
附录:中英文翻译
15SpeechSignalProcessing
15.3AnalysisandSynthesisJ esse
W. Fussell
A fte r an acousti c spee ch s i gnal i s conve rte d to an ele ctri cal si gnal by a mi crophone, i t m ay be desi rable toanalyzetheelectricalsignaltoestimatesometime-varyingparameterswhichprovideinformationaboutamodel of the speech producti on me chanism. S peech a na ly sis i s the process of e stim ati ng such paramete rs. Simil arl y , g ive n some parametri c model of spee ch production and a se que nce of param eters for that m ode
l,speechsynthesis istheprocessofcreatinganelectricalsignalwhichapproximatesspeech.Whileanalysisandsynthesistechniques maybedoneeitheronthecontinuoussignaloronasampledversionofthesignal,mostmode rn anal y sis and sy nthesis methods are base d on di gital si gnal processing.
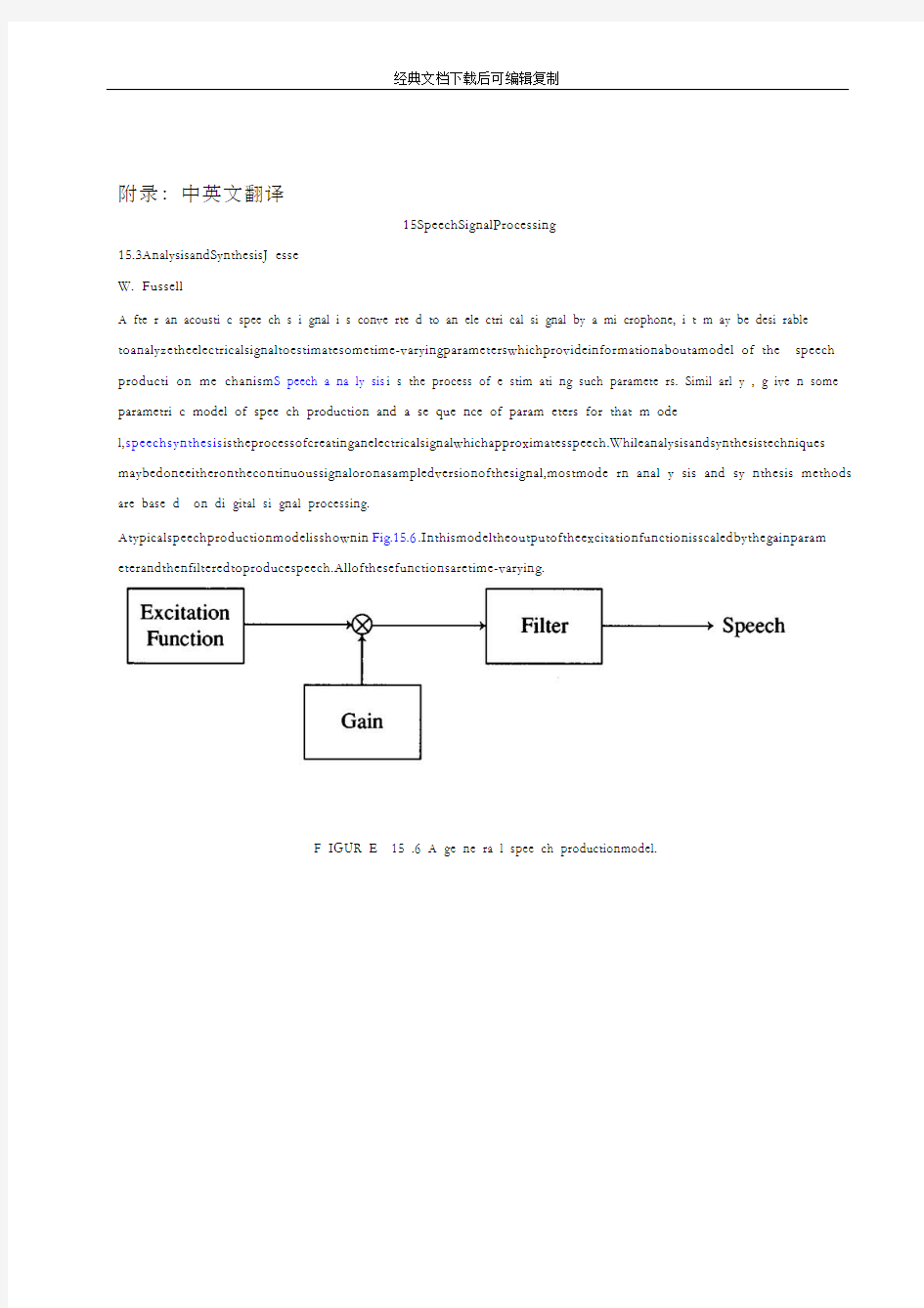
Atypicalspeechproductionmodelisshownin Fig.15.6.Inthismodeltheoutputoftheexcitationfunctionisscaledbythegainparam eterandthenfilteredtoproducespeech.Allofthesefunctionsaretime-varying.
F IGUR E 15 .6 A ge ne ra l spee ch productionmodel.
F IGUR E 1 5 .7 W ave form of a spoken phone me /i/ as i nbeet.
Formanymodels,theparametersarevariedataperiodicrate,typically50to100timespersecond.Mostspee ch inform ati on is containe d i n the porti on of the si gnal bel ow about 4 kHz.
Theexcitationisusually modeledaseitheramixtureorachoiceofrandomnoiseandperiodicwaveform.For hum an spee ch, v oi ced e x citati on occurs w hen the vocal fol ds in the lary nx vibrate; unvoi ce d e x citati onoccurs at constri cti ons i n the vocal tract w hi ch cre ate turbulent a i r fl ow [Fl anagan, 1965] . The rel ati ve mi x ofthesetw o type s ofexcitationisterme d ?v oicing.?In addition,theperiodi c e xcitation i s characterizedby afundamentalfrequency,termed pitch orF0.Theexcitationisscaledbyafactordesignedtoproducetheproperampli tude or level of the spee ch si gnal . The scaled ex citati on function i s then fi ltere d to produce the properspe ctral characte risti cs. W hile the filter m ay be nonli near, i t i s usuall y m odele d as a li nearfunction.
