GMDSS通信英语7
- 格式:doc
- 大小:186.00 KB
- 文档页数:43

GMDSS通信英语阅读修改版GMDSS英语阅读练习1一、缩略语1、GMDSSA:Global Maritime Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险与安全系统B:Global Maritime Distress and SafeSystem 全球海上遇险与安全系统C:Global Maritine Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险与安全系统D:Global Maritime Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险系统2、INMARSA TA:International Mobile Satellite Organization 国际海事卫星组织B:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国际移动卫星组织C:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国家海事卫星组织D:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国际海事卫星组织3、PORA:Pacific Ocean Region 大西洋区B:Pacific Ocean Region 太平洋区C:Pacific Ocean Region 印度洋区D:Pacific Ocean Region 北冰洋区4、DSCA:Digital Select Call 数字选择性呼叫B:Digital Search Call 数字选择性呼叫C:Digital Selective Call 数字选择性呼叫D:Digital Searching Call 数字选择性呼叫5、MSIA:Maritime Safety Information 海上安全信息B:Mobile Safety Information 海上安全信息C:Maritime Safe Information 海上安全信息D:Maritime Signe Information 海上安全信息二、单选题1、Which of the following equipments on board is for the COSPAS-SARSA T system?A:DSC B:NA VTEX C:VHF D:EPIRB2、Please choose the INMARSA T-C NCS ID of the W-AOR:A:044 B:001 C:211 D:1443、Which service does not the EGC system have?A:Safety NET B:Fleet NET C:SART D:Sending MSI 4、The VHF CH70 could be used to send ______:A:FAX B:DSC C:NBDP D:SSB5、In each NA VTEX message there is a technical code (B1B2B3B4):which character is the station identification ?A:B1 B:B2 C:B3 D:B3B46、The following radio communication systems are used in GMDSS except the INMARSA T system:A:VHFB:VHF MF and HF terrestrial systemsC:the COSPAS-ASRSA T systemD:the FLAG SIGNAL systems7、Which equipment is required to be carried in the all sea areas ?A:VHF B:MF C:HF D:SES8、Where is the INMARSA T’S headquarters?A:China B:The USAC:the United Kingdom D:Canada9、The Maritime safety information contains _________:A:distress message B:Urgency message C:Distress alertD:Navigational and meteorological warnings10、Both the satellite communication and terrestrial communications will _________:A:not be used in the GMDSSB:be used only for general communications C:be replaced by Morse D:be used in the GMDSS11、If we pass this test it may be possible for us to obtainA:The First-class Radioelectronic Certificate B:The Second-class Radioelectronic Certificate C:The General Operator’s Certificate D:The Restricted Operator?s Certificate12、Which of the following statement is correct?A:2182 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety communications using radio telegraphy which class of emission is A1AB:2187:5 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety calls using digital selective calling:C:2187:5 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety calls using narrow-band-direct-printing:D:2182 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety traffic using narrow band direct printing:13、There are VHF equipments and either a satellite EPIRB or a VHF EPIRB on board according to the equipment carriage requirement:Which sea area does the ship sail?A:A1 B:A2 C:A3 D:A414、Which of the following description of usage is suitable for 2174:5KHz frequency?A:MSI B:NBDP C:DSC D:RT15、Which of the following description about Sea Area A3 is correct?A:an area within the radiotelephone coverage of at least one VHF coast station and one MF coast stationB:an area, including Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an INMARSA T geostationary satellite.C:An area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an INMARSA T geostationary satellite.D:An area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an COSPAS—SARSA Tsystem.16、In the COSPAS-SARSA T system, there are _______types of beacons at present? A:3 B:2 C:1 D:4 17、The medical message should be preceded by the word ________.A:OBS B:TMZ C:MEDICO D:NW 18、All the distress message should be preceded by ______.A:PAN PAN B:SECURITE C:MAYDAY D:MEDICO19、What final place is a distress call/message routed to?A:CES B:NCS C:RCC D:MCC20、The date for entry into full effect for GMDSS is 1st February _______.。

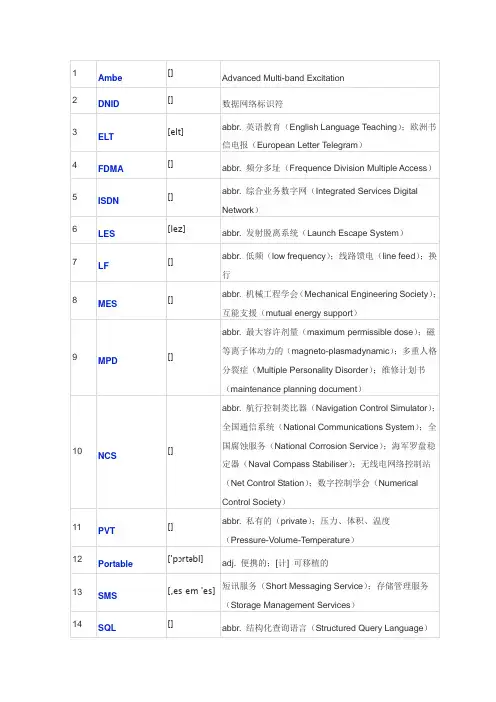
1 Ambe[]Advanced Multi-band Excitation2 DNID[]数据网络标识符3 ELT[elt]abbr. 英语教育(English Language Teaching);欧洲书信电报(European Letter Telegram)4 FDMA[]abbr. 频分多址(Frequence Division Multiple Access)5 ISDN[]abbr. 综合业务数字网(Integrated Services DigitalNetwork)6 LES[lez]abbr. 发射脱离系统(Launch Escape System)7 LF[]abbr. 低频(low frequency);线路馈电(line feed);换行8 MES[]abbr. 机械工程学会(Mechanical Engineering Society);互能支援(mutual energy support)9 MPD[]abbr. 最大容许剂量(maximum permissible dose);磁等离子体动力的(magneto-plasmadynamic);多重人格分裂症(Multiple Personality Disorder);维修计划书(maintenance planning document)10 NCS[]abbr. 航行控制类比器(Navigation Control Simulator);全国通信系统(National Communications System);全国腐蚀服务(National Corrosion Service);海军罗盘稳定器(Naval Compass Stabiliser);无线电网络控制站(Net Control Station);数字控制学会(Numerical Control Society)11 PVT[]abbr. 私有的(private);压力、体积、温度(Pressure-Volume-T emperature)12 Portable['pɔrtəbl]adj. 便携的;[计] 可移植的13 SMS[,es em 'es]短讯服务(Short Messaging Service);存储管理服务(Storage Management Services)14 SQL[]abbr. 结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)15 TDM[]abbr. 遥测数据监控器(T elemetric Data Monitor);时分多路转换(Time Division Multiplex)16 TDMA[]abbr. 分时多址(Time Division Multiple Address)17 UDI[]abbr. 单方面宣告独立(unilateral declaration ofindependence)18 Uninterruptable[]不间断的19 VDR[]abbr. 视频磁盘录像机(Video Disk Recorder);压敏电阻(Voltage Dependent Resistor)20 a part of[]一部分21 acceping[]acceping bank22 accepted[ək'septɪd]adj. 公认的;录取的;可接受的;已承兑的v. 接受(accept的过去式及过去分词)23 accepting[ək'septiŋ]adj. 承兑的;易接受的;赞同的v. 接受;同意;承担(责任等)(accept的ing形式)24 access['ækses]vt. 使用;存取;接近n. 进入;使用权;通路25 accident['æksɪdənt]n. 事故;意外;[法] 意外事件;机遇.[ə'kɒmədeɪ26 accommodatevt. 容纳;使适应;供应;调解vi. 适应;调解t][ə'kɔːd(ə)n27 accordancen. 一致;和谐s]28 according[ə'kɔːdɪŋ]adj. 相符的adv. 依照[ə'kjuːmjʊl29 accumulatorn. 蓄电池;[计] 累加器;积聚者eɪtə]30 accurate['ækjʊrət]adj. 精确的31 acronym['ækrənɪm]n. 首字母缩略词32 act[ækt]vt. 扮演;装作,举动像vi. 行动;扮演,充当;表现,举止;假装,演戏;起作用,见效n. 行为,行动;法令,法案;(戏剧,歌剧的)一幕,段;装腔作势33 action['ækʃ(ə)n]n. 行动;活动;功能;战斗;情节34 activated['æktɪveɪtɪd]adj. 活性化的;活泼的v. 使激活;使活动起来;有生气(activate的过去分词)35 activities[æk'tɪvəti]n. (activity复数形式)活动;活动区;活动性36 actually['æktjʊəlɪ;-tʃʊ-]adv. 实际上;事实上37 adequately['ædikwitli]adv. 充分地;足够地;适当地38 adjust[ə'dʒʌst]vt. 调整,使…适合;校准vi. 调整,校准;适应39 adjustment[ə'dʒʌs(t)m(ə)nt]n. 调整,调节;调节器40 adopted[ə'dɑptɪd]adj. 被收养的;被采用的v. 采用;接受(adopt的过去式和过去分词)41 adoption[ə'dɑpʃən]n. 采用;收养;接受42 advantage[əd'vɑːntɪdʒ]n. 优势;利益;有利条件vi. 获利vt. 有利于;使处于优势43 advisable[əd'vaɪzəb(ə)l]adj. 明智的,可取的,适当的44 advised[əd'vaɪzd]adj. 考虑过的;细想过的v. 建议(advise的过去分词);劝告[,ɛrə'nɔtɪk45 aeronauticaladj. 航空的;航空学的;飞机驾驶员的(等于aeronautic)l]46 affected[ə'fektɪd]adj. 受到影响的;做作的;假装的vt. 影响;假装;使…感动(affect的过去式和过去分词)47 aiming[em]n. 目标;瞄准;导航,引导v. 针对;瞄准;旨在(aim的ing形式);力求48 alarm[ə'lɑːm]n. 警报,警告器;惊慌vt. 警告;使惊恐49 allocated['æləkeitid]adj. 分配的,指派的v. 分派(allocate的过去分词)n.分配值[ælə'keɪʃ(ə)50 allocationn. 分配,配置;安置n][ə'men(d)m(51 amendmentn. 修正案;改善;改正ə)nt]52 amendments[]n. 修正(amendment的复数);修正案53 among[ə'mʌŋ]prep. 在…中间;在…之中54 amount[ə'maʊnt]vi. 总计,合计;相当于;共计;产生…结果n. 数量;总额,总数[ə'nɒm(ə)ləs55 anomalousadj. 异常的;不规则的;不恰当的][,æpə'reɪtəs56 apparatusn. 装置,设备;仪器;器官]57 appear[ə'pɪə]vi. 出现;显得;似乎;出庭[ə'plɪkəb(ə)l58 applicableadj. 可适用的;可应用的;合适的; 'æplɪk-]applies适用60 appropriate[ə'prəʊprɪət]adj. 适当的vt. 占用;拨出61 approved[ə'prʊvd]adj. 被认可的;经过检验的v. 核准;认可(approve的过去式)62 approximately[ə'prɑksɪmətli]adv. 大约,近似地;近于63 as far as[]adv. 至于,直到,远到;就…而言64 assigned[ə'saɪn]adj. 指定的;已分配的v. 分配(assign的过去分词);指定;委派65 assistance[ə'sɪst(ə)ns]n. 援助,帮助;辅助设备66 assisted[ə'sɪst]adj. 辅助的v. 协助;援助(assist的过去式)67 assisting[]v. 协助(assist的现在分词)68 associated[ə'soʃɪetɪd]adj. 关联的;联合的v. 联系(associate的过去式和过去分词)69 attract[ə'trækt]vt. 吸引;引起vi. 吸引;有吸引力70 author['ɔːθə]n. 作者;作家;创始人vt. 创作出版71 authority[ɔː'θɒrɪtɪ]n. 权威;权力;当局72 available[ə'veɪləb(ə)l]adj. 有效的,可得的;可利用的;空闲的73 avoid[ə'vɒɪd]vt. 避免;避开,躲避;消除74 bar[bɑː]n. 条,棒;酒吧;障碍vt. 禁止;阻拦prep. 除……外be carried登载be decided by[]取决77 beacon['biːk(ə)n]n. 灯塔,信号浮标;烽火;指路明灯vt. 照亮,指引vi.像灯塔般照耀78 beacons['bikn]n. 指向标;信号灯(beacon的复数)v. 照亮,指引(beacon的第三人称单数)79 beam[biːm]n. 横梁;光线;电波;船宽;[计量] 秤杆vt. 发送;以梁支撑;用…照射;流露vi. 照射;堆满笑容80 because[bɪ'kɒz]conj. 因为81 below[bɪ'ləʊ]adv. 在下面,在较低处;在本页下面prep. 在…下面82 beneficial[benɪ'fɪʃ(ə)l]adj. 有益的,有利的;可享利益的83 benefit['benɪfɪt]n. 利益,好处;救济金vt. 有益于,对…有益vi. 受益,得益84 berth[bɜːθ]n. 卧铺;停泊处,锚位;差事vt. 使……停泊;为……提供铺位vi. 停泊;占铺位85 beyond[bɪ'jɒnd]prep. 超过;越过;那一边;在...较远的一边adv. 在远处;在更远处n. 远处86 billing['bɪlɪŋ]n. 广告;记帐;开发票;演员表;总账款v. 开帐单(bill的ing形式)87 black[blæk]adj. 黑色的;黑人的;邪恶的n. 黑色;黑人;黑颜料vt. 使变黑;把鞋油等涂在…上;把(眼眶)打成青肿vi. 变黑88 both of them[]他们俩都…89 broadcast['brɔːdkɑːst]vt. 播送,播放;(无线电或电视)广播;播撒(种子)vi. 广播,播送;播放n. 广播;播音;广播节目adj. 广播的90 byte[baɪt]n. 字节;8位元组91 cabin['kæbɪn]n. 小屋;客舱;船舱vt. 把…关在小屋里vi. 住在小屋里92 caller['kɔːlə]n. 访客;[通信] 呼叫者;打电话者;召集员adj. 新鲜的['kændɪde93 candidaten. 候选人,候补者;应试者ɪt; -dət]['keɪpəb(ə)l94 capableadj. 能干的,能胜任的;有才华的]95 capacity[kə'pæsɪtɪ]n. 能力;容量;资格,地位;生产力96 carriage['kærɪdʒ]n. 运输;运费;四轮马车;举止;客车厢97 carried['kærid]adj. 被运的;入神的;忘我的v. 保持(carry的过去式和过去分词);搬运98 carrier['kærɪə]n. [化学] 载体;运送者;带菌者;货架99 carry out[]vt. 执行,实行;贯彻;实现;完成100 case[keɪs]n. 情况;实例;箱vt. 包围;把…装于容器中101 cases[kes]n. 情况(case的复数形式);案例;箱v. 把…装于容器中(case的第三人称单数形式)['kæʒjʊəltɪ102 casualtyn. 意外事故;伤亡人员;急诊室; -zj-]['kætɪg(ə)r103 categoryn. 种类,分类;[数] 范畴ɪ]104 cause[kɔːz]n. 原因;事业;目标vt. 引起;使遭受105 cautious['kɔːʃəs]adj. 谨慎的;十分小心的106 cease[siːs]vi. 停止;终了vt. 停止;结束n. 停止107 certain['sɜːt(ə)n;-tɪn]adj. 某一;必然的;确信;无疑的;有把握的pron. 某些;某几个108 charging['tʃɑːdʒɪŋ]n. 炉料;装料v. 使承担(任务等);装载;命令(charge 的现在分词)109 charging time[][电] 充电时间110 choice[tʃɒɪs]n. 选择;选择权;精选品adj. 精选的;仔细推敲的111 choose[tʃuːz]vt. 选择,决定vi. 选择,挑选112 church[tʃɜːtʃ]n. 教堂;礼拜;教派adj. 教会的;礼拜的vt. 领…到教堂接受宗教仪式113 church bell[]教堂的钟114 circle['sɜːk(ə)l]n. 循环,周期;圆;圈子;圆形物vi. 盘旋,旋转;环行vt. 画圆圈;环绕…移动115 circuit['sɜːkɪt]n. [电子] 电路,回路;巡回;一圈;环道vi. 环行vt.绕回…环行116 circuits['sɝkɪt]n. 电路(circuit的复数);环路;巡回v. 环行;巡回旅行(circuit的三单形式)117 circumstance['sɜːkəmst(ə)ns]n. 环境,情况;事件;境遇118 class[klɑːs]n. 阶级;班级;种类vt. 分类;把…分等级adj. 极好的119 climate['klaɪmət]n. 气候;风气;思潮;风土120 close[kləʊs]adj. 紧密的;亲密的;亲近的vt. 关;结束;使靠近vi.关;结束;关闭adv. 紧密地n. 结束121 combine[kəm'baɪn]vt. 使化合;使联合,使结合vi. 联合,结合;化合n.联合收割机;联合企业122 combining[kəm'bainiŋ]adj. 化合的,结合性的v. 结合(combine的ing形式)123 commercial[kə'mɜːʃ(ə)l]adj. 商业的;营利的;靠广告收入的n. 商业广告124 common['kɒmən]adj. 共同的;普通的;一般的;通常的n. 普通;平民;公有地125 communication[kəmjuːnɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n]n. 通讯,[通信] 通信;交流126 community[kə'mjuːnɪtɪ]n. 社区;[生态] 群落;共同体;团体127 compatible[kəm'pætɪb(ə)l]adj. 兼容的;能共处的;可并立的128 compelled[]v. 迫使(compel的过去式及过去分词形式);强迫129 completely[kəm'plitli]adv. 完全地,彻底地;完整地130 comply[kəm'plaɪ]vi. 遵守;顺从,遵从;答应131 complying[]依从132 components[kəm'ponənt]n. 部件;组件;成份(component复数)133 comprises[]包括134 compulsory[kəm'pʌls(ə)rɪ]adj. 义务的;必修的;被强制的n. (花样滑冰、竞技体操等的)规定动作135 concept['kɒnsept]n. 观念,概念136 concern[kən'sɜːn]vt. 涉及,关系到;使担心n. 关系;关心;关心的事137 concerned[kən'sɜːnd]adj. 有关的;关心的v. 关心(concern的过去时和过去分词);与…有关138 concerning[kən'sɜːnɪŋ]prep. 关于;就…而言v. 涉及;使关心(concern的ing 形式);忧虑139 concerns[]n. 关注;关注点;关注者(concern的复数形式)v.使关心(concern的三单形式);涉及;关系到…140 condition[kən'dɪʃ(ə)n]n. 条件;情况;环境;身份141 conferencing['kɑnfərənsɪŋ]n. 会议技术v. 开会(conference的现在分词)142 conjunction[kən'dʒʌŋ(k)ʃ(ə)n]n. 结合;[语] 连接词;同时发生143 connected[kə'nɛktɪd]adj. [计] 连接的;有联系的;连贯的v. 连接(connect的过去式)144 constructed[]vt. 构造,建造;创立,构筑;搭建(construct的过去分词)145 contact['kɒntækt]n. 接触,联系vt. 使接触vi. 联系,接触146 contained[kən'teɪnd]adj. 泰然自若的,从容的;被控制的v. 包含;遏制(contain的过去分词);容纳147 containing[kən'ten]n. 包含v. 包含;容纳;克制(contain的ing形式)adj.包含的;封闭的148 contains[kən'teinz]v. 包含;容纳;包含某字符串(contain的单三形式)n.包含149 content[kən'tent]n. 内容,目录;满足;容量adj. 满意的vt. 使满足150 continuous[kən'tɪnjʊəadj. 连续的,持续的;继续的;连绵不断的s]151 control[kən'trəʊl]n. 控制;管理;抑制;操纵装置vt. 控制;管理;抑制152 copy['kɒpɪ]vi. 复制;复印;抄袭vt. 复制;复印;抄袭n. 副本;一册;摹仿153correspondence [kɒrɪ'spɒnd(ə)ns]n. 通信;一致;相当154 cost[kɒst]vt. 花费;使付出;使花许多钱n. 费用,代价,成本;损失vi. 花费155 countries[]国家(country的复数)156 cover['kʌvə]vt. 包括;采访,报导;涉及n. 封面,封皮;盖子;掩蔽物vi. 覆盖;代替157 covered['kʌvɚd]adj. 覆盖了的;隐蔽着的;有屋顶的v. 覆盖;包括;掩护(cover的过去分词)158 create[kriː'eɪt]vt. 创造,创作;造成159 currently['kɝəntli]adv. 当前;一般地160 decided[dɪ'saɪdɪd]adj. 明确的;显然的;坚决的,果断的n. 决定(decide 的过去式)161 dedicated['dɛdə'ketɪd]adj. 专用的;专注的;献身的v. 以…奉献;把…用于(dedicate的过去式和过去分词)162 default[dɪ'fɔːlt;'diːfɔːlt]vi. 拖欠;不履行;不到场n. 违约;缺席;缺乏;系统默认值vt. 不履行;不参加(比赛等);对…处以缺席裁判163 delivered[dɪ'lɪvɚ]adj. 业已交货v. 递送(deliver的过去分词)164 description[dɪ'skrɪpʃ(ə)n]n. 描述,描写;类型;说明书165 details[]n. 细节(detail的复数);详细资料v. 详细说明(detail的三单形式)166 detected[dɪ'tɛkt]adj. 检测到的v. 发现(detect的过去分词);检测到;侦测到167 determine[dɪ'tɜːmɪn]vt. 决定;判决;使…下定决心vi. 确定;决定;判决,终止168 determines[]决心确定169 device[dɪ'vaɪs]n. 装置;策略;图案170 devices[]n. 设备;装置;器件(device的复数)171 digitally['dɪdʒɪtl]adv. 数位172 direction[dɪ'rekʃ(ə)n; daɪ-]n. 方向;指导;趋势;用法说明173 discipline['dɪsɪplɪn]n. 学科;纪律;训练;惩罚vt. 训练,训导;惩戒174 disposal[dɪ'spəʊz(ə)l]n. 处理;支配;清理;安排175 document['dɒkjʊm(ə)nt]n. 文件,公文;[计] 文档;证件vt. 用文件证明176 down link[][通信] 下行线路,[通信] 下行链路;向下联结177 downlink['daʊnlɪŋk]n. 下行线;向下链路;向地传输(数据信号等从人造卫星或航天器向地面传输)178 drawback['drɔːbæk]n. 缺点,不利条件;退税179 duration[djʊ'reɪʃ(ən. 持续)n]180 during['djʊərɪŋ]prep. 在…的时候,在…的期间181 earth[ɜːθ]n. 地球;陆地;泥土;尘世;[电] 地线[,ikə'nɑmɪ182 economicallyadv. 经济地;在经济上;节俭地kli]183 editing['ɛdɪt]adj. 编辑的v. [计] 编辑(edit的ing形式)184 effect[ɪ'fekt]n. 影响;效果;作用vt. 产生;达到目的185 effectively[ɪ'fɛktɪvli]adv. 有效地,生效地;有力地;实际上186 effort['efət]n. 努力;成就187 elected[i'lektid]vt. 选举,推选[ɪ'lektrɪk(ə188 electricaladj. 有关电的;电气科学的)l][ɪlek'trɒnɪ189 electronicsn. 电子学;电子工业ks; el-]190 element['elɪm(ə)nt]n. 元素;要素;原理;成分;自然环境[,elɪ'veɪʃ(191 elevationn. 高地;海拔;提高;崇高;正面图ə)n][ɪ'mɜːdʒ(192 emergencyn. 紧急情况;突发事件;非常时刻adj. 紧急的;备用的ə)nsɪ]193 encoded[ɪn'kod]adj. [计] 编码的v. 把…编码(encode的过去分词)194 energy['enədʒɪ]n. [物] 能量;精力;活力;精神195 engagedd; en-]adj. 使用中的,忙碌的v. 保证;约定;同…订婚(engage 的过去分词)196 enough[ɪ'nʌf]adv. 足够地,充足地n. 很多;充足adj. 充足的int.够了!197 ensure[ɪn'ʃɔː;-'ʃʊə; en-]vt. 保证,确保;使安全198 entire[ɪn'taɪə;en-]adj. 全部的,整个的;全体的199 escort['eskɔːt]n. 陪同;护航舰;护卫队;护送者vt. 护送;陪同;为…护航200 established[ə'stæblɪʃt]adj. 确定的;已制定的,已建立的201 establishes[]建立202 except[ɪk'sept;ek-]vt. 不计;把…除外vi. 反对prep. 除…之外conj. 除了;要不是203 exemption[ɪg'zempʃn]n. 免除,豁免;免税204 expensive[ɪk'spensɪv; ek-]adj. 昂贵的;花钱的205 explain[ɪk'spleɪn;ek-]v. 说明;解释206 explained[]v. 解释(explain的过去式及过去分词)207 explanation[eksplə'neɪʃ(ə)n]n. 说明,解释;辩解208 exterior; ek-]adj. 外部的;表面的;外在的n. 外部;表面;外型;外貌209 facilities[]n. 设施;工具,设备210 fact[fækt]n. 事实;实际;真相211 failure['feɪljə] n. 失败;故障;失败者;破产212 faster['fa:stə] adj. 更快的adv. 更快地213 fed[fed] abbr. 联邦调查局人员(the Federal Reserve System)214 fed to[] 被送到215 fitted['fɪtɪd] adj. 合适的;订做的;有…设备的v. 适应(fit的过去分词);合适;为…提供设备216 fix[fɪks] vt. 使固定;修理;安装;准备vi. 固定;注视n. 困境;方位;贿赂217 flash[flæʃ] vt. 使闪光;反射n. 闪光,闪现;一瞬间vi. 闪光,闪现;反射adj. 闪光的,火速的218 flow[fləʊ] vi. 流动,涌流;川流不息;飘扬vt. 淹没,溢过n. 流动;流量;涨潮,泛滥219 forbidden[fə'bɪd(ə)n] adj. 被禁止的;严禁的,禁用的220 foregoing ['fɔːgəʊɪŋ]adj. 前述的;前面的;在前的v. 发生在…之前;走在…之前(forego的ing形式)221 formal['fɔːm(ə)l] adj. 正式的;拘谨的;有条理的n. 正式的社交活动;夜礼服222 front[frʌnt] n. 前面;正面;前线vt. 面对;朝向;对付vi. 朝向adj. 前面的;正面的adv. 在前面;向前223 fulfill[fʊl'fɪl] vt. 履行;实现;满足;使结束(等于fulfil)224 fundamental [fʌndə'ment(ə)l]adj. 基本的,根本的n. 基本原理;基本原则225 general ['dʒen(ə)r(ə)l]adj. 一般的,普通的;综合的;大体的n. 一般;将军,上将;常规226 geographical[dʒɪə'græfɪk(ə)l]adj. 地理的;地理学的227 geostationary [dʒiːə(ʊ)'steɪʃ(ə)n(ə)rɪ]adj. 与地球旋转同步的228 granted['gra:ntid]conj. 算是如此,但是229 guide[gaɪd]n. 指南;向导;入门书vt. 引导;带领;操纵vi. 担任向导230 hardly['hɑːdlɪ]adv. 几乎不,简直不;刚刚231 helpful['helpfʊl;-f(ə)l]adj. 有帮助的;有益的232 here[hɪə]adv. 在这里;此时int. 嘿!;喂!n. 这里233 highly['haɪlɪ]adv. 高度地;非常;非常赞许地234 hint[hɪnt]n. 暗示;线索vt. 暗示;示意vi. 示意235 identify[aɪ'dentɪfaɪ]vt. 确定;识别;使参与;把…看成一样vi. 确定;认同;一致236 immediately[ɪ'miːdɪətlɪ]adv. 立即,立刻;直接地conj. 一…就237 impact['ɪmpækt]vt. 影响;撞击;冲突;压紧vi. 冲击;产生影响n. 影响;效果;碰撞;冲击力238 implies[]v. 意味着(imply的第三人称单数);蕴含;暗指239 improving[ɪm'pruːvɪŋ]adj. 有启发的;有教育意义的v. 