saej1268 淬透金属规范
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:4.25 MB
- 文档页数:96

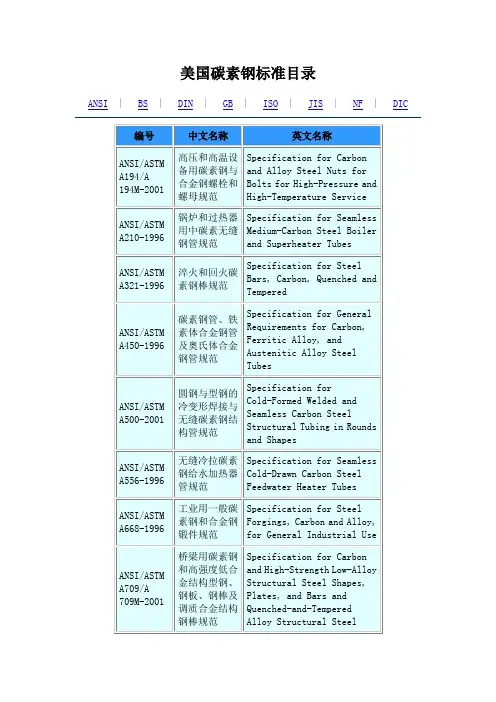
国外标准目录一、美国二、国际标准化组织三、欧洲四、英国五、日本六、德国七、法国八、澳大利亚九、俄罗斯十、韩国十一、巴西十二、奥地利十三、意大利十四、罗马尼亚十五、瑞典十六、波兰一、美国美国常用标准如下:ASTM美国材料与试验协会SAE美国汽车工程师协会UNS美国SAE和ASTM的“金属与合金统一数字体系”ASME美国机械工程师协会AMS美国航空材料规范AWS美国焊接协会ACI美国合金铸造协会API美国石油协会ANSI美国国家标准协会MIL美国军工标准FED美国政府民用采购标准 AISI美国钢铁协会一般碳钢、低合金钢 ASTM A6A6为结构钢基础性标准,规定一般交货要求和棒、板、型等尺寸及允许偏差等。
牌号、化学成分按相应专业标准的规定,例如A36碳素结构钢,A131船用结构钢,A242低合金结构钢,A283低中强度碳素钢板,A328钢板桩,A529结构级碳锰钢、A678结构用淬回火碳钢和低合金钢,A786轧制花纹钢板,A871耐大气腐蚀钢板,A992建筑框架用结构型钢等标准,这些产品标准中均规定具体牌号、化学成分、工艺和力学性能和检验等。
二、国际国际标准化组织ISO三、欧洲标准欧洲标准有两种: Euronorm标准和EN标准。
四、英国英国常用标准:BS一英国标准;BSEN一采用欧洲标准后的英国标准。
五、日本日本常用标准为JIS标准,即日本工业标准委员会标准。
钢筋钢钢筋包括:热轧生产的光圆和异型钢筋。
光圆钢筋牌号:SR235和SR295。
异型钢筋牌号:SD295A,SD295B,SD345,SD390和SD490 JIS G3112六、德国德国常用标准(手册)如下:DIN一德国标准DIN EN一采用欧洲标准(EN)的德国标准DIN ISO一采用国际标准(ISO)的德国标准SEW一德国钢铁材料手册LW一德国航空材料手册WW一德国筑坝技术材料手册七、法国标准法国常用标准:NF—法国标准;NFEN—采用欧洲标准的法国标准。


ETA-UTP001 Revision 0(SAE J1263)[P19].pdfETA-UTP001-Effective March 23,2001 Implementation of SAE J1263-1996.pdfNASA-SAE-88-1448 LDV Surveys Over Fighter Model at Moderate High Angles of Attack[P27].pdf SAE- Automotive Chassis Engineering Principles (SECOND EDITION)[P454].pdfSAE- Automotive Chassis-Engineering Principles [SECOND EDITION][P456].pdfSAE- Automotive Physical Layer SAE-J1708 DS36277.pdfSAE- Structural Steel Designer's Handbook (Brockenbrough & Merritt)(3Rd Edition)[P1201].pdf SAE-174M-MAY1998 TORQUE-TENSION TEST PROCEDURESTEEL THREADED FASTENERS,METRIC SERIES.pdfSAE-2006 Formula SAE-Chassis Design(Queen's University)[P18].pdfSAE-720709-1972 Design&Development of a High horsepower torque sensing variable speed drive.pdfSAE-AIR1228-2001 Standard Impulse Machine Equipment&Operation[P6].pdfSAE-AIR1377A-2004 Fire Test Equipment for Flexible Hose&Tube Assemblies[P22].pdfSAE-AIR3260-2006 Identification of Standard Utility Parts - Bolts&Nuts[P4].pdfSAE-AIR4002-1994 8000 psi Hydraulic Systems Experience&Test Results.pdfSAE-AIR4069A-1998 Sealing of Integral Fuel Tanks [P94].pdfSAE-AIR4069A-1998 Sealing of Integral Fuel Tanks[P95].pdfSAE-AIR4176-1995(R2005) Cost Versus Benefits of Engine Monitoring Systems.pdfSAE-AIR5120-2006 Engine Monitoring System Reliability&Validity[P27].pdfSAE-AIR797E-2001 Hose Characteristics&Selection Chart[P15].pdfSAE-AMS1376B-1992 R1998 Remover,Epoxy Paint Acid-Type,Thickened.pdfSAE-AMS1379A-1996 COMPOUND,ALKALINE RUST REMOVER Aircraft Turbine Engine Components[P7].pdfSAE-AMS1380A-1992 SCALE CONDITIONER,ALKALINE Aircraft Turbine Engine Components[P6].pdfSAE-AMS1382A-1991 OXIDE REMOVER COMPOUND,ACIDIC Aircraft Turbine Engine Components[P6].pdfSAE-AMS1383A-1999 Oxide Conditioner,Alkaline Permanganate Aircraft Turbine Engine Components.pdfSAE-AMS1384A-1991 ACID,INHIBITED PHOSPHORIC Aircraft Turbine Engine Components Room Temperature Application[P6].pdfSAE-AMS1385A-2004 Compound,Hot Carbon&Paint Remover Aircraft Turbine Engine Components.pdfSAE-AMS1386A-2004 Compound,Silicone Rubber Remover Aircraft Turbine Engine Components Room Temperature Application.pdfSAE-AMS1387A-2004 Remover,Anti-Galling Compound Aircraft Turbine Engine Components Room Temperature Application.pdfSAE-AMS1424G-2006 (R) Deicing_Anti-Icing Fluid,Aircraft SAE-Type I.pdfSAE-AMS1424H-2007 Deicing_Anti-Icing Fluid,Aircraft,SAE-Type I[P15].pdfSAE-AMS1426C-1993 FLUID,DEICINGANTI-ICING,RUNWAYS&TAXIWAYS Glycol Base.pdf SAE-AMS1428E-2006 Fluid,Aircraft DeicingAnti-Icing,Non-Newtonian (Pseudoplastic),SAE-Types II,III,&IV.pdfSAE-AMS1431B-1998 Compound,Solid Runway&Taxiway Deicing_Anti-Icing.pdfSAE-AMS1435A-1999 Fluid,Generic,Deicing_Anti-Icing Runways&Taxiways.pdfSAE-AMS1453-2004 Disinfectant Cleaner for Aircraft Interior General Purpose Liquid .pdfSAE-AMS1476B-2004 Deodorant,Aircraft Toilet.pdfSAE-AMS1526B-2000 Cleaner for Aircraft Exterior Surfaces Water-Miscible,Pressure-Spraying Type.pdfSAE-AMS1534B-2004 Cleaner,Aircraft Glass Window.pdfSAE-AMS1535C-2002 Cleaner,Transparent Plastic.pdfSAE-AMS1537B-2001 Cleaner,Alkaline Hot-Tank Type.pdfSAE-AMS1538A-1996 DEOXIDER,ACIDIC,FOR MAGNESIUM ALLOYS.pdfSAE-AMS1547-1996 Cleaner,Anodic,Electrolytic,Alkaline For Steel,Tank Type .pdfSAE-AMS1595A-1998 Qualification of Aircraft,Missile&Aerospace Fusion Welders.pdfSAE-AMS1625B-1989 DESMUTTER,ALUMINUM,POWDERED.pdfSAE-AMS1626B-1989 DESMUTTER,ALUMINUM Liquid.pdfSAE-AMS1631C-2005 Cleaner,Carpet Water Extraction Type.pdfSAE-AMS1640B-1988 CORROSION REMOVING COMPOUND For Aircraft Surfaces.pdfSAE-AMS2154-2005 Inspection,Ultrasonic,Wrought Metals,Process For.pdfSAE-AMS2154-2005 Inspection,Ultrasonic,Wrought Metals,Process For[P41].pdfSAE-AMS2175-2003 Castings,Classification&Inspection of.pdfSAE-AMS2241P-2005 Tolerances,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant Steel,Iron Alloy,Titanium,&Titanium Alloy Bars&Wire.pdfSAE-AMS2242F-2006 Tolerances Corrosion&Heat Resistant Steel,Iron Alloy,Titanium,&Titanium Alloy Sheet,Strip,&Plate.pdfSAE-AMS2243H-2006 Tolerances Corrosion&Heat-Resistant Steel Tubing.pdfSAE-AMS2244C-2003 Tolerances (R) Titanium&Titanium Alloy Tubing.pdfSAE-AMS2249F-2005 Chemical Check Analysis Limits Titanium&Titanium Alloys.pdfSAE-AMS2249F-2005 Chemical Check Analysis Limits Titanium&Titanium Alloys[1].pdfSAE-AMS2251G-1998 Tolerances Low-Alloy Steel Bars.pdfSAE-AMS2251H-2006 Tolerances Low-Alloy Steel Bars.pdfSAE-AMS2252D-2006 Tolerances Low-Alloy Steel Sheet,Strip,&Plate.pdfSAE-AMS2269F-2006 Chemical Check Analysis Limits Nickel,Nickel Alloys,and Cobalt Alloys.pdf SAE-AMS2372D 碳钢和低合金钢取样规范[中文版].pdfSAE-AMS2372D-JAN2002 Quality Assurance Sampling&Testing Carbon&Low-Alloy Steel Forgings[P6].pdfSAE-AMS2375D-2007 Control of Forgings Requiring First Article Approval [P6].pdfSAE-AMS2406L-2007 Plating,Chromium Hard Deposit [p7].pdfSAE-AMS2411F-2007 Plating,Silver for High Temperature Applications [P8].pdfSAE-AMS2412H-2007 Plating,Silver Copper Strike,Low Bake[P7].pdfSAE-AMS2417G-2004 Plating,Zinc-Nickel Alloy.pdfSAE-AMS2422E-2007 Plating,Gold[P9].pdfSAE-AMS2435G-2007 Coating,Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt Coating,Detonation Process [P8].pdfSAE-AMS2448-2004 Application of Tungsten Carbide Coatings on Ultra High Strength Steels High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process[P13].pdfSAE-AMS2448-2004 Application of Tungsten Carbide Coatings on Ultra High Strength Steels High Velocity Oxygen Fuel Process.pdfSAE-AMS2469G-2004 Hard Anodic Coating Treatment of Aluminum&Aluminum Alloys Processing&Performance Requirements.[P8].pdfSAE-AMS2470M-2007 Anodic Treatment of Aluminum Alloys Chromic Acid Process[P8].pdfSAE-AMS2482C-2006 Hard Coating Treatment of Aluminum Alloys Teflon-Impregnated or Codeposited.pdfSAE-AMS2482C-2006 Hard Coating Treatment of Aluminum Alloys Teflon-Impregnated or Codeposited[P7].pdfSAE-AMS2546-2004 Reaffirmed 2010-05 Laser Peening.pdfSAE-AMS2633C-2007 Ultrasonic Inspection Centrifugally-Cast,Corrosion-Resistant Steel Tubular Cylinders[P13].pdfSAE-AMS2643D-2007 Structural Examination of Titanium Alloys Chemical Etch Inspection Procedure [P5].pdfSAE-AMS2647C-2009 Fluorescent Penetrant Inspection Aircraft&Engine Component Maintenance.pdfSAE-AMS2649C-2008 Etch Inspection of High Strength Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2753B-1991 Liquid Salt Bath Ferritic Nitrocarburizing Non-Cyanide Bath[P8].pdfSAE-AMS2757-B-2004 气体氮碳共渗.pdfSAE-AMS2759_11-2005 Stress Relief of Steel Parts[P5].pdfSAE-AMS2759_2C-2000 低合金钢零件的热处理最小拉伸强度大于等于220KSI[中文版][P13].pdfSAE-AMS2759_3C-2000 沉淀硬化不锈钢和马氏体时效钢的热处理[中文版][P16].pdfSAE-AMS2759_3D-2005 Heat Treatment Precipitation-Hardening Corrosion-Resistant&Maraging Steel Parts[P16].pdfSAE-AMS2759_3D-2005 Heat Treatment Precipitation-Hardening Corrosion-Resistant&Maraging Steel Parts[P16][1].pdfSAE-AMS2759-11-1992 Ion Nitriding.pdfSAE-AMS2759-11-2005 Stress Relief of Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS27591-12A-2007 Gaseous Nitrocarburizing,Automatically Controlled by Potentials.pdf SAE-AMS2759-12A 2007 Gaseous Nitrocarburizing,Automatically Controlled by Potentials.pdfSAE-AMS2759-1C-2000 最低抗拉强度低于220 ksi (1517 MPa)低合金碳钢零件的热处理.pdf SAE-AMS2759-2C-2000 Heat Treatment of Low-Alloy Steel Parts Minimum Tensile Strength 220 ksi (1 51 7 MPa)&Higher.pdfSAE-AMS2759-2C-2000 中文版低合金钢零件的热处理最小拉伸强度大于等于220KSI(1517MPa).pdfSAE-AMS2759-3C-2000 中文版沉淀硬化不锈钢和马氏体时效钢的热处理.pdfSAE-AMS2759-3D-2005 Heat Treatment Precipitation-Hardening Corrosion-Resistant&Maraging Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2759-4B-2001 Heat Treatment Austenitic Corrosion-Resistant Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2759-5D-2004 Heat Treatment Martensitic Corrosion-Resistant Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2759-6A-2002 Gas Nitriding&Heat Treatment of