货币金融学 米什金 期末重点总结
- 格式:docx
- 大小:27.32 KB
- 文档页数:5
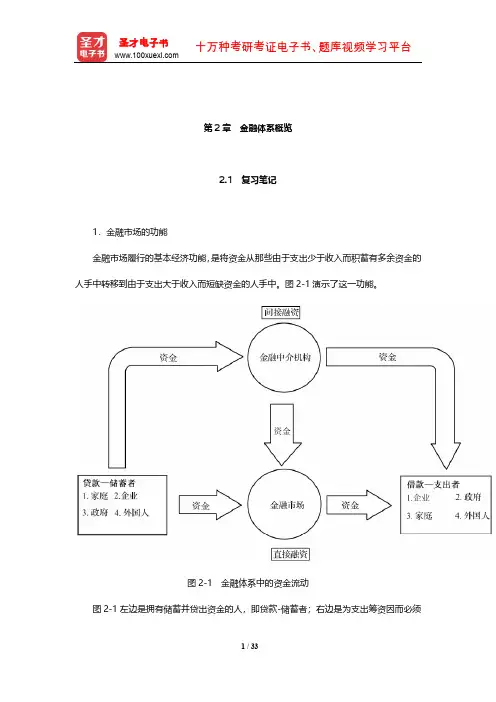
第2章金融体系概览2.1 复习笔记1.金融市场的功能金融市场履行的基本经济功能,是将资金从那些由于支出少于收入而积蓄有多余资金的人手中转移到由于支出大于收入而短缺资金的人手中。
图2-1演示了这一功能。
图2-1 金融体系中的资金流动图2-1左边是拥有储蓄并贷出资金的人,即贷款-储蓄者;右边是为支出筹资因而必须借入资金的人,即借款-支出者。
主要的贷款-储蓄者是居民,但工商企业、政府、外国人及其政府有时候也有资金剩余,因而也要贷放出去。
最主要的借款-支出者是工商企业和政府,但居民和外国人也会为购买汽车、家具和住宅而借入资金。
图中的箭头表示:资金沿着两条路线从贷款-储蓄者手中流入借款-支出者手中。
在直接融资中(图2-1底部所示的路线),借款人通过在金融市场上向贷款人出售有价证券,直接向贷款人借入资金,所发行的有价证券构成对借款人未来收入或者资产的索取权。
有价证券对于购买者来说是资产,但对于发行者(个人和企业)来说是负债。
如图2-1所示,资金从贷款人向借款人流动的第二条途径就是间接融资,之所以称之为间接融资,其原因是在贷款-储蓄者和借款-支出者之间还有一个金融中介机构,它帮助资金从一方流向另一方。
金融中介机构向贷款-储蓄者借入资金,并向借款-支出者发放贷款,从而完成资金的转移。
金融市场的功能有:(1)金融市场使资金从没有生产性投资机会的人手中流向有这种投资机会的人手中。
这样,金融市场有助于资本的合理配置,为经济社会更高的产出与效率作出了贡献。
(2)运转良好的金融市场使得消费者能够合理地选择购买时机,直接提高了他们的福利。
2.金融市场的结构(1)债务和股权市场①债务工具:是一种契约协定,借款人以契约的方式,承诺向债务工具的持有人定期支付固定的金额(利息与本金支付),直至一个确定的日期(到期日)支付最后一笔金额。
债务工具的期限就是到该工具最终偿还日的时间(期限)。
按照偿还期的不同,债务工具可以分为短期(1年以下)、中期(1~10年之间)、长期(10年或10年以上)。

中国人民大学金融专业考研米什金《货币金融学》学姐重点笔记第四篇中央银行与货币政策操作第十三章中央银行的结构与联邦储备体系目标(最重要的目标是第一个,然后是前三个,都是人民生活相关)1物价稳定(通货膨胀会抑制经济增长,恶心通货膨胀具有极强的破坏力。
名义锚是锁定物价水平以实现物价稳定目标的名义变量,前提是这个变量和物价水平有着稳定并且可靠的联系。
使用名义锚,解决时间不一致问题。
时间不一致主要是指短期政策与长期政策发生了冲突。
比如新年制定了减肥计划,可是第二天却无法自抑开始吃冰淇淋。
使得计划不能在长期保持一致)2高就业(由于存在摩擦性失业和结构性失业,所以应该追求自然失业率)3经济增长4金融市场稳定5利率稳定6外汇市场稳定物价稳定是否应该成为最主要的货币政策目标?物价稳定在长期内和其他目标是一种的,比如在长期通货膨胀和失业率就不存在菲利普斯曲线,但是在短期,比如经济扩张,失业下降,经济过热,通货上涨,为了稳定物价,银行会提高利率,但这样就会减少就业和加剧利率不稳定性。
如何破?阶梯目标和双重目标联邦储备体系的起源由于对中央集权的恐惧,导致了国民第一银行和国民第二银行的实践失败,由于缺少最后贷款人,导致银行业恐慌频发。
最终,美联储诞生。
中央银行三大法宝美联储是独立的吗?1工具独立性和目标独立性1收到立法和国会压力2委员会成员任期2总统压力3独立的收入来源中央银行的行为:官僚行为理论,增强权利和声望的愿望,包括捍卫自主权和避免利益冲突美联储应该保证独立性吗支持,受迫于政治压力会有通货膨胀压力,政治周期理论,政治家缺乏解决复杂经济事务的能力反对,精英政治不民主,财政政策,未能履行好职责,不能摆脱政治压力,第十四章多倍存款创造和货币供给过程美联储的资产负债资产负债政府证券流通中的现金贴现贷款准备金美联储的负债是货币供给的重要组成部分,美联储的货币负债总额(流通中的现金与准备金之和)与美国财政部的货币负债(流通中的财政货币,主要是铸币)被称为基础货币(又叫高能货币)负债或资产的科目的变动都会引起基础货币的增加,然后通过货币乘数和货币供给发生联系基础货币分为两种,非借入基础货币和借入准备金但美联储通过资产的运作(公开市场操作和贴现率),对基础货币实施控制公开市场购买对准备金的影响取决于债券出售方将销售所得现金以现金还是存款形式持有,但是无论哪种,对基础货币的影响是相同的。

米什金的货币金融学摘要:1.米什金的货币金融学概述2.米什金的货币理论3.米什金的金融市场理论4.米什金的政策建议及其影响正文:一、米什金的货币金融学概述《米什金的货币金融学》是著名经济学家弗拉基米尔·米什金所著的一部关于货币金融理论的著作。
该书深入浅出地讲解了货币、金融市场和货币政策等方面的知识,旨在帮助读者更好地理解金融体系的运行。
书中所提出的许多观点和理论在金融学领域具有重要意义,为后续研究提供了丰富的理论资源。
二、米什金的货币理论米什金在书中提出了一种全新的货币理论。
他认为,货币并非仅仅是一种交换媒介,而是具有资产属性的。
货币的价值取决于它所能购买的商品和服务的数量,即其实际购买力。
米什金将这一理论称为“货币资产定价理论”。
此外,米什金还探讨了货币供应、货币需求以及通货膨胀等与货币相关的现象。
他认为,货币供应的增加会导致通货膨胀,而货币需求的减少则会导致通货紧缩。
因此,要保持经济的稳定,货币供应和需求必须保持平衡。
三、米什金的金融市场理论在金融市场方面,米什金认为,金融市场的主要功能是实现资源的有效配置。
金融市场通过为投资者提供投资机会,为企业提供融资途径,从而促进了资本的流动和资源的配置。
米什金还对金融市场的各类工具和产品进行了详细的分析,包括股票、债券、期货、期权等。
他认为,这些金融工具为投资者提供了丰富的投资选择,有助于投资者根据自身的风险承受能力和收益预期进行投资。
四、米什金的政策建议及其影响在政策建议方面,米什金强调,货币政策在维护经济稳定和促进经济增长方面具有重要作用。
他主张实行稳健的货币政策,即在保持物价稳定的同时,还要关注经济增长和就业。
此外,米什金还对金融监管提出了自己的看法。
他认为,金融监管应当适度,既要防止金融市场出现过度泡沫,又要保证市场的正常运行。
这一观点对后来的金融监管理论产生了重要影响。



第一章:1.什么是金融市场,金融市场的基本功能是什么?金融市场是资金由盈余单位向短缺单位转移的市场。
金融市场履行的基本经济功能是:从那些由于支出少于收入而积蓄了盈余资金的人那里把资金引导到那些由于支出超过收入而资金短缺的人那里。
第二章:金融体系概述1.金融市场的种类划分(1) 股权市场和债权市场。
(按契约的性质)(2) 一级市场和二级市场。
(按在发行和交易中的地位)(3) 场内交易市场和场外交易市场。
(按交易的地点和场所)(4) 货币市场和资本市场。
(按所交易金融工具的期限长短)2.主要的货币市场工具和资本市场工具有哪些?货币市场工具:(1)美国国库券(贴现发行)(2)可转让银行定期存单(3)商业票据(4)回购协议(5)联邦基金资本市场工具:(1)股票(2)抵押贷款(3)公司债券(4)美国政府债券(5)美国政府机构债券(6)州和地方政府债券3.金融中介机构的概念和类型概念:金融中介机构是通过发行负债工具筹集资金,并且通过运用这些资金购买证券或者发放贷款来形成资产的金融机构。
(1)存款机构(商业银行,储贷协会,互助储蓄银行,信用社)(2)契约型储蓄机构(保险公司,养老金,退休金)(3)投资中介机构(财务公司,共同基金,货币市场共同基金,投资银行)4.直接融资和间接融资的区别(1)在直接融资中,借款人通过将证券卖给贷款人,直接从贷款人那里取得资金;在间接融资中,金融机构居于贷款人和借款人之间,帮助实现资金在二者之间的转移。
(2)直接融资的优点:短缺单位可以节约一定的融资成本,盈余单位可以获得较高的资金报酬。
缺点:盈余单位需要有一定专业知识和能力且负担的风险高;对短缺单位来说,直接融资市场门槛较高。
(3)间接融资的优点或功能:降低交易成本,实现规模经济;有助于降低投资者面临的风险;解决信息不对称问题(交易发生前:逆向选择;交易发生后:道德风险)(4)需要注意的是区别这两种融资不在于是否有金融机构的介入,而在于金融机构是否发挥了信用中介作用。

⼴外货币银⾏学期末重点全英⽶什⾦考试题型以及分数分布:⼀、选择题:1’*20=20’⼆、名词解释:4’*5=20’三、简答题:8’*5=40’四、论述题:20’*1=20’重点制作思路:1.考虑到时间关系,抓⼤放⼩2.结合⽼师提及复习内容进⾏预测3.以理顺书本架构为主,看到⼀个知识点猜⼀下可能会出什么题The economics of money,banking and financial markets----by Kyle Chapter1:Why Study Money, Banking, and Financial Markets?(本章了解⼀下这个问题即可,最多考⼀下选择)Answer:To examine how financial markets such as bond and stock markets workTo examine how financial institutions such as banks workTo examine the role of money in the economyChapter2:An Overview of the Financial System1.Function of Financial MarketsPerform the essential function of channeling funds from economic players that have saved surplus funds to those that have a shortage of fundsDirect finance: borrowers borrow funds directly from lenders in financial markets by selling them securities.Promotes economic efficiency by producing an efficient allocation(分配)of capital(资⾦), which increases production Directly improve the well-being of consumers by allowing them to time purchases better 2.Structure of Financial Markets Debt and Equity (普通股)MarketsPrimary and Secondary MarketsExchanges and Over-the-Counter (OTC不通过交易所⽽直接售给顾客的) MarketsMoney and Capital Markets(货币和资本市场)3. Financial Market Instruments(要能举出例⼦,很可能考选择)Money markets deal in short-term debt instrumentsCapital markets deal in longer-term