AnalysisofExcitation
Inasimplifiedform,theexcitationfunctionmaybeconsideredtobepurelyperiodic,forvoicedspeech,orpurel y random, for unvoi ce d. T hese tw o states correspond to voi ce d phoneti c cl asse s such as vow elsand nasalsandunvoicedsoundssuchasunvoicedfricatives.Thisbinaryvoicingmodelisanoversimplificationforsounds such as v oi ced fri cati ves, whi ch consist of a mi xture of peri odi c and random compone nts. Fi gure 15.7
is an ex ample of a time w ave form of a spoke n /i/ phoneme , w hi ch is w ell m odeled by onl y pe riodi c e x citation.
B oth ti me dom ai n and frequency dom ai n anal y s is te chni ques have bee n used to esti m ate the de greeofvoi ci ng for a short se gme nt or frame of spee ch. One ti me dom ain fe ature, te rme d the ze ro crossing rate,
i s
thenumberoftimesthesignalchangessigninashortinterval.AsshowninFig.15.7,thezerocrossingrateforvoicedsoundsisrelativ elylow.Sinceunvoicedspeechtypicallyhasalargerproportionofhigh-frequencyenergy than voi ce d spee ch, the ratio of high-fre que ncy to low -frequency e nergy is a fre que ncy dom aintechni que that provi des i nform ation on voi cing.
A nothe r measure use d to estim ate the de gree of voi ci ng is the autocorrel ation functi on, w hi ch is de fine d for
a sam pled speech se gment, S ,as
wheres(n)isthevalueofthenthsamplewithinthesegmentoflengthN.Sincetheautocorrelationfunctionofa periodi c functi on is i tsel f pe ri odi c, voi ci ng can be e sti mated from the de gree of pe ri odi city oftheautocorrel ati on function. Fi gure 15. 8 i s a graph of the nonne gati ve te rms of the autocorrel ation functi on for a64 -ms frame of the w aveform of Fi g . 15. 7. Ex cept for the de cre ase i n amplitude w ith i ncre asi ng lag, whi chresultsfromtherectangularwindowfunctionwhichdelimitsthesegment,theautocorrelationfunctionisseento be quite pe riodi c for thi s voi ce dutterance.
F IGUR E 1 5 .8 A utocorrel ati on functi on of one frame of /i/. Ifananalysisofthevoicingofthespeechsignalindicatesavoicedorperiodiccomponentispresent,another ste p i n the anal y si s process m ay be to estim ate the freque ncy ( or pe ri od) of the voi ce d com
ponent.Thereareanumberofwaysinwhichthismaybedone.Oneistomeasurethetimelapsebetweenpeaksinthetime dom ai n si gnal. For ex am ple i n Fi g . 15.7 the m aj or peaks are separate d by about 0. 00 71 s, for afundamentalfrequencyofabout141Hz.Note,itwouldbequitepossibletoerrintheestimateoffundamentalfre quency by mistaki ng the sm aller pe aks that occur betwee n the m a jor pe aks for the m aj or pe aks. Thesesmallerpeaksareproducedbyresonanceinthevocaltractwhich,inthisexample,happentobeatabouttwicethe ex citation fre quency . T his ty pe of e rror w ould re sult in an e sti m ate of pitch approxi m atel y tw i ce the corre ct fre quency.
The di stance betw ee n m ajor pe ak s of the autocorrel ation functi on is a closel y rel ate d fe ature thatisfre quentl y use d to esti m ate the pitch pe ri od. In Fi g . 15. 8, the di stance between the m aj or peaks in the autocorrelationfunctionisabout0.0071s.Estimatesofpitchfromtheautocorrelationfunctionarealsosusce pti ble to mistaking the fi rst vocal track resonance for the g l ottal e x citati on frequency.
The absol ute m agnitude di ffere nce functi on ( AM DF), de fi nedas,
is another functi on w hi ch is often use d i n estim ating the pitch of voi ce d spee ch. A n ex ample of the AM DF isshownin Fig.15.9forthesame64-
msframeofthe/i/phoneme.However,theminimaoftheAMDFisusedasanindicatorofthepitchperiod.TheAMDFhasbeenshownt obeagoodpitchperiodindicator[Rossetal.,19 74 ] and does not requi re multi pli cations.
FourierAnalysis
One of the m ore comm on processe s for e stim ating the spe ctrum of a se gme nt of spee ch is the Fourie rtransform [ Oppenheim and S chafer, 1 97 5 ]. T he Fourie r transform of a seque nce is m athem ati call y de fine das
wheres(n)representsthetermsofthesequence.Theshort-timeFouriertransformofasequenceisatimedependentfunction,definedas
F IGUR E 1 5 .9 A bsolute m agnitude diffe rence functi on of one frame of /i/.
wherethewindowfunctionw(n)isusuallyzeroexceptforsomefiniterange,andthevariablemisusedtoselectthesectionofthesequ enceforanalysis.ThediscreteFouriertransform(DFT)isobtainedbyuniformlysam pling the short-ti me Fourie r transform i n the fre quency dime nsi on. Thus an N-point DFT is computedusingEq.(15.14),
wherethe setofNsamples,s(n),may have firstbeenmultiplied by a window function.Anexampleofthemagnitudeofa512-pointDFTofthewaveformofthe/i/from Fig.15.10isshowninFig.15.10.Noteforthisfi gure, the 512 poi nts in the se que nce have been m ulti plied by a Ham ming w i ndow de fi nedby
F IGUR E 1 5 .1 0 M agnitude of 51 2-point FFT of Ham mi ng window e d/i/.
S ince the spe ctral characteristi cs of spee ch m ay change dram a ti call y in a fe w milli se conds, the le ngth, type,and l ocation of the wi ndow function are im portant consi derati ons. If the w indow is too long, changi ng spe ctralcharacteristicsmaycauseablurredresult;ifthewindowistooshort,spectralinaccuraciesresult.AHammingwi ndow of 16 to 32 m s durati on is com m onl y use d for spee ch analysis.
