制药工程专业英语--1单元
- 格式:docx
- 大小:50.67 KB
- 文档页数:17

Unit 1 Production of DrugsAbout 5000 antibiotics have already been isolated from microorganisms,but of these only somewhat fewer than 100 are in therapeutic use. It must be remembered,however,that many derivatives have been modified by partial synthesis for therapeutic use;some 50,000 agents have been semisynthetically obtained from户lactams alone in the last decade. Fermentations are carried out in stainless steel fermentors with volumes up to 400 m3. To avoid contamination of the microorganisms with phages etc. the whole process has to be performed under sterile conditions. Since the more important fermentations occur exclusively under aerobic conditions a good supply of oxygen or air(sterile)is needed. Carbon dioxide sources include carbohydrates,e. g. molasses,saccharides,and glucose. Additionally the microorganisms must be supplied in the growth medium with nitrogen-containing compounds such as ammonium sulfate,ammonia,or urea,as well as with inorganic phosphates. Furthermore,constant optimal pH and temperature are required. In the case of penicillin G,the fermentation is finished after 200 hours,and the cell mass is separated by filtration. The desired active agents are isolated from the filtrate by absorption or extraction processes. The cell mass,if not the desired product,can be further used as an animal feedstuff owing to its high protein content.关于5000抗生素已经分离出的微生物,但其中只有不到100有些治疗使用。


制药工程专业英语详细Unit..详细翻译————————————————————————————————作者:————————————————————————————————日期:Unit 1 Production of Drugs根据其生产或来源不同药物制剂可以分为三类:Ⅰ.人工合成材料(全合成材料)Ⅱ.天然产物,和Ⅲ.半合成天然产物(半合成药物)。
本书的重点是这些第一组和第三组化合物都是合成药物。
然而这并不意味着那些天然药物和其他药物就不重要。
他们可以作为很有价值的先导结构,并经常被用为重要合成药物的原料或中间体。
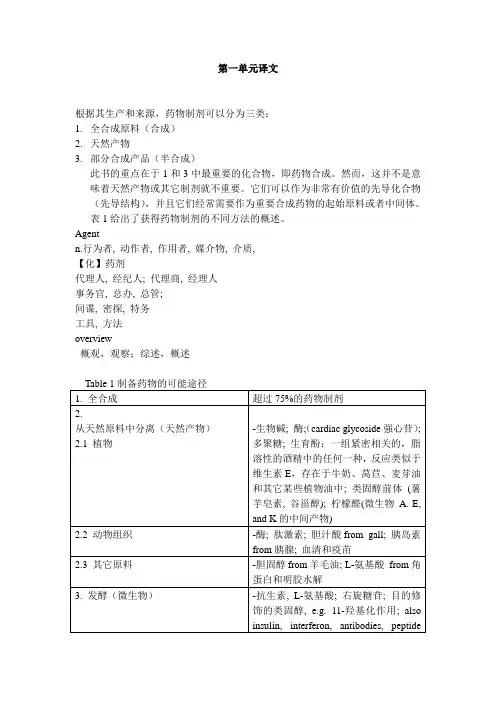
表1概述了获取药物制剂的不同方法。
Table 1 Possibilities for the preparation of drugs表1药物制备的可能性方法例子1.全合成75%以上的药物制剂都是全合成的(合成物)2.从天然产物中分离(天然产物)2.1植物生物碱;酶;强心甙;多聚糖;维生素E; 类固醇前体(薯蓣皂苷配基,谷甾醇);柠檬醛(中间产物维生素A,E,K)2.2动物器官酶;多肽;激素;胆酸;胆汁;胰岛素来自胰腺;血清和疫苗2.3其他来源胆固醇来自羊毛油;L-氨基酸来自角蛋白和明胶水解3.发酵抗生素; L -氨基酸,葡聚糖;对甾类有定向的修饰,例如11 -羟基化;胰岛素,干扰素,抗体,肽类激素,酶,疫苗生物碱化合物;半合成内酰胺类抗生素;甾类;人胰岛素4.天然产物的半合成修改(半合成药物)几种最初来自于天然原料有治疗意义天然产物如今用更有效也就是经济的全合成法制备。
这样的例子包括L-氨基酸,氯霉素,咖啡因,多巴胺,肾上腺素,左旋多巴,肽类激素,前列腺素,D -青霉胺,长春蔓胺,以及几乎所有的维生素。
在过去的几年里发酵(即微生物处理)变得极其重要。
通过现代技术和遗传选择的结果产生了高效能微生物突变株,发酵已成为广泛的底物(物质)都可以选择的一种方法。
真核微生物(酵母菌和霉菌)和原核微生物(单细胞细菌和放线菌)用于微生物。


Unit 11.Depending on their production or origin pharmaceutical agents can be splitinto three groups: Totally synthetic material (synthetics) Naturalproducts ,and Product from partial syntheses (semi-synthetic products)依据其生产或来源,药物制剂可以分为三类:I.完全的合成材料(人工合成材料),II.天然产物,和III.源自部分合成的产品(半合成产品)。
2.The emphasis of the present book is on the most important compounds ofgroups I and III-thus Drug synthesis.翻译:所以本书的重点是I和III部分的药物合成。
本书的重点是在于Ⅰ和Ⅲ类中最重要的化合物——药物合成。
3.This does not mean, however , that natural products or other agents are lessimportant.然而这并不意味着,天然产物和其他试剂不重要。
4.they can serve as valuable lead structures,and they are frequently needed as starting materials or as intermediates for important synthetic products.它们可以作为有价值的先导结构,他们常常作为重要的合成产品的起始原料或中间体产品。
5:Table1gives an overview of the different methods for obtaining pharmaceutical agents.表1列出了获取药物制剂的不同方法的概述。

制药工程的学科英语作文题目,Pharmaceutical Engineering: Bridging Science and Industry。