debt and equity instruments.4.Internationalization of Financial Markets(重点,选择、名词解释都有可能)Foreign Bonds & EurobondEurocurrencies & EurodollarsWorld Stock Markets5.Function of Financial Intermediaries: Indirect Finance(记⼀下⾦融中介机构的功能,交易成本很可能考名词解释)Lower transaction costs (time and money spent in carrying out financial transactions).Reduce the exposure of investors to riskDeal with asymmetric 不对称information problemsConclusion:Financial intermediaries allow “small” savers and borrowers to benefit from the existence of financial markets.6. Types of Financial Intermediaries(会分类即可)Depository institutionsContractual saving institutionsInvestment intermediaries7.Regulation of the Financial SystemTo increase the information available to investors:To ensure the soundness 健康稳固of financial intermediariesChapter3:What Is Money?1.Meaning of Money(即definition,必考名词解释!!)Money (or the “money supply”): anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods or services or in the repayment of debts.2.Functions of Money(重点)Medium of Exchange:A medium of exchange mustUnit of Account:Store 储藏of Value:3.Evolution of the Payments SystemCommodity 商品MoneyFiat 法定MoneyChecks ⽀票Electronic Payment (e.g. online bill pay).E-Money (electronic money):4.Measuring Money (重中之重,M1/M2都很有可能考名词解释)Construct monetary aggregates using the concept of liquidity:(构建货币总量使⽤流动性的概念)M1 (most liquid assets)= currency + traveler’s checks + demand deposits + other checkable deposits.M2 (adds to M1 other assets that are not so liquid) = M1 + small denomination time deposits + savings deposits and money market deposit accounts + money marketmutual fund shares.Chapter 4:Understanding Interest Rates1.measuring interest rates:Present Value(很可能考察名词解释)A dollar paid to you one year from now is less valuable than a dollar paid to you todaySimple Present Value:PV=CF/(1+i)n次⽅2.Four Types of Credit Market InstrumentsSimple LoanFixed Payment LoanCoupon Bond 附票债券Discount Bond 贴现债券3.Yield to Maturity(重点,很可能名词解释)The interest rate that equates the present value of cash flow payments received from a debt instrument with its value today 计算4种不同信⽤⼯具外加Consol or Perpetuity(⾦边债券或永久债券)的YM4. Yield on a Discount Basis(了解即可)Current Yield当期收益率Yield on a Discount Basis 折价收益率Rate of Return 收益率5.Rate of Return and Interest Rates(收益率与利息率的distinction)The return equals the yield to maturity only if the holding period equals the time to maturityA rise in interest rates is associated with a fall in bond prices, resulting in a capital loss if time to maturity is longer than the holding periodThe more distant a bond’s maturity, the greater the size o f the percentage price change associated with an interest-rate changeThe more distant a bond’s maturity, the lower the rate of return the occurs as a result of an increase in the interest rate Even if a bond has a substantial initial interest rate, its return can be negative if interest rates rise6.Interest-Rate RiskPrices and returns for long-term bonds are more volatile than those for shorter-term bondsThere is no interest-rate risk for any bond whose time to maturity matches the holding period7.Real and Nominal Interest Rates(重点,很可能考察简答题)Nominal interest rate makes no allowance for inflationReal interest rate is adjusted for changes in price level so it more accurately reflects the cost of borrowingEx ante real interest rate is adjusted for expected changes in the price levelEx post real interest rate is adjusted for actual changes in the price level8.Fisher Equation(重点考察)Chapter5:The Behavior of Interest Rates1.Determining the Quantity Demanded of an AssetWealth: the total resources owned by the individual, including all assetsExpected Return: the return expected over the next period on one asset relative to alternative assetsRisk: the degree of uncertainty associated with the return on one asset relative to alternative assetsLiquidity: the ease and speed with which an asset can be turned into cash relative to alternative assets(流动性很有可能考名词解释)2.Theory of Asset Demand(必考,死活都得背下来)Holding all other factors constant:1.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to wealth2.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its expected returnrelative to alternative assets3.The quantity demanded of an asset is negatively related to the risk of its returnsrelative to alternative assets4.