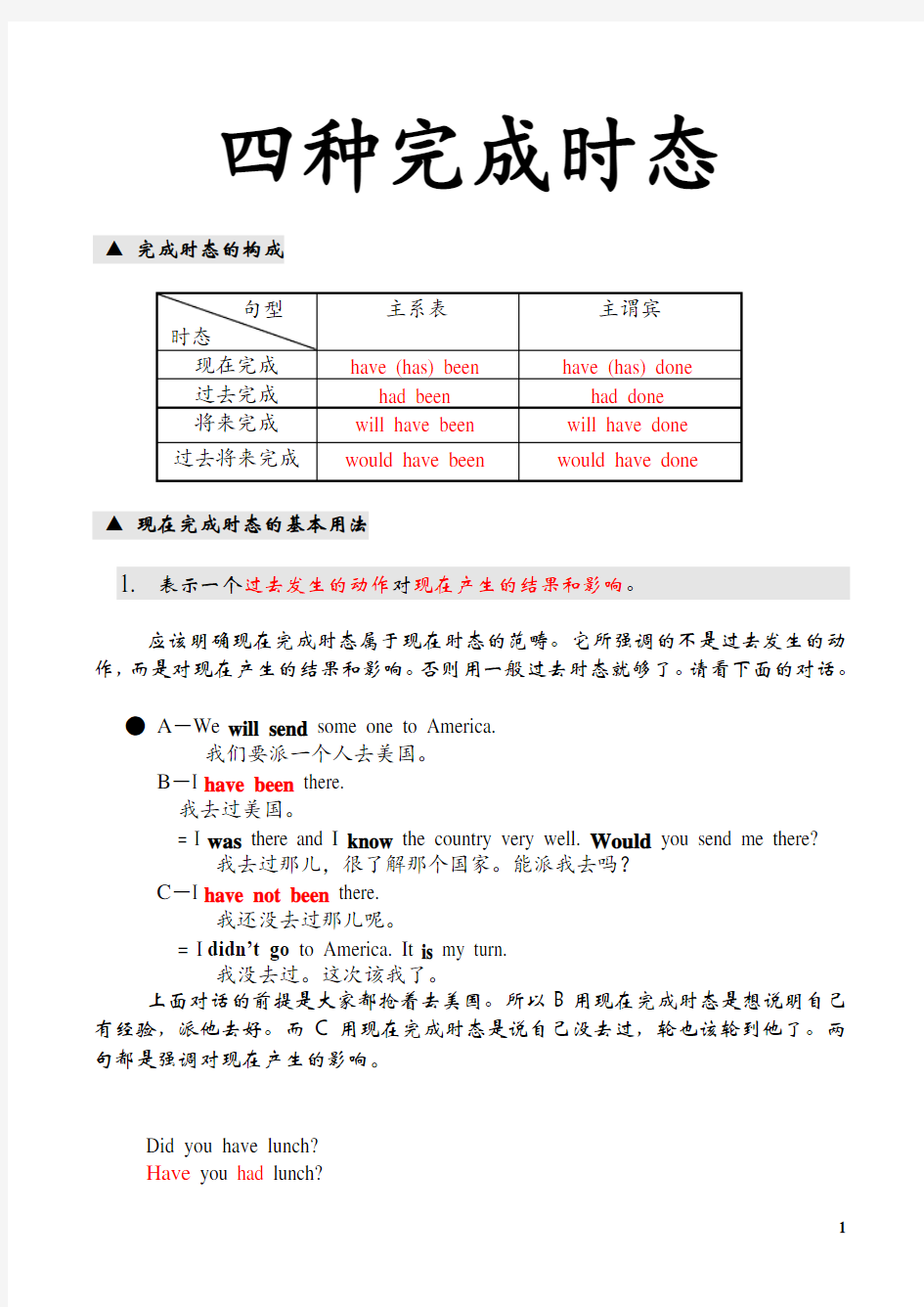

四种完成时态
▲完成时态的构成
▲现在完成时态的基本用法
1. 表示一个过去发生的动作对现在产生的结果和影响。
应该明确现在完成时态属于现在时态的范畴。它所强调的不是过去发生的动作,而是对现在产生的结果和影响。否则用一般过去时态就够了。请看下面的对话。
●A-We will send some one to America.