Low-Alloy Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2759-7A-2006 Carburizing&Heat Treatment of Carburizing Grade Steel Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2759-9_8-1992 Ion Nitriding [P12].pdfSAE-AMS2759C-2000 Heat Treatment of Steel Parts General Requirements[P15].pdfSAE-AMS2770H-2006 Heat Treatment of Wrought Aluminum Alloy Parts.pdfSAE-AMS2771C-2004 Heat Treatment of Aluminum Alloy Castings.pdfSAE-AMS2772C-2002 Heat Treatment of Aluminum Alloy Raw Materials.pdfSAE-AMS2772E-2008 Heat Treatment of Aluminum Alloy Raw Materials.pdfSAE-AMS2809-1986 R2002 Identification Titanium&Titanium Alloy Wrought Products.pdfSAE-AMS2809-2002 Identification Titanium&Titanium Alloy Wrought Products.pdfSAE-AMS2814F-2001 优质焊丝包的包装和标识.pdfSAE-AMS2814F-2001 优质焊丝包的包装和标识[P8].pdfSAE-AMS3021D-2007 Fluid,Reference for Testing Di-Ester (Polyol) Resistant Material [P4].pdfSAE-AMS3302G-1990 Silicone Rubber,General Purpose,50 Durometer.pdfSAE-AMS3650C-1991 Rods,Sheets,&Molded Shapes,Polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE),Unplasticized.pdfSAE-AMS3901C-1998 Organic Fiber (Para-Aramid),Yarn&Roving,High Modulus[P13].pdfSAE-AMS4045J-2007 Aluminum Alloy Sheet&Plate 5.6Zn-2.5Mg-1.6Cu-0.23Cr 7075 (-T6 Sheet,-T651 Plate)[P5].pdfSAE-AMS4100D-2007 Aluminum Alloy,Alclad,Sheet 5.7Zn-2.2Mg-1.6Cu-0.22Cr (Alclad 7475-T761)[P6].pdfSAE-AMS4108F-2003 Aluminum Alloy,Hand Forgings 6.2Zn-2.3Cu-2.2Mg-0.12Zr (7050-T7452)Solution Heat Treated,Compression Stress-Relieved,and Overaged.pdfSAE-AMS4111D-2007 Aluminum Alloy Forgings 7.7Zn-2.5Mg-1.5Cu-0.16Cr (7049-T73)[P8].pdf SAE-AMS4143D-2001 Aluminum Alloy Forgings&Rolled or Forged Rings 6.3Cu-0.30Mn-0.18Zr-0.10V-0.06Ti (2219-T6) Solution&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS4147D-2007 Aluminum Alloy Forgings 5.6Zn-2.5Mg-1.6Cu-0.23Cr(7075-T7352) Solution Heat Treated,Stress Relieved by Compression,&Overaged[P7].pdfSAE-AMS4150L-2003(R2008) Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions&Rings 1.0Mg-0.60Si-0.28Cu-0.20Cr-(6061-T6) Solution&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS4152M-2007 Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions 4.4Cu 1.5Mg 0.60Mn Solution Heat Treated[P5].pdfSAE-AMS4157D-2007 Aluminum Alloy Extrusions 7.7Zn-2.4Mg-1.6Cu-0.16Cr (7049-T73511)[P5].pdfSAE-AMS4162D-2003 Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions 6.3Cu - 0.30Mn - 0.18Zr - 0.10V - 0.06Ti (2219-T8511) Solution Treated,Stress Relief Stretched,Straightened,&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdf SAE-AMS4169K-2003 Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions 5.6Zn - 2.5Mg - 1.6Cu - 0.23Cr (7075-T6511)&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS4173E-2003 Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions 1.0Mg - 0.60Si - 0.30Cu - 0.20Cr (6061-T6511) Solution Heat Treated Stress.pdfSAE-AMS4206A-2006 Aluminum Alloy,Plate (7055-T7751) 8.0Zn - 2.3Cu - 2.0Mg - 0.16Zr Solution Heat Treated,Stress Relieved,&Overaged.pdfSAE-AMS4218H-2001 Aluminum Alloy Castings 7.0Si 0.35Mg (A356.0-T6P) (Formerly T61P Temper) Solution&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS4270B-2007 Aluminum Alloy,Alclad Flat Sheet 4.1Cu-1.4Mg-0.45Mn (Alclad 2424-T3) [P7].pdfSAE-AMS4279B-2006 Aluminum Alloy,Alclad Sheet 4.4Cu 1.5Mg 0.60Mn (2024-T4 Flat Sheet) Solution Heat Treated,High Formability.pdfSAE-AMS4324-2002(R2007) 固溶热处理的、消除应力的和过老化的(7055-T74511)含8.0Zn-2.3Cu-2.0Mg-0.16Zr挤压的铝合金杆材、棒材和型材.pdfSAE-AMS4329A-2006 Aluminum Alloy,Plate (7085-T7651) 7.5Zn - 1.6Cu - 1.5Mg - 0.12Zr Solution Heat Treated,Stress-Relieved,&Ove[P6].pdfSAE-AMS4337A-2006 Aluminum Alloy,Extruded Profiles (7055-T77511) 8.0Zn 2.3Cu 2.0Mg 0.16Zr Solution Heat Treated,Stress Relieved,&Overaged.pdfSAE-AMS4342E-2007 Aluminum Alloy,Extrusions 6.2Zn 2.3Cu 2.2Mg 0.12Zr (7050-T74511) Solution Heat Treated,Stress Relieved,Straightened,&Overaged.pdfSAE-AMS4484K-2007 Magnesium Alloy Castings,Permanent Mold 9.0Al-2.0Zn (AZ92A-T6) [P7].pdfSAE-AMS4500J-2007 Copper,Sheet,Strip,and Plate Soft Annealed [P4].pdfSAE-AMS4640-2005 ALUMINUM BRONZE BARS. RODS. SHAPES. TUBES.&FORGINGS 81.5 CU- 10.A1 - 4.8NI - 3.0FE DRAWN&STRESS RELIEVED (HR50) OR TEMPER ANNEALED (TQ50[P8 OCR].pdfSAE-AMS4775H-2005 Nickel Alloy,Brazing Filler Metal 73Ni - 0.75C - 4.5Si - 14Cr - 3.1B - 4.5Fe 1790 to 1970 °F (977 to 1077 °C) Solidus-Liquidus Range.pdfSAE-AMS4805E-2007 Bearings,Sintered Metal Powder 89Cu-10Sn Oil Impregnated [P6].pdfSAE-AMS4900M-2006 AEROSPACE MATERIAL SPECIFICA TION Titanium Sheet,Strip,&Plate Commercially Pure Annealed,55 ksi (379 MPa) [P6].pdfSAE-AMS4911K-2007 Titanium Alloy,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 6AI-4V Annealed [P7].pdfSAE-AMS4911L-2007 Titanium Alloy,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 6AI-4V Annealed [P7].pdfSAE-AMS4918L-2006 Titanium Alloy,Sheet,Strip,&Plate6AI - 6V - 2Sn Annealed[P7].pdfSAE-AMS4921K-2006 [P8].pdfSAE-AMS4921L-2007 Titanium Bars,Wire,Forgings,and Rings Commercially Pure 70 ksi (483 MPa) Yield Strength [P7].pdfSAE-AMS4928Q-2001 Titanium Alloy Bars,Wire,Forgings,Rings,&Drawn Shapes.pdfSAE-AMS4928R-2007 Titanium Alloy Bars,Wire,Forgings,Rings,&Drawn Shapes 6Al - 4V Annealed.pdfSAE-AMS4931B-2002 含6Al-4V超低填隙的、二次退火的、断裂韧度的钛合金棒材、锻件和环件.pdfSAE-AMS4931C-2007 Titanium Alloy bars,Forgings&Rings 6Al-4V Extra low interstitial(ELI) Duplex.pdfSAE-AMS4933D-2008 Titanium Alloy Extrusions and Flash Welded Rings 8Al-1Mo-1V Solution Heat Treated and Stabilized[P8].pdfSAE-AMS4942E-2006 Titanium Tubing,Seamless Annealed,40.0 ksi (275 MPa) Yield Strength.pdf SAE-AMS4943H-2008 Titanium Alloy.Hydraulic. Seamless Tubing 3.0Al-2.5V Annealed.pdfSAE-AMS4944G-2006 Titanium Alloy Tubing,Seamless,Hydraulic 3.0Al - 2.5V Cold Worked,Stress Relieved.pdfSAE-AMS4958C-2008 Titanium Alloy Bars and Rods 3Al-8V-6Cr-4Mo-4Zr Consumable Electrode Melted Solution Heat Treated and Centerless Ground[P6].pdfSAE-AMS4965J-2007 Titanium Alloy,Bars,Wire,Forgings,and Rings 6.0AI-4.0V Solution Heat Treated&Aged [P8].pdfSAE-AMS4971G-2007 Titanium Alloy,Bars,Wire,Forgings,and Rings 6Al-6V-2Sn Annealed,Heat Treatable[P8].pdfSAE-AMS4975J-2007 Titanium Alloy,Bars,Wire,andRings6.0Al-2.0Sn-4.0Zr-2.0Mo-0.08SiSolution&Precipitation Heat Treated[P7].pdfSAE-AMS4982D-2007 Titanium Alloy Wire 44.5 Cb [P6].pdfSAE-AMS5010K-2006 Steel Bars Free Machining Cold Drawn (SAE-1212 or SAE-1215) UNS G12120[P4].pdfSAE-AMS5046C-2007 Carbon Steel,Sheet,Strip,and Plate (SAE-1020&1025) Annealed[P5].pdfSAE-AMS5047F-2007 Steel,Sheet&Strip 0.08-0.13C,Aluminum Killed (SAE-1010) Deep Forming Grade [P4].pdfSAE-AMS5085G-2008 Steel Sheet. Strip.&Plate 0.47-0.55C (SAE-1050) Annealed.pdfSAE-AMS5349D-2007 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Investment Castings 13Cr Free Machining; Hardened&Tempered[P11].pdfSAE-AMS5352E-2007 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Investment Castings 17Cr-0.55Mo (0.95-1.20C) Annealed[P9].pdfSAE-AMS5353D-2007 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Investment Castings 16Cr-1.8Ni-0.08N ASCast [P10].pdfSAE-AMS5355H-2001 steel,corrosion resistant,investment casting[P14 OCR].pdfSAE-AMS5383E-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Investment Castings 52.5Ni-19Cr-3.0Mo-5.1Cb(Nb)-0.90Ti-0.60Al-18Fe[P11].pdfSAE-AMS5385G-1999 铸造状态的含62Co-27Cr-2.8Ni-5.5Mo耐腐蚀和耐热的钴合金熔模铸件.pdfSAE-AMS5398F-2006 Steel,Corrosion Resistant,Sand&Centrifugal Castings 16Cr 4.1Ni 0.22(Cb + Ta) 2.8Cu Solution Heat Treated[P9].pdfSAE-AMS5512L-2007 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 18Cr-10.5Ni-0.80Cb (SAE-30347)Solution Heat Treated[P5].pdfSAE-AMS5516P-2007 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 18Cr-9.0Ni (SAE-30302)Solution Heat Treated[P5].pdfSAE-AMS5542N-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Sheet,Strip,and Plate72Ni-15.5Cr-0.95Cb(Nb)-2.5Ti-0.70Al-7.0Fe[p6].pdfSAE-AMS5548P-2007 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Sheet&Strip 16.5Cr-4.5Ni-2.9Mo-0.10N 1850 to 1975 °F (1010 to 1079 °C) Annealed[P6].pdfSAE-AMS5561G-2007 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Welded&Drawn or Seamless&Drawn Tubing 9.0Mn-20Cr-6.5Ni-0.28N High-Pressure Hydraulic[P8].pdfSAE-AMS5569A-2001 Steel,Corrosion&Heat Resistant,Seamless&Welded Hydraulic Tubing 19Cr-9.5Ni-0.03C max Cold Drawn,1∕8 Hard Temper.pdfSAE-AMS5575N-2007 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Welded Tubing 18Cr-10.5Ni-0.70Cb(Nb) (SAE-30347)Solution Heat Treated[P6].pdfSAE-AMS5581D-2001 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat Resistant,Seamless or Welded Tubing 62Ni-21.5Cr-9.0Mo-3.7Cb Annealed.pdfSAE-AMS5589E-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Seamless Tubing 52.5Ni-19Cr-3.0Mo-5.1Cb (Nb)-0.90Ti-0.50Al-18Fe[P6].pdfSAE-AMS5596K-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Sheet,Strip,Foil&Plate 52.5Ni-19Cr-3.0Mo-5.1Cb (Nb)-0.90Ti-0.50Al-18Fe[P8].pdfSAE-AMS5599G-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 62Ni-21.5Cr-9.0Mo-3.7 Cb (Nb)[P5].pdfSAE-AMS5612J-2007 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Wire,Forgings,Tubing,and Rings 12CrFerrite Controlled,Annealed[P7].pdfSAE-AMS5629E-2002 真空感应加真空自耗预热处理沉淀硬化型耐蚀13Cr-8.0Ni-2.2Mo-1.1Al钢棒、丝、锻件、环和模锻件.pdfSAE-AMS5630G-2000 Steel,Corrosion Resistant,Bars,Wire,and Forgings 17Cr-0.52Mo (0.95-1.20C) (SAE-51440C).pdfSAE-AMS5639H-2002(R2007) 管口连接用备份密封圈的六角螺母[P7].pdfSAE-AMS5643Q-2003 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Bars,Wire,Forgings,Tubing,and Rings 16Cr-4.0Ni-0.30Cb-4.0Cu Solution Heat Treated,Precipitation Hardenable.pdfSAE-AMS5659K-1998 Steel,Corrosion Resistant,Bars,Wire,Forgings,Rings,&Extrusions 15Cr - 4.5Ni - 0.30Cb - 3.5Cu Consumable Electrode Melted Solution Heat Treated,Precipitation Hardenable.pdf SAE-AMS5659L-2004 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Bars,Wire,Forgings,Rings,&Extrusions[P10].pdf SAE-AMS5662M-2004 镍基高温合金[P17].pdfSAE-AMS5668J-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Forgings,and Rings 72Ni-15.5Cr-7.0Fe-2.5Ti-1.0Cb (Nb)-0.70Al[P7].pdfSAE-AMS5678F-2002(R2007) Steel,Corrosion Resistant,Wire 17Cr-7.1Ni-1.1Al Cold Drawn,Precipitation-Hardenable-UNS S17700.pdfSAE-AMS5688L-2007 Steel,Corrosion Resistant,Wire 18Cr 9.0Ni (SAE-30302) Spring Temper.pdf SAE-AMS5698G-2003(R2007) Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Wire 72Ni-15.5Cr-0.95Cb-2.5Ti-0.70Al-7.0Fe No.1 Temper,Precipitation Hardenable-UNS N07750.pdf SAE-AMS5699G-2003(R2007) Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Wire 72Ni 15.5Cr 0.95Cb 2.5Ti 0.70Al 7.0Fe Spring Temper,Precipitation Hardenable.pdfSAE-AMS5713J-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Forgings,&Rings 53Ni - 19Cr - 11Co - 9.8Mo - 3.2Ti - 1.6Al - 0.006B Vacuum Melted,Solution&Precipitation Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS5713J-2007 Nickel Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Forgings,and Rings 53Ni-19Cr-11Co-9.8Mo-3.2Ti-1.6Al-0.006B[P7].pdfSAE-AMS5732J-2006 Steel,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Wire,Forgings,Tubing,and Rings 15Cr-25.5Ni-1.2Mo-2.1Ti-0.006B-0.30V Consumable Electrode Melted 1800 °F (982 °C) Solution&P.pdfSAE-AMS5759-2004 Cobalt Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Forgings,&Rings 52Co- 20Cr- 10Ni- 15W Solution Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS5772D-2004(R2009) Cobalt Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Bars,Forgings&Rings 40Co 22Cr 22Ni 14.5W 0.07La,Solution Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS5786E-2002 Nickel Alloy,corrosion&heat-resistant,welding wire 62.5Ni-5.0Cr-24.5Mo-5.5Fe.pdfSAE-AMS5796D-2000 Cobalt Alloy,Corrosion&Heat Resistant,Welding Wire 52Co-20Cr-10Ni-15W.pdfSAE-AMS5830C-2007 Nickel-Iron Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Welding Wire 12.5Cr-42.5Ni-6.0Mo-2.7Ti-0.015B-35Fe.pdfSAE-AMS5830C-2007 Nickel-Iron Alloy,Corrosion&Heat-Resistant,Welding Wire 12.5Cr-42.5Ni-6.0Mo-2.7Ti-0.015B-35Fe[P6].pdfSAE-AMS5857B-2007 Steel,Corrosion-Resistant,Bars&Wire 19Cr-10Ni (SAE-30304)High Yield Strength Solution Heat Treated&Cold Worked[P4].pdfSAE-AMS5869C-2008 Nickel Alloy.Corrosion&Heat-Resistant.Sheet.Strip.and Plate 62Ni-21.5Cr-9.0Mo-3.7Cb Solution Heat Treated.pdfSAE-AMS6257D-2007 Steel Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 1.6Si-0.82Cr-1.8Ni-0.40Mo-0.08V (0.40-0.44C)[P9].pdfSAE-AMS6260P-2007 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 1.2Cr-3.2Ni-0.12Mo (0.07-0.13C) (SAE-9310)[P6].pdfSAE-AMS6267G-2007 Steel Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 1.2Cr-3.25Ni-0.12Mo (0.07-0.13C) (SAE-9310)[p6].pdfSAE-AMS6345B-2007 Steel,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 0.95Cr-0.20Mo (0.28-0.33C) (SAE-4130)[p7].pdf SAE-AMS6354F-2007 Steel,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 0.75Si-0.62Cr-0.20Mo-0.10Zr (0.10-0.17C)[P5].pdf SAE-AMS6359H-2007 Steel,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 0.80Cr-1.8Ni-0.25Mo (0.38-0.43C) (SAE-4340)[p6].pdfSAE-AMS6409C-2007 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 0.80Cr-1.8Ni-0.25Mo (0.38-0.43C) (SAE-4340)[p8].pdfSAE-AMS6414K-2007 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 0.80Cr-1.8Ni-0.25Mo (0.38-0.43C) (SAE-4340)[p9].pdfSAE-AMS6415S-2007 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 0.80Cr-1.8Ni-0.25Mo (0.38-0.43C) (SAE-4340)[P8].pdfSAE-AMS6417F-2006 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 1.6Si-0.82Cr-1.8Ni-0.40Mo-0.08V (0.38-0.43C)Consumable Electrode Vacuum Remelted.pdfSAE-AMS6440P-2007 Steel,Bars,Forgings,and Tubing 1.45Cr (0.93-1.05C) (SAE-52100) For Bearing Applications[p7].pdfSAE-AMS6454D-2007 Steel,Sheet,Strip,and Plate 1.8Ni-0.80Cr-0.25Mo (0.38-0.43C) (SAE-4340)Vacuum Consumable Electrode Remelted[p7].pdfSAE-AMS6501D-2007 Steel,Maraging,Welding Wire 18Ni-8.0Co-4.9Mo-0.40Ti-0.10Al Vacuum Induction Melted,Environment Controlled Packaging[p6].pdfSAE-AMS753-1998 Corrosion-Resistant Steel Parts Sampling,Inspection&Testing for Surface Passivation[P11].pdfSAE-AMS7721C-2007 Lead Alloy Sheet&Extrusions 93Pb-6.5Sb-0.50Sn ASFabricated[p5].pdfSAE-AMS7731C-2007 Gold Wire&Ribbon 99.97Au Annealed[p6].pdfSAE-AMS7881-2007 Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt Powder Agglomerated&Sintered[p5].pdfSAE-AMS7881-2007 Tungsten Carbide--Cobalt Powder Agglomerated&Sintered[P5].pdfSAE-AMS7882A-2007 Tungsten Carbide-Cobalt Chrome Powder Agglomerated&Sintered[p5].pdf SAE-AMS7882A-2007 Tungsten Carbide--Cobalt Chrome Powder Agglomerated&Sintered[P5].pdf SAE-AMS-A-22771A-2007 Aluminum Alloy Forgings,Heat Treated[p25].pdfSAE-AMS-C-5541A-2003 Chemical Conversion Coatings on Aluminum&Aluminum Alloys.pdfSAE-AMS-F-7190A-2007 Forging,Steel,For Aircraft_Aerospace Equipment&Special Ordnance Applications[p11].pdfSAE-AMS-H-6875-1998(R2006) Heat Treatment of Steel Raw Materials [P29].pdfSAE-AMS-I-23011A-2007 Iron-Nickel Alloys for Sealing to Glasses&Ceramic[P22].pdfSAE-AMS-M-7866A-2007 Molybdenum Disulfide,Technical,Lubrication Grade[p11].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-200-13B-2007 Aluminum Alloy 7178,Bar,Rod,Shapes,Tube,and Wire,Extruded[p8].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-200-14A-2007 Aluminum Alloy,Bar,Rod,Shapes,and Wire,Extruded,7178-T76 Improved Exfoliation Resistance[p8].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-200-5A-2007 Aluminum Alloy 5086,Bar,Rod,Shapes,Tube,andWire,Extruded[p7].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-200-7B-2007 Aluminum Alloy 5456,Bar,Rod,Shapes,Tube,and Wire,Extruded[p6].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-200-9-1997 Aluminum Alloy 6063,Bar,Rod,Shapes,Tube,&Wire,Extruded.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-10A-2007 Aluminum Alloy 5454,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-11A-2007 Aluminum Alloy 6061,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-12-2007 Aluminum Alloy 7075,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-13-2007 Aluminum Alloy Alclad 7075,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-14A-2007 Aluminum Alloy 7178,Plate&Sheet [p7].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-15B-2007 Aluminum Alloy Alclad 7178,Plate&Sheet[p8].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-21B-2007 Aluminum Alloy,7178-T76,Plate&Sheet Improved Exfoliation Resistant[p7].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-22B-2007 Aluminum Alloy,7178-T76,Alclad Plate&Sheet,Improved Exfoliation Resistant[p10].