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its liquidity relative toalternative assets3.Supply and Demand for Bonds(见到看⼀下图)Market Equilibrium4.Shifts in the Demand for BondsWealth: in an expansion with growing wealth, the demand curve for bonds shifts to the rightExpected Returns: higher expected interest rates in the future lower the expected return for long-term bonds, shifting the demand curve to the leftExpected Inflation: an increase in the expected rate of inflations lowers the expected return for bonds, causing the demand curve to shift to the leftRisk: an increase in the riskiness of bonds causes the demand curve to shift to the left Liquidity: increased liquidity of bonds results in the demand curve shifting right 5.Shifts in the Supply of BondsExpected profitability of investment opportunities: in an expansion, the supply curve shifts to the rightExpected inflation: an increase in expected inflation shifts the supply curve for bonds to the rightGovernment budget: increased budget deficits shift the supply curve to the right6.The Liquidity Preference Framework(重中之重)7.Demand for Money in the Liquidity Preference FrameworkAs the interest rate increases:–The opportunity cost of holding money increases…–The relative expected return of money decreases……and therefore the quantity demanded of money decreases.8.Shifts in the Demand for Money(都很重要)Income Effect:a higher level of income causes the demand for money at each interest rate to increase and the demand curve to shift to the rightPrice-Level Effect: a rise in the price level causes the demand for money at each interest rate to increase and the demand curve to shift to the rightLiquidity preference framework leads to the conclusion that an increase in the money supply will lower interest rates: the liquidity effect.Income effect finds interest rates rising because increasing the money supply is an expansionary influence on the economy (the demand curve shifts to the right). Chapter9:Banking1.The Bank Balance SheetLiabilities–Checkable deposits–Nontransaction deposits–Borrowings–Bank capitalAssets–Reserves(准备⾦)–Cash items in process of collection–Deposits at other banks–Securities–Loans–Other assets2.Basic Banking:Cash Deposit:Opening of a checking account leads to an increase in the bank’s reserves equal to the increase in checkable depositsCheck Deposit3.Inter-businessBank settlementFinance leaseFiduciary businessSafe deposit box4.Off-Balance-Sheet ActivitiesLoan sales (secondary loan participation)Generation of fee income. Examples:Chapter12:Central Banks and the Federal Reserve System(此章省略很多)1.Structure of the Fed(了解即可)12 FRBs(9⼈)Member BanksFOMC (7+1+4⼈)Federal Advisory Council (12⼈)2.Federal Reserve Bank(3+3+3⼈)Functions:Clear checksIssue new currencyWithdraw damaged currency from circulationAdminister and make discount loans to banks in their districtsEvaluate proposed mergers and applications for banks to expand their activitiesAct as liaisons between the business community and the Federal Reserve SystemExamine bank holding companies and state-chartered member banksCollect data on local business conditionsUse staffs of professional economists to research topics related to the conduct of monetary policyChapter13&14:The Money Supply Process:1.Players in the Money Supply ProcessCentral bank (Federal Reserve System)Banks (depository institutions; financial intermediaries)Depositors (individuals and institutions)2.Fed’s Balance Sheet4.Open Market PurchaseThe effect of an open market purchase on reserves depends on whether the seller of the bonds keeps the proceeds from the sale in currency or in depositsThe effect of an open market purchase on the monetary base always increases the monetary base by the amount of the purchaseOpen Market SaleReduces the monetary base by the amount of the saleReserves remain unchangedThe effect of open market operations on the monetary base is much more certain than the effect on reserves5.Fed’s Ability to Control the Monetary BaseSplit the monetary base into two components :MBn= MB - BRthe non-borrowed monetary base :MBnborrowed reserves:BR6.The Formula for Multiple Deposit Creation(很重要!必考,记住公式)7.Factors that Determine the Money SupplyChanges in the nonborrowed monetary base MBnChanges in borrowed reserves from the FedChanges in the required reserves ratioChanges in currency holdingsChanges in excess reserves8.The Money Multiplier(重点)Assume that the desired holdings of currency C and excess reserves ER grow proportionally with checkable deposits D. Then,c = {C/D} = currency ratioe = {ER/D} = excess reserves ratioThe monetary base MB equals currency (C) plus reserves (R):MB = C + R = C + (r x D) + ERM=m*MB=m*(MBn+BR)M=1+c/r+e+cChapter 15:Tools of Monetary Policy1. Tools of Monetary PolicyOpen market operationsChanges in borrowed reservesChanges in reserve requirementsFederal funds rate: the interest rate on overnight loans of reserves from one bank to another 2.Demand in the Market for ReservesSupply in the Market for Reserves3.Affecting the Federal Funds Rate4.Open Market Operations(超级重点)Advantages:The Fed has complete control over the volumeFlexible and preciseEasily reversedQuickly implemented5.Discount Policy(超级重点)Advantages:Used to perform role of lender of last resortdisadvantages:Cannot be controlled by the Fed; the decision maker is the bank6.Reserve Requirements(超级重点)Advantages:No longer binding for most banksdisadvantages:Can cause liquidity problemsIncreases