我们要派一个人去美国。
B-I have been there.
我去过美国。
= I was there and I know the country very well. Would you send me there?
我去过那儿,很了解那个国家。能派我去吗?
C-I have not been there.
我还没去过那儿呢。
= I didn’t go to America. It is my turn.
我没去过。这次该我了。
上面对话的前提是大家都抢着去美国。所以B用现在完成时态是想说明自己有经验,派他去好。而C用现在完成时态是说自己没去过,轮也该轮到他了。两句都是强调对现在产生的影响。
Did you have lunch?
Have you had lunch?
Did you study English?
Have you studied English?
Laochang died?
Laochang has died?
Who was herer?
Who has been here?
Have you done your homework
2. 表示过去发生的动作一直持续到现在。
通常用于持续性较强的动词,例如:live, study, wait for, be等等,并且常常与since, for连用,since给出的是过去的一个时间点,如since 1958, 而for往往给出的是一个时间段,如for three years。
●He has studied English for eight years.
●Since1980, they have known each other.
注:完成时态表示延续的用法不可跟非延续动词连用,如:die, go, leave, receive等。请看下面例句:
╳His father has died for three years.
●His father has been dead for three years.
第一句是错的。“死”这个动作不可能延续。但一种状态却可以延续。第二句用主系表句型是对的。
▲过去完成时态,将来完成时态和过去将来完成时态
学习完成时态应注意,所有完成时态在“态”的概念上是一样的,现在完成时态、过去完成时态、将来完成时态、过去将来完成时态所不同的只是时间上的概念。所以我们只要掌握现在完成时态,然后在时间上向过去推便是过去完成时态,向将来推便是将来完成时态。
3完成时态在主从句中的用法
完成时态除上面讲到的两种基本用法之外,在主从句中通常可以用来表示主句与从句动作发生的先后次序。
●Do you know he has finished his homework?
现在完成时态“has finished”表示发生在一般现在时态“know”之前。
●I heard he had bought a new car.
过去完成时态“had bought”表示发生在过去时态“heard”之前。
现在完成时态“have had supper”强调吃过饭之后,即强调从句动作发生在主句之前。从上面几个例句可以看出,在主从句中现在完成时态往往表示发生在另一个现在时态的动作之前,而过去完成时态则表示发生在另一个过去时态的动作之前。请注意下面的例句:
以上简单地介绍了在主从句中完成时态的用法。请同学们在做练习时多加注意。
练习
1.—What do you want ______ those old boxes?
—To put things in when I move to the new flat.
A. by
B. for
C. of
D. with
1.D do sth with sth or want sth with sth 意思是用什么东西或要什么东西做什么。
2.—______ he start at once or wait for a while?
—Let him start at once.
A.Will B.Would C.Does D.Shall
2.D.Shall shall表示征求对方意见。
3.I can’t tell you if it tomorrow.
A.will rain B.rains C.shall rain D.does rain
3.A.will rain 表示将来发生的事。
4.Did you watch the play on CCTV 1 last night? It was really good.
—No, I didn't._____?
—“Tea House”.
A. What was it
B. What's on
C. What was it about
D. How about it
4.B. What's on 意思是演的是什么。
5.—Can you give me the right answer?
—Sorry, I _______.Would you repeat that question?
A.hadn’ t listened B.haven’t listened
C.don’t listen D.wasn’t listening
5.D.wasn’t listening 表示刚才一瞬间,所以要用过去进行时。
6.I promised to get there before 5 o’clock, but now the rain is pouring down.They
_______ for me impatiently.
A.may wait B.ought to wait
C.could wait D.must be waiting
6.D.must be waiting must be or must do都可以表示对目前的推测。该话应译成:想必他们等我等的不耐烦了。
Must be must be doing
Must have been Must have done
7.—Haven't seen you for ages! Do you still work in Fuzhou?
—_____.It's two years since I worked there.
A. Yes, I have
B. Yes, I do
C. No, I haven't
D. No, I don't
7. D. No , I don't It's two years since I worked there. 此句应译成我已经有两年没
在那里工作了。
8.Goodbye, Peter, remember me to your parents.
— ______.
A. It's very kind of you to say so
B. Thanks, I will
C. You are so kind
D. Thanks, what a good idea
8.B. Thanks, I will。在答应别人时应该用will表示坚决。
9.You are talking too much.
