ASPEN_培训教材18-ASPEN_间歇精馏
- 格式:docx
- 大小:44.02 KB
- 文档页数:3
一直想用aspen plus做一个关于间歇精馏的模拟,当开始做之后才发觉困难重重。
间歇精馏和连续精馏差别比较大,面板上好多属性的设置都变了样,位置也改变了。
还多出了夹套蒸汽加热,间歇进料时间设置等。
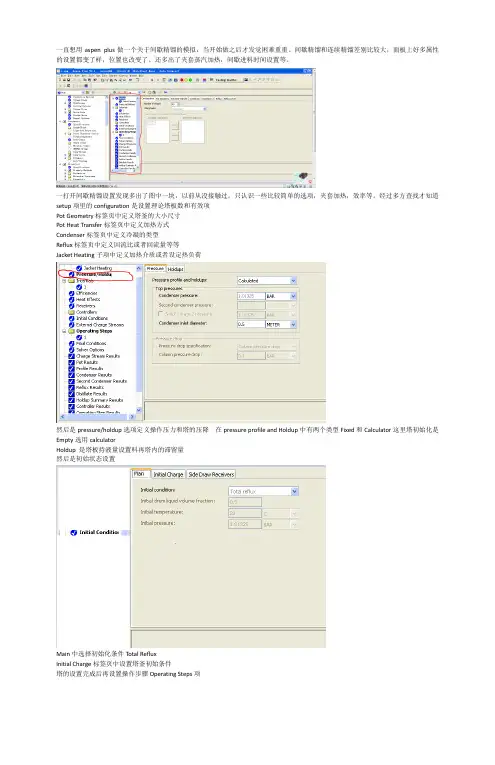
一打开间歇精馏设置发现多出了图中一块,以前从没接触过。
只认识一些比较简单的选项,夹套加热,效率等。
经过多方查找才知道setup项里的configuration是设置理论塔板数和有效项Pot Geometry标签页中定义塔釜的大小尺寸Pot Heat Transfer标签页中定义加热方式Condenser标签页中定义冷凝的类型Reflux标签页中定义回流比或者回流量等等Jacket Heating子项中定义加热介质或者设定热负荷然后是pressure/holdup选项定义操作压力和塔的压降 在pressure profile and Holdup中有两个类型Fixed和Calculator这里塔初始化是Empty选用calculatorHoldup 是塔板持液量设置料再塔内的滞留量然后是初始状态设置Main中选择初始化条件Total RefluxInitial Charge标签页中设置塔釜初始条件塔的设置完成后再设置操作步骤Operating Steps项在End Condition标签页中定义结束精馏的条件当六甲基二硅氮烷的含量为0.05时结束精馏我一直在惦记着还有两个问题没解决,一个是进料的事后属于间歇进料需要设置间歇进料的时间昨天在实验室看书刚刚找到了这方面的内容在全局设置report options中有一个batch operation选项设置进料时间。
躲得好深还有一个问题是设置成丝网填料塔,前面所设置的板数只是理论板要换算成填料高度最后终于找到了,在blocks的internals选项里面packing代表填料塔tray代表筛板塔。
运行完成之后出来结果我的间歇精馏模拟还存在问题,在添加填料性质之前核算都是正确的。

ASPEN培训课程内容1、ASPEN蒸馏模型-参考-A9-unit4塔.pdf2、普通精馏-1-ASPEN_气分.pdf3、板式塔计算、填料塔计算-参考-A10-附录 A 塔板和填料的设计和核算.pdf4、原油精馏:2-ASPEN_常压塔.pdf5、反应精馏-14-ASPEN_酯化反应精馏-动力学.pdf6、三相精馏-13-ASPEN_醇水三相精馏.pdf7、三相反应精馏-28-ASPEN_氯乙酸甲酯三相反应精馏.pdf8、共沸系统和剩余曲线-A6-共沸系统和剩余曲线.pdf均相共沸精馏-10-ASPEN_均相共沸精馏.pdf非均相共沸精馏-11-ASPEN_丁二烯脱水计算.pdf9、萃取精馏-萃取精馏.pdf萃取精馏塔-8-ASPEN_碳四萃取精馏.pdf萃取精馏及溶剂循环-9-ASPEN_萃取蒸馏及溶剂回收循环.pdf10、碱洗塔-25-ASPEN_碱洗塔.pdf11、MDEA脱硫-6-ASPEN_MDEA脱硫.pdf12、污水汽提-7-ASPEN_污水汽提.pdf13、装置模拟:15-ASPEN_MTBE装置.pdf14、热力学方法和ASPEN PLUS 热力学模型及选用:参考-5A-ASPEN物性方法和模型1-2章.pdf参考5B-ASPEN物性方法和模型5-6章.pdf参考5 C-ASPEN物性方法和模型附录B.pdf15、反应器的模拟计算:24-ASPEN_酯化反应器模拟.pdf16、再沸器、冷凝器计算:17-ASPEN_再沸器冷凝器计算.pdf17、流程设计与进料优化:18-ASPEN_流程设计及进料优化.pdf18、物性估计及应用- 21-ASPEN_非库组份物性估计.pdf19、物性数据回归-16-ASPEN_热力学数据回归.pdf以上为大致培训内容,次序和侧重点可根据需要调整,1、3和14中的参考内容太多不需复印,给大家电子文件。


间歇精馏处理含甲醇废水的工艺计算邮编:天津市 300385摘要:含甲醇废水是精细化工生产过程中经常需要处理的工况,精细化工生产普遍采用间歇小批量的方式,因而采用间歇精馏的方式处理小批量的甲醇废水是灵活高效的处理方式,本文探索采用模拟软件Aspen Plus 计算间歇精馏过程,为工程设计提供基础数据,并对操作过程进行指导。
关键词:间歇精馏;甲醇废水;模拟计算引言:间歇精馏也叫分批精馏,是在制药、轻工及精细化学品等行业中应用极为广泛的分离技术。
根据精馏的原理,间歇精馏是分批加料于塔系统中,从塔的一个或多个出料口将挥发性不同的组分顺序馏出的过程。
其主要特点包括:间歇精馏是一个动态过程;单塔可以实现多组分物系的分离;允许进料组分浓度在很大范围内变化,操作弹性大;单塔可实现多种物系的分离,即一塔多用;适用于不同分离要求的物系,而且间歇精馏具有设备简单、操作灵活等优点[1-3]。
本次处理的废水含有硫酸钠、氢氧化钠、甲醇和水。
因为含盐量高,采用连续精馏操作容易堵塞设备,故采用间歇精馏操作,将甲醇馏出回收,降低废水中的COD含量。
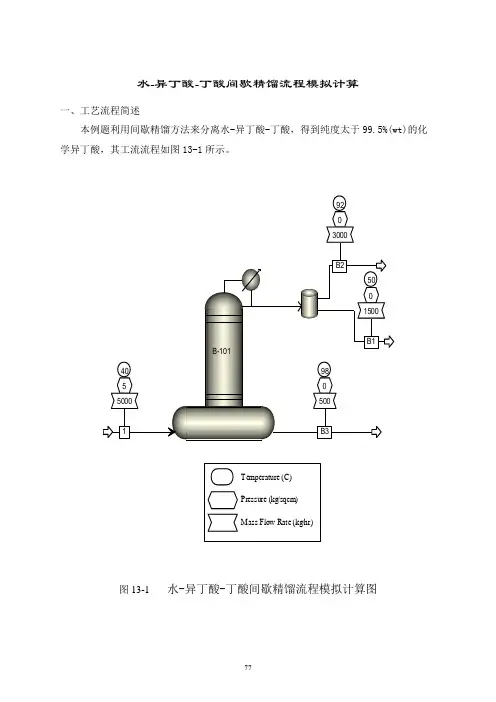
1 设计要求本设计1t废水里面的组成包括:172.5kg硫酸钠、31.5kg氢氧化钠、106kg甲醇、690kg水,每天产生量为17t。
