ANNEX 2
- 格式:doc
- 大小:3.00 MB
- 文档页数:43

© World Health Organization 世界卫生组织WHO Technical Report Series, No. 961, 2011世界卫生组织技术报告系列,编号961,2011年Annex 2 附录2WHO good practices for pharmaceutical microbiology laboratories世界卫生组织药品微生物实验室管理规范目录Background 背景 (2)Introduction and scope of document 文件介绍和范围 (2)Glossary 术语表 (3)1. Personnel 人员 (5)2. Environment 环境 (6)2.1 Premises 房屋 (6)2.3 Cleaning, disinfection and hygiene 清洁、消毒和卫生 (8)2.4 Sterility test facilities 无菌试验设施 (8)3. Validation of test methods 检验方法的验证 (10)4. Equipment 设备 (10)4.1 Maintenance of equipment 设备维护 (11)4.2 Qualification 验证 (11)4.3 Calibration, performance verification and monitoring of use 校准、性能确认和使用的监控 (11)4.3.3 Temperature measurement devices 温度测量装置 (11)4.3.4 Incubators, water-baths and ovens 培养箱、水浴和烘箱 (11)4.3.5 Autoclaves, including media preparators 高压灭菌锅,包括培养基制备器 (12)4.3.6 Weights and balances 砝码和天平 (13)4.3.7 Volumetric equipment 测定体积的设备 (13)4.3.8 Other equipment 其他设备 (13)5. Reagents and culture media 试剂和培养基 (14)5.1 Reagents 试剂 (14)5.2 Media 培养基 (14)5.3 Labelling 贴签 (16)5.4 Organism resuscitation 微生物复苏 (16)6. Reference materials and reference cultures 标准物质和标准菌株 (16)6.1 International standards and pharmacopoeial reference substances 国际标准和药典标准品 (16)6.2 Reference cultures 标准菌株 (17)7. Sampling取样 (18)8. Sample handling and identification 样品处理和鉴定 (18)9. Disposal of contaminated waste污染废物的处理 (19)10. Quality assurance of results and quality control of performance结果的质量保证和性能的质量控制 (19)10.1 Internal quality control内部质量控制 (19)11. Testing procedures检验程序 (20)12. Test reports检验报告 (20)References参考文件 (20)Further reading 补充书目 (21)Appendix 1 附件1 (22)Examples of zones in which operations could be carried out可进行操作的区域的例子 (22)Appendix 2 附件2 (23)Examples of maintenance of equipment设备维护的例子 (23)Appendix 3 附件3 (24)Examples of calibration checks and intervals for different laboratory equipment不同实验室设备校准检查和间隔的例子 (24)Appendix 4 附件4 (25)Examples of equipment qualification and monitoring设备验证和监控的例子 (25)Appendix 5 附件5 (27)General use of reference cultures 标准菌株的一般用途 (27)Background 背景The WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical Preparations adopted in 2009 a revised version of the Good practices for pharmaceutical quality control laboratories (1).世界卫生组织制剂产品的质量标准专家委员会在2009年通过了药品质量控制实验室管理规范的修订版本(1)。


DIRECTIVESCOMMISSION DIRECTIVE 2011/37/EUof 30 March 2011amending Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council onend-of-life vehicles(Text with EEA relevance)THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the EuropeanUnion,Having regard to Directive 2000/53/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 September 2000 onend-of-life vehicles ( 1 ), and in particular Article 4(2)(b) thereof,Whereas:(1) Directive 2000/53/EC prohibits the use of lead, mercury,cadmium or hexavalent chromium in materials andcomponents of vehicles put on the market after 1 July 2003, other than in cases listed in Annex II to that Directive and under the conditions specified therein. Pursuant to Article 4(2)(b) of Directive 2000/53/EC, Annex II to that Directive should be adapted to scientific and technical progress by the Commission on a regular basis.(2) Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC lists vehicle materialsand components exempted from the prohibition set outin Article 4(2)(a) thereof. Vehicles put on the market before the expiry date of a given exemption may contain lead, mercury, cadmium or hexavalent chromium in materials and components listed in Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC.(3) Certain materials and components containing lead,mercury, cadmium or hexavalent chromium shouldcontinue to be exempted from the prohibition set out in Article 4(2)(a) of Directive 2000/53/EC, since the use of such substances in those specific materials and components is still technically or scientifically unavoidable. It is therefore appropriate to prolong the expiry date of those exemptions until the use of the prohibited substances becomes avoidable.(4) The use of lead in automotive thermoelectric materials inapplications reducing CO 2 emissions by recuperation of exhaust heat is currently technically and scientifically unavoidable. Those materials should therefore be temporarily exempted from the prohibition set out in Article 4(2)(a) of Directive 2000/53/EC.(5) Certainmaterials and components containing lead, mercury, cadmium or hexavalent chromium shouldcontinue to be exempted from the prohibition set out in Article 4(2)(a) of Directive 2000/53/EC without an expiry date, since the use of such substances in the specific materials and components listed in Annex II to that Directive is still technically or scientifically unavoidable.(6) AnnexII to Directive 2000/53/EC provides that spare parts put on the market after 1 July 2003 which areused for vehicles put on the market before 1 July 2003 are exempted from the provisions of Article 4(2)(a) of that Directive. The exemption allows for the repair of vehicles put on the market before the entry into force of the prohibition set out in that Article with spare parts meeting the same quality and safety requirements as the parts with which they were originally equipped.(7) Spareparts for vehicles put on the market after 1 July 2003 but before the expiry date of a given exemption of Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC are not covered by that exemption. Hence, spare parts for those vehicles should be heavy metal free, even if they are used to replace parts which originally contained heavy metals.(8) Incertain cases it is technically impossible to repair vehicles with spare parts other than original ones as this would require changes in dimensional and functional properties of entire vehicle systems. Such spare parts cannot fit into the vehicle systems originally manu factured with parts containing heavy metals and these vehicles cannot be repaired and may need to be prematurely disposed of. Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC should therefore be amended to enable the repair of such vehicles.( 1 ) OJ L 269, 21.10.2000, p. 34.(9) Directive 2000/53/EC should therefore be amendedaccordingly.(10) The measures provided for in this Directive are inaccordance with the opinion of the Committee established under Article 18(1) of Directive 2006/12/EC ofthe European Parliament and of the Council of 5 April2006 on waste (1),HAS ADOPTED THIS DIRECTIVE:Article 1Annex II to Directive 2000/53/EC is replaced by the text set outin the Annex to this Directive.Article 2Member States shall bring into force the laws, regulations and administrative provisions necessary to comply with this Directive by 31 December 2011 at the latest.Article 3This Directive shall enter into force on the 20th day following its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.Article 4This Directive is addressed to the Member States.Done at Brussels, 30 March 2011.For the CommissionThe PresidentJosé Manuel BARROSO(1) OJ L 114, 27.4.2006, p. 9.ANNEX‘ANNEX IIMaterials and components exempt from Article 4(2)(a)Lead as an alloying elementLead and lead compounds in componentsHexavalent chromiumMercuryCadmium( 1) Dismantling if, in correlation with entry 10(a), an average threshold of 60 grams per vehicle is exceeded. For the application of this clause electronic devices not installed by the manufacturer on the production line shall not be taken into account. ( 2 ) This exemption shall be reviewed in 2015. ( 3 ) This exemption shall be reviewed in 2014. ( 4 ) This exemption shall be reviewed before 1 January 2012. ( 5) Dismantling if, in correlation with entries 8(a) to 8(j), an average threshold of 60 grams per vehicle is exceeded. For the application of this clause electronic devices not installed by the manufacturer on the production line shall not be taken into account.Notes:— A maximum concentration value up to 0,1 % by weight and in homogeneous material, for lead, hexavalent chromium and mercury and up to 0,01 % by weight in homogeneous material for cadmium shall be tolerated,— The re-use of parts of vehicles which were already on the market at the date of expiry of an exemption shall be allowed without limitation since it is not covered by Article 4(2)(a),— Spare parts put on the market after 1 July 2003 which are used for vehicles put on the market before 1 July 2003 shall be exempted from the provisions of Article 4(2)(a) (*). motors and brake linings.’。
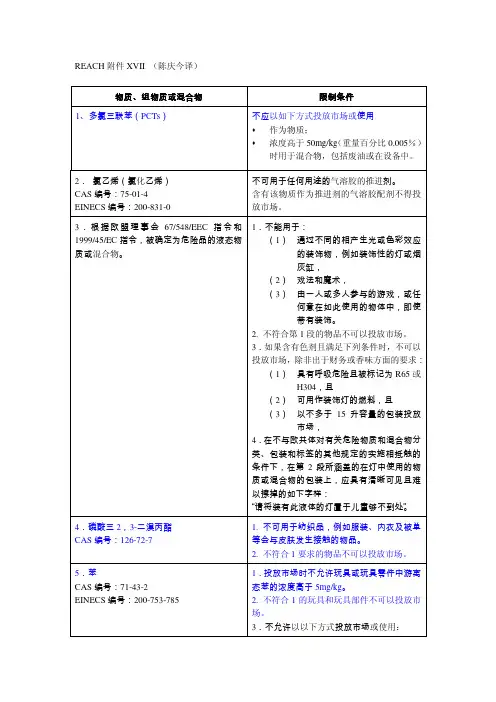
REACH 附件XVII (陈庆今译)物质物质、、组物质或组物质或混合物混合物限制条件1、多氯三联苯(PCTs )不应以如下方式投放市场或使用 作为物质;浓度高于50mg/kg (重量百分比0.005%)时用于混合物,包括废油或在设备中。
2. 氯乙烯(氯化乙烯) CAS 编号:75-01-4 EINECS 编号:200-831-0不可用于任何用途的气溶胶的推进剂。
含有该物质作为推进剂的气溶胶配剂不得投放市场。
3.根据欧盟理事会67/548/EEC 指令和1999/45/EC 指令,被确定为危险品的液态物质或混合物。
1.不能用于:(1) 通过不同的相产生光或色彩效应的装饰物,例如装饰性的灯或烟灰缸,(2) 戏法和魔术,(3) 由一人或多人参与的游戏,或任何意在如此使用的物体中,即使带有装饰。
2. 不符合第1段的物品不可以投放市场。
3.如果含有色剂且满足下列条件时,不可以投放市场,除非出于财务或香味方面的要求:(1) 具有呼吸危险且被标记为R65或H304,且(2) 可用作装饰灯的燃料,且 (3) 以不多于15升容量的包装投放市场,4.在不与欧共体对有关危险物质和混合物分类、包装和标签的其他规定的实施相抵触的条件下,在第2段所涵盖的在灯中使用的物质或混合物的包装上,应具有清晰可见且难以擦掉的如下字样:“请将装有此液体的灯置于儿童够不到处”。
4.磷酸三2,3-二溴丙酯 CAS 编号:126-72-71. 不可用于纺织品,例如服装、内衣及被单等会与皮肤发生接触的物品。
2. 不符合1要求的物品不可以投放市场。
5.苯CAS 编号:71-43-2 EINECS 编号:200-753-7851.投放市场时不允许玩具或玩具零件中游离态苯的浓度高于5mg/kg 。
2. 不符合1的玩具和玩具部件不可以投放市场。
3.不允许以以下方式投放市场或使用:物质,作为其他物质或混合物的组分且苯的浓度大于或等于0.1%。
4.但第3段不适用于:a) 指令98/70/EC所涵盖的汽车燃料;b) 用于工业生产的物质或混合物,其苯释放量不得超过现行法规规定。


Annex 2: Registration Categories and Application Information Requirements of Chemical DrugsI Registration Categories1) New chemical entity never marketed in any country.i. Drug substance and its preparations made by synthesis or semi-synthesis.ii. Chemical monomer (including drug substance and preparation) extracted from natural sources or by fermentation.iii. Optical isomer (including drug substance and preparation) obtained by chiral separation or synthesis.iv. Drug with fewer components derived from marketed multi-component drug.v. New combination products.vi. A preparation already marketed in China but with a newly added indication not yet approved in any country.2) Drug preparation with changed administration route and not marketed in any country3) Drug marketed ex-China, including:i. Drug substance and its preparations, and / or with changed dose form, but no change of administration route.ii. Combination preparations, and / or with changed dose form, but no change of administration route.iii. Preparations with changed administration route and marketed ex-China.iv. A preparation already marketed in China but with a newly added indication approved ex-China.4) Drug substance and its preparation with changed acid or alkaline radicals (or metallic elements), but without any pharmacological change, and the original drug entity already approved in China.5) Drug preparation with changed dose form, but no change of administration route, and the original preparation already approved in China,6) Drug substance or preparation following national standard.II Application Dossier ItemsA Summary1) Name of the drugs.2) Certified Documents.3) Objectives and basis for R & D.4) Summary of main study work.5) Draft of packaging insert, note to the draft, and latest literature.6) Design of packaging and labeling.B Pharmaceutical data7) Summary of Pharmaceutical Study,8) Research information and relevant literature of the production process of the drug substance, research information and relevant literature of formula and process of the preparations.9) Study information and relevant literature for the chemical structure and components determination.10) Study information and literature for quality specification.11) Draft of quality specification and notes, and providing reference standard.12) Test report of drug sample.13) The source, test report and quality specification of drug substance and excipient.14) Stability study and relevant literature.15) Selection basis and quality specification of immediate packing material and container.C Pharmacology and toxicology study information.16) Summary of pharmacology and toxicology study.17) Primary pharmacodynamics study and literature.18) General Pharmacology study and literature.19) Acute/single dose toxicity study and literature.20) Repeated dose toxicity study and literature.21) Special safety study and literature of hypersensitive (topical, systemic and photo-toxicity), hemolytic and topical irritative (blood vessel, skin, mucous membrane, and muscle) reaction related to topical and systemic use of the drugs.22) Study and relevant literature on Pharmacodynamics, toxicity and pharmacokinetics change caused by the interactions amongst multiple components in the combination products.23) Study and literature of mutagenicity test.24) Study and literature of reproductive toxicity.25) Study and literature of carcinogenicity test.26) Study and literature of drug dependence.27) Study and literature of pre-clinical pharmacokinetics.D Clinical Study Information28) Summary of global clinical study information.29) Clinical study protocol.30) Investigator’s Brochure.31) Draft of Informed Consent Form, approval of the Ethics Committee.32) Clinical study report.III Notes to Application Information Items1) Information Item 1, Name of the drugs, includes International Nonproprietary Name (INN), Chemical Name, English Name, and Chinese Phonetics. Chemical structure, Molecular Weight, Molecular Formula shall be noted. The Nomenclature of the drug should be explained for any new name.2) Information Item 2, Certified