—Only at home. No one ______ me but you.
A. is hearing
B. had heard
C. hears
D. heard
9. C. hears 表示事实用一般时。
10.—We want someone to design the new art museum for us.
—the young fellow have a try?
A. May
B. Shall
C. Will
D. Need
10.B. Shall shall表示征求对方的意见。have a try 试一试, have a look 看一看。
11.I wonder why Jenny ________us recently.We should have heard from her by
now.
A. hasn't written
B. doesn't write
C. won't write
D. hadn't written
11.A. hash' t written 因为recently表示过去延续到现在,应用过去完成时。
12.I didn't like aunt Lucy, who _____without warning and presenting
A. always turned up
B. has always turned up
C. was always turned up
D. was always turning up
12.D. was always turning up,--- be always doing表示不满。例如My wife is always watching TV. 我的妻子总是看电视。Turn up 意思是出现。该句应译成:我不喜欢我的婶子路西总不打招呼也不带礼物就突然出现。
13.—Has Tommy finished his homework yet?
—I have no idea; he it this morning.
A. was doing
B. had been doing
C. has done
D. did
13.A. was doing this morning表示一个很短的过去时间,用过去进行时。
14.The little girl ______ her heart out because she ______ her toy bear and believed
she wasn’t ever going to find it.
A. had cried; lost
B. cried; had lost
C. has cried; has lost
D. cries; has lost
14.B. cried; had lost, cry one’s heart out 哭得很伤心。在主从句中过去完成时表示动作发生在一般过去时之前,现在完成时是指动作发生在一般现在时之前。强调主从句的时间差。
15.—Hey, look where you are going?
—Oh, I’m terribly sorry_____________.
A. I’m not noticing
B. I wasn’t noticing
C. I haven’t noticed
D. I don’t notice
15. B 表示过的动作短暂用过去进行时。
16.—Do you know your town at all?
—No, this is the first time I _______ here.
A. was
B. have been
C. came
D. am coming
16. B 从过到现在的经历用现在完成时。
17.I’m sorry to keep you waiting.
--Oh, not at all. I ___________ here only a few minutes.
A. have been
B. had been
C. was
D. will be
17.A 过去的状态持续到现在用现在完成时。
18.—__________ my glasses?
— Yes, I saw them on your bed a minute ago.
A. Do you see
B. Had you seen
C. Would you see
D. Have you seen
18. D过去的动作对现在产生的影响用现在完成时
19.You don’t need to describe her.
I ______ her several times.
A. had met
B. have met
C. met
D. meet
高中英语语法(时态和语态) 一.动词的时态 时态是谓语动词所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。英语动词有16种时态,但是常见的只有九种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。 (一)一般现在时(do / does) 1.具体用法 1) 表示经常性或习惯性动作 We always care for each other and help each other. 我们总是互相关心互相帮助。 He goes to school every day. 2)表示现在的特征或状态 He is very happy. Do you sing? ----A little. 3)表示普遍真理 Light travels faster than sound. 光速比声速快。 Actions speak louder than words. 行动胜过言语。 * 常与一般现在时态连用的词或短语主要有:often, usually, sometimes, every day, every morning/afternoon, on Sundays/weekends等等。 I often go to the cinema on Sundays. 我经常星期天去看电影。 He goes to work early every day. 他每天上班很早。 (二)一般过去时( did ) (1)表示过去某一特定时间所发生的、可完成的动作或状态,常与表示确切过去时间的词、短语或从句连用。例如: We went to the pictures last night and saw a very interesting film. (2)表示过去习惯性动作。例如: He always went to class last. I used to do my homework in the library. (三)一般将来时( will / shall do) 1)表示将来打算进行或期待发生的动作或状态。例如: I shall graduate next year. 2)一般将来时有时可以表示一种倾向或习惯性动作。如 Crops will die without water. You won’t succeed with out their support. 3) 几种替代形式: *be going to +v在口语中广泛使用,表示准备做或将发生的事情。例如: I'm going to buy a house when we've saved enough money. *be to +v表示计划安排要做的事,具有"必要"的强制性意义。例如: I am to play tennis this afternoon. *be about to +v表示即将发生的事情。例如: He was about to start. *be due to +v表示预先确定了的事,必定发生的事。例如: The train is due to depart in ten minutes. 5)少数动词如:begin, come, leave, go, arrive, start, stop, return, open, close等的一般现在时可用来表示将来的动作。(多用来表示按计划事先安排好即将发生的动作,句中通常还有一个表示将来的时间状语)。例如: The meeting begins at seven.