Pharmaceutical engineering, a multidisciplinary field that integrates principles from chemistry, biology, engineering, and pharmacology, plays a pivotal role in the development, manufacturing, and optimization of pharmaceutical products. In recent years, the field has witnessed significant advancements, driven by the ever-evolving demands of the healthcare industry and the constant pursuit of innovation.At its core, pharmaceutical engineering encompasses a wide array of processes and technologies aimed at ensuring the safety, efficacy, and quality of pharmaceutical products. From drug discovery and formulation to manufacturing and distribution, every stage of the pharmaceutical lifecycle relies heavily on the expertise of pharmaceutical engineers to overcome various challenges andoptimize outcomes.One of the key areas within pharmaceutical engineering is drug formulation, where scientists and engineers work together to design dosage forms that are safe, stable, and effective. This involves selecting appropriate excipients, optimizing drug delivery systems, and ensuring proper bioavailability of the active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Through meticulous research and experimentation, pharmaceutical engineers strive to develop formulationsthat meet the diverse needs of patients while adhering to strict regulatory standards.In addition to formulation, pharmaceutical manufacturing represents another critical aspect of the field. Modern pharmaceutical manufacturing facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art equipment and technologies that enable the production of large quantities of pharmaceutical products with consistent quality and purity. Pharmaceutical engineers are responsible for overseeing these manufacturing processes, implementing Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and implementing qualitycontrol measures to minimize variability and ensure product uniformity.Furthermore, pharmaceutical engineering plays a crucial role in the development of novel drug delivery systems, such as nanoparticles, liposomes, and transdermal patches. These advanced delivery systems offer numerous advantages, including targeted drug delivery, sustained release, and improved patient compliance. By harnessing the principles of engineering and material science, pharmaceutical engineers are able to design and optimize these systems to enhance drug efficacy and minimize side effects.Moreover, pharmaceutical engineering extends beyond the laboratory and manufacturing plant to encompass the entire pharmaceutical supply chain. From raw material sourcing to distribution and logistics, pharmaceutical engineers work tirelessly to optimize efficiency, minimize waste, and ensure timely delivery of pharmaceutical products to patients worldwide. This requires a deep understanding of supply chain management principles, as well as the ability to adapt to changing market dynamics and regulatoryrequirements.In conclusion, pharmaceutical engineering serves as a bridge between science and industry, driving innovation and progress in the field of healthcare. Through the collaborative efforts of scientists, engineers, and healthcare professionals, pharmaceutical engineering continues to push the boundaries of what is possible, leading to the development of safer, more effective, and more accessible pharmaceutical products for the benefit of society as a whole. As we look to the future, the role of pharmaceutical engineering will only continue to grow in importance, shaping the landscape of healthcare for generations to come.。