现在需要用5000L釜加塔节改造进行间隙精馏,把甲醇精馏出来,要求回收的甲醇含量≥95%,计算塔节工艺尺寸。
2 模拟计算本文采用Aspen Plus间歇精馏模块计算甲醇、水体系的间歇精馏过程,物性方法选择NRTL。
间歇精馏塔的传热模型采用简捷模式,根据传热温差及塔釜换热面积,设置传热负荷为150kw。
设置塔压力为常压,塔压降10kpa。
塔顶回流比设置为2。
理论塔板数分别设置为10块和30块做计算对比。
设置停止时间为3小时。
3 计算结果选取冷凝器处时间配置文件结果,冷凝器液相中甲醇与水的质量分数如下表。
由计算结果可以看出,理论塔板选择30块的情况下,前期甲醇含量高于理论塔板数15块的情况但理论板数15的结果也满足要求,说明前一个小时内塔的分离效率没有被完全利用,后期运行过程中可以适当的减小回流比操作。


Aspen精馏模拟的步骤一、板式塔工艺设计首先要知道工艺计算要算什么?要得到那些结果?如何算?然后再进行下面的计算步骤。
其次要知道你用的软件(或软件模块)能做什么,不能做什么?你如何借助它完成给定的设计任务。
设计方案,包括设计方法、路线、分析优化方案等,应该是设计开题报告中的一部份。
没有很好的设计方案,具体作时就会思路不清晰,足见开题的重要性。
下面给出工艺设计计算方案参考,希望借此对今后的结构和强度设计作一个详细的设计方案,明确的一下接下来所有工作详细步骤和方法,以便以后设计工作顺利进行。
板式塔工艺计算步骤1.物料衡算(手算)目的:求解aspen 简捷设计模拟的输入条件。
容:(1) 组份分割,确定是否为清晰分割;(2)估计塔顶与塔底的组成。
得出结果:塔顶馏出液的中关键轻组份与关键重组份的回收率参考:《化工原理》有关精馏多组份物料平衡的容。
2.用简捷模块(DSTWU)进行设计计算目的:结合后面的灵敏度分析,确定合适的回流比和塔板数。
方法:选择设计计算,确定一个最小回流比倍数。
得出结果:理论塔板数、实际板数、加料板位置、回流比,蒸发率等等RadFarce 所需要的所有数据。
3.灵敏度分析目的:1.研究回流比与塔径的关系(NT-R),确定合适的回流比与塔板数。
2.研究加料板位置对产品的影响,确定合适的加料板位置。
方法:可以作回流比与塔径的关系曲线(NT-R),从曲线上找到你所期望的回流比及塔板数。
得到结果:实际回流比、实际板数、加料板位置。
4. 用DSTWU再次计算目的:求解aspen塔详细计算所需要的输入参数。
方法:依据步骤3得到的结果,进行简捷计算。
得出结果:加料板位置、回流比,蒸发率等等RadFarce 所需要的所有数据。
5. 用详细计算模块(RadFrace)进行初步设计计算目的:得出结构初步设计数据。
方法:用RadFrace 模块的Tray Sizing(填料塔用PAking Sizing),利用第4步(DSTWU)得出的数据进行精确设计计算。

h
催化分馏塔流程模拟计算
一、工艺流程简述
催化裂化是我国最重要的重质石油馏份轻质化的装置之一。
它由反再、主分馏及吸收稳定系统三部分所组成。
分馏系统的任务是把反再系统来的反应产物油汽混合物进行冷却,分成各种产品,并使产品的主要性质合乎规定的质量指标。
分馏系统主要由分馏塔、产品汽提塔、各中段回流热回收系统,并为吸收稳定系统提供足够的热量。
催化分馏系统分离其工流流程如图3-1所示,所涉及主要模块有进料混合罐(M1)、催化分馏塔(T2014)。
h
图3-1 催化分馏系统模拟计算流程图
FEED进分馏塔油汽; SS塔底汽提蒸汽;GAS塔顶气;COIL轻柴油,SS1柴油汽提蒸汽;HOIL回炼油;YJ油浆;
h
二、需要输入的主要参数
1、装置进料数据
h
h
h
2、 单元操作参数
3
、 设计规定及模拟技巧 三、软件版本
采用ASPEN PLUS 软件12.1版本,文件名CHT201.APW 欢迎您的下载,资料仅供参考!。

Aspen间歇精馏模拟教程Aspen间歇精馏模拟教程Use this Getting Started section to become familiar with the steps to set up a batch simulation using Aspen Batch Modeler. You will be modeling a system to recover methanol from a mixture of methanol and water.The objective is to separate methanol from the mixture with a purity of 99%. This mixture is not ideal given the polarity of the molecules; therefore, for a working pressure of 1atm, you will choose NRTL to model its physical properties.There are four steps in this process. Click a step to go the instructions for the step.Step 1 – Set up the Properties for Aspen Batch ModelerStep 2 – Enter structural data and specifications for the