般将来时: 定义:一般将来时表示将来某一时刻的动作或状态,或将来某一段时间内经常的动作或状态。 构成:(1) be going to +动词原形 (2) will + do 用法:1)表示将来的动作或状态 一般将来时常与一些表示将来的时间状语连用,女h tomorrow (明天), next week (下周), from now on (从现 在开始);in the future (将来);someday (未来的某一天) 等。 2)表示将来经常发生的动作 ril teach you English every Wednesday next month. ★★★“be going to+动词原形"表示即将发生的或最近打算进行的事。例如: ?It is going to rain.要下雨了。 ②We are going to have a meeting today. 今天我们开会。 Step Three: Do Some Exercise 一、用will或will not以及括号中的动词完成句子 1、I______________________ a Chinese song.(sing) 2、S ally ____________________ the tennis match.(not win) 3、Y ou _____________________ the one-day trip to Guangzhou.(enjoy) 4、F lora ____________________ at home this weekend.(not stay)
二、用括号内的词和be going to完成问答 1、(when/we/ have dinner? We / it / at seven o'clock) A When are we going to have dinner? B We are going to have it at seven o'clock. 2、(Where / you /meet your friends? We / them /at the school gate) A _________________________________________ B _________________________________________ 3、(you and Ling / play football/ today? No / we/ table tennis) A B 现在进行时一般过去时be+动词ingo 动词+ed 一般将来时be going to+实义动词原形; 一般现在时 动词变化 用动词原形,主语是第三人称单数时,动词要加s/es。 一般现在时主语是第三人称单数时,动词要加s/es。 动词+S的变化规则 1.一般情况下,直接加?s,如:cook-cooks, milk-milks 2.以s. x. sh? ch. o 结尾,力n-es,女u: wash-washes, watch-watches, go-goes 3.以''辅音字母+y"结尾,变y为i,再加?es,如:study-studies; 现在进行时动词加ing的变化规则 1)一般情况下,直接加ing,如cook-cooking 2)以不发音的e 结尾,去e 加ing,如:make-making, taste-tasting 3)如果末尾是一个元咅字母和一个辅咅字母,双写末尾的辅咅字母,再加ing, 如1: run-running, stop-stopping, swim-swimming 动词过去式变化规则: 1)一般在动词末尾加?ed,女n: pull-pulled, cook-cooked
高中英语语法复习讲义——动词的时态 一. 概念: 时态是英语谓语动词的一种形式,表示动作发生的时间和所处的状态.英语中的时态是通过动词形式本身的变化来实现的.英语有16种时态,但中学阶段较常用的有十种:一般现在时,一般过去时,一般将来时,过去将来时,现在进行时,过去进行时,将来进行时,过去完成时,英在完成时和现在完成进行时. 二.相关知识点精讲 1.一般现在时的用法 1) 经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频腮度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…,sometimes,at…,on Sunday。例如: I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2) 客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。例如: The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 3) 表示格言或警句。例如: Pride goes before a fall.骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 4) 现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。例如: I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。 Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. 把糖放入杯子。 I am doing my homework now. 我正在做功课。 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。 2. 一般过去时的用法 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。例如:时间状语有:yesterday,last week,an hour ago,the other day,in 1982等。例如: Where did you go just now? 刚才你上哪儿去了? 2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。例如:
时态综合练习1 填空、选择 一、用动词的适当形式填空 1. Listen!The children _______________(sing)in the classroom. 3. Look! The woman over there ______________ (look) at you. 4. Mary ______________ (visit) her grandparents next Monday. 5. Miss Li ______________(have) an English class every Tuesday. 6. I ______________ (leave) for Shanghai tomorrow evening. 7. Joan often ______________ (catch) the No.11 bus to work. 8. He _____________much about Chinese.