
3 脂环烃习题参考答案
1、用系统命名法命名或写出结构式
CH 3
(1)
(2)
3
(1)反-1,3-二甲基环己烷 (2) 2-甲基-5-环丙基庚烷 (3) 2-甲基-8-氯二环[3.2.1]辛烷
3
(5)
(4)
(6)
3
(4)7,7-二甲基-2-氯二环[2.2.1]庚烷 (5)1,4-二甲基-7-溴螺[2.4]庚烷 (6)1,6-二甲基-8-乙基螺[3.5]壬烷
(7)
(8)
2、写出符合C 5H 10的所有脂环烃的异构体(包括顺反异构体),并命名。
3
H 3H 3环戊烷
甲基环丁烷1,1-二甲基环丙烷
顺-1,2-二甲基环丙烷反-1,2-二甲基环丙烷
乙基环丙烷
3、试指出下列化合物哪些是顺式?哪些是反式?并指出构象的类型(ea 型、ee 型等)。
CH 3
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
3
3
3
3
顺式 ea 型
反式 ee 型
顺式 ea 型
反式 ae 型
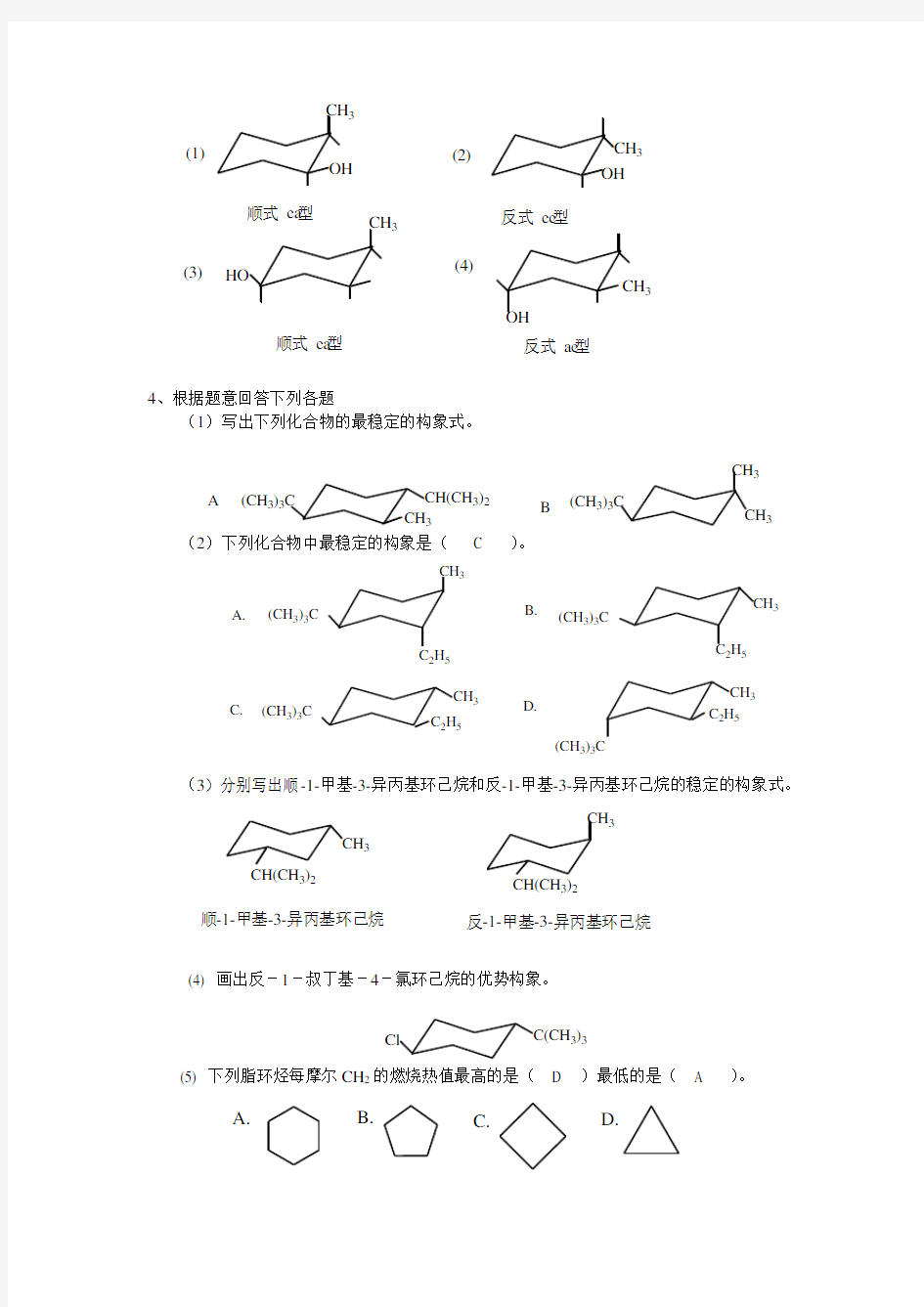
4、根据题意回答下列各题
(1)写出下列化合物的最稳定的构象式。
(CH 3)3
3)2
3
3
A
B
(CH 3)3
(2)下列化合物中最稳定的构象是( C )。
(CH 3)3C
3
25
(CH 3)3C
(CH 3)3C
(CH 3)3
A.
