涡流和趋肤效应
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:59.00 KB
- 文档页数:3




涡流的趋肤效应的主要应用1。
涡流的趋肤效应的应用当交变电流通过导体时,它所激发的交变磁场会使导体本身产生涡流,导体中的涡流使电流密度分布不再均匀,越靠近导体表面处电流密度越大,这种交变电流趋向于导体表面的效应就叫趋肤效应。
其重要应用是对金属进行表面淬火或局部淬火。
淬火时,一般是将金属工件放在用空心铜管绕成的线圈中,当线圈通有高频电流时(线圈内部通水冷却),金属工件内产生涡流的趋肤效应,金属表面的温度急剧升高,当达到淬火温度时,将工件立即浸入冷却液体中,从而达到淬火的目的.这种热处理方法既增加了金属表面的硬度,又不失去金属原有的韧性,能够保证和提高产品质量,比用一般的火焰淬火加热速度快,零件表面氧化损失少,加工成本低,劳动条件好。
2。
减少涡流的趋肤效应的影响由于高频电流趋于导体表面流动,通电的有效面积小于导体本身的截面积,使导体对交流电的电阻增大.为了减少涡流的趋肤效应的影响,在高频电路中使用的导线常做成管状,以增大导体的有效面积。
例如收音机的拉杠天线就是常见的例子。
尊敬的读者:本文由我和我的同事在百忙中收集整编出来,本文档在发布之前我们对内容进行仔细校对,但是难免会有不尽如人意之处,如有疏漏之处请指正,希望本文能为您解开疑惑,引发思考。
文中部分文字受到网友的关怀和支持,在此表示感谢!在往后的日子希望与大家共同进步,成长。
This article is collected and compiled by my colleagues and I in our busy schedule. We proofread the content carefully before the release ofthis article, but it is inevitable that there will be some unsatisfactory points. If there are omissions, please correct them. I hope this article can solve your doubts and arouse your thinking. Part of the text by the user's care and support, thank you here! I hope to make progress and grow with you in the future.。

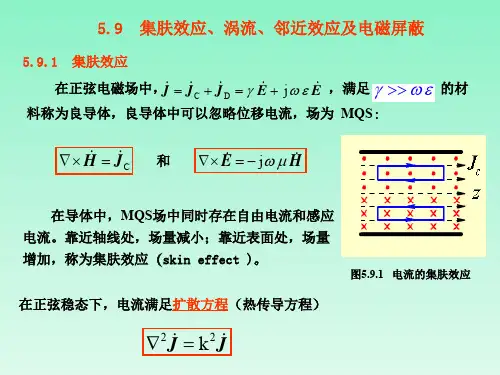
一、集肤效应1.1集肤效应的原理集肤效应也称趋肤效应,图1.1表示了集肤效应的产生过程。
图中给出的是载流导体纵向的剖面图,当导体流过电流(如图中箭头方向)时,由右手螺旋法则可知,产生的感应磁动势为逆时针方向,产生进入和离开剖面的磁力线。
如果导体中的电流增加,则由于电磁感应效应,导体中产生如图所示方向的涡流。
由图可知:涡流的方向加大了导体表面的电流,抵消了中心线电流,这样作用的结果是电流向导体表面聚集,故称为集肤效应。
在此引进一个集肤深度〈skin depth〉的概念,此深度的电流密度大小恰好为表面电流密度大小的1/e倍:一般用集肤深度Δ来表示集肤效应,其表达式为:其中:γ为导体的电导率,μ为导体的磁导率,f为工作频率。
图1.1.集肤效应产生过程示意图图1.2.高频导体电路密度分布图高频时的导体电流密度分布情形,大致如图1.2所示,由表面向中心处的电流密度逐渐减小。
由上图及式1.1可知,当频率愈高时,临界深度将会愈小,结果造成等效阻值上升。
因此在高频时,电阻大小随着频率而变的情形,就必须加以考虑进去。
1.2影响及应用在高频电路中可以采用空心导线代替实心导线。
此外,为了削弱趋肤效应,在高频电路中也往往使用多股相互绝缘细导线编织成束来代替同样截面积的粗导线,这种多股线束称为辫线。
在工业应用方面,利用趋肤效应可以对金属进行表面淬火。
考虑到交流电的集肤效应,为了有效地利用导体材料和便于散热,发电厂的大电流母线常做成槽形或菱形母线;另外,在高压输配电线路中,利用钢芯铝绞线代替铝绞线,这样既节省了铝导线,又增加了导线的机械强度,这些都是利用了集肤效应这个原理。
集肤效应是在讯号线里最基本的失真作用过程之一,也有可能是最容意被忽略误解的。
与一般讯号线的夸大宣传所言,集肤效应并不会改变所有的高频讯号,并且不会造成任何相关动能的损失。
正好相反,集肤效应会因传导体的不同成分,在传递高频讯号时有不连贯的现象。
同样地,在陈旧的线束传导体上,集肤效应助长讯号电流在多条线束上的交互跳动,对于声音造成刺耳的记号。

涡流趋肤效应计算公式
涡流趋肤效应是指在导电体中存在交变电磁场时,电流会集中在导体表面附近形成涡流,从而导致电流在导体内部的传输受到阻碍的现象。
涡流趋肤效应的计算公式如下:
$$
\delta=\sqrt{\frac{2\rho}{\pif\mu}}
$$
其中,
$\delta$是涡流趋肤深度(SkinDepth),单位为米;
$\rho$是导体的电阻率,单位为欧姆·米;
$f$是电磁场的频率,单位为赫兹;
$\mu$是导体的磁导率,单位为亨利/米。
涡流趋肤深度表示了电流在导体中的分布情况,深度越大表示电流在导体内部分布越均匀,趋肤效应越弱;深度越小表示电流在导体表面附近分布越集中,趋肤效应越明显。
一般情况下,导体的周围环境和导体的尺寸对涡流趋肤深度有一定的影响。
