发动机工作原理(中英文对照)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:31.00 KB
- 文档页数:3

中英文对照外文翻译汽车变速器设计我们知道,汽车发动机在一定的转速下能够达到最好的状态,此时发出的功率比较大,燃油经济性也比较好。
因此,我们希望发动机总是在最好的状态下工作。
但是,汽车在使用的时候需要有不同的速度,这样就产生了矛盾。
这个矛盾要通过变速器来解决。
汽车变速器的作用用一句话概括,就叫做变速变扭,即增速减扭或减速增扭。
为什么减速可以增扭,而增速又要减扭呢?设发动机输出的功率不变,功率可以表示为 N = w T,其中w是转动的角速度,T 是扭距。
当N固定的时候,w与T是成反比的。
所以增速必减扭,减速必增扭。
汽车变速器齿轮传动就根据变速变扭的原理,分成各个档位对应不同的传动比,以适应不同的运行状况。
一般的手动变速器内设置输入轴、中间轴和输出轴,又称三轴式,另外还有倒档轴。
三轴式是变速器的主体结构,输入轴的转速也就是发动机的转速,输出轴转速则是中间轴与输出轴之间不同齿轮啮合所产生的转速。
不同的齿轮啮合就有不同的传动比,也就有了不同的转速。
例如郑州日产ZN6481W2G型SUV车手动变速器,它的传动比分别是:1档3.704:1;2档2.202:1;3档1.414:1;4档1:1;5档(超速档)0.802:1。
当汽车启动司机选择1档时,拨叉将1/2档同步器向后接合1档齿轮并将它锁定输出轴上,动力经输入轴、中间轴和输出轴上的1档齿轮,1档齿轮带动输出轴,输出轴将动力传递到传动轴上(红色箭头)。
典型1档变速齿轮传动比是3:1,也就是说输入轴转3圈,输出轴转1圈。
当汽车增速司机选择2档时,拨叉将1/2档同步器与1档分离后接合2档齿轮并锁定输出轴上,动力传递路线相似,所不同的是输出轴上的1档齿轮换成2档齿轮带动输出轴。
典型2档变速齿轮传动比是2.2:1,输入轴转2.2圈,输出轴转1圈,比1档转速增加,扭矩降低。
当汽车加油增速司机选择3档时,拨叉使1/2档同步器回到空档位置,又使3/4档同步器移动直至将3档齿轮锁定在输出轴上,使动力可以从轴入轴—中间轴—输出轴上的3档变速齿轮,通过3档变速齿轮带动输出轴。


电机 electric engine; electric machine; electric (al) motor电机参数 parameter of electric machine电机槽宽 tooth ratio电机槽内导体 electric machine slot-conductor电机常数 constant of the machine电机厂 motormaker电机车 haulage motor电机车架空线保护 trolley wire guard电机车运输 electric(al) haulage电机传动辊 motorised roll电机传动轴 motor transmission shaft电机磁场 motor-field电机的电气线端 electric terminals of a machine电机的规格 rating of machine电机的输入功率 power input to a machine电机的铁间空隙 entrefer电机底座 motor base电机电刷 motor brush电机调整器 regulator generator电机定子铁芯自动焊接机 dynamo stator core automatic welder电机端部磁场 end-region magnetic field of electrical machine电机短路测试仪 electric motor short circuit test instrument电机放大器 amplidyne generator; motor amplifier; rotating amplifier 电机放大器控制部件 amplidyne control unit电机放大器伺服系统 amplidyne servomechanism电机放大伺服机构 amplidyne servomechanism电机钢 dynamo steel电机钢板 dynamo steel sheet电机工程 electric engineering电机工程师 electrical engineer电机功率 power of motor电机规格 rating of machine电机硅钢片 dynamo sheet电机黄铜合金 motor brass alloy电机减速机 motor reducer; motor reducing gear电机壳 motor casing; motor enclosure电机控制 electric machine control电机控制器 machine controller电机偏心率 motor eccentricity电机起动器 motor starter电机青铜 dynamo bronze电机驱动 motor drive电机驱动的 motor-driven电机驱动开关 motor driven switch电机驱动种子清选机 motor-driven seed cleaner电机绕组 machine winding电机设计 electric machine design电机室 motor room电机输送 motor transport电机数量 number of motors电机损耗 loss of machine电机碳刷 carbon brush for electric machine; motor carbon电机效率 electric efficiency; electrical efficiency电机械加工 electromechanical working电机械模拟 electromechanical analogy电机学 electromechanics电机用薄钢片 dynamo sheet steel电机用硅钢片 dynamo steel sheet电机用油 motor oil电机油 dynamo oil; electric engine oil电机运行特性 electric machine operating characteristic电机制造业 electric manufacturing电机轴 motor shaft电机轴承 motor bearings电机转子试验装置 motor rotor tester电机转子压铸机 die-casting machine for motor rotor电机自动继电器 motor automatic relay电机座 motor cabinet电机座位 motor cavity3-phase slip-ring induction motor 三相滑环式感应电动机3-phase squirrel cage induction motor 三相鼠笼式感应电动机battery-operated motor cycle (玩具) 电动摩托车bearing of motor 电动机轴承bin drive motor 分页格驱动电机biphase motor 两相电动机bisynchronous motor 双倍同步速度电动机blower motor 鼓风电动机; 鼓风机用马达boost motor 助推器; 加速器Boucherot (squirrel-cage) motor 双鼠笼式电动机box-frame motor 箱形机座电动机; 框形电动机brake motor 制动电动机brush and slotless motor 无电刷槽电动机brush motor 换向器电动机; 整流式电动机brush-shifting motor 移刷型电动机built-in motor drive 单独电机传动; 单独内装电机传动built-in motor 机内电动机cage motor 鼠笼式电动机cam-type axial piston motor 斜盘式轴向柱塞电动机canned motor pump 密封电动泵; 密封式电动泵; 屏蔽泵canned motor 封闭电动机; 密封式发动机capacitive motor 电容电动机capacitor induction motor 电容电动机capacitor motor 电容起动电动机; 电容器起动电动机; 电容式单相电动机; 电容式电动机capacitor split-phase motor 电容分相式电动机capacitor start and run motor 电容起动行驶式电动机capacitor start motor 电容起动电动机capacitor start-run motor 固定分相电容器式电动机capacitor-start motor 电容器起动电动机; 电容式启动电动机capacitor-start-and-run motor 电容式启动和运转的电动机capstan motor 主导电动机; 主动轮电动机cascade motor 级联电动机cascade motors 级联电动机组ceiling-fan motor 吊扇电机cell motor 电池电动机centre drvie motor mower 中央驱动动力割草机ceramic permanent-magnet motor 陶瓷永磁电动机; 铁淦氧永磁电动机chain-drive motorcycle 链动机器脚踏车chain-type side-rake for motormower 动力割草机的链指式侧向搂草器change speed motor 分级调速式电动机change-speed motor 变速电动机charge motor 充电马达; 充电用电动机chopper motor 斩波器供电电动机; 断路电动机Class I Motor Carrier 一级汽车运输公司clock motor 计时电动机; 电钟用电动机close-ratio two-speed motor 近比率双速电动机closing motor 密闭电动机clutch motor 带离合器电动机coastal motor boat 海岸汽船coller for motor 电动机冷却器combustion motor 内燃机commercial motor 商用电动机common pumpl motor base 泵与电动机的共用底座commutating pole motor 换向极电动机commutator induction motor 换向器感应电动机commutator motor 换向器式电动机; 整流式电动机; 整流子式电动机commutator variable speed motor 换向器变速电动机compass torque motor 罗盘矫正电动机compensated commutator motor 补偿整流电动机compensated induction motor 补偿感应电动机; 补偿式感应电动机compensated motor 补偿电动机compensated repulsion motor 补偿感应推斥电动机; 补偿式推斥电动机; 补偿推斥电动机; 补偿推斥式电动机compensated series motor 补偿串激式电动机; 补偿串励电动机complete motor type 配带电机型号compound motor 复励电动机compound-wound motor 复激电动机; 复励电动机compressed air motor 气动电动机concatenated motor 级联电动机; 链系电动机; 串级电动机concatenation motor 链系电动机; 串级电动机condenser motor 电容式电动机condenser run motor 电容起动电动机condenser shunt type induction motor 电容分相式感应电动机condenser start motor 电容起动电动机condenser-start induction motor 电容起动感应电动机connector motor magnet 回转电磁铁consequent-poles motor 变极式双速电动机; 交替磁极式电动机constant current motor 定流电动机constant displacement motor 定量马达constant field commutator motor 定激励整流式电动机constant power motor 恒定功率电动机constant pressure motor 等压内燃机constant speed motor 等速电动机; 恒速电动机; 定速电动机constant torque asynchronous motor 恒力矩异步电动机constant voltage motor generator 恒压电动机发电机constant voltage motor 恒压电动机; 定电压电动机constant-current motor 恒流电动机constant-speed motor 等速马达constant-voltage motor 恒定电压电动机continuously rated motor 连续额定运行电动机continuous-time-rated motor 连续运行电动机converter-fed motor 换流器供电电动机coolant pump motor 冷却液泵电动机cooled motor 冷却式发动机crane motor 吊车电动机crawler-type motor grader 履带式自动平地机crescent gear motor 内啮合齿轮马达cross feed motor 交叉馈电式电动机cumulative compound motor 积复激电动机cup motor 杯形电机current-displacement motor 深槽电动机; 深槽感应电动机cutter motor 截煤机电动机cycloid gear hydraulic motor 摆线齿轮油液压马达cycloidal gear reducing motor 摆线齿轮减速电动机cycloidal needle wheel type motor 摆线针轮电动机DC electronic motor 离子式直流电动机DC series motor 串激直流电动机dead motor 关闭的电动机decompounded motor 差复励电动机decussation motoria 运动交叉deep-bar motor 深槽鼠笼式电动机deep-slot induction motor 深槽感应电动机deep-slot motor 深槽感应电动机deep-slot squirrel cage motor 深槽鼠笼式电动机definite-purpose motor 专用电动机deluge proof motor 防水电动机Denison motor 丹尼森液压电动机; 轴向回转柱塞式液压电动机Deri motor 德里电动机Deri repulsion motor 德里推斥电动机despun motor 反旋转电动机; 反自转电动机diaphragm motor 膜片阀控制电动机; 光阑驱动电动机die-casting machine for motor rotor 电机转子压铸机diesel motor roller 柴油碾压机; 柴油压路机diesel motor 狄塞尔发动机differential compound motor 差复激电动机; 差复励电动机; 差复励电视机; 差复绕电动机; 差绕复激电动机differential motor 差绕电动机differential selsyn motor 差动自动同步电机differential shunt motor 差并励电动机differential wound motor 差励电动机differential-field motor 他激差绕直流电动机differential-field series motor 串激差绕直流电动机differentially-compound wound motor 差复激电动机differentially-wound motor 差绕电动机direct motor drive 电动机直接传动direct motor driven 单电动机传动的direct-connected motor 直连电动机direct-coupling motor converter 连轴电动换流机direct-current motor control 电动机电子控制direct-motor-driven 单电动机传动disabled motor switch 电动机故障断路器dither motor 高频振动电动机; 高频振动电机; 高频振动用电动机double armature motor 双电枢电动机double commutator motor 双整流子电动机; 双换向器电动机double motor 双电动机double squirrelcage motor 双鼠笼电动机double-casing motor 双层机壳式电机double-fed repulsion motor 双馈推斥电动机double-reduction motor 两级减速电动机double-unit motor 双电动机机组drag-cup induction motor 空心转子感应电动机drag-cup motor 拖杯式电动机; 托杯形电动机drag-cup type rotor motor 空心转子电动机drill-motor rotor vane 钻孔转子叶片drip-proof motor 防滴式电动机drip-proof type induction motor 防滴式感应电动机drive motor 传动马达driver motor 主驱动电动机driving shaft motor 传动轴电机drop-proof type motor 防滴水式电动机drum motor 鼓形电动机dual-capacitor motor 双电容器式电动机dual-frequency motor 双频率电动机dual-thrust motor 双推力发动机duocentric motor 同心双转子电动机duplex power feed type A.C. commutator motor 并联馈电整流式交流电动机dust-tight type motor 防尘式电动机dynamoelectric motor 旋转换流机eddy currents in attraction type motor 吸引型电动机中的涡流eddy-current motor 涡流电动机either-rotation motor 双向电机electric (al) motor 电机electric hoist with creep lifting motor 变速电葫芦electric motor car 电动车; 电动机车electric motor coach 电动客车electric motor drive 电动机传动electric motor driven butter churn 电动乳脂制作器electric motor for rolling way 辊道电动机electric motor generator 电动发电机electric motor movie camera 电动式活动摄影机electric motor oil 电动机油electric motor saw 电锯; 电力锯electric motor short circuit test instrument 电机短路测试仪electric motor signal mechanism 电动臂板信号机构electric motor truck 电气载重车electric motor 电动机electric motor-drawn channel scraper 电动粪槽刮铲electric motordriven point mechanism 电动转辙机构electric motor-operated fixed crane 固定式电动起重机electric pulse motor 电脉冲电动机electric starter motor 电力起动机electric vehicle motor 牵引电动机electric wiper motor 刮水器电动机electrical motor 电动机electrically operated motor car 电动车electro-hydraulic servo motor 电动液压伺服电动机electrohydraulic stepping motor 电液步进马达electromagnetic speed-adjustable motor 电磁调速电动机electromagnetic variable-speed motor 电磁调速电动机electro-motor 电动马达electronic motor control 电动机电子控制electronic motor controller 电子电动机控制器electropneumatic point motor 电动气动转辙机electropneumatic signal motor 电动气动信号机electrostatic motor 静电电动机; 静电电动机elevating motor 升降电动机elevation drive motor 仰角传动电动机; 仰角驱动电动机enclosed motor 密封式电动机; 封闭电动机; 封闭式电动机; 封闭型电动机enclosed type induction motor 封闭式感应电动机enclosed type motor 封闭式电动机enclosed ventilated motor 封闭通风式电动机engine cranking motor 发动机起动马达Enor motor 埃诺罗式叶片液压马达E-P signal motor 电动气动信号机epicycle motor 行星减速电动机erection torque motor 竖起力矩电动机; 架设转矩电动机exciter motor-generator 励磁电动发电机expiratory motor neuron 呼气运动神经元explosion motor 爆燃式发动机explosion-proof motor 防爆马达; 防爆型电机explosion-proof type induction motor 防爆式感应电动机explosion-proof ventilated synchronous motor 防爆通风型同步电动机explosive motor 内燃发动机external concrete vibrators with motor 带电动机的混凝土振动器externally reversible motor 双向启动可逆电动机external-rotor motor 外转子式电动机face-type motor 凸缘型电动机fan motor 风扇电动机; 风扇马达fan-cooled motor 全封密风冷式电动机farm motor 农用电动机feed motor 进给电动机Ferrari s motor 费拉里电动机field-control motor 磁场可控式电动机; 可调磁场型电动机fixed brush type polyphase series motor 固定电刷式多相串激电动机fixed displacement motor 定量马达fixed-displacement motor 定容量马达flame-proof 3-phase induction motor 防爆型三相感应电动机flame-proof electric motor 防爆电动机flame-proof motor 防爆式电动机flange motor 凸缘底座电动机; 凸缘型电动机flanged motor 凸缘电动机flange-mounted motor 凸缘型电动机flange-type motor 凸缘型电动机; 法兰式电动机flea-size motor 超小型电动机fluid motor 液力发动机; 液压马达fluid power motor 液压发动机fluid pressure motor 液压电动机fluid servo-motor 液压伺服马达fluidic stepping motor 射流式步进电动机fluid-power motor 液力电动机; 液力马达follower motor 随动电动机foot engine with electric motor 牙科脚踏电动二用钻机foot-mounted motor 底座安装型电动机; 落地安装型电动机force motor 执行电动机forced-ventilated motor 强制通风式电动机form-wound motorette 模绕线圈试验装置foundation bolt for motor 电动机地脚螺栓four-phase stepper motor 四相步进电动机four-pole motor 四极电动机four-stroke motor 四冲程发动机four-wheel motor vehicle 四轮机动车辆fractional electric motor 小功率电动机; 分马力电动机fractional horse power motor 分数马力电动机fractional horsepower motor 分马力电动机fractional horse-power motor 分数功率电动机fractional HP light metal induction motors 铝合金壳分马力感应电动机fractional-horsepower asynchronous motor 分马力异步电动机fractional-horsepower motor 低功率电动机fractional-horse-power motor 小马力电动机frame suspended motor 底架悬挂电动机; 底座悬挂型电动机frost-proof motor 耐寒式电动机full voltage starting motor 全电压起动电动机fully-flameproof motor 全防爆型电动机gas for motor fuel 气态发动机燃料; 动力煤气gas motor 煤气发动机; 煤气机gasoline motor car 汽油车gasoline motor 汽油发动机gas-pressurized rocket motor 气压式液体火箭发动机gate motor 栏木电动机gear head motor 齿轮减速电动机gear motor for screw conveyer 螺旋输送器减速电动机gear motor 齿轮电动机; 齿轮马达gear(ed) motor 减速电动机geared motor 齿轮传动电动机; 齿轮传动马达; 齿轮电动机; 带变速齿轮箱的电动机;带减速齿轮的电动机geared-down motor 齿轮减速发动机gear-type hydraulic motor 齿轮式液压马达gear-type motor 齿轮液压电动机gear-within-gear motor 内啮合齿轮马达general-purpose motor 通用电动机generator-motor set 发电机电动机组gimbal servo motor 万向伺服电动机gimbaled motor 悬挂式电动机gimbaling rocket motor 万向架支座火箭发动机glass reinforced plastic motor lifeboat 玻璃钢机动救生艇governor motor 调节马达; 调速电动机; 调速器电动机; 调速器用电动机; 调整机用电动机graduation of the motor currents 电动机电流级加法gramophone motor 唱机电动机grinding head motor for woodworking 木工专用磨头电动机grinding head motor 磨头电动机grinding wheel drive motor 砂轮电机gunmetals motor carriage 机械化炮车gyro motor 陀螺马达hand motor 手电动机harmonic motor 谐波电动机haulage motor 电机车head motor 头部发动机heat-pipe motor 热管冷却电动机heat-resistant motor 耐热电动机; 高温电动机heavy motor truck 重型载货汽车Hele-Shaw motor 径向活塞式液压电动机; 径向活塞式液压电动机hermetic motor 密封式电动机; 密封式电动机; 密封型电动机hermetically sealed motor 密封式电动机hermetically-sealed motor 密封型电动机heteropolar D.C. linear motor 多极直流直线电动机high capacity motor 高功率电动机high frequency motor generator 高频电动发电机high power motor 大功率电动机high slip motor 高转差率电机high speed low-noise synchronous motor 高速低噪音异步电动机high torque AC motor 大转矩交流电动机high torque and low speed motor 大转矩低速电动机high torque motor 高启动转矩电机high voltage motor 高压交流电动机high voltage wound asynchronous motor 高压卷线异步电动机high-capacity motor 大型电动机; 高功率电动机high-compression motor 高压缩发动机high-output three-phase induction motor 高功率三相感应电动机high-slip induction motor 高滑差感应电动机high-slip motor 高滑率电机high-speed motor 高速电动机high-speed servo motor 高速伺服电动机high-voltage motor 高压电动机high-voltage synchronous motor 高压同步电动机hoisting motor 升降电动机home motor 家用电动机homopolar motor 单极电动机horizontal induction motor 卧式感应电动机horizontal motor 卧式电动机horizontal-type motor 卧式发电机horse motor 马拉传动装置horse-drawn motorized duster 马拉机动喷粉机; 马拉式机动喷粉机hot mill motor 热轧电动机hot motor part detection 发动机发热部分探测hot motoring method 热机马达法hydraulic control motor 液压控制马达hydraulic motor drive 液力马达传动hydraulic motor SAE stall pressure 液压马达的SAE制动压力hydraulic motor 水力发动机; 液压发动机; 液压马达; 油压马达hydraulic slave motor 液压马达hydraulic stepping motor 液压步进马达hydraulic traversing electric motor 液压方向机电动机hydraulic-powered wiper motor 液压式风窗刮水器的液力驱动器hydro-electric motor 水力发动机hydro-motor jig 流体传动跳汰机hydro-motor 水压发动机; 液压发动机; 液压马达; 射水发动机hysteresis motor 磁滞电动机; 磁滞式电动机hysteresis synchronous motor 磁滞式同步电动机; 磁滞同步电动机igniter motor 点火发动机immersed torque motor 湿式力矩电动机; 湿式力矩马达immersible motor 浸入型电动机; 潜水电动机impulse motor 脉冲电动机; 脉冲马达impulse stepping motor 脉冲步进电动机increased-safety motor 增安型电动机independent motor drive 单独电动机传动individual drive motor 单独传动电动机individual-drive motor 单独传动电动机induction motor controller 感应电动机控制器induction motor 感应电动机; 异步电动机induction-motor meter 感应式电度表inductor motor 感应子电动机; 作为发电机的感应电动机inductor type synchronous motor 感应子同步电动机in-line (plunger) motor 直列式柱塞电动机in-line motor 直列式马达; 直列式柱塞马达in-line plunger motor 直列式柱塞马达inner tube of pneumatic tyre for motor cycle 摩托车用充气轮胎内胎inside-out motor 旋转电枢式同步电动机; 反结构同步电动机instrument motor 仪表电动机integral horsepower motor 整数马力电动机integrated motor 机内电动机; 积分马达; 积分直流电动机; 整体式电动机integrating motor 积分电动机; 积分马达; 积分直流电动机internally geared motor 内装减速器的电动机internally ventilated motor 内通风式电动机inverse speed motor 反速电动机inversed repulsion motor 反排斥电动机; 反推斥电动机inverse-speed motor 串激特性电动机inverted motor 反结构电动机inverted repulsion motor 反常推斥式电动机; 反用推斥电动机ironless A.C.servo motor 无铁交流伺服电动机Janney motor 轴向回转柱塞式液压电动机; 轴向回转柱塞液压马达jazz the motor 强化发动机jet motor 喷气发动机kick motor 加速发动机Lacour motor 拉库尔电动机large AC three-phase synchronous motor 大型交流三相同步电动机large and medium DC motor 大中型直流电动机large induction motor 大型感应电机large power motor 大功率电动机Latour motor 拉吐尔电动机leaf driving motor 过滤叶片驱动电机leak-proof motor pump 防漏式电动泵lengthened motor lorry 加长载重汽车level-compound excited motor 平复激电动机lift motor 电梯用电动机lifting motor 起重电动机light power motor 小型电动机light rail motor tractor 轻型机车lighting motor-generator set 照明用电动发电机组linear electric motor 直线电动机linear induction motor 线性感应电动机linear motor principle 直线驱动原理linear motor 直线电动机; 线性电动机linear pulse motor 直线步进电动机; 直线脉冲电动机linear reluctance motor 直线式磁阻电动机linear step motor 直线步进电动机linear stepping motor 直线步进电动机linear synchronous motor 线性同步电机line-fed motor 直接馈电电动机line-start motor 线路起动电动机; 直接起动电动机; 直接启动电动机liquid fuel motor 液体燃料发动机liquid motor fuel 液体动力燃料liquid motor 液体火箭发动机liquid-filled motor 充液式电动机load limit motor 负荷限制马达loading motor 加载电机lobed rotor motor 罗茨电动机; 罗茨马达long hour motor 持续运行电动机loom motor 织布机电动机loop motor 环流电动机low power motor 小功率电动机low speed motor 低速电动机low speed synchronous motor 低速同步电机low tension motor starter 低压电动起动机low tension motor 低压电动机low-compression motor 低压缩发动机lower motor neuron disease 下位运动神经元病lower motor neuron lesion 下运动神经元损害lower motor neuron 下运动神经元low-tension motor 低压电动机luffing motor 吊杆俯仰电动机Lundell motor 爪极式电动机; 伦德尔式电动机machine oil pump for motor 摩托车机油泵magnetic clutch motor 磁力离合器电动机magnetic stepping motor 步进电机magnetical stepping motor 磁性步进电机magnet-lagging synchronized motor 磁滞同步电动机mail motor truck 邮政汽车main drive motor 主传动电动机; 主电动机main mill drive motor 轧机主传动电机main motor contactor 主电动接触器main motor 主电动机marine flame-proof three phase asynchronous motor 船用防爆三相异步电动机marine service motor 船用电动机marine-land purpose motor 船-陆两用电机master motor 主驱动电动机medium-sized motor 中型电动机mercury motor type 水银电动机式metal-clad motor 金属加固电动机; 铠装电动机micro-stepping motor 微型步进电动机midget motor 微型电动机; 小型电动机military motor lorry 军用卡车; 军用卡车mill motor 磨坊用电动机minertial motor 小惯量电动机miniature motor 微型电动机mini-motor-home 小型旅宿车mining motor 矿用电动机mist fan motor 喷雾吹风电动机; 喷雾吹风马达mobile motor driven centrifugal pump 移动式机动离心泵model motor 模型电动机; 作为试验样品的电动机modern motor spirit 现代车用汽油Modutrol motor 莫杜特罗尔电动机monocyclic-start induction motor 单相感应电动机monocylicstart induction motor 单周期起动感应电动机monophase asynchronous motor 单相异步电动机monorail motor crab 单轨电动起重机monorail motor hoist 单轨电动绞车motor alternator 电动交流发电机motor amplifier 电机放大器motor analyser 发动机试验机; 发动机试验台motor atomizer 动力弥雾机motor auger 机力螺旋钻motor automatic relay 电机自动继电器motor bark remover 机动剥树皮机motor base (frame) 电动机座motor base (MB) 电动机基础motor base pin 电动机座销轴motor base 电机底座motor battery 电动机电池motor bearing 电动机轴承motor bearings 电机轴承motor bed-plate 电动机机座motor board 电动机配电盘motor boat 摩托艇motor body 发动机壳体motor bogie 自动转向架motor brake magnet 电动机闸磁铁motor branch circuit 电动机分支电路; 电动机馈电支路motor brass alloy 电机黄铜合金motor brass 电动机黄铜motor brush 电动机刷; 电机电刷motor cabinet 电机座motor cable 电动机电缆motor capacity 电动机容量motor car fitter 汽车修配工motor car insurance 汽车保险motor carbon 电动机碳刷; 电机碳刷motor carrier 传送机motor case 电动机壳; 发动机壳体motor casing (frame) 电动机壳motor casing 电机壳; 摩托车外胎motor cavity 电机座位motor chamber diameter 发动机燃烧室直径motor characteristic 电动机特性; 电动机特性曲线motor circuit 动力电路motor coach 长途公共客车motor combination 电动机的组合motor commutator 电动机整流子motor compressor 电动压缩机motor console 发动机试验操纵台motor constant 电动机常数motor control relay 电动机控制继电器motor control 电动机操纵; 电动机电子控制; 电动机控制motor controller 电动机控制器motor cooling jacket 发动机冷却套motor cooling 电动机冷却motor coordinating center 运动协调中枢motor coupling 电动机联轴节motor current-transformer 电动变流器motor cut-out switch 电动机停机开关motor cuts out 发动机停车motor cycle insurance 摩托车保险motor decussation 