uncertainty for banks7.Monetary Policy Tools of the European Central BankOpen market operationsLending to banksReserve RequirementsChapter16:The Conduct of Monetary Policy: Strategy and Tactics1. Goals of Monetary Policy(1)The Price Stability GoalLow and stable inflationInflationNominal anchor to contain inflation expectationsTime-inconsistency problem(2)Other Goals of Monetary PolicyHigh employmentEconomic growthStability of financial marketsInterest-rate stabilityForeign exchange market stability2.Monetary TargetingAdvantages–Almost immediate signals help fix inflation expectations and produce less inflation –Almost immediate accountability Disadvantages–Must be a strong and reliable relationship between the goal variable and the targeted monetary aggregat e3.Inflation TargetingPublic announcement of medium-term numerical target for inflationInstitutional commitment to price stability as the primary, long-run goal of monetary policy and a commitment to achieve the inflation goalInformation-inclusive approach in which many variables are used in making decisions AdvantagesDoes not rely on one variable to achieve targetEasily understoodReduces potential of falling in time-inconsistency trapStresses transparency and accountabilityDisadvantagesDelayed signalingToo much rigidityPotential for increased output fluctuationsLow economic growth during disinflation4.Monetary Policy with an Implicit Nominal AnchorThere is no explicit nominal anchor in the form of an overriding concern for the Fed.Forward looking behavior and periodic “preemptive strikes”The goal is to prevent inflation from getting started.Advantages–Uses many sources of information–Avoids time-inconsistency problemDisadvantages–Lack of transparency and accountability–Strong dependence on the preferences, skills, and trustworthiness of individuals in charge–Inconsistent with democratic principles5.Tactics: Choosing the Policy InstrumentTools–Open market operation–Reserve requirements–Discount ratePolicy instrument (operating instrument)–Reserve aggregates–Interest rates–May be linked to an intermediate targetInterest-rate and aggregate targets are incompatible (must chose one or the other).6.Linkages Between Central Bank Tools, Policy Instruments, Intermediate Targets, and Goals of Monetary Policy(中间⽬标是超级重点,死活都要背下来)Chapter19:The Demand for Money1.Velocity of Money and The Equation ofExchangeV=P*Y/MM*V=P*Y2.Quantity Theory of Money DemandSO: Demand for money is determined by:The level of transactions generated by the level of nominal income PYThe institutions in the economy that affect the way people conduct transactions and thus determine velocity and hence k 3.Keynes’s Liquidity Preference TheoryTransactions motivePrecautionary motiveSpeculative motiveVelocity is not constant:4.Friedman’s Modern Quantity Theory of Money(记住该公式及其含义)5.Differences between Keynes’s and Friedman’s Model (cont’d)Friedman–Includes alternative assets to money–Viewed money and goods as substitutes–The expected return on money is not constant; however, r b – r m does stay constant as interest rates rise–Interest rates have little effect on the demand for moneyFriedman (cont’d)–The demand for money is stable–velocity is predictable–Money is the primary determinant of aggregate spendingChapter23:Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy: The Evidence1.Framework(1)Structural Modelwhether one variable affects anotherTransmission mechanism–The change in the money supply affects interest rates–Interest rates affect investment spending–Investment spending is a component of aggregate spending (output) Advantages and Disadvantages(2)Reduced-FormAnalyzes the effect of changes in money supply on aggregate output (spending) to see if there is a high correlation Advantages and Disadvantages2.Transmission Mechanisms of Monetary Policy(1)Asset Price EffectsTraditional interest rate effectsExchange rate effects on net exports...(2)Credit ViewChapter24:Money and Inflation1.meaning of inflation(死活背下来)extremely high for a sustained period of time, its rate of money supply growth is also extremely highMoney Growth–High money growth produces high inflationFiscal Policy–Persistent high inflation cannot be driven by fiscal policy aloneSupply Shocks–Supply-side phenomena cannot be the source of persistent high inflation ?Conclusion: always a monetary phenomenon 2.Origins of Inflationary Monetary PolicyCost-push inflation–Cannot occur without monetary authorities pursuing an accommodating policy ?Demand-pull inflationBudget deficits–Can be the source only if the deficit is persistent and is financed by creating money rather than by issuing bondsTwo underlying reasons–Adherence of policymakers to a high employment target–Presence of persistent government budget deficits3.The Discretionary (Activist)/ Nondiscretionary (Nonactivist) Policy Debate(1)Advocates of discretionary policy:regard the self-correcting mechanism as slowPolicy lags slow activist policy(2)Advocates of nondiscretionary policy:believe government should not get involvedDiscretionary policy produces volatility in both the price level and output。

