第11章结构体与共用体
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:445.00 KB
- 文档页数:68



第11章结构体与共用体一、选择题(在下列各题的A)、B)、C)、D)四个选项中,只有一个选项是正确的,请将正确选项填涂在答题卡相应位置上。
)11.1 C语言结构体类型变量在程序运行期间A)TC环境在内存中仅仅开辟一个存放结构体变量地址的单元B)所有的成员一直驻留在内存中C)只有最开始的成员驻留在内存中D)部分成员驻留在内存中考生答案: 正确答案: B11.2 下列各数据类型不属于构造类型的是A)枚举型 B)共用型 C)结构型 D)数组型考生答案: 正确答案: A11.3 当说明一个结构体变量时系统分配给它的内存是A)各成员所需内存量的总和 B)结构中第一个成员所需内存量C)成员中占内存量最大者所需的容量 D)结构中最后一个成员所需内存量考生答案: 正确答案: A11.4 设有以下说明语句typedef struct{ int n;char ch[8];} PER;则下面叙述中正确的是A)PER 是结构体变量名 B)PER是结构体类型名C)typedef struct 是结构体类型 D)struct 是结构体类型名考生答案: 正确答案: B11.5 已知有如下定义:struct a{char x; double y;}data,*t;,若有t=&data,则对data 中的成员的正确引用是A)(*t).data.x B)(*t).x C)t->data.x D)t.data.x 考生答案: 正确答案: B11.6 以下程序的运行结果是#include "stdio.h"main(){ struct date{ int year,month,day; } today;printf("%d\n",sizeof(struct date));}A)6 B)8 C)10 D)12考生答案: 正确答案: A11.7 设有如下定义:struck sk{ int a;float b;} data;int *p;若要使P指向data中的a域,正确的赋值语句是A)p=&a; B)p=data.a; C)p=&data.a; D)*p=data.a; 考生答案: 正确答案: C11.8 以下对结构体类型变量的定义中,不正确的是A)typedef struct aa{ int n;float m;} AA;AA tdl;B)#define AA struct aaAA { int n;float m;} tdl;C)struct{ int n;float m;} aa;struct aa tdl;D)struct{ int n;float m;} tdl;考生答案: 正确答案: C11.9 若有下面的说明和定义struct test{ int ml; char m2; float m3;union uu { char ul[5]; int u2[2];} ua;} myaa;则sizeof(struct test )的值是A)12 B)16 C)14 D)9考生答案: 正确答案: A11.10 以下程序的输出是struct st{ int x; int *y;} *p;int dt[4]={ 10,20,30,40};struct st aa[4]={ 50,&dt[0],60,&dt[0],60,&dt[0],60,&dt[0]};main(){ p=aa;printf("%d\n",++(p->x));}A)10 B)11 C)51 D)60考生答案: 正确答案: C11.11 有以下程序:#include <stdio.h>union pw{ int i;char ch[2];}a;main(){ a.ch[0]=13;a.ch[1]=0;printf("%d\n",a.i);}程序的输出结果是A)13 B)14 C)208 D)209 考生答案: 正确答案: A11.12 已知学生记录描述为:struct student{ int no;char name[20],sex;struct{ int year,month,day;} birth;};struct student s;设变量s中的“生日”是“1984年11月12日”,对“birth”正确赋值的程序段是A)year=1984;month=11;day=12;B)s.year=1984;s.month=11;s.day=12;C)birth.year=1984;birth.month=11;birth.day=12;D)s.birth.year=1984;s.birth.month=11;s.birth.day=12;考生答案: 正确答案: D11.13 有如下定义struct person{char name[9];int age;};struct person class[10]={"John",17,"paul",19,"Mary",18,"Adam",16,};根据上述定义,能输出字母M的语句是A)printf("%c\n",class[3].name);B)printf("%c\n",class[3].name[1]);C)printf("%c\n",class[2].name[1]);D)printf("%c\n",class[2].name[0]);考生答案: 正确答案: B11.14 下列程序的输出结果是struct abc{ int a, b, c, s; };main(){ struct abc s[2]={{1,2,3},{4,5,6}}; int t;t=s[0].a+s[1].b;printf("%d\n",t);}A)5 B)6 C)7 D)8考生答案: 正确答案: B11.15 若有下面的说明和定义,则sizeof(struct aa)的值是struct aa{ int r1; double r2; float r3;union uu{char u1[5];long u2[2];}ua;} mya;A)30 B)29 C)24 D)22考生答案: 正确答案: D11.16 有以下结构体说明和变量的定义,且指针p指向变量a,指针q指向变量b。