S everal characte risti cs of a speech utte rance m ay be dete rmine d by ex amination of the DFT m agnitude. InFig.15.10,theDFTofavoicedutterancecontainsaseriesofsharppeaksinthefrequencydomain.Thesepeaks, caused by the peri odi c sampl ing acti on of the g lottal ex ci tation, are separated by the fundame ntalfrequencywhichisabout141Hz,inthisexample.Inaddition,broaderpeakscanbeseen,forexampleatabout300 Hz and at about 2300 Hz. T hese broad peaks, calle d formants, result from resonances in the vocaltract. LinearPredictiveAnalysis
Givenasampled(discrete-time)signals(n),apowerfulandgeneralparametric modelfortimeseriesanalysisis
wheres(n)istheoutputandu(n)istheinput(perhapsunknown).Themodelparametersare a(k)fork=1,p,b( l ) for l = 1, q, and G. b( 0) is assume d to be unity. Thi s m odel , describe d as an autore g ressi ve m ov ing average(ARM A)orpole-zeromodel,formsthefoundationfortheanalysismethodtermedlinearprediction.Anautoregressive(AR) orall-polemodel,forwhichallofthe?b?coe fficientsexceptb(0)arezero,isfrequentlyused for spee ch anal y si s [M arkel and Gray, 1976].
In the standard A R formul ati on of li ne ar predi ction, the model paramete rs are sele cte d to mi ni mizethemean-
squarederrorbetweenthemodelandthespeechdata.Inoneofthevariantsoflinearprediction,theautocorrelationmethod,themini mizationiscarriedoutforawindowedsegmentofdata.Intheautocorrelationmethod,minimizingthemean-squareerror of the time domain samples is equivalentto minimizing theintegratedratioofthesignalspectrumtothespectrumoftheall-polemodel.Thus,linearpredictiveanalysisisagoodmethod forspectralanalysiswheneverthesignalisproducedby an all-pole system.M ost speechsounds fi t thi s model w ell.
One ke y consi deration for li near pre dicti ve anal y si s is the order of the model, p. For spee ch, if the orde ristoosmall,theformantstructureisnot well represented. If the orderis too large, pitch pulses as well asformantsbegintoberepresented.Tenth- or twelfth-order analysis is typical forspeech.Figures15.11 and15.12 provideexamplesof the spectrum produced by eighth-order and sixteenth-order linear predictiveanalysisofthe/i/waveformofFig.15.7.Figure15.11showstheretobethreeformantsatfrequenciesofabout30 0, 23 00, and 3200 Hz , whi ch are ty pi cal for an/i/.
Homomorphic(Cepstral)Analysis
For the speech m odel of Fi g. 15. 6, the e x citati on and filter i mpulse response are convol ved to produce thespeech.Oneoftheproblemsofspeechanalysisistoseparateordeconvolvethespeechintothesetw ocom ponents. One
such te chni que is called hom omorphi c filte ri ng [ Oppe nheim and S chafer, 1968 ]. Thecharacte risti c sy ste m
for a sy ste m for hom om orphi c deconvol ution conve rts a convolution operation to anadditi on ope ration. The output of such a characteristi c sy stem is calle d the com ple x cep str u m . The complex
cepstrumisdefinedastheinverseFouriertransformofthecomplexlogarithmoftheFouriertransformoftheinput.Iftheinputseque nceisminimumphase(i.e.,thez-transformoftheinputsequencehasnopolesorzerosoutside the unit ci rcle), the se quence can be represe nted by the real portion of the transforms. Thus, the re alcepstrum can be com pute d by cal cul ati ng the inve rse Fourie r transform of the log- spe ctrum of theinput.
FIGURE15.11Eighth-orderlinearpredictiveanalysisofan?i?.
FIGURE15.12Sixteenth-orderlinearpredictiveanalysisofan?i?.
Fi gure 1 5.1 3 show s an e x ample of the cepstrum for the voi ced /i/ utterance from Fi g. 15.7 . The cepstrum ofsuch a voi ce d utterance i s characte rized by rel ati vel y la rge v alues in the fi rst one or tw o milli se conds as w ellas