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-28B-2007 Aluminum Alloy,7011 Alclad 7178 Plate&Sheet[p14].pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-4A-2007 Aluminum Alloy 2024,Plate&Sheet..pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-5A-2007 Aluminum Alloy Alclad 2024,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-8A-1998 Aluminum Alloy 5052,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250-9A-2006 Aluminum Alloy 5456,Plate&Sheet.pdfSAE-AMS-QQ-A-250A-2004 Aluminum&Aluminum Alloy,Plate&Sheet General Specification for.pdf SAE-AMS-QQ-A-367A-2007 Aluminum Alloy Forgings[p29].pdfSAE-AMS-S-13165 Issued NOV1997 Shot Peening of Metal Parts[P27].pdfSAE-AMS-W-6858A-2000 Welding,Resistance Spot&Seam[P46].pdfSAE-ARP1232B-2001 Gland Design,Elastomeric O-Ring Seals,Static Radial..pdfSAE-ARP1420B-2002 Gas Turbine Engine Inlet Flow Distortion Guidelines.pdfSAE-ARP1420B-2002 Gas Turbine Engine Inlet Flow Distortion Guidelines[P24].pdfSAE-ARP1755B-2000 Effect of Cleaning Agents on Aircraft Engine Materials Stock Loss Test Method.PDFSAE-ARP1962A-1995 TRAINING&APPROVAL OF HEAT-TREA TING PERSONNEL.PDFSAE-ARP4191-2003 C Gas Turbine Engine Performance Presentation[P9].pdfSAE-ARP4191C-2003 Gas Turbine Engine Performance PresentationDigital Computer Programs Using FORTRAN 77.pdfSAE-ARP4191C-2003Gas Turbine Engine Performance Presentation [P9].pdfSAE-ARP4754-1996 ConsiderationsHighly-Integrated or Complex Aircraft Systems[P101].pdfSAE-ARP5316B-2002 Storage of Elastomer Seals&Seal Assemblies Which Include an Elastomer Element Prior to Hardware Assembly.pdfSAE-ARP5580-2001 非机动车用的故障模式和效果分析的推荐实施规范.pdfSAE-ARP598C-2003 Aerospace Microscopic Sizing&Counting of Particulate Contamination for Fluid Power Systems[P16].pdfSAE-AS122026A THRU AS122075A-2007 WASHER-LOCK,SPRING,CADMI[p3].pdfSAE-AS123601 THRU AS123750B-2007 RIVET,SOLID,100 FLUSH HEA[p3].pdfSAE-AS1241-1997 Fire Resistant Phosphate Ester Hydraulic Fluid for Aircraft.pdfSAE-AS14101-1998 低速自调心自润滑关节轴承.pdfSAE-AS14153B-2007 CIRCUIT BREAKER-AIRCRAFT,TRIP-FREE,[P3].pdfSAE-AS14154B-2007 Circuit Breaker-Aircraft,Trip-Free,Push-P[P3].pdfSAE-AS15001B-2007 FITTING,LUBRICATION,HYDRAULIC,SURFACE CHEC[P3].pdfSAE-AS15002B-2007 FITTING,LUBRICATION,HYDRAULIC,SURFACE CHEC[P3].pdfSAE-AS15003B-2007 FITTING,LUBRICATION,HYDRAULIC,SURFACE CHEC[P3].pdfSAE-AS15005B-2007 FITTING,LUBRICATION,HYDRAULIC,THROA T OR SU[P3].pdfSAE-AS15006B-2007 FITTING,LUBRICATION,HYDRAULIC,LEAKPROOF,1_8 PIPE THREADS[P3].pdfSAE-AS155001 THRU AS155300A-2007 STUD,STEPPED,2 DIA ENGAGEME[p3].pdfSAE-AS155301 THRU AS155600A-2007 STUD,STEPPED,2 DIA ENGAGEME[p3].pdfSAE-AS155901 THRU AS156200A-2007 STUD,STEPPED,2 DIA ENGAGEMENT,CADMIUM PLATED,STEEL UNS G87400,[p2].pdfSAE-AS158901 THRU AS159200A-2007 STUD,STEPPED,NECKED,1.5 DIA ENGAGEMENT,CADMIUM PLATED,STEEL[P3].pdfSAE-AS162501 THRU AS162800A-2007 STUD,STEPPED,DRILLED,NECKED,2 DIA ENGAGEMENT,CADMIUM PLATED,STEEL[p3].pdfSAE-AS17108A-2008 (R) bearing,ball,annular,primarily for aircraft generators&motor-generators,wide cartridge,type ii.pdfSAE-AS22759-10-2000 wire,electrical,fluoropolymer-insulated,extruded tfe,nickel-coated copper conductor,1000 volt.pdfSAE-AS22759-86B-2007 wire,electrical,polytetrafluoroethylene polyimide insulated,normal weight,silver coated,copper conductor,200 °c,600 volts.pdfSAE-AS22759-87B-2007 wire,electrical,polytetrafluoroethylene-polyimide insulated,normal weight,nickel coated,copper conductor,260 °c,600 volts.pdfSAE-AS22759-89B-2007 Wire,Electrical,Polytetrafluoroethylene-Polyimide Insulated,Normal Weight,Silver Coated,High Strength or Ultra High Strength Copper Alloy,200-mDC,600 V olts.pdf SAE-AS23190-1-1999(R2006) Straps,Clamps,&Mounting Hardware,Plastic for Cable Harness Tying&Support Clamp,Loop,Nylon,Adjustable,Wire Support[P5].pdfSAE-AS23190-1998 Straps,Clamps,&Mounting Hardware,Plastic&Metal for Cable Harness Tying&Support-FSC 5975[P42].pdfSAE-AS23190-2-1998(R2003) Straps,Clamps,Plastic&Metal,&Mounting Hardware,Plastic for Cable Harness Tying&Support Clamp,Loop,Metal[P9].pdfSAE-AS23190-3-2008 Straps,Clamps,&Mounting Hardware,Plastic&Metal for Cable Harness Tying&Support Strap,Tie down[P3].pdfSAE-AS25244-2007 CIRCUIT BREAKER,TRIP-FREE,PUSH-PULL,5 THRU [P6].pdfSAE-AS25361A-2007 CIRCUIT BREAKER -AIRCRAFT,TRIP-FREE,PUSH-PULL,50 THRU 100 AMP,TYPE I,[P3].pdfSAE-AS3086A-2007 STUD-STRAIGHT,KEY LOCKED,CADMIUM PLA TED,S[p2].pdfSAE-AS3087A-2007 STUD-STRAIGHT,KEY LOCKED,CADMIUM PLA TED,S[P3].pdfSAE-AS3088A-2007 STUD,STRAIGHT,KEY LOCKED,CADMIUM PLA TED,ST[P3].pdfSAE-AS3089A-2007 STUD,STRAIGHT,KEY LOCKED,CADMIUM PLA TED,ST[P3].pdfSAE-AS33514A-2007 Fitting End,Standard Dimensions for Flareles[P3].pdfSAE-AS33515A-2007 FITTING END,STANDARD DIMENSIONS FOR BULKHEAD[P3].pdfSAE-AS39029-19A-2007 CONTACTS,ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR,PIN,CRIMP[P5].pdfSAE-AS39029-21A-2007 CONTACTS,ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR,SOCKET,CR[P5].pdf。

ASTM E1268‐01显微结构带状物或取向程度的评定方法发生在金属和合金的凝固时的偏析,随后的形变使其排列整齐。
固态相变被微观偏析所影响,可能会导致产生分层或带状组织。
最常见的例子就是锻造低碳和低碳合金钢中的铁素体-珠光体带状。
其他的例子包括热处理合金钢中共析工具钢的碳化物带及马氏体带。
这种方法包括表述带状组织形貌和程度的方法,以及利用显微硬度法测定热处理样品中带状之间的硬度差别方法。
体视学方法也可以用来描述带第二相的非带状组织沿形变方向拉长的程度差异。
1 范围1.1 本标准介绍了一种基于组织形貌来定性表述带状或取向程度的方法。
1.2 本标准介绍了定量测量带状或取向程度的体视学测量方法。
注1虽然体视学测量方法用来评估带状或取向程度,这种测量的只是在平行于形变方向的截面(即纵向面)并且不评估带状或取向的三维特征。
1.3 本标准介绍了利用显微硬度法评估热处理钢中的硬度差别程度。
对于淬火全马氏体的碳素和合金钢(0.10-0.65%C)来说,基体和偏析处的碳含量可通过显微硬度值来估算。
1.4 本标准不包括评估带状组织的化学分析方法。
1.5 本标准只涉及建议的试验方法,不包括定义的解释或可用范围的限制。
1.6 测量值用SI国际制单位表示,括号内的等效英寸-英镑值可能为近似值。
1.7本标准并非旨在解决所有的安全问题,如有的话,与其使用相关。
建立适当的安全及健康措施,并确定适用监管限制后才能使用是本标准用户的责任。
2 引用文献2.1 ASTM标准A370 钢制品力学性能的试验方法和定义A572 /A572M 低合金高强度铌钒结构钢A588 /A588M 最低屈服强度345MPa最大厚度100mm的低合金高强度钢E3 金相试样制备方法E7 与金相相关的术语E140 金属硬度换算表E384 金属材料的显微硬度试验方法E 407 金属和合金的浸蚀试验方法E562 通过系统手册计点测定体积分数的方法E883反射光学显微镜指南3 术语3.1 定义——对于本方法中使用术语的定义,见术语E7。

汽车线束热缩管标准
汽车线束热缩管的标准由国际标准化组织(ISO)和一些国家/地区的标准组织制定。
以下是一些常用的汽车线束热缩管标准:
1. ISO 6722 - 这是国际标准化组织制定的标准,用于规定汽车
线束的热缩管要求,包括材料、尺寸、性能和测试方法等方面。
2. SAE J856 - 这是由美国汽车工程师协会制定的标准,用于规
定汽车电气线束的热缩管要求,包括材料、尺寸、性能和测试方法等方面。
3. DIN 72594 - 这是由德国标准化组织制定的标准,用于规定
汽车线束的热缩管要求,包括材料、尺寸、性能和测试方法等方面。
4. JASO D 611 - 这是由日本汽车标准化组织制定的标准,用于规定汽车电气线束的热缩管要求,包括材料、尺寸、性能和测试方法等方面。
这些标准通常包括对热缩管的材料要求,如聚烯烃、聚氨酯、聚氨酯/聚酯共聚物等;热缩管的内径、壁厚和长度要求;耐
热性、耐化学品、耐油性和静电性能等要求;以及对热缩管的热收缩性能、机械性能和电气性能的测试方法等。
仿佛想了解更多信息或相关标准,建议参考这些标准的官方文档或相关汽车行业资料。



SAEJ中⽂外螺纹紧固件机械性能和材料要求原则性阐述⼏个ISO 898.1与SAE J429的材料等级相当。
本标准中表2的化学元素与ISO 898.1⼀致,像8级的允许⽤⾮合⾦钢。
值得关注的⼀个显著的差异就是ISO 898.1(2009)与SAE J429(2012)⽤来⽣产8级的合⾦钢和碳钢的含碳量⽐10.9级的含碳量⾼。
另外⼀个修订就是发现2011版的少量错误和不⼀致的地⽅。
1、范围本标准涵盖汽车和相关⼯业使⽤,尺⼨1-1/2以下英制钢制螺栓、螺丝、螺柱、sems和U型螺栓的机械性能和材料要求。
⽂中所提到“螺柱”这个词的意思是说:⼀中等长度圆棒的某⼀端搓⽛、两端都有搓⽛或整个圆棒都有搓⽛。
此产品不适⽤于加热、焊接或使⽤于类似本⽂中所要求的螺栓特征特性近似的产品。
表1包括之机械性能要求是在⼤约20℃(68F)之环境温度之下所完成。
这些性能限定于在某⼀温度界限内,此温度界限需依照所使⽤材料等级以及温度和加⼯流程⽽定。
其它疲劳测试、抗腐蚀、冲击试验等性质,都不在本标准范围内,然⽽为确保产品适⽤于这些额外性能的情况下,最终使⽤必须承担责任归属。
Sems:螺丝和垫⽚的组合U-BOLT:本SAE标准所提及的U型螺栓,其使⽤于车辆悬吊装置和其相关位置。
为了详细说明,本标准将U型螺栓视为螺柱。
因此,⽂中所提及到的STUDS (螺柱)字眼都适⽤于U-BOLT(U型螺栓)。
(设计者应要了解,在想同尺⼨、等级的U 型结构的两根螺栓和螺柱可能⽆法承受荷重;因此,U型螺栓的实际承载重量应以鞍型荷重测试⽅法来判定。
)2 参考规范2.1 适⽤的版本于本标准内所提及的范围,除⾮特别指⽰,产品应以最新版本的SAE标准来提供。
2.1.1 SAE出版品SAE J403 碳钢化学成分SAE J404 合⾦钢化学成分SAE J409 制品分析-耐热钢和铸铁的化学成分分析之允许差异标准SAE J411 碳钢和合⾦钢SAE J417 硬度测试和硬度转换SAE J1086 ⾦属盒合⾦之编号SAE J1286 碳钢和H合⾦钢的硬化带2.1.2 ASME 出版品ASME B18.2.1 美制外六⾓螺栓ASME B18.18 紧固件的检验和质量保证2.1.3 ASTM 出版品ASTM E18 ⾦属材料洛⽒硬度和洛⽒表⾯硬度的测试⽅法ASTM F606 测定外螺纹和内螺纹紧固件、垫圈及铆钉机械性能的试验⽅法 ASTM F788/788M 英制及⽶制系列的螺栓、螺钉及螺柱的表⾯不连续性ASTM F1470 特定的机械性能和功能检测⽤紧固件的抽样以下出版物仅为提供信息的⽬的⽽⾮本标准要求的⼀部分。


镀钛优点:耐磨性更高,模具寿命大大延长胶料的可流动时间更长,填模效果更佳塑料产品表面质量提高,不良率降低脱模更容易,甚至可避免使用脱模剂有效防止腐蚀性原料侵蚀模具基体模具易于清洁,且清洁周期更长塑料模具由于其结构复杂决定了加工难度大,故造价相对较高,所以提高模具的寿命就是一个主要课题,尤其镜面和蚀纹面,就特别容易磨损,这一直是一件令人十分苦恼的事情。
经过真空涂层的塑料模具表面硬度的提高,使得抗磨耗性显著提高;而且因模具表面光洁度的增强和摩擦系数的降低使得胶料的流动性更好以及塑料产品更易脱模。
同时真空涂层更因其特殊的晶格结构在模具表面形成致密的保护层,可以非常有效的解决腐蚀的弊病。
更为重要的是,由于我们的涂层完全不会改变模具的表面状况,无论是镜面还是蚀纹面,甚至要求极高的CD模具.纳米镀钛的基本条件:1.热处理回火温度:SLD﹑SKD﹑SKH,钨刚等各种经热处理后的钢材,必须高温回火,回火处理,温度最好为500℃以上.2.工作表面不可有锈斑﹑黑皮存在,且工件不得有焊补过.3.若工件为组合件,须将工件拆开成单件来处理.4.工作面其光泽度要求为0.2~0.4.注︰表面光泽度影响其附着力﹐光泽度越好其附着力越强﹐模具的使用寿命越長.5.欲留模具﹑冲棒的公差.纳米镀钛膜厚为3um~4um(双边)长江科技(东莞)镀钛厂建于2002年,长年经营:PVD纳米镀钛通常称谓:纳米镀钛,纳米镀钛厂,东莞纳米镀钛,镀膜,真空纳米镀钛,氮化钛,纳米镀钛加工,PVD,表面处理,钛板,表面处理纳米镀钛加工,真空镀钛加工,表面处理,PVD涂层,模具纳米镀钛,纳米涂层,真空纳米电镀,零件纳米镀钛,精密模具纳米镀钛,冲压模具纳米镀钛,压铸模具纳米镀铬,耐磨涂层,超硬纳米镀钛,镀钛涂层,离子镀钛,纳米涂层,冲棒纳米镀钛,五金模具纳米镀钛,塑胶模纳米镀钛,纳米镀钛,金属纳米镀钛表面处理等. 金属表面处理PVD纳米镀钛特点:增寿、增硬、增值,并以其硬高度、高耐磨、强抗腐蚀性、抗高温、抗黏着性等优越的使用性能广泛应用于模具类,刀具类,冲具类,工具类等模具工业中。
SAE Technical Standards Board Rules provide that: “This report is published by SAE to advance the state of technical and engineering sciences. The use of this report is entirely voluntary, and its applicability and suitability for any particular use, including any patent infringement arising therefrom, is the sole responsibility of the user.”SAE reviews each technical report at least every five years at which time it may be reaffirmed, revised, or cancelled. SAE invites your written comments and suggestions.QUESTIONS REGARDING THIS DOCUMENT: (412) 772-8512 FAX: (412) 776-0243TO PLACE A DOCUMENT ORDER; (412) 776-4970 FAX: (412) 776-0790Copyright 1995 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.3.Chemical Composition Limits—To permit steel producers the necessary latitude to meet the standard hardenability limits, the chemical composition limits of these steels have been broadened somewhat from those limits applicable to the same grades when specified by chemical composition only (SAE J403 and J404).These broader limits permit adjustments in manufacturing ranges of composition to compensate for individual plant melting procedures which might otherwise influence the levels and widths of the bands. The modifications have not been great enough to influence the general characteristics of the original compositions of the series under consideration.The chemical composition limits for electric furnace, open hearth, and BOF steels are outlined in T ables 1 and 2 of this document and are subject to the permissible variations for product analysis outlined in Tables 1 and 3of SAE J409.TABLE 1—CARBON AND CARBON BORON H STEEL (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown;see Figures 3 to 16 for respective H-bands)UNS No.SAE Steel No.C Mn Si P ,max (1)1.If electric furnace practice is specified or required, the limits for phosphorus and sulfur are 0.025%, respectively, and the prefix E isadded to the SAE number, for example, E1038H.S,max (1)H103801038H 0.34/0.430.50/1.000.15/0.350.0300.050H104501045H 0.42/0.510.50/1.000.15/0.350.0300.050H152201522H 0.17/0.25 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H152401524H 0.18/0.26 1.21/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H152601526H 0.21/0.30 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H154101541H 0.35/0.45 1.25/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H1521115B21H (2)2.These steels contain 0.0005 to 0.003% boron.0.17/0.240.