第^一章结构体与共用体教学内容(1) 结构体的定义与结构体变量;(2) 结构体数组;(3) 结构体指针;⑷链表;(5) 共用体;(6) 枚举类型;基本要求掌握结构体的定义方法及其作用;重点掌握链表及其应用了解共用体的概念及其应用一、概述、引入原由我们前面讲过数组,数组类型中的各个元素的类型是相同的,在日常应用中,仅仅有这些数据类型是不够的。
有时需要将不同类型的数据组合成一个有机的整体,以便于引用。
这些组合在一个整体中的数据是互相联系的。
例如:学生的信息(姓名、性别、年龄、成绩、学号)。
那么如何实现这种结构呢?采用的是结构体。
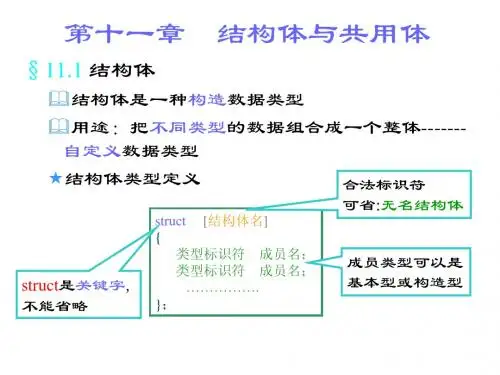
女口:struct student{ int num;char n ame[20];char sex;int age;float score;};、结构体类型的一般形式struct 结构体名{成员表列};成员表列:类型名成员名女口:struct student{int nu m;char sex;};二、结构体类型变量的定义、引用、初始化、定义方法1、先声明类型再定义变量名struct stude nt{int nu m;char sex;};struct stude nt stu1,stu2;2、在声明类型的同时定义变量struct stude nt{int nu m;char sex;} stu1,stu2;3、直接定义结构体类型变量(不给出结构体名)struct{int nu m;char sex;} stu1,stu2;4、说明:1 )类型与变量不同(变量:分配空间,可以赋值、存储、运算)2)成员与普通变量地位相当,域名可以单独使用3)成员也可以是一个结构体变量如: struct date{int mon th;int day;int year;};struct stude nt{int num;char n ame[20];char sex;struct date birthday; }stu1,stu2;4) 成员名可以与程序中的变量名相同,二者不代表同一对象。

结构体与共用体一、选择题:1.已知赋值语句wang.year=2004;则wang的变量类型是()A. 字符或文件B. 整型或实型C. 共用或结构D. 实型或指针2.Turbo C中,以下类型数据在存储器中占的字节数为 ( ) struct test{ int x;float y;char z;} ;A. 2B. 3C. 6D. 73.以下语句中,成员data的正确引用方式为( ) struct node{ int data;char name[10];}stree;struct node *p=&stree;A. p.dataB. p->dataC. (*p)->dataD. stree->data4、当执行以下程序段时,输出的结果是。
()struct data{ char a; int b; float c; };printf(“%d”, sizeof(struct data));A. 1B. 2C. 4D. 75.下面程序段的运行结果是。
struct stu{ int num; char name[10]; float scrose ; };printf(“%d\n”, sizeof (struct stu ));(A)14 (B)12 (C)16 (D)36. 若有定义:typedef char* string;#define str char *int a=4;struct {int x, *y;}z={10, &a}, *p=&z;则下列不等价的是:A. string name, sign; 与 str name, sign;B. *p->y++ 与 *(p->y++)C. ++*p->y 与 ++(*p->y)D. ++p->x与++(p->x) ()二、填空题:1.已知赋值语句zhang.year=1985;可判断zhang是类型的变量;2.若有类型定义:“typedef union{int a; char b; double c;} share;”及声明:“float r;”,则表达式:sizeof(r)+sizeof(share)的值是:。

c语言结构体与共用体课程思政下载温馨提示:该文档是我店铺精心编制而成,希望大家下载以后,能够帮助大家解决实际的问题。