运动交叉motor disturbance 运动障碍motor drill 手电钻motor drive asphalt pump 电动沥青泵motor drive oil lifter 电动油压升降机motor drive shaft 电动机驱动轴; 马达轴motor drive type 电动机传动型motor drive 电动机拖动; 电动驱动; 电机驱动motor driven blower 电动鼓风机motor driven distributor 电动分配器motor driven hoist 电动绞车motor driven layer radiographic X-ray apparatus 电动断层X射线机motor driven miniature pump set 电动微型水泵机组motor driven psychrometer 电动型通风干湿计motor driven pump 电动泵motor driven saw 电锯motor driven sludge excavator 电动挖泥机motor driven slush pump 电动泥浆泵motor driven starter 电动起动机motor driven switch 电机驱动开关motor driven turbine pump 电动涡轮泵motor driven welding machine 电动焊机; 电动机拖动式焊机motor driving time relay 电动机式时间继电器motor dynamo unit 电动直流发电机组motor dynamo 电动发电机; 电动直流发电机motor dynamometer 电动机功率计motor eccentricity 电机偏心率motor element 电动机元件; 运动元件motor enclosure 电机壳motor end closure 发动机喷口盖motor end plate 运动终板motor excitation 电动机励磁motor exciting current 电动机励磁电流motor fan 电扇motor fault 电动机缺陷motor fiber 运动纤维motor fire brigade vehicle 救火车; 救火车motor for boat 船用发动机motor for kicker and doffer 抖动器和滚筒用电动机motor for wood-working 木工电动机motor foundation 电动机基础motor frame through bolt 电动机长螺栓motor frame 电动机架motor fuel additive 发动机燃料添加剂motor fuel constituent 发动机燃料组成motor function 运动功能; 运动机能motor fuse 电动机熔断器motor gain 电动机增益motor gasoline 动力汽油motor generator arc welder 电动发电机式直流弧焊机motor glider 电动滑翔机motor grab 电动抓斗motor group 电动机组motor head 发动机前端motor hoist 电动葫芦; 电动提升机; 电葫芦motor hotel 汽车饭店motor hull insurance 汽车车身保险motor inclosure 电动机壳Motor Industry Research Association (MIRA) 汽车工业研究协会motor integrating meter 感应式电度表motor interrupter 电动断续器motor launch 汽艇motor line 电动机系列motor load control (MLC) 电动机负载控制motor load 电动机负载motor lorry (truck) 载重汽车motor machine 电动机械motor magnet 电动电磁铁motor manufacturer 电动机制造者motor meter 电动机式电度表; 电动机型仪表; 感应式电表motor method 发动机法; 发动机开车法motor mount ring 发动机安装环motor mower with binder attachment 机动青草割捆机; 带打捆装置的动力割草机motor mower with center drive 中央驱动式动力割草机motor mower with side drive 侧驱式动力割草机motor mower 动力刈草机; 机动割草机motor nozzle 发动机喷管motor nuclei 运动核motor octane number(MON) 马达法辛烷值motor off switch 电动机切断开关motor oil 电机用油; 车用机油; 马达油motor on-off switch 马达启停开关motor petrol 车用汽油motor pinion 电动机小齿轮motor pitch 电动机节距motor plough 自走犁motor plow 机动犁motor point 运动点motor power (output) 电动机功率motor power 发动机推力motor press 机动压力机motor protection against overheat 电动机过热保护; 马达过热保护motor protection relay 电动机保护继电器motor pulley 电动机皮带轮motor pump (MMP) 马达泵motor pump works 电泵厂motor pump 电动泵; 机动泵motor rear end plate 电动机后端盖motor reducer 电动机减速器; 电机减速机; 马达降速器motor reducing gear 电动机减速器; 电机减速机motor reduction unit 降速电动机motor reel 电动机轴motor repair shop 汽车修配厂motor repair 汽车修理motor road 汽车路motor room 电机室motor rotor tester 电机转子试验装置motor rotor 电动机转子motor saw 动力锯motor scooter 低座小摩托车motor scraper 自动铲运机; 自行式铲运机motor shaft 电机轴motor shell 电动机壳motor ship 汽船; 发动机推进飞行器; 内燃机船motor side 电动机侧motor siren 电笛; 电动警笛; 马达报警器motor sleigh 雪橇motor slide rails 电动机导轨motor slip 感应电动机转差率motor specification 电动机规格motor speech area 运动言语中枢motor speed control 电动机转速控制motor speed controller 发动机转速调节器motor speed 电动机转速motor spirit 车用汽油motor spring 汽车弹簧motor sprocket 电动机链轮motor squadron 汽车队motor starter 电动机起动器; 电动起动机; 电动启动器; 电机起动器motor starting and control equipment 电动机起动控制设备motor starting characteristic 发动机起动特性motor starting rheostat 电动机起动变阻器motor stator 电动机定子motor steering 汽车转向motor step 电动机距motor stirrer 电动搅拌器motor stoppage 停车motor 运动原; 电动机; 马达。
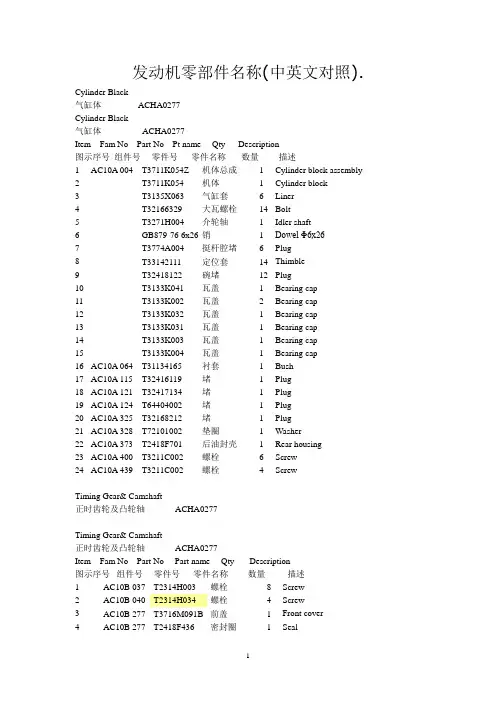
发动机零部件名称(中英文对照).Cylinder Black气缸体 ACHA0277Cylinder Black气缸体 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Pt name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10A 004 T3711K054Z 机体总成 1 Cylinder block assembly2 T3711K054 机体 1 Cylinder block3 T3135X063 气缸套 6 Liner4 T32166329 大瓦螺栓14 Bolt5 T3271H004 介轮轴 1 Idler shaft6 GB879-76 6x26 销 1 Dowel Φ6x267 T3774A004 挺杆腔堵 6 Plug8 T33142111 定位套14 Thimble9 T32418122 碗堵12 Plug10 T3133K041 瓦盖 1 Bearing cap11 T3133K002 瓦盖 2 Bearing cap12 T3133K032 瓦盖 1 Bearing cap13 T3133K031 瓦盖 1 Bearing cap14 T3133K003 瓦盖 1 Bearing cap15 T3133K004 瓦盖 1 Bearing cap16 AC10A 064 T31134165 衬套 1 Bush17 AC10A 115 T32416119 堵 1 Plug18 AC10A 121 T32417134 堵 1 Plug19 AC10A 124 T64404002 堵 1 Plug20 AC10A 325 T32168212 堵 1 Plug21 AC10A 328 T72101002 垫圈 1 Washer22 AC10A 373 T2418F701 后油封壳 1 Rear housing23 AC10A 400 T3211C002 螺栓 6 Screw24 AC10A 439 T3211C002 螺栓 4 ScrewTiming Gear& Camshaft正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Timing Gear& Camshaft正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10B 037 T2314H003 螺栓8 Screw2 AC10B 040 T2314H034 螺栓 4 Screw3 AC10B 277 T3716M091B 前盖 1 Front cover4 AC10B 277 T2418F436 密封圈 1 Seal5 AC10B 316 T2314H005 螺栓9 Screw6 AC10B 320 T2314H004 螺栓 1 Screw7 AC10B 325 T2314H034 螺栓 1 Screw8 AC10B 350 T2314H034 螺栓 2 Screw9 AC10B 436 T2314H013 螺栓 6 Screw10 AC10B 508 T62204001 检查盖 1 Inspection cover11 AC10B 508 T62004002 垫 1 Joint12 AC10B 511 T2314F036 螺栓 4 Screw13 AC10B 560 T3781N042 减震垫 1 Damping Joint14 AC10B 561 T3781N043 隔音板 1 Noiseshield Plate15 AC10B 563 T2314F003 螺栓 2 Screw16 AC10J 004 T0500012 键 1 Key17 AC10J 007 T3117C061 齿轮 1 Gear18 AC10J 013 T33426161A 轮毂 1 Hub19 AC10J 031 T4111A013 齿轮组件 1 Gear assy.20 T3117L061 齿轮 1 Gear21 T0050345 衬套 2 Bush22 AC10J 054 T3241H009 板 1 Plate23 AC10J 069 T2314J010 螺栓 3 ScrewTiming Gear& Camshaft正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Timing Gear& Camshaft正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述24 AC10J 129 T4111A008 齿轮 1 Gear25 T3117C041 齿轮 1 Gear26 T2511437 衬套 1 Bush27 AC10J 144 T33123125 垫圈 1 Washer28 AC10J 150 T2722A206 卡簧 1 Circlip29 AC10J 183 T33153121 盖板 1 Cover plate30 AC10J 189 T2116053 销子 1 Dowel31 AC10J 195 T0500012 键 1 Key32 AC10J 201 T3117L023 齿轮 1 Gear33 AC10J 207 T2314J606 螺栓 1 Screw34 AC10J 214 T3321A003 垫圈 1 Washer35 AC10J 180 T31416308 凸轮轴 1 Camshaft36 AC10B 001 T3681P009 垫 1 Joint37 AC10B 274 T3681P034 垫 1 Joint38 AC10B 010 T3716C133A 正时齿轮室 1 Timing caseCrankshaft Pistons & Connecting Rods曲轴,活塞及连杆 ACHA0277Crankshaft Pistons & Connecting Rods曲轴,活塞及连杆 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10C 005 T3131H022 曲轴 1 Crankshaft2 AC10C 044 T3111V005 轴瓦 1 Bearing3 AC10C 046 T3111V014 轴瓦 1 Bearing4 AC10C 049 T3111V005 轴瓦 4 Bearing5 AC10C 052 T3111V014 轴瓦 4 Bearing6 AC10C 055 T3111X011 轴瓦 1 Bearing7 AC10C 058 T3111X005 轴瓦 1 Bearing8 AC10C 061 T3111V005 轴瓦 1 Bearing9 AC10C 064 T3111V014 轴瓦 1 Bearing10 AC10C 067 T31137551 止推片 2 Thrust washer11 AC10C 070 T31137561 止推片 2 Thrust washer12 AC10D 005 T3135J181ETC 活塞 6 Piston13 AC10D 008 T4181A026 活塞环组件 6 Piston ring assy.14 T3136J051 气环 1 Compression ring15 T3136X021 气环 1 Compression ring16 T3137N021 油环 1 Scrape ring17 AC10D 019 T3313T005 活塞销 6 Piston pin18 AC10D 022 T2721332 卡簧12 Circlip19 AC10D 028 T4115C211 连杆组件 6 Connecting rod assy.20 T3133R001 连杆 1 Connecting rod21 T3133V001 盖 1 Cover22 T32186142 螺栓 2 Screw23 T2135A001 定位销 2 Thimble24 T3112E005 衬套 1 Bush25 AC10D 055 T31132011 轴承12 BearingCylinder Head气缸盖 ACHA02772Cylinder Head气缸盖 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10E 004 T3681H208A 缸盖垫 1 JointAC10E 004 T72505009 缸盖垫 1 Joint2 AC10E 005 TC3712L042Z 缸盖总成 1 Cylinder head assy.3 T3712L042 缸盖 1 Cylinder head4 T3342E003 进气阀座 6 Inlet valve seat5 T3314A122 排气阀座6 Exhaust valve seat6 T2431154 堵 2 Plug7 T0650586 堵 6 Plug8 T0650203 堵 1 Plug9 T2411157 垫圈 1 Washer10 T0650710 碗堵 3 Plug11 T32417156 出沙孔堵 6 Plug12 AC10E 037 T3343F041 气门导管 6 Guide13 AC10E 040 T3343J021 气门导管 6 Guid14 AC10E 064 T2114A046 定位套 2 Thimble15 AC10E 100 T32166219 螺栓12 Screw16 AC10E 103 T32166221 螺栓18 Screw17 AC10E 106 T32166222 螺栓 2 ScrewRocker Shaft摇臂轴 ACHA0277Rocker Shaft摇臂轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10F 001 T3142L072 进气阀 6 Inlet valve2 AC10F 004 T33817117 密封套 6 Seal3 AC10F 007 T31745122 弹簧 6 Spring4 AC10F 010 T31744133 弹簧 6 Spring5 AC10F 013 T33415118 垫圈6 Washer6 AC10F 016 T33424107 进气阀弹簧座 6 V alve cap7 AC10F 019 T33173108 气门锁夹12 Cotter8 AC10F 025 T3142A051 排气阀 6 Exhaust valve9 AC10F 028 T33817117 密封套 6 Seal10 AC10F 031 T31745122 弹簧 6 Spring11 AC10F 034 T31744133 弹簧 6 Spring12 AC10F 037 T33415118 垫圈 6 Washer13 AC10F 043 T33424107 排气阀弹簧座 6 V alve cap14 AC10F 046 T33173108 气门锁夹12 Cotter15 AC10F 052 T2313H331 双头螺栓 4 Stud16 AC10F 058 T2318A605 螺母 4 Nut17 AC10F 061 T2314J607 螺栓 2 Screw18 AC10F 070 T3818X901 支架 6 Bracket19 AC10F 082 T31411147 摇臂轴 1 Rocker shaft20 AC10F 091 T0650507 堵 2 Plug21 AC10F 103 T4115R306 左摇臂组件 6 Rocker level LH22 AC10F 109 T4115R305 右摇臂组件 6 Rocker level RH23 AC10F 127 T32114145 螺栓12 ScrewRocker shaft摇轴轴 ACHA0277Rocker shaft摇臂轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述24 AC10F 130 T0576052 螺母12 Nut25 AC10F 133 T31744123 弹簧 4 Spring26 AC10F 136 T31743108 弹簧 2 Spring27 AC10F 163 T33117434 垫圈 2 Washer28 AC10F 166 T0170151 卡簧 2 Circlip29 AC10J 239 T3142U031 挺柱12 Tappet30 AC10J 257 T31434307 推杆12 Push rod31 AC20N 011 T3775E012 接头 1 Connection32 AC20N 020 T2233022 螺栓 1 Screw33 AC20N 023 T33811113 橄榄体 1 Olive34 AC20N 025 T3311K015 垫片 2 WasherLubricating Oil Pump润滑油泵 ACHA0277Lubricating Oil Pump润滑油泵 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC20B 007 T4132F057 机油泵 1 Lub.Oil Assy.T3771M085 泵体 1 BodyT3753R101 盖板 1 Cover plateT2314C044 螺栓 4 ScrewT3117A038 齿轮 1 GearT2511852 衬套 1 BushT2488C509 转子 1 Rotor2 AC20B 175 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw3 AC20B 179 T2314H002 螺栓 1 Screw4 AC20D 046 T4138A033 限压阀 1 Relief valve5 T32712726 柱塞 1 Plunger6 T31744151 弹簧 1 Spring7 T32712111 弹簧座 1 Seat8 T2721130 卡簧 1 Circlip9 T3775L044 泵体 1 Body10 AC20D 127 T2314K161 螺栓 2 Screw11 AC20G 001 T3571C045 油管 1 Oil pipe12 T3617A005 法兰 1 FlangeT2415H496 O 型圈O Ring14 T3571C046 管 1 Pipe15 AC20G 076 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw16 AC20G 084 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw17 AC20L 456 T3861A027 冷却喷嘴 6 Cooling Jet18 T3317A009 喷嘴 1 NozzleLubricating Oil Pump润滑油泵 ACHA0277Lubricating Oil Pump润滑油泵 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述19 AC20L 500 T4138A017 冷却喷嘴阀 6 Cooling Jet V alve20 T33537008 阀体 1 Body21 T3174A004 弹簧 1 Spring22 T2538753 球 1 Ball23 T3271A003 座 1 RetainerFuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Fuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AF**** T73208265 喷油泵 1 Drive gear2 AF**** T3117L113G 齿轮 1 Fuel pump3 AF**** T33828108A 垫 2 Joint4 AF**** T3821D014A 支架 1 Bracket5 AF**** T3821A014B 支架 1 Bracket6 AF**** T2314J002 螺栓M10X20 2 Screw7 AF**** T2314J003 螺栓M10X25 2 Screw8 AF**** T2131A008A 垫圈 1 Washer9 AF**** T2314H005 螺栓M8X30 1 Screw10 AF**** Q1201030F3S 双头螺柱 4 Stud11 AF**** GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 4 Nut12 AF**** GB93-87D10 垫圈10 4 Washer13 AF**** T63806001B 喷油泵润滑油管 1 Lubricating oil pipe14 AF17M 002 T4184K012F 油管 1 High pressure pipe15 AF33G 030 T4126K081B 补偿管 1 Compensating pipe16 AF33G 041 T0201047 弯管头 1 Connection17 AF**** T33225412 螺母 1 Nut18 AF**** T33811112 橄榄体 1 Olive19 AF17N 001 T3558X039 油管 1 Oil return pipe20 AF17N 034 T3218R005 过油螺栓 5 Oil-pass screw21 AF17N 043 T3355V002 过油螺栓 1 Oil-pass screw22 AF17N 049 T2411101 垫圈12 Washer23 QD30Z 001 T3355M005B 三通接头 1 Connection24 QD30Z 002 T0920155 垫片 2 WasherFuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Fuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AF17E 001 T63301004 喷油器总成 6 Atomizer assy.2 AF17E 004 T3662K002 压板 6 Clamp3 AF17E 008 T2314H006 螺栓12 Screw4 AF17E 007 T0921173 垫圈 6 Washer5 AF17E 037 T33813131 密封圈6 Seal6 AF17E 035 T33813129 隔圈 6 Spacerlywheel Hosing飞轮壳 CDH00865Flywheel Hosing飞轮壳 CDH00865Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 CD**** T73639002 飞轮壳 1 Flywheel housing2 CD**** T36843154 密封条 1 Seal3 CD**** T73631005 盖板 1 Cover plate4 CD**** GB5783-86M6X10 螺栓 2 Screw5 CD**** GB93-87D6 弹簧垫圈6 2 Washer6 CD30A T2314J204 飞轮壳螺栓 6 Screw7 CD30A T2314J607 螺栓 2 Screw8 CD30A T0350025 销子 2 Dowel9 CD30A GB5783-86M12X45 飞轮壳螺栓 2 Screw10 CD30A GB93-87D16 弹簧垫圈 6 Washer11 CD30A GB93-87D12 弹簧垫圈 2 Washer1006-6TRTK01/KA01 Flywheel & Starter Ring1006-6TRTK01/KA01 飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Flywheel & Starter Ring飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 DD30B 004 T73639100K1 飞轮部 1 Flywheel assy.2 T73639001 飞轮 1 Flywheel3 T31162121B 齿圈 1 Starter ring4 DD30B 019 T2185103 飞轮螺栓10 Screw5 DD30B 031 T33117127 垫圈10 Washer6 DD**** GB/T276-94-6304-2Z 轴承6205 1 Bearing1006-6TRTN01/NA01 Flywheel & Starter Ring1006-6TRTN01/NA01飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Flywheel & Starter Ring飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 DD30B 004 T73639100 飞轮部 1 Flywheel assy.2 T73639001 飞轮 1 Flywheel3 T31162121 齿圈 1 Starter ring4 DD30B 019 T2185103 飞轮螺栓10 Screw5 DD30B 031 T33117127 垫圈10 Washer6 DD**** GB/T276-94-6304-2Z 轴承6205 1 BearingGenerator启动电机 EDGenerator启动电机 EDItem Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ED**** T2313C077 双头螺栓 3 Stud2 ED**** GB6170-86M10 螺母3 Nut3 ED**** GB93-87-10 弹簧垫圈 3 Spring washer4 ED**** T63701007 起动电机 1 GeneratorFan Drive风扇驱动装置 FBH00001Fan Drive风扇驱动装置 FBH00001Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 FB10B *** T4113H052 风扇驱动支架 1 Bracket2 FB10B *** T2314J014 螺栓 4 Screw3 FB10B *** T63906002 皮带轮 1 Pulley4 FB10B 034 T74402030 皮带 2 Belt5 MD22B T64406012 风扇 1 Fan6 MD22B T3748W241 隔圈 1 Extention7 MD22B 014 T2314H020 螺栓 4 Screw8 MD22B 014 GB93-87D8 垫圈8 4 WasherLubricating Oil Sump润滑油底壳 GBH01372Lubricating Oil Sump GBH01372润滑油底壳Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 GB10A 025 T3627P024 桥架 1 Bridge piece2 GB10A 035 T2311D039 螺栓 2 Screw3 GB20A 043 T2431A016 堵 1 Plug4 GB20A 052 T32186405 堵 2 Drain plug5 GB20A 059 T2415715 O型圈 2 O Ring6 GB20A 088 T3681M007 油底垫 1 Joint7 GB20A 001 T73803103A 油底 1 Oil sump8 GB**** GB5783-86M16X45 螺栓 6 Screw9 GB20A 200 T2314H006A 螺栓 2 Screw10 GB20A 205 T2314H008A 螺栓7 Screw11 GB20A 208 T2314H009A 螺栓 4 Screw12 GB20A 211 T2314H012A 螺栓 5 Screw13 GB20A 200 T2314H023A 螺栓 6 Screw14 GB20A 205 T2314H026A 螺栓 4 Screw15 GB20F 013 T3575K006 吸油管 1 Suction pipe16 GB20F 025 T3683H005 垫 1 Joint17 GB20F 034 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw18 GB20F 055 T2314H002 螺栓 1 Screw19 GB33V 004 T3577A125 油尺管 1 Dipstick tube20 GB33V 022 T33812116 橄榄体 1 Clive21 GB33V 130 T3178C076 油尺 1 Dipstick22 ZZ****** T76001041 左支脚 123 ZZ****** T76001042 右支脚 124 ZZ****** T73802112 过渡板 1Cover Plate盖板 ZJH00440Cover Plate盖板 ZJH00440Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ZZ23F 004 T0650586 堵 1 Plug2 HB10B 586 T3617A001 板 1 Plate3 HB10B 586 T3683H006 垫 1 Washer4 HB10B 589 T2314H003 螺栓 2 Screw5 HB10B 220 T74001002 加油口 1 Filler6 HB10B 220 T74001003 加油口盖 1 Filler cap7 HB10B 583 T3683H006 加油口垫 1 Joint8 HB10B 241 T2314H010 螺栓 1 Screw9 HB10B 241 T2314H007 螺栓 1 Screw10 HB10B GB1235-76D38X3.1 O型圈 1 O ring11 HB**** GB93-87D8 垫圈8 2 WasherCylinder Head Cover气缸盖罩 HBH02617Cylinder Head Cover气缸盖罩 HBH02617Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 HB10G 001 T3681C001 垫 1 Joint2 HB10G 006 T3718X717 缸盖罩(总成) 1 Cylinder head cover3 HB10G 040 T3274A003 螺母4 Nut4 HB10G 042 T0920009 垫圈 4 Washer5 HB10G 043 T33817135 密封垫 4 Seal6 HB10G 142 T3381J002 密封圈 1 O ring7 HB10G 145 T3781A003 加油口盖 1 Oil filler cover8 HB10G 146 T74001211 油气分离器 1 Oil air separator9 HB10G 147 T74001212 支架 1 Bracket10 HB10G 148 T2314H002 螺栓 2 Screw11 HB10G 149 T2318A603 螺母 2 Nut12 HB10G 150 T74001214 胶管 1 Hose13 HB10G 151 T2481877A 卡子 3 Clip14 HB10G 152 T73802115 胶管 1 Hose15 HB10G 153 T0180063A 卡子 2 Clip16 HB10G 154 T74001215 胶管 1 Hose17 HB10G 156 T73802114 接头 1 Connection18 HB10G 157 T73802101 垫圈 1 Washer19 HB10G 159 T73802103 铰接螺栓 1 Screw20 HB15D 443 T36241123 支架 1 Bracket21 HB20K 001 T3571C014 油管 1 Oil pipe22 HB20K 004 T36833152 垫 1 Joint23 HB20K 007 T2314H003 螺栓 2 ScrewLubricating Oil Filter润滑油滤清器 JBH01149Lubricating Oil Filter润滑油滤清器 JBH01149Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 JB20C 016 T64101001 机油滤清器2 Lub.oil filter2 JB20C 064 T3687W006 垫 1 Joint3 JB20C 079 T4134E031 机滤座 1 Lub.oil head4 JB20C 106 T2314J003 螺栓5 Screw5 JB20L 156 T3686T006 垫 1 Joint6 JB20L 182 T3766P092 接头 1 Adaptor7 JB20L 185 T2314J007 螺栓 1 Screw8 JB20L 187 T2314J003 螺栓 3 Screw9 JB20M 230 T3686A511 垫 1 Joint10 JB20M 233 T2418F602 密封垫 2 Seal11 JB20M 235 T75004281 油管 1 Oil pipe12 JB20M 236 T75004282 油管 1 Oil pipe13 JB20M 240 T2314H004 螺栓 3 Screw14 JB20M 245 T3751K121 法兰 4 Flange15 JB20M 246 T2318A603 螺母 4 Nut16 JB22H 001 T2486A993 油冷器 1 Oil cooler17 JB22H 337 T3688X008 密封垫 2 Joint18 JB22H 338 T2486A990 油冷器壳 1 Oil cooler housing19 JB22H 340 T3684N028 垫 1 Joint20 JB22H 347 T2314H002 螺栓11 Screw21 JB22H 348 T0920146 垫圈14 Washer22 ZA**** T73201640 油门拉线支架 1 Bracket23 ZA**** T2314H034 螺栓 2 Screw24 ZA**** T33134427 隔块 2 SpacerFront End Drive Input前端驱动输入 KBH00575Front End Drive Input前端驱动输入 KBH00575Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量英文描述1 KB10L 013 T0500005 键 1 Key2 KB10L 019 T3115T043 皮带轮 1 Pulley3 KB10L 080 T3311X002 隔圈 1 Spacer4 KB10L 083 T2417711 锁片 1 Cotter5 KB10L 086 T32418313 止推块 1 Block6 KB10L 089 T2415638 O 型圈 1 O Ring7 KB10L 092 T32186137 螺栓 3 ScrewWater Pump & Thermostat水泵及节温器 LBH01659Water Pump & Thermostat水泵及节温器 LBH01659Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量英文描述1 LB10E 140 T3685R005 垫 1 Joint2 LB10E 143 T3755k007 盖板 1 Cover plate3 LB10E 156 T2314H002 螺栓 3 Screw4 LB22C 049 T4131E011C 水泵 1 Water pump5 T2531A112 轴 1 Shaft6 T2415B155 O型圈 1 O Ring7 T3771D045 泵体 1 Body8 T2418M006A 密封圈 1 Seal9 T3117A035 齿轮 1 Gear10 T3746X055A 叶轮 1 Impeller11 T3243C002 盖 1 Cover12 LB22C 143 T2415H494 O 型圈 1 O Ring13 LB22C 145 T2314H015 螺栓 1 Screw14 LB22C 176 T2314N043 螺栓 3 Screw15 LB22C 177 T2314H008 螺栓 1 Screw16 LB22C 178 T2314H006 螺栓 1 Screw17 LB22D 007 T74405005 节温器 2 Thermostat18 LB22D 028 T3685F005 垫 1 Joint19 LB22D 124 T2314J013 螺栓 2 Screw20 LB22D 136 T2314H015 螺栓 1 Screw21 LB22D 160 T2314H008 螺栓 2 Screw22 LB22P 095 T3781D041C 接头 1 ConnectionLB22P 095 T3764E061 接头 1 Connection23 LB22P T2431154 堵 1 Plug24 LB22P 097 T3683N004 垫 1 JointWater Pump & Thermostat水泵及节温器 ACHA0277Water Pump & Thermostat水泵及节温器 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量英文描述25 LB22P 100 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw26 LB22P 110 T33854114 胶管 1 Hose27 LB22P 112 T0180067 卡子 2 Clip28 LD**** T62204004 接头 1 Connection29 XB10E 004 T2314J002 螺栓 2 Screw30 XB22D 007 T2314J004 螺栓 2 Screw31 LB22P T2431154 堵 1 Plug32 LB22D 040 T3771K121E 节温器壳体 1 Thermostat housing body Water Outlet & Inlet水出口及入口 LDH00439Water Outlet & Inle水出口及入口 LDH00439Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量英文描述1 LD22P 006 T3771K043 出水口 1 Water outlet2 LD22P 007 T3684A004 垫 1 Joint3 LD22P 040 T2314H010 螺栓4 Screw4 LD22P 041 T2314H008 螺栓 2 Screw1006-6TRT125N01/NA01 Alternator & Generator1006-6TRT125N01/NA01 