case15-34a. Audit sampling could be conveniently used for procedures 3 and 4 since each is to be performed on a sample of the population.b. The most appropriate sampling unit for conducting most of the auditsampling tests is the shipping document because most of the testsare related to procedure 4. Following the instructions of the auditprogram, however, the auditor would use sales journal entries asthe sampling unit for step 3 and shipping document numbers forstep 4. Using shipping document numbers, rather than thedocuments themselves, allows the auditor to test the numericalcontrol over shipping documents, as well as to test for unrecordedsales. The selection of numbers will lead to a sample of actualshipping documents upon which tests will be performed.。

Silk CentralOpenT ext Silk Central is an open solution that addresses test management by aligning goals and requirements with testing, technology, and processes. It provides an integrated framework for im-proving productivity, traceability, and visibility for all types of software testing and ensures control over application readiness.Product HighlightsEffective collaboration across teams, pro-cesses, and tools drives successful projects.Yet software delivery teams see testing astime-consuming, poorly focused, and a hin-drance to project goals. Silk Central providesgoal- and requirement-driven test manage-ment. It coordinates technologies, resources,team capabilities, and meaningful deliverablesto promote quality, collaboration, efficiency,and confidence. Silk Central scales from sup-porting a single project to being the axis thatunites software development teams in differ-ent locations, right across an organization. Silk Central delivers control over application quality by providing consistent, repeatable processes from traditional methodologies—such as waterfall—right through to more itera-tive approaches, including agile. As a unified framework for managing manual and auto-mated tests, it integrates with unit, functional, and performance test suites; issue and require-ment management systems; and continuous integration (CI) and DevOps tools. Business Process T estingThe Business Process Testing (BPT) capa-bilities in Silk Central support an organiza-tion’s need to validate end-to-end business processes implemented in the application. Besides demonstrating end-to-end process quality, BPT also enables control among tes-ters, such as the hand-off between teams and the behavior on test failure.Figure 1. Business Process T estingT est Asset WorkflowDrive improved management and controlacross your tests while maintaining auditability.Figure 2. Workflow statesData SheetData Sheet Silk CentralT ransition tests through a review process from Draft, Under Review, to Approved state with full audit control at each stage, and use dedi-cated role permissions to control the process. Redundant tests can be marked as Obsolete at any stage of the workflow, ready for final review before deletion.Collaboration Using Microsoft T eamsThe integration of Silk Central with Microsoft T eams provides a means of team collaboration for manual testers working together on a proj-ect. A set of predefined actions trigger mes-sages to be sent to Microsoft T eams. These messages deliver the crucial information and links to jump to the relevant items in Silk Central or to perform the next steps.Client and Project StructureSilk Central supports your diverse needs, and the scales of deployment, by using clients (dis-tinct units within a Silk Central instance) to sup-port a multi-tenancy structure. This enables organizations to separate projects by clients while maintaining security and control, with additional ability to manage license allocation, e ither within a single database or across mul-tiple database instances.Key FeaturesRequirement ManagementMANAGE REQUIREMENTS FROMMULTIPLE SOURCESSilk Central enables you to unite requirements, regardless of source, into a single project. Achieve a centralized end-to-end view in one location to enhance collaboration and control across your project.TEST AGILE REQUIREMENTSSilk Central offers strong integrations with leading agile planning and tracking tools such as Atlassian Jira Agile. Silk Central manual e xecution planning supports agile develop-ment through progress reporting, burndown charts, planning, and personal dashboards. Optimized to test both agile and traditional re-quirements, Silk Central accelerates test ex-ecution and increases collaboration on qualityassurance activities.MITIGATE RISK USING QUALITY GOALSSilk Central helps testers prioritize, execute,and demonstrate how their efforts respondto risk-based and requirement-driven test-ing. Silk Central reports illustrate how test-ing has responded to these defined qualitygoals, ultimately enabling the critical go/no-go decision.T est Design and Asset ManagementKEYWORD-DRIVEN TESTINGKeyword-driven testing closely couples SilkCen t ral management with Selenium or Silk T estautomation capabilities:■Involve different professional groups in thetest automation process by separatingtest design and implementation.■Achieve maintenance benefits by reusingtest code or keywords, and enjoy the easyabstraction of low-level automation andhigh-level business scenarios throughmulti-level keyword sequences.■Enable a seamless transition from manualto automated testing by basing keywordtests on current manual test steps.■Get recommended keywords based on theautomatic analysis of existing keyword-driven tests when creating a new test.SHARE TEST ASSETS ACROSS PROJECTSDrive improved reuse and lower maintenanceoverheads by sharing tests across projects.Defining a central test repository and enablingprojects to reference tests in it improves pro-cess and practice within your organization.REUSABILITY AND MAINTAINABILITYOF ASSETSSilk Central efficiently maintains and re-uses test assets. Mandatory Attributes andMandatory Properties help standardize datausage to ensure they are always used in as-set creation. Use the Global List attributesto centrally maintain a set of items and usethem in multiple projects. This enables datastandardization and increases reusability andmaintainability across requirements, tests, andexecution plans. Utilize Linked Fields for man-agement of related fields to reduce the likeli-hood of wrong input and User List attributes toautomatically populate tests or execution plansto project users.T est Planning and ExecutionADVANCED MANUAL EXECUTION PLANNINGSilk Central increases efficiency and productiv-ity by making it easy to identify, plan, and sched-ule manual tests. It allows users to decide:■What to test through quality goals andfilters■When to test by planning test cycleswithin specified timeframes■Where to test by choosing which systemsor configurations to use■Who to test by allocating based onresource and time capacityPARALLEL TEST EXECUTIONSOrganizations need efficient test execution.The parallel testing capabilities within SilkCentral execute automated tests across ev-ery execution server (physical or virtual) at thesame time—reducing overall test time anddriving project efficiency. Silk Central providesusers with the flexibility to decide what to ex-ecute in parallel and what not to.KUBERNETES PLUGINReduce resource consumption and cost bymaking Kubernetes pods available for test ex-ecution as virtual execution servers.MOBILE TESTING■Execute mobile device testing withUFT Digital Lab and Silk T est Workbenchintegration, including automated functionaltests and manual tests.■Use Silk Central when manually testing mobile applications. It mirrors the mobile device on your desktop for convenient interaction with remote test devices.■Enjoy the flexible scheduling control of manual and automated tests as if any remote iOS or Android device were connected locally. T est teams can also select mobile test devices using multiple filtering options, including device type, platform, application, or device name.TESTING FROM EVERY ANGLEIntegration with many testing tools means Silk Central offers coverage of every angle of your application through unit, functional, and perfor-mance testing, whether manual or automated. ■Unit T est: JUnit, NUnit, UFT Developer■Functional T est: UFT One, Silk T est■Performance T est: Silk Performer, LoadRunner Professional■Regression T est: UFT One, Silk T est■Any T est: The ProcessExecutor test type can be used to execute any script from command line.CODE AND CONFIGURATION COVERAGESilk Central helps identify functionality gaps in current test definitions by providing code cov-erage analysis for manual and automated tests for .NET or Java apps.Configuration testing ensures test scripts exe-cuted against multiple configurations need no duplication, providing script reuse and report-ing on coverage of test environments.EXECUTION SNAPSHOTExporting the ‘Document View’ of the Execution Planning unit to Microsoft Excel creates a snapshot of execution status and progress for management, analytics, and reporting. Filters, sorting, grouping and order settings of the col-umns in DocumentView are also applied to the exported data.T racking and ReportingTESTBOOK: INSIGHT INTO MANUAL TESTSThe T estbook delivers real-time updates onall activities during manual testing. It simplifiescollaboration among testers and test manag-ers by displaying who did what and when.SIDE-BY-SIDE RESULTS COMPARISONFOR AUTOMATED TESTSUse side-by-side result analysis for fast in-sight into the status of automated test runs.Compare runs using visual reports showingthe execution status across every individualconfiguration.TEST RESULT CONSOLIDATIONImprove result analysis by extending test ex-ecution tooling eco-systems:■Consume results for automated teststhat are executed outside of Silk Centralexecution servers.■Collect all artifacts—such as requirements,tests, and results—in a single repositoryfor holistic reporting and decision-making.REPORTING AND ANAL YTICSUse the reports to view a full audit status ofmanual test results and associated defects.Y ou can also trace issues raised, associated re-sult files, and progress status in a format view-able online or exported to a PDF. Use video andscreen capture for manual and automated testactivities to reproduce issues and compile evi-dence to support compliance and audit needs.As well as rich metrics and analytics avail-able through default reports, Silk CentralFigure 3. User defined dashboardaccommodates custom reporting needs. Itsupports Microsoft Word and BIRT for ad-vanced reporting and can export data to PDFor Microsoft Excel.BUILT-IN ISSUE TRACKINGUse the built-in issue tracking capabilities toraise, track, and manage issues against testassets and a defined workflow relevant to yourorganization.UsabilityADVANCED MANUAL TEST INTERFACEThis web-based interface requires no installa-tion and needs little or no training. Users canexecute tests and capture evidence to supporttest execution with screenshots, videos, au-dios, result files, code coverage, and defects.FACILITATE ACCESSIBILITY NEEDSBy supporting keyboard navigation and fa-cilitating audible feedback through a screenreader, Silk Central is accessible for blind orvisually impaired users. It supports both NVDAand JAWS.SIMPLIFY USER MAINTENANCE WITHLDAP OR ACTIVE DIRECTORY (AD)Automatically create and authenticate users ondemand. Eliminate the need to manually cre-ate accounts for users who are interested orinvolved in test activities with Silk Central.Supported IntegrationsFigure 4. Silk Central integrations landscapeINTEGRATIONS VIA OPENTEXT CONNECTThe OpenT ext Connect portfolio of integrations provides extensive integration capabilities. Its Silk Central T est Manager Connector simpli-fies integration setup, optimizes require m ent synchronization performance, and enables better visibility into test asset relationships and traceability between tests and defects. INTEGRATIONS VIA SILK CENTRAL APISilk Central offers SOAP-based Web Services for the integration of third-party applications, as well as a REST API for managing results of external execution plan runs.OPENTEXT SOFTWARE INTEGRATIONS■Silk Performer■LoadRunner Professional■Silk T est■UFT One■UFT Developer■StarT eam■AccuRev■Silk T estPartner■Atlas■Deployment Automation■Release Control■Solutions Business Manager ■UFT Mobile■OpenT ext Connect■Jenkins, Hudson■Microsoft TFS■SeleniumTHIRD-PARTY SOFTWARE INTEGRATIONS■IBM DOORS, DOORS Next Generation■Bugzilla■Atlassian Jira and Jira Agile■JUnit and NUnit■Subversion■Git■T eam Foundation Server■Microsoft Office Word and Excel■Microsoft T eams■Amazon and Azure Cloud execution■Kubernetes■Apache Commons Virtual File System (VFS)■Microsoft Visual Studio/Visual Studio T estAgent■Plug-in API for additional integrations Please consult your OpenT ext account repre-sentative for supported versions and additional integrations.System RequirementsOperating System Support■W indows Server 2016, 2019Additional for Mobile Device T esting■A ndroid 5.x, 6.x, 7.x, 8.x, 9.x and 10.x■i OS 10.x,11.x, 12.x and 13.xAdditional for Execution Server■W indows 8.1 (32/64bit), Windows 10 (32/64bit)■U buntu, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Debian, SUSE Linux Web Server Support■I IS 8, 10 (32/64Bit)■S tandalone web server (T omcat)Web Browser Support■I nternet Explorer 11 or later (no compatibility mode), Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome,Microsoft EdgeDatabase Support■M icrosoft SQL Server 2016 SP2, 2017, 2019■Oracle 19cPlease refer to Installation and System Con fi guration Help in Silk Central documentation for fur-ther details.。

Chapter 15 The Brain, the Spinal Cord and the NervesOnce a number of the body systems have been surveyed, it should become fairly obvious that not one of these systems is capable of functioning alone. All are interdependent, and all must work together as one unit in order that the normal conditions within the body may prevail. The agency that insures the coordination of the organs and organ systems is the nervous system.Conditions both within and outside the body are constantly changing; one purpose of the nervous system is to respond to these internal and external changes (known as stimuli) and so cause the body to adapt itself to new conditions.The nervous system has been very aptly compared with a telephone exchange in which the brain and the spinal cord act as centers and the nerve trunks serve as cables and wires for carrying messages to and from various parts of these centers.15. 1 The Nervous System as a WholeThe parts of the nervous system may be grouped according to how they are made (structure) or else on the basis of what they do (function).Structural (ANATOMIC) ClassificationThe structure of the nervous system serves as the basis for the more commonly used grouping of the parts of the nervous system, as follows:1.The central nervous system, which includes the brain and the spinal cord.2.The peripheral nervous system, which is made up of cranial and spinal nerves.Cranial nerves are those which carry impulses to and from the brain. Spinal nerves arethose which carry messages to and from the spinal cord.From the standpoint of structure, the central and peripheral nervous systems together include most of the nerve tissue in the body. However, certain peripheral nerves have a special function, and for this reason they are grouped together under the designation autonomic nervous system. The reason for this separate classification is that the autonomic nervous system has to do largely with activities which go on more or less automatically. This system carries impulses from the central nervous system to the glands, the involuntary muscles found in the walls of tubes and hollow organs and the heart. The autonomic nervous system is subdivided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, both of which will be explained later in this chapter.Some of the nerves that carry autonomic nervous system impulses are cranial, and others are spinal.15.2 On Nerves in GeneralThe basic nerve cell is called a neuron. Neurons are composed of a cell body, containing the nucleus, with the addition of threadlike projections of the cytoplasm known as nerve fibers. The nerve fibers are of two kinds: dendrites, which conduct impulses to the cell body; and axons, which conduct impulses away from the cell body. The dendrites of sensory neurons are verydifferent from those of other neuron. They are usually single and they may be very long (as much as 3 feet) or they may be short; but in any case, they do not have the treelike appearance so typical of other dendrites. Each sensory nerve fiber (dendrite) has a special structure called the receptor, or end organ, where the stimulus is received and the sensory impulse begins. Sensations such as pain, touch, hearing and seeing which involve these sensory neurons will be discussed in Chapter 11.Each neuron is a separate unit, and there is no anatomic unity between neurons. It would be logical to ask how it is possible for neurons to be in contact; in other words, how the axon of one neuron can be in functional contact with the dendrite of another neuron. This is accomplished by the synapse, from a Greek word meaning “to clasp.” Synapses, then, are points of junction fro transmission of nerve impulses.Nerve fibers that are connected with receptors (for receiving stimuli) conduct impulses to the brain and cord, and when grouped together form afferent nerves. Those fibers that carry impulses from the centers out to the muscles and glands form efferent nerves. Motor neurons, which carry impulses that lead to the contraction of skeletal muscles, are classified as efferent neurons (Fig. 15.1). Some nerves contain a mixture of afferent and efferent nerve fibers and are often referred to as mixed nerves.Fig. 15.1 Diagram of a motor neuron15.3 The Central Nervous SystemTHE BRAINMain parts of the brainThe largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which is divided into the two cerebral hemispheres, a right and a left one. The brainstem includes the deeper parts that comprise the interbrain (thalamus, etc.) that cannot be seen unless the brain is sectioned, and a series of smaller parts that extend downward. Starting at the upper part of this series, we may see a small part of the midbrain. Below it and plainly visible from the under view of the brain are the pons and the medulla oblongata, which connects with the spinal cord through a large opening in the base of the skull. The pons connects the midbrain and the medulla. Next in size to the cerebralhemispheres is the cerebellum, a word meaning :little brain.” It is located immediately below the back part of the cerebral hemispheres and is connected with the other parts of the brain only by means of the bridgelike pons.Structure of the cerebral hemispheresThe outer nerve tissue of the cerebral hemispheres is gray matter and is called the cerebral cortex. This gray cortex is arranged in folds forming elevated portions known as convolutions, separated by depressions or grooves called fissures, or sulci (Fig. 15.2). Internally the cerebral hemispheres are made largely of white matter and a few islands of gray matter. Inside the hemispheres are two spaces extending in a somewhat irregular fashion. These are the lateral ventricles, which are filled with a watery fluid common to both the brain and the spinal cord called cerebrospinal fluid, to be discussed later.Although there are many fissures (sulci), a few are especially important landmarks. These include the:1. Longitudinal fissure, which is a deep groove that separates the upper parts of the cerebralhemisphere from each other.2. Central fissure, which extends from the top of the brain near the center downward alongthe side at right angles to the longitudinal fissure.3. Lateral fissure, which curves somewhat along the side of the brain and separates thetemporal lobe from the rest of the cerebral hemisphere.Let us examine the cerebral cortex, the layer of gray matter which forms the surface of each cerebral hemisphere. It is within the cerebral cortex that all impulses are received and analyzed. These form the basis of knowledge; the brain “stores”knowledge, much of which can be produced on demand by means of the phenomenon which we call memory. It is in the cerebral cortex that all thought takes place, all association, judgment and discrimination. It is from the cerebral cortex, too, that the orders originating from conscious deliberation emanate; that is, the voluntary movements are