Aspen Batch Modeler block Step 3 – Enter Operating StepsStep 4 – Run the simulation and view the resultsStep 1 - Set up the Properties for Aspen Batch ModelerWe want to define a Properties file that has the following defined.Components Property MethodWater NRTLMethanolTo define this Properties file, follow the steps below.To set up the Problem Definition file from within Aspen Batch Modeler:1. Start Aspen Batch Modeler.2. On the Species form, click Edit Using Aspen Properties.This will start Aspen Properties.3. Enter the Components:Component ID Component name Formula WATER WATER H2O METHANOL METHANOL CH4OTip: You can use the Next button4. Click the Next button Properties Specifications form.5. On the Properties Specifications form, in the Property method field, select NRTL. Tip: Clicking the pull-down arrow on the field and typing N (the first letter of the property method name) takes you to the right choice much faster than just scrolling down the long list.6. Click NextYou are taken to the binary parameters forms, where you can view the binary parameters that will be used for Properties Calculations.7. Click NextYou are prompted to click one of the options shown below.8. There is no need for further input, so click OK to run the property setup.9. Close Aspen Properties by clicking File | Exit.You are prompted with the following:10. Click Yes to save the file.The Property setup is now complete.Step 2 - Enter structural data and specifications for the Aspen Batch Modeler blockThe column has been designed as follows:Configuration10 Stages (this includes eight trays, condenser and pot)Vapor-liquid separationPot GeometryElliptical head1m diametervolume of 1m3OverheadTotal CondenserDistillate mole flow rate = 4.5kmol/hrReflux drum is present(no need to enter dimension because we are defining fixed pressure profile/holdups; therefore reflux holdup will be entered) Pressure/HoldupsPressure profile is fixedCondenser pressure 1.01325 barColumn Pressure Drop 0.1 barHoldupsReflux Drum liquid holdup: 0.02 m3Stage holdup: 0.005 m3Heat TransferDuty: 150 kWReceiversOne receiver for liquid distillateInitial condition: total refluxInitial ConditionsInitial Charge18kmol of materialComponent mole fractionMethanol: 0.4Water: 0.6To Enter the Data1. Set the configuration to Batch Distillation