Unit 1 Production of DrugsDepending on their production or origin pharmaceutical agents can be split into three groups:I .Totally synthetic materials (synthetics),Ⅱ.Natural products,andⅢ.Products from partial syntheses (semi-synthetic products).The emphasis of the present book is on the most important compounds of groups I and Ⅲ一thus Drug synthesis. This does not mean,however,that natural products or other agents are less important. They can serve as valuable lead structures,and they are frequently needed as starting materials or as intermediates for important synthetic products.Table 1 gives an overview of the different methods for obtaining pharmaceutical agents.1单元生产的药品其生产或出身不同药剂可以分为三类:1。
完全(合成纤维)合成材料,Ⅱ。
天然产物,和Ⅲ。
产品从(半合成产品)的部分合成。
本书的重点是团体的最重要的化合物Ⅰ和Ⅲ一所以药物合成。
这并不意味着,但是,天然产品或其他代理人并不太重要。
它们可以作为有价值的领导结构,他们常常为原料,或作为重要的合成中间体产品的需要。
第一单元译文根据其生产和来源,药物制剂可以分为三类:1.全合成原料(合成)2.天然产物3.部分合成产品(半合成)此书的重点在于1和3中最重要的化合物,即药物合成。
然而,这并不是意味着天然产物或其它制剂就不重要。
它们可以作为非常有价值的先导化合物(先导结构),并且它们经常需要作为重要合成药物的起始原料或者中间体。
表1给出了获得药物制剂的不同方法的概述。
Agentn.行为者, 动作者, 作用者, 媒介物, 介质,【化】药剂代理人, 经纪人; 代理商, 经理人事务官, 总办, 总管;间谍, 密探, 特务工具, 方法overview概观,观察;综述,概述几种最初来源与天然原料的在治疗学上有重大意义的天然产物今天更加有影响力,([拉]=id est)即,通过全合成制备更加经济。
这样的例子包括L-氨基酸,氯霉素(氯霉素:一种抗生素,C11H 12Cl 2N 2O 5,来自于委内瑞拉链丝菌属土壤细菌或人工合成,是一种广谱抗菌药),咖啡因,多巴胺,肾上腺素(白色到褐色之间的晶体化合物,C9H 13NO 3,由某些哺乳动物的肾上腺提取或人工合成,用作心脏兴奋剂、血管收缩剂和支气管肌松弛剂),左旋多巴(左旋形式的多巴,用于治疗帕金森综合症也作L-dopa),肽类荷尔蒙,前列腺素(任一种产生于哺乳动物组织中的一组类似荷尔蒙的物质,由氨基酸生成,调节着一个很大范围的生理活动及神经传送),D-青霉胺(一种作为螯合剂用于治疗类风湿关节炎和铜中毒的青霉素的分解产物,C5H 11NO 2S), 长春蔓胺, 和几乎所有的维生素。
最近几年,发酵,即微生物过程,已经变得非常重要。
利用现代技术和遗传选择的结果产生了高生产性能的微生物突变株,发酵已经成为对于广泛底物都选择的一种方法。
真核微生物(酵母和霉菌)和原核微生物(单细胞细菌和放线菌)都可以作为生产菌株。
可以获得下面的典型产物:1、细胞原料(单细胞蛋白)2、酶3、初级降解产物(初级代谢产物)4、次级降解产物(次级代谢产物)不考虑从特种微生物的粘液膜组织生产右旋糖苷,例如,Leuconostoc mesenteroides,第2类和第3类对于药物的生产是一致的。


制药工程专业英语--1单元Unit 11.Depending on their production or origin pharmaceutical agents can be splitinto three groups: Totally synthetic material (synthetics) Naturalproducts ,and Product from partial syntheses (semi-synthetic products)依据其生产或来源,药物制剂可以分为三类:I.完全的合成材料(人工合成材料),II.天然产物,和III.源自部分合成的产品(半合成产品)。
2.The emphasis of the present book is on the most important compoundsof groups I and III-thus Drug synthesis.翻译:所以本书的重点是I和III部分的药物合成。
本书的重点是在于Ⅰ和Ⅲ类中最重要的化合物——药物合成。
3.This does not mean, however , that natural products or other agents areless important.然而这并不意味着,天然产物和其他试剂不重要。
4.they can serve as valuable lead structures, and they are frequently needed as starting materials or as intermediates fo r important synthetic products.它们可以作为有价值的先导结构,他们常常作为重要的合成产品的起始原料或中间体产品。
5:Table1gives an overview of the different methods for obtaining pharmaceutical agents.表1列出了获取药物制剂的不同方法的概述。
6. Several therapeutically significant natural products which were originally obtained from natural sources are today more effectively -i.e. more economically -prepared by total synthesis.最初从天然资源库获得的几个重要治疗作用的天然产品,今天可以通过全合成更有效地,即更经济地被制备出来。