提高;改善;利用(improve的ing形式)240 in addition to[]除…之外241 including[ɪn'klʊdɪŋ]prep. 包含,包括242 independent[,ɪndɪ'pendənt]adj. 独立的;单独的;无党派的;不受约束的n. 独立自主者;无党派者243 indicate['ɪndɪkeɪt vt. 表明;指出;预示;象征]244 indicated['ɪndə,ket]adj. 表明的;指示的v. 表明(indicate的过去分词);指出;显示245 indicates[]v. 表明(indicate的第三人称单数形式);指示,显示246 indication[ɪndɪ'keɪʃ(ə)n]n. 指示,指出;迹象;象征247 initial[ɪ'nɪʃəl]adj. 最初的;字首的vt. 用姓名的首字母签名n. 词首大写字母248 initialization[ɪ,nɪʃəlɪ'zeʃən]n. [计] 初始化;赋初值249 initiate[ɪ'nɪʃɪeɪt]vt. 开始,创始;发起;使初步了解n. 开始;新加入者,接受初步知识者adj. 新加入的;接受初步知识的250 installation[ɪnstə'leɪʃ(ə)n]n. 安装,装置;就职251 instruments['ɪnstrəmənt]n. 仪器(instrument的复数);工具;乐器v. 用器械装备;给乐器谱写(instrument的三单形式)252 integrated['ɪntɪgretɪd]adj. 综合的;完整的;互相协调的v. 整合;使…成整体(integrate的过去分词)253 intended[ɪn'tendɪd]adj. 故意的,有意的;打算中的n. 已订婚者v. 打算;准备(intend的过去分词)254 interco[]n. 英特科(公司名)255 interfere[ɪntə'fɪə]vi. 干涉;妨碍;打扰vt. 冲突;介入256 interference[ɪntə'fɪər(ən. 干扰,冲突;干涉)ns]257 interfering['ɪntɚ'fɪrɪŋ]adj. 干涉的;多管闲事的v. 妨碍(interfer的ing形式)258 interrogate[ɪn'terəgeɪt]vt. 审问;质问;[计] 询问vi. 审问;质问259 interrogated[]询问260 interruptions[,ɪntə'rʌpʃən]n. 瞬断,打断;中断之事(interruption的复数形式)261 intership[]实习262 introduction[,ɪntrə'dʌkʃ(ə)n]n. 介绍;引进;采用;入门;传入263 jam[dʒæm]n. 果酱;拥挤;困境;[篮球]扣篮264 knowledge['nɒlɪdʒ]n. 知识,学问;知道,认识;学科265 last[lɑːst]n. 末尾,最后;上个;鞋楦(做鞋的模型)adj. 最后的;最近的,最新的;仅剩的;最不可能…的vi. 持续;维持,够用;持久vt. 度过,拖过;使维持adv. 最后地;上次,最近;最后一点266 launcher['lɔːn(t)ʃə]n. 发射器;发射台;发射者267 level['lev(ə)l]n. 水平;标准;水平面adj. 水平的;平坦的;同高的vi.瞄准;拉平;变得平坦vt. 使同等;对准;弄平268 line of sight[][光][生理] 视线;瞄准线269 link[lɪŋk]n. [计] 链环,环节;联系,关系vt. 连接,连结;联合,结合vi. 连接起来;联系在一起;将人或物连接或联系起来270 link test[]链路测试271 load[ləʊd]n. 负载,负荷;工作量;装载量vi. [力] 加载;装载;装货vt. 使担负;装填272 location[lə(ʊ)'keɪʃ(ə)n]n. 位置(形容词locational);地点;外景拍摄场地273 login[lɑg'ɪn]n. [计] 进入系统vt. [计] 登录;注册vi. [计] 登录;注册274 logout['lɔgaʊt]n. 注销;退网;退出系统275 looked forward[]期待276 lowest[lo]adj. 最低的;最小的(low的最高级);最底下的277 mail[meɪl]n. 邮件;邮政,邮递;盔甲vt. 邮寄;给…穿盔甲vi.邮寄;寄出278 main[meɪn]n. 主要部分,要点;体力;总管道adj. 主要的,最重要的;全力的279 mainly['meɪnlɪ]adv. 主要地,大体上281 major['meɪdʒə]adj. 主要的;重要的;主修的;较多的n. [人类] 成年人;主修科目;陆军少校vi. 主修282 making['meɪkɪŋ]n. 发展;制造;形成v. 制作(make的现在分词)283 malfunction[mæl'fʌŋ(k)ʃ(ə)n]vi. 发生故障;不起作用n. 故障;失灵;疾病284 management['mænɪdʒm(ə)nt]n. 管理;管理人员;管理部门;操纵;经营手段285 mandatory['mændət(ə)rɪ]adj. 强制的;托管的;命令的n. 受托者(等于mandatary)286 manufacture[mænjʊ'fæk n. 制造;产品;制造业vt. 制造;加工;捏造vi. 制造tʃə]287 mariners[]n. 水手;西雅图水手288 mark[mɑːk]n. 标志;马克;符号;痕迹vi. 作记号vt. 标志;做标记于;打分数289 matter['mætə]n. 物质;原因;事件vi. 有关系;要紧290 maximum['mæksɪməm]n. [数] 极大,最大限度;最大量adj. 最高的;最多的;最大极限的291 member['membə]n. 成员;会员;议员292 method['meθəd]n. 方法;条理;类函数adj. 使用体验派表演方法的293 misuse[mɪs'juːz]vt. 滥用;误用;虐待n. 滥用;误用;虐待294 mountaineer[maʊntɪ'nɪə]n. 登山家,登山运动员;山地人vi. 登山295 multiple['mʌltɪp(ə)l]adj. 多重的;多样的;许多的n. 倍数;[电] 并联296 mute[mjuːt]adj. 哑的;沉默的;无声的vt. 减弱……的声音;使……柔和n. 哑巴;弱音器;闭锁音297 mutual['mjuːtʃʊəl; -tjʊəl]adj. 共同的;相互的,彼此的298 necessary['nesəs(ə)rɪ]adj. 必要的;必需的;必然的n. 必需品299noiseinterference[]噪声干扰300 normally['nɔːm(ə)l adv. 正常地;通常地,一般地ɪ]301 nowadays['naʊədeɪz]adv. 现今;时下n. 当今302 occasionally [ə'keɪʒ(ə)n(ə)lɪ;ə'keɪʒ(ə)nəlɪ;ə'keɪʒən(ə)lɪ]adv. 偶而,间或303 occupied['ɑkjupaɪd]adj. 已占用的;使用中的;无空闲的v. 占有(occupy的过去分词)304 officers['ɔfəsɚ]n. 军官,人员(officer复数形式)305omnidirectional[]全指向306 on which[]定语从句307 online['ɑn'laɪn]n. 在线;联机308 orbit['ɔːbɪt]n. 轨道;眼眶;势力范围;生活常规vi. 盘旋;绕轨道运行vt. 绕…轨道而行309 orbiting['ɔrbɪt]v. [航][天] 轨道运行;轨道运动;转圈(orbit的ing形式)310 organization[,ɔrgənə'zeʃən]n. 组织;机构;体制;团体311 original[ə'rɪdʒɪn(ə)l; ɒ-]n. 原件;原作;原物;原型adj. 原始的;最初的;独创的;新颖的312 output['aʊtpʊt]n. 输出,输出量;产量;出产vt. 输出313 panel['pæn(ə)l]n. 仪表板;嵌板;座谈小组,全体陪审员vt. 嵌镶板314 particular[pə'tɪkjʊlə]adj. 特别的;详细的;独有的;挑剔的n. 详细说明;个别项目315 party['pɑːtɪ]n. 政党,党派;聚会,派对;当事人vi. 参加社交聚会[pə'fɔːm(ə)316 performancen. 性能;绩效;表演;执行ns]317 performed[]v. 执行,表演(perform的过去分词形式)[pə'mɪʃ(ə)318 permissionn. 允许,许可n]319 personnel[pɜːsə'nel]n. 人事部门;全体人员adj. 人员的;有关人事的320 phrase[freɪz]n. 短语, 习语, 措辞, [音]乐句321 phrases[frez]n. 短语;词组;乐句;措词(phrase的复数)v. 用话表示;把…分成短句;用短语描述(phrase的三单形式)322 planned[plænd]adj. 有计划的;根据计划的v. 打算(plan的过去分词);设计323 point[pɒɪnt]n. 要点;得分;标点;[机] 尖端vt. 指向;弄尖;加标点于vi. 表明;指向324 pointing['pɔɪntɪŋ]n. 指示v. 指向;指点(point的ing形式)325 polar['pəʊlə]adj. 极地的;两极的;正好相反的n. 极面;极线326 possible['pɒsɪb(ə)l]adj. 可能的;合理的;合适的n. 可能性;合适的人;可能的事物327 possibly['pɒsɪblɪ]adv. 可能地;也许;大概328 potential[pə(ʊ)'tenʃ(n. 潜能;可能性;[电] 电势adj. 潜在的;可能的;势的ə)l]329 preamble[priː'æmb(ə)l; 'priː-]n. 序文;电报报头;先兆vi. 作序文330 preceded[]在前331 present['prez(ə)nt]vt. 提出;介绍;呈现;赠送vi. 举枪瞄准adj. 现在的;出席的n. 现在;礼物;瞄准332 prevents[]v. 阻止(prevent的第三人称单数);预防333 previous['priːvɪəs]adj. 以前的;早先的;过早的adv. 在先;在…以前334 print[prɪnt]n. 印刷业;印花布;印刷字体;印章;印记vt. 印刷;打印;刊载;用印刷体写;在…印花样vi. 印刷;出版;用印刷体写335 printer['prɪntə]n. [计] 打印机;印刷工;印花工336 prior['praɪə]adj. 优先的;在先的,在前的adv. 在前,居先337 priorities[]优先顺序338 procedure[prə'siːdʒə]n. 程序,手续;步骤339 procedures[prə'sidʒɚ]n. 程序;规程(procedure的复数)340 process['prəʊses]vt. 处理;加工n. 过程,进行;方法,步骤;作用;程序;推移vi. 列队前进adj. 经过特殊加工(或处理)的341 program['progræm]n. 程序;计划;大纲vt. 用程序指令;为…制订计划;为…安排节目vi. 编程序;安排节目;设计电脑程式342 promulgation[,promʌl'geʃən]n. 颁布;公布;宣传;普及343 propelling[prə'peliŋ]adj. 推进的n. 推进v. 推动(propel的ing形式)344 proper['prɒpə]adj. 适当的;本身的;特有的;正派的adv. 完全地345 properly['prɑpɚli]adv. 适当地;正确地;恰当地346 provision[prə'vɪʒ(ə)n]n. 规定;条款;准备;[经] 供应品vt. 供给…食物及必需品347 qualified['kwɒlɪfaɪd]adj. 合格的;有资格的v. 限制(qualify的过去分词);描述;授权予348 radius['reɪdɪəs]n. 半径,半径范围;[解剖] 桡骨;辐射光线;有效航程349 range[reɪn(d)ʒ]n. 范围;幅度;排;山脉vi. 平行,列为一行;延伸;漫游;射程达到vt. 漫游;放牧;使并列;归类于;来回走动350 rapid['ræpɪd]adj. 迅速的,急促的;飞快的;险峻的n. 急流;高速交通工具,高速交通网351 rather['rɑːðə]adv. 宁可,宁愿;相当int. 当然啦(回答问题时用)352 reasons[]n. 原因(reason的复数);理由;理智v. 推理;劝说(reason的第三人称单数)353 received[rɪ'siːvd]adj. 被一般承认的;被认为标准的v. 收到;接受;迎接(receive的过去分词)354 receiving[rɪ'siv]adj. 接受的n. 接受v. 接收(receive的ing形式)355 reception[rɪ'sepʃ(ə)n]n. 接待;接收;招待会;感受;反应356 recognized[]adj. 公认的;经过验证的v. 认识;意识到(recogniz的过去分词)357 recommended[,rɛkə'mɛnd]adj. 被推荐的v. 推荐,介绍;建议(recommend的过去分词)358 reduce[rɪ'djuːs]vt. 减少;降低;使处于;把…分解vi. 减少;缩小;归纳为359 referred[rɪ'fɝ]v. 参考,查阅(refer的过去式);归类,谈及,送交adj.援引的360 reflected[rɪ'flɛkt]adj. 反射的;得自他人的v. 反射;思考(reflect的过去式和过去分词)361 refuse[rɪ'fjuːz]n. 垃圾;废物vt. 拒绝;不愿;抵制vi. 拒绝362 regarded[]被视为363 regardless[rɪ'gɑːdlɪs]adj. 不管;不顾;不注意364 regardless of[]不顾,不管365 region['riːdʒ(ə)n]n. 地区;范围;部位366 regions[]n. 地区;地域;领域(region的复数)367 registered['redʒɪstəd]adj. 注册的;记名的;登记过的;(家畜等)附有血统证明的368 registration[redʒɪ'streɪʃ(ə)n]n. 登记;注册;挂号369 regular['regjʊlə]adj. 定期的;有规律的;合格的;整齐的n. 常客;正式队员;中坚分子adv. 定期地;经常地370 reject[rɪ'dʒekt]vt. 拒绝;排斥;抵制;丢弃n. 被弃之物或人;次品371 rejected[]adj. 被拒的;不合格的v. 拒绝,驳回(reject的过去分词形式)372 relate[rɪ'leɪt]vt. 叙述;使…有联系vi. 涉及;认同;符合;与…有某种联系373 relatively['relətɪvlɪ]adv. 相当地;相对地,比较地374 remain[rɪ'meɪn]vi. 保持;依然;留下;剩余;逗留;残存n. 遗迹;剩余物,残骸375 remedy['remɪdɪ]vt. 补救;治疗;纠正n. 补救;治疗;赔偿376 repair[rɪ'peə]vi. 修理;修复vt. 修理;恢复;补救,纠正n. 修理,修补;修补部位377 repeated[rɪ'piːtɪd]adj. 再三的,反复的v. 重复;复述(repeat的过去分词)378 replaced[rɪ'ples]v. 取代;替换;放回(replace的过去分词)adj. 被替换的379 reporting[rɪ'pɔrtɪŋ]n. 报告;报导adj. 报告的380 representative[reprɪ'zentətɪv]adj. 典型的,有代表性的;代议制的n. 代表;典型;众议员381 requested[rɪ'kwɛst]adj. 要求的;被请求的v. 要求(request的过去分词);请求382 required[rɪ'kwaɪrd]adj. 必需的;(美)必修的v. 需要(require的过去式及过去分词形式);要求383 rescue['reskjuː]vt. 营救;援救n. 营救;援救;解救384 reserve[rɪ'zɜːv]n. 储备,储存;自然保护区;预备队;[金融] 储备金vt.储备;保留;预约vi. 预订385 respond[rɪ'spɒnd]vi. 回答;作出反应;承担责任vt. 以…回答n. 应答;唱和386 response[rɪ'spɒns]n. 响应;反应;回答387 responsible[rɪ'spɒnsɪb(ə)l]adj. 负责的,可靠的;有责任的388 result[rɪ'zʌlt]n. 结果;成绩;答案;比赛结果vi. 结果;导致;产生389 returns[rɪ'tɝn]n. 回报;收益;[贸易] 退货(return的复数)v. 返回;回复;归还(return的单三形式)390 routing['raʊtɪŋ]n. [计] 路由选择;工艺路线;选择途径v. 按指定路线发送;为…规定路线(route的ing形式)391 satisfy['sætɪsfaɪ]vi. 令人满意;令人满足vt. 满足;说服,使相信;使满意,使高兴392 save[seɪv]vt. 节省;保存;储蓄;解救vi. 节省;挽救;救球prep.除...之外n. 救球,救援393 scale[skeɪl]n. 规模;比例;鳞;刻度;天平;数值范围vi. 衡量;攀登;剥落;生水垢vt. 测量;攀登;刮鳞;依比例决定394 screen[skriːn]n. 屏,幕;屏风vt. 筛;拍摄;放映;掩蔽vi. 拍电影395 second['sek(ə)nd]n. 秒;第二名;瞬间;二等品vt. 支持adj. 第二的;次要的;附加的num. 第二adv. 第二;其次;居第二位396 section['sekʃ(ə)n]n. 截面;部门;地区;章节vi. 被切割成片;被分成部分vt. 把…分段;将…切片;对…进行划分397 sector['sektə]n. 部门;扇形,扇区;象限仪;函数尺vt. 把…分成扇形[sɪ'lekʃ(ə)n398 selectionn. 选择,挑选;选集;精选品]399 sending['sendiŋ]n. 发送;[通信] 发射;信件v. 发送;派遣(send的ing形式);打发400 sentence['sent(ə)ns]n. [语][计] 句子,命题;宣判,判决vt. 判决,宣判401 separate['sep(ə)rət]vt. 使分离;使分开;使分居vi. 分开;隔开;分居adj.单独的;分开的n. 分开;抽印本402 separately['sɛprətli]adv. 分别地;分离地;个别地['siːkw(ə)ns403 sequencen. [数][计] 序列;顺序;续发事件vt. 按顺序排好]['sɪəriːz;404 seriesn. 系列,连续;[电] 串联;级数;丛书-rɪz]405 serious['sɪərɪəs]adj. 严肃的,严重的;认真的;庄重的;危急的406 set up[]v. 建立;装配;开业;竖立407 shadowing['ʃædəuiŋ]n. 遮蔽v. 遮蔽;尾随(shadow的ing形式)408 shape[ʃeɪp]n. 形状;模型;身材;具体化vt. 形成;塑造,使成形;使符合vi. 形成;成形;成长409 sharp[ʃɑːp]adj. 急剧的;锋利的;强烈的;敏捷的;刺耳的adv. 急剧地;锐利地;突然地n. 尖头;骗子;内行vt. 磨快;把音调升高vi. 打扮;升音演奏410 shipborne['ʃɪpbɔːn]adj. 用船装运的;为船运设计的;船用的411 short[ʃɔːt]adj. 短的;不足的;矮的,低的412 side[saɪd]n. 方面;侧面;旁边vi. 支持;赞助;偏袒adj. 旁的,侧的vt. 同意,支持413 simplex['sɪmpleks]adj. 单纯的;单一的n. 单形;单层公寓414 sitting['sɪtɪŋ]n. 入席,就坐;开庭;孵卵;坐着的一段时间adj. 坐着的;孵卵中的;在任期中的v. 坐;坐落(sit的ing形式)415 situation[sɪtjʊ'eɪʃ(ə)n]n. 情况;形势;处境;位置416 slot[slɒt]n. 位置;狭槽;水沟;硬币投币口vt. 跟踪;开槽于417 source[sɔːs]n. 来源;水源;原始资料418 spacecraft['speɪskrɑːft]n. [航] 宇宙飞船,航天器419 special['speʃ(ə)l]n. 特使,特派人员;特刊;特色菜;专车;特价商品adj.特别的;专门的,专用的420 spot[spɒt]n. 地点;斑点vt. 认出;弄脏;用灯光照射vi. 沾上污渍;满是斑点adj. 现场的;现货买卖的adv. 准确地;恰好421 squelch[skweltʃ]vt. 消除;镇压;压碎;使…咯吱咯吱的响vi. 嘎吱作响n. 噪声控制;嘎吱声;压倒对方的反驳;压碎的一堆422 stand for[]代表;支持;象征;担任…的候选人423 standard['stændəd]n. 标准;水准;旗;度量衡标准adj. 标准的;合规格的;公认为优秀的424 station['steɪʃ(ə)n]n. 站;驻地;地位;身分vt. 配置;安置;驻扎425 step[step]n. 步,脚步;步骤;步伐;梯级vi. 踏,踩;走vt. 走,迈步426store andforward[]储存和转送427 strength[streŋθ;streŋkθ]n. 力量;力气;兵力;长处428 strongest['strɔŋgist]adj. 最强壮的(为strong的最高级)429 subject['sʌbdʒekt;'sʌbdʒɪkt]n. 主题;科目;[语] 主语;国民adj. 服从的;易患…的;受制于…的vt. 使…隶属;使屈从于…430 successful[sək'sesfʊl;-f(ə)l]adj. 成功的;一帆风顺的431 sufficient[sə'fɪʃ(ə)nt]adj. 足够的;充分的432 suit[suːt]vt. 适合;使适应n. 诉讼;组;套装;恳求vi. 合适;相称433 suitable['suːtəb(ə)l]adj. 适当的;相配的434 superior[suː'pɪərɪadj. 上级的;优秀的,出众的;高傲的n. 上级,长官;ə; sjuː-]优胜者,高手;长者435 supervise['suːpəvaɪz; 'sjuː-]vt. 监督,管理;指导vi. 监督,管理;指导436 supply[sə'plaɪ] n. 供给,补给;供应品vt. 供给,提供;补充vi. 供给;替代437 support[sə'pɔːt] vt. 支持,支撑,支援;扶持,帮助;赡养,供养n. 支持,维持;支援,供养;支持者,支撑物438 surface['sɜːfɪs] n. 表面;表层;外观adj. 表面的,肤浅的vi. 浮出水面vt. 使浮出水面;使成平面439 survivors[sɚ'vaɪvɚ] n. 幸存者(survivor的复数)440 technique[tek'niːk] n. 技巧,技术;手法441 telephony [tɪ'lef(ə)nɪ]n. 电话(学);电话制造442 temporary ['temp(ə)rərɪ]adj. 暂时的,临时的n. 临时工,临时雇员443 terminal ['tɜːmɪn(ə)l]n. 末端;终点;终端机;极限adj. 末端的;终点的;晚期的444 thunderstorm ['θʌndəstɔːm]n. [气象] 雷暴;雷暴雨;大雷雨445 to avoid[] 避免446 to march[] 跑步447 track[træk] n. 轨道;足迹,踪迹;小道vt. 追踪;通过;循路而行;用纤拉vi. 追踪;走;留下足迹448 tracking['trækɪŋ] n. 追踪,跟踪v. 跟踪(track的ing形式)449 trading['tredɪŋ] n. 交易;贸易;购物adj. 交易的;贸易的v. 交换(trade 的ing形式);做买卖450 traditional [trə'dɪʃ(ə)n(ə)l]adj. 传统的;惯例的451 training['treɪnɪŋ]n. 训练;培养;瞄准;整枝v. 训练;教养(train的ing形式)452 transponder[træn'spɒndə; trɑːn-]n. 异频雷达收发机;转调器,变换器453 travel['træv(ə)l]vi. 旅行;行进;步行;交往vt. 经过;在…旅行n. 旅行;游历;漫游454 tune[tjuːn]n. 曲调;和谐;心情vt. 调整;使一致;为…调音vi. [电子][通信] 调谐;协调。
![GMDSS通信英语阅读修改版[1]](https://uimg.taocdn.com/5e41c7cf5fbfc77da269b1b2.webp)
阅读理解PASSAGE1.Basic description of DSC: DSC is basically a calling system .Each call consists of a “packet” of digitized information of one of four priorities : Distress , Urgency , Safety , Routine. Message can be routed to “all stations”, to an individual station or to a group of stations, using their Maritime Mobile Selective-call Identify code (MMSI):Distress messages are automatically broadcast to “All stations”. In addition to the MMSI of source and destination stations, information can be conveyed in the DSC message:For example, to aid the Rescue Service, the DSC Distress alert message is configured to contain the following: A\Ship‟s identify (the nine digit MMSI) B\Time. C\ Nature of distress (in the form of standard code) D\Ship‟s position.Where fitted ship‟s officers should ensure they are fully conversant with the procedure for entering the necessary information into DSC equipment:At sea, unless provided automatically from a navigation system, ship‟s position should be update at least once during each watch period.1. At sea, if DSC equipment can‟t get ship‟s position message from a navigation system automatically, then the position message should be renewed _______.A. .at least every 4 hours:B. at least every 8 hoursC.at least every 12 hours:D. at least every 24 hours.2. According to the message, distress message can be received by _______.A. all stations:B. coast stations.C. ship stations:D. group of specified stations3. Each DSC “packet” have _______ priority(priorities)A. 1B. 2C. 3D. 44. Which of the following statement is not true?A. A DSC message has a MMSI of source station.B. A DSC message has a MMSI of destination station.C. A DSC message has a name of source station.D. A DSC message also has other information for sending rounD.Passage2.The NA VTEX receiver is a Narrow Band Direct Printing (NBDP) device operating on the frequency 518Khz, (some equipment can also operate on 490Khz and 4209.5Khz), and is a vital part of the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS).It is automatically receives Maritime Safety Information such as Radio Navigational Warnings, Storm/Gale Warnings, Meteorological Forecasts, Piracy Warnings, Distress Alert etc.The information received is printed on the receiver‟s own paper recorder roll:Each message begins with starts of message function (ZCZC) followed by a space then four B characters:The First, (B1), identifies the station beingreceived, the second, (B2), identifies the subject i.e:Navigational Warning, Met Forecast etc, and the third and fourth, (B3+B4), form the consecutive number of the message from that station:This followed by the text of the message and ends with an end of message function (NNNN).The NA VTEX system broadcasts COASTAL WARNING which cover the area from the fairway buoy out to 250 nautical miles from the transmitter, the transmission from some transmitters can be received out to 400 nautical miles and even further in unusual propagation conditions.1. The NA VTEX receiver works on _________.A. 4209.5KhzB. 490KhzC. 518KhzD. All above.2. Which character(s) identifies station of NA VTEX?A.B1B. B2C. B3D. B43. Which statement is TRUE?A. The NA VTEX system is very important to GMDSS.B. The NA VTEX system is a part of GPS,C. The NA VTEX system is a part of EGCD. The NA VTEX system has nothing to do with the GMDSS4. Which of the following is not TRUE?A. Each message begins with starts of message function(ZCZC).B. Each message ends with an end of message function(NNNN).C. The NA VTEX system can cover the 250 miles from the transmitter.D. The NA VTEX system can not cover 400 miles from the transmitter.Passage3.Terrestrial Communications_____LONG-RANGE SERVICE_____Use of HF provides a long-rang service in both the ship-to-shore and shore-to-ship directions:In case covered by INMARSA T it can be used as an alternative to satellite communications and outside these areas it provides the only long-rang communication capability:Frequencies have been designated in the 4,6,8,12 and 16 MHz bands for this service.Digital selective calling (DSC) forms the basis of distress alerting and safety communications:Distress and safety communications following a DSC call can be performed by radiotelephone or NBDP._____MEDIUM-RANGE SERVICE_______A medium-range service is provided on frequencies in the 2 MHz banD. In the ship to shore, ship to ship and shore to ship directions 2187.5kHz will be used for distress alerts an safety calls using DSC, and 2182kHz will be used for distress and safety traffic by radiotelephone, including SAR co-ordinatind and on-scene communications:2174.5kHz will be used for radiotelex (NBDP) distress and safety traffic._____SHORT-RANGE SERVICE___VHF provides short-range service on the frequencies: A\156.525MHz (Channel 70) for distress and safety calls using DSC, and B\156.8MHz(Channel 16) for distress and safety traffic by radiotelephone, including SAR