爱因斯坦英文介绍PPT课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:4.96 MB
- 文档页数:10




爱因斯坦英文简介(配中文)
阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦(Albert Einstein)是一位著名的物理学家,他的相对论对现代物理学产生了深远的影响。
以下是一个简短的爱因斯坦英文简介,并配有中文翻译:
Albert Einstein was a German-born physicist who developed the theory of relativity and made numerous other significant contributions to physics. His work revolutionized our understanding of space, time, and gravity, and had a profound impact on the development of modern science and technology.Einstein is widely regarded as one of the greatest physicists of all time, and his name is synonymous with intellectual brilliance and scientific innovation.
阿尔伯特·爱因斯坦是一位出生于德国的物理学家,他发展了相对论,并对物理学做出了许多其他重要贡献。
他的工作彻底改变了我们对空间、时间和引力的理解,对现代科学技术的发展产生了深远的影响。
爱因斯坦被广泛认为是有史以来最伟大的物理学家之一,他的名字成为了智慧和科学创新的代名词。


Churchill Shakespeare the Beatles Music pop music football Prime Minister The Queen Commonwealth Big Ben Cambridge Oxford Scotland Wales Northern IrelandHarry porter ancientWinston Churchill is a great man of UK, he was the prime minister during the World War 2. The prime ministers work for the King or the Queen of the United Kingdom. Shakespeare is the greatest writer in ancient UK.The Beatles was the creator of modern pop music.The English football games are very popular in China.I know that Harry porter is from the UK, the story is a worldwide success. [sək'ses]Albert Einstein was considered[kən'sɪdəd]the greatest scientist of the 20th century ['sentʃʊrɪ]and one of the greatest of all time. His discoveries[dɪs'kʌvəri] and theories ['θiəriz] have greatly influenced ['ɪnflʊəns] science in many fields['fiːldz]. (还原单三至原形) Einstein was born in 1879 in Ulm [ulm], a city in Germany. As a boy, he was slow to learn to talk, but later in his childhood he showed great curiosity [kjʊərɪ'ɒsɪtɪ]about nature and ability to solve [sɒlv]difficult mathematical[mæθ(ə)'mætɪk(ə)l]problems. After he left school, he went to Switzerland, where he graduated['ɡrædjʊeɪtɪd]from a university with a degree [dɪ'griː] in mathematics. In 1905, Einstein began to publish a series of papers which shook the whole [həʊl] scientific [saɪən'tɪfɪk]and intellectual [,ɪntə'lektʃʊəl; -tjʊəl]world,and for the theories he established [ɪ'stæblɪʃt]in the papers he won the Nobel Prize for Physics ['fɪzɪks] in 1921.Because Einstein was Jewish ['dʒuːɪʃ],when Hitler took over Germany in 1933, hehad to leave the country and finally settledin the United States. There he continuedhis study on the structure ['strʌktʃə] of theuniverse ['juːnɪvɜːs] until his death[deθ]in 1955.Among the several importantdiscoveries Einstein made in his life, thegreatest is the creation of his famousTheory of Relativity1905年,爱因斯坦开始发表一系列论文,震动了整个科学和知识的世界,和他理论建立在报纸上他在1921年获得了诺贝尔物理学奖。


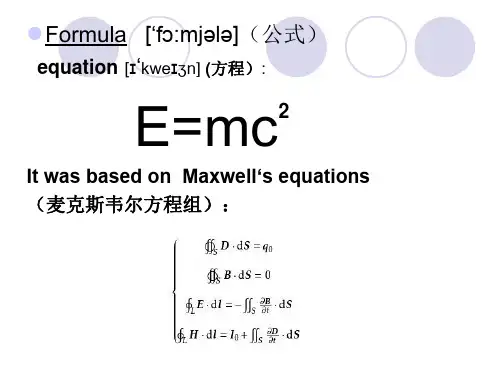
Albert Einstein ( /ˈælbərt ˈaɪnstaɪn/; German: [ˈalbɐt ˈaɪnʃtaɪn] ( listen); 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific(多产的)intellects in human history.[2][3] While best known for his mass–energy equivalence formula E = mc2, he received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect".[4] The latter was pivotal (关键的)in establishing quantum theory (量子论)within physics.Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led to the development of his special theory of relativity. He realized, however, that the principle of relativity could also be extended to gravitational(重力场)fields, and with his subsequent(后来的)theory of gravitation in 1916, he published a paper on the general theory of relativity. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory(微粒说)and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties(热力性质)of light which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, Einstein applied the general theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe as a whole.[5]He was visiting the United States when Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933, and did not go back to Germany, where he had been a professor at the Berlin Academy of Sciences. He settled in the U.S., becoming a citizen in 1940.[6] On the eve of World War II, he helped alert President Franklin D. Roosevelt that Germany might be developing an atomic weapon, and recommended that the U.S. begin similar research; this eventually led to what would become the Manhattan Project. Einstein was in support of defending the Allied forces, but largely denounced using the new discovery of nuclear fission as a weapon. Later, together with Bertrand Russell, Einstein signed the Russell–Einstein Manifesto(罗素爱因斯坦宣言), which highlighted the danger of nuclear weapons. Einstein was affiliated with(交往)the Institute for Advanced Study in Princeton, New Jersey, until his death in 1955.Einstein published more than 300 scientific papers along with over 150 non-scientific(反科学的)works.[5][7] His great intelligence and originality(创造力)have made the word "Einstein" synonymous(同义词)with genius.[8]。