交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Alternator & Generator交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ND10B 008 T2314H013 螺栓 1 Screw2 ND24A 004 T64501023 发电机 1 Alterator3 ND24A 054 T2314H007 螺栓 1 Screw4 ND24A 109 T0920497 垫圈 4 Washer5 ND24B 136 GB93-87D8 弹簧垫圈8 2 Spring washer6 ND24B 136 GB6170-86M8 螺母 2 Nut7 ND24A 94 T2314H008 螺栓 1 Screw8 ND24A 133 T2314J006 螺栓M10X40 Screw9 ND24B 136 T2131A010 平垫10 1 Washer10 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 Nut11 ND24B 004 T74502206B 支架 1 Bracket12 ND24B 016 T3827H025B 支架 1 Bracket13 ND24B 127 T2314J003 螺栓 1 Screw14 ND24B 165 T2314H002 螺栓 4 Screw15 ND24B 322 T3753V014B 调节杆 1 Adjustment level16 ND24B 192 T3753V016 支架 1 Bracket17 ND24B 367 T2314J004 螺栓 1 Screw18 ND**** T2314H018 螺栓 2 Screw19 ND**** T2314H008 螺栓 2 Screw1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 Alternator & Generator1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Alternator & Generator交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ND24A 004 T64501023 发电机 1 Alterator2 ND24A 054 T2314H005 螺栓 1 Screw3 ND24A 094 T2314H005 螺栓 1 Screw4 ND***** T74601112 支架 4 Bracket5 ND24B 127 T2314J003 螺栓12 Screw6 ND24A 008 T2314H013 螺栓 2 Screw7 ND***** T74502152 调节杆 1 Adjustment level8 ND24A 133 T2314H006 螺栓M8X45 Screw9 ND24B 136 T2314J006 平垫10X40 1 Washer10 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M8 螺母M8 Nut11 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 NutAir Compressor空气压缩机 QDH01356Air Compressor空气压缩机 QDH01356Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 QD10T 070 T3272X021 轮毂 1 Hub2 QD10T 073 T2415H213 O型圈 1 O-ring3 QD10T 076 T3117C161 齿轮 1 Gear4 QD10T 079 T2551A289 轴承 1 Bearing5 QD10T 082 T3241H011 盖板 1 Cover plate6 QD10T 085 T2314H002 螺栓 3 Screw7 QD10T 091 T3753R241 支架 1 Bracket8 QD10T 096 T2311D081 螺栓 3 Screw9 QD10T 098 T2311D560 螺栓 4 Screw1006-6TRT125K01/KA0 1Air Compressor1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 空气压缩机 QDH01356Air Compressor空气压缩机 QDH01356Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Part name图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量零件名称1 ND*** T74600123 空压机 1 AIR COMPRESSOR2 ND*** T2314J006 螺栓 1 SCREW3 ND*** T2314A604 螺母 1 NUT4 ND*** 169 T0180063A 喉箍 2 HOSE CLIP5 QD40L 010 T0470672 接头 1 CONNECTION6 QD40L 019 T3355A017 接头 1 CONNECTION7 QD40L T2411157 垫圈 1 WASHER8 QD40L T0470672 接头 2 CONNECTION9 QD40L T3355A017 接头 1 CONNECTION10 QD**** T2411157 垫圈 2 WASHER11 QD**** T0180063A 喉箍 1 HOSE CLIP12 QD**** T64601109 胶管 1 HOSEING13 QD**** T2481877A 喉箍 2 HOSE CLIP14 QD**** T74602321 胶管 2 HOSEING15 QD**** T74602322 胶管 1 HOSEING16 QD**** T64612103B 接头 1 CONNECTION17 QD30Z T64612104 锁母 118 QD20U 034 T64612105 垫片 1 WASHER19 QD10B T0206002 接头 1 CONNECTION20 QD10B T73201647 过油螺栓 2 SCREW21 QD10B T74806022 回油接头 1 CONNECTION22 QD**** T73209521 油管 1 PIPE23 QD**** T73209522 油管 1 PIPE1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 Cover Plate1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 盖板 QDH01131Cover Plate盖板 QDH01131Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 QD *** T74001209 盖板 1 COVER PLA TE2 QD *** T2314J001 螺栓 1 SCREW3 QD *** T64605001A 垫片 2 WASHERGear Drive Auxiliary Drive Option齿轮驱动/转向助力选用 QDH01131Gear Drive Auxiliary Drive Option齿轮驱动/转向助力选用 QDH01131Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 QD10B *** T4113H068A 驱动总成 1 Drive Assy2 T3751K071A 壳体 1 Housing3 GB276-82-208 轴承 1 Bearing4 T2721A537 卡簧 1 Circlip5 T3117A016A 齿轮 1 Gear6 GB276-82-106 轴承 1 Bearing7 QD10B 133 T2415H461 O型圈 1 O Ring8 QD10B 162 T2313H321 双头螺栓 1 Stud9 QD10B 164 T3254T001 双头螺栓 1 Stud10 QD10B 166 T2318A605 螺母 3 NutManifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Manifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 SB15A 010 T3777U031 进气管 1 Inducion manifold2 SB15A 016 T3688C028 垫 1 Joint3 SB15A 020 T2314J009 螺栓 6 Screw4 SB15A 022 T2314J019 螺栓 2 Screw5 SB16A 002 T3211P018 双头螺栓 4 Stud6 SB16A 003 T2313M083 双头螺栓 2 Stud7 SB16A 003 T2313M083 双头螺栓 2 Stud8 SB16A 004 T2318A634 螺母8 Nut9 SB16A 013 T3688C017 垫 1 Joint10 SB16A 014 T36862191 垫 2 Joint11 SB16A 016 T3778P001/A 排气管 1 Exhaust manifold12 SB15F 001 T3766P241 进气弯管 1 Elbow13 SB15F 031 T2314J014 螺栓 4 Screw14 SB15F 028 T3684N008 垫 1 JointManifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Manifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 SB15C 006 T3688A006 垫 1 Joint2 SB15C 007 T2674A082 增压器 1 Turbocharger3 SB15C 022 T3211P007 丝对4 Stud5 SB15C 031 T2318A634 螺母 4 Nut6 SB20K 100 T3683D006 垫 1 Joint7 SB20K 118 T2314H003 螺栓 2 Screw8 SB20K 136 T3383A024 胶管 1 Hose9 SB20K 139 T2481877 卡子 2 Clip10 SB20K 152 T3571F016D 增压器回油管 1 Oil return pipe11 SB20L 305 T3583M007 增压器进油管 1 Oil feed pipe12 SB20L 311 T36832138 垫 1 Joint13 SB20L 323 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw14 SB20L 343 T0206008 接头 1 Connection15 SB20L 344 T0576116 螺母 1 Nut16 SB20L 350 T0566007 橄榄体 1 Olive17 SB15F 004 T3383E008 胶管 1 Hose18 SB15F 007 T0180070A 喉箍 2 ClipManifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Manifolds & Air Charge Cooler进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 SB***** T33415509 垫 1 Joint2 SB***** T3688C011 垫 2 Joint3 SB***** T74707107 排气弯管 1 Elbow4 SB***** T74707108 排气弯管 1 Elbow5 SB***** T74707106 排气弯管 1 Elbow6 SB***** T74703008 排气弯管支架 1 Bracket7 SB***** T74703009 排气弯管支架 1 Bracket8 SB***** GB5783-86 螺栓M12X1.5X25 4 Screw9 SB***** GB93-87D12 弹垫12 4 Spring washer10 SB***** T2314H006 螺栓12 Screw11 SB***** T2318A633 螺母12 Nut12 SB***** GB97.1-85D12 垫 4 Washer13 SB***** T2314J003 螺栓12 Screw14 SB16D 002 T2313F059 丝对 6 Stud15 SB16A 004 T2318A633 螺母 6 NutLow Pressure Fuel System低压燃油系统 VBH01457Low Pressure Fuel System低压燃油系统 VBH01457Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 VB17C 003 T64102002A 滤清器 1 Fuel filter2 VB**** T64102003 柴滤器滤芯 23 ZE25B 311 T0650204 堵 2 Plug4 ZE25B 312 T73274309 垫圈 2 Washer5 VB17C 040 T2314J006 螺栓 2 Screw6 VB17C 070 T2318A604 螺母 2 Nut7 VB17C 220 T3818D013 支架 1 Bracket8 VB17C 295 T2314J002 螺栓 1 Screw9 VB****** T4121C031F 油管Pipe (Lift Pump to filter)10 VB****** T63201702B 油管Pipe (Filter to pump)11 VB****** T63302029 油管Pipe (Pump to filter)12 VB17N 100 T3425M006 油管 1 Pipe (Atomizer to pump)13 VB17N 118 T33225412 螺母 2 Nut14 VB17N 121 T33811112 橄榄体 2 Olive15 VB17N 148 T73217019 接头 1 Connection16 VB17N 151 T0095344A 过油螺栓 1 Nut17 VB17N 154 T73208144 密封垫 2 Nut18 V e****** T65005001A 回油管 1 Pipe19 VB17N 283 T0576113 螺母 1 Nut20 VB17N 286 T0566004 橄榄体 1 OliveBlanking Plates盖板 VBH02136Blanking Plates盖板 VBH02136Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 VB**** GB5783-86M8X20 螺栓 4 Screw2 VB**** GB93-87D8 弹簧垫圈 4 Washer3 VB**** T36856104A 垫片 1 Washer4 VB**** T63207003A 盖板 1 Cover plateCold Start System冷起动系统 WDH00033Cold Start System冷起动系统 WDH00218Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ZE25B 094 T4124E022 进气加热管 1 Pipe2 ZE25B 097 T33225412 螺母 1 Nut3 ZE25B 103 T33811112 橄榄体 1 Olive4 WD15B 010 T2666106 加热器 1 HeaterEngine Lifting发动机提升 XBH00314Engine Lifting发动机提升 XBH00314Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 XB31D 001 T74502130 吊耳 1 Left brackt2 XB31D 007 T2314J003 螺栓 3 Screw3 XB31E 004 T3654W003 吊耳 1 Left brackt4 XB31E 010 T2314J003 螺栓 2 ScrewThe Plate垫板 XBH00315The Plate垫板 XBH00315Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ND***** T73203325 垫板 1 Plate2 ND***** T74502220 支架 1 Bracket3 ND***** T2314J003 螺栓 3 Screw4 ND***** T2318A604 螺母 3 Nut5 ND***** T75701020 支架 1 Bracket7 ND***** T74502132 空调压缩机调解杆 1 Adjustment level8 ND***** T2314J005 螺栓 1 Screw9 ND***** T2318A604 螺母M10 1 Nut10 ND***** T2314H006 螺栓 1 Screw11 ND***** T2318A603 螺母M8 1 Nut12 ND***** T74502133 隔块 1 Spacer block13 ND***** GB97.1-85D8 垫圈8 2 Washer14 ND***** T2314H019 螺栓 1 ScrewWater temperature sensor水温传感器 ZJH00440Water temperature sensor水温传感器 ZJH00440Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ZL33Q 025 T65204003B 水温传感器 1 Sensor2 ZZ*** 001 T62204003 放水阀 1 Water drain valve3 ZL*** T64403007 放水管 1 Water drain pipe4 ZL*** T64403008 支架 1 Bracket5 ZL*** T0180063 喉箍 1 Clip6 ZL*** 001 T32161114 水堵 1 Plug7 QD30Z 003 T0650594 螺堵 1 PlugMountings支撑 ZCH00878Mountings支撑 ZCH00878Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 zz****** T2313C125 丝对8 Stud2 zz****** GB6170-86M16 螺母8 Nut3 zz****** GB97.1-85D16 平垫16 Washer4 zz****** GB93-87D16 弹簧垫圈16 Spring washerJoints & Gaskets-Top Service Kit垫及垫片(顶部维修组件) SACA0140Joints & Gaskets-Top Service Kit垫及垫片(顶部维修组件) SACA0140Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 TU5LT0179 顶部垫片 1 Top Joint2 T3681H208 气缸盖垫 1 Joint3 T3681C001 气缸盖罩垫 1 Joint4 T3685R005 垫 1 Joint5 T3685F005 垫 1 Joint6 T3684N008 垫 1 Joint7 T3688C017 排气管垫 1 Joint8 T36862191 排气歧管垫 2 Joint9 T3684A004 垫 1 Joint10 T36832138 垫 1 Joint11 T3683D006 垫 1 Joint12 T3683N004 垫 1 Joint13 T3688A006 增压器到排气管垫 1 Joint14 T0921173 喷油器垫圈 6 Seal15 T33817117 气门油封12 Seal16 T33813131 密封 6 Seal17 T3688C028 进气歧管垫 1 JointJoints & Gaskets-Bottom Service Kit垫及垫片(底部维修组件) SACA0140Joints & Gaskets-Bottom Service Kit垫及垫片(底部维修组件) SACA0140Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 TU5LBO158 底部垫片 1 Bottom Joint2 T3681M007 油底壳垫 1 Joint3 T3688X008 油冷器罩垫 1 Joint4 T3681P009 正室齿轮室垫 1 Joint5 T3681P034 垫 1 Joint6 T3686T006 垫 1 Joint7 T36856104A 垫 1 Joint8 T36833152 垫 1 Joint9 T3683D006 垫 1 Joint10 T3683H006 垫 1 Joint11 T2415H461 O型密封圈 1 ORing21。

Automotive engine camshaftBrief introductionThe camshaft is a part of the piston engine. Its role is to control the opening and closing operation of the valve. Although the camshaft rotational speed in a four-stroke engine is a half of the crankshaft (the same as the camshaft rotational speed in a two-stroke engine with the crankshaft), but usually it is still very high speed, but also need to withstand the large torque, so the design right demanding camshaft in terms of strength and support material is generally a special cast iron, occasionally using forgings. Valve motion law related to engine power and operation characteristics, the design in the design process of the engine camshaft occupies a very important position.StructureThe main body of the camshaft is the same as the one with the cylinder length of the cylindrical rod. The above sets have several cam for driving the valve. One end of the camshaft camshaft bearing support and the other end is connected to the drive wheels.Cam side was egg-shaped. The design aims to ensure the the cylinder sufficient air intake and exhaust, specifically, within the shortest possible time to complete the valve opening and closing movements. In addition, taking into account the durability of the engine and the smoothness of operation, the valve can not be generated due to the deceleration process of opening and closing movements too much too large the impact of serious wear and tear of the valve, otherwise it will cause an increase in noise or other serious consequences. Therefore, the cam and the power of the engine torque output as well as the operation of the ride there is a direct relationship.Generally inline engine, a cam corresponding to a valve V-type engine or horizontal opposed type engine, every two valves share a cam. The rotary engine the valveless with gas engine because of its special structure, does not need to camPositionIn the long period of time, the bottom-mounted camshaft in an internal combustion engine is most common. Typically such engines, the valve is located in the top of the engine camshaft machine, i.e., so-called the OHV (Over Head V alve, OHV) engines. Usually camshaft located on the side of the crankcase, through the gas distribution agencies (such as tappet, push rod, rocker, etc.) valve control. Bottom-mounted camshaft general also called side-mounted camshaft. Far distance valve, and each cylinder is usually only two valves in such an engine camshaft, so the speed is usually slower, ride comfort is poor, the output power is also relatively low. However, the engine output torque and low-speed performance of this structure is relatively good, relatively simple structure and easy maintenance.Now most of the production car's engine is equipped with overhead camshaft. The overhead camshafts structure closer to the camshaft valve, to reduce the kinetic energy of the waste causedby the bottom-mounted camshaft due to the larger distance between the camshaft and the valve shuttle. Overhead camshaft of the engine valve opening and closing action is relatively rapid, and hence higher speed, and the smooth running is also better. The engine of the the overhead camshafts structure appeared earlier the SOHC (Single Over Head Cam, overhead single camshaft) engine. This engine is only installed at the top of a camshaft, and therefore generally only two to three valves of each cylinder (the intake air a to two exhaust), the high-speed performance has been limited. Technology updates DOHC (Double Over Head Cam, double overhead camshaft) engine, this engine with a two camshafts per cylinder can be installed four to five valves (intake two to three, Pai gas two), high-speed performance significantly improved, but at the same time the low-speed performance will be affected to some degree, the structure will be complicated and difficult to repair.ClassificationAccording to the the camshaft number of how many, can be divided into single overhead camshaft (SOHC) and double overhead camshaft (DOHC), two kinds. The single overhead camshaft camshaft is only one camshaft, double overhead camshaft is two, this is too straightforward explanation.The single overhead camshaft with a camshaft in the cylinder head, direct drive into the exhaust valve, it has a simple structure, suitable for high-speed engine. Generally used in the past side camshaft, the camshaft in the cylinder side, is driven directly by a timing gear. The valve lifter to the rotation of the camshaft is converted into reciprocating motion of the valve must be used to transfer power. Thus, more parts of the reciprocating motion, the inertial mass, is not conducive to high-speed movement of the engine. Moreover, the slender tappet has a certain degree of flexibility, prone to vibration, accelerated component wear, even the valve control is lost.DOHC cylinder head equipped with two camshafts, one is used to drive the intake valve, the other for driving the exhaust valve. Double overhead camshaft camshaft and valve spring design less demanding, especially for the hemispherical combustion chamber of the valve V-shaped configuration, but also facilitate and used in conjunction with four-valve gas distribution agencies.FaultCamshaft common faults including abnormal wear and tear, abnormal wear of the symptoms often first appear before the occurrence of abnormal sound as well as fracture, abnormal sound and fracture.(1) Camshaft almost at the end of the engine lubrication system, lubrication situation is not optimistic. If the oil pump is too long and so insufficient oil pressure or the lubricants Road blockage caused by lubricating oil can not reach the camshaft bearing cap fastening bolts tightening torque caused by excessive oil can not enter the the camshaft gap will causing abnormal wear of the camshaft.(2) the abnormal wear of the camshaft causes the gap increases between the camshaft bearing, the camshaft movement occurs when the axial displacement, resulting in abnormal noise. Abnormal wear will lead to increased gap between the drive cam with hydraulic tappets, camcombined with hydraulic tappets will collide, resulting in abnormal noise.(3) camshaft sometimes fracture and other serious fault, common causes of hydraulic tappet cracked or severely worn, serious poor lubrication the camshaft poor quality and camshaft timing gear rupture.(4) In some cases, the failure of the camshaft is man-made causes, in particular the maintenance of the engine camshaft not correct disassembly. Such as demolition of the camshaft bearing caps with a hammer strength knocking or prying with a screwdriver, or install the bearing cap installed the wrong position does not match the result in the bearing cap and bearing, or bearing cover the fastening bolt tightening torque is too large. Install bearing cap should pay attention to the direction of the arrow and the position number marked on the surface of the bearing cap, and in strict accordance with the provisions of torque using the torque wrench tighten the bearing cap fastening bolts.RefitIn order to enhance the power of the engine, some converted stores a modified camshaft engine face lift high angle camshaft (Hi-camshaft CAM) is a common form of modified method. This modification operation is not complicated, but because of the lack of understanding of some modification cam on the camshaft angle and works so that the modified effect is not obvious even lead to the deterioration of the performance of the engine.High angle camshaft relative to ordinary camshaft cam angle of about 240°, high angle camshaft cam angle can often reach over 280°. The large angle of the camshaft can extend the valve open time, increase the valve lift, the intake valve and the exhaust valve open as early and late off, so that more air into the cylinder, in order to improve the engine, the power of the high speed output. Should choose for civilian vehicles, modified cam camshaft angle 278, will be a significant increase in working an angle greater than 278°camshaft valve overlap angle, so that the power of the engine high speed improve a lot, but engine cylinder seal is not good at low speed and cause the idling serious jitter or even turn off, so that the vehicle can not adapt to everyday use, and can only be used for competition purposes.Production technologyThe camshaft is one of the key parts of the engine, the hardness of the camshaft peach apical and white layer depth is to determine the key technical indicators camshaft life and engine efficiency. , Should be considered to ensure that the cam has a sufficiently high hardness and a fairly deep white layer premise journal does not appear high carbide, so that it has a better cutting performance.Currently, the main method of domestic and foreign production camshaft: steel forging blank by cutting the cam peach tip martensitic layer formed some of the high-frequency quenching process. The end of the 1970s, Germany and France have developed a new camshaft argon arc remelting process; hardened cast iron camshaft otherwise dominated by the United States; chilled cast iron camshaft mainly to Japan and France; well cam parts of the Cr-Mn-Mo alloy coatings casting surface alloying production.汽车发动机凸轮轴简介凸轮轴是活塞发动机里的一个部件。

