霍尼韦尔电流互感器
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:507.98 KB
- 文档页数:4

怎么选择合适自己的霍尔电流传感器目前,霍尼韦尔电流传感器主要采用了霍尔效应和磁阻效应两种工作原理,是分别利用两种原理对电流产生的磁场大小进行检测,并通过电磁互感的关系得到电流的大小。
在工作模式上,霍尼韦尔电流传感器主要有两种方式,其分别是:直接检测式和磁平衡式。
由于霍尼韦尔霍尔电流传感器有诸多优点,目前广泛应用于变频调速装置、逆变装置、UPS 电源、逆变焊机、电解电镀、电动汽车、数控机床、微机监测系统、电网监控系统和需要隔离检测电流电压的各个领域中。
泰德兰电子科技代理霍尼韦尔的霍尔电流传感器主要优点如下:1、测量范围广:它可以测量任意波形的电流和电压,如直流、交流、脉冲、三角波形等,甚至对瞬态峰值电流、电压信号也能忠实地进行反映。
2、响应速度快:快者响应时间只为1us。
3、测量精度高:其测量精度优于1%,该精度适合于对任何波形的测量。
4、线性度好:优于0.2%。
5、动态性能好:响应时间快,可小于1us;普通互感器的响应时间为10~20ms。
6、工作频带宽:在0~1MHz 频率范围内的信号均可以测量。
7、可靠性高,平均无故障工作时间长:平均无故障时间>5 10 小时。
8、过载能力强、测量范围大:0~几十安培~上千安培。
9、体积小、重量轻、易于安装。
那么,作为硬件工程师,我们该如何选择一款合适的霍尔电流传感器呢?下面我们根据霍尔电流传感器的参数来介绍一下如何选择。
1,先选择工作温度范围霍尔电流传感器一般有3种工作稳定范围,分别是-40°C ~ 85°C,-40°C ~ 125°C 和-40°C ~ 150°C。
工程师根据应用是消费类或者工业类和汽车类的温度范围来选择合适的型号。
例如Allegro的霍尔电流传感器ACS712ELCTR-30A-T,712后面的E就是表示-40°C ~ 85°C温度范围,ACS733KLATR-40AB-T中733后面的K表示-40°C ~ 125°C温度范围,ACS724LLCTR-30AB-T中724后的L表示-40°C ~ 150°C的温度范围。
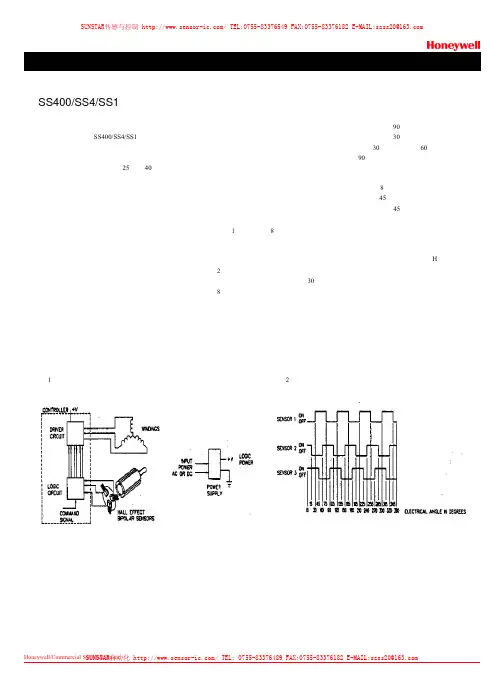
前言本说明讨论如何用SS400/SS4/SS1系列开关霍尔传感器替代直流电动机中的机械换相。
该系列传感器价格低,其动作及释放点的高斯数很低(@25℃±40℃),可作为一种低成本的磁性换相器使用。
它们与低功耗半导体配合使无刷直流电机在电机市场上极具价格竞争力。
工作原理无刷直流电机基本上与带电刷电机的内部构造相同。
电源施加于转子线圈,永久磁铁是转子的一部分。
依电动机设计方式的不同而确定旋转件是在内部还是在外部。
直流电动机的电刷和换相器也由位置传感器和电子开关所代替。
扭矩,即产生运动的力,在直流电机上是通过永久磁场与线圈电流相互作用产生。
在有刷电机中,换相器切换电枢线圈,从而提供了适当的磁通量和转子电流互相感应。
而在无电刷电机中,一个位置传感器即可通过逻辑电路和驱动电路感知旋转磁铁的位置,并激励正确的线圈。
典型驱动电路当今社会,有多种无刷直流电机正在广泛应用。
图1是一个三相8极电动机,使用双极霍尔效应传感器。
旋转的永久磁铁在传感器面前运动从而使传感器改变状态。
传感器在每次南极通过时开始工作。
图2为三个传感器的输出图,这三个传感器在无刷电机中的电角度间隔为30度。
在8极磁铁无刷电机中,相邻南极间的电角度为90度。
当三个传感器放置间隔角度为30度时,第一个传感器动作于30度,第二个为60度,第三个为90度。
北极通过传感器时,传感器会释放。
每个旋转8极磁铁的北极与相邻南极的角度为45度。
“动作”完毕后,每个传感器都会在45度角后释放。
三个传感器的输出,作为轴位置编码器使用。
传感器将磁铁位置和极性信息,提供给逻辑电路,再控制三极管的开闭,三极管的排列为“H”型桥式。
图1 典型无电刷直流电动机主要零件图2 传感器的工作SS400/SS4/SS1 低高斯双极霍尔效应传感器图3是一个使用6个三极管和三个霍尔效应传感器的驱动电路样例。
每一对三极管被开启或关闭,根据旋转磁铁的位置决定。
根据磁铁位置上,转子线圈的电流有相应的频率和时间。




Technical DataBulletin 1411 Current TransformersCatalog Numbers 1411-2xxx, 1411-8xxx, 1411-125, 1411-126, 1411-180, 1411-600, 1411-601, 1411-604, 1411-606, 1411-608, 1411-615, 1411-616, 1411-617, 1411-ALTopic PageSummary of Changes21411-2xxx Dimensions and Accuracy21411-8xxx Dimensions and Accuracy31411-125 Dimensions and Accuracy51411-126 Dimensions and Accuracy61411-180 Dimensions and Accuracy71411-600 and 1411-601 Dimensions and Accuracy91411-604 Dimensions and Accuracy101411-606 and 1411-608 Dimensions and Accuracy111411-615 Dimensions and Accuracy121411-616 Dimensions and Accuracy131411-617 Dimensions and Accuracy141411-AL Dimensions and Accuracy15Agency Certifications152Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current