Column, specify the number of stages and ensure valid phases are Vapor-Liquid on the Configuration Main form10 Stages (this includes eight trays, condenser, and pot)Vapor-liquid separation2. On the Setup | Pot Geometry tab , type the pot dimensions:Elliptical; 1m diameter; volume of 1m33. Click the Overhead form. On the Condenser tab, click Total for Total condenser.4. On the Reflux tab, type the distillate mole flow rate:Distillate mole flow rate = 4.5kmol/hrReflux drum is presentNote: You need not enter dimension because we are defining fixed pressure profile/holdups. Therefore, reflux holdup will be entered.5. Click the Jacket Heating form under Setup. On the Jacket Heating tab, enter the pot conditions:Duty: 150 kW6. Click Pressure/Holdups | Pressure.7. On the Pressure tab, type the pressure profile:Pressure profile is fixed.Condenser pressure 1.01325 barColumn Pressure Drop 0.1 bar8. On the Holdups tab, type the reflux and stage holdup information: Reflux Drum liquid holdup: 0.02 m3 Stage holdup: 0.005 m39. Click Receivers | Distillate.10. On the Distillate tab, define one liquid distillate receiver.11. Click Initial Conditions | Main.12. On the Main tab, in the Initial condition field, click Total reflux.13. On the Initial Charge tab, define the following:Total initial charge: 18 kmol of materialComponent mole fraction:Methanol: 0.4Water: 0.6Note: Do not forget to save your work regularly.To save your file for the first time:1. On the File menu, click Save As.2. In the File name field, type a name, or select a file name to overwrite an existing file:3. Click Save.Step 3 - Enter Operating StepsThere are two Operating Steps:1. Start product draw maintaining a distillate flow rate of 4.5 kmol/hr.2. Stop when the mole fraction of water in the distillate receiver approaches 0.01 from below. The batch is complete. To create the required operating steps to run the problem:1. Click Operating Steps and enter distil in the Name column of the Operating Steps table.This will create the first operating step distil.2. On the Changed Parameters tab, create an operating step to distill the methanol by maintaining a distillate flow rate of 4.5 kmol/hr.3. On the End Condition tab, specify as the end condition the mole fraction of water in the distillate receiver approaching the