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1528115B28H (2)0.25/0.34 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1530115B30H (2)0.27/0.350.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1535115B35H (2)0.31/0.390.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1537115B37H (2)0.30/0.39 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1541115B41H (2)0.35/0.45 1.25/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H1548115B48H (2)0.43/0.53 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1526115B62H (2)0.54/0.671.00/1.500.40/0.600.0300.050TABLE 2—(1)STANDARD ALLOY H STEEL COMPOSITIONS (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown(2)(3) see Figures 17 to 88 for respective H-bands)UNS No.SAESteel No.C Mn Si Ni Cr Mo VH133001330H0.27/0.33 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H133501335H0.32/0.38 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H134001340H0.37/0.44 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H134501345H0.42/0.49 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H402704027H0.24/0.300.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H40280(4)4028H(4)0.24/0.300.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H403204032H0.29/0.350.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H403704037H0.34/0.410.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H404204042H0.39/0.460.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H404704047H0.44/0.510.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H411804118H0.17/0.230.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.30/0.700.80/0.15—H412004120H0.18/0.230.90/1.200.15/0.35—0.40/0.600.13/0.20—H413004130H0.27/0.330.30/0.700.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H413504135H0.32/0.380.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H413704137H0.34/0.410.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414004140H0.37/0.440.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414204142H0.39/0.460.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414504145H0.42/0.490.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414704147H0.44/0.510.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H415004150H0.47/0.540.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H416104161H0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.65/0.950.25/0.35—H432004320H0.17/0.230.40/0.700.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.35/0.650.20/0.30—H434004340H0.37/0.440.55/0.900.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.65/0.950.20/0.30—H43406(5)E4340H(5)0.37/0.440.60/0.950.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.65/0.950.20/0.30—H462004620H0.17/0.230.35/0.750.15/0.35 1.55/2.00—0.20/0.30—H471804718H0.15/0.210.60/0.950.15/0.350.85/1.250.30/0.600.30/0.40—H472004720H0.17/0.230.45/0.750.15/0.350.85/1.250.30/0.600.15/0.25—H481504815H0.12/0.180.30/0.700.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H481704817H0.14/0.200.30/0.700.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H482004820H0.17/0.230.40/0.800.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H50401(6)50B40H(6)0.37/0.440.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H50441(6)50B44H(6)0.42/0.490.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H504605046H0.43/0.500.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.13/0.43——H50461(6)50B46H(6)0.43/0.500.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.13/0.43——H50501(6)50B50H(6)0.47/0.540.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H50601(6)50B60H(6)0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H512005120H0.17/0.230.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H513005130H0.27/0.330.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.20——H513205132H0.29/0.350.50/0.900.15/0.35—0.65/1.10——H513505135H0.32/0.380.50/0.900.15/0.35—0.70/1.15——H514005140H0.37/0.440.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H514705147H 0.45/0.520.60/1.050.15/0.35—0.80/1.25——H515005150H 0.47/0.540.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H515505155H 0.50/0.600.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H516005160H 0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H51601(6)51B60H (6)0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H611806118H 0.15/0.210.40/0.800.15/0.35—0.40/0.80—0.10/0.15H615006150H 0.47/0.540.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75-1.20—0.15 min H81451(6)81B45H (6)0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.15/0.450.30/0.600.08/0.15—H861708617H 0.14/0.200.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862008620H 0.17/0.230.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862208622H 0.19/0.250.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862508625H 0.22/0.280.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862708627H 0.24/0.300.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H863008630H 0.27/0.330.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H86301(6)86B30H (6)0.27/0.330.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H863708637H 0.34/0.410.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864008640H 0.37/0.440.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864208642H 0.39/0.460.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864508645H 0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H86451(6)86B45H (6)0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H865008650H 0.47/0.540.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H865508655H 0.50/0.600.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H866008660H 0.55/0.650.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25H872008720H 0.17/0.230.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.20/0.30—H874008740H 0.37/0.440.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.20/0.30—H882208822H 0.19/0.250.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.30/0.40—H925909259H 0.56/0.640.65/1.100.70/1.20—0.45/0.65——H926009260H 0.55/0.650.65/1.10 1.70/2.20————H93106(5)E9310H (5)0.07/0.130.40/0.700.15/0.35 2.95/3.55 1.00/1.450.80/0.15—H94151(6)94B15H (6)0.12/0.180.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—H94171(6)94B17H (6)0.14/0.200.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—H94301(6)94B30H (6)0.27/0.330.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—1.The ranges and limits on this table apply only to material not exceeding 0.13 m 2 (200 in 2) in cross-sectional area, 460 mm (18 in) in width, or 4.5 tonne (10 000 lb) per piece in weight. Ranges and limits are subject to the permissible variations for product analysis shown in Table 4 of SAE J409.2.Small quantities of certain elements may be found in alloy steel which are not specified or required. These elements are considered incidental and acceptable to the following maximum amounts: copper to 0.35%, nickel to 0.25%, chromium to 0.20%, and molybdenum to 0.06%.3.For open hearth and basic oxygen steels maximum sulfur content is 0.040% and maximum phosphorus content is 0.030%. Maximum phosphorus and sulfur in basic electric furnace steels are 0.025% each.4.Sulfur content range is 0.035/0.050%.5.Electric furnace steel.6.These steels contain 0.0005 to 0.003% boron.TABLE 2—(1)STANDARD ALLOY H STEEL COMPOSITIONS (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown (2)(3)see Figures 17 to 88 for respective H-bands) (continued)UNS No.SAE Steel No.C Mn Si Ni Cr Mo V4.Identification—As a means of identifying steels specified to hardenability band limits, the suffix letter “H” hasbeen added to the conventional series number. In the Unified Numbering System (UNS), the “H” appears as a prefix. It is important the steel consumers use this letter in specification requirements, as there is no other means of determining when hardenability band limits apply. When the letter is used, all conditions pertaining to chemical composition limits, restrictions, testing techniques, and so forth, as outlined herein apply5.Grain Size—The H-band limits set forth are intended to apply to steels exhibiting austenitic grain size ASTMNo. 