TransformersSummary of ChangesThis publication contains new and updated information as indicated in the following table.1411-2xxx Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 1 - 1411-2xxx DimensionsTable 1 - Summary of ChangesTopicPage Updated available catalog numbers.ThroughoutATTENTION: Proper safety precautions must be followed during installation by a trained electrician. Never install while bus is energized. The current transformer must have its secondary terminals that are short circuited or the burden that is connected, before energizing the primary circuit.Table 2 - 1411-2xxx AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio Models 2SFT, 2SHTModel 2DRL Accuracy at 60 Hz Burden VA at 60 HzAccuracy at 60 Hz Burden VA at 60 Hz 1411-2(1)-500(1)When ordering, prefix Cat No. with model designation required, for example, 1411-2SFT-301 or 1411-2DRL-301.50:5±3% 1.5±2% 1.51411-2(1)-80080:5±2% 2.0±2% 4.01411-2(1)-101100:5±1% 2.0±1% 5.01411-2(1)-151150:5±1% 4.0±1%8.01411-2(1)- 201200:5±1% 4.0±1%10.01411-2(1)-301300:5±1%8.0±1%15.01411-2SFT 1411-2SHT 1411-2DRLRockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 20173Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-8xxx Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 2 - 1411-8xxxDimensions1411-8SHT1411-8RL4Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current TransformersTable 3 - 1411-8xxx AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio VA for ±1% Class ANSI Metering Class at 60 Hz Secondary W inding Resistance (ohms at 75 °C (167°F))Continuous Thermal Rating Factor B0.1B0.2B0.5B0.9B1.8at 30 °C (86 °F)at 55 °C (131 °F)1411-8(1)-201(1)When ordering, prefix catalog number with model designation required, for example, 1411-8SHT-201 or 1411-8RL-301.200:5 5.0 1.2 1.2 2.4 4.8 4.80.030 2.0 2.01411-8(1)-301300:5(2)(2)Approved for revenue metering by Industry Canada No. T-188.15.00.60.6 1.2 2.4 2.40.049 2.0 2.01411-8(1)-401400:5(2)25.00.30.30.6 1.2 2.40.079 2.0 1.51411-8(1)-601600:5(2)50.00.30.30.60.6 1.20.147 1.5 1.331411-8(1)-1021000:5(2)75.00.30.30.30.60.60.246 1.33 1.01411-8(1)-1621600:5(2)100.00.30.30.30.30.60.337 1.330.81411-8(1)-2022000:5(2)120.00.30.30.30.3-0.422 1.00.81411-8(1)-3023000:560.00.30.30.30.3-0.526 1.00.81411-8(1)-4024000:580.00.30.30.30.3-0.9730.80.6Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-125 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 3 - 1411-125 DimensionsTable 4 - 1411-125 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio ANSI Metering Class at 60 HzSecondary Winding Resistance (ohms at 75 °C(167°F))Continuous