中文English轮椅升降机wheel chair lift图例legend工位station吊运装置overhead hoist更衣室restroom1号厂房工艺布置方案图proposal of the Plant I layout 合笼mate底盘平移台chassis shuttle车辆转移台bus transfer前围角板front wall angle cover后围侧板rear wall side cover保险杠bumper三类底盘three type chassis左侧围应力蒙皮R/S stretching skin (road side)中涂floating coat拼装台collector切割轮口wheel -arch cutting内饰trim线束harness返工re-doing轮罩护板wheel house发车前准备pre-delivery举升hoist小批量产品be pilot2 套two kits配电站power transformer substation裙板skirt发动机托架engine holding frame诊断报警系统diagnosis and alarming system互换性interchangeability缩微图纸microfiche files总装final assembly磷化phosphating仪表板dash board切齐trimming结构完整性structure integrity自动愈合的防腐材料self-healing corrosion preventative material 长途客车inter-city bus改装厂refitting factory遮阳板sun visor随车工具tool box钢化玻璃toughened grass异形钢管special steel pipe全天候空调系统full range A/C强制通风ram-air ventilation停机时间downtime无公害柴油clean diesel宽敞悬臂式座椅roomy cantilevered seat防滑地板no-skid floor织物纹里铝合金textured aluminum extrution 爬坡能力grade ability排水阀drain valve除湿器moisture ejector怠速时at idle琴式驱动桥banjo type drive axle通风口duct恒温控制thermostatic control平衡水箱surge tank变光开关simmer switch消音器muffler防破坏vandal resistant聚碳化透镜poly-carbonate len镀锌板galvanized plate搭接lap亮丽的外表smart apperance隐藏式固定concealed fastening水洼ponding发动机中置式客车bus with under floor engine组合式客车车身modular bus body薄壳式结构shell construction衬垫pad空气导流板air deflector搁梁shelf beam腰梁waist rail梭梁stabilizing beam腰带式安全带diagonal safety belt压条trim strip嵌条insertion strip翼板fender斜撑bracing piece转向盘回正性试验test of steering wheel returnability转向盘转角脉冲试验steering wheel impulse input test转向盘转角阶跃输入试验steering wheel step input or transient state yaw response test极限侧向加速度试验limiting lateral acceleration test汽车平顺性随机输入行驶试验automobile ride random input running test汽车平顺性单脉冲输入行驶试验automobile ride single pulse input running test汽车悬挂系统固有频率与阻尼比的测定试验measurement of natural frequency and damping raito of suspension功率突然变化影响试验test of effect of sudden power change汽车专业英语词汇大全收油门后控制试验test of control at breakway横风稳定性试验test of crosswind stability反冲试验kick-back test轮胎爆破响应时间试验test of burst response of tyre绕过障碍物试验obstacle avoidance test移线试验lane change testJ型转弯试验test of J turn频率响应时间试验frequency response test瞬态响应时间试验transient response test阶路响应时间试验step response test脉冲响应试验pulse response test静态操舵力试验static steering effort test悬架举升试验jack-up test of suspension耐翻倾试验test of overturning immunity轮辋错动试验rim slip test风洞试验wind tunnel test制动稳定性试验test of braking stability最小转弯直径试验minimum turning diameter test操舵力试验steering effort test类型type发动机engine内燃机intenal combusiton engine动力机装置power unit汽油机gasoline engine汽油喷射式汽油机gasoline-injection engine火花点火式发动机spark ignition engine压燃式发动机compression ignition engine往复式内燃机reciprocating internal combustion engine 化油器式发动机carburetor engine柴油机diesel engine转子发动机rotary engine旋轮线转子发动机rotary trochoidal engine二冲程发动机two-stroke engine四冲程发动机four-stroke engine直接喷射式柴油机direct injection engine间接喷射式柴油机indirect injection engine增压式发动机supercharged engine风冷式发动机air-cooled engine油冷式发动机oil-cooled engine水冷式发动机water-cooled engine自然进气式发动机naturally aspirated engine煤气机gas engine液化石油气发动机liquified petroleum gas engine 柴油煤气机diesel gas engine多种燃料发动机multifuel engine石油发动机hydrocarbon engine双燃料发动机duel fuel engine热球式发动机hot bulb engine多气缸发动机multiple cylinder engine对置活塞发动机opposed piston engine对置气缸式发动机opposed-cylinder engine十字头型发动机cross head engine直列式发动机in-line engine星型发动机radial engine筒状活塞发动机trunk-piston engine斯特林发动机stirling engine套阀式发动机knight engine气孔扫气式发动机port-scavenged engine倾斜式发动机slant engine前置式发动机front-engine后置式发动机rear-engine中置式发动机central engine左侧发动机left-hand engine右侧发动机right-hand engine短冲程发动机oversquare engine长冲程发动机undersquare engine等径程发动机square engine顶置凸轮轴发动机overhead camshaft engine双顶置凸轮轴发动机dual overhead camshaft engine V形发动机V-engine顶置气门发动机valve in-head engine侧置气门发动机side valve engine无气门发动机valveless engine多气门发动机multi-valve engine卧式发动机horizontal engine斜置式发动机inclined engine立式发动机vertical engineW形发动机w-engineI形发动机I-engineL形发动机L-engineF形发动机F-engine性能performance二冲程循环two-stroke cycle四冲程循环four-stroke cycle狄塞尔循环diesel cycle奥托循环otto cycle混合循环mixed cycle定容循环constant volume cycle工作循环working cycle等压循环constant pressure cycle理想循环ideal cycle热力循环thermodynamic cycle冲程stroke活塞行程piston stroke长行程long stroke上行程up stroke下行程down stroke进气行程intake stroke充气行程charging stroke压缩行程compression stroke爆炸行程explosion stroke膨胀行程expansion stroke动力行程power stroke排气行程exhaust stroke膨胀换气行程expansion-exchange stroke 换气压缩行程exchange-compression stroke汽车专业英语词汇大全止点dead center上止点top dead center(upper dead center)下止点lower dead center(bottom dead center) 上止点前budc(before upper dead center)上止点后atdc(after top dead cetner)下止点前bbdc(before bottom dead center)下止点后abdc(after bottom dead center)缸径cylinder bore缸径与行程bore and stroke空气室energy chamber气缸余隙容积cylinder clearance volume燃烧室容积combustion chamber volume气缸最大容积maximum cylinder volume压缩室compression chamber排气量displacement发动机排量engine displacement活塞排量piston swept volume气缸容量cylinder capacity单室容量single-chamber capacity容积法volumetry压缩比compression ratio临界压缩比critical compression ratio膨胀比expansion ratio面容比surface to volume ratio行程缸径比stroke-bore ratio混合比mixture ratio压缩压力compression pressure制动平均有效压力brake mean effective pressure(bmep) 空燃比air fuel ratio燃空比fuel air ratio燃料当量比fuel equivalence ratio扭矩torque单缸功率power per cylinder升功率power per liter升扭矩torque per liter升质量mass per liter减额功率derating power输出马力shaft horsepower马力小时,马力时horsepower-hour总马力gross horse power总功率gross power净功率net power燃油消耗量fuel consumption比燃料消耗率specific fuel consumption空气消耗率air consumption机油消耗量oil consumption有效马力net horse power额定马力rated horse power马力重量系数horsepower-weight factor制动功率brake horse power制动热效率brake thermal efficiency总效率overall efficiency排烟极限功率smoke limiting horsepower功率曲线power curve机械损失mechanical loss机械效率mechanical efficiency有效热效率effective thermal efficiency充气系数volumetric efficiency过量空气系数coefficient of excess air适应性系数adaptive coefficient扭矩适应性系数coefficient of torque adaptibility 转速适应性系数speed adaptive coefficient强化系数coefficient of intensification校正系数correction factor换算系数conversion factor活塞平均速度mean piston speed发动机转速engine speed (rotational frequency)怠速转速idling speed经济转速economic speed起动转速starting speed最低稳定工作转速lowest continuous speed with load 最大扭矩转速speed at maximum torque最高空转转速maximum no load governed speed调速speed governing超速overspeed怠速idling转速波动率speed fluctuation rate工况working condition(operating mode)额定工况declared working condition变工况variable working condition稳定工况steady working condition空载no-load全负荷full load超负荷overload部分负荷part load充量(进气)charge旋转方向direction of rotation顺时针clockwise逆时针counter-clockwise左转left-hand rotation右转right-hand rotation外径major diameter中径pitch diameter内径minor diameter径向间隙radial clearance发动机性能engine performance加载性能loading performance起动性能starting performance汽车专业英语词汇大全加速性能acceleration performance动力性能power performance排放性能emission performance空转特性no load characteristics负荷特性part throttle characteristics调速特性governor control characteristics万有特性mapping characteristics稳定调速率steady state speed governing rate 气缸体和气缸盖cylinder block and head气缸体cylinder block整体铸造cast inblock (cast enblock)发动机罩engine bonnet气缸体加强筋engine block stiffening rib 气缸cylinder(转子机)缸体stator缸径cylinder bore气缸体机架cylinder block frame气缸盖cylinder head配气机构箱valve mechanism casing气缸体隔片cylinder spacer气缸盖密封环cylinder head ring gasket 气缸盖垫片cylinder head gasket气缸套cylinder liner(cylinder sleeve)干式缸套dry cylinder liner湿式缸套wet cylinder liner气缸水套water jacket膨胀塞expansion plug防冻塞freeze plug气缸壁cylinder wall环脊ring ridge排气口exhaust port中间隔板intermediate bottum导板guideway创成半径(转子机)generating radius缸体宽度(转子机)operating width机柱column燃烧室combustion chamber主燃烧室main combustion chamber副燃烧室subsidiary combustion chamber预燃室prechamber涡流燃烧室` swirl combustion chamber分开式燃烧室divided combustion chamber涡流式燃烧室turbulence combustion chamber半球形燃烧室hemispherical combustion chamber浴盆形燃烧室bathtub section combustion chamberL形燃烧室L-combustion chamber楔形燃烧室wedge-section combustion chamber开式燃烧室open combustion chamber封闭喷射室closed spray chamber活塞顶内燃烧室piston chamber爆发室explosion chamber燃烧室容积比volume ratio of combustion cahmber燃烧室口径比surface-volume ratio of combustion chamber通道面积比area ratio of combustion chamber passage 曲轴箱通气口crankcase breather凸轮轴轴承座camshaft bearing bush seat定时齿轮室罩camshaft drive(gear)cover曲轴箱检查孔盖crankcase door。
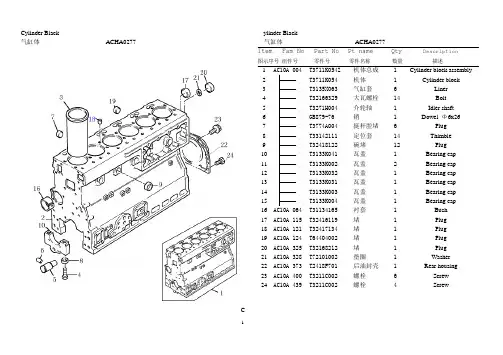
Cylinder Black气缸体ACHA0277Cylinder Black气缸体 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Pt name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10A 004T3711K054Z 机体总成1Cylinder block assembly2 T3711K054 机体1Cylinder block3 T3135X063 气缸套6Liner4 T32166329 大瓦螺栓14Bolt5 T3271H004 介轮轴1Idler shaft6 GB879-76 销1Dowel Φ6x267 T3774A004 挺杆腔堵6Plug8 T33142111 定位套14Thimble9 T32418122 碗堵12Plug10 T3133K041 瓦盖1Bearing cap11 T3133K002 瓦盖2Bearing cap12 T3133K032 瓦盖1Bearing cap13 T3133K031 瓦盖1Bearing cap14 T3133K003 瓦盖1Bearing cap15 T3133K004 瓦盖1Bearing cap16 AC10A 064T31134165衬套1Bush17 AC10A 115T32416119堵1Plug18 AC10A 121T32417134堵1Plug19 AC10A 124T64404002堵1Plug20 AC10A 325T32168212堵1Plug21 AC10A 328T72101002垫圈1Washer22 AC10A 373T2418F701后油封壳1Rear housing23 AC10A 400T3211C002螺栓6Screw24 AC10A 439T3211C002螺栓4Screw正时齿轮及凸轮轴ACHA0277正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 AC10B 037 T2314H003 螺栓 8 Screw2 AC10B 040 T2314H034 螺栓 4 Screw3 AC10B 277 T3716M091B 前盖1 Front cover 4 AC10B 277 T2418F436 密封圈 1 Seal 5 AC10B 316 T2314H005 螺栓 9 Screw 6 AC10B 320 T2314H004 螺栓 1 Screw7 AC10B 325 T2314H034 螺栓 1 Screw8 AC10B 350 T2314H034 螺栓 2 Screw 9 AC10B 436 T2314H013 螺栓 6 Screw 10 AC10B 508 T62204001 检查盖 1 Inspection cover11 AC10B 508 T62004002 垫 1 Joint 12 AC10B 511 T2314F036 螺栓 4 Screw 13 AC10B 560 T3781N042 减震垫 1 Damping Joint 14 AC10B 561 T3781N043 隔音板 1 Noiseshield Plate15 AC10B 563 T2314F003 螺栓 2 Screw 16 AC10J 004 T0500012 键 1 Key 17 AC10J 007 T3117C061 齿轮 1 Gear 18 AC10J 013 T33426161A 轮毂1 Hub 19 AC10J 031 T4111A013齿轮组件 1 Gear assy. 20 T3117L061 齿轮 1 Gear 21T0050345衬套 2 Bush 22 AC10J 054 T3241H009 板 1 Plate 23 AC10J 069 T2314J010螺栓3Screw正时齿轮及凸轮轴ACHA0277正时齿轮及凸轮轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述24AC10J 129 T4111A008齿轮 1 Gear 25 T3117C041 齿轮 1 Gear 26 T2511437衬套 1 Bush 27 AC10J 144 T33123125 垫圈 1 Washer 28 AC10J 150 T2722A206 卡簧 1 Circlip 29 AC10J 183 T33153121 盖板 1 Cover plate 30 AC10J 189 T2116053 销子 1 Dowel 31 AC10J 195 T0500012键 1 Key 32 AC10J 201 T3117L023 齿轮 1 Gear 33 AC10J 207 T2314J606 螺栓 1 Screw 34 AC10J 214 T3321A003 垫圈 1Washer 35 AC10J 180 T31416308 凸轮轴1Camshaft 36 AC10B 001 T3681P009 垫 1 Joint 37 AC10B 274 T3681P034 垫 1 Joint 38 AC10B 010 T3716C133A正时齿轮室 1 Timing caseCrankshaft Pistons & Connecting Rods曲轴,活塞及连杆ACHA0277Crankshaft Pistons & Connecting Rods曲轴,活塞及连杆 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述 1 AC10C 005T3131H022曲轴 1 Crankshaft 2 AC10C 044 T3111V005 轴瓦 1 Bearing 3 AC10C 046 T3111V014 轴瓦 1 Bearing 4 AC10C 049 T3111V005 轴瓦 4 Bearing 5 AC10C 052 T3111V014 轴瓦 4 Bearing 6 AC10C 055 T3111X011 轴瓦 1 Bearing 7 AC10C 058 T3111X005 轴瓦 1 Bearing 8 AC10C 061 T3111V005 轴瓦 1 Bearing 9 AC10C 064 T3111V014 轴瓦 1 Bearing10 AC10C 067 T31137551 止推片 2 Thrust washer 11AC10C 070 T31137561止推片2 Thrust washer12 AC10D 005 T3135J181ETC 活塞 6 Piston 13 AC10D 008 T4181A026 活塞环组件 6 Piston ring assy. 14 T3136J051 气环 1 Compression ring 15 T3136X021 气环 1 Compression ring 16T3137N021 油环 1 Scrape ring 17 AC10D 019 T3313T005 活塞销 6 Piston pin 18 AC10D 022 T2721332 卡簧 12 Circlip 19 AC10D 028 T4115C211 连杆组件 6 Connecting rod assy. 20 T3133R001 连杆 1 Connecting rod21 T3133V001 盖 1 Cover 22 T32186142 螺栓 2 Screw 23 T2135A001 定位销 2 Thimble 24T3112E005 衬套 1 Bush 25 AC10D 055T31132011轴承12BearingCylinder Head气缸盖 ACHA0277 Cylinder Head气缸盖 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AC10E 004T3681H208A缸盖垫1JointAC10E 004T72505009 缸盖垫1Joint2 AC10E 005TC3712L042Z缸盖总成1Cylinder head assy.3 T3712L042缸盖1Cylinder head4 T3342E003进气阀座6Inlet valve seat5 T3314A122排气阀座6Exhaust valve seat6 T2431154堵2Plug7 T0650586 堵6Plug8 T0650203堵1Plug9 T2411157垫圈1Washer10 T0650710碗堵3Plug11 T32417156出沙孔堵6Plug12 AC10E 037T3343F041气门导管6Guide13 AC10E 040T3343J021气门导管6Guid14 AC10E 064T2114A046定位套2Thimble15 AC10E 100T32166219螺栓12Screw16 AC10E 103T32166221螺栓18Screw17 AC10E 106T32166222螺栓2Screw2摇臂轴ACHA0277摇臂轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 AC10F 001 T3142L072 进气阀 6 Inlet valve 2 AC10F 004 T33817117 密封套 6 Seal3 AC10F 007 T31745122 弹簧 6 Spring4 AC10F 010 T31744133 弹簧 6 Spring 5AC10F 013 T33415118 垫圈 6 Washer 6 AC10F 016 T33424107 进气阀弹簧座 6V alve cap 7 AC10F 019 T33173108 气门锁夹 12 Cotter 8 AC10F 025 T3142A051 排气阀 6 Exhaust valve9 AC10F 028 T33817117 密封套 6 Seal 10 AC10F 031 T31745122 弹簧 6 Spring 11 AC10F 034 T31744133 弹簧 6 Spring 12 AC10F 037 T33415118 垫圈 6 Washer 13 AC10F 043 T33424107 排气阀弹簧座 6V alve cap 14 AC10F 046 T33173108 气门锁夹 12 Cotter 15 AC10F 052 T2313H331 双头螺栓 4 Stud 16 AC10F 058 T2318A605 螺母 4 Nut 17 AC10F 061 T2314J607 螺栓 2 Screw 18 AC10F 070 T3818X901 支架 6 Bracket 19 AC10F 082 T31411147 摇臂轴 1 Rocker shaft20 AC10F 091 T0650507 堵 2 Plug 21AC10F 103 T4115R306 左摇臂组件 6 Rocker level LH 22 AC10F 109 T4115R305 右摇臂组件 6 Rocker level RH23 AC10F 127 T32114145螺栓12Screw摇轴轴ACHA0277摇臂轴 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述 24 AC10F 130 T0576052 螺母 12 Nut 25 AC10F 133 T31744123 弹簧 4 Spring 26 AC10F 136 T31743108 弹簧 2 Spring 27 AC10F 163 T33117434 垫圈 2 Washer 28 AC10F 166 T0170151卡簧2 Circlip 29 AC10J 239 T3142U031 挺柱 12 Tappet 30 AC10J 257 T31434307 推杆 12 Push rod 31 AC20N 011 T3775E012 接头 1 Connection 32 AC20N 020 T2233022螺栓1 Screw 33 AC20N 023 T33811113 橄榄体 1 Olive 34 AC20N 025 T3311K015 垫片2 Washer润滑油泵ACHA0277润滑油泵 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 AC20B 007 T4132F057 机油泵 1 Lub.Oil Assy.T3771M085 泵体 1 Body T3753R101 盖板 1 Cover plate T2314C044 螺栓 4 Screw T3117A038 齿轮 1 Gear T2511852 衬套 1 BushT2488C509转子 1 Rotor 2AC20B 175 T2314H004 螺栓 2Screw 3 AC20B 179 T2314H002 螺栓 1 Screw 4 AC20D 046 T4138A033限压阀 1 Relief valve 5 T32712726 柱塞 1 Plunger 6 T31744151 弹簧 1 Spring 7 T32712111 弹簧座 1 Seat 8 T2721130 卡簧 1 Circlip 9T3775L044泵体 1 Body 10 AC20D 127 T2314K161 螺栓 2 Screw 11 AC20G 001 T3571C045油管 1 Oil pipe 12 T3617A005 法兰 1FlangeT2415H496 O 型圈 O Ring 14T3571C046管1 Pipe 15 AC20G 076 T2314H004 螺栓2 Screw 16 AC20G 084 T2314H004 螺栓2 Screw 17AC20L 456 T3861A027 冷却喷嘴6 Cooling Jet 18T3317A009 喷嘴1Nozzle润滑油泵ACHA0277润滑油泵 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述19 AC20L 500 T4138A017 冷却喷嘴阀 6 Cooling Jet V alve20 T33537008 阀体 1 Body 21 T3174A004 弹簧 1 Spring 22 T2538753球1Ball 23 T3271A003 座1 RetainerFuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Fuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AF**** T73208265 喷油泵 1 Drive gear2 AF**** T3117L113G 齿轮 1 Fuel pump3 AF**** T33828108A 垫 2 Joint4 AF**** T3821D014A 支架 1 Bracket5 AF**** T3821A014B 支架 1 Bracket6 AF**** T2314J002 螺栓M10X20 2 Screw7 AF**** T2314J003 螺栓M10X25 2 Screw8 AF**** T2131A008A 垫圈 1 Washer9 AF**** T2314H005 螺栓M8X30 1 Screw10 AF**** Q1201030F3S 双头螺柱 4 Stud11 AF**** GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 4 Nut12 AF**** GB93-87D10 垫圈10 4 Washer13 AF**** T63806001B 喷油泵润滑油管 1 Lubricating oil pipe14 AF17M 002 T4184K012F 油管 1 High pressure pipe15 AF33G 030 T4126K081B 补偿管 1 Compensating pipe16 AF33G 041 T0201047 弯管头 1 Connection17 AF**** T33225412 螺母 1 Nut18 AF**** T33811112 橄榄体 1 Olive19 AF17N 001 T3558X039 油管 1 Oil return pipe20 AF17N 034 T3218R005 过油螺栓 5 Oil-pass screw21 AF17N 043 T3355V002 过油螺栓 1 Oil-pass screw22 AF17N 049 T2411101 垫圈12 Washer23 QD30Z001 T3355M005B 三通接头 1 Connection24 QD30Z002 T0920155 垫片 2 WasherFuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Fuel Injection Equipment燃油喷射系统 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 AF17E 001 T63301004 喷油器总成 6 Atomizer assy.2 AF17E 004 T3662K002 压板 6 Clamp3 AF17E 008 T2314H006 螺栓12 Screw4 AF17E 007 T0921173 垫圈 6 Washer5 AF17E 037 T33813131 密封圈6 Seal6 AF17E 035 T33813129 隔圈 6 SpacerFlywheel Hosing飞轮壳 CDH00865Flywheel Hosing飞轮壳 CDH00865Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 CD****T73639002飞轮壳1Flywheel housing2 CD****T36843154密封条1Seal3 CD****T73631005盖板1Cover plate4 CD****GB5783-86M6X10螺栓2Screw5 CD****GB93-87D6弹簧垫圈62Washer6 CD30A T2314J204飞轮壳螺栓6Screw7 CD30A T2314J607螺栓2Screw8 CD30A T0350025销子2Dowel9 CD30A GB5783-86M12X45 飞轮壳螺栓2Screw10 CD30A GB93-87D16 弹簧垫圈 6 Washer11 CD30A GB93-87D12 弹簧垫圈 2 Washer1006-6TRTK01/KA01 飞轮及启动齿圈DDH01188飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 DD30B 004 T73639100K1 飞轮部 1 Flywheel assy.2 T73639001 飞轮 1 Flywheel 3T31162121B齿圈 1 Starter ring 4 DD30B 019 T2185103 飞轮螺栓 10Screw 5 DD30B 031 T33117127 垫圈10Washer 6 DD****GB/T276-94-6304-2Z 轴承6205 1Bearing1006-6TRTN01/NA01飞轮及启动齿圈DDH01188飞轮及启动齿圈 DDH01188Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 DD30B 004 T73639100 飞轮部 1 Flywheel assy.2 T73639001 飞轮 1 Flywheel 3T31162121齿圈 1 Starter ring 4 DD30B 019 T2185103 飞轮螺栓 10Screw 5 DD30B 031 T33117127 垫圈10Washer 6 DD****GB/T276-94-6304-2Z 轴承6205 1BearingGenerator启动电机EDGenerator启动电机 EDItem Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 ED**** T2313C077 双头螺栓 3 Stud2 ED**** GB6170-86M10 螺母3 Nut 3 ED**** GB93-87-10 弹簧垫圈 3 Spring washer4 ED****T63701007起动电机1GeneratorFan Drive风扇驱动装置 FBH00001Fan Drive风扇驱动装置 FBH00001Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 FB10B *** T4113H052 风扇驱动支架 1 Bracket2 FB10B *** T2314J014 螺栓 4 Screw3 FB10B *** T63906002 皮带轮 1 Pulley4 FB10B 034 T74402030 皮带 2 Belt5 MD22B T64406012 风扇 1 Fan6 MD22B T3748W241 隔圈 1 Extention7 MD22B 014 T2314H020 螺栓 4 Screw8 MD22B 014GB93-87D8 垫圈8 4 WasherLubricating Oil Sump润滑油底壳GBH01372Lubricating Oil Sump GBH01372 润滑油底壳Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 GB10A 025 T3627P024 桥架 1 Bridge piece2 GB10A 035 T2311D039螺栓 2 Screw 3 GB20A 043 T2431A016 堵 1 Plug 4 GB20A 052 T32186405 堵 2 Drain plug 5 GB20A 059 T2415715 O 型圈 2 O Ring 6 GB20A 088 T3681M007 油底垫 1 Joint 7 GB20A 001 T73803103A 油底 1Oil sump 8 GB****GB5783-86M16X45 螺栓 6Screw 9 GB20A 200 T2314H006A 螺栓 2 Screw 10 GB20A 205 T2314H008A 螺栓 7 Screw 11 GB20A 208 T2314H009A 螺栓 4 Screw 12 GB20A 211 T2314H012A 螺栓 5 Screw 13 GB20A 200 T2314H023A螺栓 6 Screw 14 GB20A 205 T2314H026A 螺栓 4 Screw 15 GB20F 013T3575K006吸油管 1 Suction pipe16 GB20F 025 T3683H005 垫 1 Joint 17 GB20F 034 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw 18 GB20F 055 T2314H002 螺栓 1 Screw 19 GB33V 004 T3577A125 油尺管 1 Dipstick tube20 GB33V 022 T33812116 橄榄体 1 Clive 21 GB33V 130 T3178C076 油尺 1 Dipstick22 ZZ****** T76001041 左支脚 1 23 ZZ****** T76001042 右支脚 1 24ZZ******T73802112过渡板1Cover Plate盖板 ZJH00440Cover Plate盖板 ZJH00440Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ZZ23F 004 T0650586 堵 1 Plug2 HB10B 586 T3617A001 板 1 Plate3 HB10B 586T3683H006 垫 1 Washer4 HB10B 589 T2314H003 螺栓 2 Screw5 HB10B 220 T74001002 加油口 1 Filler6 HB10B 220 T74001003 加油口盖 1 