Documents, includes,i. Certified Documents of lawful registration of the Applicant, copies of Drug Manufacturing License, GMP Certificate. For the application of production of new drugs, copies of GMP Certificate for the workshop where the sample product of the drugs was manufactured should be provided.ii. Certified Documents stating patent status and ownership of this entity and formula, production process of the drug, and letter of guarantee stating that no infringement upon the patent rights of others.iii. Copies of official approvals of the research proposal of narcotics, psychotropic, medical-use toxic drugs and radioactive drugs.iv. For the application of production of new drugs, copy of Approval of Clinical Study of New Drugs and the quality standard of investigational drugs should be provided for the market authorization approval.v. For the application of production of preparation, certified documents to evidence the legal channels of drug substance should be provided, including copies of certified approval document of drug substance, drug standards, test report, business licenses of manufacturers of drug substance, Drug Manufacturing License, GMP Certificate, sales invoice, and supply contract. vi. Copies of the Drug Packing Material and Container Certificate or Import Drug Packing Material and Container Certificate for the immediate packing material and container.3) Information Item 3, objectives and basis of the application, includes R&D, marketing status, and the related literature of the drugs, as well as the summary of the use and production of the drugs, domestically and overseas,4) Information Item 4, summary and evaluation of main research results, includes the summary of main research results by the Applicant, and a comprehensive analysis of safety, efficacy, and quality controllability of the drugs of the application.5) Information Item 5, draft of insert sheet, notes to the draft and latest literature, includes the sample of draft of packaging insert sheet drafted in accordance with the relevant regulations, notes on how each items of the insert sheet were drafted, latest relevant literature.6) Information Item 7, Summary of Pharmaceutical Study, refers to the summary of experiment and global literature of Pharmaceutical Study of the drug in the application (synthesis process, selection of dosage form, screening of formula, determination of structure, quality study and determination of quality standards, and stability study).7) Information Item 8, research information of the production process of the drug substance, includes technology process and chemical reaction equation, initial raw material and organic menstruum, reaction conditions (temperature, pressure, duration, catalyst) and operation procedure, refining method and main physical-chemical constants. The raw material input, and output yield, as well as possible impurities or other by-products produced or mixed during the production process should be explained.8) Information Item 10, experiments information and literature for quality research, includes physical-chemical properties, purity inspection, dissolution, assay, and methodology validation, as well as the data and results collected at various stages.9) Information Item 11, draft of drug quality specification and notes, and reference standard shall be provided: Quality specification shall comply with the format of the current version ofChinese Pharmacopoeia, and the terminology and units of measure of Chinese Pharmacopoeia should be used. Reagents, reagent solution, buffer solution, titrant and others used and their concentration should follow the current version of Chinese Pharmacopoeia. In the event of a different one was used, detailed explanations should be provided. Reference standard shall be provided with separate information attached to explain the source, physical-chemical constants, purity, content, and measurement method and data of the drugs.Notes to the draft of drug standards shall include the selection of items to be controlled, selection of method, inspection and purity and limitation range, as well as the basis to decide each item.10) Information Item 12, the test report of the sample products, means the self-test report of the sample products of the drugs in the application. Self-test report for at least one batch of sample product should be provided before the clinical study. Self-test reports of the consecutive 3 batches of sample products should be provided for the market authorization approval after completion of the clinical study.11) Information item 14, experiments information and literature of the stability study of the drugs, includes stability test conducted together with the use of the immediate packing material and container.12) Information item 16, Summary of pharmacology and toxicology study, refers to the summary of experiment and global literature of pharmacology and toxicology study of the drug in the application (including pharmacodynamics, mechanism of action, general pharmacology and toxicology, and pharmacokinetics).13) Information item 27, summary of pre-clinical pharmacokinetics, refer to the summary of experiment and literature of pre-clinical pharmacokinetics (animal) of the drug in application (absorption, metabolite, distribution, execration)14) Information item 28, Summary of global clinical study information, refers to summary of global literature, abstract and latest updating regarding the clinical trial of the drug in the application.15) Information item 29, Clinical study protocol: Clinical study protocol should cover details to deal with the critical items including proposed indication, usage and dosage, which should be supported with submission of study information. Clinical study protocol should be scientific, complete and there should be a comprehensive summary of pre-clinical and clinical information related to the key analysis of the potential risks and benefit of proposed trials.16) Information item 29, Investigator’s Brochure, refers to summary of existing pre-clinical and clinical information of the drug in the application, for the purpose to provide Investigator and other participators with information to aid them in understanding the characteristic of the drug and Clinical study protocol. Investigator’s Brochure should be concise and objective.IV Table of Application Information Item and NotesA Table of Application Information ItemInformation category information item Registration category and information item requirement1 2 3 4 5 6Summary information 1 ++++++2 ++++++3 ++++++4 ++++++5 ++++++6 ++++++Pharmaceutical Information 7 ++++++8 + *5 ++ *5 *59 ++++++10 ++++++11 ++++++12 ++++++13 ++++++14 ++++++15 ++++++Pharmacology and toxicology study information 16 ++++++17 + *16 ± *18 --18 + *16 ± *18 --19 + *16 ± *18 --20 + *16 ± *18 --21 *19 *19 *19 *19 *19 *1922 *13 -----23 + ± ± ±--24 + ± ± ±--25 *8 - *8 *8 --26 *9 -----27 + *20 *20 + *20 -Clinical Study information 28 ++++++29 +++++△30 +++++△31 +++++△32 +++++△Notes:1. + Denote the information must be submitted,Denote±2. literature can be used instead of test information,Denote the-3. information may be exempted,Denote the information shall be submitted*4. 8 refer to note 8.*according to the requirement,5. △denote that the provisions 4 of “V , Requirement For Clinical Study” shall apply.6. literature refers to literature and / or summary of literature of all Pharmacology and toxicology study information of the drug in the application (including pharmacodynamic, mechanism of action, general pharmacology and toxicology and pharmacokinetics)B Notes1) Drugs under Registration Categories 1-5 refer to as new drugs. Drugs under Registration Category 6 refer to as the drugs already following National Standards. New indications referred in Registration Categories 1.6 and 3.4 mean the cases where preparation already marked in China add new indications that are different with the original indication in term of作用机制.2) Information Items 1-30 (except Information Item 6) shall be submitted for the application for new drugs as required under the Table of Application Information Items. Re-compiled summary Information Items 1-6, Information Item 12 and 14, clinical Information Items 28-32 and other changes and supplemental information shall be submitted and numbered with the numbers of Information Items upon the completion of the clinical study.For the drugs under Registration Category 1, upon the completion of the clinical study, all the required information of Information Items 1-30 should be re-edited according to the result of trails conducted during clinical study, and then be re-submitted.When the registration of drug substance and registration of preparation of the chemical drug under Registration Category 3 and 4 are applied at the same time, the registration of drug substance should comply with the requirement for production.3) Information Items 1-16 and 28-30 shall be submitted for the application for a drug already with National Standard as required under the Table of Application Information Items. If the clinical study was required, upon completion of the clinical study, Information Items 28-32 and other changes and supplemental information shall be submitted and numbered with the numbers of Information Items.4) During the registration of the drug already with National Standards, there should be a comprehensive quality study of the process and formula of the drug, and quality comparison with the already marketed drugs according to the national standards. When it is not possible to conduct the quality comparison with the already marketed drugs according to the national standards, a quality study should be conducted according to the requirement for registration of new drug, and if necessary, quality provisions in the national standard can be appended and /or revised.5) During the application only for preparations, the lawful Certified Documents to evidence the lawful sourcing of the drug substances shall be provided in 2 duplicates, which should be respectively categorized into information item 2 (certified document) and information item 13 (The source, test report and quality specification of drug substance and excipient). For the applicant using domestic drug substance, the documents that should be provided include copies of certified approval document of drug substance, drug standards, test report, business licenses of manufacturers of drug substance, Drug Manufacturing Certificate, and GMP Certificate, supply contract signed with manufacturers of drug substance, purchasing receipts.When the import drug substances were used, copies of supply contract signed with manufacturers of drug substance or its legal domestic agent, Import Drug Certificate, or Pharmaceutical Product Certificate, test report from Drug Control Institute of the local Customs, and drug standards shall be provided. During drug registration, use in investigative preparation with the drug substances without Import Drug Certificate, or Pharmaceutical Product Certificate must be approved by SFDA.6) For the registration of the drugs transformed among injections, powder for injection and intravenous infusion, the application shall be applied by the qualified enterprise with the production scope of the corresponding dosage form.7) The reproductive toxicity research information corresponding to the drug used for the people at child-bearing age should be submitted based on the natures of the indications and characteristic of the new drug8) For any of the drugs with expected treatment period longer than 6 months inclusive, or used for treatment of chronic and recurrent disease, or intermittent use for a regular period of time, experiment information or literature on Carcinogenicity should be provided, and information of carcinogenicity test or literature should be submitted for the following new drugs, based on the indication and characteristic of action:i. New drugs with chemical structure relating to the known carcinogen or the metabolite of the new drugs are similar to the known carcinogen.ii. During long-term toxicity experiment, cytotoxic effects were shown or extraordinary activation on the growth of cells in certain visceral organs and tissues were caused.iii. Drug with a positive test result during mutagenicity test.9) For new drugs acting on central nervous system, such as analgesics, depressants, stimulants, and drugs with chemical structure related to those compounds liable to cause drug dependence, experiment information of drug dependence should be submitted.10) For the new drug under Registration Category 1, toxicokinetics study should usually be conducted during the repeated doses toxicity study.11) Under the Registration Category 1, the optical isomer obtained from a known drug through chiral separation or synthetic method and its preparation, the research information and relevant literature compared between racemate and mono-isomer in areas on pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and toxicology (normally acute toxicity) should be provided to indicate the justification of the R&D. When the safety range of racemate is narrow, and the available information indicates that the unexpected toxicology (irrelevant to pharmacology) is considerably high, the toxicology test of mono isomer with repeated doses (normally lasting for 3 months) or other toxicology tests (such as