co-ordinating and on-sense communications.1. In GMDSS system, terrestrial communications can be divided into ____parts.A. oneB. TwoC. ThreeD. four2.2187.5kHz can be used for________.distress and safety calls on radiotelex system in MEDIUM-RANGE service.A. distress and safety calls on digital selective calling system in MEDIUM-RANGE service.B. distress and safety calls on radiotelex system in LONG-RANG service.C. distress and safety calls on radiotelex system in SHORT-RANGE service.D. distress and safety calls on telex system in satellite service.3. VHF CH 16 is a distress and safety frequency in short-rang service, so it should be used for ____.A. distress and safety radiotelex calls in short-rang serviceB. distress and safety DSC calls in short-rang serviceC. distress and safety radiotelex calls in MEDIUM-RANG serviceD. distress and safety radiotelephone calls in short-rang service4. The HF can provide the service which is ____________.A. not covered by INMARSA T:B. only Short-Range Service .C. only Medium-Range ServiceD. Covered by INMARSA T.5. Which of the following is true?A. Digital selective calling (DSC) follows a telephone call.B. Distress and safety communications by radiotelephone or NBDP follows a DSC distress call.C. Digital selective calling (DSC) follows NBDP:traffic.D. Radio telephone alert forms the basis of distress alerting and safety communications: Passage4.Terrestrial Communications_____LONG-RANGE SERVICE_____Use of HF provides a long-rang service in both the ship-to-shore and shore-to-ship directions:In case covered by INMARSA T it can be used as an alternative to satellite communications and outside these areas it provides the only long-rang communication capability:Frequencies have been designated in the 4,6,8,12 and 16 MHz bands for this service.Digital selective calling (DSC) forms the basis of distress alerting and safety communications:Distress and safety communications following a DSC call can be performed by radiotelephone or NBDP._____MEDIUM-RANGE SERVICE_______A medium-range service is provided on frequencies in the 2 MHz banD. In the ship to shore, ship to ship and shore to ship directions 2187.5kHz will be used for distress alerts an safety calls using DSC, and 2182kHz will be used for distress and safety traffic by radiotelephone, including SAR co-ordinatind and on-scene communications:2174.5kHz will be used for radiotelex (NBDP) distress and safety traffic._____SHORT-RANGE SERVICE___VHF provides short-range service on the frequencies: A\156.525MHz (Channel 70) for distress and safety calls using DSC, and B\156.8MHz(Channel 16) for distress and safety traffic by radiotelephone, including SAR co-ordinating and on-sense communications.1. The acknowledgement of a DSC test call is transmitted as follows:A. first, you should tune a transmitter to 2187.5 kHz.B. then key in or select “test call acknowledgement”.C. key in or select 9-digit identity of the calling ship station.D. all above.2. The section 6 describing is about .A. HFB. MFC. VHFD. All above3. Ships in distress may transmit the DSC distress alert on .A. Only a HF bandB. Only two HF bandsC. A number of HF bandsD. A and B4. Who shall transmit DSC acknowledgement on all HF DSC distress channels on which the DSC alert was received?A. a ship stationB. a coast stationC. many ship stationsD. many coast station5. The DSC distress acknowledgement should be received by .A. ship in distressB. rescue shipC. all ships which received the DSC alert:D. A and C6. The distress traffic should be initiated on the appropriate .A. radiotelephony distress traffic channel:B. NBDP distress traffic channelC. A or BD. DSC distress calling channel7. Which of the following statement is not true?A. The distress traffic should proceed in the same band in which the DSC alert was received.B. Radiotelephone may be used for the distress communication.C. NBDP may be used for the distress traffic.D. NBDP should not be used for the distress traffic.Passage5.The IMO also introduced digital selective calling (DSC) on VHF, MF and HF maritime radios as part of the GMDSS system: DSC is primarily intended to initiate ship/ship, ship/shore, and shore/ship radiotelephone and MF/HF radiotelex calls: DSC calls can also be made to individual ships or groups of ships: DSC distress alerts, which consist of a preformatted distress message, are used initiate emergency communications with ships and rescue coordination centers: When fully implemented, DSC will eliminate the need for persons on a ship's bridge or on shore to continuously guard radio receivers on voice radio channels, including VHF channel 16 (156:8 MHz) and 2182 kHz now used for distress, safety and calling: A listening watch aboard GMDSS-equipped ships on 2182 kHz ended on 1 February 1999, and on VHF channel 16 is scheduled to end on 1 February 2005: We urge that the DSC-equipped VHF and MF/HF radios beexternally connected to a satellite navigation receiver: That connection will ensure accurate location information is sent to a rescue coordination center if a distress alert is ever transmitteD. FCC regulations actually require that ship's position be manually entered into the radio every four hours on ships required to carry GMDSS equipment, while that ship is underway (47 CFR 80:1073): Once SOLAS ships are allowed to disband watch-keeping on VHF and MF radiotelephone channels, other ships are going to need DSC-equipped radios to contact these ships, particularly in a passing situation, especially when outside U:S: waters: We believe VHF, MF and HF radiotelephone equipment carried on ships should include a DSC capability as a matter of safety: To achieve this, the FCC requires that all new VHF and MF/HF maritime radiotelephones type accepted after June 1999 to have at least a basic DSC capability: VHF digital selective calling also has other capabilities beyond those required for the GMDSS: The Coast Guard uses this system to track vessels in Prince William Sound, Alaska, V essel Traffic Service: IMO and the USCG also plan to require ships carry a Universal Automatic Identification System, which will be DSC-compatible: Countries having a GMDSS A1 Area will be able to identify and track AIS(自动识别系统)-equipped vessels in its waters without any additional radio equipment:1. Which of the following is the best answering?A. Only VHF equipment can used DSC.B. Only MF equipment can used DSCC. Only HF equipment can used DSC.D. DSC will use on VHF, MF and HF equipment2. According to this message, which of the following is wrongA. When fully implemented, for persons to continuously guard will eliminateB. DSC is used for watchingC. DSC is only used for watching:D. DSC is used to initiate emergency communication:3. According to this message, the watch-keeping of VHF CH16 will be ended _______:A. on 1 February 1999:B. on 1 February 2005:C. on 1 February 2000:D. on 1 February 2010:4. The writer intends that the VHF/MF/HF radio equipment _______:A. should have its own satellite navigator;B. have nothing to do with the satellite navigation system;C. should be connected to a satellite navigator:D. should change the ship‟s position manually every hours:5. Which statement is not correct?A. DSC can initiate radio-telephone and radiotelex calls on VHF/MF/HF bands:B. DSC can initiate radio-telephone calls on VHF/MF/HF bands:C. DSC can initiate radiotelex calls on MF/HF bands:D. DSC can initiate VHF/MF/HF radio-telephone and MF/HF radiotelex calls:6. The AIS equipment will be used to ________:A. identify and track vessels in A1sea area;B. identify and track vessels in A2sea area;C. identify and track vessels in A3sea area;D. identify and track vessels in A4sea areA.7. The meaning of word “radios” in the passage is :A. radio equipmentsB. radio wavesC. radio programsD. no meaningPassage6.Satellite systems operated by the International Mobile Satellite Organization (Inmarsat), are also important elements of the GMDSS: Three types of Inmarsat ship earth station terminals are recognized by the GMDSS: the Inmarsat A, B and C. The Inmarsat A and B, an updated version of the A, provide ship/shore, ship/ship and shore/ship telephone, telex and high-speed data services, including a distress priority telephone and telex service to and from rescue coordination centers: The Inmarsat C provides ship/shore, shore/ship and ship/ship store-and-forward data and telex messaging, the capability for sending preformatted distress messages to a rescue coordination center, and the SafetyNET service: The Inmarsat C SafetyNET service is a satellite-based worldwide maritime safety information broadcast service of high seas weather warnings, NA V AREA navigational warnings, radionavigation warnings, ice reports and warnings generated by the USCG-conducted International Ice Patrol, and other similar information not provided by NA VTEX: SafetyNET works similarly to NA VTEX in areas outside NA VTEX coverage: Inmarsat C equipment is relatively small and lightweight, and costs much less than an Inmarsat A or B. Inmarsat A and B ship earth stations require relatively large gyro-stabilized antennas; the antenna size of the Inmarsat C is much smaller: Inmarsat also operates an EPIRB system, the Inmarsat L, which is similar to that operated by COSPAS-SARSA T: Under a cooperative agreement with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), combined meteorological observations and AMVER reports can now be sent to both the USCG AMVER Center, and NOAA, using an Inmarsat C ship earth earth station, at no charge: There is also no charge to register for this service and to receive the necessary Inmarsat C software: For more information, see the NOAA Shipboard Environmental (data) Acquisition System, or SEAS: We strongly urge that Inmarsat C equipment have an integral satellite navigation receiver, or be externally connected to a satellite navigation receiver: That connection will ensure accurate location information to be sent to a rescue coordination center if a distress alert is ever transmitteD.1. According to the passage, which type of Inmarsat SES terminals are approved by the GMDSS?A. INMARSA T-C;B. INMARSA T-M;C. INMARSA T MINI-M;D. INMARSA T-P2. The writer suggests that INMARSA T-C ship earth stations ______A. should have an satellite navigator;B. should be connected to a satellite navigation receiverC. A & BD. A or B3. The SafetyNET (satellite-based worldwide maritime safety information broadcast service) service is provided by _____________A. INMARSA T-AsystemB. INMARSA T-B systemC. INMARSA T-C systemD. INMARSA T-M system4. Which ship earth station does not requires relatively large gyro-stabilized antenna?A. INMARSA T-AB. INMARSA T-BC. INMARSA T-CD. Both A & B5. The meaning of phrase “store-and-forward” in the passage isA. first memorize, then relayB. memorizing messageC. directly send messageD. store a file6. INMARSA T-L isA. INMARSA T-C systemB. INMARSA T-BC. EPIRB system of INMARSA TD. COSPAS-SARSA T7. According to the passage, which of the following is not true?A. a meteorological observation can be transmited to NOAA with Inmarsat-C SES at free of chargeB. A AMVER reports can be transmited to the USCG AMVER Center at chargeC. It is no charge to register for AMVER serviceD. It is no charge to receive Inmarsat-C softwarePassage7.The GMDSS installation on ships include one or more search and rescue radar transponders (SART), devices which are used to locate survival craft or distressed vessels by creating a series of dots on a rescuing ship's 3 cm radar display: The detection range between these devices and ships, dependent upon the height of the ship's radar mast and the height of the SART, is normally about eight nautical miles: Note that a marine radar may not detect a SART even within this distance, if the radar settings are not optimized for SART detection1. Which statement is true according to the passage?A. SART can send alert signals to RCC through INMARSA T system;B. SART can send alert signals to RCC through COSPAS-SARSA T system;C. SART can send alert signals to RCC through VHF/HF/MF communication system;D. SART is used to locate survival craft or distressed vessels2. The detected distance of SART is determined by_________A. The position of the SARTB. The frequency of the marine radarC. The height of the radar antenna and the SARTD. The frequency of the SART3. If the radar settings are not optimized for SART detection,maybeA. can not see returns of SART on radar screenB. can see returns of SART on radar screenC. affect function of SARTD. be independent of radar detectingPassage8.Radar should not be regarded as more than an aid to the detection of other vessel, and collisions in poor visibility can be averted for certain only if the information provided by the radar set is correctly interpreted。

IMO=International Maritime Organization 国际海事组织introduction 引入,引进mark 标志maritime 海上的;海事的invention 发明amendment 修改改正convention 公约SOLAS= Safety of life at sea 海上人命安全公约adopt 正式通过,采用replace 取代,代替phase in 强调entry into force 生效,实施stage 阶段SAR= Search and Rescue 搜索和救助coordinate 协调authority 主管机关ashore 岸上vicinity 附近alert 报警emergency 紧急coordinate 协调on-scene 现场locate 定位distress 遇险bridge 驾驶台community 实体,社会Beneficial 有益的;受益的INMARSAT 国际海事卫星put into orbit 送入轨道announcement 宣布;通告establish 建立shipyard 船坞;船厂as a general rule 通常shipment 装船,装运的货物provide by 提供;供给terrestrial 地面的travel =sail 航行high sea 公海carry 携带;配备facility 设备;设施in addition to 除。
以外dissemination 播发;传播meteorological 气象的warning 警告comprehensive 全面的available 可利用的;有用的enhanced 增强的combination 组成;组合take out 退出;去掉contributing 贡献;起作用voyage 航次;航海;航行install 安装Pacific 太平洋Atlantic 大西洋GT =gross tonnage 总吨位Navigate 航行Abbreviation 缩写component 部分SART=Search and Rescue Radar Transponders 搜救雷达应答器interrogate 触发;询问airborne 飞机载lay down 制定;规定irrespective 不论;不考虑primarily 主要地imminent 急迫的;危急的relate to 涉及;与。

《GMDSS通信英语》理论复习题单选题(每题1分,共403题)1、_____ means the finding of ships, aircraft, units or persons in distress.A、shore-based radar assistanceB、locatingC、search and rescueD、salvage参考答案:B_____是指船舶,航空器,单位或遇险人员发现。
A,岸基雷达援助B,定位C,搜索和救援D, 打捞2、_____ will form the basis for distress alerting and safety calling.A、GMDSSB、EGCC、MSID、DSC参考答案:D______将提醒遇险和安全呼叫的基础上形成的。
A,GMDSS B,EGC C,微星D, DSC3、______ are used for distress alerting as a rule .A、SES/DSC/EPIRBB、SART/radiotelephoneC、COSPAS-SARSATD、both a and c参考答案:A,______是用于遇险报警作为一个规则。
A,SES/ DSC / EPIRB B,SART /无线电话C,COSPAS-SARSAT系统,D, 同时A和C4、A digital calling system used to call ships and coast stations using frequencies in the MF, HF or VHF bands, as is defined by CCIR recommendations 493 and 541, is a ______ .A、DSC systemB、EGCC、Terrestrial RadioD、Alerting information参考答案:A,数字电话系统,用来调用船舶和海岸电台在MF,HF或VHF频段使用频率,定义和CCIR建议493和541,是______。