(not know) 9.Tom often ______________(go) to school on foot. But yesterday was rainy. He ______________ (go) to school by bus. 10. My mother usually ____________(watch) TV and ___________(wash) clothes on Sunday morning? 12. Today is a sunny day. We ______________ (have) a picnic this afternoon. 13. ______________your sister often ______________(go)shopping? 14. The boys ________________ (swim)in the river now. 16. Everyone in my family_________ (be) busy now. But my brother ____________(play) with the cat. 二、单项选择。 ( ) 1.They ____ climbing mountains. A. like B. likes C. liking ( ) 2.Tom and Jack _____ some reading every day. A. do B. does C.doing ( ) 3.My brother_____ hard. A. study B. studys C. studies ( ) 4.Joe doesn’t _____ any money now. A. have B. has C. having ( ) 5.Tom’s English teacher _____ him questions very often. A. ask B. asks C. asking ( ) 6.Mary and May ______ exercise under the tree now. A. take B. are taking C. taking
高考英语语法专题复习动词时态和语态 Document number:PBGCG-0857-BTDO-0089-PTT1998
高考英语语法复习专题:动词时态和语态 一、考点聚焦 1、动词时态考查要点简述 (1)一般现在时考点分析 ①表示客观事实或普通真理(不受时态限制) The geography teacher told us the earth moves around the sun. Water boils at 100o C. ②表示现状、性质、状态时多用系动词或状态动词;表示经常或习惯性的动作,多用 动作动词,且常与表频率的时间状语连用。 Ice feels cold. We always care for each other and help each other. ③表示知觉、态度、感情、某种抽象的关系或概念的词常用一般现在时:see、hear、smell、taste、feel、notice、agree、believe、like、hate、want、think、belong seem等。如: I know what you mean. Smith owns a car and a house. All the students here belong to Middle School. ④在时间、条件状语从句中常用一般现在时代替将来时。但要注意由if 引导的条件状语从句中可以用shall或will表“意愿”,但不表示时态。 If you will accept my invitation and come to our party, my family will be pleased.如果你愿意接受并参加我们的舞会,我的家人会非常高兴。 ⑤少数用于表示起止的动词如come、go、leave、arrive、fly、return、start、begin、pen、close、end、stop等常用一般现在时代替将来时,表示一 个按规定、计划或安排要发生的动作。当be表示根据时间或事先安排,肯定会出现的状态,只用一般现在时。 The shop closes at 11:00 . every day. Tomorrow is Wednesday.
高中英语语法系统全解 第一章动词时态 在英语中,不同时间发生的动作或存在的状态,要用不同的动词形式来表示,这就叫做动词的时态。一、一般时 一般时包括一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时和一般过去将来时。 A.一般现在时 1.一般现在时的构成 一般现在时主要用动词原形来表示。主语是第三人称单数时,动词后面要加-s 或-es。 They want good jobs. 他们想要好的工作。 The coat matches the dress. 外衣和裙子很相配。 This work does not satisfy me. 这项工作我不满意。 Do you understand? 你懂了吗? 2.一般现在时的用法 ①一般现在时的基本用法 a. 表示现在习惯性的动作或存在状态 He always takes a walk after supper. 晚饭后他总是散散步。 Everyone is in high spirits now. 现在大家都情绪高涨。 b. 表示客观事实或普遍真理 The sun rises in the east and sets in the west. 太阳从东方升起在西方落下。 Sound travels faster through water than it does through air. 声音在水中的传播速度要比在空气中快。
Time and tide wait for no man. 时间不等人。 c. 表示主语的特征、能力和状态 This cloth feels soft. 这布摸上去很软。 I love classical music. 我喜欢古典音乐。 The President still seems able to find time to go fishing. 看来总统仍能有时间去钓鱼。 d. 表示按计划或安排将要发生的动作 The meeting begins at 7:00. 会议七点钟开始。 We leave here at 8:00 sharp. 我们八点整离开这里。 e. 在时间、条件、让步状语从句中表示将来动作 When you come next time, bring me some magazines. 你下次来时,给我带几本杂志。 If time allows, we shall go there tomorrow. 如果时间允许的话,我们明天去那里。 Whether he agrees or not, I will stay at home. 不管他同意与否,我都会待在家里。 ②一般现在时的特殊用法 a. 用于新闻标题或图片说明中 China Declares Manned Spaceflight Successful 中国宣布载人航天飞行圆满成功 Laura Bush Arrives in Moscow 劳拉·布什抵达莫斯科 b. 用于体育运动、表演等实况报道中 Francis slips past, passes the ball to Yao Ming, who jumps, catches and shoots it into the basket.