reproductive toxicology) shall be provided based on the comprehensive information such as clinical course of treatment, dosage, and indications of the drugs, as well as the people using the drugs.12) For drugs under Registration Category 1 with fewer components derived from already marketed multi-component drugs, if the component did not include the substance explained in note 8 herein, then Information Items 23-25 may be exempted.13) For the new combination products under Registration Category 1, Information Item 22 should be submitted.14) For the new combination products under Registration Category 1, information of toxicity test of repeated dosage compared with single dosage should be provided, and if the - toxicitytest of repeated dosage indicated no increase in toxicity, and no change in the target tissue, Information Item 27 should be exempted.15) For the new combination products under Registration Category 1, if there is no significant change in animal pharmacokinetic study results, then Item 23-25 should be exempted.16) For the new drugs under Registration Category 2, the route of administration during the pharmacology and toxicology study should be the same with that to be used in clinical study. Generally, the pharmacokinetic test or the related toxicology study information (such as topical and repeated dose toxicity) compared with the original route of administration should be provided.17) For the drugs under Registration Category 3, the preparations with change in route of administration and already marketed overseas, emphasis should be focused more on the drug absorption or topical toxicity influenced by the excipient, and if necessary, the pharmacokinetic test or other toxicology study should be provided.18) For the new drugs under Registration Category 4, pharmacokinetic, main pharmacodynamic, normal pharmacology and acute toxicity test information compared with the already marketed drugs should be provided to reflect the difference before and after the changes, and if necessary, the research information on repeated doses toxicity and other relevant pharmacology and toxicology study should be provided. If the preparation is made by changing the acidic or alkaline radicals (or metallic elements) of the salt of a marketed drug, it has been already marketed overseas, then the application information requirement under Registration Category 3 shall be provided.19) For the drugs for topical use, in addition to the information required under the relevant Registration Category and Information Items, the information under Information Item 21 should also be submitted; topical absorption test should be conducted, if necessary.20) When there is an obvious safety concerns in the immediate, sustained and controlled released preparations (narrow safety range, significant increase in dosage), animal pharmacokinetic study information compared with the marketed immediate, sustained and controlled released preparations regular preparations should also be provided at single dose.V Requirement for Clinical Study1) For the new drugs under Registration Category 1 and 2, clinical trials should be conducted.i. Cases of patients for clinical trials should meet the statistical requirement and the minimal cases required.ii. The minimal cases required (trial group) of clinical trials are as following, 20-30 for Phase I, 100 for Phase II, 300 for Phase III, 2000 for Phase IV,iii. Phase I clinical trial of the contraceptives should be conducted following this Regulation. In Phase II clinical trial, a randomized controlled clinical study should be conducted on at least 100 pairs of subjects for at least 6 menstruation cycles. In Phase III trial, an open trial on at least 1000 cases for 12 menstruation cycles should be accomplished. In Phase IV trial, variable factors of such kind of drugs should be carefully considered to finish the trial with adequate numbers of cases.2) For the new drugs under the Registration Categories 3 and 4, human pharmacokinetic study and randomized controlled clinical trials on at least 100 pairs of subjects should be conducted.In the event of more than one indication, cases for each main indication shall not be less than 60 pairs. Human pharmacokinetics study and an open trial on at least 500 cases for 12 menstruation cycles should be accomplished for contraceptives.Human pharmacokinetics study may be exempted for the following 2 cases:preparation of topcial use with only topical treatment effect.oral preparation that not be absorbed.3) The clinical study for the new drug under Registration Category 5 should be conducted in accordance with the following principles,i. Bioequivalence trials should be conducted for oral solid preparations on normally 18-24 cases. ii. When a bioequivalence trial is difficult to be conducted for oral solid preparations or other non- oral solid preparations, clinical trails should be conducted, and cases for the clinical trials should be at least 100 pairs.iii. For the preparations of sustained and controlled released preparations, controlled human pharmacokinetic study and clinical trials related to therapeutics should be conducted on single dose and repeated doses of the drugs, and the cases for clinical trials should be at least 100 pairs.iv. For registration of drug transformed among injections, powder for injection and intravenous infusion, if the route of administration, dosage, and usage are identical with the original dosage form, the clinical study can be exempted.4) For the oral solid preparations under the Registration Category 6, bioequivalence tests should be conducted on normally 18-24 cases.If the quality of drug needs to be controlled by process and standards, clinical tests should be conducted on normally 100 cases.5) During the new drug registration of chemical drug, when at the same time the registration of injection, powder injection and intravenous infusion that made of this chemical drug is also applied, if the preparations are from the same applicant, clinical trial is only needed for one of the preparation. For other preparation, as long as requirement of exemption of clinical trail are met, clinical trail may be exempted. If the preparations are from different applicants, clinical trail should be conduction respectively.6) Application for reduction or exemption of clinical trial should be made during the application of drug registration with detail of reasons and information for reduction or exemption of clinical trials. If a clinical trial is already approved, with exception of the case where reduction or exemption of clinical trial is allowed by this Regulation, reduction or exemption of clinical trial generally should not be allowed. If there is indeed difficulty to complete the clinical trial, application should be made with detail of the basis and plan for reduction or exemption of clinical trial, where the rational should be justified in term of clinical statistic, status of group of patients in the clinical trials.7) The comparative drug used for the controlled clinical trails shall be already marketed in China. If the comparative drug must be imported, there need to be approval from SFDA. Priority in choosing the comparative drug of positive clinical test should according to the following:i. Drug from the original manufacturerii. The same drug of definite clinical test dataiii. Drug of the same active substance and route of administration but different dosage form iv. Other drug of similar mechanism of action effect and the same indication.VI Requirement on Import Chemical Drug.A Requirement of Application Information Items1) Application Information should be submitted in accordance with the requirement under Table of the Application Information Items of Chemical Drugs. For the application of the new chemical entity not yet marketed in any country, Application Information should be submitted in accordance with the Registration Category 1. For other drugs, Application Information should be submitted in accordance with the Registration Category 3. Drug under Registration Category1 refers to those that are at least in the stage of Phase II Clinical Trials ex-China.2) Information Item 5, include draft of packaging insert sheet, notes to the draft and the updated literature, the original PI from the manufacturing country, the actual commercial sample of PI used in the manufacturing country and the Chinese translation. The original commercial packaging and labeling should also be provided for Registration Category 6.3) All the clinical study information used for the market authorization approval in the original manufacturing countries shall be submitted for Information Item 28.4) All the application information shall be in Chinese with the original text attached, information in other language (ex-English) may be attached as reference. The Chinese translation shall be consistent with the original language.5) The Chinese translation of quality specification must comply with the format of the National Drug Standards of China.B Requirement and notes to the Information Item 2, Certified Documents1) Information Item 2, Certified Documents, includes,i) Certified Documents, notarized document for the free sale certificate (FSC) issued from the competent authorities of the local country or region where the manufacturer is located, and the GMP Certificate of the manufacturer, and the Chinese translation.Application for the drugs under Registration Category 1, the above Certified Documents can be submitted together with the clinical study report upon the completion of the clinical study in China. However, during the application of Clinical Trails, certified documents of GMP Certificate of the manufacturer issued by local competent drug administration where the drug is manufactured must be provided.ii) When the registration of a foreign drug manufacturer is conducted by manufacturer’s office in China, copies of Registration Certificate Of Resident Office Of Foreign Enterprise should be provided.。

REACHREACH RestrictionsREACH foresees a restriction process to regulate the manufacture, placing on the market or use of certain substances, either on their own or in mixtures or articles, within the EU territory if they pose an unacceptable risk to health or the environment. Such activities may be limited or even banned, if necessary. The restriction is designed to manage risks that are not addressed by the other REACH processes or by other Union legislation.From 1 June 2009, Annex XVII of the REACH Regulation replaced Directive 76/769/EEC on the approximation of the laws, regulations and administrative provisions of the Member States, relating to restrictions on the marketing and use of certain dangerous substances and mixtures.Regulations amending Annex XVII of REACHCommission Regulation (EU) 2021/2204 of 13 December 2021 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), as regards carcinogenic, mutagenic or reproductive toxicant (CMR) substancesCommission Regulation (EU) 2021/2030 of 19 November 2021 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regardsN,N-dimethylformamideCommission Regulation (EU) 2021/1297 of 4 August 2021 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards perfluorocarboxylic acids containing 9 to 14 carbon atoms in the chain (C9-C14 PFCAs), their salts and C9-C14 PFCA-related substancesCorrigendum to Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1297 of 4 August 2021 amending AnnexXVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council asregards perfluorocarboxylic acids containing 9 to 14 carbon atoms in the chain (C9-C14PFCAs), their salts and C9-C14 PFCA-related substances (Official Journal of the EuropeanUnion L 282 of 5 August 2021)Corrigendum: In Latvian language version only, OJ L 89, page 11, 17.03.2022Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1199 of 20 July 2021 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards polycyclic-aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in granules or mulches used as infill material in synthetic turf pitches or in loose form on playgrounds or in sport applicationsCommission Regulation (EU) 2021/57 of 25 January 2021 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards lead in gunshot in or around wetlandsREACHCommission Regulation (EU) 2020/2096 of 15 December 2020 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), as regards carcinogenic, mutagenic or reproductive toxicant (CMR) substances, devices covered by Regulation (EU) 2017/745 of the European Parliament and of the Council, persistent organic pollutants, certain liquid substances or mixtures, nonylphenol and testing methods for azocolourants (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/2081 of 14 December 2020 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards substances in tattoo inks or permanent make-up (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2020/1149 of 3 August 2020 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards diisocyanates (Text with EEA relevance)Regulation (EU) 2019/1148 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 20 June 2019 on the marketing and use of explosives precursors, amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 and repealing Regulation (EU) No 98/2013Commission Regulation (EU) 2019/957 of 11 June 2019 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards (3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,8-tridecafluorooctyl) silanetriol and TDFAs (Text with EEA relevance.) Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/2005 of 17 December 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regardsbis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP), benzyl butyl phthalate (BBP) and diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP) (Text with EEA relevance.)Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/1513 of 10 October 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards certain substances classified as carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic for reproduction (CMR), category 1A or 1B (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/675 of 2 May 2018 amending the Appendices to Annex XVII to Regulation EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards CMR substances (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/589 of 18 April 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards methanol (Text with EEA relevance)Corrigendum to Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/589 of 18 April 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerningthe Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards methanolREACHCommission Regulation (EU) 2018/588 of 18 April 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards 1-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2018/35 of 10 January 2018 amending Annex XVII to Regulation EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards octamethylcyclotetrasiloxane ('D4') and decamethylcyclopentasiloxane ('D5') (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1510 of 30 August 2017 amending the Appendices to Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards CMR substances (Text with EEA relevance)Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/1000 of 13 June 2017 amending Annex XVII to Regulation EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA), its salts and PFOA-related substanceCommission Regulation (EU)2017/227 of 9 February 2017 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regardsbis(pentabromophenyl)ether –Link to Eur-LexCorrigendum to Commission Regulation (EU) 2017/227 of 9 February 2017 amending AnnexXVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Councilconcerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards bis(pentabromophenyl)etherCommission Regulation (EU) 2016/2235of 12 December 2016 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards bisphenol A –Link to Eur-LexCommission Regulation (EU) 2016/1017ED of 23 June 2016 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards inorganic ammonium saltsCommission Regulation (EU) 2016/1005ED of 22 June 2016 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards asbestos fibres (chrysotile)Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/217 ED of 16 February 2016 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards cadmium.REACHCommission Regulation (EU) 2016/26of 13 January 2016 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards nonylphenol ethoxylates.Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/1494 of 4 September 2015 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards benzene.Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/628of 22 April 2015 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Regist ration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (‘REACH’) as regards lead and its compounds.Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/326of 2 March 2015 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalates.Commission Regulation (EU) No 474/2014 of 8 May 2014 amending Annex XVII toRegulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (‘REACH’) as regards 1,4-dichlorobenzene.Commission Regulation (EU) No 317/2014 of 27 March 2014 amending Regulation(EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII (CMR substances).Commission Regulation (EU) No 301/2014 of 25 March 2014 amending Annex XVII toRegulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards chromium VI compounds.Commission Regulation (EU) No 1272/2013of 6 December 2013 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Corrigendum: In German language version only, OJ L 109, page 49, 12.4.2014Commission Regulation (EU) No 126/2013of 13 February 2013 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH). This Regulation corrects several entries in the Annex XVII to REACH in terms of terminology and recent update of CEN methods.Commission Regulation (EU) No 848/2012of 19 September 2012 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation,REACHAuthorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards phenylmercury compounds, prohibits the manufacture, placing on the market and use of 5 phenylmercury compounds as well as placing on the market of articles containing any of those substances at a concentration level of 0.01% or more.Commission Regulation (EU) No 847/2012of 19 September 2012 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards mercury, extends the scope of entry 18a to mercury measuring devices used in industrial and professional applications.Commission Regulation (EU) No 836/2012of 18 September 2012 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards lead, prohibits the placing on the market and the use of lead in jewellery articles at a concentration level of 0.05% or above.Commission Regulation (EU) No 835/2012of 18 September 2012 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 ofthe European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII (Cadmium), in particular the use in a list of plastic materials.Commission Regulation (EU) No 412/2012of 15 May 2012 amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) in order to prohibit the use of dimethylfumarate (DMF) in articles or parts thereof, in concentrations greater than 0.1 mg/kg, as well as the placing on the market of articles or parts thereof containing DMF in concentrations greater than 0.1 mg/kg. It makes permanent an existing temporary prohibition adopted under Directive 2001/95/EC on general product safety.Commission Regulation (EU) No 109/2012of 9 February 2012 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of theEuropean Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII (CMR substances) amended Annex XVII of REACH in order to include a number of newly classified CMR substances in Appendices 1 to 6 so that they are aligned to the entries concerning CMR substances in Regulation (EC) No 790/2009 amending Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures.Commission Regulation (EU) No 494/2011of 20 May 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of theEuropean Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII (Cadmium), and, related Corrigendum OJ L 136/105of 24 May 2011. More on RestrictionsREACHCommission Regulation (EU) No 366/2011of 14 April 2011 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of theEuropean Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII (Acrylamide). More on RestrictionsCommission Regulation (EU) No 207/2011adopted on 2 March 2011 deleted Entry 44 concerningpentabromodiphenyl ether and Entry 53 concerning PFOS from Annex XVII as these substances are now regulated under Regulation (EC) No 2004/850 on Persistent organic pollutants as amended by Commission Regulation (EU) No 757/2010of 24 August 2010.Commission Regulation (EU) 276/2010adopted on 31 March 2010 amended Annex XVII of REACH in order toinclude the last restrictions adopted in 2009 under Directive 76/769/EEC that is to say the modification of the restrictions concerning lamp oils and grill lighter fluids (entry 3) and organostannic compounds (entry 20) and the new restriction concerning dichloromethane (entry 59).Commission Regulation (EC) No 552/2009of 22 June 2009 amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of theEuropean Parliament and of the Council on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) as regards Annex XVII.。

附录II技术文档制造商拟定的技术文档及其摘要(如适用)应以清晰、有条理、易于搜索和明确的方式呈现,尤其应包括本附录中列出的要素。
1、产品描述和特征,包括变体和附件/配件1.1、产品描述和规格a)产品或贸易名字和产品基本描述包括预期用途和预期使用人群b)附录VIPartC提到的制造商分配给器械的UDI-DL基于UDI系统,或产品代码,序列号或其他可参考的标识就会被立马识别c)预期用途包括以下信息:I)检测或测量物质II)功能,例如:筛查、监测、诊断或辅助诊断、预测、伴随诊断III)旨在检测、定义或区分特定疾病、情况和风险因素IV)自动或非自动V)定性、半定量或定量VI)样本类型VII)预期检测人群VIII)预期使用者IX)另外,伴随诊断需要有相关目标人群和相关药品d)检测方法或仪器操作原则的描述e)产品作为医疗器械的理由f)风险等级和分类规则的应用遵循附录VIIIg)组分的描述,和相关组分里活性成分:抗体、抗原、核酸引物(如适用)如适用:h)样本采集、和器械一起提供的运输材料,或推荐使用规格的描述i)对于自动检测的仪器:描述适用的检测性能或专用检测性能j)对于自动检测试剂:描述适用的仪器性能或专用的仪器性能k)描述与器械一起使用的软件引申:TUV l) 拟投放市场的器械的各种配置/变体的说明或完整列表m )描述预期与器械联合使用的配件、其他器械和非器械引申:TUV 解读,单独提供的配件需要单独的标签、说明书、包装和证书1.2、a) 己上市同类产品或制造商已制造产品的概览b) 已在国际市场上销售的类似产品的概览2、制造商提供的信息a) 器械上的标签或包装(例如单一包装、销售包装、运输包装)的语言应被预想销往的成员国接受b )使用说明书语言应该被预想销往的成员国接受3、设计和制造消息3.1、设计信息用于理解器械设计阶段的信息应包括:a )描述与器械一起提供或推荐一起使用的关键组分如抗体、抗原、酶和核酸引物b )对于仪器:描述主要子系统、分析技术例如操作原则、控制原理、专用电脑硬件或软件c )对于仪器和软件:描述整个系统d )对于软件:描述数据解读技术及算法e )对于预期用于自我测试或近患者测试的器械:描述自我测试或近患者测试的适用性设计方面3.2、制造信息a )生产制造过程信息,例如生产过程、装配、成品测试、成品的包装信息。

国际航行船舶货物系固手册CARGO SECURING MANUAL本手册是按照《国际海上人命安全公约》、国际海事组织Msc/Circ745号通函和“货物积载和系固安全操作规则<A.714(17)决议>”编制的。
This manual has been prepared according to the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), the IMO Msc/circ745, the Code of Safe Practice for Cargo Stowage and Securing (IMO Resolution A.714(17) ).序言(PREAMBLE)本手册是按照1974年《国际海上人命安全公约》、国际海事组织第Msc/Circ745号通函、国际海事组织决议A.714(17)以及“货物积载和系固安全操作规则”编制的。
This manual has been prepared according to the International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea , 1974(SOLAS)1994 amendment, the IMO Msc/circ745,the Code of Safe Practice for Cargo Stowage and Securing (IMO Resolution A.714(17) ).本手册应永久保留在船上, 以便船级社的验船师、港口国检查的官员以及其他有关人员的随时检查。
The manual shall always be kept on board and available for inspection by class surveyors , port/flag state inspectors and others to whom it may concern.如系固装置和对系固手册的要求有变化, 本手册应修订并送船级社或主管当局重新批准。


OMCL Network of the Council of Europe QUALITY ASSURANCE DOCUMENTPA/PH/OMCL (16) 17 RQUALIFICATION OF EQUIPMENTANNEX 2: QUALIFICATION OF GC EQUIPMENTFull document titleand referenceQualification of EquipmentAnnex 2: Qualification of GC EquipmentPA/PH/OMCL (16) 17 RDocument type GuidelineLegislative basis The present document was also accepted by EA asrecommendation document to be used in the context of QualityManagement System audits of OMCLsDate of first adoption May 2006Date of original entryinto forceJune 2006Date of entry intoforce of reviseddocumentJuly 2016Previous titles/otherreferencesThis document replaces PA/PH/OMCL (06) 86 DEFCustodianOrganisationThe present document was elaborated by the OMCLNetwork/EDQM of the Council of EuropeConcerned Network GEONANNEX 2 OF THE OMCL NETWORK GUIDELINE“QUALIFICATION OF EQUIPMENT”QUALIFICATION OF GC EQUIPMENTIntroductionThe present document is the second Annex of the core document “Qualification of Equipment”, and it should be used in combination with it when planning, performing and documenting the GC equipment qualification process.The core document contains the general introduction and the Level I and II of qualification, common to all type of instruments, and the present annex contains GC instrument-related recommendations on parameters to be checked and the corresponding typical acceptance limits, as well as practical examples on the methodology that can be used to carry out these checks.The tests proposed in the Level III and IV of qualification are based on an overall approach, in which several parameters are checked at the same time in a combined test procedure, to obtain information on the overall system performance (e.g. peak area precision, retention time precision, temperature programme reproducibility, etc).Nevertheless, it should be noted that it is also acceptable to check these parameters individually by using other well-defined procedures.Level III. Periodic and motivated instrument checksExamples of requirements for GC instruments with FIDInstrumentmoduleParameter to be checked Typical tolerance limits1. Inlet system1.1 Injector leak testPressure drop ≤ 15 kPawithin 5 minutes1.2. Pressure/flow accuracy and stability Covered by overall test 1 1.3. Repeatability of GC injections (overall test 1)Peak areas:- In split mode- In split less modeRetention times:RSD ≤ 3.0%RSD ≤ 3.0%RSD ≤ 2.0%1.4. Injector temperature accuracy and stability Covered by overall test 2 1.5. Carry-over (overall test 3) ≤ 0.2%Head space injector1.6. Repeatability of Headspace injections- Peak areas:- Retention times:1.7Vial heater temperatureRSD ≤ 5.0 %RSD ≤ 2.0%± 4°C from set point2. Oven 2.1. Repeatability of oven temperature characteristics Covered by overall test 23. FID detector 3.1. Linearity (overall test 3) r2≥ 0.9993.2. Constant detector response Covered by overall test 1 or 2 3.3. Noise See Annex I3.3. Drift See Annex ILevel IV. In-use instrument checksExamples of requirements for GC instruments with FID Parameter to be checked Typical tolerance limits1. System suitability check for the method According to Ph. Eur. or MAH dossier or validated in-house method2. Peak area precision- GC injections- Headspace injections RSD ≤ 3.0% unless otherwise prescribed* RSD ≤ 5.0% unless otherwise prescribed*3. Retention time repeatability RSD ≤ 2.0%4. Sensitivity (where relevant, e.g. for related substances tests) According to Ph. Eur. or MAH dossier or validated in-house method* This is to be defined in conjunction