Chapter 1 Passage 1 Human Body In this passage you will learn: 1. Classification of organ systems 2. Structure and function of each organ system 3. Associated medical terms To understand the human body it is necessary to understand how its parts are put together and how they function. The study of the body's structure is called anatomy; the study of the body's function is known as physiology. Other studies of human body include biology, cytology, embryology, histology, endocrinology, hematology, immunology, psychology etc. 了解人体各部分的组成及其功能,对于认识人体是必需的。研究人体结构的科学叫解剖学;研究人体功能的科学叫生理学。其他研究人体的科学包括生物学、细胞学、胚胎学、组织学、内分泌学、血液学、遗传学、免疫学、心理学等等。 Anatomists find it useful to divide the human body into ten systems, that is, the skeletal system, the muscular system, the circulatory system, the respiratory system, the digestive system, the urinary system, the endocrine system, the nervous system, the reproductive system and the skin. The principal parts of each of these systems are described in this article. 解剖学家发现把整个人体分成骨骼、肌肉、循环、呼吸、消化、泌尿、内分泌、神经、生殖系统以及感觉器官的做法是很有帮助的。本文描绘并阐述了各系统的主要部分。 The skeletal system is made of bones, joints between bones, and cartilage. Its function is to provide support and protection for the soft tissues and the organs of the body and to provide points of attachment for the muscles that move the body. There are 206 bones in the human skeleton. They have various shapes - long, short, cube - shaped, flat, and irregular. Many of the long bones have an interior space that is filled with bone marrow, where blood cells are made. 骨骼系统由骨、关节以及软骨组成。它对软组织及人体器官起到支持和保护作用,并牵动骨胳肌,引起各种运动。人体有206根骨头。骨形态不一,有长的、短、立方的、扁的及不规则的。许多长骨里有一个内层间隙,里面充填着骨髓,这即是血细胞的制造场所。 A joint is where bones are joined together. The connection can be so close that no movement is possible, as is the case in the skull. Other kinds of joints permit movement: either back and forth in one plane - as with the hinge joint of the elbow - or movement around a single axis - as with the pivot joint that permits the head to rotate. A wide range of movement is possible when the ball - shaped end of one bone fits into a socket at the end of another bone, as they do in the shoulder and hip joints. 关节把骨与骨连接起来。颅骨不能运动,是由于骨与骨之间的连接太紧密。但其它的关节可允许活动,如一个平面上的前后屈伸运动,如肘关节;或是绕轴心旋转运动,如枢轴点允许头部转动。如果一根骨的球形末端插入另一根骨的臼槽里,大辐度的运动(如肩关节、髋关节)即成为可能。 Cartilage is a more flexible material than bone. It serves as a protective, cushioning layer where bones come together. It also connects the ribs to the breastbone and provides a structural base for the nose and the external ear. An infant's skeleton is made of cartilage that is gradually replaced by bone as the infant grows into an adult. 软骨是一种比一般骨更具韧性的物质。它是骨连结的保护、缓冲层。它把肋骨与胸骨连结起来,也是鼻腔与内耳的结构基础。一个婴儿的骨骼就是由软骨组成,然后不断生长、
大事记格式 大事记格式大事记作为一种公务文书,大事记忠实地记载着一个地区、一个部门的重要工作活动和重大事件,因此,它首先可以为本地区、本部门的工作总结、工作检查、工作汇报、工作统计和上级机关掌握面上情况提供系统的、轮廓性的材料。其次,大事记具有史料价值,可以起到录以备查的作用。大事记是党政机关、企事业单位、社会团体记载自己重要工作活动或自己辖区所发生的重大事件的一种应用文体。大事记 - 分类国际大事记根据制文机构职权范围的不同,大事记可以分为:1、世界大事记; 2、全国大事记; 3、地区大事记; 4、部门大事记; 5、单位大事记等;根据制文机构性质的不同,大事记可以分为:1、党政组织大事记;2、国家行政机关大事记;3、社会团体大事记;4、企业或事业单位大事记等;根据记载内容、性质的不同,可以分为:1、综合性大事记; 2、专题性大事记;根据时间跨度的不同,可以分为:1、古今大事记; 2、断代大事记; 3、年度大事记; 4、季度大事记; 5、每月大事记; 6、每旬大事记; 7、每周大事记; 8、每日大事记等。大事记 - 格式大事记格式示例大事记的格式单 一、固定,由标题和主体两部分组成。标题。主要有这样几种形式:由制文单位、事由和文种构成,如《中国医学大事记》;由制文单位和文种构成,如《××人民政府大事记》;由事由和文种构成,如《解放以后中国科技发展大事记》;由制文单位、时间和文种构成,如《××市人民政府八月份大事记》等。主体。一般由时间和事件两部分组成。时间按年、月、日的顺序依次排列;事件是指重要工作活动和重大事件。具体内容包括以下几个方面:1、党和国家方针政策贯彻执行中所产生的重大反响和出现的重大问题;2、机构设置、体制变动、重要人事调动等机构和组织变动情况;3、重要会议和重大活动,包括内务和外事活动;4、上级到本地区、本部门参加重大活动,或检查、指导工作并作出重大决策或重要部署、指示等;5、本地区、本部门的重要工作或重大事件等。大事记 - 记录范围大事记属大事、要事的记录范围 1.人事变动事。包括:本地区和本机关批准的主要领导人的任免、调动;本机关所属干部的重要奖励、处分、离休、退休和逝世等事。 2.组织变动事。包括:本地区和本机关批准的机构的成立、撒销、合并;本机关及所属下级名称的更改、职权范围的调整、内部组织机构的变更、办公地址的迁移,人员编制增减等事。 3.其他事。包括:本地区、本机关之外发生的重大事件在本地区、本机关发生的影响,以及本地区、本机关发生的重大社会动态、事故;气象的重大变化,以及遭受严重的自然灾害与善后处理等事。
企业创新战略外文翻译文献(文档含中英文对照即英文原文和中文翻译) 翻译之一: Choosing an innovation strategy: theory and practice Author:Joseph T. Gilbert Nationality:America Derivation:Business Horizons, Nov-Dec, 1994 Innovations come as both inventions and adoptions. They come in many types and vary greatly in complexity and scope. Companies attempting to