计算 Term structure Expectations theory:i nt =i t +i t +1e +i t +2e +⋯+i t + n−1e n Liquidity premium theory:i nt =i t +i t +1e +i t +2e +⋯+i t + n −1e n +l ntBecause of people preferred short- term bonds, there is a larger liquidity premium as the term to maturity lengthens. (上升图)Yield curves tend to have an especially steep upward slope. (下降图)Yield curves will not tend to have a steep downward slope, and maybe will slope upward. Stock pricing modelOne-Period Valuation Model :P 0=Div 11+k e +P 11+k eP 0=the current price of the stockDiv 1=the dividend paid at the end of year 1.k e =the required return on investments in equity.P 1=the price at the end of the first period .Generalized Dividend Valuation Model :P 0= D t1+k e t ∞t =1Gordon Growth Model :P 0=D 0× 1+g(k e −g )=D 1(k e −g )D 0=the most recet dividend paid .g =the expected constant growth rate in dividends. Interest-Rate Risk A change in its interest rate:percent change in market value of security≈−persentage-point change in interest rate×duration in yearsA1:The assets fall in value by $8 million(=$100 million ×−2%×4 years )while the liabilities fall in value by $10.8 million(=$90 million ×−2%×6 years ). Because the liabilities fall in value by $2.8 million more than the assets do, the net worth of the bank rises by $2.8 million. The interest-rate risk can be reduced by shortening the maturity of the liabilities to a duration of 4 years or lengthening the maturity of the assets to a duration of 6 years. Alternatively, you could engage in an interest-rate swap, in which you swap the interest earned on your assets with the interest in another bank’s assets that have a durati on of 6 years.A2: The gap is $10 million ($30 million of rate-sensitive assets minus $20 million of rate-sensitive liabilities). The change in bank profits from the interest rate rise is +$0.5 million (5%×$10 million); the interest rate risk can be reduced by increasing rate-sensitive liabilities to $30 million or by reducing rate-sensitive assets to $20 million. Alternatively, you could engage in an interest rate swap in which you swap the interest in $10 million of rate-sensitive assets for the interest on another bank ’s $10 million of fixed-rate assets.The Money MultiplierM is money supply.MB is the monetary base.M=m×MBc = {C/D} = currency ratioe = {ER/D} = excess reserves ratioC is currency.ER is excess reserves.D is checkable deposits.r is the required reserve ratio.D=1r+e+c×MBM=1+cr+e+c×MBm=1+cr+e+c问答Present Value: A dollar paid to you one year from now is less valuable than a dollar paid to you today.Yield to Maturity and the Bond Price for a Coupon Bond: have 3 facts.1.When the coupon bond is priced at its face value, the yield to maturity equals the coupon rate.2.The price of a coupon bond and the yield to maturity are negatively related; that is, as the yield to maturity rises, the price of the bond falls. AS the yield to maturity falls, the price of the bond rises.3.The yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate when the bond price is below its face value.Yield to Maturity(到期收益率):1.The interest rate that equates the present value of cash flow payments received from a debt instrument with its value today.2.Also called internal rate of return.3.Most accurate measure of i.Rate of Return:The payment to the owner plus the change in value expressed as a fraction of the purchase price.RET=CP t +P t+1−P tP tRET=return from holding the bond from time t to t+1. P t=price of bond at time tP t+1=price of the bond at time t+1C=coupon paymentCP t=current yield=i cP t+1−P tP t=rate of capital gain=gRate of Return and Interest Rates:1.The return equals the yield to maturity only if the holding period equals the time to maturity.2.A rise in interest rates is associated with a fall in bond prices, resulting in a capital loss if time to maturity is longer than the holding period.3.The more distant a bond’s maturity, the greater the size of the percentage price change associated with an interest-rate change.4.The more distant a bond’s maturity, the lower the rate of return that occurs as a result of an increase in the interest rate.5.Even if a bond has a substantial initial interest rate, its return can be negative if interest rates rise.Real and Nominal Interest Rates:1.Nominal interest rate makes no allowance for inflation.2.Real interest rate is adjusted for changes in price level so it more accurately reflects the cost of borrowing.3.Ex ante real interest rate is adjusted for expected changes in the price level.4.Ex post real interest rate is adjusted for actual changes in the price level.4 Factors of Asset Demand:An asset is a piece of property that is a store of value, such as money ,bond, stocks, and houses.1.Wealth: the total resources owned by the individual, including all assets2.Expected Return: the return expected over the next period on one asset relative to alternative assets3.Risk: the degree of uncertainty associated with the return on one asset relative to alternative assets4.Liquidity: the ease and speed with which an asset can be turned into cash relative to alternative assetsTheory of Asset Demand:1.