综合英语二教案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:150.90 KB
- 文档页数:17
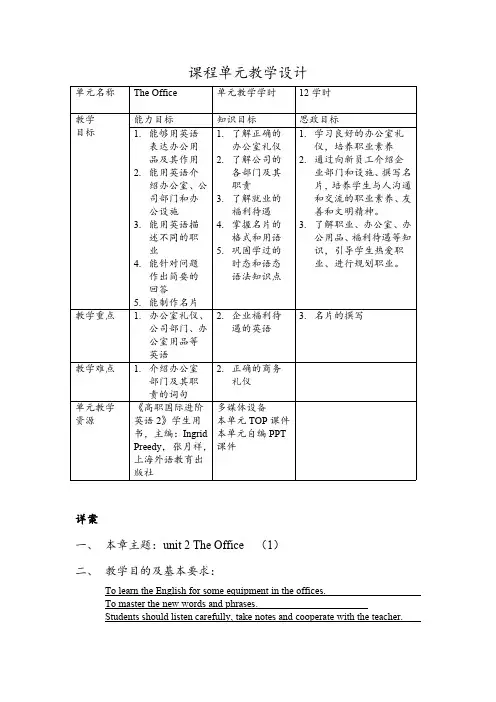
课程单元教学设计单元名称The Office单元教学学时12学时教学目标能力目标知识目标思政目标1.能够用英语表达办公用品及其作用2.能用英语介绍办公室、公司部门和办公设施3.能用英语描述不同的职业4.能针对问题作出简要的回答5.能制作名片1.了解正确的办公室礼仪2.了解公司的各部门及其职责3.了解就业的福利待遇4.掌握名片的格式和用语5.巩固学过的时态和语态语法知识点1.学习良好的办公室礼仪,培养职业素养2.通过向新员工介绍企业部门和设施、撰写名片,培养学生与人沟通和交流的职业素养、友善和文明精神。
3.了解职业、办公室、办公用品、福利待遇等知识,引导学生热爱职业、进行规划职业。
教学重点 1.办公室礼仪、公司部门、办公室用品等英语2.企业福利待遇的英语3.名片的撰写教学难点 1.介绍办公室部门及其职责的词句2.正确的商务礼仪单元教学资源《高职国际进阶英语2》学生用书,主编:IngridPreedy,张月祥,上海外语教育出版社多媒体设备本单元TOP课件本单元自编PPT课件详案一、本章主题:unit2The Office(1)二、教学目的及基本要求:To learn the English for some equipment in the offices.To master the new words and phrases.Students should listen carefully,take notes and cooperate with the teacher.三、教学重点:Expressions of office equipment;New words and expressions四、教学难点Expressions of office equipment五、教学时数:_2_学时,其中实践性教学_____学时六、参考资料:materials from the internet 七、教学内容(上课内容、步骤和方法):项目教学内容和步骤说明时间(分)Study English for office equipment 办公用品英语学习和练习PPT 课件1.Which office do you like?Does the office influence your decision of taking a job?---ask students to talk about the queations.2.Can you name some of these office equipment in English?3.According to students’answers,the teacher then show students the names of the supplies.4.Is office etiquette important?--ask students to watch a video and speak out the mistakes in English.Then,conclude the mistakes in PPT.教师引导,学生回答并学习教师布置,学生互动回答教师评论,给予答案观看视频,用英语描述错误。

Unit 1 Ways of LearningTeaching Aims:1.Understanding the main idea (that it would be ideal if we can strike a balance between theChinese and western learning styles) and structure of the text(introduction of the topic by an anecdote-elaboration by comparison and contrast-conclusion by a suggestion)2.Appreciate the difference between comparison and contrast, as well as different ways tocompare and contrast (point-to-point method or one-side-at-time method)3.Grasp the key language points in Texts A and grammatical structures in the text4.Understand the cultural background related to the content5.Conducting a series of theme-related reading, listening, speaking, and writing activities6.Learn to write notices, etc.Teaching Keypoints:1.Grasp the main idea of Text A and language points in Text A2.Cultural background about Chinese and western ways of learning3.Analysis of the difficult sentences in Text ATeaching Difficulties:1.Writing strategy and style demonstrated in Text A2.Learn how to understand the structure of difficult and long sentencesTeaching Aids:Teacher-guided, discussion, exercises, group-activities, student-centredTeaching period: 12 classesTeaching Procedure:Step 1Warming up1.Have students read the overview of page 2, students will understand the main topic of unit(ways of learning in Chinese and western countries)2.Have students listen to the script of listening part, explain some difficult sentences andphrases, lead them to finish the exercises on page3, check the answer3.How to understand the following sentences:Standing on the shoulders of giants4.Explain the cultural notes of education in the west5.In class, students form two camps to debate the following issue: If you have a baby , whichway would you prefer to use , to pay more attention to develop more skills or to creativity?Step 2 Global analysis of Text AⅠ. ScanningScan Text A and decide whether the following statements are true or false.1 Benjamin was worried that he couldn’t put the key into the box. (F)(=Benjamin was not bothered at all.)2. In the Chinese staff’s opinion, the parents should guide Benjamin to insert the key. (T)3. The author and his wife didn’t care whether Benjamin succeeded in inserting the key into the slot. (T)4. For the Westerners, learning should take place by continual careful shaping and molding. (F) (= The Chinese think that learning should take place by continual careful shaping and molding.) 6.Chinese teachers hold the opinion that skills should be acquired as early as possible, whileAmerican educators think that creativity should be acquired early. (T)7.Add more questions about the text:Where and when did the incident take place?Who are the main characters in this incicent?What is Howard Gardner?Why do the couple come to China?How old is the son of the author?Through what does the baby get pleasure in the incident?What is the attitude of his parents ?What is the attitude of the hotel staff towards Benjamin effort?8.Answer the questions of on page 10-11ⅱUnderstanding the main idea of the text Division of the Text AStep 3 Detailed Reading of Text AⅠ. Difficult Sentences1. (LL. 13~15) Because of his tender age and incomplete understanding of the need to position the key just so, he would usually fail.Paraphrase the sentence. (= Because he was so young and didn’t quite know that he should position the key carefully to fit into the narrow key slot, he would usually fail.)2. (L. 15) Benjamin was not bothered in the least.(= Benjamin was not bothered at all.)3. (L. 30) … and to throw light on Chinese attitudes toward creativity.And to help explain Chinese attitudes toward creativity.4. (LL. 37~39) …since the child is neither old enough nor clever enough to realize the desired action on his own, what possible gain is achieved by having him struggle?What does the desired action refer to? (= Positioning the key carefully to fit into the slot.)5. (L. 39) He may well get frustrated and angry. (= He is likely to get frustrated and angry.)Eg . You use “may well” when you are saying what you think is likely to happen.6. (L. 47~48) He was having a good time and was exploring, two activities that did matter to us. What do the two activities refer to?(= Having a good time and exploring.)“activities that did matter to us”.(= activities that were important to us.)7. (L. 52) …whether it be placing a key in a key slot, drawing a hen or making up for a misdeed…= No matter whether it is placing a key in a key slot, drawing a hen or making up for some mistakes.) the subjunctive moodeg. Whether he be present or absent, we shall have to do our part.)8. (LL. 80~81) …young Westerners making their boldest departures first and then gradually mastering the tradition…(西方的年轻人先是大胆创新,然后逐渐深谙传统。

Listen and RespondTask One Focusing on the Main IdeasChoose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences according to the information contained in the listening passage.1 One day in school Monty Roberts was asked to ________.A) write a term paper about the courses he learnedB) write about his dream of the futureC) describe a horse ranchD) draw a picture of a horse ranch2 Monty Roberts’goal was to become ________.A) a horse trainer like his fatherB) a painter who draws horses and horse ranchesC) an owner of a large horse ranchD) an owner of a large farm3 When Monty Roberts turned in the paper, his teacher ________.A) was not satisfied with itB) helped to improve itC) gave a good comment about itD) asked him to discuss the topic with his father4 The teacher asked the boy to rewrite the paper because ________.A) his father had helped him write the paperB) his paper was full of empty wordsC) his dream was not properly described in the paperD) his goal of life described in the paper was not realistic5 A week later, the boy finally decided ________.A) to follow his father’s professionB) to keep his dreamC) to make some changes in his paperD) to follow his teacher’s adviceTask Two Zooming In on the DetailsListen to the recording carefully and fill in each of the blanks according to what you have heard.1 Monty Roberts was the son of a horse trainer . His dream was to own a large horse ranch. That night he wrote about his dream in great detail and he even drew a picture of a 200-acre ranch .2 He put a great deal of his heart into the dream ranch and the next day he handed the paper in to his teacher .3 When Monty Roberts asked his teacher why he got a large red F for his paper, his teacher explained to him that his dream was impossible for him. He had no money. But he needed a lot of money to buy the land, the house and the machines for his dream ranch.4 When Monty Roberts asked his father for advice, his father just asked him to make up his own mind on his dream because it is a very important decision for him to make.5 When Monty Roberts turned in the same paper, he said to his teacher, “You can keep the F and I’ll keep my dream . I will follow my heart , no matter what happens.”Read and ExploreTask One Discovering the Main Ideas1 Answer the following questions with the information contained in Text A.1) According to Alex Haley, why does many a young man want to be a writer?Because they think that being a writer can bring them wealth and fame.2) Does writing mean glory and wealth in the author’s opinion?No. The author thinks that writing is a lonely, private and poor-paying affair. Only a few can succeed after long periods of neglect and poverty.3) What was the author’s life in Greenwich Village like?His life in Greenwich Village was very poor. He barely made enough to eat.4) Did he ever doubt his ability to write? Why or why not?Yes. Because he didn’t receive a break after writing for a year or so.5) Why did the call from his old acquaintance change his life? Because his doubt of his resolution to write was cleared. He was determined to keep on writing.6) In what way did people like Delaney and Belafonte become role models for the author?From them he learned that one had to make sacrifices and live creatively to keep working hard to realize one’s dreams.7) How many years did the author keep on writing before his great success?He kept on writing for 17 years before his great success.8) What did the two sardine cans and 18 cents in the brown paper bag symbolize?They symbolized his courage and persistence to stick to his dream of writing.9) What is the meaning of the Shadowland of dreams?The Shadowland of dreams means all the difficulties (e.g. neglect, poverty, doubt, uncertainty, and fear of failure) people meet with in pursuing their dreams.2 Text A can be divided into three parts with the paragraph number(s) of each part provided as follows. Write down the main idea of each part.Part: One; Paragraph(s): 1-2; Main Idea: Alex Haley explains the difference between “being a writer”and “writing”.Part: Two; Paragraph(s): 3–18; Main Idea: The author tells about his struggle to stick to his dream of writing and his final success.Part: Three; Paragraph(s): 19-22; Main Idea: The author tells about his struggle to stick to his dream of writing and his final success.Task Two Reading Between the LinesRead the following sentences carefully and discuss in pairs what the author intends to say by the italicized parts.1) For every writer kissed by fortune, there are thousands more whose longing is never rewarded. (Para. 2)Compared with those lucky writers who have become famous, thousands of people who devote themselves to writing are never given recognition as successful writers.2) Next time I make a sale. (Para. 6)Considering the rather difficult circumstances the author was in, it is easy to see that there was a degree of irony and self-sarcasm when he promised his friend that he would pay back the money next time he made a sale, for it was something that had not happened before and would not be very likely to happen in the near future, thus pushing the repayment of the debt into the remote future.3) What’s more, I could write on the side. (Para. 8)More importantly, I could take writing as a part-time job.4) There’s everything you’ve made of yourself so far. (Para. 10)The two cans of sardines and 18 cents are all you have.5) Another Village neighbor was a handsome young singer who ran a struggling restaurant. (Para. 13)…a restaurant that has few customers and is about to close down.6) As I absorbed the lesson, I gradually began to sell my articles. (Para.15)As I became aware of what it meant to live in the Shadowland, …7) For the first time I had money and open doors everywhere. (Para. 18)…I had a lot of opportunities.Checking Your VocabularyWord Detective1 Choose the definition in Column B that best matches each italicized word in Column A.1)d2)g3) f4) e5) b6) h7) a8)c2 Spell out the words from Text B with the help of the given definitions, the initial letters and paragraph numbers. Example: e stablish : set up; begin; create (Para. 1)1) w orthy : deserving respect or serious consideration (Para. 1)2) c reep : move slowly, quietly, and carefully, esp. so as not to attract attention (Para. 1)3) r esolve : make a determined decision; decide firmly (Para. 2)4) r efresh : make less hot or tired; bring back strength and freshness to (Para. 5)5) o ccurrence : an event or happening (Para. 6)6) s urplus : an amount additional to what is needed or used (Para. 6)7) f avourable : winning favour and approval (Para. 7)8) r emark : say esp. sth. that one has just noticed; give as an opinion (Para. 9)3 Some phrases or expressions from Text B are hidden in the following picture. Find the phrases or expressions and then use them to complete the sentences with the help of the clues.1) He sweeps the floor for the hotel to work out (以工作抵偿) the cost of board. (Para. 1)2) She was unused to (不习惯) talking about herself. (Para. 4)3) After waiting for a long time,the little boy is out of patience(不耐烦). (Para. 4)4) The bad weather has added to (增加) the difficulties in our work. (Para. 4)5) The homeless people in the city have to walk the streets (走街串巷), begging for food and money. (Para. 5)6) We were terrified when we came on / upon (发现) a snake behind the little cottage on the edge of the wood. (Para. 5)7) Eva was cutting the grass, and in the meantime (与此同时) Adam was planting roses. (Para. 7)8) From this book written by a movie star we get / have got the idea (领悟到) that those people in the limelight are just ordinary people —even famous faces have flaws! (Para. 7)Checking Your Comprehension1 Answer the following questions with the information contained in Text B.1) How did the author get to know about the school for coloured people in Virginia?He overheard two miners talking about it while working in the coal-mine.2) Why did the author resolve to go to the school?Because he heard that the school was established for coloured people and opportunities were provided to poor but worthy students to work out all or a part of the cost of board and learn some trade or industry at the same time.3) What kind of situation was he in when he reached the city of Richmond late one night?He was tired, hungry and dirty. And he was completely out of money. He had not a single acquaintance in the city, and, being unused to city ways, he didn’t know where to go.4) How did he spend his first night in Richmond?He walked the streets till he became too exhausted to walk any longer. Then he found an elevated sidewalk and lay under it for the night upon the ground.5) How did he earn some money for his breakfast the next morning?He helped unloading a cargo of pig iron from a large ship.6) Why didn’t the head teacher admit the author to the institution at first?Because of being so long without proper food, a bath and change of cloth, he didn’t make a very favourable impression upon her.7) How did the author get a chance to prove his worthiness to the head teacher?The head teacher asked him to sweep the adjoining classroom and he did an excellent job,which proved his worthiness as a student in the institute.2 Read the following statements and then decide whether each of them is true or false based on the information in the text. Write T for True and F for False in the space provided before each statement. 