controlled here.Fig. 15.2 External surface of the brain showing the main partsand some of the lobes and fissures of the cerebrum.Division and functions of the cerebral cortexThe cerebral cortex of each hemisphere is divided into four lobes, areas named from the overlying cranial bones. It has been found that each area controls a certain category of functions. The four lobes, with some of their characteristic functions, follow:1. The frontal lobe, which is relatively much larger in the human being than in any otherorganism. This contains the motor cortex which controls the voluntary muscles. The left side of the brain governs the right side of the body and the right side of the brain governs the left side of the body. The upper portion of the center controls the lower parts of the body. The frontal lobe also contains two areas used in speech (the speech centers will be discussed later).2. The parietal lobe, which occupies the upper part of each hemisphere, just behind thecentral fissure. This contains the sensory area, in which the general senses such as pain, touch and temperature are interpreted. Also, such interpretations as the determination of distances, sizes and shapes take place here.3. The temporal lobe, which is lateral (at the side) and folds under the hemispheres on eachside. This contains the auditory center for interpreting impulses from the ear.4. The occipital lobe, which is the most posterior, and extends over the cerebellum. Thiscontains the visual area for interpreting messages from the retina of the eye.Speech centersThe speech centers are among the most interesting groups of areas in the cerebral hemispheres (Fig. 15.3). Their development and use are closely connected with the processes of learning. These areas are called the:1. Auditory speech center, located in the temporal lobe near the auditory center. While theauditory center enables a person to interpret sounds, it does not have anything to do with the understanding of words. Such an understanding of language requires the development of the auditory speech center. Often, this is the first speech center to develop in the child.Babies often seem to understand what is being said long before they do any talking themselves. It is usually several years before children learn to read or write words. In many parts of the world people never learn to read or write their language.2. Visual speech center, which is somewhat above and in front of the visual center. In thisarea the ability to read with understanding is developed. You may see the writing in the Japanese language, for example, but this would involve only the visual center in the occipital lobe unless you could read the words.3. Motor speech center, located just in front of the lowest part of the motor cortex in thefrontal lobe. Since the lower part of the motor cortex controls the muscles of the head and the neck, it seems logical to think of the speech area as an extension forward to make possible the control of the muscles of speech in the tongue, the soft palate and the larynx.4. Written speech center, located above the motor speech center, and in front of the corticalarea that controls the muscles of the arm and the hand. Again this center is an extension forward from the motor cortex. The ability to write words usually is one of the last phases in the development of learning words and their meaning, although occasionally a person may write words more readily than he can vocalize them.Fig. 15.3. Functional areas of cerebrumOther parts of the cerebral hemispheresBeneath the gray matter of the cerebral cortex is the white matter, consisting of nerve fibers which connect the cortical areas with each other and with other parts of the nervous system. Among the most important of these large collections of nerve fibers is the internal capsule, a crowded strip of white matter where any injury is apt to cause extensive damage. At the base of each hemisphere are the nerve cell groups called basal ganglia, which regulate the body movements originating in the cerebral cortex. On the underside of each cerebral hemisphere is the olfactory area, concerned with the sense of smell, which is stimulated by the impulses arising in the nerve receptors of the nose.The interbrainThe interbrain, or diencephalon, can be seen only by cutting into the central section of the brain. It includes the thalamus and the hypothalamus. The two masses of gray matter that form the thalamus are relay centers and act to monitor sensory stimuli, suppressing some and magnifying others. The hypothalamus is located in the midline area below the thalamus and contains cells that control body temperature, water balance, sleep, appetite and some of our emotions, such as fear and pleasure. Both divisions of the autonomic nervous system are under the control of the hypothalamus. Thus it influe nces the heart‟s beating, the contractions of the walls of the bladder and other vital body functions.The midbrainThe midbrain is located just below the center of the cerebrum. It forms one of the forward parts of the brainstem. Four rounded masses of gray matter that are hidden by the cerebralhemispheres form the upper part of the midbrain. These four bodies, the corpora quadiigemina, act as relay centers for certain eye and ear reflexes. The ventral white matter of the midbrain conducts impulses between the higher centers of the cerebrum and the lower centers in the pons, cerebellum, medulla and spinal cord.The cerebellumThe cerebellum is made up of three parts: the middle portion, called the vermis (meaning …'wormlike‟‟), and two lateral hemisphere s at the sides. As in the case of the cerebral hemispheres, the cerebellum has an outer area of gray matter and an inner portion that is largely white matter. The functions of the cerebellum are:1. To aid in the coordination of voluntary muscles so that they will function smoothly and inan orderly fashion. Disease of the cerebellum causes muscular jerkiness and tremors.2. To help maintain balance in standing, walking and sitting, as well as during morestrenuous activities. Messages from the internal ear and from the tendon and muscle sensory end organs aid the cerebellum.3. To aid in maintaining muscle tone so that all muscle fibers are slightly tensed and readyto produce necessary changes in position as quickly as may be necessary.The ponsThe pons is white in color because it is composed largely of myelinated nerve fibers. These fibers in the pons carry messages from one side of the cerebellum to the other, from the cerebellum to the higher centers in the cerebrum and midbrain, and from the cerebellum to the lower centers, including the medulla and the spinal cord. Not only is the pons an important connecting link between the cerebellum and the rest of the nervous system, but it also contains connections with four pairs of cranial nerves. Further it contains nerve fibers that carry impulses to and from the centers located above and below it. Certain reflex (involuntary) actions are controlled in the pons; namely, some occurring in respiration.The medulla oblongataThe medulla of the brain is located between the pons and the spinal cord. It appears white externally because, like the pons, it contains many covered (myelinated) nerve fibers. Internally it contains collections of cell bodies (gray matter), which are called centers or nuclei. Among these are the very important vital centers including:1. The respiratory center, which controls the muscles of respiration in response to chemicaland other stimuli.2. The cardiac center, which tends to slow the heart rate so that it will not beat too rapidly tobe effective.3. The vasomotor center, which affects the muscles in the blood vessel walls and hencehelps to determine blood pressure.The last four pairs of cranial nerves are connected with the medulla. The nerve fibers that carry messages up through the spinal cord to the brain continue through the medulla also, as do similar descending or motor fibers. These groups of nerve fibers form tracts (bundles) and are grouped together according to function. The motor fibers from the motor cortex of the cerebral hemispheres .extend down through the medulla, and most of them cross from one side to the other (decussate) while going through this part of the brain. It is in the medulla that the shifting of nerve fibers occurs which causes the right cerebral hemisphere to control muscles in the left side of the body, and the upper portion of the cortex to control of muscles in the lower portions of the person. The medulla is an important reflex centfer, and it is here that certain neurons end and impulses are relayed to other neurons.Ventricles of the brainWithin the brain are four fluid-filled spaces called the ventricles. These extend into the various parts of the brain in a somewhat irregular fashion. We have already mentioned the largest, the lateral ventricles in the two cerebral hemispheres. Their extensions into the lobes of the cerebrum are called horns. These paired ventricles communicate with a midline space, the third ventricle, by means of the openings called foramina. The third ventricle is bounded on each side by the two parts of the thalamus, while the floor is occupied by the hypothalamus. Continuing down from the third ventricle a small canal, called the cerebral aqueduet, extends through the midbrain into the fourth ventricle. The latter is continuous with the near microscopic neural, or central, canal of the spinal cord. Do not confuse this tiny canal inside the cord with the much larger vertebral, or spinal, canal that is a part of the dorsal cavity enclosing the entire cord, together with its membranes and surrounding fluid. .In the roof of the fourth ventricle are three openings that allow the escape of fluid to the area that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. This will be discussed later.After removal of some of the fluid, air or other substances may be injected, and x-rays called encephalograms or ventriculograms are taken. Tumors or other brain disorders may sometimes be located by this means.Another kind of study of the brain and other soft tissues involves the use of high frequency sound impulses. This is called echoencephalography.BrainwavesThe interactions of the billions of nerve cells in the brain give rise to measurable electric currents. These may be recorded by an instrument called the electroencephalograph, which was Mentioned in Chapter 3. Tfie recorded tracings dr brain waves produce an electroencephalogram, not to be confused with the encephalogram mentioned earlier.Disorders of the brainSince the scientific name for the brain is encephalon, infection of, the brain is known asencephalitis. There are many causes of such disease, but the two chief pathogens are:1. Viruses, which cause some of the epidemic types of, sleeping sickness sometimes foundin the United States and in other parts of the world.2. Certain one-celled animals (protozoa) called trypanosoma, which cause the so-calledAfrican sleeping sickness. These protozoa are carried by a kind of fly (tsetse) and are capable of invading the cerebro-spinal fluid of man.Other infections that may involve the brain and related parts include abscesses and meningitis (explained later). As in the case of encephalitis a variety of organisms may cause these disorders. Viruses, bacteria, protozoa and fungi may travel from the centers of infection in the teeth, the sinuses, the tonsils and in the middle ear.Stroke, or cerebral apoplexy, is by far the most common kind of brain disorder. Rupture of a blood vessel (with a consequent cerebral hemorrhage), thrombosis or embolism may cause destruction of brain tissue. Such disorders are more frequent in the presence of artery wall disease, and hence are more common after the age of 40. The onset may seem to be sudden and often is referred to as a cerebrovascular accident. The effects of a stroke will depend on the extent and location of the artery involvement. A hemorrhage into the white matter of the internal capsule in the lower part of the cerebrum may cause extensive paralysis on the side opposite to the affected area. Such a paralysis is called hemiplegia, and the person so afflicted is known as a hemiplegic.Cerebral palsy is a disorder present at birth. It is characterized by diverse disorders of muscles varying in degree from weakness to complete paralysis, and in extent from a slight disorder of the lower extremity muscles to a multiplicity of paralyses involving all four extremities and the speech muscles as well. With patient and continuous muscle reeducation, speech training and other corrective procedures these victims may be helped considerably.Epilepsy, or so-called falling sickness, is a chronic disorder in which there is abnormality of brain function without apparent changes in tlte nerve tissues. In most cases the cause is not known. The study of brain waves obtained with the electroencephalograph usually shows abnormalities and is helpful both in diagnosis and treatment. Research is constantly improving and increasing the knowledge concerning the various forms of epilepsy. Many of these sufferers can be helped to live a normal active life if they follow a very careful hygienic regimen and use appropriate medication as outlined by a physician.Tumors of the brain may develop at any age, but are somewhat more common in young and middle-aged adults. The majority of brain tumors originate from the neuroglia and are called gliomas. The symptoms produced depend on the location of the growth, its destructiveness and the amount it compresses the brain tissue. Involvement of the frontal portions of the cerebrum often causes mental symptoms, such as changes in personality, disordered conduct and drowsiness. Early surgery offers hope of cure in some cases.Aphasia is a term that refers to the loss of the ability to speak or write, or the loss of the understanding of written or spoken language. There are several different kinds of aphasia,depending on what part of the brain is affected. Usually damage to a speech center causes more disturbance in the well-educated person than it does in the illiterate. It also has been noted that there is a tendency for the last language to be acquired to be the first to be lost; and conversely, the speech concepts that were obtained first (in childhood) remain the longest. The lesion that causes aphasia is likely to be in the left cerebral hemisphere in the right-handed person. Often much can be done for these people by patient retraining and much.understanding. The brain is an organ that has a marvelous capacity for adapting itself to different conditions, and its resources are tremendous. Often some means of communi¬cation can be found even though speech areas are damaged.THE SPINAL CORDLocation of the spinal cordIn the embryo the spinal cord occupies the entire spinal canal and so extends down into the tail portion of the vertebral column. However, the column of bone grows much more rapidly than the nerve tissue of the cord, so that the end of the cord soon fails to extend into the lower part of the spinal canal. This disparity in growth increases so that in the adult the cord ends in the region just below the area to which the last rib attaches (between the first and second lumbar vertebrae).Structure of the spinal cordExamination of the spinal cord reveals that it has a small irregularly shaped internal section made of gray matter (nerve cell bodies), and a larger area surrounding this gray part that is made of white matter (nerve fibers). A cross section of the cord shows that the gray matter is so arranged that a column of cells extends up and down dorsally, one on each side; another column is found in the ventral region; while a third less conspicuous part is situated on each side. These three pairs of columns of gray matter give this cross section an H-shaped appearance. The white matter can be seen to be made of thousands of nerve fibers arranged in three areas external to the gray matter on each side.Functions of the spinal cordThe functions of the cord may be divided into three aspects;1. Reflex activities, which involve the transfer and integration of messages that enter thecord, so that a sensory (afferent) impulse entering the center will become a motor (efferent) message leaving the cord.2. A pathway for conducting sensory impulses from afferent nerves upward throughascending tracts to the brain.3. A pathway for conducting motor impulses from the brain down through descending tractsto the nerves that will supply muscles or glands.The reflex pathway through the spinal cord usually involves three or more nerve cellstogether with their fibers, including:1. The sensory neuron, which has its beginning in a receptor and its nerve fiber in a nervethat leads to the cord.2. One or more central neurons, which are entirely within the cord.3. The motor neuron, which receives the impulse from a central neuron and then carries itvia its long axon through a nerve to a muscle or a gland.The knee jerk is an example of a spinal reflex. The pathway for the impulses that make this reflex possible includes a sensory neuron which has its receptor in the tendon just below die knee, its sensory nerve fiber in the nerves that extend to the spinal cord, central neurons inside the lower part of the cord and motor neurons that send processes through nerves from the cord to the effectors in the thigh‟s kicking muscle.Disorders involving the spinal cordAn acute virus disease affecting both the spinal cord and the brain is poliomyelitis, which is most commonly found in children. The polio virus is spread from the nose and the throat; from here it travels to the central nervous system, possibly by way of the respiratory passages and the blood. The virus may destroy the motor nerve cells in the spinal cord, in which case paralysis of one or more limbs results. The virus also can attack some of the cells of the brain and cause death. Prevention of poliomyelitis by means of the oral Sabin vaccine (which was preceded by the Salk vaccine) is one of the many significant advances in preventive medicine.Injuries to the spinal cord occur in traffic accidents in which bones of the spinal column are broken or dislocated. In wars gunshot or shrapnel wounds may damage the cord in varying degrees. Since the nerve tissue of the brain and the cord cannot repair itself, severing the cord causes paralysis below the injury, together with loss of all sensation from this area. Loss of sensation and of motion in the lower part of the body is called paraplegia.Other disorders of the spinal cord include tumors that grow from within the cord or that compress the cord from outside.Multiple sclerosis (sclerosis means hardening) involves the entire spinal cord as well as the brain. In this disease the myelin, a fatlike substance that forms a sheath around certain nerve fibers, disappears and the nerve axons themselves degenerate. It is an extremely disabling disease; however, it usually progresses very slowly so that the patient may have many years of relatively comfortable life remaining to him.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a motor disorder of the nervous system in which certain cells are destroyed. The progressive destruction causes muscle atrophy and loss of motor control, until finally the victim is unable to swallow, or to talk.Spinal puncture and anesthesiaFluid may be removed from the space below the spinal cord. Since the cord is only about 18 inches long and ends some distance above the level of the hip line, a spinal puncture is usuallydone between the third and fourth lumbar vertebrae, about the level of the top of the hip bone. This cerebro-spinal fluid may be studied in the laboratory for evidence of disease or injury.Anesthetics are sometimes dissolved in. cerebrospinal fluid and then injected into the space below the cord, thus temporarily removing all sensation from the lower part of the body. In the hands of a trained operator this method of giving an anesthetic may have a number of advantages for certain types of surgery in selected patients. Under this type of anesthetic the patient is “awake” during the operation, but of course feels nothing in his lower body.COVERINGS OF THE BRAIN AND THE SPINAL CORDThe meninges are three layers of connective tissue that surround the brain and the spinal cord to form a complete enclosure; The outermost of these membranes is called the dura mater. It is the thickest and toughest of these meninges. Inside the skull, the dura mater splits in certain places to provide channels for the blood coming from the brain tissue. The second layer around the brain and the spinal cord is the arachnoid membrane (so-called because it resembles the webs produced by spiders, which belong to a group of animals called the Arachnida). The arachnoid membrane is loosely attached, to the deepest of the meninges by weblike fibers allowing a space for fluid located between the arachnoid and the innermost membrane. The third layer around the brain, the pia mater, is attached to the .nerve tissue of the brain and spinal cord and dips into all the depressions, unlike the other two meninges. It is made of a delicate Connective tissue in which there are many blood vessels. The blood supply to the brain is carried, to a large extent, by the pia mater (Fig. 15.4).Fig. 15.4 Frontal (coroal) section of top of head, showing meninges andrelated parts.。