make a profit cannot continue for long periods without innovating. If they try, their customers will leave them for firms with more up-to-date products or services. It is an observed fact that different companies take different approaches to the use of innovation in attempting to improve their performance. Both academic and practitioner publications in recent years have contained a great deal of writing about innovation, the subjects of which have ranged from comparisons of national patterns of innovation to studies of individual innovations. However, little has been published regarding one issue of both theoretical and practical importance: the innovation policy or strategy of individual firms. Business strategy as a field of study is concerned with how a company competes in its chosen business. It deals with the analysis of a firm's strengths and weaknesses and the opportunities and threats presented by the firm's environment. Strategy looks toward consistent execution of broad plans to achieve certain levels of performance. Innovation strategy determines to what degree and in what way a firm attempts to use innovation to execute its business strategy and improve its performance. To choose an innovation strategy, managers might logically start by thinking about various kinds of innovations and their requirements. We shall discuss three major features of innovation, and analyze each in terms of distinct opposites, even though innovations found in the real world more often appear at various points between these opposites. Innovation is sometimes used in a limited sense to refer only to inventions (products, services, or administrative procedures that no other firm has introduced). More often, however, it applies in a more general sense that includes both invention as described above and imitation (adoption by a firm of a product, service, or administrative procedure that is not an invention but is new to that firm). We use the term in this second sense. Innovations can be characterized in a variety of ways. In the following
汤soup 羹soup 高汤thin soup; light soup; clear soup; consommé 清汤thin soup; light soup; clear soup; consommé 浓汤thick soup; pottage/potage 老汤soup stock 肉汤broth 骨头汤bone broth 肉片汤soup with meat slices 黄瓜肉片汤soup with meat and cucumber slices 肉片鱼羹sliced meat with fish paste in broth 丸子汤soup with meat balls; pork balls soup 氽丸子soup with meat balls; pork balls soup 肉圆粉丝汤pork balls soup with bean noodles 白肺汤pork lung soup 牛肉汤beef soup 羊肉汤mutton soup 鸡汤chicken soup; soup with chicken 鸡块汤soup with chicken slices; soup with sliced chicken; sliced chicken soup 鸡丝汤soup with shredded chicken; shredded chicken soup 草菇鸡片汤sliced chicken with mushrooms in soup 鸡茸玉米汤corn soup with minced chicken
鸡茸芦笋汤asparagus soup with mashed chicken 鸡茸黄鱼羹yellow croaker potage with minced chicken 鸡杂汤chicken giblets soup 鸡什汤chicken giblets soup 蔬菜鸡什汤chicken giblets soup with vegetables 鸭汤duck soup 火鸭芥菜汤sliced roasted duck with leaf mustered in soup 芥菜鸭汤duck soup with pickled mustard leaves 鸭掌汤duck web soup 竹笋鸭掌汤du ck’s feet with bamboo shoots in soup 鸭肝汤duck liver soup 冬菇鸭杂汤duck giblets soup with black mushrooms 鸭骨菜汤duck bone soup with vegetables 汤泡肫球gizzard balls in soup 三鲜汤soup with fish, shrimps and pork balls 红鱼汤fish soup with tomato 黄鱼羹yellow croaker chowder 鲫鱼汤soup with gold carp; gold carp soup 鱼翅汤soup with shark’s fins 鲍鱼汤soup with abalone; abalone soup 鲍鱼鸡片汤 abalone soup with sliced chicken 鲍鱼芦笋汤 abalone soup with asparagus 干贝汤dried scallop soup; soup with dried scallops 燕窝汤bird‘s nest soup 燕窝羹bird‘s nest soup 蛇羹snake soup; soup with snake 酸辣汤sour and pepper hot soup 豆腐汤bean-cud soup 蔬菜汤vegetables soup 榨菜汤hot pickled tuber mustard soup 榨菜肉丝汤hot pickled tuber mustard soup with shredded pork 榨菜粉丝汤hot pickled tuber mustard soup with bean noodles 什锦瓜丁汤 assorted meat soup with diced white gourd 鸡蛋羹steamed egg custard 鸡蛋汤eggdrop soup; egg soup 木须汤eggdrop soup; egg soup 蛋花汤eggdrop soup; egg soup 蕃茄鸡蛋汤egg soup with tomatoes 锅巴口蘑汤 mushroom soup with fried rice crust