1) F At Hampton Normal and Agricultural Institute poor but worthystudents had opportunities to pay just a part of the cost of board. (Poor but worthy students were provided opportunities to earn money to pay all or a part of the cost of food in the school and at the same time learn some trade or industry.)2) T On the first day of his journey, he realized that he didn’t haveenough money to go to Hampton.3) F He reached the city of Richmond by walking and begging for anumber of days.(He reached the city of Richmond by walking and begging rides for a number of days.)4) T Though he was tired and hungry, he still believed that he wouldreach Hampton.5) F By helping unload a big ship, he earned enough money to buy achicken leg and an apple pie for his breakfast.(By helping unload a big ship, he earned enough money for his breakfast.)6) F He felt that a new kind of existence had begun because he arrived atthe school with a surplus of 50 cents.(He felt that a new kind of existence had begun because he could begin his education in the school.)7) T He worked hard to clean the classroom because his future dependedupon the impression he made upon the head teacher.8) F The head teacher admitted the author on condition that he shouldclean the classroom thoroughly after class.(The head teacher admitted the author because he proved his worthiness by cleaning the classroom thoroughly.)Enhance Your Language AwarenessWords in ActionWorking with Words and Expressions1 In the box below are some of the words you have learned in this unit. Complete the following sentences with them. Change the form where necessary.1) A smart appearance tends to make a(n) favourable impression at an interview.2) The scientist failed in his experiments many a time, but he was never discouraged ; instead, he stuck it out and finally made a great scientific discovery.3) When I asked my mother if I could marry George, she consented but rather unwillingly.4) The garden has fallen into a state of neglect since its owner died two years ago.5) Coming home late, the boy crept quietly into the house to avoid waking his parents.6) If you want to learn a language well, sufficient time is necessary.7) The origin of Chinese writing can be traced back to ancient China although we are not certain of the date of its invention.8) The price was somewhat higher than I had expected. However, it was still acceptable.9) When you feel tired, a rest and a cool drink will refresh you.10) As I sit here today, I couldn’t be more grateful for the opportunity, not only to be alive, but also to apply my life to such a(n) worthy effort.11) More and more people in big companies are enrolling in English courses to improve their promotion(晋升) prospects .12) I made full preparations for my journey to London on foot and I resolved to get there in five days.13) At the end of the interview, she remarked , “You’ve proved your worthiness more than well enough.”14) I hope that I shall never again have to undergo such a terrible experience.15) Susan started singing to her baby and was rewarded with a smile.2 In the boxes below are some of the expressions you have learned in this unit. Do you understand their meanings? Do you know how to use them in the proper context? Now check for yourself by doing the blank-filling exercise. Change the form where necessary.1) Since the summer vacation has started, let’s pack up and spend a week in the country with my grandparents.2) The boy is so interested in the popular novel entitled Harry Porter and the Deathly Hallows(圣徒) that he has read it for many a time.3) I admire Steve very much, for in his pursuit of a successful life, he always stays the course and never gives up in spite of the many difficulties and risks he has encountered.4) The couple’s love was put to the test when the husband was crippled in a car accident.5) I mailed out 250 letters to complete strangers for help and within 6 weeks the stream of money came flooding in from all over the country.6) When searching for some news online(在线的) last night, I came across an interesting website(网址) devoted to computer games.7) He is so clever that he can always come up with solutions at the last moment.8) At the sight of the big fish, the fisherman plunged his hands into the water and caught it with graceful ease.Increasing Your Word Power1 Listed in the box below are some unit nouns. Discuss their meanings and then complete the following table by filling in the appropriate unit noun. The same unit noun may be used for more than once. Consult a dictionary if necessary.a(n) slice of bread a(n) particle of rocka(n) bunch of keys a(n) bar of soapa(n) can of orange juice a(n) sheet of glassa(n) item of business a(n) article of furniturea(n) slice of meat a(n) particle of dusta(n) can of beer a(n) bar of chocolatea(n) article of luggage a(n) bunch of flowersa(n) sheet of paper a(n) item of expense2 Words such as respectful, respectable and respective may cause confusion because they are similar either in meaning or in spelling. To communicate effectively, we need to pay special attention to such confusable words. In each of the following sentences you are given two or three words in brackets. Choose the appropriate one to fill in the blank. You may consult a dictionary if necessary.1) Now your father has retired, you should go and see him now and then. This should not be neglected (neglectful, neglected).2) Some boy students are neglectful (neglectful, neglected) of their appearance in school.3) In this book the writer describes his colourful (coloured, colourful) experiences in Africa.4) To celebrate the Spring Festival, they tie many coloured (coloured, colourful) lamps on the trees.5) The coat is made of a kind of cloth that is rough (rough, tough) to touch.6) The meat was tough (rough, tough) and hard and I did not like it at all.7) The article is all nonsense. It’s not worth (worth, worthy) the paper it’s printed on.8) These young men will prove worthy (worth, worthy) of our trust.9) The situation will develop in a direction favourable (favourite, favourable) to China.10) I like oranges very much; they are my favourite (favourite, favourable) fruit.11) The boys here are well mannered and respectful (respective, respectable, respectful) toward grown-ups.12) My uncle is a respectable (respective, respectable, respectful) doctor in our town.13) After the meeting we will take our respective (respective, respectable, respectful) ways home.14) It was very considerate (considerate, considerable) of you to send mea birthday card yesterday.15) There has been a considerable (considerate, considerable) growth of light industry in the city in the last five years.3 Word BuildingNow match each of the English words in Column A with its Chinese meaning in Column B. You may consult a dictionary if necessary.1)d2) i3) l4) a5)k6) o7) p8) b9)m10) n11) e12) c13) f14) g15) h16) jGrammar in ContextTask 1: Fill in the blanks in the following sentences by choosing proper connectives from the box below.1) He gave us a vivid description of what he had seen in Africa.2) The only way to avoid being miserable is not to have enough leisure to wonder whether you are happy or not.3) I looked around and was not certain whose house I was in.4) The students here will give their used books to whoever need them in the countryside schools.5) The situation today is obviously different from what it was only 50 years ago.6) Persistent people begin their success where others end in failure.7) I didn’t realize how difficult it was to get the tickets for the performance.8) You say you are brave. Now let’s see which of us is the more timid(胆小的).9) I know nothing about her except that she is an English teacher in our school.10) We all thought it a pity that the sports meet should have been put off.Task 2: Complete the following sentences using a preposition and a relative pronoun.1) He took out a square green bottle, the content of which he poured into a dish.2) The goals for which he has fought all his life are all achieved now.3) An investigation was made into the accident, in which fifty people were killed.4) We need a chairman in whom everyone has confidence.5) A survey was carried out on the death rate of the new-born babies in the region, the results of which were shocking.6) I am grateful to him for his advice, to which I owe all my success.7) This depends on the purpose for which nuclear energy is used.8) The time at which each control signal is sent is carefully controlled by a digital(数码的) clock.ClozeComplete the following passage with words and phrases chosen from Text A. The initial letter of each is given.There’s a difference between “being a writer”and writing. As a matter of fact, many who wish to be writers are longing f or (1) wealth and fame, not the long hours alone at the type-writer. They are not a ware (2) of the fact that writing is a lonely, private and poor-paying a ffair (3). Iremember when I became a freelance writer, I had no p rospects (4) at all. What I did have was a friend and a small s torage (5) room in an apartment building. It didn’t even m atter (6) that it was cold and had no bathroom. Immediately I bought a used manual typewriter and p lunged(7) myself into writing. After a year or so, however, I still hadn’t receiveda b reak (8) and began to doubt myself. Then one day I was o ffered (9) a job earning $ 6,000 a year. As the dollars were d ancing (10) in my head, something c leared (11) my senses. From deep inside a bull-headed resolution w elled u p (12). I heard myself saying, “I’m going to s tick (13) it out and write.”I realized that you had to make s acrifices (14) and live creatively to keep working at your dreams. Then, in 1970, 17 years after I left the Coast Guard, Roots was p ublished (15). The shadows had turned into dazzling limelight.TranslationTranslate the following sentences into English, using the words and expressions given in brackets.1) 听说他的新书是根据发生在田纳西州一个小镇上一家人的真事写的。
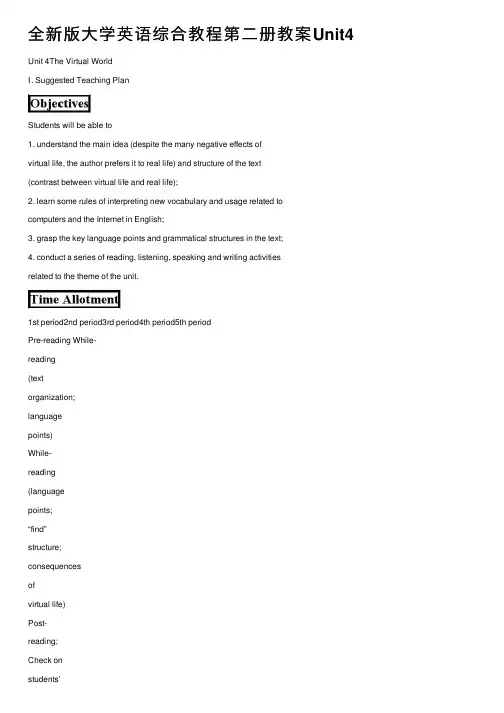
全新版⼤学英语综合教程第⼆册教案Unit4 Unit 4The Virtual WorldⅠ. Suggested Teaching PlanStudents will be able to1. understand the main idea (despite the many negative effects ofvirtual life, the author prefers it to real life) and structure of the text(contrast between virtual life and real life);2. learn some rules of interpreting new vocabulary and usage related tocomputers and the Internet in English;3. grasp the key language points and grammatical structures in the text;4. conduct a series of reading, listening, speaking and writing activitiesrelated to the theme of the unit.1st period2nd period3rd period4th period5th periodPre-reading While-reading(textorganization;languagepoints)While-reading(languagepoints;“find”structure;consequencesofvirtual life)Post-reading;Check onstudents’homereading(Text B)Theme-RelatedLanguageLearn-ing Tasks1. T asks Ss the following questions on the poem Surfing the Internet:(5minutes)* What was the hero doing when his boss came in? (surfing the Internet) * How did he act in front of his boss? (He pretended to be surprised at the computer which had crashed “unexpectedly”.)2. Ss look at the theme of this unit (The Virtual World) and the title of TextA (A Virtual Life), then try to: (10 minutes)* find antonyms of “virtual world” and “virtual life”; (real world, real life) * suggest synonyms for “virtual world”; (cyberspace, cyberia, etherworld, virtual reality, Internet world, net world, etc.)* say what people can do on the Internet, (communicating with people, shopping, reading, entertainment, education, working, hacking, publishing, etc.)3. Imaginative writing(28 minutes)1) T dictates to Ss the following paragraph:For the past two weeks, other participants of the Net Survival Contest (⽹络⽣存竞赛)and I have been shut up in bare hotel rooms.Our only link to the real world has been a computer that is hooked up to the Internet (联⽹电脑). We have relied on it, not only for food, bed sheets and other daily necessities, but also to set up an e-business (电⼦商务)of our own.2) Now Ss will complete the next paragraph beginning with: “Now it istime for me to walk out into the light of day again...” They willgive their imagination full play. They will write no more than 100words.3) Ss form groups of four to five, and read aloud to each other theirown writings.4) T asks some groups to recommend the best piece in their group tothe class.4. T may lead in to Text A by saying: Some of us like to live a life in contact with real things and real people, but others favora virtual existence. Which life is better? I’m sure you have different opinions. Now let’s read Text A to find out what Maia Szalavitz has to say about these two life styles. (2 minutes)1. Text organization (15 minutes)1) T draws Ss’ attention to Text Organization Exercise 1, and lets themread its instructions as well as what has already been done for them in this exercise.2) Ss try to complete the exercise by simply reading the first sentence ofeach paragraph in Text A.1) Ss compare answers with each other; if necessary, T may help.2. T explains the key language points and gives Ss practice (see LanguageStudy). (45 minutes)3. T guides Ss through Structure Exercise 2. (10 minutes)2. Ss re-read Paras 4-10, work in pairs to find out consequences of “my”virtual life. Can they use the “find oneself + adj./ past participle/present participle” structure when summing up the conse-quences? (10 minutes)3. Some pairs report to the class their findings, using the “find” structure.(5 minutes)1. Computer-related vocabulary items (20 minutes)1) Ss scan Text A to find out vocabulary items related to computer andthe Internet. (They are: virtual life, the net, telecommuter, email,Internet mailing lists, computer-assisted, data, link, cyber-interaction, on line, system crash, click on the modem, connection,password)2) T tells Ss that new terms related to computer and the Internet areconstantly added to the English vocabulary, so much so that many ofthem are not included in any English dictionary. However, if weapply certain rules, their meanings are easy to deduce.3) T gives Ss more examples of computer-related vocabulary items (seeText Analysis).2. T guides Ss through some after-text exercises. (25 minutes)3. T checks on Ss’ home reading (Text B). (3 minutes)4. Ss do Part IV: Theme-Related Language Learning Tasks. (1 period)5. T asks Ss to prepare the next unit: (2 minutes)1) do the pre-reading task;2) preview Text A.Ⅱ.Text AnalysisThe most dynamic combining forms/prefixes for new computer-and-Internet-related vocabulary in English are cyber-, virtual, Net- (net-), Web-(web-), and E- (e-).New English vocabulary items derived from them usually appear in the following forms:1. combining forms/prefixes + noun: this is the most common type, e.g.virtual life (虚拟⽣活), virtual world (虚拟世界), virtualcommunity(虚拟社区), virtual office (虚拟办公室), virtual pet (虚拟宠物),virtual reality (虚拟现实),cyber-interaction (⽹络互动),cyberculture(⽹络⽂化),cybernut (⽹⾍), cyberpet(电⼦宠物),cyberspace (⽹络空间), netwriter(发送电⼦邮件的⼈),nethead (⽹⾍), Webmaster (⽹站维护者), Web page (⽹页), website (⽹站),WebTV (⽹络电视机), E-book (电⼦书籍), E-shopper (⽹上购物者), e-card (电⼦贺卡), e(-)mail (电⼦邮件), e-journal (电⼦杂志),e-business (电⼦商务), e-cash (电⼦货币), e-commerce (电⼦商务). 