2024年1月浙江省首考普通高等学校招生全国统一考试英语试题一、阅读理解Tom Sawyer Play Is an AdventureA 35-minute hand-clapping, foot-stomping musical version of a Mark Twain favorite returns with this Tall Stacks festival.“Tom Sawyer: A River Adventure” has all the good stuff, including the fence painting, the graveyard, the island and the cave. It is adapted by Joe McDonough, with music by David Kisor. That’s the local stage writing team that creates many of the Children’s Theatre of Cincinnati’s original musicals, along with the holiday family musicals at Ensemble Theatre.This year Nathan Turner of Burlington is Tom Sawyer, and Robbie McMath of Fort Mitchell is Huck Finn.Tumer, a 10th-grader at School for Creative and Performing Arts, is a familiar presence on Cincinnati’s stages. He is a star act or of Children’s Theatre, having played leading roles in “The Legend of Sleepy Hollow” and “The Wizard of Oz,” and is fresh from Jersey Production “Ragtime”.McMath is a junior at Beechwood High School. He was in the cast of “Tom Sawyer” when it was first performed and is a Children’s Theatre regular, with five shows to his credit. This summer he attended Kentucky’s Governor’s School for the Arts in Musical Theatre.Note to teachers: Children’s Theatre has a study guide demonstrating how math and science can be taught through “Tom Sawyer.” For downloadable lessons, visit the official website of Children’s Theatre.1.Who wrote the music for “Tom Sawyer: A River Adventure”?A.David Kisor.B.Joe McDonough.C.Nathan Turner.D.Robbie McMath.2.What can we learn about the two actors?A.They study in the same school.B.They worked together in ”Ragtime“.C.They are experienced on stage.D.They became friends ten years ago.3.What does Children’s Theatre provide for teachers?A.Research funding.B.Training opportunities.C.Technical support.D.Educational resources.【答案】1.A 2.C 3.D【解析】1.根据第二段中的“It is adapted by Joe McDonough, with music by David Kisor.(本剧由乔·麦克多诺改编,大卫·基索作曲。

单元质量检测(三)(时间:100分钟满分:120分)Ⅰ.阅读理解(共15小题;每小题2分,满分30分)阅读下列短文,从每题所给的A、B、C和D四个选项中,选出最佳选项。
ABullets (子弹) to Bandages: Life Inside the Israel Defense ForcesMark Terris, M.D.www.xlibris. com$34.99 hardcover | $23.99 softcover | $3.99 ebookThe book explores the daily life inside the Israeli Defense Forces.These are true stories that center on the experiences of four Israeli soldiers and provide readers with a personal view of life in the Israeli army, the meaning of friendships and the soldiers' comingofage.The One Who Shows the Way: Evolving Humanity From Psychological To Psychospiritual LivingBilly Grant$39.92 hardcover |$23.28 softcover | $4.99 ebook“This book tells my 12year journey through midlife crisis (危机). Seen as a microcosm (缩影) of what is going on in religion, society and humanity, it shows what we need to do to develop.” — Billy GrantBless (祝福) Your Little Cotton Socks: Beyond the Quirky Saying of My Eccentric Scottish MumDiane Radford$27.99 hardcover | $16.95 softcover | $9.99 ebookIn this delightful essay collection, readers enter the pleasant world of Diane Radford's parents and share in laughoutloudfunny, at times moving, events that show how Diane is altogether blessed — not just her cotton socks.The readers will be too.Ni a CubetadasAngélica González$26.99 hardcover | $19.99 softcover | $3.99 ebookNi a Cubetadas is the second book of Lorenza's amazing adventures.This book guides readers through several extreme and funny situations to deal with the boring bath time.This story promotes environment preservation and animal welfare.语篇解读:本文是应用文。


亨格瑞管理会计英文第15版练习答案04CHAPTER 4 COVERAGE OF LEARNING OBJECTIVESLEARNING OBJECTIVE FUNDA-MENTALASSIGN-MENTMATERIALCRITICALTHINKINGEXERCISESANDEXERCISES PROBLEMSCASES,EXCEL,COLLAB. &INTERNETEXERCISESLO1: Describe the purposes ofcost management systems.31, 34 50LO2: Explain the relationshipbetween cost, cost object, costaccumulation, and costassignment.45 56LO3: Distinguish between direct and indirect costs. A1,B1 36, 37, 38, 39,4445, 49 56LO4: Explain the majorreasons for allocating costs.B2 33, 41 46 54LO5: Identify the main types ofmanufacturing costs: directmaterials, direct labor, andindirect production costs.36, 37, 38, 39LO6: Explain how the financialstatements of merchandisersand manufacturers differbecause of the types of goodsthey sell.A2 57, 60, 61LO7: Understand the main A3, A4, B3, 33, 40, 41, 42 48, 49, 50 55, 56, 57, 58,Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.124B4 59, 60, 61differences between traditionaland activity-based costingsystems and why ABC systemsprovide value to managers.A4, B4 32, 37, 43 48, 49, 50 55, 56, 60LO8: Use activity-based costinformation to make strategicand operational controldecisions.CHAPTER 4Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.125Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.124TABLE 4-A1STATEMENT OF OPERATING INCOME OPERATING INCOME BY PRODUCT LINEEXTERNAL REPORTING PURPOSE INTERNAL STRATEGIC DECISION MAKING PURPOSECustom Large SmallDetailed Std. Std. Cost Type, Assignment Method Sales $155,000 $30,000 $45,000 $80,000Cost of goods sold:Direct material 40,000 5,000 15,000 20,000 Direct, Direct TraceIndirect manufacturing 41,000 28,0001 5,000 8,000 Indirect, Alloc. – Mach. Hours81,000 33,000 20,000 28,000Gross profit 74,000 (3,000) 25,000 52,000Selling and administrative expenses:Commissions 15,000 1,500 3,500 10,000 Direct, Direct TraceDistribution to warehouses 10,400 1,0002 3,000 6,400 Indirect, Allocation - WeightTotal selling and admin. expenses 25,400 2,500 6,500 16,400Contribution to corporate expensesand profit 48,600 $(5,500) $18,500 $35,600Unallocated expenses:Administrative salaries 8,000Other administrative expenses 4,000Total unallocated expenses 12,000Operating income before tax $ 36,6001 Total machine hours is 1,400 + 250 + 400 = 2,050. Indirect manufacturing cost per machine hour is then $41,000 ÷ 2,050 = $20. The allocation to custom detailed is $20 × 1,400 machine hours = $28,000.2 Total weight shipped is 25,000 kg + 75,000 kg + 160,000 kg = 260,000 kg. Indirect distribution costs per kilogram is then $10,400 ÷ 260,000 kg = $0.04. The allocation to custom detailed is $0.04 × 25,000 kg = $1,000.Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.1244. ORINOCO, INC.Statement of Operating IncomeFor the Year Ended December 31, 20X9Sales (9,000 units at $170) $1,530,000Cost of goods manufactured and sold:Beginning finished goods inventory $ 0Cost of goods manufactured:Beginning WIP inventory $ 0Direct materials used 530,000Direct labor 290,000Indirect manufacturing 150,000Total mfg. costs to account for $970,000Less ending work-in-process inventory 0 970,000Cost of goods available for sale $970,000Less ending finished goods inventory 97,000Cost of goods sold (an expense) 873,000Gross margin or gross profit $ 657,000 Less other expenses: selling and administrative costs 185,000Operating income (also income before taxesin this example) $ 472,000 5. The balance sheet for the merchandiser (Nile) has just one line for inventories, theending inventory of the items purchased for resale. The balance sheet for themanufacturer (Orinoco) has three items: direct materials inventory,work-in-process inventory, and finished goods inventory.The income statements are similar except for the computation of cost of goodsavailable for sale. The merchandiser (Nile) simply shows purchases for the yearplus beginning inventory. In contrast, the manufacturer (Orinoco) shows beginning work-in-process inventory plus the three categories of cost that comprisemanufacturing cost (direct materials used, direct labor, and factory (ormanufacturing) overhead) and then deducts the ending work-in-process inventory.The manufacturer then adds the beginning finished goods inventory to this cost ofgoods manufactured to get the cost of goods available for sale.6. The purpose is providing aggregate measures of inventory value and cost of goodsmanufactured for external reporting to investors, creditors, and other externalstakeholders.Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.1254-A3 (10-15 min.)There can be many justifiable answers for each item other than the listed cost driver and behavior. The purpose of this exercise is to generate an active discussionregarding those chosen by First Bank’s managers. One point that should beemphasized is that many times managers choose cost drivers that are not the mostplausible or reliable because of lack of data availability. Cost drivers are also used asa basis to allocate activity and resource costs and so the availability of data is often animportant consideration.ActivityOr CostResource Cost Driver Behaviora.* R Number of square feet Fb.** R Number of person hours Fc. R Number of computer transactions Vd. A Number of schedulese. R Number of person hours Ff. R Number of loan inquiries Vg.*** A Number of investmentsh. A Number of applicationsi. R Number of person hours Vj. R Number of minutes Vk. R Number of person hours Fl. A Number of loans* An argument can be made that maintenance of the building is an activity. If this was the case, resources such as supplies and labor would be resources consumed, and several resource cost drivers would be needed. In addition, a separate resource and associated cost driver would be needed for insurance costs. However, the company had a contract for maintenance (fixed price), so this was a fixed-cost resource that was added to other occupancy costs such as insurance. The cost driver chosen for all these occupancy costs was square feet occupied by the various departments.** Normally, the cost driver used for any labor resource is person hours. It is assumed that the staff person hours used are regular hours rather than overtime or temporary labor hours. Thus, the cost is fixed with respect to changes in hours used. As the hours used increases (decreases) the utilization of the resources increases (decreases) and eventually, management will need to make a decision whether to expand capacity (or whether to cut back on labor). This is an example of a step cost that is fixed over wide ranges of cost-driver level.*** Students may try to determine the cost behavior of activities even though the problem requirements do not ask for it. Point out that activities almost always have mixed cost behavior because they consume various resources. Some of these are fixed-cost and others variable-cost resources. For example, the activity “research to evaluate a loan application” consumes such fixed-cost resources as manager labor time and computers (assumed owned Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.126by the bank). This activity also consumes variable-cost resources such as telecommunications time and external computing services.4-A4 (20-30 min.)1. The first step is to determine the cost per cost-driver unit for each activity:Monthly Cost- Cost perManufacturing Driver Driver Activity [Cost driver] Overhead Activity Unit Material Handling [Direct materials cost] $12,000 $200,000 $0.06 Engineering [Engineering change notices] 20,000 20 1,000.00 Power [Kilowatt hours] 16,000 400,000 0.04 Total Manufacturing Overhead $48,000Next, the costs of each activity can be allocated to each of the three products:PHYSICAL FLOW / ALLOCATED COSTCost Senior Basic DeluxeMaterial Handling$.06 × 25,000 = $1,500$.06 × 50,000 = $ 3,000 $.06 × 125,000 = $ 7,500 Engineering $1,000 × 13 = 13,000 $1,000 × 5 = 5,000 $1,000 × 2 = 2,000 Power $.04 × 50,000 = 2,000$.04 × 200,000 = 8,000$.04 × 150,000 = 6,000 Total $16,500 $16,000 $15,500 2. Overhead rate based on direct labor costs:Rate = Total manufacturing overhead ÷ Total direct labor cost= $48,000 ÷ $8,000 = $6.00/DL$Overhead allocated to each product is:Senior: $6.00 × 4,000 = $24,000Basic: $6.00 × 1,000 = 6,000Deluxe: $6.00 × 3,000 = 18,000Total $48,000Notice that much less manufacturing overhead cost is allocated to Basic using directlabor as a cost driver. Why? Because Basic uses only a small amount of labor butlarge amounts of other resources, especially power.3. The product costs in requirement 1 are more accurate if the cost drivers are goodindicators of the causes of the costs -- they are both plausible and reliable. Forexample, kilowatt hours is certainly a better measure of the cost of power costs thanis direct labor hours. Therefore, the allocation of power costs in requirement 1 iscertainly better than in requirement 2. Materials handling and engineering arelikewise more plausible. A manager would be much more confident in themanufacturing overhead allocated to products in requirement 1. Remember,however, that there are incremental costs of data collection associated with the moreaccurate ABC system. The benefit/cost criteria must be applied in deciding whichcosting system is “best.”Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.1274-B1 (20-30 min.)See Table 4-B1 on the following page.4-B2 (25-30 min.)1. $1,080,000 ÷ 45,000 hours = $24 per direct-labor hour2. (a) $585,000 ÷ 15,000 hours = $39 per direct-labor hour(b) $495,000 ÷ 30,000 hours = $16.50 per direct-labor hour3. (a) $585,000 ÷ 97,500 hours = $6 per machine hour(b) $495,000 ÷ 30,000 hours = $16.50 per direct-labor hour4. (a) $24 × (1.0 + 14.0) = $360.00$24 × (1.5 + 3.0) = $108.00$24 × (1.3 + 8.0) = $223.20(b) ($39 × 1.0) + ($16.50 × 14.0) = $39.00 + $231.00 = $270.00($39 × 1.5) + ($16.50 × 3.0) = $58.50 + $ 49.50 = $108.00($39 × 1.3) + ($16.50 ×8.0) = $50.70 + $132.00 = $182.70(c) ($6 × 12.0) + ($16.50 × 14.0) = $ 72.00 + $231.00 = $303.00($6 × 17.0) + ($16.50 × 3.0) = $102.00 + $ 49.50 = $151.50($6 × 14.0) + ($16.50 ×8.0) = $ 84.00 + $132.00 = $216.00(d) First consider using departmental instead of firm-wide rates (part b vs. part a).Departmental rates that use direct-labor hours as the base decrease the costapplied to units of A and C and leave B unaffected. Other products that userelatively less assembly time will increase in cost. Now examine changing to abase of machine hours in machining (part c vs. part a). Product B is the only onewith an increase in cost in (c) compared to (a). Why? Because B's uses only16% of the direct labor hours used for A, B, and C, so it is is allocated only 16%of the costs allocated on the basis of direct labor hours. But it uses 40% of themachine hours, and there is allocated 40% of costs that are allocated on thebasis on machine hours. Therefore, it receives relatively more costs with abase of machine hours than with a base of direct-labor hours.Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.128TABLE 4-B1STATEMENT OF OPERATING INCOME OPERATING INCOME BY PRODUCT LINE Thousands of Dollars Lawn HandScooter Mower Tool Cost Type,Parts Parts Parts Assignment Method Sales $990 $350 $380 $260Cost of goods sold:Direct material 400 175 125 100 Direct, Direct Trace Indirect manufacturing 94 68 1 14 12 Indirect – Mach.Hrs494 243 139 112Gross profit 496 107 241 148Selling and administrative expenses:Commissions 55 25 20 10 Direct, Direct Trace Distribution to warehouses 150 20 2 80 50 Indirect - Weight Total selling and administrative expenses 205 45 100 60Contribution to corporate expenses and profit 291 $ 62 $141 $ 88Unallocated expenses:Corporate salaries 11Other general expenses 17Total unallocated expenses 28Operating income before tax $2631 Total machine hours is 8,500 + 1,750 + 1,500 = 11,750. Indirect manufacturing cost per machine hour is then $94,000 ÷ 11,750= $8. The allocation to scooter parts is $8 × 8,500 machine hours = $68,000.2 Total weight shipped is 100,000 kg + 400,000 kg + 250,000 kg = 750,000 kg. Indirect distribution costs per kilogram is then$150,000 ÷ 750,000 kg = $0.20. The allocation to scooter parts is $0.20 × 100,000 kg = $20,000.Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.1294-B3 (30-35 min.)1.The existing system allocates all costs based on direct labor cost. The rate forallocating indirect production costs is:Estimated indirect production cost ÷ Estimated direct labor cost= ¥24,500,000 ÷ ¥35,000,000 = 70%That is, each time ¥1 is spent on direct labor, Watanabe adds ¥0.7 of indirect production cost to the cost of the product.2. Under an ABC system, Watanabe would allocate indirect production costs separately for each activity. This would result in the following four allocation rates:Receiving: Receiving costs ÷ Direct material cost=¥4,800,000 ÷ 60,000,000 = ¥0.08 per ¥1of dir. mat.Assembly: Assembly costs ÷ Number of control units=¥13,800,000 ÷ 92,000 = ¥150 per control unitQual. Control: Quality control cost ÷ QC hours=¥1,800,000 ÷ 600 = ¥3,000 per QC hourShipping: Shipping cost ÷ # of boxes shipped=¥4,100,000 ÷ 8,200 = ¥500 per box shipped3. (a) The cost will contain 3 components (in thousands of yen):Direct material ¥8,000Direct labor 2,000Indirect production cost (¥2,000 × .7 = 1,400) 1,400Total cost ¥11,400Price (¥11,400 × 1.3) ¥14,820(b) The cost will have 7 components, 4 of them allocating indirect production costs (totals in thousands of yen):Direct materials ¥8,000Direct labor 2,000Receiving (¥0.08 × 8,000) ¥640Assembly (¥150 × 5,000) 750Quality control (¥3,000 × 50) 150Shipping (¥500 × 600) 300Total indirect production cost 1,840Total cost ¥11,840Price (11 ,840 × 1.3) ¥15,3924. The order from Nissan requires a relatively large amount of receiving, quality control, and shipping resources compared to the relative amount of labor required. This makes its indirect production costs are relatively expensive relative to the labor required. The following illustrates why an allocation on the basis of labor cost results in less costs than allocations based on the four activities:Budgeted Cost- Nissan Cost- NissanActivity Allocation Base Allocation Base Percentage Direct materials 60,000,000 8,000,000 13.3% Direct labor 35,000,000 2,000,000 5.7 Receiving 60,000,000 8,000,000 13.3 Assembly 92,000 5,000 5.4 Quality control 600 50 8.3 Shipping 8,200 600 7.3Using the single direct-labor cost-allocation base, this order would receive 5.7% of all indirect production costs. The main reason that indirect production costs for this order under the ABC system are relatively high is the large relative cost of materials that drives a large allocation (13.3%) of receiving costs to this order. The allocations of both quality control and shipping costs are slightly larger that they would be using a direct-laborcost-allocation base, while the allocation of assembly costs is slightly smaller.4-B4 (50-60 min.)1. A summary of the analyses follows.Pen Cell-PhoneCasings Casings Company Base Gross Profit Percentage* 1.25% 38.75% 8.07% Plan Gross Profit Percentage** 10.80% 37.20% 17.40% Support of Product Manager? Strong NoneSupport of President? Moderate* See Exhibit 4-6 on p. 136 of the text.