with the target concentration of the analyteAll parameters given here should be checked when performing analyses under the working conditions for the actual sample determinations. Normally, the test and reference solutions to be prepared for this purpose are given as a part of the method.Level III. Periodic and motivated instrument checksPractical examples of tests and their associated tolerance limits for several parameters related to the performance of the different modules of a GC are presented below.These examples can be considered by the OMCLs as possible approaches to perform the Level III of the equipment qualification process: “Periodic and motivated instrument checks”. Several tests are proposed to check various parameters at the same time (overall tests). In order to run the tests in a more economical way, other suitable solutions can be used, as for example, the “Grob Test” mixture, available from different suppliers (e.g. Alltech, Sigma, Thames Restek). This commercial solution should be appropriate to the column material used. It is recommended to run the overall tests by using always the same test column, exclusively dedicated to qualification purposes, to guarantee reproducible conditions.1. INLET SYSTEMThe following tests are proposed for the periodic and motivated check of the GC Inlet System.1.1. INJECTOR LEAK TESTMethod:If not otherwise specified by the instrument manufacturer, the leak test is carried out according to the procedure laid down in the instrument manual or by the built in automatic leak check procedure of the instrument.Otherwise use the test described below:Disconnect the column from the injector and close the injector outlet with a sealed cap.Close the septum purge and the bypass.Adjust the flow and pressure controller to the maximal possible value of the pressure gauge. Adjust the flow controller to zero.Read the pressure after 1 minute and record the value.Record the pressure after 5 minutes.Limits:Pressure drop ≤ 15 kPa within 5 minutes.1.2. INLET PRESSURE/FLOW ACCURACY AND STABILITYA direct measurement of these parameters was not deemed practical or necessary, but the optimal conditions of flow/pressure can be verified by the overall test 1.Limits: refer to overall test 1.1.3. REPEATABILITY OF GC INJECTIONThe verification of this parameter is covered by the overall test 1.This test is to be performed in both split and split less mode.Limits: refer to overall test 1.1.4. INJECTOR TEMPERATURE ACCURACY AND STABILITYDue to the fact that the temperature cannot be reliably measured without opening and modifying the system and due to the difficulties of introducing a probe inside this module, the verification of this parameter is considered to be covered by the overall test 2.Limits: refer to overall test 2.1.5. INJECTOR CARRY OVERAfter having injected the solutions for the linearity test of the FID detector, in increasing order, inject the blank and measure the peaks that correspond to the major peaks (= analytes) in the linearity solutions.The verification of this parameter is covered by the overall test 3.Limits: refer to overall test 3.HEAD SPACE INJECTORS1.6. REPEATABILITY OF HEADSPACE INJECTIONSMethod:The GC-HS operating conditions below are provided as an example, adjustments may be needed depending on the equipment used.Test solution: 0.5 % ethanol in water R (V/V)GC-Settings:Column: 95% Dimethyl / 5% diphenylpoly siloxane 30 m x 0.25 µm; 0.25 mm (HP-5 was found suitable)Carrier gas: HeliumColumn Flow: 1.2 ml/minInjector temperature: 200 °CSplit ratio: 1:50Oven temperature: 40°C isothermDetector temperature: 250 °CRun time: 1.5 folds the retention time of the main peakRetention time: about 2.2 minHeadspace-Settings:Carrier pressure: 9.9 psiVial pressure: 14.2 psiShake: lowOven Temperature: 80 °CLoop Temperature: 90 °CTransfer line Temperature: 100 °CVial size: 20 mLVolume of sample solution/vial: 5 mLVial Equilibration Time: 15.0 minInject Time: 1.0 minLoop Equilibration Time: 0.1 minLoop Fill Time: 0.5 minVial Pressurization Time: 0.08 minCarry out 6 consecutive injections of the test solution and calculate the RSD of the different peak areas and retention times.Limits:Peak areas: the RSD should be ≤ 5.0%Retention time: the RSD should be ≤ 2.0%1.7 VIAL HEATER TEMPERATUREThe heater temperatures are to be set up at values which depend on the operating conditionsof the methods applied.Suitable calibrated temperature devices are to be used.Put the calibrated device in the oven of the head space compartment. Set the temperature at the required values. When equilibration is achieved, record the value displayed on the calibrated device.Limits: ± 4°C from set point2. OVEN2.1. REPEATABILITY OF THE OVEN TEMPERATURE CHARACTERISTICSDue to the fact that the temperature cannot be reliably measured without opening and modifying the system conditions and that even when introducing a probe inside the oven, its location would not reflect the real temperature conditions at all points, the verification of this parameter is covered by the overall tests 2A and 2B.Limits: refer to overall test 2.3. FID DETECTORThe following tests are proposed for the periodic and motivated check of the GC FID detector.3.1. FID DETECTOR LINEARITYIncreasing amounts of analyte are injected and a linear response should be obtained.The verification of this parameter is covered by the overall test 3.Limits: refer to overall test 3.3.2. CONSTANT FID DETECTOR RESPONSEThe proper and reproducible functioning of the FID can be demonstrated by checking the peak areas obtained from a pre-defined standard solution.The verification of this parameter is covered by the overall test 1 or 2.Limits: refer to overall test 1 or 2.3.3. FID DETECTOR NOISE AND DRIFTIf the instrument has a built-in automatic system for the verification of the noise and drift, follow the manufacturer’s instructions and apply the defined acceptance criteria. Otherwise, use the test described below:Settings:Column installedSuitable flow, depending on column length/diameterNo injectionOven temperature: 40°CDetector on and heated at working temperature (270-300°C)Method:After stabilisation of the system, record the signal for 15 minutes.Noise: evaluate 10 periods of 1 minute and calculate the mean value.Drift: evaluate the slope of the baseline over the 15 minutes.Limits:The acceptance criteria for these parameters have to be chosen in accordance with the instrument vendor’s instructions and the intended use of the instrument. If no instructions are given, the user has to pre-define these acceptance criteria by taking into account the previous experience and the intended use of the instrument.No fixed values can be pre-defined in this guideline due to the high variety of integration systems used and consequently the acceptance criteria may be expressed in different units (voltage, current, arbitrary units per time).OVERALL TEST 1The overall test 1 covers the following parameters:-Pressure/flow accuracy and stability in the inlet system: Retention time repeatability -Repeatability of injection: peak area precision-In split mode-In split less modeThe test may be combined with overall test 3.Split mode:Test solution:1-octanol in n-hexane 1% (V/V).Settings:Column: 100% Dimethylpolysiloxane 30m x 0.32mm ID x 0.25µm film (SPB-1 was found suitable)Carrier gas: HeliumVelocity: 25cm/secSplit: 1:100Injection: 1µlInjector temperature: 220°COven temperature: 100°C isothermDetector temperature: 300°CRun time: 1.5 folds the retention time of the main peakRetention time of 1-octanol: about 5 minSplit less mode:Stock solution: 1-octanol in n-hexane 1% (V/V)Test solution: Dilute 10 ml of the stock solution with n-hexane to 100 ml (corresponds to 1µl/ml of 1-octanol in n-hexane)Settings:Column: 100% Dimethylpolysiloxane 30m, 0.32mm ID, 0.25µm film (SPB-1 was found suitable)Carrier: HeliumVelocity: 30cm/secSplit less injection: purge valve closed during 2 minInjection: 0.2µl of the test solutionInjector Temperature: 220°COven Temperature: Initial 60°C for 4 min, 15°C/min. up to 135°C, final time 1minDetector temperature: 300°CRuntime: 1.5 folds the retention time of the main peakRetention time of 1-octanol: about 8 minMethod:Carry out 6 consecutive injections of the test solution and calculate the RSD of the different peak areas and retention times.Limits:Retention time repeatability: the RSD of the retention times should be ≤ 2.0%Peak area precision (split and split-less mode): the RSD of the peak areas should be ≤3.0%OVERALL TEST 2The overall test 2 covers the following parameters:-Injector, oven and detector temperature accuracy and stability: retention timerepeatabilityTwo alternative tests are proposed:Overall test 2ATest solution:0.035 ml 1-octanol0.035 ml 2-octanone0.035 ml 2,6-dimethylanilin0.035 ml n-tridecane0.035 ml n-tetradecane35 mg n-eicosanedissolved in 50 ml DichloromethaneSettings:Column: 100% Dimethylpolysiloxane 30m x 0.32mm ID x 0.25µm film (SPB-1 was foundsuitable)Carrier gas: HeliumVelocity: 25 cm/sSplit: 1:100Injection volume: 1 µlInjector temperature: 220°CDetector: FIDDetector temperature: 300°CGradient programme: 60°C (4 min), 5°C/min, 270°C (3 min)Method:Inject the solution twice and calculate the relative retention (RR) times in relation to n-eicosane (RR = 1)The following table shows the approximately expected relative retention times.Analyte 1-octanol 2-octanone 2,6-dimethylaniline n-tridecane n-tetradecaneRRT 0.30 0.22 0.37 0.52 0.60Limits:The RSD of each RR from two consecutive injections should be ≤1.0%Overall test 2BTest Solution:1.0% (m/m) n-Nonane and Hexadecane in Tetradecane.Settings:Column: 100% Dimethylpolysiloxane 25m x 0.32mm ID x 0.52µm film (Ultra-1 was found suitable)Injection volume: 1 μlSolvent: TetradecaneOven temperature: 110°CGradient programme: 110°C, 20°C/min, 180°C (final time: 3.5 min)Detector temperature: 250°CInjector temperature: 200°CDetector: FIDFlow rates: as defined by the instrument manufacturerSplit ratio: 1:15Split vent: 30 ± 3.0 ml/minSeptum purge: 3-5 ml/minMethod:Allow the system to equilibrate.Injection sequence:1)blank (Tetradecane)2) 6 replicates of the test solution. Calculate the mean of the retention times and peakareas and the relative standard deviation of n-Nonane and n-Hexadecane.Limits:Retention time repeatability: RSD of the peak retention times of the 6 replicates ≤ 2.0% Retention time (Rt) accuracy: for this example, the retention time ranges shown in the table below are proposed. Nevertheless, individual ranges should be predefined by the laboratory depending on the column used (e.g. Rt ± 0.2 min).(min)Compound Rtn-Nonane (C9) 1.3 – 1.7Tetradecane (C14) 4.0 – 4.7Hexadecane (C16) 5.1 – 6.0OVERALL TEST 3This test is a modified version of the overall test 1 to be used for the verification of: -Detector linearity: linearity of the areas recorded-Injector carry-over: area recorded in the blank runIt is described for both split and split less mode and may be combined with overall test 1.Split mode:Test solution: 1-octanol in n-hexane 1% (V/V)Prepare further reference solutions by diluting the test solution as described below. Settings: see overall test 1Injection sequence:5.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (2 µl/ml): 2 injections10.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (4 µl/ml): 2 injections15.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (6 µl/ml): 2 injections20.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (8 µl/ml): 2 injectionsi f combined with overall test 1 for repeatability: test solution (10 µl/ml): 6 injectionsn-hexane as blank (carry over)Split-less mode:Stock solution: 1-octanol in n-hexane 1% (V/V)Test solution: Dilute 10 ml of the stock solution with n-hexane to 100 ml (corresponds to 1µl/ml of 1-octanol in n-hexane).Prepare further reference solutions by diluting the test solution with n-hexane.Settings: see overall test 1Injection sequence:5.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (0.2 µl/ml): 2 injections10.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (0.4 µl/ml): 2 injections15.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (0.6 µl/ml): 2 injections20.0 ml of the test solution diluted to 25.0 ml with n-hexane (0.8 µl/ml): 2 injectionsif combined with overall test 1 for repeatability: test solution (1 µl/ml): 6 injectionsn-hexane as blank (carry over)Limits:Linearity: coefficient of correlation of the calibration line obtained with the reference solutions and the test solution: r2≥ 0.999.Carry-over: the percentage of the peak area corresponding to the analyte in the blank solution should be ≤0.2% of the peak area of this analyte in the chromatogram obtained with the solution with the highest concentration within the sequence.。