Thermal Rating FactorB0.1B0.2B0.5B0.9B1.8at 30 °C(86 °F)at 55°C(131 °F)1411-125-1021000:50.30.30.30.6 1.20.187 1.6 1.331411-125-1621600:50.30.30.30.30.60.304 1.6 1.331411-125-2022000:50.30.30.30.30.60.280 1.6 1.01411-125-3023000:50.30.30.30.30.60.421 1.33 1.01411-125-4024000:50.30.30.30.30.30.696 1.00.8Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 201756Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-126 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 4 - 1411-126 DimensionsTable 5 - 1411-126 AccuracyCat. No.Current RatioVA for ±1% ClassANSI Metering Class at 60 HzSecondaryWinding Resistance (ohms at 75 °C (167°F))Continuous Thermal Rating Factor B0.1B0.2B0.5B0.9B1.8at 30 °C (86 °F)at 55 °C (131 °F)1411-126 -401400:5 4.00.6 1.2 2.4 2.4 4.80.116 2.0 2.01411-126-601600:510.00.60.6 1.2 1.2 2.40.173 2.0 2.01411-126-1021000:525.00.30.30.60.6 1.20.289 2.0 1.51411-126-1621600:550.00.30.30.30.30.60.462 1.5 1.01411-126-2022000:560.00.30.30.30.30.30.578 1.33 1.01411-126 -3023000:590.00.30.30.30.30.30.722 1.33 1.01411-126-4024000:5126.00.30.30.30.30.30.962 1.00.81411-126-6026000:5140.00.30.30.30.30.31.2781.00.8Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 20177Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-180 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 5 - 1411-180 Dimensions1411-180RL1411-180SHT8Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current TransformersTable 6 - 1411-180 AccuracyCat. No.Current RatioVA for ±1% ClassANSI Metering Class at 60 HzSecondary Winding Resistance (ohms at 75 °C (167°F))Continuous Thermal Rating B0.1B0.2B0.5B0.9B1.8at 30 °C (86 °F)at 55 °C (131 °F)1411-180(1)-500(1)When ordering, prefix catalog number with model designation required, for example, 1411-180RL-301 or 1411-180SHT-301.50:5 1.5 2.4----0.009 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-101100:5 2.5 1.2 2.4 4.8--0.021 1.33 1.01411-180 (1)-151150:5 (2)(2)Approved for revenue metering by Industry Canada. No. T-189.5.00.6 1.2 2.4 4.8-0.038 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-201200:5 (2)12.50.60.6 1.2 2.4-0.051 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-301300:5 (2)25.00.30.30.6 1.2 2.40.076 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-401400:5 (2)50.00.30.30.30.6 1.20.102 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-601600:5 (2)50.00.30.30.30.6 1.20.177 1.33 1.01411-180 (1)-1021000:5 (2)100.00.30.30.30.30.60.253 1.33 1.01411-180(1)-1621600:5 (2)175.00.30.30.30.30.30.359 1.25 1.01411-180(1)-2022000:5 (2)200.00.30.30.30.30.30.4491.00.75Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-600 