** See Panel B of Exhibit 4-B4 that follows.Exhibit 4-B4, Panels A and B on the following pages can be used to explain the impact of the controller’s idea using the process map of the traditional costing system and the related financial reports. Notice that the $80,000 annual decrease in the cost of engineers needs to be converted to a $20,000 quarterly savings. The controller’s idea will result in an increase of 9.55% in the gross profit of the pen-casings line but a decrease of 1.55% in the cell-phone line. The product manager of pen casings would probably give strong support to the idea but the cell-phone casings manager would most likely not support the idea.Although the company-level gross profit margin improves, the president’s support may not be strong. Why? There is not a strong consensus among product-line managers. Top management is normally hesitant to support actions that do not have the unanimous support among product-line managers unless there is solid evidence of material improvement inprofitability. While the current loss would be reversed, the return on sales is still nominal at3,500 ÷ $480,000 = .73%.Exhibit 4-B4: Panel AProcess Map of Traditional Cost SystemUnallocated $80,000 Direct Materials for Pen Casings $22,500 Direct Labor for Pen Casings$135,000 Direct Materialsfor Cell Phone Casings $24,000 DirectLaborfor CellPhoneCasings$15,000Pen Casings Sales $360,000 Cell Phone CasingsSales $120,000AllIndirectResources$200,000All Unallocated Value Chain Costs $80,000 Cost Driver[Direct Labor Hours = 4,500 +Exhibit 4-B4: Panel BPRO-FORMA FINANCIAL REPORTS:TRADITIONAL COST ALLOCATION SYSTEMSTATEMENT OF OPERTING INCOME CONTRIBUTION TO CORPORATE COSTSAND PROFIT[EXTERNAL REPORTING PURPOSE] [INTERNAL STRATEGIC DECISION MAKINGAND OPERATIONAL-CONTROL PURPOSE]Pen Casings Cell Phone CasingsSales $480,000 $360,000 $120,000 1Cost of goods sold:Direct material 46,500 22,500 24,000 2Direct labor 150,000 135,000 15,000Indirect manufacturing 200,000 163,636 336,364 4Cost of goods sold 396,500 321,136 75,364Gross profit 83,500 $ 38,864 $ 44,636Corporate expenses (unallocated) 80,000Operating income $ 3,500Gross profit margin 17.40% 10.80% 37.20%1. $80,000 × .75 × 22. $12,000 × 23. $200,000 × [4,500/(4,500 + 1,000)]4. $200,000 × [1,000/(4,500 + 1,000)]5. $83,500/$480,000Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.133Perhaps the most important factor bearing on the president’s support is lack of confidence in the accuracy of the cost and hence gross margin figures. She probably will inquire whether the shift in the consumption percentages by the two activities is captured by the traditional costing system. Does the change in allocation rates from 90:10 to 82:18 based on direct labor hour changes accurately capture the impact of the operational changes? An informal analysis of the controller’s idea might look like t he following table.Operational Change Likely Impact on the Consumption of Resources that Support: Pen CasingsCell-PhoneCasingsLess purchasing work to supply parts for cell-phonecasings ↓Less engineering design work on cell phone casings ↓Less equipment used to support cell-phoneproduction ↓Increase in cell-phone production ↑Based on the informal analysis, the President probably would expect the profitability of cell-phone casings to improve and the profitability of pen casings to be unaffected. This disagrees with the numerical analysis. Given the propensity of managers to embrace numerical results, less weight will likely be given this analysis compared to the “objective” numbers. As a result, she may question the validity of the numerical analysis as well as the value of the traditional costing system!Finally, the focus of improvement efforts should be directly on the pen-casing product line. This initiative deals mostly with the cell-phone line. What can be done to improve profitability of the pen casings? Can prices be raised without losing too much volume? Can operational improvements be made to lower the indirect manufacturing costs? The controller’s idea is worthy of some support but it does not address the profitability issue head on.2. Exhibit 4-B4, Panel C on the following page is a process map that can be used to explain the impact of the controller’s idea. Panel D at the end of the solution provides a detailed evaluation of the controller’s idea.Pen Cell-PhoneCasings Casings Company Base Gross Profit Percentage* 16.22% (28.63%) 8.07%Plan Gross Profit Percentage** 17.26% 17.81% 17.40% Support of Product Manager? Neutral StrongSupport of President? Strong* See the table on p. 139 of the text.** See panel D of Exhibit 4-B4 that follows.ProcessingActivity$154,00080%All Unallocated Value Chain Costs$80,000Plant &Machinery$180,000[Direct Labor Hours = 4,500 + 1,000]UNALLOCATED $80,000Engineers & CAD Equip. $20,000Production Support Activity $46,000Cost Driver [Distinct Parts = 5 + 11]50%50%20%Direct Materials for Pen Casings $22,500Direct Materials for Cell Phone Casings $24,000Direct Labor for Cell Phone Casings $15,000Direct Labor for Pen Casings $135,000SALES $360,000SALES $120,000The controller’s idea will result in a slight increase in the gross pro fit of the pen-casings linebut a dramatic turnaround in the profitability of the cell-phone line. The product managerof pen casings would probably be neutral or slightly positive about the idea because the ideadoes not focus on operational improvements that directly affect the pen-casings line. Thecell-phone casings manager would give strong support to the idea – this may save his/her job!The president would strongly support this idea while encouraging all managers involved tokeep up the good work. Also, note that the numbers agree with the informal analysis –generating confidence in the integrity of the cost accounting system.Exhibit 4-B4, Panel CProcess Map for ABC SystemExhibit 4-B4: Panel DPRO-FORMA FINANCIAL REPORTS FOR LOPEZ PLASTICS COMPANY:ACTIVITY-BASED COST ALLOCATION SYSTEMSTATEMENT OF OPERTING INCOME CONTRIBUTION TO CORPORATE COSTSAND PROFIT [EXTERNAL REPORTING PURPOSE] [INTERNAL STRATEGIC DECISION MAKINGAND OPERATIONAL-CONTROL PURPOSE]Pen Casings Cell Phone CasingsSales $480,000 $360,000 $120,000Cost of goods sold:Direct material 46,500 22,500 24,000Direct labor 150,000 135,000 15,000Processing activity 154,000 126,000 128,000 2 Production support activity 46,000 14,375 331,625 4Cost of goods sold 396,500 297,875 98,625Gross profit 83,500 $ 62,125 $ 21,375Corporate expenses (unallocated) 80,000Operating loss $ 3,500Gross profit margin 17.26% 17.81%1. $154,000 ×[4,500 labor hours/(4,500 labor hours + 1,000 labor hours)]2. $154,000 ×[1,000 labor hours/(4,500 labor hours + 1,000 labor hours)]3. $46,000 ×[5 distinct parts/(5 distinct parts + 11 distinct parts)]4. $46,000 ×[11 distinct parts/(5 distinct parts + 11 distinct parts)]Copy right ©2011 Pearson Education, Inc., Publishing as Prentice Hall.1363. As vice president, you probably are pleased with the new ABC system. The cost drivers that are used to allocate activity costs appear to be plausible and reliable and thus probably represent a sound cause-effect model of operations. This will improve both the accuracy of produ ct costing and operating managers’ control over costs. Operating managers will be pleased with the ABC system because it helps them understand how their day-to-day work impacts costs and profits. From a behavioral perspective, this should be highly motivational. This problem emphasizes the importance of the cost-accounting system to managers. Different systems can result in significantly different management decisions. In this case, the product-line managers’ support for the controller’s idea changes when an ABC system is used to evaluate the idea. Although the company-level gross margins do not change, it is possible that the president would strongly support the idea based on ABC data. Why? Neither of the product-line managers is against the idea, and one strongly supports it. In addition, the president may have more confidence in the accuracy of the ABC analysis. The substantial losses of the current quarter have been completely eliminated and the serious profitability problem of the cell-phone casing product line has been reversed.4-1 A cost management system is a collection of tools and techniques that identifies how management’s decisions affect costs. The thr ee purposes of a CMS are to provide1.cost information for operational control,2.cost information for strategic decisions, and3.measures of inventory value and cost of goods manufactured (or purchased) forexternal reporting to investors, creditors, and other external stakeholders.4-2 a. The production manager needs operational control information.b. Setting the product mix is a strategic decision.c. The cost of inventory that appears on the balance sheet is information that is used by external investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.4-3 Cost objects are any items for which decision makers desire a separate measurement of costs. They include departments, products, services, territories, and customers.4-4 No. Products are one of the main cost objects for most companies, but departments are also important cost objects because they represent a logical grouping of activities for which managers desire a separate determination of costs.4-5 The major purpose of a detailed cost-accounting system is to measure costs for decision making and financial reporting. Cost accounting systems become more detailed as management seeks more accurate data for decision making.4-6 The two major processes performed by a cost accounting system are cost accumulation and cost assignment. Cost accumulation is collecting costs by some “natural” classification, such as materials or labor, or by activities performed such as order processing or machine processing. Cost assignment is attaching costs to one or more cost objects, such as activities, processes, departments, customers, or products.4-7 Managers make important decisions on a daily basis. They base these decisions in large part on financial data provided by the cost accounting system. So it is critically important that the cost accounting system provide accurate and reliable financial information.4-8 Managers can specifically and exclusively identify direct costs with a given cost object (that is, directly trace them) in an economically feasible way. Indirect costs cannot be so identified. However, managers can usually identify a plausible and reliable cost driver to use to allocate resource costs to cost objects that consume the resources. When direct tracing is not economically feasible and a plausible and reliable cost driver cannot be found, costs should remain unallocated.4-9 Yes, the same cost (for example, the department supervisor's salary) can be direct with respect to a department but indirect with respect to the variety of products flowing through a department (e.g., tables, chairs, and cabinets).4-10 Some costs can be physically linked with a department (or a product), but not in an economically feasible way. An example is the use of departmental meters for measuring power usage. Such devices could measure power costs as direct costs of a department.The alternative is to regard factory power costs as indirect costs of individual departments. Managers often decide whether the resulting increased accuracy provided by individual power meters is worth their additional cost; thus, the test of economic feasibility will decide whether a particular cost is regarded as direct or indirect.4-11 The four purposes of cost allocation are (1) to predict the economic effects of strategic and operational control decisions, (2) to obtain desired motivation, (3) to compute income and asset valuations, and (4) to justify costs or obtain reimbursement.4-12 Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) require publically-held companies to allocate all production-related costs and only production-related costs to its products for financial reporting to the public.4-13 No. The costs in a cost pool are not physically traced to cost objects. Only direct costs are traced to cost objects. A cost pool contains indirect costs that are allocated to cost objects using a single cost-allocation base.4-14 Some possible terms are reallocate, assign, distribute, redistribute, load, apportion, reapportion, and burden.。
新SAT官⽅指南阅读第⼗五篇全解析新SAT官⽅指南阅读第⼗五篇全解析This passage is adapted from Richard J.Sharpe and Lisa Heyden,“Honey Bee Colony Collapse Disorder is Possibly Caused by a Dietary Pyrethrum Deficiency.”?2009by Elsevier Ltd.Colony collapse disorder is characterized by the disappearance of adult worker bees from hives.Honey bees are hosts to the pathogenic large ectoparasitic mite Varroa destructor(Varroa mites).These mites feed on bee hemolymph(blood)and can kill bees directly or by increasingtheir susceptibility to secondary infection with fungi,bacteria or viruses.Little is known about the natural defenses that keep the mite infections under control.Pyrethrums are a group of flowering plants which include Chrysanthemum coccineum,5Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium,Chrysanthemum marschalli,and related species.These plantsproduce potent insecticides with anti-mite activity.The naturally occurring insecticides are known as pyrethrums.A synonym for the naturally occurring pyrethrums is pyrethrin and syntheticanalogues of pyrethrums are known as pyrethroids.In fact,the human mite infestation known as scabies(Sarcoptes scabiei)is treated with a topical pyrethrum cream.10We suspect that the bees of commercial bee colonies which are fed mono-crops are nutritionally deficient.In particular,we postulate that the problem is a diet deficient in anti-mite toxins:pyrethrums,and possibly other nutrients which are inherent in such plants.Without,atleast,intermittent feeding on the pyrethrum producing plants,bee colonies are susceptible to mite 15infestations which can become fatal either directly or due to a secondary infection ofimmunocompromised or nutritionally deficient bees This secondary infection can be viral,bacterial or fungal and may be due to one or more pathogens.In addition,immunocompromised or nutritionally deficient bees may be further weakened when commercially produced insecticidesare introduced into their hives by bee keepers in an effort to fight mite infestation.We furtherpostulate that the proper dosage necessary to prevent mite infestation may be better left to the bees, 20who may seek out or avoid pyrethrum containing plants depending on the amount necessary todefend against mites and the amount already consumed by the bees,which in higher doses could be potentially toxic to them. This hypothesis can best be tested by a trial wherein a small number of commercial honey25bee colonies are offered a number of pyrethrum producing plants,as well as a typical bee foodsource such as clover,while controls are offered only the clover.Mites could then be introduced to each hive with note made as to the choice of the bees,and the effects of the mite parasites on the experimental colonies versus control colonies.It might be beneficial to test wild-type honey bee colonies in this manner as well,in case there could be some genetic difference between them that affects the bees’preferences for30pyrethrum producing flowers.42、How do the words“can,”“may,”and“could”in the third paragraph(lines11-23) help establish the tone of the paragraph?A)They create an optimistic tone that makes clear the authors are hopeful about the effects of their research on colony collapse disorder.B)They create a dubious tone that makes clear the authors do not have confidence in the usefulness of the research described.C)They create a tentative tone that makes clear the authors suspect but do not know that their hypothesis is correct.D)They create a critical tone that makes clear the authors are skeptical of claims that pyrethrums are inherent in mono-crops.正确答案:C分析:⽂章当中,作者讨论蜂群问题时,使⽤了“我们猜想”(we suspect)和“我们推测”(we postulate)这样的句式,还采⽤了“can””may”和“could”这样表⽰可能的情态动词,是为了强调作者是猜测但是不确定的语⽓。
护士学士学位英语考试真题及答案In the realm of nursing education, the Bachelor of Nursing degree examination is a crucial milestone. The English component, particularly, poses a significant challenge to many aspirants. To excel in this segment, a thorough understanding of the exam pattern, familiarization with past exam questions, and a well-defined study plan are essential.**Exam Overview**The Bachelor of Nursing English exam typically comprises reading comprehension, vocabulary and grammar, writing skills, and possibly a section on nursing-related terminology. The reading comprehension section tests the candidate's ability to understand and interpret passages from a variety of sources, such as medical journals, research articles, and patient education materials. The vocabulary and grammar section评估候选人的词汇量和语法知识的掌握程度,而写作技能部分则侧重于评估候选人的表达能力,如撰写病历报告、护理计划等。
The questions contained in this AP ® M i croeconomics Practice Exam are written to the contentspecifications of AP Exams for this subject. Taking this practice exam should provide students with an idea of their general areas of strengths and weaknesses in preparing for the actual AP Exam. Because this AP M i croeconomics Practice Exam has never been administered as an operational AP Exam, statistical data are not available for calculating potential raw scores or conversions into AP grades.This AP M i croeconomics Practice Exam is provided by the College Board for AP Exam preparation. Teachers are permitted to download the materials and make copies to use with their students in a class-room setting only. To maintain the security of this exam, teachers should collect all materials after their administration and keep them in a secure location. Teachers may not redistribute the files electronically for any reason.© 2008 The College Board. All rights reserved. College Board, Advanced Placement Program, AP , AP Central, SAT, and the acorn logo are registered trademarks of the College Board. PSAT/NMSQT is a registered trade-mark of the College Board and National Merit Scholarship Corporation. All other products and services may be trademarks of their respective owners. Visit the College Board on the Web: .Practice ExamAdvanced Placement ProgramAP ®M i croeconomicsContentsDirections for Administration (ii)Section I: Multiple-Choice Questions (1)Section II: Free-Response Questions (15)Student Answer Sheet for Multiple-Choice Section (18)Multiple-Choice Answer Key (19)Free-Response Scoring Guidelines (20)The College Board: Connecting Students to College SuccessThe College Board is a not-for-profit membership association whose mission is to connectstudents to college success and opportunity. Founded in 1900, the association iscomposed of more than 5,000 schools, colleges, universities, and other educationalorganizations. Each year, the College Board serves seven million students and theirparents, 23,000 high schools, and 3,500 colleges through major programs and services incollege admissions, guidance, assessment, financial aid, enrollment, and teaching andlearning. Among its best-known programs are the SAT®, the PSAT/NMSQT®, and theAdvanced Placement Program® (AP®). The College Board is committed to the principlesof excellence and equity, and that commitment is embodied in all of its programs,services, activities, and concerns.Visit the College Board on the Web: .AP Central is the official online home for the AP Program: .AP® MicroeconomicsDirections for AdministrationThe AP Microeconomics Exam is 2 hours and 10 minutes in length and consists of a multiple-choice sectionand a free-response section.•The multiple-choice section is 1 hour and 10 minutes, contains 60 questions, and accounts for two-thirds of the final grade.•The free-response section is 60 minutes, contains 3 questions, and accounts for one-third of the final grade. Ten minutes of the Section II time are reserved for reading the questions and planning answers.Students should be given a 10-minute warning prior to the end of each section of the exam. A 10-minute break should be provided after Section I is completed.The actual AP Exam is administered in one session. Students will have the most realistic experience if a complete morning or afternoon is available to administer this practice exam. If a schedule does not permit one time period for the administration of the entire practice exam, it would be acceptable to administer Section I one day and Section II on a subsequent day.Many students wonder whether or not to guess the answers to the multiple-choice questions about which they are not certain. It is improbable that mere guessing will improve a score. However, if a student has some knowledge of the question and is able to eliminate one or more answer choices as wrong, it may be to the student’s advantage to answer such a question.•The use of calculators, or any other electronic devices, is not permitted during the exam.•It is suggested that the practice exam be completed using a pencil for Section I and a pen with black or dark blue ink for Section II to simulate an actual administration.•Teachers will need to provide paper for the students to write their free-response answers. Teachers should give the students directions indicating how they wish the responses to be labeled so that the teacher will be able to associate the student’s response with the question the student intended to answer.