第二部分 控制理论 第1章 1.1控制系统的引入 人类控制自然力量的设计促进人类历史的发展,我们已经广泛的能利用这种量进行在人类本身力量之外的物理进程?在充满活力的20世纪中,控制系统工程的发展已经使得很多梦想成为了现实?控制系统工程队我们取得的成就贡献巨大?回首过去,控制系统工程主要的贡献在机器人,航天驾驶系统包括成功的实现航天器的软着陆,航空飞机自动驾驶与自动控制,船舶与潜水艇控制系统,水翼船?气垫船?高速铁路自动控制系统,现代铁路控制系统? 以上这些类型的控制控制系统和日常生活联系紧密,控制系统是一系列相关的原件在系统运行的基础上相互关联的构成的,此外控制系统存在无人状态下的运行,如飞机自控驾驶,汽车的巡航控制系统?对于控制系统,特别是工业控制系统,我们通常面对的是一系列的器件,自动控制是一个复合型的学科?控制工程师的工作需要具有力学,电子学,机械电子,流体力学,结构学,无料的各方面的知识?计算机在控制策略的执行中具有广泛的应用,并且控制工程的需求带动了信息技术的与软件工程的发展? 通常控制系统的范畴包括开环控制系统与闭环控制系统,两种系统的区别在于是否在系统中加入了闭环反馈装置? 开环控制系统 开环控制系统控制硬件形式很简单,图2.1描述了一个单容液位控制系统, 图2.1单容液位控制系统 我们的控制目标是保持容器的液位h 在水流出流量V 1变化的情况下保持在一定 可接受的范围内,可以通过调节入口流量V 2实现?这个系统不是精确的系统,本系 统无法精确地检测输出流量V 2,输入流量V 1以及容器液位高度?图2.2描述了这 个系统存在的输入(期望的液位)与输出(实际液位)之间的简单关系, 图2.2液位控制系统框图 这种信号流之间的物理关系的描述称为框图?箭头用来描述输入进入系统,以及
大事记格式范文 一、大事记的概念 大事记是党政机关、社会团体、企事业单位记载自己重要工作活动或自己辖区所发生的重大事件的一种应用文体。 二、大事记的使用 作为一种公务文书,大事记服务于社会管理。由于它忠实地记载着一个地区、一个部门的重要工作活动和重大事件。因此,它首先可以为本地区、本部门的工作总结、工作检查、工作汇报、工作统计和上级机关掌握面上情况提供系统的材料。其次,大事记具有史料价值,可以起到录以备查的作用。它既可以为今人提供一个地区的政治、经济、文化、宗教等方面的状况,提供一个地区、一个部门自成立到发展,以及随着体制改革而变迁的轨迹,使人们从中去探索一些规律性的东西,作为指导现在和规划将来的借鉴;又可以为后人编年写史、从事历史研究保留可贵的资料。因此,各部门和单位,应该重视并不间断地编写大事记。 三、大事记的分类 根据制文机构职权范围的不同,大事记可分为世界大事记、全国大事记、地区大事记、部门大事记、单位大事记等;根据制文和机构性质的不同,大事记可以分为党政组织大事记、国家行政机关大事记、社会团体大事记、企业或事业单位大事记等;根据记载内容、性质的不同,可以分为综合性大事记和专题性大事记;根据时间跨度的不同,
可以分为贯通古今大事记、断代大事记、年度大事记、季度大事记以及每月大事记、每旬、每周、每日大事记等等。 四、大事记的格式、内容和写法 大事记的格式单一、固定,由标题和主体组成。 (一)标题。主要有几种形式:一种是由制文单位、事由和文种构成。如《中国新文学大事记》;一种是由制文单位和文种构成,如《××大事记》;一种是由事由和文种构成,如《企业改革大事记》;还有的是由制文单位、时间和文种构成,如《××公司三月份大事记》。 (二)主体。其内容一般由时间和事件两部分组成。其中时间是按年、月、日的顺序依次排列;事件是指重要工作活动和重大事件。具体内容大致包括以下几个方面:一是党和国家方针政策贯彻执行所产生的重大反响和出现的重大问题;二是机构设置、体制变动、重要人事调动,如任免、离退休等机构和组织变动情况;三是重要会议和重大活动,其中包括内务和外事活动;四是上级到本地区、本部门参加重大活动,或检查、指导工作并作出重大决策或重要部署、指示等;五是本地区、本部门的重要工作或重大事件,如取得的重大成绩,获取的重要数据,发生的重大事件、事故、案件、灾情等,群众反映的重大问题,提出的重要建议和意见,以及其他重要动态和需要记载的大事等等。 大事记主体的写法一般是以时系事,或一日一事,或一日几事,每事一条,每条一记。 由于大事记具有内容的史料性,记载的摘要性和表述的概括性等
营销策略外文翻译文献 (文档含中英文对照即英文原文和中文翻译)
译文: 营销策略 内容提要:为了组织的销售能是成功的,它需要根据一个营销策略计划来帮助保证其努力的目标和宗旨与市场的需要想吻合。营销策略审查市场以确定潜在顾客的需要,竞争者的战略和市场地位,并且尝试制定出一套能使组织在市场上获取或维护竞争优势的相关战略。有一些因素会对营销策略计划的发展造成冲击性的影响,它包括内部因素例如组织的财产、技能和组织文化,外在因素例如各种各样的市场驱动者、市场或产业运作方式、战略窗口和竞争的本质。一个优选的营销策略计划也需具备一套意外情况防备策略以应对市场治理及组织生产能力的不确定性。 关键词:竞争优势竞争策略市场地位市场份额营销销售计划组织文化营销策略 营销策略简述 无论组织的产品或服务多么好,除非它们的价值能被传达给潜在的顾客,否则组织依然无法实现它的使命。这种传达和交流是组织内市场营销功能的职责。根据美国市场协会,营销是“一个组织效能和一套创造过程、交流和传达产品价值给顾客、处理与顾客关系的有益于组织和它的利益共享者的方式”。营销作用包括相辅相成的两方面。营销策略在市场上审查市场来确定潜在顾客和竞争者本质的需要,并且试图开发
出在市场上将使组织获取或维护竞争优势的战略。操作的营销被建立在营销策略作用和贯彻各种各样的计划和策略(包括适当的混合营销的发展)吸引顾客和促进顾客忠实的基础之上的。 产品和服务营销的方法 有很多的方式能用来销售你的产品或服务包括做广告,直接响应、推销活动和宣传。然而,除非你能了解顾客、市场和产业的需要并且竞争的优势和劣势,否则这些方法是不太可能成功的。营销策略帮助一个组织尖化它的焦点和在市场顺利地竞争。营销策略与二个组分有关:目标市场和用最佳的方式传达你的产品价值或服务到那个市场。一个可实行的销售方针的发展取决于几个关键维度。首先,与组织之内的所有全球性战略一样,一个成功的销售方针需要由在组织之内的最高管理层签名。销售方针本质上也具有政治性的色彩:在组织之内的强有力的单位在最佳的销售方针也许不同意,并且协议也许需要谈判达成。销售方针也许受组织文化的也影响,并且那得假定这发生。例如,如果组织总是销售它的装饰物给商业主管,它也许就看不到组织之内的低层人员甚至是成人或少年的个人消费潜力。 实施战略销售计划发展的因素 存在一些能冲击战略销售计划发展的因素,这些因素首先包括组织已经拥有或它可能欣然获取的财产和技能。例如,如果组织拥有一个重大编程的部门,就为它能做和销售应用软件提供了可行性的条件。然而,如果这些人员已经在其他工作介入并且不能自由研究一个新的软件项目,并且组织没能力聘用另外的程序员,起始一条新的软件线是不妥当
附录:中英文翻译 15SpeechSignalProcessing 15.3AnalysisandSynthesisJ esse W. Fussell A fte r an acousti c spee ch s i gnal i s conve rte d to an ele ctri cal si gnal by a mi crophone, i t m ay be desi rable toanalyzetheelectricalsignaltoestimatesometime-varyingparameterswhichprovideinformationaboutamodel of the speech producti on me chanism. S peech a na ly sis i s the process of e stim ati ng such paramete rs. Simil arl y , g ive n some parametri c model of spee ch production and a se que nce of param eters for that m ode l,speechsynthesis istheprocessofcreatinganelectricalsignalwhichapproximatesspeech.Whileanalysisandsynthesistechniques maybedoneeitheronthecontinuoussignaloronasampledversionofthesignal,mostmode rn anal y sis and sy nthesis methods are base d on di gital si gnal processing. Atypicalspeechproductionmodelisshownin Fig.15.6.Inthismodeltheoutputoftheexcitationfunctionisscaledbythegainparam eterandthenfilteredtoproducespeech.Allofthesefunctionsaretime-varying. F IGUR E 15 .6 A ge ne ra l spee ch productionmodel.