and 1411-601 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 6 - 1411-600 and 1411-601 DimensionsTable 7 - 1411-600 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio VA at 1% Class ANSI Metering Class at 60 Hz B0.1B0.2B0.51411-600-301300:5 A 2.0 2.4--1411-600-401400:5 A 1.5 2.4 4.8-1411-600-601600:5 A 2.5 2.4 2.4-1411-600-1021000:5 A7.5 1.2 1.2 2.4 1411-600-1621600:5 A20.00.60.6 1.2 1411-600-2022000:5 A30.00.60.60.6 Table 8 - 1411-601 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio VA at 1% Class ANSI Metering Class at 60 Hz B0.1B0.2B0.51411-601-301300:5 2.0 2.4--1411-601-401400:5 A 1.0 4.8--1411-601-601600:5 A 2.0 2.4-1411-601-1021000:5 A 5.0 1.2 1.2 4.8 1411-601-1621600:5 A15.0 1.2 1.2 1.2 1411-601-2022000:5 A20.00.60.6 1.2*Modell 1411-600Modell 1411-601Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 20179Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-604 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 7 - 1411-604 DimensionsCat. No.Current Ratio Burden VA Accuracy1411-604-101100:51±5% 1411-604-151150:51±4% 1411-604-201200:51±2% 1411-604-301300:52±1.5% 1411-604-401400:5 2.5±1.5%10Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-606 and 1411-608 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 8 - 1411-606 and 1411-608 DimensionsTable 10 - 1411-606 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio Burden VA Accuracy at 60 Hz1411-606-201200:5 2.52%1411-606-301300:5 3.51%1411-606-401400:551%1411-606-601600:581%1411-606-1021000:5151%1411-606-1221200:5201%Table 11 - 1411-608 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio Burden VA Accuracy1411-608-601600:581%1411-608-801800:5121%1411-608-1021000:5131%1411-608-1621600:5271%1411-608-2022000:5331%1411-608-3023000:5501%1411-608-3223200:5541%Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 201711Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-615 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 9 - 1411-615 DimensionsTable 12 - 1411-615 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio Burden VA Accuracy 1411-615-101100:515% 1411-615-201200:523% 1411-615-301300:5 3.51% 1411-615-401400:58.51%12Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 201713Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-616 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 10 - 1411-616 DimensionsTable 13 - 1411-616 AccuracyCat. No.Current RatioBurden Accuracy 1411-616-201200:52VA 3%1411-616-401400:55VA 1%1411-616-801800:55VA1%14Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-617 Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 11 - 1411-617 DimensionsTable 14 - 1411-617 AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio VA at 1% Class ANSI Metering Class B0.1B0.2B0.51411-617-401400:5 A 1.5 2.4 4.8-1411-617-801800:5 A 5.0 1.2 1.2 2.41411-617-1021000:5 A 7.5 1.2 1.2 2.41411-617-1221200:5 A15.00.61.21.2Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 201715Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers1411-AL Dimensions and AccuracyFigure 12 - 1411-AL DimensionsAgency CertificationsTable 15 - 1411-AL AccuracyCat. No.Current Ratio Accuracy at 60 Hz Burden VA at 60 Hz 1411-AL-50050:5±3% 1.51411-AL-80080:5±2% 2.01411-AL-101100:5±1% 2.01411-AL-151150:5±1% 4.01411-AL-201200:5±1% 4.01411-AL-301300:5±1%8.01411-AL-401400:5±1%10.0Cat. No.1411-2xxx1411-8xxx1411-1251411-1261411-1801411-600 and 1411-6011411-6041411-6061411-6081411-6151411-6161411-6171411-ALX X X X X X X X XX X X X X X X X X X X X ANSI/IEEE C57.13X X X X X X X X X X X X X IEC 44-1XXXXXXXXXXXXX16Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Bulletin 1411 Current TransformersAdditional ResourcesThese documents contain additional information concerning related products from Rockwell Automation.Y ou can view or download publications at /global/literature-library/overview.page . T o order paper copies of technical documentation, contact your local Allen-Bradley distributor or Rockwell Automation sales representative.ResourceDescriptionBulletin 1411 Current Transformer Selection Matrix, publication 1411-SG001Provides selection information for the current transformers.Industrial Automation Wiring and Grounding Guidelines, publication 1770-4.1Provides general guidelines for installing a Rockwell Automation industrial system.Product Certifications website, /global/certification/overview.pageProvides declarations of conformity, certificates, and other certification details.Bulletin 1411 Current Transformers Notes:Rockwell Automation Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 201717Allen-Bradley, LISTEN. THINK. SOLVE., Rockwell Software, and Rockwell Automation are trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.Trademarks not belonging to Rockwell Automation are property of their respective companies.Publication 1411-TD001B-EN-P - June 2017Supersedes Publication 1411-TD001A-EN-P - August 2013Copyright © 2017 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the U.S.A.Rockwell Automation SupportUse the following resources to access support information.Documentation FeedbackY our comments will help us serve your documentation needs