•Remember that students are not allowed to remove any materials, including scratch work, from the testing site.Section IMultiple-Choice QuestionsThe inclusion of source material in this exam is not intended as an endorsement by the College Board or ETS of the content, ideas, or values expressed in the material. The material printed here reflects various aspects of the course of study on which this exam is based and is therefore appropriate to use to measure the skills and knowledge of this course.MICROECONOMICSSection ITime—70 minutes60 QuestionsDirections: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and place the letter of your choice in the corresponding box on the student answer sheet.1. The diagram above shows the production possibil-ities curve for Country Y. Which of the following statements is true?(A) If Country Y is producing at point C, it isusing all its resources efficiently.(B) The opportunity cost of producing moremachines is constant.(C) Producing at point C is the most preferable,because butter is a nondurable good.(D) Country Y cannot produce at point E.(E) The economy is not producing at its potential,since it is not producing at point D.2. Which of the following is the definingcharacteristic of a capitalistic economy?(A) Well-functioning capital markets(B) Private ownership and protection of propertyrights(C) Fair distribution of income and low incometaxes(D) Equality of opportunity(E) Efficient allocation of resources 3. Assume that the government increases the unitexcise tax on gasoline suppliers and also thatpeople commute longer distances to work as more houses are built in city suburbs. As a result, theequilibrium price and quantity of gasoline willmost likely change in which of the followingways?(A) Decrease Decrease(B) Increase Decrease(C) Increase Increase(D) Increase Indeterminate(E) Indeterminate Increase4. The graph above shows the market demand forgood X. A movement from point A to point Bwould most likely be caused by(A) an increase in the price of good Z, asubstitute(B) an increase in consumers’ income(C) a decrease in consumers’ income(D) a decrease in production costs for good X(E) a decrease in the supply of good X5. To maximize utility, a consumer with a fixedbudget will purchase quantities of goods sothat the ratios of the marginal utility of eachgood to its(A) total utility are the greatest(B) total utility are the same(C) price are the greatest(D) price are equal to one(E) price are equal6. In the short run, which of the following is true ofa firm’s average total cost of production?(A) It is equal to marginal cost plus averagevariable cost.(B) It is equal to marginal cost plus averagefixed cost.(C) It is equal to average fixed cost plus averagevariable cost.(D) It always increases when a firm increasesproduction.(E) It is zero if the firm shuts down.7. Let W denotes the nominal wage, P the outputprice, and MP L the marginal product of labor.Which of the following relationships correctlyestimates the marginal cost (MC) of productionfor a perfectly competitive firm in the short run?(A) MC = P/MP L(B) MC = P x MP L(C) MC = W x MP L(D) MC = W/MP L(E) MC = MP L/W8. JC pizzeria has a year remaining on anunbreakable lease on its building, requiring apayment of $20,000 a year. If JC operates overthe next year, it estimates that its revenues willbe $200,000 and that its expenses, in additionto the lease, will be $190,000. Which of thefollowing statements is true?(A) JC should shut down, since it will incura loss of $20,000.(B) JC should shut down to break even.(C) JC should operate, since its loss is less thanits fixed cost.(D) JC should operate, since it will earn a profitof $10,000.(E) JC will break even, whether it operates orshuts down. 9. Which of the following statements abouta monopolistically competitive firm inlong-run equilibrium is true?(A) It has excess capacity, even though itslong-run profit is zero and its outputprice equals its marginal cost.(B) It has excess capacity and its long-runprofit is positive, even though itsmarginal revenue equals its marginal cost.(C) It has excess capacity and its output priceexceeds its marginal cost, even though itslong-run profit is zero.(D) It has no excess capacity and its long-runprofit is zero.(E) It has no excess capacity and its marginalrevenue equals its marginal cost.10. The cartel model of oligopoly predicts that(A) all the firms in the industry act in unisonto set a monopoly price(B) each producer acts independently of others(C) firms follow the low-price firm in theindustry(D) differences in cost of production discourageindividual firms from cheating(E) the markup on marginal cost should bethe same for all firms11. Which of the following is true about themarginal revenue of a firm in a perfectlycompetitive industry?(A) It is constant.(B) It increases as output sold increases.(C) It decreases as output sold increases.(D) It increases at first, then decreases.(E) It decreases at first, then increases.12. A firm produces truffles by using labor andcapital. The price of labor is $10 per unit, and the price of capital is $20 per unit. At current output level, the marginal product of labor is 40 truffles and the marginal product of capital is 60 truffles.To reduce the total cost of producing the current quantity of truffles, how should the firm changeits spending on labor and capital?Labor Capital(A) No change Increase(B) Decrease No change(C) Decrease Increase(D) Increase No change(E) Increase Decrease13. In the current labor market, suppose that the wagerate for accountants is significantly higher thanthe wage rate for economists. In the long run, ifyou observed that the wage rate for economistsrose while the wage rate for accountants fell,which of the following would best explain yourobservation?(A) The supply of economists must haveincreased, and the supply of accountantsmust have decreased.(B) The supply of economists must havedecreased, and the supply of accountantsmust have increased.(C) The demand for economists must haveincreased, and the supply of accountantsmust have decreased.(D) The demand for economists must havedecreased, and the supply of accountantsmust have increased.(E) The demand for both economists andaccountants must have decreased.14. The primary purpose of antitrust laws is to(A) protect consumers from fraudulent businesspractices(B) protect small businesses from unfair foreigncompetition(C) prevent firms from monopolizing trade andto promote competition(D) reduce lawsuits and limit the liabilities ofbusinesses(E) grant the government the right to take overprivate property15. A pure public good is a good that is(A) provided efficiently by markets(B) rivalrous and excludable in consumption(C) nonrivalrous and excludable in consumption(D) rivalrous and nonexcludable in consumption(E) nonrivalrous and nonexcludable inconsumption16. The diagram above shows the production possi-bilities curves for two countries, Country X andCountry Y. Assume that both countries use equal amounts of resources in production. If the twocountries engage in trade, both would be better off under which of the following conditions?(A) Country X produced both cars and planes,because it has an absolute advantage in theproduction of both goods.(B) Country Y produced both cars and planes,because it has a comparative advantage inthe production of both goods.(C) Country X specialized in the production ofcars, because it has an absolute advantagein the production of cars.(D) Country X specialized in the productionof cars, because it has a comparativeadvantage in the production of cars.(E) Country Y specialized in the productionof cars, because it has a comparativeadvantage in the production of cars.17. If resources were perfectly substitutable in allactivities, which of the following would be true?(A) Output of all goods could be increased atzero opportunity cost.(B) The production possibilities curve would be astraight line.(C) Specialization and mutually beneficial tradewould be impossible.(D) No country or individual would havea comparative advantage in any activity.(E) Scarcity of resources would be eliminated.18. Assume that the price elasticity of demand forgood X is constant and equal to −0.5 and theprice elasticity of demand for good Y is constant and equal to -2. Assume that goods X and Y have identical upward-sloping elastic supply curves. Ifa per-unit excise tax of the same amount is leviedon good X and on good Y, which of thefollowing would be true?(A) The percentage decrease in the quantity ofgood X demanded would be greater thanthe percentage decrease in the quantity ofgood Y demanded.(B) The tax share paid by consumers of good Xwould be relatively higher than that paid byconsumers of good Y.(C) The tax share paid by consumers of good Ywould be relatively higher than that paid byconsumers of good X.(D) The tax share paid by sellers of good Ywould be relatively lower than that paid bysellers of good X.(E) The tax share paid by sellers of goods X andY would be the same.19. Assume that demand for bottled water isrelatively price elastic. An increase in supplyof bottled water will result in which of thefollowing?(A) A decrease in price, leading to an increasein total revenue(B) A decrease in price, leading to a decreasein total revenue(C) An excess supply of bottled water(D) An excess demand for bottled water(E) A relatively small decrease in price andno change in equilibrium quantity 20. A leftward shift in the supply curve of watchescould be caused by(A) an increase in the price of watches(B) an increase in wages paid to workers whoproduce watches(C) an improvement in the technology associatedwith watchmaking(D) a decrease in the price of parts used in theproduction of watches(E) an increase in population21. If growing corn becomes more profitable thangrowing wheat, which of the following willoccur?(A) The supply of corn will decrease.(B) The price of wheat will decrease.(C) The price of corn will decrease.(D) The demand for wheat will increase.(E) The demand for corn will increase.Number of WorkersBushels ofApples Picked0 01 42 93 154 205 2422. The table above shows the short-run productionfunction for picking apples. Based on theproduction data, which of the followingstatements about the marginal product of thefifth worker is true?(A) It is the maximum that can be attained.(B) It is greater than the marginal product ofthe first worker due to increasing returns.(C) It is greater than the combined marginalproducts of all the other workers.(D) It is less than the marginal product of thethird worker due to diminishing returns.(E) It is rising due to increasing marginal returns.23. If a firm’s average total cost decreases as thefirm increases its output, the firm’s marginalcost must be(A) greater than the average variable cost(B) less than the average fixed cost(C) less than the average total cost(D) decreasing(E) negative24. Suppose that a firm is producing the profit-maximizing output under conditions ofdiminishing returns. Its output price is $25, and its marginal cost of production at its current outputlevel is $25. Based on this information, it can beconcluded that this firm must(A) be a single-price monopoly(B) be a perfectly competitive firm(C) decrease its output to maximize profitif it is a monopoly(D) increase its output to maximize profitif it is a monopoly(E) exit the industry if it is a perfectlycompetitive firm 25. Suppose that the two biggest producers of gold,Bmine and Gmine, form a cartel to set price.However, each has the option to cheat or to notcheat on the agreement. The table below showsthe payoffs from these strategies, with the firstentry in each cell representing the payoff toBmine and the second representing the payoffto Gmine.GmineCheatNotCheatCheat $10, $5 $25, $20Bmine NotCheat $5, $15 $20, $25Which of the following correctly describes thedominant strategy of each firm?(A) Neither Gmine nor Bmine has a dominantstrategy.(B) Gmine’s dominant strategy is to not cheat;Bmine does not have a dominant strategy.(C) Gmine’s dominant strategy is to cheat; Bminedoes not have a dominant strategy.(D) Gmine’s dominant strategy is to cheat;Bmine’s dominant strategy is to not cheat.(E) Gmine’s dominant strategy is to not cheat;Bmine’s dominant strategy is to cheat.26. Assume that a firm that produces a good in aconstant-cost perfectly competitive industry is in long-run equilibrium. If the demand for the good increases, the profit-maximizing output by thefirm will change in which of the following waysin the short run and long run?ShortRun LongRun(A) Return to original Return to originallevel level(B) Increase Increase(C) Increase Return to originallevel(D)Decrease Decrease(E) Decrease Return to originallevel27. Which of the following is true of bothmonopolistically competitive and perfectlycompetitive firms in long-run equilibrium?(A) Marginal revenue equals average total cost.(B) Marginal cost equals average total cost.(C) Price equals average total cost.(D) Price is greater than marginal cost.(E) Production occurs at minimum averagetotal cost.28. Assume that both the product and labor marketsare perfectly competitive. It would be profitablefor a firm to hire additional labor if the ratio ofthe wage to the marginal product of labor is(A) less than the output price(B) less than the marginal cost(C) greater than the output price(D) greater than the marginal cost(E) equal to the output price29. If positive externalities exist in the market for flushots, which of the following is true?(A) Taxing flu shots will lead to the sociallyefficient level of output.(B) Subsidizing flu shots will lead to the sociallyefficient level of output.(C) The firm making the flu shots is charging toolow a price to reach the socially efficientlevel of output.(D) The firm making the flu shots is producingwhere marginal social cost equals marginalsocial benefit.(E) The firm making the flu shots is producingthe socially efficient quantity if the marketfor flu shots is perfectly competitive. 30. Pollution abatement policies will improveefficiency if the(A) marginal benefit of abatement is less thanthe marginal cost of abatement(B) marginal cost of abatement is less than themarginal benefit of abatement(C) marginal cost of abatement is positive(D) marginal benefit of abatement is positive(E) marginal cost of abatement is zero31. Individuals in any society must make choicesregarding the types of goods and services to beproduced because(A) free markets do not always allocate resourcesefficiently(B) free markets only satisfy the demands ofpaying consumers(C) opportunity costs increase as more of a goodor service is produced(D) resources are scarce and human wants areunlimited(E) resources must be allocated for the benefit ofthe entire society32. In the market shown in the graph above, at a priceof $5, there will be(A) a surplus and the price will eventually fall(B) a surplus generating a decrease in demand(C) a shortage and the price will eventually rise(D) a shortage generating an increase in supply(E) an increase in supply and a decrease indemand33. Assume that the market for tomatoes is inequilibrium at a price of $35 per bushel. If thedemand for tomatoes decreases, which of thefollowing will occur?(A) A shortage at $35, creating an increasein price, leading to an increase in quantitysupplied(B) A shortage at $35, leading to an increasein supply and a decrease in price(C) A surplus at $35, leading to a decreasein price and in quantity supplied(D) A surplus at $35, leading to a decreasein supply and an increase in price(E) A surplus at $35, leading to an increase inprice and a decrease in quantity demanded 34. If the income elasticity of demand for good Xis negative and the cross-price elasticity ofdemand between good X and good Y is negative, which of the following must be true of good X?(A) X is a normal good and is a substitute for Y.(B) X is a normal good and is a complementto Y.(C) X is an inferior good and is a substitute for Y.(D) X is an inferior good and is a complementto Y.(E) X is a normal good and Y is an inferior good.35. When total utility is at its maximum, marginalutility is(A) increasing(B) negative(C) equal to zero(D) at a maximum(E) at minimum 36. If a firm’s long-run average total cost increasesas output increases, the firm is experiencing(A) economies of scale(B) diseconomies of scale(C) increasing returns to scale(D) efficiency in plant size(E) maximum economic profit37. A monopolistically competitive profit-maximizingfirm is currently producing and selling 2,000 units of output. At this output level, marginal revenue is $9, average revenue is $10, and the averagevariable cost is $8. The product price is(A) $8(B) $9(C) $10(D) greater than $10(E) less than $838. The short-run supply curve for a firm ina perfectly competitive industry is(A) its entire marginal cost curve(B) its average variable cost curve above itsmarginal cost curve(C) its average total cost curve above its marginalcost curve(D) its marginal cost curve above the minimumpoint of its average total cost curve(E) its marginal cost curve above the minimumpoint of its average variable cost curveQuestions 39-40 refer to the diagram below, which shows the cost and revenue conditions of a monopolist.39. If the monopolist chooses to maximize totalrevenue rather than total profit, it will choose which combination of price and output?Price Output(A) P 1Q 5 (B) p 2 Q 4 (C) P 3 Q 3 (D P 4 Q 4 (E) P 5 Q 540. If the monopolist produces the allocativelyefficient level of output rather than the profit-maximizing level of output, consumer surplus will(A) decrease by the area P 5JKP 4(B) decrease by the area P 5JMP 2 (C) increase by the area P 5JGP 1 (D) increase by the area P 5JKP 4 (E) increase by the area P 5JMP 2Questions 41-42 refer to the table below, whichshows the short-run production function of a perfectly competitive firm that produces potatoes using one variable input, labor.Number of Workers Potatoes Harvested(pounds per hour)0 0 1 3 2 7 3 10 4 12 5 136 1241. After which worker does diminishing marginalproduct first occur?(A) Second worker (B) Third worker (C) Fourth worker (D) Fifth worker (E) Sixth worker42. If the firm can sell as many potatoes as it wantsfor $2 per pound and has to pay each worker $5per hour, how many workers should the firmemploy to maximize profits?(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4 (E) 543. Suppose that the market for low-wage labor isperfectly competitive and initially in equilibrium. If the government establishes an effective minimum wage, which of the following will occur?(A) Employment of low-wage workers willdecrease and unemployment will increase.(B) The quantity of low-wage workers suppliedwill be less than the quantity demanded.(C) The total wage payment received by alllow-wage workers will increase.(D) Economic efficiency will increase, sincefirms were paying workers less than thevalue of their marginal revenue product.(E) Low-wage workers will be motivated to forma union.44. Which of the following is most likely to reduceinequality in a country’s distribution of income?(A) An increase in the population growth rate (B) Job training for low-skill workers (C) An increase in the trade deficit (D) A decrease in funding for training unemployed workers (E) A regressive tax rate45. If an industry ignores the external costs it generates in its production, which of the following will be true at the competitive market equilibrium output? (A) Price will be greater than the marginal social cost. (B) Price will be less than the marginal social cost. (C) Price will be equal to the marginal social cost.(D) Marginal private cost will be equal to marginal social cost. (E) Marginal private cost will be greater than the marginal social cost.46. Karen works part-time at a local conveniencestore and earns $10 per hour. She wants to spend next Saturday afternoon attending a musicconcert. The full price of a concert ticket is $75,but Karen was able to get a discounted price of$50 from a friend who purchased the ticket buthas become unable to attend. If Karen took4 hours off from her job to attend the concert,what was her opportunity cost of attending theconcert?(A) $40(B) $50(C) $75(D) $90(E) $11547. Assume that the price of good X decreases from$10 to $9 per unit and that the quantity demanded of good X increases from 25 to 30 units. In thisprice range, the demand for good X is(A) inelastic(B) elastic(C) unit elastic(D) perfectly inelastic(E) perfectly elastic48. The difference between the price a consumerwould be willing to pay for a cone of ice creamand the actual market price that she pays givesa measure of her(A) consumer surplus(B) producer surplus(C) marginal utility(D) marginal cost(E) ability to pay49. Which of the following is true of the substitutioneffect of an increase in the price of a normalgood?(A) It works to offset the income effect.(B) It works to reinforce the income effect.(C) It is less than the income effect.(D) It causes an increase in the quantitydemanded of the good.(E) It causes an increase in the demand forthe good.50. The graph above shows the cost curves for acompetitive firm that produces 20 units of output.What are the total cost and the total fixed cost ofproducing 20 units of output?TotalCost Total Fixed Cost(A) $10 $0(B) $120 $100(C) $120 $20(D) $200 $100(E) $200 $2051. A profit-maximizing monopolist selects its outputlevel in the(A) inelastic region of its demand curve(B) elastic region of its demand curve(C) range of output where marginal revenueis rising(D) range of output where total cost is falling(E) range of output where marginal cost is falling52. Which of the following enables a seller to capturethe entire consumer surplus in a market?(A) Perfect price discrimination(B) Perfect competition(C) An excise tax on buyers(D) Effective price ceiling(E) Effective price floor。