文档下载后可定制随意修改,请根据实际需要进行相应的调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种各样类型的实用资料,如教育随笔、日记赏析、句子摘抄、古诗大全、经典美文、话题作文、工作总结、词语解析、文案摘录、其他资料等等,如想了解不同资料格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by the editor. I hope that after you download them, they can help you solve practical problems. The document can be customized and modified after downloading, please adjust and use it according to actual needs, thank you!In addition, our shop provides you with various types of practical materials, suchas educational essays, diary appreciation, sentence excerpts, ancient poems, classic articles, topic composition, work summary, word parsing, copy excerpts, other materials and so on, want to know different data formats and writing methods, please pay attention!C语言中的结构体与共用体是编程领域中非常重要的概念,在计算机科学的世界里扮演着不可或缺的角色。

结构体与共用体笔记定义结构体C语言允许用户自己建立由不同类型数据组成的组合型的数据结构,它称为结构体(structre)。
在其他一些高级语言中称为“记录”.定义后的结构体类型和系统提供的标准类型(如int, char, float, double 等)具有相似的作用,都可以用来定义变量,只不过int等类型是系统已声明的,而结构体类型是由用户根据需要在程序中指定的。
定义一个结构体类型的一般形式为:struct 结构体名{ 成员表列};注意:1.结构体类型的名字是由一个关键字struct和结构体名组合而成的(例如struct Student) ,结构体名是由用户指定的,又称“结构体标记”,以区别于其他结构体类型。
上面的结构体声明中Student就是结构体名(结构体标记)。
2.花括号内是该结构体所包括的子项,称为结构体的成员。
“成员表列"(member list)也称为“域表”(field list),成员表列由若干个成员组成,每一个成员是结构体中的一个域。
对每个成员也必须作类型说明,其形式为:类型说明符成员名;成员名的命名应符合标识符的书写规定。
例如:struct stu{int num;char name[20];char sex;float score;};3.一个结构体的成员可以属于另一个结构体类型(嵌套)。
例如:struct Date //声明一个结构体类型struct Date{ int month;//月int day;//日int year;//年}struct Student//声明一个结构体类型struct Student{ int num;char name[20];char sex;int age;struct Date birthday;//成员birthday属于struct Date 类型char addr[30];};结构体类型变量1.定义结构体类型变量说明结构变量有以下三种方法。



第十一章 结构体与共用体1、 填空(1) 为了建立如图所示的存储结构(即每个结点含两个域,data 是数据域,next 是指向结点的指针域),请填空。
Struct link{char data;;}node;(2) 以下程序的输出结果是 。
main(){struct cmplx{int x;int y;} cnum[2]={1,3,2,7};printf(“%d\n ”,cnum[0].y/cnum[0].x*cnum[1].x);}2、 选择(1) 根据以下定义,能输出字母M 的语句是A.printf(“%c\n ”,class[3].name);B.printf(“%c\n ”,class[3].name[1]);C.printf(“%c\n ”,class[2].name[1]);D.printf(“%c\n ”,class[2].name[0]); struct person { char name[9];int age;};struct person class[10]={ “John ”,17,“Paul ”,19,“Mary ”,18,“Adam ”,16,};(2) 对整个结构能够进行的操作是 。
A. 对结构进行赋值data nextB.对结构进行存取C.对结构进行运算D.对结构进行&操作(3)不是结构类型的特点的选项为。
A.结构体变量可以有不同类型的成员B.结构体中的成员都占有存储空间C.结构体变量既可以做函数参数,又可以从函数中返回D.结构体变量的成员既可以读又可以写3、判断(1)能在一个存储区内处理不同的类型的数据叫结构。
()(2)在编译时对结构类型不分配空间,只能对变量分配空间。
()(3)结构一旦定义,系统就给它分配所需的内存单元。
()4、程序设计(1)设有以下结构类型说明:struct stud{char num[5],name[10];int s[4];double ave;}请编写:<1>readrec把30名学生的学号、姓名、四项成绩及平均分放在一个结构体数组中,学生的学号、姓名和四项成绩由键盘输入,然后计算出平均分放在结构提对应的域中。
结构体与共用体
例如:20020945
有如下定义:struct sk
{int a;float b;} data;
int *p 则要使p指向data中的a域,正确的赋值语句是:C (A)p=&a;错误在于结构体变量的成员,必须通过定义的结构
体变量的名来引用其成员
(B)p=&data.a; data.a就是变量的值,而不是成员a地址
(C)p=&data.a;
(D)*p=data.a 同B解释
“()”优于“->”(指向)优于“++”
结构体类型还允许嵌套定义!