高中英语语法(时态语态篇)练习题精选 ( ) 1. –Where is the morning paper?–I ________ for you at once. A. get B. am getting C. to get D. will get ( ) 2. ________ a concert next Saturday? A. There will be B. Will there be C. There can be D. There are ( ) 3. If they come, we ________ a meeting. A. have B. will have C. had D. would have ( ) 4. If it ________ tomorrow, we’ll go roller-skating. A. isn’t rain B. won’t rain C. doesn’t rain D. doesn’t fine ( ) 5. Tomorrow he ________ a kite in the open air first, and then ______ boating in the park. A. will fly; will go B. will fly; goes C. is going to fly; will goes D. flies; will go ( ) 6. There ________ a birthday party this Sunday. A. shall be B. will be C. shall going to be D. will going to be ( ) 7. They ________ an English evening next Sunday. A. are having B. are going to have C. will having D. is going to have ( ) 8. Sorry, I can’t open the door, for I the key to it. A. lost B. lose C. had lost D. have lost ( ) 9. —It’s good to see you again, Agnes. —This has been our first chance to visit since from Iran. A. you return B. you returned C. you have returned D. returning ( ) 10. — Did you expect Frank to come to the party? — No, but I had hoped . A. him coming B. him to come C. that he comes D. that he would come ( ) 11. — Bob must be very wealthy. — Yes, he more in one day than I do in a week.
第四讲初中英语时态综合讲解(2) 现在完成时 一、现在完成时定义: 1、表示过去发生的或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果; 2、也可表示动作或状态在过去已经开始,一直持续到现在的动作或状态,还有可能继续持续下去。 二、基本结构:主语+ have/has + 动词的过去分词+ 其他。 1、当主语是第三人称单数时用has,其余人称用have。 2、当have被用在现在完成时态中时,它可以和前面的代名词一起组成缩写形式。 3、现在完成时用not来表达否定形式。当有not出现的时候,have可以和not组成缩写,但是此时不能和前面的代名词组成缩写。 4、过去分词:规则动词的过去分词构成与动词过去式相同;不规则动词需要特殊记忆。 三、基本句式:否定式: 主语+ haven't/hasn't + 过去分词+ 其他。 疑问式: Have /Has + 主语+ 过去分词+ 其他? 简略答语: Yes, 主语+ have/has. (肯定) No, 主语+ haven't/hasn't. (否定) 四、基本用法: 1、动作发生在过去某个不确定的时间,但对现在有某种影响和结果。常被just、already、yet 等副词修饰。 如:(1)-Have you had lunch yet? 你(已经)吃午饭了吗? -Yes,I have. I've just had it.我刚刚吃过。(现在我不饿了) (2)-I have already watched the TV play. 我已经看过这部电视剧了。 (3)-Have you found your lost pen yet?你找到丢失的钢笔了吗? -No,I haven't found it yet.没,我还没有找到。 2、表示从过去某一时刻开始一直持续到现在的动作或状态。这个动作可能刚停止,可能仍然在进行。常带有for 和since等表示一段时间的状语,多为延续性动词。 如:He has taught here since 1981.他自1981年就在这教书。(可能还要继续教) I haven't seen her for four years.我有四年没见到她了。 3、表示说话前发生过一次或多次的动作,现在成为一种经验,一般译为汉语“过”,常带有twice, ever, never, three times等时间状语。 如:I have been to Beijing twice.我去过北京二次。 4、现在完成时的含义之一是过去完成的动作对现在仍有影响,用以下四大标志词可以表达这种含义: 以already, just和yet为标志:already, just和yet 表示到现在为止动作或状态已经、刚刚或还没有发生。 以ever和never为标志:ever和never 表示到现在为止动作或状态曾经或从来没有发生过。 以动作发生的次数为标志:若某一动作到现在为止已经发生了若干次,则要使用现在完成时。 以so far为标志:so far往往表示到目前为止动作或状态已经发生。 五、现在完成时的时间状语: For+一段时间(时间段) since+时间点或时间状语从句 so far (到目前为止,迄今为止) ever(曾经) never(从来不) just(刚刚) yet(还)
人教版高中英语必修二 知识点梳理 重点题型(常考知识点)巩固练习 限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句 概念引入: He is a person who never gives up. 他是个永远不服输的人。 I found him in the woods, where has a well-known tree. (我是在树林里找到他的,那里有一棵很有名的树。) Our guide,(who was a Frenchman, ) was an excellent cook. 我们的导游是个很优秀的厨师,他是个法国人 She was not on the train which arrived just now。 她没在刚刚到达的那辆车上 语法点拨 什么是定语从句? 修饰主语、宾语、表语的句子就叫做定语从句。引导定语从句的关系词有: 关系代词:who, whom, whose, which, that 关系副词:when, where, why 我们把下面两个句子组合成一个复合句: 1. This is our school. It is beautiful. →This is our school which is beautiful. 2. This is our school. We study in our school. →This is our school which we study in. →This is our school in which we study. →This is our school where we study. 3. Do you know the room? It is made of amber. →Do you know the room which is made of amber? 4. I have read the newspaper. It carries the important news. →I have read the newspaper which carries the important news. 从上述定语从句的组合我们可以看出: 先行词和关系词的关系:关系代词实际上是先行词的复指;关系词whose 实际上是先行词的所有格。 1. A plane is a machine that can fly. the machine = that 2. The boy who broke the window is called Wangkai. the boy =who 3. The boy whose parents are working outside was brought up by his grandfather. the boy’s =whose 【高一英语语法(二)定语从句(二)356521限制性定语从句和非限制性定语从句】