涡流趋肤效应的计算公式可以通过导体的材料参数、导体尺寸和电磁场的频率来确定,它在电磁学、电路设计以及电磁兼容性等领域中都有重要的应用。

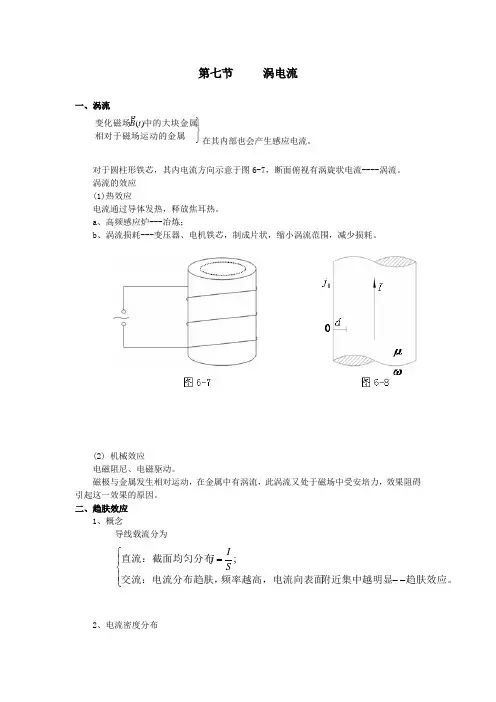
第七节 涡电流
一、涡流
在其内部也会产生感应电流。
对于圆柱形铁芯,其内电流方向示意于图6-7,断面俯视有涡旋状电流----涡流。
涡流的效应
(1)热效应
电流通过导体发热,释放焦耳热。
a 、高频感应炉---冶炼;
b 、涡流损耗---变压器、电机铁芯,制成片状,缩小涡流范围,减少损耗。
(2) 机械效应
电磁阻尼、电磁驱动。
磁极与金属发生相对运动,在金属中有涡流,此涡流又处于磁场中受安培力,效果阻碍引起这一效果的原因。
二、趋肤效应
1、概念
导线载流分为
2、电流密度分布
⎭⎬⎫相对于磁场运动的金属中的大块金属变化磁场)(t B ⎪⎩⎪⎨⎧--=趋肤效应。
附近集中越明显频率越高,电流向表面交流:电流分布趋肤,直流:截面均匀分布;S I
j
式中叫做趋肤深度。
对于,为表面附近处的电流分布,而则为处的分布大小,如图6-8。
当,则。
3、趋肤效应的说明
电流的频率越高,进而的变化也越快,产生也越大,涡流也越大,分析一个
周期内的情况,大部分时间内,轴线处与
方向相反。
表面处与方向相同。
4、应用
金属表面淬火。
高频表面电阻增大,可镀银或辫线使电阻,导线可中空省材料。
s d d e
j j -=0s d e j j 0=0j j s d d =σωμμ02
=s d ↑ω↓s d B φεi 涡i i 涡i ↓R。


电流的趋肤效应概述说明以及解释1. 引言:1.1 概述在电磁学领域中,电流的趋肤效应是一种重要的物理现象。
当交变电流通过导体时,由于磁场的作用,电流会在导体表面形成一个类似于“皮肤”的分布,这种现象称为趋肤效应。
趋肤深度与导体材料、频率和电流密度等因素有关,对于高频交变电流尤为明显。
1.2 背景信息电流的趋肤效应不仅在理论物理学中具有重要意义,而且在实际工程中也有广泛的应用。
通过充分理解电流的趋肤效应原理和特点,可以更好地设计和优化各种电路和设备,并提高其性能和效率。
1.3 研究意义深入研究电流的趋肤效应对于改善能源传输、无损检测技术、工业加热与焊接等领域具有重要意义。
通过探索其基本原理和机制,可以为相关领域提供更科学合理的解决方案,并推动技术进步和产业发展。
2. 电流的趋肤效应原理:2.1 定义和基本概念电流的趋肤效应是指当交变电流通过导体时,电流主要分布在导体表面附近,而深层部分的电流密度迅速减小至很小的数值的现象。
这种现象是由于导体内部感应出相互抵消的涡流,使得整个导体内部只有少量电流能够通过。
2.2 形成机制当交变电流通过导体时,原初产生的磁场会刺激导体内感应出涡流。
这些涡流在导体内部形成并阻碍了除了表面以外其他位置的电流传输。
由于涡流越靠近表面处于高密度状态,所以大多数电流集中在导体表面周围,形成所谓的“趋肤”效应。
2.3 物理解释根据麦克斯韦方程组和洛伦茨力定律,在交变磁场中运动带电粒子(即导体内自由电子)会受到感生电场及洛伦茨力作用而发生运动。
这样一来就会形成一个新的阻碍条件,使得整个导体对于穿过它的交变电流呈现出一种“挤压”的现象,将大部分电流推向表面。
因此,了解和掌握电流的趋肤效应原理对于提高交变电路及设备的设计、效率和性能具有重要意义。
3. 应用领域与实际案例分析:电流的趋肤效应在各个领域都有广泛的应用。
其中,以下是一些实际案例分析:3.1 电力输送中的应用:在电力输送系统中,电流的趋肤效应被广泛应用于减小导线损耗和提高传输效率。
五彩斑斓的树叶英语作文## The Kaleidoscope of Autumn Leaves.As summer draws to a close and the days grow shorter, a magical transformation begins to unfold in the world of nature. The leaves of deciduous trees, once a vibrant canopy of green, begin to don a kaleidoscope of colors that paint the landscape in breathtaking hues. This seasonal spectacle, known as autumn foliage, is a symphony ofnature's artistry, showcasing the diversity and beauty of the plant kingdom.The vibrant colors of autumn leaves are the result of a complex interplay between light, pigments, and biochemical processes within the leaves. As the days shorten and the nights grow longer, trees prepare for winter by reducing their production of chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs sunlight and gives leaves their green color. With the decrease in chlorophyll, other pigments, such as carotenoids and anthocyanins, become more prominent,revealing a spectrum of colors ranging from golden yellow and fiery orange to deep crimson and vibrant purple.