Rev. 2.1, 08/2009© Copyright RapidIO Trade AssociationRapidIO ™ Interconnect Specification Annex 2: Session Management Protocol SpecificationRevision HistoryRevision Description Date2.0First release06/14/20072.0Public release03/06/20082.1No technical changes MM/DD/200Y2.1Removed confidentiality markings for public release08/13/2009NO WARRANTY.THE RAPIDIO TRADE ASSOCIATION PUBLISHES THE SPECIFICATION “AS IS”. THE RAPIDIO TRADE ASSOCIATION MAKES NO WARRANTY, REPRESENTATION OR COVENANT, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, OF ANY KIND CONCERNING THE SPECIFICATION, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, NO WARRANTY OF NON INFRINGEMENT, NO WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY AND NO WARRANTY OF FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. USER AGREES TO ASSUME ALL OF THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH ANY USE WHATSOEVER OF THE SPECIFICATION. WITHOUT LIMITING THE GENERALITY OF THE FOREGOING, USER IS RESPONSIBLE FOR SECURING ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY LICENSES OR RIGHTS WHICH MAY BE NECESSARY TO IMPLEMENT OR BUILD PRODUCTS COMPLYING WITH OR MAKING ANY OTHER SUCH USE OF THE SPECIFICATION.DISCLAIMER OF LIABILITY. THE RAPIDIO TRADE ASSOCIATION SHALL NOT BE LIABLE OR RESPONSIBLE FOR ACTUAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, EXEMPLARY OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS) RESULTING FROM USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE SPECIFICATION, ARISING FROM ANY CAUSE OF ACTION WHATSOEVER, INCLUDING, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, WARRANTY, STRICT LIABILITY, OR NEGLIGENCE, EVEN IF THE RAPIDIO TRADE ASSOCIATION HAS BEEN NOTIFIED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.Questions regarding the RapidIO Trade Association, specifications, or membership should be forwarded to:12343 Hymeadow, Suite 2-R(non-US mail deliveries to Suite 3-E)Austin, TX 78750512-401-2900 Tel.512-401-2902 FAX.RapidIO and the RapidIO logo are trademarks and service marks of the RapidIO Trade Association. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1Table of ContentsChapter 1 Overview1.1Introduction (11)1.2Overview (11)1.3Features of the Session Management Protocol (12)1.4Contents (12)1.5Terminology (13)1.6Conventions (14)1.7Useful References (14)Chapter 2 Managing Data Streams2.1Introduction (15)2.2System Example (15)2.3Establishing Data Streams (16)2.4Data Streaming System Configurations (17)Chapter 3 Session Management Operation3.1Introduction (19)3.2Initialization of Session Management Advertisement CSRs (19)3.3Contacting a Participating End point (20)3.4Establishing Conduits (21)3.4.1Master/Slave Configuration Conduit Establishment (22)3.4.2Peers Configuration Conduit Establishment (23)3.4.3Conduit Establishment Algorithm (24)3.5Management Messages (26)3.5.1Session Management Message Types (26)3.5.1.1REQUEST (26)3.5.1.2ADVERTISE (26)3.5.1.3OPEN (27)3.5.1.4ACCEPT (27)3.5.1.5REFUSE (27)3.5.1.6FLOW-CONTROL (27)3.5.1.7DATA (27)3.5.1.8CLOSE (27)3.5.1.9STATUS (28)3.5.2Message Header Fields (28)3.5.2.1Command Header Field: <CMD><VER> (28)3.5.2.2SourceID and DestID (28)3.5.2.3Protocol Identifier: <ProtoID> (29)3.5.2.4Class of Service: <COS> (29)RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1Table of Contents3.5.2.5Stream Identifier: <StreamID> (29)3.5.3Session Management Protocol Attributes (30)3.5.3.1VENDOR Attribute (31)3.5.3.2DATA_OFFSET_VENDOR Attribute (31)3.5.3.3DATA_OFFSET Attribute (32)3.5.3.4REQUEST_RETRY_PERIOD Attribute (32)3.5.3.5REQUEST_TIMEOUT_PERIOD Attribute (32)3.5.3.6FLOW_CONTROL_XON_TIMEOUT_PERIOD Attribute (33)3.5.3.7OPEN_MESSAGE_NUMBER Attribute (33)3.5.3.8CONDUIT_STREAM Attribute (33)3.5.3.9DATA_HEADER_FORMAT Attribute (34)3.5.3.10CONVEYANCE Attribute (34)3.5.3.11Other Attributes (34)3.6Message Sequence Examples (35)3.6.1Stream Initiation (35)3.6.2Refusal to Initiate a Stream (35)3.6.3Stream Shutdown (36)3.6.4Uses of the STATUS command (37)3.6.5Use of the FLOW_CONTROL Command (38)3.7Session Management Error Conditions and Recovery (39)3.7.1Message Loss (39)3.7.2Session Management Protocol Congestion Management (40)3.7.3Session Management Protocol Non-Compliance (40)3.8Rules for Session Management (41)3.8.1Optional Features (41)3.8.2Attribute Related Rules (41)3.8.3Rules Related to Virtual Stream Status (42)3.8.4Rules Related to Vendor-Specific Commands (42)3.8.5Rules Related to Reserved Fields (43)3.9Notes on Optional Features and Inter-Operability (43)3.9.1Optional Attributes (43)3.9.2REQUEST and ADVERTISE (44)Chapter 4 Message Format Descriptions4.1Introduction (45)4.2Control Message Formats (45)4.2.1REQUEST (45)4.2.2ADVERTISE (46)4.2.3OPEN (47)4.2.4ACCEPT (48)4.2.5REFUSE (49)4.2.6FLOW_CONTROL (49)4.2.7CLOSE (50)4.2.8STATUS (51)4.2.9User Defined (52)RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1 Table of Contents4.3Data Formats (53)4.3.1DATA Message Format, MAILBOX (53)4.3.2DATA1 Message Format, Large PDU (54)4.3.3DATA2 Message Format (54)4.3.4DATA3 Zero-length DATA header (54)4.3.5Data Streaming (55)Chapter 5 Registers5.1Introduction (57)5.2Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block (58)5.2.1Session Management Protocol Register Block Header (Block Offset 0x0) (58)5.2.2Session Management Protocol Register Write Enable CSR(Block Offset 0x4) (59)5.2.3Session Management Advertisement CSR (Block Offset 0x8) (60)5.2.4Session Management Attribute Range CSR (Block Offset 0xC) (61)5.2.5Session Management Protocol Attributes 0-508 CSRs(Block Offset 0x10-0x7F8) (63)5.3Component Tag CSR Session Management Protocol Advertisement (64)Chapter 6 Vendor-Defined Protocols6.1ProtoID (67)6.2Attributes (67)6.2.1VENDOR attribute (67)6.2.2PROTOCOL_NAME attribute (67)6.2.3Other attributes (67)6.3Other Requirements for Vendor-Defined Protocols (67)Chapter 7 Ethernet Encapsulation7.1ProtoID (69)7.2Attributes (69)7.2.1MTU Attribute (69)7.2.2CONVEYANCE Attribute (69)7.2.3MAC_ADDRESS Attribute (69)7.3Other Requirements of Ethernet Encapsulation (69)7.3.1Dropped Messages (70)7.3.2Broadcast (70)7.3.2.1Broadcast With Multicast Extensions (70)7.3.2.2Broadcast Without Multicast Extensions (70)7.3.2.3Vendor defined Broadcast Server (70)7.3.3Ingress/Egress Nodes (70)RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1 Table of ContentsBlank pageRapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1List of Figures1-1Data Streaming (11)2-1Example of a RapidIO-Based Networking System (15)2-2Stream Process (16)3-1Normal Stream Initiation (35)3-2Use of REFUSE Command (35)3-3Normal Stream Shutdown (36)3-4Use of the STATUS Command (37)3-5Use of the FLOW_CONTROL Command (38)RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1 List of FiguresBlank pageRapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1List of Tables2-1Data Streaming System Configurations (17)3-1StreamID Assignments (29)3-2System Management Protocol Attribute Sizes (30)3-3Vendor-Specific Attribute Ranges (30)3-4System Management Protocol Attribute Sizes (31)3-5System Management Protocol Attribute Sizes (31)3-6DATA_OFFSET Attribute Format (32)3-7DATA_HEADER_FORMAT Attribute Values (34)3-8Ethernet Encapsulation Conveyance (34)4-1REQUEST Message Format (45)4-2ADVERTISE Message Format - Protocol Attributes (46)4-3ADVERTISE Message Format - Protocol List (47)4-4OPEN Message Format (48)4-5ACCEPT Message Format (48)4-6REFUSE Message Format (49)4-7FLOW_CONTROL Message Format (50)4-8CLOSE Message Format (50)4-9STATUS Message Format (51)4-10Status Bit Values (51)4-11USERDEFINED Message Format (52)4-12DATA Message Format (53)4-13DATA Message Format (54)4-14DATA Message Format (54)5-1Bit Settings for Session Management Protocol Register Block Header (58)5-2Bit Settings for Session Management Protocol Register Write Enable Register (59)5-3Bit Settings for Session Management Protocol Advertisement Register (60)5-4Bit Settings for Session Management Attribute Range Register (61)5-5Bit Settings for Session Management Protocol Attributes 0-508 Registers (63)5-6Component Tag CSR Bit Usage (64)RapidIO Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1 List of TablesBlank pageChapter 1 Overview1.1 IntroductionThe Session Management Protocol permits system software to establish, manage, and remove virtual streams as defined in RapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 10: Data Streaming Logical Specification Rev. 2.1. The data streaming protocol allows data of any format to be transported between two end points. The Session Management Protocol provides a method for two end points to negotiate the characteristics of the data stream and assign those characteristics so the receiving entity can use the appropriate software layers upon receiving the data stream.1.2 OverviewA stream, is a unidirectional connection between two end points. Bidirectional traffic is carried over two streams, one in each direction.Figure 1-1. Data Streaming The end points must have a common understanding of what the data within the stream is, and associate the stream with the right end point process. One of the principles of the data streaming protocol is the use of virtual streams . A virtual stream contains a generic tag called the virtual stream ID (VSID). The VSID is assigned by the destination, based on the destination’s method for decoding, and may be a software or a hardware feature.VSIDs are unique between any pair of source and destinations. The Session Management Protocol allows a source and destination to discover what protocols the two can use to communicate, assign a VSID to carry that protocol, establishing an open stream. Once open, a stream can carry any number of protocol data units (PDUs) until the stream is not longer needed. The Session Management Protocol is then used to close the stream.Stream A Stream BEnd pointProtocolSoftware End point Protocol SoftwareThe Session Management Protocol is intended to manage streams of communication. When data is passed using Type 9 (Data-Streaming Class) as the conveyance, the streamID used for Session Management Protocol is the same as the streamID used for Type 9 data traffic. When the data are passed using Type 11 (Message Class) as the conveyance, the streamID used for Session Management Protocol can be encapsulated in the command header of the DATA or DATA1 commands, as defined in Section 4.3.1.3 Features of the Session Management ProtocolThe Session Management Protocol provides the following features:• A method to contact the session management software running on any end point.• A method to discover which protocols an end point is capable of receiving.• A method to discover and assign streams.• A method to manage the status of streams.• A method to close active streams.• A method to handle errors and to handle protocol violations.1.4 ContentsFollowing are the contents of the RapidIO Interconnect Specification Annex 2: Session Management Protocol Specification Rev. 2.1:• Chapter 1, “Overview,” is an overview of the Session Management Protocol specification.• Chapter 2, “Managing Data Streams,” introduces system issues such as discovery and transport configurations.• Chapter 3, “Session Management Operation,” describes the set of messages defined by the protocol and their use.• Chapter 4, “Message Format Descriptions,” contains the packet format definitions for the session management messages.• Chapter 5, “Registers,” describes the visible register set that allows an external processing element to discover and contact a session management process onanother end point.• Chapter 6, “Vendor-Defined Protocols,” describes how to specify vendor- defined protocol attributes.• Chapter 7, “Ethernet Encapsulation,” contains the specific use caserequirement for tunneling Ethernet using this protocol and data streaming, aswell as requirements for vendor-specific attributes.1.5 TerminologyThe following terms are used in this document. The terms are consistent with their usage in RapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 10: Data Streaming Logical Specification.Refer to the Glossary at the back of this document for additional definitions.Class of service - (cos) a term used to describe different treatment (quality of service) for different data streams. Support for class of service is provided by a class of service field in the data streaming protocol. The class of service field is used in the virtual stream ID and in identifying a virtual queue.The value of the cos field is not defined by this specification, but is implementation dependent. The requirements for this field are that every message with a given cos must be transmitted with equal priority.Conduit - A bidirectional data path, consisting of one stream for data transfer in each direction.Conveyance - The RapidIO logical layer protocol used to transmit and receive data within a stream. This specification defines the use of RapidIO Type 11 (Message Class) and Type 9 (Data-Streaming Class) conveyances.Egress - Egress is the device or node where traffic exits the system. The egress node also becomes the destination for traffic out of the RapidIO fabric. The terms egress and destination may or may not be used interchangeably when considering a single end to end connection.Ingress - Ingress is the device or node where traffic enters the system. The ingress node also becomes the source for traffic into the RapidIO fabric. The terms ingress and source may or may not be used interchangeably when considering a single end to end connection.Process - When a node communicates with a remote, some element of execution is responsible for managing the data communication. In this specification such element of execution is referred to as a process. No implication is intended regarding the internal structure of the operating system or other system organization.Protocol Data Unit - (PDU) A self contained unit of data transfer comprised of data and protocol information that defines the treatment of that data.Virtual Stream ID - (VSID) an identifier comprised of several fields in the protocol to identify individual data streams. When using Type 9 (Data-Streaming Class) as the conveyance for data transfers, the VSID is encapsulated in the Type 9 protocol.When using Type 11 (Message Class) as the conveyance for data transfers, the VSID is encapsulated in fields in the DATA or DATA1 Session Management Protocol commands.StreamID - a specific field in the data streaming protocol that is combined with the data stream’s transaction request flow ID and the source ID or destination ID from the underlying packet transport fabric to form the virtual stream ID.Segment - A portion of a PDU.Segmentation - a process by which a PDU is transferred as a series of smaller segments.Segmentation context - Information that allows a receiver to associate a particular packet with the correct PDU.Suspect - A node which, for some reason, is not behaving according to the specification. See “Section 3.7, Session Management Error Conditions and Recovery” on page 39 for more information.1.6 ConventionsAll fields and message formats are described using big endian format.