B.
C.
D.3
33255
5
(3)分别写出顺
-1-甲基-3-异丙基环己烷和反-1-甲基-3-异丙基环己烷的稳定的构象式。
32
3
3
3
2
顺-1-甲基-3-异丙基环己烷反-1-甲基-3-异丙基环己烷
(4) 画出反-1-叔丁基-4-氯环己烷的优势构象。
3)3
(5) 下列脂环烃每摩尔CH 2的燃烧热值最高的是( D )最低的是( A )。
A. B.
C. D.
(6) 下列化合物催化氢化时,最容易开环的是( C )。
A. B. C.
D.
(7)
下列脂环烃,最容易与溴发生加成反应的是( C
)。
A. B. C.
D.
(8) 下列化合物与HBr 加成能生成2-溴丁烷的是( C )。
CH 3?
CH 3?
CH 3?
A.
B.
C.
D.
(9) 什么是直立键和平伏键?
答:在环己烷的椅式构象中与分子的对称轴平行的C-H 键,叫做直立键或a 键。与直立键形成接近109.5°的夹角,平伏着向环外伸展的C-H 键,叫做平伏键或e 键 5、完成下列反应式
1、
C 2
H 2、
3
C 2
+ HCl
4、
3
3、
3)2
4H
3
3
3
3
+O=C(CH
3)
2
3
3
5、
6、用化学方法区别下列各化合物:
(1)
(2)
(3)
答:加溴的四氯化碳溶液不褪色的是(2),剩下的加高锰酸钾溶液,不褪色的是(1)。 7、推测结构
(1)化合物A 和B 是分子式为C 6H 12 的两个同分异构体,在室温下均能使Br 2-CCl 4 溶液褪色,而不被KMnO 4氧化,其氢化产物也都是3-甲基戊烷;但A 与HI 反应主要得3-甲基-3-碘戊烷,而B 则得3-甲基-2-碘戊烷。试推测A 和B 的构造式。
A 为
B 为
3
2H 53
(2)化合物A (C 6H 12),在室温下不能使高锰酸钾水溶液褪色,与氢碘酸反应得B (C 6H 13I )。A 氢化后得3-甲基戊烷,推测A 和B 的结构。
A 为
或
3
2H 53
B
为
或
(3)有A 、B 、C 、D 四个互为同分异构体的饱和脂环烃。A 是含一个甲基、一个叔碳原子及四个仲碳原子的脂环烃;B 是最稳定的环烷烃;c 是具有两个不相同的取代基,且有顺、反异构体的环烷烃;D 是只含有一个乙基的环烷烃。试写出A 、D 的结构式,B 的优势构象,C 的顺反异构体,并分别命名。
A 为
B 为
3
C 2
C 为3
C 2
D 为
2H 5
(资料素材和资料部分来自网络,供参考。可复制、编制,期待你的好评与关注)
大学英语四级模拟题十五 7’) Directions: In this section, you will hear three news reports. At the end of each news report, you will hear two or three questions. Both the news 一二三四五主观题客观题总分核查人 report and the questions will be spoken only once. After you hear a question, you must choose the best answer from the four choices marked A), B), C) and D). Then mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet with a single line Part I Writing through the center. (1 5’) Directions: For this part, you are allowed 30 minutes to write a letter to News Report One express your Questions 1 and 2 are based on the news report you’ve just heard. thanks to one of your friends whohelped you most whenyou were in difficulty. 1. A) 250, 000 at 50 centres. C) 255, 000 at 50 centres. You B) 250, 000 at 55 centres. D) 255,000 at 55 centres. should write at least 120 words but no more than 180 words. 2. A) Electronic detection. B) Telephone call screening. C) Fingerprints identification. Part II Listening Comprehension D) Sunday’s dress rehearsal. (2 5’) Section A (1 ’×7 = News Report Two word 版本整理分享
一、单项选择题:本大题共10个小题,每小题1分,共10分。在每小题给出的四个选项中,只有一项是符合题目要求的,把所选项的字母填在题后的括号内。 1.下列哪一个事件是心理学脱离思辨性哲学成为一门独立学科的标志?() A. 1879年,德国学者冯特在莱比锡大学建立了世界上第一个心理学实验室 B.1890年美国学者詹姆斯发表了他的经典著作《心理学原理》 C.瑞士心理学家皮亚杰通过一系列精心设计的试验,研究儿童思维发展的规律 D.俄国生理学家巴浦洛夫提出条件发射说 2. 个体在3~6岁处于()期。 A.童年 B.幼儿 C.少年 D.青年 3. 广义的学习是指人和动物在生活过程中获得个体经验并有经验引起相对()。 A.升华 B.发挥 C.表现 D.持久的变化 4. .看到一朵红花,这时的心理活动为()。 A.感觉 B.知觉 C.视觉 D.色觉 5. 艾宾浩斯遗忘曲线显示,遗忘是有规律的,其规律是()。 A.先快后慢 B. 逐步减慢 C.先慢后快 D.逐步加快 6. 思维的主要特征为( ) A.间接性和概括性 B.分析性和概括性 C.间接性和整合性 D.分析性和整合性 7. 意识的()是意识的最基本特征。 A.觉知性 B.能动性 C.目的性