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to wealth2.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its expected return relative to alternative assets3.The quantity demanded of an asset is negatively related to the risk of its returns relative to alternative assets4.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its liquidity relative to alternative assetsThe Structure of Interest Rates风险结构:Bonds with the same maturity have different interest rates due to: Default risk违约风险, Liquidity流动性, Tax considerations所得税因素.1. Default risk: probability that the issuer of the bond is unable or unwilling to make interest payments or pay off the face value.Conclusion: a bond with default risk will always have a positive risk premium, and an increase in its default risk will raise the risk premium. 具有违约风险的债券通常具有正的风险溢价,而违约风险的增长将会提高风险溢价水平。

学习内容(章节要求、知识点)第一章第一章为什么研究货币、银行与金融市场附录了解性的内容,掌握基本概念,能简要回答出课后问答和思考题即可。
本章可能以判断题形式出题,但涉及不会太多。
第二章金融体系概览本章主要内容是金融市场的基础功能、参与者、工具等。
头脑中要形成市场分类体系,掌握基本概念。
以下术语可能会考名词解释:逆向选择、道德风险、回购协议、规模经济、金融中介化,等等,这些概念都比较基本,所以掌握也比较容易。
要能回答出:金融市场的主要分类金融市场主要工具金融中介机构的类型一级市场与二级市场的区别与联系欧洲债券、外国债券、欧洲货币、欧洲美元的区别与联系政府为避免金融恐慌的发生,通常采取的六种监管类型……以上问题出问答题的概率不大,主要是常识性的理解和选择题第三章什么是货币本章知识点较少,而且关于货币基础概念的内容重点参考货币银行学,所以本书这一章非重点了解。
需掌握货币的含义、货币的职能(参考货币银行学)、支付体系的演进、货币供应量层次分类(中外分类不同,都需掌握,具体参考货币银行学)第四章理解利率本章知识点较少,提醒以判断题和选择题形式为主需掌握几种收益率的含义和计算公式,特别需注意债券到期收益率或利率与价格的联系,注意费雪效应和费雪方程式的区别等。
注意课后题中的计算。
第五章利率行为本章属于重点章节,需要深入理解重点掌握资产需求决定理论、债券需求曲线决定因素及变动、债券供给曲线决定因素及变动、流动性偏好理论等。
特别注意本章各专栏中的相关知识,同样重要,需认真学习并掌握。
第六章利率的风险结构与期限结构本章属于重点章节,需深入理解重点掌握利率风险结构定义及决定因素,利率期限结构定义,收益率曲线定义及三种形式,熟记利率期限结构中的三种理论及其对应可以解释的三个经验事实。
本章内容各种题型都可能出现,而且也需要总结出上述几个知识点的定义描述语言。
第七章股票市场、理性预期理论与有效市场假定本章内容涉及知识点并不在本书中,主要需在公司理财课本中掌握知识点如下:适应性预期、套利的定义、戈登增长模型、最优预测、随机游走的定义、有效市场的假定和三种形式市场分类以及市场异象举例。

第3章什么是货币3.1 复习笔记1.货币的含义(1)货币(money)是在商品和劳务支付或债务偿还中被普遍接受的东西,包括可用于购物的通货(纸币和硬币)、活期存款和其他形式能用于支付的货币。
(2)财富(wealth)是作为价值储藏的各项财产的总和,不仅包括货币,还包括其他各种资产,比如债券、普通股、艺术品、土地、家具、汽车和房产等。
(3)收入(income)是指在单位时间内收益的流量,而货币是存量概念,是某一特定时点上的一个确定的金额。
2.货币的功能货币在任何经济社会中都有三个基本功能:交易媒介、记账单位、价值贮藏。
(1)交易媒介货币的交易媒介功能是指货币被用来购买产品和服务。
货币的交易媒介功能能够极大地减少花费在交换物品和劳务上的时间,从而提高经济运行效率。
对于任何行使交易媒介功能的商品来说,它必须满足几个条件:①便于标准化,其价值易于确定;②被广泛接受;③易于分割,以方便“找零”;④便于携带;⑤不易变质。
(2)记账单位货币的记账单位功能是指货币用于衡量经济社会中的价值。
由于货币的记账功能的发挥,需要考虑的价格数量减少,从而减少经济社会中的交易成本。
(3)价值储藏价值储藏是一种超越时间的购买力的储藏。
利用货币的价值储藏功能将取得收入和支出的时间分离开来。
流动性,即某项资产转化为交易媒介的相对难易和快慢程度。
货币是所有资产中流动性最高的,因为它本身就是交易媒介,它不需要转换为任何东西,直接就表现为购买力。
其他资产在转化为货币的时候,还涉及到交易成本。
货币是最具流动性的资产这一事实,就解释了为什么人们愿意持有货币,尽管它不是最好的价值储藏手段。
货币作为价值储藏手段的优劣取决于物价水平,因为货币价值依赖于价格水平。
3.支付体系的演进(1)支付体系(payments system)是指经济社会中进行交易的方法。
支付制度在不同的时期一直在发展变化,而货币形式也在随之发展变化。
支付制度的演变过程如下:商品货币→不兑现纸币→支票→电子支付→电子货币。

1,measurement of moneyM0:流通中的现金Currency in circulation refers to that circulated in nonbank publics, this is the money in the narrowest sense,We use M 0 to denote. Eg: coins, paper moneyM1: narrow money 狭义货币currency in circulation and checkable deposits 反应了社会的直接购买支付能力M2: broad money 广义货币 M 1+Saving deposits既反映了现实的购买力也反映了潜在的购买力,中央银行货币政策调节的主要中介目标2,function definition:(会判断)Measurement of money 价值尺度Medium of exchange 流通手段Medium of payment 支付手段Means of storage 储藏手段World currency 世界货币3,Gold standard 大致了解Gold coin standard is the typical example (金铸币本位制)4,fiat money standard (不兑现信用货币制度)Lecture2 money and monetary systems2011年11月20日0:231,components of financial system 看一下定义2,funds flows 流动的载体、原则、监管Indirect financing 间接融资:●3,直接融资和间接融资(了解)Indirect financing is a means of financing via financial intermediaries which mainly includes commercial banks.Commercial banks, insurance companies, investment funds, etc., are bridges for indirect financing.Theory of financial intermediation focusing on the reason why there is financial intermediary, the nature of financial intermediary, and the division of labor between financial markets and intermediaries.Direct financing●Financing activities between demanders for funds and suppliers of funds are conducted in financial markets directly.It is worth pointing out that direct financing also involves financial institutions such as investment banks, security brokers, and market makers, etc.Financial market theory focusing on allocation efficiency of capitals, and asset pricing, etc.Disadvantages of direct financing●Advantages vs. disadvantages of different financingsExpertise requirementsHigher risks involvedIndirect financing●Tough requirements for issuersReducing information and contract costsReducing risks by diversificationsTransformation of maturities4,两种结构,大致理解比较bank-based and market-based市场,伙伴关系相对少,股权分散银行,贷款,商业往来,合作伙伴,允许交叉持股直接融资:市场间接融资:银行Lecture3 financial system and financial structure2011年12月9日15:495,中国的金融体系概览(有所了解)A glimpse at china's financial system中国以商业银行主导的间接融资模式为主● 非简单的银行主导,政府干预太多在直接融资中,通过发行企业债券方式所筹集的资金比例低于股票融资。