better. If you have any suggestions on how to improve this document, complete the How Are W e Doing? form at /idc/groups/literature/documents/du/ra-du002_-en-e.pdf .Technical Support CenterKnowledgebase Articles, How-to Videos, FAQs, Chat, User Forums, and Product Notification /knowledgebase Local Technical Support Phone Numbers Locate the phone number for your country./global/support/get-support-now.pageDirect Dial Codes Find the Direct Dial Code for your product. Use thecode to route your call directly to a technical support engineer./global/support/direct-dial.pageLiterature LibraryInstallation Instructions, Manuals, Brochures, and Technical Data./literatureProduct Compatibility and Download Center (PCDC)Get help determining how products interact, check features and capabilities, and find associated firmware./global/support/pcdc.pageRockwell Otomasyon Ticaret A.Ş., Kar Plaza İş Merkezi E Blok Kat:6 34752 İçerenköy, İstanbul, T el: +90 (216) 5698400Rockwell Automation maintains current product environmental information on its website at /rockwellautomation/about-us/sustainability-ethics/product-environmental-compliance.page .。

首先要确定一下基本的技术参数,如:1、被测电流值大小2、被测电缆或者铜牌的尺寸(根据尺寸来选择产品的穿孔尺寸,尽量充满穿孔)3、输出信号(一般是± 4V或者± 5V)4、供电电源(一般是DC ±12-15V)等以上这些是主要技术参数,其他次级的技术参数如下:1、使用环境是否有高低温、海拔、强震、潮湿等要求2、对于精度是否有要求(一般闭环电流传感器多为0.2-1%不等,开环传感器精度多为1%)3、安装方式(一般包含PCB式和固定式,也有导轨式的,不过比较少)合理选择霍尔电流传感器,就是要根据实际的需要与可能,做到有的放矢,物尽其州,达到实用、经济、安全、方便的效果。
为此,必须对传感器测量的目的、测量对象、使用条件等诸方面有较全面的了解;这是考虑问题的前提。
一是要依据测量对象和使用条件确定霍尔电流传感器的类型众所周知:同一霍尔电流传感器.可用来分别测量多种被测量;而同一被测量,义常有多种原理的霍尔电流传感器可供选用。
在进行一项具体的测量量工作之前,首先要分析并确定采用何种原理或类删的霍尔电流传感器更合适。
这就需要对与霍尔电流传感器工作有关联的方方面面作番调查研究。
要了解被测量的特点:如被测量的状态、性质,测量的范围、幅值和频带,测量的速度、时间、精度要求、过载的幅度和和出现频率等。
二是要了解使用的条件,这包含两个方面:(1)现场环境条件:如温度、湿度、气压,能源、光照,尘污、振动、噪声,电磁场及辐射干扰等;(2)现有基础条件:如财力(承受能力),物力(配套设施),人力(技术水平)等。
选择霍尔电流传感器所需考虑的方面和事项很多,实际中不可能也没有必要面面俱到满足所有要求。
设计者应从系统总体对霍尔电流传感器使用的目的、要求出发,综合分析主次,权衡利弊,抓住要方面,突出重要事项加以优先考虑。
在此基础七.就可以明确选择霍尔电流传感器类型的具体问题:量程的大小和过载量;被测对象或位置对霍尔电流传感器重量和体积的要求;测量的方式是接触。



第1篇随着科技的飞速发展,电器自控系统在工业生产、家居生活等领域扮演着越来越重要的角色。
为了提高生产效率、降低能耗、保障安全,电器自控系统解决方案的研究与应用成为当务之急。
本文将从系统设计、设备选型、实施步骤、维护保养等方面,详细介绍电器自控系统解决方案。
一、系统设计1. 系统架构电器自控系统采用分层分布式架构,分为以下几个层次:(1)感知层:负责采集现场设备、环境等数据,如温度、压力、流量、电流等。
(2)网络层:负责数据传输,采用工业以太网、无线网络等通信方式。
(3)控制层:负责数据处理、逻辑控制、决策支持等,采用PLC、DCS、FCS等控制设备。
(4)应用层:负责实现各类功能,如数据监控、设备控制、报警处理等。
2. 系统功能(1)数据采集与处理:对现场设备、环境等数据进行实时采集,并进行处理与分析。
(2)设备控制:根据预设逻辑,实现对设备的启动、停止、调节等操作。
(3)监控与管理:实时监控设备运行状态,实现远程监控、故障报警等功能。
(4)决策支持:根据采集的数据和预设逻辑,为生产管理提供决策支持。
二、设备选型1. 感知层设备(1)传感器:根据现场需求,选择合适的温度、压力、流量、电流等传感器。
(2)执行器:根据控制要求,选择合适的开关、调节阀等执行器。
2. 网络层设备(1)交换机:采用工业以太网交换机,保证数据传输的稳定性和安全性。