D.社会历史性 8. ()是指个人对于自己认为重要的或有价值的事力求达成的欲望。 A.成就需要 B.交往需要 C.权利需要 D.进食需要 9. ()是构成一个人的思想、情感及行为的特有模式,这个独特模式包含了一个人区别与他人的稳定而统一的心理品质。 A.气质 B.性格 C.人格 D.自我 10. ()是信息的载体或媒介,即信息通过什么方式、用什么工具从信息源把信息传递给接受者。 A.信息源 B.信息 C.信息渠道 D.接受者 二、多项选择题:本大题共10个小题,每小题2分,共20分。在每小题给出的五个选项中,有两项或两项以上是符合题目要求的,把所选项前的字母填在题后的括号内。 1.人格特征是个人身上经常表现出来的稳定的心理特征。它集中反映了人心理活动的独特性,包括()。 A.兴趣 B.能力 C.气质 D.性格 E.理想 2. 1.中枢神经系统包括()。 A.脑垂体 B.脑 C.面神经 D.脊髓 E.脊神经 3. 技能按其本身的性质和特点可以分为()。 A.逻辑技能 B.动作技能 C.具体技能 D.抽象技能 E.智力技能 4. 产生深度知觉的单眼线索有多种,如:()。
教育心理学试题及答案 时间:2015-03-07 分类:期末试题 一、选择题(共15小题,每小题2分,共30分) 1、下列哪项不归之于学习与教学的系统过程中。(C ) A、学习过程 B、教学过程 C、反应过程 D、评价/反思过程 2、在皮亚杰看来,当学生的思维已超越对具体的可感知事物的依赖,能作出一定的概括时,他的思维水平已进入( D ) A、感知动作阶段 B、前运算阶段 C、具体运算阶段 D、形式运算阶段 3、下列规律中,不属于尝试——错误学习论的主要规律的是(D ) A、效果律 B、练习律 C、准备律 D、接近律 4、学生由过分重视成绩名次而产生的学习动机属于(B ) A、认知内驱力 B、自我提高内驱力 C、附属内驱力 D、交往内驱力 5、举一反三属于(A ) A、水平迁移 B、垂直迁移 C、一般迁移 D、负迁移 6、学习正方体、长方体的体积计算公式后,再学习一般立方体的体积计算公式,这属于(C ) A、并列结合学习 B、下位学习 C、上位学习 D、相关类属学习 7、运算技能属于哪种技能(B ) A、操作技能 B、心智技能 C、动作技能 D、运动技能 8、通过对要学习的新材料增加相关信息来达到对新材料的理解和记忆的方法,如补充细节、举出例子,或使之与其他观念形成联想等。这种促进知识保持的方法是( B ) A、过度学习 B、深度加工 C、组块化编码 D、及时复习 9、创造思维的核心是(C ) A、直觉思维 B、形象思维 C、发散思维 D、聚合思维 10、根据柯尔伯格的分类,中学生的道德主要处在 A、前习俗水平 B、习俗水平 C、后习俗水平 D、他律水平 11、心理辅导的主要目标是学会调适和(D ) A、诊断问题 B、克服障碍 C、行为矫正 D、寻求发展 12、在教学设计时,下列哪项不是分析教学任务涉及的主要内容(D ) A、确定学生原有基础 B、分析使能目标 C、分析支持性条件 D、分析学习结果 13、课堂里某种占优势的态度与情感的综合状态被称为(C ) A.群体凝聚力B.群体规范C.课堂气氛D.人际关系 14、衡量一个测验能否测量出所要测量的特征或品质的指标被称为(A ) A.效度B.区分度C.信度D.难度 15、福勒等认为,当教师较多地关注"学生是否喜欢我"、"同事怎样看我"、"领导怎样评价我" 时,他此时主要处在教师成长历程的( A ) A、关注生存阶段B 、关注情境阶段C、关注学生阶段D、关注成就阶段 二、填空题:每小题1分,共20分。 16、教育心理学是一门研究学校情境中学与教的基本心理规律的科学。 17、在中学生人格发展的过程中,随着年龄的增长,同伴的影响在某种程度上甚至超过父母的影响。
Part II Reading Comprehension (35 minutes) Directions: There are 4 passages in this part. Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked A), B), C) and D). You should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet with a single line through the center. Passage One Questions 21 to 25 are based on the following passage. Unless we spend money to spot and prevent asteroids (小行星) now, one might crash into Earth and destroy life as we know it, say some scientists. Asteroids are bigger versions of the meteoroids (流星) that race across the night sky. Most orbit the sun far from Earth and don’t threaten us. But there are also thousands of asteroids whose orbits put them on a collision course with Earth. Buy $50 million worth of new telescopes right now. Then spend $10 million a year for the next 25 years to locate most of the space rocks. By the time we spot a fatal one, the scientists say, we’ll have a way to change its course. Some scientists favor pushing asteroids off course with nuclear weapons. But the cost wouldn’t be cheap. Is it worth it? Two things experts consider when judging any risk re: 1) How likely the event is; and 2) How bad the consequences if the event occurs. Experts think an asteroid big enough to destroy lots of life might strike Earth once every 500,000 years. Sounds pretty rare—but if one did fall, it would be the end of the world. “If we don’t take care of these big asteroids, they’ll take care of us,” says one scientist. “It’s that simple.” The cure, though, might be worse than the disease. Do we really want fleets of nuclear weapons sitting around on Earth? “The world has less to fear from doomsday (毁灭性的) rocks than from a great nuclear fleet set against them,” said a New York Times article. 