Test 15 Inversion and Tag-QuestionsPart I Multiple-choice questions1. More remarkable than those planets ( ), a few of which are of great brightness.A. comets areB. is the cometsC. the comets areD. are the comets2. I wonder how many years ago ( ).A. did your father retireB. your father retiredC. has your father retiredD. your father has retired3. ( ) there can be no avoiding it.A. However the decision is difficultB. However difficult the decision isC. The decision however difficultD. However the difficult decision4. “They couldn’t have done that, you know,” she gently remarked.“They were ill.”“( )”, said the man, “very ill.”A. So they wereB. So were theyC. So they had beenD. So had they been5. Most people would agree that only in exceptional circumstances ( ) the truthfrom the patient.A. a doctor should hideB. should a doctor hideC. a doctor would hideD. a doctor will hide6. ( ) a certain about among the students as to the necessity of the work.A. It existedB. There existedC. There hadD. Existed there7. ( ) but he also proved himself a good athlete.A. He showed himself not only a good student.B. He showed not only himself a good studentC. Not only he showed himself a good studentD. Not only did he show himself a good student8. Einstein seldom wore strange clothes, nor ( ) a cruel man.A. is heB. he wasC. he couldn’t beD. was he9. ( ) who had arrested him three times for drug-taking.A. Before George stood the policemanB. Before the policeman George stoodC. Before the policeman George stoodD. Before the policeman stood the George10. “That house belongs to the Greens.”“( ) living in it now, is there?”A. Aren’t there any peopleB. Isn’t there anyoneC. There’s nobodyD. There’re no people11. California relies heavily on income from fruit crops. ( ).A. Florida alsoB. Florida tooC. Florida is as wellD. So does Florida12. He was told under no circumstances ( ) the computer.A. he may useB. he use mayC. may he useD. may use13. Nowhere in the world ( ).A. travelers can buy so much beauty with so little money as in HawaiiB. no one can buy so much beauty for so little money as in HawaiiC. so much beauty can be bought for so little money in HawaiiD. can travelers buy so much beauty for so little money as in Hawaii14. ( ) absurd was his manner that everyone stared at him.A. TooB. soC. SuchD. Much15. ( ) visiting that city, but we have been too busy.A. We often have thought ofB. Often we have thought ofC. Often have we though ofD. Often we did think of16. ( ) who had been in prison for seven years.A. In the robbery a man involvedB. Involved a man in the robberyC. Was a man involved in the robberyD. Involved in the robbery was a man17. ( ), I must do another experiment.A. Be it ever so lateB. it is ever so lateC. It be ever so lateD. So late it ever be18. By no means ( ) their own language well.A. it is true that all English people knowB. is it true that do all English people knowC. it is that do all English people knowD. is it true that all English people know19. ( ) was his anger that his face turned red.A. SuchB. greatC. SoD. It20. Up went the prices and ( ).A. the living standard came downB. came down the living standardC. down the living standard cameD. down came the living standard21. He believed, ( ), that people should start as early as possible to look at theworld and at nature and to think about what they saw.A. as does his motherB. as his mother doesC. as did his motherD. his mother as did22. ( ) where we can have Chinese food.A. Next to it another restaurant is thereB. Next to it another restaurant standsC. Next to it does another restaurant standD. Next to it is another restaurant23. It is the first time that she has been to the United States, ( )?A. hasn’t sheB. isn’t itC. has sheD. is it24. I don’t suppose he cares, ( )?A. does heB. doesn’t heC. do ID. don’t I25. You ought to finish the task in time, ( )?A. shouldn’t youB. mustn’t youC. couldn’t youD. won’t you26. Still beginners have to learn from their mistakes, ( ) they?A. haven’tB. mustn’tC. don’tD. aren’t27. John isn’t a diligent student, for it is the third time he has been late, ( )?A. wasn’t itB. hasn’t itC. isn’t itD. hasn’t he28. “Your uncle told me that he overslept.”“Oh, my uncle rarely used to oversleep, ( )?”A. wasn’t heB. was heC. didn’t heD. did he29. Peter oughtn’t to have done it in the first place, ( )?A. hasn’t heB. oughtn’t heC. hadn’t heD. ought he30. Everything seems all right, ( )?A. doesn’t itB. won’t itC. hasn’t itD. don’t they31. There has not been a great response to the sale, ( )?A. does thereB. hasn’t itC. hasn’t thereD. has there32. I wish to attend the evening party, ( )?A. wish I B do I C. don’t I D. may I33. James was very pleased, if he hadn’t spoken to the salesgirl beforehand, he mighthave spent more money than he could really have afforded, ( )?A. didn’t heB. couldn’t heC. hadn’t heD. mightn’t he34. You’d better remain here, ( )?A. hadn’t youB. shouldn’t youC. couldn’t youD. wouldn’t you35. He never used to swim in winter, ( )?A. did heB. didn’t heC. was heD. wasn’t he36. I am the only person who is to blame, ( )?A. am notB. aren’t IC. am not ID. am I37. We have to do another experiment today, ( )?A. don’t weB. shouldn’t weC. did weD. have we38. She must be looking forward to your return, ( )?A. mustn’t sheB. wasn’t sheC. isn’t sheD. didn’t she39. Don’t tell him the matter, ( )?A. will youB. do youC. don’t youD. won’t you40. What a pleasant day, ( )?A. is itB. won’t itC. isn’t itD. aren’t theyPart II Proof-reading41. (A) Not until the 19th and 20th centuries (B) did modern nationalism in Europe (C)produced its ripest fruit and its (D)lethal poisons.42. Few of the gold seekers (A) who flocked to California (B) were experiencedminers, and (C) so did they feel that they (D) had to be.43. (A)So is (B) the length of the bridge (C)that the shape of the earth (D) had to betaken into account by its designer.44. It was (A) not until dark (B) that did he realize it was (C) too late to return (D)home.45. (A) Anyone who did (B) that was (C) wasting their time and money, (D) wasn’tit?46. He (A) would have bought the house, if he had (B)only had (C) enough money,(D) hadn’t he?47. Black (A) told me that there (B) wasn’t anyone in the classroom (C) at that time,(D) was there?48. (A) It is (B) high time that we (C) left, (D) didn’t we?49. “What was the assignment (A)for today?”“We (B) had to read (C) the first chapter, (D) hadn’t we?”50. (A) Let’s go (B) swimming and boating (C) together, (D) will you?Answer SheetName: No. Class:1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10. 11.12.13.14.15.16.17.18.19.20.21.22.23.24.25.26.27.28.29.30.31.32.33.34.35.36.37.38.39.40.41.42.43.44.45.4647.48.49.50.。
Practice Test Chapter 115-17 and 21Multiple ChoiceIdentify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.____ 1. For a typical natural monopoly, average total cost isa. falling and marginal cost is above average total cost.b. falling and marginal cost is below average total cost.c. rising and marginal cost is below average total cost.d. rising and marginal cost is above average total cost.Figure 15-7The figure below depicts the demand, marginal revenue, and marginal cost curves of a profit-maximizingmonopolist.____ 2. Refer to Figure 15-7. If the monopoly firm perfectly price discriminates, then the deadweight loss amounts toa. $0.b. $100.c. $200.d. $500.____ 3. Refer to Figure 15-7. If the monopoly firm perfectly price discriminates, then consumer surplus amounts toa. $0.b. $250.c. $500.d. $1,000.____ 4. Refer to Figure 15-7. If the monopoly firm is NOT allowed to price discriminate, then the deadweight loss amounts toa. $50.b. $100.c. $500.d. $1,000.____ 5. Refer to Figure 15-7. If there are no fixed costs of production, monopoly profit without price discrimination equalsa. $500.b. $1,000.c. $2,000.d. $4,000.____ 6. A monopolist faces the following demand curve:The monopolist has fixed costs of $1,000 and has a constant marginal cost of $2 per unit. If the monopolistwere able to perfectly price discriminate, how many units would it sell?a. 400b. 500c. 900d. 4,200Table 15-5Dreher's Designer Shirt Company, a monopolist, has the following cost and revenue information. Assume that Dreher’s is able to engage in perfect price discrimination.____ 7. Refer to Table 15-5. What is the marginal revenue from selling the 5th shirt?a. $80b. $100c. $110d. $120____ 8. Refer to Table 15-5. What is total profit at the profit-maximizing quantity?a. $325b. $435c. $565d. $1000____ 9. Refer to Table 15-5. What is the marginal revenue from selling the 8th shirt?a. $45b. $60c. $80d. $95____ 10. Refer to Table 15-5. What is the total revenue when 7 shirts are sold?a. $650b. $700c. $910d. $1080____ 11. Refer to Table 15-5. What is the quantity that maximizes economic profit?a. 5b. 6c. 7d. 8____ 12. When an industry has many firms, the industry isa. an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products, but it is monopolistically competitiveif the firms sell identical products.b. an oligopoly if the firms sell differentiated products, but it is perfectly competitive if thefirms sell identical products.c. monopolistically competitive if the firms sell differentiated products, but it is perfectlycompetitive if the firms sell identical products.d. perfectly competitive if the firms sell differentiated products, but it is monopolisticallycompetitive if the firms sell identical products.____ 13. Crude oil is primarily supplied to the world market by a few Middle Eastern countries. Such a market is an example of a(n)(i) imperfectly competitive market.(ii) monopoly market.(iii) oligopoly market.a. (i) and (ii)b. (ii) and (iii)c. (i) and (iii)d. (iii) onlyTable 16-1The following table shows the percentage of output supplied by the top eight firms in four different industries.____ 14. Refer to Table 16-1. What is the concentration ratio in Industry C?a. 29%b. 39%c. 45%d. 56%Table 16-2The following table shows the total output produced by the top six firms as well as the total industry outputfor four industries.____ 15. Refer to Table 16-2. What is the concentration ratio for Industry A?a. 71%b. 81%c. 86%d. 88%____ 16. In markets characterized by oligopoly,a. the oligopolists earn the highest profit when they cooperate and behave like a monopolist.b. collusive agreements will always prevail.c. collective profits are always lower with cartel arrangements than they are without cartelarrangements.d. pursuit of self-interest by profit-maximizing firms always maximizes collective profits inthe market.____ 17. As a group, oligopolists would always be better off if they would act collectivelya. as if they were each seeking to maximize their own individual profits.b. in a manner that would prohibit collusive agreements.c. as a single monopolist.d. as a single perfectly competitive firm.____ 18. The theory of oligopoly provides a reason as to whya. perfect competition is not a useful object of study.b. price is less than marginal cost for many firms.c. all countries can benefit from free trade among nations.d. firms do not want to capture larger shares of their markets.____ 19. Consider the diagram below which shows the market demand curve for a particular product. Suppose thismarket is served by two duopolists who each face the marginal cost curve shown in the diagram. Themarginal revenue curve that a monopolist would face in this market is also shown. Which of the following statements is true?a. The total output in this market will likely be 2 units when the market is served by aduopoly.b. The price in this market will likely be $6 when the market is served by a duopoly.c. The total revenue to each firm will likely be more than $16 when the market is served by aduopoly.d. The total output in this market will likely be less than 4 units when the market is served bya duopoly.____ 20. An equilibrium in which each firm in an oligopoly maximizes profit, given the actions of its rivals, is calleda. a general equilibrium.b. a dominant equilibrium.c. a Nash equilibrium.d. an oligopoly equilibrium.Table 16-8Two cigarette manufacturers (Firm A and Firm B) are faced with lawsuits from states to recover the healthcare related expenses associated with cigarette smoking. Both cigarette firms have evidence thatindicates that cigarette smoke causes lung cancer (and other related illnesses). State prosecutors do not have access to the same data used by cigarette manufacturers and thus will have difficulty recovering full costs without the help of at least one cigarette firm study. Each firm has been presented with an opportunity to lower its liability in the suit if it cooperates with attorneys representing the states.Firm BConcede that cigarette smokeArgue that there is no evidence that smoke causes cancerFirm AConcede that cigarette smoke causes lung cancer Argue that there is no evidence that smoke causes cancer____ 21. Refer to Table 16-8. If both firms follow a dominant strategy, Firm B's profits (losses) will bea. $-50b. $-15c. $-10d. $-5Table 16-11 BAUp Down____ 22. Refer to Table 16-11. This table shows a game played between two players, A and B. The payoffs in thetable are shown as (Payoff to A, Payoff to B). Which outcome is the Nash equilibrium in this game? a. Up-Right b. Up-Left c. Down-Right d. Down-LeftTable 16-16Consider a small town that has two grocery stores from which residents can choose to buy a gallon of milk. The store owners each must make a decision to set a high milk price or a low milk price. The payoff table, showing profit per week, is provided below. The profit in each cell is shown as (Store 1, Store 2). Store 2Store 1Low Price High Price____ 23. Refer to Table 16-16. If grocery store 1 sets a high price, what price should grocery store 2 set? And whatwill grocery store 2's payoff equal? a. Low price, $800 b. High price, $100 c. Low price, $500 d. High price, $650Figure 17-1____ 24. Refer to Figure 17-1. The firm depicted in panel b faces a horizontal demand curve. If panel b depicts a profit-maximizing firm,a. it could be operating in either a perfectly competitive market or in a monopolisticallycompetitive market.b. it would not have excess capacity in its production as long as it is earning zero economicprofit.c. it is able to choose the price at which it sells its product.d. the firm can always raise its profit by increasing production since consumers will buy asmuch as the firm can produce.Figure 17-2____ 25. Refer to Figure 17-2. Which of the graphs shown would be consistent with a firm in a monopolistically competitive market that is earning a positive profit?a. Panel ab. Panel bc. Panel cd. Panel dFigure 17-3The lines in the figures below illustrate the potential effect of entry and exit in a monopolistically competitivemarket on either the demand curve or the marginal cost curve of existing firms.____ 26. Refer to Figure 17-3. Panel (d) illustrates the change that would occur if existing firms faceda. long-run economic losses.b. a decrease in the diversity of products offered in the market.c. new entrants in the market.d. firms exiting the market.____ 27. The free entry and exit of firms in a monopolistically competitive market guarantees thata. both economic profits and economic losses can persist in the long run.b. both economic profits and economic losses disappear in the long run.c. economic profits, but not economic losses, can persist in the long run.d. economic losses, but not economic profits, can persist in the long run.Figure 17-4____ 28. Refer to Figure 17-4. Which of the panels depicts a firm in a monopolistically competitive market earning positive economic profits?a. Panel ab. Panel bc. Panel cd. Panel d____ 29. Since a firm in a monopolistically competitive market faces aa. downward-sloping demand curve, it will always operate with excess capacity.b. downward-sloping demand curve, it will always operate at its efficient scale.c. perfectly elastic demand curve, it will always operate with excess capacity.d. perfectly inelastic demand curve, it will always operate at efficient scale.____ 30. Because a monopolistically competitive firm has some market power, in the long-run the price of its good exceeds itsa. average revenue.b. average total cost.c. marginal cost.d. profit per unit.____ 31. Which of the following markets impose deadweight losses on society?(i) Perfect competition(ii) Monopolistic competition(iii) Monopolya. (i) and (ii)b. (ii) and (iii)c. (i) and (iii)d. (i) only____ 32. A firm in a monopolistically competitive market is similar to a monopoly in the sense that(i) they both face downward-sloping demand curves.(ii) they both charge a price that exceeds marginal cost.(iii) free entry and exit determines the long-run equilibrium.a. (i) onlyb. (ii) onlyc. (i) and (ii)d. (i), (ii), and (iii)____ 33. Consider two goods, books and hamburgers. The slope of the consumer's budget constraint is measured by thea. consumer's income divided by the price of hamburgers.b. relative price of books and hamburgers.c. consumer's marginal rate of substitution.d. number of books purchased divided by the number of hamburgers purchased.____ 34. A budget constrainta. shows the prices that a consumer chooses to pay for products he consumes.b. shows the purchases made by consumers.c. shows the consumption bundles that a consumer can afford.d. represents the consumption bundles that give a consumer equal satisfaction.Figure 21-1____ 35. Refer to Figure 21-1. A consumer that chooses to spend all of her income could be at which point(s) on the budget constraint?a. Ab. Ec. B, C, or Dd. A, B, C, or DFigure 21-3(a) (b)40101242____ 36. Refer to Figure 21-3. In graph (a), what is the price of good y relative to good x (i.e., P y/P x)?a. 1/3b. 1/4c. 3d. 4____ 37. Suppose a consumer is currently spending all of her available income on two goods: music CDs and DVDs. If the price of a CD is $9, the price of a DVD is $18, and she is currently consuming 10 CDs and 5 DVDs, whatis the consumer's income?a. $90b. $180c. $270d. $360____ 38. Budget constraints exist for consumers becausea. their utility from consuming goods eventually reaches a maximum level.b. even with unlimited incomes they have to pay for each good they consume.c. they have to pay for goods and they have limited incomes.d. prices and incomes are inversely related.____ 39. Suppose the only two goods that Brett consumes are wine and cheese. When wine sells for $10 a bottle and cheese sell for $10 a pound, he buys 6 bottles of wine and 4 pounds of cheese — spending his entire incomeof $100. One day the price of wine falls to $5 a bottle and the price of cheese increases to $20 a pound, whilehis income does not change. If you place wine on the vertical axis and cheese on the horizontal axis, thena. the slope of Brett's budget has not changed.b. the slope of Brett's budget constraint is flatter at the new prices.c. the slope of Brett's budget constraint is steeper at the new prices.d. Brett's budget constraint has shifted in parallel to the budget constraint with the old prices.Figure 21-4____ 40. Refer to Figure 21-4. Which of the following statements is true for a consumer who moves from point A to point D?a. It is difficult to compare the level of consumer satisfaction between points D and A.b. The consumer is indifferent between point A and point D.c. The consumer is definitely worse off.d. The consumer is likely to place a higher relative value on Twinkies at point A than at pointD.