Table of Contents Uuit 1 What is Geomatics? (什么是测绘学) (2) Unit 2 Geodetic Surveying and Plane Surveying(大地测量与平面测量) (6) Unit 3 Distance Measurement(距离测量) (10) Unit 4 Angle and Direction Measurement(角度和方向测量) (14) Unit 5 Traversing (导线测量) (17) Unit 6 Methods of Elevation Determination(高程测量方法) (21) Unit 7 Robotic Total Station (智能型全站仪) (25) Unit 8 Errors in Measurement(测量工作中的误差) (29) Unit 9 Basic Statistical Analysis of Random Errors (32) Unit 10 Accuracy and Precision (准确度和精度) (35) Unit 11 Least-Squares Adjustment (38) Unit 12 Geodesy Concepts (40) Unit 13 Geoid and Reference Ellipsoid (42) Unit 14 Datums, Coordinates and Conversions (44) Unit 15 Map Projection (46) Unit 16 Gravity Measurment (48) Unit 17 Optimal Design of Geomatics Network (50) Unit 18 Construction Layout (施工放样) (53) Unit 19 Deformation Monitoring of Engineering Struvture (56) Unit 20 Understan ding the GPS(认识GPS) (59) Uuit 21 Understanding the GPS (II) 认识GPS(II) (62) Unit 22 Competition in Space Orbit(太空轨道上的竞争) (64) Unit 23 GIS Basics(GIS 的基础) (69) Unit 24 Data Types and Models in GIS GIS中的数据类型和模型 (75) Unit 25 Digital Terrain Modeling(数字地面模型) (79) Unit 26 Applications of GIS (83) Unit 27 Developments of photogrammetry (87) Unit 28 Fundamentals of Remote Sensing (遥感的基础) (90) Unit 29 Digital Image Processing and Its Applications in RS (94) Unit 30 Airborne Laser Mapping Technology(机载激光测图技术) (99) Unit 31 Interferometric SAR(InSAR) (102) Unit 32 Brief Introduction toApplied Geophysics (104) Unit 33 Origon of Induced Polarization (105) Unit 34 International Geoscience Organization (108) Unit 35 Prestigious Journals in Geomatics (110) Unit 36 Relevant Surveying Instrument Companies (115) Unit 37 Expression of Simple Equations and Scientific Formulsa (116) Unit 38 Professional English Paper Writing (119) Unit 39 Translation Techniques for EST (127)
妙文翻译公司翻译样稿 中国汽车工业大事记 1901: 欧洲和美国第一批汽车进入中国 1913: 进口福特汽车公司T型轿车 1920: 中国2000英里的马路上行驶着7000辆汽车和600辆卡车,主要从美国进口 亨利.福特红河工厂培训中国学生 1923: 100名中国学生在底特律学习与工作 1929: 通用汽车公司在中国建立销售站,20世纪20年代到30年代,通用每年向中国销售10000到15000辆别克 福特在爱尔兰的工厂向中国出口拖拉机 1936: 梅赛德斯-奔驰在上海建立工厂生产公共汽车和卡车 1949: 共产党击败国民党,成立中华人民共和国 1950: 中国借助苏联的帮助筹建汽车厂 1953: 中华人民共和国第一家第一汽车制造厂(一汽)成立,根据苏联ZIS 150模型,生产4吨解放牌卡车 1958: 一汽模仿梅赛德斯-奔驰220开始生产红旗牌轿车 上海汽车组装厂(上海汽车工业集团的前身)成立 1964: 中国拥有147家工厂,生产卡车、汽车、摩托车和汽车零部件1966: 文化大革命开始 1967: 为防备可能的入侵,中国在湖北偏远山区建立东风汽车厂(第二汽车厂) 1972: 美国总统尼克松访华 1976: 中国有1500多家汽车及其零部件制造厂 1983: 美国汽车公司与北京汽车工业联合成立中国第一家汽车合资企业-北京吉普 1984: 大众汽车与上汽成立合资公司-上海大众 1985: 北京吉普开始生产吉普-切诺基 1986: 天津汽车厂开始生产大发查拉得-一款颜色永远不变的红色夏利主要为出租车
1988: 政治领导推出“三大,三小”术语描述中国汽车工业结构。第一梯队为第一汽车制造厂、东风和上汽,第一梯队为北京吉普、广州标致和 天津汽车厂 1991: 大众与一汽成立合资企业。截至2003年生产了捷达、宝来和高尔夫。 1991年中国客运汽车总生产量为81055辆 1992: 东风雪铁龙汽车公司生产ZX富康客用汽车 1994: 中国日报(中国政府机关报)报告中国效率低下的汽车制造厂将在“竞争面前萎缩” 宝马开始向中国出口汽车 1995: 福特持有江铃摩托车公司20%的股份 轻骑销量达到125万辆 1996: 奥迪加入一汽-大众合资企业,持有10%股份 1997: 标致从遇到麻烦的广州标致撤资 1998: 中国选择本田(而非通用欧宝)接管标致撤出的工厂,但是通用击败福特取得与上海汽车合资的批准,投资16亿美元 上海开始制造别克新世纪、此后增加别克GL8微型车、赛欧(基于欧 宝可赛)、SR-V、君威和凯越 1999: 北京第一个实行标准排放政策 一汽-大众开始生产奥迪 A6. 2000: 丰田获得与大发长期合作伙伴-天津汽车夏利建立合资企业的许可。 2002年开始生产丰田威驰 2001: 福特汽车与长安集团成立长安福特,各持一半股份。2003年1月开始生产福特嘉年华汽车 宝马和华晨集团成立华晨(中国),生产宝马3和5系列 中国加入WTO 2002: 1月,中国削减关税,到2006年中期最终减少25%。 价格战爆发,库存却在增加。一汽收购天津汽车。一汽和丰田就2010年前每年生产 200000至300000辆丰田汽车达成一致。北京现代汽车由北京汽车厂和现代汽车组合。 上汽集团收购韩国的通用大宇10%的股权,这是上汽首次在中国境外投资。上汽集团 和通用汽车公司成立通用五菱汽车并收购烟台车身公司。 与标致雪铁龙签定协议后,神龙汽车有限公司(DCAC)更名为东风标致雪铁龙汽车公 司( DPCA)以增加DCAC的产量,有4个新车型,并重新将标致品牌引进中国。 一汽与丰田联手生产高档轿车、微型车,中高档SUV车。新的合资企业计划截至2010 年,生产300000-400000辆汽车。 东风与日产组成合资企业,东风汽车有限公司,各占一半股份。