## The Science Behind the Hues.Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red pigments that are always present in leaves, even during the spring and summer. However, they are often masked by the abundance of chlorophyll. As chlorophyll levels decline in autumn, carotenoids become more visible, contributing to the warm and inviting hues of fall foliage.Anthocyanins are red, purple, and blue pigments that are not typically found in leaves during other seasons. Their production is triggered by a combination of factors, including exposure to sunlight, cool temperatures, and drought stress. When these conditions are met, trees produce anthocyanins to protect their leaves from the harmful effects of UV radiation and dehydration.The intensity and variety of autumn colors can vary greatly from year to year and from tree to tree. Factorssuch as climate, soil conditions, and genetic makeup all play a role in determining the vibrancy of fall foliage.## A Symphony of Colors.The diversity of tree species and their unique responses to environmental conditions give rise to a breathtaking array of colors each autumn. Some of the most common and visually striking autumn trees include:Sugar Maples are renowned for their brilliant crimson and orange leaves, which often create a fiery blaze of color in the forests of North America.Red Maples produce vibrant shades of scarlet and burgundy, adding a touch of drama to the autumn landscape.Aspen Trees are known for their shimmering golden leaves, which tremble in the slightest breeze, creating a shimmering curtain of light.Birch Trees display a delicate and elegant yellow hue,adding a subtle touch of warmth to the autumn palette.Sweetgum Trees showcase a stunning range of colors, from deep crimson to golden yellow, creating a vibrant tapestry of foliage.Oak Trees exhibit a rich and varied palette, ranging from deep browns and oranges to fiery reds and purples, adding depth and complexity to the autumn landscape.