2. combining forms/prefixes + verb: e.g. cybersurf (⽹络漫游), netsurf (⽹络漫游), websurf (⽹络漫游),email (发送电⼦邮件)3. words like cyber, net, etc. + suffix: e.g. cyberian (cyber + ian, ⽹络⽤户), cyberphobia (cyber + phobia, 电脑恐惧症), cybernaut (cyber +naut ⽹络⽤户), netter (net + er ⽹民), Webify (web + fy 使万维⽹化), cyberize (cyber + ize, 使联⽹).4. clipped word: cyberdoc (cyber + doctor, ⽹络医⽣), Netcast (Net +broadcast,⽹络播放), Netiquette (Net + etiquette, ⽹规), Netizen (Net+ citizen, ⽹民,), Netpreneur (Net + entrepreneur, ⽹络企业家),Webcam (Web + camera, ⽹络摄像机), Webcasting (Web + broadcasting,⽹络播放), Webliography (Web + bibliogrpahy, ⽹络书⽬), Webnomics (Web + economics, ⽹络经济), Webzine (Web +magazine, ⽹络杂志), e-tailing (electronic + retailing,电⼦零售), e-zine (electronic + magazine,电⼦杂志)Ⅲ. Cultural Notes1. the Internet: an international computer network for the exchange of information. It was originally used mainly in the academic and military worlds but has since become available to the large and increasing number of people with personal computers. Other services, e.g. the World Wide Web, are available through it.The Internet is changing our lives and a parallel universe is rapidly emerging online. Today there’s scarcely an aspect of our life that isn’t being upended by the torrent of information available on the hundreds of millions of sites crowding the Internet, not to mention its ability to keep us in constant touch with each other via electronic mail. The Internet is saving companies billions of dollars in producing goods and serving the needs of their customers. Nothing like it has been seen since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, when power-driven machines began producing more in a day than men could turn out in nearly a year. The Internet and e-commerce are viewed as a global megatrend along the lines of the printing press, the telephone, the computer and the electricity.You would be hard pressed to name something that isn’t available on the Internet. Consider: books, health care, movie tickets, baby clothes, stocks, real estate, toys and airline tickets. American kids today are so computer savvy that it virtually ensures the United States will remain the unchallenged leader in cyberspace for the foreseeable future. Most kids use computers to play games and have email chats with friends.What’s clear is that, whether we like it or not, the Internet is an ever-growing part of our lives and there is no turning back. 2. NBC (the National Broadcasting Company): the first of the originalthree US national broadcasting companies. It was established in 1926by Radio Corporation of America as two groups of radio stations. Thefirst NBC television channel opened in 1940. The company is nowowned by General Electric. Its main offices are at Rockefeller Centerin New York.3. PBS (the Public Broadcasting Service): (in the US) a televisionsystem that broadcasts programs to an association of local stationswhich use no television advertisements and do not make a profit. Itwas established by the Public Broadcasting Act and is supported bymoney from the US Government, large companies and the public.PBS is known for the high quality of its programs.4. ABC (the American Broadcasting Company): one of the original threemajor television networks in America. It began in 1943 as the BlueNetwork of six radio stations. ABC is now owned by the Walt DisneyCompany .Ⅳ. Language Study1. virtual: 1) created and existing only in a computerExamples: I can visit a virtual store and put what I want in my basket atthe click of a mouse button.Some people spend too much time escaping from reality intothe virtual world conjured up on their computer screens.2) being or acting as what is described, but not accepted as such inname or officiallyExamples: Our deputy manager is the virtual head of the business.Now that the talks have broken down, war in the region looks like a virtual certainty.2. interpret: 1) understand (sth. said, ordered, or done)Examples: They are worried that the students might interpret the new regulation as a restriction of their rights. She interprets the dream as an unconscious desire to be young again.2) give or provide the meaning of,explainExamples: How do you interpret his refusal tosee us?This dream can be interpreted in several different ways.3) translate what is said in one language into anotherExamples: I am terribly sorry, but I don’t understand a word. Could you interpret for me?No one in the tour group spoke Spanish so we had to ask the guide to interpret.3. tone: a particular quality or intonation of the voiceExamples: From the tone of her voice I could tell she was very angry.Suddenly he laughed again, but this time with a cold, sharptone.4. stretch: (cause to) become longer, wider, etc. without breakingExamples: My working day stretches from seven in the morning toeight at night.The child stretched the rubber band to its full extent.5. submit: give (sth.) to sb. so that it may be formally considered (followed by to)Examples: You should submit your reports to the committee.I am going to submit an application for that job in Microsoft.Peter submitted his plans for the new town square to the local government.6. edit: revise or correctExamples: Jack is busy editing Shakespeare’s plays for use in schools.John didn’t finish editing the annual report until the end of lastmonth.7. email: electronic mailExamples: Young people like to keep in touch with their friends via email.I received an email from my studentyesterday.vt. send an email toExamples: I will email you the instant I get thenews.She’ll email me a question before she calls so I can think it overin advance.8. communicate: contact sb. in any way, esp. by speaking to them, writing to them or calling them (followed by with) Examples: Some young people depend heavily on email to communicate with each other.They have been divorced for years and never communicated with each other.9. the Internet: the worldwide network of computer links which allows computer users to connect with computers all over the world, and which carries electronic mailExamples: Whether we like it or not, the Internet is an ever-growing partof our lives.You can take online courses and earn your degree via theInternet whenever and wherever you want to.It’s believed the Internet was born in 1969 when twocomputers at the University of California, Los Angeles wereconnected by a 15 foot cable.10. relationship: state of being connectedExamples: What is the relationship between language and thought?The scientist had a good working relationship with his Americancolleagues.11. at times: sometimesExamples: She has been away from her home for about a year. At times she wishes she had never left. He went on listening to her, at times impatient and at times fascinated.12. take in: absorb (sth.) into the body by breathingor swallowingExamples: The earth takes in heat and light fromthe sun.Fish take in oxygen through their gills.13. data: information, usu. in the form of facts or statistics thatyou can analyzeExamples: This data is stored on the network and can beaccessed by anybody.The data is still being analyzed, so I can’t tell you the results.14. spit: send (liquid, food, etc.) out from the mouth (used in the pattern: spitsth. (out) (at/on/onto sbJsth.))Examples: The baby spat its food out on the table.He took one sip of the wine and spat it out.15. on line: connected to or controlled by a computer(network)Examples: Our system is on line to the maincomputer.The largest online institution is the University of Phoenix, withsome 1000 students today and hopes of reaching 200,000 studentsin 10 years.16. symptom: 1) sign of the existence of sth. badExamples: High interest rates are a symptom of a weak economy.They regard the increase in crime as a symptom of a more generaldecline in moral standards.2) change in the body that indicates an illnessExamples: A cold, fever and headache are the usualsymptoms of flu.If the symptoms persist, it is important to go to your doctor.17. nightmare: a terrifying dreamExamples: Tom didn’t eat fish because it gives him nightmares.Watching horror films gives menightmares.I had a nightmare about falling off theskyscraper.18. conversely: in a way that is opposite to sth.Examples: $1 will buy 100 yen worth of Japanese goods. Conversely, 100 yen will buy $1 worth of American goods. You can add the fluid to the powder or, conversely, the powder to the fluid.19. but then: yet at the same timeExamples: The failure of China’s soccer team looks inevitable. But then, anything can happen in football.Mary performed better than the others in the final exam; but then,she spent much longer on it than they did.20. jar: have a harsh or an unpleasant effect (used in the pattern: jarsth., jar on sbJsth.)Examples: You shouldn’t have too many colors in a small space as the effect can jar.The loud bang jarred my nerves.Her squeaky voice jarred on me.21. suck in: (usu. passive) involve (sb.) in an activity, an argument, etc., usu.against their will (used in the pattern: suck sb. in/into sth.; suck in)Examples: I don’t want to get sucked into the debate about school reform.Some teenagers don’t want to get involved with gangs, but theyfind themselves getting sucked in.22. keep up with: learn about or be aware of (thenews, etc.)Examples: Carrie likes to keep up with the latestfashions.He didn’t bother to keep up with the news. His only concern wasto study.23. Work moves into the background: Work becomes secondary to me.24. in sight: 1) visibleExamples: It was early in the morning and there wasn’t anyone in sight oncampus.As the train pulled into the station my parents standing on theplatform were soon in sight.2) likely to come soonExamples: Two months passed, and victory was not yetin sight.The end of the economic nightmare is still nowhere in sight.A solution to the problem of environmental pollution now seemsin sight.25. remark: thing said or written as a commentExamples: The principal of the school made some remarks about educational reform at the meeting. Mr. Smith approached us and made a couple of remarks aboutthe weather.His rude remark about my book jarred on me.26. emotional: 1) of the emotionsExamples: She is grateful to him for his emotional support while she wasin trouble.It’s quite difficult to handle emotional problems.2) having emotions that are easily excitedExamples: Marie got very emotional when we parted, andstarted to cry.It’s said that the Italians are more emotional than we are.27. cue: anything that serves as a signal about what to do or say (followedby to / for)Examples: When he started to talk about the finances, that was our cue toget up quietly and leave.When I nod my head, that’s your cue to giveflowers to him.Mr. Clinton’s excitement was the cue for acampaign.28.1 say a line: I type a line on the screen.29. routine: a fixed and regular way of doing things (oftenadjectival)Examples: The job is really just a dull series of fairly routine tasks. I don’t think you’ll take it.He established a new routine after retirement.30. rely on/upon: depend confidently on, put trust inExamples: Nowadays we rely increasingly on computers to control theflow of traffic.Some children relied heavily on the advice of theirparents.31.abuse: wrong or bad use or treatment of sth./sb.Examples: The World Health Organization (WHO) has published a report on drug abuse and addiction.The policemen are making an investigationof child abuse.32. restore: bring back to a former condition (used in the pattern: restoresth.; restore sb. to sth.)Examples: Law and order will be quickly restored after the incident.Winning three games restored their confidence.Doing sports every day restored the old man to good health.The deposed king was restored to power.33. arrange: prepare or plan (used in the pattern: arrange sth.; arrange todo sth.; arrange for sb./ sth. to do sth.)Examples: Her marriage was arranged by her parents.Let’s arrange to have a dinner together some time before wegraduate.I have arranged for a taxi to pick us up at 8:00 a.m.I could arrange for you to come along with us if you like.34. flee: run away (from) (used in the pattern: flee from/to; fleesomeplace)Examples: The customers fled from the bank when the alarmsounded.During the war, thousands upon thousands of Afghans fled the country.Up to five million political refugees have fled to other countries.35. interview: 1) a meeting at which a journalist asks sb. questions inorder to find out their newsExamples: In an exclusive interview with our reporter, the film star revealed some of his personal affairs.Radio interviews are generally more relaxed than television ones.2) a formal meeting at which sb. applying for a job is askedquestions, as a way of judging how suitable they are Examples: I have been asked to go for an interview for a project I applied for at Harvard University.She has had a couple of job interviews, but nooffers.v.Examples: As a journalist, he interviewed manygovernment officials.After the press conference, the journalist interviewed the UN Secretary General about the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.I will be interviewed next week for the Chief Executive’s job.36. appointment: an arrangement to meet or visit sb. at a particular time (followed by with)Examples: You can’t see the president of the university unless you make an appointment.I’ve made an appointment to see my tutor tomorrow.37. click: press or release a mouse button rapidly, as to select an icon (followed by on)Example: When shopping online, you just click the mouse and order what you want to buy.38. tune: a series of musical notes that is pleasant andeasy to rememberExamples: She whistled a happy tune all the wayhome.He was humming a merry tune while cooking.。