(2)无线设备:根据现场需求,选择合适的无线设备,如无线模块、无线网关等。
3. 控制层设备(1)PLC:根据控制要求,选择合适的PLC型号,如西门子、三菱等。
(2)DCS:根据现场规模和需求,选择合适的DCS系统,如霍尼韦尔、ABB等。
4. 应用层设备(1)人机界面:根据需求,选择合适的工控机、触摸屏等设备。
(2)服务器:负责数据存储、处理、分析等任务,选择性能稳定的设备。
三、实施步骤1. 需求分析:了解现场需求,明确系统功能、性能、规模等。
2. 设计方案:根据需求分析,制定详细的系统设计方案,包括系统架构、设备选型、实施步骤等。

霍尼韦尔电流环
霍尼韦尔电流环通常指霍尼韦尔(Honeywell)公司生产的电流环(current loop)产品。
电流环是一种电气工程中常见的连接方式,通常用于传感器与控制器之间的信号传输。
霍尼韦尔公司的电流环产品通常包括传感器、转换器、放大器和其他电子元件,用于测量和控制电流信号。
这些产品广泛应用于工业自动化、过程控制、仪表和传感器等领域,常用于监测温度、压力、流量等参数,并将这些参数转换成标准的电流信号进行传输和处理。
霍尼韦尔电流环产品通常具有高精度、可靠性强、抗干扰能力强等特点,能够满足工业现场对信号传输和控制的严格要求。
这些产品的应用范围广泛,涉及到工业自动化的各个方面,为工业生产提供了重要的技术支持。
电流传感器原理、分类以及应用电流传感器,也称磁传感器,是一种检测装置,能感受到被测电流的信息,并能将检测感受到的信息,按一定规律变换成为符合一定标准需要的电信号或其他所需形式的信息输出,以满足信息的传输、处理、存储、显示、记录和控制等要求。
例如开关电源、硬开关、软开关等。
下面给大家简单介绍一下电流传感器的分类及其应用电流传感器也称磁传感器,可以在家用电器、智能电网、电动车、风力发电等等,在我们生活中都用到很多磁传感器,比如说电脑硬盘、指南针,家用电器等等。
分类电流传感器依据测量原理不同,主要可分为:分流器、电磁式电流互感器、电子式电流互感器等。
电子式电流互感器包括霍尔电流传感器、罗柯夫斯基电流传感器及专用于变频电量测量的AnyWay变频功率传感器(可用于电压、电流和功率测量)等。
泰德兰电子代理的霍尼韦尔电流传感器主要采用了霍尔效应和磁阻效应两种工作原理,是分别利用两种原理对电流产生的磁场大小进行检测,并通过电磁互感的关系得到电流的大小。
在工作模式上,霍尼韦尔电流传感器主要有两种方式,其分别是:直接检测式和磁平衡式。
直接检测式电流传感器。
霍尔效应开环电流传感器是霍尼韦尔的一种直接检测式电流传感器。
众所周知通电导线周围产生的磁场与流过电流成正比。
该磁场经软磁材料聚集后,用霍尔器件来检测。
由于它们有良好的线性,因此可用标定后的霍尔输出来测出电流的大小。
与电磁式电流传感器相比较,电子式电流互感器没有铁磁饱和,传输频带宽,二次负荷容量小、尺寸小、重量轻、是今后电流传感器的发展方向。
应用电流传感器应用于风力发电:风能作为一种清洁的可再生能源,越来越受到世界各国的重视。
其蕴量巨大,全球的风能约为2.74&TI mes;109GW,其中可利用的风能为2&TI mes;107GW,比地球上可开发利用的水能总量还要大10倍。
风很早就被人们利用--主要是通过风车来抽水、磨面等,而新世纪,人们感兴趣的是如何利用风来发电,以及如何才能发电量最大化。
霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器广州南创蔡工霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器是一家财富100强公司发明和生产技术,以解决与全球宏观趋势,如安全性,安全性和能源的严峻挑战。
霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器全球约132,000名员工,其中包括超过19,000名工程师和科学家,霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的产品在多个国家设立了国外办事处及售后服务中心,并在中国设立了广州南创传感事业部,为美国Honeywell 流量传感器提供最佳的服务与解决方案。
有质量,交货,价值,和霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器做的一切技术的不懈重点。
霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的能力不断提高,来自成功实现两个看似竞争的一次任务- 生产力和经济增长。
美国Honeywell流量传感器公司的核心内部业务流程,传动效率和服务质量。
促成带来世界一流的产品和服务更快地推向市场和更具成本效益航天霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的航空航天产品和服务用于全球几乎所有的商业和商务飞机经营的今天,以及国防和空间应用。
霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器提供综合航空电子系统,发动机,系统和服务解决方案,认真听取霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的客户和重点放在最能满足他们的需求,使飞行更安全,更可靠,更高效,更具成本效益的技术。
自动化和控制解决方案霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的环境控制,生命安全,安全,遥感,扫描,移动产品,以及建筑和工艺解决方案是在工作中,在150万个家庭,10万座建筑物,5000工业设施,以及数以百计的全球天然气和电力公用事业。
霍尼韦尔Honeywell传感器的产品和解决方案,使客户能够捕获更多和更好的数据,更快的速度和整个无线景观,提高生产率,安全性和安全性,推动更好的决策,并降低了成本。