高考英语——动词的时态和语态(专项练习题) 单句语法填空 1.We can achieve a lot when we learn to let our differences unite,rather than ________ (divide) us. 2.Silk ________(become) one of the primary goods traded along the Silk Road by about 100 BC. 3.When the time came to make the final decision for a course,I decided to apply for the one that ________(reflect) my interest. 4.More efforts,as reported,________(make)in the years ahead to accelerate the supply-side structural reform. 5.Dashan,who ________ (learn)crosstalk,the Chinese comedic tradition,for decades,wants to mix it up with the Western stand-up tradition. 6.When walking down the street,I came across David,whom I ________ (see) for years. 7.Two years ago,while Cathy ________ (watch) the Olympics,a dream came into her sweet little head—to be a swimmer. 8.Jack ________(work)in the lab when the power cut occurred. 9.I ________(read)half of the English novel,and I’ll try to finish it at the weekend. 10.The students have been working hard on their lessons and their efforts ________ (reward)success in the end. 11.—Excuse me,which movie are you waiting for? —The new Star Wars.We ________ (wait)here for more than two hours. 12.Secret codes keep messages private.Banks,companies,and government agencies use secret codes in doing business,especially when information ________ (send)by computer. 13.People in this area are in fact French citizens because it________(be) a colony of the French Republic since 1946.
必修一 语法点一:Be+v.ing表将来 use the present continuous tense for future plans In English, we have lots of ways of talking about the future. The most common ways of talking about the future we encounter use ‘will’ or ‘be going to’ followed by an infinitive(动词原形), and we tend to use ‘be going to’ most often for talking about future plans. Sometimes, we also use the present continuous tense to talk about future plans. Ex. ①we are going to Mexico next Sunday. ② Are you coming to the cinema? ③ He is leaving for London in two hours. ④ We are spending next winter in Australia. Only some verbs can be used in this situation, such as: go, arrive, come, leave, start, stay, return, play, have, work, wear, spend, see, meet, etc. 扩展: What’s the difference between using ‘be going to’ and the present continuous to talk about future plans? Let’s look at some more examples: “I’m going to play football on Saturday” You have made a plan in your head but possibly not taken any real action to confirm it. Also, playing football on Saturday is probably not a regular event for you. “I’m playing football on Saturday” You have made a plan and taken some real action to confirm it (e.g. called your friends or booked a place to play). In this case, it’s likely that playing football on Saturdays is a common activity for you. 