天水师范学院外国语学院2006-2007学年第二学期教案课程名称:大学英语使用教材: 大学英语(全新版)第二册(综合教程) 主编: 李荫华上海外语教育出版社授课班级:2006级物理三班授课时间:2007年3月5日------2007年7月8日授课教师:姜炳生Lesson Plan of College English Book IICourse Description:Course Objectives: The objective of College English is to develop students‘ ability to use English in an all-round way, especially in listening and speaking, so that in their future work and social interactions they will be able to exchange information effectively through both spoken and written channels, and at the same time they will be able to enhance their ability to study independently and improve their cultural quality so as to meet the needs of China‘s social development and international exchanges.Textbook:College English (Integrated Course 2, Listening and Speaking course 2 New Edition)Course Duration: from March 5th of 2007 to July 8th, 2007Teaching Hours: 4 hours each week (two hours is subtracted every week to enhance listening and speaking in the Multimedia Lab.Subjects of Teaching: 2006Class Three, Department of PhysicsTopics:Week 1: Integrated Course 2: Unit one Ways of LearningWeek 2: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 1 Sports, Unit 2 WeatherWeek 3: Integrated Course 2: Unit two ValuesWeek 4: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 3 Food and drinks, Unit 4 Health Week 5: Integrated Course 2: Unit Three The Generation GapWeek 6: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 5 Music, Unit 6 BusinessWeek 7: Integrated Course 2: Unit Four The Virtual WorldWeek 8: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 7 Fashion, Unit 8 SocietyWeek 9: Integrated Course 2: Unit Five Overcoming ObstaclesWeek 10: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 9 Unusual Happenings,Unit 10 DisastersWeek 11: Integrated Course 2: Unit Six Women, Half the skyWeek 12: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 11 Famous People, Unit 12 Invention Week 13 Integrated Course 2: Unit Seven Learning about EnglishWeek 14: Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 13 Human Virtues, Unit 14 BiodiversityWeek 15 Integrated Course 2: Unit Eight Protecting Our EnvironmentWeek 16: Text Reciting Listening and Speaking course 2: Unit 15 Environment, Unit 16 InternetWeek 17: Oral ExaminationWeek 18: RevisionTeaching Format:This course uses a variety of learning methods: Lectures, collaborative tasks, group discussions and presentations.Required work for the students:Students are required to1.write a short essay every week2.do translation exercise of each unit3.recite at least two paragraphs of each text4.read at least 5000 words of reading materials that suit their levels5.have conversational oral practice with their roommates or classmates every day6.get up at 6:30 Am and read English every dayAssessment:Autonomous Learning through Internet: 10%, Test of each Unit: 10%, Students Performance in class: 10%, Homework and Text Reciting: 10%, Oral Exam: 10%, Final Exam: 50%Course Instructor: Jiang BingshengUNIT 1 Ways of LearningTeaching Objectives: Students are required to1.grasp the main idea (that it would be ideal if we can strike a balance between theChinese and Western learning styles) and structure of the text (introduction of the topic by an anecdote-elaboration by comparison and contrast—conclusion by a suggestion);2.appreciate the difference between comparison and contrast, as well as differentways to compare and contrast (point-by-point method or one-side-at-a-time method);3.master the key language points and grammatical structures in the textTeaching Procedures:Activity 1:1. Teacher asks students some questions.Q1: Is Learning a one-way street? (Parents and children should teach each other and learn from each other. Learning is a two-way interaction.)Q2: Can you guess what the theme of this unit, ways of learning, refers to? (Different people have different learning styles.)Activity 2:Teacher goes through the text with the students, helps them with words, phrases, sentences etc.New words and expressions1. attach: fasten or join (one thing to another)attach sth.to sth; eg. to attach a photo to a letter, be attached to sb./sth.eg. Most guys are attached to her beauty. attach importance to sb. /sth.eg. In English learning, people attach great importance to five basic skills. Namely, they are listening, speaking, reading, writing and translating as well.e.g. Scientists measure wind speed by attaching a wind meter to a kite and sending it up.e.g. You will find a copy of the document which is attached to this letter you asked for.2.not in the least: not at alle.g. I am not in the least touched by the Marilyn Monroe kind of beauty.e.g. Ann didn' t seem in the least concerned about her study.3.find one' s way: reach a destination naturally; arrive ate.g. Shanghai is not an easy city to find your way around.4.phenomenon:(pl.phenomena) sth.that happens or exists and that can be seen or experienced.e.g. Stress-related illness is a common phenomenon in big cities.e.g. Thunder and lightening are natural phenomena.5.initial: of or at the beginning, first(adj., used only before n.)e.g. Their initial burst of enthusiasm died down when they realized how much work the job involved.6. assist: help(used in the pattern: assist sb. To do sth, assist sb. with sth.)e.g. The professor was assisting his students to prepare their project.e.g. The college student decided to assist the boy with his study.7.somewhat: to some degree, a littlee.g. It is reported that conditions in the village have improved somewhat since November.8.await: (fml) wait forAwait is a fairly common word in formal writing, but you do not usually use it in conversation. Instead you use ―wait for.‖9. on occasion: now and thene.g. Steve spent almost all his time doing his research, but, on occasion, he would take his son to see a film.e.g. We must await the results of field studies yet to come.9.relevant: directly connected with the subject (followed by to, opposite irrelevant)e.g. Only a few people feel the debate about the cloning of human beings is relevant to their daily lives.10. on one’s own: a. without anyone‘s helpe.g. You needn‘t g ive me any help, I‘m able to manage on my own.e.g. I‘d rather not go to dance on my own. I do wish you‘d come with me.11. in due course: at the proper time; eventuallye.g. Your book will be published in due course.12. make up for: compensate fore.g. Her husband bought her a present to make up for quarreling with her the day before.13.view…as…:regard…as…14.in retrospect: on evaluating the past; upon reflectione.g. The young man knew in retrospect that he should have married his first love Emily.15. apply:a. be relevant (to sb./sth.); have an effect (used in the pattern apply to sb./sth.)e.g. The new pension arrangements won‘t apply to people born before 1960b. write a letter or fill in a form in order to ask formally for sth. (used in the pattern: apply for sth., apply to do sth.)e.g. We went to the sports club so often that we decided that we might as well apply to join.16.work at/on: try hard to achieve or improve (sth.);从事于/致力于e.g. John came back ahead of time to continue working on his thesis.at work:在工作priority: a. sth.that one must do before anything elsee.g. Being a qualified teacher is her first priority.b. sth. that holds a high place among competing claimse.g. The school will give priority to English and computer studies.17.evolve: (cause to) develop gradually (followed by into/from)e.g. The story evolves into a violent tragedy.Ss make sentences by means of ―evolve‖:通俗歌曲是由民歌演变而来。
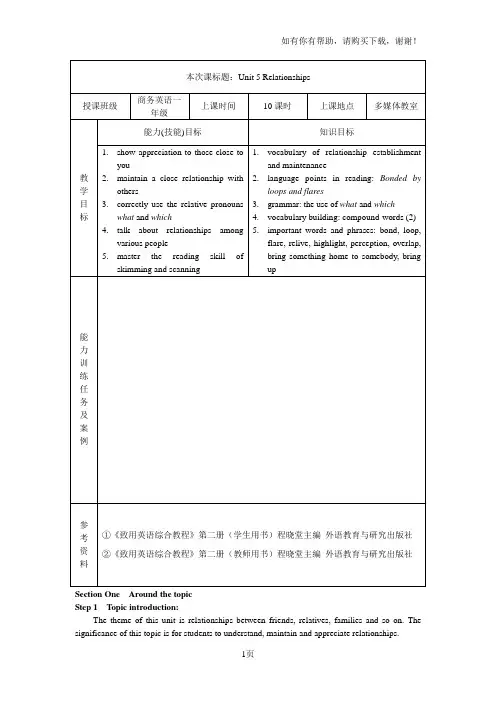
Section One Around the topicStep 1 Topic introduction:The theme of this unit is relationships between friends, relatives, families and so on. The significance of this topic is for students to understand, maintain and appreciate relationships.Step 2 Your ideas1.Listen to the song. Fill the blanks in the lyrics while listening.I believe I can loveYou give me your loving careI believe in what we areI don’t know where I would beWithout you staying with meSometimes, I’m lost in miseryYou will take me all the wayI’m not afraidOh, you and mehand in hand to everywhereAmazing be my friend, oh friendWe are forever friendsOh babyYou give me all the love I needYou are the only onePlay the song twice constantly and then encourage students to tell the answer by themselves. Step 3 vocabularyA.Work in pairs and think of as many English words as possible that havemeanings similar to friendly and unfriendly. Compare your list with anotherpairThis is a pair-work task. Ask students to brainstorm as many related words as possible.Then ask them to exchange opinions with other pairs. You may let them read out thewords they have got in front of the class.B.The underlined adjectives in the sentences below are all about friendliness.Read them and work out the meanings.Ask students to read these sentences carefully and discuss their meanings in pairs. Havethem explain the meanings in English.Answers:Friendly: acting or ready to act as a friendSociable: fond of making friends with people and enjoying being with othersAmiable: having a pleasant and friendly nature; good temperedIntimate: close in relationshipClose: near in relationship, friendshipWarm: friendly in a pleasant wayStep 4 discussionPut the class into small groups. Each group selects one student to note down the opinions of each speaker. After the discussion, you may collect their ideas by having some students give a report. This can be really interesting when show diverse opinions.1). In your opinion, what is a friend? What does friendship mean to you? What do youthink are the most important factors that can keep a long-lasting close relationship with your friends?2). What about with your family members and relatives?3). How can we make our close relationships last long?Step 5 listening and speakingA: Do you have family members, relatives or friends who live in a faraway place? What do you do to keep in touch with them? Do you do the following?●phone them●write letters to them●send them recorded cassettes●send them postcards●have flowers or other gifts delivered to them●e-mail them●send them text messages●visit them during holidays●chat with them onlineB: listening: John lives in Manchester. His sister, Mary, is studying French in Paris. She’s been there for five weeks. He wants to visit her in Paris and he wrote to her about it through an e-mail. He’s just received a message on the answer phone from her.This activity involves skills of both speaking and listening. Use the questions in task A to start a talk among students. The items listed in the text can give students some topics for continuing their talk.After the activity in task A, move on to the listening section. At the same time, ask students to pay attention to decide whether they are true or false. Have a class feedback when they finish. Section 2 Reading: Bonded by loops and flaresThe text Bonded by loops and flares is taken from the newspaper International Herald Tribune, written by David Brooks. Students may find the ideas expressed in this article quite new. Ask students to read the text carefully and have them do exercises individually. When they finish, ask them to exchange and discuss the answers with their partners.Step 1 Pre-reading questionsRead these questions and then put students into small groups for a brief discussion. Give them a few minutes to prepare. Ask one or two groups to tell the whole class their conclusions and reasons when they finish.Do you think people’s perception and thinking are greatly influenced by others? If so, by whom are people most probably influenced? Discuss these questions in groups.Step 2 Text illumination1) Ask several students to read the whole text in order to check whether they preview the textand get a general understanding about it or not beforehand.2) Ask students to summarize the text3) The teacher can put the comprehension check either before or after illuminating the textaccording to the needs of class and the students’ comprehension ability.4) Illuminate the text, during the process of which the teacher can encourage students tohighlight or underline the important parts when they read the text in detail. Try to explain that it can help students to grasp the important details and review important points Language points:1. loop n. a shape like a curve or circle made by a line curving back towards itself 环形,圈状。

《全新版大学英语》第二册之《综合教程》教案Unit One Ways of LearningPart I Pre-reading1.Listen to the song and discuss two questions: (10 minutes)2.Who should teach whom? Is learning a one-way street?3.In your opinion, what is the best teaching method?Part II Text: Learning, Chinese-style1.Main idea of the text:It would be ideal if we can strike a balance between the Chinese and the Western learning styles.2.Structure of the text:Para.1-5------introduction of the topic by an anecdotePara.6-13------elaboration by comparison and contrastPara14---------conclusion by a suggestion3. Discourse comprehension of Part I:a. Ss skim Paras 1-5 and be ready to answer the following questions:-----Where and when did the incident take place?(Jinling Hotel in Nanjing, spring 1987)-----Who are the main characters in this incident?(author, his wife Ellen, their son Benjamin, hotel staff)-----What is the attitude of the author and his wife toward Benjamin' s efforts ininserting the key into the slot?(They let him explore and enjoy himself.)------What is the attitude of the hotel staff toward Benjamin' s efforts?(They held his hand and taught him how to insert the key correctly.)。

新世纪⼤学英语综合教育教案第⼆册Unit3规范标准答案Listen and RespondTask One Focusing on the Main IdeasChoose the best answer to complete each of the following sentences according to the information contained in the listening passage.1 One day in school Monty Roberts was asked to ________.A) write a term paper about the courses he learnedB) write about his dream of the futureC) describe a horse ranchD) draw a picture of a horse ranch2 Monty Roberts’goal was to become ________.A) a horse trainer like his fatherB) a painter who draws horses and horse ranchesC) an owner of a large horse ranchD) an owner of a large farm3 When Monty Roberts turned in the paper, his teacher ________.A) was not satisfied with itB) helped to improve itC) gave a good comment about itD) asked him to discuss the topic with his father4 The teacher asked the boy to rewrite the paper because ________.A) his father had helped him write the paperB) his paper was full of empty wordsC) his dream was not properly described in the paperD) his goal of life described in the paper was not realistic5 A week later, the boy finally decided ________.A) to follow his father’s professionB) to keep his dreamC) to make some changes in his paperD) to follow his teacher’s adviceTask Two Zooming In on the DetailsListen to the recording carefully and fill in each of the blanks according to what you have heard.1 Monty Roberts was the son of a horse trainer . His dream was to own a large horse ranch. That night he wrote about his dream in great detail and he even drew a picture of a 200-acre ranch .2 He put a great deal of his heart into the dream ranch and the next day he handed the paper in to his teacher .3 When Monty Roberts asked his teacher why he got a large red F for his paper, his teacher explained to him that his dream was impossible for him. He had no money. But he needed a lot of money to buy the land, the house and the machines for his dream ranch.4 When Monty Roberts asked his father for advice, his father just asked him to make up his own mind on his dream because it is a very important decision for him to make.5 When Monty Roberts turned in the same paper, he said to his teacher, “You can keep the F and I’ll keep my dream . I will follow my heart , no matter what happens.”Read and ExploreTask One Discovering the Main Ideas1 Answer the following questions with the information contained in Text A.1) According to Alex Haley, why does many a young man want to be a writer?Because they think that being a writer can bring them wealth and fame.2) Does writing mean glory and wealth in the author’s opinion?No. The author thinks that writing is a lonely, private and poor-paying affair. Only a few can succeed after long periods of neglect and poverty.3) What was the author’s life in Greenwich Village like?His life in Greenwich Village was very poor. He barely made enough to eat.4) Did he ever doubt his ability to write? Why or why not?Yes. Because he didn’t receive a break after writing for a year or so.5) Why did the call from his old acquaintance change his life? Because his doubt of his resolution to write was cleared. He was determined to keep on writing.6) In what way did people like Delaney and Belafonte become role models for the author?From them he learned that one had to make sacrifices and live creatively to keep working hard to realize one’s dreams.7) How many years did the author keep on writing before his great success?He kept on writing for 17 years before his great success.8) What did the two sardine cans and 18 cents in the brown paper bag symbolize?They symbolized his courage and persistence to stick to his dream of writing.9) What is the meaning of the Shadowland of dreams?The Shadowland of dreams means all the difficulties (e.g. neglect, poverty, doubt, uncertainty, and fear of failure) people meet with in pursuing their dreams.2 Text A can be divided into three parts with the paragraph number(s) of each part provided as follows. Write down the main idea of each part.Part: One; Paragraph(s): 1-2; Main Idea: Alex Haley explains the difference between “being a writer”and “writing”.Part: Two; Paragraph(s): 3–18; Main Idea: The author tells about his struggle to stick to his dream of writing and his final success.Part: Three; Paragraph(s): 19-22; Main Idea: The author tells about his struggle to stick to his dream of writing and his final