value of 0.01 from below.Step 4 - Run the simulation and view the resultsThe simulation is now ready to run.Before running the simulation, it is a good idea to create plots for key variables such as: the composition and holdup in the Receiverthe composition and temperature in the potand so onTo create plots for key variables:1. On the Plots form, click the Temperature and Composition to create time plots for pot temperature and mole fractions.2. Use the Custom plots feature to create plots of the receiver holdups and compositions. Click New on the Custom plots table and specify H2O_distil as the name of the plot.3. Go to the Holdups Summary Results\Distillate tab. Select the field that displays the WATER mole fraction and drag it on to the plot (H2O_distil) created in the previous step.4. Use the same approach to create plots of holdups in the receiver and/or the plot.5. You can change the time units displayed in the plots by clicking the Run Options toolbar button Select the time units in which the user interface should display time field.14. Click the Run button and view the Simulation Messages window for any relevantmessages.Once the problem has run successfully you can view results in the forms.Batch time: 1.49 hours/ 89.4 minutesPot temperature: 101.05 ℃Methanol recovery: 6.636 kmolNote: It is always good practice to restart your simulation in order to restore it to time zero before saving your work.。
1.2 间歇精馏1.2.1 概述间歇精馏是把批量液体混合物精馏成产品的过程,它是典型的非稳态过程。
在一个精馏周期中,塔内各点的温度、组成等参数都在不断地改变,因而一些操作参数就必须随之作相应的变动,才能保证获得合格的产品和满意的分离效果。
间歇精馏适用于:①小规模、批量生产;②在同一设备中完成不同的分离,如根据季节不同处理不同的原料,得到不同的产品;或出于评价的需要,由同一进料得到不同纯度的产品;③进料组成时常变化,难以进行有效的连续操作;④处理含固体,或易形成固体沉淀、焦油等污垢的物料。
由于间歇精馏的适用性强,操作灵活,投资少,适于处理原料成分复杂的多元物系,在精细化工等部门得到了广泛的应用。
由于在本科生《传质分离过程》课程中已讲述了间歇精馏的基础知识,故本小节仅就与操作、控制和模拟有关的间歇精馏特性做简要叙述。
一、间歇精馏塔的形式常规间歇精馏塔也称精馏式间歇精馏塔是最常见的间歇精馏塔,塔釜内装有被分离料液,塔顶采出产品,很像连续精馏的精馏段。
这种流程适用于除去重组分杂质而轻组分纯度要求较高的过程。
对分离要求不高的除去轻组分杂质的分离过程,这种操作可节省时间。
提馏式间歇精馏塔,塔顶设有贮料罐,从塔底采出馏分,类似于连续精馏的提馏段。
适用于难挥发组分为目标产物或难挥发组分为热敏性物质的分离情况。
带有中间贮罐的间歇精馏塔或称复杂间歇精馏塔,其料液贮存于塔中部的贮罐内,塔顶、塔底同时出料,除了进料不是连续之外,与常规连续精馏相同。
这种流程综合了常规间歇精馏和提馏式间歇精馏的优点,生产能力高,节能效果明显,并对某些热敏性物料的分离有特殊优异的效果,是有潜在优势的间歇精馏过程。
二、间歇精馏塔的操作典型的精馏式间歇精馏塔一个操作周期可分为以下若干阶段:(1)全回流开工阶段全回流开工阶段的目的是在塔内建立起浓度梯度,全回流开工的结束条件一般为回流罐中的液相组成达到第一个产品的浓度要求。
(2)产品采出段某产品采出段一般是从塔顶液相组成刚刚达到该产品浓度要求时开始,持续到塔顶馏出物组成刚降至低于该产品浓度要求时结束。