GMDSS通信英语包过500题带答案翻译(不全)GMDSS通信英语500题(带答案)第一部分单项选择题第一章GMDSS通信基础知识001. Which of the following is a required GMDSS function?A. Bridge-to-bridge communications.B. Reception of weather map facsimile broadcasts.C. Both of these.D. None of these.下述哪一项是GNDSS功能所要求的?驾驶台对驾驶台通信A002. Which of the following is a required GMDSS function?A. Transmit and receive location signals.B. Transmit and receive general communications.C. Both of these.D. None of these.下述哪一项是GNDSS功能所要求的?(A发送和接收寻位信号;B 常规通信);两者都是C003. GMDSS is required for which of the followings?A. All vessels capable of international voyages.B. SOLAS Convention ships of 300 gross tonnage or more.C. Vessels operating outside of the range of VHF coastal radio stations.D. Coastal vessels of less than 300 gross tons.GMDSS适用于下面哪一项?300总吨及以上的SOLAS船舶 B004. What is the fundamental concept of the GMDSS?A. It is intended to automate and improve existing digital selective calling procedures and techniques.B. It is intended to automate and improve emergency communications in the maritime industry.C. It is intended to provide more effective but lower cost commercial communications.D. It is intended to provide compulsory vessels with a collision avoidance system when they are operating in waters that are also occupied by non-compulsory vessels.GMDSS的基本概念是什么?在航运业,它用来使紧急通信自动化并提高通信B005. What equipment can be used to receive Maritime Safety Information?A. HF NBDP.B. NA VTESC. EGC receiver.D. All of these.什么设备可以用来接收海上安全信息?(HF NBDP,NA VTEX,EGC receiver ),以上都是D006. Which statement is false regarding the radio operator requirements for a GMDSS-equipment ship station?A. One of the qualified GMDSS operators must be designated to have primary responsibility for radio communications during distress incidents.B. A qualified GMDSS operator, and a qualified backup, must be designated to perform distress, urgency and safety communications.C. Maintaining a record of all incidents connected with the radio communication service which appear to be of importance to safety of life at sea is not required.D. While at sea, all adjustments or radio installations, servicing or maintenance of such installations which may affect the proper operation of the GMDSS station must be performed by, or under the supervision of, a qualified GMDSS operator.关于配备有GMDSS的船台对无线电操作员的要求的描述,下列哪个是错误的?不要求记录对海上人命安全重要的无线电通信业务的有关事件C007. Which statement is false regarding the maintenance of GMDSS equipment at sea?A. The GMDSS operator may not be the person designated to have primary responsibility for radio communications during distress incidents.B. Ships must carry at least one person who qualifies as a GMDSS maintainer for the maintenance and repair of equipment if the at sea maintenance option is selected.C. All at sea maintenance and repairs must be performed by, or under the supervision of a person holding aGMDSS First/Second Class Radio Electronic Certificate.D. The GMDSS maintainer may be the person responsible for ensuring that the watches are properly maintained and that the proper guard channels and the vessel’s position are entered in the DSC equipment.关于海上GMDSS的维修哪一项是错误的?GDMSS操作员不能是遇险事件时的专门通信操作员A 008. What is defined as an area outside sea areas A1, A2 and A3?A. AOR-E.B. AOR-W.C. Coastal and inland waters.D. A4.什么被定义为除A1,A2,A3海区以外的区域?A4 D009. Which radio equipment is not necessary for the ships sailing in the sea area A1?A. NA VTES receiver.B. VHF EPIRB.C. 406MHz EPIRBD. VHF DSC.在A1海区航行的船舶不必配备哪种无线电设备?C010. Which of the following is a functional or carriage requirement for compulsory vessels?A. A compulsory vessel must satisfy certain equipment carriage requirements that are determined by where the vessel sails.B. A compulsory vessel must carry licensed GMDSS operators, the number should be determined by the associated administration.C. A compulsory vessel must be bale to transmit and respond to distress alerts.D. All of these.对强制船舶来讲,下面哪一项是功能或是必要配备?A.强制船舶无论航行在哪里都必须配备某种安全运输设备;B.强制船舶必须配备GMDSS操作员,人数应由主管机关来决定的;C.强制船舶必须发送和回应遇险报警。

航海GMDSS通信英语题库+答案航海GMDSS英语阅读500题单选题一第三部份英语阅读单项选择题1. IMO has decided that all ships over 300TGt must be fitted with a NAVTEX receiver ______ .A. by 01 Feb 1992B. by 01 Aug 1993C. between 01 Feb 1992 and 01 Feb 1999D. before 01 Feb 1992 2. GMDSS is to provide ______ with reliable communication . A. all large passenger vesselsB. freighters of more than 300gt in coastal watersC. all passenger ships and cargo ships engaged in international-voyagesD. all passenger ships and cargo ships of 300gt upwards in open sea3. The complying vessels can transmit ship-to-shore distress alertsby at least ______ .A. One means, whether satellite or terrestrial techniquesB. Two means, whether satellite or terrestrial techniquesC. Two separate and independent means, each using different radio communication servicesD. Two means, such as MF DSC and HF DSC4. The quality of the message can be affected by ______ .A. climateB. sunshineC. human beingsD. both a and b5. Within the polar areas it is ______ to see a satellite in geo-stationary orbit .A. impossibleB. possibleC. easyD. difficult 6. The Inmarsat system is open for use by ______ countries on anon-discriminatory basis .A. someB. lots ofC. manyD. all7. With the help of GMDSS ______ can be alerted to a distressincident as soon as possible .A. all ships in a large sea areaB. only the sea authorities ashoreC. the SAR units ashore and at seaD. the port radios and thecoast stations 8. In areas covered by Inmarsat HF can be used as an______ to satellite communications.A. alternationB. alternateC. alterD. alternative 9. When receiving a distress alert, the SAR authorities ashore and the ships inthe vicinity of the ship in distress will ______ in a coordinated search andrescue operation with the minimum delay .A. assistB. send a rescue vesselC. search the distress areaD. reach the distress position atonce 10. In which year was the COSPAS-SARSAT system established ? A.1980 B. 1981 C. 1979 D. 198211. It is quite ______ for an SES operator to send a distressalert . A. easy and expensive B. simple and certain C.dangerous and stable D. difficult and compulsory12. Any ships fitted with SES can ______ and _______ through thesatellite system when sending a distress alert . A. enter the system / contactan RCCB. access to INMARSAT / establish contact with a CESC. have absolute priority to enter the system / make contact with a CESD. enter the system gradually / wait for rescue13. What’s the advantage when using the satellites ? A. Themessage can be directed to the desired location B. The message canfollow the earth’s curvature C. The quality of message can not beaffected by climaticD. The range of the message extend and the quality of reception isimproved 14. The DSC frequency for distress alerting in Area A2 is______ . A. 2182KHZ B. 2174.5KHZ C. 2192KHZ D. 2187.5KHZ 15. What channel is general communication used ? A. any appropriate channel exceptpublic communication B. any appropriate channel except for public communications C. any appropriate channel besides public communicationD. any appropriate channel beside public communication 16. why do somestations keep silence ?A. Because they are not engaged in the distress trafficB. theywill affect the transmission of the distress traffic C. The powers ofthese stations are very weak D. They are not in charge of search andrescue17. General radio communications in the global system are those between ______ concerning the management and operation of the ships and may have impact on their safety .A. SAR party and the ship in distressB. SAR authorities and the ship in distress and survival craftC. A ship station and any coast stationD. Ship stations and shore-based communication network18. It is required that ships proceeding at sea should keep continuous watch on ______ .A. VHF channels 16 and 13B. Appropriate DSC distress and safety frequenciesC. INMARSAT TDM message channelD. VHF channel 70 andchannel 819. The ARQ mode should be applied ______ . A. when two stations communicate with each other B. in any radio system and at any timeC. when one ship sends a message to another stationD. for communication among some stations20. What information will a distress alert contain ? A. nature of distressB. type of assistance requiredC. course and speed and time at which the information was recordedD. A, B, C are all right21. A radio determination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals reflected , or retransmitted from the position tobe determined, is ______ .A. DFB. Radar SystemC. DSC SystemD. COSPAS-SARSAT 22. With the help of modern technology, ships are able to receive automated broadcast of safety messages ______.A. by day or at nightB. almost round the clockC. somewhat and sometimeD. from sunrise and sunset23. The WWNWS is a coordinated global service for the broadcast by radioof vital information on ______ to marine navigation.A. ship’s movementB. safetyC. ship’s managementD. hazards24. distress alerts will be relayed on the ______ when the RCC considersit necessary .A. dedicated systemB. MSI broadcastsC. 518KHZD. channel 1625. The frequency 518KHZ will be used to transmit ______ and ______ wanings in NAVTEX .A. navigational / typhoonB. traffic / meteorologicalC. marine / hurricaneD. navigational / meteorological 26.It is possible for ships to receive safety message transmitted by Navtexstation ______ .A. in any INMARSAT regionsB. in each NAVTEX areaC. atany distance D. in Areas A3 and A427. A Navtex station in each NAVAREA is usually allowed to have ______ for transmission .A. 10 minutes every 4 hoursB. half an hour every other hourC. irregular period of timeD. 5 minutes every two hours 28.The difference between international and national Navtex Service is limited to______ .A. frequency allocatedB. both language and frequencyC. language usedD. transmission power and time 29. Navtex transmitter identification character ______ is used to identify the感谢您的阅读,祝您生活愉快。


GMDSS通信英语习题Part one The introduction of GMDSS(GMDSS概述)1.The radio equipment to be carried on board GMDSS ship depends upon .(船舶GMDSS通信设备配置根据船舶的。
)A.Gross tonsB.kind of shipC.sea area(航行海区)D.A+B2.Which of the following indicates that a station transmit concerning navigation safety message by radio telephone?(下列哪个是无线电话安全信号)A.MAYDAYB.PAN PANC.SECURITE(安全)D.SAFETY3.Which of the following indicates a grave(危险的)and imminent即将来临的danger requesting immediate assistance on the radio telephone?(危险事件即将发生而且需要立即援助)A.MAYDAY(遇险)B.PAN PANC.SECURITED.SAFETY4.If we pass exam, it may be possible for us obtain .(通过考试,我们取得---)A.First class radio electronic certificationB. Second class radio electronic certificationC.General operation’s certificationD. Restricted operation’s certification5.All the distress message should be preceded by . (遇险信号处在---之面)A.MAYDAY(遇险)B.PAN PANC.SECURITED.SAFETY6.The sea area A3 will be within the coverge of .(A3海区在----覆盖范围之内)A.MF coast stationB.VHF coast stationC.Inmarsat StatelliteD.COSPAS/SARSA T7. Urgency message should be preceded by . (紧急信号处在---之面)A.MAYDAY(遇险)B.PAN PANC.SECURITED.SOS8.Which of the following equipment does not belong to GMDSS?下列哪个不属于GMDSS设备A.EPIRBB.GPSC.DSCD.INMARSAR—F9.The equipment carriage requirement of the ships of which sea area can be summarized(概括)as:carry VHF equipment and either a satellite EPIRM or a VHF EPIRB?(哪个海区需配置的设备:VHF设备和S-EPIRB或VHF EPIRB)A.A1B.A2C.A3D.A410.“CHANGED ETD PILOT STN”means .(预计离开引水站时间已经改变)A.ETD is not changedB.ETD has changedC.ETA has changedD.ETA is not changed11.What is AAIC of traffic system in China?交通部系统中国对外无线电资费结算单位代码是:01O2O30412.Which equipment is required to be carried in various sea areas?(在不同海区都必须配置的设备)A.VHFB.MFC.HFD.MES13.Which of the following description about Sea A3 is correct?下列哪个对A3海区描述是正确。
航海GMDSS英语阅读500题单选题一第三部份 英语阅读单项选择题1. IMO has decided that all ships over 300TGt must be fitted with a NAVTEX receiver ______ .A. by 01 Feb 1992B. by 01 Aug 1993C. between 01 Feb 1992 and 01 Feb 1999D. before 01 Feb 19922. GMDSS is to provide ______ with reliable communication .A. all large passenger vesselsB. freighters of more than 300gt in coastal watersC. all passenger ships and cargo ships engaged in international-voyagesD. all passenger ships and cargo ships of 300gt upwards in open sea3. The complying vessels can transmit ship-to-shore distress alerts by at least ______ .A. One means, whether satellite or terrestrial techniquesB. Two means, whether satellite or terrestrial techniquesC. Two separate and independent means, each using different radio communication servicesD. Two means, such as MF DSC and HF DSC4. The quality of the message can be affected by ______ .A. climateB. sunshineC. human beingsD. both a and b5. Within the polar areas it is ______ to see a satellite in geo-stationary orbit .A. impossibleB. possibleC. easyD. difficult6. The Inmarsat system is open for use by ______ countries on a non-discriminatory basis .A. someB. lots ofC. manyD. all7. With the help of GMDSS ______ can be alerted to a distress incident as soon as possible .A. all ships in a large sea areaB. only the sea authorities ashoreC. the SAR units ashore and at seaD. the port radios and the coast stations8. In areas covered by Inmarsat HF can be used as an ______ to satellite communications.A. alternationB. alternateC. alterD. alternative9. When receiving a distress alert, the SAR authorities ashore and the ships in the vicinity of the ship in distress will ______ in a coordinated search and rescue operation with the minimum delay .A. assistB. send a rescue vesselC. search the distress areaD. reach the distress position at once10. In which year was the COSPAS-SARSAT system established ?A. 1980B. 1981C. 1979D. 198211. It is quite ______ for an SES operator to send a distress alert .A. easy and expensiveB. simple and certainC. dangerous and stableD. difficult and compulsory12. Any ships fitted with SES can ______ and _______ through the satellite system when sending a distress alert .A. enter the system / contact an RCCB. access to INMARSAT / establish contact with a CESC. have absolute priority to enter the system / make contact with a CESD. enter the system gradually / wait for rescue13. What’s the advantage when using the satellites ?A. The message can be directed to the desired locationB. The message can follow the earth’s curvatureC. The quality of message can not be affected by climaticD. The range of the message extend and the quality of reception is improved14. The DSC frequency for distress alerting in Area A2 is ______ .A. 2182KHZB. 2174.5KHZC. 2192KHZD. 2187.5KHZ15. What channel is general communication used ?A. any appropriate channel except public communicationB. any appropriate channel except for public communicationsC. any appropriate channel besides public communicationD. any appropriate channel beside public communication16. why do some stations keep silence ?A. Because they are not engaged in the distress trafficB. they will affect the transmission of the distress trafficC. The powers of these stations are very weakD. They are not in charge of search and rescue17. General radio communications in the global system are those between ______ concerning the management and operation of the ships and may have impact on their safety .A. SAR party and the ship in distressB. SAR authorities and the ship in distress and survival craftC. A ship station and any coast stationD. Ship stations and shore-based communication network18. It is required that ships proceeding at sea should keep continuous watch on ______ .A. VHF channels 16 and 13B. Appropriate DSC distress and safety frequenciesC. INMARSAT TDM message channelD. VHF channel 70 and channel 819. The ARQ mode should be applied ______ .A. when two stations communicate with each otherB. in any radio system and at any timeC. when one ship sends a message to another stationD. for communication among some stations20. What information will a distress alert contain ?A. nature of distressB. type of assistance requiredC. course and speed and time at which the information was recordedD. A, B, C are all right21. A radio determination system based on the comparison of reference signals with radio signals reflected , or retransmitted from the position to be determined, is ______ .A. DFB. Radar SystemC. DSC SystemD. COSPAS-SARSAT22. With the help of modern technology, ships are able to receive automated broadcast of safety messages ______.A. by day or at nightB. almost round the clockC. somewhat and sometimeD. from sunrise and sunset23. The WWNWS is a coordinated global service for the broadcast by radio of vital information on ______ to marine navigation.A. ship’s movementB. safetyC. ship’s managementD. hazards24. distress alerts will be relayed on the ______ when the RCC considers it necessary .A. dedicated systemB. MSI broadcastsC. 