使用共用体类型数据时要注意:1,同一段程序可以用来存放几种不同的数据,但是在读写瞬间只能存放其中一种,而不是同时存放几种。
系统分配的空间为其中一个所需内存最大的成员的空间,不累加!!!
共用体变量的地址和他的各成员的地址都相同,即无论哪个成员起始地址都相同(参考19960946)。
typedef 原类型名新类型名
typedef v1 int v3
typedef 可以声明各种类型名,但是不能用用来定义变量。
他只为已存在的类型增加一个类型名,并不是创造新类型。
(参考20000930和20020947)。
一、结构体(structure)
C语言允许用户自己指定这样一种数据结构,即将不同类型的数据组合成一个有机的整体以便于引用。
二、共用体
使几个不同的变量共占同一段内存的结构。
三、枚举类型
1、如果一个变量只有几种可能的值,可以用此方法定义。
2、声明枚举类型用enum开头。
3、说明:(1)在C编译中,对枚举元素按常量处理;
(2)C语言编译按定义时的顺序使它们的值为0,1,2…,也可以改变枚举元素的值,在定义时由程序员指定;
(3)枚举值可以用来作判断比较;
(4)一个整数不能直接赋给一个枚举元素,只有进行强制类型转换才能赋值:workday=(enum weekday)2;
四、用typedef定义类型。
第1章C语言概述(一)选择题1.一个C程序的执行是从 A 。
答案AA) 本程序的main函数开始,到main函数结束B) 本程序文件的第一个函数开始,到本程序文件的最后一个函数结束C) 本程序文件的第一个函数开始,到本程序main函数结束D) 本程序的main函数开始,到本程序文件的最后一个函数结束2.以下叙述不正确的是 D 。
A) 一个C源程序必须包含一个main函数B) 一个C源程序可由一个或多个函数组成C) C程序的基本组成单位是函数D) 在C程序中,注释说明只能位于一条语句的后面3.以下叙述正确的是 C 。
A) 在对一个C程序进行编译的过程中,可发现注释中的拼写错误B) 在C程序中,main函数必须位于程序的最前面C) C语言本身没有输入输出语句D) C程序的每行中只能写一条语句4.一个C语言程序是由 B 。
A)一个主程序和若干个子程序组成B) 函数组成C) 若干过程组成D) 若干子程序组成5. C语言程序编译时,程序中的注释部分______D______.A) 参加编译,并会出现在目标程序中B) 参加编译,但不会出现在目标程序中C) 不参加编译,但会出现在目标程序中D) 不参加编译,也不会出现在目标程序中(二)填空题1、C语句结束符为____;_____________.2、C语句注释符号为:_/* */______________.3、一个C程序总是从____main函数______________开始执行的。
第3章数据类型、运算符与表达式(一)选择题1. 若x、i、j、k都是int型变量,则计算下面表达式后,x的值为( C )。
x=(i=4,j=16,k=32)A) 4 B) 16 C) 32 D) 522.下列四组选项中,均不是C语言关键字的选项是( A )。
A) define IF typeB) getc char printfC) include case scanfD) while go pow3. 下列四组选项中,均是不合法的用户标识符的选项是( B )。