Filler cap7 HB10B 583 T3683H006 加油口垫 1 Joint8 HB10B 241 T2314H010 螺栓 1 Screw9 HB10B 241 T2314H007 螺栓 1 Screw10 HB10B GB1235-76D38X3.1 O型圈 1 O ring11 HB****GB93-87D8 垫圈8 2 WasherCylinder Head Cover气缸盖罩HBH02617Cylinder Head Cover气缸盖罩 HBH02617Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 HB10G 001 T3681C001 垫1 Joint2 HB10G 006 T3718X717 缸盖罩(总成) 1 Cylinder head cover3 HB10G 040 T3274A003 螺母4 Nut 4 HB10G 042 T0920009 垫圈 4 Washer5 HB10G 043 T33817135 密封垫 4Seal6 HB10G 142 T3381J002 密封圈1O ring 7 HB10G 145 T3781A003 加油口盖 1 Oil filler cover 8 HB10G 146 T74001211 油气分离器 1 Oil air separator9 HB10G 147 T74001212 支架 1Bracket 10 HB10G 148 T2314H002 螺栓 2 Screw 11 HB10G 149 T2318A603 螺母 2 Nut 12 HB10G 150 T74001214 胶管 1Hose 13 HB10G 151 T2481877A 卡子 3Clip 14 HB10G 152 T73802115 胶管 1 Hose 15 HB10G 153 T0180063A 卡子 2 Clip 16 HB10G 154 T74001215 胶管 1 Hose 17 HB10G 156 T73802114 接头 1 Connection 18 HB10G 157 T73802101 垫圈 1 Washer 19 HB10G 159 T73802103 铰接螺栓 1 Screw 20 HB15D 443 T36241123 支架 1 Bracket 21 HB20K 001 T3571C014 油管 1 Oil pipe 22HB20K 004 T36833152 垫 1 Joint 23 HB20K 007 T2314H003 螺栓 2 ScrewLubricating Oil Filter润滑油滤清器JBH01149Lubricating Oil Filter润滑油滤清器 JBH01149Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 JB20C 016 T64101001 机油滤清器2 Lub.oil filter2 JB20C 064 T3687W006 垫 1 Joint3 JB20C 079 T4134E031 机滤座 1 Lub.oil head4 JB20C 106 T2314J003 螺栓5 Screw 5 JB20L 156 T3686T006 垫 1 Joint 6 JB20L 182 T3766P092 接头 1 Adaptor7 JB20L 185 T2314J007 螺栓 1 Screw8 JB20L 187 T2314J003 螺栓 3 Screw9 JB20M 230 T3686A511 垫 1 Joint 10 JB20M 233 T2418F602 密封垫 2 Seal 11 JB20M 235 T75004281 油管 1 Oil pipe 12 JB20M 236 T75004282 油管 1 Oil pipe 13 JB20M 240 T2314H004 螺栓 3 Screw 14 JB20M 245 T3751K121 法兰 4 Flange 15 JB20M 246 T2318A603螺母 4 Nut 16 JB22H 001 T2486A993 油冷器 1 Oil cooler 17 JB22H 337 T3688X008 密封垫 2 Joint 18 JB22H 338 T2486A990 油冷器壳 1 Oil cooler housing19 JB22H 340 T3684N028 垫 1 Joint 20 JB22H 347 T2314H002 螺栓 11 Screw 21 JB22H 348 T0920146 垫圈 14 Washer 22 ZA**** T73201640 油门拉线支架 1 Bracket 23ZA**** T2314H034 螺栓 2 Screw 24 ZA**** T33134427 隔块 2 SpacerFront End Drive Input前端驱动输入KBH00575Front End Drive Input前端驱动输入 KBH00575Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 英文描述1 KB10L 013 T0500005 键 1 Key2 KB10L 019 T3115T043 皮带轮 1 Pulley 3 KB10L 080 T3311X002 隔圈 1 Spacer4 KB10L 083 T2417711 锁片 1 Cotter5 KB10L 086 T32418313 止推块 1 Block 6 KB10L 089 T2415638O 型圈1 O Ring 7 KB10L 092 T32186137 螺栓3Screw水泵及节温器LBH01659水泵及节温器 LBH01659Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 英文描述1 LB10E 140 T3685R005 垫 1 Joint2 LB10E 143 T3755k007 盖板 1 Cover plate 3 LB10E 156 T2314H002 螺栓 3 Screw4 LB22C 049T4131E011C 水泵 1 Water pump 5 T2531A112 轴 1 Shaft 6 T2415B155 O 型圈 1 O Ring 7 T3771D045 泵体 1 Body 8 T2418M006A 密封圈 1 Seal9 T3117A035 齿轮 1 Gear10 T3746X055A 叶轮 1 Impeller 11T3243C002 盖 1 Cover 12 LB22C 143 T2415H494 O 型圈 1 O Ring 13 LB22C 145 T2314H015 螺栓 1 Screw 14 LB22C 176 T2314N043 螺栓 3 Screw 15 LB22C 177 T2314H008 螺栓 1 Screw 16 LB22C 178 T2314H006 螺栓 1 Screw 17 LB22D 007 T74405005 节温器 2 Thermostat 18 LB22D 028 T3685F005 垫 1 Joint 19 LB22D 124 T2314J013 螺栓 2 Screw 20 LB22D 136 T2314H015 螺栓 1 Screw 21 LB22D 160 T2314H008 螺栓 2 Screw 22 LB22P 095 T3781D041C 接头 1 Connection LB22P 095 T3764E061 接头 1 Connection 23LB22P T2431154 堵 1 Plug 24LB22P 097T3683N004垫1Joint水泵及节温器ACHA0277水泵及节温器 ACHA0277Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 英文描述25 LB22P 100 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw 26 LB22P 110 T33854114 胶管 1 Hose 27 LB22P 112 T0180067 卡子 2 Clip 28 LD****T62204004接头 1 Connection 29 XB10E 004 T2314J002 螺栓 2 Screw 30 XB22D 007 T2314J004 螺栓 2 Screw 31 LB22PT2431154堵1Plug32 LB22D 040 T3771K121E 节温器壳体 1Thermostat housing bodyWater Outlet & Inlet水出口及入口LDH00439Water Outlet & Inle水出口及入口 LDH00439Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 英文描述1 LD22P 006 T3771K043 出水口 1 Water outlet2 LD22P 007 T3684A004 垫 1 Joint3 LD22P 040 T2314H010 螺栓4 Screw 4 LD22P 041 T2314H008 螺栓2Screw1006-6TRT125N01/NA01 交流发电机及发电机NDH01533交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1ND10B 008 T2314H013 螺栓 1 Screw 2 ND24A 004 T64501023 发电机 1 Alterator 3 ND24A 054 T2314H007 螺栓 1 Screw 4 ND24A 109 T0920497 垫圈 4Washer 5 ND24B 136 GB93-87D8 弹簧垫圈8 2 Spring washer6 ND24B 136 GB6170-86M8 螺母 2 Nut7 ND24A 94 T2314H008 螺栓 1Screw 8 ND24A 133 T2314J006 螺栓M10X40 Screw 9 ND24B 136 T2131A010 平垫10 1 Washer 10 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 Nut 11 ND24B 004 T74502206B 支架 1 Bracket 12 ND24B 016 T3827H025B 支架 1 Bracket 13 ND24B 127 T2314J003 螺栓 1 Screw 14 ND24B 165 T2314H002 螺栓 4 Screw 15 ND24B 322 T3753V014B 调节杆 1 Adjustment level16 ND24B 192 T3753V016 支架 1 Bracket 17 ND24B 367 T2314J004 螺栓 1 Screw 18 ND**** T2314H018 螺栓 2 Screw 19 ND****T2314H008螺栓2Screw1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533交流发电机及发电机 NDH01533Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ND24A 004T64501023发电机1Alterator2 ND24A 054T2314H005 螺栓 1 Screw3 ND24A 094T2314H005 螺栓1Screw4 ND*****T74601112 支架4Bracket5 ND24B 127 T2314J003 螺栓12 Screw6 ND24A 008 T2314H013 螺栓2Screw7 ND*****T74502152 调节杆 1 Adjustment level8 ND24A 133 T2314H006 螺栓M8X45 Screw9 ND24B 136 T2314J006 平垫10X40 1 Washer10 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M8 螺母M8 Nut11 ND24A 136 GB6170-86M10 螺母M10 NutAir Compressor空气压缩机QDH01356Air Compressor空气压缩机 QDH01356Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 QD10T 070 T3272X021 轮毂 1 Hub2 QD10T 073 T2415H213 O 型圈 1 O-ring 3 QD10T 076 T3117C161 齿轮 1 Gear4 QD10T 079 T2551A289 轴承 1 Bearing5 QD10T 082 T3241H011 盖板 1 Cover plate6 QD10T 085 T2314H002 螺栓 3 Screw7 QD10T 091 T3753R241 支架 1 Bracket8 QD10T 096 T2311D081 螺栓 3 Screw9 QD10T 098T2311D560螺栓4Screw1006-6TRT125K01/KA0 1Air Compressor1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 空气压缩机 QDH01356Air Compressor空气压缩机 QDH01356Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Part name图示参号组件号零件号零件名称数量零件名称1 ND***T74600123 空压机1AIR COMPRESSOR2 ND***T2314J006 螺栓 1 SCREW3 ND***T2314A604 螺母 1 NUT4 ND*** 169T0180063A 喉箍 2 HOSE CLIP5 QD40L 010T0470672 接头1CONNECTION6 QD40L 019T3355A017 接头1CONNECTION7 QD40L T2411157 垫圈 1 WASHER8 QD40L T0470672 接头 2 CONNECTION9 QD40L T3355A017 接头 1 CONNECTION10 QD**** T2411157 垫圈 2 WASHER11 QD****T0180063A 喉箍1HOSE CLIP12 QD**** T64601109 胶管 1 HOSEING13 QD****T2481877A 喉箍2HOSE CLIP14 QD****T74602321 胶管2HOSEING15 QD****T74602322 胶管 1 HOSEING16 QD****T64612103B 接头 1 CONNECTION17 QD30Z T64612104 锁母 118 QD20U 034T64612105 垫片 1 WASHER19 QD10B T0206002 接头 1 CONNECTION20 QD10B T73201647 过油螺栓 2 SCREW21 QD10B T74806022 回油接头 1 CONNECTION22 QD**** T73209521 油管 1 PIPE23 QD**** T73209522 油管 1 PIPE1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 Cover Plate1006-6TRT125K01/KA01 盖板QDH01131Cover Plate盖板 QDH01131Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 QD *** T74001209 盖板 1 COVER PLATE2 QD *** T2314J001 螺栓 1 SCREW3 QD *** T64605001A 垫片 2 WASHERGear Drive Auxiliary Drive Option齿轮驱动/转向助力选用QDH01131Gear Drive Auxiliary Drive Option齿轮驱动/转向助力选用 QDH01131Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 QD10B *** T4113H068A 驱动总成 1 Drive Assy2 T3751K071A 壳体 1 Housing3 GB276-82-208 轴承1 Bearing 4 T2721A537 卡簧 1 Circlip 5 T3117A016A 齿轮 1 Gear 6GB276-82-106 轴承1 Bearing 7 QD10B 133 T2415H461 O 型圈 1 O Ring 8 QD10B 162 T2313H321 双头螺栓 1 Stud 9 QD10B 164 T3254T001 双头螺栓 1 Stud 10 QD10B 166T2318A605螺母 3Nut进、排气歧管及空气冷却器SBH00616进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 SB15A 010 T3777U031 进气管 1 Inducion manifold2 SB15A 016 T3688C028 垫 1 Joint3 SB15A 020 T2314J009 螺栓 6 Screw4 SB15A 022 T2314J019 螺栓 2 Screw5 SB16A 002 T3211P018 双头螺栓 4 Stud6 SB16A 003 T2313M083 双头螺栓 2 Stud7 SB16A 003 T2313M083 双头螺栓 2 Stud8 SB16A 004 T2318A634 螺母 8 Nut9 SB16A 013 T3688C017 垫 1 Joint 10 SB16A 014 T36862191 垫 2 Joint 11 SB16A 016 T3778P001/A 排气管1 Exhaust manifold12 SB15F 001 T3766P241 进气弯管 1 Elbow 13 SB15F 031 T2314J014 螺栓 4 Screw 14 SB15F 028 T3684N008垫1Joint进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 SB15C 006 T3688A006 垫 1 Joint2 SB15C 007 T2674A082 增压器 1 Turbocharger3 SB15C 022 T3211P007 丝对4 Stud5 SB15C 031T2318A634螺母 4 Nut6 SB20K 100T3683D006垫 1 Joint7 SB20K 118T2314H003螺栓 2 Screw8 SB20K 136T3383A024胶管 1 Hose9 SB20K 139T2481877卡子 2 Clip10 SB20K 152T3571F016D 增压器回油管 1 Oil return pipe11 SB20L 305T3583M007增压器进油管 1 Oil feed pipe12 SB20L 311T36832138垫 1 Joint13 SB20L 323 T2314H004 螺栓 2 Screw14 SB20L 343 T0206008 接头 1 Connection15 SB20L 344T0576116 螺母 1 Nut16 SB20L 350T0566007 橄榄体 1 Olive17 SB15F 004 T3383E008 胶管 1 Hose18 SB15F 007 T0180070A 喉箍 2 Clip进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616进、排气歧管及空气冷却器 SBH00616Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 SB***** T33415509 垫 1 Joint2 SB***** T3688C011 垫 2 Joint3 SB***** T74707107 排气弯管 1 Elbow4 SB***** T74707108 排气弯管 1 Elbow5 SB***** T74707106 排气弯管 1 Elbow6 SB***** T74703008 排气弯管支架 1 Bracket7 SB***** T74703009 排气弯管支架 1 Bracket8 SB***** GB5783-86 螺栓M12X1.5X25 4 Screw9 SB***** GB93-87D12 弹垫12 4 Spring washer10 SB***** T2314H006 螺栓12 Screw11 SB***** T2318A633 螺母12 Nut12 SB***** GB97.1-85D12 垫 4 Washer13 SB***** T2314J003 螺栓12 Screw14 SB16D 002 T2313F059 丝对 6 Stud15 SB16A 004 T2318A633 螺母 6 NutLow Pressure Fuel System低压燃油系统 VBH01457Low Pressure Fuel System低压燃油系统 VBH01457Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 VB17C 003T64102002A滤清器1Fuel filter2 VB****T64102003柴滤器滤芯23 ZE25B 311 T0650204 堵2Plug4 ZE25B 312 T73274309 垫圈2Washer5 VB17C 040T2314J006螺栓2Screw6 VB17C 070T2318A604螺母2Nut7 VB17C 220T3818D013支架1Bracket8 VB17C 295T2314J002螺栓1Screw9 VB****** T4121C031F 油管Pipe (Lift Pump to filter)10 VB****** T63201702B 油管Pipe (Filter to pump)11 VB****** T63302029 油管Pipe (Pump to filter)12 VB17N 100T3425M006油管1Pipe (Atomizer to pump)13 VB17N 118T33225412螺母2Nut14 VB17N 121T33811112橄榄体2Olive15 VB17N 148T73217019 接头1Connection16 VB17N 151T0095344A 过油螺栓1Nut17 VB17N 154T73208144 密封垫2Nut18 Ve****** T65005001A 回油管1Pipe19 VB17N 283 T0576113 螺母 1 Nut20 VB17N 286 T0566004 橄榄体 1 OliveBlanking Plates盖板VBH02136Blanking Plates盖板 VBH02136Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示参号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 VB**** GB5783-86M8X20 螺栓 4 Screw2 VB**** GB93-87D8 弹簧垫圈 4 Washer3 VB**** T36856104A 垫片 1 Washer4 VB**** T63207003A 盖板 1 Cover plateCold Start System冷起动系统WDH00033Cold Start System冷起动系统 WDH00218Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 ZE25B 094 T4124E022 进气加热管 1 Pipe 2 ZE25B 097 T33225412 螺母 1 Nut3 ZE25B 103 T33811112 橄榄体 1 Olive4 WD15B 010 T2666106 加热器 1 HeaterEngine Lifting发动机提升 XBH00314Engine Lifting发动机提升 XBH00314Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 XB31D 001T74502130吊耳1Left brackt2 XB31D 007T2314J003螺栓3Screw3 XB31E 004T3654W003吊耳1Left brackt4 XB31E 010T2314J003螺栓2ScrewThe Plate垫板XBH00315The Plate垫板 XBH00315Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 ND***** T73203325 垫板 1 Plate2 ND***** T74502220 支架1 Bracket 3 ND***** T2314J003 螺栓 3 Screw 4 ND***** T2318A604 螺母3 Nut 5 ND***** T75701020 支架1 Bracket 7 ND***** T74502132 空调压缩机调解杆 1 Adjustment level8 ND***** T2314J005 螺栓 1 Screw 9ND*****T2318A604螺母M101Nut 10 ND***** T2314H006 螺栓 1 Screw 11 ND***** T2318A603 螺母M8 1 Nut 12 ND***** T74502133隔块 1 Spacer block 13 ND***** GB97.1-85D8垫圈82 Washer 14 ND***** T2314H019 螺栓1ScrewWater temperature sensor水温传感器 ZJH00440Water temperature sensor水温传感器 ZJH00440Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 ZL33Q 025 T65204003B 水温传感器 1 Sensor2 ZZ*** 001 T62204003 放水阀 1 Water drain valve3 ZL***T64403007 放水管 1 Water drain pipe4 ZL***T64403008 支架 1 Bracket5 ZL***T0180063 喉箍 1 Clip6 ZL*** 001T32161114水堵 1 Plug7 QD30Z 003 T0650594 螺堵 1 PlugMountings支撑 ZCH00878Mountings支撑 ZCH00878Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description 图示序号组件号零件号零件名称数量描述1 zz****** T2313C125丝对8 Stud2 zz****** GB6170-86M16螺母8 Nut3 zz****** GB97.1-85D16平垫16 Washer4 zz****** GB93-87D16 弹簧垫圈16 Spring washer垫及垫片(顶部维修组件)SACA0140垫及垫片(顶部维修组件) SACA0140Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1TU5LT0179 顶部垫片 1 Top Joint 2T3681H208 气缸盖垫 1 Joint 3 T3681C001 气缸盖罩垫1 Joint 4 T3685R005 垫 1 Joint 5 T3685F005 垫 1 Joint 6 T3684N008 垫 1 Joint 7 T3688C017 排气管垫 1 Joint 8 T36862191 排气歧管垫2 Joint 9 T3684A004 垫 1 Joint 10 T36832138 垫 1 Joint 11 T3683D006 垫 1 Joint 12 T3683N004 垫 1 Joint 13 T3688A006 增压器到排气管垫 1 Joint 14 T0921173 喷油器垫圈 6 Seal 15 T33817117 气门油封 12 Seal 16 T33813131 密封 6 Seal 17 T3688C028 进气歧管垫 1 Joint垫及垫片(底部维修组件)SACA0140 垫及垫片(底部维修组件) SACA0140Item Fam No Part No Part name Qty Description图示序号 组件号 零件号 零件名称 数量 描述1 TU5LBO158 底部垫片1 Bottom Joint2 T3681M007 油底壳垫1 Joint 3 T3688X008 油冷器罩垫 1 Joint4 T3681P009 正室齿轮室垫 1 Joint5 T3681P034 垫 1 Joint6 T3686T006 垫 1 Joint7 T36856104A 垫 1 Joint8 T36833152 垫 1 Joint9 T3683D006 垫 1 Joint 10 T3683H006 垫 1 Joint 11 T2415H461 O型密封圈 1 ORing。

发动机engine汽油机gasoline engine汽油喷射式汽油机gasoline-injection engine内燃机internal combustion engine动力机装置power unit火花点火式发动机spark ignition engine压燃式发动机compression ignition engine往复式内燃机reciprocating internal combustion engine 化油器式发动机carburetor engine柴油机diesel engine转子发动机rotary engine旋轮线转子发动机rotary trochoidal engine二冲程发动机two-stroke engine四冲程发动机four-stroke engine直接喷射式柴油机direct injection engine间接喷射式柴油机indirect injection engine增压式发动机supercharged engine风冷式发动机air-cooled engine油冷式发动机oil-cooled engine水冷式发动机water-cooled engine自然进气式发动机naturally aspirated engine煤气机gas engine液化石油气发动机liquified petroleum gas engine柴油煤气机diesel gas engine多种燃料发动机multi-fuel engine石油发动机hydrocarbon engine双燃料发动机duel fuel engine热球式发动机hot bulb engine多气缸发动机multiple cylinder engine对置活塞发动机opposed piston engine对置气缸式发动机opposed-cylinder engine十字头型发动机cross head engine直列式发动机in-line engine星型发动机radial engine筒状活塞发动机trunk-piston engine斯特林发动机stirling engine套阀式发动机knight engine气孔扫气式发动机port-scavenged engine倾斜式发动机slant engine前置式发动机front-engine后置式发动机rear-engine中置式发动机central engine左侧发动机left-hand engine右侧发动机right-hand engine径超程发动机oversquare engine长行程发动机undersquare engine短冲程发动机short stroke engine长冲程发动机long stroke engine等径程发动机square engine顶置凸轮轴发动机overhead camshaft engine双顶置凸轮轴发动机dual overhead camshaft engineV形发动机V-engine顶置气门发动机valve in-head engine侧置气门发动机side valve engine无气门发动机valveless engine多气门发动机multi-valve engine卧式发动机horizontal engine斜置式发动机inclined engine立式发动机vertical engineW形发动机w-engineI形发动机I-engineL形发动机L-engineF形发动机F-engine二冲程循环two-stroke cycle四冲程循环four-stroke cycle狄塞尔循环diesel cycle奥托循环otto cycle混合循环mixed cycle定容循环constant volume cycle工作循环working cycle等压循环constant pressure cycle理想循环ideal cycle热力循环thermodynamic cycle冲程stroke活塞行程piston stroke长行程long stroke上行程up stroke下行程down stroke进气行程intake stroke充气行程charging stroke压缩行程compression stroke爆炸行程explosion stroke膨胀行程expansion stroke动力行程power stroke排气行程exhaust stroke膨胀换气行程expansion-exchange stroke换气压缩行程exchange-compression stroke止点dead center上止点top dead center(upper dead center)下止点lower dead center(bottom dead center) 上止点前budc(before upper dead center)上止点后atdc(after top dead cetner)下止点前bbdc(before bottom dead center)下止点后abdc(after bottom dead center)缸径cylinder bore缸径与行程bore and stroke空气室energy chamber气缸余隙容积cylinder clearance volume燃烧室容积combustion chamber volume气缸最大容积maximum cylinder volume压缩室compression chamber排气量displacement发动机排量engine displacement活塞排量piston swept volume气缸容量cylinder capacity单室容量single-chamber capacity容积法volumetry压缩比compression ratio临界压缩比critical compression ratio膨胀比expansion ratio面容比surface to volume ratio行程缸径比stroke-bore ratio混合比mixture ratio压缩压力compression pressure制动平均有效压力brake mean effective pressure(bmep) 空燃比air fuel ratio燃空比fuel air ratio燃料当量比fuel equivalence ratio扭矩torque单缸功率power per cylinder升功率power per liter升扭矩torque per liter升质量mass per liter减额功率derating power输出马力shaft horsepower马力小时,马力时horsepower-hour总马力gross horse power总功率gross power净功率net power燃油消耗量fuel consumption比燃料消耗率specific fuel consumption空气消耗率air consumption机油消耗量oil consumption有效马力net horse power额定马力rated horse power马力重量系数horsepower-weight factor制动功率brake horse power制动热效率brake thermal efficiency总效率overall efficiency排烟极限功率smoke limiting horsepower功率曲线power curve机械损失mechanical loss机械效率mechanical efficiency有效热效率effective thermal efficiency充气系数volumetric efficiency过量空气系数coefficient of excess air适应性系数adaptive coefficient扭矩适应性系数coefficient of torque adaptability转速适应性系数speed adaptive coefficient强化系数coefficient of intensification校正系数correction factor换算系数conversion factor活塞平均速度mean piston speed发动机转速engine speed (rotational frequency) 怠速转速idling speed经济转速economic speed起动转速starting speed最低稳定工作转速lowest continuous speed with load 最大扭矩转速speed at maximum torque最高空转转速maximum no load governed speed 调速speed governing超速overspeed怠速idling转速波动率speed fluctuation rate工况working condition(operating mode) 额定工况declared working condition变工况variable working condition稳定工况steady working condition空载no-load全负荷full load超负荷overload部分负荷part load充量(进气)charge旋转方向direction of rotation顺时针clockwise逆时针counter-clockwise左转left-hand rotation右转right-hand rotation外径major diameter中径pitch diameter内径minor diameter径向间隙radial clearance发动机性能engine performance加载性能loading performance起动性能starting performance加速性能acceleration performance动力性能power performance排放性能emission performance空转特性no load characteristics负荷特性part throttle characteristics调速特性governor control characteristics万有特性mapping characteristics稳定调速率steady state speed governing rate 气缸体和气缸盖cylinder block and head气缸体cylinder block整体铸造cast inblock (cast enblock)发动机罩engine bonnet气缸体加强筋engine block stiffening rib气缸cylinder(转子机)缸体stator缸径cylinder bore气缸体机架cylinder block frame气缸盖cylinder head配气机构箱valve mechanism casing气缸体隔片cylinder spacer气缸盖密封环cylinder head ring gasket气缸盖垫片cylinder head gasket气缸套cylinder liner(cylinder sleeve)干式缸套dry cylinder liner湿式缸套wet cylinder liner气缸水套water jacket膨胀塞expansion plug防冻塞freeze plug气缸壁cylinder wall环脊ring ridge排气口exhaust port中间隔板intermediate bottom导板guideway创成半径(转子机)generating radius缸体宽度(转子机)operating width机柱column燃烧室combustion chamber主燃烧室main combustion chamber副燃烧室subsidiary combustion chamber预燃室prechamber涡流燃烧室` swirl combustion chamber分开式燃烧室divided combustion chamber涡流式燃烧室turbulence combustion chamber半球形燃烧室hemispherical combustion chamber浴盆形燃烧室bathtub section combustion chamberL形燃烧室L-combustion chamber楔形燃烧室wedge-section combustion chamber开式燃烧室open combustion chamber封闭喷射室closed spray chamber活塞顶内燃烧室piston chamber爆发室explosion chamber燃烧室容积比volume ratio of combustion chamber燃烧室口径比surface-volume ratio of combustion chamber 通道面积比area ratio of combustion chamber passage 曲轴箱通气口crankcase breather凸轮轴轴承座camshaft bearing bush seat定时齿轮室罩camshaft drive(gear)cover曲轴箱检查孔盖crankcase door曲轴箱防爆门crankcase explosion proof door主轴承盖main bearing cap气缸盖罩valve mechanism cover飞轮壳flywheel cover扫气储器scavenging air receiver活塞piston裙部开槽活塞split