518KHZD. channel 1625. The frequency 518KHZ will be used to transmit ______ and ______ wanings in NAVTEX .A. navigational / typhoonB. traffic / meteorologicalC. marine / hurricaneD. navigational / meteorological26. It is possible for ships to receive safety message transmitted by Navtex station ______ .A. in any INMARSAT regionsB. in each NAVTEX areaC. at any distanceD. in Areas A3 and A427. A Navtex station in each NAVAREA is usually allowed to have ______ for transmission .A. 10 minutes every 4 hoursB. half an hour every other hourC. irregular period of timeD. 5 minutes every two hours28. The difference between international and national Navtex Service is limited to ______ .A. frequency allocatedB. both language and frequencyC. language usedD. transmission power and time29. Navtex transmitter identification character ______ is used to identify the broadcasts which are to be accepted by the receiver and those are to be rejected .A. B2B. B1C. MARD. NNN30. The receiving stations can use the B2 character to ______ different, classes of messages .A. identifyB. CorrectC. RejectD. Print out31. If EGC receiver shares a same antenna with Inmarsat SES, it means thatit can receive MSI ______ .A. from any Inmarsat satelliteB. from any appropriate Navtex and EGC stationC. via the satellite the SES is trackingD. from any RCC and coast station32. Why should the SES operators be very careful when the ship enters the area where three ocean regions overlap ? Because ______ .A. the weather is always terribleB. the condition there is complicatedC. the signals are too strongD. their SES may receive the signals from unwanted satellite33. The establishment of INMARSAT as an independent organization marked a great step forward for maritime radio communications . What does “marked a great step” mean in the sentence ?A. To run faster than everB. To go forwardC. To march without stoppingD. A significant symbol of a great improvement in maritime communication .34. In addition to meeting the requirement of Sea area A1, every ship engaged on voyage in Sea area A2 shall be provided with ______ .A. MF radio installation with DSCB. SESC. MF/HF radio telephone installationD. 2187.5KHZ watch receiver35. ______ is a space system using one or more artificial earth satellites .A. satellite networkB. Satellite LinkC. INMARSATD. Satellite System36. The satellites over the major ocean regions cover the globe ______ .二A. besides the polar regionsB. including the North Pole and the South PoleC. above 70N and below 70SD. as far north and south 7037. There are some back-up satellites in the event of failure. If the operational satellite is out of work, ______ .A. communications in the whole system will stopB. the global system will be damagedC. the back-up one will take its placeD. the whole system will not work38. The position if the IOR satellite in the INMARSAT system is ______ above the equator .A. 64.5EB. 178EC. 15.5WD. 54W39. The GMDSS defines four sea area based on the ______ .A. location and capacity of the facilities located on board shipsB. Position and type of a sincere sintionC. Capacity and location of shore based communication facilitiesD. Position and capacity of mobile communication stations.40. The NCS of INMARSAT-A system in the IOR is in ______ .A. Goonhilly, UKB. Yamaguchi, JapanC. Perth, AustraliaD. Southbury, USA41. The Network Coordination station for the INMARSAT-A coast stations in the Pacific ocean region is in ______ .A. Yamaguchi, JapanB. Beijing, ChinaC. Nakhodka, RussiaD. Perth, Australia42. Any ship with SES can ______ and ______ through the Inmarsat satellites when sending a distress alert .A. enter the system rapidly / wait for rescueB. have an absolute priority to enter the system / contact with a CESC. establish contact with the RCC / enter the portD. enter the system gradually / get the rescue43. A mobile earth station in the maritime mobile-satellite service, which is located on board ship, is called ______ .A. an LESB. an SESC. a ship stationD. a Land Mobile Station44. After successful commissioning , the ______ will permit the SES access to system.A. INMARSATB. IMOC. MSCD. CES45. In general, there are two parts in an SES, One of these is antenna eqipment also referred to as ______ .A. BDEB. UDEC. AEPD. ADE46. To establish a communication channel for the telex service in the INMARSAT-A terminal, you should first ______ .A. establish a communication channel from the CES, via the International Telex Network to the final destinationB. set up a communication channel from your SES, via a satellite, to a CES within your ocean regionC. set up a channel directly to the addressee at the destinationD. establish a channel from your terminal , via the International Telex Network to a CES within your ocean region47. The maritime access code for the AOR-E is ______ in INMARSAT-A Telex Service .A. 581B. 582C. 583D. 58448. When you have received GA+ from the CES for the INMARSAT-A telex communication, you should immediately select ______ and ______ you required .A. an CES / telex modeB. an SES telex serviceC. the service /the subscriberD. a satellite /an ocean region49. Every ship must be fitted with SART, and two-way VHF radio telephone .A. 1, 2B. 2, 3C. 2, 1D. 3, 250. The maritime access code of telephone mode in INMARSAT-A terminal forthe IOR is _____.A. 871B.872C.873D. 87451. ______ are operated as a secondary method of alerting in the GMDSS .A. satellite EPIRBsB. Non-satellite EPIRBsC. SES and DSCD. a+b52. Which Inmarsat system applies store-and-forward messaging ?A. Inmarsat-AB. Inmarsat-CC. Inmarsat-BD.Inmarsat-M53. Distress signal are always stored in the memory so as to start ______ .A. local-mode coverageB. SAR operationsC. data processD. continuous broadcast54. EGC is a ______ part of INMARSAT-C .A. componentB. supportableC. combinedD. complimentary55 An area within the coverage of at least one VHF shore station in which continuous DSC distress alerting is available is ______ .A. sea area A1B. sea area A2C. distress areaD. GMDSS areas56. An area within the coverage of at least one MF shore station in which continuous DSC distress alerting is available is ______ .A. Sea area A1B. Sea area A2C. Distress areaD. GMDSS areas57. In area A2, the DSC frequency for distress alerting is ______ .A. 2182KHzB. 2174.5KHzC. 2191KHzD. 2187.5KHz58. If a DSC distress relay is transmitted from coast station , it will______ .A. indicate the ship in distress that the alert has been receivedB. alert ships in the area of a distress incident that a distress has occurredC. inform other coast station of distress incidentD. repeat the distress alert in 5 minutes59. Ship-to-ship distress alerting should be conducted by ______ .A. Inmarsat SESB. VHF/DSC or MF/DSCC. SART and VHF/DSCD. Satellite EPIRB and VHF/DSC60. If the DSC controller is configured for MF/HF operation, the distress will be sent on ______.A. double frequenciesB. single frequencyC. dedicated frequencyD. multiple frequencies61. Maritime Safety Information ______ International SafetyNet Service and NAVTEX Service .A. consists ofB. can be receivedC. is transmitted byD. Are made on62. IMO has decided that all ships over 300TGT must be fitted with a NAVTEX receiver.A. by 01 Feb 1992B. 01 Aug 1993C. between 01 Feb 1992 and 01 Feb 1999D. before 01 Feb 199263. Ships sailing in ______ are able to receive and print out EGC messages.A. a fixed area or Navarea in any ocean regionB. a Navarea or weather forecast areaC. the designated area or given geographic positionD. anywhere of the world64. Ships sailing in ______ are able to receive and print out EGC messages .A. a fixed area or Navarea in any ocean regionB. a Navarea or weather forecast areaC. the designated area or given geographic positionD. anywhere of the world65. ______ can receive MSI sent by coast station .A. A NAVTEX receiverB. An EGC receiverC.. MF/HF radio telephoneD. HF radio telephone with NBDP66. SafetyNet is a maritime safety information broadcast service offering ______ on suitably equipped ships.A . free reception B. free transmissionC. dedicated receptionD. dedicated transmission67. COSPAS-SARSAT has the function of ______ .A. distress alertingB. communicationC. broadcasting MSID. on-scene communication68. The COSPAS-SARSAT 406MHZ system was adopted as an element of the GMDSS by IMO in ______ .A. 1992B. 1980C. 1984D. 198869. ______ is capable of finding any 406MHZ beacons no matter where they are.A. Local User TerminalB. Spacecraft三C. Local-mode coverageD. Near polar orbiting satellites70. COSPAS-SARSAT cannot fulfill the function of :A. determining the position of a distress vesselB. both a andcC. distress communicationD. distress alerting and position fixing in Area A471. the beacon located on board aircraft is termed _____ .A. EPIRBB. PLBC. ELTD. MCC72. for COSPAS-SARSAT system, _____ transmit distress alert and location information to appropriate rescue authorities all over the world . A. Polar orbiting satellites B. Ground receiving stations C. MCC D. ROC73. Distress alerting is usually transmitted to _____ .A. ships near distress positionB. rescue coordination centerC. all ships in a large areaD. both a and b74. Exchange of answer-backs acts a confirmation that the messages_____ at the destination.A. have receivedB. have been receivedC. are receivedD. are being received75. The range of a MF coast station is normally _____ nm.A. 20 to 30B. 200C. 100D. 45076. _____ process the distress signal from EPIRB to determine its position and identity.A. COSPAS-SARSATB. ground receiving stationsC. storing distress signalD. Near polar orbiting satellites77. A station in the mobile service the emissions of which are intended to facilitate search and rescue operations is _____ .A. EPIRBB. SARTC. Mobile StationD. Distress Alerting78. Every ship, while at sea, shall be capable.A. of receiving shore-to-ship distress alertsB. of transmitting and receiving MSIC. of transmitting and receiving ship-to-ship distress alertsD. A, B, C are all right79. Every radio installation shall be clearly marked with the _____ , the ship station identity and other codes as applicable for the use of the radio installation.A. call signB. port of registerC. radio nameD. signal label80. Bridge-to-bridge communication means _____ communications between ships from the position from which the ships are normally navigated.A. distressB. urgentC. safetyD. general81. Every lifeboat which is fitted with a fixed _____ VHF radiotelephone apparatus with an antenna which is separately mounted shall be provided with arrangements for sitting and securing the antenna effectively in its operating position.A. one-wayB. two-wayC. double-effectD. one-effect82. Every lifeboat which is fitted with a fixed two-way VHF radiotelephone apparatus with_____ which is separately mounted shall beprovided with arrangements for sitting and securing the antenna effectively in is operating position.A. a dummy antennaB. a supporting facilitiesC. a back-up equipmentD. an antenna83. At least _____ two-way VHF radiotelephone apparatus shall be provided on every cargo ship of 300 tons gross tonnage and upwards but less than 500 tons gross tonnage.A. oneB. twoC. threeD. four84. Stations in the United States of America are grouped by states arranged in the alphabetical order of their _____.A. countriesB. statesC. namesD. groups85. According to the basic concept of GMDSS, _____ can be rapidly alerted to a distress incident.A. only SAR authorities on landB. all ships in a very large sea areaC. the nearest coast stations and port radiosD. the SAR authorities ashore as well as ships in the vicinity of the casualty86. Having studied the INMARSAT document, GMDSS document, SOLAS Convention and other international navigation documents, we all know that the Chapter IV of SOLAS Convention is mainly about _____ .A. the radio regulationsB. the technical terms and definitionsC. how to operate the GMDSS SES equipmentD. Maritime Communications87. What following is not among the functions of SOLAS ships ?A. receive shore-to-ship distress alertingB. transmit ship-to-shore distress alertingC. receive message for public correspondenceD. transmit and receivelocating signals88. Vessel in distress _____ indicate their position by any method.A. cannotB. are no allowedC. have the rightD. should get permission to89. The distress alert should _____ the ship in distress.A. identityB. identicalC. identifyD. identification90. General radio communications in the global system may _____ ship’s safety .A. be responsible forB. have an impact onC. commandD. give a guidance to91. In the case of a ship in distress , the need exists to create a temporary geographic area to _____ locating potential assisting ships.A. increaseB. improveC. facilitateD. develop92. Distress traffic is the communication _____ between the stationin distress and the ships, aircraft, coast radio stations, coast earth stations and rescue centers participating in the rescue work.A. exchangeB. to exchangeC. exchangingD. exchanged93. A SART provides the main means _____ a survival craft or the mother ship in distress under the global maritime distress and safety system.A. to locateB. for locatingC. in locatingD. by locating94. The portable SART is designed _____ on the bridge in its container.A. to stowB. for stowingC. being stowedD. to be stowed95. What did you say on board _____ any part of the message is considered sufficiently important to need safe guarding ?A. whichB. ifC. whyD. that96. The advantage of geo-stationary satellites is _____ .A. the range of antennal can cover everywhere in the worldB. we can know the ship’s exact positionC. that the distress alert can be located as soon as possibleD. antenna of permanrent earth stations may be directed towards fixed points in the sky97. Some words in English have meanings _____ the context in which they appear.A. depended onB. which depend onC. which depends onD. to which depends on98. The fishing vessel _____ the distress area until the assistance vessel arrived.A. leaveB. leftC. has leftD. didn’t leave99. All coast radio stations _____ DSC installed for VHF and HF.A. haveB. hadC. are havingD. have had100. By using previous communication system, rescue is often a matter of chance. What does “a matter of chance “ mean ?A. occasionallyB. accidentallyC. oftenD. usually101. SOLAS vessels should be able to communicate with a shore station _____.A. no matter where they are and what time it isB. at scheduled time and in major ocean regionsC. at fixed time and positionD. when they get permission102. The basic concept of GMDSS is _____.A. Search and rescue authorities ashore will rapidly received an distress alert and acted uponB. SAR units will be rapidly alerted to a distress incident and assist in a coordinated SAR operationC. Ships navigating in the immediate vicinity of the ship in distress will rapidly alerted to the alert and give their help accordinglyD. The RCC will rapidly alerted to a distress alert through satellite and terrestrial communication techniques and conducted a rescue operation immediately103. The complying vessels will transmit ship-to-shore distress alert by _____ in area A4.A. MF DSCB. HF DSCC. 406MHZ S-EPIRBD. Both b and c104. The INMARSAT safety-net service covers _____.A. the whole worldB. all NAVAREASC. areas from A1 to A2D. only four Inmarsat regions105. Which Inmarsat system applies store-and-forward messaging ?A. Inmarsat-AB. Inmarsat-BC. Inmarsat-CD. Inmarsat-F106. The