success.Task Two Reading Between the LinesRead the following sentences carefully and discuss in pairs what the author intends to say by the italicized parts.1) For every writer kissed by fortune, there are thousands more whose longing is never rewarded. (Para. 2)Compared with those lucky writers who have become famous, thousands of people who devote themselves to writing are never given recognition as successful writers.2) Next time I make a sale. (Para. 6)Considering the rather difficult circumstances the author was in, it is easy to see that there was a degree of irony and self-sarcasm when he promised his friend that he would pay back the money next time he made a sale, for it was something that had not happened before and would not be very likely to happen in the near future, thus pushing the repayment of the debt into the remote future.3) What’s more, I could write on the side. (Para. 8)More importantly, I could take writing as a part-time job.4) There’s everything you’ve made of yourself so far. (Para. 10)The two cans of sardines and 18 cents are all you have.5) Another Village neighbor was a handsome young singer who ran a struggling restaurant. (Para. 13)…a restaurant that has few customers and is about to close down.6) As I absorbed the lesson, I gradually began to sell my articles. (Para.15)As I became aware of what it meant to live in the Shadowland, …7) For the first time I had money and open doors everywhere. (Para. 18)…I had a lot of opportunities.Checking Your VocabularyWord Detective1 Choose the definition in Column B that best matches each italicized word in Column A.1)d2)g3) f4) e5) b6) h7) a8)c2 Spell out the words from Text B with the help of the given definitions, the initial letters and paragraph numbers. Example: e stablish : set up; begin; create (Para. 1)1) w orthy : deserving respect or serious consideration (Para. 1)2) c reep : move slowly, quietly, and carefully, esp. so as not to attract attention (Para. 1)3) r esolve : make a determined decision; decide firmly (Para. 2)4) r efresh : make less hot or tired; bring back strength and freshness to (Para. 5)5) o ccurrence : an event or happening (Para. 6)6) s urplus : an amount additional to what is needed or used (Para. 6)7) f avourable : winning favour and approval (Para. 7)8) r emark : say esp. sth. that one has just noticed; give as an opinion (Para. 9)3 Some phrases or expressions from Text B are hidden in the following picture. Find the phrases or expressions and then use them to complete the sentences with the help of the clues.1) He sweeps the floor for the hotel to work out (以⼯作抵偿) the cost of board. (Para. 1)2) She was unused to (不习惯) talking about herself. (Para. 4)3) After waiting for a long time,the little boy is out of patience(不耐烦). (Para. 4)4) The bad weather has added to (增加) the difficulties in our work. (Para. 4)5) The homeless people in the city have to walk the streets (⾛街串巷), begging for food and money. (Para. 5)6) We were terrified when we came on / upon (发现) a snake behind the little cottage on the edge of the wood. (Para. 5)7) Eva was cutting the grass, and in the meantime (与此同时) Adam was planting roses. (Para. 7)8) From this book written by a movie star we get / have got the idea (领悟到) that those people in the limelight are just ordinary people —even famous faces have flaws! (Para. 7)Checking Your Comprehension1 Answer the following questions with the information contained in Text B.1) How did the author get to know about the school for coloured people in Virginia?He overheard two miners talking about it while working in the coal-mine.2) Why did the author resolve to go to the school?Because he heard that the school was established for coloured people and opportunities were provided to poor but worthy students to work out all or a part of the cost of board and learn some trade or industry at the same time.3) What kind of situation was he in when he reached the city of Richmond late one night?He was tired, hungry and dirty. And he was completely out of money. He had not a single acquaintance in the city, and, being unused to city ways, he didn’t know where to go.4) How did he spend his first night in Richmond?He walked the streets till he became too exhausted to walk any longer. Then he found an elevated sidewalk and lay under it for the night upon the ground.5) How did he earn some money for his breakfast the next morning?He helped unloading a cargo of pig iron from a large ship.6) Why didn’t the head teacher admit the author to the institution at first?Because of being so long without proper food, a bath and change of cloth, he didn’t make a very favourable impression upon her.7) How did the author get a chance to prove his worthiness to the head teacher?The head teacher asked him to sweep the adjoining classroom and he did an excellent job,which proved his worthiness as a student in the institute.2 Read the following statements and then decide whether each of them is true or false based on the information in the text. Write T for True and F for False in the space provided before each statement. 1) F At Hampton Normal and Agricultural Institute poor but worthystudents had opportunities to pay just a part of the cost of board. (Poor but worthy students were provided opportunities to earn money to pay all or a part of the cost of food in the school and at the same time learn some trade or industry.)2) T On the first day of his journey, he realized that he didn’t haveenough money to go to Hampton.3) F He reached the city of Richmond by walking and begging for anumber of days.(He reached the city of Richmond by walking and begging rides for a number of days.)4) T Though he was tired and hungry, he still believed that he wouldreach Hampton.5) F By helping unload a big ship, he earned enough money to buy achicken leg and an apple pie for his breakfast.(By helping unload a big ship, he earned enough money for his breakfast.)6) F He felt that a new kind of existence had begun because he arrived atthe school with a surplus of 50 cents.(He felt that a new kind of existence had begun because he could begin his education in the school.)7) T He worked hard to clean the classroom because his future dependedupon the impression he made upon the head teacher.8) F The head teacher admitted the author on condition that he shouldclean the classroom thoroughly after class.(The head teacher admitted the author because he proved his worthiness by cleaning the classroom thoroughly.) Enhance Your Language AwarenessWords in ActionWorking with Words and Expressions1 In the box below are some of the words you have learned in this unit. Complete the following sentences with them. Change the form where necessary.1) A smart appearance tends to make a(n) favourable impression at an interview.2) The scientist failed in his experiments many a time, but he was never discouraged ; instead, he stuck it out and finally made a great scientific discovery.3) When I asked my mother if I could marry George, she consented but rather unwillingly.4) The garden has fallen into a state of neglect since its owner died two years ago.5) Coming home late, the boy crept quietly into the house to avoid waking his parents.6) If you want to learn a language well, sufficient time is necessary.7) The origin of Chinese writing can be traced back to ancient China although we are not certain of the date of its invention.8) The price was somewhat higher than I had expected. However, it was still acceptable.9) When you feel tired, a rest and a cool drink will refresh you.10) As I sit here today, I couldn’t be more grateful for the opportunity, not only to be alive, but also to apply my life to such a(n) worthy effort.11) More and more people in big companies are enrolling in English courses to improve their promotion(晋升) prospects .12) I made full preparations for my journey to London on foot and I resolved to get there in five days.13) At the end of the interview, she remarked , “You’ve proved your worthiness more than well enough.”14) I hope that I shall never again have to undergo such a terrible experience.15) Susan started singing to her baby and was rewarded with a smile.2 In the boxes below are some of the expressions you have learned in this unit. Do you understand their meanings? Do you know how to use them in the proper context? Now check for yourself by doing the blank-filling exercise. Change the form where necessary.1) Since the summer vacation has started, let’s pack up and spend a week in the country with my grandparents.2) The boy is so interested in the popular novel entitled Harry Porter and the Deathly Hallows(圣徒) that he has read it for many a time.3) I admire Steve very much, for in his pursuit of a successful life, he always stays the course and never gives up in spite of the many difficulties and risks he has encountered.4) The couple’s love was put to the test when the husband was crippled in a car accident.5) I mailed out 250 letters to complete strangers for help and within 6 weeks the stream of money came flooding in from all over the country.6) When searching for some news online(在线的) last night, I came across an interesting website(⽹址) devoted to computer games.7) He is so clever that he can always come up with solutions at the last moment.8) At the sight of the big fish, the fisherman plunged his hands into the water and caught it with graceful ease.Increasing Your Word Power1 Listed in the box below are some unit nouns. Discuss their meanings and then complete the following table by filling in the appropriate unit noun. The same unit noun may be used for more than once. Consult a dictionary if necessary.a(n) slice of bread a(n) particle of rocka(n) bunch of keys a(n) bar of soapa(n) can of orange juice a(n) sheet of glassa(n) item of business a(n) article of furniturea(n) slice of meat a(n) particle of dusta(n) can of beer a(n) bar of chocolatea(n) article of luggage a(n) bunch of flowersa(n) sheet of paper a(n) item of expense2 Words such as respectful, respectable and respective may cause confusion because they are similar either in meaning or in spelling. To communicate effectively, we need to pay special attention to such confusable words. In each of the following sentences you are given two or three words in brackets. Choose the appropriate one to fill in the blank. You may consult a dictionary if necessary.1) Now your father has retired, you should go and see him now and then. This should not be neglected (neglectful, neglected).2) Some boy students are neglectful (neglectful, neglected) of their appearance in school.3) In this book the writer describes his colourful (coloured, colourful) experiences in Africa.4) To celebrate the Spring Festival, they tie many coloured (coloured, colourful) lamps on the trees.5) The coat is made of a kind of cloth that is rough (rough, tough) to touch.6) The meat was tough (rough, tough) and hard and I did not like it at all.7) The article is all nonsense. It’s not worth (worth, worthy) the paper it’s printed on.8) These young men will prove worthy (worth, worthy) of our trust.9) The situation will develop in a direction favourable (favourite, favourable) to China.10) I like oranges very much; they are my favourite (favourite, favourable) fruit.11) The boys here are well mannered and respectful (respective, respectable, respectful) toward grown-ups.12) My uncle is a respectable (respective, respectable, respectful) doctor in our town.。

2014-2015学年第二学期大学英语教案授课教师:崔俊学授课班级:2014级数学教育1、2班教研室:大学英语教研室Unit 1 Invitation EtiquetteTopic: Good MannersObjectives: S tudents should be able to:1. Talk about good manners;2. Understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage;3. Know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text;4. Grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patterns for expressing ideas on related topics;5. Learn how to write a note of thanks;6. get some tips about English modal verbs.Important/Difficult Point(s):1.Grammar2.Raise the awareness of good manners.Materials and Resources:1.Multimedia2.PPTs3.Colorful chalks4.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm upWarm-up Discussion:Ask students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic: “D o you think good manners are important in our life? Why?”Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Tryto scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: Word study1. Read new words2. Memories them all.Step 2: Word analysisPlan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded atthe end of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2.The next class will be structured through passage analysis and languagestudy.Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number ofstudents will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students watch a short video about the mannersStep 2: Passage Aprehensive study of passage Aa.main ideab.structure analysisnguage studyPeriod 4Step 1:Finish all the after-reading exerciseStep 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and discuss on the topic “What is the Golden Rule in dealing with others?” Group leaders present the result. Step 2: Fast-reading of Passage BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 3: Word StudyPeriod 6:Step 1: Passage Analysis1. Comprehensive study of passage B1)main idea2) structure analysis2. Language studyStep 2: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar studyStep 3: Finish exercise of Modal VerbsPeriod 8:Step 1: ExerciseStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a note of thanksThe teacher will explain what a note of thanks is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the example a note of thanks.Students are required to write a note of thanks in a group.Plan for follow-up class1.Our next class will begin with Unit2. The students will be reminded at the end ofthis class to prepare the readings for next week.2.The next class will be structured through small group work and whole classdiscussions.Unit 2 E-mailTopic: Living EnvironmentObjectives: S tudents should be able to:1. Talk about Living Environment;2. Understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage;3. Know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text;4. Grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patterns for expressing ideas on related topics;5. Learn how to write a note of apology;6. Get some tips about adverbial clauses of time in English.Important/Difficult Point(s):1.Grammar2.Raise the awareness of environmental protection.Materials and Resources:1.Multimedia2.PPTs3.Colorful chalks4.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm upWarm-up Discussion:Ask students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic: “What suggestions do you have for environmental protection?” Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Tryto scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: Word study1. Read new words2. Memories them all.Step 2: Word analysisPlan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded at theend of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2.The next class will be structured through passage analysis and language study. Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number ofstudents will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students watch a short video about the environmental protection.Step 2: Passage A1. Comprehensive study of passage Aa.main ideab.structure analysis2. Language studyPeriod 4Step 1:Finish all the after-reading exerciseStep 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and discuss on the topic “What does noise mean to ordinary people like you?” Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Fast-reading of Passage BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 3: Word StudyPeriod 6:Step 1: Passage Analysis1. Comprehensive study of passage Ba)main idea2) structure analysis2. Language studyStep 2: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar studyStep 3: Finish exercise of A dverbial Clauses of time.Period 8:Step 1: ExerciseStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a note of apologyThe teacher will explain what a note of thanks is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the example a note of apology.Students are required to write a note of apology in a group.Plan for follow-up class1.Our next class will begin with Unit 3. The students will be reminded at the end ofthis class to prepare the readings for next week.2. The next class will be structured through small group work and whole class discussions.Unit 3 Communication by phoneTopic: Fast foodObjectives: S tudents should be able to:1. Talk about fast food2. Understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage;3. Know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text;4. Grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patterns for expressing ideas on related topics;5. Learn how to write a note of congratulations6. get some tips about the adverbial clause of purpose in EnglishImportant/Difficult Point(s):nguage points2.GrammarMaterials and Resources:1.PPTs2.Colorful chalks3.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm upWarm-up Discussion:Ask students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic: “Do you like the food at McDonald’s or KFC? What attracts you most there?” Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Try to scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out thecorresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: Word study1. Read new words2. Memories them all.Step 2: Word analysisPlan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded atthe end of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2. The next class will be structured through passage analysis and language study.Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number ofstudents will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students watch a short video about the fast food.Step 2: Passage Aprehensive study of passage Aa.main ideab.structure analysisnguage studyPeriod 4Step 1:Finish all the after-reading exerciseStep 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and discuss on the topic “What is your healthy diet?” Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Fast-reading of Passage BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 3: Word StudyPeriod 6:Step 1: Passage Analysis1. Comprehensive study of passage Ba)main idea2) structure analysis2. Language studyStep 2: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar studyStep 3: Finish exercise of Adverbial ClausePeriod 8:Step 1: ExerciseStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a note of congratulationsThe teacher will explain what a note of congratulations is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the example a note of congratulations.Students are required to write a note of thanks in a group.Plan for follow-up class1.Our next class will begin with Unit 4. The students will be reminded at the end ofthis class to prepare the readings for next week.2.The next class will be structured through small group work and whole classdiscussions.Unit 4 Hotel ServicesTopic: Daily shoppingObjectives: S tudents should be able to:1. Talk about shopping;2. Understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage;3. Know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text;4. Grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patterns for expressing ideas on related topics;5. Learn how to write a note of announcement6. get some tips about the gerund in English grammarImportant/Difficult Point(s):nguage points2.GrammarMaterials and Resources:1.PPTs2.Colorful chalks3.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm upWarm-up Discussion:Ask students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic: “Do you like shopping? Why or why not?” Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Try to scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage.Step 1: Word study1. Read new words2. Memories them all.Step 2: Word analysisPlan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded at theend of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2.The next class will be structured through passage analysis and language study. Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number ofstudents will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students watch a short video about the shopping.Step 2: Passage Aprehensive study of passage Aa)main ideab)structure analysisnguage studyPeriod 4Step 1:Finish all the after-reading exerciseStep 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and discuss on the topic “Why is it convenient to do shopping on line?” Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Fast-reading of Passage BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 3: Word StudyPeriod 6:Step 1: Passage Analysis1. Comprehensive study of passage Ba)main idea2) structure analysis2. Language studyStep 2: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar studyStep 3: Finish exercise of gerundPeriod 8:Step 1: ExerciseStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a note of AnnouncementThe teacher will explain what a note of announcement is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the example a note of announcement.Students are required to write a note of thanks in a group.Plan for follow-up class1.Our next class will begin with Unit 5. The students will be reminded at the end ofthis class to prepare the readings for next week.2.The next class will be structured through small group work and whole classdiscussions.Unit 5 Food BlogsTopic: Modern CommunicationObjectives:1. Students will be able to enlarge the vocabulary relating to modern communication.2. Students will be able to understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage.3. Students will be able to know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text.4. Students will come to know the importance of managing incoming email.5. Students will be able to learn how to write a public notice.6. Students will be able to get some tips about the use of the infinitive in English. Important/Difficult Point(s):1.Grammar2. Experiences with cell phones and emails.Materials and Resources:1.Multimedia2.PPTs3.Colorful chalks4.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm up1. Warm-up DiscussionQuestions: What is your favorite way of daily communication?Do you use the Internet?.2. Group DiscussionAsk students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic of Internet: How has the Internet influenced your life? Is the influence good or bad? Why?Appoint a team leader for each group.Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Try to scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: New word studyStep 2: (Homework)1. Read new words2. Memorize them all.Plan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded atthe end of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2.The next class will be structured through passage analysis and languagestudy.Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number ofstudents will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students will go to spot dictation to practice their listening.Step 2: Text Aa.Guide the students to get the main idea.b.structure analysisPeriod 4Step 1:Language studyStep 2: Finish all the after-reading exercisePeriod 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and talk about making telephone calls based on the following questions:What advantages does making phone cells have?Do you prefer making phone cells to sending short messages to your parents while you are in college? Why or why not?Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 6:Step 1: Fast-reading of Text BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 2: Brief Text Analysis1. The main idea of the text2. Questions relating to the major points of the textWhat problem is troubling email users and corporations around the world?What is the importance of managing emails?Who should be responsible for managing emails?Step 3: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar Study: the infinitive in EnglishGuide students to learn the grammar points of this unit.Step 3: Exercises of the infinitive in EnglishPeriod 8:Step 1: ExercisesStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a public noticeThe teacher will explain what a public notice is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the samples.Students are required to write two notices according to the assignments in the textbook.Plan for follow-up class1.Our next class will begin with Unit 6. The students will be reminded at the end ofthis class to prepare the readings for next week.2. The next class will be structured through small group work and whole class discussions.Unit 6 Shopping and SightseeingTopic: Health CareObjectives:1.Students will know the background information related to the text.2.Students will be able to understand the content, the organization of the text andwriting devices of the text.3.Students will be able to grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patternsfor expressing ideas on related topics.4.Students will enlarge their vocabulary of diseases.5.Students will learn about the past participle in English.6.Students will learn how to write a name card.Important/Difficult Point(s):Key words and expressionsGrammarMaterials and Resources:1.PPTs2.Multimedia3.Colorful pens and markers4.Chalk, chalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm up:1. Ask students questions about healthDo you often get sick? What should we do if we want to stay healthy?2. Group DiscussionAsk students to form groups of four and discuss on the topic of health: What can we do in order to have a healthy, happy and long life?Appoint a team leader for each group.Group leaders will be asked to present group opinions.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Try to scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: New word studyStep 2: (Homework)1. Read new words2. Memorize them all.Plan for Follow Up Lesson:1. Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded at the end of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2. The next class will be structured through passage analysis and language study. Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students will go to spot dictation to practice their listening.Step 2: Text A1. Guide the students to get the main idea.2. Structure analysisPeriod 4Step 1:Language studyStep 2: Finish all the after-reading exercisePeriod 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and talk about experiences with doctors based on the following questions:1. What was your most unforgettable experience with doctors?2. What kind of doctor do you like best? Why?Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Active Words1. Teacher explains the usage and examples2. Students make sentences and try to memories the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1. Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2. Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 6:Step 1: Fast-reading of Text BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 2: Brief Text Analysis1. The main idea of the text2. Questions relating to the major points of the textWhat are the secrets of a good night’s sleep?How many phases are there in the course of sleep?Step 3: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2. Students do listening practice.Step 2: Grammar Study: the past participle in EnglishGuide students to learn the grammar points of this unit.Step 3: Finish exercises of the past participle in EnglishPeriod 8:Step 1: Comprehensive ExercisesStudents are required to do comprehensive exercises in class within a certain timeframe. The teacher will check the answer.Step 2: Writing Practice --- How to write a name cardThe teacher will explain what a name card is and how to write it. Students will be shown with the samples.Students are required to design a name card for themselves according to the assignment in the textbook.Plan for follow-up class1. Our next class will begin with Unit 7. The students will be reminded at the end of this class to prepare the readings for next week.2. The next class will be structured through small group work and whole class discussions.Unit 7 FarewellTopic: Generation gapObjectives: S tudents should be able to:1. Talk about generation gap2. Understand the content, the organization of the text and the writing devices of the passage;3. Know and make use of the language points, especially expressions, learned from the text;4. Grasp some key words, expressions and sentence patterns for expressing ideas on related topics;5. Learn how to write invitation cards or letters6. get some tips about the relative clause in EnglishImportant/Difficult Point(s):1.active verbs: start, concern, throw, care, count2.mean, major, concerned, dorm, save, sake, wear, exaggerate, collect, can, charge, priority, ruin, vacation,3.the relative clause in EnglishMaterials and Resources:1.PPTs2.Colorful chalks3.ChalkboardProcedure:Period 1Step 1: Warm upWarm-up Discussion:Ask students to form groups of four and discuss on the topics: 1) differences between my parents and 2) suggestions for bridging the generation gapDivide the students into groups of three or four. Appoint a team leader for each group. Invite some students to talk about the topics. Each speaker has two minutes for thepresentation.Step 2: Reading StrategyAsk students to read through the whole passage without referring to the word list. Try to scan through to find out the main idea. And skim the passage to find out the corresponding part of the passage to the comprehension exercise after the passage. Period 2Step 1: Word studyStep 2: Word analysisPlan for Follow Up Lesson:1.Our next class will begin with the passage. The students will be reminded at the end of this class to prepare the readings for next class.2.The next class will be structured through passage analysis and language study. Period 3Step 1: Warm-up1.Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of students will be called to read some words out for the teacher to check pronunciation.2.Students watch a short video about the generation gap.Step 2: Passage Aprehensive study of passage Ac.main idead.structure analysisnguage studyi.You don’t really feel the generation gap until a son or daughter comeshome form college fro Christmas.ii.What difference does it make?iii.Why don’t you do it for our sake?iv.But it’s very hard for us to realize you’re an adult when you throw all your clothes on the floor.Period 4Step 1:Finish all the after-reading exerciseStep 2: Active Words1.Teacher explains the usage and examples2.Students make sentences and try to memorize the usagesStep 3: HomeworkFinish Vocabulary Check after the Active Words.Plan for follow-up lesson1.Students should prepare for the study of Text B.2.Students should prepare for group discussion and writing.Period 5Step 1: Warm-upGroup Study: Students are asked to form groups of four and discuss on the topics “What do you do when you and your parents have different ideas about the same thing?” And “what suggestions do you have for bridging the generation gap?”Group leaders present the result.Step 2: Fast-reading of Passage BStudents are required to take advantage of fast reading strategies to do comprehension work.Step 3: Word StudyPeriod 6:Step 1: Passage Analysis1. Comprehensive study of passage B1)main idea2) structure analysis2. Language studyStep 2: (Homework)Ask students to finish after-reading activities.Period 7Step 1: Warm-up1. Students are asked to take out a piece of paper and recite new words. A number of。