skirt pistonU形槽活塞U-slot piston滚花修复活塞knurled piston圆顶活塞dome head piston平顶活塞flat head piston凸顶活塞crown head piston(convex head piston)凹顶活塞concave head piston阶梯顶活塞step-head piston筒形活塞trunk piston椭圆形活塞oval piston抗热变形活塞autothermic piston不变间隙活塞constant clearance piston镶因瓦钢片活塞invar strut piston直接冷却式活塞direct-cooled piston间接冷却式活塞indirect cooled piston滑裙活塞slipper piston活塞速度piston speed活塞顶部piston head活塞裙部piston skirt整体活塞裙solid skirt活塞裙扩大衬簧piston skirt expander滑履式活塞裙slipper skirt隔热槽heat dam活塞标记piston mark活塞销piston pin活塞销孔piston pin boss活塞销衬套piston pin bushing全浮式活塞销full-floating piston pin半浮式活塞销semifloating piston pin固定螺钉式活塞销set screw piston pin活塞环piston ring组合式活塞环compound piston ring同心活塞环concentric piston ring偏心活塞环eccentric piston ring自由环free ring闭合环closed ring梯形环keystone ring半梯形环half keystone ring矩形环rectangular ring油环oil control ring开槽油环slotted oil control ring螺旋弹簧加载双坡口油环coil spring loaded slotted oil control ring 涨环expander双坡口油环double bevelled oil control ring内上坡口internal bevel top内下坡口internal bevel bottom边缘坡口油环bevelled-edge oil control ring刮油环scrapper ring钩形环napier ring镀铬活塞环chrome plated piston ring活塞衬环piston ring expander活塞环槽piston ring groove活塞环区ring zone活塞环岸piston ring land活塞环内表面back of ring曲柄连杆机构connecting rod中心曲柄连杆机构central-located connecting rod偏心曲柄连杆机构offset connecting rod铰接曲柄边杆机构hinged connecting rod连杆connecting rod连杆小头connecting rod small end连杆大头connecting rod big end连杆杆身connecting rod shank副连杆slave connecting rod叉形连杆fork-and-blade connecting rod主连杆main connecting rod方形连杆boxed rod绞链式连杆hinged type connecting rod活节式连杆articulated connecting rod连杆盖connecting rod cap连杆轴承connecting rod bearing曲轴crankshaft整体式曲轴one-piece crankshaft组合式曲轴assembled crankshaft右侧曲轴right-hand crankshaft左侧曲轴left-hand crankshaft改变行程的曲轴stroked crankshaft曲轴前端crankshaft front end曲轴主轴颈crankshaft main journal轴颈重叠度shaft journal overlap圆角fillet主轴承main bearing曲轴止推轴承crankshaft thrust bearing薄臂轴瓦thin wall bearing shell曲轴油道crankshaft oil passage曲柄crank曲柄臂crank arm曲柄销crank pin轴套bush曲柄转角crank angle曲柄半径crank radius抛油圈oil slander角度轮degree wheel动平衡机dynamic balancer平衡重balancer weight扭振减振器torsional vibration damper扭振平衡器torsion balancer谐振平衡器harmonic balancer振动平衡器vibration balancer曲轴链轮crankshaft sprocket转子轴颈rotor journal偏心轴eccentric shaft曲轴箱crankcase闭式曲轴箱通风装置closed-crankcase ventilating system 飞轮flywheel飞轮齿圈flywheel ring gear飞轮芯棒cantilever飞轮芯轴flywheel spindle飞轮的惯量矩flywheel moment of inertia飞轮标记flywheel mark当量系统equivalent system当量轴长equivalent shaft length一级往复惯性力reciprocating inertia force,1st order 二级往复贯性力reciprocating inertia force, 2nd order 离心惯性力centrifugal inertia force配气机构valve gear凸轮轴camshaft凸轮cam整体式凸轮轴one-piece camshaft组合式凸轮轴assembled camshaft凸轮轴驱动机构camshaft drive赛车用凸轮轴race camshaft凸轮轴轴颈camshaft bearing journal凸轮轴轴承camshaft bearing凸轮轴偏心轮camshaft eccentric凸轮轴链轮camshaft sprocket凸轮轴正时齿轮camshaft timing gear凸轮轴齿轮camshaft gear wheel进口凸轮inlet cam排气凸轮exhaust cam快升凸轮quick lift cam快升缓降凸轮quick lift gradual clsing cam凸轮轮廓cam contour凸轮包角cam angle凸轮升程cam-lobe lift凸轮尖cam nose凸轮从动件cam follower齿轮传动机构gear drive正时齿轮timing gear链传动机构chain drive链轮sprocket wheel链轮盘chain sprocket正时链条timing chain带齿皮带toothed timing belt链条张紧轮chain tension gear半速齿轮half speed gear正时齿轮刻印记号timing gear punch mark气门valve进气过程intake process换气过程gas exchange process扫气过程scavenging process给气比delivery ratio分层充气stratified charge充量系数volumetric efficiency涡流比swirl rate进气涡流intake swirl螺旋进气道进气helical duct intake导流屏式气门进气masked valve intake切向进气道进气tangential duct intake进气紊流intake turbulence进气提前角intake advance angle进气持续角intake duration angle进气迟后角intake lag angle进面值time-area value气门升程valve lift气门正时valve timing扫气口面积scavenging port area菌形气门mushroom valve, poppet valve钠冷却气门sodium filled valve(natrium cooled valve) 双气门dual valve进气门intake valve (suction valve,inlet valve)排气门exhaust valve顶置气门overhead valve侧置气门side valve倾斜气门inclined overhead valve直立气门vertical overhead valve套筒式滑阀sleeve valve气门机构valve gear直接式气门驱动机构direct valve gear间接式气门驱动机构indirect valve gear气门杆valve stem加大气门杆oversize valve stem气门头valve head气门工作面valve face气门边限valve margin气门弹簧座valve-spring retainer气门锁片valve key气门间隙调节螺钉valve lash adjusting screw气门旋转器valve rotator气门室valve cage气门油封valve oil seal气门口valve port气门座valve seat气门座镶圈(嵌镶式气门座圈)valve seat insert(valve seat ring)气门座锥角valve seat angle气门座宽度valve seat width气门挺杆valve tappet(valve lifter)液力挺杆hydraulic tappet(lifter)无间隙挺杆zero-rush tappet (non-clearance tappet) 筒形挺杆barrel type tappet油压挺杆oil tappet滚轮挺杆roller tappet(lifter)挺杆转位tappet rotation排气门挺杆exhaust valve lifter气门导管valve guide气门杆导管stem guide气门重叠度stem overlap气门开启持续时间valve duration气门正时标记valve timing sign气门弹簧valve spring气门内弹簧inner valve spring气门外弹簧outer valve spring刚性缓冲弹簧stiff buffer spring上紧弹簧energizing spring防振气门弹簧non-surging spring弹簧座圈spring retainer蝶形弹簧belleville spring滚柱roller气门室盖valve chamber cover摇臂rocker arm高升程摇臂high lift rocker arm摇臂轴rocker arm shaft推杆push-rod摇臂支架rocker arm bracket气门摇臂室罩valve rocker chamber cover导向轮guide wheel导杆slide bar导轨slide rail张紧轮tensioning wheel链条张紧调节装置assembly chain tension adjuster 张紧带轮tensioning pulley传动带张紧装置belt tensioner同步驱动皮带synchronous belt同步驱动皮轮synchronous belt pulley供油系fuel system控制燃烧系统controlled combustion system 反湿气装置antipercolator电子燃油喷射electronic fuel injection蒸气回收装置vapor recovery system燃油蒸气回收系统fuel vapor recovery system液体回收装置liquid withdrawal system恒量净化管constant purge line碳罐净化管canister purge line供油量fuel delivery循环供油量fuel delivery per cycle额定供油量rated fuel delivery怠速供油量idling speed fuel delivery供油规律fuel supply rate curve油量调节装置fuel control unit供油提前角fuel supply advance angle进油计量inlet metering几何供油行程geometric fuel delivery stroke 供油率fuel supply rate燃油通道fuel gallery有效行程effective stroke剩余行程remainder stroke变行程计量variable stroke metering等容卸载constant volume unloading变容卸载variable volume unloading收缩容积retraction volume燃油喷油装置fuel injection equipment燃油喷射泵fuel injection pump滚轮式燃油喷射泵roll fuel injection pump凸轮轴式燃油喷射泵camshaft fuel injection pump直列式燃油喷射泵in-line fuel injection pump伺服式燃油喷射泵servo fuel injection pump底部突缘安装燃油喷射泵base flanged mounted fuel injection pump 上部安装燃油喷射泵high flanged-mounted fuel injection pump 侧向安装燃油喷射泵side-mounted fuel injection pump端部突缘安装式燃油喷射泵end flange-mounted fuel injection pump V形燃油喷射泵vee fuel injection pump脉动式燃油喷射泵jerk fuel injection pump螺纹安装燃油喷射泵screw-mounted fuel injection pump蓄能式燃油喷射泵accumulator fuel injection pump往复式燃油喷射泵reciprocating fuel injection pump驱动轴式燃油喷射泵driveshaft fuel injection pump单缸式燃油喷射泵single cylinder fuel injection pump圆柱式燃油喷射泵cylindrical fuel injection pump旋转式燃油喷射泵rotary fuel injection pump分配式燃油喷射泵distributor fuel injection pump多缸燃油喷射泵multicylinder fuel injection pump框架安装式燃油喷射泵cradle mounted injection pump喷油始点fuel injection beginning喷油终点fuel injection end喷油持续角fuel injection duration angle喷油延迟injection delay引燃喷射pilot injection启喷压力injection starting pressure峰值喷油扭矩peak injection torque峰值喷油压力peak injection pressure喷油泵油缸数目number of cylinders of an injection pump 无气喷射solid injection喷射正时injection timing集中喷射group injection喷油器injector整体式喷油器unit injector喷嘴nozzle轴针式喷嘴pintle type nozzle环槽式喷嘴annular slot nozzle孔式喷嘴hole type nozzle长杆喷嘴long stem nozzle孔板式喷嘴orifice plate nozzle开式喷嘴open nozzle闭式喷嘴closed nozzle喷油提前器timing advance unit喷射泵壳体injection pump housing针阀needle芯轴central spindle喷嘴壳体nozzle body针阀升程needle lift喷嘴盖形螺母nozzle cap nut喷油器壳体nozzle holder突缘安装喷油器壳体flanged-mounted injection nozzle holder燃油喷射泵传动装置transmission of an injection pump喷嘴锥体nozzle hole cone柱塞plunger柱塞套barrel柱塞行程plunger stroke喷孔spray orifice海拔控制器altitude control提前器飞锤flyweight喷孔长径比ratio of nozzle hole length nozzle diameter 喷嘴液动力特性nozzle hydrokinetic characteristics动态相位dynamic phase喷孔面积nozzle hole area喷嘴流通特性nozzle flow characteristic喷油背压injection back pressure高压油管high pressure pipe平均喷油扭矩mean injection torque喷油总效率overall pumping efficiency峰值喷油压力injection peak pressure预行程prestroke收缩行程retraction stroke燃油箱fuel tank油箱盖fuel tank cover油位表fuel level gauge注油控制装置fill control system汽油箱gasoline tank( petrol tank)汽油供给管gasoline feed pipe加油管filler tube放油螺塞drain plug吸油管suction pipe刚性燃油管rigid fuel pipe进油孔fuel feed hole供油管supply pipe通气管bleeding pipe通气管bleeding pipe泄油阀spill valve泄油孔口spill port进油阀inlet valve最大油量限制器maximum fuel stop滴油dribble燃油表fuel gauge输油泵feed pump燃油泵fuel pump附装燃油箱中的电动燃油泵tank-mounted electric fuel pump机械式燃油泵mechanical fuel pump膜片式燃油泵diaphragm fuel supply pump叶片式供油泵vane fuel supply pump活塞式输油泵piston type fuel supply pump齿轮式输油泵gear fuel supply pump电动燃油泵electric fuel pump带真空泵的汽油泵vacuum pump with fuel pump起动加油器primer起动给油杆primer lever燃油泵上体fuel pump body燃油泵下体fuel pump base燃油泵盖bowl cover进油口接头fuel inlet neck出油口接头fuel discharge port输出阀delivery valve泵油元件pump element回油阀部件fuel return valve assembly化油器carburetor化油器系统carburetor circuit简单化油器elementary carburetor单腔化油器single-barrel carburetor双腔并动化油器two-barrel dual carburetor双腔分动化油器two-barrel duplex carburetor四腔化油器four-barrel carburetor上吸式化油器updaught carburetor下吸式化油器downdraught carburetor平吸式化油器horizontal carburetor侧吸式化油器side-draft-carburetor高海拔补偿式化油器altitude compensating carburetor 化油器附加器adaptor carburetor双腔式化油器twin-choke carburetor固定喉管式化油器fixed venturi carburetor可变喉管化油器variable venturi carburetor化油器接头carburetor adaptor阻风门choke valve阻风活塞choke piston阻风板choke plate自动阻风门automatic choke阻风门拉钮choke button电控自动阻风门electric-assisted choke阻风管choke tube喉管venturi双重或三重喉管double & triple venturi阻风门拉线choke cable化油器小喉管booster venturi浮子系float system浮子float环形浮子annular float同心式浮子concentric float浮子支销float hinge pin浮子针阀float needle valve阀针valve needle浮子油面float level浮子臂float arm侧置浮子室式side float type怠速阀idle valve怠速针阀idle needle省油器economizer省油器阀economizer valve辅助空气阀auxiliary air-valve加速油井accelerating well加速泵accelerating pump加速泵喷嘴accelerating pump nozzle油门throttle手油门hand throttle节气门操纵手柄throttle control lever真空加浓器vacuum booster加浓器excess fuel device量孔体jet block怠速量孔idle metering jet主量孔main metering jet剂量阀活塞dosage valve piston空气量孔air jet燃油滤清器fuel filter沉淀杯sediment bowl串联过滤器in-line filter燃油箱内装过滤器in-tank filter调速器governor飞球式调速器flyball governor调速器governor飞球式调速器flyball governor液压调速器hydraulic governor真空转速调速器vacuum speed governor惯性调速器inertia governor离心调速器centrifugal governor调速器重锤governor weight空气滤清器及进排气系统air cleaner and intake and exhaust system 空气滤清器air filter冲压式空气滤清器ram air cleaner恒温控制式空气滤清器thermostatic controlled air cleaner油浴式空气滤清器oil bath air cleaner纸质空气滤清器paper air cleaner旋流管式空气滤清器swirl tube air filter滤清器滤芯filter element空气滤清器壳体air filter housing空气滤清器盖air filter cover滤清器密封圈filter seal ring滤网sieve滤纸盘或膜filter paper disc or membrane进气和排气系统intake and exhaust system排气管exhaust pipe排气抽气管exhaust extraction duct扫气泵scavenging pump进气预热装置intake preheater进气歧管intake manifold进气歧管真空度intake manifold vacuum冷式进气歧管cold manifold冲压式进气歧管ram intake manifold排气歧管exhaust manifold脉冲式排气歧管pulse exhaust manifold等压排气歧管constant pressure exhaust manifold排气歧管热量控制阀exhaust manifold heat control valve超高度歧管high-rise manifold升温横跨管道heat crossover排气横跨管道exhaust crossover预热点hot spot阻风门加热器choke heater热空气导流管hot air duct隔热板heat shield排气再循环阀exhaust -gas-recirculation消声器silencer进气消声器intake silencer排气消声器exhaust silencer金属垫片式消声器steel pack muffler玻璃丝消声器glass pack muffler空洞消声器gutted muffler前排气管front exhaust pipe尾管tail pipe消声器联接管intermediate pipe热空气管hot air pipe曲轴箱通风管crankcase bleed pipe隔声罩acoustic hood进气消声器元件silencer element真空泵vacuum pump指示功率indicated power指示热效率indicated thermal efficiency指示油耗率indicated specific energy consumption示功图indicator diagram冷却系cooling system风冷air cooling水冷water-cooling循环流冷却系cooling recovery system自然循环液冷却系统natural circulation type cooling system热流循环液冷却系统thermo-siphon circulation type cooling system 温差循环液冷却系统gravity circulation water cooling system压力式水冷却系统positive circulation cooling system加压式冷却法pressure type cooling水泵循环冷却系统pump circulation cooling system强制循环式化冷系统forced-feed water circulation system封闭式液冷系统sealed cooling system散热器radiator片式散热器finned radiator管式散热器tubular radiator蜂窝式散热器cellular radiator哈里逊式散热器Harrison type radiator带板式散热器ribbon type radiator上水箱upper tank下水箱lower tank涨溢箱expansion tank散热器芯radiator core之字形管散热器芯film core管-片式散热器芯fin and tube core散热器加水口盖radiator filter cap压力式水箱盖radiator-pressure cap蒸气-空气泄放阀vapor-air release valve散热器护罩radiator cowl散热器百叶窗radiator shutter散热器保温帘radiator roller blind散热片cooling fin缸盖散热片cylinder head fin缸体散热片cylinder block fin控温装置temperature regulating device 恒温器thermostat恒温器主阀thermostat main valve恒温器旁通阀thermostat by-pass valve恒温器挠性波纹筒thermostat flexible bellows液体冷却设备liquid cooling equipment水泵water pump水泵体pump casing水泵叶轮water pump impeller旁通进水口water by-pass inlet neck循环泵circulating pump主进水口water main inlet port出水口water outlet port自调式水封self-adjusting seal unit溢流管overflow pipe导流板deflector风扇fan(blower)轴流式风扇axial flow fan离心式风扇centrifugal fan风扇壳体blower casing风扇导流罩fan cowl风扇毂fan hub风扇叶片fan blade风扇叶轮blower impeller风扇导流定子blower stator风扇皮带轮fan pulley三角皮带v-belt风扇护罩fan shroud风扇叶轮叶片impeller vane冷却用空气cooling air风扇导流叶片stator vane强制风冷forced-air cooling自然风冷natural air cooling风道air ducting润滑系lubrication system润滑lubrication气缸上部润滑upper cylinder lubrication压力润滑pressure-feed lubrication压力润滑法forced lubrication自动润滑automatic lubrication飞溅润滑splash lubrication润滑周期lubrication interval边界润滑borderline lubrication曲轴箱机油油盘crankcase oil pan油底壳oil pan机油盘放油塞sump plug集油器oil collector机油泵oil pump计量式机油泵metering oil pump齿轮式机油泵gear type oil pump转子式机油泵rotor-type oil pump机油泵出油管oil pump outlet pipe放油口oil drain hole油道oil duct断油开关cut-off cock机油散热器oil cooler机油滤清器oil filter机油粗滤器primary oil filter机油精滤器secondary oil filter全流式机油滤清器full-flow oil filter分流式机油滤清器by-pass oil filter离心式机油滤清器centrifugal oil filter整体式滤芯integral filtering element细滤器滤芯filter element滤清器壳filter box滤片filtering disc机油减压器oil pressure relief valve旁通阀by-pass oil filter机油滤网oil strainer加机油孔oil filter cap滤芯轴filter shaft刮片组件cleaning edge机油量尺dipstick增压器supercharger增压和扫气装置pressure-charging and scavenging unit 增压装置supercharging device涡轮增压器turbo-charger气波增压器comprex pressure wave supercharger 增压器阻风阀supercharger blast gate增压器调节容气量的旁通阀supercharger control bypass增压器叶轮supercharger impeller惯性增压inertia supercharging机械增压mechanical supercharging涡轮增压turbo-charging增压比supercharge ratio增压压力boost pressure增压中冷inter-cooling中冷度inter-cooling level增压度supercharging level喘振surge喘振线surge line轴流式涡轮axial-flow turbine脉冲进气ram charging发动机试验engine test发动机试验规程engine test procedure发动机技术要求engine technical requirements标准大气状况standard atmospheric conditions大气压力atmospheric pressure进气温度inlet air temperature进气温度inlet air temperature功率校正power correction功率标定power rating功率换算power conversion校正系数correction factor换算系数performance test性能试验performance test起动性能试验starting ability test怠速试验idle running test道路负荷试验road load test各缸工作均匀性试验cylinder variation test背压试验back pressure test最低稳定工作转速试验lowest continuous speed test with load 背部泄漏试验back-leakage test调整试验adjustment test热平衡试验heat balance test快速磨损试验accelerated wear test热冲击试验thermo-shock test空载特性试验no-load characteristic test模拟增压试验simulated supercharging test停缸试验cylinder fuel-cut test增压机匹配试验turbo-charger matching test排气分析试验exhaust analysis test突变负荷试验sudden load change test稳定性试验stability test单缸熄火试验one cylinder shut off test例行检查试验routine inspection test验证试验verification test鉴定试验approval test可靠性试验reliability test耐久性试验durability test定型试验type approval test验收试验acceptance test现场试验field test出厂试验delivery test抽查试验spot check test复查试验re-check test台架试验bench test强化试验hop-up test发动机试验台engine test bed底盘测功机chassis dynamometer测功机dynamometer水力测功机hydraulic dynamometer电涡流测功机eddy current dynamometer电力测功机electric dynamometer扭矩仪torque meter转速表tachometer温度测量thermometry温度测量仪器thermometric instruments空气流量测量air flow measurement热线风速仪hot wire anemometer电子示功仪electronic indicator燃烧分析仪combustion analyzer压力传感器pressure transducer精密声级计precision sound level meter排放emission排放物emission排气污染物gaseous pollutant蒸发排放物evaporative emission曲轴箱排放物crankcase emission漏气blowby gas氨氧化物oxids of nitrogen一气化碳carbon monoxide碳氢化合物hydrocarbon甲烷methane无甲烷碳氢化合物non-methane hydrocarbons光化学活性碳氢化合物photochemically reactive hydrocarbons微粒物particulated matter黑烟black smoke蓝烟blue smoke白烟white smoke碳烟soot光化学烟雾smog臭味odor丙烷propane排放浓度concentration of emission排气烟度exhaust smoke先期排气initial exhaust亚临界排气subcritical exhaust超临界排气supercritical exhaust强制排气forced exhaust自由排气free exhaust排气提前角exhaust advance angle排气迟后角exhaust lag angle排气热损失exhaust heat loss排气净化exhaust purification排气背压exhaust back pressure残余废气residual gas排气有害成分poisonous exhaust composition柴油机排烟diesel smoke综合排放浓度composite concentration of exhaust emission 综合排放质量composite mass of exhaust emission排放系数emission factor排放率emission index质量排放量mass emission比排放量brake specific emission排放物控制系统emission control system排气排放物控制系统exhaust emission control system二次空气secondary air二次空气分配歧管secondary air distribution二次空气控制阀secondary air control valve二次空气转换阀secondary air switching valve二次空气转流阀secondary air diverter valve二次空气喷射装置secondary air injection system二次空气喷射管secondary air injection tube二次空气喷射减速压阀secondary air injection relief valve脉动空气装置pulsating air system二次空气泵secondary air pump曲轴箱排放物控制系统crankcase emission control system 曲轴箱双通风系统crankcase closed system曲轴箱单通风系统crankcase sealed system曲轴箱强制通风装置positive crankcase ventilationPCV阀PCV valve蒸发排放物控制系统evaporative emission control system 活性碳罐贮存装置charcoal canister storage system活性碳罐charcoal canister曲轴箱贮存装置crankcase storage system空气滤清器贮存装置air filter storage system燃油箱止回阀fuel tank check valve油气分离器fuel and vapor separator清除阀furge valve催化转化系统catalytic converting system催化燃烧分析仪catalytic combustion analyzer催化剂catalyst转化器converter催化转化器catalytic converter轴流式转化器AXIAL FLOW TYPE CONVERTER 径流式转化器RADIAL FLOW TYPE CONVERTER 下流式转化器down flow type converter上流式转化器up flow type converter双床式转化器dual bed converter单床式转化器single bed converter氧化型催化剂oxidation catalyst还原型催化剂reduction catalyst三元催化剂three-way catalyst贵金属催化剂noble metal catalyst普通金属催化剂base metal catalyst稀土催化剂rare earth catalyst催化剂耗损catalyst attrition催化剂收缩catalyst shrinkage催化剂中毒catalyst poisoning比表面积specific surface area空速space velocity载体涂料washcoat双重催化系统dual -catalyst system催化箱catalyst container载体substrate整体式载体monolithic substrate颗粒式载体pelleted substrate转化效率conversion efficiency熄灯温度light-off temperature热态反应系统thermal reacting system热反应器thermal reactor反应式歧管reactive manifold过热保护装置over heating protection system过热警报装置over heating warning system排气口衬套exhaust port liner后燃器after burner排气再循环系EGR system排气再循环exhaust gas recirculation节气门前EGR系统above throttle valve EGR system节气门后EGR 系统below throttle valve EGR system空气比例式EGR系统air proportional EGR system负荷比例式EGR系统load proportional EGR system孔口真空控制式EGR 系统ported vacuum controlled EGR system喉管真空控制式EGR系统venturi vacuum controlled EGR system排气压力控制式EGR系统exhaust pressure controlled EGR system 声速控制式EGR系统sonic controlled EGR system电子控制式EGR系统electronic controlled EGR system EGR冷却器 EGR cooler EGR过滤器 GER filter EGR控制阀 EGR control valve EGR调压阀 EGR pressure regulator EGR再循环排气EGR gas再循环排气率EGR rate点火和喷油时刻控制系统ignition and injection timing control system 点火时刻控制系统ignition timing control system减速点火提前控制装置deceleration spark advance control推迟喷油时刻控制系统retarded injection timing control system转速控制的推迟喷油时刻 retarded injection timing with speed负荷控制的推迟喷油时刻retarded injection timing with load燃油控制系统fuel control system反馈控制feedback control空燃比反馈控制系统air-fuel ratio feedback control system理论配比stoichiometric高效带window氧传感器oxygen sensor稀混合气lean mixture浓混合气rich mixture分层充气stratified charge温度补偿temperature compensating海拔补偿altitude compensating气压补偿atmospheric pressure compensating电子控制化油器electronic controlled carburetor电子燃油喷射系统electronic fuel injection system怠速限制器idle limiter。