Inmarsat system is open for use by _____countries on a non-discriminatory basis .A. someB. lots ofC. manyD. all107. Sea Area A3 is an area within the coverage of _____in which continuous alerting available .A. VHF stationsB. MF/HF stations四C. Radio stationsD. INMARSAT stations108. The GMDSS must combine all various subsystems, because _____.A. they all have different limitations with respect to coverageB. they all have different limitations in the technology they useC. different systems apply to different shipsD. all of above109. In addition to communication equipment, the GMDSS will introduce requirements of SARTs and EPIRBs designed to improve the _____.A. living standardsB. survival conditionC. chance of survivalD. technical specification110. Ships equipped with Inmarsat SES send distress alerts both _____and _____.A. quick and goodB. convenient and certainC. easily and simplyD. important and difficult111. Some radio waves _____ the surface of the earth because of its _____ .A. are capable of following / distanceB. can follow / altitudeC. can hardly follow / shapeD. are unable following / angle112. Ships in areas A3 and A4 will transmit, as appropriate, _____ .A. a ship to ship alert on MF/VHFB. a ship to shore alert by SES/HF DSCC. a ship to shore alert by satellite EPIRBD. all of a, b, c113. What’s the advantage when using the satellites ?A. The message can be directed to the desired locationB. The message can follow the earth’s curvatureC. The quality of message can not be affected by climaticD. the range of the message extend and the quality of reception is improved114. General communications are those communications _____ .A. between ship stations and shore-based communication networksB. concern the management and operation of shipsC. may have an impact of the safety on shipsD. all of A, B, C115. What channel is general communication used ?A. any appropriate channel except public communicationB. any appropriate channel except for public communicationsC. any appropriate channel besides public communicationD. any appropriate channel beside public communication116. A ship station on receiving a shore-to-ship distress alert should _____ .A. keep silenceB. interfere with such communicationC. establish communication as directed and render such assistance as is required and appropriateD. refuse communication as directed and render such assistance as is required and appropriate 117. Signals for locating will be transmitted in the 9GHz band by means of _____ .A. SARTB. DSCC. NBDPD. RT118. Which of the following optional equipment can be used by a ship in Area A3 for ship to shore distress alerting ?A. VHF DSCB. MF DSCC. INMARSAT SESD. VHF 70CH EPIRB119. The ARQ mode should be applied _____ .A. when two stations communicate with each otherB. in any radio system and at any timeC. when one ship sends a message to another stationD. for communication among some stations120. The SART should provide a _____ indication of its correct operation and should also inform survivors when it is interrogated by radar.A. sight or soundB. seeing or soundingC. visual or audibleD. seeing or hearing121. When the power of a SART is on , it will _____ .A. transmit distress signalB. send response signalC. transmit the signal of ship’s positionD. be interrogated by X-band radar122. With the help of modern technology, ships are able to receive automated broadcast of safety messages _____ .A. by day or at nightB. almost round the clockC. somewhat and sometimeD. from sunrise to sunset123. International SafetyNet and Navtex Services promulgate MSI by means of _____ .A. FEC and ARQB. satellite and terrestrial communicationsC. radio and telexD. NBDP124. In the GMDSS, MSI broadcasts will be made on two dedicated systems: _____ and _____ .A. NBDP/VHF radioB. Inmarsat safetyNet/NAVTEXC. Safety service / Inmarsat-AD. Long range / short range125. Ships at sea are in urgent need of MSI because they are _____ various kinds of danger .A. subject forB. liable toC. easy to meetD. always encounter126. The NAVTEX receiver can be mounted on _____ .A. on the bridgeB. in the coast stationC. on the forecastleD. on starboard side127. The distance between the two Navtex stations with the same B1 character should be not exceed _____ nautical miles .A. 400B. 400C. 450D. 180128. NAVTEX transmissions have a designed range of about _____ nautical miles .A. 300B. 400C. 500D. 600129. The transmitter identification character B1 is a single unique letter which is allocated to each NAVTEX _____ .A. receiverB. SESC. CESD. Transmitter五130. In NAVTEX service, the subject indicate character B means _____ .A. meteorological warningsB. navigational warningsC. search and rescue informationD. meteorological forecast131. In NAVTEX service, VITAL warnings will _____ by transmitting station .A. be transmitted at once though the frequency is not clearB. be transmitted as soon as the frequency is cleared coordinatelyC. be transmitted at its scheduled transmissionsD. be transmitted at next scheduled transmissions132. The satellites over the major ocean regions cover the globe _____ .A. besides the polar regionsB. including the North Pole and the South PoleC. above 70°N and below 70°SD. as for north and south as 70°133. The establishment of INMARSART as an independent organization marked a great step forward for maritime radio communications. What does “marked a great step” mean in the sentence ?A. To run faster than everB. To go forwardC. To march without stopping。
1 IMO, International Maritime Organization. 国际海事组织2 INMARSAT, International Maritime Satellite Organization. 国际海事卫星组织3 GMDSS, Global Maritime Distress and Safety System.全球海上遇险和安全系统4 1974SOLAS, Convention International Convention for the Safety of life at Sea.1974年国际海上人命安全公约5 SAR Convention, International Convention for maritime search and rescue.国际海上搜寻救助公约6 STCW, international convention on standard of training certification and watchkeeping for seafares,1978. 1978年国际海员培训、发证和值班标准公约7 Contracting Government. 缔约国政府8 GMDSS areas. 全球海上遇险和安全系统区域9 area A1 A1海区area A2 A2海区areaA3 A3海区areaA4 A4海区10 ship carriage requirements 船舶配备要求11 diatress alerting 遇险报警12 SAR co-ordinating communications 搜救协调通信13 on-scene communications 现场通信14 on-scene commander 现场指挥15 positioning 示位16 locating 寻位17 MSI maritime safety information 海上安全信息18 general radio communications 常规无线电通信19 bridge-to-bridge communication 驾驶台对驾驶台通信20 DOE, duplication of equipment 双套设备方法21 UTC, Co-ordinated universal time 世界协调时22 ship reporting system 船舶报告系统23 continuous watch 连续值守24 space radio communication 空间无线电通信25 space system 空间系统26 satellite system 卫星系统27 satellite network 卫星网略28 satellite link 卫星链路29 muliti-satellite link 多卫星链路30 feeder link 馈线链路31 geostationary satellite 静止卫星32 geostationary satellite orbit 静止卫星轨道33 INMARSAT system, international maritime satellite system 国际海事卫星系统INMARSAT –A system 国际海事卫星A系统INMARSAT –B system 国际海事卫星B系统INMARSAT –C system 国际海事卫星C系统INMARSAT –E system 国际海事卫星E系统34 L-band EPIRB L-波段卫星紧急无线电示位标EPIRB, emergency position-indicating radio beacon.35 EGC system, enhanced group call system 增强群呼系统36 Ocean regions 洋区37 AOR-E, Atlantic Ocean Region east. 大西洋东区AOR-W, Atlantic ocean region west, 大西洋西区POR, pacific ocean region, 太平洋区IOR, indian ocean region 印度洋区38 space segment 空间段39 NCS, network co-ordination station , 网络协调站40 NCC, network control centre , 网络控制中心41 earth station 地球站42 space station 空间站43 land earth station,LES 陆地地球站44 coast earth station, CES 海岸地球站45 mobile earth station, MES 移动地球站46 ship earth station, SES 船舶地球站47 inmarsat mobile number, IMN 国际海事卫星移动号码48 maritime distress channel 海上遇险信道49 distress priority 遇险优先级50 urgency priority 紧急优先级51 safety priority 安全优先级52 routine priority 日常优先级53 MES signalling channel移动地球站信令信道54 MES message channel移动地球站信息信道55 closed network 闭合网络56 public switching telephone network, PSTN 公众电话交换网57 packet swithing data network, PSDN 分组数据交换网58 data report 数据报告59 data circuit terminating equipment, DCE 数据线路终端60 data terminal equipment,DTE 数据终端设备61 enhanced group call service code, EGC service code 增强群呼业务码62 mobile earth station status, MES status 移动地球站状态62 open network 开放网络63 packet switching 分组交换64 PVT, performance verification test 性能验证测试65 Polling 轮询66 Signalling packet 信号分组67 SFU, store and forward unit 存储转发单元68 EGC receiver 增强群呼接收机69 EGC decoder 增强群呼译码器70 EDI, electronic data interchange 电子数据交换71 Handshake 交接72 space system for search of distress vessels (COSPAS) 搜索遇险船舶空间系统73 SARSAT search and rescue satellite-aided tracking 卫星搜救跟踪系统COSPAS-SARSAT system 低级轨道搜救卫星系统74 SPOC. SAR point of contact 搜救联络点75 Service area 服务区76 system information 系统信息77 alert data, 报警数据78 filtered alert data, 报警数据滤除79 time of approach, TCA 最接近点时间80 beacon identification data, 示位标识别数据81 coded information, 编码信息82 emergency locator transmitter,ELT 紧急示位发信机83 realtime mode 实时方式84 全球覆盖方式global coverage mode85 信标检测概率beacon detection probability86 信标定位概率beacon location probability87 地面无线电通信terrestrial radio communications88 地面通信系统terrestrial communication systems, [tə'restrɪəl]89 地面通信网络terrestrial communication networks90 海上无线电话marine radiotelephone91 单边带无线电话single-side band radiotelephone, SSB RT92 窄带直接印字电报narrow-band direct-printing telegraphy, NBDP93 数字选择呼叫digital selective calling, DSC数字选择呼叫系统digital selective calling system, DSC system国际数字选择呼叫(DSC)频率international DSC frequencies国内数字选择呼叫(DSC)频率national DSC frequencies94船舶电台数字选择呼叫自动操作automatic DSC operation at a ship station95 呼叫尝试call attempt96 搜救雷达应答器search and rescue radar transponder ,SART97 中频通信medium frequency communication. MF communication高频通信high frequency communication. HF communication甚高频通信very high frequency communication. VHF communication98 普遍呼叫general call to all stations99 无线电导航radio navigation100 无线电定位radiolocation101 电台station102 地面电台terrestrial station103 救生艇(筏)电台survival craft station104 移动电台mobile station105 陆地电台land station106 基地电台base station107 海岸电台coast station108 船舶电台ship station109 船上通信电台on-board communication station110 港口电台port station111 无线电导航陆地电台radio navigation land station112 无线电导航移动电台radio navigation mobile station113 无线电定位陆地电台radio location land station114 无线电定位移动电台radio location mobile station115 无线电测向电台radio direction-finding station116 无线电信标电台radio beacon station117 标准频率和时间信号电台standard frequency and time signal station118 双向甚高频无线电话设备two-way VHF radiotelephone apparatus119 甚高频紧急无线电示位标VHF emergency position indicating radiobeacon, VHF EPIRB120 对讲电话机intercommunication telephone set121 数据电话机data phone122 气象传真接收机weather facsimile receiver123 甚高频无线电装置VHF radio installations124 前向纠错方式forward error correcting mode, FEC mode125 选择前向纠错方式selective forward error correcting mode, SELFEC mode 126 指配频率assigned frequency127 成对频率paired frequencies128 指配频带assigned frequency band129 有害干扰harmful interference遇险和安全通信130 遇险和安全通信distress and safety communications131 遇险信号distress signal132 遇险优先呼叫distress priority call133 遇险呼叫distress call134 遇险呼叫格式distress call format135 数字选择呼叫遇险报警DSC distress alerts136 船到岸遇险报警ship-to-shore distress alerting岸到船遇险报警shore-to-ship distress alerting船到船遇险报警ship-to-ship distress alerting137 遇险报警转发distress alert relay138 遇险收妥承认distress acknowledgement139 遇险优先申请信息distress-priority request message140 遇险报告distress message141 遇险通信distress communication142 遇险信道distress channel143 紧急信号urgency signal144 紧急呼叫urgency call145 紧急报告urgency message146 紧急通信程序urgency communication procedure147 紧急通信urgency communication148 安全信号safety signal149 航警电传系统navigational telex NA VTEX国际奈伏泰斯业务international NA VTEX service国内奈伏泰斯业务national NA VTEX service奈伏泰斯优先电文NA VTEX priority message奈伏泰斯紧急警告NA VTEX VITAL warning奈伏泰斯重要警告NA VTEX IMPORTANT warning奈伏泰斯日常警告NA VTEX ROUTINE warning150 航行警告navigational warning N/W151 世界航行警告业务world-wide navigational warning service WWNWS 152 航行警告区域协调国NA V AREA co-ordinator153 国内协调人national co-ordinator154 航行警告区NA V AREA155 航行警告区警告NA V AREA warning156 沿海警告coastal warning157 本地警告local warning158 气象警告meteorological warning气象预报meteorological forecast159 冰况报告ice report160 国际冰况巡视报告international ice patrol bulletin161 公海海上安全信息high seas maritime safety information162 卫星转发海上安全信息maritime safety information via satellite163 航行安全通信navigation safety communications164 航行警告信号navigational warning signal165 搜救区search and rescue region. SRR166 救助协调中心rescue co-ordination center RCC167 海上救助协调中心maritime rescue co-ordination center MRCC168 联合救助协调中心associated rescue co-ordination center169 救助分中心rescue sub-centre RSC170 海上搜救计划maritime SAR plan171 移动单元mobile unit172 搜救单元search and rescue unit SAR unit173 现场通信管制control of on-scene communications174 寻位信号locating signal引航信号homing signal175 主管部门administration176 公众通信public correspondence177 电信telecommunication178 无线电通信telecommunication179 无线电通信radiocommunication180 无线电通信业务radiocommunication service181 移动业务mobile service182 卫星移动业务mobile-satellite service183 水上移动业务maritime mobile service184 卫星水上移动业务maritime mobile-satellite service185 港口营运业务port operation service186 船舶动态业务ship movement service187 广播业务broadcasting service188 卫星广播业务broadcasting-satellite service189 极轨道卫星业务polar orbiting satellite service190 无线电测定业务radiodetermination service191 卫星无线电测定业务radiodetermination-satellite service192 无线电导航业务radionavigation service193 卫星无线电导航业务radionavigation-satellite service194 海上无线电导航业务maritime radionavigation service195 卫星海上无线电导航业务maritime radionavigation-satellite service196 无线电定位业务radio location service197 气象辅助业务meteorological aids service198 卫星气象业务meteorological-satellite service199 Standard frequency and time signal service 标准频率和时间信号业务200 Standard frequency and time signal service 卫星标准频率和时间信号业务201 safety service 安全业务202 special service 特别业务203 temporary radio beacon service 临时无线电信标业务204 frequency-shift telegraphy 移频电报205 FAX. facsimile 传真206 telephony 电话技术207 radiotelephone call 无线电话通信208 radio telex call 无线电用户电报通信209 radiotelex service 无线电用户电报业务210 simplex operation 单工操作211 duplex operation 双工操作212 semi-duplex operation 半双工操作213 space tracking 空间跟踪214 ship radio license 船舶无线电执照215 call sign 电台呼号216 radio log 无线电台日志217 MMSI maritime mobile service identies 海上移动业务识别218 MID maritime identification digit 海上识别数字219 ship station identity 船舶电台识别220 group ship station call identity 海岸电台群呼识别221 coast station identity 海岸电台识别222 group coast station call identity 海岸电台群呼识别223 identification of stations using radiotelephony 无线电话电台识别224 EPIRB identification 紧急无线电示位标识别225 SELCALL NO. selective calling number 选择呼叫号码226 RO. routing organization 执行机构227 safetyNET 安全通信网228 international safetyNET service 国际安全通信网业务229 national safetyNET service 国内安全通信网业务230 fleetNET 船队通信网231 geostationary satellite service 静止卫星业务232 electronic mall 电子邮件233 station call 叫号电话234 personal call 叫人电话235 date communication 数据通信236 general communication channels 常规通信信道237 LL land-line charge 陆线费238 CC coast station charge 海岸费239 SC special charge 特别业务费240 medical advice by radio 无线电医疗指导241 medical transports 医疗运输242 plain language 明语243 secret language 密语。
1.此通知你我们的ARPA雷达已经无法工作。
Now we advise you that our ARPA radar has not been able to work.2.卫星船站电话质量差,有噪音。
The communication quality of the SES telephone to satellite is poor, there is noise in it.3.经你岸站到巴拿马的电传费是多少?What are the telex charges to Panama via your CES?4.通信已被切断,你是否再重新接通线路。
The call has been cut off, whether you reconnect it for me?5.你要的电传号码有错,请查实。
The telex number you required is incorrect, please check and confirm.6.当用VHF数字选呼开始呼叫时,显示出“发射错误”。
“SEND ERROR” is displayed, when a call is initialed with VHF DSC.7.请告诉我打到东京电话的费用和时间好吗?Could you tell me the charges and duration of the telephone to TOKYO?8.你与被叫用户处于通信状态中。
You are in communication with the called user.9.我轮请求紧急医疗援助。
I require urgent medical assistance.10.国际海事卫星C船站终端打印机故障。