College English Integrated Course 2Teaching Designs逯静Unit OneSection A W ays of Learning(一)Content of the Course(教学内容)Section A. Learning, Chinese-Style (精讲)(二)Audience(教学对象)(三)Teaching Span(教学时间)6---7学时(四)Teaching Aims(教学目的)1. Appreciate the text to know something about different ways of learning.2. Learn to use some important words, expressions and sentence patterns.3. Practice listening, speaking, reading and writing.4. Learn some translation skills(五)Instruction Objectives &. Teaching Procedures(教学任务及步骤)Step One Pre-reading Activities(导入)Themes(文章主题)10 minutes1. 课文A向我们讲述了一次偶然的经历让作者发现了中美在教育和艺术实践上的差异,并呼吁能否将这两种教育方式有机地结合产生一种既不失创造性又有利于培养娴熟技艺的教育方法。
2. 课文B讨论的是如何教育孩子珍惜钱财的问题,应该给孩子更多的自主权和适当的刺激,让他们学会理性地支配属于自己的钱财。
Step Two While-reading Activities1. Language Points(语言知识) 140 minutes(1) Key words &. Expressions (重点单词及短语)Style attach slot tender phenomenon insert occasionneglect relevant anecdote in due course self-reliance validsuperior foster(2) Key Grammar and Structures (重点语法及结构)a. confusable wordsb. usage: subject or object emphasizers ( oneself, by oneself, on one’sown)2. Sentence Interpretation (难句精析) 50 minutes(1) Benjamin was not bothered in the least.(2) He may well get frustrated and angry- certainly not adesirable outcome.(3) “Teaching by holding his hand”- so much so that he would happilycome back for more.Step Three Post-reading Activities100 minutes1.Reading Skill (阅读技能)2.Reading between the lines (找出段落中隐含之意)3.Language Practice (语言技能训练)Exercises after Text A Page 9—29 (课本后练习)4.Writing Practice (写作技能训练)5.Discussion (探讨设计)Topic: a. Who should teacher whom? Is learning a one-way street ?b. What can you learn from the story about? Try to say as much aspossible about different ways of learning?(六)Assignments(作业)1. Page 20. Translation ( Homework)2. Review and Preview.3. Read Aloud (New words and text)Unit TwoSection A V alues(一)Content of the CourseSection A. The Richest Man in America, Down Home(精讲)Section B. The Restoration of Jimmy Carter(略讲)(二)Audience(三)Teaching Span6---7 periods(四)Teaching Aims1. Appreciate the text to know something about value point of view.2. Learn to use some important words, expressions and sentence patterns.3. Practice listening, speaking, reading and writing.4. Learn some translation skills(五)Instruction Objectives &. Teaching ProceduresStep One Pre-reading Activitie sThemes 10 minutes1. 课文A向我们讲述了美国最富者沃尔顿先生过着非常简朴的生活,但他总是全心全意地投入到沃尔玛公司的事务中去,这一切造就了个人和公司的巨大成功。
Unit 5 Fourteen StepsSection One Pre-reading Activities ..............................................................错误!未定义书签。
I. Audiovisual supplement ............................... 错误!未定义书签。
II. Cultural information ................................ 错误!未定义书签。
Section Two Global Reading .................................. 错误!未定义书签。
I. Main idea ............................................ 错误!未定义书签。
II. Structural analysis ................................. 错误!未定义书签。
Section Three Detailed Reading .............................. 错误!未定义书签。
Text I .................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
Section Four Consolidation Activities ........................ 错误!未定义书签。
I . Vocabulary Analysis ................................. 错误!未定义书签。
II Grammar Exercises .................................... 错误!未定义书签。
III. Translation exercises .............................. 错误!未定义书签。
Unit 1 The Snake BiteI .Teaching Objectives1.Functions : Expressing distress & annoyance2.Grammar points : Indirect command with infinitives such as He wantedto see you / Tell him to wait .3.Vocabulary : all at once , figure , seem , forbid , show up , strike ,make for , pick out , light out for , must have done ,every now and then , at length , hold on toII . Focal Points1. Functions : Expressing distress & annoyance2. Grammar points : Indirect command with infinitives such as He wantedto see you / Tell him to wait .3.ConversationIII . Teaching Process1. Listening and Speaking Activities1)Introduction to the formulas of expressing distress & annoyance2)Listen to the conversation twice3)Correct the answers4)Pair workPracticing : Read ConversationExplanationSpeak before the classMake up another dialogue using the cues in the box5)Make your own dialogueTeam & group workPresentation6)Matching exercises :What are they for ?If you want to learn more2.Reading Comprehension1)Warm-up questions2)Listening to the text twice3)Doing the comprehension work :Reading the textDiscussion :Read the text carefully to find the answers to the questions and look to the evidence from the text to support the answers Retelling the text using the key words4)Extended ActivityExercisesStep 1 Listening and Speaking Activities1.Formulas for expressing distress & annoyanceIt sickened me to see how chickens were raised in the mechanical production . They were bald . They were forced to live in a small cage and had to climb over each other in order to get around .It really shocked me to know how chickens were raised in mechanical production .I just can’t remember that girl’s name , it’s really bugging me .Why on earth didn’t you tell me the truth ?You kept me waiting for over an hour . What have you been busy with ?I can’t say I’m at all pleased about your delay .I wish you’d stop pestering me .We’re not going to the beach and that’sfinal .I’m most unhappy at his bragging .Having to stay in and working on a sunny day like this is a real drag .We’d be OK if we could get this stupid gate to open properly .She never stopped complaining while we were on vacation .It really got on my nerves .It really annoys me that she never returns the books she borrows .It galled him bitterly that his father gambled again .Turn that music down -------It’s driving me mad .What really gets under my skin is people who talk while I’m trying to concentrate on my work .My tape-recorder’s broken down again . It’s a nuisance , isn’t it ?2.Listen and speak :Listen to the following conversation twice and try to tick what you have heard as the correct answer to the questions .3.Try to speak more1)Listen to the tape2)Explanation of the conversation :three chickens to one single cage :three chickens living in one cage bald : (of people ) having little or no hair on the scalpdisgraceful : causing disgrace ; very bad3)Read the conversation by themselves and then try to memorizethem .Invite two pairs of students to speak before the class and then exchange their roles .Depending on the cue box on the right , ask them to make up another conversation .Act out the conversation.4)Make your own dialogueExplanation :Without regard for sth : not care for sthPoultry : hens , ducks , geese , turkeys , etc. kept for eating or for their eggsBattery hens : hens mechanically raised for laying eggsPeck : (try to ) strike (sth ) with the beakPluck : gather or remove sth by pullingTeam workPresentation5)What are they for ?Explanation:Bug :If something bugs you , it annoys you because it is always there or is always happening , so that you cannot stop thinking kaboutit or noticing it . Eg. , I wish you’d tell me whatever it is that’sbugging you .Much to my annoyance : You say much to my annoyance when you are talking about something that has annoyed you very much , eg. , Much to myannoyance , the hotel hadn’t received our reservation .Pester : to annoy someone by repeatedly asking questions or making requests , especially when they are trying to pay attention tosomething else , eg. , Everyone pestered me so much that I gaveit up .Pair work : matching the exercises6)If you want to learn moreExplanation :Get on someone’s nerves :If someone gets on your nerves , they annoy you ,especially by continually saying or doing somethingthat you do not like . eg. , Sit down ,James . You’regetting on my nerves pacing up and down like that . Drive someone mad / crazy / nuts / up the wall : to annoy people very much ,so that they feel unable to stand the situation .eg. , Being in the house all day with these twoscreaming kids is driving me nuts . This noise isdriving me mad .Get under someone’s skin : If someone gets under your skin , they dosomething that annoys you a lot but which may notannoy other people . eg. , He really gets under myskin sometimes .Be a drag : If someone or something is a drag , they annoy you especiallybecause they are boring or prevent you from enjoyingyourself . Eg. , Don’t invite John ------- he’s sucha drag .Step 2 Reading Comprehension and LanguageActivities1.Warm-up questions and discussion2.Listen to the text twice3.Read the text and try their best to answer the questions .①the beginning of the story ------- What happened first ?★What did the boy start out to do and where ?(He was going to get a watermelon for his own use from the family’smelon-and –garden patch ehich was back of the barn on the edge ofthe cane field .)★What did the boy take with him ? And why did he take that ?(He took a corn knife with him . It was the best thing to cut amelon . One swipe and the melon was in two .)★What happened to the boy when he was thumping for a ripe melon ?(All at once , he seemed to step on something like a needle .Actually , he was bitten by the rattler in the foot . )★What are rattlers supposed to do before they strike ?(Rattlers are supposed to make some sound as warning before theystrike .)★Why did the boy fail to hear the snake rattle ?(Maybe this snake didn’t have time to rattle .)②asking for help -------- What did his mother do ?★How did the boy’s mother treat his wound ?(The mother tied apron strings around her son’s leg above the knee ,made him lie on the sofa and put Martha to watch him .)★Why did the mother decide not to go to the Howell place ? And howfar away was the Anderson house ?(The Howell would not be of much help because they had no horse .The Anderson place was exactly half a mile away by the short cutthrough a field .)★What did the mother do when she found that Martha had taken offthe strings ?(She got the apron strings back , yanking them tight .)③waiting for help --------- What did her mother do then ?★Who should Herb Anderson look for first ? Who else should he lookfor next ?(Herb Anderson was told to first look for the boy’s father . Ifhe failed to find him , he should look for a doctor .)★Why did the mother go to the porch ? And who showed up at last ?(The mother went to the porch to watch the road from town . At last ,the boy’s father showed up .)4.Practicing asking and answering the questions in pairs .5.Retell the text using the key words .6.Explanation of the new words and phrases .⑴the background of the story :The story , as told by an American boy , is set against the background of the American countryside in the 19th century .The narration , therefore exhibits features of both cultural pictures of the countryside of that period , and the way that a teenager spoke . Words like sandbur , claim jumper , buggy , porch , lot , rig are characteristic of American culture .Besides , the text contains many colloquial phrases to reflect a child’s style of speaking . Phrasal verbs are preferred over single verbs , for instance , light out for depart ; pick out for recognize ;show up for appear ; break into forb egin ab ruptly . The use of child phrases (Mamma , Papa ) and somecausative verbs in make me lie , put Martha to watch , get me to stop yelling also help render the text fitting a child’s tone .⑵ the house melon-and –garden patch : a piece of land for growingvegetables and melons for family use .⑶back of : Although it is now established as standard in American Englishmeaning“behind ” , many considered it as a sloppy colloquial way ofspeaking inthe 19th century English .⑷ on the place ; in the lot : both refer to the boy’s home . Lot : apiece of land having a special use . Eg. , aparking lot ; a used –car lot ; a building lot ⑸ porch : (mainly used in American English ) a raised platform builtalong thewalls of a house and often covered with a roof . After supper ,peopleusually sit on chairs or rockers on the porch for relaxation .Houses withporches can still be seen in many places in America , especiallyin ruralareas .⑹ between the Anderson and the Howell claims : In the 19th century ,many Americans moved to the West where there was vastland for the taking . They staked out some pieces of landas their own property . Formal request for the land wasmade for mining . Claims refers to the pieces of landof this kind .⑺ anxious to get his nose in the manger : A manager is a feeding boxin a stable or barn . Here it means that the horse wasanxious to eat .⑻ rig : referring to the horse and the buggy⑼ all at once : suddenly⑽ figure : think (sth) ; calculateeg. I figured that you wouldn’t come .⑾ seem : appearseem (to sb ) (to be ) + n./ adj .seem to doseem likeIt seems that …It seems as if /as though …There seem(s) to be …⒀ forbid : Order (sb ) not to doOrder sth shall not be doneForbid sth.Forbid sb to doForbid doing⒁ show up : (colloquial ) arrive , often after a delay ; appear eg. It was ten o’clock when she finally showed up .⒂ strike : attack , esp. suddenlyeg. Enemy troops struck just before dawn .⒃ make for sb./sth. : move in the direction of sb./sth.