21. What does the passage say about asteroids and meteoroids? A) They are heavenly bodies different in composition. B) They are heavenly bodies similar in nature.
2021年心理学考试发展心理学知识全真模拟试 卷及答案(一) 一、选择题 1.儿童心理学是研究()的科学。 A.儿童心理发展规律 B.儿童各年龄阶段的心理特征 C.A和B D.儿童个体心理发展 2.从动物到人类的演化过程中,心理发生发展的历史是指()A.动物心理发展 B.人类心理发展 C.心理的个体发展 D.心理的种系发展 3.儿童发展心理学是研究()的科学。 A.儿童心理发展规律 B.儿童各年龄阶段的心理特征 C.儿童心理发展的规律和年龄特征 D.儿童个体心理发展 二、填空题 1.所谓心理的种系发展,是指从动物到人类的演化过程中的历史。2.儿童心理学是研究儿童心理发展的基本规律和儿童各年龄阶段的的科学。
3.儿童心理研究的类型从时间的延续上,可分为和横断研究。三、名词解释 1.儿童发展心理学 2.心理的种系发展 3.心理的个体发展 4.纵向研究 5.横向研究 四、简答题 1.简述儿童心理学研究对象的基本内容。 2.简述心理的种系发展。 3.简述心理的个体发展。 4.简述儿童心理发展的基本规律。 五、论述题 1.结合教育实际,论述遗传、环境和教育在儿童心理发展上的作用。2.结合教育实际,论述儿童心理发展的动力。 3.论述教育与发展的辩正关系。 4.论述儿童心理不断发展和发展阶段的关系。 第一章参考答案 一、选择题 1、C 2、D 3、C 二、填空题 1、心理发生发展 2、心理特征 3、纵向研究
三、名词解释 1、儿童心理学是研究儿童心理发展的基本规律和儿童各年龄阶段的心理特征的科学。 2、所谓心理的种系发展,是指从动物到人类的演化过程中心理发生发展的历史。 3、心理的个体发展是指人的个体从出生到成熟到衰老的过程中心理发生发展的历史。 4、纵向研究就是对同一人群在不同的时间里对他们的某种心理活动进行评价,比较两次或两次以上的研究结果,以此作为这种心理活动在这些年内发展变化的依据。 5、这种研究设计就是在同一个评价时间内,对不同年龄的人群进行心理观察或实验,比较各个年龄的人群在所观察或实验的某种心理活动上的差异,作为这种心理活动发展变化的依据。 四、简答题 1.儿童心理发展是儿童心理学的研究对象。 ①儿童心理发展首先是一种心理现象。 ②关于心理发展的研究,一般是从心理的种系发展和心理的个体发展进行的。 ③儿童心理发展是个体心理发展中的一个具有自己特点的部分。2.心理的种系发展是指从动物到人类的演化过程中心理发生发展的历史。 ①心理这一反映形式是在动物出现以后才开始产生的,是跟神经系统、
Questions 47 to 56 are based on the following passage. Have you ever been afraid to talk back when you were treated ____47 ___? Have you ever bought something just because the salesman talked you into it? Are you afraid to ask someone for a date. Many people are afraid to assert(表现)themselves. Dr. Alberti thinks it's because their self-respect is low. "Our whole ____48 ___ is designed to make people distrust themselves," says Alberti. "There's always '____49 ___' around-a parent, a teacher, a boss-who 'knows better'. These superiors often gain when they chip(削弱) away at your self-image." But Alberti and other scientists are doing something to help people ____50 ___ themselves. They ____51 ___ "assertiveness training" courses-At for short. In the AT courses people learn that they have a right to be themselves. They learn to speak out and feel good about doing so. They learn to be more ____52 ___ without hurting other people. In one way. learning to speak out is to ____53 ___ fear. A group taking a course will help the timid person to lose his fear. But AT uses an even stronger ____54 ___-the need to share. The timid person speaks out in the group because he wants