||Concatenation, used to indicate that two fields are physicallyassociated as consecutive bitsitalics Book titles in text are set in italics.REG[FIELD]Abbreviations or acronyms for registers are shown in uppercase text.Specific bits, fields, or ranges appear in brackets.TRANSACTION Transaction types are expressed in all caps.operation Device operation types are expressed in plain text.n A decimal value.[n-m]Used to express a numerical range from n to m.0b nn A binary value, the number of bits is determined by the number ofdigits.0x nn A hexadecimal value, the number of bits is determined by thenumber of digits or from the surrounding context; forexample, 0x nn may be a 5, 6, 7, or 8 bit value.x This value is a don’t care.<variable>Identifies a logical variable that may be a specific field of a registeror packet or data structure.1.7 Useful ReferencesRapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 2: Message Passing Logical Specification RapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 3: Common Transport SpecificationRapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 10: Data Streaming Logical SpecificationChapter 2 Managing Data Streams2.1 IntroductionData streaming provides a common layer in RapidIO that allows any protocol to simultaneously share the same physical transport with any and all other protocols. The system can be comprised of many end points, supporting multiple protocols, and utilizing a variety of hardware and software acceleration features. Using data streaming and this management protocol, any standard or proprietary protocol data format can be tunneled on a RapidIO fabric.2.2 System ExampleFigure 2-1 shows an example of a system using two methods to perform file transfers, one interworking with an Ethernet bridge and one tunneling FTP directly.Figure 2-1. Example of a RapidIO-Based Networking System Stream 1Ethernet Link MAC to RIO Switching Stream 2FTPI P E N E T R a p i d I OL a y e rStream 1I PE N E T FTPTCP UDP TCP UDP R a p i d I OL a y e r Stream 2FTP End point #1End point #2End point #3R a p i d I O L a y e r2.3 Establishing Data StreamsThe data streaming process is separated into two phases, with the management phase separated from the data phase. All the information about the stream is exchanged separately from the actual data transfer. Once established, a stream can support many data transfers. The data transfer only contains the information necessary to recover the original data. The received data must then be associated with an end process.The method of association makes use of both the streamID and class of service (cos) to identify the stream. For example, the streamID can be linked directly to a given process which receives information for that stream. The cos may be used to determine the real time behavior necessary for the data, for example, guaranteed latency of X for responses.Figure 2-2. Stream Process The Session Management Protocol begins with a discovery process. That discovery process detects which end points can perform session management negotiations. The discovery process is described in “Section 3.3, Contacting a Participating End point” on page 20.Once two management end points are connected, they exchange a series of Session Management Protocol messages to discover the data streaming capabilities of the other. If both have the right capabilities, then one or more streams are opened for a given protocol.With an open stream data can be transferred at any time. A stream may be persistent, existing even though there is no data to transfer at any given time.Any stream may be closed by either end point, however most streams should remain open as long as the hardware and software might need to transfer data. If an end point is shutting down, or is terminating the process that handles data on that stream, it may close a stream.As previously described, streams are unidirectional. However, many systems have Source Destination MgmtProcess Mgmt Process Stream AMake Contact, Open Stream Stream AMgmtProcess Mgmt ProcessClose Stream (optional)RecvProcessData Transfers T I M Erequirements that communication be bidirectional. A bidirectional data path is created out of two streams, one in each direction. Such a bidirectional data path is called a conduit. When there is a requirement for bidirectional data transfer, one system may initiate the connection. The recipient of the initial negotiation is expected to start negotiation for the connection in the other direction. The resulting pair of streams should be grouped together, so that whenever one stream of the conduit is opened or closed, the other stream is treated the same. For more information, see “Section 3.4, Establishing Conduits” on page 21.2.4 Data Streaming System ConfigurationsRapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 10: Data Streaming Logical Specification defines a logical layer for streaming data transfer. Hardware designed to this specification can transfer data using hardware or software resources to encapsulate data. The data streaming protocol uses a segmentation and reassembly protocol to manage variable sized PDUs.Other methods may be used to transfer variable sized PDUs as long as they include the elements of segmentation and reassembly and contain a virtual stream ID. This specification also defines a method to encapsulate data using the RapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 2: Message Passing Logical Layer Specification.The management protocol may also be run over a number of conveyances. The messages may be embedded in a predesignated stream in the data streaming logical layer, or it may be run over the message passing logical layer, even if the data is on the data streaming logical layer. Additional conveyances may be available as vendor-specific conveyances or in future versions of the RapidIO specifications.Table 2-1 shows the system configurations that are currently defined by this specification.Table 2-1. Data Streaming System ConfigurationsManagement Data TransfersMessaging (Type 11)Messaging (Type 11)Messaging (Type 11)Data Streaming (Type 9)Data Streaming (Type 9)Messaging (Type 11)Data Streaming (Type 9)Data Streaming (Type 9)The protocol first establishes how to contact the management process. Once contacted, the management processes then exchange the necessary information to transfer the data.When a single node supports Session Management Protocol on multiple conveyances, the initial information required to establish a Session Management Protocol connection on each conveyance must be put in a separate Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block, as described in “Section5.2, Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block” on page 58.Therefore, multiple Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Blocks may be required.Chapter 3 Session Management Operation3.1 IntroductionThis chapter describes the RapidIO Session Management Protocol. The protocol consists of a sequence of messages to establish capabilities, open streams, manage streams, and close streams. The protocol includes methods for handling abnormal conditions.3.2 Initialization of Session Management AdvertisementCSRsBefore any management messages can be exchanged, an end point must first establish which end points support data streams, and discover how to contact their management process. The Session Management Protocol allows each end point to use its own resources as needed for the process of data streaming.Participating end points place information in the Session Management Advertisement CSR, indicating that it supports the session management protocol, and identifies which conveyance to use to contact the management process. Legacy devices may also advertise participation in this protocol using the Component TAG CSR (see RapidIO Interconnect Specification Part 3: Common Transport Specification and “Section 5.3, Component Tag CSR Session Management Protocol Advertisement” on page 64).On hardware power-up and on hardware reset, the Session Management Advertisement CSR and the Component Tag CSR must be initialized by hardware to indicate non-participation in Session Management Protocol. During software initialization, implementations conforming to this specification must indicate participation in the Session Management Protocol by modifying the Session Management Advertisement CSR, or optionally by modifying the Component Tag CSR if the Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block is not available.The Session Management Advertisement CSRs, defined in “Section 5.2, Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block” on page 58, may be initialized by a processor which is part of the device implementing the Session Management Advertisement CSRs, by a processor remote from the device, or through a combination of the two. For example, protocol support related attributes could be initialized by the local processor, while system related attributes such asmessage timeout values could be initialized by a remote processor.The Session Management Advertisement CSRs include a number of registers to facilitate initialization by local and remote processors. These are:• “Section 5.2.2, Session Management Protocol Register Write Enable CSR (Block Offset 0x4)” on page 59• “Section 5.2.4, Session Management Attribute Range CSR (Block Offset 0xC)” on page 61The Session Management Protocol Register Write Enable CSR implements mutual exclusion between processors attempting to write to the attribute registers. If the Session Management Protocol Register Write Enable CSR is locked, other processors must respect the lock and not attempt to modify the attribute registers.The Session Management Attribute Range CSR indicates how many attributes have been initialized. It also supports encoding up to 16 stages of initialization, to allow sequencing of the attribute initialization process.For more information, refer to the definitions of the named registers.3.3 Contacting a Participating End pointThe Session Management Advertisement CSR contains the following information:<Conveyance> indicates which conveyance can be used for the Session Management ProtocolIf the conveyance is Type 11 (messaging) then the CSR has the following information:• <Mailbox ID> identifies a mailbox dedicated for the reception of management messages.If the conveyance is Type 9 (streaming) then the CSR has the following information:• <StreamID> identifies a stream dedicated for the reception of management messages.• <COS> identifies the class of service dedicated for the reception ofmanagement messages.The conveyance used to create and manage all streams is specified in the Session Management Advertisement CSR, or in the Component Tag CSR if the Session Management Protocol Extended Features Register Block is not available. Unless otherwise specified, the conveyance used to transmit DATA and FLOW_CONTROL messages for a stream is the same as the conveyance used to create and manage all streams. Specification of other conveyances for DATA and FLOW_CONTROL traffic is performed by including the CONVEYANCE attribute as described in Section 3.5.3.10.A special case may be needed when a system is required to create and managestreams using both Type 11 (messaging) and Type 9 (streaming). This will occur on mixed systems, where some nodes provide support for only Type 11 conveyance and other nodes provide support for only Type 9 conveyance. When necessary, this can be accomplished by use of the Session Management Advertisement CSR to contain contact information for Type 9 management, and using the Component Tag CSR to contain contact information for Type 11 management. Other configurations may be possible, but are implementation specific.End points have two options to determine whether a remote node participates in this protocol. First, they may choose an implementation-specific mechanism, such as a built-in table, to check only for specified remote systems. Second, they may scan management space for all remote nodes, collecting information on participating end points. In either case, the end point is then expected to contact remote end points as appropriate, asking for their capabilities. See Chapter 5, “Registers”, for the bit definitions.3.4 Establishing ConduitsConduits consist of a pair of unidirectional streams for transferring data for a single protocol between two end points. In every conduit, one stream transfers protocol data in one direction while the other stream transfers protocol data in the other direction.Conduits are established using the same command set as unidirectional streams. The Session Management Protocol requires that the sender initiate the process of opening a stream. One consequence of these two facts is that for conduits to be established, both end points are required to send an OPEN command, and there must be a mechanism to link the two streams into a single conduit. Linking the two streams into a conduit is accomplished by use of the CONDUIT_STREAM attribute during OPEN/ACCEPT negotiation. The CONDUIT_STREAM attribute is a 32-bit attribute, as described in Section 3.5.3.8. The data associated with this attribute consists of two streamIDs involved in the conduit.One difficulty arises, based on whether a known end point is required to establish the conduit based on some external criteria, or whether it is possible for either end point to initiate establishment of the conduit.The simple case, where one end point initiates establishment of the conduit, is referred to as a master/slave configuration. In this case, the master may send an OPEN message at any time to initiate establishment of the conduit, but the slave may only send the corresponding OPEN message after receiving the OPEN message from the master.The more general case is referred to as a peers configuration. In this case, either node may send an OPEN message at any time to initiate establishment of the conduit. The peers configuration is more complex, because there must be a mechanism to handle。