PP Production Proveout 生产验证TTO Tool Try-Out 工装设备试运行(J1) Job 1 整车投产DFMEA Design Failure Mode Effects Analysis 故障模式影响分析设计DVP Design Verification Plan 设计验证计划DVP&R Design Verification Plan & Report 设计验证计划和结果FMEA Failure Mode Effects Analysis 故障模式影响分析FPDS Ford Product Development System 福特产品开发系统GYR Green-Yellow-Red 绿-黄-红MRD Material Required Date 物料要求到厂日OTT OK-TO-TOOL 可以开模TKO Tooling-Kick-Off 工装启动OEM original Equipment Manufacturer 设备最初制造厂FtF/F2F Face To Face 面对面会议PV Production Validation 产品验证OTS Off-Tooling-Sample 完全工装样件QOS Quality Operating System 质量运作体系TS-16949 Technical Specification –16949 技术规范-16949APQP Advanced Product Quality Planning 先期产品质量计划IPD In Plant Date 进厂日PPM Parts per Million (applied to defective Supplier parts) 零件的百万分比率(适用于供应商不合格零件)PPAP Production Part Approval Process 生产件批准程序Pre-PV Pre -Production Validation 产品预先验证1PP- First Phase of Production Prove-Out 第一次试生产3C Customer(顾客导向)、Competition(竞争导向)、Competence(专长导向)4S Sale, Sparepart零配件, Service, Survey信息反馈5S 整理,整顿,清理,清洁,素养8D- 8 DisciplineABS Anti-lock Braking SystemAIAG 美国汽车联合会ANPQP Alliance New Product Quality ProcedureApportionment 分配APQP Advanced Product Quality PlanBacklite Windshield 后窗玻璃Benchmark Data 样件资料bloodshot adj.充血的, 有血丝的BMW Bavarian Motor WorksC.P.M Certified Purchasing manger 认证采购经理人制度CB- Confirmation Build 确认样车制造CC- Change CutOff 设计变更冻结CC\SC- critical/significant characteristicCCR Concern & Countermeasure RequestCCT Cross Company TeamCharacteristics Matrix 特性矩阵图COD Cash on Delivery 货到付现预付货款(T/T in advance) CP1- Confirmation Prototype 1st 第一次确认样车CP2- Confirmation Prototype 2nd 第二次确认样车Cpk 过程能力指数Cpk=Zmin/3CPO Complementary Parts orderCraftsmanship 精致工艺Cross-functional teams 跨功能小组CUV Car-Based Ultility VehicleD1:信息收集;8DD2:建立8D小组;D3:制定临时的围堵行动措施,避免不良品流出;D4:定义和证实根本原因,避免再发;D5:根据基本原因制定永久措施;D6:执行和确认永久措施;D7:预防再发,实施永久措施;D8:认可团队和个人的贡献。

•中文译文•发动机缸盖加工工艺概述•一、发动机缸盖的功用气缸盖是发动机的主要零件之一,位于发动机的上部,其底平面经汽缸衬垫,用螺栓紧固在气缸体上。
主要功用如下:1、封闭气缸上部,并与活塞顶部和汽缸壁一起形成燃烧室。
2、作为定置气门发动机的配气机构、进排气管和出水管的装配基体。
3、气缸盖内部有冷却水套,其底面上的冷却水孔与气缸体冷却水孔相通,以便利用循环水带走发动机的高温。
二、气缸盖的结构特点气缸盖应具有足够的强度和刚度,以保证在气体的压力和热应力的作用下,能够可靠的工作。
气缸盖的形状一般为六面体,系多孔薄壁件,其中我们现在481缸盖上,加工的数量多达100个。
铸造最薄处只有4.5毫米。
三、缸盖材料与毛坯制造1、缸盖的材料:缸盖的材料,现在的发动机厂家一般选用铝合金。
因为铝合金导热性能较好,有利于适当提高压压缩比,质量也较轻,可以降低整车、整机的重量。
但是铝合金缸盖的刚度差,使用过程中容易变形。
缸盖附件上,以前气门座材料一般采用耐热合金铸铁,气门导管一般采用铸铁。
现在粉末冶金在气门阀座和导管上运用的越来越多了,而且很多复杂的形状也能铸造成型,不需要再加工了。
但耐磨性不如铸铁。
•裂纹:铸造应力造成;•冷隔:浇注过程中铝水冷却速度不一致造成;•表面疏松:浇注温度不当或铝水成分不当;•气孔:浇注铝水中夹杂了空气;•砂眼:浇注铝水中夹杂了杂质;•沾砂:工件出炉温度不当或没有喷丸等。
四、缸盖的加工难点:1、平面加工工艺•缸盖的顶面、底面和进、排气面都是大面积平面,精度要求高(平面度0.04,垂直度0.05,位置度0.10),而且有可能是全部工艺过程的基础,例如480缸盖就是。
•这就对机床的几何精度和刀具的调整精度要求比较高。
•以前缸盖大平面加工,采用硬质合金刀片加工,并配一个金刚石修光刃。
现在,如果毛坯情况好的话,全部采用金刚石刀片进行加工,可以很好的提高加工后的表面粗糙度。
2、高精度孔的加工•气缸盖上的气门阀座、导管孔、挺杆孔和凸轮轴孔等孔系,有配合关系。
第一类 MOTOR VEHICLE 汽车一、Vehicle classification 汽车分类1.2 Bus 客车1.3 Motor truck 货车1.4 special purpose vehicle 专用汽车二、Vehicle construction 汽车构造2.1 Main components of vehicle 汽车主要组成2.2 Vehicle performance 汽车性能2.3 engine position 发动机布置三、Vehicle dimensions汽车尺寸五、Diameter of turning circle 转弯直径第二类ENGINE 发动机Timing components : 发动机时规组件一、Engine construction 发动机构造二、Essential term 基本术语三、Engine operation principle发动机工作原理3.1 Four-stroke gasoline engine operation principle四冲程汽油机工作原理3.2 Four-stroke diesel engine operational principle四冲程柴油机工作原理3.3 Two-stroke gasoline engine operation principle二冲程汽油机工作原理3.4 Two-stroke diesel engine operation principle二冲程柴油机工作原理四、Engine performance 发动机性能曲柄连杆机构5.2 Piston,connecting rod 活塞连杆组5.3 Crankshaft,flywheel 曲轴飞轮组六、Valve mechanism 配气机构6.1 Side valve 侧置气门6.2 Overhead valve 顶置气门6.3 Overhead valve 顶置气门6.4 Valve-timing diagram 配气相位图七、Gasoline engine-fuel system汽油机供油泵7.1 Fuel system 供油泵7.2 Air cleaner 空气滤清器7. 3 Fuel pump,fuel filter 汽油泵,汽油滤清器7.4 Simple carburetor 简单化油器7.5 Carburetor 化油器7.6 Carburetor elements 化油器零件7.7 Carburetor control 化油器操纵件7.8 Gasoline injection 汽油喷射7.9 Electric fuel pump,Injector电动汽油泵,喷油器7.10 Sensor 传感器八、Diesel engine-fuel system柴油机工友系8.1 Fuel system 供油泵8.2 Combustion chamber 燃烧室8.3 Injection pump 喷油泵8.4 Injection 喷油器8.5 Speed governor 调速器九、Exhaust system 排气系统十、Turbo-supercharging 蜗轮增压10.1 Turbocharging system 蜗轮增压系统10.2 Turbocharger 蜗轮增压器十一、Emission control 排污控制11.1 Emission control system 排污控制系统11.2 Catalytic convertor 催化转化器十二、Engine-cooling system 发动机冷却机12.1 Water cooling system 水冷系12.2 Radiator 传感器12.3 Fan,water pump 风扇,水泵12.4 Air cooling system 风冷系十三、Engine-lubrication system发动机润滑系13.1 Pressure lubrication 压力润滑13.2 Oil pump 机油泵13.3 Oil cleaner 机油滤清器13.4 Oil cooling radiator 机油散热器发动机点火系14.2 Lead battery 铅蓄电池14.3 Ignition coil 点火线圈14.4 Distributor 分电器14.5 Spark plug 火花塞14.6 Electronic ignition 电子点火十五、Engine-starting system发动机起动系15.1 Starting system 起动系15.2 Electric starter 电动起动机十六、New type engines 新型发动机16.1 Rotary piston engine 旋转活塞发动机16.2 Gas turbine 燃气轮机16.3 Stirling engine 斯特林发动机(热气机)第三类CHASSIS 底盘一、Drive line 传动系1.1 Layout of drive line 传动系示意图1.2 Friction clutch 摩擦离合器1.3 Hydrodynamic coupling 液力偶合器1.4 Gearbox-housing 变速器外壳1.5 Gearbox-gearing 变速器齿轮传动1.6 Gearbox-gear-shift 变速器换档机构1.7 Automatic transmission 自动变速器1.8 Transfer case 分动器1.9 Cardan shaft 万向传动器1.10 Flexible coupling 挠性联轴节1.11 Constant-velocity joint 等速万向节1.12 Drive axle 驱动桥1.13 Final drive 主减速器1.14 differential 差速器1.15 Half-axle,rear axle housing二、Running gear 行驶系2.1 Layout of main components 主要组成示意图2.2 Frame 车架2.3 Front axle 前桥2.4 Wheel 车轮2.5 Tire 轮胎2.6 Tire type 轮胎类型2.7 Front wheel independent suspension前轮独立悬架2.8 Rear wheel independent suspension后轮独立悬架2.9 Leaf spring 钢板弹簧2.10 Air suspension 空气悬架2.11 Hydro-pneumatic spring 液压充气弹簧2.12 Telescopic hydraulic shock absorber伸缩式液压减振器2.13 Cam hydraulic shock absorber凸轮式液压减振器三、Steering system 转向系Mechanical steering system 机械转向系 3.2 Power steering system 动力转向系3.3 Steering mechanism 转向机构3.4 Steering gear 转向器3.5 Power steering 动力转向3.6 steering linkage 转向杆系四、Braking system 制动系4.1 Braking principles 制动原理4.2 Drum brake 鼓式制动器4.2 Drum brake4.4 Hand brake 手制动器(parking brake 驻车制动器)4.5 hydraulic brake system 液压制动系4.6 Brake master cylinder,Wheel cylinder制动主缸,制动轮缸4.7 Compressed-air brake system 气压制动系4.8 Anti-lock braking system 防抱死制动系第四类、BODY AND ACCESSORIES 车身及附属装置一、Car body 轿车车身二、All-steel body 全钢车身三、Car door 轿车车门四、Bus body 大客车车身五、Truck body 货车车身六、Special-transport vehicle body专用汽车车身七、Cab 驾驶室八、Drivers place 驾驶员位置九、Instrument panel仪表板十、Seat,Safety belt 座椅,安全带十一、Air conditioning 空调十二、Compressor 压缩机十三、Lighting 照明十四、Head Lamp 前大灯十五、Turnsignal lamp 转向灯十六、Windshield wiper 风窗刮水器十八、Horn 喇叭十九、Tools 工具。
电机行业常用的中英文对照induction machine 感应式电机horseshoe magnet 马蹄形磁铁magnetic field 磁场eddy current 涡流right-hand rule 右手定则left-hand rule 左手定则slip 转差率induction motor 感应电动机rotating magnetic field 旋转磁场winding 绕组stator 定子rotor 转子induced current 感生电流time-phase 时间相位exciting voltage 励磁电压slot 槽lamination 叠片laminated core 叠片铁芯short-circuiting ring 短路环squirrel cage 鼠笼rotor core 转子铁芯cast-aluminum rotor 铸铝转子bronze 青铜horsepower 马力random—wound 散绕insulation 绝缘ac motor 交流环电动机end ring 端环alloy 合金coil winding 线圈绕组form—wound 模绕performance characteristic 工作特性frequency 频率revolutions per minute 转/分motoring 电动机驱动generating 发电per-unit value 标么值breakdown torque 极限转矩breakaway force 起步阻力overhauling 检修wind—driven generator 风动发电机revolutions per second 转/秒number of poles 极数speed—torque curve 转速力矩特性曲线plugging 反向制动synchronous speed 同步转速percentage 百分数locked-rotor torque 锁定转子转矩full-load torque 满载转矩prime mover 原动机inrush current 涌流magnetizing reacance 磁化电抗line-to—neutral 线与中性点间的staor winding 定子绕组leakage reactance 漏磁电抗no-load 空载full load 满载Polyphase 多相(的)iron—loss 铁损complex impedance 复数阻抗rotor resistance 转子电阻leakage flux 漏磁通locked—rotor 锁定转子chopper circuit 斩波电路separately excited 他励的compounded 复励dc motor 直流电动机de machine 直流电机speed regulation 速度调节shunt 并励series 串励armature circuit 电枢电路optical fiber 光纤interoffice 局间的waveguide 波导波导管bandwidth 带宽light emitting diode 发光二极管silica 硅石二氧化硅regeneration 再生,后反馈放大coaxial 共轴的,同轴的high-performance 高性能的carrier 载波mature 成熟的Single Side Band(SSB) 单边带coupling capacitor 结合电容propagate 传导传播modulator 调制器demodulator 解调器line trap 限波器shunt 分路器Amplitude Modulation(AM 调幅Frequency Shift Keying(FSK)移频键控tuner 调谐器attenuate 衰减incident 入射的two—way configuration 二线制generator voltage 发电机电压dc generator 直流发电机polyphase rectifier 多相整流器boost 增压time constant 时间常数forward transfer function 正向传递函数error signal 误差信号regulator 调节器stabilizing transformer 稳定变压器time delay 延时direct axis transient time constant 直轴瞬变时间常数transient response 瞬态响应solid state 固体buck 补偿operational calculus 算符演算gain 增益pole 极点feedback signal 反馈信号dynamic response 动态响应voltage control system 电压控制系统mismatch 失配error detector 误差检测器excitation system 励磁系统field current 励磁电流transistor 晶体管high-gain 高增益boost-buck 升压去磁feedback system 反馈系统reactive power 无功功率feedback loop 反馈回路automatic Voltage regulator(A VR)自动电压调整器reference Voltage 基准电压magnetic amplifier 磁放大器amplidyne 微场扩流发电机self-exciting 自励的limiter 限幅器manual control 手动控制block diagram 方框图linear zone 线性区potential transformer 电压互感器stabilization network 稳定网络stabilizer 稳定器air-gap flux 气隙磁通saturation effect 饱和效应saturation curve 饱和曲线flux linkage 磁链per unit value 标么值shunt field 并励磁场magnetic circuit 磁路load-saturation curve 负载饱和曲线air—gap line 气隙磁化线polyphase rectifier 多相整流器circuit components 电路元件circuit parameters 电路参数electrical device 电气设备electric energy 电能primary cell 原生电池energy converter 电能转换器conductor 导体heating appliance 电热器direct—current 直流time invariant 时不变的self—inductor 自感mutual-inductor 互感the dielectric 电介质storage battery 蓄电池e。
挖掘机英语、工程机械英语(常用中英文对照)教程本文介绍了挖掘机和工程机械的常用英语术语,包括部件名称、功能、分类、品牌等。
本文旨在帮助从事挖掘机和工程机械行业的人员提高英语水平,便于与国外客户或同行进行沟通和交流。
一、挖掘机部件名称中英文对照挖掘机是一种主要用于挖掘土方、破碎岩石、开凿沟渠等工作的工程机械。
挖掘机由动臂、斗杆、铲斗、回转支承、驾驶室、发动机、液压系统等部件组成。
以下是挖掘机部件名称的中英文对照表¹²:中文英文柴滤滤心Diesel filter机油滤芯Engine oil filter空滤滤芯Air filter element吸油滤芯(铜沙格)Suction oil filter回油滤(滤芯)Return oil filter element油水分离器滤芯Water separator filter先导滤芯1(先导系统,制动系统)Pilot filter 1(Braking and steering system)电子输油泵Electronic priming pump发动机上水管Engine upper water hose发动机下水管Engine lower water hose空调皮带Air conditioner belt熄火电磁阀Stop solenoid空调压缩机Air conditioner compressor空调水阀Water valve水温传感器Water temperature sensor联轴器Connector24V 接触器24V Contactor起动开关Starting switch24V水壶 (带电机)Water bottle (with motor)雨刮器电机Window wiper motor呼吸器Aspirator中心管道油封Central joint seals伸缩油缸密封Seal kits of extended cylinder动臂缸油封Boom cylinder seals斗杆缸油封Arm cylinder seals铲斗缸油封Bucket cylinder seals燃油盖Fuel cap拖链轮(上辊)Up roller(Carrier roller)支重轮(下辊)Low roller(Track roller)引导轮(前导轮)Idler (front idler)中文英文驱动轮(链轮)Drive gear (sprocket wheel)24V电磁阀线圈24V solenoid coil液位计 (油标尺)Oil dipstick二、挖掘机功能分类中英文对照挖掘机根据其功能和用途,可以分为不同的类型,如履带式挖掘机、轮式挖掘机、液压挖掘机、迷你挖掘机等。
Electric / 电器A/Con,Heater assy / 空调,暖气设备总成Air conditioner / 空调调节器Heater / 暖气设备A/Con compressor / 空调压缩机A/Con fan / 空调风扇Reciver drier / 烘干器A/Con condenser / 空调冷凝器Defroster / 防结冰装置A/Con others / 空调其他MDU / MDU ( 스위치보드)Switch panel / 开关板Cluster / Cluster ( 게이지판넬) Rotary switch / 旋转开关Diesel heater / 柴油加热器Warning buzzer / 警告蜂鸣器Horn / 喇叭Back alarm / 倒车警告器Travel alarm / 行走警告器Bicorn lamp / 操作警告灯Head light / 顶灯Working lamp / 工作灯Extra lamp / 附加灯Combination lamp / Kombilampe Direction lamp / 指示灯Tail lamp / 尾灯Emergency lamp / 事故备用灯Backward lamp / 倒车灯Room lamp / 室内灯License lamp / Kennzeichenbeleuchtung Cassette / 录音带盒Antena / Antenne ( 라듸오안테나) Speaker / 扬声器Safety lever / 安全手柄Wiper assy / 刮水器总成Wiper blade / 刮水片Wiper motor / 刮水器马达Wiper nozzle / 刮水器喷嘴Washer tank / 洗涤液箱Step motor / 步进马达Battery / 电池Master switch / 总开关Fuse box / 保险丝盒Relay box / 继电器盒Fuel filler pump / 燃料补充泵Start key / 启动钥匙Preheater / 预热器Cigar lighter / 点烟器Other electrics / 电器其他Under Carriage / 下部车架Track A'ssy / 履带总成Track link / 履带链Track shoe / 履带板Track master pin / 履带主销Idler / 惰轮Sprocket / 链齿轮Adjust cylinder / 调节油缸Recoil spring / 反冲弹簧Track guard / 履带防护装置Carrier roller / 履带托轮Lower roller / 下部滚轮Other under carriages / 下部车架其他Lower roller / 下部滚轮Other under carriages / 下部车架其他Hydraulic / 液压Main pump / 主泵Gear pump / 齿轮泵Rotator(X3) pump / 旋转(X3)泵Swing motor / 回转马达Swing reduction / 回转减速器Track motor / 行走马达Track reduction / 行走减速器Travel motor(Wheel) / 行走马达(轮式) H/Tank / 液压油箱Hyd oil cooler / 液压油冷却器Turning joint / 回转接头Accumulator / 蓄能器Slewing ring gear / 回转环形齿轮Breaker(X1) line / 破碎器(X1)线路Boom cylinder / 大臂油缸2nd boom cylinder / 第二大臂油缸Arm cylinder / 小臂油缸Bucket cylinder / 铲斗油缸Outrigger cylinder / 悬臂支架油缸Blade cylinder / 推土板油缸Cylinder others / 油缸其他Main control valve / 主控阀Valve others / 阀其他RCV lever / 遥控操纵杆Breaker(X1) pedal / 破碎器(X1)踏板Other levers / 控制杆其他Other hydraulic / 液压其他Accessory / 附属物CAB A'ssy / 驾驶室总成Cab door / 驾驶室门Cab sunroof / 驾驶室遮阳顶棚Cab front window / 驾驶室前窗Cab side window / 驾驶室侧窗Cab inner interior / 驾驶室内部件Cab inner FRP / 驾驶室内部玻璃钢Control box / 控制盒Seat A'ssy / 椅子总成Back of seat / 椅子靠背Seat head restraint / 椅子头枕Seat arm rest / 椅子扶手Safety belt / 安全带Engine hood / 发动机罩Side door / 侧门Rearview mirror / 后视镜Guard rail / 保护扶手RCV lever box / 遥控操纵杆箱Sun shield / 遮阳板Rain shield / 遮雨板Ashtray / 烟灰缸Other accessories / 附件其他Attachment / 附件Boom / 大臂Second boom / 第二大臂Arm / 小臂Bucket / 铲斗Bucket tooth / 铲斗牙齿Bucket link / 铲斗链Dozer blade / 推土平铲Outrigger / 悬臂支架Breaker / 破碎器Quick Fit / 快速安装Other attachments / 附件其他Standard Parts / 标准零件Bolt / 螺栓Rivet / 柳钉Nut / 螺母Washer / 垫圈Pin / 销Cotter pin / 开口销Bearing(Bushing) / 轴衬Nipple / 黄油加注口Plug / 塞子Spring / 弹簧Shim / 垫片Cover(Plate) / 盖板B.K.T(Support) / 支架Link / 链环Rod / 杆Clamp / 夹子Hinge / 铰链Guard / 防护装置Grill / 护罩Other standard parts / 标准零件其他General Parts / 普通零件Cap / 帽子Catch / 钩Pusher / 推动器Key / 钥匙Cable / 电缆Stay / 支柱Gas spring / 气体弹簧Name plate / 铭牌Stop bar / Stopschiene ( 각종문에부착되어있는데문을열고닫을때손상을방지하는고무류부품)--> 잘모르면,사진으로설명한다Step / 台阶Yoke / 轭Lever / 操纵杆Handle / 把手Pedal / 踏板Anti slip / 防滑板Drain hose / 排水软管Other general parts / 普通零件其他Nonmetal parts / 非金属零件Sponge / 海绵Packing / 包装Seal / 密封条Knob / 旋钮Decal / 帖膜Belt / 皮带Grommet / 套环Boot / 波纹管Cushion rubber / 缓冲橡胶Mat / 橡胶垫子Glass / 玻璃Duct / 输送管Fan / 扇Other nonmetal parts / 非金属零件其他Electric Parts / 电器零件Switch / 开关Motor / 马达Connector / 连接器Fuse / 保险丝Relay / 继电器Limit switch / 限位开关ECU / ECU Wire harness / 线束Lamp / 灯Lamp cover / 灯罩Gauge / 量表Sensor / 传感器Other electric parts / 电器零件其他Hydraulic Parts / 液压零件Head / 油缸端部Rod / 杆Hose / 软管Pipe / 硬管Connector / 连接器Flange / 法兰Breather / 呼吸器O-ring / O型环Filter / 过滤器Cylinder cushion / 油缸缓冲装置Sight gauge / 观测计Dipstick gauge / 量油计Spool / 线轴Relief valve / 安全阀Check valve / 止回阀Solenoid valve / 电磁阀Regulator / 调节器Anti drop valve / 防落阀Other valves / 阀门其他Other hydraulic parts / 液压零件其他Fluid Parts / 流体Oil / 油Air / 气体Coolant / 冷却液Fuel / 燃料Grease / 黄油Washing liquid / 洗涤液Refrigerant / 制冷剂Battery acid /电解液(电瓶) Silicone / 硅胶Other fluid parts / 流体其他General defect location code / 普通缺陷位置代码ASS'Y / 总成Internally / 内部Externally / 外部Around / 周围Both front and rear/ 前后Front / 前面Rear / 后面Both right and left / 左右Left / 左边Right / 右边Front, left / 前左Rear, left / 后左Front, right / 前右Rear, right / 后右Both above and under / 上下Above / 上面Under / 下面Horizontally / 水平地Vertically / 垂直地Attach region / 组装部Welding region / 焊接部Cutting region / 切削部Edge region / 末端Corner region / 棱角Hole / 孔Block / 块Other general location / 普通位置其他Unit Code / 单位代码Pressure / 压力Temperature / 温度Speed / 速度RPM / 转速Power / 功率Weight / 重量Length / 长度Height / 高度Gap(Clearance) / 间隙Angle / 角度Volume / 体积Specific gravity / 比重Inspection sheet / 检验表No location / 无正确位置Other unit location / 单位其他Leakage Type / 泄漏Leakage(oil/fuel) / 泄漏(油/燃料)Leakage(coolant) / 泄漏(冷却液)Leakage(air) / 泄漏(空气)Overplus / 过多Insufficiency / 不足Oil contamination / 油的沾污Washing fault / 洗涤不良Leakage(grease) / 泄漏(油脂)Overflow / 溢出Other leaks / 泄漏其他Welding Type / 焊接Welding bead fault / 焊缝不良Welding missing / 焊接漏掉Welding pores / 焊接气孔Spatter / 溅滴Finish fault / 完成阶段不良Lack of fusion / 未熔合Softball / 小颗粒Other welding faults / 焊接其他不良Appearance / 外观Surface bending / 表面弯曲Crack / 裂缝Broken / 破损Burnt / 烧损Damage / 损伤Deformation / 变形Rust / 生锈Discoloration / 变色Rustprotection fault / 防锈不良Carve fault(s/no etc) / 刻印不良(S/No etc)Other appearances / 外观其他不良Loose / 松散Not tighten / 未拧紧Separation / 分离Loosen / 晃动Gap / 缝隙Poor adhesion / 粘贴不良Not attached / 没有Not fitted / Nicht eingebaut ( 볼트및기타부품의체결력불량)Wrong parts / 错误的零件Removal(No need) / 不需要Others / 其他Blow hole / 砂眼Other loose / 松散其他Painting / 油漆Painting missing / 油漆漏掉Painting drop / 油漆流挂Painting damage / 油漆损伤Lifting&flaking / 油漆接合不良Painting contamination / 油漆污染Painting dust / 漆雾Orange peel / 桔皮Painting blushing / 油漆白化Painting bubbles / 油漆起泡Brilliance fault / 光泽度不良Cleanliness / 清洁不良Foreign object fault / 有异物附着Film thickness fault / 厚度不良Other painting faults / 油漆其他不良Operation / 动作Malfunction / 故障Self-drop / 自动落下Noise / 噪音locking fault / 锁不良Open&close fault / 开闭不良Light fault / 开灯不良Tightness / 紧Sticking / 固定Over clearance / 间隙过大Shaking / 过分晃动Hunting / 摆动Impact / 冲击Cushion fault / 缓冲不良Smoking / 煤烟Check omission / 确认漏掉Other operation / 动作其他Adjustment / 调整Routing fault / 整齐不良Adjustment fault / 调整不良Alignment fault / 单差不良Interference / 接触Worn / 磨损Bending fault / 弯曲不良Position fault / 位置不良Height fault / 高度不良Horizontally fault / 水平不良Wrong dimension / 尺寸不良Other assembly faults / 组装其他不良Silicone faults / 硅胶不良Other adjustment / 调整其他不良Crawller excavater Mini Excavators / 迷你型挖掘机Medium Excavators / 中型挖掘机Heavy Excavators / 重型挖掘机Usage DecisionAccept / 接收Rejected / 拒收Work CenterLower Frame SUB / 下部结构过程Upper Frame SUB / 上部结构过程Attachment SUB / 附件过程Attachment Mtg / 附件装配Self Insp. Repair / 自我检验修理Final Inspection / 最终检验Touch up Paint-A / 油漆润色-A Touch up Paint-B / 油漆润色-B Track SUB / 行走过程Spec. Change / 规格变更KD Semi-Painting / LackierungTotal Quality Management EU-RAM / 全面质量管理EU-RAMManufacturing Engineering EU-RAM / 制造工程EU-RAMAddministration EU-RAM / 服务EU-RAM Purchasing Department / 采购部门Inventory Management / 库存管理Order Desk / Production Planning / Produktplanung。