to tell how he feels. Whether or not you speak up for yourself depends on your self-image. If someone you face is more "important" than you, you may feel less of a person. You start to ____55 ___ your own good sense. You go by the other person's ____56___ . But, why should you? AT says you can get to feel good about yourself. And once you do, you can learn to speak out. [A] doubt [I] peace [B] active [J] demand [C] system [K] ask [D] offer [L] superior [E] unfairly [M] overcome [F] unfortunately [N] confidence [G] motive [O] roar [H] image Section B Directions: There are 2 passages in this section. Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked [A], [B], [C] and [D]. You should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding letter on Answer Sheet 2 with a single line through the center. Passage One Question 57 to 61 are based on the following passage. Among all the animals, the ape is most like human beings. Both people and apes have the similar brain structure, the similar nerve system, and the similar kind of blood. There are four kinds of apes: the chimpanzee(黑猩猩), the orangutan(猩猩), the gorilla(大猩猩), and the gibbon(长臂猿). They live in the deep forests and warm tropical regions of Africa and of Southeast Asia, including Indonesia.
2012年中学心理学模拟题及答案1(1) 一、选择题:本大题共15小题,每小题2分,共30分。在每小题给出的四个选项中,只有一个是符合题目要求的,把所选项的字母填在题后的括号内。 1.某教师通过调查、访谈、观察等方式研究本地区十几所学校语文教师的课堂教学行为,他所采用的研究方法属()。 A.实验研究B.个案实验C.描述性研究D.实验室实验 2.某学生对待事物的态度容易受到同学、老师的影响,善于察言观色,其知觉方式属于()。A.沉思型B.场依存型C.冲动型D.场独立型 3.某同学每周都对自己的学习情况做出小结,分析自己在学习上取得的进步,找出自己的薄弱环节。他这种行为属()。 A.自我认识B.自信C.自我体验D.自我调控 4.新课程倡导的研究性学习、合作学习、教学对话等教学方式,其主要理论依据是()。A.建构学习论B.结构学习论C.认知学习论D.联结学习论 5.学生在英语学习中对相似的单词不能加以正确区分的现象属于()。 A.分化B.泛化C.消退D.遗忘 6.学生学习是为了改变自己在班集体中的排名,这样的学习动机属于()。 A.认知的驱力B.附属内驱力C.自我提高内驱力D.交往内驱力 7.学生原有知识对新学习的影响属于()。 A.逆向迁移B.负迁移C.顺向迁移D.正迁移 8.学习正方体、长方体的体积计算公式后,再学习一般立方体的体积计算公式V=Sh,这属于()。 A.并列结合学习B.下位学习C.上位学习D.相关类属学习 9.通过对要学习的新材料增加相关信息来达到对新材料的理解和记忆的方法,如补充细节、举出例子,或使之与其他观念形成联想等。这种促进知识保持的方法是()。 A.过度学习B.深度加工C.组块化编码D.及时复习 10.下列哪种学习策略属于元认知策略()。 A.设置目标B.列提纲C.寻求同学帮助D.做笔记 11.学生在学习弹奏钢琴曲的练习中,当练习到一定阶段时,常会感到自己的进步似乎停了,这种现象属技能学习中的()。 A.高原现象B.倒摄抑制C.生理极限D.及时反馈 12.画线是阅读时常用的一种()。 A.精加工策略B.复述策略C.组织策略D.资源管理策略 13.在解几何证明题中,学生常从问题的目标状态往回走,先确定达到该目标所需要的条件,然后再将达到目标所需要的条件与问题提供的已知条件进行对比,完成证明过程。这种方法属于问题解决中的()。 A.反推法B.算法式C.简化法D.类比法 14.某儿童开始认识到规则不是绝对的、一成不变的,而是可以协商或修改的。按照皮亚杰的道德发展阶段论,该儿童道德发展处于()。 A.他律阶段B.前习俗阶段C.自律阶段D.寻求认可取向阶段 15.在课堂上,某教师注重创造自由气氛,鼓励学生自由发表意见,不把自己的意见强加于学生。该教师对课堂管理的领导方式主要属于()。 A.参与式B.监督式C.放羊式D.控制式
2020年自考《心理学》模拟试题及答案(卷一)单选题 1.格式塔心理学派的代表人物是( BCD )。 A.佛洛依德 B.魏特墨 C.考夫卡 D.苛勒 2.根据活动任务的要求,有意识地主动地把注意从一个对象转移到另一个对象称为( C )。 A.注意的稳定性 B.注意的分心 C.注意的转移 D.注意的分配 3.我们知觉到月亮在动,而浮云是静止的,是因为( B )。 A.动景运动 B.诱发运动 C.自主运动 D.真实运动 4. ( ABD )属于深度知觉的单眼线索。 A.线条透视 B.相对大小 C.辐合 D.遮挡 5. 语言的基本语音单元是( B )。 A.短语 B.音位 C.语素 D.单词 6. 支持语言获得的后天学习论的研究者是( ACD )。 A.巴甫洛夫 B.乔姆斯基 C.班杜拉 D.斯金纳 7.“情绪。只是一种身体状态的感觉”是( D ) 的观点。