## A Symbol of Change and Renewal.Autumn foliage is not merely a visual delight but also a powerful symbol of change and renewal. As the leaves fall from the trees, they decompose and enrich the soil, providing essential nutrients for new growth in the spring. In this way, autumn foliage represents the cyclical nature of life and the promise of rebirth.Autumn foliage has captivated poets, artists, and nature lovers throughout history, inspiring countless works of art, literature, and music. From the vibrant landscapesof the Hudson River School to the haiku of Matsuo Bashō, the beauty of autumn leaves has been celebrated and immortalized in countless cultural traditions.## Preserving the Autumn Spectacle.The beauty of autumn foliage is a gift that should be cherished and preserved for future generations. However, climate change, deforestation, and other human activities are posing threats to this natural wonder.To protect and preserve the autumn foliage, it is important to:Reduce our carbon footprint by adopting sustainable practices that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which contribute to climate change.Support sustainable forestry practices that promote the health and longevity of forests.Plant native trees in our communities to enhance thediversity and resilience of local ecosystems.By taking these steps, we can ensure that the kaleidoscope of autumn leaves continues to enchant and inspire for generations to come.。
什么是涡流?什么是集肤效应?
当交流电流通过导线时,在导线周围产生交变的磁场。
处在交变磁场中的整块导体的内部会产生感应电流,由于这种感应电流在整块导体内部自成闭合回路,形似水的旋涡,所以称做涡流。
因为金属导体电阻很小,因此这种感生电流很大,造成发热损耗。
在直流电路内,均匀导线的横截面上的电流密度是均匀的,而当交流电通过导线时,由于交变磁场的作用,在导线截面上各处电流分布不均匀,中心处电流密度小,而越靠近表面电流密度越大,这种电流分布不均匀的现象称为集肤效应(也称趋肤效应)。
集肤效应的原因也是因为涡流的存在。
交流电的频率越高,则集肤效应越严重。
此外集肤效应也使得线棒内部的导线载流能力下降。
发电机的线棒截面都比较大,涡流和集肤效应都会使线棒造成严重的发热,所以克服发电机线棒发热的办法是将线棒内的导体设计成由若干股相互绝缘的细小导线并联组成。
如某发电机其设计的支路电流为2000A,其每根线棒由44股2.5×8mm规格的双玻璃丝包线并联并经换位编织而成。
趋肤效应的原理及应用
趋肤效应,也称为集肤效应,是一种物理现象。
当交流电或交变电磁场通过导体时,电流会集中在导体的表面,这种现象就是趋肤效应。
这是因为电流在导体的内部产生交变磁场,而在导体的表面产生感应电动势,这个感应电动势会阻碍电流的变化。
趋肤效应的原理可以追溯到涡流的产生。
当电流流过导体时,在导体的垂直平面内形成交变磁场,这个磁场在导体内部产生感应电动势。
这个感应电动势的方向总是与电流的变化趋势相反,因此它会阻碍电流的变化。
在导体内部,由于感应电动势的存在,会产生涡流电流,其方向与原电流相反,而在导体表面,涡流电流的方向与原电流相同,加强了原电流。
这就导致了电流在导体表面流动更为容易,而在内部流动较为困难。
因此,交变电流倾向于在导体的表面流动,形成了趋肤效应。
趋肤效应的影响主要表现在电阻的变化上。
由于电流主要集中在导体的表面,导体的等效电阻变大,因为电流的有效截面积减小了。
此外,趋肤效应与电流的频率有关,频率越高,趋肤效应越显著,交流电阻越大。
趋肤效应的应用主要在于改善导体的高频传输性能。
例如,在传输高频电流的导线中,可以通过增加导线的表面积、镀银或镀金降低表面电阻、或者制作成空心导线等方法来改善其传输性能。
另外,趋肤效应还可应用于金属表面热处理,例如表面淬火等过程。
如需了解更多关于趋肤效应的原理和应用的详细信息,建议查阅物理类书籍或文献,也可以咨询物理专家或学者获取专业解答。