The Inmarsat-C SES terminal printer was out of order.11.停止发送,等待进一步的指示。
Please stop sending, wait for further advice.12.遇险船的位置在哪里?What is the position of the vessel in distress?13.卫星船站的接收电平不稳定。
GMDSS 通信英语(青岛)Part One The Introduction of GMDSS1.The radio equipment to be carried on board GMDSS ship depends upon____.A. Gross tonsB. kind of shipC. sea areaD. A + B2.Which of the following indicates that a station transmit concerning navigation safety messages by radio telephone? .A. MAYDAYB. PAN PANC. SECURITED. SAFETY3.Which of the following indicates a grave and imminent danger requesting immediate assistance on the radio telephone? .A. MAYDAYB. PAN PANC. SECURITED. SAFETY4.If we pass the exam, it may be possible for us to obtain: ___.A. F irst Class Radio Electronic CertificateB. S econd Class Radio Electronic CertificateC. G eneral Operator's CertificateD. R estricted Operator's Certificate5.All the distress messages should be preceded by____A.MAYDAYB. PAN PANC. SECURITED. SAFETY6.The sea area A3 will be within the coverage of____.A. MF Coast StationB. VHF Coast StationC. Inmarsat SatelliteD. COSPAS/SARSAT7.Urgency message should be preceded by____.A. PAN PANB. MAYDAYC. SECURITED. SOS8.Which of the following equipment does not belong to GMDSS ?A. EPIRBB. GPSC. DSCD. Inmarsat-F9.The equipment carriage requirement of the ships of which sea area can be summarized as: carry YHF equipment and either a satellite EPIRB or a YHF EPIRB?A. A1B. A2C. A3D. A 410. "CHANGED ETD PILOT STN" means .____A. ETD is not changedB. ETD has changedC. ETA has changedD. ETA is not changed11. What is AAIC of traffic system in China? ____A. CN01B. CN02C. CN03D. CN0412. Which equipment is required to be carried in various sea areas?A. VHFB.MFC. HFD. MES13. Which of the following description about Sea Area A3 is correct?____A. a n area within the radiotelephone coverage of at least one VHF coast station and one MF coast station.B. a n area, including Sea Area A1 and A2 , within the coverage of an Inmarsat geostationary satellite.C. A n area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an Inmarsat geostationary satellite.D. A n area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an COSPAS-SARSAT system.14. The following radio communication systems are used in the GMDSS except .A. the Inmarsat systemB. VHF MF and HF terrestrial systemsC. The COSPAS-SARSAT systemD. The FLAG SIGNAL systems15. Which of the following frequency is NOT used for GMDSS? ____A. 2,182 kHzB. 500 kHzC.518kHzD.2,187.5kHz16. 'AMENED ETA PILOT STA TION" means____ .A. ETA pilot station has been changedB. ETA pilot station will be given afterwardsC. ETA pilot station was not givenD. ETA pilot station is given17. Which frequency band does the 518 kHz belong to?A. LF B .MF C. HF D. VHF18. GMDSS is the abbreviation of_____.A. T he Global Maritime Distress and Safety SystemB. T he Global Mariners Distress and Safety SystemC. T he Global Marines Distress and Safe SystemD. T he Global Marines Disco and Safe System19. If we only want to sail in A1, which certificate will fit for us?____A. t he First-class Radio electronic CertificateB. t he second-class Radio electronic CertificateC. t he General Operator's CertificateD. t he Restricted Operator's Certificate20. Both the satellite communication and terrestrial communications will ____.A. not be used in the GMDSSB. be used only for general communicationsC. be replaced by MorseD. be used in the GMDSS21. The medical message should be preceded by the word ____.A. OBSB.TMZC. MEDICOD. N/W22. The date for entry into full effect for GMDSS is 1st February____ .A. 1999B.1992C.1995D.199723. How does the GMDSS enable a ship in distress to send a message?A. in many waysB. in a wayC. only by DSCD. only by Inmarsat24. In the case of a ship in Sea Area A4, the primary means of ship-to-shore distress alerts would have to be____A. VHF DSCB. MF DSCC.406 MHz EPIRBD. InmarsatC25. The primary function of the GMDSS is____ .A. d aily communicationB. b ridge to bridge communicationC. M SI broadcastD. d istress communication of the distressed ships26. If we want to communicate with Guangzhou station by RT, we find out the channel of the station in the ADMIRALTY LIST OF RADIO SIGNALS____ .A. V olume 1B. Volume2C. Volume3D. V olume527. What kinds of ships may not comply with SOLAS convention?A. c argo ships less than 300 tonsB. C argo ships more than 300 tonsC. p assenger ships sail on international serviceD. B&C28. Every ship shall be provided with a VHF radio installation capable of transmitting and receiving on____ .A. CH 70 and CH 16B.CH06C. CH 13D. all of above29. The "on-scene" frequency .3 023 kHz for radiotelephone is used for____ communication.A. ship-aircraftB. intershipC. ship-shoreD. bridge-bridge30. Who have primary responsibility for radio communications during distress incidents? .A. the first mateB. the second mateC. the captainD. the operator31. The call sign of coast' stations of China are between____ .A. BAA-BZZB. XSA-XSZ C3HA-3UZ D. AAA-AZZ32. Availability of radio equipment maintenance options onboard in A3 is____ .A. at-sea maintenanceB. shore-based maintenanceC. duplication of equipmentD. nominate two options of above '33. Regulation of the GMDSS applies to_____.A. a ll cargo ships above 300 gross tonsB. a ll passenger ships on international voyagesC. a ll shipsD. A&B34. Which device has not the function of alerting?A. EPIRBB. SARTC. MESD. DSC35. The GMDSS supports two independent systems for broadcasting MSI, viz ____ .A. NA VTEX & EGCB. SafetyNET & FAXC. InmarsatC & EGCD. DSC & NBDP36. Which terminal is used to alert to ships by distressd vessel?A. EPIRBB.SARTC. MESD. DSC37. When distressed vessel in A4, which terminal is used for routine communication in long range servies?A. 406 MHzEPIRBB. InmarsatFC. InmarsatBD. HF terminal38. Which of the following frequencies is used for international distress and safety frequencies on MF radio telephony?A.2,182 kHzB.2,187.5 kHzC.2,177 kHzD.2,414.5kHz39. Which of the following descriptions of usage is suitable for 8,414.5 kHz frequency?A. D istress alerting frequency on HF DSCB. D istress communication frequency on HF RTC. D istress alerting frequency on MF DSCD. D istress communication frequency on HF NBDP40. Which of the following (lescription of usage is suitable for 2,174. 5 kHz frequency-?A. M F NBDP distress and safety traffic frequencyB. M F TELEPHONE distress and safety traffic frequencyC. M F DSC distress and safety call frequencyD. H F NBDP distress and safety traffic frequency41. The call sign of ship stations of China are between____ .A. BAA-BZZB.XSA-XSZC.3HA-3UZD. AAA ~ AZZ42. Which of the following frequencies is used for intership MF DSC calll?A.2,182 kHzB.2,187.5 kHzC.2J..77 kHzD.2,414.5 kHz43. Which frequencies can not be used for ship-aircraft communications?A.CH06B.3,023 kHzC.2,182 kHzD.5,680 kHz.44. If a ship is on fire in the Sea Area A3 , which of the following equipments would be used to make ship-to-shore distress alerts?A. HF DSCB. 406 MHz EPIRBC. Imarsat-CD. All of above45. To insure the maintenance of the radio equipments, the vessel sailing in A1 area should selectA. at-sea maintenanceB. shore-based maintenanceC. duplication of equipmentD. any one of above46. The transition period in implementation of the new GMDSS system is____ years.A. 6B.7C. 8D.947. What is the basic concept of GMDSS?A. S horeside authorities and vessels can assist in a coordinated SAR operation with minimum delayB. S earch and rescue authorities ashore can be alerted to a distress situationC. S hipping in the immediate vicinity of a ship in distress will be rapidly alertedD. A ll of these48. What statement is generally correct regarding the maintenance requirements for ships under GMDSS?A. S horeside maintenance and scheduled tests and inspections will partially meet this requirementB. R edundancy of functions of .certain equipment will partially meet this requirementC. O n-board maintenance provided by a person holding a GMDSS Maintained license will partially meet therequirementsD. A ll of the above49. What is the primary reason GMDSS imposes the carriage requirement for different radio subsystems on vessels?A. B ecause the different radio subsystems have individual limitations with respect to the geographical coverageand services providedB. R edundancy in duplicating all operational functions in.the event of a system failureC. D ifferent radio systems may be used by the various authoritiesD. T he ability to communicate in all modes with any of the shore stations50. GMDSS is primarily a system based on ____.A. V HF digital selective calling from ship to shoreB. S hip-to-ship distress communication using MF or HF radiotelephonyC. T he linking of search and rescue authorities ashore with shipping in the immediate vicinity of a ship indistress or in need of assistanceD. D istress, urgency and safety communication carried out by the use of narrow-band direct printing telegraphy51 ____is the orbit of a geosynchronous satellite whose circular and direct orbit lies in theplane of the Earth's equator, and it is approximately 35 ,700 kilometers above the equator.A. Polar OrbitingB. GPS Satellite OrbitC. Geostationary Satellite OrbitD. The North and South Poles52.____ is a service which is based on,polar orbiting satellites which receive and relay distressalerts from satellite EPIRBs and which provides their position.A. Inmarsat Satellite ServiceB. Polar Orbiting Satellite ServiceC. GPS Satellite ServiceD. NNSS Satellite Service53 ___includes navigational and meteorological warnings, meteorological forecasts and otherurgent safety related messages broadcast to ships.A. Distress trafficB. Urgency communicationC. Public correspondenceD. Maritime Safety Information54 .____is an area, outside Al, A2, A3, which mostly in the North Pole Area (as the areanear to South Pole is mostly land).A. Sea Area AlB. Sea Area A2C. Sea Area A3D. Sea Area A455. What system provides accurate vessel position information to the GMDSS equipment?A. GPSB. Cospas-SarsatC. InmarsatD. NBDP56. Which of the following is a functional or carriage requirement for compulsory vessels?A. A compulsory vessel must carry at least two (2) licensed GMDSS Radio Operators.B. A compulsory vessel must satisfy certain equipment carriage requirements that are determined by where thevessel sails.C. A compulsory vessel must be able to transmit and respond to distress alerts.D. A ll of the above.57. GMDSS-equipped ships will be required to perform which of the following communications functions?A. D istress alerting and maritime safety informationB. S earch and Rescue coordination and on-scene communicationsC. B ridge-to-bridge and general radio communicationsD. A ll of these58. Which of the following is a required GMDSS function?A. T ransmit and receive locating signalsB. T ransmit and receive general communicationsC. B ridge-to-Bridge communicationsD. A ll of the above59. What statement is generally correct regarding the maintenance requirements for ships under GMDSS?A. R edundancy of functions of certain equipment will partially meet this requirementB. O n-board maintenance provided by a person holding a GMDSS Maintainer' s license will partially meet therequirementsC. S horeside maintenance and scheduled tests and inspections will partially meet this requirementD. A ll of the above60. GMDSS began a phased implementation on Feb. ____.A.1999B.2000C.1992D.200261. The GMDSS defines sea areas based on the location and capability of shore based communication facilities.A. threeB. sixC. fiveD. four62. In addition to meeting the requirement of Sea area Al and A2, every ship engaged on voyage in Sea area A3 shall be provided with___ .A. MF radio installation with DSCB. MES or HF with DSCC. MF/HF radio telephone installationD.2 187.5 kHz watch receiver63. Every ship must be fitted with___ SART, and ___two-way VHF radio telephone.A.1,2B.2,3C.2, 1D.3,264. The communication arrangements are designed to enable distress alerting to be performed in all three directions;____ in all Sea Areas.A. e ast, west, southB. s hip, shore, crewC. s hip-to-shore, ship-to-ship, shore-to-shoreD. s hip-to-shore, ship-to-ship, shore-to-ship65. For ship-to-shore distress alerts, you can use ____.A. Inmarsat, EPIRB and DSCB. NA VTEX, NBDP and R/TC. Inmarsat,' VHF and SARTD. EPIRB, DSC and radar66. Ships which operate in area A4 will have to carry .A. HF equipmentB. MF, VHF equipment and MES'C. Inmarsat equipmentD. EGC receiver67.____ are used for distress alerting as a rule.A. MES / DSC / EPIRBB. SART / radiotelephoneC. COSPAS-SARSATD. both A and C68. Besides distress alerting, the GMDSS can also provide ____communication.A. urgencyB. safetyC. broadcast of MSID. all of A, B and C69. According to the basic concept of the GMDSS, distress alerting can be sent by___to SARauthorities ashore or ships in vicinity of a distress incident.A. e ither satellite or terrestrial communicationB. o nly satellite communicationC. o nly terrestrial communicationD. V HF DSC or MES70. On-scene communications will be between ___and___ .A. the ship in distress / SARB. the ship in distress / RCCC. the ship in distress / vessel in vicinityD. the ship in distress / assisting units71. Every ship, while at sea, shall be capable of .A. t ransmitting and receiving search and rescue co-ordination communicationsB. t ransmitting and receiving on-scene communicationsC. t ransmitting and receiving bridge-to-bridge communicationsD. A, B, C are all right.72. If operating within Ocean Area Al, and outside of NA VTEX coverage, a GMDSS-equipped vessel must carry____ .A. A n Inmarsat-A terminalB. A GPS receiverC. E quipment capable of maintaining a continuous DSC watch on 2,187.5 kHzD. E quipment capable of reception of maritime safety information by the Inmarsat enhanced group call system,or HF NBDP73. What information should be included in a distress follow on voice transmission?A. Ship's Name and Call SignB. Ship's positionC. Ship' s MMSI numberD. All of the above74. What action should you take after sending a false distress alert on VHF?A. Send a DSC cancellation message on CH70B. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on CH16C. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on CH13D. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on CH2275. What action should you take after sending a false distress alert on MF? .A. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on 2,187.5 kHzB. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on 2,174. 5 kHzC. M ake a voice announcement to cancel the alert on 2,182.0 kHzD. S end another DSC alert and follow on with voice on 2,182.0 kHz76. What action 'should you take after sending a false distress alert on 8 MHz?A. M ake an "'ALL SHIPS" call on all 5 HF telex channels canceling the alert.B. M ake an "ALL SHIPS" call on,8,291.0 kHz canceling the alertC. M ake a "MAYDAY" call on 8 ,414.5 kHz canceling the alertD. M ake an "URGENT" call on 8,614.0 kHz canceling the alert77. Which of the following frequencies and modes is allocated for distress alertifig in GMDSS?A. 406 MHz to via EPIRBB. 1,626. 5 ~ 1 ,645. 5 MHz via InmarsatC. C hannel 70 DSC plus six (6) MF/HF DSC frequenciesD. A ll of the above78. Which of the following frequencies have been designated for "On-scene" communications in the Global Maritime Distress and Safety System?A. V HF CH22B. H F radiotelephone on 21. 820 MHzC. N BDP on 2,177.0 kHz and VHF CH16D. V HF CH16 and NBDP on 2,174.5 kHz.79. SafetyNET messages can be received by which of the following shipboard equipment?A. NA VTEXB. MF and HF NBDPC. EGC receiverD. All of these80 .