中国人民大学金融专业考研米什金《货币金融学》重点章节第六篇货币政策第十九章货币需求IS-LM模型是分析利率和总产出水平的关系,而ad-as曲线是分析物价和总产出水平的.货币理论研究的是货币对经济的影响机制货币数量论:探讨名义总收入如何决定的理论.MV=PY(交易方程式,它阐释了名义收入与货币数量和流通速度的联系)交易方程式并不是说当货币供给(M)变动时,名义收入(PY)就会同向变动,因为还要考虑到货币流通速度(V)。
费雪认为由于经济体中的制度和技术特征只在较长的时间里才会对流通速度产生影响,所以,货币流通速度在短期内相当稳定。
这样交易方程式就转化为货币数量论。
该理论认为,名义收入仅仅取决于货币数量的变动。
又由于古典经济学家认为工资和价格是具有完全弹性的,所以Y总是维持在充分就业水平上的,即Y是相当稳定的。
最后得出结论:物价水平的变动仅仅源于货币数量的变动如果两边同时除以V,人们持有的货币数量M等于货币需求量Md,就可以得出货币需求的数量论Md=k*名义收入,也就是说,在流通速度一定的条件下,既定水平的名义收入所支持的交易规模决定人们的货币需求量。
所以,费雪的货币数量论表明,货币需求仅仅是收入的函数,利率对货币需求没有影响。
但是货币流通速度的变动是剧烈的,因而导致了更好解释货币流通速度行为的一些货币需求理论:凯恩斯的流动性偏好理论:交易动机预防动机投机动机(注意分析过程)综合三种动机,使用实际货币余额注意:可以通过对凯恩斯的流动性偏好函数变形,从而得出1.流通速度和利率的关,因为利率波动剧烈,所以流通速度波动距离2.流通速度顺周期3对未来正常利率水平的预期不稳定将导致货币流通速度的不稳定。
凯恩斯理论的进一步发展:货币需求的交易部分与利率水平负相关预防需求与利率负相关投机需求:利用资产组合来解释弗里德曼的现代货币数量论:认为主要和永久收入相关,和利率几乎没有什么影响。
所以弗里德曼认为活剥需求的随机波动很小。
货币金融学第一章为什么研究货币、银行和金融市场?金融市场债券市场股票市场外汇市场……………..证券(security)又称金融工具,是对发行人未来收入与资产的的索取权。
债券是债务证券,承诺在特定的时间段的定期支付,是决定利率的场所,所以利率决定理论,无论是债券需求理论还是流动性偏好理论,都是将债券作为利率的传导机制。
股票,代表的是所有权,是对公司收益和资产的索取权。
金融市场中,资金从拥有闲置货币的人手中转移到资金短缺的人手中,债券市场和股票市场等金融市场将资金从没有生产用途的人转向有生产用途的人手中。
经济周期的误解,经济周期是不规则的,无法预测的,时间跨度变幻不定的,因为有时候经济周期也被称为经济波动。
金融机构银行保险公司共同基金其他金融机构货币经济周期(货币的供给变动是经济周期波动的推动力之一)通货膨胀(货币的持续增加是无价水平持续上涨的一个重要原因)利率货币政策国际金融外汇市场第二章金融体系概览金融市场的功能金融市场最基本的功能就是实现资金盈余者和资金短缺者之间的资金转移,通过直接融资(借款人直接发行债券)或者间接融资,完成了资本的合理配置(包括生产性用途或者物质消费)金融市场的结构债务市场和股权市场一级市场和二级市场交易所和场外市场货币市场和资本市场金融市场工具货币市场工具美国国库券可转让存单商业票据回购协议联邦基金(容易困惑,不是联邦,而是银行间的贷款)资本市场工具股票抵押贷款企业债券美国政府债券美国政府机构债券州和地方政府债券消费者贷款和商业银行贷款金融中介机构的功能为什么金融中介结构和间接融资对金融市场而言如此重要?交易成本(金融中介具有降低成本的专门技术和规模经济)风险分担(资产转换和资产组合多样化)信息不对称造成的逆向选择和道德风险(甄别信贷风险技术和监督)而金融机构为经济社会提供了流动性服务,承担风险分担职能,并解决信息问题,金融中介机构的类型存款机构商业银行储蓄和贷款协会和互助储蓄银行信用社契约性储蓄机构保险公司和养老基金人寿保险公司火灾和意外伤害保险公司养老基金和政府退休基金投资中介机构财务公司共同基金货币市场共同基金投资银行金融体系的监管金融体系受到最严格的监管,旨在帮助投资者获得更多的信息和确保金融体系的健全性。
货币金融学复习资料米什金货币金融学复习资料米什金货币金融学是经济学中的一个重要分支,研究货币和金融体系的运行机制以及对经济活动的影响。
在学习货币金融学的过程中,米什金是一本非常经典的教材,被广泛应用于全球各大高校。
本文将对米什金的内容进行回顾和总结,以帮助读者更好地复习货币金融学知识。
首先,米什金详细介绍了货币的定义和功能。
货币作为一种交换媒介,具有价值尺度、支付手段和价值储藏等功能。
它的价值来自于人们对其信用的认可和社会的广泛接受。
货币的供给和需求决定了货币的价值,而货币的价值又对经济活动产生重要影响。
接着,米什金对货币供给和需求进行了深入分析。
货币供给由中央银行控制,通过货币政策的调控来影响经济。
货币需求受到人们的收入水平、利率水平、预期通货膨胀率等因素的影响。
米什金通过图表和实例生动地展示了货币供给和需求的关系,以及它们对经济的影响。
在货币市场方面,米什金对货币市场的均衡分析进行了详细阐述。
货币市场的均衡由货币供给和货币需求的交叉确定,而利率则是货币市场均衡的结果。
米什金通过提供货币需求和货币供给曲线的图表,解释了利率如何根据货币市场的供求关系来决定。
此外,米什金还介绍了货币政策的工具和目标。
货币政策的工具包括利率、准备金率和公开市场操作等,通过调整这些工具,中央银行可以影响货币供给和经济活动。
货币政策的目标主要包括稳定物价水平、促进经济增长和维护金融稳定等。
米什金详细解释了这些工具和目标的作用和实施方法。
此外,米什金还讨论了货币与经济增长、通货膨胀、失业等重要经济问题之间的关系。
货币供给的增加可以刺激经济增长,但如果供给过多,可能导致通货膨胀。
米什金对这些问题进行了深入分析,并提出了一些解决方案。
最后,米什金还介绍了国际货币体系和货币政策的国际协调。
国际货币体系的稳定对于全球经济的发展至关重要,而货币政策的国际协调可以减少不同国家之间的冲突和不稳定性。
米什金通过具体案例和理论分析,探讨了这些问题,并提出了一些思考。
第1章为什么研究货币、银行与金融市场1.1 复习笔记1.为什么研究金融市场金融市场是指将资金剩余方的资金转移到资金短缺方的市场。
通过债券市场和股票市场等金融市场,资金从没有生产用途的人向有生产用途的人转移,从而提高了经济效率。
此外,金融市场上的变化还直接影响着个人财富、企业和消费者的行为以及经济周期。
(1)债券市场和利率证券是对发行人未来收入与资产的索取权。
债券是债务证券,它承诺在一个特定的时间段中进行定期支付,债券包括长期债务工具和短期债务工具。
债券市场可以帮助政府和企业筹集到所需要的资金,并且是决定利率的场所,因此在经济活动中有着重要的特殊意义。
利率是借款的成本或为借入资金支付的价格(通常以一定时期内的利息额同本金额的比率来表示)。
利率对整个经济的健康运行有着很大的影响:对于个人来说,利率过高倾向于使其减少消费,增加储蓄;对于企业来说,利率还影响着企业的投资决策,利率的高低决定着企业投资成本的高低。
(2)股票市场普通股(简称为股票)代表持有者对公司的所有权,是对公司收益和资产的索取权。
股票市场是指人们交易股票的市场。
股票市场的价格波动会影响到人们的财富水平,进而对他们的消费意愿产生影响。
股票市场也是影响投资决策的一个重要因素,因为股票价格的高低决定了发行股票所能筹集到的资金数量,从而限制了企业可用于投资的资金。
企业股票的价格高,则他们可以筹集到更多的资金,用于购买更多的生产设施以及装备。
2.为什么研究金融机构和银行银行与其他金融机构是金融市场能够运行的关键所在。
没有金融机构,金融市场就无法实现资金由储蓄者向有生产性投资机会的人的转移。
因此,银行和其他金融机构对于经济运行具有十分重要的作用。
(1)金融体系的结构金融体系是由银行、保险公司、共同基金、财务公司、投资银行等不同类型的私人金融机构构成的复杂系统。
金融中介是指向拥有储蓄的个人借入资金并转而贷给其他资金需求者的金融机构。
(2)银行与其他金融机构银行是吸收存款、发放贷款的金融机构,包括商业银行、储蓄与贷款协会、互助储蓄银行与信用社。
计算Term structureExpectations theory:i nt =i t +i t+1e +i t+2e +⋯+i t+(n−1)e nLiquidity premium theory:i nt =i t +i t+1e +i t+2e +⋯+i t+(n−1)e n +l ntBecause of people preferred short - term bonds, there is a larger liquidity premium as the term to maturity lengthens. (上升图)Yield curves tend to have an especially steep upward slope. (下降图)Yield curves will not tend to have a steep downward slope, and maybe will slope upward. Stock pricing modelOne -Period Valuation Model :P 0=Div 1(1+k e )+P1(1+k e ) P 0=the current price of the stockDiv 1=the dividend paid at the end of year 1.k e =the required return on investments in equity.P 1=the price at the end of the first period .Generalized Dividend Valuation Model :P 0=∑D t(1+k e )t ∞t=1Gordon Growth Model :P 0=D 0×(1+g )(k e −g)=D 1(k e −g)D 0=the most recet dividend paid .g =the expected constant growth rate in dividends.Interest -Rate RiskA change in its interest rate:percent change in market value of security≈−persentage -point change in interest rate×duration in yearsA1:The assets fall in value by $8 million(=$100 million ×−2%×4 years )while the