5 or finer (see SAE J418). In cases where coarse grain steel is desired, the hardenability limits shall be a matter of agreement between the producer and the consumer.e of Hardenability Limits—H-band limits are shown graphically and are so depicted for convenience inestimating the hardness value obtainable at the various locations on the end quench test specimen and for quick comparisons of the various H grades.The values of Diameter of Rounds, with Same As-Quenched Hardness shown above each H-band, are approximate and were selected from the ranges appearing in Figure 7 of SAE J406.It should be noted that hardenability limits are presented graphically in both U.S. customary units and metric (SI) units. The metric hardenability bands were prepared by careful conversion from existing bands in U.S.customary units.In either case, for specification purposes, the tabulated values of Rockwell C hardness (HRC) are used.Values below 20 HRC are not specified because such values are not as accurate.Two points from the tabulated values are commonly designated according to method A, B, C, D, or E, which are defined in the following paragraphs. Those various methods are illustrated graphically in Figures 1 and 2.Note that nearest whole integers of distance and hardness are to be used, not fractions.6.1Method A—The minimum and maximum hardness values at any desired distance. This method is illustratedin Figures 1 and 2 as points A-A.6.2Method B—The minimum and maximum distance at which any desired hardness value occurs. This methodis illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points B-B. If the desired hardness does not fall on an exact mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position, the minimum distance selected should be the nearest mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position toward the quenched end and the maximum should be the nearest mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position away from the quenched end.6.3Method C—Two maximum hardness values at two desired distances, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as pointsC-C.6.4Method D—Two minimum hardness values at two desired distances, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points D-D.6.5Method E—Any minimum hardness plus any maximum hardness, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points E-E.When hardenability is specified according to one of the aforementioned methods, the balance of the hardenability band is not applicable.In cases when it is considered desirable, the maximum and minimum limits at a distance of 1.5 mm (1/16 in) from the quenched end can be specified in addition to the other two points as previously described in methodsA to E, inclusive.HARDENABILITY REQUIREMENTS IN METRIC (SI) UNITSHARDENABILTY REQUIREMENTS IN U.S. CUSTOMARY UNITSWhen the full h-band is specified, the hardenability can be reported by listing hardness values for 1.5, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, and 50 mm from the quenched end of the test specimen. In the case of the test specimen made to U.S. customary units, hardness values would be reported for each 1/6 to 16/16 in and 1/8 in increments from there to 32/16 in.It is customary to accept a tolerance of two points HRC for a 5mm or 3/16 in portion of the curve, except at the1.5 mm or 1/6 in position. This tolerance is necessary because curves for individual heats may vary somewhatin shape from the standard band limits and thus deviate slightly at one or more positions in the full length of the curves.For shall hardening carbon H steels, distances form the quenched end may be reported by listing hardness values for 1 mm or 1/32 in intervals near the quenched end, as described more fully in SAE J406.Acceptance testing shall be performed in accordance with SAE J406.7.General—The hardenability limits in this document are those for regular quality steels produced in accordancewith the Steel Products manuals published by the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI). Some of the steels in this document can be specified to more restricted hardenability ranges, as presented in SAE J1868.FIGURE 3—UNS H10380—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1038HFIGURE 4—UNS H10450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1045HFIGURE 5—UNS H15220—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1522HFIGURE 6—UNS H15240—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1524HFIGURE 7—UNS H15260—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1526HFIGURE 8—UNS H15410—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1541HFIGURE 9—UNS H15211—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B21HFIGURE 10—UNS H15281—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B28HFIGURE 11—UNS H15301—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B30HFIGURE 12—UNS H15351—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B35HFIGURE 13—UNS H15371—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B37HFIGURE 14—UNS H15411—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B41HFIGURE 15—UNS H15481—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B48HFIGURE 16—UNS H15621—HARDENABILITY BNAD—SAE 15B62HFIGURE 17—UNS H13300—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1330HFIGURE 18—UNS H13350—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1335HFIGURE 19—UNS H13400—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1340HFIGURE 20—UNS H13450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1345HUNS H40280—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4028H*FIGURE 22—UNS H40320—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4032HFIGURE 23—UNS H40370—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4037HFIGURE 24—UNS H40420—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4042HFIGURE 25—UNS H40470—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4047HFIGURE 26—UNS H41180—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4118HFIGURE 27—UNS H41200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4120HFIGURE 28—UNS H41300—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4130HFIGURE 29—UNS H41350—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4135HFIGURE 30—UNS 41370—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4137HFIGURE 31—UNS H41400—HARDENABILITY BAND—4140HFIGURE 32—UNS H41420—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4142HFIGURE 33—UNS H41450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4145HFIGURE 34—UNS H41470—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4147HFIGURE 35—UNS H41500—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4150HFIGURE 36—UNS H41610—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4161HFIGURE 37—UNS H43200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4320HFIGURE 38—UNS H43400—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4340HFIGURE 39—UNS H43406—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE E4340HFIGURE 40—UNS H46200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4620HFIGURE 41—UNS H47180—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4718HFIGURE 42—UNS H47200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4720HFIGURE 43—UNS H48150—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4815HFIGURE 44—UNS H48170—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4817H。
QJ 1268--87 着色渗透探伤方法中华人民共和国航天工业部部标准QJ1268--87着色渗透探伤方法──────────────────────────────────1 适用范围1.1本标准适用于检查致密性金属材料(包括焊缝)、非金属材料(如玻璃、陶瓷、氟塑料)及其制品表面开口性的缺陷,如暴露于表面的裂纹、气孔、疏松、分层、未焊透及未熔合等缺陷。
1.2 本标准可用于产品的最终检验和工序间检验。
1.3 本标准不能保证发现以下开口缺陷:a.由于热变形(拉制、轧制及锻造等)所产生的折叠和非金属夹杂;b. 由于外来因素造成堵塞的缺陷。
1.4 本标准的检测灵敏度:a. 在试块上能检出裂纹最小宽度1μm左右;b.在实际应用中要使用对比试块进行比较,根据被检表面的粗糙度,确定检测灵敏度。
2 原理利用液体的渗透现象、毛细作用和吸附原理来检查材料、制品表面的开口缺陷。
探伤时,将红色渗透剂施加在被检表面,如果被检表面存在缺陷,渗透剂便渗入缺陷内,当把表面多余渗透剂去除后,再施加白色显象剂,缺陷内的渗透剂便被吸出,从而在白色背景上呈现出红色缺陷迹痕。
3 对工件被检表面的要求3.1 被检表面及其周围25mm区域内应无油污、锈蚀、切屑、漆层及其它污物。
3.2检查焊缝时,在焊缝表面及距焊缝边缘30mm内不应有氧化皮、焊渣、飞溅等污物。
_ __ 3.3 机加工件表面的粗糙度应不大于6.3√(光洁度∨5)。
4 渗透剂、清洗剂、显象剂的选择原则4.1渗透剂应有良好的渗透性能、颜色鲜艳、对被检表面无腐蚀、对人体毒性小、剌激性小、挥发性小、易于清洗、并与被检容器内所使用的介质相容。
4.2 清洗剂应能去除被检表面的多余渗透剂又不会过洗。
对被检表面无腐蚀、对人体毒性小和剌激性小。
4.3 显象剂应能在被检表面上形成均匀的白色背景,对渗透剂有强的吸附性能,显示缺陷迹痕对比度好。
4.4 推荐几种着色探伤剂,见附录A。
4.5 用于检验和选用渗透探伤剂的对比试块见附录B。