____consists of all messages relating to the immediate assistance required by the ship indistress, including SAR communication and signals for locating.A. Distress trafficB. Routine communicationC. Port operation trafficD. Public correspondencePart Two The Satellite Communication System1. The following number is Inmarsat-C MES's number, which one is Chinese vessels?A. 421256545B.441212345C.415701234D.4124123452. If we want to cancel the false alert to RCC, we should find out the telephone number of the RCC in the ADMIRALTY LIST OF RADIO SIGNALS____.A. Volume2B. Volume3C. Volume4D. V olume53. The EGC service is composed of___ .A. SAFETY NETB. FLEET NETC. DATA REPORTD. A&B4. Which of the following are included in mandatory services LES of Inmarsat-C? __A. FleetNETB. NBDPC. DSCD. SafetyNET5. Which of the following statements about Distress call is correct?A. D istress call is only available on fleet77 systemsB. D istress call is only available on fleet 55 systemsC. D istress call is only available on fleet77/55/33 systemsD. b oth A and B6. The difference between the mobile ISDN and MPDS is that ____.A. T he mobile ISDN is charged by connection time and MPDS is charged by Mbits transferredB. T he mobile ISDN is charged by Mbits transferred and MPDS is charged by connection timeC. T here is no difference between the mobile ISDN and MPDSD. T he communication fee of the mobile ISDN is inexpensive than that of MPDS7. Which of the following IMN is used for Inmarsat-F MES voice service?A. 76 x x x x x x xB.60xxxxxxxC. 3412 xxxxxD.66xxxxxxx8. Which type of the following services is excluded from Inmarsat-F services?A. telephoneB. high speed data transmissionC. telexD. E-mail9. The PIN becomes blocked if the PIN code is entered incorrectly several times when operating cap-sat F77 MES. The maximum of input is ____.A. 4B. 5C. 6D. 310. Which of the following ID number is used for BEIJING LES telephone access code in AOR-E?A.118B.868C.311D.21111. Which terminal equipment of ship is for COSPAS/SARSAT system?A. EPIRBB. InmarsatCC. SARTD. EGC12. COSPAS-SARSAT is intended to be used for .A. Distress alarm and locatingB. Daily communications •C. Send messagesD. E-mail13. The low polar orbiting satellite system provides the coverage of ____.A. AlB.A1+A2 + A3C. A4D. Al + A2 + A3 + A414. Which service does not EGC have? .A. N/WB. MSIC. SafetyNETD. FAX15. Where is the geostationary orbit of Inmarsat situated.?A. equator orbitB. pole orbitC. oblique orbitD. A&B16. Which frequency is used on line from LES to satellite in the Inmarsat system?A. 4 GHzB. 6 GHzC. 1.6 GHzD. 1.4 GHz17. Which frequency is used on line from MES to satellite in the Inmarsat system?A. 4 GHzB. 1.6GHzC. 3 GHzD. 6 GHz18. Which number of the following Inmarsat-C ID numbers is the ID number distributed to Chinese vessel "VICTORY"?A.494601513B.404120000C.441258112D.04126004119. Which is the Inmarsat-C LES access code of MCN( Beijing) in POR?A. 211B.311C.868D.21020. Which 2 digit code is Medical Assistance offered by all LES as specified in the Radio Regulations under GMDSS?A. 32B. 38C. 39D.4121. Please choose the Inmarsat-C NCS ID of the AOR-W .A. 044B.001C.211D.14422. Which type of MES of Inmarsat does not have the telex service?A. Inmarsat-AB. Inmarsat-BC. Inmarsat-CD. Inmaisat-F23. Where is the Inmarsat's headquarters?A. ChinaB. The U. S. AC. the United KingdomD. Canada24. The ground segment of Inmarsat consist of .A. Land Earth StationsB. Network Co-ordination StationsC. Network Operations CentreD. A. B and C25. Which of the following are usually used for distress alerting by Inmarsat-C?A. d irectly press the distress button on the panelB. p ick up phone and report distress information to RCCC. s end distress information by satellite EPIRBD. s end telex to LES26. How many Geo-stationary satellites are employed in the Inmarsat?A. 3B.4C.5D. 627. COSPAS-SARSAT can not fulfill the function of .A. d etermining the position of a distress vesselB. d istress communication 'C. d istress alerting and position-fixing in AeroD. b oth A and C28. The Inmarsat satellites are controlled by .A. NOCB. LESC. NCSD. SCC29. Where is the distress alerting made by MES in the Inmarsat system passed to?A.MCCB. RCCC. LESD. NCS30. Before the communication, the Inmarsat-C MES must login ____ of the located oceanregion. .A. dominated MES by NCSB. RCCC. anyone of the MESD. NCS31. In the Inmarsat system, the services code 00 meansA. position reportB. relay serviceC. automatic serviceD. medical advice32. Which service is a more cost-effective solution for applications where there is no need for constant transmission of data in both directions?A. ISDNB. MPDSC. ISDLD. CDMA33. The command of breaking the radio connection of the Inmarsat-B telex service is___.A.NNNNB.…..C. KKKKD. OVER34. The distress message of the Inmarsat-C radiotelex does not include the information of .A. the time of distressB. the nature of distressC. the position of distressD. the number of the distress people35 The Inmarsat Mobile Numbers (IMN) has digits except InmarsatA MES.A. 7B. 9C. 10D. 336. Communication using fax of Inmarsat-F, the country code of China is .A. 868B. 11C. 86D. 85 ,37. Which institution monitor and control the communications traffic of the LES within the Ocean Region? .A. RCCB. NCSC. NOCD. MCC38. Which orbit is the COSPAS/SARSAT satellite situated?A. equator orbitB. pole orbitC. oblique orbitD. A&B '39. Which equipment does not belong to COSPAS-SARSAT system?A. EPIRBB. SARTC. PLBD. ELT40. Which type of Inmarsat mobile earth station terminals is approved by the GMDSS?A. Inmarsat-CB. Inmarsat-MC. Inmarsat mini-MD. Inmarsat-F5541. Which institue processes the signals to determine the beacon location?A. MCCB. RCCC. LUTD. NCC42; When a vessel in distress making On-scene communications, which one of the following radio equipments can be used____ .A. VHFB. MF/HF radio equipmentC. Inmarsat MESD. all of above43. Any ships fitted with MES can ____and through the satellite system when sendinga distress alert.A. e nter the system/contact an RCCB. a ccess to Inmarsat/establish contact with a LESC. h ave the absolute priority to enter the system/make contact with a LESD. e nter the system gradually/wait for rescue44. Where does the RCC of the China locate in?____A. BeijingB. ShanghaiC. DalianD. Tianjin45. Which of the following optional equipment can be used by a ship in Area A3 for ship to shore distress alerting?A. VHF DSCB.MF DSCC. Inmarsat MESD. VHF 70CH EPIRB46. The maritime access code for the IOR is in Inmarsat-C Telex Service.A.581B.582C.583D.58447. In Inmarsat-C, "Priority 0" means communication.A. routineB. distressC. urgencyD. safety48. The maritime access code of telephone mode in Inmarsat-F,. terminal for the AOR ( E) isA.871B.870C.581D.58049. Which Inmarsat system applies store-and-forward messaging?A. Inmarsat-AB. Inmarsat-CC. Inmarsat-BD. Inmarsat-M50. The Inmarsat SafetyNet services covers .A. the whole worldB. all NavareaC. areas from Al to A4D. only four Inmarsat regions51. Sea Area A3 is an area within the coverage of in which continuous alerting available.A. VHF stationsB. MF/HF stationsC. Radio stationsD. Inmarsat stations52. The NCS of Inmarsat-C system in the AOR(E) is in____.A. Goonhilly, UKB.Yamaguchi, JapanC.Perth, AustraliaD. Southbury, USA53. An MES operator can choose the most suitable LES according to___.A.the routing agreement for a particular ocean regionB.the communication service he requiredC.the positions of his ship and the LESsD. B and C54. In Inmarsat-B service code "32"means____ .A. medical assistanceB. medical adviceC. maritime assistanceD. technical assistance55. What is the primary function of a NCS?A.To monitor and control communications through the Inmarsat satellite for which it is responsi¬bleB.To provide direct communications between the Inmarsat station placing a call and the station receiving thecallC.To provide multi-mode communications between the Inmarsat station placing a call and the coast radiostation that will deliver itD.To determine which satellite is best suited to provide communications between the Inmarsat station placinga call and the station receiving the call56.How does a distress message normally initiated through Inmarsat?A. A ll Inmarsat units have a dedicated key that can be pressed for immediate actionB. B y adding the word "DISTRESS" in the first line of the message's preambleC. C ertain Inmarsat units have a dedicated key that can be pressed for immediate action, while other systemsprovide menu-driven featuresD. By transmitting the distress message on the U. S. Coast Guard's dedicated monitoring channel 57.57.How will communication fee of Inmarsat-C be paid?A. i n accordance with duration of communicationB. i n accordance with size of message transferredC. s ame as billing method of telecommunication of radio coast stationsD. s ame as billing method of Inmarsat-B58; Which of the following is a correctly formatted Inmarsat-C address book entry for sending communications to a fax machine number (045 ) 334-5678 in Japan (voice country code 81)?A. 810453345678#B. 81(045)3345678C. 819453345678D. 81 (045) 334-567859. Which of the following is a correctly formatted Inmarsat-C address book entry for sending communications toa shoreside telex terminal number 45992 in Taiwan (telex country code 769) ?A. (769)45992B. 76945992 +C. 76945992D. None of the above.60. It is possible to transmit all of the following via Inmarsat-C from a vessel except? .A. TelexB. Text for delivery by FaxC. V oiceD. Comtex mail and x. 400 data services61: Inmarsat-C provides for which of the following?A. P olling, enhanced group call, and one-way position and data reporting via satelliteB. F M voice communications via satelliteC. T wo-way messaging and data communications on a store-and-forward basisD. P olling, enhanced group call, one-way position and data reporting via satellite, two-way messaging and datacommunications on a store-and-forward basis62. Which mode of communications is possible through an Inmarsat-F MES?A. SITORB. TelexC. telephoneD. DSC。
第一部英语听力习题1.Utopia Forward Station. This is Utopia Bridge. Single up forward to head line and breastline.Utopia船首台,我是驾驶台,请单绑,只剩头缆和横缆。
2.Utopia Aft Station. This is Utopia Bridge. Single up aft to breast line and stern buoy line.Utopia船尾台,我是船首台,请单绑,只剩横缆和尾浮筒系缆。
3.Utopia Aft Station. Take tug’s towing line to capstan then make fast on starboard quarter.Utopia船尾台,请把拖轮拖缆带上绞缆机并在右舿挽牢。
4.Oredock Pilot. This is Huanghe. My draught forward 10.2m, aft 11.0m, fresh waterallowance 200 millimeters.Oredock引航员,我是黄河轮,我船首吃水为10,2米,尾吃水为11米,淡水限额为200毫米5.Gargantua. This is Utopia. Visibility is expected to decrease to 200m in four hours.Gargantua,我是Utopia,预计四小时后能见度将下降到200米。
6.Euphoria. This is Red Sea. Visibility at Diexieville is 500 meters. It is expected to increaseto 1500 meters in the next two hours.Euphoria,我是Red Sea,在Diexieville处的能见度为500米,预计两小时后将增加到1500米。
一、缩略语1、GMDSSA:Global Maritime Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险与安全系统B:Global Maritime Distress and SafeSystem 全球海上遇险与安全系统C:Global Maritine Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险与安全系统D:Global Maritime Distress and Safety System 全球海上遇险系统2、INMARSA TA:International Mobile Satellite Organization 国际海事卫星组织B:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国际移动卫星组织C:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国家海事卫星组织D:International Maritime Satellite Organization 国际海事卫星组织3、PORA:Pacific Ocean Region 大西洋区B:Pacific Ocean Region 太平洋区C:Pacific Ocean Region 印度洋区D:Pacific Ocean Region 北冰洋区4、DSCA:Digital Select Call 数字选择性呼叫B:Digital Search Call 数字选择性呼叫C:Digital Selective Call 数字选择性呼叫D:Digital Searching Call 数字选择性呼叫5、MSIA:Maritime Safety Information 海上安全信息B:Mobile Safety Information 海上安全信息C:Maritime Safe Information 海上安全信息D:Maritime Signe Information 海上安全信息6、EPIRBA: Urgency Position Indicating Radio Beacon 紧急无线电示位标B:Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon 紧急无线电示位标C:Emergency Positive Indicating Radio Beacon 紧急无线电示位标D:Emergency Position Identification Radio Beacon 紧急无线电示位标7、LESA: Lord Earth Station 陆地地球站B:Land Earth Station 陆地地球站C:Land Earth State 陆地地球站D:Land Earth Station 移动地球站8、MSIA: Maritime Safety Information 海上安全信息B:Maritine Safety Information 海上安全信息C:Maritime Safe Information 海上安全信息D:Maritime Safety Identification 海上安全识别9、ETAA: Estimate Time of Arrival 预计抵达时间B:Estimated Time of Arrival 预计离港时间C:Estimated Time of Arrival 预计抵达时间D:Estimated Timing of Arrival 预计抵达时间10、IMOA: International Maritime Organization 国际海事组织B:Internation Maritime Organization 国际海事组织C:International Mobile Organization 国移动组织D:International Maritime Organize 国际海事组织二、单选题1、Which of the following equipments on board is for the COSPAS-SARSA T system?A:DSCB:NA VTEXC:VHFD:EPIRB2、Please choose the INMARSA T-C NCS ID of the W-AOR:A:044B:001C:211D:1443、Which service does not the EGC system have?A: Safety NETB: Fleet NETC:SARTD: Sending MSI4、The VHF CH70 could be used to send ______:A:FAXB:DSCC:NBDPD:SSB5、In each NA VTEX message there is a technical code (B1B2B3B4):which character is the station identification ?A:B1B:B2C:B3D:B3B46、The following radio communication systems are used in GMDSS except the INMARSA T system:A:VHFB:VHF MF and HF terrestrial systemsC:the COSPAS-ASRSA T systemD:the FLAG SIGNAL systems7、Which equipment is required to be carried in the all sea areas ?A:VHFB:MFC:HFD:SES8、Where is the INMARSA T’S headquarters?A: ChinaB: The USAC: the United KingdomD: Canada9、The Maritime safety information contains _________:A: distress messageB: Urgency messageC: Distress alertD: Navigational and meteorological warnings10、Both the satellite communication and terrestrial communications will _________:A: not be used in the GMDSSB: be used only for general communicationsC: be replaced by MorseD: be used in the GMDSS11、If we pass this test it may be possible for us to obtainA:The First-class Radioelectronic CertificateB:The Second-class Radioelectronic CertificateC:The General Operator’s CertificateD:The Restricted Operator‟s Certificate12、Which of the following statement is correct?A:2182 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety communications using radiotelegraphy which class of emission is A1AB:2187:5 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety calls using digital selective calling:C:2187:5 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety calls using narrow-band-direct-printing:D:2182 KHz is a carrier frequency used for distress and safety traffic using narrow band direct printing:13、There are VHF equipments and either a satellite EPIRB or a VHF EPIRB on board according to the equipment carriage requirement:Which sea area does the ship sail?A:A1B:A2C:A3D:A414、Which of the following description of usage is suitable for 2174:5KHz frequency?A:MSIB:NBDPC:DSCD:RT15、Which of the following description about Sea Area A3 is correct?A:an area within the radiotelephone coverage of at least one VHF coast station and one MF coast station B:an area, including Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an INMARSAT geostationary satellite.C:An area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an INMARSAT geostationary satellite.D:An area, excluding Sea Area A1 and A2, within the coverage of an COSPAS—SARSAT system.16、In the COSPAS-SARSA T system, there are _______types of beacons at present?A:3B:2C:1D:417、The medical message should be preceded by the word ________.A:OBSB:TMZC:MEDICOD:NW18、All the distress message should be preceded by ______.A:PAN PANB:SECURITEC:MAYDAYD:MEDICO19、What final place is a distress call/message routed to?A:CESB:NCSC:RCCD:MCC20、The date for entry into full effect for GMDSS is 1st February _______.。