liabilities fall in value by $10.8 million(=$90 million ×−2%×6 years ). Because the liabilities fall in value by $2.8 million more than the assets do, the net worth of the bank rises by $2.8 million. The interest -rate risk can be reduced by shortening the maturity of the liabilities to a duration of 4 years or lengthening the maturity of the assets to a duration of 6 years. Alternatively, you could engage in an interest -rate swap, in which you swap the interest earned on your assets with the interest in another bank’s assets that have a duration of 6 years.A2: The gap is $10 million ($30 million of rate -sensitive assets minus $20 million of rate -sensitive liabilities). The change in bank profits from the interest rate rise is +$0.5 million (5%×$10 million); the interest rate risk can be reduced by increasing rate -sensitive liabilities to $30 million or by reducing rate -sensitive assets to $20 million. Alternatively, you could engage in an interest rate swap in which you swap the interest in $10 million of rate -sensitive assets for the interest on another bank’s $10 million of fixed -rate assets.The Money MultiplierM is money supply.MB is the monetary base.M=m×MBc = {C/D} = currency ratioe = {ER/D} = excess reserves ratioC is currency.ER is excess reserves.D is checkable deposits.r is the required reserve ratio.D=1r+e+c×MBM=1+cr+e+c×MBm=1+cr+e+c问答Present Value: A dollar paid to you one year from now is less valuable than a dollar paid to you today.Yield to Maturity and the Bond Price for a Coupon Bond: have 3 facts.1.When the coupon bond is priced at its face value, the yield to maturity equals the coupon rate.2.The price of a coupon bond and the yield to maturity are negatively related; that is, as the yield to maturity rises, the price of the bond falls. AS the yield to maturity falls, the price of the bond rises.3.The yield to maturity is greater than the coupon rate when the bond price is below its face value.Yield to Maturity(到期收益率):1.The interest rate that equates the present value of cash flow payments received from a debt instrument with its value today.2.Also called internal rate of return.3.Most accurate measure of i.Rate of Return:The payment to the owner plus the change in value expressed as a fraction of the purchase price.RET=CP t +P t+1−P tP tRET=return from holding the bond from time t to t+1. P t=price of bond at time tP t+1=price of the bond at time t+1C=coupon paymentCP t=current yield=i cP t+1−P tP t=rate of capital gain=gRate of Return and Interest Rates:1.The return equals the yield to maturity only if the holding period equals the time to maturity.2.A rise in interest rates is associated with a fall in bond prices, resulting in a capital loss if time to maturity is longer than the holding period.3.The more distant a bond’s maturity, the greater the size of the percentage price change associated with an interest-rate change.4.The more distant a bond’s maturity, the lower the rate of return that occurs as a result of an increase in the interest rate.5.Even if a bond has a substantial initial interest rate, its return can be negative if interest rates rise.Real and Nominal Interest Rates:1.Nominal interest rate makes no allowance for inflation.2.Real interest rate is adjusted for changes in price level so it more accurately reflects the cost of borrowing.3.Ex ante real interest rate is adjusted for expected changes in the price level.4.Ex post real interest rate is adjusted for actual changes in the price level.4 Factors of Asset Demand:An asset is a piece of property that is a store of value, such as money ,bond, stocks, and houses.1.Wealth: the total resources owned by the individual, including all assets2.Expected Return: the return expected over the next period on one asset relative to alternative assets3.Risk: the degree of uncertainty associated with the return on one asset relative to alternative assets4.Liquidity: the ease and speed with which an asset can be turned into cash relative to alternative assetsTheory of Asset Demand:1.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to wealth2.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its expected return relative to alternative assets3.The quantity demanded of an asset is negatively related to the risk of its returns relative to alternative assets4.The quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its liquidity relative to alternative assetsThe Structure of Interest Rates风险结构:Bonds with the same maturity have different interest rates due to: Default risk违约风险, Liquidity流动性, Tax considerations所得税因素.1. Default risk: probability that the issuer of the bond is unable or unwilling to make interest payments or pay off the face value.Conclusion: a bond with default risk will always have a positive risk premium, and an increase in its default risk will raise the risk premium. 具有违约风险的债券通常具有正的风险溢价,而违约风险的增长将会提高风险溢价水平。