SAE Technical Standards Board Rules provide that: “This report is published by SAE to advance the state of technical and engineering sciences. The use of this report is entirely voluntary, and its applicability and suitability for any particular use, including any patent infringement arising therefrom, is the sole responsibility of the user.”SAE reviews each technical report at least every five years at which time it may be reaffirmed, revised, or cancelled. SAE invites your written comments and suggestions.QUESTIONS REGARDING THIS DOCUMENT: (412) 772-8512 FAX: (412) 776-0243TO PLACE A DOCUMENT ORDER; (412) 776-4970 FAX: (412) 776-0790Copyright 1995 Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.3.Chemical Composition Limits—To permit steel producers the necessary latitude to meet the standard hardenability limits, the chemical composition limits of these steels have been broadened somewhat from those limits applicable to the same grades when specified by chemical composition only (SAE J403 and J404).These broader limits permit adjustments in manufacturing ranges of composition to compensate for individual plant melting procedures which might otherwise influence the levels and widths of the bands. The modifications have not been great enough to influence the general characteristics of the original compositions of the series under consideration.The chemical composition limits for electric furnace, open hearth, and BOF steels are outlined in T ables 1 and 2 of this document and are subject to the permissible variations for product analysis outlined in Tables 1 and 3of SAE J409.TABLE 1—CARBON AND CARBON BORON H STEEL (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown;see Figures 3 to 16 for respective H-bands)UNS No.SAE Steel No.C Mn Si P ,max (1)1.If electric furnace practice is specified or required, the limits for phosphorus and sulfur are 0.025%, respectively, and the prefix E isadded to the SAE number, for example, E1038H.S,max (1)H103801038H 0.34/0.430.50/1.000.15/0.350.0300.050H104501045H 0.42/0.510.50/1.000.15/0.350.0300.050H152201522H 0.17/0.25 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H152401524H 0.18/0.26 1.21/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H152601526H 0.21/0.30 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H154101541H 0.35/0.45 1.25/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H1521115B21H (2)2.These steels contain 0.0005 to 0.003% boron.0.17/0.240.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1528115B28H (2)0.25/0.34 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1530115B30H (2)0.27/0.350.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1535115B35H (2)0.31/0.390.70/1.200.15/0.350.0300.050H1537115B37H (2)0.30/0.39 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1541115B41H (2)0.35/0.45 1.25/1.750.15/0.350.0300.050H1548115B48H (2)0.43/0.53 1.00/1.500.15/0.350.0300.050H1526115B62H (2)0.54/0.671.00/1.500.40/0.600.0300.050TABLE 2—(1)STANDARD ALLOY H STEEL COMPOSITIONS (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown(2)(3) see Figures 17 to 88 for respective H-bands)UNS No.SAESteel No.C Mn Si Ni Cr Mo VH133001330H0.27/0.33 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H133501335H0.32/0.38 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H134001340H0.37/0.44 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H134501345H0.42/0.49 1.45/2.050.15/0.35————H402704027H0.24/0.300.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H40280(4)4028H(4)0.24/0.300.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H403204032H0.29/0.350.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H403704037H0.34/0.410.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H404204042H0.39/0.460.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H404704047H0.44/0.510.60/1.000.15/0.35——0.20/0.30—H411804118H0.17/0.230.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.30/0.700.80/0.15—H412004120H0.18/0.230.90/1.200.15/0.35—0.40/0.600.13/0.20—H413004130H0.27/0.330.30/0.700.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H413504135H0.32/0.380.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H413704137H0.34/0.410.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414004140H0.37/0.440.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414204142H0.39/0.460.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414504145H0.42/0.490.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H414704147H0.44/0.510.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H415004150H0.47/0.540.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.75/1.200.15/0.25—H416104161H0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.65/0.950.25/0.35—H432004320H0.17/0.230.40/0.700.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.35/0.650.20/0.30—H434004340H0.37/0.440.55/0.900.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.65/0.950.20/0.30—H43406(5)E4340H(5)0.37/0.440.60/0.950.15/0.35 1.55/2.000.65/0.950.20/0.30—H462004620H0.17/0.230.35/0.750.15/0.35 1.55/2.00—0.20/0.30—H471804718H0.15/0.210.60/0.950.15/0.350.85/1.250.30/0.600.30/0.40—H472004720H0.17/0.230.45/0.750.15/0.350.85/1.250.30/0.600.15/0.25—H481504815H0.12/0.180.30/0.700.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H481704817H0.14/0.200.30/0.700.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H482004820H0.17/0.230.40/0.800.15/0.35 3.20/3.80—0.20/0.30—H50401(6)50B40H(6)0.37/0.440.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H50441(6)50B44H(6)0.42/0.490.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H504605046H0.43/0.500.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.13/0.43——H50461(6)50B46H(6)0.43/0.500.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.13/0.43——H50501(6)50B50H(6)0.47/0.540.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H50601(6)50B60H(6)0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.30/0.70——H512005120H0.17/0.230.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H513005130H0.27/0.330.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75/1.20——H513205132H0.29/0.350.50/0.900.15/0.35—0.65/1.10——H513505135H0.32/0.380.50/0.900.15/0.35—0.70/1.15——H514005140H0.37/0.440.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H514705147H 0.45/0.520.60/1.050.15/0.35—0.80/1.25——H515005150H 0.47/0.540.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H515505155H 0.50/0.600.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H516005160H 0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H51601(6)51B60H (6)0.55/0.650.65/1.100.15/0.35—0.60/1.00——H611806118H 0.15/0.210.40/0.800.15/0.35—0.40/0.80—0.10/0.15H615006150H 0.47/0.540.60/1.000.15/0.35—0.75-1.20—0.15 min H81451(6)81B45H (6)0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.15/0.450.30/0.600.08/0.15—H861708617H 0.14/0.200.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862008620H 0.17/0.230.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862208622H 0.19/0.250.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862508625H 0.22/0.280.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H862708627H 0.24/0.300.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H863008630H 0.27/0.330.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H86301(6)86B30H (6)0.27/0.330.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H863708637H 0.34/0.410.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864008640H 0.37/0.440.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864208642H 0.39/0.460.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H864508645H 0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H86451(6)86B45H (6)0.42/0.490.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H865008650H 0.47/0.540.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H865508655H 0.50/0.600.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25—H866008660H 0.55/0.650.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.15/0.25H872008720H 0.17/0.230.60/0.950.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.20/0.30—H874008740H 0.37/0.440.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.20/0.30—H882208822H 0.19/0.250.70/1.050.15/0.350.35/0.750.35/0.650.30/0.40—H925909259H 0.56/0.640.65/1.100.70/1.20—0.45/0.65——H926009260H 0.55/0.650.65/1.10 1.70/2.20————H93106(5)E9310H (5)0.07/0.130.40/0.700.15/0.35 2.95/3.55 1.00/1.450.80/0.15—H94151(6)94B15H (6)0.12/0.180.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—H94171(6)94B17H (6)0.14/0.200.