____ 41. The following diagram shows one indifference curve representing the preferences for goods x and y for oneconsumer.What is the marginal rate of substitution between points A and B?a. 1/2b. 4/3c. 2d. 3____ 42. Each of the following are characteristics of an indifference curve map excepta. moving northeast to a new indifference curve will increase utility.b. points on the same indifference curve yield equal utility.c. the axes represent levels of utility for each of the goods.d. indifference curves cannot cross.Figure 21-9____ 43. Refer to Figure 21-9. Assume that the consumer depicted in the figure has an income of $80. If the price of chocolate chips is $4.00 and the price of marshmallows is $4.00, the optimizing consumer would choose topurchasea. 9 marshmallows and 6 chocolate chips.b. 10 marshmallows and 10 chocolate chips.c. 5 marshmallows and 5 chocolate chips.d. 3 marshmallows and 9 chocolate chips.Practice Test Chapter 115-17 and 21Answer SectionMULTIPLE CHOICE1. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 15-4 TOP: Natural monopolyMSC: Analytical2. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 15-5 TOP: Perfect price discriminationMSC: Analytical3. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 15-5 TOP: Perfect price discriminationMSC: Analytical4. ANS: D DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: Deadweight lossMSC: Applicative5. ANS: C DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: ProfitMSC: Applicative6. ANS: C DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: Perfect price discriminationMSC: Analytical7. ANS: D DIF: 2 REF: 15-5 TOP: Marginal revenueMSC: Applicative8. ANS: B DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: ProfitMSC: Applicative9. ANS: D DIF: 2 REF: 15-5 TOP: Marginal revenueMSC: Applicative10. ANS: C DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: Total revenueMSC: Applicative11. ANS: C DIF: 3 REF: 15-5 TOP: Profit maximizationMSC: Applicative12. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 16-1 TOP: MarketsMSC: Interpretive13. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 16-1 TOP: OligopolyMSC: Interpretive14. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 16-1 TOP: Concentration ratioMSC: Applicative15. ANS: B DIF: 3 REF: 16-1 TOP: Concentration ratioMSC: Applicative16. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 16-2 TOP: CartelsMSC: Interpretive17. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 16-2 TOP: CartelsMSC: Interpretive18. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 16-2 TOP: OligopolyMSC: Interpretive19. ANS: D DIF: 3 REF: 16-2 TOP: DuopolyMSC: Interpretive20. ANS: C DIF: 1 REF: 16-2 TOP: Nash equilibriumMSC: Definitional21. ANS: C DIF: 1 REF: 16-3 TOP: Game theoryMSC: Applicative22. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 16-3 TOP: Game theoryMSC: Applicative23. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 16-3 TOP: Game theoryMSC: Applicative24. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Profit maximizationMSC: Interpretive25. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Monopolistic competitionMSC: Interpretive26. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Long-run equilibriumMSC: Interpretive27. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Long-run equilibriumMSC: Interpretive28. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Monopolistic competitionMSC: Interpretive29. ANS: A DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Demand curveMSC: Interpretive30. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: Long-run equilibriumMSC: Interpretive31. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: MarketsMSC: Interpretive32. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 17-1 TOP: MarketsMSC: Interpretive33. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Interpretive34. ANS: C DIF: 1 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Definitional35. ANS: C DIF: 1 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Applicative36. ANS: B DIF: 3 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Applicative37. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Applicative38. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Interpretive39. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 21-1 TOP: Budget constraintMSC: Applicative40. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 21-2 TOP: Indifference CurveMSC: Analytical41. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 21-2 TOP: Marginal rate of substitutionMSC: Analytical42. ANS: C DIF: 2 REF: 21-3 TOP: Indifference CurveMSC: Interpretive43. ANS: B DIF: 2 REF: 21-3 TOP: Consumer choiceMSC: Applicative。
Computing Essentials 2008练习答案Chapter 1: Information Technology, The Internet, and YouCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer1 The most essential part of an information system. People7 Coordinates computer resources. Operating System10 Modifies signals for processing. Modem12 Data that has been processed by the computer. Information13 Unprocessed facts. Data14 Notebook computer that accepts handwritten input.. Tablet PCDownNum. Clue Answer2 Uses computers to become more productive.End User3 Rules or guidelines to follow when using software, hardware, and data. Procedures4 Created by word processors.Document Files5 Specialized programs that allow input and output devices to communicate. Device Drivers6 Created by database management programs.Database Files8 The physical equipment of a microcomputer.Hardware9 The world’s largest computer network.Internet13 Provides step-by-step instructions to the computer.SoftwareMultiple Choice AnswersB B A B D D ACD DMatching AnswersE F I H A C G B D JChapter 2: The Internet, The Web, and Electronic CommerceCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer2 Provide users a connection to the Internet. ISP3 Unwelcome e-mail. Spam5 Explore the Web. Surf7 Internet uploading and downloading service. FTP8 Steals credit card information. Carder9 A file, such as a document or worksheet, that is attached to an e-mail message.Attachment10 Involves the sale of a product to another business. B2B13 Connection to Web resources. L ink15 Process of transferring information from a remote computer to the computer one is using.DownloadDownNum. Clue Answer1 The sites that a search engine returns after running a keyword search. Hits4 Special program written in Java. Applet5 Locates information online. Search Engine6 Location of Web resource. URL11 Program that provides access to Web Browser12 Used to block certain sites. Filter14 Provides high-speed connection using existing telephone lines. DSLNum Multiple Choice AnswersD A C C A A A A D BMatching Answersi d g e f c h j a bChapter 3: Basic Application SoftwareCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer4 Rectangular area that contains messages. Window5 System to organize and retrieve data. DBMS8 Collection of individual applications. Software Suite10 Rearrange records using a field. Sort11 Formed by intersection of row and column. Cell14 Collection of related data. Database16 Flyer, report, newsletter, Web page. Document17 These make up a presentation. Slides18 Question or request for data in a database. QueryDownNum. Clue Answer1 List of commands. Menu2 Rectangular grid of rows and columns used in programs like Excel. Worksheet3 Has records and fields. Table叮叮小文库6 Controls format and placement of slides. Master Slide7 Requests user input. Dialog Box9 Moves insertion point to next line. Word Wrap12 Series of cells. Range13 A vertical block of cells one cell wide. Column15 Contain buttons and menus. ToolbarsNum Multiple Choice AnswersD D B D D A B B C DMatching Answersj a c h b d i e g fChapter 5: System SoftwareCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer5 Program that makes copies of files in case of damage or loss. Backup6 Boot that occurs when the computer is already on. Warm boot8 Combination of several utility programs in one package. Utility Suite9 Allows communication between devices and the operating system. Driver11 Concentric rings on a disk. Tracks12 Used to control and coordinate networked computers. NOSDownNum. Clue Answer1 Location to store related files. F older2 Computer that coordinates all communication between other computers.Network server3 Uses graphical elements to communicate with the operating system. GUI4 Broken-up file stored in different sectors. Fragmented5 Starting or restarting a computer. Booting7 Operating system with over 80 percent of the market. Windows10 Graphic objects on the desktop used to represent programs and other files. IconsNum Multiple Choice AnswersC D C A A A C B B A CMatching Answersj d f b g h a e i cChapter 7: Input and OutputCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer6 Used to grade multiple choice exams. OMR9 Specialized digital camera that broadcasts images over the Internet. WebCam10 Records images digitally on a disk. Digital camera13 Most popular input device used for computer games. Joystick14 Delivers much clearer picture than regular TV. HDTV16 Resolution is expressed as a matrix of these dots. Pixel17 Keyboard that rolls up for storage and transport. FlexibleDownNum. Clue Answer1 The distance between each pixel. Dot pitch2 Most commonly used way to input data. Keyboard3 Button rotated to scroll through information displayed on the monitor.Wheel Button4 Most widely used type of mouse. Mechanical5 Type of terminal that does no processing. Dumb7 Number of times a screen is redrawn each second. Refresh rate8 Measure of resolution. dpi11 Keys that turn features on and off. Toggle12 Translates processed information into hard copy. Printer15 Bar code system used in supermarkets. UPCNum Multiple Choice AnswersA B A B D A D C D BMatching Answersi e f j a b g d c hChapter 9: Communications and NetworksCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer5 Interprets and routs incoming radio frequencies. Base station7 Continuous electronic waves. Analog9 Configuration of a network. topology10 Network interface card. NIC11 Transfer speed or transfer rate. bps12 Short range wireless communication standard. bluetooth14 Measurement of the width of the communication channel. bandwidthDownNum. Clue Answer1 Node that requests and uses resources available from other nodes. client2 Each device in the network handles its own communications. Bus network3 Device that allows links between LANs. Network gateway4 Process that converts digital to analog. modulation6 Pieces of a message sent over the Internet. packets8 Global positioning system. GPS13 Any device that is connected to a network. node15 Uses existing telephone lines to provide high-speed connections. DSL16 Central node for other nodes. hubNum Multiple Choice AnswersC B AD C D B B D DMatching Answersg b a i h e c j d fChapter 11: Information SystemsCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer3 Level of management concerned with strategic planning. Top5 Identifies, investigates, and develops new products and services. Research9 Report produced upon request. Demand10 Someone who makes decisions in a DSS. User11 Model that helps middle-level managers in long-range planning. Tactical12 Information worker involved in the creation of information. Knowledge worker 14 Concerned with calculating employee paychecks. Payroll16 Specialized information system that knowledge workers use. KWS17 Keeps track of summaries of all foregoing transactions. General ledgerDownNum. Clue Answer1 The buying of materials and services. Purchasing2 Plans, prices, promotes, sells, and distributes goods and services. M arketing4 Form that shows supply and order information. Purchase order6 Report that calls attention to unusual events. Exception7 Help top-level managers oversee operations and develop plans. ESS8 Information worker that distributes information. Data worker13 Use data from TPS to support middle managers. MIS15 Level of management concerned with decision making. MiddleNum Multiple Choice AnswersB B A D D AC C CC BMatching Answersh j f d g b a c i eChapter 13: Systems Analysis and DesignCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer3 Systems implementation Conversion8 Collection of activities and elements organized to accomplish a goal. System9 Build a model that can be modified before the system is installed. Prototyping10 Automated design tool. CASE12 Approach where new system is tried in only one part of an organization. Pilot14 Shows levels of management and formal lines of authority. Organization chart15 List of questions. ChecklistDownNum. Clue Answer1 1st step in the design phase. Feasibility2 St udy an organization’s systems.Systems analysis4 System’s performance is compared to the original specifications.System audit5 Approach where new system is implemented slowly over time. Phased6 Conversion done by abandoning old system and starting the new. Direct approach7 Diagram that shows the information flow within an organization. Data flow11 Shows the relationship between input and output documents. Grid chart12 Old and new systems are operated side by side. Parallel13 The most commonly overlooked activity in the implementation phase. TrainingNum Multiple Choice AnswersA D A C D D A D A CMatching Answersg h f d c a b i j eChapter 15: Your Future and Information TechnologyCrossword Puzzle Answers:AcrossNum. Clue Answer4 Inputs customer information and other data. Data entry worker6 Repairs and installs computer components and systems. Computer Technician8 Acting in anticipation of future problems, needs, or changes. Proactive9 Develops and maintains Web sites. W ebmaster10 Plans and designs information systems. System analyst11 Prepares instruction manuals and technical reports. Technical writer12 Designs, tests, and researches encryption procedures. CryptographerDownNum. Clue Answer1 Person that is unfamiliar with computers. Na?ve2 Creates, tests, and troubleshoots computer programs. Programmer3 Person that feels learning about computers is an imposition.F rustrated4 Creates and formats publication-ready material. Desktop publisher5 Instructs users on the latest software and hardware. Computer trainer7 Person that feels the idea of using a microcomputer is overrated. Cynic叮叮小文库Num Multiple Choice AnswersD B A D C D C A D BMatching Answersd j h ae i b g c f欢迎有需要的朋友下载!!11。
Chapter 15: Practice Tests15.1 The difference in hearing loss between men and women is thought to be due toA.similar factors that reduce the maximum lifespan of men.B.exposure to environmental noise in male-dominated occupations.C.physical damage to the eardrum due to participation in conact sports.D.X-linked chromosomal abnormalities15.2 The inner fatty layer of skin that softens and rounds the edges of our body is called theA.epidermisB.protodermisC.dermisD.hypodermis15.3 All of the following are benefits of hormone replacement therapy EXCEPTA.protection against bone deterioration and cardiovascular disease.B.an increase in hot flashes until menopause is completeC.improvement of memory and other aspects of cognition.D.maintenance of cognitive functioning in late adulthood.15.4 A man’s level of the sex hormone testosterone will generallyA.peak in middle age, then drop off.B.peak in early adulthood, then drop off.C.rise steadily throughout adulthood.D.remain stable throughout adulthood.15.5 Which of these is the best description of the relationship between a couple’s sexualactivity and their marital happiness?A.Sexual activity makes couples happier.B.Being happy makes them have more sex.C.It is bi-directional; each affects the other.D.There is no scientific relationship between them.15.6 Currently, the death rate from many common types of cancer isA.increasing sharply.B.increasing somewhat.C.leveling off or dropping.D.fluctuating widely.15.7 In some individuals, indigestion-like or crushing chest pains, called _______, revealan oxygen-deprived heart.A.a heart attackB.atherosclerosisC. a strokeD.angina pectoris15.8 Frequent and angry outbursts; rude, disagreeable behavior; and critical andcondescending nonverbal cues during social interactions are all aspects ofA.mental illnessB.insensitivitypetitivenessD.expressed hostility15.9 Sharon decided that she was unhappy at work. She realized that the primary cause wasfrustration with an irresponsible co-worker. She met with the individual, came up withstrategies to help the young woman meet her responsibilities, and subsequently enjoyedher job more. Sharon usedA.Stress Identification Therapy (SIT)B.an emotion-centered coping strategyC. a problem-centered coping strategyD.an indirect method of stress management15.10 When a person has a sense of control over life events, a commitment to importantactivities, and the tendency to see change as a challenge rather than a disappointment, this person is said to displayA.a Type A behavior patternB. a Type B behavior patternC.fluidityD.hardiness15.11 In American society, the ideal woman is portrayed as _____, and represents the heart ofthe double standard of aging.A.passive and submissiveB.young and sexually attractiveC.indecisive and dependentD.assertive and competent15.12 Which of these tasks most clearly makes use of crystallized intelligence?A.learning to speak a new languageB.finding hidden figures in a drawinging the right words to express an ideaD.creating unusual, challenging art work15.13 Basic information-processing skills decline throughout adulthood, but overall cognitivefunctioning remains quite steady. The author suggests that this apparent contradictioncan be reconciled by noting thatA.adults use stronger abilities to compensate for weaker onesB.basic information-processing skills don’t affect most abilitiesC.declines occur, but only for highly practiced, automatic skillsD.cognitive declines are masked by social bias against older people15.14 The viewpoint that the general slowing of cognitive processes is due to breaks in theconnections in the brain, which must then be bypassed, is called the ______ view.A.neural networkrmation-lossC.interconnectionistD.path construction15.15 As Clarissa gets older, which type of memory activity will be LESS likely to suffer?A.matching names with faces of people she has metB.memorization of digits such as phone numbersC.memorization of list itemsD.memorization of prose15.16 Expertise tends to developA.in those who are highly educatedB.in those at the top of administrative laddersC.in those from high SES backgroundsD.at all levels in any field of endeavor15.17 Research on the ability to solve everyday problems effectively shows that this abilityA.peaks about age 30 and then drops offB.peaks between the ages of 40 and 59C.doesn’t reach a peak until after age 60D.is constant throughout adulthood15.18 When solving an everyday problem, middle-aged adults will do all of the followingEXCEPTA.select better strategiesB.make decisions based on emotionC.solve it though logical analysisD.reinterpret it from a different perspective15.19 The impact of a challenging job on cognitive growth is greatest forA.individuals of any ageB.people in their twenties and thirtiesC.those in administrative or supervisory positionsD.people living in Japan or Poland15.20 The most important factor in the success of an adult college student isA.receiving social supportB. a high intelligence levelC.taking a full course loadD.studying at regular timesChapter 16: Practice Test16.1 At age 43, Darryl is a successful lawyer who gets a lot of satisfaction from guiding younglawyers starting out in the firm, coaching his daughter’s basketball team, and being camp leader for his son’s Boy Scout troop. According to Erikson, he has most clearlydeveloped a sense ofA.intimacyB.generativityC.autonomyD.integrity16.2 Although Inez has a stable marriage, three successful grown children, and a good job, sheis very self-centered and self-indulgent. She has little involvement with her children ortheir families, other than to remind them what gifts she wants for her birthday orMother’s Day. She “puts in her hours” at work, but is indifferent to how she couldimprove her productivity or that of her office. Erikson would say that InezA.has developed a strong sense