A.拉扎勒斯 B.阿诺德 C.兰格 D.詹姆斯 8.独立、果断、勇敢、坚韧等属于性格的( B )特征。 A.态度 B.意志 C.情绪 D.理智 9.有些原本学习很好的学生在升入高中之后,会出现学习成绩下降、心情烦躁、无所事事,甚至出现想退学的想法,这种现象通常属于( A )。 A.适应性障碍 B.急性应激障碍 C.心境障碍 D.情绪障碍 10.下列运动中,容易出现沉浸体验的是( AD )。 A.运动 B.逛街 C.做家务 D.从事自己喜欢的活动 二、名词解释 11.感觉:是人们认识和理解外部世界的最初阶段。外部的物理刺激作用于人的感觉器官,人的头脑接受和加工了这些刺激的属性,进而认识了这些属性的过程,这就是感觉。 12.定势:在问题解决过程中,如果先前曾采用某种方法解决某类问题并多次获得成功,以后再次遇到同类问题时还会重复采用同样的方法,这就是问题解决过程中的定势。 13.情绪:是有机体反映客观事物与主体需要之间关系的态度体验。
试题库(习题) 第四章 脂环烃 一、命名下列化合物 1. 2. 1-甲基-2-异丙基环戊烷 1,6-二甲基螺[4.5]癸烷 3. CH 3 C 2H 5 4. 1-甲基-2-乙基环戊烷 螺[3.4]辛烷 5. 6. CH 3 CH 3 二环[2.2.1]庚烷 反-1,2-二甲基环丙烷 7. CH(CH 3)2 8. Br 异丙基环丙烷 5-溴螺[3.4]辛烷 9. 3)23 10. 顺-1-甲基-2-异丙基环己烷 2,7,7-三甲基二环[2.2.1]庚烷 11. CH 3 12. Cl Cl 6-甲基螺[2.5]辛烷 7,7-二氯二环[4.1.0]庚烷 二、写出下列化合物的结构式 1、环戊基甲酸 2、4-甲基环己烯 COOH CH 3 3、二环[4.1.0]庚烷 4、反-1-甲基-4-叔丁基环己烷 (CH 3)3CH 3 5、3-甲基环戊烯 6、5,6-二甲基二环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯 CH 3 CH 3CH 3 7、7-溴双环[2.2.1]庚-2-烯 8、2,3-二甲基-8-溴螺[4.5]癸烷
H Br CH 3CH 3 Br 9、4-氯螺[2.4]庚烷 10、反-3-甲基环己醇 Cl CH 11、8-氯二环[3.2.1]辛烷 12、1,2-二甲基-7-溴双环[2.2.1]庚烷 Cl CH 3 H CH 3 Br 二、完成下列反应式 1.+ CH 3 O 2. + CH 2 CHCl C O CH 3 3.CH 3 CH CH 2CH 2 + HBr 4. + COOEt COOEt CH CH 2CH 3 CH 3Br COOEt COOEt 5.CH 3CH CH 2CH 2 + HCl 6. CH 3 + COOCH 3 COOCH 3 Cl CH CH 2CH 3CH 3 COOCH 3CH 3 COOCH 3 7.CH 3 + CH 3 COOCH 3 COOCH 3 8. H 3C H 3C CH 2CH 3Cl 2 + COOCH 3CH 3 CH 3 COOCH 3 C 2H 5Cl C CH 2CH CH 3Cl CH 3 9. + O CH 3 10. HBr H 3C H 3C CH 2CH 3+ C O CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH C CH CH 3 Br
2.3.2 环烷烃的命名
单环烷烃的命名 A. 当支链不复杂时,以环烷烃为母体 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane 1,2-二甲基环戊烷 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopentane 1-甲基-3-乙基环戊烷
单环烷烃的命名methylcyclopentane 2-ethyl-4-methyl-1-propylcycloheptane 甲基环戊烷 4-甲基-2-乙基-1-丙基环己烷A. 当支链不复杂时,以环烷烃为母体 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclopentane 1,2-dimethylcyclopentane 1,2-二甲基环戊烷1-甲基-3-乙基环戊烷
B. 当支链较复杂或不易命名时,以环烷基为取代基 3-cyclohexylhexane 3-环己基己烷 C. 两环相连时 Cyclopropylcyclohexane 环丙基环己烷Cyclopropylcyclopropane 环丙基环丙烷
多环烷烃的命名 A. Spiro cycloalkanes 螺环烃 1)选母体:根据成环的总碳原子数,称为“螺某烷”。 2)编号:从小环开始;从第一个非螺原子开始。3)书写:先写词头“螺”方括号内沿着编号方向写出每个环中除螺原子外的每个环的碳原子数数字之间用圆点隔开最后写出包括螺原子在内碳原子数的烷烃名称12 345678910螺[4.5]癸烷
“小原则”:在不违背螺环烃命名的“大”原则基础上,在编号时应尽可能令取代基的位号最小。 1 2 3 45 67 8 9 10 1-甲基螺[4.5]癸烷思考!
大学英语四级模拟题四 Part One Reading Comprehension (2’×10 = 20’) Directions: There are 2 passages in this section. Each passage is followed by some questions or unfinished statements. For each of them there are four choices marked A), B), C) and D). Y ou should decide on the best choice and mark the corresponding letter on the Answer Sheet with a single line through the centre. Passage One Air pollution can spread from city to city. It even spreads from one country to another. Some northern European countries have had “black snow”from pollutants