7.Such example include L-amino acids, Chloramphenicol , Caffeine, Dopamine, Epinephrine, Levodopa, peptide hormorres, Prostaglandins,D-Penicillamine, Vincamine, and practically all vitamins.这样的例子包括L-氨基酸、氯霉素、咖啡因、多巴胺、肾上腺素、左旋多巴、肽类激素、前列腺素、D -青霉胺、长春胺,以及几乎所有的维生素。
8.Over the last few years fermentation–i.e. microbiological processes–has become extremely important.在过去的几年里,发酵,即微生物过程,变得极其重要。
9.through modern technology and results from genetic selection leading to the creation of high performance mutants of microorganisms, fermentation has already become the method of choice for a wide range of substances.通过现代技术和基因选择导致的微生物的高性能突异变种的结果,发酵已成为选择宽范围物质的方法。
10.Both Eukaryonts(yeasts and moulds) and Prokaryonts(single bacterial cells,and actinomycetes) are used as microorganisms.真核细胞(酵母菌和霉菌)和原核细胞(单细胞细菌,放线菌)都可用作微生物。
11.The following product types can be obtained: 1. cell material(single cell protein),2. enzymes,3. primary degradation products(primary metabolites)翻译:下列产品类型可以得到:1。
细胞的物质(单细胞蛋白),2。
酶,3。
初级降解产物(初级代谢物),4。
二级降解产物(次生代谢物)。
12:Disregarding the production of dextran from the mucous mem branes of certain microorganisms e.g. Leuconostoc mesenteroides cl ass2and3are the relevant ones for the preparation of dru gs.尽管从诸如肠膜状明串球菌的某些微生物的黏膜可以生产葡萄聚糖,但第2和3类产品类型只与药品生产的有关。
13.Dextran itself , with a molecular weight of50,000~100,000, is used as a blood plasma substitute.葡聚糖自身的分子量5万〜10万,可用作血浆代用品。
14.Among the primary metabolites the L-amino acids from muta nts of Corynebacterium glutamicum and Brevibacterium flavum ar e especially interesting.而来自谷氨酸棒杆菌和黄色短杆菌突变体的初级代谢产物中,L-氨基酸尤其令人感兴趣。
15.From these organisms some350000tones of monosodium L-glutamate(foodadditive)and some70000tones of L-lysine(supplement for vegetable proteins)are produced.从这些生物体中,可以生产约35万吨L-谷氨酸单钠盐(味精,食品添加剂)和约70,000吨L-赖氨酸(用于植物蛋白补充物质)。
16.Further important primary metabolites are the purina nucleotides,organic acids,lactic acid,citric acid,and vitamins,for example vitamin B,12from Propionibacterium shermanii.此外,重要的初级代谢产物还有嘌呤核苷酸、有机酸、乳酸、柠檬酸和维生素,。
例如源自谢氏丙酸杆菌的维生素B1217、Among the secondary metabolites the antibiotics must be mentioned first.在次生代谢产物中首先必须提到的是抗生素。
18、The following five groups represent a yearly worldwide value of US-$17billion:以下五组药品代表了全球每年价值170亿美元:penicillins (Penicillium chrysogenum),青霉素(青霉)cephalosporins (Cephalosporium acremonium),头孢菌素(头孢枝顶)tetracyclines (Streptomyces aureofaciens),四环素(金色链霉菌)erythromycins (Streptomyces erythreus),红霉素类(红霉素链霉菌)aminoglycosides(e.g.streptomycin from Streptomyces griseus).氨基糖苷类(如链霉素从灰色链霉菌)19.About5000antibiotics have already been isolated from microorganisms, but of these only somewhat fewer than100are in therapeutic use.从微生物中已分离出约5000种抗生素,但其中只有不到100种有治疗用途。
20.It must be remembered,however that many derivatives have been modified by partial synthesis for therapeutic use some50,000agents have been semisythetically obtained fromβ-lactams alone in the last decade.但是,必须记住,许多衍生物已通过部分合成法来修饰以获得治疗用途;在过去的十年里,采用半合成方法已从ß-内酰胺获得了约50,000种制剂。
21. To avoid contamination of the microorganisms with phages etc , the whole process has to be performed under sterile conditions.为了避免受到噬菌体等微生物的污染,(发酵)全过程都必须在无菌条件下进行。
22. Fermentations are carried out in stainless steel fermenters with volumes up to400m^3.发酵是在体积高达400m3的不锈钢发酵罐中进行。
23.Since the more important fermentations occur exclusively under aerobic conditions a good supply of oxygen or air(sterile)is needed.由于更重要的是,发酵只在有氧条件下才能发生;因此,需要提供有足够量的氧气或(无菌)空气。