of stagnationB.is typical of those in middle adulthoodC.is going through a midlife crisisD.is a pain in the neck16.3 Which person is likely to have the largest gap between subjective and objective age?A.Maria, age 25B.Martin, age 35C.Mathew, age 55D.MaryAnne, age 5516.4 Which person is more likely to pursue a satisfying life structure successfully?A.Parker, a blue-collar workerB.Peter, who lives in povertyC.Patsanne, a corporate executive who works only the hours she wants toD.Penny, who is unemployed16.5 The majority of adults experiencing a midlife transition demonstrateA.a sharp, sudden change in careersB. a great increase in family responsibilitiesC.major depression or anxiety attacksD.small, slow changes in life structure16.6 Which of the following early adulthood characteristics is NOT associated with crisisduring middle adulthood?A.strong gender rolesB.low income or povertyC.strong family pressuresD.divorce16.7 Researchers who are proponents of the _____ approach say that middle adulthood is anadaptation to events like children growing up or an impending retirement.A.stageB.developmentC.life eventsD.social pressure16.8 Because ________, they cannot be the single cause of midlife change.A.external pressures are less during middle adulthoodB.life events are not as age graded as in early adulthoodC.changing gender roles are more commonD.pressures to positively impact the world occur at all age levels16.9 As a young adult, Christian wanted to be a great athlete and a very successfulbusinessman. As he enters middle adulthood, he will probablyA.strive harder to make his current self match his possible selfB.become depressed that he didn’t achieve his goalsC.focus less on the business success and more on the athleticism in an attempt to regainhis youthD.concentrate more on enhancing personal relationships and being competent at work16.10 In a study of well-educated individuals throughout adulthood, which of these traitsshowed an increase from early to middle adulthood?A.insecurityB.depressionC.self-acceptanceD.isolation16.11 Shakira, an office supervisor, is well liked and respected by those who work for her. Shecan find the “silver lining” to a stressful situation, anticipates and plans for possibleproblems, and uses humor to express ideas and feelings. Shakira is probablyA.a middle-aged individualB.not effective as a supervisor, even though she is well likeding emotion-centered strategies for coping with stressD.a young adult16.12 Warren is generous, kind, and good-natured. he always has good words to say about hisfriends and tries to find the best qualities in everyone he meets. Warren best exemplifies which of these “big five” personality traits?A.extroversionB.conscientiousnessC.agreeablenessD.neuroticism16.13 The modern view of the period between the departure of the last child and retirement isviewed as a time ofA.expansion and new horizonsB.sadness and the “empty nest”C.increasing marital stressD.isolation from social activities16.14 Your friend’s children will be growing up and leaving home in the next five years or so,and your friend is concerned about how satisfying life can be after they are gone.According to the book, the best advice you can give for ensuring increased life happiness after they leave is for her toA.develop a strong work orientationB.spend as much time with them as possible nowC.keep them in the family unit as long as possibleD.separate completely from them after they go16.15 Middle-aged adults who balance the needs of aging parents and financially dependentchildren are calledA.real troopersB.kinkeepersC.economically challengedD.the sandwich generation16.16 Which event tends to cause an increase in sibling ties during middle adulthood?A.the birth of childrenB.beginning a new jobC.the birth of grandchildrenD.parental illness16.17 Eighteen-year old Tim believes that government programs for the elderly are too costly.Which of the following activities could increase his endorsement of these benefits?cation on the tax structure of the United StatesB.increased awareness of health care costs for elderly adultsC.frequent contact with his grandparentsD.eventually becoming a senior citizen himself16.18 Which aspect of a worker’s job satisfaction changes the most during adulthood?A.intrinsic satisfactionB.extrinsic satisfactionC.borderline satisfactionD.corporate satisfaction16.19 The most important factor in helping middle-aged worker cope with losing their job isA.leaving them alone to preserve their dignityB.social contact with those who share their valuesC.getting them involved with household managementD.pretending that nothing has really changed16.20 Retirement can be stressful since it leads to a loss of two important work-related rewards,A.income and benefitsB.interaction with others and a steady incomeC.income and statusD.intrinsic and extrinsic satisfactionChapter 17: Practice Test17.1 Charlie, at age 82, is vigorous, healthy, and looks younger than he really is. Charliewould be classified asA.immatureB.postmatureC.old-oldD.young-old17.2 The percentage of elderly people in the population of the United States is lower than inmany other industrialized nation due in part toA.particularly strong strains of influenza during the last five yearsB.low birthrates among America’s poverty-stricken groupsC.less effective public policies ensuring health and well-being throughout the lifespanD.zero population growth during the last decade17.3 Ellen is worried about developing macular degeneration. What can she do to reduce herrisk of acquiring this condition?A.avoid reading, as it strains the eyesB.wear bifocalsC.eat lots of spinachD.wear reading glasses17.4 Compared with vision loss in elderly people, hearing loss has a larger effect on a person’sA.safety and enjoyment of lifeB.ability to live independentlyC.self-esteemD.employment17.5 An important reason elderly people become more out of breath while exercising thanyounger adults do is thatA.their hearths pump blood more quicklyB.their lungs fill and empty less effectivelyC.their brains demand more oxygenD.their muscles demand more oxygen17.6 All of the following contribute to a higher incidence of sleep disturbances in men than inwomen EXCEPTA.sleep apnea.B.enlargement of the prostate glandC.restless legsD.lower levels of both testosterone and estrogen17.7 Weight changes after age 60 typically involveA.less fat accumulated on the torsoB.weight gain due to decreased activityC.weight loss due to less lean body massD.weight gain from fat accumulations17.8 In several studies, 12 to 20 percent of elders with disabilitiesA.died within 2 years of becoming disabledB.showed improvement 2 to 6 years laterC.maintained their independent living status with no outside support from othersD.had become disabled due to injuries that occurred during early adulthood that had notbeen treated properly17.9 Your elderly neighbor is wondering whether or not to take a vitamin-mineral nutritionalsupplement. What advice should you give?A.There is no evidence that supplements make any differenceB.Vitamin supplements are not necessary if you are eating wellC.These supplements are only useful for very active peopleD.These supplements have proven benefits for most elders17.10 Which of these is the best example of primary aging?A.far-sightedness forma stiffening lensB.lung cancer from smoking cigarettesC.weight gain from a sedentary lifestyleD.high blood pressure from prolonged stress17.11 An autoimmune response that leads to inflammation of connective tissue and subsequentoverall stiffness, inflammation, and aching is calledA.osteoarthritisB.adult-onset diabetesC.rheumatoid arthritisD.bursitis17.12 At which age is the death rate from unintentional injuries highest?A.middle adulthoodB.adolescencete adulthoodD.young adulthood17.13 The most common form of dementia isA.cerebrovascular dementiaB.cardiovascular diseaseC.Alzheimer’s diseaseD.retrograde amnesia17.14 Bundles of twisted threads inside neurons that are the product of collapses neuralstructures are calledA.amyloid plaquesB.cerebrovascular bundlesC.neurofibrillary tanglesD.brain breaks17.15 Which person is MOST likely to be placed in a nursing home?A.Neva, an 83-year-old African-AmericanB.Natasha, an 80-year-old Caucasian-AmericanC.Nyree, a 90-year old Japanese great-grandmotherD.Nyung, a 95-year-old Asian-American17.16 When older adults engage in selective optimization with compensation, theyA.select only activities that are personally valued to optimize their energy and they alsodevelop ways to compensate for lossesB.tend to show gains in fluid intelligenceC.show losses in crystallized intelligence onlyD.attend to only certain parts of a conversation (selective optimization) and then thry tofill in the missing pieces later (compensation).17.17 Which of these language abilities remains the most constant as adults grow older?A.retrieving words from long-term memorynguage comprehensionC.planning and organizing speechD.inventing new words and phrases17.18 According to your text, wisdom can be summed up asA.a cumulative benefit of ageB.expertise in the fundamental pragmatics of lifeC.an intrinsic characteristic that develops with ageD.general familiarity with human problems17.19 A steady, marked decrease in cognitive functions shortly before death is referred to asA.increased morbidityB.the cognitive slopeC.mental despairD.terminal decline17.20 One serious drawback to the Elderhostel program is thatA.it is not accessible to low-SES peopleB.it gives elders a gales sense of importanceC.there is no screening for the program’s teachersD.most programs are too demanding physicallyChapter 18: Practice Test18.1 According to Erikson, developing a sense of ego integrity depends onA.viewing one’s life in the context of all of humanityB.the willingness to open up one’s life to another personC.deciding who one is and what one wants from lifeD.the desire to make a contribution to the next generation18.2 Yin-sing, at age 80, can’t face the idea that she will die and the world will go on. She haschildren and grandchildren, but is not interested in their lives or fortunes. According toPeck, Yin-sing needs to work onA.body transcendenceB.ego transcendenceC.ego differentiationD.future differentiation18.3 When asked, approximately one-third of elders claimed that the best part of their life was_________, thus _______ the belief that older adults wish to be young again.A.childhood; verifyingB.“right now”; contradictingC.young adulthood; verifyingD.“still to come”; contradicting18.4 Which of these personality traits tends to DECREASE as adults grow old?A.AgreeablenessB.Acceptance of changeC.SociabilityD.Satisfaction18.5 Because Mahatma Gandhi and Martin Luther King, Jr., stood up against persecution andinjustice in order to promote their visions of an all-inclusive human community, they had att ained which of Fowler’s stages of faith development?A.synthetic-conventionalB.conjunctiveC.individuative-reflectiveD.intuitive-projective18.6 Because of the gender-related life changes in very old age, women are more likely toreport _______ than are men.A.a higher sense of psychological well-beingB. a lower sense of psychological well-beingC.more dependence on othersD.more frequent thoughts of suicide18.7 Ethnic minority elders who are offered formal agency services to help with their liveswill generallyA.accept formal agency services quite readilyB.resist unless the agencies are culturally sensitiveC.resist all types of formal agency servicesD.accept only formal services that are family based18.8 According to the ________, when society arranges conditions that permit elders toremain engaged in roles and relationships, life satisfaction is improved and socialinteractions increaseA.mutuality theoryB.activity theoryC.socioemotional selectivity theoryD.disengagement theory18.9 Although the social networks of older adults are ________, they report being _______than younger adults with their current number of friendsrger; more dissatisfiedrger; happierC.smaller; happierD.smaller; more dissatisfied18.10 Which of the following is the primary reason that elders residing in small and mid-sizedcommunities are more satisfied with life?A.children tend to live closerB.more opportunities for interaction with others of the same ethnic backgroundC.higher participation in local governmentD.lower crime rates18.11 Although increasing numbers of ethnic minority elders want to live on their own, ______prevent(s) them from doing so.A.prideB.cultural valuesC.their childrenD.poverty18.12 An elder’s autonomy is restricted most sharply if he or she is living inA.his or her own homeB. a nursing homeC.congregate housingD.an adult child’s home18.13 The increase in marital satisfaction in late adulthood is due to all of the followingEXCEPTA.increased perceptions of fairness as men contribute more to household tasksB.engagement in more joint leisure activitiesC.greater financial securityD.more positive interactions due to greater emotional understanding18.14 Compared with younger adults, elders who must cope with the death of a spouse typicallyshowB. a less intense but longer-lasting reactionC.more problems adjusting to the deathD.fewer problems adjusting to the death18.15 Elderly women who are asked to list the functions of close friendships in their lives giveprimary importance toA.living assistanceB.acceptanceC.links to the outside worldpanionship18.16 The kind of assistance that elders expect from their adult children most often involves.A. Help with day-to-day living tasksB. advice and emotional supportC. financial assistance with living expensesD. help in dealing with medical emergencies18.17 Elder abuse is more common if the elder’s caregiver isA. a sibling or other close relative of the elderB. an adult who is at least middle-aged or olderC. emotionally or financially dependent on the elderD. working in a challenging, rewarding career18.18 Women are more likely to retire earlier than men becauseA. they are typically better off financiallyB. they tend to be in better healthC. they work in unstimulating environmentsD. of family events18.19 Miguel works for a community center and wants to recruit elders as volunteers for anafter-school reading program. Which of the following people is NOT a likely candidate?A. Carl, a lifelong community activist and volunteerB. Marcos, who has never volunteered and retired 4 years agoC. Maria, who has never volunteered for anything and retired 6 months agoD. Reuben, a highly educated and financially secure elder18.20 Modern definitions of successful aging have shifted the focus AWAY fromA. specific achievements in health or cognitive functioningB. the processes elders use to reach personally valued goalsC. accepting and learning to compensate for personal declinesD. the ways in which elders minimize losses and maximize gains19.1 Death is long and drawn out for _____ of people due to _____.A. only a small percentage; life-saving medical technologyB. only a small percentage; the increasing popularity of living willsC. three-fourths; life-saving medical technologyD. nearly 90 percent; increases in diseases like cancer and AIDS19.2 Brianna was found unconscious is a swimming pool. Her heartbeat and breathing hadstopped, and her dilated pupils indicated lack of oxygen to her brain. yet, paramedicswere able to revive her. Brianna was in the _____ phase of dying.A. agonalB. clinicalC. mortalityD. miracle19.3 The term used by the medical profession for individuals whose brain stems continue tofunction but who show no electrical activity at all in the cortex isA. brain deathB. persistent vegetative stateC. imminent mortalityD. coma19.4 Karim had grown up in the United States, in a suburban neighborhood. As a result, he isprobably _____ death.A. comfortable withB. used to dealing withC. very familiar withD. insulated from19.5 Which of these aspects of the death concept is most difficult for children to comprehend?A. Dead people no longer eat, breathe, or moveB. Dead people will not wake up or come alive againC. Dead people cannot think, feel, or understandD. All people will die at some time or other19.6 Among elders in Western cultures such as the United States, the most important factor inreducing death anxiety isA. a spiritual sense of life’s meaningB. commitment to an organized religionC. the conviction that there is an afterlifeD. good physical health for one’s age19.7 When going through Kubler-Ross’s phases of dying, peopleA. move through each stage in a sequential mannerB. move back and forth between stagesC. often linger at the anger stage and must be pushed to the next stage by family orhealth care professionalsD. rarely progress to the acceptance stage19.8 According to Kubler-Ross, once a dying patient has reached the stage of acceptance he orshe will oftenA. appear cheerful and eager for deathB. become more sociable and outgoingC. feel no hope at all of avoiding deathD. withdraw from most or all people19.9 _____ is an alternative to Kubler-Ross’s stages that theorists say makes sense in terms ofthe individual’s pattern of living and values, preserves or restores significant relationships, and is as free of suffering as possible.A. Passive euthanasiaB. Voluntary active euthanasiaC. Assisted suicideD. An appropriate death19.10 The primary reason some caregivers join in a dying patient’s denial by pretending thatthey will get better and continue to live is thatA. the patient seems so healthy they forget he or she is dyingB. the patient becomes too angry whenever dying is mentionedC. it is difficult to face the impending death and to close off relationshipsD. they don’t want to be bothered with discussing death19.11 When a dying person feels a strong sense of spirituality, it tends to produceA. less fear of dying and more acceptance of dyingB. more anger at a God who should have prevented thisC. confusion and distress at what dying really meansD. anger and resentment at those who go on living19.12 In the United States today, passive euthanasia for patients whose death is imminent orwho are in a permanent coma is consideredA. an ordinary part of normal medical practiceB. an unusual procedure that must be court orderedC. immoral and unethical and almost never occursD. permissible only for patients who are very old19.13 _____ is a written statement of desired medical treatment should a person becomeincurably ill. Two types are recognized is most states.A. An advance medical directiveB. A living willC. Durable power of attorney for health careD. a codicil19.14 The durable power of attorney for medical care is a particularly useful for ensuring thepartner’s roleA. in states in which euthanasia is illegalB. in situations other than terminal illnessC. in relationships not recognized or sanctioned by lawsD. when mental as well as physical difficulties are present19.15 A central philosophy of the _____ is that the dying person and his or her family should beoffered choices that guarantee an appropriate death.A. home-choiceB. intensive care unitC. hospice approachD. emergency room procedure19.16 After Jada’s sister died, she experienced intense physical and psychological distress. Jadawas experiencingA. bereavementB. griefC. a near-death experienceD. mourning19.17 Many of the reactions of the confrontation phase-such as anxiety, anger, frustration,sleeplessness and loss of appetite- are symptoms ofA. depression, an invariable component of grievingB. avoidanceC. mourning, a necessary phase of grievingD. poor coping strategies19.18 During the accommodation phase of the grieving process, a bereaved person’s focus shiftstoA. a strong yearning or desire to be with the deceased againB. anger at those who survived when the loved one didn’tC. putting the deceased in the past and forgetting him or herD. the surrounding world and going on with one’s life19.19 Parents of children who have close family members who are dying would be best advisedtoA. remove the children from the household until the death is overB. be honest about what is happening and answer their questionsC. keep the truth from them as long as pos sible so they won’t worryD. use comforting phrases such as “he’s going to be with the angels.”19.20 Research indicates that the LEAST effective method of providing death education isA. a program to help students confront their own mortalityB. discussions with terminally ill patients and their familiesC. visits to mortuaries, cemeteries, and funeral homesD. lectures giving factual information about the dying process。