that have traveled through the air from other countries and have fallen with the snow. So air pollution is really a global problem. Air pollution can kill babies, older people, and those who have respiratory(呼吸的)diseases. As found in cities, air pollution increases the risks of certain lung diseases. Air pollution can cause both airplane and car accidents because it cuts down visibility(能见度). There are other possible health dangers from air pollution that we don’t know much about. For example, scientists are trying to find out whether chemicals that reach us from the air may cause changes in our cells. These changes might cause babies to be born with serious birth defects. Scientists are trying to learn how all the many chemicals are apt(易于的)to take into our bodies from air, water, food, and even medicines act together to affect our health and the way our bodies work. That is another reason why it is so important to begin to control pollution now instead of waiting until we learn all the answers. Air pollution costs us a lot of money. It corrodes(腐蚀)our buildings. It damages farm crops and forests. It has a destructive effect on our works of art. The cost of all this damage to our government is great. It would be much more worthwhile, both for us and for the government, to spend our tax dollars on air pollution control. 1.Air pollution may lead to airplane accidents because . A. it may cause pilots to be ill B. engines may fail from the air-borne dirt C. visibility is reduced D. it brings a lot of black snow 2. Scientists are trying to find a link between pollution and . A. intelligence levels B. birth problems C. man’s behavior D. the nervous system 3. Scientists have not yet determined . A. all of the effects of pollution on the human body B. how pollution can be controlled successfully C. when the atmosphere first became polluted D. how some snow becomes black 4. The author suggests that before air pollution becomes more serious, . A. factories will be forced to stop operating B. buildings should be protected C. the earth will begin to grow colder D. more money should be spent to solve the problem 5. We can conclude that . A. civilization may be ruined if pollution is not controlled B. pollution is more serious in Europe than it is in America C. most people do not know that pollution is a serious problem D. we should learn all the answers before we begin to control pollution Passage Two Stiletto heels could be banned from the workplace because of health and safety reasons, according to British Trade Union bosses. The Trade Union Congress, predominantly male, has proposed a motion arguing that high heels are disrespectful to women while they also contribute to long term injuries. They propose instead that women wear “sensible shoes” with an inch heel limit in an