战略管理研究参考文献 (总目录) 项保华2003-5-31 重要说明:本目录经过多届博士生的共同努力,于2003年5月整理完成,主要提供本人指导的战略管理研究方向的博士生学习参考之用。可以认为,只要通读了本目录的大部分文献,必将能够对战略管理领域的当前及经典理论、方法有比较系统的把握。若能在此基础上潜心感悟,加强与同行的交流探索,定可具备解决具体战略理论与实践问题的创新思路与实用技能,从而顺利完成博士学位论文的选题与撰写。作为战略管理研究方向博士生培养的业务目标定位为,通过对战略理论与实践的系统学习,达到胜任国内重点高等院校战略领域的教学、研究、咨询工作之要求。所以,对于硕士生以及非战略管理研究方向的博士生而言,不作全面通读本目录文献之要求,各位可以根据自己的兴趣,从本目录中选取部分文献阅读,以作为参与战略课程学习之补充。 学习建议:以具体老师为师的范围终有限,而以文献为师则可延请古今中外名家赐教,广泛借鉴吸收多方面的见解。多读、多思、多写,书山无路勤为径,以学为乐恒则成!谨以此与各位共勉! 1、中文部分 为人经世 ?孔子, 论语(网上下载) ?老子, 道德经(网上下载) ?孙子, 孙子兵法(网上下载) ?马基雅维里(1469-1527), 君主论, 中国社会出版社, 1999 ?葛拉西安(1601-1658), 智慧书——永恒的处世经典(网上下载) ?何兆武, 西方哲学精神, 清华大学出版社, 2002 ?墨顿·亨特, 心理学的故事, 海南人民出版社, 1999 ?维克托·E.弗兰克尔, 人生的真谛, 中国对外翻译出版公司, 1994
? E. 迈尔, 生物学思想发展的历史, 四川教育人民出版社, 1990(网上下载) ?威尔逊, 新的综合:社会生物学(李昆峰编译), 四川人民出版社, 1985(网上下载) 战略总论 ?项保华, 战略管理——艺术与实务(第3版), 华夏出版社, 2003 ?明茨伯格等, 战略历程:纵览战略管理学派, 机械工业出版社, 2002 ?拜瑞·J·内勒巴夫;亚当·M·布兰登勃格, 合作竞争(Co-Opetition), 安徽人民出版社, 2000 ?迈克尔·波特, 竞争战略(原著1980年出版), 华夏出版社, 2003 ?迈克尔·波特, 竞争优势(原著1985年出版), 华夏出版社, 2003 ?迈克尔·波特, 国家竞争优势(原著1990年出版), 华夏出版社, 2002 ?迈克尔·波特等, 未来的战略, 四川人民出版社, 2000 ?格里·约翰逊;凯万·斯科尔斯, 公司战略教程, 华夏出版社, 1998 ?小乔治·斯托尔克等, 企业成长战略, 中国人民大学出版社、哈佛商学院出版社, 1999 专题探讨 ?保罗·索尔曼、托马斯·弗利德曼, 企业竞争战略, 中国友谊出版公司, 1985 ?罗伯特·艾克斯罗德, 对策中的制胜之道:合作的进化, 上海人民出版社, 1996 ?约瑟夫·巴达拉克, 界定时刻——两难境地的选择, 经济日报出版社、哈佛商学院出版社, 1998 ?芝加哥大学商学院、欧洲管理学院、密歇根大学商学院、牛津大学赛德商学院, 把握战略:MBA战略精要, 北京大学出版社, 2003 ?哈默尔、普拉哈拉德, 竞争大未来, 昆仑出版社, 1998 ?尼尔·瑞克曼, 合作竞争大未来, 经济管理出版社, 1998 ?卡尔·W.斯特恩、小乔治·斯托克, 公司战略透视, 上海远东出版社, 1999 ?乔尔·布利克、戴维·厄恩斯特, 协作型竞争, 中国大百科全书出版社, 1998
1、应力和应变 应力和应变的概念可以通过考虑一个棱柱形杆的拉伸这样一个简单的方式来说明。一个棱柱形的杆是一个遍及它的长度方向和直轴都是恒定的横截面。在这个实例中,假设在杆的两端施加有轴向力F,并且在杆上产生了均匀的伸长或者拉紧。 通过在杆上人工分割出一个垂直于其轴的截面mm,我们可以分离出杆的部分作为自由体【如图1(b)】。在左端施加有拉力P,在另一个端有一个代表杆上被移除部分作用在仍然保存的那部分的力。这些力是连续分布在横截面的,类似于静水压力在被淹没表面的连续分布。 力的集度,也就是单位面积上的力,叫做应力,通常是用希腊字母,来表示。假设应力在横截面上是均匀分布的【如图1(b)】,我们可以很容易的看出它的合力等于集度,乘以杆的横截面积A。而且,从图1所示的物体的平衡,我们可以看出它的合力与力P必须的大小相等,方向相反。因此,我们可以得出 等式(1)可以作为棱柱形杆上均匀应力的方程。这个等式表明应力的单位是,力除以面积。当杆被力P拉伸时,如图所示,产生的应力是拉应力,如果力在方向是相反,使杆被压缩,它们就叫做压应力。 使等式(1)成立的一个必要条件是,应力,必须是均匀分布在杆的横截面上。如果轴向力P作用在横截面的形心处,那么这个条件就实现了。当力P没有通过形心时,杆会发生弯曲,这就需要更复杂的分析。目前,我们假设所有的轴向力都是作用在横截面的形心处,除非有相反情况特别说明。同样,除非另有说明,一般也假设物体的质量是忽略的,如我们讨论图1的杆
一样。 轴向力使杆产生的全部伸长量,用希腊字母δ表示【如图1(a)】,单位长度的伸长量,或者应变,可以用等式来决定。 L是杆的总长。注意应变ε是一个无量纲的量。只要应变是在杆的长度方向均匀的,应变就可以从等式(2)中准确获得。如果杆处于拉伸状态,应变就是拉应变,代表材料的伸长或者延长如果杆处于受压状态,那么应变就是压应变,这也就意味着杆上临近的横截面是互相靠近的。 当材料的应力和应变显示的是线性关系时,也就是线弹性。这对多数固体材料来说是极其重要的性质,包括多数金属,塑料,木材,混凝土和陶瓷。处于拉伸状态下,杆的应力和应变间的线性关系可以用简单的等式来表示。E是比例常数,叫做材料的弹性模量。 注意E和应力有同样的单位。在英国科学家托马斯·杨(1773 ~ 1829)研究杆的弹性行为之后,弹性模量有时也叫做杨氏模量。对大多数材料来说,压缩状态下的弹性模量与处于拉伸时的弹性模量的一样的。 2、拉伸应力应变行为 一个特殊材料中应力和应变的关系是通过拉伸测试来决定的。材料的试样通常是圆棒的形式,被安置在测试机上,承受拉力。当载荷增加时,测量棒上的力和棒的伸长量。力除以横截面积可以得出棒的应力,伸长量除以伸长发生方向的长度可以得出应变。通过这种方式,材料的完整应力应变图就可以得到。 图1所示的是结构钢的应力应变图的典型形状,轴向应变显示在水平轴,对应的应力以纵坐标表示为曲线OABCDE。从O点到A点,应力和应变之间是