Two-stroke cycle 二冲程循环Four-stroke cycle 四冲程循环Diesel cycle 狄塞尔循环Otto cycle 奥托循环Mixed cycle 混合循环Constant volume cycle 定容循环Constant pressure cycle 等压循环Working cycle 工作循环Ideal cycle 理想循环Thermodynamic cycle 热力循环Stroke 冲程,行程Piston stroke 活塞行程Long stroke 长行程Up stroke 上行程Down stroke 下行程Intake stroke 吸气行程Charging stroke 充气行程Compression stroke 压缩行程Working stroke 工作行程Explosion stroke 爆炸行程Expansion stroke 膨胀行程Power stroke 动力行程Exhaust stroke 排气行程Expansion-exchange stroke 膨胀-换气行程Exchange-compression stroke 换气-压缩行程Dead center 止点Top dead center 上止点Lower dead center 下止点Before top dead center 上止点前After top dead center 上止点后Before bottom dead center 下止点前After bottom dead center 下止点后Cylinder bore 缸径Bore and stroke 缸径与冲程Air-cell 空气室Cylinder clearance volume 气缸余隙容积Combustion chamber volume 燃烧室容积Maximum cylinder volume 气缸最大容积Compression chamber 压缩室Displacement (swept volume) 排气量Engine displacement 发动机排量Piston displacement 活塞排量Cylinder capacity 气缸容量Single-chamber capacity 单室容量V olumetry 容积法Compression ratio 压缩比Critical compression ratio 临界压缩比Expansion ratio 膨胀比Surface to volume ratio 面容比Stroke-bore ratio 行程-缸径比Mixture ratio 混合比Compression pressure 压缩压力Brake mean effective pressure (BMEP) 制动平均有效压力Air fuel ratio 空燃比Fuel air ratio 燃空比Fuel equivalence ratio 燃料当量比Torque 扭矩Power per cylinder 单缸功率Power per liter 升功率Torque per liter 升扭矩Mass per liter 升质量Derating power 减额功率Output power 输出功率Gross power 总功率Net power 净功率Fuel consumption 燃油消耗量Specific fuel consumption 比燃料消耗量Air consumption 空气消耗量Oil consumption 机油消耗量Rated power 额定功率Brake power 制动功率Brake thermal efficiency 制动热效率Indicted thermal efficiency 指示热效率Overall efficiency 总效率Smoke limiting power 排烟极限功率Power curve 功率曲线Mechanical loss 机械损失Mechanical efficiency 机械效率Effective thermal efficiency 有效热效率V olumetric efficiency 容积效率Excess air coefficient 过量空气系数Adaptive coefficient 适应性系数Torque adaptive coefficient 扭矩适应性系数Speed adaptive coefficient 转速适应性系数Intensification coefficient 强化系数Correction factor 校正系数Conversion factor 换算系数Mean piston speed 活塞平均速度Engine speed 发动机速度Idling speed 怠速转速Economic speed 经济转速Starting speed 起动转速Lowest continuous speed with load 最低稳定工作转速Lowest idling temperature 发动机怠速转动最低温度Maximum torque speed 最大转矩转速Maximum noload governed speed 受控最高空转转速Speed governing调速Overspeed超速Idling怠速Speed fluctuation rate转速波动率Working condition (operating condition)工况Rated working condition额定工况Variable working condition变工况Steady working condition稳定工况No –load空载Full load 全负荷Over load 超负荷Part load 部分负荷Charge 充量(进气)Direction of rotation 旋转方向Clockwise 顺时针Anticlockwise 逆时针Left-hand rotation 左转Right-hand rotation 右转Major diameter 外径Pitch diameter 中径Minor diameter 内径Radial clearance 径向间隙Engine performance 发动机性能Loading performance 加载性能Starting performance 起动性能Acceleration performance 加速性能Power performance 动力性能Emission performance 排放性能No load characteristics 空转特性Partial throttle characteristics 负荷特性Governor control characteristics 调速特性Mapping characteristics 万有特性Steady-state speed governing rate 稳定调速率Working medium 工质Practical cycle 实际循环Firing order 点火次序Timing 定时Stroke-bore ratio 行程缸径比Number of cylinders 气缸数Piston area 活塞面积Connecting rod length 连杆长度Crank radius 曲柄半径Crank radius-connecting rod length ratio 曲柄连杆比Working medium volume 气缸体积Piston swept volume 气缸工作体积Effective piston swept volume 气缸有效工作体积Cylinder clearance volume 气缸余隙体积Maximum cylinder volume 气缸最大体积Effective cylinder volume 气缸有效体积Engine swept volume 发动机排量Engine cylinder volume 发动机气缸总体积Clearance 余隙高度Injector protrusion 喷嘴端伸出量Intake process 进气过程Intake temperature 进气温度Intake pressure 进气压力Natural aspiration 自然进气Stratified charge 层状充气Intake advance angle 进气提前角Intake lag angle 进气迟后角Intake duration angle 进气持续角Intake swirl 进气涡流Intake turbulence 进气紊流Helical duct intake 螺旋进气道进气Tangential duct intake 切向进气道进气Masked inlet valve intake 导流屏进气Time-area value 时面值Valve lift 气阀升程Scavenging port area 气阀开度Gas exchange process 换气过程Scavenging process 扫气过程Scavenging duration 扫气持续期Scavenging pressure 扫气压力Uniflow scavenging 直流扫气Loop scavenging 回流扫气Cross scavenging 横流扫气Crankcase scavenging 曲轴箱扫气Scavenging by blower 扫气泵扫气Piston underside pump scavenging 活塞底泵扫气Exhaust-pulse scavenging 排气脉冲扫气Coefficient of scavenging 扫气系数Trapping efficiency 扫气利用系数Scavenging efficiency 扫气效率Coefficient of scavenging loss 扫气漏失系数Delivery ratio 给气比Valve timing 配气定时Valve overlap 气阀重叠Swirl rate 涡流比Compression process 压缩过程Compression pressure 压缩压力Compression beginning pressure 压缩始点压力Compression beginning temperature 压缩始点温度Compression end pressure without combustion 压缩终点压力Compression end temperature without combustion 压缩终点温度Fuel injection starting compression pressure 喷油始点压缩压力Ignition starting compression pressure 着火始点压缩压力Ratio of pressure rise 压力升高比Effective compression ratio 有效压缩比Polytropic index of compression 压缩多变指数Compression swirl 压缩涡流Injection process 喷油过程Direct injection 直接喷射Indirect injection 间接喷射Electronic-controlled injection 电控喷射Fuel supply advance angle 供油提前角Fuel injection advance angle 喷油提前角Injection lag 喷油延迟角Injection duration 喷油持续角Nozzle hole area 喷孔面积Total area of nozzle holes 喷孔总面积Ratio of nozzle hole length-nozzle hole diameter 喷孔长径比Nozzle hole cone 喷孔锥体Nozzle hole cone angle 喷孔锥角Needle lift 针阀升程Sac volume 针阀压力室体积Retraction volume of delivery valve 出油阀卸载体积Injection pressure 喷油压力Injection starting pressure 启喷压力Injection peak pressure 喷油峰值压力Inject back pressure 喷油背压Spray 喷注Spray penetration 喷注贯穿距离Spray penetration curve 喷注贯穿规律Spray penetration ratio 喷注贯穿率Fuel delivery per cycle per cylinder 循环喷油量Minimum fuel delivery per cycle per cylinder 最小循环喷油量Fuel supply rate 供油率Fuel injection rate 喷油率Accumulated fuel delivery rate 累计喷油率Fuel supply rate curve 供油规律Fuel injection rate curve 喷油规律Fuel delivery curve at constant speed 喷油泵负荷特性Fuel delivery curve at fixed rack 喷油泵速度特性Nozzle flow characteristic 喷嘴流通特性Nozzle hydrokinetic characteristic 喷嘴液力特性Spray characteristic 喷雾特性Spray cone angle 喷雾锥角Atomization 雾化Sauter mean diameter (SMD) 索特平均直径Abnormal injection 异常喷油Secondary injection 二次喷油Fluctuating injection 波动喷油Intermittent injection 间断喷油Disorder injection 不齐喷油Nozzle dribbing 喷油滴漏Mixture formation process 混合气形成过程Mixture concentration 混合气浓度Mixture ratio 混合比V olumetric mixture ratio 体积混合比Mole mixture ratio 摩尔混合比Theoretical mixture ratio 理论混合比Theoretical mixture gas 理论混合气Film mixture 油膜混合Combustible mixture 可燃混合气Total air-fuel ratio 总空燃比Total excess air ratio 总过量空气系数Air untilization ratio 空气利用系数Chamber mixture 雾化混合Compound mixture 复合混合Peripheral mixture 周边混合Thermo-mixture effect 热混合效应Thermo-hamper effect 热束缚效应Micro swirl 微涡流Combustion chamber 燃烧室Divided combustion chamber 分开式燃烧室Semi-open combustion chamber 半开式燃烧室Open combustion chamber 开式燃烧室Direct injection combustion chamber 直喷式燃烧室Piston chamber 活塞顶内燃烧室M-process chamber 球型燃烧室Basin shaped combustion chamber 盆形燃烧室Swirl combustion chamber 涡流燃烧室Prechamber 预燃燃烧室Pre-swirl combustion chamber 涡流预燃室Heat-reserve combustion chamber 储能燃烧室Main combustion chamber 主燃室Subsidiary combustion chamber 副燃室L-combustion chamber L形燃烧室Wedge shaped combustion chamber 楔型燃烧室Bathtub shaped combustion chamber 盆形燃烧室Hemispherical combustion chamber 半球形燃烧室V olume ratio of combustion chamber 燃烧室体积比Calibre ratio of combustion chamber 燃烧室口径比Surface-volume ratio of combustion chamber 燃烧室面容比Area ratio of combustion chamber passage 燃烧室通道面积比Ignition 着火Ignition process 着火过程Ignition temperature 着火温度Compression ignition 压燃Spark ignition 点燃Cold flame 冷焰Blue flame 蓝焰Hot flame 热焰Pre-flame reaction 焰前反应Chain reaction 链反应Pre-mixing combustion 预混合燃烧Diffusion combustion 扩散燃烧Lean mixture combustion 稀薄燃烧Stratified combustion 层状燃烧Ignition delay period 滞燃期Rapid combustion period 速燃期Main combustion period 主燃期Normal combustion period 缓燃期After combustion period 后燃期Combustion duration 燃烧持续期Heat release beginning 放热始点Heat release end 放热终点Duration of heat release 放热持续期Combustion rate 燃烧率Heat release rate 放热率Heat release rate curve 放热规律Heat utilization ratio 热量利用率Spark advance angle 点火提前角Spark lag 点火延迟Pre-ignition 早燃Surface ignition 热面点火Miss-fire 失火Back fire 回火Flame propagation velocity 火焰传播速度Detonation 爆燃Squish area 挤气面积Quench effect 冷激效应Combustion swirl 燃烧涡流Squish swirl 挤压涡流Anti-squish swirl 反挤压涡流Maximum combustion pressure 最高燃烧压力Maximum combustion temperature 最高燃烧温度Pressure rise rate 压力升高率Alternative fuel 代用燃料Emulsified fuel 乳化燃料Main fuel 主燃料Pilot-ignition fuel 引燃燃料Basic fuel 基础燃料Lower calorfic value of fuel 燃料低热值Cetane number 十六烷值Octane number 辛烷值Antiknock quality index 抗爆指数Antiknock sensitivity 抗爆敏感度Antiknock quality 抗爆性Polytropic index of expansion 膨胀多变指数Coefficient of molecular change 分子变更系数Initial exhaust 先期排气Free exhaust 自由排气Forced exhaust 强制排气Supercritical exhaust 超临界排气Subcritical exhaust 亚临界排气Exhaust advance angle 排气提前角Exhaust lag angle 排气迟后角Exhaust duration 排气持续期Exhaust pressure 排气压力Exhaust back pressure 排气背压Exhaust temperature 排气温度Residual gas 残余废气Coefficient of residual gas 残余废气系数Exhaust purification 排气净化Poisonous exhaust composition 排气有害万分Emission 排放物Concentration of emission 排放浓度Emission rate 排放分数Exhaust pollution 排气污染Exhaust smoke 排气烟度Soot 黑烟Exhaust particulate 排气微粒Exhaust gas recirculation 废气再循环Indicated work 指示功Indicated power 批示功率Mean indicated pressure 平均指示压力Indicated thermal efficiency 指示热效率Indicated specific fuel consumption 指示油耗率Indicated specific energy consumption 指示能耗率Indicator diagram 示功图Motoring indicator diagram 拖动示功图Low pressure indicator diagram 低压示功图Heat balance 热平衡Exhaust heat loss 排气热损失Cooling heat loss 冷却热损失Remainder heat loss 余项热损失Supercharging 增压Supercharging level 增压度Pressure ratio 增压比Boost pressure 增压压力Low pressure-charging 低增压Medium pressure-charging 中增压High pressure-charging 高增压Super high pressure-charging 超高增压Mechanical supercharging 机械增压Turbo-charging 废气涡轮增压Combined supercharging 复合增压Pulse turbo-charging 脉冲增压Constant-pressure turbo-charging 定压增压Inertia supercharging 惯性增压Intake fluctuation effect supercharging 气波增压器增压Two stage supercharging 两级增压pulse converter supercharging 脉冲转换增压sequential turbocharging 相继涡轮增压tuned intake supercharging 谐波增压modular pulse converter supercharging 模件式脉冲转换增压inter-cooling 增压中冷inter-cooling level 中冷度exhaust expansion ratio through turbine 涡轮膨胀比equivalent area of turbine nozzle 涡轮当量喷嘴面积surge 喘振surge line 喘振线supercharger speed 增压器转速supercharger outlet temperature 增压器出口温度starting speed 起动转速declared speed 标称转速idling speed 最低空载转速maximum no-load speed 最高空载转速lowest continues speed with load 最低工作稳定转速economic speed 经济转速speed at maximum torque 最大转矩转速right-hand rotation 右转left-hand rotation 左转overspeed 超速coefficient of speed reserve 转速储备系数speed governing 调速coefficient of speed fluctuation 转速波动率maximum transient speed 最高瞬时转速minimum transient speed 最低瞬时转速speed recovery time 转速稳定时间transient speed regulation 瞬时调速率steady-state speed regulation 稳定调速率hunting 游车load 负荷full load 全负荷partial load 部分负荷overload 超负荷no-load 空载working condition 工况steady working condition 稳定工况variable working condition 变工况transient working condition 过渡工况declared working condition 标定工况economic working condition 经济工况mechanical loss 机械损失功率brake power 有效功率declared power 标称功率15-minute rated power 15 min功率one hour rated power 1h功率12-hour rated power 12h功率continues power 持续功率power per piston area 活塞面积功率power per cylinder 单缸功率power to bulk ratio 体积功率economic power 经济功率normal power 常用功率maximum power 最大功率gross power 总功率net power 净功率smoke limit power 冒烟极限功率derating power 减额功率power take-off 功率分支输出power reserve 储备功率adjusted power 修正功率standard power 标准功率coefficient of power reserve 功率储备系数mechanical power 机械功率。
1史上最全的汽车术语中英文对照表第一类 MOTOR VEHICLE 汽车一、Vehicle classification 汽车分类1.1 Car 轿车1.2 Bus 客车1.3 Motor truck 货车1.4 special purpose vehicle 专用汽车二、Vehicle construction 汽车构造 2.1 Main components of vehicle 汽车主要组成2.2 Vehicle performance 汽车性能2.3 engine position 发动机布置三、Vehicle dimensions 汽车尺寸 四、Wheel alignment 前轮定位第二类一、Engine construction 发动机构造二、Essential term 基本术语发动机工作原理3.1 Four-stroke gasoline engineoperation principleoperational principleoperation principle二冲程汽油机工作原理34operation principle四、Engine performance 发动机性能曲柄连杆机构5.2 Piston,connecting rod 活塞连杆组55.3 Crankshaft,flywheel 曲轴飞轮组六、Valve mechanism 配气机构 6.1 Side valve 侧置气门6.2 Overhead valve 顶置气门6.3 Overhead valve 顶置气门66.4 Valve-timing diagram 配气相位图七、 Gasoline engine-fuel system汽油机供油泵7.1 Fuel system 供油泵7.2 Air cleaner 空气滤清器7. 3 Fuel pump,fuel filter 汽油泵,汽油滤清器7.4 Simple carburetor 简单化油器77.5 Carburetor 化油器7.6 Carburetor elements 化油器零件7.7 Carburetor control 化油器操纵7.8 Gasoline injection 汽油喷射87.9 Electric fuel pump,Injector电动汽油泵,喷油器7.10 Sensor 传感器八、Diesel engine-fuel system柴油机工友系8.1 Fuel system 供油泵8.2 Combustion chamber 燃烧室8.3 Injection pump 喷油泵8.4 Injection 喷油器8.5 Speed governor 调速器九、Exhaust system 排气系统10.1 Turbocharging system 蜗轮增压系10.2 Turbocharger 蜗轮增压器91011.1 Emission control system 排污控11.2 Catalytic convertor 催化转化器却机12.2 Radiator 传感器12.3 Fan,water pump 风扇,水泵12.4 Air cooling system 风冷系十三、Engine-lubrication system发动机润滑系13.1 Pressure lubrication 压力润滑13.2 Oil pump 机油泵13.3 Oil cleaner 机油滤清器13.4 Oil cooling radiator 机油散热器发动机点火系14.2 Lead battery 铅蓄电池14.3 Ignition coil 点火线圈14.4 Distributor 分电器14.5 Spark plug 火花塞14.6 Electronic ignition 电子点火十五、Engine-starting system发动机起动系15.1 Starting system 起动系15.2 Electric starter 电动起动机16.1 Rotary piston engine 旋转活塞发16.2 Gas turbine 燃气轮机第三类一、Drive line 传动系1.1 Layout of drive line 传动系示意1.2 Friction clutch 摩擦离合器1.3 Hydrodynamic coupling 液力偶合器1.4 Gearbox-housing 变速器外壳1.5 Gearbox-gearing 变速器齿轮传动1.8 Transfer case 分动器1.9 Cardan shaft 万向传动器1.10 Flexible coupling 挠性联轴节1.12 Drive axle 驱动桥1.13 Final drive 主减速器1.14 differential 差速器1.15 Half-axle,rear axle housing2.1 Layout of main components 主要组2.2 Frame 车架2.3 Front axle 前桥2.4 Wheel 车轮2.5 Tire 轮胎2.6 Tire type 轮胎类型suspension2.8 Rear wheel independent suspension后轮独立悬架2.9 Leaf spring 钢板弹簧2.10 Air suspension 空气悬架absorber2.13 Cam hydraulic shock absorber凸轮式液压减振器Mechanical steering system 机械转向3.2 Power steering system 动力转向系3.3 Steering mechanism 转向机构3.4 Steering gear 转向器3.5 Power steering 动力转向3.6 steering linkage 转向杆系四、 Braking system 制动系4.1 Braking principles 制动原理4.2 Drum brake 鼓式制动器4.2 Drum brake4.4 Hand brake 手制动器 (parking brake 驻车制动器)4.5 hydraulic brake system 液压制动系4.6 Brake master cylinder,Wheelcylinder制动主缸,制动轮缸第四类、BODY AND ACCESSORIES 车身及附属装置一、Car body 轿车车身二、All-steel body 全钢车身三、Car door 轿车车门四、Bus body 大客车车身五、Truck body 货车车身六、Special-transport vehicle body专用汽车车身七、Cab 驾驶室八、Drivers place 驾驶员位置九、Instrument panel 仪表板十、Seat,Safety belt 座椅,安全带 十一、Air conditioning 空调十二、Compressor 压缩机十三、Lighting 照明十四、Head Lamp 前大灯十五、Turnsignal lamp 转向灯十六、Windshield wiper 风窗刮水器十七、Wiper-washer equipment 刮水器-洗涤器装置十八、Horn 喇叭十九、Tools 工具。
发动机工作原理 大多数汽车的发动机是内燃机,往复四冲程汽油机,但是也有使用其它类型的发动机,包括柴油机,转子发动机,二冲程发动机和分程燃烧发动机。 往复的意思就是上下运动或前后运动,在往复发动机中,气缸中活塞的上下运动产生发动机的动力,这种类型几乎所有的发动机都是依赖气缸体即发动机缸体,缸体是铸铁或铸铝制的,它包括发动机气缸和冷却液循环用的水套。缸体的顶部是气缸盖,它组成了燃烧室,缸体底部是油底壳。 气缸内活塞的直线运动产生动力,然而,必须将直线运动转化成旋转运动,使汽车车轮转动,活塞销将活塞连接在连杆顶部,连杆底部与曲轴连接,使汽车车轮转动,活塞销将活塞连杆顶部,连杆底剖与曲轴连接,连杆将活塞的往复运动传递给曲轴,曲轴将其转化为旋转运动,连杆是用连杆曲轴安装在曲轴上的,用类似的轴承即主轴承将曲轴固定在缸体内。 气缸的直径称为发动机的内径,排量和压缩比是两个常用的发动机参数,排量是指发动机的大小,压缩比是气缸总容积与燃烧室压缩容积之比。 术语: 冲程是用来说明活塞在气缸内的运动,也就是活塞行程的距离根据发动机类型的需要二冲程或四冲程来完成一个工作循环四冲程发动机也叫做奥托发动机,为了纪念德国工程师奥托,他是在1876年第一个应用该原理的,在四冲程发动机中,要求气缸活塞四冲程来完成一个完整的工作循环,每个冲程根据其行为命名分别为: 进气冲程,压缩冲程,作功冲程和排气冲程。 1、 进气冲程 当活塞下移时,雾化后的可燃混合气通过打开的进气门进入气缸,为了达到最大的进气量,进气门在活塞到达上止点前10°打开,使进、排气门有20°打开重叠角,进气门一直打开到活塞到达下止点充分进入混合气之后50°左右。 2、 压缩冲程 活塞开始向上移动时,进气门关闭,混合气在燃烧室中压缩,根据不同因素包括压缩比,节气门开度,发动机转速压力上升到约1兆帕,接近冲程顶部时,火花塞产生的电火花击穿点火间隙点燃可燃混合气。 3、 作功冲程 燃烧膨胀的气体产生的压力上升到3.5个兆帕时,推动活塞下移,接近气缸底时,排气门打开。 4、 排气冲程 随着排气门开启约下止点前50°,活塞回升,使气缸内压力下降在排气冲程,减少对活塞回压,派出废气,为下一个进气冲程作准备,通常情况下,进气门在排气冲程完成前打开。 只要发动机保持运转,每个气缸内四个冲程循环连续不断地重复下去。 两冲程发动机也同样通过四行程来完成,一个工作循环但是进气冲程,压缩冲程合为一个冲程,作功冲程形成另一个冲程,术语两行程循环和两行程就是所谓的术语双循环但实际上并不太准确。 在所用的汽车发动机中,所有的活塞都是固定在一个曲轴上的,气缸中发动机越多,每转为发动机的作功冲程产生越多的动力,这就意味着八缸发动机运转的越平顺,因为发动机在作功冲程中运转时间和旋转角度紧密。 多气缸发动机有三种排列形式,任其一种 1、 直列式发动机用一个气缸体,大多数四缸发动机和一些六缸发动机都采用这种型式,这种气缸不必垂直分布,它们可以向任一方向倾斜。 2、 V-型发动机用两排同样的气缸,通常夹角为60°或90°,大多数有六缸或八缸,尽管四缸和十二缸也有采用V型的。 3、 卧式或者对置式发动机有两排互为180°的气缸,这些节省窨发动机设计通常采用风冷式,在雪弗兰、富士、大众车采用这种型式,富士汽车采用水冷式,在顶置式风冷发动机中,大众的新型厢式汽车采用水冷式。
Engine Operating Principles Most automobile dngines are internal combustion, reciprocating 4-stroke gasoline engines, but other types have been used, including the diesel, the rotary ( Wankel ) , the 2-srtoke, and stratified charge. Reciprocating means up and down or banck and forth, It is the up and down action of a piston in the cylinder blick, or engine block. The blick is an iron or aluminum casting that contains engine cylinders and passges called water jackets for coolant circulation. The top of the block is covered with the cylinder head. Which forms the combustion chanber. The bottom of the block is covered with an oil pan or oil sump. Power is produced by the linear motion of a piston in a cylinder. However, this linear motion must be changed into rotary motion to turn the wheels of cars of trucks. The piston is attached to the top of a connecting rod by a pin, called a piston pin or wrist pin. The bottom of the connecting rod is attached to the crankshaft. The connecting rod transmits the up-and-down motion of the piston to the crankshaft, which changes it into rotary motion. The connecting rod is mounted on the crankshaft with large beaings called rod bearings. Similar bearings, called main bearings, are used to mount the crankshaft in the block. Shown in Fig. 1-1 The diameter of the cylinder is called the engine bore. Displacement and compression ratio are two frequently used engine specifications. Displacement indicates engine size, and compression ratio compares the total cylinder volume to compression chamber volume. The term stroke is used to describe the movement of the iston within the cylinder, as well as the distance of piston travel. Depending on the type of engine the operating cycle may require either two or four strokes to complete. The 4-stroke engine is also called Otto cycle engine, in honor of the German engineer, Dr. Nikolaus Otto, who first applied the principle in 1876. In the 4-stroke engine, four strokes of the piston in the cylinder are required to complete one full operating cycle. Each stroke is named after the action it performs intake, compression, power, and exhaust in that order, shown in Fig1-2. 1、 Intake stroke As the piston moves down, the vaporized mixture of fuel and air enters the cylinder through open intake valve. To obtain the maximum filling of the cylinder the intake valve opens about 10°before t.b.c., giving 20°overlap. The inlet valve remains open until some 50°after b.d.c. to take advantage of incoming mixture. 2、 Compression stroke The piston turns up, the intake valve closes, the mixture is compressed within the combustion chamber, while the pressure rise to about 1Mpa, depending on various factors including the compression ratio, throttle opening and engine speed. Near the top of the stroke the mixture is ignited by a spark which bridges the gap of the spark plug. 3、 Power stroke The expanding gases of combustion produces a rise in pressure of the gas to some 3.5Mpa, and the piston is forced down in the cylinder. The exhaust valve opens near the bottom of the stroke. 4、 Exhust stroke