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—H94301(6)94B30H (6)0.27/0.330.70/1.050.15/0.350.25/0.650.25/0.550.80/0.15—1.The ranges and limits on this table apply only to material not exceeding 0.13 m 2 (200 in 2) in cross-sectional area, 460 mm (18 in) in width, or 4.5 tonne (10 000 lb) per piece in weight. Ranges and limits are subject to the permissible variations for product analysis shown in Table 4 of SAE J409.2.Small quantities of certain elements may be found in alloy steel which are not specified or required. These elements are considered incidental and acceptable to the following maximum amounts: copper to 0.35%, nickel to 0.25%, chromium to 0.20%, and molybdenum to 0.06%.3.For open hearth and basic oxygen steels maximum sulfur content is 0.040% and maximum phosphorus content is 0.030%. Maximum phosphorus and sulfur in basic electric furnace steels are 0.025% each.4.Sulfur content range is 0.035/0.050%.5.Electric furnace steel.6.These steels contain 0.0005 to 0.003% boron.TABLE 2—(1)STANDARD ALLOY H STEEL COMPOSITIONS (ladle chemical composition, weight %, for elements shown (2)(3)see Figures 17 to 88 for respective H-bands) (continued)UNS No.SAE Steel No.C Mn Si Ni Cr Mo V4.Identification—As a means of identifying steels specified to hardenability band limits, the suffix letter “H” hasbeen added to the conventional series number. In the Unified Numbering System (UNS), the “H” appears as a prefix. It is important the steel consumers use this letter in specification requirements, as there is no other means of determining when hardenability band limits apply. When the letter is used, all conditions pertaining to chemical composition limits, restrictions, testing techniques, and so forth, as outlined herein apply5.Grain Size—The H-band limits set forth are intended to apply to steels exhibiting austenitic grain size ASTMNo. 5 or finer (see SAE J418). In cases where coarse grain steel is desired, the hardenability limits shall be a matter of agreement between the producer and the consumer.e of Hardenability Limits—H-band limits are shown graphically and are so depicted for convenience inestimating the hardness value obtainable at the various locations on the end quench test specimen and for quick comparisons of the various H grades.The values of Diameter of Rounds, with Same As-Quenched Hardness shown above each H-band, are approximate and were selected from the ranges appearing in Figure 7 of SAE J406.It should be noted that hardenability limits are presented graphically in both U.S. customary units and metric (SI) units. The metric hardenability bands were prepared by careful conversion from existing bands in U.S.customary units.In either case, for specification purposes, the tabulated values of Rockwell C hardness (HRC) are used.Values below 20 HRC are not specified because such values are not as accurate.Two points from the tabulated values are commonly designated according to method A, B, C, D, or E, which are defined in the following paragraphs. Those various methods are illustrated graphically in Figures 1 and 2.Note that nearest whole integers of distance and hardness are to be used, not fractions.6.1Method A—The minimum and maximum hardness values at any desired distance. This method is illustratedin Figures 1 and 2 as points A-A.6.2Method B—The minimum and maximum distance at which any desired hardness value occurs. This methodis illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points B-B. If the desired hardness does not fall on an exact mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position, the minimum distance selected should be the nearest mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position toward the quenched end and the maximum should be the nearest mm (or sixteenth of an inch) position away from the quenched end.6.3Method C—Two maximum hardness values at two desired distances, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as pointsC-C.6.4Method D—Two minimum hardness values at two desired distances, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points D-D.6.5Method E—Any minimum hardness plus any maximum hardness, illustrated in Figures 1 and 2 as points E-E.When hardenability is specified according to one of the aforementioned methods, the balance of the hardenability band is not applicable.In cases when it is considered desirable, the maximum and minimum limits at a distance of 1.5 mm (1/16 in) from the quenched end can be specified in addition to the other two points as previously described in methodsA to E, inclusive.HARDENABILITY REQUIREMENTS IN METRIC (SI) UNITSHARDENABILTY REQUIREMENTS IN U.S. CUSTOMARY UNITSWhen the full h-band is specified, the hardenability can be reported by listing hardness values for 1.5, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, and 50 mm from the quenched end of the test specimen. In the case of the test specimen made to U.S. customary units, hardness values would be reported for each 1/6 to 16/16 in and 1/8 in increments from there to 32/16 in.It is customary to accept a tolerance of two points HRC for a 5mm or 3/16 in portion of the curve, except at the1.5 mm or 1/6 in position. This tolerance is necessary because curves for individual heats may vary somewhatin shape from the standard band limits and thus deviate slightly at one or more positions in the full length of the curves.For shall hardening carbon H steels, distances form the quenched end may be reported by listing hardness values for 1 mm or 1/32 in intervals near the quenched end, as described more fully in SAE J406.Acceptance testing shall be performed in accordance with SAE J406.7.General—The hardenability limits in this document are those for regular quality steels produced in accordancewith the Steel Products manuals published by the American Iron and Steel Institute (AISI). Some of the steels in this document can be specified to more restricted hardenability ranges, as presented in SAE J1868.FIGURE 3—UNS H10380—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1038HFIGURE 4—UNS H10450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1045HFIGURE 5—UNS H15220—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1522HFIGURE 6—UNS H15240—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1524HFIGURE 7—UNS H15260—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1526HFIGURE 8—UNS H15410—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1541HFIGURE 9—UNS H15211—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B21HFIGURE 10—UNS H15281—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B28HFIGURE 11—UNS H15301—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B30HFIGURE 12—UNS H15351—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B35HFIGURE 13—UNS H15371—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B37HFIGURE 14—UNS H15411—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B41HFIGURE 15—UNS H15481—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 15B48HFIGURE 16—UNS H15621—HARDENABILITY BNAD—SAE 15B62HFIGURE 17—UNS H13300—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1330HFIGURE 18—UNS H13350—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1335HFIGURE 19—UNS H13400—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1340HFIGURE 20—UNS H13450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 1345HUNS H40280—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4028H*FIGURE 22—UNS H40320—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4032HFIGURE 23—UNS H40370—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4037HFIGURE 24—UNS H40420—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4042HFIGURE 25—UNS H40470—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4047HFIGURE 26—UNS H41180—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4118HFIGURE 27—UNS H41200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4120HFIGURE 28—UNS H41300—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4130HFIGURE 29—UNS H41350—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4135HFIGURE 30—UNS 41370—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4137HFIGURE 31—UNS H41400—HARDENABILITY BAND—4140HFIGURE 32—UNS H41420—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4142HFIGURE 33—UNS H41450—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4145HFIGURE 34—UNS H41470—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4147HFIGURE 35—UNS H41500—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4150HFIGURE 36—UNS H41610—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4161HFIGURE 37—UNS H43200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4320HFIGURE 38—UNS H43400—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4340HFIGURE 39—UNS H43406—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE E4340HFIGURE 40—UNS H46200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4620HFIGURE 41—UNS H47180—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4718HFIGURE 42—UNS H47200—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4720HFIGURE 43—UNS H48150—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4815HFIGURE 44—UNS H48170—HARDENABILITY BAND—SAE 4817H。