高性能材料和技术以开发和制造先进的材料和工艺技术,是人每天使用,以减少温室气体排放,阻止子弹,使生产的绿色燃料,增加炼油能力,加速药物发现,和保护药品的全球领先地位。
对钒电池磁力驱动泵进行安全监控的电流传感器
钒电池全称全钒液流电池,是一种新型清洁化学能源存储装置。
随着风能、太阳能等新能源的崛起,以电池为主要表现形式且不受自然条件限制的化学储能迎来了增长的机遇。
并且由于全钒液流电池具有使用寿命长、规模大、安全可靠等优势,因而成为大规模储能的首选技术之一。
作为一优良的储能装置,钒电池性能的发挥取决于正常工作的情况,在监测钒电池运行中,电流传感器是一种必不可少的测量元件。
在钒电池储能系统中,电流传感器主要作用体现在对电磁泵和电堆充放电电流的测量上。
在钒电池中有两个分别盛放氧化和还原溶液的容器,构成电池系统的正负极,电池能量的存储和释放是靠电磁泵驱动下正负极溶液的交换实现的。
一旦磁力泵发生故障,钒电池将不复正常工作。
因此,作为保证钒电池系统正常运行的核心部件,利用电流传感器对磁力驱动泵进行安全监控是必要的。
此外电堆的放电电流,以及充电时的充电电流,也要监控起来,以监测电堆内部是否发生故障。
霍尼韦尔电流传感器是利用霍尔或者专利磁阻器件,通过对导体中电流所产生磁场大小的检测来间接测量电流的,从原理上主要可分为霍尔效应闭环电流传感器、磁阻效应闭环电流传感器和霍尔效应开环电流传感器。
霍尼韦尔电流传感器能够覆盖从毫安级到几百安的交、直流和脉冲电流的测量,主要有CSDA系列数字电流传感器、CSN系列闭环电流传感器、CSCA-A系列。
温度补偿霍尔传感器内含集成 在方形集成电路上的方块霍尔传感元件。
外封装为含玻璃的热固性压模材料,小型SOT89封装可安装在PCB 的柔性板上。
热平衡的集成电路提供可预知的性能,在-40~+125˚C 整个温度范围内。
内含的温度补偿为负的曲线(动作/释放点随温度上升下降)。
这种特性与低成本磁钢的负温度系数最佳匹配,有双极、单极、锁存型可选。
带宽间隙调整提供3.8~30VDC 电源电压范围内非常稳定的工作性能,消耗电流可低至10mA (最大值)。
SS100能连续输出20 mA 沉电源,并能承受短时50 mA 电流。
传感器可在许多应用中利用现有的电源,并可与许多电路直接相连不用另加缓冲及补偿电路。
SS100系列有用于自动器安装带状或卷状包装型号,每个卷带包含1000个传感器。
注:不要波峰焊此器件,此工艺可能影响传感器的性能和可靠性,并得不到MICRO SWITCH 质量保证,MICRO SWITCH 建议红外波峰焊,最高温度不超过220℃,10秒内。
特点:●方块霍尔设计实上消除了机械引力效应●(磁特性)温度特性 ● 双极,单极,锁存型 ● 特别高的灵敏度● 动作/释放磁场(双极/锁存) ● 工作温度范围-40~+125˚C● 低消耗电流(7mA 典型@5V,25˚C ) ● 3.8 ~ 30VDC 供电电压● 高输出电流—绝对最大电流50mASS111A 双极3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µs G 70-701565-651560-601560-601265-6512mT 7.0-7.01.56.5-6.51.56.0-6.01.56.0-6.01.26.5-6.51.2最大动作点最小释放点最小回差最大动作点最小释放点最小回差最大动作点最小释放点最小回差最大动作点最小释放点最小回差最大动作点最小释放点最小回差型号磁性能供电电压(VDC )供电电流(最大值)输出类型输出电压(最大值)输出电流(最大值)漏电流(最大值)输出开关时间上升下降磁特性-40℃0℃25℃85℃125℃SS113A 双极3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsSS141A 单极3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsSS143A 单极3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsSS149A 单极3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsSS161A 锁存3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsSS166A 锁存3.8-3010mA 电流沉.40V 20mA 10µA1.5µs 1.5µsG 140-14020140-14020140-14020140-14020140-14020mT 14.014.02.014.014.02.014.014.02.014.0-14.02.014.0-14.02.0G 1352015117201811520201201515123158mT 13.52.01.511.72.01.811.52.02.012.01.51.512.31.50.8G 21580251908025180752518070151906010mT 21.58.02.519.08.02.518.07.52.518.07.01.519.06.01.0G 110-1105090-905085-855085-8550100-10050mT 11.0-11.05.09.09.05.08.5-8.55.08.5-8.55.010.0-10.05.0G 200-200200185-185200180-180200180-180190180-180160mT 20.0-20.00.018.5-18.520.018.018.020.018.0-18.019.018.018.016.0选型指南G 4402103040023030390235304002153041020030mT 44.021.03.040.023.03.039.023.53.040.021.53.041.020.03.0G=Guass mT=milliTesla动作点和释放点注:当锁存型传感器掉电后,上电时输出状态会发生改变,如过足够强的磁场,传感器输出由所在磁场决定。