attempt to avoid future foot and back pain as well as injuries. The motion is due to be debated at next month’s conference. The motion states: “Congress believes high heels may look glamorous on the Hollywood catwalks but are completely in appropriate for the day-to-day working environment. Feet bear the burden of daily life, and for many workers prolonged standing, badly fitted footwear, and in particular high heels can be a hazard. Around two million days a year are lost through sickness as a result of lower limb disorders. Wearing high heels can cause long-term foot problems and also serious foot, knee and back pain and damaged joints. Many employers in the retail sector force women workers to wear high heels as part of their dress code. More must be done to raise awareness of this problem so that women workers and their feet are protected.” Nadline Dorries, the Tory Member of Parliament, however criticized the motion and said the extra height heels give women can help them when in the workplace. “I’m 5ft 3in and need every inch of my Christian Louboutin heels to look my male colleagues in the eye,” she said. “If high heels were banned in Westminster, no one would be able to find me. The Trade Union leaders need to get real, stop using obvious sexist tactics by discussing women’s stilettos to divert tension away from Labor chaos.” Michelle Dewberry, a former winner of The Apprentice, said the motion was patronizing(自认为高人一等的). “This is absolutely ridiculous and I think these union officials should be spending their time dealing with more important issues”, she said. “I’m at work in five-inch heels and perfectly able to do my job. Heels are sexy, they boost your confidence and they are empowering to women. I can’t imagine these officials debating a motion about how tightly men should wear their ties. Wearing heels is a personal choice.”
2020年考研专业课心理学预测试题及答案(1) 一、单项选择题 1、心理过程包括() A、理解过程、情感过程、行为过程 B、知觉过程、情感过程、行为过程 C、感觉过程、知觉过程、意志过程 D、理解过程、情感过程、意志过程 2.用信息加工的观点来研究人的感觉、知觉、记忆、思维等心理过程的心理观点是( )。 A.行为的观点 B.生物学的观点 C.现象学的观点 D.认知的观点 3.去过几次小朋友的家,就能画出具体的路线图来。认知发展到哪一阶段的儿童能做到这种水准( )。 A.感知运动阶段 B.前运算阶段 C.具体运算阶段 D.形式运算阶段 4.下面不属于内部感觉的是( )。 A.动觉 B.痛觉 C.平衡觉 D.内部感觉 5.()认为,不同性质的感觉是由不同的神经元传递信息的 A神经特殊能量学说B模式理论C特异化理论D行波理论 6.下列哪个现象反映的是视觉适合() A夜幕下,蓝色物体要比黄色物体更亮一些 B不管是白天还是夜晚,看到树叶的颜色总是绿色的 C直升机的螺旋桨高速旋转后,不再能观察到每片桨叶 D值夜班的消防员佩戴红色眼镜在室内灯光下活动
7.()能够很好地解释在某些情况下人为什么对一些刺激“视而不见,充耳不闻”现象 A衰减理论B过滤器理论C认知资源理论D双加工理论 8.人在每一瞬间,将心理活动选择了某些对象而忽略了另一些对象,这个特点指的是注意的() A指向性B集中性C目的性D能动性 9.幼儿获得概念的主要方式是() A典型事例B定义C言语讲解和概括D概念名称的组合 10.学习形成两个或更多的刺激与反应联结,即形成一系列的刺激 与反应联结的是() A连锁学习B信号学习C辨别学习D概念学习 11.具有加工信息和与存储信息双重功能的记忆是() A感觉记忆B短时记忆C工作记忆D长时记忆 12.内容效度主要用于考察()的有效性 A智力测验B人格测验C特殊水平测验D成绩、技能测验 13.既影响信度又影响效度的误差是() A随机误差B系统误差C抽样误差D评分误差 14.考察学生某次考试的分数与教师评定学术等级之间的相关水准,应采用() A积差相关B斯皮儿曼等级相关C肯德尔和谐系数D二列相关 15.创造性思维的主要成分是() A集中思维B抽象思维C发散思维D直觉思维