语法点二:Direct speech and indirect speech(直接引语和间接引语) Let's first define the terms, then look at how to talk about what someone said, and how to convert speech from direct to indirect or vice-versa. You can answer the question What did he say? in two ways: by repeating the words spoken (direct speech) by reporting the words spoken (indirect or reported speech). Direct speech repeats, or quotes, the exact words spoken. When we use direct speech in writing, we place the words spoken between quotation marks (" ") and there is no change in these words. Reported or indirect speech is usually used to talk about the past, so we normally change the tense of the words spoken. We use reporting verbs like 'say', 'tell', 'ask', and we may use the word 'that' to introduce the reported words. Quotation marks are not used. 1、declarative sentence陈述句 ①Change in pronoun:The pronoun (subject) of the reported speech is changed according to the pronoun of reporting verb or object (person) of reporting verb (first part of sentence). Sometimes the pronoun may not change. In following example the pronoun of reported speech is “I” which will be changed
初中英语时态综合讲解训练 学习英语时态的意义: 英汉两种语言在时态表达方式上有很大的差异: 如,“他经常帮助我。”“他昨天帮助我了。”和“他一直在帮助我。”这三句话当中,汉语的动词“帮助”没有任何变化,而是用“经常”、“一直”和“昨天”分别表达出时间的区别。 英语就不同,它必须用动词本身的形态变化来完成任务。 He often helps me. 他经常帮助我。 He helped me yesterday. 他昨天帮助我了。 He has been helping me. 他一直在帮助我。 在这几句中,动词help的意义没有变化,但形态变了. 我们初中英语需要掌握多少个时态呢? 一.初中英语常见的八种时态 1 一般现在时 1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。 时间状语:often ,usually, always, every day/week…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday。 例如:I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 提醒:当第三人称单数作主语时,别忘了动词的变化 He usually goes to school by bike. 2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。例如: The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 3)表示格言或警句。例如: Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。 例:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 2 一般过去时 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。时间状语有:yesterday, yesterday morning/afternoon/evening, last week/month/year, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982等。 例如:Where did you go just now? 刚才你上哪儿去了? 2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。 例如:When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 我是个孩子的时候,常在马路上踢足球。 Whenever the Browns went during their visit, they were given a warm welcome.
宾语从句综合分析(时态、语序、引导词,每部分均含讲解、练习及答案)目录:(一)宾语从句基础讲解 (二)宾语从句的转化 (三)典例讲解 因此,简单地来说,整个句子担当宾语成分,那么这样的句子就叫宾语从句。 (一)宾语从句基础讲解 1. 概念: 在句中担当宾语的从句叫宾语从句,宾语从句可作谓语动词的宾语,也可做介词的宾语。 E.g. He said he was good at drawing. (动词宾语) He asks him how long Mike has been down . (动词宾语)
Miss Zhang is angry at what you said. (介词宾语) 2. 连接词 (1) 陈述句转化成宾语从句时,引导词用that,口语中常常省略。 e.g, She told me (that) she would like to go with us. (2) 以 whether 或if 引导的宾语从句, 主要用来引导一般疑问句意思或选择疑问句意思的宾语从句,从句同样是陈述语序 E.g. I wonder if /whether u have told the new to Li Lei . (3) 特殊疑问句转化成宾语从句时,引导词用特殊疑问词;引导词后要用陈述句语序。 E.g. Could you tell me what's the matter/wrong with you? 特殊情况:当do you think后接特殊疑问句转化成宾语从句时,句式结构应为引导词+do you think+陈述句语序。
3. 宾语从句时态 a. 当主句是一般现在时,一般将来时或祈使句时,从句不受主句的限制,根据自身的需要选用相应的时态。例如: Do you know(if/whether he has seen the film)? b. 当主句是一般过去时,从句要用过去时的相应时态。例如: I didn't know (if/whether he had seen the film.) 注意:当主句是一般过去时,而从句表示的是客观真理,自然现象,科学原理,格言等,从句仍然要用一般现在时。 例如: He said (that the earth moves round the sun.) The teacher told us (that light travels much faster than sound.) 4. 人称的变化和标点的使用 a. 从句的主语如果是第一人称,变为宾语从句则与主句的主语一致;如果是第二人称,则与主句的宾语一致;如果是第三人称,不用变化。 (一主二宾三不变) “May I use your knife?”He asked me. →He asked me if he might use my knife. “Do you know her telephone number?” He asked me. →He asked me if I know her telephone number. b. 宾语从句的标点均由主句决定。 主句是陈述句,用句号;主句是疑问句,用问号。如: Who will give us a talk? I don’t know. → I don’t know who will give us a talk.