Annex 2 附件2WHO good manufacturing practices: water for pharmaceutical useWHO GMP:制药用水1. Introduction 介绍1.1 Scope of the document文件范围1.2 Background to water requirements and uses 水的要求和使用背景1.3 Applicable guides 适用的指南2. General principles for pharmaceutical water systems 制药用水系统的一般原则3. Water quality specifications 水质量标准3.1 General 概述3.2 Drinking-water 饮用水3.3 Bulk purified water散装纯化水3.4 Bulk highly purified water散装高纯水3.5 Bulk water for injections散装注射用水3.6 Other grades of water 其它类型水4. Application of specific types of water to processes and dosage forms 不同类型水在工艺和剂型中的应用5. Water purification systems 水纯化系统5.1 General considerations 一般考虑5.2 Production of drinking-water 饮用水的制备5.3 Production of purified water 纯化水的制备5.4 Production of highly purified water高纯水的制备5.5 Production of water for injection(s) 注射用水的制备6. Water storage and distribution systems 水存贮和分配系统6.1 General 概述6.2 Materials that come into contact with systems for water for pharmaceutical use 与制药用水系统接触的材质6.3 System sanitization and bioburden control 系统消毒和微生物控制6.4 Storage vessel requirements 贮罐要求6.5 Requirements for water distribution pipework 水分配管道要求7. Operational considerations 运行时的考虑7.1 Start-up and commissioning of water systems 水系统开机和运行7.2 Qualification 确认7.3 Continuous system monitoring 对系统的持续监控7.4 Maintenance of water systems 水系统维护7.5 System reviews 系统回顾8. Inspection of water systems 水系统检查Further reading 扩展阅读1. Introduction 介绍1.1 Scope of the document 文件范围1.1.1 The guidance contained in this document is intended to provide information about the available specifications for water for pharmaceutical use (WPU), guidance about which quality of water to use for specific applications, such as the manufacture of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and dosage forms, and to provide guidance on good manufacturing practices (GMP) regarding the design, installation and operation of pharmaceutical water systems. Although the focus of this document is on water for pharmaceutical applications, the guidelines may also be relevant to other industrial or specific uses where the specifications and practices can be applied.本文件中包括的本指南目的在于提供以下信息,关于制药用水(WPU)的可获得的质量标准,哪种质量的水适用于特定用途,例如活性药用物质(API)生产和制剂生产,提供关于药用水系统设计、安装和运行GMP指南。
COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2016/1005of 22 June 2016amending Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of theCouncil concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals(REACH) as regards asbestos fibres (chrysotile)(Text with EEA relevance)THE EUROPEAN COMMISSION,Having regard to the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union,Having regard to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), establishing a European Chemicals Agency, amending Directive 1999/45/EC and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1488/94 as well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC (1), and in particular Article 68(1) thereof,Whereas:(1) Entry 6 of Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 prohibits the manufacture, placing on the market anduse of asbestos fibres, and of articles and mixtures containing these fibres added intentionally.(2) Member States could exempt the placing on the market and use of diaphragms containing chrysotile fibres forexisting electrolysis installations. This included the possibility to exempt the placing on the market of chrysotile fibres for use in the manufacture or maintenance of such diaphragms and the use of chrysotile fibres for these purposes.(3) Out of five electrolysis installations in relation to which Member States reported (2) in 2011 that they hadgranted exemptions, only two, in Sweden and Germany, remain in operation.(4) On 18 January 2013, pursuant to the obligation in paragraph 1 of entry 6, the European Commission requestedthe European Chemicals Agency (‘the Agency’) to prepare an Annex XV dossier in accordance with Article 69(1) of REACH with a view to prohibiting the placing on the market and use of diaphragms containing chrysotile. On17 January 2014, the Agency finalised the Annex XV dossier, which proposed to amend the existing restrictionby limiting the duration of the exemptions granted by Member States for the placing on the market and use of diaphragms containing chrysotile and of chrysotile fibres used exclusively in their maintenance to 31 December 2025 and enabling Member States to impose a reporting requirement to allow better monitoring and enforcement.(5) The dossier was subsequently put out to public consultation and submitted for examination by the Committeefor Risk Assessment (hereinafter ‘RAC’) and the Committee for Socio-Economic Analysis (hereinafter ‘SEAC’).(6) On 26 November 2014 RAC adopted an opinion concluding that there is no worker exposure to chrysotile inone plant and that in the other exposure is minimised by risk management measures which are effective in controlling potential risks from the use of chrysotile to a risk level of low concern. The opinion further concluded that there is no release of chrysotile to the environment and therefore the health and environment benefits of immediate closure of the two plants would be negligible. Furthermore, due to process and technologyspecific considerations in one of the plants, no suitable alternative was available.(1)OJ L 396, 30.12.2006, p. 1.(2)Exemptions granted by EU countries and EEA-EFTA States on asbestos contained in articles pursuant to Entry 6 of Annex XVII toRegulation (EC) No 1907/2006 (REACH).http://ec.europa.eu/DocsRoom/documents/13170(7) In order to further the objective of phasing out the use of chrysotile in the EU and to improve the clarity andtransparency of the existing exemption, RAC agreed with the proposed amendment set out in the Annex XV dossier. The opinion also concluded that action on a Union-wide basis is necessary.(8) On 9 March 2015, SEAC adopted an opinion noting that in one plant the existing asbestos containing cellswould be dismantled by 2025 and that in the other, the operator claimed that ongoing production level testing using chrysotile-free diaphragms in its current installation would lead to full substitution at the latest by 2025.SEAC also concluded that immediate closure of this plant would result in costs in terms of lost value added and jobs and took note of the commitment of the operator of the latter plant to cease all imports of chrysotile by the end of 2017. Given the overall objective of phasing out the use of chrysotile in the EU and in order to improve the clarity and transparency of the existing exemption, SEAC advised that the duration of the exemptions granted by Member States for the placing on the market of diaphragms and fibres should be limited to the end of 2017 and concluded that the proposed amendment of the existing restriction, as modified by SEAC, is the most appropriate Union wide measure.(9) Commission Implementing Decision 2013/732/EU (1), establishing the best available techniques (BAT)conclusions under Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council (2) on industrial emissions (IED), stipulates that the use of asbestos diaphragms is not considered BAT and accordingly permit conditions for chlor-alkali installations operated in the Union must be updated by 12 December 2017 so that those installations do no longer use asbestos diaphragms from that date. However, unlike for mercury cells which are not considered BAT under any circumstances, Member States may determine that, in specific and exceptional circumstances, asbestos diaphragms may be used in a particular installation for a well-defined longer period and under conditions consistent with the environmental objectives of the IED, provided that the conditions and duration of such use are specified in a legally binding way.(10) Since the adoption of the SEAC opinion, the operator of the plant in which full substitution is envisaged by 2025has entered into a binding agreement with the authorities of the Member State concerned with a view to guaranteeing the gradual substitution of diaphragms containing chrysotile by a non-asbestos alternative material from 2014 on and achieving full substitution at the latest by 30 June 2025. Therefore it is appropriate that the duration of the exemption granted by Member States to permit the use of diaphragms containing chrysotile and of chrysotile fibres used exclusively in their maintenance is limited to 30 June 2025 at the latest.(11) Moreover, although under the binding agreement the operator undertook to stop importing chrysotile fibres anddiaphragms containing chrysotile by the end of 2017, it subsequently confirmed that imports have already ceased as it has acquired sufficient chrysotile fibres to manage the transition to an alternative material. Therefore it is appropriate to terminate the possibility that allows Member States to permit the placing on the market of diaphragms containing chrysotile and of chrysotile fibres exclusively for their maintenance.(12) A report indicating the amount of chrysotile used in diaphragms in the installations benefiting from exemptionsshould be transmitted to the Commission. Union legislation on the protection of workers' health and safety already provides that employers must reduce workers' exposure to chrysotile fibres to a minimum and in any case below an established limit value. Member States may set more stringent limit values for such fibres in air and may require their regular measurement/monitoring. The results of any such measurement/monitoring should be included in the report.(13) The Forum for Exchange of Information on Enforcement was consulted and its recommendations were taken intoaccount.(14) Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 should therefore be amended accordingly.(15) The measures provided for in this Regulation are in accordance with the opinion of the Committee establishedunder Article 133 of Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006,(1)Commission Implementing Decision 2013/732/EU of 9 December 2013 establishing the best available techniques (BAT) conclusions,under Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on industrial emissions, for the production of chlor-alkali (OJ L 332, 11.12.2013, p. 34).(2)Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 November 2010 on industrial emissions (integratedpollution prevention and control) (OJ L 334, 17.12.2010, p. 17).HAS ADOPTED THIS REGULATION:Article 1Annex XVII to Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006 is amended in accordance with the Annex to this Regulation.Article 2This Regulation shall enter into force on the twentieth day following that of its publication in the Official Journal of the European Union.This Regulation shall be binding in its entirety and directly applicable in all Member States.Done at Brussels, 22 June 2016.For the CommissionThe PresidentJean-Claude JUNCKERANNEXIn Annex XVII, entry 6, paragraph 1 of column 2 is replaced by the following:。
100 floors 攻略1-100 ANNEX第二关1-5随时更新请关注:/499834593/blog/1339030540#!app=2&p os=1338127322更多精彩请点击:/499834593/main iphone游戏100 Floors 图文攻略随时更新点击此处1. 直接点击绿色向上按钮开启电梯门。
2. 搬开垃圾桶,取得绿色三角物品,点击物品在点击向上按钮开启电梯门。
3. 左右摇晃手机就可以开启电梯门。
4. 两手放在门上,向左右同时拉开。
5. 把手机面朝下,梯子就会倒下了。
6. 搬开右边的植物,看见太阳装饰,将4个太阳装饰点亮,电梯门开启。
7. 把手机向左慢慢倾斜,直到右边的石头压住红色按钮。
8. 找到猩猩最爱的水果...9. 根据电梯门四个角落的图案,相应调整门上图案。
10. 把睡著的蛇摇醒离开,依照门上键头的指示画线即可。
11. 将两个铁球保持在中间位置三秒就可以了。
12. 不停的敲击地下的红色按钮,直到铁球撞亮柱子顶端的灯。
13. 晃动手机,左上方的铁鎚自然掉落,用铁锤将砖墙击碎即可。
14. 将手指放在指纹辨识器上五秒。
15. 这层我是蒙对的!依据门框上图形在九宫格上画下来,每次离得最远的数字164316. 捡起地上的改锥,将中间的板子取下,轻晃手机就OK啦。
17. 仔细观察门上的条纹,移动铁球触碰蓝色按钮,次数与条纹相对应左1右2左3右218. 同时点亮点击门上的五个蓝点,每个蓝点发光的时间长短都不同。
19. 这关简单,只要捡起地上的抹布,把电梯门擦的干干净净就哦了20. 首先一开黄色的维修标志,捡起螺丝后放在空缺处,再用改锥锁紧即可。
21. 门上的眼睛图案是会上下看的,手机保持垂直状让眼睛向上看五秒就可以了。
22. 用铁锤将右边石狮子敲碎,N-E-W-S按指示划过电梯门,从下往上,从左往右,从右往左,从上往下。
23. 黑漆漆的一片,所以要先开灯,嘿嘿...将工具栏中的板子方在门上,从右往左点依序按下就可图案以了。