⒄ pick (sb./sth.) out :a.choose fromeg. He picked out the ripest peach .b.distinguish sb./sth. Fromeg. Pick out sb’s face in a crowd⒅ light out for sp. : depart for sp.Assignments1.Do the exercises on the textbook .2.WritingP 43 Exercise 63.Oral practice :The Snake BiteUnit 2 He Was My FatherI .Teaching Objectives1.Functions :Expressing possibility & impossibility2.Grammar points : Use of prepositional phrases on the pattern : bybus , by post , in the car ; Used to as modalindicating past habit or state ; Adverbial of frequencywith past tense : I never used to go by car .3.Vocabulary : fall into , live on , apprehension , tuition , regard/ disregard , decent , recite , on one’s own , stare at ,pick up , grow up , put in , follow in one’s footsteps II . Focal Points1. Functions : Expressing possibility & impossibility4.Grammar points : Use of prepositional phrases on the pattern : bybus , by post , in the car ; Used to as modalindicating past habit or state ; Adverbial of frequencywith past tense : I never used to go by car .5.ConversationIII . Teaching Process1. Listening and Speaking Activities1)Introduction to the formulas of expressing possibility & impossibility2) Listen to the conversation twice3) Correct the answers4) Pair workPracticing : Read ConversationExplanationSpeak before the classMake up another dialogue using the cues in the box5)Make your own dialogueTeam & group workPresentation6)Matching exercises :What are they for ?If you want to learn more3.Reading Comprehension1) Warm-up questions2) Listening to the text twice3) Doing the comprehension work :Reading the textDiscussion :Read the text carefully to find the answers to the questions and look to the evidence from the text to support the answers Retelling the text using the key words4) Extended ActivityExercisesStep 1 Listening and Speaking Activities1.Formulas for expressing possibility & impossibilityIt is possible for you to get into the university if you pass the examination .You may have a point there .It could be a bad start .You might be right to a certain extent .The job can be done by Wednesday if I get extra help .Take your umbrella – you might need it .There’s possibility that she’ll lose her job .It’s still possible to make some money if you invest wisely . Perhaps it was the coffee .Possibly for the first time in their lives .There’s just a chance that she may have left her keys in the office , so I’m going to look .You might be lucky .But it is impossible if you fail .It may not be .It will be impossible for him to see you today .Alice can’t be at home .There’s no way you’re going to get the job without good references . Sending Sandra a letter was out of the question , because her …… , but she knew it was hopeless .2.Listen and speak :Listen to the following conversation twice and try to tick what you have heard as the correct answer to the questions .3.Try to speak more1) Listen to the tape2) Explanation of the conversation :nonsense : foolish talk , ideas , etc .blah : talk that sounds impressive , but actually says very little have a point : be rightheaps of : great number / amount ; plentybe reluctant to :be unwilling and therefore slow to co-operate , agree , etc.put the blame on sb : blame sb for sth.3) Read the conversation by themselves and then try to memorizethem .Invite two pairs of students to speak before the class and then exchange their roles .Depending on the cue box on the right , ask them to make up anotherconversation .Act out the conversation.4) Make your own dialogueTeam workPresentation5) What are they for ?ExplanationPair work : matching the exercises6) If you want to learn moreExplanation:You never know :an informal expression that you use when you think thatsomething may happen , but you are not certain becauseit is difficult to say what will happen in the future .Eg.It might have been better if she’d had kids , thoughyou never know .There’s no way : You say there’s no way to someone when you stronglybelieve that something is impossible . Eg. My legs wereaching and I knew that there was no way I would make itup the hill .Out of the question : If an idea , suggestion , etc. , is out of thequestion , it is completely impossible , especiallybecause it is not allowed . Eg ., That’s out of thequestion : Mary is much too busy to look after thechildren .Step 2 Reading Comprehension and LanguageActivities7.Warm-up questions and discussion8.Listen to the text twice9.Read the text and try their best to answer the questions .①Paragragh 1 and 2 :Before eating his ★ What would the father do before eatingthe dinner and why ?(When the father washed his hands beforedinner , he would talk to his son or tellhim tales of his own childhood in order tolet drops of moral tuition fall into theboy’s lap .)②Paragraph 3 , 4 and 5Father’★What was the father’s job and how many hours wouldhe work each week ?(The father was a London taxi – driver . He had to work12 hours a day , 6 days a week to earn decent wage .)★Was a taxi-driver respected by people and how do youknow ?(No . A taxi –driver is not respected very much by manypassengers . They treat him with patronizing disregardand address him rudely as cabbie , you or driver . ) ③Paragraph 6 :Father’★How do you understand “powerful enough to crywhen he felt the need ?” Explain in your own words . (This is an open-ended question . The teacher shouldencourage the students to discuss the problem ofstrength and power . But generally speaking , a mandoes not believe in tears . And crying is normallyassociated with weakness . So it calls for greatcourage and strength for a man to cry before others .The father is not only powerful and strong , he alsohas deep love for his mother and family . )④Paragraph 7 :★How did the father feel when his son went touniversity ?(When his son went to university , the father felt very happyandexcited , because the boy was the first in the father’s familytoreceive higher education .)★Was the narrator satisfied with his father’s behaviour at hisgraduation ceremony and why ?(Yes . The father seemed to be out of place at the graduationceremony from the boy’s point of view ------- he felt gauche ,took the matter too seriously by taking many pictures , anddidn’t understand the Latin before the ceremonial meal . Butthis was not important . He knew that his father wasoverjoyed because his son would have a better life .)⑤Paragraph 8 :★Why didn’t the father go on holiday ? And how did he liveand work when the family was away ?(The father could not afford to go on holiday with the family .There was just not enough money . When the family was away ,he would stay on his own , work even longer hours , and liveon sandwiches and tea .)⑥Paragraph 9 :★ What was the message from his father’s eyes when thenarrator had his first child ?(He seemed to say with his eyes : Son , let him say just onething when he grows up : “he was my father .”) Conclusion :★Why does the narrator repeat “he was my father ” so many times ? (This is again an open-minded question . Encourage the students to talk about their understanding . The father was seen as a great man in the boy’s eyes . He kept promises , he worked hard , he was powerful and he showed tender love for the family . Besides , his father was an understanding father , selfless and self-sacrificing , a man of conviction , believing in the power of love and hoping the love could be passed from generation to generation as a family tradition . The repeated use of “He was my father ”showed how much the boy loved his father and how proud he was of his father .) ★In what way was the father an extraordinary ordinary father ?(The father was ordinary as a worker , labourer , and taxi-driver . But he is extraordinary as a father , as a model for the younger generation . He was a man of integrity with power and profound love .)10.Practicing asking and answering the questions in pairs .11.Retell the text using the key words .12.Explanation of the new words and phrases .①Let drops of moral tuition fall into my lap :teach me moral standardslittle by little②Decent wage : a wage which is considered satisfactory③… with such patronizing disregard :patronizing is often used todescribe a person’s manner or tone which seemsfriendly , but which shows that they think theyare superior to you in some way .④…didn’t understand the Latin that was spoken before the ceremonialmeal : Latin is the Italic language spoken nearancient Roman , and was the official language ofthe Roman Empire . Until the middle ages , it wasthe dominant language of school , church , andstate in West Europe . Now , Latin is still usedin religious ceremonies of Roman Catholic Church .Besides , it is also used for ceremonial purposesin cases such as school graduation ceremony .⑤So what ? :an informal colloquial expression , meaning that the remarkor statement which has just been made seems unimportant ,uninteresting , or irrelevant . Here it means what does itmatter if my father doesn’t understand the Latin that wasspoken in the ceremony ? Another similar expression is Whatof it ? Eg. , Someone will see . ------- So what ?Your parents are coming tomorrow .-------- What of it ?⑥Disregard (for / of sb. / sth.) : lack of attention or careEg. She shows a total disregard for other people and their feelings .⑦Decent :a.satisfactory ;quite goodeg. Earn a decent wage , living , etcb.not likely to shock or embarrass others ; modesteg. That dress isn’t decent .⑧apprehension : anxiety about the future ; fearrecite (sth to sb ) : say (a poem , passage , etc.) aloud frommemory , esp. to an audience⑨(all ) on one’s own :a.aloneeg. She lives on her own .b.without help or supervision ; aloneeg. Although her father is in the firm , she got the job on her own . ⑩put sth in : spend (a period of time ) working at stheg. She often puts in twelve hours’ work a day .put sth in / into (doing ) stheg. We’ve put a great deal of time and effort in this project .⑾follow in sb’s footsteps : do as sb else does ; follow a similaroccupation or life-style as sb elseeg. She works in theatre , following in her father’s footsteps .Assignments4.Do the exercises on the textbook .5.WritingP 57 Exercise 66.Oral practice :He Was My FatherUnit 3 Understanding Your OwnerI .Teaching Objectives4.Functions : Expressing anger2. Grammar points : -ing as objectives of vt./v.+prep.3.Vocabulary : desperate , represent , be aware of , interpret , fitin with , put … into danger , keep away , work out , trydoing , end up , vary from , all too , force onII . Focal Points1.Functions : Expressing anger2. Grammar points : -ing as objectives of vt./v.+prep.3.ConversationIII . Teaching Process1. Listening and Speaking Activities2)Introduction to the formulas of expressing anger3)Listen to the conversation twice3) Correct the answers4) Pair workPracticing : Read ConversationExplanationSpeak before the classMake up another dialogue using the cues in the box5)Make your own dialogueTeam & group workPresentation6)Matching exercises :What are they for ?If you want to learn more4.Reading Comprehension1) Warm-up questions2) Listening to the text twice3) Doing the comprehension work :Reading the textDiscussion :Read the text carefully to find the answers to the questions and look to the evidence from the text to support the answers Retelling the text using the key words4) Extended ActivityExercisesStep 1 Listening and Speaking Activities1.Formulas for expressing angerI simply can’t bear to hear them bark.I’m disgusted . How could you be so rude to my guests !I really hate being kept waiting . Can you make it earlier next time ?My orders have been disobeyed . I must teach them a lesson .I’m going to get very angry with you . Pick your things up now !Look at the way people just throw litter down in the street ------ it makes you sick , doesn’t it ?Look , how they treat the innocent animals ! It makes my blood boil .It’s typical of him to behave like that !Why don’t you pick someone your own size ?!It really makes me angry the way he talks .I’ve had enough of that .Steve never apologises for anything .That’s what gets me down !You can often see Sam picking flowers in the park . It really makes me see red .I can’t stand his arrogance .Do you always stick your nose in other’s business ?How would you like somebody to litter around in your own doorway ?2. Listen and speak :Listen to the following conversation twice and try to tick what you have heard as the correct answer to the questions .5. Try to speak more1) Listen to the tape2)Explanation of the conversation :walk :①行走;步行②cause (sb./sth.)to walk , esp. by accompanying him / it 使(某人/某物)行走(尤指与之同行)eg.He walked the horse up the hill .He walked her to her car .keep sb. company : remain with sb. So that he is not aloneeg.I’ll stay here and keep you company .pessimist : person who expects the worst to happen 悲观主义者3) Read the conversation by themselves and then try to memorizethem .Invite two pairs of students to speak before the class and then exchange their roles .Depending on the cue box on the right , ask them to make up another conversation .Act out the conversation.4) Make your own dialoguePresentationTeam work5) What are they for ?ExplanationPair work : matching the exercises6) If you want to learn moreStep 2 Reading Comprehension and LanguageActivities13.Warm-up questions and discussion14.Listen to the text twice15.Read the text and try their best to answer the questions .Section 1 --------- In the two ways : a set of sounds and a set of marks ,humans have developed their eyes and ears to a higher level of interpretation than the dogs .Questions :①What does the phrase “a set of sounds” mean ? Why do some humans have difficulty communicating with others by a set of sounds ?(“A set of sounds” refers to the spoken form of human language . Some people have difficulty in understanding people from other places because they speak different languages . As the dog understands , human beings have to be either raised in the same place or receive special training in order to understand a different language .)②What does the phrase “a set of marks on paper?” mean ? What is the use of the marks for human beings ?(“A set of marks on paper” refers to the written form of human language and is used to represent the sounds of language . These marks can be used to record human messages so that humans at a different time and in a different place can understand those messages .)③Why should a dog not develop the same communicating means /skills as human beings ?(Humans have lost the other abilities and senses for gatheringinformation while they have developed their eyes and ears . If adog develops these two skills too far , it would put its otherabilities into danger .)④What cost have human beings paid for having developed their seeing and hearing senses ?(When human beings have developed their eyes and ears to a higher level , they have lost the ability to get much of the information that dogs are able to do by other means .)Conclusion : the advantage and disadvantage of developing seeing and hearing sensesThe advantage : have developed their eyes and ears to a higherlevel of interpretationfor humans Humans at a different time and in a differentplace can understand their messages .The disadvantage : have lost the ability of other senses excepteyes and ears to get much informationThe advantage : can get information not only from ears and eyesbut also from otherfor dogs sensesThe disadvantage : have a lower level of interpretationSection 2 --------- How to please a human .Questions : What gesture of a dog’s can best please human beings ?(A dog who can behave like a human , such as sitting down in frontof him , and raising a front paw in a gesture to shake hands witha human will please a human most .)Section 3 --------- Don’t forget the true nature — you are a dog .Questions :①According to the passage , what is the best policy for a dog to livepeacefully with humanbeings ?(Even when a dog is behaving like a human to please a man , he should always remember that he is a dog . He is not a human and needs to live as a dog . It is all very well for a dog to change himself slightly to fit in with human beings, but he should not deny his true nature . Besides , he should accept whatever is forced upon him . In other words , he should be faithful to his master no matter who the master is . )②What are the reasons that human beings hold for keeping a dog ? (Human beings need dogs for various reasons . They may need a dog to help with some specific tasks like hunting or guiding , or want a dog to keep burglars away . Looking after a dog may give their children a sense of responsibility .They may want other people to admire their dogs if the dogs are of an expensive and fashionable breed . Or they may simply need some sort of companionship or love .)Conclusion :Should : need to live as a dogFor a dog change yourself slightly to fit in with a human pack accept anything forced on youShould not : deny your true naturehelp with some specific tasks like hunting or guidingkeep burglars awayreasons for keeping a dog give their children a sense of responsibilitywant other people to admire their dogsneed some sort of companionship or love16.Practicing asking and answering the questions in pairs .17.Retell the text using the key words .18.Explanation of the new words and phrases .①be aware of sb./sth.that …②vary from sth to sth : change from … to…vary with : change according to some factorseg.Her mood varied from optimism to extreme depression .Prices vary with the seasons .③represent : stand for or be a symbol or equivalent of (sb/sth);。