北京化工大学材料导论PPT
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:4.92 MB
- 文档页数:7


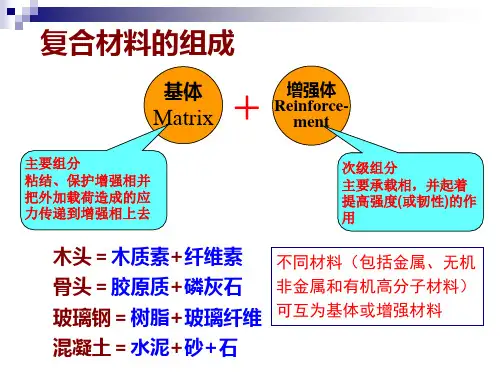
一,英译中1. BMC, bulk molding compound,块状模塑料2. CMC, ceramic matrix composite,陶瓷基复合材料3. DP, degree of polymerization,聚合度4. FRP(GRP), fiber-reinforced plastics(glass fiber-reinforced plastics),纤维增强塑料5. LCPs, liquid crystal polymers,液晶聚合物6. MMC, metal matrix composite,金属基复合材料7. PMC, polymer matrix composite,聚合物基复合材料8. RTM, resin transfer molding,树脂转移模塑9. SMC, sheet molding compound,片状模塑料10. TP, thermoplastic,热塑性塑料11.TG,class transition temperature,玻璃化转变温度12.SBR,styrene butadiene rubber,丁苯橡胶二,连线1.A chainlike molecule made up of smaller molecular units. Polymer 聚合物2.The linking together of smaller units into long chains. Polymerization 聚合3.A chemical that serves as molecular matchmaker necessary to begin polymerization reaction.Catalyst 催化剂anic,ceramic,synthetic,or metallic materials with a length of 100 times the diameter, with aminimum length of at least 5mm. Fiber 纤维5.The individual fibers of indefinite length used in tows ,yarns, or roving. Filament 单丝6.The binder material of a composite, whether organic ,ceramic ,or metallic, that distributes theload among fibers or particulates. Matrix 基体7.A human-made, nearly perfect, single crystal with a diameter ranging from about 1 to10μm andlengths up to 3 cm. Whisker 晶须8.A reference to cross-linking ,which designates the number of cross-links per 100 linear bonds.Netting index 网数9.Materials used to work like adhesives, provide protective coatings, and keep out liquids and gases. Sealants 密封胶10.Attraction of molecules between an adhesive and substrate. Adhestion 粘合11.Any material that is capable of holding two materials together by surface attachment.Adhesive 粘合剂12.A material upon the surface of which an adhesive is spread for the purpose of bonding orcoating. Adherend 被粘物13.The ratio of the tensile strength of a fiber material to its weight density or mass density.Specific strength 比强度14.The term used to describe the crystallinity of polymers. Degree of crystallinity结晶度15.The number of repeating units in the polymer materials.Degree of polymerization聚合度16.The amount of reinforcement in a composite material. Fiber loading 纤维载量17.V ariation in the molecular structure of the same composition. Isomers 异构体18.The point at which polymers act as glass or become viscous liquids. TG 玻璃化转变温度19. A property unique to polymers that incorporates two properties of viscosity and elasticity.另一种解释:A combination of viscous and elastic properties in a material with the relative contribution of each being dependent on time,temperature,stress and strain rate. Viscoelasticity 粘弹性20. Energy loss through heating in elastomers, which creates problems in applications such as cartires. Hysteresis滞后作用21.The time-dependent permanent deformation that occurs under stress. Creep 蠕变22.The decrease in stress after a given time at constant strain. Stress relaxation 应力松弛23.Attrction of molecules within an adhesive or substrate. Cohesion 内聚力24.Wood’s ability to char when burned. Ablation 烧蚀25.An indicator of a material’s resistance to the extension of a preexisting crack. Fracturetoughness 断裂韧性26.The additive can be selected to moderate the plastics that are used for aircraft storage compartments subject to fire。







This time7.3.1.6 High-performance polymeric fibers 7.3.1.4 Kevlar fiber7.3.1.7 Smart fibersThis time 7.3.2.1 Fiber strength7.3.2.2 Specific tensile strength 7.3.2.3 Specific stiffness7.3.2.4 Fiber loading7.3.2.5 Fiber orientation7.3.1.6 High-performance ManufacturedPolymeric FibersPage 343PolyesterNylonAramid 芳香族聚酰胺Polyolefins聚烯烃Aramid fibers 芳香族聚酰胺纤维Country Trade name CompositionAmerican, DuPont kevlarNomex聚对苯二甲酰对苯二胺聚间苯二甲酰间苯二胺Japan ConexTechnora聚间苯二甲酰间苯二胺聚对苯二甲酰对苯二胺荷兰阿克苏Twaron聚对苯二甲酰对苯二胺Kevlar TM fiberPage 342(aramidaromatic, polyamideMelt-spunStructure of Kevlar fiberStiff, rodlikemolecule lineup in parallelarray.Aromatic ringstructureWhat are the properties of kevlar fibers?Anisotropy [7Anai5sCtrEpi ]fiber-longitudinal Page 342Que. ?Page 342 Three grades of kevlarKevlar 29Kevlar 49Kevlar149Bending stress-strain curves showing the relation of Kevlar 49 to other common reinforcing fibers Undirectional composite bending stress-strain curves (epoxy resion matrix)Page 342Poly imidazole[7pClibenzimE5dAzEul] PBI 聚苯并咪唑Sulfar or Polyphenylene Sulfide耐纶Polyolefins聚烯烃丙纶(Polypropylene, 缩略为PP)Spectra 900Page 343 Polyolefin.U ltrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylenehas a low specific gravity of 0.9, higher specific strength and specific stiffness, and has 7 to 10 times abrasiveresistance than aramid, with low moistureabsorptionPage 343 7.3.1.7 Smart fibersSmart fibersSmart fibersOne example of smart fibers Antimicrobialsprevent the spread of bacteriareduce odors 气味For exampleRef.Examples of smart fibers Athletic wearSmart fibers using photonics7.3.2.1 Fiber strengthPage 343 The strength of an individual fiber is dependent onMicrocracks localized stressload concentrationfailure of fiber7.3.2.1 Fiber strength The properties of a fiber are mainlydependent onQue.1补充How do the fiber’s length,diameter, and orientation affect the fiber strength ?Page 343Relationship between tensile strength and gauge length (规长)Tensile strength of CF versus gauge lengthWhy?补充补充adversely affected defects flaw (缺陷)How are the amount of defects in fibers reduced? macro reducing the amount of cross-sectional area in the fiber.Que.2补充补充Fiber-aspect ratio (L/D)Page 343Fig. 7-11 Strength versusfiber-aspect ratioDifferent Strength of the same materials in different forms Page 344MaterialsStrengthIn fiber form in bulk formGlass around 3.5GPa a few mega pascal(MPa) Plain-carbon steel around 4 GPa around 0.5 GPaValues of strength of materials in fiber form is much over the same materials in bulk form, why?the crystals aligning themselves along the fiber axis in ordered fashion Que.3Page 344Page 344 7.3.2.2 Specific tensile strengthThe ratio of the tensile strengthmaterial to its weigh density in KN/mmillimeters (mm)inches (in.)kilometers (km)Table 7-4 Specific Strength of materialsMaterials WeightDensity(KN/m3)Tensilestrength(GN/m2 )Specificstrength(Km)S-glass197 E-glass137 Boron137Carbon and Graphite123 Page 3457.3.2.3 Specific stiffnessPage 344 Stiffness(or specific modulus) ratio of the modulus of elasticityelasticity ) to the weight densityTable 7-5 Specific Stiffness/ModulusMaterials WeightDensity(KN/m3)Tensileelasticity(GN/m2 )Specificstiffness(Mm)Boron16Carbon and Graphite14 Page 345Page 344of the mass densityweight density.Mass density to weightdensity)to mass density Kg/m 3Tab. Units of parameters Page 344Page 346 7.3.2.4 Fiber Loading (填充量)Fiber loadingThe strength of the composite is directly proportional toIf all fibers are placed parallel toBe inversely proportional to 成反比的Fiber loading and the arrangement ororientation of the fibersPage 346-347if all fibers are placed parallel tounidirectionalreached if half the fibers are arranged atright angles to fabricsA random arrangementchopped strands7.3.2.5 Fiber orientationunidirectionalBidirectionalMultidirectional RandomPage 348Page 347 Directional orientedIf continuous fiberstheir length is in the directionof the loading, this type of arrangement isdirectional orientedloadingloadingdecreases to (降低至)Page 347‘7.4.1 Structure and propertiesof CompositesPage348their composition and their structure.Que.1What does the structure of acomposite material refer to?In monolithic materials macroscopic major ingredients or constituents Page349Structure of CompositesPage 348 Properties of compositesdesignedisotropic[properties (nearly homogeneous2) anisotropic[E7naisEu5trCpik]3) directionalReview What is directional oriental? (Page 347)7.4.1.1 Rules of mixtureconstituents of a composite interact in various ways to produce the collective properties ( rule of mixtures (ROM) 混合原则Page 348What ?Page 349 Rules of mixturesuch as modulus of elasticity, follow ROM. Que.?relative amounts properties of thecomponents。